
1 minute read
‘NATIVE’ TOWNSHIPS IN SOUTH AFRICA
from APPROPRIATING MODERNISM: APARTHEID AND THE SOUTH AFRICAN TOWNSHIP ERROL HAARHOFF School of Architect
(Calderwood, 1953, p31)
• Mass housing system - Cost minimization
Advertisement
• Largely technical approach
• Apartheid remains the “elephant in the room’’
• Scientific (Housing standards and neighborhood planning)
• Stresses the importance social surveys
• Works used : P. Geddes, L. Mumford, C. Stein
• “Neighborhood unit", "British New Town Movement"
• Calderwood : "(social, scientific) survey before plan" - core principle, but Apartheid did not follow . Focused on technical, not social surveys
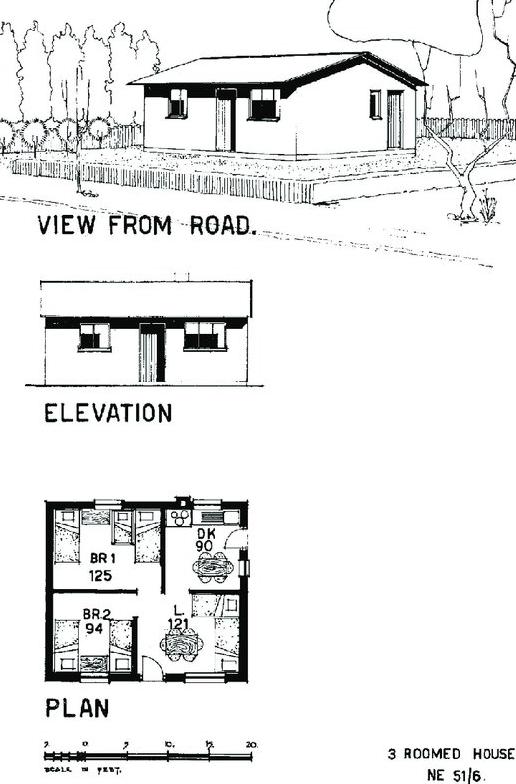
• minimum standards - 3 housing types
• First we must erect a standard of living In terms of housing, the minimum standards are set by objective criteria of air, water, sunlight, heat, privacy and so forth (Mumford cited in Calderwood, 1953 p 14
• HOWEVER ‘’ information of this type relating to the urbanizing Black population was either not available or still to be obtained‘’
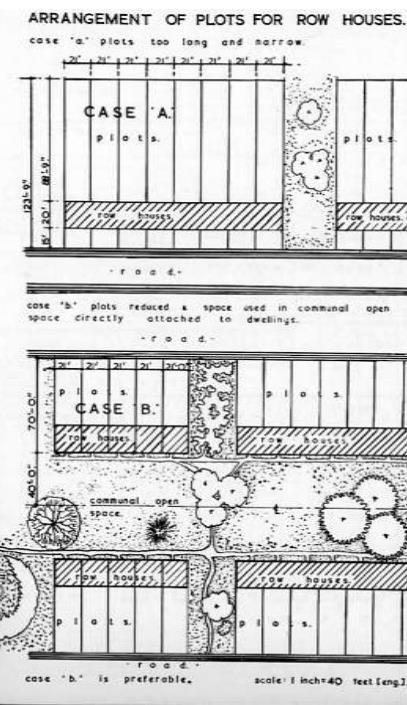
Case A plots too long and narrow Case B plots reduced a space used in communal open space directly attached to dwellings. Accommodating pedestrian movement Case B is preferable.

• Suggested to:
• Humanizing the inevitable monotony of the township
• Landscaping and the encouragement of individual private gardens
• Reflective of the Modernist position „pre machine age Garden City ‟ to the modern world
• Strong advocacy for home ownership > contradiction to the government stance temporary residents of „white ‟ urban areas)
• WAIVER
• Administrative point of view > easier to administer .
• National point of view > main bastions against Communism and other social ills
Conclusion
• Modernism's failure : too focused on technical, not social ,(FOR US, 1962 )
• 16 June 1976, police fired into a large crowd of schoolchildren in the township of Soweto, Johannesburg
• Native townships became symbol of revolt to end apartheid leading to democratic elections in 1993
• Apartheid : embedded in South African systems, hard to change (beyond laws) due to " spatial segregation "
• “Most inefficient cities“ ( Mabin & Smit, 1997) . - spatial separation, fragmentation, sprawling, social and economic inequalities




