
1 minute read
Policy and Framework
EQ iSearch
Advertisement
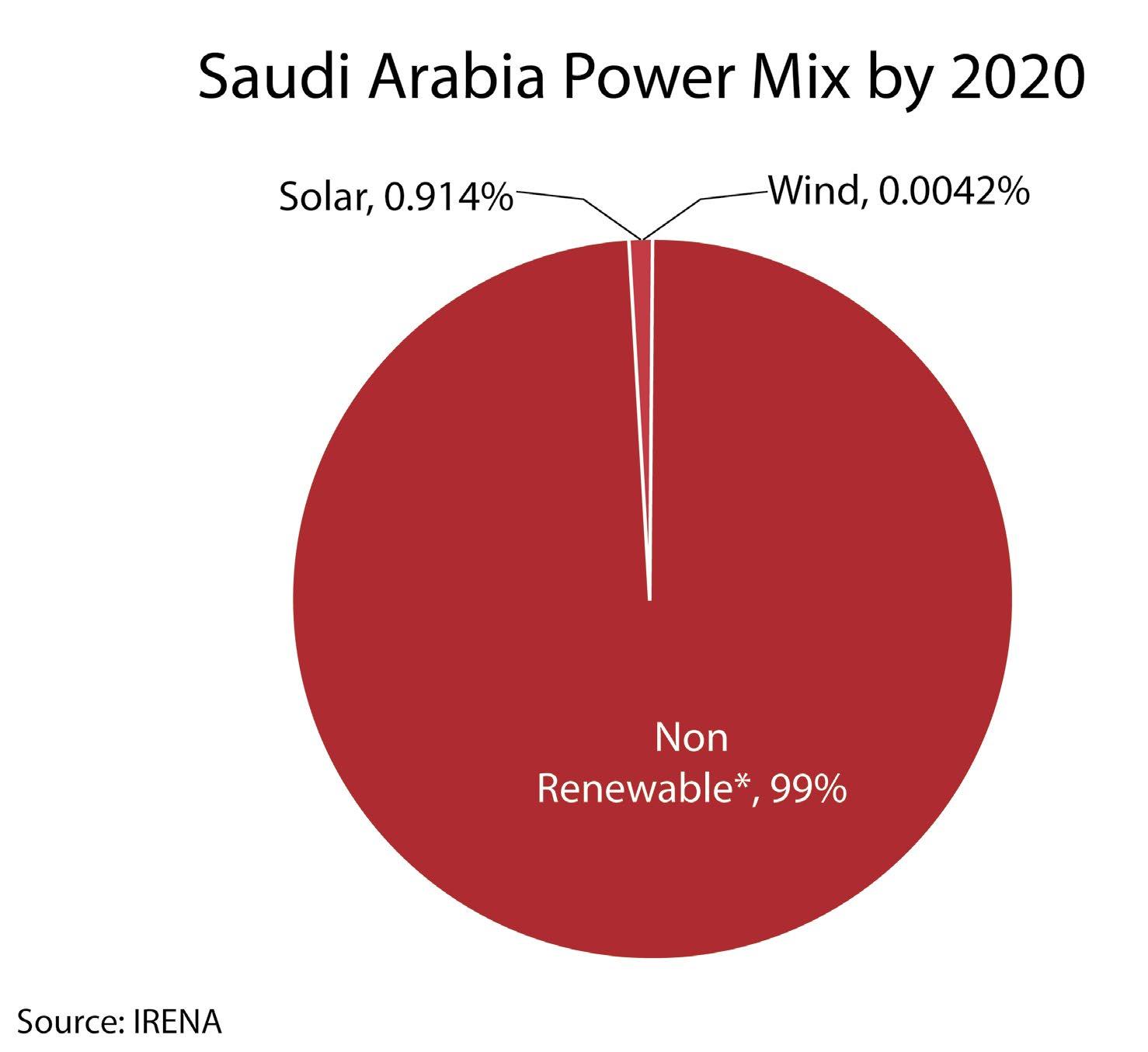
Due to the Covid situation and tariff issue, none of the renewable projects got commissioned in 2020, but in 2021 one Solar project in Sakaka got commissioned, and Wind projects will get commissioned by 2022.
Round Three projects will carry a minimum requirement of 18% local content as calculated by the mechanisms defined by the Local Content & Government Procurement Authority (LCGPA), which aims to increase the value-added contribution of products and services in the national economy. The Electricity & Cogeneration Regulatory Authority (ECRA) launched a regulatory framework for addressing households and smallscale solar distribution systems connected to the utility grid. Introduction of net billing and a cap for each Solar system’s capacity per facility ranging from 1 kW to 2 MW. However, the total installed small-scale Solar PV system capacity may not exceed 15% of a substation’s transformer rated capacity. This came into effect on July 1, 2020.
30 percent of the resources required to complete the solar project must be sourced locally, creating demand for employees, finance, and components locally. Distribution Service Provider (DSP) shall provide the Net Billing arrangement to all Eligible Consumers provided that the Small-Scale Solar PV Systems aggregated capacity to be allowed in parallel with the Distribution System shall not exceed 3% of the preceding year peak load of the power system within the distribution operating area.
Electricity & Cogeneration Regulatory Authority (ECRA) could have a positive impact on the Kingdom’s solar commercial and industrial (C&I) sector. The key elements of the framework are that exported electricity is planned to be credited to the monthly electricity bill of the Solar-powered facility owner.



