
2 minute read
Drama
Design and Technology Board: AQA Specification: 8552
Entry requirements
Why study GCSE Design and Technology?
The course develops your capacity to critically analyse and evaluate a problem from a technical and aesthetic viewpoint. Creative design solutions are developed and manufactured through a thorough understanding of materials, an awareness of environmental constraints, new technologies and modern manufacturing processes.
Although it is extremely advantageous if you can sketch in three dimensions with ease, this skill is not essential to access the top grades. Having the willingness and curiosity to experiment with the form and function of a design is much more important. The non-exam assessment element of the course requires students to adopt an iterative approach which is best achieved through the use of modelling, computer aided design, the manufacture of test pieces and sketches.
Important information
The Key Stage three curriculum at Ashford School has been designed to equip you with the skills required to access and flourish in Design and Technology at GCSE. Our most successful students have a creative, inquisitive and analytical mind, the ability to communicate and visualise their design solutions and have a good grasp of basic mathematical principles. Above all, they enjoy the subject and have an interest in shaping the world that they live in.
Course Overview and Content
The specification consists of two assessed units: a written design examination and a product design project (non-exam assessment).
The examination (50% of overall grade):
This is a two-hour written paper which is divided into three sections: Core technical principles (20%) The questions are presented in a mixture of multiple choice and short answer questions that relate to new and emerging technologies, developments in materials and material properties and control systems.
Specialist technical principles (30%) These questions focus on a range of material categories in more depth, for example: compliant and resistant materials and electronic and mechanical systems.
Designing and making principles (50%) This section includes short and extended written and graphical responses to questions on design in society, the work of others and modern industrial manufacturing techniques.
3 7
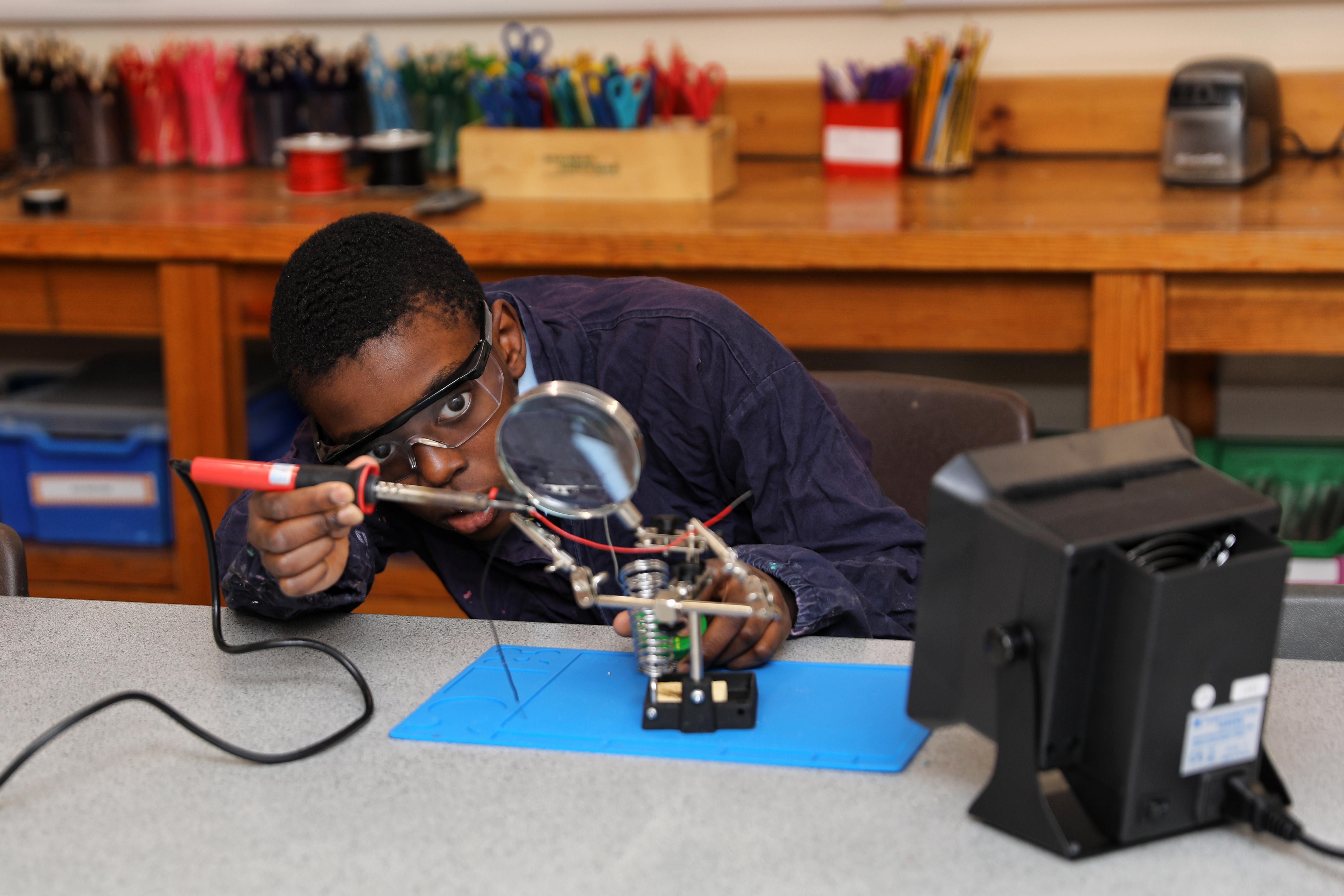
The Non-Exam Assessment (50% of overall grade):
This element affords you the chance to explore an everyday design opportunity and through the iterative design process, design, develop and manufacture a prototype. A design e-portfolio consisting of no more than 20 A3 PowerPoint slides will accompany the prototype and developmental models.
Enrichments
The course encourages students to become more observant and to question the products and systems that surround them and play a pivotal role in their lives. Therefore, in its simplest form students will become progressively more enriched by their surroundings and what they witness on the news and in social media.
To further enhance and broaden their experiences, students have visited the Victoria and Albert Museum, various local high-end manufacturing companies and the Jaguar and Morgan car plants. Students have also had the pleasure of engaging in workshops run by a silversmith.
Future pathways
The GCSE course naturally feeds into the A Level Product Design course which combined with Mathematics, the Sciences or Art and Design provide a strong foundation for a wealth of degree courses and careers.The following are just a few: Product Design, Industrial Design, Fashion, Video gaming platforms, Broadcast Media Design and Technology Communication, Engineering, Sports Technology, Medical and Surgical Engineering, Interior Design and Architecture. Due to the nature of the subject, it can also be paired with contrasting subjects to provide a broad platform with problem solving at its heart.










