
6 minute read
Indian Army shows its mettle
Apart from successfully resisting Chinese incursions along the LAC, the Indian Army was busy in other sectors also during 2020 protecting the nation’s sovereignty
General Manoj Mukund Naravane
Advertisement
PVSM, AVSM, SM, VSM, ADC Chief of Indian Army 2020 was a significant year for the Indian Army as it was kept engaged in several sectors, especially along the Line of Actual Control (LAC). The confrontation with Chinese troops on the LAC also led to emergency troop buildups and inductions.
Historically, Indian Army’s acquisitions are focused on building new capabilities as well as making up deficiencies in inventory. Modernization of the mechanized forces is intended to meet the requirements of the future battlefield. Indigenous development of future vehicle combat vehicle platforms is also being carried out. Upgrading gun and missile systems is yet another area of importance. The Army has also enhanced its interactions with Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) for the purpose.
One of the major events related to India’s Armed Forces during 2020 was the Ministry of Defence (MoD) releasing the Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020 to achieve the goal of ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ or self-reliance in Defence production. Subsequently, Defence Acquisition Council (DAC), headed by the Defence Minister, approved acquisition of weapon systems worth 28,000 crore of which equipment costing Rs 27,000 crore are to be sourced from Indian industry. Meanwhile, steps were initiated to clear the first set of Acceptance of Necessity (AoNs), with the majority of them in the category of Indigenously Designed Developed and Manufactured (IDDM). The proposals approved include Modular Bridges for the Indian Army.
Earlier, DAC had delegated powers to make emergency purchases worth up to Rs 300 crore to the three services to meet their emergent operational requirements. The devolution of financial powers came against the backdrop of the border

tensions with China.
In 2020, the Government of India also approved the acquisition of arms and military equipment worth Rs 2,290 crore considering the military standoff with China. Proposals cleared by DAC include the acquisition of around 72,000 SIG Sauer assault rifles at a cost of Rs 780 crore. The Indian Army inducted more than 72,400 of the rifles under a fast-track procurement deal signed last year, said a report. Moreover, the DAC approved procurement of Static HF Tans-receiver sets and Smart Anti Airfield Weapon (SAAW), under the Buy Indian category. The field units of the Army will be equipped with HF radio sets to enable seamless communication under a procurement costing around Rs 540 crore.
LAC issue
In May 2020, tensions started between India and China at Galwan River Valley. Indian Army resisted Chinese incursion, resulting in the martyrdom of 20 Indian soldiers, including an officer, and reportedly 43 armed forces personnel belonging to China.
The tension soon spread to other areas along the LAC such as near Pangong Lake in Ladakh, Hot Springs and Gogra. India rushed more troops, weapons and equipment to counter the Chinese threat. The nation also spruced up its Armed Forces to enhance its military capabilities through procurements, acquisitions and tests.
India was taken by surprise by the Chinese action as the Chinese soldiers mobilised into areas where there has historically been no dispute over the LAC. Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic had led India to cancel its annual training exercise in Ladakh, which brings a brigade to the area to react quickly.
Satellite images showed that China had carried out construction activities in the areas that are claimed by India. In Hot Springs, Chinese soldiers intruded into three areas of PP14, PP15 and Gogra, backed by a large number of armed personnel and heavy equipment. There was similar massive Chinese deployment in the Galwan River Valley area.
Dialogues at various levels prevented escalation of violence but the stand-off continues.
DRDO’s efforts
Rising to the occasion, DRDO launched a series of successful tests and introduced advanced weapons and systems. For instance, the maiden launch of MRSAM (Medium Range Surface-to-Air Missile) and the successful flight test of QRSAM (Quick Reaction Surface-to Air Missile System) took place in 2020.
Moreover, an enhanced version of the PINAKA rocket system was successfully flight-tested. The transfer of the Authority Holding Sealed Particulars (AHSP) responsibility of PINAKA weapon system by DRDO to the Directorate General of Quality Assurance (DGQA) also took place. This would support the production of the PINAKA missile system, which has a range of around 37.5 km.
DRDO also completed the final user trial of the NAG missile during the year. Yet another achievement was the successful flight test of the indigenouslydeveloped Anti-Radiation Missile (RUDRAM). Test firings of laser-guided ATGM (Anti-Tank Guided Missile) and Abhyas – High-speed Expendable Aerial Target (HEAT) also were a success.

TESTING SIMULATOR FOR FUZE YDB – 60

Charudatta Alegaonkar
CEO Pune Polytronics Pvt. Ltd.
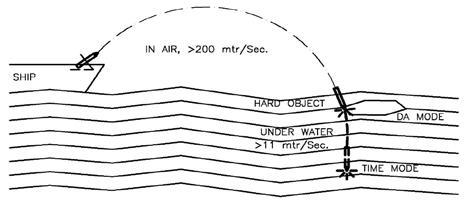
Pune Polytronics Pvt. Ltd., Pune, India has developed a Testing Simulator to test the fuze YDB-60 for Navy’s one of the oldest proven rocket RGB-60. Its an anti submarine weapon with a range of 1500 to 6000 mtrs that can function inside a water column of 500 mtrs.
Now, with the development of the simulator, the fuze YDB-60 is possible to test in a laboratory. Going for sample testing / inspection of fuzes in deep sea waters is very expensive and time-consuming proposition.
The new simulator developed first time in India will save lot of Govt. funds and months delays in testing. Development of simulator was a big challenge as the fuze functioning is very complex. There are two main safeties provided in the fuze, one is at the time of releasing from the rocket and another is releasing while entering the waters. The second safety event triggers a ‘Time Mechanism’ provided in the simulator as well as allows the firing of chain of events inside the fuze to act in ‘Direct Action’ (DA) mode once the rocket hits any hard surface inside the water viz. submarine or in ‘Sympathetic’ mode of explosion of a nearby RGB-60 rocket.
Process of testing:
In this simulator, we had to simulate ‘g’ value of a certain set-back force generated while launching the rocket. And simultaneously to simulate ‘g’ value of a certain set forward force actually generated while entering the rocket in water. The time, which corresponds to the set depth value is measured and compared in specified accuracy limits. The whole test cycle of simulation is fully automatic, robotic, and remote controlled as the fuze is filled with ammunition. No manual intervention is allowed in testing area / room. You can start the auto test cycle after entering fuze details and monitor the progress through CCTV camera. The results of the test with all required details as decided, get logged continuously on a computer.
FUZE YDB-60

Developed by: PUNE POLYTRONICS PVT. LTD., PUNE, INDIA.
Indian Coast Guard Celebrates 45th Raising Day
Indian Coast Guard celebrates its 45th Raising Day on 01 Feb 2021. From a modest beginning with just 07 surface platforms in 1978, ICG has grown into a formidable force with 156 ships and 62 aircraft in its inventory and is likely to achieve targeted force levels of 200 surface platforms and 80 aircraft by 2025.
As the fourth largest Coast Guard in the world, Indian Coast Guard has played a significant role in securing the Indian Coasts and enforcing regulations within the Maritime Zones of India. True to its motto “Vayam Rakshamah” meaning “We Protect”, the service has to its credit saving over 10,000 lives and apprehending around 14,000 miscreants since inception in 1977. On an average, Coast Guard saves one precious life every second day at sea.
Despite the restrictions imposed by the ‘COVID-19’ pandemic, Indian Coast Guard has maintained 24×7 vigil in the Exclusive Economic Zone, by deploying about 50 ships and 12 aircraft daily. The deterrence at sea and coordinated air surveillance by the service enabled seizure of contraband worth about ₹ 1,500 Crore and apprehension of more than 10 foreign fishing boats with 80 miscreants illegally operating in the Indian EEZ alone in year 2020.










