FARM/RANCH MANAGER: FARMING IN TENNESSEE


LESSON PLAN OVERVIEW

Career: Farmers and ranchers grow crops and raise animals to supply our food.
Lesson: This lesson plan provides activities for students to learn where our food comes from. Students will learn about some of the crops grown in Tennessee and will calculate crop yield to determine the best use of land to make the most money. Students will also explore hydroponics (growing plants in water) and will create a classroom hydroponic garden
Grade Level: Elementary Grades
Learning Objectives:
〉 Students will explore the career of a farm/ranch manager and learn about what they do.
〉 Students will learn about crops grown in Tennessee and will calculate crop yield to determine the best use of land to make the most money.
〉 Students will explore hydroponics and learn how plants can grow without soil and then perform a hydroponic experiment.
Materials Needed:

Activity #1: Agriculture in Tennessee
〉 Student worksheet
〉 Calculator
Activity #2: What is Hydroponics?
〉 Student worksheet
〉 2-liter plastic bottle – 1 per group
〉 Scissors to cut the top off the 2-liter bottles
〉 Growing media – clay pellets or coconut coir*
〉 Nutrients – Miracle-Gro Water Soluble Plant Food or other similar plant nutrients*
〉 Water – tap water or filtered water
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is
〉 Wick material – use thin cotton rope or cut a towel in 6 to 8-inch strips
〉 Seeds – herbs such as basil and mint or strawberries
〉 Aluminum foil (optional) – helps reduce the amount of algae in the water
〉 Light source – windows for natural sun light or a lamp with LED lights
*You can find these materials at your local garden center.


TEACHER GUIDE
Lesson Instructions: The following activities will help you introduce students to careers in agriculture. Begin the lesson by reading the Class Message below to your students, then have them watch the recommended career video. Afterwards, facilitate a discussion using the Class Questions listed below.
After the discussion, students will work on two activities. Each activity has a printable worksheet with student instructions and areas to record their work. Have students read their worksheets before beginning each activity.
You should also familiarize yourself with the student worksheets to provide assistance when needed, help demonstrate any procedures, and help in facilitating the discussion that ends each activity.


Class Message: Today, we are going to learn about farmers and ranchers. Do any of you know what farmers and ranchers do? Farmers and ranchers grow and supply our food.
Farmers grow fruits, vegetables, nuts, cotton, trees, and other crops for fuel, clothing, and shelter. Ranchers raise animals for meat, eggs, milk, cheese, ice cream, and other dairy products we enjoy!
In this lesson, you will learn about the food that Tennessee farmers grow and then use a graph to calculate crop yield to find out what crops will make the most money from farmland. Crop yield is the measurement of how much of a crop can be grown on an acre of land. Some crops yield more for each acre of land than other crops do. You will also learn about a different way of farming by exploring hydroponics. Hydroponics is growing plants in water instead of soil. We will work together to make a hydroponic garden in our classroom.
Let’s watch this short video to learn more about careers in farming and ranching




Class Discussion Questions:
〉 Do you live on a farm or have any of you visited a farm? If so, share your experience. Allow students to share their experience.
〉 What are some crops that are grown in Tennessee? - Response suggestions: corn, wheat, hay, soybeans, cotton, and sorghum (is a grain that grows like corn and is used as a sweetener, livestock feed, and can be turned into ethanolfuel.)
〉 What are some things plants need in order to grow? - Response suggestions: water, light, air, nutrients, and a base such as the ground for anchorage.
〉 What does the word hydroponics mean? - Response suggestions: hydroponics is growing plants in water without soil. It is an alternative growing method to conserve land space?
Activities Overview: This lesson plan includes two student activities. Activity #1 challenges students to use graphs to calculate crop yield to determine the best use of land to make the most money. In Activity #2, students will learn about an alternative farming method by creating a hydroponic garden

Activity #1: Agriculture in Tennessee
Students will learn about the different crops grown in Tennessee. They will then use graphs to calculate the crop yield for 5 crops to determine the best use of their land for making the most money.
Activity Instructions:
〉 Hand out the student worksheet.
〉 Introduce the activity and guide students as needed.

〉 After completion, facilitate a discussion using the questions for the activity.
Activity Results: This activity introduces students to the crops that are grown in Tennessee and how farmers decide on which crops to plant.
〉 Which crop would make the most money? – Cotton


Activity Discussion:
〉 What are some things that could affect how much profit a farmer makes from a crop? - Sample answers may include: the cost of preparing the soil to plant; labor costs for planting and harvesting the crop; the cost of watering, fertilizing, and pest control.
〉 What things could reduce the amount of a crop that is grown? - Sample answers may include: bad weather, insect infestation, bad seeds, not enough rain, farm equipment repair.
〉 What do you think determines the Unit Price for crops? - Sample answers may include: the amount of crop available, supply and demand, Farmers’ Cooperative (Co-Op) - a group of farmers that pool their resources together to share profits from the co-op.

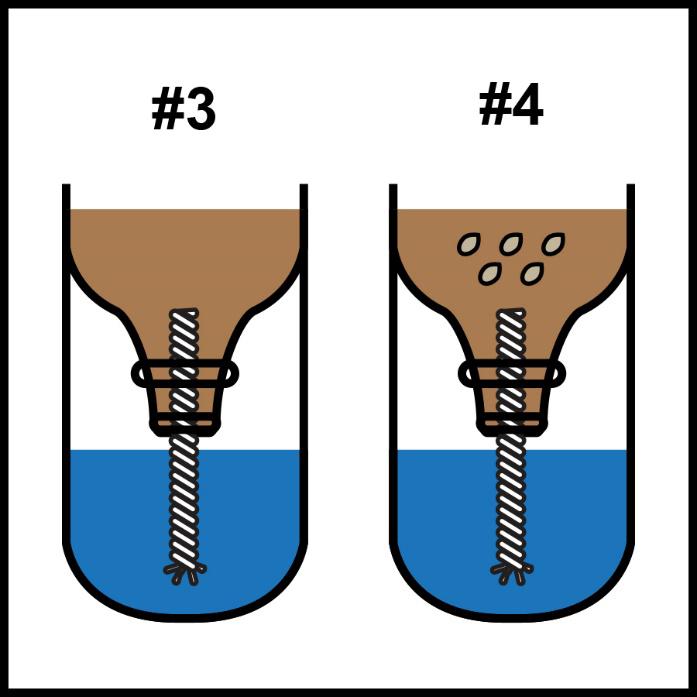
Activity #2: What is Hydroponics?
Students will learn about the use of alternative farming by creating a hydroponic garden in the classroom.
Activity Instructions:
〉 Prior to activity, cut off the top part of the 2-liter bottles, cut the cotton rope or a towel in 6 to 8-inch strips to make wicks (one for each group), and pre-mix Miracle-Gro Water Soluble Plant Food - 1 tablespoon per gallon of water.
〉 Before the experiment, show this video on Vertical Farming: (http://tn-caps.com/r/35FM1)
〉 Hand out the student worksheet.
〉 Divide the class into groups.
〉 Distribute the activity materials.

〉 Introduce the activity and guide students as needed.
〉 After completion, facilitate a discussion using the questions for the activity.
Activity Results: Students will learn about alternative farming by creating a hydroponic garden and monitoring its growth.

Activity Discussion:
〉 How is growing plants in water different from growing plants in soil? - Sample answers may include: plants that grow in water get their nutrients from plant food and artificial light, where plants in soil get their nutrients from the soil, sunlight, water, and air.
〉 Do you think that hydroponics is a good way to produce food? - Allow students to share their opinion.
〉 Do you think hydroponics could feed the world in the future? - Allow students to share their opinion.
〉 What do you think are some of the benefits of having a hydroponic system? What are some downfalls? - Sample answers may include: Benefits – grow indoors vertically taking up less space than farming, requires less manual labor, avoids issues like drought, insects, and weather. Downfalls – costs more than traditional farming which increases the cost of products; system malfunctions affect plants faster; power outages; requires special water; waterborne diseases spread quickly.


CAREER INSIGHT
Career Highlight: This lesson plan highlights some of the concepts and skills farmers and ranchers use daily to grow our food. See the Employers in My Area section to contact businesses and organizations in your area about classroom demonstrations, on-site visits, or other additional career exposure opportunities.
Featured Career:
Farm & Ranch Manager
Career Descriptions: Farmers and ranchers plan, direct, or coordinate the management or operation of farms, ranches, greenhouses, aquaculture operations, nurseries, timber tracts, or other agricultural establishments. May hire, train, or supervise farm workers or contract for services to carry out the day-today activities of the managed operation. May engage in or supervise planting, cultivating, harvesting, financial, or marketing activities.

Farmers, ranchers, and other agricultural managers typically do the following:
〉 Supervise all steps of the crop production and ranging process, including planting, fertilizing, harvesting, and herding
〉 Determine how to raise crops or livestock by evaluating factors such as market conditions, disease, soil conditions, and the availability of federal programs
〉 Select and purchase supplies, such as seed, fertilizers, and farm machinery
〉 Ensure that all farming equipment is properly maintained
〉 Adapt their duties to the seasons, weather conditions, or a crop’s growing cycle
〉 Maintain farm facilities, such as water pipes, hoses, fences, and animal shelters
〉 Serve as the sales agent for livestock, crops, and dairy products
〉 Record financial, tax, production, and employee information
Other Names for this Career: Farmer, Rancher, Grain Farmer, Ranch Manager, Sow Farm Manager, Accredited Farm Manager (AFM), Farm Operator, Farm Manager, Dairy Farmer, Cash Crop Farmer