1 minute read
Octopuses I Squid I Blowfish
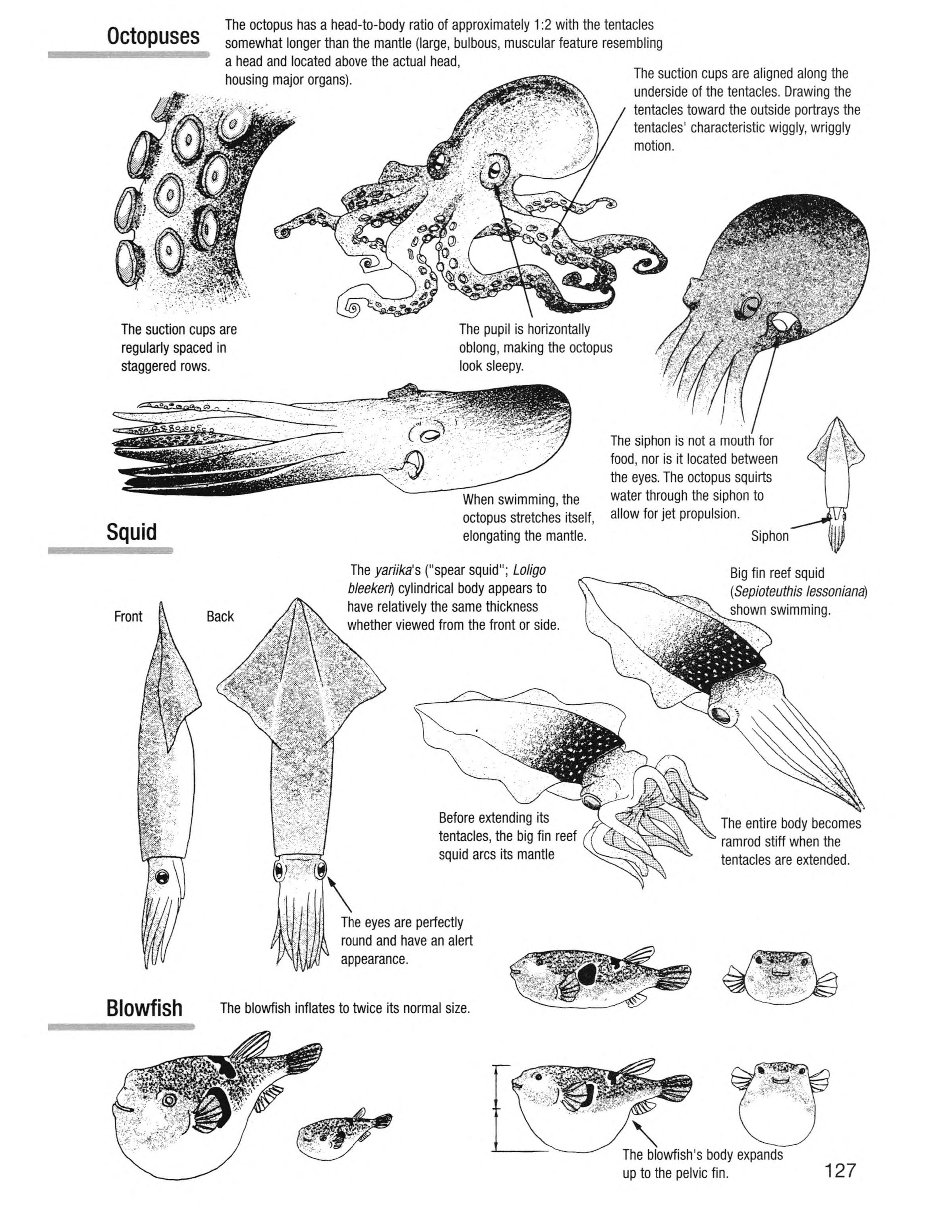
Octopuses The octopus has a head-to-body ratio of approximately 1 :2 with the tentacles somewhat longer than the mantle (large, bulbous, muscular feature resembling a head and located above the actual head, housing major organs). The suction cups are aligned along the underside of the tentacles. Drawing the tentacles toward the outside portrays the tentacles' characteristic wiggly, wriggly motion.
The suction cups are regularly spaced in staggered rows.
Advertisement
Squid
Back The pupil is horizontally oblong, making the octopus look sleepy.
When swimming, the octopus stretches itself, elongating the mantle.
The yariika's ("spear squid"; Loligo cylindrical body appears to have relatively the same thickness whether viewed from the front or side. The siphon is not a for food, nor is it located between the eyes. The octopus squirts water through the siphon to allow for jet propulsion.
Siphon
Big fin reef squid (Sepioteuthis lessoniana) shown swimming.
Blowfish
Before extending its tentacles, the big fin reef squid arcs its mantle
The eyes are perfectly round and have an alert appearance.
The blowfish inflates to twice its normal size. The entire body becomes ramrod stiff when the tentacles are extended.
"The blowfish's body expands up to the pelvic fin. 127










