
•
•
•
•
•


•
•
•
•
•















In an especially difficult year for many, Meridian employees rallied round for their communities with a Holiday Food & Toy Drive and doubled down to give more time and money through its Employees Corporate Giving Program. Senior leaders made a surprise donation of $67,000, which is being shared with three charities. Employees unlocked nearly $800,000. In 2022 through Meridian’s award-winning employee giving program, My Commitment to Communities, Meridian employees logged $486,000 in donations unlocking an additional $310,000 in donation matching for a total impact of nearly $800,000. Meridian capped off our impact with our annual Year End Giving Campaign launched on Giving Tuesday, November 29th. During the campaign, employee donations were double matched and annual matching allowances increased to $2,000 per employee, up from $1,000. The Year End Giving Campaign drove $312,000 of total impact.
CIBC announced today that $6 million was raised for children’s charities globally during the 38th annual CIBC Miracle Day. Every year CIBC Capital Markets traders and CIBC Wood Gundy investment advisors donate their fees and commissions to help kids access vital support programs and services that help them thrive. This year’s CIBC Miracle Day brought together celebrities, athletes, musicians, singers, charities and CIBC team members — all with the goal of raising funds to improve the lives of children around the world. Longstanding supporters Scott McGillivray, Tessa Virtue, Pinball Clemons, Mira Sorvino, Simple Plan, Charles Oakley and Bruce Croxon, were among the special guests who brought their energy and enthusiasm to highlight the incredible and inspiring work of children’s charities. CIBC Miracle Day is an annual event that supports invaluable work done by children’s charities around the world. CIBC began this giving tradition in 1984, and has since raised more than $272 million globally, helping to transform the lives of children and communities worldwide. The new CIBC Foundation, which serves to advance social and economic equity, administers the funds raised on CIBC Miracle Day. Funds are distributed throughout the year and play an instrumental role in helping children access vital support services and programs.
BMO employees have pledged more than $31 million to the United Way and thousands of other community organizations across North America, setting a new BMO record and exceeding the bank’s annual Employee Giving Campaign target by $5 million. Since kicking off their annual campaign, 88 per cent of BMO employees across North America came together to reach beyond and Boldly Grow the Good in business and life, by making donations to thousands of organizations. These donations will help address the disproportionate impacts felt more acutely by the most vulnerable in our society, and drive progress in a year which saw higher costs for basic life essentials. Over the last decade, the BMO employee-driven campaign, has raised more than $200 million delivering on its aim to be a Purpose-driven organization with a culture of giving back.
McDonald’s Canada and 4-H Canada launched of the National Youth Scholarship program as a part of the next iteration of a longstanding relationship between the two organizations. As part of this partnership, sixteen scholarships totaling $80,000 will be awarded over two years to senior youth leaders from coast to coast to coast and will be aimed at advancing important work in sustainability and educational pursuits in agriculture. 4-H Canada is empowering youth to be responsible, caring and contributing leaders that affect positive change in the world around them. The Leadership Development Pillars of 4-H Canada -Sustainable Agriculture & Food Security, Science & Technology, the Environment & Healthy Living, Community Engagement & Communications - are all areas that are incredibly relevant and important to the current generation of youth, and which align with the concerns of Canada’s government, global community, and McDonald’s Canada.



Publisher / Corporate Sales Steve Lloyd steve@totalfinance.ca
Leigh Anderson, Senior Economist, FCC Thomas Anderson, Managing Director, Moneycorp Americas
Fiona Roach Canning, Co-Founder & President, Pollinate
Andrew Eppich, Managing Director, Equinix Canada
Anthony Messina, President, Guardian Partners Inc.
Jon Purther, Director Market Insights, Payments Canada
Creative Direction / Production Jennifer O’Neill, jennifer@totalfinance.ca




Photographer Gary Tannyan
President Steve Lloyd, steve@totalfinance.ca
For subscription, circulation and change of address information, contact: subscriptions@totalfinance.ca

Publications Mail Agreement No. 40050803 Return undeliverable Canadian addresses to:
Circulation Department 302-137 Main Street North Markham ON L3P 1Y2 t: 905.201.6600 • f: 905.201.6601 info@totalfinance.ca www.totalfinance.ca
Twitter: @totalfinancemag Subscriptions
The Ontario Securities Commission (OSC) is announcing that Kevan Cowan began his term as OSC Chair of the Board effective December 15, 2022, by way of an Order in Council approved and ordered by the Lieutenant Governor of Ontario.
“I am honoured to take on this leadership role with the OSC, an organization I have long admired, and with which I have worked closely both as a director and throughout my career,” said Mr. Cowan. “I look forward to further collaboration with the talented staff at the OSC who continually demonstrate their deep commitment to public service and to strengthening Ontario’s capital markets.”
Cowan was appointed Chair of the OSC by the Ontario government on November 30, 2022. His term as Chair continues until April 29, 2024, which corresponds with the term of his initial two-year appointment as part-time director that began with the proclamation of the Securities Commission Act, 2021, on April 29, 2022.
“The OSC will benefit tremendously from Kevan’s sound judgement and deep capital markets experience as we continue to fulfil our expanded mandate within our new governance structure,” said the OSC’s Chief Executive Officer, Grant Vingoe. “With Kevan’s leadership and the strength of our board and team, we are wellpositioned to continue modernizing regulation and facilitating financial innovation while promoting safe, fair, efficient and competitive capital markets in Ontario.”
Kevan Cowan is a financial services executive and lawyer with more than 30 years of experience in capital markets operational, regulatory and policy matters. He is the past Chief Executive Officer of the Capital Markets Authority Implementation Organization, the past President of TSX Markets responsible for all TSX stock exchanges, and the past President of the TSX Venture Exchange. Kevan has served on many boards and in advisory roles, including with the Investment Industry Regulatory Organization of Canada, the Ontario Capital Markets Modernization Taskforce Expert Advisory Group, and as Chair of the Board of the Toronto Financial Services Alliance / Toronto Finance International.
The mandate of the OSC is to provide protection to investors from unfair, improper or fraudulent practices, to foster fair, efficient and competitive capital markets and confidence in the capital markets, to foster capital formation, and to contribute to the stability of the financial system and the reduction of systemic risk.
AutoCanada Inc., a multi-location North American automobile dealership group, announced today that Azim Lalani will be appointed as its new Chief Financial Officer, effective in the first quarter of 2023. He will be based at the Company’s Edmonton headquarters.
Azim has over 25 years of financial experience and has held senior management roles in several public and private real estate and operating companies with responsibility for financial reporting, treasury, corporate finance, taxation, investor relations and risk management. He joins AutoCanada from a real estate development and management company, where he has served as Senior Vice President, Finance and Accounting. Previously, Azim was the Chief Financial Officer of American Hotel Income Properties REIT LP (TSX: HOT.UN), where he oversaw the REIT’s growth from an enterprise value of US$350 million to over US$1.1 billion with a diversified portfolio of franchised hotels located across the United States.
Azim is currently Co-Vice Chair of the Board of Governors and Chair of the Finance Committee at the University of British Columbia. He is also a Corporate Director with UBC Investment Management Trust and the Chair of the Audit Committee of the Family Services of the North Shore.
Azim is a CPA (CA) and CBV, and started his career with KPMG LLP in Vancouver.
easily align operations to extract further synergies and learnings at the core of our business. Alex is uniquely positioned to take on this new role with his impressive leadership experience in convenience and fuel operations as well as his extensive contributions growing the business across all our geographies.”
Miller, who is currently the Corporation’s Executive Vice President, Operations North America and Global Commercial Optimization, brings over 25 years of management experience in the retail fuel/convenience store industry including over 10 years at Couche-Tard. During his tenure at the Corporation, Mr. Miller has demonstrated outstanding leadership skills that engage and empower effective and collaborative teams across multiple functions and business channels.
“I am humbled and honored to take on this new role of Chief Operating Officer for CoucheTard,” says Mr. Miller. “I believe we have one of the best operations teams in the industry and by pulling together across our many geographies and programs, we can better fulfill our mission of making our customers’ lives a little easier every day as well as our vision of becoming the world’s preferred destination for convenience and mobility. I am excited by the strategic opportunities and future that lies ahead for our team members, customers, and stakeholders.”
Alimentation Couche-Tard Inc. is pleased to announce the appointment of Mr. Alex Miller to its newly created position of Chief Operating Officer effective January 2, 2023. In his new role, he will be overseeing North America, Europe and Asia operations, including its food program, merchandise procurement and supply chain activities.
Miller will be responsible for translating the strategic vision of the business into executable plans and activities to drive revenue growth and operating efficiency, while controlling expenses. As Chief Operating Officer, Miller will continue to report to the Corporation’s President & CEO, Brian Hannasch.

Brian Hannasch, Couche-Tard’s President and Chief Executive Officer adds: “By bringing together all the operational reporting lines under the Chief Operating Officer, the regional teams can more
Couche-Tard is a global leader in convenience and fuel retail, operating in 24 countries and territories, with more than 14,300 stores, of which approximately 10,900 offer road transportation fuel. With its well-known Couche-Tard and Circle K banners, it is one of the largest independent convenience store operators in the United States and it is a leader in the convenience store industry and road transportation fuel retail in Canada, Scandinavia, the Baltics, as well as in Ireland. It also has an important presence in Poland and Hong Kong SAR. Approximately 122,000 people are employed throughout its network.
SEI announced that Karla Webster Gill has been named Managing Director and Head of Asset Management Distribution for SEI Investments Canada Company (SEI Canada). A 16-year SEI veteran, Gill brings more than 27 years of industry experience.
Wayne Withrow, Head of SEI Global Asset Management, said: “Karla’s commitment to helping our clients achieve greater results and the tremendous relationships she’s built are a testament to SEI’s mission to build brave futuresSM through the power of connection. Her expertise
and experience will be critical in expanding our strategic partnerships in Canada. I’m confident that Karla will continue to drive our growth strategy and deliver enhanced solutions that help our clients succeed.
“As we focus on seizing opportunities to execute against SEI’s key strategic areas of talent, culture, and growth, her appointment reflects our efforts to promote internal mobility and evolve leadership.”
In her role, Gill is responsible for supporting the distribution of SEI’s investment strategies and solutions, developing customized asset management programs, and guiding the vision and business strategy in Canada. She previously served as Director of Business Development for SEI Asset Management Distribution, and prior to joining SEI, Gill held roles at BMO Nesbitt Burns. She holds a Personal Financial Planner designation and was as a 2022 recipient of the RIA’s financial credentials in recognition of expertise in responsible investing.

Commenting on her appointment, Gill said: “I’m excited to expand my role in helping wealth management organizations face and embrace change, overcome challenges, and grow their businesses. I look forward to continue strengthening our client relationships and building new ones to deliver investment management solutions aligned to investors’ financial goals.”
This role was previously held by Andy Mitchell, who is leaving SEI to pursue another opportunity.
SEI founded its Canadian business in 1983, pioneering innovative asset management techniques for institutional investors. SEI delivers technology and investment solutions that connect the financial services industry. With capabilities across investment processing, operations, and asset management, SEI works with corporations, financial institutions and professionals, and ultrahigh-net-worth families to solve problems, manage change and help protect assets — for growth today and in the future. As of Sept. 30, 2022, SEI manages, advises, or administers approximately $1.2 trillion in assets.
Jo Taylor. “Charley has played a pivotal role in delivering service excellence to our 333,000 active and retired teachers, through a focus on self-funded growth, digital transformation and innovation. Under her strong leadership, we are wellpositioned to further strengthen our mission to deliver outstanding service and retirement security for our members.”
Charley brings more than 20 years of experience in client services operational management, business transformation and strategy to her new role. She joined Ontario Teachers’ in 2015 to oversee all aspects of services delivered to our members. Charley holds an LLB from the University of East London, U.K. and an MBA from the University of Toronto, Rotman School of Management.
Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan Board (Ontario Teachers’) is a global investor with net assets of $242.5 billion as at June 30, 2022. We invest in more than 50 countries in a broad array of assets including public and private equities, fixed income, credit, commodities, natural resources, infrastructure, real estate and venture growth to deliver retirement income for 333,000 working members and pensioners.
Dr. Puffer brings with her an excellent investment track record and a wealth of experience in traditional and alternative investments, capital markets, and pension governance. She has held CEO, senior roles and board positions at major Canadian pension funds and investment dealers. Most recently, she was the President and Chief Executive Officer at CN Investment Division, accountable for all aspects of the investment management and organizational oversight of the CN Pension Trust Funds. She is the former vice-chair of the Board of the Healthcare of Ontario Pension Plan (HOOPP) and past president of Women in Capital Markets. Dr. Puffer is a CFA charterholder and received her Ph.D. in Finance and Statistics from the Simon Business School, University of Rochester.
“I am delighted to have Marlene join AIMCo. She is both a fantastic addition to the company and a complement to our leadership team,” said Evan Siddall, CEO of AIMCo. “I look forward to Marlene’s guidance and investment acumen, to ensure we are at the forefront of global asset management, as we aim to fulfill our purpose for our clients and build a better financial future for all Albertans.”

As Chief Investment Officer, Dr. Puffer will serve as Head of both Public and Private Investments –responsible for Real Estate, Infrastructure, Private Equity and Private Debt and Loan, Fixed Income, Private Mortgages, Economics and Fund Strategy and Public Equities – addressing clients’ needs for both liquid and illiquid investments.
With Dr. Puffer’s appointment, Sandra Lau, who most recently served as Interim CIO, has decided to leave AIMCo.
“I want to acknowledge and thank Sandra Lau for her deep commitment to AIMCo and trackrecord of delivering client value over the past 24 years. Her passion for AIMCo is undeniable and her contributions to the organization, especially her commitment to our DEI principles, will continue to position AIMCo for success in the future,” said Siddall. “While we are very sad to see her go, we wish Sandra the very best for the future. She would be an asset to any investment organization.”
Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan Board appointed Charley Butler as Chief Pension Officer, effective January 1, 2023. Based in Toronto, Butler will become a member of Ontario Teachers’ Executive Team and report to Jo Taylor, President and Chief Executive Officer. Charley takes on this role from Tracy Abel, currently Chief Operations and Pension Officer, who will continue to be Chief Operations Officer and a member of the Executive Team.
“I am very pleased to welcome Charley to the Executive Team as Chief Pension Officer,” said
Alberta Investment Management Corporation appointed Dr. Marlene Puffer as Chief Investment Officer. She will assume her new role on January 30, 2023. Dr. Puffer is an accomplished investor and leader with over 25 years of experience in both cross-asset class portfolio management and liability driven investment.
Sandra began her career at AIMCo in 1999, and her tenacity and investment expertise gave her opportunity to hold progressively more senior positions. Prior to her role as Co-CIO and Head of Public Investments, a role she held before her current interim role, Sandra successfully led Global Fixed Income investments with record top quartile performance for over a decade.
AIMCo is one of Canada’s largest and most diversified institutional investment managers with more than $160 billion of assets under


















































































































































































management. AIMCo was established on January 1, 2008 with a mandate to provide superior long-term investment results for its clients. AIMCo operates at arms-length from the Government of Alberta and invests globally on behalf of 32 pension, endowment and government funds in the Province of Alberta.
as a leader in Bitcoin mining and high-performance computing.”
Hut 8 is one of North America’s largest innovation-focused digital asset miners, led by a team of business-building technologists, bullish on bitcoin, blockchain, Web 3.0, and bridging the nascent and traditional high performance computing worlds.
practice serving clients across North America and Europe.
“I’m delighted to welcome Nav into Aviva’s executive leadership team. Nav brings with him a broad range of experience in corporate strategy, investor relations and performance management and I’m looking forward to him playing a key role in our continued growth and success,” says Jason Storah, Chief Executive Officer of Aviva Canada.
Hut 8 Mining Corp., one of North America’s largest, innovation-focused digital asset mining pioneers and high performance computing infrastructure provider, is pleased to announce the appointment of Shenif Visram, CPA, CMA as the company’s Chief Financial Officer (CFO), effective immediately. With more than 20 years of financial management experience in the infrastructure and technology businesses, Shenif brings a wealth of leadership expertise working in medium and large public and private companies.
Shenif, who will be based in Toronto and will report to CEO Jaime Leverton, is replacing Hut 8’s CFO Shane Downey, who is moving on to pursue new opportunities after 20 months with the organization.
“With deep financial experience at IBM Canada, Cogeco Peer 1, and Aptum Technologies, Shenif is a senior leader with excellent financial acumen and the skill set we need to lead us through the next crucial growth period at Hut 8,” said Jaime Leverton, Chief Executive Officer of Hut 8. “The Board and I would like to thank Shane for his dedication through a significant period of change at Hut 8, including the strategic expansion of our business into high performance computing.”
Shenif began his finance career with IBM Canada, quickly progressing to take on CFO roles within key business units including Global Business Services, Global Technology Services, and leading as Chief Operating Officer in Global Business Services. He then moved to Cogeco Peer 1 as Vice President, Finance, before assuming the CFO role, which he led through the company’s rebranding to Aptum Technologies, a multi-cloud managed services provider delivering complex, high performance computing solutions.
“I am incredibly energized by the opportunity to work with a team of seasoned executives with robust backgrounds in this exciting industry,” said Shenif. “Leveraging my previous experience in M&A and driving growth in the infrastructure technology space, I am eager to make a meaningful contribution at Hut 8 by building on our established balance sheet-first approach as we continue to successfully navigate the market by executing on our differentiated strategy and grow
iAnthus Capital Holdings, Inc., which owns, operates and partners with regulated cannabis operations across the United States, is pleased to announce the appointment of Philippe Faraut as Chief Financial Officer of the Company, effective immediately.
“We are very excited for Philippe to join iAnthus as Chief Financial Officer. Philippe brings over 20 years of senior CPG financial management and leadership expertise to the Company, and we are thrilled to work with him as we drive iAnthus forward,” commented Interim CEO, Robert Galvin.
Philippe was most recently the CFO of Irwin Naturals, a mass market nutraceutical brand. Philippe led Irwin’s initial public offering and entrance into the psychedelic mental health care space. Prior to that, he was a Managing Partner of the investment banking services firm Bastiat Partners from 2016 to 2021, and served as Chief Investment Officer for Knight Global, a family office with a diversified asset portfolio from 2015 to 2016. Philippe started his finance career at Merrill Lynch in the Consumer Retail group in New York and held senior positions at the Sage Group and Intrepid Investment Bankers. He holds a Master of Business Administration degree from the Anderson School at UCLA and a Bachelor of Science degree from Glion Institute – Hotel Management School.
Philippe is replacing Julius Kalcevich who served as the Company’s CFO since October 2016. “On behalf of the Company’s board of directors, I want to thank Julius for his years of service to iAnthus. We wish him every success in his future endeavors,” said Galvin.
iAnthus owns and operates licensed cannabis cultivation, processing and dispensary facilities throughout the United States.
Aviva Canada says Nav Dhillon will join Aviva Canada as Chief Financial Officer (CFO) from December 2022. Dhillon has served in senior leaderships roles in financial planning & analysis for RSA Canada Group and most recently, Intact Financial Corporation. He also previously held leadership positions in E&Y’s insurance advisory
“I’m thrilled to join Aviva Canada, a fantastic brand within the Canadian marketplace. I look forward to working with my colleagues across the business to help Aviva achieve its potential as a best-in- class operator for our customers, partners and shareholders,” says Dhillon.
Aviva Canada is one of the leading property and casualty insurance groups in the country, providing home, automobile, lifestyle, and business insurance to 2.4 million customers
Roots, the premium outdoor lifestyle brand, announced Chief Financial Officer, Mona Kennedy, will be leaving the company to pursue other interests in the Canadian CPG sector. Leon Wu, Vice President of Finance and Strategy, will replace Ms. Kennedy as the Chief Financial Officer effective January 13, 2023.
“I have enjoyed partnering with Mona over the last few years and appreciate her contributions to the company. On behalf of the Roots team and our Board of Directors, we wish her well,” said Meghan Roach, President and CEO, Roots.
Leon Wu is to take on the role of Chief Financial Officer. Wu has played a leading role in developing the chain’s long-term strategy and has an intimate knowledge of Roots from his tenure with the brand. A talented and experienced executive, Leon will continue to build a strong foundation for future growth at Roots.
Wu joined Roots in 2016 and has increasingly taken on major roles in financial and operational matters. Over the last seven years, he has acted as a key management representative to the Roots Board of Directors as well as its investors and lenders. Most recently, he served as Vice President of Finance and Strategy, where he led the functional areas of financial reporting, financial planning and analysis, and corporate strategy.
Established in 1973, Roots is a global lifestyle brand. Starting from a small cabin in northern Canada, Roots has become a global brand with over 100 corporate retail stores in Canada, two stores in the United States, and an eCommerce platform, www.roots.com, that serves over 55 international markets.
Digitalization has been central to banking since the introduction of ATMs in the late 1960s. It has led to a rapid change in the way customers want to interact with money or matters related to it. With accelerating digital transformation changing operational risks, there has been a fundamental shift in the way businesses perceive banks or want to engage with them.
The pandemic forced almost all industries to reflect on their customer experience strategy which also meant assessing their current banking partners for seamless digital payments. According to the World Retail Banking Report 2022, 95

percent of executives found the current outdated legacy systems and technological capabilities of banks unable to fully optimize their data for customer-centric growth strategies. While scaling banking technologies to meet customer needs can be challenging, 80 percent of financial institution (FI) executives believe that banks can profit by embracing platform business models.
Business platforms: Opportunity in disruption Considering the present economic and technological disruptions, banks have shown readiness in business platforms that can help

them thrive in the new environment. By offering personalized products and services to their clients, banks have been able to gain access to profitability, innovation, and market growth. Businesses alike have benefited from this converged style of operations, helping them with risk management and providing valuable services to their partners, customers and / or employees.
By breaking down barriers in a move to scale technology, leading banks and FinTechs are already working to build an inclusive and flexible financial ecosystem that is customer focused. This includes partnering with financial third parties to offer Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) through their ecosystem. This model has shown promise especially in B2B transactions by allowing businesses to scale their financial service offerings based on their customer needs.
Flexibility and ease-of-use, a unique characteristic
Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) makes it easier for banks and businesses to send and receive payments using application programming interfaces (APIs). Transforming the B2B banking ecosystem, APIs offer scalable business opportunities to each stakeholder involved in making B2B payments. In comparison to traditional systems, they are flexible, cost-effective, and easy-to-use, which is paramount to what customers want in this digital age. Its novel banking capabilities have helped businesses run operations across the globe leading to emergence of new sectors such as the gig economy. However, just over half of a bank’s B2B APIs are currently used to connect its internal systems, according to McKinsey’s latest global survey on the State of APIs in Global Transaction Banking (GTB). While some traditional banks remain wary of this FinTech innovation, the ratio is expected to shift with most new APIs connecting banks to systems outside the organization.
This also presents an opportunity for banks to leverage APIs in order to expand their products and service offerings,
thereby creating a new revenue stream that previously did not exist.
With a potential to reach $7 trillion value globally in close to a decade, BaaS empowers businesses with new functions that unites customers in a single ecosystem. It wraps seamlessly around banks’ existing infrastructure making the solution cost-effective and easy to launch. While the majority use the service to offer domestic payments, some are already planning for the future.
The digital disruption has empowered businesses to expand their operations cross-border, making foreign exchange a greater part of their day-to-day business needs. Therefore, finding partners who can not only provide the API technology, but also help with evolving customer demands is critical to the future of banking. This includes protection against cybercrime, regulatory excellence, and personalized services to create real-time experiences for the customers. However, adapting to new banking platforms would mean that banks need to find the right talent, strategy, and operational techniques to drive growth and market expansion.
International B2B payments and FX needs
BaaS is creating rapid changes and innovations in the payment space, but B2B cross-border transactions still have significant hurdles that have yet to be overcome. One key factor that hinders many fintechs looking to tackle global payment problems is the inability to issue an International Bank Account Number
(IBAN). Being able to offer IBAN accounts to customers can allow fintechs to easily set up cross-border transactions and remove the need for complex reconciliation processes that often come packaged with international payments.
However, being able to just offer IBANs alone is not sufficient. Crossborder payments come with many other challenges such as high transaction fees, unfavourable exchange rates, and payment regulations in different jurisdictions. BaaS providers that can issue IBANs and have multi-currency management tools can make it easier for businesses to integrate their payment flows into an all-in-one ecosystem. An alternative solution to these challenges is to offer personalized services to clients, having account managers that are experts in currency markets and have a full understanding of a specific business’ needs. With either solution, one thing remains clear — BaaS providers and fintechs looking to innovate cross-border B2B payments must find a solution for the FX needs involved.
The digitalization of banking has come a long way since ATMs and with the advent of fintechs, is now an indispensable part of the financial space. This movement of digitalization, combined with a global market landscape, has caused a massive shift in how consumers make payments and has subsequently made companies dissatisfied with the status quo. The pace of business and the need for international B2B payments has increased significantly, but the backend processes are still stuck in the bygone era of paper cheques. Crossborder transfers face many hurdles but through BaaS and APIs, these challenges can be overcome. The partnership of banks and fintechs, combining established infrastructure with quick and agile innovation, will drive the future of crossborder transfers. While it may not happen immediately, BaaS will become the core of a digital revolution for international B2B payments.
ANDERSON is Managing Director, Moneycorp Americas.THOMAS
“With a potential to reach $7 trillion value globally in a decade, BaaS...unites customers in a single ecosystem.”
 BY ANDREW EPPICH
BY ANDREW EPPICH
Financial institutions in Canada and around the world are facing increased pressure to transform their offerings and systems to remain competitive and relevant with quickly evolving customers. Additionally, with continued pressure from rapidly evolving regulations, increased competition and the financial impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the banks, credit unions and other financial service providers have had to accelerate their digital transformation plans deploying hybrid public and private cloud architectures.
According to Equinix’s latest Globe Interconnect Index Vol. 5, Toronto and Montreal are tied as the second fastest growing edge metros in North and South America behind Mexico City. Toronto is forecast to continue to be the largest metro in Canada, with growth led by Financial Services. As more customers expect digital first services such as instant payment
services like Apply Pay and as e-transfers eclipse cheques as the standard way to send payments, Canada’s financial service providers will need to rethink how they approach their infrastructure needs.
As such, banks in Canada and around the world will need to make their digital infrastructure more flexible and distributed through hybrid and sustainable digital infrastructure. However, that is often easier said than done. What can they do to meet customers evolving need for digital-first services, improve agility, while futureproofing their infrastructure and embracing a sustainable approach?
Core, edge, and ecosystems are driving modern digitalization
In today’s digital economy, the most agile and adaptive business generally wins. A fixed approach to infrastructure that most financial institutions operate through is no longer feasible or sustainable.
As banks evolve and expanding their businesses locally and globally, continuing to operate traditional infrastructure
that wasn’t built using sustainability innovations can be detrimental from a carbon emissions perspective. Optimizing digital infrastructure to thrive sustainably in the future economy is the next step.
Many financial institutions are shifting their digital cores into vendor-neutral colocation facilities to enable a hybrid multicloud approach to maximize agility and realize greater efficiencies. Moving into the cloud, allows them to decommission some data centres while still running certain workloads with special security requirements on-premises.

This means banks can strike the right balance of gaining an agile infrastructure in the cloud, while meeting the strict regulatory requirements around data by leveraging their on-prem direct and secure, private interconnection.
From a sustainability perspective, there are “sunk costs” that come with operating a legacy / traditional data centre. Firstly, many of the existing data centres weren’t
built using the latest sustainability innovations. A hyperconverged infrastructure can help organizations meet their sustainability goals by run applications on fewer servers as well as adopting the latest cooling solutions employed within next-gen data centres.

The best experience for end users of financial institutions can’t be provided by relying solely on the core. To deliver the best user experience possible, transactions need to be distributed through infrastructure at the edge, allowing them to be processed in proximity to the customers and devices that initiate those transactions.
For Canadian organizations, there are data privacy and sovereignty regulations requiring data to be processed and stored locally. This means financial institutions are building out their edge infrastructures to meet regulatory requirements. To reduce the carbon footprint impact, many of these facilities are being built to run on local renewable energy sources, such as wind or
solar power.
For example, Equinix’s TR2 facility in Toronto leverages a deep lake water cooling system to reduce its power consumption. By using the city’s system to draw water from the cold depths of Lake Ontario, Equinix reduces fossil fuel energy needs by 50% or more and obviates the need for make-up water intensive heat rejection systems like cooling towers.
As hybrid multi-cloud grows more important in the financial services sector, being able to connect with more global partners quickly and securely is important as well. Implementing a simplified platform that allows financial institutions to access multiple digital and business ecosystems physically and virtually — and does not compromise performance, reliability, security or control — would be the ideal integration.
Additionally, a software-defined interconnection provides an agile, high-performance option that allows
financial institutions to spin up new secure virtual connections to multiple clouds on demand via a single physical port, without the need for additional physical hardware investments. Canadian financial institutions are already shifting to the public cloud and taking advantage of sustainable innovations from partner ecosystems, further decreasing carbon footprints and helping their customers meet their own sustainability goals.
In today’s digital economy, speed and agility can be competitive differentiators; but to be THE leader, financial institutions must take a balanced approached in transforming their services and underlying infrastructure. Doing so means meeting today’s consumers changing needs with a great end-user experience, future-proofing systems for tomorrow’s challenges, while improving embracing innovative solutions that allows them to meet increasingly aggressive sustainability goals.
 BY JON PURTHER A
BY JON PURTHER A
s we continue to move into an increasingly digital world, we are seeing major shifts in payment trends. These shifts are driven by consumers’ changing expectations, behaviours and needs — and are facilitated by payment innovation and evolving technologies.

One of the most prominent trends in Canada is an ongoing acceleration in contactless and digital payments, while cash and cheque usage continue to decline among consumers. We are also seeing the emergence of new payment methods that we can anticipate will shape Canada’s payment landscape. Some of these new ways to pay include biometric-facilitated payments, QR (quick response) codes, and buy now, pay later (BNPL) services.
BNPL is a form of short-term loan in which consumers take immediate possession of their purchases and pay for them through a series of instalment payments. While BNPL is an emerging payment service in Canada, it is gaining traction as a popular payment option offered by retail
merchants to their customers for both online and in-store purchases around the world.
The BNPL model is provided by two key players: the merchant and the BNPL provider, usually a fintech, financial institution or global payment network provider. Payments are structured so the payment amounts are equal and the payment dates follow a pre-set schedule, with the first payment due at checkout. BNPL providers collect their revenue mainly from the fees they charge the merchants that accept the loans as a customer payment option. Additional revenue is obtained from late fees or penalties charged to customers who do not fulfill the repayment terms, although most BNPL providers do not charge interest.
Currently, BNPL services in Canada have a relatively low adoption rate. According to recent research commissioned by Payments Canada, while 62 per cent of Canadians are aware of BNPL services, only one in ten Canadians have used it to make a purchase in the last 12 months. Its
limited adoption in Canada stems from a few factors. While generally, consumers can be hesitant to use new types of payments, to date few businesses in Canada offer this service, reducing the opportunity for consumers to use this new way to pay. However, we can anticipate a continued increase in the adoption of BNPL as more and more retailers and other businesses begin offering this payment option.
BNPL offers a number of benefits to consumers. Customers can apply and receive loan approval almost immediately and then pay for the first instalment easily and quickly during checkout. It can make it easier for consumers to budget spending because the payment streams are predictable (following a set amount and timeframe), and some BNPL apps come with budgeting tools. It’s also a convenient way to pay since the BNPL payment option is embedded in the e-commerce platform. Approval usually takes a few minutes to complete, compared to days for new credit card approvals, and it makes it possible for consumers to afford to pay for purchases upfront. For Canadians who either do not have access to traditional forms of credit, such as credit cards or a personal line of credit or have lower income, BNPL allows them to make purchases that otherwise would not fit their budget. Convenience, avoidance of interest, payment deferral and reduced credit card usage are key drivers cited by Canadians for using BNPL services. Another key benefit is that consumers are able to immediately take possession of a product while they are still paying for it.
In Canada, younger Canadians aged 1834 are significantly more likely than older age groups to have used BNPL to make a purchase (14 per cent report they have used it to make a purchase in the last 12 months; 17 per cent plan to make a purchase using BNPL in the next 12 months).
Canadians aged 35-54 seem willing to learn about BNPL but are more hesitant to use these services than younger generations. Canadians aged 55+ are less inclined to start using BNPL as they tend to favour other payment types to make their purchases, likely due to having more experience with making payments or having higher income or savings. Around 95 per cent of this age group have not used BNPL services before and 80 per cent said they
have no plans to use BNPL in the next year.
Young Canadians are also particularly drawn to the fact that BNPL makes it easier to budget their spending (43 per cent), it’s an easy, convenient way for making purchases (41 per cent), and it allows them to defer payment for their purchases (38 per cent). People in this age group might not have access to credit facilities, such as a credit card or personal line of credit, whereas that accessibility is much higher amongst older generations. For Canadians aged 55+, the primary appeal of BNPL services is being able to defer payments for their purchases without incurring interest payments (40 per cent).
Among Canadian BNPL service users, it is most commonly used to pay for a vacation (54 per cent), out-of-home entertainment events (38 per cent) and recurring bills like rent, utilities and internet service (36 per cent). When it comes to day-to-day purchases, such as groceries and gas, it is again younger or middle-aged Canadians who are much more likely to use BNPL.
Canadians report feeling more comfortable using BNPL services provided by their bank or credit union than any other provider. This sentiment may shift as these services become more prevalent and consumers gain familiarity and experience with BNPL services in Canada.
Beyond the benefits to consumers, BNPL also offers benefits to businesses and can ultimately support greater overall sales revenue. This can be achieved through consumers being more likely to make a purchase, spending more money per shopping visit, and shopping more regularly. Another benefit of BNPL services is that merchants are able to settle sales quickly, and it may eliminate a merchant’s chargeback and fraud risks because BNPL providers assume those risks. Merchants can also benefit from having BNPL providers directly market their product offers to consumers and by providing their customers with a seamless checkout experience via direct API integration capabilities.
While there are many benefits to consumers, BNPL services also present risks. Even though services are often interest-free, if consumers miss or are late in making payments, they can incur fees
or be sent to collections. This, in turn, can negatively impact credit scores. BNPL providers are not obligated to qualify a consumer’s ability to repay loans, unlike credit card providers. As a result, these consumers can potentially find themselves getting into an unmanageable debt load, especially if they use multiple BNPL services. The availability of BNPL credit could also encourage impulse buying.
Conversely, despite the potential benefits to merchants of offering BNPL services, there are associated risks as well. The cost of a BNPL transaction for merchants can be anywhere from two per cent to eight per cent of the purchase price of the item sold. By comparison, the typical cost of a credit or debit card transaction is between one and three per cent. Therefore, merchants rely on a bump in their overall sales volume, so that the increased revenue helps to more than offset the increased transaction cost. Related to this point is the risk that having a BNPL payment option will cause existing customers to switch away from payment options, such as credit, debit and prepaid cards that cost the merchant less to accept.
According to the Research and Markets Canada Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) Market Report 2022, BNPL is estimated to grow 48.2 per cent annually in Canada, with its value increasing from CAD$8.3 billion in 2021 to upwards of CAD$53.2 billion by 2028. As of right now, limited retailers choose to offer BNPL services but we can expect this to rapidly change. For example, in September of 2022 Amazon and Square both made BNPL options available to Canadian customers. Consumer demand may also accelerate this trend due to the prevailing economic climate with the rising cost of goods, inflationary pressures and increased interest rates. As BNPL services increase in popularity, particularly among younger consumers, merchants may gain or maintain a competitive advantage by offering BNPL as a payment option because consumers may choose to only shop where BNPL is offered. Ultimately, there is no doubt that buy now, pay later services are here to stay and that they are poised to evolve the payment landscape in Canada.
JON PURTHER is Director of Market Insights at Payments Canada

Inside The Value of Institutional DeFi SPECIAL REPORT
Decentralized finance (DeFi), which uses blockchainbased smart contracts to execute a variety of financial services activities, has seized the attention of technology developers, investors, and financial institutions. DeFi protocols have already enabled nascent markets in the crypto-asset industry on public blockchains, such as borrowing and lending as well as decentralized exchanges. Imagine the potential if the technology were to be applied to streamline transactions in foreign exchange, equities, bonds, and other real-world assets.


institutions that can adapt their technology and business models.
That’s an alluring prospect, but many DeFi protocols today are not designed for use in mainstream finance. Firms that wish to apply DeFi in their client offerings must incorporate the same, if not higher, levels of safeguards and security standards that have been developed over decades in the finance industry.
This is where we look to the idea of Institutional DeFi — a system that combines the power and efficiency of DeFi protocols with a level of safeguards to meet regulatory compliance and customersafety requirements. Many existing DeFi protocols lack identity solutions to enable institutions to meet anti-money laundering (AML), know your customer (KYC), and combatting the finance of terrorism (CFT) requirements.
Cybersecurity is another major risk, as recent high profile hacks demonstrate. There is also limited, if any, recourse for investors should something go wrong. Firms need to develop safeguards to address these challenges before DeFi protocols can be adopted at scale in mainstream finance.
To create viable Institutional DeFi solutions that fit their purpose and ambitions, we believe financial institutions need to make several key design choices to implement appropriate safeguards and drive innovation. These design choices will influence everything from the level of privacy and efficiency in transactions to the pace of user adoption and the extent of interoperability with other tokenized assets.
The choices lie in three critical areas: 1) Blockchain – which underlying network to build on and what information is visible to whom;
2) Participation – the mechanisms that determine who can develop and access solutions, and
3) Token Design– how tokens are issued, transacted, settled, and standardized.
In an effort to advance industry thinking on these issues, the Monetary Authority of Singapore launched Project Guardian in May 2022. The project aims to test the feasibility of applications in asset
tokenization and DeFi while managing risks to financial stability and integrity. Project Guardian will help MAS build a framework for a digital asset ecosystem, develop and enhance relevant policies, and provide direction on required technology standards. The project’s first pilot was being led by our co-authors DBS, Onyx by J.P. Morgan, and SBI Digital Asset Holdings. The Project Guardian pilot carried out transactions involving foreign exchange with tokenized deposits and separate transactions with government bonds, in each case, on a public blockchain network, using digital identity solutions and logic adapted from existing DeFi protocols.
The pilot demonstrated the feasibility and transformative potential of using DeFi protocols in financial markets with appropriate guardrails. It also validated the crucial role of two key factors in this process: 1) the use of regulated institutions to act as “trust anchors,” issuing and verifying the credentials of participating entities to establish the identities of transacting parties and connect with existing legal frameworks, and 2) the need for an agreed set of technical standards around business logic and token standards for interoperability.
Both are essential elements for Institutional DeFi and can be helpful across systems and jurisdictions to drive adoption, and improve transaction efficiency for a globally integrated finance industry. Broader efforts are needed, however, to unlock the full potential of Institutional DeFi and make it scalable.
The Project Guardian pilot identified seven key areas where further work is needed, such as legal clarity, adoption incentives, and technical standards alignment. We believe these areas need joint actions from multiple parties across regulators, financial intermediaries, clients, and other third parties, including DeFi communities.
The joint actions should address legal and regulatory uncertainties, establish shared standards, and seek to forge a common vision of how the industry should operate.
Given the transformative potential of Institutional DeFi, financial institutions need to develop a playbook for getting the most value out of it. Institutional DeFi will likely vary by jurisdiction and market structure, and the report suggests three
ways financial institutions should start responding:
◉ Develop a house view on Institutional DeFi implications across business portfolios. We share potential future paradigms and their implications for key sectors.
◉ Decide on a participation strategy to adapt existing business and embrace new opportunities enabled by Institutional DeFi. We suggest several questions that can help firms on their journey.
◉ Get the organization ready to fulfill its ambitions by developing the required capabilities. We identify three areas, including organizational structure, delivery model, and talent strategy.
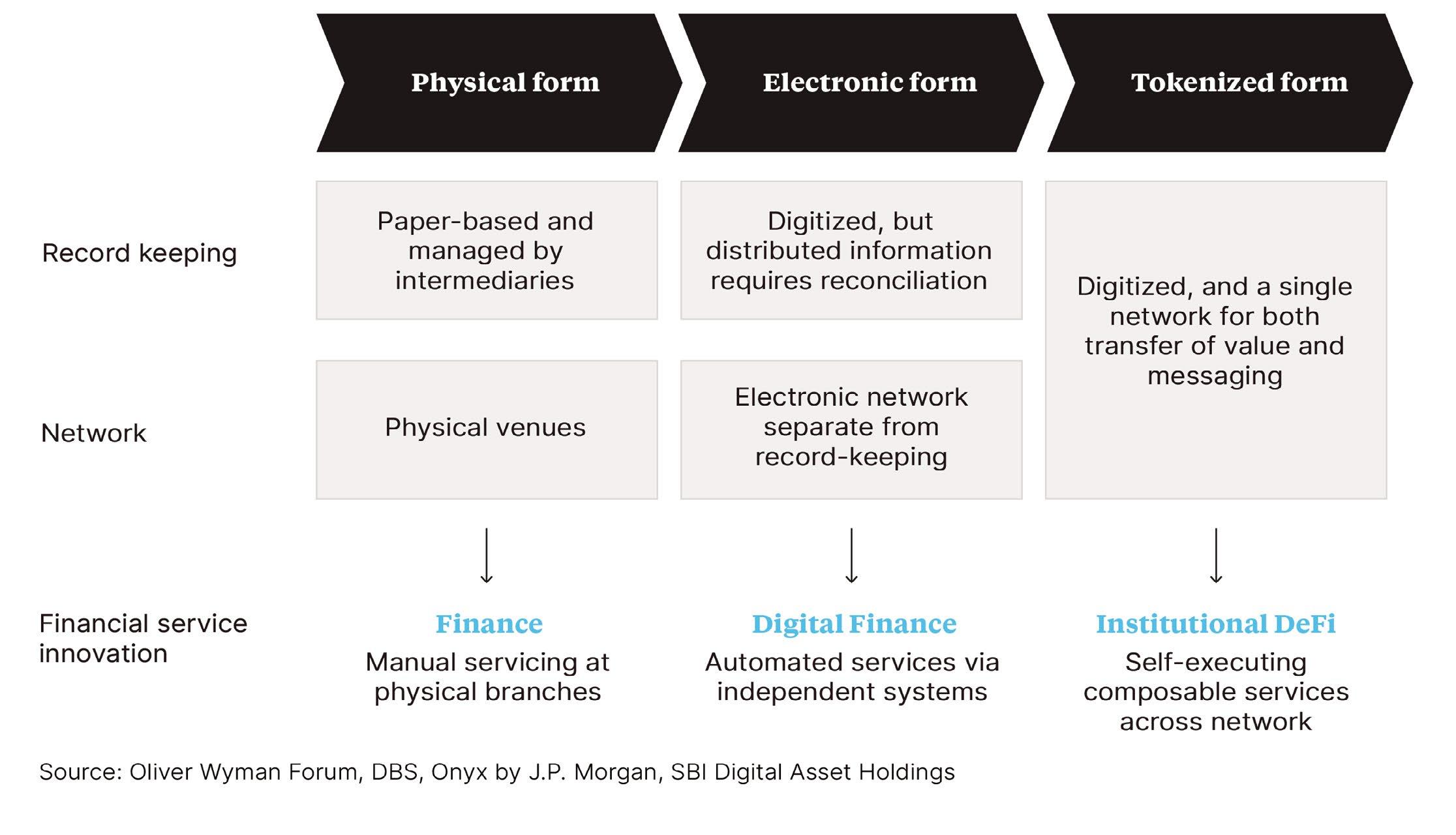
Financial services are built on trust and empowered by information. This trust rests on financial intermediaries who maintain the integrity of records covering ownership, liabilities, conditions, and covenants, among other areas, across a variety of siloed ledgers that are separate from the means they use to communicate. As each intermediary has a different piece of the puzzle, the system requires much post-transaction coordination to reconcile the various ledgers and settle transactions. For example, many securities transactions, particularly cross-border ones, can take anywhere from one to four days to settle.
Distributed ledger technology (DLT), such as blockchain, has the potential to resolve some of those inefficiencies by presenting transactional and ownership information on a single shared ledger. The growing acceptance of tokenization, which creates digital representations of assets such as a stocks and bonds on a blockchain, can extend the benefits of DLT to enable exchange and settlement of a wide range of asset classes.
Institutions can generate further efficiency by adopting DeFi protocols, which use software code to automatically execute a range of financial transactions pursuant to present rules and conditions.
We define Institutional DeFi as the application of DeFi protocols to tokenized real-world assets, combined with appropriate safeguards to ensure financial integrity, regulatory compliance, and
customer protection. (It is important to note that in the joint paper they do not refer to Institutional DeFi as institutional players participating in crypto DeFi.) The prize for innovators who hone this model for use in the world’s trillion-dollar finance industry could be substantial.
Institutional DeFi is: Real-world asset tokenization
Representation of real-world assets on a mutualized ledger, shifting from siloed records to a shared one viewable by all participants
Rapidly evolving area at the vanguard of financial services and digital assets; providing services on a blockchain settlement layer; such as lending, trading, investments, insurance, and asset management
Controls and security standards for investor protection and financial stability, for example, Know Your Customer, trade
surveillance; using a public blockchain could require more safeguards.
Tokenization is already bringing new potential to money and assets Technology continually evolves and modernizes financial services by creating new ways of executing and recording transactions. Each step in this evolution brings new business opportunities. For example, dematerialization replaced paper certificates with digital ones in the form of electronic book-entries, fostering the rise of electronic payments and trading. That, in turn, made securitization possible, which added value to previously illiquid assets such as mortgages.
Despite recent waves of digitization, trillions of dollars’ worth of real-world assets are recorded in a multiplicity of ledgers that remain separate from messaging networks. This means that financial intermediaries have to record transactions on siloed ledgers and then message each other to reconcile their books and finalize settlement. The need for coordination across ledgers and networks
between entities creates inefficiencies that increase costs and risks, lengthens settlement times, and in general adds overhead to financial services.
The past few years have witnessed an increased focus on blockchain technology as a potential panacea for resolving these inefficiencies. The promised value of blockchain comes from combining ledgers and networks in a way that allows multiple parties to see the same information, hence greatly reducing the need for reconciliation after a trade or transaction. In addition to creating a shared view of information (transaction balances, ownerships, etc.), blockchains also enable business rules and logic to be executed and viewed with high transparency and in a deterministic manner.
For example, lending business logic can be codified transparently in smart contracts, thereby enforcing adherence to rules and automating settlement.
In the process of adopting blockchain technology, financial firms are exploring the concept of representing real-world assets as tokens on a blockchain. Such tokenization can reduce settlement risk
and decrease settlement times, which typically takes one to two days even for low-risk assets such as G10 government bonds, by enabling so-called “atomic” settlement – the instant exchange of two assets on the condition that assets are simultaneously transferred. No party to a transaction is then left waiting for delivery.
The application of smart contracts in asset tokenization also has delivered a number of benefits, including enhanced and new offerings. For example, J.P. Morgan leverages tokenization to offer intra-day repo solutions for clients on its Onyx Digital Assets platform, and DBS Digital Exchange offers corporates a platform to raise capital through the digitization of their securities and assets, with options to offer smaller denominations.
These tokenization benefits are also welcomed by asset managers, as 70 percent of institutional investors expressed willingness to pay extra for increased liquidity and faster asset turnover, according to a recent survey conducted by Celent.
Tokenization efforts in the industry are well under way covering both payment instruments and assets, which creates the potential for end-to-end asset exchange on blockchain.
Tokenized payment instruments are gaining scale through public- and privatesector efforts Tokenized assets are growing as multiple pilots have validated their feasibility and value
Eighty-eight percent of global institutional investors are comfortable with digital representations of cash using blockchain-based technology, according to a 2022 Celent survey.
Tokenized payment instruments are being explored by both the public and private sector. On the public sector side, a 2021 survey of 81 central banks by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) found that 90 percent of central banks were investigating the potential of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), including 26 percent that were actively developing CBDCs or conducting pilot projects.3 The transaction volume of China’s digital yuan, or e-CNY, reached RMB 100 billion ($13.9 billion) at the end of August 2022,4 nearly three years after its launch. The European
Central Bank in September selected five companies to develop potential user interfaces for a digital euro; it expects to complete its investigation on whether to launch a CBDC in October 2023.
Central banks are broadening the scope of their CBDC experiments. As of October 2022 the BIS was running seven CBDC projects with various member central banks. More recently, the Banque de France announced a new project to look at using DeFi for wholesale CBDC liquidity management.
On the private sector side, privately issued stablecoins, which are cryptocurrencies typically pegged to fiat money such as the US dollar, have grown to a nearly $150 billion market.
There are increasing efforts from regulators to clarify the status of stablecoins. Recently, MAS published a consultation paper to support the development of stablecoins as a credible medium of exchange in the digital asset ecosystem.
In 2022, the European Union agreed on the first major regulatory framework for the cryptoasset industry, including stablecoins. Japan also passed a bill providing a legal framework for stablecoins that allows licensed banks, money transfer agents, and trust companies to issue them.
Ninety-one percent of institutional investors are interested in investing in tokenized assets, according to a 2022 Celent survey.
We see many firms entering the space across multiple asset classes including equities, bonds, real estate, commodities and others. For example, J.P. Morgan’s intra-day repo application on Onyx Digital Assets has processed more than $430 billion of repo transactions since its launch in November 2020; the daily transaction volume of Broadridge’s Distributed Ledger Repo platform using tokenized government bonds reached $35 billion in the first weeks after launch; DBS has successfully issued the DBS Digital Bond in May 2021 via security token offering (STO); Mata Capital, a French asset manager, tokenized €350 million ($343 million) worth of funds.
Last year, Switzerland implemented a so-called DLT Act granting tokenized securities the same legal status as traditional ones. Furthermore, in May 2021 Germany’s parliament passed a
law allowing securities to be issued in electronic form, not paper, enabling the issuance of tokenized assets. The European Investment Bank subsequently issued a digital bond on a public blockchain in 2021 under this German law.
DeFi protocols enable new ways to deliver financial services In parallel to industry efforts to develop real-world asset tokenization, the concept of decentralized finance has flowered in the public cryptoasset space. DeFi, as it is popularly known, refers to decentralized applications (DApps), which provide financial services via sophisticated and automated computer code on a blockchain as the settlement layer. These services include payments, lending, trading, investments, insurance, and asset management. DeFi protocols are the code and procedures that govern these applications. These protocols typically operate without centralized intermediaries or institutions, use open-source code, and allow for flexible composability (code or applications can be taken from one protocol/service and plugged into another).
DeFi has rapidly emerged in the past three years and grew more than tenfold to $160 billion in 2021 in terms of total value locked before retreating to stand at a little over $50 billion as of October 2022. DeFi innovations have flourished across various financial ecosystems and attracted billions of dollars of liquidity across decentralized exchanges (such as Curve and Uniswap), lending protocols (such as Aave and Compound), and other DeFi solutions, such as liquidity staking and collateralized debt positions, which lock up collateral in a smart contract in exchange for stablecoins. Some noteworthy innovations in the DeFi space involve crypto lending/borrowing protocols and decentralized exchanges:
Liquidity pools, for instance, create all-to-all markets. These pools link buyers and sellers along with liquidity providers in decentralized exchanges, or DEXes, and lenders and borrowers in lending protocols. Aave and Compound are examples of large crypto lending and borrowing protocols in terms of total value locked, whose operations involve liquidity pools. Both retail and institutional investors can deposit,
borrow, or trade crypto from the pool using business logic that is governed by smart contracts. If pools are on the same chain or made interoperable, this aggregates liquidity by attracting more investors.
Automated market markers (AMM) provide a new method of price discovery. An AMM facilitates buy and sell orders in a self-executing manner, always standing ready to provide quotes and setting a price based on a predefined, transparent formula considering supply and demand. Uniswap and Curve are examples of a decentralized crypto exchange that uses an AMM. When a user wants to swap crypto A for crypto B, the AMM automatically calculates how much crypto B the user can get and at what price rather than relying on a market maker to quote a price or to match a buyer and a seller.
DeFi, as described above, is prevalent in the public blockchain space and applies mostly to transactions in the largely unregulated crypto-asset industry. Yet the logic embedded in DeFi protocols, which are programmable, self-executing business processes, can be applied to interact with any tokenized asset.
Building full-scale financial services
that leverage tokenization and programmability could have far-reaching implications for the finance industry. It could generate substantial cost savings, as code dramatically reduces middle and back-office operations across firms and intermediaries. In the exhibit below we list some notable benefits of DeFi solutions. New business opportunities are also likely to emerge as financial institutions take advantage of the composability of DeFi protocols, packaging multiple DeFi protocols together to offer new solutions. First, however, firms must adapt the DeFi protocols to the regulatory standards of today’s trillion-dollar markets for money, stocks, bonds, and other assets.

Today’s finance industry rests on an array of safeguards that protect investors from fraud and abusive practices, combat financial crime and cyber malfeasance, maintain investor privacy, ensure that industry participants meet certain minimum standards, and provide a mechanism for recourse in case things go wrong.
Institutional DeFi will need to incorporate the same, if not higher, level of
standards to meet regulatory requirements, create trust, and drive adoption by issuers, investors, and financial institutions.
Here are some of the key safeguards needed to build DeFi-based solutions for institutions:
◉ AML/KYC risk controls. Mechanisms that ensure AML/KYC compliance for participants can avert the potential legal liability of dealing with sanctioned parties or unqualified investors, and also prevent inadvertently enabling or participating in money laundering. Designing appropriate risk controls however are not easy. In 2021, financial institutions were fined $2.7 billion for their deficiencies and failures in AML compliance policies, procedures, and processes.18 To avoid the severe consequences that could arise from control failures, the average mid-size to large organization spends $22.7 million annually on financial crime compliance operations to build up effective standards.19 Appropriate controls are needed if regulated financial activity is to take place through DeFi protocols, and regulators have begun to set expectations.
In August 2022, the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) imposed sanctions on Tornado Cash, a cryptocurrency mixer that facilitates anonymous transactions by obfuscating their origin, destination, and counterparties, alleging that it had facilitated the laundering of more than $7 billion worth of cryptocurrency.20 Blockchain technologies may offer novel ways of ensuring appropriate controls at lower cost. For example, there are methods for ensuring compliance with AML/KYC without necessarily revealing one’s personal information, such as using zero-knowledge proofs combined with pseudonymous identity mechanisms.
◉ Data privacy. Data privacy is crucial for clients in certain segments, in particular to protect their trading history and positions for certain asset markets. Information on public blockchains is permanently visible to all by default, and investor orders can at times be inferred from publicly available data, something that becomes increasingly more likely as time goes on and data
is accumulated. For example, whale tracking tools on Twitter and Telegram are widely used by the public to track large crypto-asset transactions done via decentralized exchanges and other DeFi protocols, whereby people have strong assumptions or hypotheses on who these whales (investors holding a vast number of crypto-assets) are. In the finance industry, client information in respective transactions is masked and protected through brokers, without being revealed to the market. Appropriate privacy protections will be necessary.
◉ Cybersecurity protections. While almost anything digital can be vulnerable to hackers, cybersecurity protections are especially important for digital assets and DeFi protocols due to the nature of blockchain. Although the underlying blockchain technology makes it difficult to alter data, firms seeking to develop Institutional DeFi solutions must address cybersecurity vulnerabilities in cross-chain bridges, private digital keys, and on-chain price oracles, as well as guarding against market
manipulation. Such controls are needed to enhance client trust and protect the safe ownership of digital assets. A rise in thefts from DeFi protocols led to a 58 percent increase in crypto hacking losses, to $1.9 billion, in the first seven months of 2022. Bridges connecting different networks are particularly vulnerable, as hackers demonstrated in July 2021 by attacking the crosschain DeFi platform Poly Network, and causing roughly $600 million in losses in Ethereum and other tokens. Users manage their own private keys to access their crypto assets, which can also compromise security. Losses due to compromised private keys have totalled $274 million in the first eight months of 2022 alone.
◉
Mature governance and conduct models. Reliable DeFi protocol governance and stakeholder conduct standards are needed to ensure that the quality of Institutional DeFi solutions offered are in alignment with financial services professional standards. Financial institutions are highly regulated with

mature quality assurance processes. For example, there are more than nine different federal financial regulators in the United States on top of multiple regulators in each of the 50 states. Multilateral organizations help coordinate financial regulation internationally. Banks invest over $270 billion a year and dedicate an average of 10 percent to 15 percent of their staff to comply with regulatory obligations. Standards for conduct exist for both institutions and individuals. Existing DeFi protocols are based on different governance and conduct assurance mechanisms, most often done through governance tokens that bestow holders with voting rights. This is similar to most common equity structures but without the same level of corporate governance. Also, many DeFi protocols have a very high concentration of voting control: Research by Chainalysis into ten major governance tokens found that fewer than one percent of token holders held 90 percent of the voting rights. Indeed, participants could consider whether to and how to cover DeFi protocols under a corporation construct — such as trusts, special purpose vehicles, or other limited purpose corporations — to allow for structured governance and liability recourse.
◉ Proper recourse mechanisms. Recourse and dispute management should be properly established upfront. Incidents such as theft or loss due to operational errors can occur in any financial system. The finance industry today is built with robust recourse mechanisms or legal remedies to protect users and investors in most cases. For instance, the London Court of International Arbitration, one of the world’s leading arbitral institutions, managed 86 international dispute cases from the banking and finance industry in 2021. Such mechanisms are lacking in public DeFi solutions, giving rise to uncertainty in arbitration procedures. When a hacker stole $130 million in crypto assets from users of DeFi platform BadgerDAO, they were unable to afford full restitution immediately with a mere $53 million in their treasury and no insurance coverage. Without an available legal recourse mechanism,
this left a handful of affected users uncompensated.
◉ Legal clarity around smart contract-based business activity. The legal status of financial business activity has been continuously clarified by countless acts of legislation and major litigation efforts over past decades. The UK High Court, for example, typically hears 80 to 100 important banking and finance cases annually. That level of clarity does not yet exist for smart contract-based DeFi activity. According to international law firm Norton Rose Fulbright, it remains unclear which smart contracts are legally enforceable, which could depend on the intentions of contracting parties or local jurisdictions. In the United States, the enforceability and interpretation of contracts in the United States is commonly governed by state law. Some states such as Arizona and Nevada have amended their respective laws (such as the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act) to explicitly incorporate blockchains and smart contracts. Some code-only smart contracts would be enforceable under state laws governing contracts. The International Swaps and Derivatives Association (ISDA) also developed legal guidelines for smart derivatives contracts to provide general guidance for different jurisdictions. More legal clarity in commercial law is necessary to reinforce these requirements and foster a trusted environment for smart contractbased business.
Now is the time to actively explore Institutional DeFi The foundation for Institutional DeFi is being established by the growth of real-world asset tokenization and the innovations observed in DeFi. Financial institutions have the opportunity to transform parts of their business by adapting DeFi protocols and combining them with the level of safeguards that regulators and clients expect. Institutional investors’ appetite for digital assets is growing and they are willing to pay extra for increased liquidity and faster transactions. 88 percent said they are still planning to move forward with current plans around digital assets despite market downturn. In May 2022, the
Monetary Authority of Singapore launched Project Guardian to test the feasibility of applications in asset tokenization and DeFi while managing risks to financial stability and integrity.
Project Guardian will help MAS build the digital asset ecosystem framework, enhance and develop relevant policies, and provide direction on the technology standards. The full report also explores how financial services providers could adopt Institutional DeFi based on different considerations, leveraging findings from the first pilot under Project Guardian. It also discusses how financial institutions should collaborate to get the most out of the transformation.
From the carrier pigeon to the telegraph, the transistor to the mainframe, technology has shaped the finance industry for generations. We believe Institutional DeFi has the potential to be the next great transformative force. It may be too early to predict the end-game scenario, but there are no-regret moves executives can take now to prepare their organization for future options. There is no single right answer, but an answer is needed at both the institution and industry level to move from debates and pilots to scalable, industrialized solutions. Given the challenges discussed in this paper, we expect first movers will have an advantage because they will learn how best to deploy the technology and create a talent environment that fosters innovation.
This article is based on the special report Institutional-DeFi: The Next Generation of Finance? Produced by a collaboration of the OliverWyman Forum, DBS, onyx by J.P. Morgan and SBI Distal Asset Holdings, an SBJ Company.
Authors credits. Oliver Wyman: Jason Ekberg, Partner, Corporate and Institutional Banking, Netherlands; Michael Ho, Partner, Corporate and Institutional Banking Hong Kong; Larissa de Lima, Senior Fellow, Future of Money Initiative, Oliver Wyman Forum, New York; Teddy Hung, Engagement Manager, Financial Services Hong Kong; DBS: Keith Desouza, Group Head, Liquidity Funding Management, Treasury & Markets, Singapore; Peng Khim Ng, Group Head of Institutional Banking Group & Future Ready, Technology, Singapore; Nova Cygni Pelupessy, Head, Financial Market Infrastructure Ecosystems, Group Strategy and Planning, Singapore; Yu Song Low, Financial Market Infrastructure Ecosystems, Group Strategy and Planning, Singapore; Onyx by J.P. Morgan: Naveen Mallela, Global Head of Coin Systems, Singapore; Naveen.Mallela@jpmchase.com, Tyrone Lobban, Head of Blockchain Launch and Onyx Digital Assets, Onyx by J.P. Morgan, London; Nikhil Sharma, Senior Product Manager, Blockchain Launch and Onyx Digital Assets, Nelli Zaltsman, Lead Product Designer, Coin Systems, Onyx by J.P. Morgan, New York; SBI Digital Asset Holdings: Jason Beale Head of Product, SBI Digital Asset Holdings, Japan; Pablo Argibay, Chief Scientist, SBI Security Solutions, Japan. This joint report would not have been possible without ideas and contributions from numerous other members from these organizations.












Those working and running foundations have more to accomplish in a day than ever before. They are tasked with fundraising, event planning, evaluating giving options and the oversight of the portfolio. All of this while functioning within a budget and dealing with human resources and other operational issues. Wouldn’t it be a blessing to have the aspects of overseeing a portfolio and the ongoing reporting, decision-making and governance delegated to a trusted third party? What if that opportunity existed and likely at a cost comparable to or below your current cost structure? This article will describe an option to optimize the investment goals of the foundation while affording you with more time on the things that you are passionate about.
Today more than ever, it is important to have independent and aligned investment advice. Foundations that have partnered with an Outsourced Chief Investment Officer (OCIO) have been well served in the past decade, but today we are at an inflection point. The last 10 years can be referred to as the “Goldilocks” era, where we had low interest rates and good economic growth — fairly simple portfolios were able to generate strong returns. The next decade will have the drag of higher interest rates and likely muted growth — hence the inflection point.
The OCIO model is much more prevalent in the US than here in Canada, where we have few firms that can tick all the boxes. However, this does not preclude many from marketing themselves as OCIO’s or multifamily offices, which can prove detrimental to both their clients and, over time, the firms themselves. With this in mind, today may be the most important time in decades for foundations and endowments to step back and evaluate their strategy, ensuring they receive the best investment guidance possible and partner with a firm that is fully aligned with them.
Many of the very large foundations, pension plans and family offices have investment employees that execute on their
plan. Generally, these are organizations that have investible assets exceeding $500 million. The people working at these entities are directly aligned with their clients’ goals and objectives, and may manage some of the money internally. They often have dedicated research teams to explore and assess external managers for mandates that they do not have the skillset to manage in-house. An OCIO replaces the duties and functions of those investment employees and delivers them to a foundation in a seamless and costeffective manner.
This is why it is so important to clarify what an OCIO actually is and isn’t. Allow me to go through a checklist of key attributes:
◉ OCIO’s are conflict-free. Investment solutions are managed exclusively by external parties. Using in-house products creates a conflict and as a result will often exclude banks and boutique firms. OCIO’s are only paid by their client and receive no referral or third-party fees. This eliminates any bias and ensures alignment with the client’s goals and objectives. In our view, this is the best framework for creating a portfolio of best-of-breed managers and appropriate portfolio construction.
◉ OCIO’s are investors first. The culture is rooted in research, portfolio construction and decision-making. Their people are investment professionals with a pedigree in broad and diverse investment classes. They are often credentialed (generally Chartered Financial Analysts) and they must meet regulatory standards - integrity, code of conduct and proficiency requirements. While a true OCIO, along with its people, are registered with the securities regulators, this is often not the case with a consultant.
◉ OCIO’s have research and service as their cornerstone. The research team is accomplished and has a mandate to evaluate and continually assess investment solutions locally and globally. The investment they make is in people, practices and processes, leading to the construction of robust, resilient
portfolios. Seasoned relationship managers are dedicated to each client for guidance and discussion that is continuous and coordinated.
◉ OCIO’s have purchasing power. Fees are top of mind for everyone and having scale allows for the negotiation of optimal pricing and terms. All fee discounts and rebates go directly to the benefit of the client. Investment minimums are often lower and include preferential terms. As an aside, an OCIO with scale also affords it the opportunity to attract and retain top talent.
◉ OCIO’s will have valuable intangibles beyond investments. Given their knowledge in the space, they will have relationships with industry experts in accounting, legal, insurance and custody providers that can benefit the foundation. Experience in the foundation space will also allow for advice on board governance and succession, board education and regulator awareness.
Leadership in the foundation space is generally occupied by a very talented group. They have a genuine passion for the cause, for raising funds and for deploying the portfolio for the good of society. These significant talents aside, more often than not, leadership and their team do not have a strong background in investment strategy and management – because of this, OCIO’s can provide significant value. In other cases where knowledge and experience does exist, the presence of an OCIO preserves the independence, in fact and appearance, of leadership and the Board.
There are many compelling reasons for foundations large and small to consider working with an OCIO. When reviewing a firm, make sure it ticks all the boxes.
ANTHONY MESSINA, President, Guardian Partners Inc. and Head of Private Wealth, Guardian Capital Group Limited. Guardian is a prominent, independent outsourced CIO and multi-family office. Guardian Partners manages assets approaching $4 billion and has been working for 25 years with many of Canada’s wealthiest individuals, families and institutional clients that include public and private foundations, endowments and pension plans. The information provided is for illustrative/educational purposes only.

PNC EQUIPMENT FINANCE | Your CAPEX budget has never been tighter. We get it. That’s why numerous clients across the U.S. and Canada choose PNC Equipment Finance to power their future. Deep experience allows our team to offer leading asset-specific financing solutions, including loans, leases and lines of credit, to help you drive maximum ROI. If you’re looking for stability and flexibility from one of the nation’s largest financial institutions, know we have the energy to help you be ready for today.
To learn more, visit pnc.com/ef
PNC is a registered mark of The PNC Financial Services Group, Inc. (“PNC”).

Equipment fi nancing and leasing products are provided by PNC Equipment Finance, LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of PNC Bank.


In Canada, PNC Bank Canada Branch, the Canadian branch of PNC Bank, provides bank deposit, treasury management, lending (including asset-based lending) and leasing products and services. Deposits with PNC Bank Canada Branch are not insured by the Canada Deposit Insurance Corporation or by the United States Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation.
Lending and leasing products and services, as well as certain other banking products and services, require credit approval.
©2021 The PNC Financial Services Group, Inc. All rights reserved.
0321-014-1798101


FCC Economics helps you make sense of the top economic trends and issues likely to affect your agri-business in 2023. Overall demand for farm equipment is projected to remain strong into 2023, despite rising interest rates and a weakening Canadian US exchange rate. Demand is supported by strong farm cash receipts, even with commodity prices softening from peak levels. As supply chains recover, equipment manufacturers are expected to increase the delivery of new equipment orders. However, inventory levels will remain below pre-pandemic levels as we project inventory levels could remain tight beyond 2024.
Sale trends for the remainder of 2022 are expected to be mixed. Higher horsepower tractors, combines, and implement sales are expected to have positive year-over-year growth, while lower horsepower tractor sales are
expected to decline in 2022 because of slowing economic growth. Sales of smaller equipment are projected to decline as broad economic conditions worsen in Canada. A slowdown in low-horsepower tractor sales may allow manufacturers to allocate production to higherhorse-powered tractors utilized in agriculture. Further delays in equipment arrival before the end of the year could change these projections.

Farm equipment sales projections for 2023 are projected higher for high horse-powered tractors, combines, and implement sales driven by strong crop receipts: ◉ 100+ HP tractor sales to rise 8.7 percent ◉ 4WD tractor sales to rise 13.9 percent ◉ Combine sales to rise 19.3 percent ◉ Canadian agricultural implement manufacturing to rise 32.2 percent
However, small horsepower tractor sales, which are largely driven by the health of the Canadian
BY LEIGH ANDERSONeconomy, are expected to slow in 2023:
◉ < 40 HP tractor sales to decline 0.4 percent
◉ 40 – 100 HP tractor sales to rise 0.4 percent
However, the wild card for 2023 sale projections continues to be the arrival of equipment from manufacturers. Canadian agricultural implement manufacturers are still recovering from supply chain disruptions. Strong demand for farm equipment since 2021 significantly reduced new and used inventories at the dealer level, creating further opportunities for manufacturing sales. Canadian agricultural implement manufacturing sales increased 10 percent in 2021 and are up 22.3 percent year-to-date in 2022 through the first 8 months. Canadian agricultural implement manufacturing sales are projected to rise 32.2 percent in 2023 due to strong demand and price inflation.
Inventory is projected to remain tight
We are anticipating inventory levels will remain tight through 2024 as producer demand remains strong for farm equipment and manufacturers catch up on pre-orders. Inventory levels of new farm equipment have trended below the five-year average (tractors are down 42 percent and combines down 47 percent). Strong demand for farm equipment for the remainder of 2022 is expected to reduce inventory levels further and support higher prices. The good news is that equipment manufacturers are expected to adjust their production upward due to the changing economic environment as North American equipment dealers begin to rebuild their inventories. We expect farm equipment dealers to remain 100 percent sold on new equipment. However, individual dealer revenue remains uncertain and tied to deliveries and allocations from manufacturers. Overall, dealer sale revenue will come down to the number of trades that materialize once new equipment arrives.
Combine inventory projected to remain pressured into 2024 4WD tractor inventory levels are projected to recover slowly while inventory levels are recovering for smaller horse-powered units.
Farm equipment prices are expected to be higher in 2023 due to the depreciation of the Canadian dollar and inflationary pressures in the supply chain that occurred in the last half of 2022. The Canadian dollar has a direct impact on equipment prices. Most new tractors and combines sold in Canada are manufactured south of the border, so an expected depreciation of the loonie through 2023 should lead to price increases on farm machinery. Domestic manufactured equipment, including air drills and seeding equipment, tillage, grain carts, swathers and other “shortline” equipment prices, are less directly connected to the Canadian dollar.
Supply chain disruptions because of the pandemic-related shutdowns directly impacted the availability of new equipment and parts. Strategic planning on farms meant having additional used equipment available in the event parts and services were unavailable. These farms either kept their older machines or sought used equipment at auctions. Dealers also shifted strategically to servicing or overhauling used equipment to ensure customers could continue using their existing equipment for another year or longer. Inventory in the used equipment market declined as a result. This has had a profound impact on the used equipment market. Throughout 2021-2022 used equipment (e.g., 4-5-yearsold) was selling for prices like what they were worth two years earlier.
Interest rates rose throughout 2022 from their historical lows as the Bank of Canada lifted its overnight rate from 0.25 percent to 3.75 percent. The Bank of Canada is committed to returning inflation to its 2 percent target. As a result, borrowing costs are forecasted to rise further in 2022 and possibly early in 2023. In some cases, farm operations have seen their interest expenses more than double. In other instances, prudent financial risk management mitigated the negative influence of higher rates on profit margins. Historically as interest rates rose,
farm operators have lengthened their replacement cycle of farm equipment, and farm equipment sales have slowed. Given the backlog in deliveries of new equipment and low inventory levels, we expect that higher borrowing costs will not impact the demand for farm equipment in the short term. Farm income appears strong enough to offset higher short-term input and interest rate costs.
FCC Economics’ current forecast of the Canadian dollar is to average USD$0.72 through 2023. A declining Canadian dollar will impact both the used and new equipment market. A low Canadian dollar will push prices higher, forcing dealers to re-evaluate their prices on used equipment, given they will have demand from U.S. dealers and farmers, at least adjusting their USD sticker price.
We will continue to monitor these two financial trends. Check back with us in early December when our next Economic and Financial Market Update is released for the latest outlook.
The 2023 farm equipment market will be characterized by a recovery in deliveries of new equipment as supply chains slowly recover. In addition, strong commodity prices will continue to support the demand for farm equipment, so higher interest rates and a lower Canadian dollar may not weaken the demand for farm equipment in the short term. We expect the used equipment market to stay robust for most of 2023 and 2024. Prices in the used equipment market may moderate as delivery of new equipment results in additional trades and inventory of new equipment slowly recovers. Revenue growth for Canadian equipment dealers will continue to come from service and parts as inventories recover for both new and used.
LEIGH ANDERSON is a Senior Economist at FCC with experience in agricultural markets and risk. He specializes in monitoring and analyzing FCC’s portfolio, industry health and providing industry risk analysis. In addition to his speaking engagements on agriculture and economics, Leigh is a regular contributor to the FCC Economics blog.
SMBs account for around one-fifth ($850 billion) of global banking revenues, with annual growth predicted to reach up to 10 percent over the next five years1. This is a critical revenue stream that banks can’t ignore.

Customer expectations of digital services are being shaped by the battle to become the SuperApp of choice; becoming the single marketplace and closed-loop ecosystem for users every need (e.g. Apple). SMB banking is just one sector that is being disrupted by this model, with new challenger banks, FinTechs, and digital disruptors focused on creating experiences that drive customer primacy.
Traditional banks already have the assets needed to respond and secure customer primacy. They have an established product and distribution advantage, backed by a wealth of customer data that can drive new experiences and interactions. The key to success is harnessing this data, at speed and scale, but if traditional banks fall short in delivering a competitive offering, this could open the door to digital disruptors who excel at experience.
Our global research among nearly 1,000 business banking leaders shows that there
is a disconnect between the wealth of customer data traditional banks can access, and how they use it to build relationships. The majority of traditional banks in Canada (74 percent) rank collecting data as a key strength, but 37 percent reveal they have lost customers because they cannot offer SMBs the data and insights they require about their business.
In order to build data-driven experiences at the required scale and pace for the modern market, any investment by traditional banks needs to be focused on collaboration, both internally and externally, including securing strong partnerships with FinTechs that can work as smart partners, and accelerate and elevate the delivery of data-led experiences.
Currently, 95 percent of Canadian banks recognize the need to work with capable FinTech partners, who they trust. However, traditional banks and competitors differ in why these partnerships are created. In Canada, 17 percent of traditional banks partner with FinTechs collaboratively to build specific digital solutions from scratch, compared to 60 percent of challenger banks, and 50 percent of neobanks
Banks need FinTech partners that go far beyond a basic transactional relationship or plugging in services. They want smart partners who can build alliances based on key qualities including safety and security;
working collaboratively; being a trusted partner; understanding business needs; sharing financial expertise, and advising on security or compliance. Smart partners work collaboratively to not just implement tech, but also create a successful business for the bank.
Investing in such deep relationships with FinTech partners can play a fundamental role in the rapid deployment of data-driven experiences, which will be key to traditional banks gaining a critical advantage in the fight for customer primacy.
Traditional banks have the ingredients of success, now they must focus investment on harnessing the power of their data through smart partnerships. With the right strategy and partners, traditional banks can gain a long-term competitive advantage and overcome the threat from disruptors.
*Source: McKinsey’s Global Banking Annual Review 2021
FIONA ROACH CANNING is Co-Founder and President of Pollinate, leading Product, Marketing, Sales and Solutions. Her career has included working on the launch of Egg, the first internet bank in 1998, running European Insights for Visa, and leading operations and customer experience for Nectar, the UK’s largest and most successful loyalty scheme, with 20 million members. Fiona has been named one of the UK’s top 30 female entrepreneurs by the FT and one of the Top 25 Women Leaders in European Financial Technology, as well as being one of Beauhurst’s 50 Female Entrepreneurs to Watch. She is also featured in the 2021 Women in FinTech Powerlist

Findings of the 2022 LexisNexis True Cost of Fraud™ Study: Financial Services and Lending. This sixth edition of the report examines current fraud trends for more than 500 United States and Canadian financial services and lending companies and highlights key pain points related to the addition of new payment mechanisms, online and mobile channel transactions and international expansion. The survey was conducted between May and July 2022.
The new survey found Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL), increased bots and mobile channel fraud are among the key concerns for financial services and ending firms.
U.S. and Canadian financial services firms’ fraud costs continue to rise. Every $1 lost to fraud now costs U.S. financial services firms $4.23 compared to $3.64 in 2020, a 16.2 percent increase. The cost for Canadian financial services firms rose 19.6 percent, from $3.16 in 2020 to $3.78 in 2022.
The costs for credit and mortgage lending firms remain above pre-pandemic levels, although they are trending downward after substantial increases observed at the start of the pandemic. According to U.S. loan companies, each $1 in fraud losses costs $4.08. Canadian lending firms find that each $1 in fraud losses actually costs $3.74.
Attacks and Costs: Fraud costs and attack volumes for financial services firms remain significantly higher compared to before the pandemic. Costs continued to rise above early 2020 levels, with banks reporting the highest figure of $4.36 for every $1 of fraud loss. Mortgage firms also had a comparably higher cost of $4.20 for every $1 lost to fraud.
Trends to Watch: Fraudsters targeting mobile channels, increased bot attacks, various scams and the rapid adoption of buy now, pay later (BNPL) are causing concern for
financial services and lending firms. Mobile channels now generate a sizeable level of transaction volume and fraud costs. Banks and credit lenders are beginning to accept BNPL as a digital payment method, which respondents indicated represents one-third of the overall average transaction volume.
creation. Canadian lending firms and U.S. mortgage lenders saw the biggest increase in identity-related fraud across account creation, with a 9 percent rise and 11 percent rise respectively since 2020.
“It’s clear that fraud has become more complex with various risks occurring simultaneously,” said Chris Schnieper, senior director of fraud and identity strategy, LexisNexis Risk Solutions. “To minimize fraud, organizations can no longer rely on manual processes or point solutions to reduce fraud, manual reviews and costs. Firms using a multi-layered solutions approach that integrates identity verification and authentication within digital consumer experience can lower their cost and volume of successful fraud. This approach improves identity verification and fraud detection effectiveness and lowers friction for trusted consumers.”
Scams Impacting Customer Journey Risks:
Scams are contributing to increased fraud costs, particularly creating more risk at the new account creation stage of the consumer journey. Scams impact fraud detection across consumer touchpoints by heightening challenges associated with digital identity verification, distinguishing bots from legitimate customers and balancing fraud detection with customer friction. Those dealing with multiple types of scams had a higher cost of fraud based on more labor/investigation efforts.
Identity-Related Fraud: Lack of identity verification is a top challenge that contributes to fraud across the customer journey. With new account creation still trending upward, U.S. banks that deal with multiple types of scams attributed more identity-related fraud to new account
The report’s findings stem from a survey of financial services and lending companies. The 426 U.S. and 76 Canadian respondents consisted of risk and fraud management executives in retail and commercial banks, credit unions, trusts and wealth management along with auto lenders, mortgage companies, finance companies and non-bank credit card and personal loan issuers.
The cost of fraud is more than the actual dollar value of a fraudulent transaction. It includes additional costs related to labor/ investigation, fees incurred during the applications/underwriting/processing stages, legal fees and external recovery expenses. The LexisNexis Fraud Multiplier determines the actual cost of fraud based on calculating these additional costs.
LexisNexis Risk Solutions harnesses the power of data and advanced analytics to provide insights that help businesses and governmental entities reduce risk and improve decisions to benefit people around the globe.

