8 Leading Business Stories Across Europe - June 2024
13 The rush to adopt generative AI may have long term repercussions on technology
14 Tapping on the Realm of Multifarious Opportunities
18 Open Banking Payments for High-Value Purchases
20 Raj Brahmbhatt
24 Revolutionizing Identities, Governance, Intellectual Property, and Impact
28 Angelika Hellweger of Rahman Ravelli assesses the development of ESG-related litigation
30 New data begs the question - is an AI power struggle in the C-suite imminent?
32 Rytis Ulys, Analytics Team Lead at Oxylabs
36 Why growth-focused businesses must supplement ERP Systems with payments
38 An Overview of the Current Technology Landscape
40 Navigating the emerging AI cybersecurity risk
42 The current state of banking fraud
44 Navigating hidden ransomware pitfalls
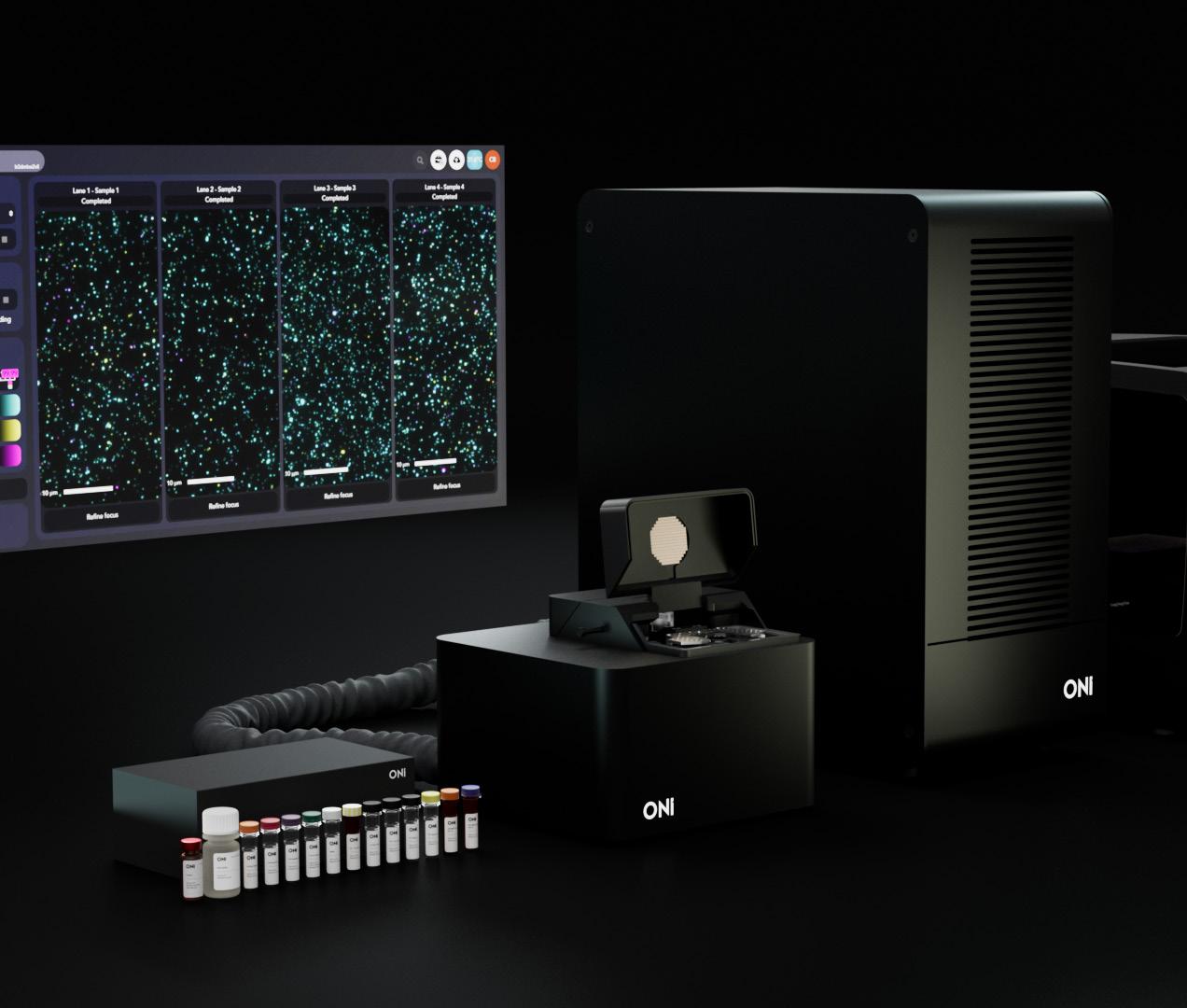
46 Paul Scagnetti Ceo of ONI
50 Advancements in Super-Resolution Microscopy and Personalized Medicine
54 DGFEZ, Dashing Toward 2030
56 One Year of Foreign Subsidies Regulation
58 Retailer Sunglass Hut Aims to Change Marketing Strategies
60 Revolutionary Technology or Overhyped Trend?
62 Exploring the Boundless Potential of Tokenization
64 Global Business Vanguards Aligning with 2045 Net Zero Goals
66 An Unsustainable Practice for the World’s Biggest Brands
68 Sustainability growing influence on financial due diligence process
70 Redefining Industries and Reshaping the Future
74 Operating Effectively when Crisis Hits
76 $13.5 Trillion Investment Needed to Fast-Track Decarbonization of Key Hard-to-Abate Industry Sectors
78 Sustainable Business Practices in Satellite Communications
80 Why Europe is catching the US in the cloud adoption race
82 “Electrification of Automotive Industry: How Electric Commercial Vehicles Are Changing the Game”
86 Attractive opportunities in the Payment Gateway Market
88 Lamia Tazi
Secretary General of the Moroccan Federation of Pharma Industry and Innovation
90 A New Generation of Civil Servants Paving the Way for Industry 2.0
92 36 Pioneer Cities Chart a Course Towards a More Ethical and Responsible Future
Publisher Nick Staunton
Editor
Patricia Cullen
Deputy Editor
Anthony Gill
Associate Publisher Brad Adams
Features Editor Katie Winearls
Head of Production
Paul Rogers
Head of Design Vladimir Mladenovski
Subscriptions Manager
Rebecca Hill
Head of Business Development
Paul Matthews
Advertising Sales
Brad Adams Tara Duckworth
Advertising Sales
Tara Duckworth, Mike Ray, Andy Ellis, Mark Holburn
Contributing writers
Patricia Cullen, Richard Fitzpatrick, Bala Murali Krishna, Shilpa Meen, Argee Laraya, Aimee Ni Mhaolcraibhe, Gordana Ristic, Jonathan Hooker, Jose Ignacio Latorre
Head of Digital
Stephen Scott
Photographer Ben Fisher
NST Publishing Ltd, 19 Leamington Spa (studio 1) Leamington Spa,Cv324tf, UK
The information contained has been contained from sources the proprietor believes to be wholly correct however no legal liability can be accepted for any errors. No part of this publication can be reproduced without consent of the publisher.
Reclaiming duties means more money in your pocket. Discover how duty reclaim can significantly impact your bottom line, contributing to increased profitability.
Stay ahead of the competition by understanding the importance of duty reclaim. Gain a competitive edge and attract more customers with lower prices without sacrificing quality.
Duty reclaim is not just about savings; it’s about optimising your cash flow. Learn how this crucial piece of the puzzle can help you manage your finances more efficiently.
Wondering about the complexity of duty reclaim? Discover the simplified process that ensures you get the maximum from returns with minimal effort. Let duty reclaim work for you!




Chancellor Rachel Reeves unveiled a comprehensive fiscal assessment, revealing significant economic challenges inherited from the previous government. The report highlights a complex mix of high public debt, rising interest rates, and sluggish economic growth. Reeves indicated potential spending cuts and tax adjustments to restore fiscal discipline and stimulate growth. This assessment sets the stage for a pivotal autumn Budget, where tough decisions will be made to balance the public finances while prioritizing investment in infrastructure and public services to foster sustainable economic recovery.

The European Central Bank (ECB) announced that Eurozone inflation has fallen to its lowest level in two decades, sparking concerns about deflationary risks. The inflation rate dropped to 0.5% in May, driven by declining energy prices and weaker consumer demand. ECB President Christine Lagarde emphasized the need for continued accommodative monetary policy to support economic recovery. The ECB is considering further interest rate cuts and expanding its bond-buying program to boost liquidity and encourage spending. This unprecedented low inflation rate underscores the challenges facing the Eurozone economy in achieving sustainable growth.

Volkswagen announced a major expansion of its electric vehicle (EV) production, aiming to double its EV output by 2026. The German automaker will invest €10 billion in new factories and technology development, focusing on battery production and autonomous driving capabilities. This move aligns with the European Union’s stringent emission targets and the growing demand for sustainable transportation. Volkswagen’s CEO, Oliver Blume, stated that the expansion would create thousands of new jobs and solidify the company’s position as a leader in the EV market. The initiative is part of Volkswagen’s broader strategy to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.

Air France-KLM posted record profits for Q2 2024, driven by a surge in post-pandemic travel demand and successful cost-cutting measures. The airline group reported a net profit of €1.2 billion, a significant turnaround from the losses incurred during the COVID-19 pandemic. CEO Benjamin Smith credited the strong financial performance to increased passenger numbers, higher ticket prices, and strategic partnerships. The company plans to reinvest profits into fleet modernization and sustainability initiatives, including the purchase of new fuel-efficient aircraft and the development of sustainable aviation fuels.






The UK and the EU have commenced renegotiations on the Brexit trade deal to address lingering issues and improve trade relations. Key topics include resolving disputes over fishing rights, Northern Ireland trade arrangements, and regulatory divergence. Both sides aim to reach a mutually beneficial agreement that enhances economic cooperation and reduces trade barriers. The renegotiations come amid growing pressure from businesses for more certainty and stability in post-Brexit trade policies. Successful talks could pave the way for stronger economic ties and boost investor confidence in both regions.

Siemens unveiled a €2 billion investment in a new green hydrogen initiative to support the EU’s climate goals. The project involves developing advanced electrolysis technology and building large-scale hydrogen production facilities across Europe. Siemens aims to produce 500,000 tons of green hydrogen annually by 2030, significantly reducing carbon emissions in industrial processes and transportation. The initiative aligns with the EU’s Green Deal and aims to position Siemens as a leader in the emerging hydrogen economy. CEO Roland Busch emphasized the importance of green hydrogen in achieving a sustainable energy transition.










































































































































































































Sorare, the French fantasy football platform, announced its global expansion plans after raising €500 million in a Series B funding round. The company will use the funds to enter new markets, enhance its platform, and expand its partnerships with major football leagues. Sorare’s blockchain-based platform allows users to trade digital player cards and participate in fantasy football competitions. The expansion aims to capitalize on the growing popularity of digital collectibles and fantasy sports. CEO Nicolas Julia highlighted the potential to revolutionize sports entertainment and engage millions of fans worldwide.


Gucci, the iconic Italian luxury fashion brand, announced its plans to go public on the Milan Stock Exchange. The initial public offering (IPO) is expected to raise approximately €4 billion, which will be used to expand the brand’s digital presence and global retail network. Gucci’s CEO, Marco Bizzarri, stated that going public would provide the capital needed to accelerate growth and innovation. The IPO marks a significant milestone in Gucci’s history and reflects the brand’s strong market position and continued demand for luxury fashion.

The Spanish government approved a €5 billion renewable energy mega-project, aiming to enhance the country’s clean energy capacity. The project includes the construction of large-scale solar and wind farms, expected to generate 3 GW of electricity annually. This initiative is part of Spain’s broader strategy to transition to a sustainable energy future and meet EU climate targets. Energy Minister Teresa Ribera highlighted the project’s potential to create jobs, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and ensure energy security. The project is slated to begin construction in early 2025.

Deutsche Bank is under increased regulatory scrutiny following allegations of compliance failures and lapses in anti-money laundering controls. The European Central Bank and Germany’s financial regulator, BaFin, are conducting investigations into the bank’s practices. CEO Christian Sewing pledged full cooperation with regulators and announced a comprehensive review of the bank’s compliance framework. The scrutiny comes amid broader efforts to strengthen financial oversight and prevent illicit activities within the banking sector. Deutsche Bank faces potential fines and reputational damage, underscoring the importance of robust compliance measures.

Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, the world’s largest, announced a significant investment in green bonds, committing $2 billion to support sustainable projects globally. The investment focuses on renewable energy, sustainable infrastructure, and climate resilience projects. CEO Nicolai Tangen emphasized the fund’s commitment to aligning its investments with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. The move reflects a growing trend among institutional investors to prioritize sustainability and address climate change risks. Norway’s investment aims to promote global environmental sustainability while ensuring long-term returns for future generations.

IKEA, the Swedish furniture giant, announced plans to phase out all plastic packaging by 2028 as part of its sustainability strategy. The company will transition to renewable and recyclable materials, such as paper and biodegradable options. IKEA’s Chief Sustainability Officer, Lena Pripp-Kovac, stated that the initiative aims to reduce plastic waste and minimize the company’s environmental footprint. This move aligns with IKEA’s broader goals to achieve a circular business model and promote sustainable living. The company will work with suppliers to develop innovative packaging solutions that are ecofriendly and cost-effective.

European aerospace giant Airbus secured a $10 billion order from Turkish Airlines for 50 new A320neo aircraft. The deal, one of Airbus’s largest this year, reflects strong demand for fuel-efficient aircraft amid rising fuel costs and environmental concerns. Turkish Airlines CEO Bilal Ekşi highlighted the importance of the new fleet in enhancing operational efficiency and reducing carbon emissions. Airbus CEO Guillaume Faury emphasized the strategic partnership with Turkish Airlines and the growing market for sustainable aviation solutions. The first deliveries are scheduled for 2026, supporting the airline’s expansion plans.

Nokia, the Finnish telecommunications giant, announced the acquisition of FastMile, a leading 5G technology startup, for €600 million. The acquisition aims to enhance Nokia’s 5G capabilities and accelerate the rollout of next-generation networks. FastMile’s innovative solutions for fixed wireless access and small cell technology will complement Nokia’s existing portfolio. CEO Pekka Lundmark stated that the acquisition aligns with Nokia’s strategy to lead in 5G innovation and deliver high-speed connectivity solutions globally. The deal is expected to boost Nokia’s competitive position in the rapidly evolving 5G market.

Maersk, the Danish shipping conglomerate, announced plans to expand its green fleet with an investment of $1.5 billion in new eco-friendly vessels. The new ships, powered by methanol and other sustainable fuels, aim to reduce carbon emissions and meet stringent environmental regulations. CEO Søren Skou emphasized Maersk’s commitment to achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. The investment includes the construction of 10 new container ships and the retrofitting of existing vessels with green technology. Maersk’s initiative highlights the shipping industry’s efforts to transition to sustainable operations and combat climate change.

UBS Group, Switzerland’s largest bank, reported strong Q2 earnings, driven by robust performance in its wealth management and investment banking divisions. The bank posted a net profit of CHF 2.3 billion, surpassing analysts’ expectations. CEO Ralph Hamers attributed the success to increased client activity, favorable market conditions, and strategic cost management. UBS plans to reinvest the profits into digital transformation and expanding its global footprint. The positive earnings report underscores UBS’s resilience and adaptability in a challenging economic environment, bolstering investor confidence in the bank’s growth strategy.

Royal Philips, the Dutch health technology company, completed the divestment of its domestic appliances unit for €3.7 billion to a global investment firm. The sale aligns with Philips’ strategic focus on healthcare technology and innovation. CEO Frans van Houten stated that the divestment allows Philips to concentrate resources on its core health tech businesses, including medical imaging, patient monitoring, and digital health solutions. The proceeds will be used to strengthen Philips’ R&D capabilities and pursue strategic acquisitions in the healthcare sector. The transaction marks a significant step in Philips’ transformation journey.

EDP, Portugal’s leading energy company, announced a major renewable energy project in Brazil, investing €1 billion in new wind and solar farms. The project aims to add 1.5 GW of renewable capacity, supporting Brazil’s clean energy transition and EDP’s global expansion strategy. CEO Miguel Stilwell d’Andrade emphasized the importance of international growth and sustainable energy investments. The new facilities will supply power to millions of Brazilian households and contribute to reducing carbon emissions. EDP’s investment highlights the growing role of European companies in the global renewable energy market.

Alpha Bank, one of Greece’s largest financial institutions, announced a comprehensive digital transformation program, investing €500 million over the next five years. The initiative aims to enhance digital banking services, improve customer experience, and streamline operations.
CEO Vassilios Psaltis highlighted the strategic importance of digital innovation in maintaining competitiveness and meeting evolving customer needs. The program includes the development of a new mobile banking platform, advanced cybersecurity measures, and the implementation of AI-driven financial services. Alpha Bank’s digital transformation underscores the broader trend of digitalization in the European banking sector.

Anheuser-Busch InBev, the world’s largest brewing company, announced a €1 billion investment in sustainability initiatives to achieve carbon neutrality by 2040. The investment focuses on renewable energy, water conservation, and sustainable packaging. CEO Michel Doukeris emphasized the company’s commitment to environmental stewardship and responsible business practices. The initiatives include installing solar panels at breweries, reducing water usage in production, and transitioning to fully recyclable packaging materials. Anheuser-Busch InBev’s sustainability investment reflects the growing demand for eco-friendly products and the importance of corporate responsibility in the beverage industry.
London, UK – July 11, 2024 – Businesses who rush to adopt generative AI tools will encounter prolonged challenges with their existing infrastructure, new research from Console Connect, a global Network-as-a-Service provider, has revealed.
According to its latest global survey, more than three quarters of business IT leaders and CTOs (76%) agreed the fast adoption of generative AI (Gen AI) will have long-term repercussions on technology infrastructure planning for their organisation.
Additionally, two-thirds of CTOs (66%) said their network infrastructure does not have the capacity to embrace Gen AI to its full potential; while 76% believe their IT teams are under increasing pressure to adopt Gen AI within their organisation.
The large volumes of additional data being generated by Gen AI and the requirement to move this data to and between private and public clouds is already starting to introduce greater cost and complexity to enterprise networks.
As enterprises build hybrid and multi-cloud architectures to deliver and support generative AI, they need to re-examine how they access the cloud.
The survey conducted by Arlington Research engaged 1,000 CTOs and senior IT leaders across the UK, US, Australia, Hong Kong, and Singapore, providing a comprehensive perspective on the challenges and demands associated with Gen AI adoption.
The findings underscore a growing awareness among industry leaders regarding the potential long-term repercussions of embracing Gen AI without strategic planning.
“The rapid development of generative AI creates a demand on networks

that we
says Paul Gampe, CTO of Console Connect. “As CTOs and senior IT leaders adopt Gen AI tools within their organisation, they need to consider the short and long-term implications of moving larger volumes of sensitive data to and between private and public clouds.”
Security is also a big concern when it comes to the adoption of Gen AI. Seven-in-ten (70%) feared the use of Gen AI is going to put their organisation’s network at risk of cyberattacks or data breaches – a figure which rises to 90% in Australia.
Cybersecurity risks and lack of IT skills/expertise to support it are seen as the main barriers to adopting Gen AI in their organisations.
“These survey results demonstrate that when it comes to deploying mission-critical AI applications, businesses are growing increasingly concerned about the need to be securely connected and that the public internet is no longer suitable for handling many of these applications and workloads. Automation and the move to Network-as-a-Service presents a way for businesses to break away from traditional network infrastructure and the public internet, and instead utilise automated, private and secure network connections to the cloud that can be dynamically adapted to meet the needs of generative AI,” said Gampe.
You can read the full ‘2024 Interconnection Report: The impact of generative AI on networks.

As the world of social media is expanding, the creator economy is also flourishing like never before. The total number of internet users has reached a whopping 5.3 billion in the beginning of year 2024. Due to this, market players are reaching out to content creators, community builders, and curators to spread the message of their brands on a humongous level. Some of the below-written data is the testimony of the rising
importance of digital creators in the growth of business:
- Almost 25.1% of market players declared that they have got 2nd highest ROI in comparison to other marketing approaches.
- In the year 2022, it was estimated that almost 54.2% of 18-29-yearold social media users confess that social media influences their purchases.
- Almost 67.2% of the consumers acquired knowledge of a new
product through the creator’s videos.
- In the year 2021, YouTube paid more than USD 15.1 billion to content creators.
These statistics proclaim that the creator’s economy is playing a prominent role in today’s business operations. Before going forward, let us briefly understand the historical evolution of the creator economy.

Let us understand some of the factors contributing to the surge of the creator economy:
A plethora of factors are contributing to the rapid growth in the domain of the creator economy. Some of the key growth-propelling factors are:
1- Increase in internet users, high screen time and globalization.
A study conducted at the beginning of 2024 revealed that on average people render almost 3 hours
Beginning of 2000s Advent of blogging
- People initiated sharing content online
- Monetization was conducted mainly through sponsors and advertisements
Mid 2000s YouTube began operations in 2005
Ending of 2000s Mushrooming Social Media Platforms
Preliminary years of the 2010s
Middle of the 2010s
The initiation of other social media platforms
Diverse content formats were fabricated
2017 onwards Widespread expansion of platforms
The 2020s onwards Mainstreaming
- Video creators started monetizing through AdSense
- Expansion of platforms such as Twitter and Facebook
- Brand partnerships became widely popular
- Instagram, Tiktok, and Snapchat were launched
- Creators started getting money directly from fans
- Thriving of Live streaming and e-commerce integrated services
- Emergence of creator-focused start-ups
- The arrival of the pandemic raised the consumption of online content
- Creator economy valued at USD 104.2 billion
and 16 minutes on their smartphones every day. Other than this, the potential of Meta advertising garnered almost 2 billion people. As people are spending more time hovering over the internet, the scope of advertisement on social media platforms has increased exponentially. The wider access to the internet is narrowing the gap between products and consumer awareness. The last mile of internet reach is certainly giving economic thrust to the creator economy.
2- Mushrooming popularity of short-term video content
It has been estimated that almost 75.2% of people confessed that they
prefer marketing through video content. With almost 96.2% favoring videos of shorter duration for efficacious service or product education. Consumers are loving short form video content as these are highly effective in acquiring the attention of audience and raising brand visibility and awareness.
3- A rising number of creator economy tools and platforms
There has been a surge in the development of a myriad of creator economy tools such as All-in-one tools, community and engagement tools, and AI tools. Other than this, there is widespread availability of content creation courses. There is the
advent of numerous monetization platforms that are helping creators earn a decent income from their work. With the utilization of platforms such as Snapchat, Instagram, YouTube, TikTok, etc content creators can earn money through:
- Fan clubs
- Advertising revenue share
- Tipping
- Product placement
- Live and virtual event
- VIP meetups
- Merchandise
- Paid subscriptions
Moreover, Instagram has evolved as the most promising influencer marketing place for customers.
- About 89.2% of the marketers said that Instagram was essential for their influencer marketing strategy
- Almost 65.2% of consumer confessed that they follow their favorite influencers on Instagram.
- Moreover, 71% of women prefer using Instagram over other social media channels to follow their favorite influencers.
Let us enumerate the platforms that are most popular for influencer marketing:
The above data illustrates that content creator economy is going to thrive in the future. Let us now delve into the market analysis:
The creator economy market size is anticipated to reach almost USD 600 billion by the end of year 2036. Furthermore, the market garnered almost USD 200 million in the year 2023. Some of the prominent companies in the domain are Meta, YouTube, Bytedanc, Alphabet, Spotify AB, Netflix, Snap Inc, Pinterest etc. The creator economy holds enormous potential for growth in multiple aspects. Some of the key points are as follows:


- By the beginning of 2024, there were almost 206.9 million content creators present globally.
- Almost 10.1% of influencers earn USD 100,000 or more in a year.
- Approximately 46% of people identify as full-time content creators.
- Almost 1 billion accounts on Instagram have over 500k followers
- There were almost 42,000 YouTube channels with over 1 million subscribers in the year 2023.
- Almost 67.2% of the consumers learned about new products through creator videos.
Some of the future trends in creator economy domain are:
- Advent of Web 3 technologies is opening new opportunities for content creation
- Non fungible tokens are going to play a prominent role in creator economy
- Growth of the community based platform
- Huge future demand for the influencer marketing
The above information illustrates that the creator economy market is offering plethora of lucrative opportunities for the future. However, market players are required to understand the intricacies of the market by analysis market research reports. An exhaustive market research report include information related to the growth opportunities, market constraints, regional analysis, etc.
Source -https://www.researchnester.com/reports/reator-economy-market /5691
“As online shopping, live selling, and social commerce continue to grow, the luxury shopping experience must evolve to be more immersive, customised, and secure”
By Donal McGuinness, CEO of Prommt
Personalised experiences are the hallmark of luxury retail. When a brand tailors its offerings to match individual desires and tastes, it speaks directly to the customer, creating a unique and powerful connection. It’s not just about the product - it’s about how the customer feels when buying and using it.
Payments are a vital part of this experience. Often the final touchpoint, it can leave a lasting impression that can influence a customer’s decision to return. The payment journey is an extension of the brand, making it crucial to remove friction at checkout, and offer a choice of safe and convenient payment options.
By 2025, Gen Z and Millennials will drive 70 percent of luxury spending As hybrid shoppers, they easily move between physical stores, online platforms, and virtual experiences. In addition, they expect seamless payment options across all channels, allowing them to engage anytime, anywhere. As online shopping, live selling, and social commerce continue to grow, the luxury shopping experience must evolve to be more immersive, customised, and secure. Businesses can capitalise on this trend by integrating pay-by-link features into social media and messaging apps, allowing customers to make purchases directly from live videos hosted by influencers and brand reps.

Moreover, luxury retailers can offer remote personal consultations and follow up with secure, branded payment requests via SMS, email, web chat, and messaging apps, incorporating modern payment options like open banking.
To date, these payment links have largely been based on card transactions, however, more and more luxury retailers are now beginning to experience the transformational benefits that a Pay By Bank option offers. Based on the European Open Banking payments initiative, Pay by Bank is a game-changer for highvalue transactions. There’s no hassle of card limits and expensive processing fees. It is a safer, faster, and more cost-effective alternative to time-consuming manual bank transfers, drafts, or cheques.
Open banking payments are a winwin for customers and businesses. Backed by the EU Payment Services Directive and the CMA 9 banks in the UK, it helps retailers cut costs and protect margins by significantly reducing high transaction fees, card fraud, chargebacks, and payment operations costs.
Customers enjoy a quick, secure, and seamless way to pay directly from their bank accounts. With open banking payments, clients no longer need to worry about mistyping lengthy account details. In a few simple taps, they select their bank, log in to their mobile banking app, and authorise the payment in a native environment. They have more control over who accesses their personal data and

enjoy greater visibility into their transactions and account balances. Sensitive payment information becomes ‘invisible’, making it harder for fraudsters to exploit. Customers authenticate payments directly through their own banking app, with their personal information encrypted and safeguarded by industry-standard banking security. Unlike direct debits, the payment is initiated by the payer and pushed to the merchant, and not initiated by the merchant and pulled from the payer.
All providers of open banking solutions must adhere to stringent security standards to safeguard customer data. Open banking technology is safe because the banks themselves designed and built the API endpoints, which play a crucial role in verifying account information and facilitating
payments between accounts. Initially developed for online banking, this technology has seen substantial investments in security measures over time. The expertise gained from these investments forms the bedrock of open banking technology.
Traditional payment methods like manual bank transfers are slow and carry high operational costs. Merchants usually share their bank details in PDF format, making it necessary for customers to manually set them up as payees before making a payment. This process involves multiple authentication steps and the hassle of entering and verifying lengthy account numbers. Consequently, it causes delays in business communication, as sales
staff need to coordinate with the finance team to confirm payments before shipping goods. Moreover, sharing bank details in this way isn’t safe and exposes sensitive data to potential misuse by malicious middlemen.
Advanced pay-by-link solutions facilitate smarter invoicing with merchant-branded payment requests, providing a direct link for customers to settle bills effortlessly. With preset payee information, payments can be authenticated securely in just a few clicks. This highlights how open banking can significantly improve businesses’ accounts receivable processes. Furthermore, with SEPA Instant and Faster Payments in the UK, open banking transfers are immediate, and all parties are promptly notified, so deals can be completed more quickly.
With smart payment orchestration controls, luxury retailers can set automated thresholds to present their desired payment method, depending on factors such as the value, location, product, or transaction type. For instance, a jeweller could accept card payments for deposits and take the final balance through open banking. This enables customers to benefit from credit card protections, and the merchant to benefit from the lack of card fees on the larger balance payment.
Retailers can easily set automatic chase paths for failed transactions or where the cart has been abandoned, and present an alternative payment method to complete the transaction –via bank or card. This strategy allows them to achieve substantial savings on transaction fees and operational costs, while also mitigating card fraud and minimising chargebacks.
Open banking payments are the ideal choice for luxury purchases. Customers experience a seamless, secure payment process directly from their banking app, while merchants enjoy reduced processing and operational fees, as well as strengthened fraud prevention measures.
a trailblazer in the rapidly expanding tokenization market. As digital transformation accelerates across Europe, Zeebu stands at the forefront of leveraging blockchain technology to revolutionize how businesses operate and transact. Today, we are privileged to gain insights from the visionary leader driving this innovation.
Zeebu has distinguished itself by developing cutting-edge solutions that enable the seamless tokenization of assets, enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency in various industries. From real estate to finance, Zeebu’s platform empowers businesses to tokenize physical and digital assets, creating new opportunities for investment and liquidity.
In this session, we will explore the intricacies of the tokenization market, delve into Zeebu’s unique offerings, and understand the strategic vision guiding the company. Our discussion will cover the potential of tokenization to reshape traditional business models, the challenges and opportunities within this emerging market, and Zeebu’s role in shaping the future of digital assets.
Zeebu is focused on tokenization solutions across various domains. Can you explain what tokenization means and why it’s become such an important concept in recent years?
Absolutely. At Zeebu, we’re primarily focused on transforming the telecom carrier industry through

blockchain-based payments and settlement layer. Tokenization is central to this transformation. In simple terms, tokenization converts realworld assets, digital art, intellectual properties, and even processes into digital tokens that exist on blockchain networks.
For Zeebu, tokenization is about streamlining and securing transactions within the telecom sector using ZBU tokens. This integration ensures automated settlements and realtime transaction processing, making operations more flexible, secure, and efficient for telecom businesses. As the digital world evolves, Zeebu’s approach to tokenization is setting new standards in decentralization, security, and global accessibility.
Tokenization has become an important concept in recent years due to its transformative benefits in various sectors. One of the key advantages is fractional ownership, which allows assets that were previously illiquid, like real estate or fine art, to be divided into smaller, tradable units. This opens up investment opportunities to a broader audience and enhances liquidity in the market.
Efficiency is another significant benefit. Tokenization automates many processes through smart contracts, reducing the need for intermediaries and speeding up transaction times. This leads to lower costs and more streamlined operations.
Transparency and traceability are also crucial. Blockchain technology ensures
that every transaction is recorded in a secure, immutable ledger that can be audited in real-time. This transparency builds trust among all parties involved and reduces the risk of fraud and errors.
Overall, tokenization is revolutionizing how we manage and transfer assets, making these processes more accessible, secure, and efficient.
One of Zeebu’s areas of focus is DeFi (Decentralized Finance). How can tokenization contribute to the growth and adoption of DeFi applications and services?
At Zeebu, we’re passionate about the transformative potential of decentralized finance (DeFi). Integrating DeFi into traditional financial systems can create a faster, more affordable, and inclusive digital economy. DeFi empowers users with decentralized, permissionless protocols, reducing dependence on large institutions that have historically struggled to safeguard consumers during economic crises.
Speaking of tokenization, it lies at the heart of DeFi applications, acting as the crucial first step for bringing real-world assets into the DeFi space. This process not only opens new doors for asset utilization but also significantly propels the growth of DeFi. Tokenization enables innovative financial products such as decentralized insurance, lending and borrowing platforms, and synthetic assets. These advancements diversify and strengthen the DeFi ecosystem, making it more robust and versatile.
We believe in a future where financial services are faster, cheaper, and accessible to everyone, regardless of location or background.
Governance tokens are used to enable decentralized decision-making and voting within blockchain-based organizations. How does Zeebu facilitate the creation and management of governance tokens for projects built on its platform?
We’re actively developing our governance framework. Our goal is to create a democratic and decentralized ecosystem where community members can significantly influence the platform’s direction and decisions. The governance feature will allow users to participate in key processes like validation, deployment, and liquidity provision. This participatory model is crucial for driving the decentralization of telecom transactions and fostering an engaged, active community.
As Zeebu is operating in the Telecom Market, what is the biggest benefit for traditional companies leveraging blockchain technology?
Stemming from our experience in transforming traditional industries, the biggest benefit for traditional companies leveraging blockchain technology is the significant enhancement in automation, efficiency, and transparency. The telecom industry, involving numerous participants like operators, carriers, and service providers, faces chronic issues such as delays in settlements, lack of transparency, high transaction fees, and substantial FX conversion losses.
Blockchain technology directly addresses these inefficiencies. At Zeebu, we use blockchain to automate payment processes, ensuring realtime settlements that reduce transaction times from days to seconds. This automation minimizes operational costs and FX conversion losses.
Additionally, blockchain provides an immutable ledger that enhances transparency and security, eliminating the need for intermediary approvals and reducing the risk of fraud.
By integrating blockchain, traditional companies can streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve the overall efficiency and reliability of their process. The applications for every industry must be unique and benefits are endless, ranging from enhanced data security and transparent supply chains to improved compliance and streamlined auditing processes. Each industry can tailor blockchain technology to address its specific challenges, thereby unlocking new levels of innovation and operational excellence.
There are many buzzwords such as tokenization, RWA, and DeFi; Where do you see these sectors going and what are you at Zeebu actually trying to achieve in the near future?
The financial landscape is undergoing a transformative shift with the integration of tokenization, Real World Assets (RWA), and Decentralized Finance (DeFi). These innovations are redefining various sectors by enabling more efficient use of traditional market liquidity and bringing capital markets on-chain. This movement is critical as it leverages the vast pools of liquidity in traditional markets, making assets more accessible and tradable.


In the trading and investment sector, DeFi is revolutionizing how trades are conducted, making them faster, more cost-effective, and globally accessible. Similarly, the lending and borrowing landscape is being reshaped by DeFi platforms, which offer easier access to loans and better returns, appealing to a wide range of users.
The potential of DeFi to disrupt the traditional payments and remittances industry is becoming increasingly evident. With the ability to conduct robust cross-border transactions seamlessly, DeFi protocols are providing a more efficient alternative to conventional methods.
The majority of the industries are moving towards greater integration of these technologies, with increased adoption in highly regulated

jurisdictions playing a pivotal role. As regulatory frameworks evolve to accommodate these innovations, we can expect to see substantial growth and mainstream acceptance. This regulatory clarity will foster an environment that supports innovative growth, efficient market participation, and provides more utility for asset holders to leverage on-chain capabilities.
At Zeebu, one of our most anticipated updates is the rollout of our liquidity protocol. This development will enhance our platform’s capabilities, facilitating smoother and more efficient transactions while introducing a greater degree of decentralization. By implementing these initiatives, we aim to drive innovative growth, enable efficient market participation, and provide more utility for asset holders to leverage on-chain.
In essence, the future of finance and beyond lies in the seamless integration of these technologies to create a more inclusive, transparent, and efficient system. At Zeebu, we are committed to being at the forefront of this transformation, continuously working towards setting new standards in the industry.
What is your biggest challenge and what do traditional companies need to change to take advantage of new technologies? Tokenization is a powerful tool as we know, but how can companies “get over the hump” and actually integrate it into daily operations?
We see the biggest challenge lies in bridging the gap between traditional business practices and the innovative potential of blockchain technologies,

including tokenization. While the benefits of these technologies are clear— greater efficiency, transparency, and cost savings—many traditional companies struggle with the complexity of integration and the inertia of established systems.
One major challenge is the need for greater understanding and awareness of tokenization among the public. Many people are still unfamiliar with the benefits and mechanisms of tokenization, which can hinder widespread adoption. Another challenge is navigating the complex and uncertain regulatory environment surrounding tokenization. Finally, making the technology more seamless and user-friendly is essential for broader acceptance.
To take full advantage of new technologies, traditional companies need to undergo a fundamental shift in mindset. Moreover, companies need
to adopt a phased approach to integration. Instead of a complete overhaul, businesses can start by implementing tokenization in specific, manageable areas where it can have the most immediate impact. It is crucial to leverage tokenization to bring assets and processes onto the blockchain while maintaining an easy-touse interface. The transition should not feel overwhelming; rather, it should involve simple, straightforward steps. Developing custom-built applications for different industries can ensure that these solutions are tailored to meet specific needs, making the adoption process smoother and more effective.
By focusing on making the technology accessible and user-friendly, companies can ensure that the transition to tokenization is as seamless as possible.
What factors are hindering the wider adoption of blockchain payments by online merchants and businesses? Are UI/UX issues or technological limitations the main obstacles? How is Zeebu addressing these challenges?
Yes, That still stands true, adoption of blockchain payments by online merchants and businesses is largely hindered by technical complexities and less intuitive user interfaces compared to traditional systems. The onboarding process, which includes steps like setting up digital wallets and using decentralized applications, can be daunting for many users. However, the core issue is the lack of enterprise-specific solutions tailored to the unique needs and workflows of businesses.
At Zeebu, we recognize that for blockchain payment solutions to be widely adopted, they must be as seamless and user-friendly as traditional systems. This means developing interfaces that are intuitive and easy to navigate, reducing the learning curve associated with new technologies.
Another focus of Zeebu has been to build tailored solutions for the telecom industry, addressing the unique challenges in their settlement processes. By providing custom-built applications that integrate smoothly with existing business operations, we ensure that the transition to blockchain payments is straightforward and efficient. Our solutions are designed to simplify the setup and use of blockchain technology, making it accessible even for those who may not be tech-savvy.
By prioritizing user experience and offering industry-specific solutions, Zeebu helps businesses overcome the technical and logistical barriers to adopting blockchain payments. This approach ensures that companies can easily leverage the benefits of blockchain technology while maintaining their existing workflows and processes.

The advent of blockchain technology has ushered in a new era of digital transformation, and at the heart of this revolution is the concept of tokenization. By converting rights and assets into digital tokens, we are witnessing a profound shift in how we manage identities, governance, intellectual property, and even our approach to environmental and social challenges. This 2000-word feature explores the multifaceted impact of tokenization on these critical areas, highlighting the
transformative potential and future prospects of this groundbreaking technology.
In our increasingly digital world, the need for secure and verifiable identities is paramount. Traditional methods of identity verification, often cumbersome and prone to fraud, are being challenged by the promise of tokenized identities. By leveraging blockchain technology, tokenized identities offer a secure, decentralized, and user-centric approach to managing personal information.
Tokenized identities involve the creation of a digital representation of an individual’s identity, which is stored on a blockchain. This digital identity can include a wide range of personal information, from basic details like name and date of birth to more complex data such as educational qualifications, professional credentials, and even biometric information. The use of blockchain ensures that this information is immutable, tamper-proof, and easily verifiable.

One of the most significant advantages of tokenized identities is their ability to provide users with full control over their personal data. In traditional systems, personal information is often stored in centralized databases, making it vulnerable to breaches and unauthorized access. With tokenized identities, individuals can manage their data through private keys, sharing only the necessary information with trusted parties. This approach not only enhances security but also fosters greater privacy and user autonomy.
The tokenization of credentials is revolutionizing the verification process across various sectors. In education, for instance, academic institutions can issue digital diplomas and certificates on the blockchain, which students can then present to employers or other educational entities. This method not only simplifies the verification process but also eliminates the risk of fraudulent claims.
Similarly, professional credentials can be tokenized to facilitate seamless verification in the job market. Employers can quickly verify an applicant’s qualifications and work history without the need for lengthy background checks. This efficiency is particularly valuable in industries where rapid hiring processes are essential.
Several projects and platforms are already pioneering decentralized identity solutions. Microsoft’s Azure Active Directory, for example, integrates decentralized identity technology to empower users with self-sovereign identities. Similarly, platforms like Sovrin and uPort are developing decentralized identity networks that allow individuals to manage and share their credentials securely.
The potential applications of tokenized identities extend beyond individual use cases. Governments can implement digital identity systems to streamline public services, while financial institutions can leverage them for more efficient KYC (Know Your Customer) processes. As adoption grows, tokenized identities are poised to become the cornerstone of a more secure and efficient digital ecosystem.
In the realm of decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain-based projects, governance tokens have emerged as a powerful tool for community-driven decision-making. These tokens enable token holders to participate in the
governance of a project, influencing key decisions and shaping the future direction of the platform.
Governance tokens are central to the operation of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). DAOs are entities governed by smart contracts and driven by community consensus rather than centralized leadership. Token holders can propose and vote on changes to the protocol, ranging from technical upgrades to financial decisions and community initiatives.
The use of governance tokens democratizes decision-making, giving stakeholders a direct say in the development and management of the project. This inclusivity fosters a sense of ownership and accountability among participants, aligning their interests with the success of the platform.
Several prominent DeFi projects have successfully implemented governance tokens. MakerDAO, for example, uses MKR tokens to govern its decentralized stablecoin platform. MKR holders can vote on proposals related to risk parameters, collateral types, and other critical aspects of the protocol.
Similarly, Uniswap, a leading decentralized exchange, introduced UNI tokens to enable community governance. UNI holders can participate in the decision-making process, influencing the future development and direction of the platform. This model not only empowers users but also enhances the resilience and adaptability of the project.
While governance tokens offer significant benefits, they also present challenges. Ensuring active and informed participation among token holders can be difficult, and the risk of concentration of power in the hands of a few large holders remains a concern. Additionally, navigating regulatory frameworks and ensuring compliance
is a complex task for projects operating in the decentralized space.
Despite these challenges, the potential of governance tokens to revolutionize organizational structures and decision-making processes is immense. As the technology matures and more projects adopt decentralized governance models, we can expect to see a shift towards more transparent, inclusive, and community-driven ecosystems.
The digital age has brought about new challenges in protecting and monetizing intellectual property (IP). Tokenization offers a promising solution by enabling the creation of digital tokens that represent ownership and rights to intellectual property. This innovation has far-reaching implications for creators, artists, and innovators across various fields.
Tokenizing intellectual property on a blockchain provides a secure and transparent record of ownership. This immutable ledger ensures that the provenance and ownership history of an asset are verifiable and tamper-proof. For creators, this means enhanced protection against infringement and unauthorized use of their work.
In the art world, for instance, tokenization allows artists to issue digital certificates of authenticity for their works. Collectors can purchase these tokens, confident in the knowledge that their ownership is securely recorded on the blockchain. This approach not only protects the artist’s rights but also enhances the value and marketability of the artwork.
Tokenization also opens up new avenues for monetizing intellectual property. Creators can issue tokens that represent fractional ownership of their work, allowing investors to purchase shares in a song, film, or invention. This fractionalization democratizes access to investment opportunities and enables creators to raise funds more efficiently.

Moreover, smart contracts can automate licensing agreements and royalty distributions. For musicians, this means receiving payments instantly whenever their music is streamed or used commercially. Smart contracts ensure that all parties involved in the creation and distribution of a work are fairly compensated, reducing the administrative burden and potential for disputes.
Several platforms are pioneering the tokenization of intellectual property. One notable example is Ascribe, a platform that allows artists to register their digital creations on the blockchain, ensuring proof of ownership and enabling secure transfers.
Another example is the Musicoin project, which uses blockchain to manage music rights and royalties, providing transparent and fair compensation for artists.
In the patent industry, platforms like IPwe are exploring the use of blockchain to create a global patent registry. By tokenizing patents, inventors can easily prove ownership, facilitate licensing, and attract investment. This approach has the potential to streamline the patenting process and foster innovation by making it easier to share and monetize intellectual property.
Beyond the realms of finance and commerce, tokenization holds significant potential for driving positive environmental and social impact. By creating transparent, traceable, and

efficient systems, tokenization can address some of the most pressing challenges facing our planet and society.
Tokenization can play a crucial role in environmental conservation efforts. One application is the tokenization of carbon credits. By representing carbon credits as digital tokens on a blockchain, we can create a transparent and efficient market for trading these credits. This approach enhances accountability and ensures that carbon offset projects are accurately tracked and verified.
Additionally, tokenization can support sustainable supply chains. By tracking the provenance of raw materials and products through digital tokens, companies can ensure that their goods
are sourced ethically and sustainably. Consumers, in turn, can make more informed purchasing decisions, driving demand for environmentally friendly products.
Tokenization can also promote social impact and financial inclusion. In the charitable sector, for instance, blockchain technology can enhance transparency and accountability in the distribution of funds. Donors can track their contributions through digital tokens, ensuring that their donations reach the intended beneficiaries and are used effectively.
Furthermore, tokenization can empower underserved communities by providing access to financial services.
In regions with limited banking infrastructure, tokenized assets and decentralized finance platforms can offer individuals and businesses access to credit, savings, and investment opportunities. This inclusivity fosters economic growth and resilience, particularly in developing economies.
Several initiatives are leveraging tokenization for environmental and social good. Veridium, for example, uses blockchain technology to tokenize carbon credits and other environmental assets, creating a transparent and efficient market for sustainable investments. Similarly, the Plastic Bank initiative uses blockchain to incentivize plastic recycling by issuing tokens to collectors, who can then exchange them for goods and services.
In the realm of social impact, the GiveTrack platform allows donors to follow their contributions in real-time, ensuring transparency and accountability in charitable projects. By tokenizing donations, GiveTrack enhances trust and encourages greater participation in philanthropic efforts.
Tokenization is not merely a technological advancement; it is a paradigm shift that has the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives. From secure digital identities and decentralized governance to the protection and monetization of intellectual property, and the promotion of environmental and social impact, tokenization offers a more transparent, efficient, and inclusive future.
As we continue to explore and embrace the possibilities of tokenization, it is essential to navigate the challenges and ensure that the technology is used responsibly and ethically. Regulatory frameworks, education, and collaboration will play critical roles in shaping the tokenized world and unlocking its full potential.
When it comes to the issue of ESG (environmental, social and governance) litigation, there seems to be plenty to report. But while developments show little sign of slowing down, the future may well depend on a number of factors. We are certainly seeing more courts worldwide issuing judgments in favour of protecting the climate. The recent example of Verein KlimaSeniorinnen Schweiz saw the European Court of Human Rights hold that the right to a private life imposes a positive obligation on states to ensure effective protection against the adverse effects of climate change. It was the first time an international court had definitively ruled on the intersection between climate and human rights.
In addition, Friends of the Earth, Client Earth and Good Law Project vs Secretary of State for Energy, Security and Net Zero saw the UK High Court rule that the UK government’s climate strategy was not fit-for-purpose and so was in breach of the UK Climate Change Act. We have also seen the US case of Held v Montana, in which the court found in favour of protecting the constitutional right to a healthy environment, and the French ruling, in Notre Affaire à Tous and Others v France, that the state needs to take immediate action to comply with commitments to reduce emissions under the Paris Agreement; the international treaty on climate change that was adopted in 2015.
Then there’s the Supreme Court of India’s ground-breaking ruling that recognised a right to be free from the adverse effects of climate change, and

South Korea’s constitutional court currently hearing the country’s first major climate litigation. There is certainly a move to the courts when it comes to the environment.
The future of ESG litigation is an intriguing proposition. The International Tribunal for the Law of the Sea recently confirmed that states are under a legal obligation to protect our oceans and seas from climate change. This includes an obligation to restore habitats and ecosystems where they have been damaged due to anthropogenic (man-made) emissions, and where restoration is needed to regain ecological balance. States are even under an obligation to anticipate risks
to the marine environment that may be created by climate change.
At present, the world is currently awaiting the outcome of further requests for advisory opinions from the International Court of Justice and the Inter-American Court of Human Rights. These bodies’ interpretations of states’ climate change obligations will not be binding, in the same way as the International Tribunal for the Sea opinion was not binding. But their opinions on matters such as protection of the marine environment, human rights and the environment, and greenhouse gases will carry substantial legal weight. They may be decisive in defining the human rights

obligations of states (and possibly corporations) regarding the climate crisis.
Against this backdrop, we can also expect an increase in climate-related litigation against non-financial institutions and a more diverse range of corporate actors. Cases based on the principle of polluter pays and citing the Paris Agreement could become more commonplace. Claims based on tort law, action brought under corporate due diligence legislation, use of consumer protection and competition law, and challenges to directors over breaches of fiduciary duties under company law are all viable options for those looking to hold to account companies or individuals.
But there are hurdles to be overcome by those looking to bring such cases. The most prominent of these is that rights enshrined in constitutions and regional conventions impose obligations on the state but not on private actors. In many jurisdictions, powerful constitutional rights, most notably the right to a healthy environment, can be asserted vertically against the State but not horizontally against private actors.
The issue of insufficient direct legal rights and procedural Issues is a serious challenge to those looking to bring ESG cases. This applies both to the aforementioned climate-related issues as well as to other matters
such as greenwashing, modern slavery and poor health and safety in supply chains.
English law needs to adapt to the complexities of group litigation. The current arrangements can make bringing action an unbelievably challenging exercise in paperwork, while also giving scope to corporate defendants to do what they can to avoid having to answer for their actions. It is proposed that the UK needs a legal framework for human rights and environmental violations, modelled on the Bribery Act 2010 and Criminal Finances Act 2017; which contain failure to prevent offences.
There can be little argument that something needs to be done. Currently, applicants are usually the ones having to shoulder the burden of proof while up against corporates that can boast large legal teams who face few obligations to disclose information that could be crucial to the case. This has been why a number of claims have been unsuccessful. Added to this, the often slow pace of such proceedings can mean that the harm to people or the environment that is at the heart of the legal action can continue unchecked for long periods of time.
Applicants will often struggle to raise the funds to bring a legal action. Even if they do manage this, they then face the daunting prospect of having to keep finding funds to keep it going. All this has to be done while their opponent is likely to be a sizeable company that can find all the money that is necessary to thwart the case. It is a far from level playing field, which probably explains why the biggest UK group litigation – relating to the Mariana Dam disaster case – required third-party litigation financing.
As a result, many individuals have extremely limited access to justice, which can often only serve to perpetuate injustice. So while we can see signs of progress, much needs to be done to ensure such advances do not remain the exception rather than the rule.

Recent research from Dialpad found that over 69% of executives in the C-suite reporting to the CEO - or what is commonly known as CxOs - are expecting to spearhead their organisation’s AI efforts. The research also found that three quarters (75%) of respondents believe AI will have a significant impact on their roles in the next three years, and more than 69% are already using the technology. Does this mean that an AI power struggle is imminent in the C-suite?
It’s no surprise that AI is top of mind for the C-Suite, but with everyone expecting to lead the charge - does this risk confusion, duplication of efforts, and even a power struggle over who holds the keys to an organisation’s AI-related decisions? And
what can help tackle these challenges and cut out confusion?
Whilst most (69%) of executives are already using AI, this doesn’t mean they all feel comfortable with the technology. In fact, there are some notable concerns, with 54% of leaders worried about AI regulation and 38% moderately to extremely concerned about AI in general. In light of this, the case for Chief AI Officers (CAIOs) is a strong one - something which the Biden administration in the US has called for recently. In theory, a CAIO will be able to take on these concerns and act as the main point of contact and the final authority on all things AI. It will be their responsibility to understand regulatory developments,
shielding other executives and teams, and to dictate how AI is used across the business. Crucially, a CAIO can also stop any AI ‘power struggle’ from forming, acting as a figurehead for AI-related decisions and planning in a business.
“We will likely begin to see other governments echo the Biden administration’s call for more Chief AI Officer roles to be created,” said Jim Palmer, CAIO of Dialpad. “The CAIO role is one that can manage and mitigate much of the risk that comes with AI development, ensuring privacy and security standards are met and that customers understand how and why data is being used. The specifics of the CAIO role are far from fully mapped out, but as the AI boom continues, this will no doubt change in the coming months and years.”


The research also found that, often, leaders across the business are using multiple AI solutions - 33% executives are using at least two AI solutions, 15% are using three, and 10% are using four or more. If multiple different AI solutions are being used across a business, it runs a real risk of duplication across different departments - meaning companies are often unnecessarily paying for tools with the same functionality. Disparate tools and solutions can also tamper with a single source of truth, making it harder to align teams around the same data, goals and objectives - fuelling the potential AI power struggle among executives even further.
This is another area where the role of a CAIO can be so important, reducing
duplication and ensuring the business invests smartly into AI.
Half (50%) of executives are moderately to extremely concerned about the possibility of a data leakage. On top of this, they have security concerns (22%), accuracy worries (18%), and fears over the cost of models, compute power, and expertise (12%). Additionally, 91% of companies will determine they do not have enough data to achieve a level of precision their stakeholders will trust.
It’s clear that, for all its value, AI is still full of unknowns for many leaders. A CAIO can, again, take on the responsibility to tackle these concerns head on. Alongside this, partnering with AI native companies that develop their
own, proprietary AI services can offer much reassurance. Companies built upon their own proprietary AI stack will have greater control over data, privacy, security, performance and cost – key topics of discussion by organisations and regulators currently. Additionally, partnering with an AI native should, in theory, ensure more accuracy. Why? Because, while public AI is trained off the entire world wide web of data, AI natives can train their models on data that is relevant - making it faster and more accurate. It’s like writing a history book with guaranteed facts versus a combination of facts and lies, with no way to distinguish between the two. By embracing distributed leadership, fostering alignment, and standardising AI tools, businesses can navigate the evolving landscape of AI with confidence and clarity.

What key trends do you see shaping the future of data analytics in business intelligence?
In a little more than a decade, data analytics went through several big transformations. First, it became digitized. Second, we witnessed the emergence of ‘big data’ analytics, driven partly by digitization and partly by massively improving storage and processing capabilities. Finally, in the last couple of years, analytics has been transformed once again by emerging generative AI models that can analyze data at a previously unseen scale and speed. Gen AI is becoming a data analyst’s personal assistant, taking over less exciting tasks— from basic code generation to data visualization.
I believe the key effect of generative AI—and the main future trend for data analytics—is data democratization. Recently, there’s been a lot of activity around “text to SQL” products to run queries in natural language, meaning that people without specialization in data sciences get the possibility to dive deeper into data analysis. However, we shouldn’t get carried away with the hype too quickly. Those AI-powered tools are neither 100% accurate nor error-free, and noticing errors is more difficult for less experienced users. The holy grail of analytics is precision combined with a nuanced understanding of the business landscape—skills that are impossible to automate unless we reach some sort of a “general” AI.
The second trend that is critical for business data professionals is moving towards a single umbrella-like AI system capable of integrating sales, employee, finance, and product analytics into a single solution. It could bring immense business value due to cost savings (ditching separate software) and also help with the data democratization efforts.
Can you elaborate on the role of machine learning and AI in next-generation data analytics for businesses?
Generative AI somehow drew an artificial arbitrary line between next-gen analytics (powered by Gen AI) and “legacy” AI systems (anything that came before Gen AI). In the public discourse

around AI, people often miss the fact that the “traditional” AI isn’t an outdated legacy; Gen AI is intelligent only on the surface; and both fields are actually complementary.
In my previous answer, I highlighted the main challenges of using generative AI models for business data analytics. Gen AI isn’t, strictly speaking, intelligence—it is a stochastic technology functioning on statistical probability, which is its ultimate limitation.
Increased data availability and innovative data scraping solutions were the main drivers behind the Gen AI “revolution”; however, further progress can’t be achieved by simply pouring in more data and computational power. Moving towards a “general” artificial intelligence, developers
will have to reconsider what “intelligence” and “reasoning” mean. Before this happens, there’s little possibility that generative models will bring to data analytics something more substantial than they have already done. Saying this, I don’t mean there are no methods to improve generative AI accuracy and make it better at domain-specific tasks. A number of applications already do it. For example, guardrails sit between an LLM and users, ensuring the model provides outputs that follow the organization’s rules, while retrieval augmented generation (RAG) is increasingly employed as an alternative to LLM fine-tuning. RAG is based on a set of technologies, such as vector databases (think Pinecone, Weaviate, Qdrant, etc.), frameworks (LlamaIndex, LangChain, Chroma), and semantic analysis and similarity search tools.
How can businesses effectively harness big data to gain actionable insights and drive strategic decisions?
In today’s globalized digital economy, businesses don’t have a choice of avoiding data-driven decisions, unless they operate in a very confined local market and are of limited size. To
drive competitiveness, an increasing number of businesses are collecting not only consumer data they can get from their owned channels but also publicly available information from the web for price intelligence, market research, competitor analysis, cybersecurity, and other purposes.
Up to a point, businesses might try to get away without using data-backed decisions; however, when the pace of growth increases, companies that rely on gut feeling only unavoidably start lagging behind. Unfortunately, there are no universal approaches to harnessing data effectively that would suit all companies. Any business has to start from the basics: first, define the business problem; second, answer, very specifically, what kind of data might help to solve it. Over 75% of data businesses collect ends up as “dark data.” Thus, deciding what data you don’t need is no less important than deciding what data you need.
In what ways do you envision data visualization evolving in the context of business intelligence and analytics?
Most data visualization solutions today have AI-powered functionalities
that provide users with a more dynamic view and enhanced accuracy. Further, AI-driven automation also allows businesses to analyze patterns and generate insights from larger and more complex datasets while freeing analysts from mundane visualization tasks.
I believe data visualization solutions will have to evolve towards more democratic and noob-friendly alternatives, bringing data insights beyond data teams and into sales, marketing, product, and client support departments. It is hard to tell, unfortunately, when we could expect such tools to arrive. Up until now, the focus of the industry hasn’t been on finding the single best visualization solution. There are many different tools available on the market, and they all have their advantages and disadvantages.
Could you discuss the importance of data privacy and security in the era of advanced analytics, and how businesses can ensure compliance while leveraging data effectively?
Data privacy and security were no less important before the era of advanced analytics. However, the increased scale and complexity of data collection and processing activities also increased the risks related to data mismanagement and sensitive data leaks. Today, the importance of proper data governance cannot be understated: mistakes can lead to financial penalties, legal liability, reputational damage, and consumer distrust.
In some cases, companies deliberately “cut corners” in order to cut costs or gain other business benefits, resulting in data mismanagement. In many cases, however, improper data conduct is unintentional.
Let’s take an example of Gen AI developers who need massive amounts of multifaceted data to train and test ML models. When collecting data at such a scale, it is easy for a company to miss that parts of these datasets contain personal data or copyrighted material that the company wasn’t authorized

to collect and process. Even worse, getting consent from thousands of internet users who might be technically regarded as “copyright” owners is virtually impossible.
So, how can businesses ensure compliance? Again, it depends on the context, such as the company’s country of origin. US, UK, and EU data regimes are quite different, with the EU having the most stringent one. The newly released EU AI Act will definitely have an additional effect on data governance as it tackles both developers and deployers of AI systems within the EU. Although generative models fall in the low-risk
zone, in certain cases, they might still be subject to transparency requirements, obliging developers to reveal the sources of data the AI systems have been trained on as well as data management procedures.
However, there are basic principles that apply to any company. First, companies must thoroughly evaluate the nature of the data they are planning to fetch. Second, more data doesn’t equal better data—deciding which data brings added value for the business and omitting data that is excessive or unnecessary is the first step towards better compliance and fewer data management risks.

How can businesses foster a culture of data-driven decision-making throughout their organizations?
The first step is, of course, laying down the data foundation—building the Customer Data Platform (CDP), which integrates structured and cleaned data from various sources the company uses. To be successful, such a platform must include no-code access to data for non-technical stakeholders, and this isn’t an easy task to achieve.
No-code access means that the chosen platform (or “solution”) must hold
both an SQL interface for experienced data users and some sort of “drag and drop” function for beginners.
At Oxylabs, we chose Apache Superset to advance our self-service analytics. However, there is no solution that would fit any company and would only have pros and no cons. Moreover, these solutions require well-documented data modeling.
When you have the necessary applications in place, the second big challenge is building data literacy and confidence of non-technical users. It requires proper training to ensure that employees handle data, interpret it, and draw insights correctly.
Why is this a challenge? Because it is a slow process, and it will take time away from the data teams.
Fostering a data-driven culture isn’t a one-off project—to turn data into action, you will need a culture shift inside the organization, as well as constant monitoring and refinement efforts to ensure that non-technical employees feel confident about deploying data in everyday decisions. Management support and well-established cooperation between teams are key to making self-service analytics (or data democratization, as it is often called) work for your company.

Attributed to: Brian Gaynor, VP of Product & EU CEO at BlueSnap
The B2B payments landscape is constantly changing. Maintaining pace is vital to keep up with buyer demands, payment trends, and new regulations. The right payment provider for your ERP System is key to this as it can provide a better buyer experience by offering more ways to pay. It also helps avoid costly fees, which in turn improves agility and gives an edge over competitors. At the same time, it provides businesses with better cash flow and accurate reporting and reconciliation. All this becomes particularly important when companies are looking to scale and need to cater to the differences in payment practices. Last year, 57% of businesses stated that their ERP System helped them become more agile. However, many businesses are still missing out. Business leaders should be incorporating the right payment provider with their ERP System so that it acts as a catalyst

for growth and increases Return on Investment (ROI).
ERP Systems are an excellent way to gather payment data, consolidate workstreams, maintain a growth trajectory, and get an accurate picture of the payment landscape. Adding a Global Payment Orchestration Platform to your ERP System can enable payment acceptance in multiple currencies and payment methods. This brings the dexterity firms need to cater to buyers’ preferences and makes it easier for buyers to complete transactions.
Buyers too, have their own preferred ways to pay. Offering customers their chosen payment types leads to more revenue via repeat business, a reduction in checkout abandonment, and even increased order volume. When adding payments to an ERP System, offering a variety of payment types can satisfy current and future customer preferences while steering the business toward future growth.
Finally, working with the right payment provider gives companies the flexibility to handpick functionalities to cater to multiple use cases across the B2B and B2C spaces. This agility enables businesses to customise services received and optimise their payment strategy at each stage of growth and in every

geography. For example, BlueSnap offers additional services like fraud prevention and chargeback management, which can be added on demand. This gives small and medium enterprises the tools they need to compete with large corporations.
Several factors need to be considered when searching for the right payment provider. Businesses operating across regions have to tackle high cross-border payment fees, low authorisation rates, differences in preferred payment methods, and global and regional regulatory standards. However, these pain
points can be overcome by supplementing an ERP System with a payment provider that has global capabilities to manage multiple currencies, payment types, and fraud and tax regulations in each country.
It’s worth noting that payment providers manage information flow differently and subtle variations like file formats can make or break an onboarding process. The same is the case with additional payment options, which you’ll likely need as the company expands. Your payment partner should guarantee easy assimilation and deployment with little to no additional coding and development requirements - avoiding surplus costs while supporting business expansion.
Your chosen payment provider must also be PCI compliant and update merchant agreement terms, privacy policy, and cookie usage in line with GDPR requirements so that you mitigate data security risks and steer clear of fines for non-compliance. By choosing a payment provider capable of this, you also avoid the need for additional partnerships in different regions, which reduces your overall technical debt.
Ultimately, ERP-supplemented payments are an asset for any business. By choosing a payment partner that combines the functionalities of a payment gateway and a merchant account, businesses can simplify onboarding and management, reduce costs, prepare for business expansion, and improve efficiency and data security. All this goes a long way in improving buyer trust and satisfaction. Fully incorporating the new payment provider into a corporation’s existing ERP System minimises friction and leverages the capabilities of both platforms efficiently. This also sidesteps duplication of data and gives you a clear overview of the payment landscape.
To maximise the benefits of the assimilation, businesses must automate as much as possible. This could mean standardised reporting or fraud prevention strategies across geographies, but the more your payment partner handles, the less there is to be outsourced.
In a dynamic and competitive landscape, it’s the subtle differences that can give a business the edge it needs to stand out and generate higher revenue.
Adding payments to your ERP System is a great way to maximise efficiency and streamline operations, which goes a long way in reducing costs and improving the buyer experience and consequently, profit margins. The seemingly small differences brought about by supplementing your ERP System with a payments provider are the edge enterprises need to flourish.
Consider face-id, which allows access to machine controls on a factory floor. It is obvious why using AI in embedded applications is appealing. AI has several applications, such as voice control, facial recognition, and anomaly detection. Face-id will be used as an example in this post. Much more intelligent, robust, and intuitive than traditional passwords and UIs for humans and machines. Plus, all the other people are doing it. Though AI’s workings may seem enigmatic, what it is capable of is rapidly becoming commonplace. No one wants to use antiquated technology to evaluate things candidly.
Since AI improves the intelligence and capacities of IOT devices, the worldwide AI industry is integrating IOT more and more. These gadgets don’t need centralized cloud servers or a constant internet connection to make judgments because they can process and analyze data locally. According to a recent study, the average American home currently contains 21 connected devices, based on examination of 41 million houses and 1.8 billion connected devices.
Economic opportunities are expanding since there is a growing demand for processors that are more powerful, energy-efficient, and capable of handling complex artificial intelligence algorithms. AI algorithms are becoming more sophisticated and resource-intensive. Consequently, there is an increasing demand for

processors that can effectively handle these demands. High-performance CPUs, GPUs, and specialized AI accelerators are examples of processors that are in higher demand. These processors create chances for embedded AI solution providers to offer cutting-edge technology. In order to leverage the expanding market need and deliver high-performance embedded AI solutions that satisfy customers’ changing needs, suppliers ought to concentrate on creating advanced processors, edge computing capacities, energy-conserving solutions, and alliances.
The market adoption of these solutions will be expedited by the growing
demand for improved technology that can provide clients with customized and adaptable experiences. AI is becoming a part of many embedded systems since personalized experiences are needed. By utilizing these solutions, devices and software are able to evaluate user information, preferences, and actions in order to provide personalized recommendations, suggestions, and reactions. As such, there is an increase in user pleasure and engagement. Through enabling devices and systems to comprehend user preferences, adapt to changing circumstances, make educated judgments, and provide personalized experiences, these solutions eventually

increase consumer satisfaction and encourage market expansion.
Embedded AI systems frequently operate on resource-constrained hardware with limited memory, processing power, and energy. Inadequate processing resources may limit the performance of AI systems, leading to longer inference times, lower accuracy, and a less satisfying user experience. When computational limitations make it impossible for AI models to run on embedded devices, adoption of these solutions is hindered since the models might not meet the performance requirements of the intended applications. As the market continues to grow in
these areas, overcoming these challenges will enable the deployment of more powerful and effective AI applications on resource-constrained devices and accelerate the acceptance of embedded AI solutions in several domains.
Asia Pacific is expected to hold a significant market share by 2036. One major factor driving embedded AI is the retail industry’s digital revolution and the fast expansion of e-commerce. It is estimated that e-commerce in Asia Pacific will generate USD 3.5 trillion in sales. Embedded AI technologies provide intelligent infrastructure, effective energy management, and improved public services
as nations invest in creating technologically sophisticated and sustainable cities.
To sum up, the investigation of artificial intelligence in marketing could involve two distinct approaches: “Applied AI” to utilize external data sources and “Embedded AI” to improve in-platform functionality. Marketers need to understand how AI is essential to establishing their company’s presence in digital marketing as Google continues to progress its use of AI in ad tech solutions.
Source: https://www.researchnester.com/ reports/embedded-ai-market/5715

of Engineering
The cybersecurity threat landscape is constantly evolving. Each day, we see new threat variants emerge. Hackers, and the technologies they use, become more sophisticated and targeted. At the same time the widespread adoption of IoT devices and remote working technologies has introduced opportunities for cybercriminals.
The proliferation of AI, especially generative AI, is fundamentally transforming how companies use software. This is simultaneously complicating software’s attack surfaces and making it more susceptible to vulnerabilities.
enterprise
Add all this together and it’s easy to see why we continue to experience a rapid rise in cyber-attacks globally. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, the global cost of cybercrime is expected to reach $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, up from $3 trillion in 2015.
Indicative of this escalating issue, a report by Metomic said a recent survey of 400 Chief Information Security Officers from businesses in the UK and the US found that 72% believe that AI solutions would lead to security breaches. Conversely, 80% said they intended to implement AI tools
to defend against AI. This is another reminder of both the promise and the threat of AI. On one hand, AI can be used to create unprecedented security arrangements and enable cybersecurity experts to go on the offensive against hackers. On the other hand, AI will lead to industrial-scale automated attacks and incredible levels of sophistication
For tech companies caught in the middle of this double-edged sword, the big questions are how worried they should be and what can they do to protect themselves.
To begin, it’s important to consider the challenge of identifying the AI risk. One of the most pressing issues we have is that because generative AI can craft realistic and personalised phishing emails and mimic the writing style of colleagues or trusted contacts, it can be incredibly hard to establish whether it has been used in a cybersecurity incident.
As a result, we don’t yet know the scale of generative AI-driven attacks or their effectiveness. If we cannot yet quantify the problem, it becomes difficult to know just how concerned we should be.
For tech startups, that means the best course of action is to focus on
and mitigate threats more generally. All evidence suggests that existing cybersecurity measures and solutions underpinned by best practice data governance procedures are up to the task of the existing threat from AI.
With some irony, the biggest existential threat to organisations isn’t necessarily from AI being used in a diabolically brilliant way, it’s from their own very human employees using it carelessly or failing to follow existing security procedures.
For example, employees sharing sensitive business information while using services such as ChatGPT holds the risk of that data being retrieved at a later date and could lead to leaks of confidential information and subsequent hacks. Reducing this threat means having proper data protection systems in place and better education for generative AI users on the risks involved. Education extends to helping employees understand the current capabilities of AI – particularly when countering phishing and social engineering attacks.
Recently, a finance officer at a major company paid out $25 million to fraudsters after being tricked by a deep fake conference call mimicking the company’s CFO. So far, so scary. However, reading into the incident you find that this was not ultra-sophisticated from the perspective of AI – it was only one small step above a scam a few years ago that tricked the finance departments at scores of businesses (many of which were startups) to send money to fake client accounts by mimicking the email address of their CEO.
In both instances, if basic security and compliance checks, or even common sense, had been followed, the scam would have quickly been uncovered. Teaching your employees how AI can be used to generate the voice or appearance of other people and how to spot these hacks is as important as having a robust security infrastructure.
Also, the good news in all of this is that the EU is currently at the forefront of creating new legislation for different topics in information technology geared towards elevating standards and ensuring a more ethical digital space. Most pertinent in this, earlier this year the European Parliament approved the EU Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) aimed at bolstering cybersecurity across various sectors.
At this point, some tech businesses may not be convinced the effort is necessary. However, it’s important that we view this as a big opportunity to make the web and future developments in this space much more secure. This is a huge chance to fix a lot of problems from the past. As digital services are part of our everyday lives we should demand best security practices. It is similar to other omnipresent things like food, or cars where we expect a basic level of security which is required also by law.
As a general rule, those companies who comply with these regulations will keep if not grow their market share. With this, it’s a great time for tech companies to go back to the drawing board and reassess their approach to cyber security now. Starting this process now means that when the final version comes into force, your business already has the knowledge and procedures in place to make compliance a much smoother and cheaper process. It also goes without saying that developing a more robust cyber approach will confer commercial benefits.
Even with all the media hype, the reality is that we do not yet fully understand the cyber security implications of widespread generative AI use. However, that is not to say that tech businesses can afford to lose sight of the conversation or continue to operate outdated cybersecurity practices, processes, and architecture. As with all major technological shifts, it will be those that keep pace and continue to follow best practices as the market evolves that will remain better protected and future-ready in the long run.

Rapid advancements in technologies such as cloud computing, IoT, AI, ML, and big data analytics present opportunities for
enterprises to stay ahead of fraudsters and detect fraudulent activities in real-time, fueling the fraud detection and prevention market
growth. Regulatory bodies impose strict compliance standards on large enterprises, particularly in finance, healthcare, and e-commerce industries. Compliance requirements such as PCI-DSS, GDPR, HIPAA, and others compel organizations to implement effective fraud detection and prevention measures to ensure data security and integrity, driving the FDP market growth.
The banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) sectors have increasingly embraced fraud detection and prevention solutions to combat the rising threat of financial fraud. The BFSI vertical is a primary target for cybercriminals as it holds sensitive information about employees, customers, assets, offices, branches, and operations. Owing to the number of transactions (both monetary and data-centric), the number of transactions, technological advancements, and digitalization of the financial sector, the possibility of fraud in this vertical is increasing significantly. Therefore, robust fraud detection and prevention solutions are critical for safeguarding sensitive financial data, preventing monetary losses, and maintaining customer trust. By adopting these solutions, BFSI institutions can effectively detect anomalies, authenticate transactions, and mitigate risks, ultimately enhancing security and ensuring regulatory compliance in an ever-evolving threat landscape. The significant rise of FaaS has largely been attributed to criminal entities’ incorporation of generative AI (GenAI). Generative AI ability to quickly process large amounts of data helps criminal groups gather information on potential targets with unprecedented speed.
In 2024, criminals are expected to continue exploiting weak IT protocols, setting up fake investment websites, targeting e-commerce businesses, and carrying out social engineering scams like phishing, smishing, and vishing. Synthetic identity fraud, which includes the use of stolen data, is predicted to remain the most common form of identity theft.







RE: THINK, RE: DUCE, RE: USE, RE: CYCLE. DISCOVER


















The dilemma of ransomware: to pay or not to pay? More than just a financial decision, organisations must navigate a complex legal and ethical minefield, warns Rob Smith, CTO of Creative ITC. Here he outlines hidden dangers and the steps organisations can take to avoid them.
Ransomware remain an escalating problem. Last year, groups achieved record-breaking payments by increasing the scope and complexity of attacks, hitting almost three quarters (73%) of organisations. Ransom demands shot up by 20% over the past 12 months and gangs managed to extort an unprecedented $1 billion from victims.
No wonder ransomware attacks remain high on the list of business leaders’ anxieties, with their potential to cause huge operational disruption and losses extending far beyond the ransom payment itself.
It can be tempting for victims to pay the ransom to regain access to encrypted as quickly as possible. The financial demands may seem insignificant compared to the potential losses
incurred from operational downtime and the need to uphold commitments to clients and stakeholders
However, before deciding to pay, organisations must consider a range of more complex considerations that often go overlooked.
First and foremost, ransom payment doesn’t guarantee the return of data. Ransomware groups notoriously don’t always do as they promised upon receiving ransom payments; victims frequently don’t regain access to their data or find it to be incomplete or corrupted. Attackers also withhold decryptors despite payment, or those provided prove to be faulty.
Capitulating to ransom demands also marks an organisation as an easy target, encouraging repeat attacks. Ransomware attackers often publicise information about compliant victims, making it easy for others to use the












































same vulnerability or exploit. This creates a vicious cycle, with businesses becoming more and more vulnerable.
Worryingly, attacks are growing more aggressive with groups deploying high-pressure tactics to increase payments and provoke greater reputational damage and additional penalties. Ransomware groups have begun to expand their hitlist to target the clients of organisations they successfully attack, and to report victims to their insurers and even to the US Securities and Exchange Commission
At the point of a ransomware attack, overwhelming financial and business continuity pressures make it easy for victims to overlook the wider implications. Recovering data is one thing; the long-term regulatory and moral implications are quite another.














With no organisation immune from attack, here are some of the most effective measures business leaders can implement to reduce risk and bolster resilience.
organisations to enforce MFA rules are adhered to.
Many organisations find out the hard way that their data and resources aren’t backed up by their cloud providers. Ensure you backup all your data, wherever it resides. Cloud security incidents can often be traced back to weak access policies and misconfigurations, emphasizing the importance of IAM and cloud utilities.



Only 1 in 5 businesses have a formal incident response plan and many leaders say they aren’t sure of their firm’s position on ransom payments. Establish a clear ransomware attack response plan and be aware of company policies and laws on cybercrime. Regular drills and policy reviews will prepare the organisation for an actual incident.








Organisations paying a ransom can find themselves in legal and ethical hot water. Payment poses significant moral dilemmas by perpetuating the cycle of cybercrime. Those capitulating to ransom demands could be in breach of company policies which prohibit payment to avoid organisational support of criminal activities.
Ransom payments may also contravene legislation banning the funding of crime. In October, a coalition of 50 countries and organisations was announces, including Interpol and the European Union, pledging never to pay ransomware groups. Furthermore, paying a ransom may expose individuals and any organisations involved to civil and criminal penalties. Victims must report ransomware attacks promptly to law enforcement and government agencies and cooperate their investigations.
Robust backup and recovery practices are an effective way to boost resilience to ransomware attacks. While they won’t prevent data exfiltration, the ability to retrieve data and restore business operations quickly can limit the impact of an attack.
IT teams need holistic visibility with continuous monitoring across the entire attack surface to enable early detection of threats. It’s also vital to make use of the information logged to strengthen defences and inform future cybersecurity strategies.
An effective patching programme greatly reduces cyber risk. Consider managed patching services to overcome challenges of managing patching long-term and ensure your machines up to date with the latest OS and security patches.
Implementing multi-factor authentication is an effective way to strengthen cyber defences, particularly password-less approaches. Once in place, it’s also essential for
Collaboration with peers, cybersecurity specialists and MSPs can help business and IT leaders stay informed about cyber threats and resilience strategies to enhance their organisation’s security posture. Cooperation with law enforcement agencies also helps track and apprehend cybercriminals.
The ransomware landscape has evolved. In response to increased cyber-risk, businesses and governments have upped their game to defeat cyber attackers - strengthening defences, upweighting international law enforcement and stopping ransom payments. Faced with a growing refusal to pay, ransomware groups have grown more aggressive, demanding higher payments, applying more pressure on victims and extending their list of targets.
The importance of a proactive strategy on detection, recovery and prevention has never been greater. By fully considering the long-term financial, legal and ethical considerations now, organisations can remove uncertainty from the equation when a ransomware attack strikes, de-risking fraught decision-making and business recovery measures. Defeating ransomware groups is not simply about choosing not to pay; it’s also about establishing a state of preparedness to reduce risk and eradicate the need to make highly-charged, reactive decisions in the first place.
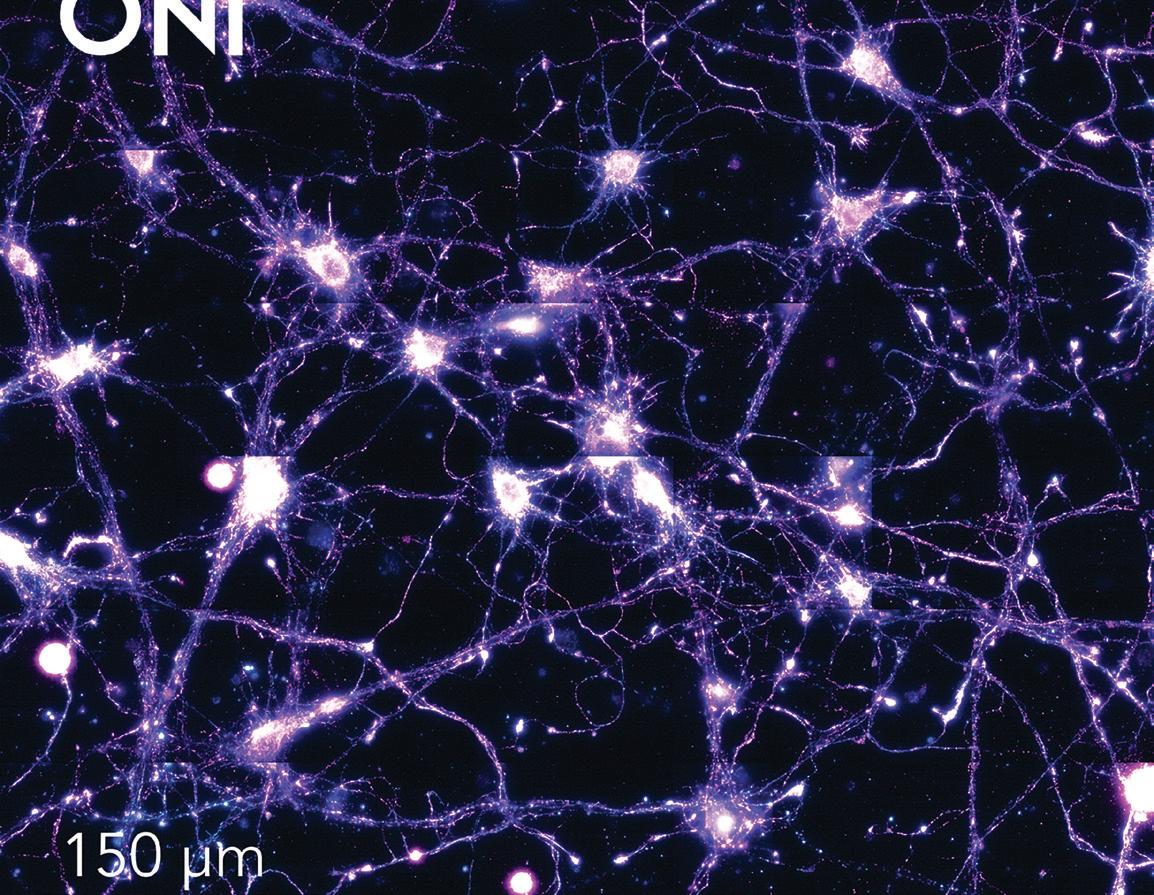

Paul Scagnetti is the visionary CEO of ONI, a groundbreaking technology company renowned for its cutting-edge super-resolution technology. With a robust foundation in artificial intelligence and deep roots in Oxford, Scagnetti has positioned ONI at the forefront of technological innovation.
Scagnetti’s journey into the tech world began with his academic pursuits at MIT, where he earned his PhD in mechanical engineering. His time at this prestigious institution not only
provided him with a solid technical foundation but also exposed him to a network of leading researchers and innovators. This environment fostered his interest in artificial intelligence, ultimately guiding him towards developing transformative technologies.
Under Scagnetti’s leadership, ONI has made significant strides in the field of super-resolution imaging. The company’s flagship innovation, the Nanoimager, exemplifies Scagnetti’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of what is possible. This advanced imaging technology offers unprecedented clarity and detail, revolutionizing fields within scientific research. By leveraging AI, super-resolution can analyze images in real-time, providing insights that were previously unattainable.
Scagnetti’s strategic vision extends beyond technological development. He has cultivated a corporate culture at ONI that prioritizes innovation, collaboration, and ethical AI deployment. His leadership style emphasizes continuous learning and adaptability, ensuring that ONI remains agile in the fast-evolving tech landscape. Scagnetti is also a strong advocate for responsible AI, emphasizing the importance of ethical considerations in the development and implementation of new technologies.
Through his work at ONI, Paul Scagnetti has demonstrated a remarkable ability to blend technical expertise with visionary leadership. His contributions to AI and super-resolution imaging are not only advancing the industry but also setting new
standards for innovation and ethical responsibility in technology. With the company’s deep roots in Oxford and a forward-thinking approach, Scagnetti continues to steer ONI toward a future where technology and humanity progress hand in hand.
How do you see ONI’s super-resolution technology evolving to support advancements in personalised medicine and pharmacogenomics?
The important thing to understand about what we do is we help people see molecules interacting in real time and in the site of the interaction. And so if you think about it, your cells and most of the things in your body are ultimately made up with molecules. And it has historically been very
difficult to observe interactions at that level. And in particular with interactions, what we do is enable therapeutic discovery by helping people see through previous blind spots.
And so what we mean by that is, with a regular microscope, you can observe cells and tissues, but not individual molecules. We enable that level of detailed observation with far greater simplicity than the alternative methods.But a lot of cellular structures ultimately break down to things that are in the nanometer scale, which is almost an unfathomably small scale of things. And so things like the antibodies that are associated with fighting disease in your body are also a means of delivering drugs. If you look at viruses, if you look at the way that, for example, the COVID vaccine that many of us took,
they’ve packaged mRNA into a lipid particle. And those particles are typically in the 50 to 100 nanometer range.
Basic microscopes can’t reach this level of detail. Even high-power, non-super-resolution microscopes can only show cells and organelles. To watch a COVID vaccine particle with mRNA entering your cells, traditional microscopes fail; it’s a blind spot.
You might know that the COVID vaccine contains mRNA and you can monitor the tissue’s response, but our tools allow you to visualize the entire movie of the vaccine’s journey into the cells. And so that’s the fundamental thing that we do. It’s important when you are trying to understand exactly what the process is, so that you could make vaccines or drugs that are very specific to the cells you want to target, or even to sites within a certain cell.
Your Nanoimager platform has made super-resolution microscopy more accessible. What breakthroughs in life sciences do you anticipate this democratisation of technology will enable?
A lot of them will be associated with therapeutic discovery, as the main area, but there will also be new biomarkers that we find, for example, new proteins that participate in a process and can be targeted by drugs. I think fundamentally these are the two biggest areas where we will enable pharmaceutical companies to develop better therapeutics.
And then we’ll enable diagnostic companies to find better, more precise diagnostics, so that when people are dealing with a particular disease state, they’ll have better diagnostics. These advancements in therapeutics and diagnostics are the two biggest areas where we can make a significant impact.
How is ONI integrating AI and machine learning into its imaging systems, and what impact do you foresee this having on drug discovery processes?
There are two ways. In one sense, people often divide AI into generative AI and then machine learning. So in the near term, the most obvious way is through machine learning. When you look at things that are at the scale that we’re at, they’re so small, that you have to look at gigabytes, and gigabytes of data to have a sense.
You don’t want to just watch one particle of a therapeutic molecule being up-taken, you want to watch that a million times, and then make some sense of it and distill that. And so, one way is to synthesise a lot of information and to pull out the bits and pieces that are the most important for a researcher doing discovery work. The other way is through generative AI. I think that there is going to be a combination of different techniques that are going to put together molecular movies effectively — which will be based on super-resolution and also known structural information of the molecules.
I think in the very near future, you’ll be able to see almost as though you were a molecule. You’ll be able to shrink yourself down and watch molecules interacting and get a generated molecular movie animation of what’s happening with a molecule entering the cell.
And not just an animation — like a pretend thing, but a real thing that is showing a real mechanism of action. So I think it’s going to be twofold. In terms of the way AI, super-resolution and other molecular techniques come together.
ONI has roots in Oxford but has expanded globally. How are you leveraging international collaborations to drive innovation in super-resolution microscopy and beyond?
The best thing that we have in our business is that we sell to both leading academic researchers and we sell to biopharma companies. So one of the most fun parts of our job is that we deal with academic researchers at leading universities and many of

those leading universities have our microscopes.
And then we deal with the pharma companies and they each want slightly different things. The academics want to develop methods and want to do fundamental discovery. The pharma companies are doing it for purposeful, more targeted application specific discovery — for the purpose of discovery and new therapies.
And so you could picture it as a triangle, sometimes where we’re providing a technology, we provide it to the leading academics, and then those academics also work with pharma companies, and vice versa. So that’s one way to think of how this works. We are global, and we’re working with both
the academic researchers, and also pharma researchers, but we are all on the same team and we are excited to hear about the discoveries that scientists make using our products.
What has been the main barriers to drive overall adoption of super-resolution in research and discovery?
The main one has been that it’s complex to do molecular scale imaging. And that’s true. In any area where a new life science tool technology comes in or a new discovery tool comes of age, it’s always extremely valuable, but a little finicky to use. And so one of the challenges in our case is getting the chemistry, the

software, and the hardware to all work in unison — in a way that’s easy and consistent for researchers. And that they get consistent results day after day.
And so if you and I were to go into the lab today, and to try and get a result, it would be substantially less time than it would have been two or three years ago, to get a single super-resolution image.
So really, it’s been about simplifying and making the technique more consistent, more foolproof, easier, and more accessible to people who don’t have all the time in the world to study a particular technique and want to use the technique to get a result. So I think ease of use and a
sort of bullet proofing have been two of the biggest things that have been barriers to adoption.
What are the blind spots that you believe exist in current drug design which super-esolution can help reveal?
I think it depends on the particular type of therapy. But in general, one of the biggest blind spots is what people refer to as a mechanism of action, which means how exactly is a therapy being up-taken and working in a biological system with cells.
And so that general blind spot plays out in different ways, whether you’re looking at antibody based therapeutics, and there’s a couple different
flavours of those antibody drug conjugates by specific antibodies. Then the same thing on drugs that are packaged into, say, lipid particles.
Even though we often see the effect of drugs, the biggest blind spot is understanding how exactly they are up-taken into the cells. That’s one of the main things that we work on with customers. We see it as our job to give people a new kind of camera into the molecular world.
Again, our goal is to enable researchers to go beyond just observing the end states, such as ‘I put this chemistry in’ or at the macro scale, ‘I see this result in a patient.’ We want them to actually see down to the level of molecular interactions and watch what is happening in real-time.
With the increasing complexity in drug design and biological manufacturing, how could you see ONI’s technology contributing to make manufacturing more efficient and safer?
Once a company has discovered a molecule and discovered that it works; whether it’s an antibody, whether it’s a lipid nanoparticle that’s packaging RNA, or something else; the question then becomes when they’re manufacturing, how consistent is what they’re manufacturing, whether it’s a set of antibodies, a set of lipid particles — how consistent are those relative to the intended molecule?
And super-resolution is one of a multitude of technologies that is capable of giving people that quality control of saying, “Hey, this is what we intended.” Now, let’s take a sample out of the large batches that are being manufactured, and see if those are consistent with what we developed in the clinical trials.
So that’s the conceptual link in the way that we contributed. We’re not the only technique, of course—there are many others. However, we can help companies examine large batches of manufactured products and compare them to what was used in earlier stages of research.
Personalized medicine, often termed precision medicine, tailors healthcare to individual patients based on their genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. This approach promises more effective treatments with fewer side effects, ushering in a new era of healthcare. One of the key enablers of personalized medicine is the ability to observe and understand the intricate details of biological systems at the molecular level. Super-resolution microscopy (SRM) has emerged as a critical tool in this regard, breaking the diffraction limit of conventional light microscopy to provide unprecedented insights into cellular and molecular processes. This article explores how advancements in SRM are transforming personalized medicine.
Super-resolution microscopy encompasses several techniques that surpass the resolution limits of traditional light microscopy, which is typically around 200 nanometers. The key SRM methods include:
1. STED (Stimulated Emission Depletion) Microscopy: STED microscopy uses a pair of laser beams to selectively deactivate fluorescence in all but a nanometer-sized region, achieving higher resolution.
2. PALM (Photoactivated Localization Microscopy) and STORM (Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy): These methods rely on the precise localization of individual fluorescent molecules that are activated and deactivated in a controlled manner, allowing the reconstruction of high-resolution images from multiple imaging cycles.

3. SIM (Structured Illumination Microscopy): SIM enhances resolution by illuminating the sample with patterned light and using computational algorithms to reconstruct high-resolution images.
These techniques have evolved rapidly, with continuous improvements in resolution, imaging speed, and compatibility with living cells, making them indispensable in modern biomedical research.
One of the primary benefits of SRM is its ability to visualize cellular structures and molecular interactions with unparalleled clarity. This capability is crucial for understanding the complex mechanisms underlying various diseases, which is the foundation of personalized medicine.
Cancer Research: In cancer research, SRM has been instrumental in studying the behavior of cancer cells at

the molecular level. For instance, researchers can observe the dynamics of protein interactions that drive cancer progression, metastasis, and resistance to therapies. This detailed understanding can lead to the identification of novel therapeutic targets and the development of personalized treatment strategies.
Neuroscience: SRM has also made significant contributions to neuroscience by enabling the visualization of synaptic structures and the
mapping of neural circuits. Understanding these intricate networks is essential for developing personalized treatments for neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and autism spectrum disorders.
: In the study of infectious diseases, SRM allows researchers to observe the interactions between pathogens and host cells at the nanoscale. This information can inform the design of targeted
therapies and vaccines, tailored to the specific mechanisms employed by different pathogens.
Biomarkers are measurable indicators of biological processes, diseases, or responses to treatments. They are central to personalized medicine, as they enable the stratification of patients based on their specific biological profiles. SRM enhances the detection and analysis of biomarkers

by providing detailed images of their localization, abundance, and interactions within cells and tissues.
Single-Molecule Detection: SRM techniques such as PALM and STORM allow the detection and quantification of single molecules within cells. This capability is crucial for identifying low-abundance biomarkers that may be overlooked by conventional imaging methods. By accurately quantifying these biomarkers, clinicians can better predict disease progression and
response to therapy, tailoring treatments to individual patients.
Multiplex Imaging: SRM enables the simultaneous imaging of multiple biomarkers within a single sample. This multiplexing capability is essential for understanding the complex interplay between different molecular pathways in health and disease. For example, in cancer, the ability to simultaneously image multiple oncogenes and tumor suppressors can provide a comprehensive
view of the molecular landscape of a tumor, guiding personalized treatment decisions.
The development of new drugs is a complex and costly process, often hampered by the inability to observe drug-target interactions in detail. SRM addresses this challenge by providing high-resolution images of how drugs interact with their targets at the molecular level. This information is

invaluable for drug development and testing, ensuring that new therapies are both effective and safe.
Understanding the precise mechanism of action of a drug is crucial for optimizing its efficacy and minimizing side effects. SRM allows researchers to observe how drugs bind to their targets, induce conformational changes, and affect cellular processes. This detailed knowledge can inform the design of more effective drugs with fewer off-target effects.
Drug resistance is a major challenge in the treatment of diseases such as cancer and infectious diseases. SRM can reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying resistance, such as mutations in drug targets or changes in drug uptake and efflux. By understanding these mechanisms, researchers can develop strategies to overcome resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
SRM can be used to screen potential drugs in patient-derived cells or tissues, providing personalized insights into drug efficacy and toxicity. This approach allows for the identification of the most promising candidates for further development and clinical testing, reducing the time and cost associated with drug development.
Personalized medicine relies on the ability to monitor how individual patients respond to treatments in real-time. SRM enables the real-time imaging of cellular responses to drugs, providing critical information for optimizing treatment regimens.
Live-Cell Imaging: Advances in SRM have made it possible to image living cells with high resolution, allowing researchers to observe dynamic processes in real-time. This capability is essential for understanding how cells respond to treatments over time, including changes in signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular behavior.
Treatment Optimization: By monitoring cellular responses in real-time, clinicians can adjust treatment regimens to maximize efficacy and minimize side effects. For example, in cancer therapy, SRM can be used to monitor how tumor cells respond to chemotherapy or targeted therapies, allowing for the timely adjustment of treatment plans based on individual responses.
The integration of super-resolution microscopy into personalized
medicine is still in its early stages, but the potential is enormous. As SRM techniques continue to advance, they will become even more powerful tools for understanding disease mechanisms, identifying biomarkers, developing new therapies, and monitoring treatment responses.
Integration with Other Technologies:
The future of personalized medicine will likely involve the integration of SRM with other advanced technologies, such as genomics, proteomics, and artificial intelligence. This multidisciplinary approach will provide a comprehensive view of individual patients’ biological profiles, enabling highly personalized and effective treatments.
Clinical Applications: While SRM is currently primarily used in research settings, its clinical applications are expanding. Improved imaging speed, ease of use, and compatibility with clinical samples will facilitate the adoption of SRM in diagnostic and therapeutic contexts, bringing the benefits of personalized medicine to more patients.
Accessibility and Cost: Advances in technology and reductions in cost will make SRM more accessible to researchers and clinicians worldwide. This democratization of SRM will drive innovation and accelerate the adoption of personalized medicine, ultimately improving patient outcomes on a global scale.
Advancements in super-resolution microscopy are revolutionizing personalized medicine by providing unprecedented insights into the molecular underpinnings of diseases. By enabling high-resolution imaging of cellular and molecular processes, SRM is transforming our ability to diagnose, treat, and monitor diseases on an individual level. As SRM technologies continue to evolve, their integration into personalized medicine will pave the way for more effective, targeted, and patient-specific healthcare, heralding a new era of medical innovation and improved patient outcomes.

The Daegu-Gyeongbuk Free Economic Zone Authority (DGFEZ) held the ‘DGFEZ Vision 2030’ announcement ceremony on June 13, 2024, at Hotel Inter-Burgo Daegu. The ceremony was attended by approximately 150 personnel from relevant institutions and enterprises, as well as DGFEZ committee council and staff.
At the event, DGFEZ unveiled its new vision, ‘Global Business Base Leading the 2030 New Airport Era’, and detailed development strategies. This new vision is part of a mid- to long-term strategy extending to 2030, designed to prepare for the Daegu-Gyeongbuk New Airport era. This era is expected to be a turning point for regional development, marked by the opening of the new airport in 2029. The vision focuses on three key areas: Daegu-Gyeongbuk New Airport,
Business, and Global Base, aiming to transform the business environment from a regional to a global scale.
To achieve this goal, DGFEZ has outlined three core implementation strategies: 1) [Space] Sustainable Space Innovation, 2) [Industry] Revitalization of Innovation Ecosystems, and 3) [Company] Reinforcement of Corporate Support Services. Eighteen core tasks have been identified to support these strategies, and the commitment to these goals was reinforced by informing the participants and the public at the ceremony. These strategies are designed to coexist with the local economy in the long term, aligning with the 3rd Basic Plan for Free Economic Zones announced by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy in 2023 and reflecting the updated development environment in the region.
Following the vision announcement ceremony, DGFEZ hosted a seminar on AI technology convergence and autonomous vehicles in the future mobility industry. This seminar, part of the key strategic industry strengthening project, is one of four seminars/forums planned for the year. These seminars provide tenant companies with opportunities to interact, enhance their capabilities, and foster an innovation ecosystem within DGFEZ’s eight investment districts.
Byeong Sam Kim, the 6th commissioner of DGFEZ, expressed a strong commitment to proactively preparing for the new airport era, which is expected to drive future development. He emphasized focusing all capabilities on transforming DGFEZ from a regional economic hub into a global business base, in line with the
new mid- to long-term development strategy, coinciding with DGFEZ’s 16th anniversary.
The status of the Republic of Korea, which was once considered a small country located in East Asia, has changed drastically over the last decade. It has gained a worldwide reputation with its many specialized R&D centers, a resource pool with outstanding capabilities, and overwhelming state-of-the-art technologies, winning the hearts of investors around the world.
The Daegu-Gyeongbuk region, located in the central part of the Republic of Korea, has traditionally been the largest domestic industrial and manufacturing center. More than $52 billion worth of exports are generated annually in Daegu-Gyeongbuk region. Daegu-Gyeongbuk Free Economic Zone Authority (DGFEZ), which is at the center of Korea, has been developing a total of eight districts (18.41 km2) as an environment that can cooperate with global companies.
DGFEZ was established in August 2008 with the goal of creating the “world’s best” business environment for domestic and foreign companies. This upcoming August marks its 16th anniversary. Approximately 1,000 companies have exerted their best efforts to build a sustainable investment district by achieving about USD 5.94 billion in investments. As a result, it earned the best evaluation among Free Economic Zones in 2022 by the Korean government. At present, there are nine designated free economic zones in operation in Korea.
DGFEZ has designated three key strategic industries: 1) ICT·Robot, 2) Medical·Bio, and 3) Future Mobility to attract systematic and strategic investment. Based on this, it is intensively creating business infrastructure, fostering industries, and attracting excellent companies.
In addition, it is further enhancing the investment attractiveness of DGFEZ by creating an innovation ecosystem, that is, an innovation ecosystem, among innovators in free economic zones.


In today’s rapidly changing society, the time for synergy effects through convergence between different types of industries has arrived. To preemptively respond to this, the “innovation cluster foundation construction” project is underway to establish a corporate support system by connecting industry, academia, and research institutes in DGFEZ. The “corporate business capabilities reinforcement” project is also being promoted to solve the difficulties of resident companies. DGFEZ has been taking the lead in creating an innovative ecosystem by actively collaborating with the central government. It promises to provide full corporate support to resident and prospective companies. Moreover, if you take advantage of the wide range of benefits, such as
various tax reductions, labor deregulation, and incentives given to foreign-invested companies, and the one-stop service for providing management support to resident companies, your investment in Korea will settle in a stable orbit.
Currently, more than half of the eight investment districts have successfully completed their development and recorded a sale rate of about 81%. However, in response to the steadily increasing demand for moving into free economic zones, we are planning to expand existing investment districts and designate new investment districts to strengthen the competitiveness of DGFEZ. This will be good news for those looking for new opportunities in Asia, especially Korea.
Happy birthday, Foreign Subsidies Regulation! You took effect on 12 July 2023 and provided your guardian, the European Commission, with new powers to ensure a level playing field within the EU’s internal market. It may now investigate distortive effects of foreign subsidies in contexts such as company acquisitions and public tenders
By
Christoph Heinrich and Dr. Cathleen Laitenberger (ADVANT Beiten), Manuela Becchimanzi and Francesco Mazzocchi (ADVANT NCTM)
Companies need to notify acquisitions, mergers and joint ventures to the European Commission when the target company/joint venture achieves an EU-wide turnover of at least EUR 500 million and the parties were granted at least EUR 50 million in combined financial contributions from non-EU countries in the previous three years. Financial contributions in this context not only include state guarantees, equity contributions or loans but also tax benefits, project grants and revenues from sales to state entities.
Notification obligations started on 12 October 2023. Since then, the Foreign Subsidies Regulation has been applied to more deals than initially assumed. In the first 100 days alone, the Commission engaged in pre-notification discussions for 53 transactions, of which 14 were then formally notified. Out of those transactions,

many were subject to parallel assessment under the EU Merger Regulation, some to parallel assessment under national merger control procedures in the EU and roughly half also to parallel assessment under foreign direct investment screening in the EU. The Commission has so far found sufficient indications of distortive foreign subsidies in one case. In June 2024, it opened an in-depth investigation of the planned acquisition by Emirates Telecommunications Group Company PJSC of Eastern European telecommunication operator PPF Telecom Group B.V. Emirates Telecommunications Group Company PJSC is a telecommunication operator based in
Abu Dhabi and has allegedly received unlimited guarantees, loans and further financial contributions from the United Arab Emirates. The investigation is still ongoing.
New ex-ante notification obligations also apply to public procurement procedures that exceed certain thresholds. Again, the tool aims at identifying and controlling direct or indirect financial contributions by non-EU countries that are limited to one or more companies or industries, and thus confer the beneficiaries an unfair competitive advantage in the EU market. If the European Commission finds

such distortive effects caused by the foreign subsidies, it may issue structural and behavioral remedies.
The Commission has already opened several in-depth investigations into public tenders:
z In February 2024, the Commission opened an in-depth investigation following the notification of a bid by Chinese state-owned company CRRC Qingdao Sifang Locomotive Co. Ltd. for providing and maintaining electric trains in Bulgaria.
z In April 2024, the Commission opened in-depth investigations following two notifications of bidding consortia for the construction
The European Commission has embraced its new child and has so far used its tools more eagerly and broadly than many would have expected. These are the main Foreign Subsidies Regulation enforcement actions and trends so far
and operation of a solar plant in Romania. One consortium included a German subsidiary of LONGi Green Energy Technology Co. Ltd, which is listed on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. The other consortium included Shanghai Electric UK Co. Ltd. and Shanghai Electric Hong Kong International Engineering Co. Ltd., both ultimately controlled by the P.R. China.
The Commission didn’t need to take a final decision as each bidder withdrew its offer.
The European Commission may as well start investigations on its own initiative: It may request notifications for smaller M&A deals and public procurement procedures, and it may also conduct dawn raids. During dawn raids, the Commission may examine all digital and physical company records, take copies thereof, seal business premises, and ask staff members for explanations on facts or documents relating to the subject matter of the inspection.
The Commission made first use of the latter option in April 2024: It carried out an unannounced inspection at the Dutch and Polish offices of the Chinese state-owned company Nuctech. The Commission claims that Nuctech may have received foreign subsidies that could distort the internal market at the expense of other security equipment companies. Nuctech is currently challenging the Commission’s actions before the EU’s General Court.
The European Commission is using its new tools under the Foreign Subsidies Regulation very actively and extensively. Some priorities are already becoming apparent: while the Commission’s focus on Chinese companies had
been anticipated from the start, the heightened scrutiny for state-owned Arab companies is a more recent trend. Still, the regulatory burden of the Foreign Subsidies Regulation is also felt by businesses based in the EU, the US, the UK or Switzerland when planning and implementing M&A deals.
Energy, transportation, telecommunication and security equipment are so far the sectors in the spotlight of the Commission’s actions. However, we expect the Commission to extend its investigations to further sectors –like other services for critical infrastructure – in the coming years.
Companies operating in these sectors and receiving financial contributions from non-EU countries should be particularly aware of the risk of investigations and prepare for them. For them, it is advisable to make themselves familiar with the European Commission’s dawn raid procedures. Notably, these rules may differ significantly from those applicable to investigations by national authorities in other contexts.
More generally, when preparing large M&A deals or offers for public tenders, the potential notification requirements need to be considered. First experiences show that, for example, the pre-notification discussions with the Commission for company acquisitions can be quite lengthy and can include several requests for information. The implementation of internal reporting systems to continuously gather information on all forms of financial contributions from non-EU governments helps in preparing for such scenarios.
Companies should also watch out for sectoral market investigations –a tool that the Commission has not used so far but will likely use in the mid-term.

Any business today must innovate and adapt its marketing strategies to shifting customer demands. In a previous post, we highlighted how Spanish sunglasses enterprise Hawkers adapts to customer preferences , including the sustainability trend among young adult customers. At the same time, the business is well aware of the need to be more sensitive about pricing due to increased competition. Investors in the business noted
the importance of using data and considering how to access customers as the best way to attract existing and new customers.
Likewise, sunglasses retailer Sunglass Hut continues to expand its services to reach more customers around the world. In 2023, the retailer brought holiday cheer to central London with a festive pop-up truck activation. Part of the company’s #ShadesofHoliday campaign, the activation featured a festive arcade game where
visitors can play to win prizes such as in-store discounts and eyewear. Guests also received “bounce back” cards that provided 20% off eyewear redeemable in any Sunglass Hut store.
Aside from the pop-up truck and games, however, Sunglass Hut also continues to invest in innovating the company’s marketing strategies to appeal to newer generations of consumers in this increasingly digital age. Below, we’ll take a look at some of the

notable marketing strategies employed by Sunglass Hut in recent years:
With the rise of social media, influencer marketing has quickly become a popular means of reaching new customers through online channels. Likewise, Sunglass Hut has actively partnered with celebrities and Internet influencers to market its variety of products.
On Sunglass Hut’s homepage, visitors and customers can find new and trending sunglasses as well as the retailer’s celebrity and influencer campaigns. This includes Clémence Bertrand’s Paris Fashion Week appearance, featuring stylish shades from Michael Kors, Swarovski, and Burberry. Aside from highlighting specific models, these campaigns are provide style inspirations for potential customers who may be interested in specific sunglasses brands or models.
Another key marketing strategy Sunglass Hut introduced was its partnership with avatar platform Ready Player Me in 2023. The partnership offered digital sunglasses for users to put onto their avatars, merging virtual worlds and physical retail. In the US, customers were able to visit select Sunglass Hut stores to claim free virtual sunglasses for their avatars, including virtual counterparts of featured brands from retailers like Oakley and Ray-Ban.
The collaboration was an interesting step into the world and development of virtual fashion, allowing users to customise their virtual looks and style just as they would in real life. At the same time, the campaign also allowed known eyewear brands and models to be showcased to an increasingly Internet-bound customer base. Additionally, as tech companies continue to innovate in the virtual reality segment, this will likely be the first of more virtual campaigns to come from retailers like Sunglass Hut.
Finally, another crucial marketing strategy helping Sunglass Hut boost its reach and offerings is by constantly boosting customer loyalty. In March 2024, the company launched a firstof-its-kind customer loyalty program called The Sun Club. The program provides a gamified approach for customers to earn rewards. For example, each Sunglass Hut purchase would grant special gifts, access to exclusive products, as well as personal services like free expedited shipping and same-day delivery.
There are four levels to the loyalty program, with each level offering more rewards as you go. Other benefits include birthday and anniversary promotions, gifts with purchase, access to exclusive product launches and sales, branded gifts, and more.
If you found this post helpful, you can check out our homepage for more insights on European business and finance, as well as the latest developments in business and technology.

By Ann Keefe, Regional Director – UK and Ireland at Kingston Technology EMEA.
In recent months, AI PCs have dominated technology headlines, with hardware manufacturers announcing new models at an unprecedented pace. The emergence of this new type of hardware reflects broader AI trends, but the speed of innovation begs the question: Are AI PCs truly revolutionary, or simply the latest tech industry hype?
AI PCs represent a significant evolution in computing, featuring dedicated Neural Processing Units (NPUs) within their System on Chip (SoC). These NPUs are specifically designed to handle AI applications and experiences, offering enhanced computational power for language models, focused tasks, security, and privacy. The key advantage of AI PCs lies in their ability to provide low latency and
greater personalisation, meeting the growing demand for more independent computing experiences.
Essentially, AI PCs enable computation to occur at the edge, closer to the data source or end-user, rather than relying solely on cloud processing. This approach combines the strength of cloud computing for intensive tasks with the speed and privacy advantages of local processing. By utilising local hardware like GPUs and NPUs to enable AI tasks, AI PCs can reduce latency, conserve bandwidth, and improve data security by minimising the amount of sensitive information transferred to the cloud.
The evolution of AI PCs has been closely tied to advancements in chip technology. Early examples of this approach can be traced back to the
iPhone’s A11 bionic processor. However, recent innovations like Intel’s Ultra Core processor have introduced a new CPU design tailored for multiple purposes. This tilebased CPU architecture allows for dedicated allocation of resources to the GPU (for compute tasks), the main processor, and the SoC (which includes the NPU) to support local AI functions.
The combination of CPU, GPU, and NPU is crucial for modern computing tasks. While the CPU handles general-purpose processing and runs the operating system, the GPU excels at parallel computations ideal for AI and deep learning. The NPU, designed specifically for AI tasks, accelerates neural network computations while maintaining low power consumption. This trio allows for flexibility, with each processor type fully optimised for specific tasks, leading to significant

improvements in both performance and energy efficiency.
As AI PC technology advances, questions arise about the memory and storage requirements needed to support these systems effectively. Currently, there are very few standardised specifications with AI PC systems ranging from 8GB to 32GB of memory. However, as AI applications become more sophisticated and demanding, we can expect a shift in memory requirements.
It’s the same situation when it comes to storage, with current systems offering anywhere from 256GB to 2TB of SSD storage. When considering AI PCs, it’s key for enterprises to look beyond their needs right now, and instead anticipate future requirements as applications evolve.
AI PCs are finding applications across various domains, with business productivity tools leading the charge. Microsoft Copilot, Zoom, Webex, and Slack are breaking new ground in project management and collaboration. Creative professionals are benefiting from AI-enhanced tools like the Adobe suite, Audacity for audio editing, and GIMP for design work.
These early applications primarily focus on communication and creativity, areas where AI can make an immediate impact. However, as the technology matures, we can expect to see AI PC applications diversify into numerous industries and use cases.
1. Enhanced Security and Privacy: By processing data locally, AI PCs reduce the risks associated with cloud storage and transmission and use of sensitive information, by public AI models.
2. Improved Performance: The combination of specialised processors enables faster, more efficient handling of AI-related tasks.
3. Greater Autonomy: AI PCs can operate independently of cloud services, ensuring functionality even during network outages or cyber-attacks targeting cloud infrastructure.
4. Personalisation: The ability to process data locally allows for more tailored user experiences and faster response times.
As enterprises consider adopting AI PCs, several factors should be considered:
1. Assess Current Needs: Evaluate your organisation’s immediate requirements and how they align with available AI PC capabilities.
2. Application Compatibility: Identify which AI-enhanced applications are crucial for your business operations.
3. Refresh Cycle Timing: Consider where you are in your current hardware refresh cycle and whether immediate adoption or a wait-and-see approach is more appropriate.
4. Staff Training: Ensure your team is prepared to optimise and securely operate AI PC systems.
5. Regulatory Compliance: Stay ahead of AI-related policies and practices to ensure smooth adoption and operation.
6. Phased Approach: Consider a nuanced strategy, such as upgrading key components incrementally rather than overhauling entire systems at once.
While there’s undoubtedly excitement surrounding AI PCs, dismissing them as mere hype would be shortsighted. Analyst predictions from firms like Gartner, IDC, and Canalys suggest a significant market shift towards AI PCs in the coming years.
For enterprises, AI PCs represent a genuine opportunity to enhance productivity, security, and user experiences. However, the key to success lies in thoughtful adoption. Organisations must carefully consider their specific needs, the current state of AI PC technology, and their readiness to implement and manage these advanced systems.
As with any emerging technology, there are trade-offs to consider. Early adopters may gain competitive advantages but also face the challenges of working with less mature ecosystems. Others may benefit from a more measured approach, allowing time for the technology and application landscape to evolve further.
Ultimately, AI PCs are not just hype –they represent a significant shift in computing paradigms. Whether your organisation dives in now or waits for further developments, staying informed and prepared for this technological evolution is crucial for future success in an AI-driven world
The financial world is undergoing a seismic shift, driven by the transformative power of tokenization. This revolutionary process, which involves converting rights to an asset into a digital token on a blockchain, is poised to reshape industries and redefine the concept of ownership. From decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) to the tokenization of real-world assets, security tokens, and cross-chain interoperability, tokenization is unlocking unprecedented opportunities and efficiencies.
DeFi, or decentralized finance, is at the forefront of the tokenization revolution. It leverages blockchain technology to create an open and permissionless financial system, eliminating intermediaries and offering users direct control over their assets. DeFi platforms provide services such as lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest, traditionally offered by banks and financial institutions.
The appeal of DeFi lies in its inclusivity and accessibility. With a smartphone and internet connection, anyone can participate in the global financial system. This democratization of finance is particularly impactful in regions with limited access to traditional banking services. Moreover, DeFi protocols are built on smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code. This reduces the need for trust and enhances transparency and security.
The growth of DeFi has been meteoric. According to DeFi Pulse, the total value locked in DeFi protocols surged

from under $1 billion in early 2020 to over $100 billion in 2022. This exponential rise underscores the growing confidence in decentralized financial services and their potential to disrupt the conventional financial landscape.
Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have taken the world by storm, representing a new frontier in digital ownership and creativity. Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum, NFTs are unique digital assets that cannot be exchanged on a one-to-one basis. They are typically used to represent ownership of digital art, music, videos, virtual real estate, and even tweets.
NFTs leverage blockchain technology to provide verifiable proof of authenticity and ownership. This has profound implications for creators and artists, who can now monetize their work directly and receive royalties through smart contracts whenever their creations are resold. The explosion of the NFT market was epitomized by the sale of digital artist Beeple’s “Everydays: The First 5000 Days” for $69.3 million at Christie’s auction house.
Beyond art and collectibles, NFTs are finding applications in various industries. For instance, in gaming, players can own and trade in-game assets, creating new economic ecosystems. In the music industry, artists can release exclusive content and

engage with fans in innovative ways. The versatility of NFTs is driving a digital renaissance, reshaping how value is created, exchanged, and perceived.
Tokenization extends far beyond digital assets, offering the potential to revolutionize the ownership and trading of real-world assets. This involves creating digital representations of physical assets such as real estate, commodities, and even fine art on a blockchain. These tokenized assets can be divided into smaller units, enabling fractional ownership and increasing liquidity.
Real estate tokenization is particularly promising. Traditionally, real estate investment has been accessible
only to those with significant capital. Tokenization democratizes access by allowing investors to buy fractions of properties, thereby lowering the barrier to entry. This not only broadens the investor base but also enhances liquidity in the real estate market, which has historically been illiquid. Tokenization also facilitates more efficient and transparent transactions. Blockchain’s immutable ledger ensures accurate and traceable records, reducing the risk of fraud and eliminating the need for intermediaries. The potential applications are vast, spanning from luxury goods and fine art to commodities and intellectual property, each benefiting from enhanced liquidity, accessibility, and security.
Security tokens represent a digital evolution of traditional securities such as stocks and bonds. These tokens are regulated financial instruments that confer ownership rights and entitlements to dividends or interest payments. Security tokens offer several advantages over traditional securities, including faster settlement times, lower transaction costs, and increased liquidity through fractional ownership.
The issuance of security tokens is governed by regulatory frameworks, ensuring compliance with securities laws. This regulatory oversight provides a level of trust and legitimacy, attracting institutional investors and enabling broader market participation. Security tokens also facilitate global investment opportunities, allowing investors to access markets and assets that were previously out of reach.
Furthermore, security tokens can be programmed with smart contracts to automate functions such as dividend distributions and voting rights. This automation reduces administrative overhead and enhances transparency, providing a more efficient and streamlined investment process. As the market matures, security tokens
are expected to play a pivotal role in the future of capital markets.
One of the significant challenges in the blockchain space is the lack of interoperability between different blockchain networks. Cross-chain interoperability aims to address this by enabling seamless communication and transfer of assets across disparate blockchain platforms. This interconnectedness is crucial for the widespread adoption and scalability of blockchain technology.
Interoperability solutions, such as Polkadot, Cosmos, and Chainlink, are developing protocols that facilitate the exchange of data and value between blockchains. These solutions allow different blockchain networks to interact, enhancing their functionality and opening up new possibilities for decentralized applications (dApps).
For instance, in the DeFi ecosystem, interoperability enables users to leverage the strengths of multiple blockchain networks, optimizing their investment strategies and accessing a broader range of financial services. In supply chain management, cross-chain solutions can integrate various stakeholders and streamline operations across different platforms, enhancing efficiency and transparency.
The advent of tokenization heralds a new era in finance and beyond, transforming how assets are created, owned, and traded. DeFi, NFTs, tokenization of real-world assets, security tokens, and cross-chain interoperability are key pillars of this transformation, each contributing to a more inclusive, efficient, and interconnected global economy.
As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, the potential applications of tokenization will continue to expand, driving innovation and creating new opportunities. The future is tokenized, and those who embrace this paradigm shift stand to reap significant rewards in the digital age.

As the urgency of the climate crisis intensifies, the global business community has found itself at a pivotal crossroads, with the imperative to transition towards sustainable practices colliding with the realities of a complex and interconnected global economy. However, amid this daunting challenge, a vanguard of forward-thinking corporations has emerged, embracing innovative sustainability programs that not only align with the ambitious 2045 net zero targets but also pave the way for a greener, more resilient future.
Leading the charge in this transformative journey are companies that have recognized the inextricable link between environmental stewardship and long-term business success. These trailblazers are not only mitigating their carbon footprints but also fostering a corporate culture that embraces sustainability as a core tenet, driving innovation and inspiring industry-wide change.
One such pioneer is Unilever, the global consumer goods giant, whose ambitious ‘Rethinking Plastic’ initiative has set a new benchmark for circular economy practices. By 2025, the company aims to ensure that all of
its plastic packaging is reusable, recyclable, or compostable, a bold target that has already catalyzed significant progress. Through strategic partnerships with recycling organizations and innovative materials development, Unilever is not only reducing its environmental impact but also creating a blueprint for sustainable packaging that other industries can emulate.
“Sustainability is not just a moral imperative; it’s a business imperative,” asserts Alan Jope, Unilever’s CEO. “By reimagining our approach to plastic, we are future-proofing our operations, reducing costs, and fostering a more circular economy that benefits both our bottom line and the planet.”
In the realm of renewable energy, Spanish utility giant Iberdrola stands as a beacon of progress, with its ambitious ‘Net Zero by 2050’ strategy leading the way. Through massive investments in wind, solar, and hydroelectric power generation, the company has rapidly decarbonized its energy portfolio, positioning itself as a global leader in clean energy production. Notably, Iberdrola’s innovative ‘Smart Grids’ initiative has revolutionized energy distribution, utilizing cutting-edge technologies to optimize
efficiency and reduce transmission losses, further minimizing the company’s environmental impact.
“The transition to a sustainable energy future is not just a choice; it’s an imperative,” affirms Ignacio Galán, Iberdrola’s Chairman and CEO. “By embracing renewable energy and pioneering innovative solutions, we are not only safeguarding the planet but also securing our long-term competitiveness in an increasingly carbon-conscious global marketplace.”
The transportation sector, long a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, has also witnessed transformative sustainability initiatives from industry titans. Swedish automaker Volvo Cars, for instance, has set an audacious goal of achieving complete climate neutrality across its manufacturing operations and supply chain by 2040. The company’s comprehensive ‘Climate Plan’ encompasses everything from electrifying its vehicle lineup and optimizing logistics to leveraging renewable energy sources and promoting sustainable materials in production.
“We recognize that the automotive industry has a crucial role to play in mitigating climate change,” states Jim
Rowan, President and CEO of Volvo Cars. “By embracing electrification and sustainable practices throughout our operations, we are not only reducing our environmental impact but also positioning ourselves as a leader in the transition to a greener, more sustainable mobility future.”
Beyond individual corporate initiatives, cross-industry collaborations have emerged as a powerful force driving sustainability efforts. The Renewable Energy Buyers Alliance (REBA), a consortium of leading multinational corporations, is at the vanguard of this movement. REBA’s members, including tech giants like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft, have collectively committed to procuring over 60 gigawatts of renewable energy by 2030, a monumental undertaking that has catalyzed the development of new renewable energy projects and accelerated the transition to a low-carbon economy.
“Collective action is key to achieving our ambitious sustainability goals,” asserts Miranda Ballentine, CEO of REBA. “By pooling our resources and leveraging our collective buying power, we are not only accelerating the deployment of renewable energy but also creating a ripple effect that inspires other industries to follow suit.”
While the initiatives of these sustainability pioneers are undoubtedly impressive, their impact extends far beyond their respective operations. By demonstrating the economic viability and competitive advantages of sustainable practices, these companies are effectively reshaping the business landscape, inspiring smaller enterprises and suppliers to embrace similar initiatives.
“Sustainability is not just a box to be ticked; it’s a mindset that permeates every aspect of our operations,” remarks Marc Engel, Chief Supply Chain Officer at Unilever. “By engaging our entire supply chain and fostering a culture of environmental stewardship, we are creating a ripple effect that amplifies our impact exponentially.”
This ripple effect is further amplified by the growing investor scrutiny of

environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. As socially responsible investing gains traction, companies with robust sustainability programs are increasingly attractive to investors seeking long-term value creation and risk mitigation. This shift in investor sentiment has not only elevated the importance of sustainability initiatives but has also provided a powerful financial incentive for businesses to align with the 2045 net zero targets.
“Investors are increasingly recognizing that sustainability is not just a feel-good exercise; it’s a critical factor in assessing a company’s long-term viability and risk profile,” notes Lauren Taylor, Head of ESG Research at Morningstar. “Companies that fail to prioritize sustainability risk not only missing out on growth opportunities but also facing heightened scrutiny from investors and stakeholders alike.”
However, the road to net zero emissions is not without its challenges. Navigating complex supply chains, fostering buy-in from stakeholders, and overcoming technical and regulatory hurdles are just a few of the obstacles that companies must confront. Yet, the sustainability pioneers have demonstrated that these challenges are not insurmountable, and their unwavering commitment to innovation and collaboration holds the key to surmounting these barriers.
“Achieving our sustainability goals is not a sprint; it’s a marathon,” acknowledges Jim Rowan of Volvo Cars. “But
by embracing a culture of continuous improvement, investing in cutting-edge technologies, and fostering strategic partnerships, we are well-positioned to overcome the hurdles that lie ahead.”
As the global community grapples with the existential threat of climate change, the actions of these sustainability pioneers offer a beacon of hope and a roadmap for a greener, more sustainable future. By aligning their operations with the 2045 net zero targets, these companies are not only mitigating their environmental impact but also positioning themselves as industry leaders, driving innovation, and inspiring systemic change.
“The path to a sustainable future is not an easy one, but it is a necessary one,” affirms Alan Jope of Unilever. “By embracing sustainability as a core tenet of our operations, we are not only safeguarding the planet for future generations but also securing our own long-term success in an increasingly carbon-conscious global marketplace.”
As the world eagerly awaits the pivotal 2045 milestone, the sustainability initiatives pioneered by these global business leaders serve as a testament to the power of corporate responsibility and the potential for businesses to be agents of positive change. By leading the charge towards a net zero future, these companies are not only shaping the trajectory of their respective industries but also inspiring a broader cultural shift towards a more sustainable and resilient global economy.

In the era of heightened environmental consciousness and growing consumer demand for corporate responsibility, the world’s biggest brands find themselves confronted with a paradoxical challenge: to communicate their sustainability efforts transparently or to remain silent, a practice known as “greenhushing.” As the urgency of climate action intensifies, this strategic dilemma has far-reaching consequences, not only for brand reputation but also for the very future of our planet.
At the heart of the greenhushing debate lies a fundamental tension between the imperative for businesses to demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship and the risk of perceived greenwashing – the practice of misleading or exaggerating sustainability claims for marketing purposes. In an attempt to avoid scrutiny and potential backlash, some companies have chosen
to adopt a low-key approach, downplaying or even concealing their sustainability initiatives altogether.
However, as concerns over climate change and environmental degradation continue to mount, this strategy of silence is increasingly being called into question. Critics argue that greenhushing not only undermines transparency and accountability but also represents a squandered opportunity to drive positive change and inspire industry-wide action.
“Greenhushing is essentially a form of self-sabotage,” asserts Dr. Emily Huddart Kennedy, a leading expert on corporate sustainability at the University of Cambridge. “By failing to communicate their sustainability efforts, companies are not only missing out on the reputational benefits but also failing to leverage their influence as catalysts for broader societal change.”
The costs of this silence are not merely intangible. According to a recent study by the consultancy firm Deloitte, companies that effectively communicate their sustainability initiatives can expect to see a 1.7% increase in sales revenue and a 3.9% increase in share price performance. In a highly competitive global marketplace, these financial implications are too significant to be ignored.
“Greenhushing is not only an ethical misstep but also a strategic blunder,” remarks Mark Lewis, a partner at Deloitte and co-author of the study. “By remaining silent, companies are effectively letting billions go to waste in terms of lost revenue, investor confidence, and brand equity.”
At the forefront of this debate are some of the world’s most recognizable brands, whose actions – or inactions – resonate across the global business landscape. Take, for instance, the case

of Amazon, a company that has faced intense scrutiny over its environmental impact, particularly in the realm of packaging waste and carbon emissions.
While Amazon has implemented numerous sustainability initiatives, including its commitment to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2040 and its investment in electric delivery vehicles, the tech giant has been criticized for its muted communication efforts. This perceived lack of transparency has fueled skepticism and criticism from environmental advocates and consumers alike.
“Amazon has the potential to be a true sustainability leader, but their reluctance to effectively communicate their efforts is a missed opportunity,” says Katharine Wilkinson, co-editor of the bestselling book “All We Can Save.” “By embracing transparency and amplifying their sustainability story, they could not only bolster their brand
reputation but also inspire other companies to follow suit.”
In stark contrast, brands like Patagonia and Levi Strauss & Co. have embraced a proactive approach to sustainability communication, leveraging their platforms to educate consumers, showcase their initiatives, and advocate for broader environmental action.
“We believe that transparency is not just a moral imperative but also a strategic advantage,” says Chip Bergh, President and CEO of Levi Strauss & Co. “By openly sharing our sustainability journey, we not only hold ourselves accountable but also inspire our customers, employees, and industry peers to join us in creating a more sustainable future.”
Patagonia, the outdoor apparel brand renowned for its environmental activism, has taken this approach to new heights. Through its “Footprint Chronicles,” the company provides detailed information on the environmental impact of its products, from the raw materials used to the supply chain and manufacturing processes involved.
“We believe that transparency is the foundation of trust,” says Ryan Gellert, Patagonia’s General Manager for Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. “By empowering our customers with information, we not only build stronger relationships but also inspire them to make more informed and sustainable choices.”
Beyond the realm of consumer goods, the greenhushing debate has also permeated the financial sector, where investors and stakeholders are increasingly demanding greater transparency on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues.
“Greenhushing in the financial sector is not only a missed opportunity but also a potential risk,” warns Gillian Tett, Chair of the Editorial Board at the Financial Times. “As ESG considerations become increasingly integral to investment decisions, banks and financial institutions that fail to communicate their sustainability efforts risk losing out on capital and
falling behind their more transparent competitors.”
The consequences of greenhushing extend far beyond the realm of brand reputation and financial performance. By remaining silent on their sustainability efforts, companies are effectively abdicating their responsibility to drive broader societal change and contribute to the collective effort to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
“Businesses have a moral obligation to use their influence and resources to tackle the existential threat of climate change,” asserts Paul Polman, former CEO of Unilever and co-founder of IMAGINE, a platform dedicated to accelerating business leadership on global priorities. “By embracing transparency and actively communicating their sustainability initiatives, companies can inspire broader action and catalyze the systemic change that is so desperately needed.”
As the world grapples with the escalating consequences of environmental degradation, the choice between greenhushing and transparency has never been more consequential. By remaining silent, companies risk not only financial and reputational repercussions but also the erosion of trust and credibility among consumers, investors, and society at large.
“Greenhushing is ultimately an unsustainable practice,” concludes Dr. Huddart Kennedy. “In an era where transparency and accountability are paramount, companies that fail to communicate their sustainability efforts risk being left behind, both in terms of their bottom line and their ability to contribute to a more sustainable future.”
As the global community confronts the existential threat of climate change, the world’s biggest brands face a pivotal choice: to embrace transparency and leverage their influence as catalysts for positive change, or to remain silent and squander the opportunity to drive meaningful progress. The path forward is clear – greenhushing is no longer a viable option, and the time to amplify sustainability efforts is now.
Written by Nick Staunton- Editor

Achieving a sustainable future is one of the most significant organisational risks of the 21st century. This creates an opportunity for organisations to ensure that their merger and acquisition (M&A) processes make a material, positive contribution to a sustainable operating model. Failure to adequately assess the impact of sustainability risks and can threaten the success of M&A transactions.
As accountancy and finance professionals are at the heart of the transaction process they have a crucial role using their skills to assess complex risk to help organisations transform
their operating models to become more sustainable.
With sustainability-related issues an increasingly becoming a driver for M&A activity, an important joint report Sustainability in transactions from ACCA (the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants) and Chartered Accountants Australia and New Zealand, examines how the interrelationship between M&A and sustainability is crucial for the corporates and their stakeholders.
The report sets out three key messages: sustainability forms a fundamental part of the strategic intent of
M&A transactions and of the valuation of an entity, and the related opportunities and risks cannot be ignored;
assessing sustainability-related risk and opportunities must be comprehensively considered as part of the due diligence process, both as a specific workflow and as an integral part of other forms of due diligence; and
organisations need to ensure that they have an appropriate level of expertise to handle the transaction cycle and to understand the sustainability-related aspects of

a target’s operations, assets and liabilities.
CFOs must identify sustainability considerations during the investment and divestment cycles. Critical business risks are now arising from sustainability-related issues, and these can pose a threat to the outcome of transactions.
Sustainability can be a driver for an acquisition and – in the case of a sunset industry – the reason for divestment or demerger. Sustainability considerations in transaction are not uniform. The research suggests that in some sectors and industries
it is barely a subtle noise, in others it is a loud drumbeat. It is clear from the research that sustainability is a multi-dimensional issue and the breadth of areas to be considered in a due diligence process is broad and interconnected.
The report examines the sustainability considerations in the due diligence process under strategic, environmental, social economic and governance. Sustainability should be a consideration through each step of the transaction workflow: from strategy and acquisition planning through to due diligence and closing. The report provides tips to help guide CFOs and their
finance teams when considering sustainability-related issues in the M&A transaction process.
Clive Webb, Head of Business Management, ACCA, said: ‘It cannot be stated too loudly that in the M&A process there are significant numbers of risks which could derail an organisation’s journey towards a sustainable operating model. Failure to adequately assess the impact of those risks, and the opportunities which arise, can create a threat to the success of the transaction. As accountancy and finance professionals we are best placed to lead that assessment.
‘Four main factors determine why sustainability matters in a transaction –financial institutions and investors; supply chains; regulators; and customers; clients and employees. They vary according to location and whether they are sunrise or sunset industries.’
Simon Grant, Group Executive APS and International, CA ANZ, said: ‘Accountancy and finance professionals need to grow the appropriate skills and knowledge and capitalise upon ‘on-the-job’ learning opportunities. They also need to constantly bear in mind the ethical dimension. Ethics must be at the heart of everything that we do.
‘Assessing the impact of sustainability-related risks and opportunities requires a significant familiarity with social, economic and environmental issues. Professional scepticism is also required when considering risks of greenwashing and bluewashing against the potential upside of investment.’
Prof Dr Christopher Kummer, President, Institute of Mergers, Acquisitions and Alliances (IMAA), Austria, said: ‘In the context of evaluating new investments or acquisition opportunities, organisations are now employing ESG criteria to gauge the extent to which the prospective target aligns with their sustainability objectives.’
Visit ACCA’s website for more information.
In the dynamic world of entrepreneurship and innovation, Europe has emerged as a fertile ground for disruptive startups to thrive and flourish. Among these trailblazers are a select few that have achieved the coveted “unicorn” status, representing their rare and elusive nature within the business realm. These billion-dollar companies are not only redefining industries but also reshaping the future, propelling Europe to the forefront of the global startup ecosystem. In this article, we explore some of the most prominent European unicorns poised for even greater success and uncover the secrets behind their meteoric rise.
Founded in 2015 by Nikolay Storonsky and Vlad Yatsenko, Revolut has swiftly ascended the ranks of the fintech world, disrupting traditional banking practices with its innovative digital banking platform. Based in London, this unicorn has garnered a staggering valuation of $33 billion, solidifying its position as one of Europe’s most valuable startups.
At the core of Revolut’s success lies its comprehensive suite of financial services, which includes multi-currency accounts, seamless money transfers, and investment options, all accessible through a sleek and user-friendly mobile app. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and a customer-centric approach, Revolut has captivated millions of users globally, empowering them to manage their finances with unparalleled convenience and transparency.
With ambitious expansion plans and a relentless drive for innovation, Revolut is well-positioned to continue its
ascent, reshaping the financial services landscape and cementing its status as a true industry disruptor.
Hailing from Sweden, Klarna has rapidly emerged as a game-changer in the world of online payments and digital shopping. Founded in 2005 by Sebastian Siemiatkowski, Niklas Adalberth, and Victor Jacobsson, this unicorn has revolutionized the way consumers shop and pay for goods and services.
With a valuation of $45.6 billion, Klarna has become a household name in Europe, offering innovative solutions such as “buy now, pay later” and seamless checkout experiences. By leveraging advanced technology and data analytics, Klarna empowers retailers to enhance customer engagement, increase sales, and mitigate risks associated with online transactions.
As the demand for frictionless and personalized shopping experiences continues to soar, Klarna’s innovative approach positions it as a frontrunner in shaping the future of retail, both within Europe and beyond.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of sustainable energy solutions, Northvolt stands tall as a European unicorn driving the electric vehicle (EV) revolution. Founded in 2016 by former Tesla executives Peter Carlsson and Paolo Cerruti, this Swedish company has quickly amassed a valuation of $11.75 billion, capturing the attention of investors and industry giants alike.
Northvolt’s mission is to establish Europe as a global leader in sustainable battery production, leveraging

cutting-edge technology and renewable energy sources. With ambitious plans to construct Europe’s largest battery manufacturing facility, the company aims to meet the surging demand for high-performance batteries in the EV and energy storage markets.
Backed by strategic partnerships with automotive giants like Volvo and BMW, Northvolt is poised to play a pivotal role in the transition towards a more sustainable future, cementing its position as a driving force in the rapidly expanding EV industry.

Checkout.com: Streamlining Global Payments
Founded in 2012 by Guillaume Pousaz, Checkout.com has rapidly emerged as a leading force in the global payments landscape. Headquartered in London, this unicorn has achieved a valuation of $40 billion, cementing its position as one of Europe’s most valuable startups.
Checkout.com’s success lies in its innovative payment solutions that streamline and simplify the checkout process for businesses of all sizes, across various industries and
geographies. By leveraging advanced technology and a comprehensive suite of payment options, the company empowers merchants to enhance their customers’ shopping experiences, reduce operational costs, and mitigate fraud risks.
With a strong focus on international expansion and continuous innovation, Checkout.com is well-positioned to capitalize on the rapidly evolving digital commerce landscape, further solidifying its position as a leading player in the global payments industry.
In a world grappling with the challenges of food security and sustainability, Infarm stands out as a pioneer in urban agriculture. Founded in 2013 by Osnat Michaeli, Guy Galonska, and Erez Galonska, this Berlin-based unicorn has achieved a valuation of $1 billion, captivating investors and consumers alike with its innovative approach to food production.
Infarm’s revolutionary concept involves the deployment of modular, vertically stacked farming units in cities,
enabling the local and sustainable production of fresh produce. By leveraging advanced technologies such as hydroponics, IoT, and data analytics, the company optimizes growing conditions and maximizes yields, while minimizing the environmental impact of traditional agriculture.
As urbanization and climate change continue to shape global food systems, Infarm’s cutting-edge solutions position the company as a frontrunner in the realm of urban farming, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient food supply chain.
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence (AI), Graphcore stands out as a European unicorn at the forefront of technological innovation. Founded in 2016 by Nigel Toon and Simon Knowles, this Bristol-based company has achieved a valuation of $3.2 billion, attracting significant investments from industry giants such as Microsoft and BMW.
Graphcore’s groundbreaking contributions lie in the development of intelligent processing units (IPUs), which are specifically designed to accelerate AI workloads and enable more efficient and powerful computing capabilities. By addressing the computational bottlenecks of traditional hardware, the company’s IPUs hold the potential to unlock new realms of possibility in fields such as machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing.
With a strong focus on research and development, Graphcore is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of AI, driving advancements that could have far-reaching implications across various industries and sectors.
In the realm of process optimization and digital transformation, Celonis has emerged as a true European unicorn, achieving a valuation of $13 billion.
Founded in 2011 by Bastian Nominacher, Martin Klenk, and Alexander Rinke, this Munich-based company has revolutionized the way organizations analyze and optimize their business processes.
Celonis’s flagship product, the Execution Management System, leverages advanced process mining techniques and machine learning algorithms to provide organizations with unprecedented insights into their operational processes. By identifying
inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement, Celonis empowers businesses to streamline their operations, enhance productivity, and drive sustainable growth.
With a rapidly expanding global footprint and a strong focus on innovation, Celonis is well-positioned to maintain its leadership in the process mining space, enabling organizations across industries to unlock new levels of operational excellence and competitive advantage.

Wise (formerly TransferWise): Revolutionizing International Money Transfers
Founded in 2011 by Taavet Hinrikus and Kristo Käärmann, Wise (formerly TransferWise) has disrupted the traditional cross-border money transfer market with its innovative and transparent approach. Based in London, this unicorn has achieved a valuation of $11 billion, making it one of Europe’s most valuable fintech startups.
Wise’s mission is to provide a fast, secure, and cost-effective way for individuals and businesses to transfer money across borders. By leveraging its proprietary technology and a peerto-peer model, the company eliminates the hidden fees and unfavorable exchange rates often associated with traditional money transfer services.
With a rapidly expanding global presence and a strong focus on customer experience, Wise is well-positioned to continue its disruption of the cross-border payments industry, empowering millions of people and businesses to move money seamlessly and affordably across the globe.
In the rapidly evolving world of digital collectibles and blockchain-based gaming, Sorare has emerged as a trailblazing European unicorn. Founded in 2018 by Nicolas Julia and Adrien Montfort, this Paris-based company has achieved a valuation of $4.3 billion, captivating the attention of investors and sports enthusiasts alike.
Sorare’s innovative platform combines the excitement of fantasy sports with the world of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), allowing users to collect, trade, and manage digital trading cards representing real-life athletes. By leveraging blockchain technology and partnerships with major sports leagues, Sorare has created a unique ecosystem where fans can engage in a new form of fantasy sports, while unlocking opportunities for digital ownership and potential financial rewards.
With a rapidly growing user base and ambitious plans for expansion into new sports and markets, Sorare is poised to shape the future of digital collectibles and blockchain-based gaming, solidifying its position as a pioneering force in the intersection of sports, technology, and innovation.
In the realm of virtual worlds and distributed computing, Improbable stands as a visionary European
unicorn, achieving a valuation of $3 billion. Founded in 2012 by Herman Narula and Rob Whitehead, this London-based company is at the forefront of developing cutting-edge technologies for creating and operating largescale, persistent virtual environments.
Improbable’s flagship product, SpatialOS, is a groundbreaking platform that enables the creation of vast, interconnected virtual worlds by harnessing the power of distributed computing and cloud infrastructure. This innovative solution has the potential to revolutionize industries such as gaming, simulations, and the emerging metaverse, enabling the seamless integration of massive virtual environments with real-world data and applications.
With a strong focus on research and development, as well as strategic partnerships with industry giants, Improbable is poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of virtual worlds and distributed simulations, unlocking new realms of possibility in the rapidly evolving digital landscape.
These trailblazing European unicorns represent the vanguard of innovation and entrepreneurship, redefining industries and reshaping the future with their disruptive ideas and cutting-edge technologies. From fintech and retail to sustainable energy and urban agriculture, these billion-dollar startups are not only driving economic growth but also addressing global challenges and shaping a more sustainable, efficient, and connected world.
As Europe continues to nurture its vibrant startup ecosystem, these unicorns serve as beacons of inspiration, attracting top talent, fostering innovation, and positioning the continent as a global hub for entrepreneurial excellence. With their unwavering commitment to pushing boundaries and their ability to adapt to ever-changing market dynamics, these companies are poised to continue their ascent, rewriting the rules of their respective industries and leaving an indelible mark on the global business landscape.
By James Wood, Regional Security Director at International SOS
In an era marked by global unrest and conflict, businesses face the considerable challenge of maintaining operations amidst uncertainty. It is not always possible to predict when or where the next security issue will come, so thorough planning is vital. Businesses should develop comprehensive risk management planning and evacuation strategies to prepare and react in a timely manner and keep any potentially affected staff safe. If evacuations do become necessary, organisations need reliable intelligence to inform timely decision making. The rapid escalation of crises seen recently in locations like Sudan, Niger, Israel, and Gaza serves as a stark reminder that security threats are deeply complicated and interconnected. Hence, it is paramount businesses are equipped with the knowledge and guidance necessary to navigate these challenges successfully.
At the heart of effective risk management lies meticulous preparation. Businesses need to craft robust risk management planning strategies that draw insights from various parts of the organisation. These plans should encompass a thorough analysis of the geopolitical landscape, potential disruptions to business operations and supply chains, and an assessment of local market impacts. It is important that flexible strategies which allow for agile responses to evolving situations can be formulated.
Third party security risk management organisations can be an invaluable resource for businesses operating in

conflict-prone regions. They can provide not only immediate security support but also a broader spectrum of assistance. International SOS actively monitors security incidents, gauging their potential to spread and impact wider regions. For example, there are ongoing concerns about the Israel-Gaza crisis spilling across borders in the region and tensions within European urban centres rising in response. If a business already has planning in place, then these secondary effects of security crises can be better mitigated.
Beyond addressing physical safety concerns in Israel and Gaza, International SOS has also been providing
support for mental health issues, trauma, and crisis fatigue among clients’ employees. This is due to the sensitive and emotive nature of the conflict, which has far-reaching repercussions. A comprehensive approach ensures that businesses can attend to the long-term wellbeing of their employees and the future of the company.
In the rare situations where the security landscape deteriorates to the point where it is no longer feasible to operate safely and securely,

businesses should be prepared to undertake evacuations. Evacuations can be facilitated through various means, including commercial flights, chartered flights, and local road or maritime transportation. However, executing evacuations is no simple feat; road, border or airspace closures may occur unexpectedly, or infrastructure could be compromised, demanding flexible logistics.
Evacuations present multifaceted challenges, particularly as they usually occur in very dynamic environments. The current situation in Israel and Gaza underscores the unpredictable nature of on-the-ground conditions.
With a diminishing number of commercial flight options available from the country, numerous businesses made the decision to evacuate staff from Israel. International SOS has, so far, successfully transported over 100 people and organised multiple chartered flights across Israel during a period of active conflict, some of whom were as close as 6 miles from the Gaza border.
Assistance as complicated as this is only possible with the ability to accurately assess the risks stemming from rocket fire or similar activity. So, crucial to successful evacuations are in-country partners, providing
on-the-ground insights, effective risk assessments and support. The International SOS Incident Management Team coordinated the movement of travellers across various locations in Israel, who had to meet at Ben Gurion International Airport. It also ensured reliable information on their status was fed back to businesses – at a time where the spread of misinformation poses a substantial challenge for businesses across the globe.
The most effective crisis management structures empower the pre-crisis phase. This focuses on identifying and collecting information to make timely decisions and rehearsing the potential response. Information remains key in successful crisis management and can be prepared in advance by researching key players, assessing the historical context of the conflict, and predicting its trajectory.
This information needs to be shared with those on the ground, but communication in conflict zones poses unique challenges, especially when infrastructure is compromised. Businesses need contingency plans to address communication blockages and disruptions, ensuring that alternative channels are available and staff know how to access them. Establishing a dedicated team and maintaining strong links with vetted on-the-ground partners is fundamental to this.
The ability of businesses to continue to operate when a security crisis hits lies in thorough preparation, empowered Crisis Management Teams, strategic partnerships, and access to reliable information. By prioritising comprehensive risk management plans and staying informed on the situation on the ground, businesses can bolster their resilience and, in turn, reduce the risks for their employees. In an era defined by uncertainty, adaptability and preparedness stand as the essentials for sustaining operations and prioritising the safety and wellbeing of employees.
Transitioning to a more sustainable and carbon-neutral future, $13.5 trillion in investments will be needed by 2050, particularly in the production, energy and transport sectors, according to a new World Economic Forum report.
The Net-Zero Industry Tracker 2023, published in collaboration with Accenture, takes stock of progress towards net-zero emissions for eight industries – steel, cement, aluminum, ammonia, excluding other chemicals, oil and gas, aviation, shipping and trucking – which depend on fossil fuels for 90% of their energy demand and pose some of the most technological and capital-intensive decarbonization challenges.
The report, published the same week as the United Nations called at COP28 for “dramatic climate action” to close an “emissions canyon”, outlines pathways to accelerate the decarbonization of emission-intensive production, energy and transport industries. While the pathway to net zero in these sectors will differ based on unique sectoral and regional factors, investments in clean power, clean hydrogen and infrastructure for carbon capture, utilization and storage (CCUS) will be needed to accelerate industrial decarbonization across most sectors.
“Decarbonizing these industrial and transport sectors, which emit 40% of global greenhouse gas emissions today, is essential to achieving net zero, especially as demand for industrial products and transport services will continue to be strong,” said Roberto Bocca, Head of Centre for Energy and Materials, World Economic Forum. “Significant infrastructure investments are required, complemented
by policies and stronger incentives so industries can switch to low-emission technologies while ensuring access to affordable and reliable resources critical for economic growth.”
According to the report, the $13.5 trillion in investments is derived from average clean power generation costs of solar, off-shore and on-shore wind, nuclear and geothermal, electrolyzer costs for clean hydrogen and carbon transport, as well as storage costs.
The Net-Zero Industry Tracker proposes a comprehensive framework of emissions drivers and enablers to measure progress and identify gaps, scorecards for each industry,
and opportunities for cross-sector collaboration. Building on the 2022 edition, the updated report includes transportation sectors and applies the framework to identify strategies for net-zero industrial transformation.
The report’s findings underscore the urgency for creating a robust enabling environment, including low-emissions technologies, infrastructure, demand for green products, policies and investments. In addition to increasing capital expenditures to decarbonize existing industrial and transport asset bases, further investment is needed to build a clean-energy infrastructure.
Share of global GHG emissions for heavy industrial and transport sectors
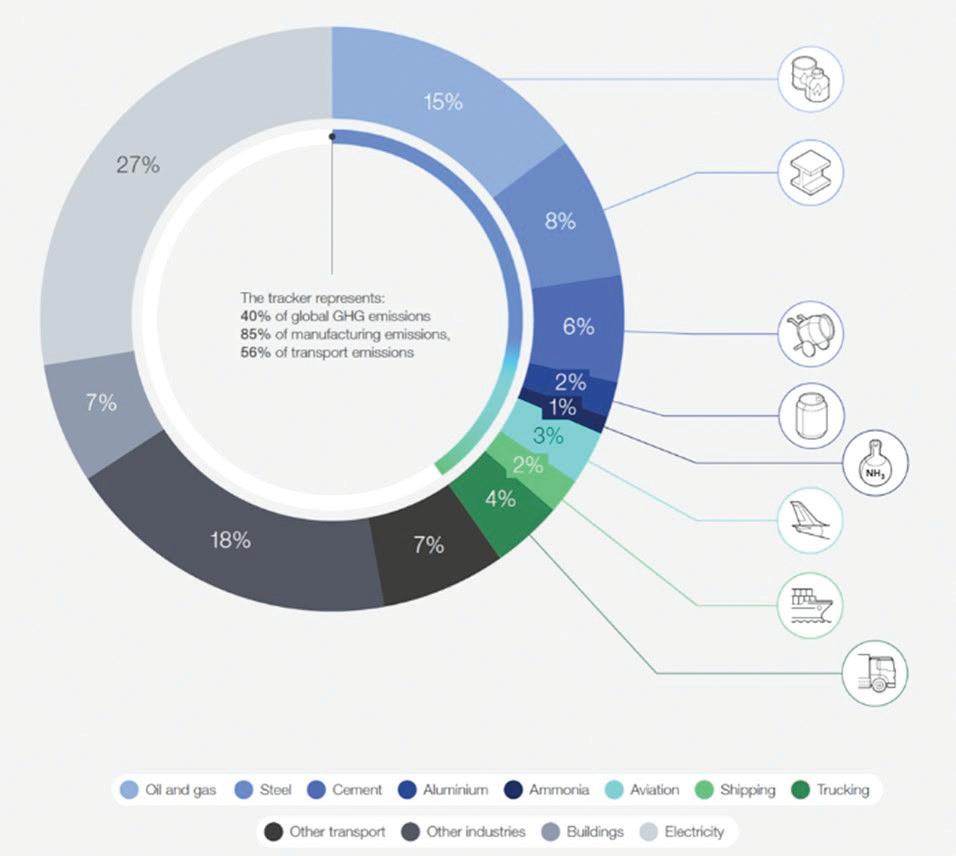

The majority of the technologies needed to deliver net-zero emissions are expected to reach commercial maturity after 2030, highlighting the need for collaborative approaches to research, develop and scale them. This includes substituting legacy technologies with low-emission alternatives, increasing efficiency of processes and machinery, electrification and driving circularity.
“It is imperative that action is taken soon to both decarbonize and improve energy efficiency; otherwise, unabated fossil-fuel demand in the key industry sectors, which have grown 8% on average the past three years, will increase very significantly by 2050,” said Bocca. “But industrial leaders can respond through new collaborative ways of working and innovating, for example within industrial clusters and by fostering best practices, sharing infrastructure in important areas like clean hydrogen and CCUS and building demand for lower-emissions products.”
According to the report, carbon pricing, tax subsidies, public procurement and development of strong business cases can support in mobilizing necessary investments. However, raising capital for high-risk projects with unproven technologies could be challenging in the current macroeconomic environment. Institutional investors and multilateral banks, therefore, can play an important role by providing access to
low-cost capital linked to emissions targets; equally vital is adapting financial models to the needs of various industries and regions.
“Collaboration between the public and private sectors is critical to a successful energy transition, and technology can be a key enabler in both managing affordable and reliable access to clean energy and addressing the incremental cost of decarbonization,” said Muqsit Ashraf, who leads Accenture Strategy. “Widespread scaling and adoption of clean power, carbon capture and storage, and energy efficiency technologies across sectors are vital for progress. Additionally, business model innovations can also help stimulate demand and accelerate industrial decarbonization — achieving net-zero objectives and a resilient energy transition.”
The report acknowledges that recent policy developments can push the industrial net-zero transformation in the right direction. While some advanced economies are enacting large-scale policy measures, emerging economies – which will account for a larger share of future demand for industrial products and transport services – will need help accessing low-emission technologies and solutions.
The report also calls for industrial sectors to focus on the following five areas, and details specific actions for each of the sectors as part of its individual scorecard:
Technology – Prioritize clean power technology across most sectors, commercially scale CCUS in cement, and improve technology to reduce costs for clean hydrogen development.
Infrastructure – Promote shared infrastructure, such as industrial hubs and clusters.
Demand – Create a standardized framework for low-emissions products, a simple emissions-intensity calculator and an auditable carbon-footprint assessment process, improving consumer transparency.
Policy – Align on emissions reduction requirements globally, with policies customized to suit individual country needs and enhance market transparency to increase emission intensity visibility.
Capital – Improve transparency for low-emissions and low-carbon alternatives, strengthen demand signals and reduce capital expenditures through shared infrastructure development.
“The Net-Zero Tracker 2023 explores in detail how low-carbon solutions and infrastructure will contribute to increasing the pace of decarbonization in hard-to-abate industries,” said Stephanie Jamison, Accenture’s global Resources industry practice lead and global sustainability services lead. “This depth is essential to help companies create sustainable value and impact as they strive to achieve netzero carbon emissions.”

By Brian Allen, Head of Product Design
and Development at equipment case manufacturers CP Cases, provides his expertise.
As businesses increasingly come to rely on automated technologies in a digital landscape, the focus turns to satellite communication as the most efficient means of connectivity.
While satellite internet offers a number of benefits – particularly in locations where traditional telecom infrastructure is lacking – the environmental impacts cannot be ignored. It’s up to businesses investing in and benefitting from satellite technologies to take accountability and drive for responsible and ethical usage as
satellite-based connectivity systems gain popularity across the UK.
For its numerous benefits, satellite internet comes at a price. Mass satellite groups including SpaceX’s Starlink have garnered criticism for their detrimental environmental impacts. Astronomers have panned such schemes, blaming failed observations of sensitive radio telescopes on light pollution and radiation leaks. Astronomers from the Netherlands Institute for Radio Astronomy (ASTRON) have detected radiation between 110 and 188 MHz from 47 out of the 68 satellites observed, with such levels of radiation contributing to global
warming upon passing through the atmosphere. Radiation emitted from satellite internet systems has also been linked with the decline of nesting success for birds, as well as disruptions to seasonal animal behaviours.
Furthermore, while the satellites themselves are solar-powered, the ground stations responsible for sending and receiving signals require immense amounts of energy – the majority of which is sourced from fossil fuels. As a result, satellite communication systems accumulate larger carbon footprints than other forms of internet access; energy consumption by satellite internet systems is estimated to be four times higher than traditional internet services, such as cable or fibre optic.
With such an environmental cost attached to the implementation and use of satellite technologies, action must be taken to mitigate and minimise impacts to the climate. While much of the onus is on the proprietors of these satellite systems, accountability also lies with the businesses that benefit from such systems. They need to initiate positive change towards a greener and more sustainable future.
Four steps towards connectivity sustainability:
There are numerous ways in which a business can contribute to minimising satellite communication’s effect on the environment, with tangible change possible through small shifts in day-to-day operations.
1. Investment in energy-efficient satellite designs
With satellite communication promising to surpass the efficiency and effectiveness of traditional telecom systems, satellite-based internet systems are here to stay. With that in mind, businesses must actively look to invest in the development of greener technologies and continue to reap the benefits of satellite communication while safeguarding the environment.
2. Adoption of environmentally friendly materials and production processes
Businesses can look to offset carbon emissions created by satellite communication through small changes to their ground-level day-to-day operations, countering global warming’s effects through green business practices. They might shift energy solutions towards renewable energy sources, cutting down greenhouse gas emissions in the process. For example, business premises and production facilities might integrate solar power, or optimise production processes to reduce waste.
3. Environmental advocacy
While individual businesses can ‘do their bit’, it‘s vital for action to be taken on a systemic level. Without

the cooperation of the government, industry associations and regulatory bodies, any change will be limited. Through lobbying, raising awareness and outspoken advocacy of sustainable connectivity systems, legislation may be introduced to enforce ethical and environmentally friendly satellite communication practices. From responsible satellite disposal to regulation of radiation exposure, systemic change must come from positions of authority, while initiated at grassroots levels.
4. Environmental consciousness
With the rapid onset of a climate crisis and projections of net zero by 2050, environmental consciousness must be at the forefront of all business decision-making. It’s vital that concentrated efforts are made to curb global warming, avoid climate catastrophe and establish future-proofed connectivity solutions at the same time. This extends from offsetting satellite
communication’s carbon footprint to responsibly investing in greener satellite technologies. With sustainable methods of operation and green business practices, businesses are able to move forward with technological advances, reducing uncertainty and securing a responsible, sustainable and successful future.
It’s paramount that businesses are aware of the environmental impacts of satellite communication. And with the continued uptake of satellite-based connectivity systems, environmental agencies must work alongside proprietors to find sustainable solutions as we look to the future. With satellite communication here to stay, a balance must be struck whereby technological innovation and environmental consciousness can coexist. As we service businesses and communities with improved connectivity, we must also protect the environment from potential climate disasters.


By Paul Mackay, Vice President Cloud - EMEA & APAC, Cloudera
The story is a familiar one. American organisations have often been early adopters of advanced technologies, while their
European peers lagged. Cloud computing is no different. US organisations have outspent their EU counterparts for many years. A Gartner market analysis from 2019 showed the US clearly out in front, with countries across the Atlantic relegated to the “tracking” or “laggard” groups. However, things have rapidly changed over the last few years.
Cloudera research reveals that 92% of EMEA organisations are planning to move more data to the public cloud
over the next three years. As the old world catches up with the new, innovative data management platforms like Cloudera’s will accelerate the process – enabling organisations to extract value from their data wherever it resides.
Cloud has become the foundation for the digital transformation projects that drive customer engagement, business agility and competitive

advantage across virtually every industry. Given the role cloud plays in driving this value, early adoption has undoubtedly given US organisations an advantage over the years.
Why did the US jump out of the starting blocks so quickly on cloud? Most obviously, because all the main hyperscalers are American companies. It follows that they sold locally and gained deeper market penetration at home first, before expanding abroad. Amazon Web Services (AWS) launched its pioneering S3 cloud storage service
in the US in 2006, four years before it made landfall in Europe.
The likes of AWS, Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud Platform were also blessed with a large domestic market in which to grow. Data sovereignty concerns weren’t an issue at the time, as cloud datacentres were located in the same jurisdiction as customers’ corporate headquarters. Contrast that with Europe, where legal concerns over transatlantic data transfers persist to this day. As a result, US organisations had a significant head start on cloud.
However, over the past few years, there’s been a shift. New data reveals that 45% of European organisations bought cloud services in 2023 – up four percentage points annually –compared to 48% in the US. But why?
As cloud adoption slowed and the market reached something close to saturation in the US, the hyperscalers launched European business units that have grown rapidly. And they have been able to satisfy local and regional governments over security and sovereignty concerns. AWS last year announced a European Sovereign Cloud, which should help allay long-running fears over data transfers and access by US government intelligence/law enforcement agencies. The European Commission now wants 75% of regional organisations to use “cloud-edge” technologies by 2030.
The European market is also benefitting from a kind of “second-mover” improvement in performance. Cloud technologies have matured, providers are offering price reductions and optimised products, and roadblocks to adoption have now eased. In this context, there’s actually a lot to be said for not adopting new technology first. You can learn from the mistakes of those that were quickly out of the blocks and benefit from additional tools that enable you to drive full value from innovations like cloud.
This is where the likes of Cloudera have stepped up to address key customer pain points, breaking down silos and ensuring strict governance. In truth, few organisations go all-in on the public cloud. Although there are significant cost, agility and scalability benefits from migrating workloads to the public cloud, some data may need to remain on-premises or in private clouds for reasons such as compliance – especially in heavily regulated industries such as banking. That’s why 68% of organisations store data in a hybrid environment according to our research. A further 72% have a multi-cloud model, meaning that they work with two or more hyperscalers. This complexity can quickly erode any value organisations gain from moving to the cloud in the first place.
Cloudera Data Platform enables seamless management of data, regardless of whether it sits on-premise or in the cloud. It means organisations can finally start to capitalise on all those business benefits of cloud migration, whilst applying company-wide policies to keep governance, risk and compliance (GRC) teams happy. Platforms like Cloudera have made cloud a much more viable, profitable proposition for European organisations.
The future of business is undoubtedly digital, and therefore built on cloud computing – whether that means traditional centralised data centres or more dispersed edge computing locations. US businesses arguably still have an advantage having moved so quickly on cloud. But Europe is undoubtedly making up ground.
When it comes to the cloud market, it’s the perfect time for organisations in Europe to peak, with innovations from AI, quantum computing and the Internet of Things (IoT) to biotech and cleantech all primed to dominate the business landscape. But their ability to harness the transformative potential in these technologies will depend on how seamlessly they can manage data across their hybrid cloud environments.
The transportation industry is one of the most prominent contributors to worldwide emissions of greenhouse gases, and numerous countries are intensifying efforts to adopt electric commercial vehicles toward zero-emission electric alternatives. With impending government mandates targeting vehicle emissions, the automotive industry is transitioning towards adopting emission-free vehicles and advanced technologies to increase vehicle range in EVs. This shift underscores a pressing need for sustainable transportation solutions, prompting heightened investment and research into electric vehicle technology to meet regulatory requirements and environmental imperatives. Increasing e-commerce, logistics, delivery, and mobility growth in urban areas have significantly boosted the market for electric commercial vehicles, especially for electric pick-up trucks

and electric vans, due to their wide applications in the e-commerce and logistics industries. Additionally, companies such as Mercedes-Benz Group AG (Germany), AB Volvo (Sweden), BYD (China), GM (US), Volkswagen (Germany), Scania AB (Sweden), and Peterbilt (US) are launching a new model in electric truck segment of electric commercial vehicle
MONTH & YEAR COMPANY
May 2023
May 2023
Mercedes-Benz Group AG Electric Van EQT van
Mercedes-Benz Group AG Electric Van eCitan
April 2023 Scania AB Electric Truck Scania P 25
March 2023 Yutong Light Truck Light Truck T Series
March 2023 Rivian Electric Van Rivian EDV
Source: Press Release and Company Website
market which will support the market growth in the near future. For instance, In October 2023, MercedesBenz Trucks, the European division of commercial vehicle maker Daimler, premiered its battery-electric longhaul truck, eActros 600. The series production of this truck is planned for the end of 2024.
The EQT van has a 90-kW electric motor, two sliding doors, the MBUX infotainment system, and numerous safety and assistance systems.
Mercedes-Benz Vans launched its electric small van eCitan, equipped with a 45kWh battery that can be charged from 10 to 80 percent (state of charge) within 38 minutes with the optionally installed 80 kW DC charger.
Scania AB launched an all-electric car transporter with a GVWR of 42 tons and a battery capacity of 230 kWh.
Yutong launched its T-series light truck with a battery capacity of 100.46 kWh
The Rivian EDV is a battery-electric cargo van built by Rivian exclusively for its investor, Amazon, which uses the van for package delivery.
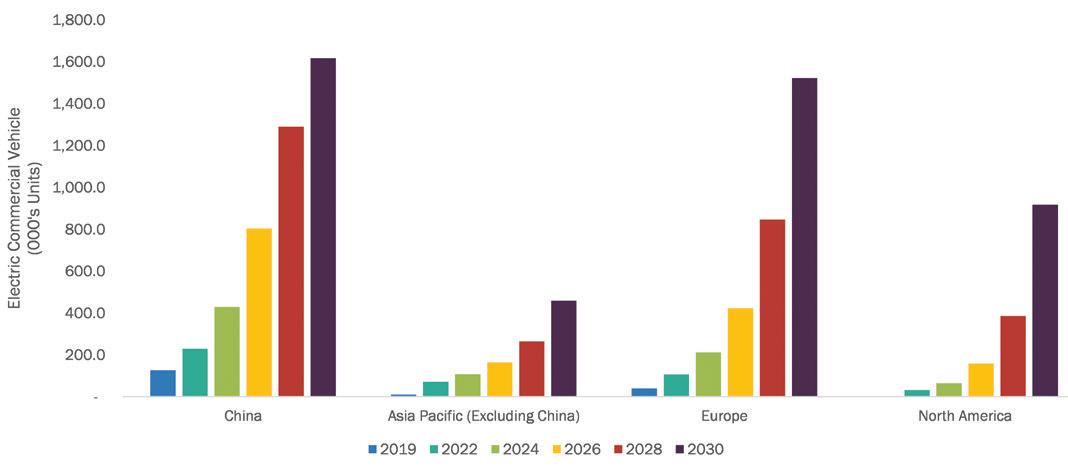
Source: Global EV Outlook 2023, Secondary Websites, News Portals, Automotive Databases, Company Annual Reports, and MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Further, increasing demand for emission-free public transport options in developed and emerging economies is projected to boost the electric bus segment in the near future. For instance, In January 2024, Yutong and BYD signed a contract to supply electric buses to the Italian cities of Bari and Taranto. Yutong will supply 99 electric buses to Bari, with a length ranging from 11.5 to 13 meters. On the
other hand, BYD will supply 45 electric buses with a length of 18 meters to the city of Taranto. The manufacturers are focused on the launch of electric commercial vehicle models. The table below covers a few of the new models launched by key manufacturers.
Transitioning to electric commercial vehicle options can yield significant cost savings for businesses with
ELECTRIC COMMERCIAL VEHICLE LAUNCHES BY OEMS, 2024-2026
lower operating costs due to cheaper electricity than diesel fuel, leading to long-term financial benefits and making it an attractive choice. Key OEMs such as BYD (China), Mercedes Benz Group AG (Germany), Yutong (China), AB Volvo (Sweden), and Ford Motor Company (US) have launched electric light trucks, electric vans, electric buses, electric medium and heavyduty trucks in recent years.
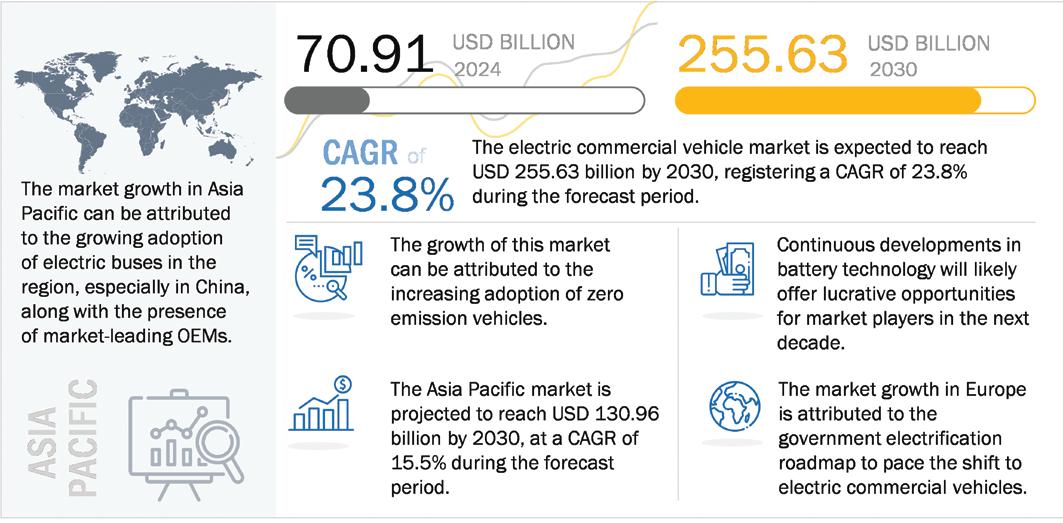
Source: MarketsandMarkets Analysis
As per Atin Jain, Team Lead (Automotive and Transportation) at MarketsandMarkets Research, “The growth of electric commercial vehicle market is driven by factors such as government favorable policies, investment in ECV charging infrastructure, adoption of electric fleets for e-commerce and logistic, delivery and others end -use purpose. In addition, electric vehicles have lower operating costs due to the lower running cost of electricity compared to
diesel/gasoline and have fewer maintenance requirements, resulting in a lower total cost of ownership over the vehicle’s lifespan. Ongoing advancements in battery technology, electric drivetrains, and a decrease in battery prices would support the adoption of electric commercial vehicles for a wider range of end-use applications.
According to MarketsandMarkets research, the global electric commercial vehicle market is projected
to reach 4,512.4 thousand units by 2030, starting from 812.9 thousand units in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 33.1%. Innovations in battery technology have led to increased energy density, longer driving ranges, and faster charging times, eliminating some of the primary concerns associated with ECVs end-use applications. Further, R&D activities are being carried out to enhance battery technology, reduce battery cost, decrease charge time, and increase vehicle
PURCHASE ORDER/SUPPLY CONTRACT/expansion FOR ELECTRIC commercial vehicles
MONTH/YEAR PURCHASE ORDER/ SUPPLY CONTRACT/EXPANSION
January 2024 BYD announced its plan to invest USD 1.3 billion to build an electric vehicle factory in Indonesia. The factory will have a production capacity of 150,000 vehicles.
November 2023 AB Volvo acquired Proterra’s battery business for USD 210 million in a bankruptcy auction. The deal is expected to be finalized in early 2024
October 2023 The Infrastructure & Transport Ministry of Greece signed a contract with Yutong for 250 e-buses. This contract will facilitate green and sustainable development and improve the conditions of public transport in Greece.
September 2023 FedEx Express Europe, a subsidiary of FedEx Corporation, announced the addition of 23 Mercedes-Benz eSprinter vans to its UK operations. The battery-electric eSprinter vans assist FedEx Express in achieving its objectives for locally emissions-free delivery and pickup.
May 2023 PACCAR Inc. and Toyota Motor North America, Inc., a subsidiary of Toyota Motor Corporation, collaborated to expand their joint efforts to develop and produce hydrogen fuel cell (FCEV) Kenworth and Peterbilt trucks powered by Toyota hydrogen fuel cell modules.
Source: Secondary Research, Company Websites, EV Associations, and Country-level Automotive Organizations
COUNTRY TYPE
China Electric Vehicle
South Korea Battery Technology
DESCRIPTION
The government offers a tax exemption on purchases of new energy vehicles (NEVs). This exemption applies to both domestically produced NEVs and imported models. The exemption was initially set to expire in 2020 but was extended to 2022 and then again to cover NEV purchases in 2023.
The South Korean government and its top battery companies plan to jointly invest USD 15.1 billion through 2030 to develop advanced battery technologies, including solid-state batteries.
Germany EV Charging Infrastructure Up to USD 51,000 subsidy for private commercial charging infrastructure.
US EV Charging Infrastructure Up to USD 700 million in funding over fiscal years 2022 and 2023 for strategic deployment of EV charging and alternative fueling infrastructure projects in publicly accessible locations, urban and rural communities, and designated Alternative Fuel Corridors (AFCs).
China EV Charging Infrastructure
The government also offers subsidies for charging points and battery-swapping installations, varying rates for community or commercial projects, and subsidized taxi charging.
Canada Government Investment Clean Energy Fund (CEF)—Budget of USD 975.2 Million over Five Years
Source: Secondary Research, Press Release and MarketsandMarkets Analysis
range. With countries worldwide setting targets to reduce vehicle emissions, the demand for electric commercial vehicles will grow during the forecast period.
Electric commercial vehicles (ECVs) are revolutionizing various industries by offering efficient and sustainable transportation solutions tailored to specific end uses. In urban delivery and logistics, ECVs are preferred due to their quiet operation, zero-emission propulsion, and cost-effectiveness over distances. These vehicles are well-suited for last-mile delivery services, supporting companies in meeting stringent emission regulations
implemented by the government. Various retail, logistics, and courier companies, such as DHL (Germany), UPS (US), FedEx (US), and Amazon (US), have included electric vehicles in their operations. For instance, in September 2023, FedEx announced the addition of 23 Mercedes-Benz eSprinter vans to its UK operations. Furthermore, ECVs find applications in public transportation, providing clean and reliable mobility options for commuters while lowering city carbon footprints. Thus, electric commercial vehicles are poised to play an increasingly pivotal role across diverse industries, driving a sustainable transportation revolution.

Disclaimer: MarketsandMarkets™ provides strategic analysis services to a select group of customers in response to orders. Our customers acknowledge when ordering that these strategic analysis services are solely for internal use and not for general publication or disclosure to any third party.
MarketsandMarkets™ does not endorse any vendor, product, or service profiled in its publications. MarketsandMarkets’™ strategic analysis constitutes estimations and projections based on secondary and primary research and is therefore subject to variations.
MarketsandMarkets™ disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness, for any particular purpose.
MarketsandMarkets™ takes no responsibility for incorrect information supplied to it by manufacturers or users.
Trademarks, copyrights, and other forms of intellectual property belong to MarketsandMarkets™ or their respective owners and are protected by law. Under no circumstance may any of these be reproduced, copied, or circulated in any form without the prior written approval of MarketsandMarkets™ or its owner—as the case may be.
No part of this strategic analysis service may be given, lent, resold, or disclosed to any third party without express permission from MarketsandMarkets™.
Reproduction and/or transmission in any form and by any means, including photocopying, mechanical, electronic, recording, or otherwise, without the permission of MarketsandMarkets™, is prohibited. For information regarding permission, contact: Tel: 1-888-600-6441

The current trends for payment technology are the future path for merchant services. This involves automation, usability and security. The driving forces are technological businesses new to the payment arena including Google, Samsung and Apple. Blockchain technology holds immense potential to revolutionize payment processing
by offering a secure, decentralized, and transparent ledger system. Payment gateways that explore blockchain integration can position themselves for future advancements in the industry. By leveraging blockchain technology, payment gateways can streamline transaction processes, reduce fees, and enhance security through cryptographic protocols and
distributed consensus mechanisms. Additionally, blockchain-based payment solutions offer greater transparency, enabling real-time tracking of transactions and providing an immutable record of payment history. This transparency not only enhances trust between merchants and consumers but also mitigates the risk of fraud and disputes.

Furthermore, blockchain technology enables cross-border payments to be executed more efficiently, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing transaction times and costs. As the adoption of blockchain technology continues to grow, payment gateways that embrace blockchain integration stand to benefit from greater efficiency, security, and

innovation in payment processing, positioning themselves as leaders in the evolving fintech landscape.
Integrating with local banks presents a significant opportunity for payment gateways to leverage existing security protocols and fraud prevention measures implemented by these institutions. By aligning with the security infrastructure of trusted local banks, payment gateways can enhance the overall security and reliability of their payment processing services. This integration not only helps to mitigate the risk of fraud but also builds trust with customers who may be hesitant to use unfamiliar payment methods or platforms. Customers often place a high value on the security measures implemented by their banks, and by partnering with these institutions, payment gateways can reassure customers that their financial transactions are conducted in a secure environment. Moreover, integrating with local banks allows payment gateways to offer a wider range of payment options, including bank transfers and direct debits, catering to the preferences of customers who prefer traditional banking methods. Overall, this collaboration between payment gateways and local banks not only enhances security but also fosters customer trust and satisfaction, driving greater adoption and usage of digital payment solutions.
“The media & entertainment segment to register the fastest growth rate during next five years
In-game virtual currencies have become a staple of modern gaming, serving as a means for players to make microtransactions for various in-game items, enhancements, or additional content. Payment gateways play a crucial role in facilitating these transactions by integrating with the systems managing these virtual currencies. By doing so, users can securely purchase these virtual currencies with real money, enhancing their gaming experience without the need for cumbersome payment processes. This integration not only streamlines the purchasing process for gamers but also ensures the security and reliability of transactions, instilling confidence in users as they engage in microtransactions within the gaming ecosystem. Furthermore, by enabling seamless integration with in-game virtual currency systems, payment gateways contribute to the monetization strategies of game developers, allowing them to leverage microtransactions as a lucrative revenue stream. As the gaming industry continues to evolve and embrace digital economies, payment gateways that facilitate the seamless exchange between real money and in-game virtual currencies are poised to play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of gaming commerce.
Secretary General of the Moroccan Federation of Pharma Industry and Innovation, about the Moroccan pharmaceutical industry, the new federation FMIP and accessibility to medicines.
The Moroccan pharmaceutical industry went from 80% of the local market in the late 90s to less than 60% now. What, in your opinion, are the main factors that hinder the sustainable growth of this sector and what actions are needed to help boost and develop it?
During the period to which you refer, there has been a regression in the share of manufactured drugs compared to those imported. In 2013, this phenomenon was particularly exacerbated after the price decree came into force. The latter clearly favours the imported drug by granting it an additional margin of 10%. The domestic pharmaceutical industry has posed this problem to the government. When addressing the development of the Moroccan pharmaceutical sector, several parameters must be evaluated. The Moroccan pharmaceutical industry has experienced continuous growth for more than three decades, sometimes in double digits. In 2019, the turnover amounted to 1.5 billion Euros, representing 5% of the national industrial GDP. The sector provides some 50,000 jobs in 49 pharmaceutical companies. Despite the current crisis of COVID-19, these jobs have been preserved, as well as the second position of our pharmaceutical industry in Africa, behind that of South Africa. In terms of investments, the Moroccan pharmaceutical sector mobilizes significant budgets annually, both for the opening of new production units and for the maintenance and renovation of existing ones. These investments have enabled our industry to position itself in the therapeutic areas of the future such as biotherapies, which is sought-after by pharmaceutical players.

Today, more than ever, local production must be supported in order to ensure health autonomy. This must be done through a shortening of the product registration deadline, the establishment of a fast track for the essential and/or innovative products, the national preference for manufactured products, the extension of social security coverage and finally support for exports.
Morocco stands to benefit as European firms, hurt by COVID-19, look to shorten their supply chains, reduce their overreliance on China and bring manufacturing closer to home. The country could become the best platform south of the Mediterranean to build a prosperity hub based on co-investment between the north and the south. Can you elaborate on the opportunities that exist here? Can you tell European Business Magazine readers about Morocco's strengths in the global value chain? Where do the weaknesses exist, and how can they be handled?
Morocco is well positioned to be the ideal partner of the old continent especially in industrial sectors with high added value such as the pharmaceutical industry. Thanks to its political stability, its geographical proximity to Europe and above all to the quality of its medicine production recognized European quality. Indeed, the COVID-19 pandemic has shown a great dependence of Europe towards Asian countries in terms of the pharmaceutical industry, whether for finished products or API (Active Pharmaceutical ingredients). I believe that this pandemic represents an opportunity for

both Europe and Morocco to put into practice a policy of co-location and co-investment advocated in recent years by several European officials. This policy can take the form of pharmaceutical joint ventures whose production could be intended for both Europe and Africa. Morocco has several assets to make such cooperation effective. In terms of quality, Moroccan drugs are produced and registered in accordance with European regulations. In terms of human resources, Morocco has the skills at all levels, including a new generation of researchers and innovators, capable of making these pharmaceutical projects a success. In terms of logistics, Morocco has developed advanced and quality infrastructure in terms of highway, rail, port and airport networks. Morocco's financial sector, thanks to its African roots, also offers several advantages to investors. In terms of economic policies, the industrial and technological cities created particularly in the north of the country offer a range of advantages and facilities for the establishment of leading Euro-Moroccan pharmaceutical units. Furthermore, Morocco's commitment to the production of renewable energies represents a guarantee of compliance with international environmental standards for European partners.

The new federation, the Moroccan Federation of the Pharmaceutical Industry (FMIP), aims to unite pharmaceutical operators in Morocco and strengthen the national industrial fabric. What benefits will FMIP bring, and how will it support the Moroccan pharmaceutical sector on the international stage?
The members of the Moroccan Association of the Pharmaceutical Industry (AMIP) unanimously agreed about the creation of the Moroccan Federation of the Pharmaceutical Industry (FMIP) at the end of the Ordinary General Assembly of the association held on Tuesday, September 29th. This new federation aims to bring together all the pharmaceutical players in Morocco to strengthen the pharmaceutical industrialization. Whether its generic or multinationals operating in Morocco via industrial sites, we all have a single goal which is to ensure Morocco's autonomy in the manufacture of drugs, and a quality and accessible product for the consumer. FMIP is created to support the various development initiatives of the sector, especially in terms of industrial tools, Research and Development or innovation.
In your opinion, what are the legal and technical constraints to overcome in order to promote and encourage a stronger national pharmaceutical industry? And what methods do you advise to create an adequate framework for this field of activity?
From a legal perspective, the last two decades have seen several law reforms governing the pharmaceutical sector; some of these reforms are positive and some are not. The entry into force of Law 17.04, the Pharmacy and Medicines Code, for example, has made it possible to open up the capital of pharmaceutical companies to national or foreign investors other than pharmacists. This is a major step forward and this legal framework can play a positive role in the Euro-Moroccan cooperation I mentioned earlier. However, there are certainly challenges to be met at the regulatory level. One of these challenges is the long process of granting Marketing Authorizations (MA) for new pharmaceutical specialties. I think that France's response to the impact of COVID-19 on its drug industry can serve as a model in this field. As a matter of fact, one of the key measures recently taken by the French authorities to boost the French pharmaceutical industry is precisely to facilitate the registration formalities for new drugs and to shorten the time to obtain the MA.
What impact has the COVID-19 crisis had on the Moroccan pharmaceutical industry, and what opportunities have come about directly because of the pandemic? Did the crisis directly impact the sector's international development strategy, particularly in Africa?
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a rich learning experience for the pharmaceutical sector. It was necessary to react quickly through the activation of business continuity plans that respond both to the country's needs for drugs - especially those included in the COVID treatment protocol - and to the imperatives of preventing contamination within the production units. There
was huge pressure on the industrial teams, who have doubled their creativity to maintain the delivery of medicines on time, along with safeguarding the health of employees and avoiding the formation of contamination clusters. In terms of medical promotion, containment simply stopped medical representatives from visiting doctors and organizing scientific events. This was an opportunity for our teams to imagine other forms of communication. In that respect, thanks to digital technology, we were able to maintain our medical and pharmaceutical information efforts through the organization of virtual congresses and webinar trainings. In brief, I think that the pandemic has had the merit of pushing pharmaceutical players to make major transformations in their operations. This will positively impact the future of the sector.
How would you qualify accessibility of medicines and the system of health insurance in Morocco? Is it possible to ensure the adequacy between the price of medicines, the level of citizens' income, accessibility to innovation and R&D and the capacity of the AMO?
I believe that the project of generalization of social security coverage recently announced by His Majesty the King, will resolve this question of accessibility to medicines. The will to solve this problem by focusing on the sole parameter of prices and margins of medicines has proved to be fruitless, because the consumption of medicines per capita has not changed despite all the price cuts announced in recent years by the government. We have the weakest per capita drug consumption in the Maghreb region. It is only 35 Euros per inhabitant per year. This low consumption is essentially due to the fact that in Morocco two thirds of the population do not have reliable social security coverage. Consequently, the project of generalization of social security should contribute to better accessibility to medicines for citizens, as well as promoting the development of the national pharmaceutical sector.

Over the last decade a new generation of civil servants has been working to improve the attractiveness of Morocco’s industrial sector, especially in areas such as automotive, aeronautics, electronics and biotech. With youth on their side, many of them are in their thirties or early forties, and they all have extensive experience in the private sector in Morocco or abroad.

Youssef El Bari, Secretary General
Acting as the global coordinator of Morocco’s “industry team”, Youssef El Bari is the secretary general of the Ministry of Industry, trade, green and digital economy. Prior to this, a graduate from the prestigious French engineering school Polytechnique, El Bari was the director of industrial innovation in Phosphate Giant OCP. El Bari is laser-focused on execution and deals with numerous challenges in the transformation of the administration, alongside coordinating the different departments and interactions with other ministries. A seasoned jogger who used to run long distance, El Bari is a rising star in the Moroccan administration. Renowned for his solutions-oriented character and his constant search for common ground, he is also well known for being a tough negotiator.
Ali Seddiki, 35 years old, is one of the most esteemed actors of the Moroccan public industry. A graduate from HEC Paris, Ali started his career in a strategy consulting firm based in Paris, and specialized in Aeronautics, before joining the minister’s cabinet in 2014. He became director in charge of Aeronautics, Rail, Naval and Renewable Energies and was project leader for the 1$ billion Boeing ecosystem in Morocco. He currently serves as General Director in charge of industry, and is in charge of developing the Moroccan industrial sector, which currently employs more than 800,000 people and generates $24 billion in exports. Seddiki’s scope of intervention encompasses regulation improvement, FDI development and industrial supply chain densification.
Morocco’s industry is no longer a “boy’s club”:
Following Morocco’s journey towards gender equality, the Kingdom’s industry is no longer a “boy’s club”, and two high profile female leaders are in charge of some of the most crucial sectors.

Kenza El Alaoui, 39 years old, is currently the director of automotive industry in the ministry, the most dynamic sector when it comes to exports. Automotive is also one of the most important sectors for employment, with more then 700 000 vehicles produced per year. El Alaoui, a graduate from Engineering School Ecole des Mines, spent a great deal of her career in French automotive giants Peugeot and Renault, before being scouted by the ministry in April 2018.

Afaf Saaidi is an engineer and is currently preparing a PHD in Business. Saaidi accomplished most of her career in the public sector, and is the director overseeing the development of aeronautics, railways and renewable energies. Prior to this, Saaidi was responsible for innovation, head of division for advanced technologies and head of division for industrial ecosystems.

The World Economic Forum announced on the 17th of November in the face of extraordinary challenges that 36 cities across 22 countries and six continents have agreed to pioneer a new roadmap for safely adopting new technology as part of the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance.
Cities are facing urgent challenges from the COVID-19 pandemic and other major disruptions, which are expected to culminate in a budget crisis that could reach $1 trillion in the United States alone. They need data and innovation to become more resilient, responsive and efficient. Yet there is no global framework for how cities should use these technologies, or the data they collect, in a way that protects the public interest.
This is set to change with the launch of a new global policy roadmap by the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance, designed to give cities the procedures, laws and regulations they need to use new technology responsibly. The secretariat of the alliance is hosted at the World Economic Forum
“This roadmap is not about theoretical ideas and pipe dreams, it is built on practical, real-world policies from leading cities around the globe,” said Jeff Merritt, Head of the Internet of Things and Urban Transformation, World Economic Forum. “City governments are on the frontline of a global crisis and need to be able to act quickly and decisively to curtail this pandemic and set course for their economic recovery. Technology is an essential tool in this fight but governments cannot risk falling into the usual traps related to privacy, security and vendor lock-in.

That’s where the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance can help.”
To kickstart adoption of the roadmap, the alliance has recruited a group of 36 “pioneer cities” that will collaborate with global experts to enhance their city policies, in areas ranging from privacy protection and cyber security to better services for disabled people and better broadband coverage.
The pioneer cities are launching their activities today at a global event broadcast by Smart City Expo World Congress, the world’s premier smart cities event.
“This initiative originated in Japan last year from our Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, a fact I’m very proud of,” said Koichi Akaishi, Vice Minister for Science, Technology and Innovation for the Cabinet Office of the Government of Japan. “I hope to

see more cities participating in the Alliance following the model set by these first pioneer cities.”
Leaders of organizations participating in the programme:
Miguel Eiras Antunes, Global Smart Cities Leader, Deloitte Global, said “The transformation from a traditional city to a ‘smart city’ does not just happen overnight. Success depends
on the quality of the decisions that are made and the way those decisions are executed. Deloitte is committed to working closely together with the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance on Technology Governance to co-design policy frameworks that will empower governments to accelerate smart cities initiatives for sustainable developments.”
“Being a pioneer city in the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance is an excellent
opportunity for us to promote the innovative work that is taking place in Leeds right now, but also facilitates the opening of doors where we can learn from other leading cities around the world and implement best practice in our city,” said Stephen Blackburn, Head of Smart Cities, Leeds.
London’s Chief Digital Officer, Theo Blackwell , said “We need to work together to realize the potential of data to solve city challenges by
Discover the molecules that make life work