1 minute read
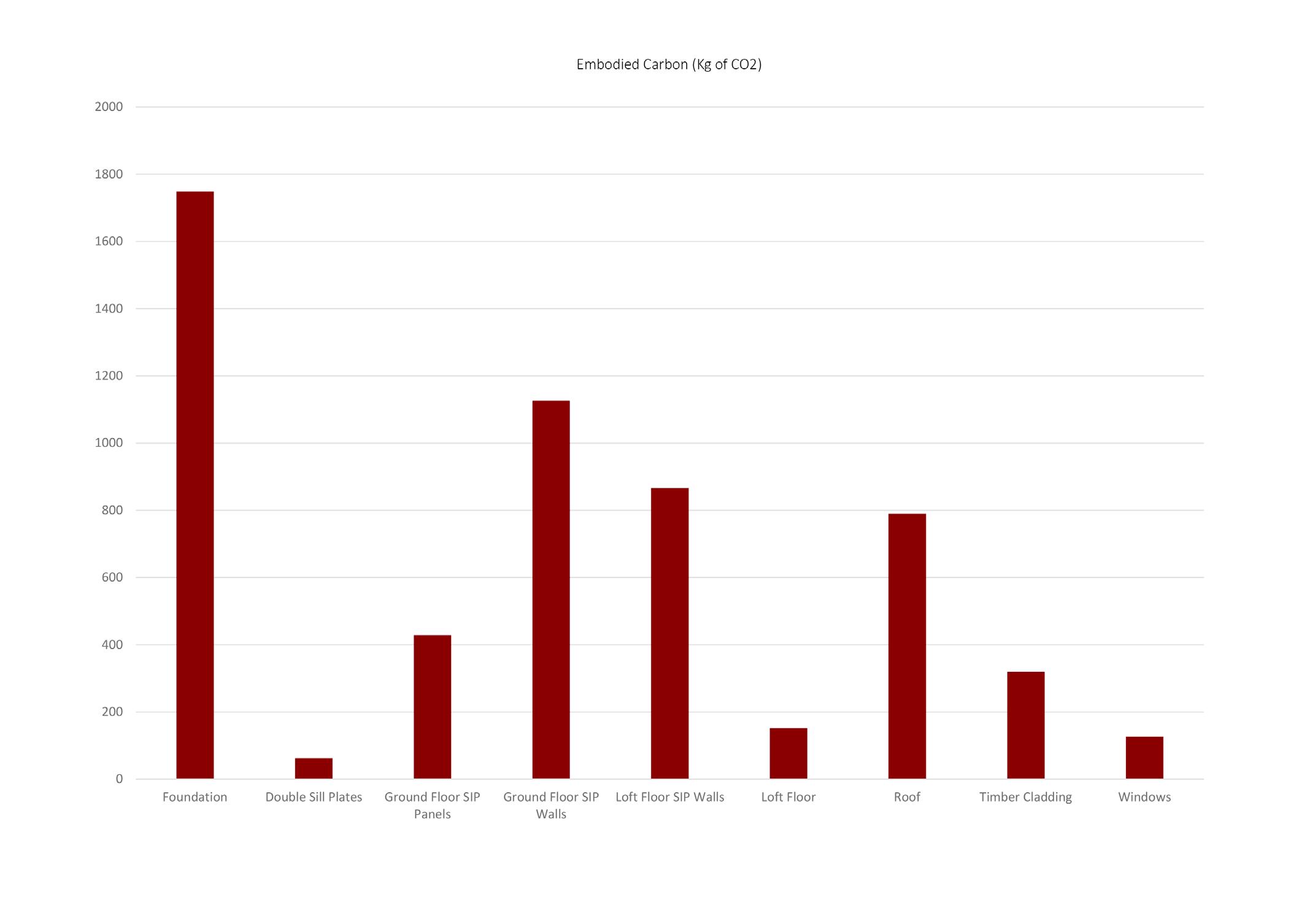
CARBON ANALYSIS FINDINGS
Heating And Cooling
Heating and cooling account for 50% of energy use in the average home, making insulation the natural starting point to profoundly impact a structure’s energy performance. SIPs provide high-performance continuous insulation that maintains its stated R-value for the lifetime of the structure.
Advertisement
Rather than offsetting the carbon emissions and energy usage directly through domestic technology, the SIPs focus on reducing the heating and cooling needs of the building through its airtightness, reduced thermal bridging and insulation.
The external walls and roof panels contain SIP block splines to connect the panels with minimal timber only on the top, bottom and endplates. The block splines lower the chances of thermal bridging and heat loss by being an insulated block rather than a timber stud.

Shading and cooling can be reduced by 10% during the summer through the trees on the site. The shade from the trees is able to reduce the cooling costs typically used during summer.
Based on the Insulation for Environmental Sustainability A Guide by XCO2, Buildings are responsible for 50% of EU energy use. The diagram highlights that insulation is the greatest potential in saving C02 emissions compared to other building measures. Using the SIPs significantly improves the thermal insulation of the building compared to traditional timber frame construction. The SIPs have a U-value of 0.13 which is within the Passivhaus standards.