1 minute read
Conclusions
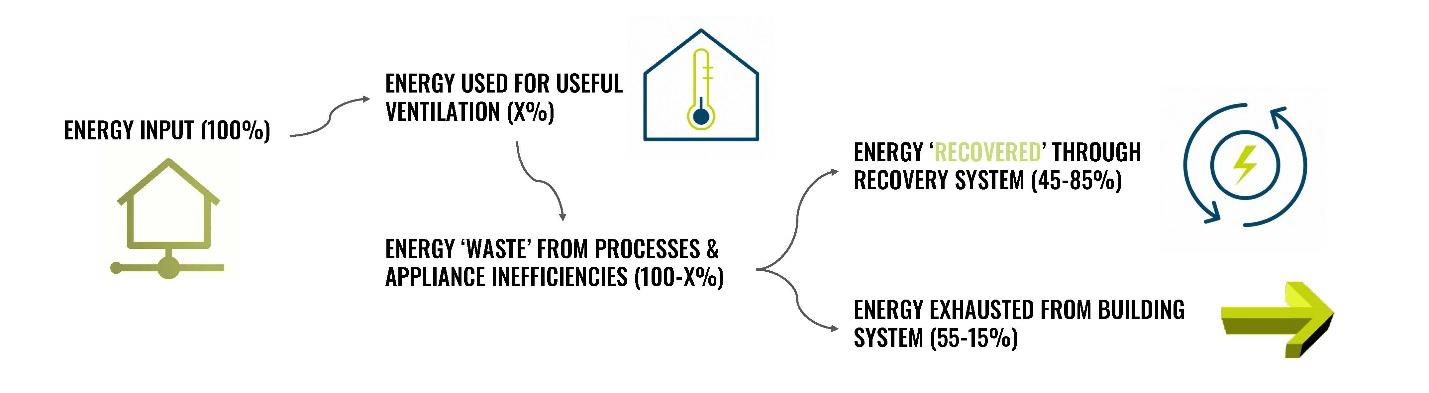
The greenhouse gases that are released in the operation of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems are one of the leading contributors of climate change. Because HVAC costs and energy expenditure are among the highest of all building systems and almost 30-60% of that is expelled as waste heat, it becomes imperative to find ways to reduce that loss. On top of saving energy and cost, providing clean and fresh indoor air into buildings and improving indoor air quality is essential for occupant health. Heat recovery is a cost effective and efficient technology to incorporate into the mechanical system of any structure and recycle the waste heat from a building or process and reuse it for the same or a different purpose. With studies being conducted around the varying types of energy recovery technology and the integration of it into architectural components, there are many opportunities in the realm of design to reduce greenhouse gas emissions while improving indoor air quality and thermal comfort by using heat recovery. Regulations and standards are constantly being updated to push for the incorporation of heat recovery into mechanical design strategies and encourage high performance ventilation strategies. Initial costs might be higher than a typical HVAC unit, but the overall benefits of global and occupant health outweigh the cost within a short payback period of a few years.
Advertisement