UNCERTAIN GUERRILLA GARDEN
Landscape Architecture Mla Y2 2023-2024
BARC0113: Advanced Landscape Design 2
Module Administrator: Laura Allen
Design Tutor: Douglas Miller
Katya Larina
Student Name: Shihui Zhou
Submission Date: 2024.09.03
Guerrilla gardening refers to an unauthorized, grassroots gardening activity typically organized spontaneously by the public. It aims to improve unmanaged lands in urban or rural areas. This project uses famous guerrilla gardening community “Grow Heathrow” as introduction, studies how people collaborate with nature in an off-grid style: stick to recycling, producing food and protecting environment. Even though this guerrilla garden has been evicted, the communities near heathrow airport are still at risk of being displaced, as the Heathrow Airport Expansion plan is implemented. In order to make better use of the gap period of time before runway construction, The author aims to establish an uncertain-future landscape within the next 15 years. Responding to studio 4 brief ‘Uncertain Sitopias’ this year, the basic design intention is to construct productive lands for people near Heathrow Airport. They could be small scale like personal micro garden field, to large field ridges that can block aircraft’s noise. People are invited to occupy these lands, and take their own plants away once the site is abandoned. The highlight of this project is to create landscapes in the most rapid and economical way to address an uncertain future.
GENERAL INFORMATION OF GUERRILLA GARDENING
Guerrilla gardens consist of networks of volunteers. In its most basic form, guerrilla gardening is the ‘illicit cultivation of someone else’s land’ (Reynolds, 2008, p.16). According to Reynolds, there are mainly two types of guerrilla gardening regards to the aims: for personal purpose and for political purpose.

HISTORY OF GUERRILLA GARDENING IN UK

Reynolds records it on the website:guerrillagardening.org and makes guerrilla garden a community in UK history (Fraser,2010)
Salford, one city in North West region of the UK integrate guerrilla gardening with regeneration project, sponsored by the city council (Hardman, 2018)




HM Land Registry is actively encouraging landowners to register their land and has committed to achieving 100% registration in England and Wales by 2030. However, as of now, about 13% of the land remains unregistered (HM Land Registry, 2018). Among these unregistered plots, ranging from abandoned lots to neglected corners, guerrilla gardens have emerged across London, transforming forgotten spaces into thriving green sanctuaries.
Guerrilla gardening, as a grassroots movement does not have much written record in British history. Richard Reynolds’ website provides a channel for people to gather and engage in guerrilla gardening activities.
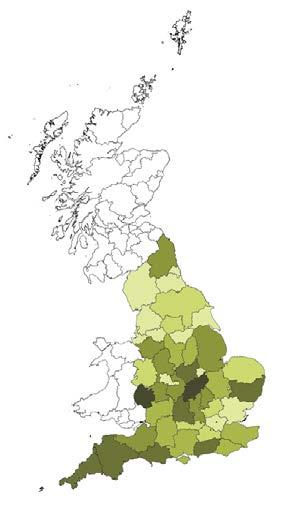
LGS (Local Green Space) designation is a way to provide special protection against development for green areas of particular importance to local communities. Among 6515 LGs in England, London only takes part of 112 of them. These data reflect London’s insufficient protection of green spaces, providing people with opportunities for guerrilla greening.

" GROW HEATHROW": EVICTED ECO-VILLAGE


Sipson&Harmondsworth


On 16 December 2020, the UK Supreme Court lifted the ban on the third runway, allowing a planning application via a Development Consent Order to go ahead.However as of 2023 largely post-COVID pandemic, falling passenger numbers and concerns about investment costs have stalled the project.
2010, that a group of activists, calling themselves ‘Transition Heathrow’ squatted a former market garden in Sipson to create ‘Grow Heathrow’.


They cleaned up the site which had been an unauthorised car parking lot, repaired the site’s old greenhouse, and became a community skills resource .



trees give funding guide on permac -


While grow heathrow was evicted in 2021, Its team members continue to work on projects in the harmondsworth town.

(“Grow Heathrow [Squat!net],” n.d.) (new


hire members organize activities education on susatainability holding events
The guerrilla gardening near Heathrow Airport has undergone a transition from radical squatting (gray area in the diagram) to volunteer-led activities (colorful area in the diagram). Throughout this process, the purpose of the activities has remained unchanged: to protest against the construction of the third runway in a sustainable manner. However, the stakeholders involved in individual guerrilla gardening have increased. Apart from the support and guidance of the Transition Network, other artistic organizations and schools have also built connections with individual guerrilla gardeners. This has contributed to the sustainable development and expansion of gardening activities, thereby influencing the decisions of local governments.



TEMPORARY LANDSCAPE&RECONSTRUCT
CASE: GROW HEATHROW




Seed bomb is a method of planting without requiring people to visit the site as they would in traditional planting methods. They bombs require less preperation work, such as tilling and maintenance. What is more, they contain nutrients that support seed germination and growth, reducing the need for additional fertilization.

Use fungi for mycoremediation in order to clean polluted soil (adapted from Millson,2023)
Use drainage pipe for windrow composting (adapted from Millson,2023)

WATER CATCHMENT WITH EARTHWORK: SWALE
STEP1: EVALUATE SLOPE
Deciding whther to turn Site A from the current community garden into green space surrounding the future runway will take approximately 15 years. This process is highly unpredicable. However, people will have enough time to change it through guerrilla gardening methods before Site A is changed. During guerrilla gardening, the designers often use local materials to construct temporary landscapes. These practices can be referred to for the process of constructing site A. These graphs show how people collect tree branches from the site to build the structures inside the tents. After the tents are abandoned, these branches become composting materials.

STEP2:LAY OUT THE SWALE LINES

contour lines
use A-frame to locate the contours on the land
STEP3: DIG OUT THE SOIL
How the swales work on sites with different slopes (“Install Swales | Permaculture Conversion,” n.d.)
bio-swale:cobble, stone & gravel mixturé

There are many sustainable methods that can be used to regenerate soil in community gardens, such as using fungi for mycoremediation and windrow composting. The former enphysize the purifying power of fungi, while the latter recycles drainage pipes to provide suppoting materials for compost. Such practices not only reduce costs but also decrease pollution.
How to dig the soil for swales (“Install Swales | Permaculture Conversion,” n.d.)

vegetation selected to tolerate wet & dry conditions roots to stable the soil
Typical section of a vegetated swales (www.Deercreekliving.Com, 2011,redrawn by author)
m construction, the design, layout, and implementation of swales are quite affordable. They can be established on gentle slopes ranging from 0 to 15 degrees. (Barnes, n.d.)

Roadside Unregistered Land
Building

Refilled
Sipson & Harmondsworth are villages in the London Borough of Hillingdon, the westernmost borough of Greater London, England. It is on the north side of Heathrow Airport. Due to the proximity to Heathrow Airport, there are many waste management facilities around the community to centrally handle waste, such as construction debris and household garbage. Meanwhile, because of the preparation for the construction of a third runway, some pits in two communities have been filled in and turned into agricultural land. Some quarries are still in operation. There is also a wetland park in the community, converted from a landfill, designed to attract birds.
According to noise map in 2024, the average noises of the two towns reach up to above 60dB and 68dB seperatly. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines noise above 65 dB as noise pollution.

Harmondsworth Moor is owned by British Airways. The open parkland contains a variety of habits including meadows, rivers, lakes and ponds.

The former volunteer group continues their work in the recreation ground, primarily focusing on tree planting and cultural restoration.

The main users of this site are primary school students from the surrounding schools.



Local residents visit the site primarily for outdoor activities such as dog walking and tennis.

The area surrounding the site is mostly agricultural land. This picture, taken by the author, shows Brassica carinata being planted on these fields.




From a north to south, the site is located between agricultural land and residential area, with no vegetations or terrains to block noises coming from the south. From an east-west perspective, the site is surrounded by a wetland park, residential areas, and a stretch of agricultural land. Trees in the wetland can help reduce the noise slightly. In the future, this recreation ground has the potential to block noise for the surrounding community.


bricks and wooden boards from

As unmanaged land, this small space is filled with overgrown plants and litter discarded by passersby.

An aging steel fence separates the site from the road to the south.



Apart from Grow Heathrow, other unregistered roadside spaces in the Harmondsworth community could be transformed in the future using unofficial horticultural methods. Photo taken by the author.


By practicing guerrilla gardening on these unmanaged sites, people have transformed them from neglected areas into thriving gardens. These efforts provide a blueprint for others in the UK who want to assert their right to engage in productive planting.
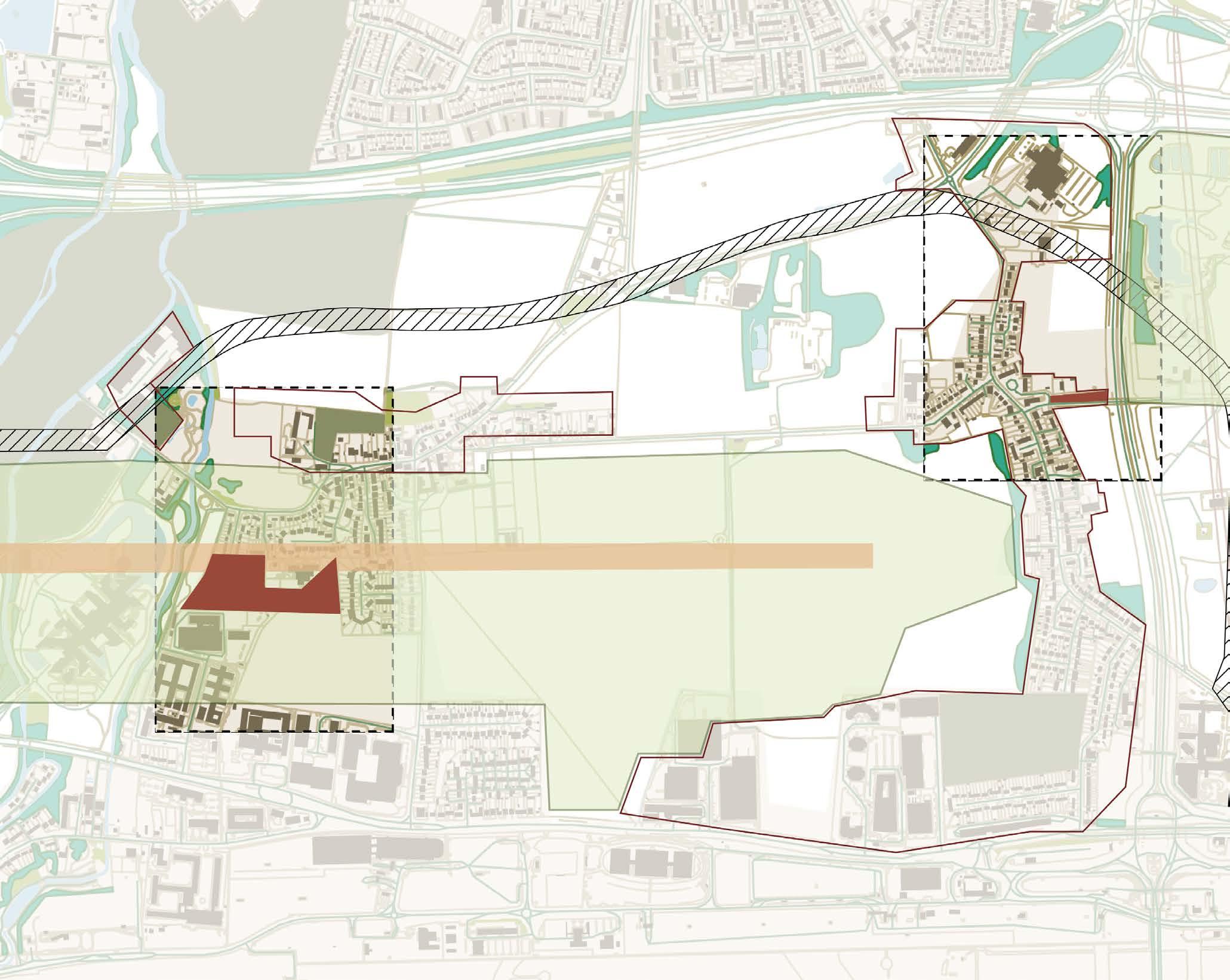
Proposed Runway Added Route

Presevered Community Boundries
Future Buffer Green Space
Due to the expansion of the third runway at Heathrow Airport, If the proposal to build a third runway is approved in the future. Nearly 1/3 part of Harmondsworth and Sipson will become the preperation lands for runway in the future.
As a result, many new green spaces will be created: some of them will be partly built on the basis of gravel pits in refill sites. Most of the community in Sipson will be preserved, while the buildings in Harmondsworth Village will be demolished. Additionally, the expansion of the airport will add a new road within the area.
(picture redrawn from heathrow airport expansion – consultation document, june 2019)

1. SELF-SUSTAINABLE
An self-sustainable site will be established for local residents to provide natural resources, offering the necessary food for daily living.
2. PROTEST LANDSCAPE
By creating gardens and land art in public spaces, the local residents’ demand for unpolluted land is communicated to the outside world. It is conveyed by daily activities of people who squatting here.
3. HANDLE UNCERTAIN FUTURE
In preparation for the uncertain future of the garden 15 years from now, materials will be gradually transferred over the course of the next 15 years.

In the construction phase, the local councils will publish relevant policies after consulting the local community and provide funding to construction firm. During this process, the local community will also provide feedback on earthwork.



Once the entire site is fully constructed, stakeholders will collaborate on its management. The Transition Network and other social organizations associated with Post Grow Heathrow will provide support for managing the site.



RECREATION GOUND NEW GROW HEATHROW
















The design strategy is divided into three distinct stages. In the first stage, earthworks and planting on the recreation ground site will be completed. During this period, preparations including the collection of demolished waste materials and pruning on the new Grow Heathrow site will also be finished.
In the second stage, people will be invited to occupy the recreation ground, which features four main landscape typologies serving different functions. Simultaneously, materials such as seeds and planters will be transferred from the recreation ground to the new site during this period of time.

In the future, if the campaign for the third runway continues, the recreation ground may be abandoned, while the new Grow Heathrow site could be preserved as a permanent location. Alternatively, if the recreation ground receives approval from the local council, and the third runway is not going to be constructed. It will be maintained as a permanent productive space for community members.

Excavate soil from the site to shape a sunken landform, and use the excavated soil to create a sound barrier.
Step 1: Cut Step 2: Fill
Water-concentrated areas

Sunlight duration low high

Analyze the site’s sunlight exposure and water accumulation patterns to determine the location of water catchment areas, and create shade with raised berm swales.




Fill:8840M^3
Unbalanced Amount=1340^3 (Supplemented by demolished waste))

Prototype A: cut landform to form noise reduction mounds

Use berm in landscape architecture for reducing noise in airport (Fabrique, 2010)

11m is equal to the length of sound wave made by aircrafts distance between two lanform=11m

Prototype B: cut landform to enclose underground activitie, extra soil used for plantation crops. Rainwater collected from the terrain is gathered in bioretention channels for irrigation. Any excess rainwater is discharged back into the river channels of harmondsworth moor




Build tents on top of curved ground to provide shadow. The place is used for tool storage and composting.
Slope stablization by adding concrete retaining walls or pile retaining wall. People will be ensured with safe places to do horticulture in micro gardens.
Plant floral meadows on the topsoil of noise reduction landforms to create habitats for bees and butterflies.
Enhance productivity by shaping the topsoil of noise reduction landforms into ridge system.

An elevated walkway atop the curved-down landform serves as both a tourist attraction and a site for seed restoration.

Residents help prune the plants in noise reduction area.


















The selection of plants mainly focuses on three points: 1 Revegetation to create different habitats. 2. Attract local residents’ participation by using various forms of field ridges and planting beds, allowing them to grow plants they can consume themselves. 3.functional planting, including noise reduction barrier vegetation.
1.DECORATION LAWN& FLOWERAL MEADOW:
-community residents are invited to maintain and play inside
-providing space for insect pollination -Providing shelter for invertebrates
2.CROP RIDGES& TARGET GARDEN:
-stablize the soil on the ridges -community members are invited to grow their own plants to consume





3.NOISE REDUCTION BARRIER:
-Dense forests can better absorb noise from aircraft takeoffs and landings -with a rapid growth cycle, no need for longterm maintenance
4.POND/MARSH:
- Provide habitat for birds in Harmondsworth Moor
- Stabilize the bank -Purify water



IRRIGATION
WATER RESTORATION
SWALE RESTORATION POND

FLOW OF WATER
BIORETENTION CELL
water catchment The water from irrigation on crop rifges will be collected and recycled.
To manage rainwater flow from the landforms on the site, a stormwater management system has been implemented. This includes a bioretention cell, water restoration ponds, and drainage channels. Part of the collected water will be used for irrigation, while the remainder will be redirected to Harmondsworth Moor.

The main maintenance tasks for the site include mowing and pruning. The lawn area, depending on the vegetation species, should be mowed every two weeks. Additionally, the vegetation used for sound barriers needs to be pruned every 3 to 4 months.



Bricks and concrete from demolished construction waste can be recycled into hard materials for use on the design site or transferred to another location for future use.

London clay is easily to be found near Heathrow Airport. It’s impermeable feature allows it to be used as a pond lining.

Remove the nails and coating from the wooden planks, and ensure that the beams and boulders are securely joined with gravity, roots, and the ground.

Crop Ridges, they are situated on the ridge, and the excess irrigation water is collected in channels for viewing and reuse in irrigation.

This page discusses how to integrate productive landscapes with recreational landscapes on functional landforms.
NOISE-REDUCTION FOREST
A combination of local groundcover plants, shrubs, and trees is used to block noise.
PRODUCTIVE FIELD
RAIN WATER COLLECTION
Viewing platform, with the space below used for storing and making seed bombs. The seeds from the trees on site are transported here for storage.
CIRCULATION ROUTES
GUERRILLA GARDENING PLAYGROUND






By placing targets above the terrace planting beds, visitors are encouraged to throw seed bombs. A planting bed already filled with plants grown from seed bombs can be set up as an example, encouraging people to throw seed bombs into other planting beds to achieve similar results.

The ravine garden is built on an excavated landform. The main design strategy of the site focuses on two aspects: protest and functional planting.



prepare basic landform

cut the retention pond, use the soil refill to build the edges of micro gardens grow plants



The design of New Grow Heathrow primarily handles the various plants and hard materials transported from the recreation ground. These scattered green spaces provide local residents with areas where they can engage in daily gardening and connect with nature.
VEGETATION FROM RECREATION GROUND: BAMBOO

bamboo’s growth speed is quite fast, suitable for a temporary landscape

BAMBOO TRELLIS


Bamboo is a plant with a short growth cycle, typically maturing in about three years. Once mature, bamboo can be crafted into fences, trellis, and other structures, depending on its thickness.
bamboo fence separate New Grow Heathrow from the surrounding refilled land

marsh plants and reeds help filter the rainwater before residents take them for irrigation their crops.
Steps made from reclaimed concrete and wood planks from the recreational ground.

The local residents are harvesting beans and vine plants from the vertical tower. These towers were converted from bee hive towers on the recreational ground. Little soil and maintenance are needed for them.
The stalls in the recreational ground were dismantled, and the remaining pallets were used to create movable planters. Edible plants like carrots and lettuce are being grown there.
The site’s original terrain lines have been utilized to collect water, while the abundant planting beds create ample gardening spaces.



Once the noise reduction landform construction is complete, people begin to take the gardening tools they need from the guerrilla stalls in preparation for the occupation.
People begin greening the site and take their own garden sites.
A complete production system begins to take shape on the site, including planting, irrigation, fertilization, and storage.
Through pruning and maintaining the recreation ground site, people gradually begin transferring materials to New Grow Heathrow, where they establish smaller-scale guerrilla gardens.
This depends on whether the recreation ground can effectively function as a protest landscape. If it succeeds in halting the Heathrow runway project, the sound barriers will be permanently preserved and expanded throughout the community to shield residents from noise generated by the existing Heathrow runway. If the protest fails, New Grow Heathrow will still serve as a permanent site and provide a model for constructing guerrilla gardens in other parts of London.




THANK YOU!
(APPENDIX NEXT)
