








In the evolving landscape of global consciousness, the concept of carbon net-zero has transcended mere environmental policy; it has become a cultural imperative. As societies grapple with the urgency of climate change, embracing sustainability has shifted from a trend to a foundational aspect of our collective identity.
Executive Mat Service has taken a leadership role In this cultural movement. Carbon netzero is part of our core values and mindset. It represents a commitment to stewardship of our planet, a recognition of our interconnectedness with the environment, and a pledge to future generations.
 Kim Caron Founder / President Executive Mat Group of Companies
Kim Caron Founder / President Executive Mat Group of Companies
Executive Mat Service is at the forefront of achieving carbon neutrality, committed to mitigating environmental impacts and promoting a sustainable future. Our approach centers on extensive education, collaborative policy development, innovative solutions, and rigorous environmental stewardship.
Key Components of Our Strategy:
1. Scope 1 and 2 Carbon Accounting: We have established robust carbon accounting practices for Scope 1 and 2 emissions, significantly enhancing our ability to monitor and manage both direct and indirect carbon emissions.
2. Innovating Scope 3 Challenges: Addressing the complexities of Scope 3 emissions, which constitute the largest portion of our carbon footprint, we have streamlined this category by focusing on "Internal Operations." This approach simplifies accounting and emphasizes that Scope 3 emissions can represent up to 80% of total emissions.
3. Emission Factor Development: By formulating specific emission factors, we've simplified the calculation and reporting of Scope 3 emissions, improving accuracy and manageability.
4. Carbon Net-Zero Education: Through targeted educational programs, we raise awareness and facilitate the transition to net-zero operations, ensuring all stakeholders grasp the essential concepts and actions required.
5. Collaboration on Policy Frameworks: In partnership with FRAS-Canada, we play a key role in creating streamlined frameworks for reporting Scope 3 emissions, enhancing both transparency and accountability.
6. Technology Innovation and Commercialization: Our associated enterprises, such as CDFSystems, Eco-Growth Environmental, Weather-Stopper, and Gravitas Energi, develop technologies that address specific environmental issues.
7. VER Marketplace Development: We have launched a marketplace for Verified Emission Reductions to encourage the adoption of technologies that reduce Scope 3 emissions and promote sustainability.
8. Advanced Methane Modeling: We utilize sophisticated mathematical models to better understand and reduce methane emissions from landfills, advancing our strategies for landfill avoidance.
9. Green Thumb Initiative: Focused on reducing landfill waste, this initiative plays a crucial role in our strategy to lower greenhouse gas emissions and foster a circular economy.
Executive Mat Service is dedicated not only to achieving carbon neutrality but also to setting an industry standard for environmental responsibility. Our integrated strategy provides a blueprint for others to emulate, demonstrating the feasibility and benefits of a comprehensive approach to carbon management.



The Green Wash Company is a fictitious entity created to highlight companies that claim a net-zero strategy set far in the future without taking genuine action. It is not intended to represent any actual company but serves to expose and critique such disingenuous practices
The Green Wash Company's purported commitment to environmental and net-zero goals appears more like a superficial effort rather than a genuine attempt to make meaningful changes. Here’s a critical assessment of their so-called sustainability initiatives:
• LED Lighting Transition: The Green Wash Company is nearing the completion of a multi-year project to switch to LED lighting across its facilities in the United States and Canada, aiming for Net Zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2050. (Why 2050? This seems like a convenient way to defer responsibility to future generations rather than addressing the issue immediately.)
• Energy Reduction: By installing LED lights in older, more energy-intensive locations, The Green Wash Company has installed LED lighting in over 6 million square feet of space, expecting to reduce annual energy use by almost 23.3 million kilowatt-hours. (This is a mature technology that should have been implemented years ago. Boasting about it now shows a lack of genuine proactive measures.)
• CO2 Emissions Reduction: The switch to LED lighting is estimated to prevent more than 16,500 metric tons of CO2 emissions annually. (Again, this is something that should have been done years ago. It’s not a milestone to be proud of, but rather an overdue action.)
• Energy Consumption Intensity: From FY’21 to FY’22, The Green Wash Company reduced its energy consumption intensity by 7.9%, including the impact of the LED lighting transition project. (Once again, focusing on lighting. What about addressing Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions comprehensively?)
• Beyond Lighting: The Green Wash Company is exploring other energy-efficient solutions, including testing solar technology. (What does "testing solar technology" mean? Is it a single solar panel in an obscure location? This feels disingenuous and lacks transparency.)
The Green Wash Company's approach to achieving their net-zero goal is touted as strategic and multifaceted, focusing primarily on lighting practices. (In reality, it is a joke and represents the worst form of greenwashing. They are far from making a genuine impact on sustainability.)

The world is facing an unprecedented climate emergency. Extreme weather events, rising sea levels, and catastrophic loss of biodiversity are no longer distant threats but present realities. As global temperatures soar, the urgency for climate action has never been clearer. This blog post explores how we arrived at this critical juncture and highlights how Executive Mat Service is not waiting for a distant net-zero future but is taking decisive, impactful action today.
The roots of the climate crisis lie in the Industrial Revolution, which marked the beginning of large-scale fossil fuel consumption and wide-spread use of landfills. Progress, however, came with a steep environmental cost.
1. Industrial Emissions: Factories and power plants began emitting vast quantities of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases (GHGs) into the atmosphere. These emissions have trapped heat, leading to global warming.
2. Deforestation: Massive deforestation for agriculture and urban development has reduced the planet's capacity to absorb CO2, exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
3. Waste Management: Inadequate waste management, particularly in landfills, has led to substantial methane emissions as organic waste decomposes anaerobically.
These activities have led to a dramatic increase in atmospheric GHG concentrations, resulting in the climate crisis we face today.
Executive Mat Service: Leading the Charge for Immediate Action
While many organizations are making long-term commitments to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 or later, Executive Mat Service stands out by taking real, impactful action now. Here's how we are leading the way in climate action:
1. Carbon-Lowering Technology: We have developed the CDF low-carbon mat cleaning machine, a groundbreaking technology that significantly reduces carbon emissions within our processing facilities.
2. Landfill Waste Avoidance: Through our GREEN THUMB Initiative and the development of the Eco-Growth suite of technologies, we actively avoid landfill waste. This initiative ensures that organic waste is composted efficiently, preventing methane emissions from anaerobic decomposition in landfills.
3. Gravitas Energi: This game-changing technology delivers low-cost, reliable electricity with zero carbon emissions. By harnessing innovative techniques, Gravitas Energi is set to revolutionize the energy sector and drastically cut down on greenhouse gas emissions.
4. Carbon Offsetting: For the emissions we cannot eliminate, we use high-quality Verified Emission Reductions (VERs) from Pericarbon.org. These offsets ensure that our operations achieve true carbon neutrality today, rather than in some distant future.
The time for vague promises and distant goals is over. The climate crisis demands immediate and meaningful action. Executive Mat Service is committed to being a leader in this space, demonstrating that it is possible to operate a successful business while significantly reducing environmental impact.
Our approach is grounded in the belief that every action counts and that businesses have a critical role to play in mitigating climate change. By taking bold steps today, we are not only safeguarding our planet for future generations but also setting a standard for others to follow.
You can't manage what you can't measure –Understanding how to measure (carbon emission factors)
In light of upcoming Government-led mandatory carbon emission reporting over all scopes of carbon (including scope 3) there is an urgent need for simplistic and effective carbon accounting protocols. One powerful tool is the use of emission factors. Emission factors provide a straightforward and standardized approach to calculating greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions across various scopes.
• Definition: An emission factor is a coefficient that quantifies the emissions produced per unit of activity, such as kilograms of CO₂ per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity consumed.
• Calculation Method:
• Determine Consumption: Identify the total quantity of the item being measured, for example kWh of electricity consumed within a specific period.
• Apply Emission Factor: Multiply the quantity being measured by the emission factor specific to the region or energy source.
• Example:
2. Benefits of Using Emission Factors
• Simplicity: Eliminates the need for complex data collection and analysis.
• Consistency: Ensures standardized and comparable emissions data to form baseline greenhouse gas emissions over all scopes of carbon emissions.
• Efficiency: Reduces the time and resources required for carbon accounting. Simplifies compliance with reporting standards and frameworks, such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol and ISO 14064.
1. Adoption of Emission Factors
• Widespread Use: As emission factors become more widely adopted, organizations can achieve greater transparency and consistency in their carbon reporting and strategic plans to minimize carbon emissions.
2. Driving Innovation
• Continuous Improvement: Emission factors allow innovators to develop new technologies and processes to drive carbon emission reduction. Using current industry-standard baseline emission factors to measure meaningful reductions.
• Encouraging Participation: Simplified carbon accounting encourages more organizations to engage in carbon management and adoption of carbon lowering technologies and processes.
Getting Started: Net-Zero Analytics Inc. is a Canada-based firm specializing in assisting innovators calculate emission factors surrounding their new technology developments and processing solutions.

In the global effort to combat climate change, achieving carbon net-zero has emerged as a crucial target for businesses, governments, and individuals alike. 83 out of the Fortune 500 companies have committed to netzero, carbon-neutral, or related targets. Carbon net-zero refers to balancing the amount of carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere with the amount removed or offset. This typically involves following a 2-step process.
The initial and most impactful step towards achieving carbon net-zero is reducing your existing carbon footprint. This involves a series of strategic actions aimed at minimizing carbon emissions associated with your activities. This involves accounting for all Scopes of carbon, specifically Scope 3 “Internal Operations” emissions which can represent most of overall emissions.
Reduction strategies include seeking certified low-carbon goods and services within your supply chain. Eliminating landfill waste altogether is probably the most impactful strategy that signifies a commitment to operational changes that genuinely reduce the reliance on carbon-based resources.
Once you have reduced your carbon emissions as much as practically possible, the next step involves neutralizing the remaining emissions. This is done through the purchase of Verified Emission Reductions. VERs are carbon offsets that have been certified by third-party organizations to ensure they provide genuine, measurable environmental benefits. These offsets support projects that either avoid emissions (like landfill methane avoidance) or capture carbon directly from the atmosphere (such as reforestation i.e., treeplanting).
Achieving carbon net-zero is more than just an environmental responsibility; it’s a competitive edge for businesses, a marker of commitment to sustainability, and a significant step towards safeguarding our planet for future generations. As more entities commit to this goal, it catalyzes broader changes in policy, industry standards, and consumer expectations, leading to a more sustainable economy.

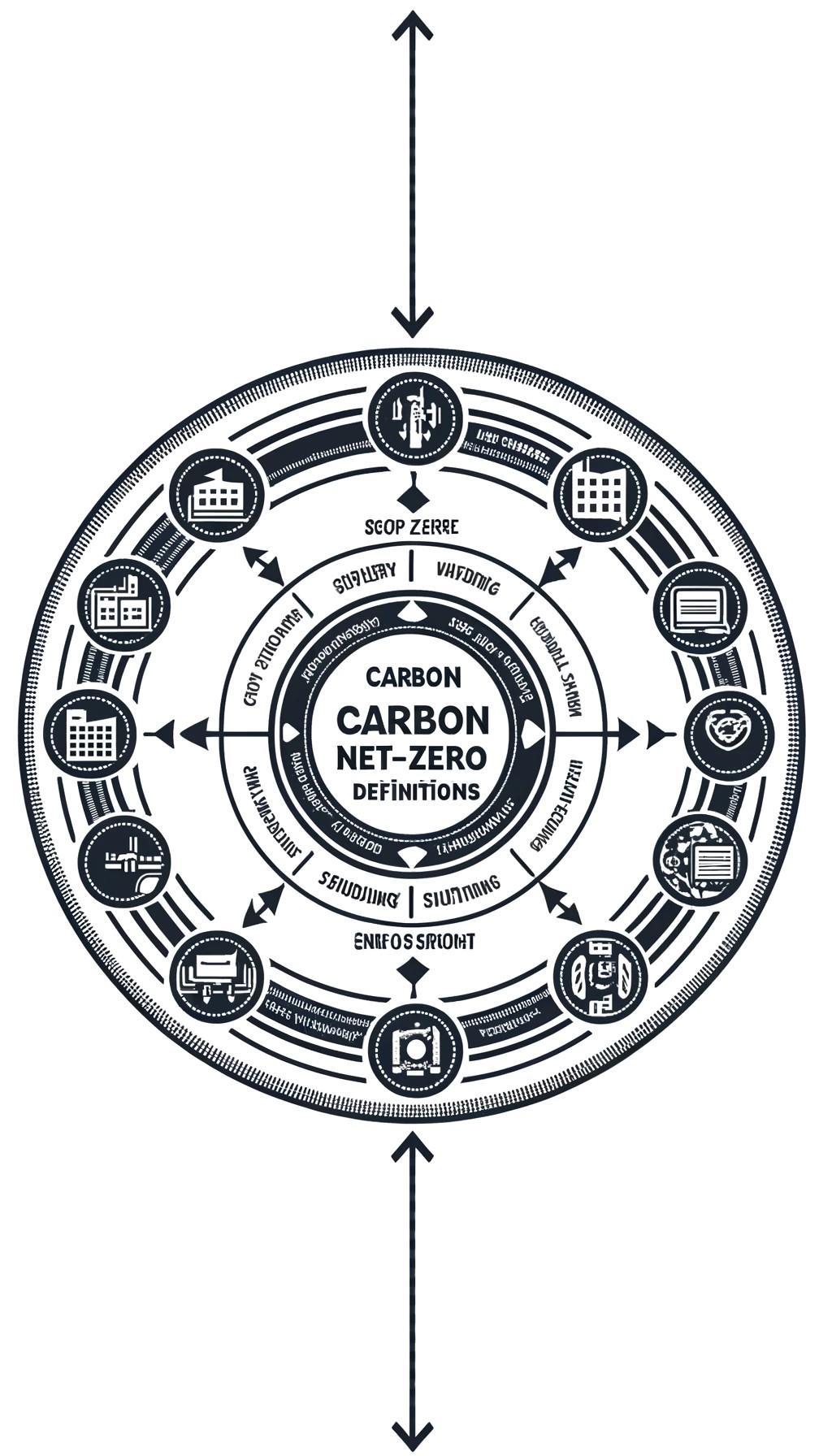
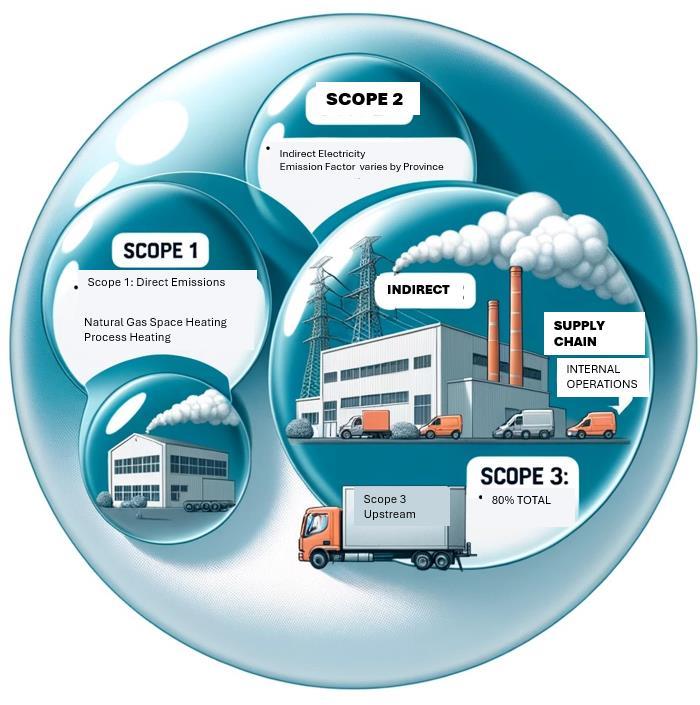
In the era of increasing environmental awareness, organizations are under growing pressure to not only track but also manage their carbon emissions. Understanding the full extent of one's carbon footprint involves delving into the "scopes" of emissions defined by the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol, which categorizes them into three parts: Scope 1, Scope 2, and Scope 3. This comprehensive approach helps organizations identify effective strategies to reduce their carbon impact, especially considering that Scope 3 emissions can constitute as much as 80% of a total carbon footprint for many companies.
Scope 1 emissions are direct emissions from owned or controlled sources. This includes fuel combustion on-site such as gas boilers or company-owned vehicles. Mitigation strategies here are often focused on switching to renewable energy sources or improving energy efficiency.
Scope 2 emissions cover indirect emissions from the generation of purchased electricity consumed by the reporting company. Companies can reduce these emissions by opting for electricity from renewable sources, such as wind, solar or gravity (Gravitas Energi), and by increasing the energy efficiency of their buildings and processes.
Scope 3 emissions, also known as value chain emissions, however, are the most elusive as they include all other indirect emissions that occur in a company’s value chain. This encompasses emissions related to business travel, procurement, and waste disposal. Scope 3 can often account for the majority of an organization’s carbon footprint up to 80% or more. This makes it a critical target for those aiming to make a significant impact on their overall emissions.
Image depicts a building whose management have committed to carbon net-zero.
In an era where sustainability shapes market landscapes and investor priorities, the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation has introduced pivotal changes aimed at enhancing how companies report on sustainability and climate-related matters. These changes are encapsulated in two new standards, IFRS S1 and IFRS S2, which seek to refine and expand the scope of corporate disclosures concerning sustainability-related risks and climate impacts. Here’s a closer look at these new standards and what they mean for businesses globally.
IFRS S1 marks a significant shift in how companies communicate sustainability issues to investors. The standard mandates a comprehensive set of disclosure requirements, enabling companies to articulate the sustainability-related risks and opportunities they face over the short, medium, and long term. This includes any information that might reasonably impact the company's cash flows, access to finance, or cost of capital. By focusing on ‘sustainability-related risks and opportunities that could reasonably be expected to affect the entity’s prospects’, IFRS S1 aims to integrate sustainability into the core financial disclosure framework, making it a pivotal factor in investment decisions.
While IFRS S1 sets the stage for broad sustainability reporting, IFRS S2 drills down into the specifics of climate-related issues. This standard requires companies to disclose information regarding how they are managing the potential negative effects of climate change. This encompasses physical risks such as extreme weather events, transition risks including policy and regulatory changes, and opportunities that
may arise from the global shift towards a greener economy. IFRS S2 is designed to work in tandem with IFRS S1, ensuring that climate-related disclosures are both comprehensive and contextual.
With these standards, the IFRS Foundation encourages organizations not just to passively await legal mandates but to adopt a proactive approach in addressing climate change. Companies are urged to begin by assessing and implementing action plans to reduce Scope 3 "Internal Operations" emissions. Scope 3 emissions, which are not directly produced by the company but are a consequence of their internal and external activities, often represent the bulk of an organization’s carbon footprint. By focusing on these emissions, companies can significantly influence their overall environmental impact.
Organizations that move swiftly to align their reporting with IFRS S1 and S2 standards will likely gain a competitive edge. Early adoption can enhance a company's reputation, improve investor confidence, and facilitate access to green financing options. More importantly, it prepares businesses to be resilient and adaptable in a future where sustainability and climate resilience are not just regulatory requirements but also critical business imperatives.

Image is from Canadian Sustainability Standards Board Exposure. Drafts CSDS 1 and CSDS 2. Executive Mat Service Ltd. Has provided input into developing Scope 3 “Internal Operations” Emissions standard.

In the evolving landscape of environmental accountability, accurate and efficient carbon emissions reporting is paramount for companies committed to sustainability. Executive Mat Service Ltd., in collaboration with "Financial Reporting and Assurance Standards Canada," is pioneering a groundbreaking framework for Scope 3 carbon emissions reporting. This initiative introduces the concept of "Internal Operations - IO" emissions, aimed at simplifying the reporting process through a structured, two-step approach
Scope 3 emissions encompass all indirect emissions that occur in a company’s value chain. These include emissions associated with both upstream and downstream activities which traditionally are complex to track and report. The difficulty lies in the diverse range of activities and interactions that contribute to these emissions, making them challenging to quantify and manage.
Executive Mat Service has developed a strategic method to simplify this complexity through the categorization of emissions into two distinct types: Upstream IO and Downstream IO emissions.
1. Upstream IO Emissions:
• Definition: These are emissions associated with inputs to an organization that are consumed onsite.
Details: This category records the carbon intensity of goods and services procured by the company. By focusing on the direct inputs and their immediate impacts, this
• method allows for a more manageable approach to capturing data and encourages suppliers to adopt greener practices.
• Definition: Emissions that occur from the disposal of a company’s waste generated onsite within the organization.
• Details: Particularly, this approach uses the gold-standard Scholl-Canyon landfill methane model with “Caron-Refinements” to measure emissions from landfill waste. This model provides a detailed and refined assessment of the methane emissions resulting from waste disposal, offering a clear view of the downstream impact.
The introduction of the IO emissions reporting structure by Executive Mat Service is set to transform how companies report their carbon footprints. This method not only simplifies the complex nature of Scope 3 emissions but also enhances transparency and accuracy in environmental reporting. By categorizing emissions into upstream and downstream activities, companies can more effectively identify hotspots for carbon reduction and engage in more targeted sustainability strategies.
Additionally, this structured approach fosters a better understanding among stakeholders about where emissions are generated and how they can be mitigated. It empowers businesses to take concrete steps toward sustainability by focusing on specific areas within their control and influence.
As Executive Mat Service Ltd. continues to lead in sustainability initiatives, their work with "Financial Reporting and Assurance Standards Canada" on simplifying Scope 3 carbon emissions reporting is a testament to their commitment to environmental stewardship. This innovative approach not only aids in fulfilling regulatory requirements more efficiently but also aligns with global efforts to combat climate change through better business practices.
The adoption of the IO emissions framework could serve as a model for other companies striving to enhance their environmental reporting and impact. As more organizations adopt these practices, the collective impact on reducing global carbon emissions could be substantial, marking a significant step forward in corporate environmental responsibility.










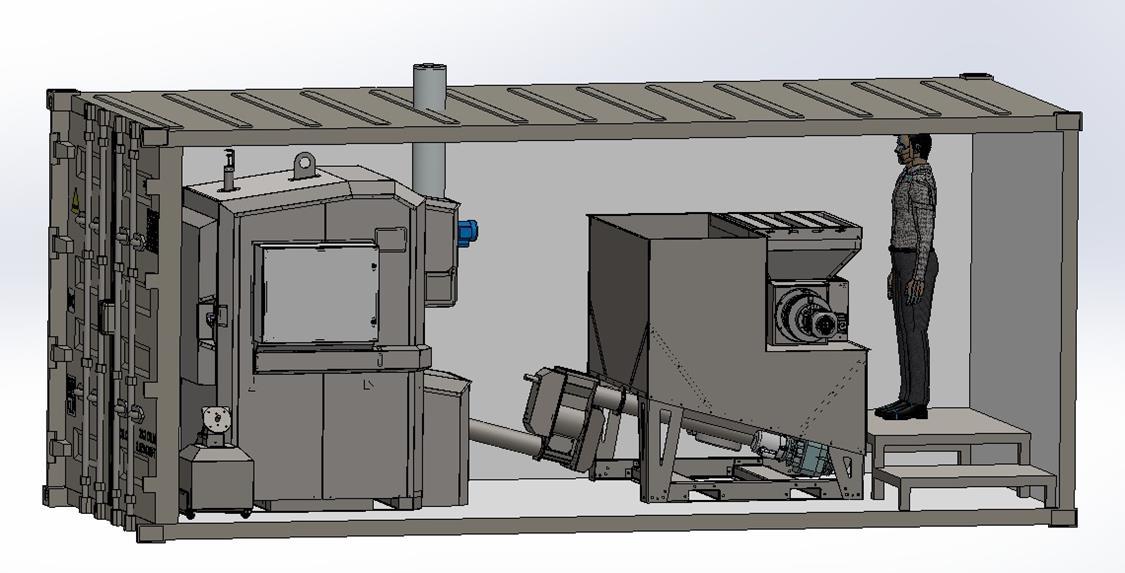
As industries and organizations strive to reduce their carbon footprint, Scope 1 emissions, which encompass direct emissions from owned or controlled sources, are a critical focus. One innovative approach to mitigating these emissions is through energy recovery, specifically by utilizing biomass energy devices. This method not only reduces dependence on fossil fuels but also aligns with global climate goals.
When biomass is used as a feedstock, it is considered carbon neutral under the Paris Agreement on Climate Change. This designation stems from the fact that the carbon dioxide released during the energy recovery process is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by the plants during their growth. As a result, biomass energy systems do not contribute to a net increase in atmospheric CO2 levels, making them a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
One notable example of a biomass energy device is the Eco-Growth Environmental ER500 system. With a maximum output of 500,000 BTU (145 kilowatts), the ER500 efficiently converts dry organic waste into valuable thermal energy. This high-output system is capable of handling various types of biomass feedstocks, making it versatile for different industrial and commercial applications.
The thermal energy generated by the ER500 system can replace the direct use of fossil fuels for space heating or process water heating. By doing so, organizations can significantly reduce their Scope 1 emissions. The adoption of biomass energy devices like the ER500 not only helps in cutting down greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes the use of renewable energy sources.
1. Emission Reduction: Utilizing biomass for energy recovery directly reduces emissions from fossil fuels, lowering the overall carbon footprint.
2. Sustainability: Biomass energy is renewable and abundant, providing a sustainable energy source that supports waste management and recycling efforts.
3. Cost Efficiency: Converting waste to energy can reduce waste disposal costs and provide a cost-effective energy solution.
4. Energy Independence: Biomass energy systems can enhance energy security by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Emission Factor – Energy Recovery
Greenhouse Gas Quantification Assessment Report CE0163185
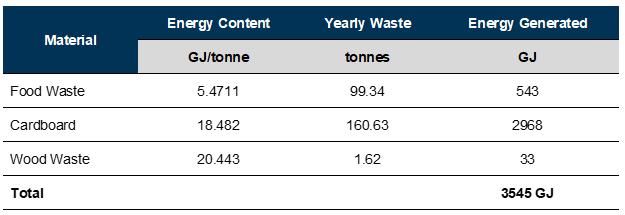
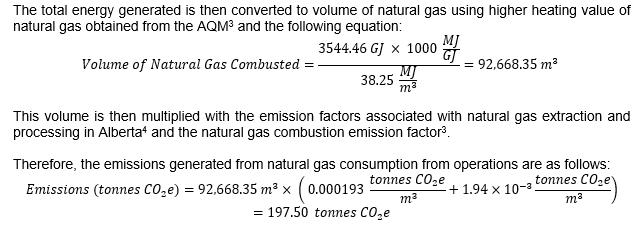
Based on calculations made by Emissions Reduction Alberta there is 182.9 mt available biomass feedstock with a net reduction in Scope 1 CO2 emissions of 197 mt. Energy Recovery Emission factor = 1 mt dry feedstock = 1.08 mt CO2 reduction.
Kona EV vs. Gasoline: Carbon Footprint Comparison in British Columbia and Alberta
As electric vehicles (EVs) gain popularity, understanding their environmental benefits compared to traditional gasoline vehicles is crucial. Executive Mat Service management in British Columbia and Alberta adopted Kona all-electric vehicles for management travel. The following details the Scope 1 carbon footprint reduction achieved by the Hyundai Kona EV compared to a gasoline powered Kona in the two Canadian provinces. The focus is on the emission factor reductions per 100 km driven.
Before diving into the comparison, it’s essential to understand the emission factors for electricity generation in BC and Alberta:
• British Columbia: Known for its clean energy mix, primarily hydroelectric power, BC has a low carbon intensity of electricity at 15 grams CO2 per kWh.
• Alberta: Predominantly reliant on fossil fuels, particularly coal and natural gas, Alberta’s electricity generation has a higher carbon intensity at 540 grams CO2 per kWh.
Kona EV vs. Gasoline Vehicle: Emission Factor Reductions
To compare the carbon footprints, we’ll examine the emission factor reductions achieved by the Kona EV compared to a gasoline vehicle, which consumes 8.6 liters of gasoline per 100 km.
• British Columbia:
• Electricity Emission Factor: 15 grams CO2 per kWh (0.015 kg CO2 per kWh).
• Kona EV Carbon Footprint:
• Electricity Consumption: 15.8 kWh per 100 km.
• Calculation: 15.8 kWh × 0.015 kg CO2/kWh = 0.237 kg CO2 per 100 km.
• Gasoline Vehicle Carbon Footprint: 19.87 kg CO2 per 100 km.
• Emission Factor Reduction:
• Calculation: 19.87 kg CO2 (Gasoline) - 0.237 kg CO2 (Kona EV) = 19.633 kg CO2 reduced per 100 km.
• Alberta:
• Electricity Emission Factor: 540 grams CO2 per kWh (0.54 kg CO2 per kWh).
• Kona EV Carbon Footprint:
• Electricity Consumption: 15.8 kWh per 100 km.
• Calculation: 15.8 kWh × 0.54 kg CO2/kWh = 8.532 kg CO2 per 100 km.
• Gasoline Vehicle Carbon Footprint: 19.87 kg CO2 per 100 km.
• Emission Factor Reduction:
• Calculation:
• Table shows Gasoline versus EV emission standards comparison by Canadian Province. 1 Source Canada – Environment Climate Change.

The Gravitas Energi TA150 system is a groundbreaking technology poised to transform the landscape of electricity generation. With its ability to produce electricity 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, the TA150 system is not just a game-changer: it's a beacon of hope for a greener future.
1. Unmatched Efficiency: The Gravitas Energi TA150 system boasts unparalleled efficiency, capable of generating a net 150 kilowatts of continuous output resulting in a staggering 1,314,000 kilowatt hours of electricity per year.
2. Environmental Benefits: One of the most compelling aspects of the TA150 system is its minimal environmental footprint. By harnessing the power of gravity, the system achieves remarkable results in emissions reduction. In Alberta with an emissions factor of 540 grams CO2/kWh x 1,314,000 kWh the annual Scope 2 emission reduction is 709.56 mt.
3. Cost Savings: Beyond its environmental benefits, the Gravitas Energi TA150 system also delivers tangible economic advantages. By generating electricity efficiently and reliably, the system helps save money on energy production and distribution. Additionally, the reduced reliance on fossil fuels translates into long-term cost savings, as volatile fuel prices become less of a concern.
4. Scope 2 Emissions Reduction: The adoption of the TA150 system contributes to the reduction of Scope 2 emissions, which encompass indirect emissions associated with the generation of purchased electricity



Bathroom/Restroom Consumables
Hand soaps and sanitizers
Paper towels and tissues
Toilet paper
Cleaning chemicals
Floor Matting Services
Entrance mats -fatigue mats
Specialty mats (anti-static, scraper, etc.)
Services
Regular cleaning and disinfection
Deep cleaning services
Window cleaning
Services
Landscape maintenance • Plant care and tree services • Snow removal and winter services • Pest control
/ Mechanical / Plumbing Services • System maintenance and repairs
Duct cleaning and inspection
Maintenance • Regular maintenance supplies
Paints and finishes
Executive Mat Service's two-stage approach to reducing Scope 3 indirect emissions for our Floor Mat Service includes:
Embodied Carbon Reduction: Utilizing sustainable and recycled materials for mat production to lower the carbon footprint.
Service Provision Efficiency: Streamlining delivery routes and employing energy-efficient cleaning technologies to reduce carbon intensity during servicing.



Scope 3: Internal Operations/ Floor
Embodied carbon in floor mats refers to the total amount of carbon dioxide emissions (CO2) associated with the production and transportation of floor mats. This encompasses all greenhouse gas emissions released from the extraction of raw materials used in its manufacture to the point where the matting is ready for installation.
The concept of embodied carbon is critical for understanding the environmental impact of products like floor mats in a comprehensive manner. It helps businesses and consumers make more informed decisions regarding their product choices, aiming to select options that minimize environmental footprints and support sustainability goals. For Executive Mat Service, reducing embodied carbon is a significant part of our environmental strategy.
Assessing the embodied carbon of three different floor matting options to determine level of alignment towards environmental objectives. Here is an overview based on the emission factors provided:
1. Nylon/Nitrile Rubber Carpet-Top Matting:
• Materials: Nylon and synthetic rubber (nitrile).
• Analysis: This matting type, with a high nylon content, results in a higher carbon footprint due to the significant emission factor of nylon. The overall embodied carbon footprint is offset through use of smaller volume of nitrile rubber. It is less favorable due to its relatively high embodied carbon.
2. PET/Nitrile Bi-Level Matting:
• Materials: Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and synthetic rubber (nitrile).
• Analysis: The PET component brings down the overall carbon footprint compared to pure synthetic (nylon) options; the matting incorporates significantly more nitrile rubber making it the most carbon intense of the 3 matting types..
3. PET/Natural Rubber (Weather-Stopper Matting):
• Materials: Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and natural rubber.
• Analysis: This type of matting exhibits the lowest embodied carbon of the three options. The inclusion of natural rubber, which has a significantly lower emission factor, alongside PET, results in a more environmentally friendly solution ideal for sustainability-driven specifications like those of the LCBO.
Executive Mat Service is at the forefront of environmental sustainability. As part of the journey towards achieving carbon net-zero, Executive Mat Service has implemented a two-step strategy that effectively combines technological advancements with strategic environmental initiatives.
1. Reduction of Carbon Intensity: The first step in our approach has been to significantly reduce the carbon intensity of our products. By developing the Weather-Stopper matting, Executive Mat Service has utilized materials such as PET and natural rubber, which have much lower embodied carbon compared to traditional materials.
2. Purchase of High-Quality VERs (Carbon Offsets): To address any remaining emissions and achieve a net-zero carbon footprint, Executive Mat Service has committed to purchasing high-quality Verified Emission Reductions (VERs). The company has successfully purchased and retired a substantial amount of VERs through the Pericarbon.org Carbon Registry. The transparency of these transactions are bolstered by their visibility on the Pericarbon.org blockchain, providing clear and accessible proof of the company's environmental commitments.
Factors
Floor Mat Material Input


on: 4x6
Table 3 shows embodied carbon footprint in kg. for a 4’x6’ by matting type. Carbon footprint was divided by mat trade size to achieve kg. CO2 per square foot (ft2). Carbon footprint associated with transporting each mat type from factory to Brantford Ontario was added to report total embodied carbon footprint.
4:
Embodied Carbon Footprint KG,/CO2 by size
Table 4 shows embodied carbon footprint in kg. for a range of sizes. Currently sizes: 4’x8’, 6’x6’ and 6’x10’ are not available in the Weather-Stopper format.


1. Weather-Stopper lowest embodied carbon footprint floor mat on the market.
2. Emission Factor - Industry baseline for carpet-top on nitrile rubber is 1.61 kg CO2 per square foot.

3. Emission Factor – Weather-Stopper is .28 kg CO2 per square foot.

4. 100% of all Weather-Stopper floor mats have been certified net-zero through purchase and retirement of VERs at a rate of .28 kg CO2 per square foot.

Emission factors expressed as kilograms CO2 per square foot of floor matting delivered. Includes carbon intensity of cleaning & sanitizing, delivery and overheads.
Calculating carbon reductions is a vital process in assessing the environmental impact of product or service innovations. It begins with establishing an industry baseline, which serves as a reference point for measuring carbon emissions. By comparing emissions before and after implementing innovations, organizations can quantify the reduction in carbon emissions achieved. This method enables businesses to track progress towards sustainability goals and evaluate the effectiveness of their initiatives in reducing environmental impact.

Floor mat rental baseline carbon intensity has been established in a sustainability report prepared for Textile Rental Institute of America.
Table 5: Reported Baseline Carbon Intensity
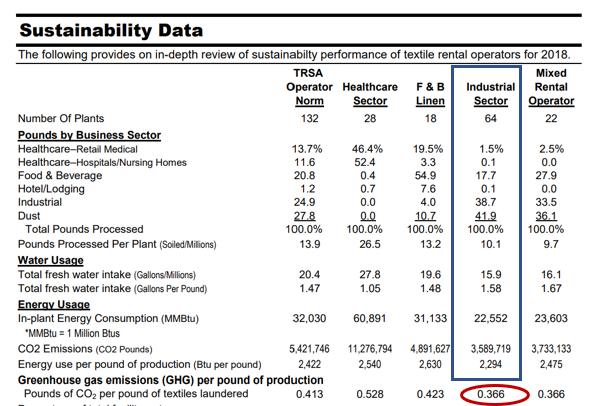
Table 5 shows the average carbon footprint associated with cleaning floor mats in an industrial processing facility. Average carbon intensity was reported as .366 pounds CO2/pound processed or .166 kilograms CO2 per pound processed.
Table 6: Reported Baseline Carbon Intensity by Square Foot. (Carpet-Top is 30% lighter and 10% smaller)
Table 6 shows the average carbon footprint associated with cleaning floor mats by ft2.Standard 4’x6’ floor mat was used in the comparison. Carpet-top matting shows lowest carbon intensity per square foot due to light weight and smaller size. A 4’x’6 carpet-top measures 10% smaller than 4’x6’ Weather-Stopper mat.
• Delivery CO2 calculation: .0263 kg. CO2 / ft2. Derived from ISO14001 audit conducted across 5 Canadian floor mat locations over 12-months.
• Overheads estimation .0009 kg. CO2 / ft2 sourced from ISO14001 audit findings.

May 2024
In the commercial cleaning industry, the traditional methods of washing and drying nylon floor mats have been a significant source of carbon emissions. According to a TRSA report, approximately 0.366 pounds of CO2 pollution is emitted for every pound of floor matting cleaned. However, a groundbreaking advancement in this field has been introduced by CDF-Systems, which promises to drastically reduce these emissions and contribute positively to environmental conservation.
CDF-Systems has developed a revolutionary dry technology that cuts down the carbon intensity of washing and drying nylon floor mats by more than 90%. Considering the billions of pounds of floor matting cleaned annually the potential carbon savings from this technology are staggering. This innovation not only helps businesses who consume mat services reduce their Scope 3 "Internal Operations" emissions significantly but also aligns with global carbon reduction goals.
In addition to its carbon-saving benefits, the CDF-Systems technology addresses another critical environmental issue: water scarcity. The system is designed to virtually recycle 100% of the water used in the cleaning process, making it an invaluable asset in drought-prone areas. This feature not only helps conserve water but also reduces the overall environmental footprint of the cleaning process.
From an operational perspective, the CDF-Systems cleaning technology offers simplicity and efficiency. It is a one-touch process where soiled matting is fed into the machine face up and exits clean, dry, and sanitized ready for immediate reuse. This process significantly cuts down on labor and utility costs compared to traditional cleaning methods. Moreover, the technology can handle a broader range of matting types, including advanced bi-level systems like Weather-Stopper technology, which outperforms conventional nylon matting in controlling tracked in dirt, debris and moisture.
In today's market, where consumers and businesses alike are increasingly conscious of their environmental impact, goods and services that are certified as low-carbon or carbon net-zero are more appealing. CDF technology not only meets these standards but has also been third-party certified as low carbon. Operators using this system can generate Verified Emission Reductions (VERs), which are tradable on the Pericarbon.org Carbon Registry blockchain. These VERs serve as carbon offsets, allowing other entities who purchase them to balance their emissions, thereby fostering a broader commitment to climate action.
The CDF-Systems mat cleaning technology represents a triple win: for consumers, it ensures safer and cleaner floors with significantly reduced carbon footprints; for operators, it lowers operating costs and provides a competitive edge; and for society, it offers substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. As businesses and consumers increasingly prioritize sustainability, technologies like those developed by CDF-Systems are not just beneficial but essential for a sustainable future.
Executive Mat Service, a Canadian National floor mat service provider, has positioned itself at the forefront of environmental sustainability by being an early adopter of the innovative CDF cleaning technology. With mat cleaning facilities located in Vancouver, Calgary, Edmonton, Regina, and Toronto, Executive Mat Service has collectively reduced their carbon emissions by an impressive 30,000 metric tonnes compared to industry baselines since 2017.
Here’s why EMS’s adoption of CDF-Cleaning Technology is a game-changer:
Efficient Processing of High-Performance Matting: With CDF-Cleaning Technology in place, EMS can streamline the processing of top-tier matting solutions like the WeatherStopper. This advanced technology ensures that even the most durable and specialized mats receive thorough cleaning and maintenance, extending their lifespan and performance.
Dramatic Reduction in Carbon Footprint: By implementing CDF-Cleaning Technology across all its operations, EMS is making a tangible commitment to sustainability. This innovative approach significantly minimizes the carbon footprint associated with traditional mat cleaning methods. From reduced water usage to optimized energy consumption, every aspect of the cleaning process is engineered to be eco-friendly.
Table 7: Emission Factor for electricity across Canada
Table 7 CDF technology uses displacement drying process that uses electricity instead of natural gas. Based on an average production rate of 4,000 ft2 processed per hour and electricity consumption of 120 kW/h. Virtually 100% of water is recycled using electricity therefore is considered a factor contributing to reported CO2.
• Delivery CO2 calculation: .0263 kg. CO2 / ft2. Derived from ISO14001 audit conducted across 5 Canadian floor mat locations over 12-months.
• Overheads estimation .0009 kg. CO2 / ft2 sourced from ISO14001 audit findings.
Weather-Stopper floor matting surpasses carpet-top style matting in performance, necessitating fewer service intervals.
1. Studies reveal that Weather-Stopper matting, serviced every 4 weeks, excels in floor safety and cleanliness compared to weekly serviced carpet-top matting.
2. CDF cleaning technology sanitizes and cleans floor matting with significantly lower carbon intensity, marking a notable advancement in environmental sustainability.
Table 8: Scope 3 Internal Operations / Floor Mat Service Comparison
Table 8 shows the carbon footprint reduction associated with converting an Ontario client with 28 locations from weekly carpet-top service using a supplier utilizing industry baseline cleaning systems. Weather-Stopper matting was introduced on an every-4-week service program and mats were processed in a CDF equipped facility
1 TRSA includes reported production CO2 intensity of .166 kg CO2/ Square Foot processed plus .0272 kg for Delivery and Overhead. CDF production numbers are based on 4,000 ft2 processed per hour using 125 kWh (no natural gas). The same .0272 was applied for Delivery and Overhead. EmissionComparisonPerService
Magnifying Carbon Reductions: To illustrate the tangible environmental benefits of Executive Mat Service's approach, consider a typical scenario in Ontario. Traditionally, businesses in the region might require weekly matting service in winter and bi-weekly service in summer, totaling 39 deliveries annually. Assuming an average organization requires 200 square feet of floor matting for safety, this equates to a significant carbon footprint of 1,507 kg CO2 per year (39 x 200 ft2 x emission factor of .1932 kg CO2/ft2).
In contrast, by adopting Executive Mat Service's OPTIMIZED solutions, the carbon emissions associated with matting services can be dramatically reduced. With only 13 deliveries per year, the same 200 ft2 x emission factor of .0281 kg CO2/ft2 the carbon footprint plummets to just 73 kg CO2 annually, representing a staggering 95% reduction compared to traditional practices.
Scope 3 Upstream Reductions are not just a theoretical concept; they are a practical and impactful strategy for businesses looking to enhance their sustainability efforts. Through the adoption of cutting-edge technologies like CDF and high-performance products like Weather-Stopper mats, Executive Mat Service is leading the charge towards a greener, more sustainable future.


In today’s fast-paced, delivery-dependent world, the efficiency of service routing isn’t just a logistical concern it's also a critical environmental one. Companies across the globe are under increasing pressure not only to cut costs but also to reduce their carbon footprints. Interestingly, while fuel emissions from delivery vehicles are typically accounted for under a service provider's Scope 1 emissions, they also considerably impact the Scope 3 emissions of the end client. By optimizing delivery routes, companies can significantly enhance cost efficiencies and lower carbon emissions, creating a ripple effect of benefits.
At its core, the principle of routing efficiency is about doing more with less. For delivery companies, this means maximizing the number of stops they can make in a single journey without extending the delivery day beyond workable hours. Advanced routing algorithms can now calculate the quickest and shortest routes between multiple delivery points, allowing drivers to cover more ground in less time. This reduction in drive time and distance directly correlates with decreased fuel consumption, which not only lowers operational costs but also reduces wear and tear on delivery vehicles, thereby saving on maintenance costs and extending the lifecycle of a delivery fleet.
From an environmental perspective, the benefits of optimized delivery routes are even more compelling. Transportation is a major contributor to global CO2 emissions, and reducing the distance traveled by delivery vehicles directly lowers their carbon outputs. By decreasing the
number of trips required to deliver goods and services, companies not only adhere to their Scope 1 responsibilities but also positively influence the Scope 3 emissions of their clients. This is particularly important for businesses committed to achieving net-zero emissions, as Scope 3 encompasses all indirect emissions that occur in a company's value chain, including those associated with procured goods and services.
Efficient delivery routing also extends beyond just the roads traveled; it encompasses minimizing the time spent at each delivery location as well. By streamlining on-site processes, service representatives can achieve greater in-and-out efficiencies, allowing for more deliveries to be completed within the same working day. This not only maximizes productivity but also substantially decreases the carbon emissions per delivery. Technologies such as FotoFinish streamline the onsite delivery process, reducing waiting times, further enhancing the efficiency of the delivery process. As each minute saved per stop accumulates, the overall environmental impact is significantly reduced, demonstrating how operational efficiencies can directly contribute to sustainability goals.
Executive Mat Service has implemented a three-step approach to enhance delivery efficiency and environmental sustainability:
1. Development of the Weather-Stopper Floor Mat: This high-performance mat features a bi-level construction that outperforms traditional carpet-top mats, reducing the need for frequent service visits and thus lowering associated carbon emissions.
2. Adoption of Advanced Route Scheduling Software: By optimizing delivery sequences, this software ensures the most efficient travel paths are used, decreasing travel time and fuel consumption.
3. Integration of FotoFinish Technology: This tool automates quality assurance and proof of delivery processes, saving time at each stop and increasing service reliability, further enhancing overall operational efficiency.
In conclusion, Executive Mat Service is deeply committed to carbon efficiency across all facets of our operations. We understand that true environmental responsibility extends beyond the cleaning and sanitizing of our products to include every step of our delivery process. By innovating with highperformance products like the Weather-Stopper floor mat, utilizing advanced route scheduling software, and integrating FotoFinish technology, we are not only enhancing our service quality but also significantly reducing our carbon footprint.

In the competitive world of floor mat services, efficiency and quality assurance are paramount. Companies need to ensure that each stop on their delivery routes, typically averaging 30-40 stops per day, is optimized to avoid delays that can throw off an entire day’s schedule. Drawing a parallel to urban garbage collection, where trucks make 500-800 stops daily, even minor delays can significantly extend working hours. This principle is exactly where artificial intelligence (AI) comes into play, transforming operational efficiency and service quality in surprising ways.
Introducing FotoFinish: AI-powered Quality Assurance and Efficiency
FotoFinish, a remarkable application of Large Language Model AI technology, is at the forefront of this transformation in the floor mat service industry. Designed to streamline operations and enhance quality control, FotoFinish simplifies the process of service delivery verification with a quick snap and upload of a photo.
Upon delivery, service technicians are required only to take a photo of the placed mat(s) and upload it via their smart device. From there, AI takes over with the following checks:
• Quality Standards: The AI assesses if the mat meets or exceeds predefined quality benchmarks.
• Proper Placement: It checks whether the mat is positioned in the designated area, ensuring optimal usage and safety.
• Cleanliness: The AI evaluates the cleanliness of the mat, crucial for maintaining a professional and hygienic appearance.
If any issues are detected that don’t meet the company’s high standards, an automated alert is sent to the quality assurance director to initiate corrective measures promptly.
FotoFinish also serves as an automated "Proof of Delivery" system. Each uploaded picture is time-stamped and securely stored on a cloud server, providing irrefutable evidence of service delivery. This feature is especially useful for:
• Customized Reporting: Stakeholders can receive tailored reports or review individual delivery details, enhancing transparency and accountability.
• Integration with Third-party Software: FotoFinish can seamlessly integrate with other software solutions, facilitating automated reconciliations and streamlining backend processes.
In an era where litigation over floor safety is a rising concern, FotoFinish offers more than just operational efficiency. It provides concrete proof of due care and attention to floor safety, significantly mitigating legal risks associated with slip-and-fall accidents and other liabilities.
The application of AI into Executive Mat Service’s floor matting program is a game-changer. By automating quality assurance and proof of delivery, Executive Mat not only ensures topnotch service quality but also optimizes operational efficiency, saving precious time and resources which translates to lower pricing for clients.


This image was captured using the AI-powered FotoFinish tool, which scans for product quality and placement deficiencies. If any issues are detected, the tool automatically generates a notification to the quality assurance director, ensuring prompt remedial action to maintain the highest standards of service quality and customer satisfaction.
Life is full of surprises, and sometimes those surprises come in the form of unforeseen circumstances that can disrupt the smooth operation of a business. One such unexpected event is the soiling of floor mats, which can create health and safety concerns and impact the cleanliness and appearance of a facility. Recognizing the need for a reliable solution, Executive Mat Service has introduced a comprehensive program designed to act like an insurance policy for your floor mats, ensuring your business remains prepared and compliant.
The Unforeseen Circumstances Program is a proactive service offering that helps businesses effectively manage unexpected floor mat soiling events. Here’s how it works:
• Custom Inventory Planning: We collaborate closely with your custodial team to assess your facility’s specific needs and determine the additional mat inventory required. This ensures that enough replacement mats are available on-site for immediate use.
Isolation Protocols: To address health and safety concerns, we supply bags labeled "Danger Biological Soiling" for the custodial staff. These bags are
• used to isolate contaminated mats, preventing the spread of contaminants, and ensuring compliance with safety protocols.
• Training & Support: We provide training and support to your custodial staff on the proper handling and isolation of soiled mats, enhancing their readiness to manage such situations.
2. Notification – Communication is Key
• Notification: In the event of a biological soiling incident, the customer simply notifies Executive Mat Service Customer Service.
• Reserved Mat Replacement: Our service team, on the next scheduled service day, retrieves the contaminated mat and replaces it with a freshly laundered mat to be held in reserve, minimizing disruption to your operations and maintaining a clean and safe environment.
• Special Handling Procedures: We initiate special handling procedures to manage the contaminated mat. This includes high-temperature cleaning and sanitization, ensuring the mat is safe for future use.
1. Enhanced Preparedness: By maintaining a reserve inventory of mats, your facility is always ready to handle unexpected soiling events without delay.
2. Health & Safety Assurance: The program’s focus on isolation and proper handling of contaminated mats ensures compliance with health and safety standards.
3. Operational Continuity: With immediate mat replacement, your business can continue operating smoothly, even during unforeseen circumstances.
4. Cost-Effective Solution: The program acts as an insurance policy, mitigating the potential costs and disruptions associated with emergency mat replacement.
Executive Mat Service is committed to providing innovative and reliable solutions that enhance the safety and efficiency of your facility. Our Unforeseen Circumstances Program reflects our dedication to customer satisfaction and our proactive approach to facility management.

Floor mats are common in commercial settings, but when they become wavy or buckled, they can present significant risks. Understanding the implications of these hazards is crucial for maintaining safety and compliance.
1. Why It Matters: Wavy floor mats can lead to trips and falls, posing serious injury risks to customers and employees alike. Ensuring mats lie flat and secure minimizes the likelihood of accidents, protecting individuals and safeguarding businesses against potential liability.
2. Who is Responsible: Property owners and managers are primarily responsible for maintaining safe premises. This includes regular inspections of floor mats and immediate action to correct any issues. Failing to manage these risks can lead to negligence claims if accidents occur.
3. Accounting for Risk: Identifying trip hazards from wavy floor mats is an essential part of risk management. Businesses must proactively address these issues, using proper matting solutions and adhering to safety standards to prevent accidents and ensure a safe environment for all visitors.
By recognizing the dangers of wavy floor mats and taking steps to mitigate these risks, businesses can uphold their duty of care and promote a safer community. WeatherStopper™ floor matting is the solution.

Floor mats are tested for friction coefficient when new. Our competitors state this mat is floor safety certified?

The floor mat service industry is currently grappling with a significant challenge: the emergence of rippled or buckled floor mats. This issue has become prevalent due to several critical factors in the manufacturing and maintenance of these mats:
• Removal of DEHP: DEHP, or Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, a key plasticizer previously used in the production of nitrile rubber, has been phased out. Nitrile rubber, a blend of the monomers acrylonitrile (CH₂=CH-CN) and butadiene (CH₂=CH-CH=CH₂), is a crucial component in the construction of nylon carpet-top floor matting. The absence of DEHP, without a viable alternative, has affected the mat's durability and flatness.
• Incompatible Substrate: The substrate, which is the fabric to which the nylon is mechanically attached to create the mat's carpet-top, tends to shrink during the laundering process. This shrinkage occurs at a different rate than the nylon fibers and the rubber backing, leading to distortions in the mat as it goes through repeated wash cycles.
• Modern Washing Equipment: The use of newer washer-extractors, which are primarily designed for cleaning everyday clothing items like pants and shirts, has introduced higher levels of extraction force to the mats. Typically handling 450 pounds of mats per load, these machines can apply up to 400 G-force during the extraction cycle. This intense force causes the mats to stretch and often results in permanent rippling or buckling.
These issues collectively contribute to the "wavy mat epidemic," affecting not just the aesthetic appeal of the mats but also their functionality and safety. As the industry scrambles to address these challenges, the need for innovations in both material composition and care processes is becoming ever more apparent.


The mat service industry is witnessing a revolutionary change with the introduction of Weather-Stopper Technology, which promises to solve the persistent issue of wavy floor mats. This innovative approach utilizes several key developments:
1. Natural Rubber Base: Unlike synthetic rubbers such as nitrile, natural rubber does not require the use of plasticizers like DEHP. This shift not only enhances the environmental appeal of the mats but also improves their durability and stability.
2. Needle-Punch PET Fabric: By using recycled PET (polyethylene terephthalate) from plastic water bottles, Weather-Stopper mats eliminate the need for a separate substrate. The needle-punch process mechanically entangles fibers to create a robust, non-woven fabric that maintains its form without the usual shrinkage issues seen in traditional mats.
3. CDF-Systems Mat Washing Technology: This cutting-edge technology cleans and sanitizes mats while keeping them flat, eliminating the need for high G-force centrifugal extraction. This process prevents the stretching that typically causes ripples and buckles, maintaining the mats' integrity and safety.
Weather-Stopper Technology represents a significant leap forward in addressing the functional and aesthetic challenges faced by the mat service industry, promising a new era of durable, reliable, and eco-friendly floor mats.

Scope 3 Internal Operation/Dust Mop

In the world of cleaning, dust mops play an essential role in maintaining pristine environments in both retail and commercial spaces. Traditional dust mop programs have long relied on cotton mop heads, often 6 inches wide, fitted to metal frames for easy handle attachment. This setup is typically treated with a heavy oil coating, enhancing the mop's ability to trap dust and dirt. However, while effective, this traditional method presents several sustainability challenges that are increasingly hard to ignore in our environmentally conscious world.
1. Cotton Mop Heads: Cotton, while a natural fiber, requires extensive water and energy to produce and maintain. In the context of dust mops, oil-treated cotton is particularly burdensome for laundry processes, requiring lengthy drying times and thus consuming considerable energy.
2. Oil Coatings: The application of oil is designed to enhance dust capture but introduces environmental issues during the cleaning phase. As the oil is washed from the mop, it enters the sanitary sewer system, complicating water treatment processes and posing risks to water quality.
In response to these sustainability concerns, advancements in material science have led to the development of dust mops that utilize a unique blend of synthetic fibers. These modern dust mops are not only more effective but also significantly reduce environmental impact.
1. Unlike the traditional oil-coated cotton, these advanced synthetic fibers work on the principle of static electricity. As the mop moves across the floor, it generates a static charge. This static charge creates an attractive force between the negatively charged dust mop fibers and the positively charged dust particles on the floor.
2. This electrostatic attraction ensures that dust, dirt, and debris cling to the mop rather than resettling on the floor surfaces, providing a superior cleaning effect without the need for chemical enhancers.
1. The synthetic fibers used in modern dust mops have a quick-drying nature, which significantly reduces the time and energy required for drying after washes.
2. These fibers are lighter and less dense than traditional cotton, which allows them to dry rapidly, decreasing the energy consumption and carbon footprint associated with their maintenance.
The switch to synthetic fiber dust mops offers substantial environmental benefits:
1. Reduced Water and Energy Usage: The quick-drying nature of synthetic fibers lowers energy consumption in laundry processes, aligning with sustainability goals.
2. Decreased Chemical Discharge: By eliminating the need for oil coatings, these mops reduce the risk of chemical pollutants entering wastewater systems, easing the burden on public water treatment facilities.
Conclusion
We are committed to developing ways to minimize our ecological footprint by embracing technologies that offer both performance and sustainability The evolution of our dust mop program from traditional cotton and oil to synthetic fiber technology is another example of our steadfast commitment to science-based improvements in our product offering and processing systems.

When it comes to maintaining a clean and safe environment, choosing the right dust mop technology is not as straightforward as one might think. The evolution from traditional oiltreated cotton dust mops to synthetic static-based systems marks a significant technological breakthrough, offering improved efficiency and cleanliness. However, the method of replacing dust mop heads plays a crucial role in determining overall productivity and hygiene.
A typical dust mop program using synthetic mop heads involves sliding a metal frame in and out of the mop head to replace a dirty mop with a freshly laundered one. This process, while seemingly simple, can be deceptively time-consuming and messy.
In-the-field studies have shown that it can take between 7-10 minutes for an untrained operator to perform a mop head exchange. This process often results in the transfer of soil from the soiled mop head to the operator, leading to further cleaning needs and potential frustration.
Understanding that time is money, Executive Mat Service has pioneered their "Concierge Dust Mop Program," designed to streamline and simplify the mop replacement process.
1. Pre-installed Mop Heads: Freshly laundered mop heads are delivered with the frame already installed in a reusable nylon bag. This eliminates the need for operators to handle dirty mop heads directly.
2. Quick and Easy Replacement: The operator simply unclicks the handle from the soiled mop frame and connects it to the clean mop head, a process that takes less than 10 seconds. This is a significant reduction from the 7-10 minutes required for traditional mop head exchanges.
3. Efficient Disposal: The soiled dust mop is placed into the same reusable nylon bag that housed the clean mop and is stored for removal on the next scheduled service day. This not only ensures a cleaner and more efficient process but also reduces the environmental impact by reusing the nylon bags.
Conclusion
Choosing the right dust mop technology and replacement method can significantly impact the efficiency and cleanliness of your facility. Executive Mat Service’s Concierge Dust Mop Program exemplifies how innovative solutions can save time, reduce mess, and enhance overall productivity. The cost savings in time and the reduction in frustration far exceed any additional costs associated with the Concierge Dust Mop Program. In the world of floor maintenance, it's clear that time truly is money. By adopting more efficient and cleaner dust mop systems, businesses can ensure their operations run smoothly, ultimately benefiting their bottom line.

The floor cleaning industry has seen numerous advancements over the years, yet the fundamental design of dust mops has remained relatively unchanged. Traditional synthetic dust mops, while effective, come with their own set of challenges. These challenges include unnecessary weight and carbon intensity, as well as time-consuming mop head exchanges. However, a new innovation using Velcro technology is poised to revolutionize dust mop design and functionality.
Traditional synthetic dust mops are designed with a metal frame that slides into the mop head, accommodating the addition of a pole. This design requires extra fabric to house the frame, which serves no purpose in the actual dusting process. This extra fabric adds unnecessary weight to the mop, increasing the carbon footprint associated with its production, transportation, and use.
Moreover, the process of changing mop heads can be cumbersome and time-consuming. In-the-field studies show that it can take between 7-10 minutes for an untrained operator to perform a mop head exchange. This often involves handling dirty mop heads, which can lead to further frustration and inefficiency.
1. Reducing Carbon Footprint and Weight: The innovative use of Velcro technology in dust mops addresses the issue of excess weight and unnecessary fabric. By eliminating the need for extra fabric to accommodate a metal frame, Velcro microfiber dust mops are
significantly lighter. This reduction in weight translates to a smaller carbon footprint, making these mops a more environmentally friendly option.
The Velcro system maintains the same high-performance characteristics as traditional dust mops, effectively capturing dust and dirt without the added bulk. This innovation not only enhances the sustainability of the product but also improves its overall usability.
2. Simplifying Mop Head Exchanges: One of the most significant advantages of Velcro microfiber dust mops is the ease of changing mop heads. With the Velcro system, operators can simply pull the mop head away from the Velcro frame in one easy movement. This process is quick, clean, and efficient, taking mere seconds compared to the lengthy and messy traditional method.
This streamlined process reduces downtime and increases productivity, allowing cleaning staff to focus more on maintaining cleanliness rather than struggling with equipment. The "no fuss, no muss" approach of Velcro microfiber dust mops significantly enhances the user experience, making them a preferred choice for modern cleaning operations.
Conclusion
Executive Mat Service has integrated Velcro technology into our microfiber dust mops, marking a significant improvement in floor cleaning technology. By addressing the issues of excess weight, carbon intensity, and time-consuming mop head exchanges, Velcro microfiber dust mops offer a sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional dust mops.
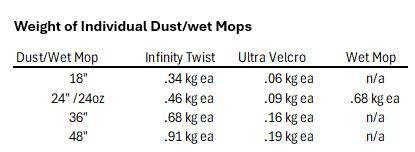
Weights are based on product specifications detailed at GoldenStar.com
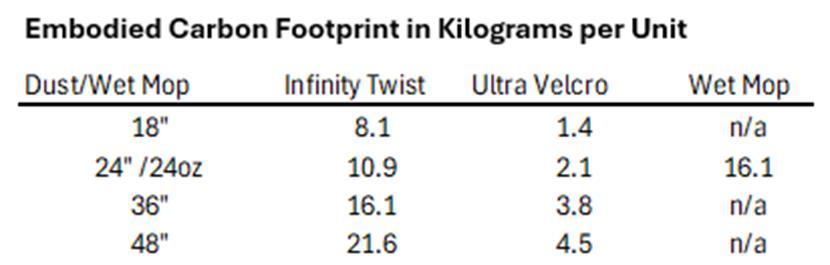
Source:greenly.earth/carbonaccounting for embodied carbon of raw materials and manufacturing processes 21.5 kg CO2e/kg fiber. Add additional 10% carbon intensity was added for logistics.
Based on TRSA published average carbon footprint of .366 lbs. CO2 per lb processed converted to metric. No carbon intensity was considered for delivery as mops are delivered the same time as floor mats and carbon intensity of delivery is included in with the floor mats.
48% of the mop’s content is PostConsumer Content (PCC)

Executive Mat Service synthetic dust mops work by creating a static charge that attracts and holds dirt particles. Here’s how the process works:
1. Charging the Fibers: When you push the mop across the floor the synthetic fibers of the dust mop become charged with static electricity. This causes the fibers to stand on end and become negatively charged.
2. Attraction of Dust: Dust particles are naturally positively charged. Because opposites attract, the negatively charged fibers of the dust mop will pull in the positively charged dust particles.
3. Capturing the Dirt: Once the dust particles encounter the charged fibers, they are held in place by the static cling. This effectively captures the dirt and prevents it from being redistributed around the room.
4. Cleaning the Mop: The industrial laundering process releases the static charge and dislodges the captured dirt.
Executive Mat Service dust mop service is an efficient way to clean floor surfaces without spreading dust particles into the air.


Executive Mat Service synthetic dust mops work by creating a static charge that attracts and holds dirt particles. Here’s how the process works:
1. Charging the Fibers: When you push the mop across the floor the synthetic fibers of the dust mop become charged with static electricity. This causes the fibers to stand on end and become negatively charged.
2. Attraction of Dust: Dust particles are naturally positively charged. Because opposites attract, the negatively charged fibers of the dust mop will pull in the positively charged dust particles.
3. Capturing the Dirt: Once the dust particles encounter the charged fibers, they are held in place by the static cling. This effectively captures the dirt and prevents it from being redistributed around the room.
4. Cleaning the Mop: The industrial laundering process releases the static charge and dislodges the captured dirt.
Executive Mat Service dust mop service is an efficient way to clean floor surfaces without spreading dust particles into the air. Safeguarding Steps,


Opting for a wet mop rental service over limited-life disposable wet mops offers numerous benefits, both economically and environmentally. Our wet mop rental services provide high-quality, durable mops that are professionally laundered and maintained, ensuring optimal cleanliness and longevity. Our wet mop program minimizes waste while reducing the environmental footprint, lowers operational costs, and maintain a higher standard of cleanliness.



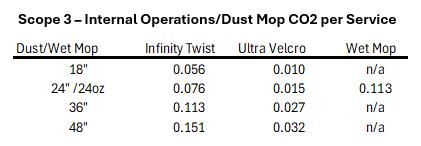
Scope 3 emissions encompass the indirect greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions that occur in a company’s value chain, both upstream and downstream. A significant aspect of downstream emissions is the release of methane from organic waste decomposition in landfills. Methane, a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential (GWP) 87x greater than CO2 over a 20-year period.
To accurately estimate methane emissions from landfills, scientists use methane propensity models such as the Scholl-Canyon model. This model helps calculate the carbon dioxide equivalent (CO₂e) emissions resulting from the anaerobic decomposition of organic waste. The Scholl-Canyon model considers various factors, including the type and moisture content of the waste, to predict methane generation over time.
Key Components of the Scholl-Canyon Model:
1. Waste Composition: Differentiates between wet and dry organic waste.
2. Decomposition Rate: Estimates the rate at which organic waste breaks down anaerobically.
3. Methane Correction Factor: Adjusts for the proportion of methane in the landfill gas.
4. Methane Capture Efficiency: Accounts for the efficiency of landfill gas collection systems.
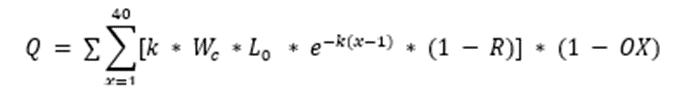
K value represents how quickly a waste will decay and considers the relative moisture content. For example: organic food waste has a lower K value due to high moisture content (80%) and corresponding lower level of carbon.
Applying this model using methane’s 87x GWP and the non-linear rate of decay in landfill (40% of 40-year methane generation occurs in the first 5-years), we can determine Emission Factors (Efactor) of individual waste streams. Applying Efactors to individual waste streams being disposed of in landfill provides a quick and easy methodology to determine the 5-year impact of wastes on atmospheric carbon dioxide levels.
companies can better understand the methane emissions associated with their products' end-oflife disposal and develop strategies to mitigate these emissions.
Following FOD modeling generated by Brightspot Climate and Emissions Reduction Alberta the following Efactors were determined for 2-broad categories of organic waste1 The Efactors were restated using methane’s 87x global warming potential and a 5-year window instead of the 40-year total expressed in the FOD model.
Emission Factors:
1. Wet Organic Waste Emission Factor: 43.5 kg CO₂e per kg of waste.
2. Dry Organic Waste Emission Factor: 126.8 kg CO₂e per kg of waste.
• Data Collection: Companies need to identify organic waste going to landfill by wet and dry and collect annual weight data. on the type and amount of organic waste generated downstream.
• Emission Calculation: Multiply the quantity of waste in each classification by the corresponding emission factor to estimate the CO₂e emissions.
• Reporting: Include these emissions in the company’s Scope 3 downstream emissions inventory.
Mitigation Strategies
To reduce Scope 3 downstream emissions related to methane, companies can now look to adopt strategies to prevent organic wastes from entering a state of anaerobic decay.
1: ERA Greenhouse Gas Quantification Assessment Report CE0163185 Hotel Blackfoot
1: ERA Greenhouse Gas Quantification Assessment Report CE0163185 Hotel Blackfoot

At Executive Mat Service, we recognize the urgent need to address the environmental impact of our single-use disposable culture. As convenience increasingly dictates lifestyle choices, it has led to an exponential rise in waste that ends up in our landfills, contributing significantly to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions and, consequently, climate change. In response, we have launched the Green Thumb Initiative, a comprehensive program aimed at drastically reducing landfill contributions by upcycling waste materials into valuable resources.
Landfills are not just dumping grounds; they are active environmental hazards. As organic and inorganic waste decomposes, it releases methane and other GHGs, which are up to 87 times more potent than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period. This makes landfills one of the most significant contributors to global warming and underscores the need for sustainable waste management solutions.
The Green Thumb Initiative
The Green Thumb Initiative represents a bold step towards sustainability. It is designed to intercept and upcycle various waste streams that are conventionally destined for landfills. By leveraging our existing delivery logistics, these materials are collected and brought back to our processing plant, minimizing additional carbon emissions that would have been generated through separate collection processes.
At the heart of the Green Thumb Initiative is our innovative approach to upcycling waste. Much of the collected waste is transformed into biomass feedstock, which is then utilized in our Eco-Growth Energy
Recovery boiler system. This system plays a crucial role in our operations by heating laundry water an essential resource in our business. Utilizing biomass feedstock not only diverts waste from landfills but also replaces the need for fossil fuels, creating a double environmental benefit.
Heating laundry water with waste-derived biomass is not just an environmentally sound practice; it's also economically advantageous. By repurposing what would otherwise be landfill waste, we significantly reduce our energy costs and allows us the opportunity to reinvest in other carbon-lowering technologies
Our dedication to reducing environmental impact is not just about innovative solutions but also about being accountable and transparent in our practices. Executive Mat Service has been ISO14001 certified since 2010, a testament to our commitment to effective environmental management systems. We engage annually with ISO consultants to explore new ways to reduce our carbon intensity. These efforts contribute not only to lowering our own carbon footprint but also to assisting our customers in reducing their Scope 3 emissions related to "Internal Operations."
The Green Thumb Initiative by Executive Mat Service is more than just a program—it's a part of our mission to lead the industry towards a sustainable future. By turning waste into energy, we showcase how businesses can operate both economically and sustainably, setting a benchmark for others in the industry. As we continue to innovate and expand our sustainable practices, we invite our partners and customers to join us in making a meaningful impact on the planet, one step at a time.



the
"Tackling
Synopsis: In today's convenience-driven world, the environmental toll of single-use coffee pods has become alarmingly evident. With the disposal of 62 billion pods annually in the US and Europe alone, approximately 1.55 billion kilograms of organic waste end up in landfills each year.
The Impact of Methane Emissions: This massive waste volume leads to significant landfill methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas. Using established models, it's estimated that these pods could contribute to 6.665 billion tonnes of greenhouse gas pollution annually, equivalent to 1 kilogram of pollution per pod.
Local Example: Calgary's Contribution: In Calgary, with a population of 1.4 million, the annual landfill contribution from single-use pods reaches 2,205 tonnes, resulting in 95,256 tonnes of CO2 equivalent emissions.
The Urgency of Action: The reliance on single-use pods highlights a broader issue of disposable culture, posing unsustainable consequences for the planet. Urgent action is needed to address this global crisis.
A Sustainable Solution: Executive Mat Service, based in Calgary, is leading the charge with its GREEN THUMB INITIATIVE. Through a single-serve pod recycling program, in partnership with Eco-Growth Environmental, millions of pods are upcycled into emissions-neutral energy and dimensional lumber. This initiative showcases a practical approach to combatting single-use waste and invites broader participation.


 Image depicts
problem with single-service coffee pods ending up in landfill turning into landfill methane.
Image depicts
problem with single-service coffee pods ending up in landfill turning into landfill methane.

Eco-Growth Environmental represents a pioneering venture in the realm of sustainable waste management and energy production, initially incubated within Executive Mat Service. This innovative initiative was born out of the need to convert "GREEN THUMB WASTE operations into clean thermal energy, specifically to heat process water for laundry operations.

Transition to a Standalone Business Entity: Capitalizing on its early successes and the growing demand for sustainable waste management solutions, Eco-Growth Environmental soon expanded into a separate business unit. The company has since positioned itself as a global leader in the development of landfill avoidance technologies, including Rapid Dehydrators and micro waste-to-energy systems. These technologies are designed not only to reduce waste but to transform it into valuable energy resources, minimizing environmental impact while maximizing efficiency.
Strategic Expansion and Global Impact: As a dedicated business unit, Eco-Growth Environmental has continued to innovate, focusing on the scalability of its technologies to meet global challenges. The company's systems are engineered for a variety of applications, particularly appealing to regions and industries seeking to reduce landfill use and convert waste into clean energy.
Circular City Consortium and Recognition: Eco-Growth Environmental is a proud member of the Circular City consortium, a collective focused on advancing sustainable urban development. This membership underscores Eco-Growth’s commitment to collaborative, innovative solutions for environmental challenges. The consortium recently achieved significant recognition, capturing the $2 million first-place prize in Canada's IDEaS challenge. This accolade was awarded for the consortium's revolutionary approach to upcycling military camp solid waste into clean energy, providing a sustainable energy source for Canadian forces and their NATO allies.
Future Directions:
Eco-Growth Environmental is actively addressing global sustainability challenges, particularly focusing on waste management in underdeveloped countries. The company has accepted a United Nations challenge to implement landfill waste avoidance strategies in these regions. This initiative not only aims to curb the escalating issue of landfill methane pollution but also promises to spur economic development through innovative, sustainable practices.

As organic waste decomposes anaerobically in landfills, it produces methane (CH4), a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential (GWP) 87 times greater than carbon dioxide (CO2) over a 20-year period. Using the Scholl-Canyon model for a 5-year analysis, the astronomical impact of these emissions becomes clear, underscoring the urgent need for better waste management practices.
Methane emissions from landfills are significantly influenced by the type of organic waste. According to the Scholl-Canyon model, which assesses the methane production potential of different waste types.
1. Wet Organics: With an emissions factor of 43.5, 1 kg of wet organic waste produces 43.5 kg of CO2e (carbon dioxide equivalent) over five years.
2. Dry Organics (Cardboard): With a higher emissions factor of 126.8, 1 kg of dry organic waste, such as cardboard, results in 126.8 kg of CO2e GHG emissions over the same period.
These figures illustrate the substantial GHG emissions generated by even small quantities of organic waste in landfills.
To grasp the broader impact of landfill methane emissions, consider this: organic waste in landfills globally is 14 times a larger contributor to GHG emissions than the entire oil and gas industry. This startling statistic highlights the critical role of waste management in climate mitigation strategies.
Why Landfill Methane is a Problem
Methane is significantly more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere compared to CO2, making it a crucial target for reducing short-term climate impacts. The high emissions factors for wet and dry organics illustrate the substantial climate burden posed by improper waste disposal.
1. Emission Factors: Wet organics and dry organics produce vastly different levels of methane emissions, with dry organics like cardboard being particularly problematic.
2. Global Impact: The sheer volume of organic waste in landfills makes it a dominant source of GHG emissions, far surpassing sectors traditionally viewed as major polluters.
3. Urgency for Action: Reducing landfill methane emissions is as easy as implementing a zero-waste to landfill strategy.
Eco-Growth Environmental Solutions
Eco-Growth Environmental specializes in landfill waste avoidance through development of Rapid Dehydration systems. With 3-sizes of systems available: EGOR218 – 75kg / day, EGOR1018 – 200 kg /day and EGOR1224 – 750 kg /day. This technology quickly dehydrates wet organic materials rendering the waste inert or no longer biological alive. Cycle times are normally less than 16 hours after which time the dehydrated waste can be used as a biomass feedstock for energy recovery or back to soil as a nutrient rich fertilizer.
Table shows: Daily waste volumes multiplied by 365 days x emission factors of 43.5 for wet organics and 126.8 for dry.
Summary: Annual Landfill GHG Emissions from a Canadian Donut Shop's Organic Waste
Daily Organic Waste Production:
75 kg of wet organic waste per day
Emissions Factor:
43.5 kg CO2e per kg of wet organic waste
Calculation:
Daily Emissions:
75 kg/day×43.5 kg CO2e/kg=3,262.5 kg CO2e/day 75kg/day×43.5kg CO2e/kg=3,262.5kg CO2e/day
Annual Emissions:
3,262.5 kg CO2e/day×365 days/year=1,190,812.5 kg CO2e/year3,262.5kg CO2e/day×365days/year= 1,190,812.5kg CO2e/year
Summary:
An average Canadian donut shop producing 75 kg of wet organic waste daily generates approximately 1,190,812.5 kg of CO2e greenhouse gas emissions annually when this waste is sent to landfills.

Introduction
Eco-Growth Environmental is making significant strides in global climate action by partnering with the United Nations Climate Hub to address landfill emissions in underdeveloped countries. This collaboration is part of a broader initiative by the UNDP Climate Hub, which manages over $2 billion in grants to foster comprehensive climate action worldwide.
The UNDP Climate Hub is pivotal in advancing global climate goals, leveraging the United Nations Development Program’s (UNDP) extensive expertise. Linked to Climate Promise 2025, this hub actively supports over 125 developing countries in aligning their Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) with the Paris Agreement. The goal is to cap the global temperature rise at 1.5°C, a critical target for mitigating climate change impacts.
Canada has significantly bolstered its commitment to global climate finance, doubling its pledge to CAD 5.3 billion through 2026. This includes a notable contribution of CAD 40 million to the UNDP in 2023, specifically aimed at aiding climate adaptation and mitigation efforts in vulnerable regions.
Compost derived from food waste often contains broken glass and other contaminants, making it unsuitable for use in gardens or agricultural fields as a soil amendment. In addition, local market demand for compost may not always match the available supply, leading to challenges in effectively utilizing this resource. It has become popular for largescale compost facilities to provide finished compost to landfill operators for use as a daily cover (US Federal regulations mandate six inches of soil daily1).
When considering composting, many people envision a sustainable method to recycle organic waste into nutrient-rich soil, reducing landfill waste and benefiting the environment. However, when organic compost is used as a daily cover in landfills, the reality is more complex and problematic, especially regarding methane emissions.
Landfills are engineered to isolate waste from the environment. Typically, waste is layered in cells, with each layer compacted and covered to reduce odor, deter pests, and limit exposure to the elements. Organic compost is often used as a covering layer due to its availability and perceived environmental benefits. However, this practice can have unintended consequences.
1. Anaerobic Conditions: When organic compost is buried under layers of garbage or additional compost, it lacks sufficient oxygen. Composting is ideally an aerobic process, requiring oxygen to break down organic matter efficiently. In the confined, oxygen-poor environment of a landfill, compost quickly shifts to anaerobic decomposition.
2. Anaerobic Decomposition: Without adequate oxygen, anaerobic bacteria dominate the decomposition process. Unlike their aerobic counterparts, these bacteria produce methane (CH4) and carbon dioxide (CO2) as by-products. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential 87 times higher than CO2 over a 20-year period.
3. Methane Emissions: The layers of garbage and compost in a landfill trap methane, which eventually escapes into the atmosphere if not properly managed. This contributes to the greenhouse effect, exacerbating climate change. Methane is significantly more effective than carbon dioxide at trapping heat in the atmosphere, making its release from landfills a critical environmental concern.
4. Environmental Impact: While compost is beneficial in garden soils, its anaerobic decomposition in landfills negates these benefits, instead contributing to harmful greenhouse gas emissions. This contradiction underscores the need for improved waste management practices and composting strategies to mitigate environmental impacts.
By understanding these issues, solutions such as those proposed by Eco-Growth Environmental offer better solutions. Their proprietary rapid dehydration processes effectively sterilizes food waste leaving the material suitable for other uses, such as biomass feedstock for their line of Energy Recovery thermal hot water boilers.
1 waste today magazine

A platform to help with the adoption of carbon lowering technologies


"Pericarbon.org:
• Members-Driven Education and Advocacy
• Pericarbon.org is dedicated to educating and advocating for Carbon Net-Zero across all scopes of carbon emissions.
• Members actively participate in educational initiatives and advocacy campaigns aimed at promoting carbon neutrality.
• Protocol Development for Carbon Emission Reporting
• The organization develops protocols for accurately reporting carbon emission reductions.
• These protocols ensure transparency and consistency in measuring and verifying carbon reduction efforts.
• Registry for High-Quality Carbon
• Pericarbon.org operates a registry to facilitate the supply and demand of high-quality carbon offsets, known as Verified Emission Reductions (VER).
• This registry connects buyers and sellers of VERs, fostering a marketplace for reliable carbon offsetting solutions.
The Pericarbon.org Carbon Offset (VER) Registry offers an innovative platform to encourage the invention of carbon-lowering products or services to gain recognition and facilitate their adoption. Here's a breakdown of its key features:
1. Validation Process: Innovators seeking recognition for their carbon-lowering innovations start by creating a White Paper detailing their product or service. This White Paper undergoes rigorous review by an impartial accredited third party to validate its carbonlowering claims. Executive Mat Service “White Paper” was submitted to Alberta Institute of Technology for validation – see validation letter.
2. Inclusion on VER Registry: Once the White Paper is validated, it is submitted for inclusion on the Pericarbon.org VER Registry. This registry serves as a centralized repository for verified carbon offset innovations. Reporting protocols are established to guide innovators on the information required for submission, typically done at the end of each calendar year. Executive Mat Service reporting protocols were established by Net-Zero Analytics – see protocol letter.
3. Transparency through Blockchain: Entries on the VER Registry are serialized and recorded on the blockchain for maximum transparency. This ensures that information about each carbon-lowering innovation is publicly accessible, promoting trust and accountability.
4. Purchase and Retirement: VERs are made available for purchase, but with the condition that they can only be immediately retired upon acquisition. Ownership of VERs cannot be transferred to speculators, maintaining the integrity of the offsetting process. Each retirement of VERs is recorded on the blockchain for transparency purposes. Purchasers typically retire VERs in blocks.


Executive Mat Service is proud to announce that its technology adoption 'White Paper' has received third-party validation for inclusion on the prestigious Pericarbon.org VER Registry. This recognition underscores the credibility and impact of EMS's commitment to sustainability. Additionally, the quantification protocols associated with EMS's initiatives have been independently determined by third parties for inclusion on the Pericarbon.org VER Registry, solidifying the company's position as a leader in environmental responsibility."

1. Validated Projects that reduce atmospheric carbon emissions.




1. Reduce your carbon footprint
2. Purchase VER to offset remaining carbon footprint

In an era where transparency and accountability are paramount, Pericarbon.org is revolutionizing the management of Verified Emission Reductions (VERs) by leveraging cutting-edge blockchain technology. This innovative approach not only enhances the integrity of carbon offset tracking but also sets a new standard for the industry.
Verified Emission Reductions (VERs) are a critical component in the fight against climate change, allowing organizations to offset their carbon footprint by investing in projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, traditional methods of tracking and verifying these reductions are often plagued by inefficiencies, lack of transparency, and the potential for fraud. This is where blockchain technology comes into play, offering a robust solution to these challenges.
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable ledger, provides an ideal platform for managing VERs. By recording each transaction on a blockchain, Pericarbon.org ensures that every step in the VER lifecycle from generation to retirement is transparent, secure, and verifiable.
1. Transparency: Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger, accessible to all stakeholders. This transparency helps build trust among participants and ensures that all VERs are accounted for accurately.
1. Security: The hash-protected nature of blockchain technology makes it highly resistant to tampering and fraud. Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating a secure chain of data that is virtually impossible to alter.
2. Efficiency: Blockchain streamlines the process of tracking and verifying VERs, eliminating the need for intermediaries. This results in faster, more efficient transactions.
Pericarbon.org’s blockchain-based VER registry operates as a centralized ledger. Through a public access portal project developers, auditors, buyers, and regulators, all of whom have access to the same, up-to-date information.
1. VER Generation: When a project generates VERs, the details are recorded on the blockchain, including the project’s location, the amount of emissions reduced, and the verification status.
2. Verification and Validation: Independent auditors verify the project’s emissions reductions. Once verified, this information is added to the blockchain, ensuring that all stakeholders have access to the same verified data.
3. Trading and Retirement: Buyers can purchase VERs and immediately retire through the blockchain platform. Once a VER is retired (i.e., used to offset emissions), this action is recorded on the blockchain, preventing the same VER from being sold or used more than once.
By integrating blockchain technology into its VER registry, Pericarbon.org is setting a new benchmark for transparency and security in the carbon offset industry. This pioneering approach not only enhances the credibility of VERs but also promotes greater participation in carbon offset initiatives, driving us closer to a sustainable, low-carbon future.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change, innovative solutions like Pericarbon.org’s blockchain-based registry are essential for building a transparent, trustworthy, and effective carbon market. By ensuring that every VER is accurately tracked and verified, Pericarbon.org is helping to pave the way for a greener, more sustainable world.


Screen shot of blockchain entry on Pericrbon.org blockchain.
To render a product or service carbon net-zero using the Pericarbon.org Registry, follow these steps:
1. Identify the Carbon Footprint:
Determine the total carbon emissions associated with the product or service you aim to make net-zero. This involves calculating the emissions from production, distribution, usage, and disposal.
2. Purchase Verified Emission Reductions (VERs):
Access the Pericarbon.org Registry to purchase a block of VERs equivalent to the identified carbon footprint. These VERs represent verified projects that reduce or remove emissions, helping offset your product or service's carbon footprint.
3. Allocate the Block of VERs:
Clearly specify how the purchased VERs will be allocated to offset the emissions. Document the allocation details, ensuring that each VER is effectively retired to achieve the carbon net-zero status for your product or service.

High-quality Voluntary Emission Reductions (VERs) are characterized by several key factors that ensure their effectiveness and reliability. Here are some of the main factors that contribute to the quality of VERs:
1. Real: The emission reductions must have actually occurred and be measurable.
2. Permanent: The reductions should represent a long-term change and not be reversible.
3. Verifiable: There should be a clear and transparent method to verify the reductions.
4. Additional: The reductions should be above and beyond what would have happened without the project.
5. Quantifiable: The amount of reduction should be accurately calculated and reported.
6. Avoidance of Leakage: The project should not result in increased emissions outside the project boundary.
7. Sustainable Development: The project should contribute to sustainable development goals and not cause social or environmental harm.
These factors ensure that VERs are robust and can be trusted by those who purchase them to offset their emissions It’s also important that the projects generating VERs have a clear baseline to compare against business-as-usual scenarios and that they are aligned with broader climate change goals
In the rapidly evolving landscape of carbon reduction technologies, understanding when an innovation transitions from being "new" to becoming a standard baseline is crucial. This transition is governed by the principles of the "Diffusion of Technology" protocol, which plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and relevance of Verified Emission Reductions (VER) on the blockchain.
When Does Technology Cease to be New?
1. Defining the Transition Point
• New to Baseline: A new carbon-lowering technology or innovation ceases to be considered new when it achieves 15% market penetration, called “Early Adopter” .
• Exclusion from VER Blockchain: Once a technology is no longer considered new, it no longer qualifies for inclusion on the VER blockchain as a source of verified emission reductions.
2. The 15% Market Share Threshold
• Establishing a New Baseline: At this point, technology becomes the new baseline, setting a standard from which subsequent innovations will seek to improve.
Ensuring Continuous Innovation
1. Driving Further Improvements
• Encouraging Innovation: By establishing a clear threshold for when a technology is no longer considered new, the Diffusion of Technology protocol ensures that innovators are continuously motivated to develop further and better improvements.
• Sustaining Momentum: This approach sustains the momentum of technological advancement, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in carbon reduction.
2. Example: The Evolution of LED Lighting
• Introduction of LEDs: When energy-efficient LED lights were first introduced, they represented a significant technological breakthrough, driving substantial reductions in energy consumption.
• Maturity of LEDs: Today, LED lighting is widely considered a mature technology. As a result, switching to LED lighting is no longer eligible for inclusion on the VER blockchain, as it has become the baseline standard for energy-efficient lighting.
1. Maintaining Integrity of VERs
• Ensuring Relevance: Excluding mature technologies from the VER blockchain ensures that only genuine, cutting-edge innovations qualify for verified emission reductions.
• Promoting Transparency: This approach enhances the transparency and credibility of the VER market, providing assurance to investors and stakeholders that they are supporting truly impactful technologies.
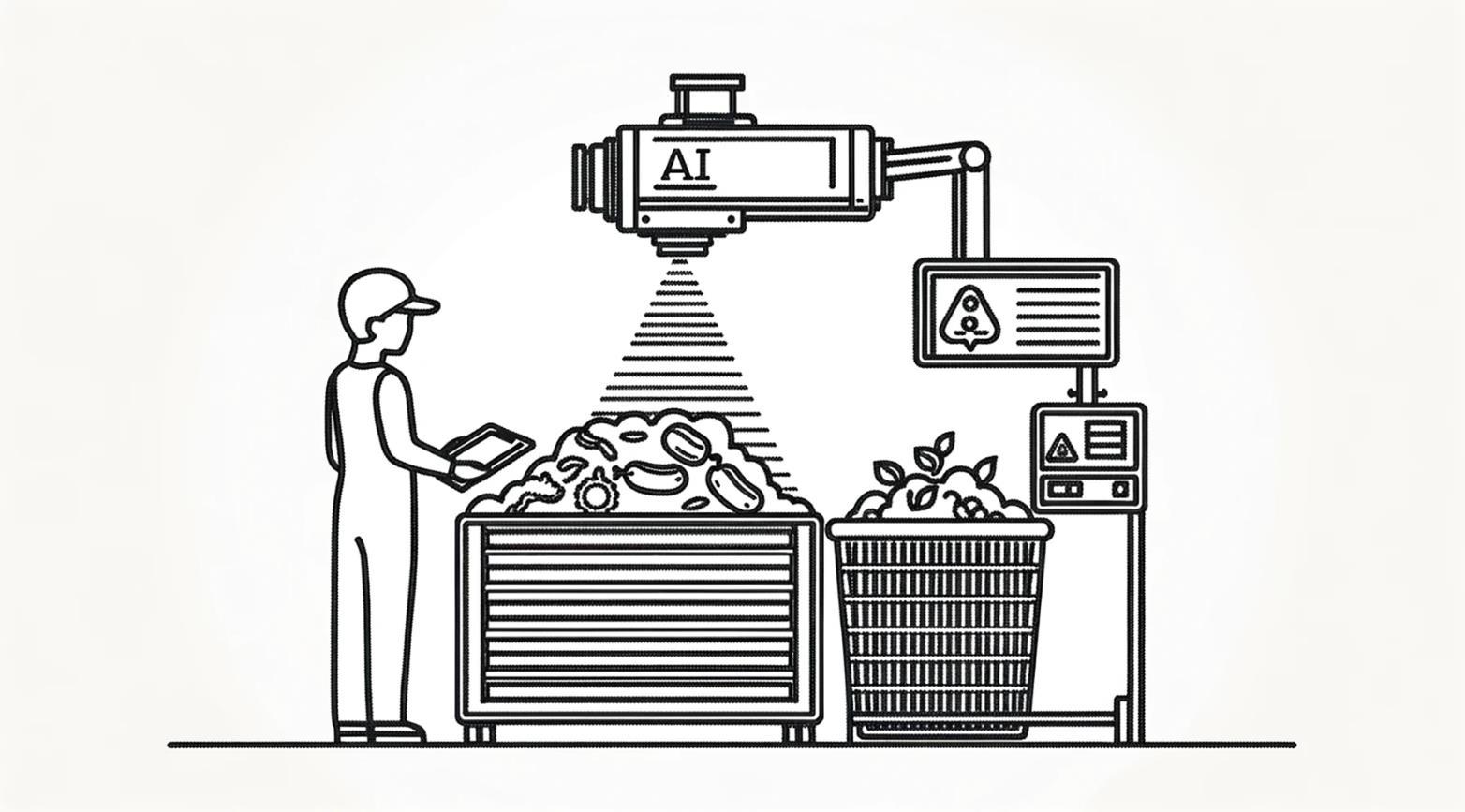
As the world intensifies its efforts to achieve sustainability and reduce carbon footprints, the accurate reporting of organic waste diversion from landfills has become paramount.
1. Ensuring Transparency with AI-Based Verification
The integrity of waste diversion reporting is crucial for VER monetization. Over-reporting of organic waste diversion can undermine integrity and quality of VER accounting. To address this, the development of AI-based verification tools is essential. These tools are designed to:
• Accurately Track Waste Volumes: AI algorithms analyze key data points, such as weight and volume measurements, ensuring that reported figures align with actual waste diverted.
• Detect Anomalies: Our advanced machine learning models easily identifies discrepancies in waste identification and reporting, flagging unusual patterns or inconsistencies that may indicate over-reporting.
• Enhance Auditability: By maintaining a transparent and traceable record of waste diversion activities, AI tools facilitate easier auditing and verification by regulatory bodies.
A critical component in managing organic waste is the accurate scanning and verification of each waste load before it enters processing equipment like the Rapid Dehydrator. This step is crucial for maintaining the quality and integrity of the waste management process. Here’s how AI scanning applications contribute:
• Real-Time Load Scanning: AI-driven cameras and sensors scan each load of organic waste as it arrives, analyzing its composition and volume in real time.
• Data Integration: The application integrates with existing waste management systems, providing seamless data flow and real-time updates on waste processing.
• Automated Compliance Checks: AI algorithms compare the scanned data against predefined criteria, ensuring that only compliant organic waste loads proceed to the dehydration stage.
To maintain the integrity of the waste management process and prevent contamination, it is crucial to enforce strict material conformity. AI tools play a vital role in this enforcement by:
• Identifying Non-Conforming Materials: The AI system is trained to recognize materials that do not meet the required specifications for organic waste, such as contaminants or non-organic items.
• Automating Rejection Processes: Upon detecting non-conforming materials, the AI system automatically disqualifies and rejects the entire batch, preventing it from entering the Rapid Dehydrator.
• Feedback and Reporting: The system provides immediate feedback to waste management personnel, detailing the reasons for rejection and suggesting corrective actions.
The development of AI tools for accurate accounting in organic waste diversion is a significant step towards enhancing transparency, efficiency, and compliance in waste management. By implementing AI-based verification, real-time scanning applications, and strict material conformity measures, we can ensure that organic waste diversion efforts are both accurate and reliable. These innovations not only support environmental sustainability but also bolster trust and accountability in waste reporting practices, paving the way for a greener and more transparent future.

1. Helping the disadvantaged find meaningful employment.
2. Helping the hungry.
3. Helping Indigenous business succeed Executive Mat Service
At the Executive Mat Service Calgary Eco-Center, Eco-Growth Environmental is pioneering a transformative approach to address local hunger and reduce Scope 3 emissions through an innovative vertical indoor farming system. This initiative, equivalent to a 4-acre farm, represents a significant leap forward in sustainable agriculture and community support.
The vertical farm, strategically located at the Calgary Eco-Center, is operated by a local charity dedicated to feeding the community. This modern farming technique utilizes vertical grow towers, optimizing space and resources to produce leafy greens year-round, regardless of external weather conditions.
1. Efficient Space Utilization:
o The vertical farm maximizes productivity within a compact footprint, equivalent to a traditional 4-acre farm, allowing for high-density cultivation of various leafy greens.
2. Community Impact:
o All produce harvested from the farm is donated to the local community, providing fresh, nutritious greens to those in need and supporting local food security initiatives.
Traditional agriculture often involves transporting produce over long distances from southern regions to Canada. This lengthy supply chain contributes significantly to the carbon footprint and results in substantial food spoilage, leading to increased landfill waste.
1. Reducing Food Miles:
• By producing leafy greens locally, the vertical farm eliminates the need for longdistance transportation, thereby reducing the associated carbon emissions (Scope 3 emissions) and ensuring fresher produce for the community.
2. Minimizing Food Waste:
• Local production drastically cuts down on spoilage, as greens are consumed shortly after harvest, reducing the volume of spoiled produce that would otherwise end up in landfills.
Sustainable Practices: Enhancing Environmental Impact
Eco-Growth Environmental’ s vertical farm incorporates several sustainable practices, further enhancing its positive environmental impact.
1. Water Efficiency:
o The farm uses a closed-loop hydroponic system, recycling water and nutrients to minimize waste and maximize efficiency.
2. Energy Efficiency:
o Advanced LED lighting and climate control systems ensure optimal growing conditions while reducing energy consumption.
3. Carbon Capture Integration:
o The facility integrates carbon capture technology, directing CO2 from exhaust streams into the farm to enhance plant growth, further reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits of Vertical Indoor Farming
1. Local Food Production:
• Supports local agriculture, reduces dependency on imported produce, and strengthens the community’s food resilience.
2. Lower Carbon Footprint:
• Significantly reduces emissions associated with transportation and food spoilage, contributing to overall sustainability goals.
3. Year-Round Availability:
• Provides a consistent supply of fresh greens, regardless of season or weather conditions, enhancing food security.
4. Community Engagement:
• Encourages community involvement and awareness of sustainable practices, fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
According to the "Food Waste in Canada" report:
Production Stage: In the production stage, which includes farming and harvesting, the report estimates that approximately 32% of all food produced in Canada is lost or wasted.
Processing and Distribution: In the processing and distribution stages, around 5% of food is wasted.
Retail Stage: At the retail level, the report suggests that approximately 15% of food is lost or wasted.
Consumer Stage: Finally, at the consumer level, it's estimated that households waste about 47% of all food in Canada.
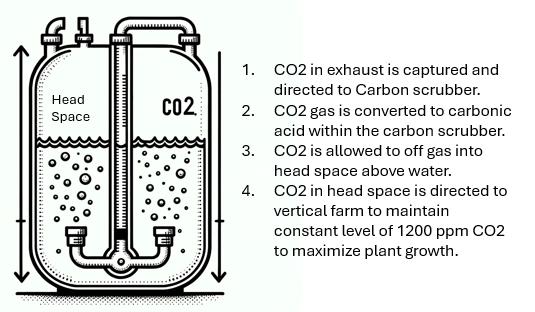
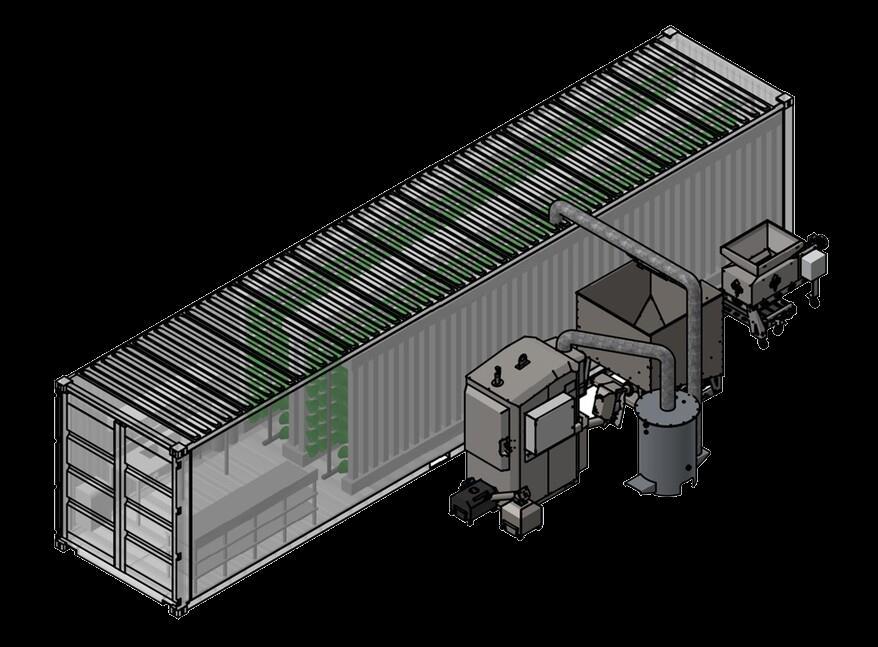
Carbon Capture: Increasing Food Supply and Reducing Scope 1 Emissions
In the quest for sustainable solutions, Eco-Growth Environmental has developed carbon capture technology not only to reduce Scope 1 emissions but also enhance food supply.
Exhaust from the Eco-Growth Energy Recovery systems, particularly those using biomass as feedstock, is considered carbon neutral under the Paris Agreement on Climate Change. This is because the carbon released during combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed by the plants during their growth. However, the exhaust still contains CO2, which, if not managed properly, can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
A groundbreaking technology has been developed to scrub CO2 from the exhaust stack by converting it into carbonic acid in a sealed tank half filled with water. This process involves directing the CO2-laden exhaust into the tank, where it dissolves in water to form carbonic
acid (H2CO3). This simple yet effective method captures CO2 efficiently, reducing its direct release into the atmosphere.
The carbonic acid in the tank slowly off-gasses back into CO2. This off-gassing process is carefully controlled within the tank, ensuring that CO2 is released in a manageable and predictable manner. This controlled release is crucial for the next step in the carbon capture cycle.
The off-gassed CO2 from the tank is then directed into an indoor farm, where it is used to optimize CO2 levels to around 1,200 parts per million (ppm). This concentration is ideal for maximizing plant growth and yields. By providing plants with an optimal CO2 environment, the indoor farm can achieve higher productivity and more efficient use of resources.
The captured CO2 from the exhaust stream is ultimately absorbed by the growing plants, bringing the carbon cycle full circle. This process not only prevents CO2 from contributing to atmospheric greenhouse gases but also enhances the growth and yield of crops. By integrating carbon capture with agricultural practices, we can significantly reduce Scope 1 emissions and boost food production simultaneously.
• Reduction in Scope 1 Emissions: By capturing CO2 from exhaust streams, we directly reduce emissions from energy recovery systems, aligning with sustainability goals. Emission factor calculations are not yet available at the time of this report.
• Increased Food Supply: Optimizing CO2 levels in indoor farms enhances plant growth, leading to higher crop yields and a more stable food supply.
• Sustainable Agriculture: Utilizing CO2 in agricultural practices promotes a sustainable approach to farming, reducing the need for external CO2 sources.
• Efficient Resource Utilization: This technology maximizes the use of available resources, turning waste CO2 into a valuable asset for food production.


Pictured is Val Favel receiving recognition from Spectrum Advantage for successful participation in the Autism Placement Program .

A Healthier Alternative: Eco-Growth Environmental’ s Food-Waste Derived Pellets
In response to the pressing health issues caused by traditional cooking and heating fuels, Eco-Growth Environmental has introduced an innovative solution: food-waste derived cooking and heating pellets. These pellets offer a low-particulate alternative to the commonly used dung and coal, significantly reducing the health risks associated with indoor air pollution.
In many developing countries, particularly in rural areas, dung and coal are primary sources of fuel for cooking and heating. Unfortunately, burning these materials releases a high level of particulate matter and other harmful pollutants. This can lead to chronic respiratory diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and increase the risk of acute respiratory infections like pneumonia, particularly in children (over 50% of premature deaths among children under five in India are attributable to pneumonia caused by inhaling particulate matter – soot. Source: timesofindia.indiantimes.com, indiaclimatedialogue.net).
Eco-Growth Environmental’ s food-waste derived pellets are designed to address these health hazards. Made from recycled food waste, these pellets burn more cleanly and efficiently than traditional fuels, producing significantly lower levels of particulate matter and harmful gases. This not only helps to improve indoor air quality but also reduces the risk of respiratory illnesses.
• Cleaner Combustion: These pellets produce fewer emissions, resulting in less smoke and fewer pollutants released into the air.
• Sustainable and Renewable: Using food waste as a resource helps to reduce waste and create a sustainable fuel source.
• Cost-Effective: Food-waste pellets can be a more affordable option compared to other cleaner fuels like liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and biogas.
• Accessible: They are easy to produce and can be made locally, ensuring that even remote communities can benefit from this cleaner fuel source.
By switching to Eco-Growth Environmental’ s food-waste derived pellets, communities can significantly reduce their exposure to harmful pollutants, leading to better respiratory health and a reduction in child mortality rates due to pneumonia. This innovative solution provides a practical, low-cost way to improve health outcomes while also promoting environmental sustainability.

Wood pellets have long been touted as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Initially, these pellets were produced from waste woods such as tree branches and lumber mill sawdust, effectively recycling what would otherwise be discarded. However, the rapidly growing demand for biomass energy in countries like England and Japan has raised serious environmental concerns. Evidence is mounting that valuable, untouched forests are being felled to feed the burgeoning wood pellet sector. (source: theguardian.com)
The shift from using waste wood to harvesting intact forests for wood pellet production has significant environmental implications. Old-growth forests, rich in biodiversity and crucial for carbon sequestration, are being cut down to supply the wood pellet industry. This practice not only destroys vital ecosystems but also releases large amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere. When these mature trees are burned, the carbon they have sequestered over decades is released almost immediately, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
One of the most critical issues with cutting down old-growth forests is the carbon footprint. These forests act as significant carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When they are cut down and burned, the carbon stored in their biomass is released, creating a substantial carbon debt. Replanting trees to offset this carbon is a
lengthy process. It can take up to 100 years for newly planted forests to sequester the same amount of carbon that was released by cutting and burning old-growth trees. During this period, the immediate increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide contributes to climate change, exacerbating global warming.
To mitigate these issues, producing wood-like pellets from organic food and agricultural waste presents a promising solution. For example, in many agricultural regions, flax stubble is traditionally burned in the fields after harvest, releasing carbon dioxide and other pollutants. Instead of burning this waste, it can be converted into biomass pellets. This approach offers a two-fold environmental benefit.
1. Avoiding Landfill Methane: Organic waste, if left to decompose in landfills, generates methane a potent greenhouse gas that is far more effective at trapping heat in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide. By diverting organic waste from landfills to pellet production, methane emissions can be significantly reduced.
2. Reducing Reliance on Virgin Forests: Using agricultural waste and other organic materials for pellet production decreases the demand for wood from untouched forests. This not only helps preserve these critical ecosystems but also ensures that the carbon sequestration capacity of old-growth forests is maintained.
While wood pellets remain a viable renewable energy source, it is crucial to address the environmental impact of their production. Shifting towards using organic waste and agricultural residues for pellet production can help alleviate the pressure on virgin forests and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Policymakers and industry leaders must prioritize sustainable practices and support innovations that make use of waste materials. By doing so, we can continue to harness the benefits of biomass energy without compromising the health of our planet.

Since 2009, the United Nations has pledged $100 billion annually to help developing countries tackle climate change. While this significant financial commitment aims to support climate action and adaptation, there are growing concerns that the fund is falling short in addressing critical areas of emissions reductions, particularly landfill methane emissions. Here’s why landfill methane emissions need more attention and how EcoGrowth Environmental’ s innovative technology can be a game-changer for climate action and economic development.
Landfill methane emissions are a major source of greenhouse gases (GHGs). Methane is a potent GHG, with a global warming potential 87 times greater than carbon dioxide over a 20-year period. Despite its significant impact, landfill methane avoidance has been neglected in climate action plans. Most developing countries lack the infrastructure and resources to manage landfill emissions effectively, resulting in unchecked methane release and missed opportunities for significant emissions reductions.
Eco-Growth Environmental offers a promising solution to this problem through its microsized rapid dehydration systems. These systems can be deployed within communities where food waste is generated, providing an efficient and sustainable method for
converting food waste into biomass energy. This approach addresses multiple challenges simultaneously:
1. Mitigates Greenhouse Gas Emissions: By diverting food waste from landfills and converting it into biomass energy, methane emissions can be significantly reduced. This not only helps mitigate climate change but also makes use of waste that would otherwise contribute to environmental degradation.
2. Promotes Clean Energy Solutions: Biomass energy derived from food waste offers a renewable and cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. It reduces reliance on coal and dung, which are commonly used for cooking and heating in many developing countries. The shift to biomass energy can significantly cut down on air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Protects Vulnerable Populations: The health impacts of burning coal and dung are well-documented, including respiratory diseases and increased mortality rates. By providing a cleaner fuel source, biomass energy helps protect vulnerable populations from adverse health effects, improving overall public health outcomes.
Eco-Growth Environmental’ s technology also spurs economic development and engages communities in meaningful ways:
• Localized Processing: The micro-sized rapid dehydration systems allow food waste to be processed within the community. Residents are encouraged to bring their food waste to the local processor, which converts it into clean-burning wood-like pellets.
• Incentivizing Participation: Community members receive clean-burning pellets in exchange for their food waste, providing them with a valuable resource while reducing waste.
• Real-Time Verification and Payment: The processors are paid based on the volume of food waste they process, with real-time verification through a cloud-based interface. This system ensures transparency and efficiency, rewarding processors for their contributions to sustainability.
• Job Creation: Establishing these facilities within communities creates jobs in waste management, processing, and distribution, contributing to local economic growth.
• Economic Diversification: Developing a biomass energy sector can diversify the economy, reducing dependence on traditional agricultural and fossil fuel industries. This diversification can make economies more resilient and sustainable.
The Way Forward
Policymakers need to leverage the fund in two key ways:
1. Technology Installation: Invest in installing technology that can effectively reduce emissions, such as Eco-Growth Environmental’ s rapid dehydration systems for converting food waste into biomass energy.
2. Monetization of Landfill Methane Emissions: Establish pre-agreements to purchase Verified Emission Reductions (VERs) in real-time through a carbon registry, such as Pericarbon.org. This approach ensures that landfill methane emissions are financially incentivized and accounted for immediately, promoting sustainable practices and emissions reductions.
Conclusion
While the United Nations' $100 billion per year climate fund is a commendable effort, it must be more effectively allocated to address critical areas like landfill methane emissions. Eco-Growth Environmental’ s technology for converting food waste into biomass energy presents a powerful solution that not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes clean energy, protects public health, and stimulates economic development. By focusing on these multifaceted benefits, we can enhance the effectiveness of climate action and foster a more sustainable future for all.

In many developing countries, managing waste effectively is a critical challenge. Landfills, often overflowing with organic waste, emit significant amounts of methane a potent greenhouse gas contributing to climate change. To tackle this issue, innovative solutions like Eco-Growth's rapid dehydration technology are being implemented. However, the success of such initiatives hinges on data integrity. Ensuring that data is believable and free of tampering is essential for effective landfill avoidance and environmental sustainability.
Data integrity refers to the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data throughout its lifecycle. In the context of landfill avoidance, maintaining data integrity is crucial for several reasons:
1. Trustworthiness: Stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and local communities, need to trust that the reported data reflects the actual amount of waste processed. This trust is foundational for ongoing support and funding.
2. Efficiency: Accurate data ensures that resources are used efficiently. Misreported data can lead to over or underutilization of the system, affecting its overall performance.
3. Verification: For initiatives that rely on generating Verified Emission Reductions (VERs), accurate data is necessary to prove the environmental benefits and secure funding or credits.
To ensure data integrity, Eco-Growth Environmental utilizes advanced AI image recognition technology. Here’s how it works:
1. AI Image Recognition: Every load of food waste brought to the processing site is scanned using AI image recognition technology. This system verifies the contents of each pail, ensuring that only acceptable food waste is processed.
2. Prevention of Overreporting: The AI technology prevents overreporting by accurately identifying and verifying the waste. This step is critical to avoid inflating the actual weights and ensures that the data remains credible.
3. Automated Weighing and Processing: Once a load of food waste is verified by the AI system, it is automatically weighed on a load cell. This weight data is recorded in real-time, providing an accurate measure of the waste being processed.
4. Processing and Rejection: Verified loads are dumped into the rapid dehydrator for processing. Loads that do not meet the criteria are rejected and automatically dumped into a bin located behind the 40-foot sea container. This automated sorting ensures that only appropriate waste is processed, maintaining the integrity of the system.
The use of real-time data is another critical component of maintaining data integrity. By leveraging cloud-based interfaces, Eco-Growth ensures that the data is immediately available for verification and analysis. This transparency allows for:
1. Immediate Verification: Real-time data allows for immediate verification of the waste being processed, reducing the likelihood of errors or tampering.
2. Accurate Reporting: Stakeholders can access accurate and up-to-date reports on the amount of waste processed and the resulting environmental benefits.
3. Enhanced Accountability: With real-time data, it is easier to hold all parties accountable for their role in the waste management process.
In the quest for sustainable solutions to global environmental challenges, innovative technologies are paving the way for a greener future. One such groundbreaking innovation is the Gravitas Energi gravitational electricity generation system. This system is revolutionizing the way we approach renewable energy by providing a reliable and sustainable power source without relying on traditional grid power systems. A prime example of its application is in powering the Eco-Growth rapid dehydration and pellet system, which processes food waste into valuable biomass energy.
The Gravitas Energi system utilizes the fundamental force of gravity to generate electricity. This ingenious technology works by converting gravitational potential energy into electrical energy, providing a continuous and reliable power supply. The system captures potential energy from a rotating mass using a series of push rods (pistons). As the push rods descend under heavy load, they drive a generator to produce electricity. An ingenious mechanism effortlessly repositions the push rods back to their starting position, readying them for the next downward push from the weighted mass. This method is environmentally friendly, highly efficient, and sustainable.
Many third-world countries lack access to affordable power. The Eco-Growth Landfill Methane Avoidance technology addresses this issue by providing its own power source, allowing the technology to be installed anywhere with internet access. Eco-Growth Environmental’ s rapid dehydration and pellet system transforms food waste into biomass pellets, which can be used for cooking and heating. This process significantly reduces landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions while providing a renewable energy source. However, such a system requires a consistent and reliable power supply. This is where the Gravitas Energi gravitational electricity generation system comes into play.
1. Independence from Grid Power: One of the most significant advantages of using the Gravitas Energi system is that it eliminates the need to connect to existing grid power systems. This independence is particularly beneficial in remote or underserved areas where access to grid power is limited or unreliable.
2. Sustainable and Renewable Energy: The Gravitas Energi system harnesses the power of gravity a perpetual and abundant resource. By using this clean energy source, the Eco-Growth system reduces its carbon footprint and contributes to a more sustainable future.
3. Reliable Power Supply: Unlike solar or wind energy, which are dependent on weather conditions, gravitational energy is consistently available. This reliability ensures that the Eco-Growth dehydration and pellet system can operate continuously without interruptions.
4. Cost-Effective Solution: By eliminating the need for grid power, the Gravitas Energi system reduces operational costs. This cost-effectiveness makes it an attractive option for communities and businesses looking to invest in sustainable technologies.
The combination of Gravitas Energi’s gravitational electricity generation system and EcoGrowth Environmental’ s food waste processing technology presents a powerful solution to several pressing issues. It addresses waste management challenges by converting food waste into valuable energy, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and promotes sustainability using renewable energy.
Moreover, this innovative approach has the potential to transform communities, particularly in developing countries where waste management and energy access are significant challenges. By providing a reliable and sustainable power source, the Gravitas Energi system empowers these communities to implement eco-friendly technologies and improve their quality of life.
Exploring New Horizons: Executive Mat Service and Askiy Mat Service Discuss Potential Joint Venture
In the dynamic world of business services, strategic partnerships can redefine markets and set the stage for groundbreaking innovations. A thrilling development in this arena is the ongoing joint venture discussions between Executive Mat Service Ltd. and Askiy Mat Service. This potential collaboration aims to leverage the unique strengths of both companies to create a formidable force in the mat service industry.
Founded by Sandy Sanderson at a challenging time right before the global COVID-19 crisis Askiy Mat Service has exemplified resilience and entrepreneurial spirit. Despite the daunting circumstances, Sandy's unwavering dedication and robust business acumen enabled Askiy Mat to not only survive but thrive. His commitment to hard work, quality products, and efficient service has built a dynamic business that stands as a testament to overcoming adversity with determination.
Seeing the remarkable journey and the solid foundation laid by Sandy, Kim Caron, founder of Executive Mat Service, identifies Askiy Mat as an ideal partner. This admiration is not just based on Askiy Mat’s resilience but also on the synergistic potential between the two companies. Kim envisions a partnership where Askiy Mat would acquire a controlling interest in the Service Delivery division of Executive Mat Service. This move would allow Executive Mat Service to concentrate on innovating within their Cleaning Technology Centers, serving as the processing powerhouse behind the scenes.
The proposed business model is a strategic realignment that aims to optimize the strengths of both entities. Askiy Mat's prowess in service delivery and customer relations would be at the forefront of the joint operation, ensuring that clients receive top-tier service. Simultaneously, Executive Mat Service would enhance its focus on technological advancements and operational efficiencies within its Cleaning Technology Centers.
This collaboration not only promises growth and expansion but also a sharing of values and visions that are fundamental to both companies. It reflects a mutual recognition of potential and a shared goal of excellence. By combining Askiy Mat’s customer-focused approach with Executive Mat’s technological edge, the joint venture is poised to set new standards in the industry.
Nestled in the heart of our community, Askiy Mat Service stands as a proud Indigenous-owned business, operating under the leadership of Sandy Sanderson, a dedicated member of the Mikisew Cree First Nation. At Askiy Mat Service, we are not just providing mats; we are offering a gateway to safer, greener, and more sustainable environments with every step you take on our products.
Askiy Mat Service combines safety and sustainability with its product line, including Waterhog Mats and Weather Stop Mats, which feature non-skid backings made from 20% recycled vehicle tires and surfaces crafted from 100% recycled plastic bottles. The company's patented cleaning process not only enhances mat durability and extends their lifespan but also significantly reduces water usage by 99%, underlining a commitment to eco-friendly practices. Furthermore, the effectiveness of this cleaning technology in reducing carbon emissions has been validated by the Southern Alberta Institute of Technology (SAIT), reinforcing Askiy Mat's dedication to environmental stewardship and community well-being.
Askiy Mat Service is more than a business; it is a reflection of our culture, heritage, and commitment to the principles of respect and sustainability taught by our ancestors. Owned and operated by a member of the Mikisew Cree First Nation, our company is a testament to the strength and resilience of our community. We bring these values to the forefront of our operations, ensuring that every interaction honors our heritage and contributes to the wellbeing of our planet.
As we continue to grow, Askiy Mat Service remains dedicated to innovating and expanding our sustainable practices. We are committed to providing products and services that meet the highest standards of quality and environmental responsibility, aiming to inspire other businesses to join us in making a meaningful impact.
At Askiy Mat Service, every mat tells a story of tradition, resilience, and hope for a more sustainable future.




As we progress on our path to carbon net-zero, it is essential to pause and express my deepest gratitude to those who have been instrumental in this journey. Achieving our environmental goals is a collective effort, and I want to acknowledge the invaluable contributions of just some of the many that have been assisting on this journey.
To our esteemed customers and dedicated team members, your unwavering support has been the cornerstone of our journey. Your belief in our vision, even when ideas didn’t always pan out as planned, has been a source of motivation and resilience. Your feedback, patience, and commitment have driven the refinement of our approaches to carbon netzero. I am immensely grateful for your trust and partnership.
To my family, your patience and understanding have been nothing short of extraordinary. Enduring countless late-night research sessions and the constant hum of computer keystrokes, you have been my silent strength. Your unwavering support and encouragement have fueled the passion and perseverance to the pursuit of carbon netzero.
To our ISO14001 auditing team and Val, our sustainability coordinator, your expertise has been crucial in providing a robust management framework, enabling us to implement new technological ideas in an orderly and effective manner. Your guidance has ensured that our processes align with international standards, paving the way for sustainable innovation. I appreciate your meticulous work and unwavering support.
A special thank you to Naveed, our E&Y SR&ED advisor, whose exceptional support has been invaluable. His expertise in preparing our paperwork has freed up much-needed capital, allowing us to continue our journey towards carbon net-zero. Your dedication and strategic insights have been instrumental in navigating the complexities of our projects. I am profoundly grateful for your contributions.
Sincerely,
Kim Caron

