New Drugs in Myeloma – What, How and When?

What Patients and Care Partners Need to Know
Joseph Mikhael, MD, MEd Chief Medical Officer, International Myeloma Foundation

















 Dr. Joseph Mikhael Chief Medical Officer International Myeloma Foundation
Dr. Joseph Mikhael Chief Medical Officer International Myeloma Foundation


• Review the key classes of drugs we use in myeloma
• Provide an overview of how myeloma drugs work in simple terms
• Discuss the concept of immunotherapy and what it means in myeloma

• Outline the process of drug development where clinical trials start in the relapsed setting and then move up to the frontline
Introduce the newest drugs in myeloma and how they will be used

Multiple Myeloma* is a blood cancer that starts in plasma cells of the spongy center of bones (bone marrow).
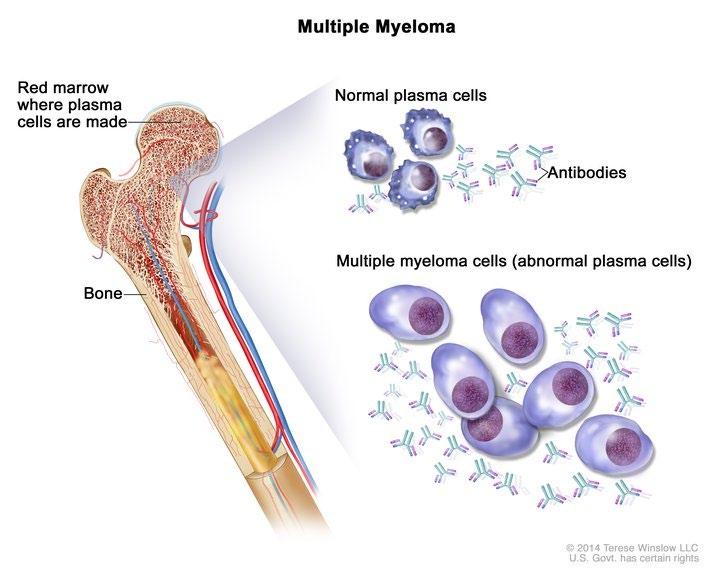
–
This is where stem cells mature into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
– Myeloma cells are abnormal plasma cells that make an abnormal antibody called “M protein”.
* Myeloma is NOT a bone cancer or skin cancer (melanoma), it is a type of blood cancer.


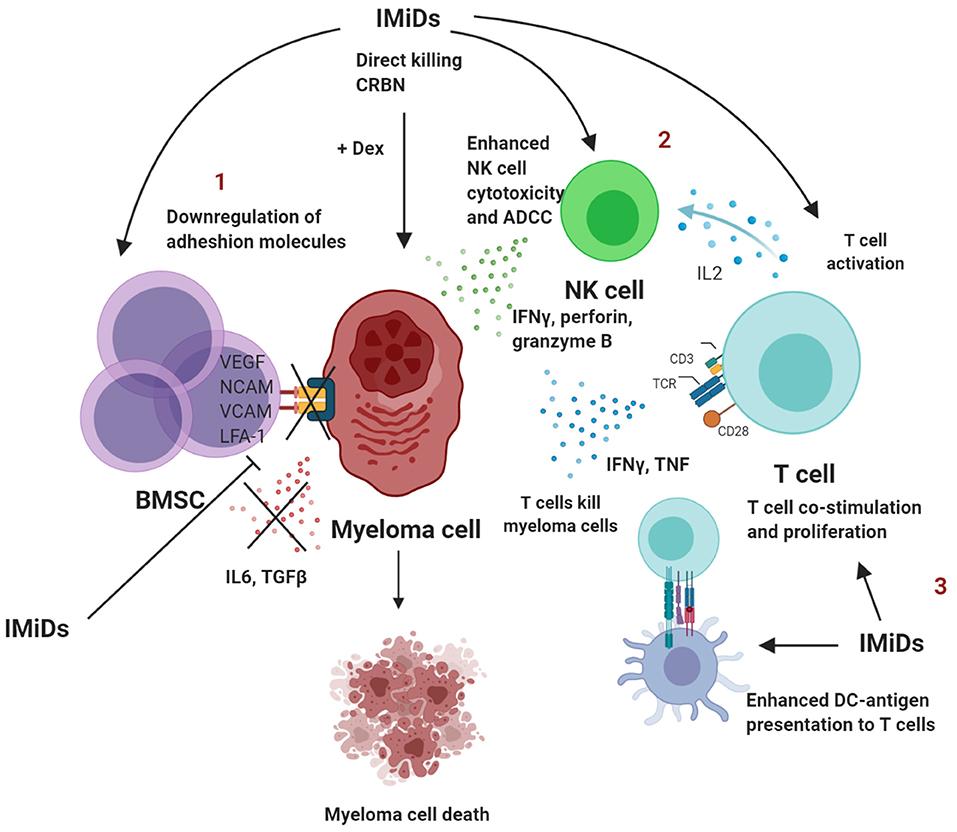
Increase in cytokine production and adhesion molecules







Block of programmed cell death FAS (CD95)






Pro-caspase B FAS ligand


fibers
NFkB Binding Site
Angiogenesis Migration Growth

Natural-Killer Cells TNFα


Inhibition of Anti-Myeloma Immunity Dendritic Cells

Monocytes




















Daratumumab (Darzalex)




Classic Chemotherapy
These drugs work by generally destroying cancer cells and are often very effective at reducing the burden of myeloma cells.
Melphalan is one of the most effective drugs in myeloma and has been for over 60 years!
They can often be given at lower doses (often orally) or at higher doses intravenously (high dose melphalan is the drug we give for stem cell transplant)


“Eligible” Patient
Induction Therapy
Collect PBSCs
Freeze
High-dose
Chemotherapy
Reinfuse PBSCs +/- Post-ASCT therapy
Steroids – Dexamethasone (Dex)
These drugs interefere with the communication between myeloma cells and can be effective on their own. They tend to be used to “boost” the effect of nearly all other myeloma drugs. I think of them like booster rockets…

#downwithdex



Proteasome inhibitor Velcade (bortezomib) V or Vel or

Intravenous (IV) or
subcutaneous injection (under the skin) Kyprolis (carfilzomib)
(ixazomib)
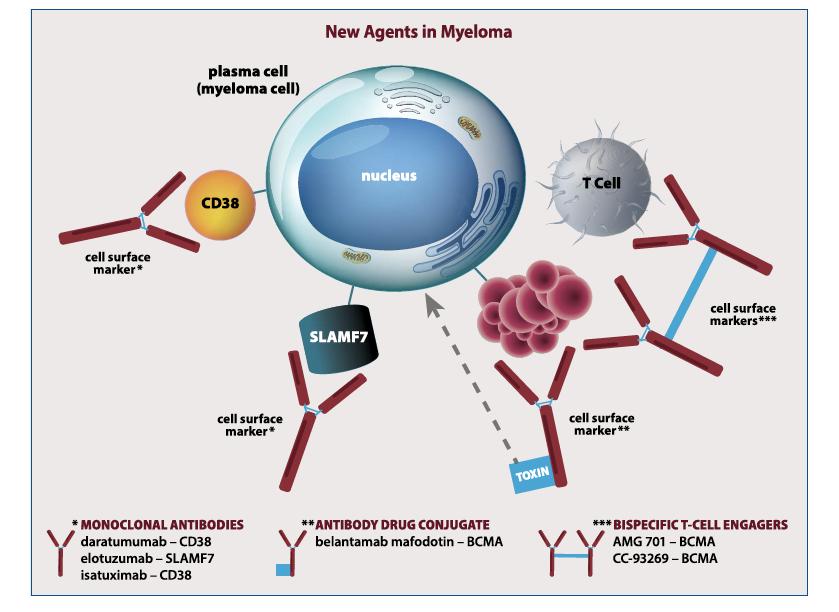

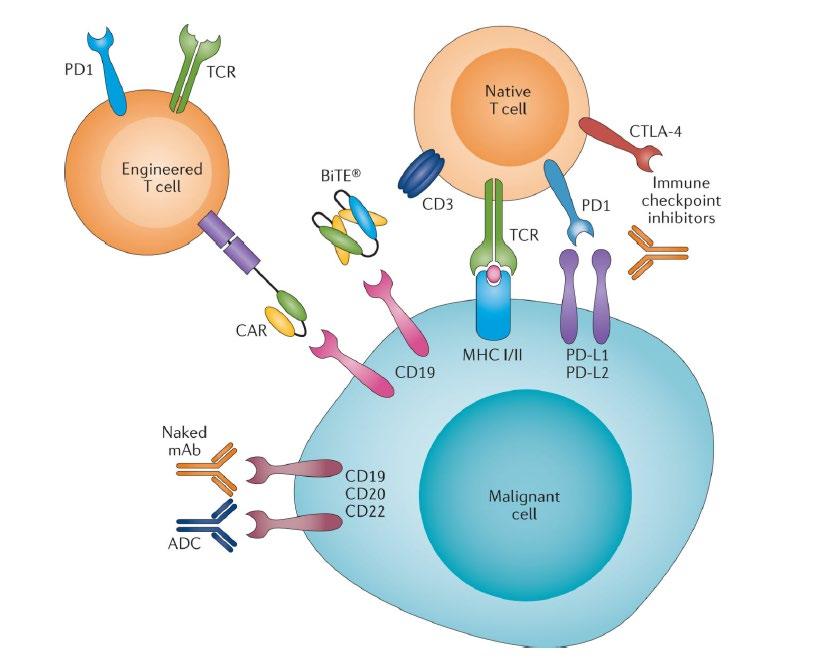
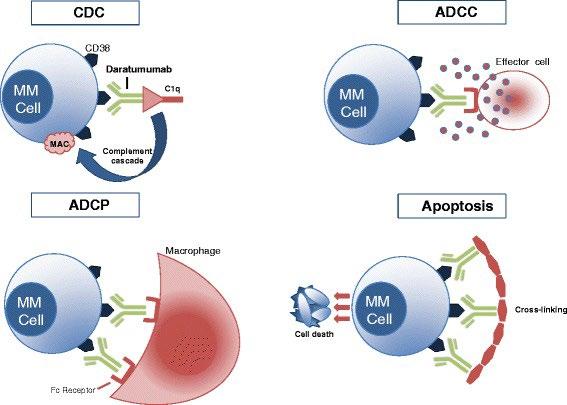
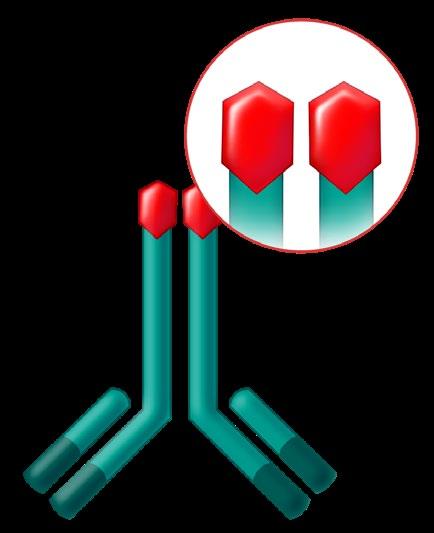
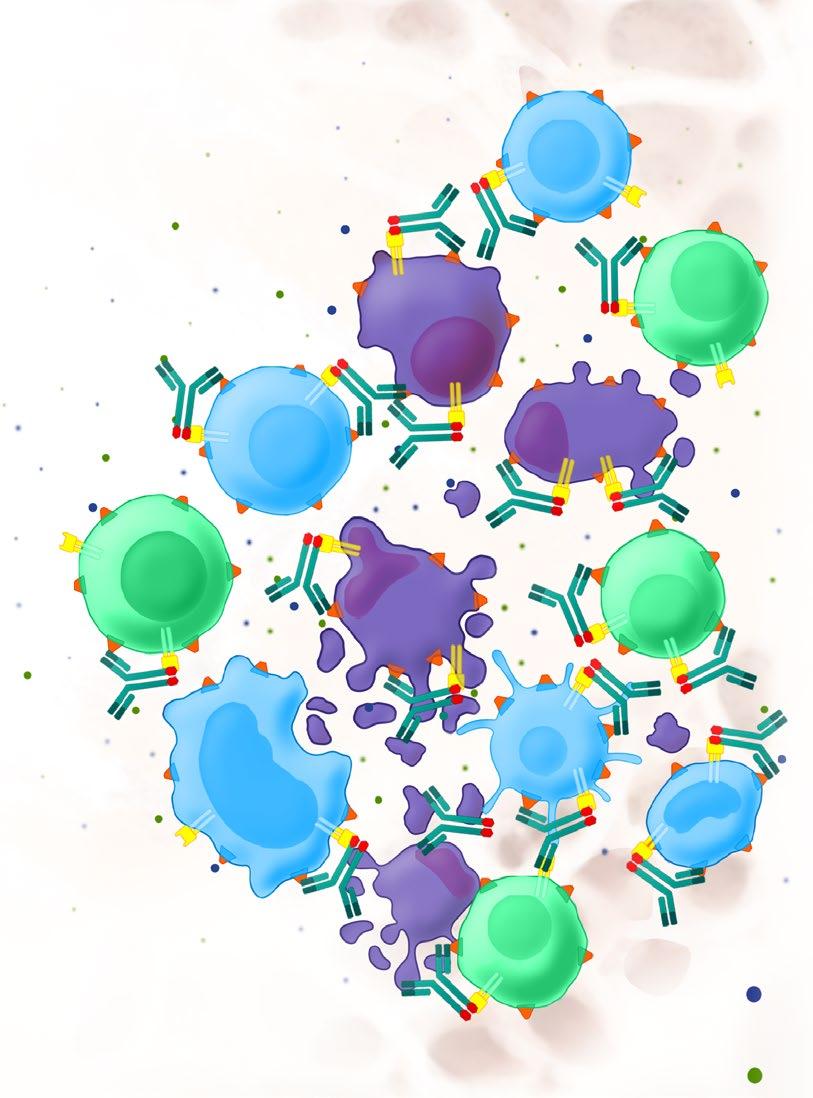
Monoclonal Antibodies

Daratumumab (Darzalex)
Dara or D
Subcutaneous or Intravenous (IV)
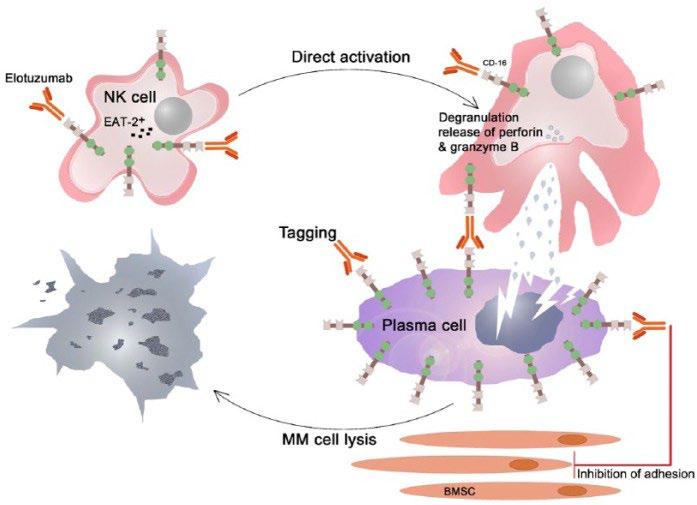
Empliciti (Elotuzumab)

Elo or E
Intravenous (IV)
Isatuximab (Sarclisa) Isa Intravenous (IV)
CD38-Targeted mAb

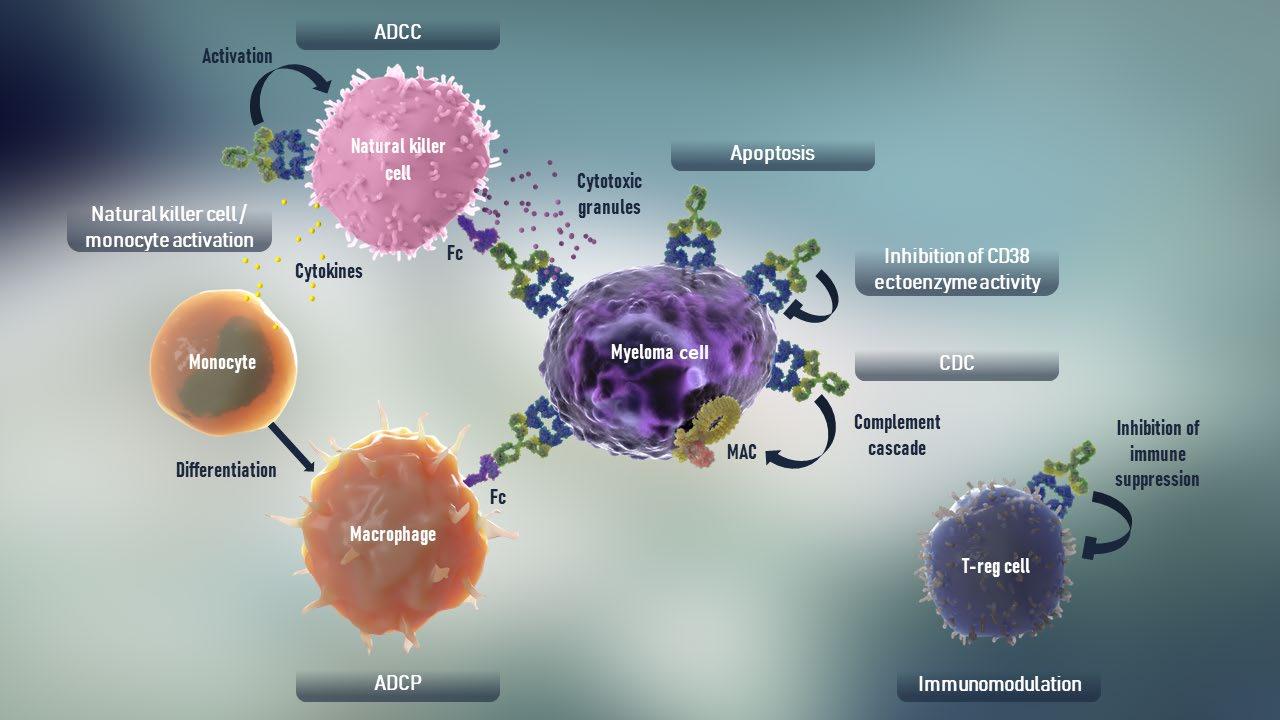
dependent cytotoxicity; MAC = membrane attack complex; ADCC = antibody
SLAMF7-Targeted mAb

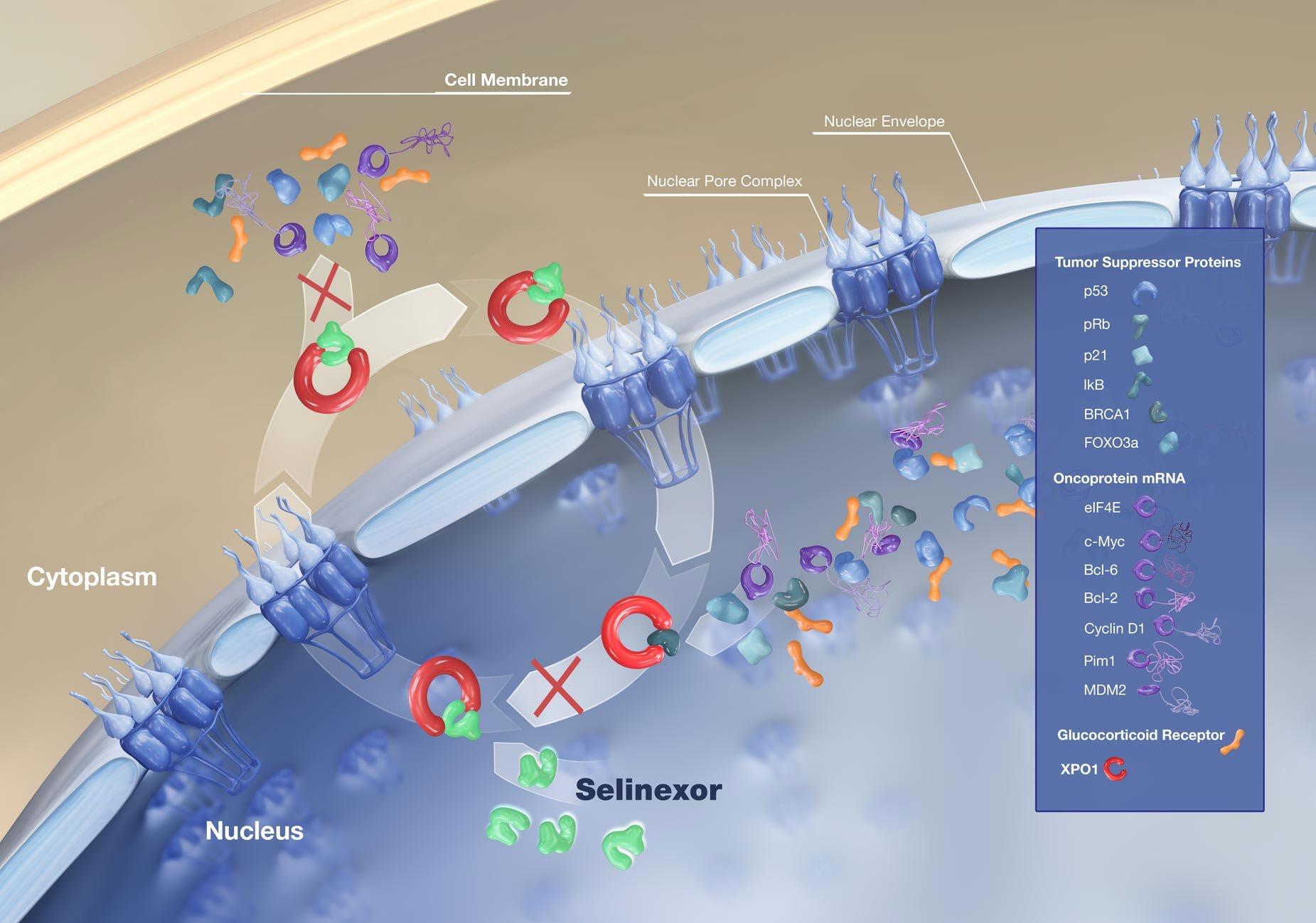


Melflufen


Amino-peptidase
Alkylating moiety






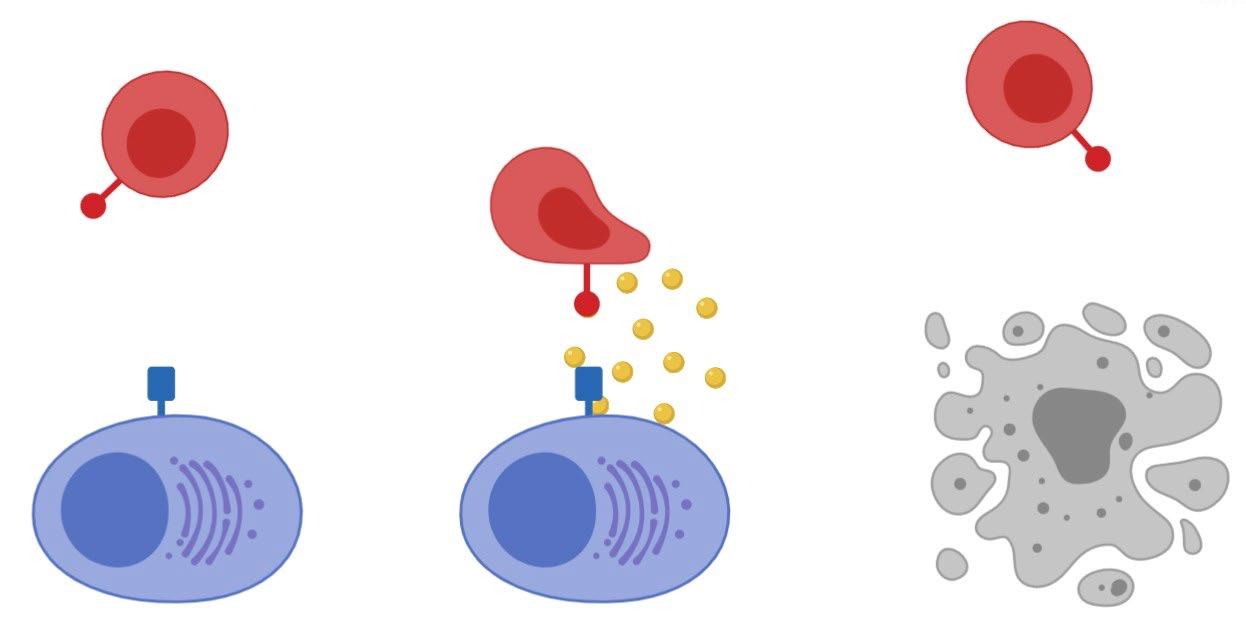
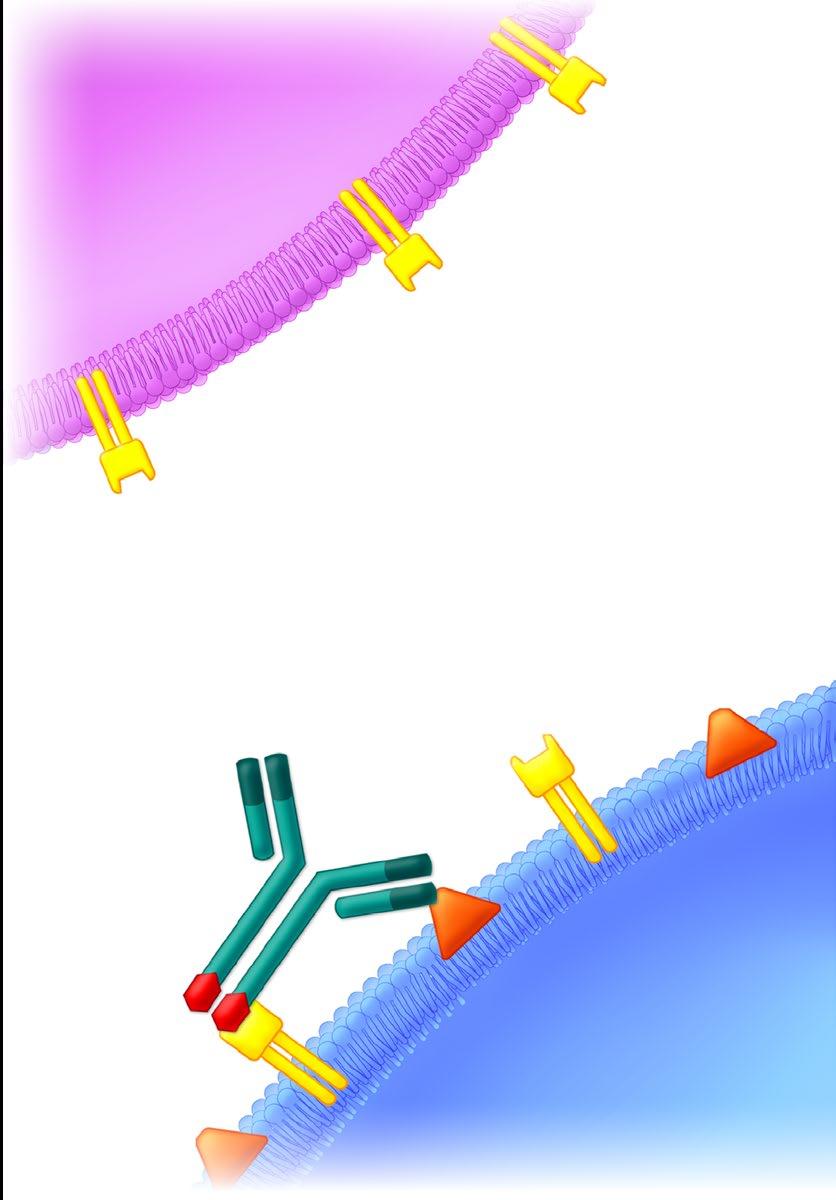
• Incorporates 2 antibody fragments to target and bind both tumor cells and T cells

• Brings target-expressing MM cells and T cells into close proximity, enabling T cells to induce tumor-cell death
• BCMA = B Cell Maturation Antigen



Talquetamab is a novel first-in-class, off-theshelf, T-cell redirecting bispecific antibody directed against a new antigen target called GPRC5D1,2

GPRC5D is a novel antigen target in myeloma that is highly expressed on malignant plasma cells with limited expression in normal human tissues,3-6 including hematopoietic stem cells7
Talquetamab has shown an ORR of 64–70% with QW and Q2W dosing in the phase 1 MonumenTAL-1 study (NCT03399799)8



• Cevostamab has also shown activity in relapsed myeloma with a response rate around





Median previous lines: 4-6
In Cohort E, >50% CD 38 ab refractory
In Cohort F, >60% PI refractory
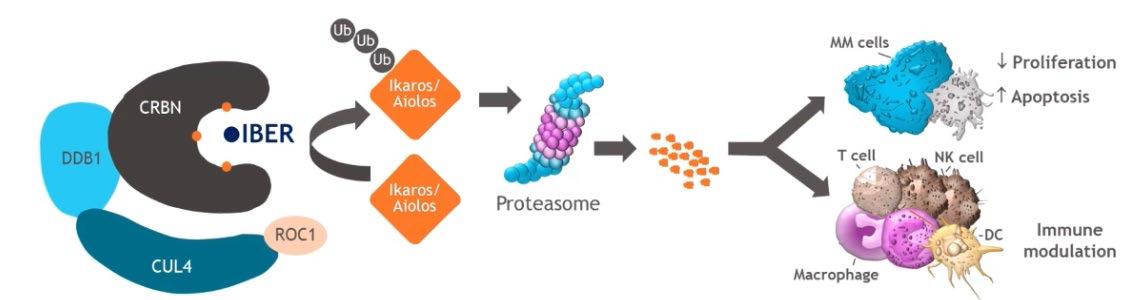
Modakafusp alfa is a first-in-class, innate immunity enhancer that functions through targeted next-generation IFN signaling
The CD38-targeted attenuated IFNα fusion protein displays a 10,000-fold greater specificity than native IFNα for CD38+ vs CD38− cells2
Modakafusp alfa
Binds with high affinity to unique epitope of CD381,2
Signals through IFNAR to:2
• Activate innate and adaptive immune cells1
• Elicit direct antiproliferative/ apoptotic signals to tumor cells2,3
*hIgG4 is a poor inducer of Fc-mediated effector functions, such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and phagocytosis.4
Fc, fragment crystallizable; hIgG4b, human immunoglobulin 4b; IFN, interferon; IFNAR, interferon α receptor; MDSC, myeloid-derived suppressor cell; MM, multiple myeloma; NK, natural killer; Treg, regulatory T cell
Attenuated IFNα

Innate immune cell activation2,4
IFNAR
hIgG4b* with limited Fc functionality2,4
Unique CD38 epitope specificity
Unique CD38 epitope
Adaptive immune cell activation

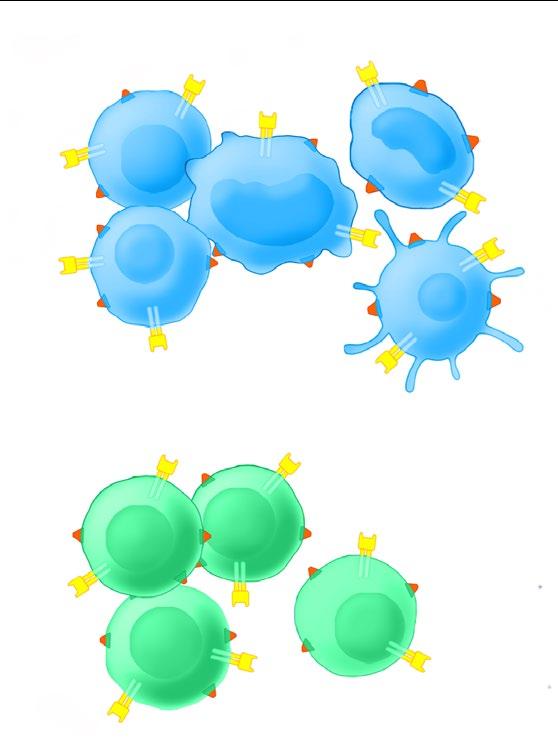
CD38 is widely expressed on innate and adaptive immune cells, MM cells, and subsets of tumor cells of other hematologic malignancies2,5
MM cell anti-tumor effects

Cytokines
MM cell death2,3
Chemokines
1. Vogl DT, et al. Blood 2020;136(Suppl. 1):3197; 2. Pogue SL, et al. PLoS One 2016;11:e0162472; 3. Anguille S, et al. Leukemia 2011;25:739–48; 4. Crescioli S, et al. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2016;16:7;In patient with t(11;14) the bcl2 pathway is upregulated giving the cell
Venetoclax inhibits that pathway…


“immortality”

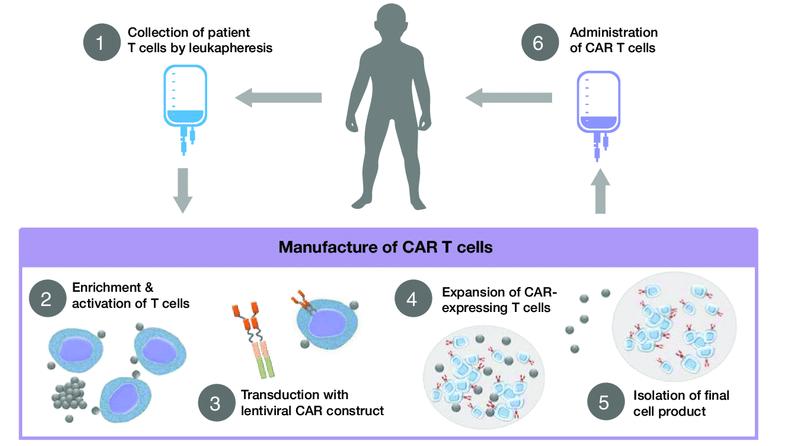
CAR T cell therapy – both Auto and Allo
Bispecifics and tri-specifics – including NK Cell engagers
Targeting BCMA but also: –
GPRC5D – FCRH5
CelMods – Iberdomide and Mezigdomide
Modakafusp • And many combinations of the above!
cereblon

thalidomide lenalidomide pomalidomide
iberdomide
CC-92480
CFT7455
venetoclax
melphalan cyclophosphamide melflufen*












proteasome
daratumumab CD38
isatuximab
BCMA
belantamab mafodotin
idecabtagene vicleucel
ciltacabtagene autoleucel
bispecific antibodies
panobinostat†
HDAC
glucocorticoid receptor

dexamethasone
prednisone
GPRC5D
talquetamab
RG6234
FcRH5
cevostamab
*withdrawal from US market October 2021 withdrawn January 2022
†withdrawn from US market November 2021
• The importance of preliminary research – in the lab

• Animal studies • Phase 1 clinical trials – first in human
Phase 2 and 3 trials
• General principle – start in the areas of “unmet need” = late stage disease – Then agents move up earlier in the disease course – Example – Daratumumab
We are now seeing this process with many drugs like CAR T Cell therapy…
GREAT resources at the IMF homepage – http://myeloma.org

IMF FDA approved drug page (https://www.myeloma.org/multiple-myeloma-drugs)
IMF publications page (https://www.myeloma.org/publications)
“Drugs in Current use for MM”
https://issuu.com/international-myeloma-foundation/docs/myelomadrugs-current-use?fr=sYjBiYTQzNTE1OTI
International Myeloma Foundation

Professor, Translational Genomics Research Institute (TGen)
City of Hope Cancer Center
Director of Myeloma Research and Consultant Hematologist, HonorHealth Research Institute
jmikhael@myeloma.org





