
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Ravindra Murlidhar Gaikwad
At.Po. I-24 floor 4th Datt mehar Heritage Bulding , Pisadewi Chtrpati Sambhajinagar pin code:- 431008
Professor : Anurag Gahalod, Dept. of civil Engineering, GH Raisoni University, Maharashtra, India
Abstract - The comprehensive plan for environmental restoration, rejuvenation, and beautification of khokad lake aims to assess, design, and implement effective strategies for revivingandsustainingfreshwaterecosystems.Lakesarevital natural resources, providing ecological services, supporting biodiversity, and serving as social and recreational spaces. However, many lakes face degradation due to pollution, encroachment, and climate change. This study compares variousrestorationapproachesbasedonecological,economic, and social outcomes.
The plan emphasizes habitat restoration, water quality improvement, erosion control, and sustainable landscaping, ensuring the lake's ecological function is preserved while enhancingitsvisualappeal.Thisresearchprovidesaroadmap for policy makers, environmentalists, and urban planners to restore lake ecosystems as resilient, beautiful, and functional landscapes.
The Khokad Lake, once a vital ecological and cultural resource,hassufferedfromenvironmentaldegradationdueto urbanization, encroachment, pollution, and insufficient management. This comprehensive plan aims to restore and rejuvenate the lake ecosystem, improve water quality, and enhance the surrounding landscape to ensure long-term sustainability and beauty. The plan also advocates for community participation and collaborative governance to ensure successful implementation and maintenance. By adopting a multi-disciplinary approach, this plan seeks to transform Khokad Lake into a thriving, resilient ecosystem thatservesasarecreational,educational,andecologicalasset for future generations.
In this Research comprehensive plan for environmental restorationandrejuvenation&beautificationofkhokadlake: Pilot project on khokad lake at. Chandwad district Nashik
Keywords: - 1. Water Quality Assessment, 2. Ecosystem Health, 3. Sediment Removal, 4. NativeSpecies Plantation, 5. Aquatic Habitat Restoration, 6. Algal Bloom Control, 7. Eco-Tourism Initiatives, 8. Habitat and Biodiversity Monitoring
The degradation of Khokad Lake is not just an environmental concern but a socio-economic one as well. The lake's declining state has limited its potential as a recreationalandtourismresource,whilealsoposinghealth risksduetocontaminationandreducedwateravailability. Thesurroundingareas,onceahubforbiodiversity,havealso seenadeclineinfloraandfauna,furthercontributingtothe lossofecosystemservices.
Recognizingtheurgentneedforaholisticintervention, this Comprehensive Plan for Environmental Restoration, Rejuvenation, and Beautification of Khokad Lake aims to addressthechallengesfacingthelakeanditssurroundings. The plan proposes a multi-dimensional approach that combinesecologicalrestoration,waterqualityimprovement, biodiversityconservation,andlandscapebeautification.By focusing on both environmental health and community engagement,thisinitiativeseekstotransformKhokadLake intoavibrant,sustainable,andaestheticallypleasingnatural resource.
UltimatelythevisionistorejuvenateKhokadLakeintoan ecologicallyresilient,recreationallyaccessible,andvisually appealing site that can serve as a model for urban water body restoration, contributing to the overall well-being of theregionanditsinhabitants.
The Khokhad lakesite issituated 743.00 mabove meansealevel.
Mumbai–Agra National Highway Road passes adjacenttothesite.
Proposed lake site is located at Latitude:20.337212°,Longitude:-74.246375°
Silentfeaturesofproposedproject
Maximumspaceforwaterrestores.
Spaceavailableforhawker’szone.
Theaestheticscopeforspaceisvery.
scopefordevelopingjoggingtrackforcitizens
As the surrounding area of lake having 900m1200mhigh
Hillsspacehasbecomeeffectivecatchmentareafor rainwaterfall.

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

WaterQualityImprovement,HabitatRestoration,Sediment Management, Biodiversity Conservation, Hydrological Restoration,RejuvenationofaLake
Keycomponentsoflakerejuvenationinclude.
Enhancing aesthetics Beautification projects such as landscaping,thecreationof parksorgreenspacesaround the lake, and installing recreational infrastructure like walking trails, viewing platforms, and picnic areas. Improvingthevisualappealofthelakebyaddressinglitter, debris,oranyunsightlyinfrastructure
CommunityEngagementandEducation EcotourismandRecreation
SustainableManagementPractices: FloodControlandClimateResilience:
1.2 Aim
The aim of comprehensive Plan for Environmental Restoration, Rejuvenation, and Beautification of Khokad Lakeistorestoreecologicalbalance,improvewaterquality enhancebiodiversity,andcreateasustainable,aesthetically pleasing natural habitatthatservesboththeenvironment andthelocalcommunity.
1.3 Objectives
ImprovementofWaterQuality
RestorationofAquaticandTerrestrialEcosystems: SedimentandPollutionManagement
FloodControlandClimateResilience
BeautificationandPublicEngagement
Development of Sustainable Recreation and Ecotourism Opportunities
Long-TermSustainabilityandMaintenance
CapacityBuildingandCommunityParticipation
1.4 Outcome Goals:
A healthy, biodiverse lake ecosystem that supports both aquatic and terrestrial life. Improved water quality with reducedpollutionandrestoredecologicalfunctions.
Resilientcommunitiesthatbenefitfromthelake'secological services, such as water supply, flood protection, and educationalopportunities.
A model for sustainable lake management, providing a blueprint for the restoration and management of similar waterbodiesintheregion.
Through this comprehensive approach, the plan aims not only to restore the ecological balance of Khokad Lake but alsotocreateathriving,sustainableresourcethatenhances the well-being of the surrounding communities and promotesenvironmentalstewardshipforfuturegenerations.
1.5 SCOPE
The scope of the Comprehensive Plan for Environmental Restoration, Rejuvenation, and Beautification of Khokad Lake covers a wide range of activities, interventions, and strategies aimed at restoring the ecological health of the lake, enhancing its recreational and aesthetic value, and ensuring long-term sustainability. This scope includes scientific, technical, social, and governance aspects to provide a holistic approach to lake management and revitalization.
1.5.1EcologicalRestorationandBiodiversityConservation RestorationofAquaticEcosystems
ReforestationandRiparianHabitatRestoration
InvasiveSpeciesManagement
BiodiversityMonitoringandConservation
1.5.2WaterQualityImprovement
PollutionControl and WasteManagement:
The scope includes the identification of pollution sources suchasuntreatedsewage,industrialeffluents,agricultural runoff,andsolidwasteandtheimplementationoftreatment measures like constructed wetlands, sediment traps, and stormwatermanagementsystemstoimprovewaterquality.
NutrientLoad Reduction
SedimentManagement
1.5.3HydrologicalManagementandFloodControl
RestorationofNatural Hydrology:
Theplanwillrestorethenaturalflowpatternsofwaterinto andoutofthelaketoimprovewaterretentionandprevent flooding. This may include regulating the inflow of water through channels, canals, or constructing check dams to

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
control water levels during monsoons. Flood Mitigation: Riparianbuffers,wetlands,andfloodplainrestorationwillbe implemented to absorb excess water, reducing the risk of floodsinthesurroundingcommunitiesandprotectingthe lake'secosystemfromtheimpactsofclimatechange.
1.5.4BeautificationandPublicAmenities
LandscapeDesign andGreen Spaces: The plan will develop green spaces and parks around the lake,includingwalkingtrails,gardens,andscenicareasthat enhance the aesthetic appeal of the lake and create recreationalspacesforthepublic.
Public Engagement Zones:Areasforpublicinteraction withnature,includingpicnicspots,educationalcentres,and observationpoints,willbedevelopedtoincreasecommunity involvementandappreciationofthelake.
RestorationofScenicViews:Thelake'svisualappealwillbe enhancedthroughlandscapearchitecture,ensuringitisboth anaturalhabitatandapleasantareaforpublicenjoyment.
1.5.5CommunityEngagementandEducation
CommunityParticipation in Restoration Efforts: Local communities,schools,NGOs,andvolunteerswillbeengaged in the restoration process through awareness campaigns, treeplantingdrives,wastecollectionactivities,andcitizen scienceprograms.
Environmental Education and Awareness Programs: Educationalprogramsontheimportanceoflakeecosystems, sustainablepractices,andtheroleofthelakeinlocalwater supplyandclimateresiliencewillbeestablished,involving localschools,environmentalgroups,andthegeneralpublic.
1.5.6SustainableRecreationandEcotourismDevelopment
Recreational Infrastructure Development: Theplanwilldevelopinfrastructuretosupportsustainable recreation, such as eco-friendly boating, fishing, and birdwatching zones, along with cycling and walking trails aroundthelake.
EcotourismInitiatives:KhokadLakewillbedevelopedasan ecotourismdestination,offering guided tours, educational programs,andwildlifeobservation,allaimedatpromoting environmental conservation and contributing to local economicgrowththroughtourism.
VisitorEducationandResponsibleTourismPractices
1.5.7.SustainabilityandLong-TermManagement
Monitoring and Maintenance Systems: Long-term monitoringofwaterquality,biodiversity,andthesuccessof restoration efforts will be a key part of the plan. Regular
assessmentandadaptivemanagementpracticeswillensure thelake’srestorationcontinueseffectively.
IntegratedGovernanceandStakeholderCoordination:The restoration plan will involve collaboration between local authorities,environmentalagencies,communitygroups,and the private sector to create a governance framework that ensurescoordinatedmanagementofthelake.
1.5.8.ClimateResilienceandAdaptation
Climate Change Adaptation Strategies: The restoration effortswillincorporateclimateresiliencemeasurestohelp thelakeadapttofutureenvironmentalchallenges,suchas changesinrainfallpatterns,temperaturefluctuations,and extreme weather events. These measures will include enhanced flood control, drought-resistant vegetation, and the strengthening of ecosystem services to buffer against climateimpacts.
2.1 Tourbier, J.T., &Piovar, R.A “Managing Urban Runoff: Urban Land Institute Handbook. Urban Land Institute” (1984).
Intermsofwaterqualitymanagement,theplanincorporates strategiessuchascontrollingurban runoff and improving wastemanagementsystems,whichisdirectlyinformedby the work of Tourbier&Piovar (1984). Their focus on managingurbanrunoffthroughsustainablepractices,such as stormwater management systems and treatment measures like biofiltration and constructed wetlands, resonateswiththeapproachesproposedforKhokadLake. This alignment indicates a well-considered approach to mitigating pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial effluents,andurbanwastewater.
The plan also proposes reducing nutrient loading and controllingalgalblooms,whichareknowntodegradewater quality.
2.2 Ostrom E. “Governing the Commons: The Evolution of Institutions for Collective Action” Cambridge University press(1990).
Drawing on Ostrom's (1990) work on governing the commons, the plan's inclusion of a robust governance frameworkforKhokadLakeiscrucial.Ostromarguesthat effective institutions for collective actionin this case, management systems for the lakeare essential for sustainable environmental management. The plan's proposed collaboration between local authorities, environmentalagencies,NGOs,andthecommunityfitswell withOstrom’semphasisonpolycentricgovernance,where multiplelayersofdecision-makingandresponsibilityhelp

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ensure the sustainability of common-pool resources like lakes.
2.3 Pretty,J.“SocialCapitalandtheCollectiveManagementof Resources”.Science,302(5652),1912(2003).
The plan’s focus on community engagement and public education reflects key social principles of social capital as discussed by Pretty (2003). Pretty argues that collective actionandcommunityinvolvementarevitalformanaging environmental resources effectively. This participatory approachhelpsfosterasenseofownership,responsibility, andstewardship,whichiscrucialforthelong-termsuccess ofenvironmentalprojectsliketherejuvenationofKhokad Lake. The social capital framework from Pretty (2003) supports the idea that building trust, enhancing communication,andfosteringcommunitycooperationcan leadtomoresuccessfulmanagementofnaturalresources.
2.4 Ostrom(1990)andPretty“SustainabilityandLong-Term Management”(2003)
The focus on long-term sustainability and adaptive managementisanimportantaspectoftheplanthatreflects an understanding of dynamic environmental change. Incorporating continuous monitoring and adaptive management practices aligns with adaptive governance models as promoted by both Ostrom (1990) and Pretty (2003). The establishment of a monitoring framework to trackthehealthofthelake,coupledwiththeinvolvementof stakeholders in ongoing management, ensures that future ecologicalchallengescanbeaddressedproactively.
2.5 Louv, “Urban Green Spaces and Health: A Review of Evidence”(2008),
Green Urban Spaces: The concept of creating green recreational spaces around water bodies is explored in "Urban Green Spaces and Health: A Review of Evidence" (Louv, 2008), which links the development of parks, walkways,andnaturalrecreationareastoimprovedmental andphysicalheal.
2.6 W.J., & Gosse link, J. G John Wiley & Sons “Mitsch, Wetlands”(2015)
EcologicalRestorationandBiodiversityConservation
ThefirstobjectiveoftheKhokadLakerestorationplanisto improve water quality and restore aquatic ecosystems, whichaligns with the principlesof wetland restoration as outlinedbyMitsch&Gosselink(2015).Wetlands,including lakeslikeKhokad,arecriticaltomaintainingwaterquality, controllingfloods,andprovidinghabitatfordiversespecies. Byfocusingonhabitatrestoration,reforestation,andnative speciesintroduction,theplandrawsfromsoundecological principles, especially the importance of restoring natural hydrologicalfunctions.Mitsch&Gosselink(2015).
2.7 “Maharashtra Pollution Control Board Nashik and MunicipalCorporationChandwaddistrictNashik”Integration withBroaderEnvironmentalManagementPolicies
The plan’s scope also involves policy and regulatory frameworks that align with local environmental laws and regulations, which is in line with the suggestions of MaharashtraPollutionControlBoardandlocalgovernance structures.
2.8 “LakesandReservoirManagement”(NALMS):
Technical Manuals and Handbooks : The North American LakeManagementSocietypublishestechnicalresourceson lake management practices, including erosion control, nutrient reduction, and habitat restoration."Watershed ManagementforPotableWaterSupply
The research and methodology for a comparative plan focused on environmental restoration, rejuvenation, and beautification of lakes requires a structured approach to assess existing conditions, evaluate different restoration techniques,anddesignasustainableactionplan.
Belowisastep-by-stepoutlineoftheresearchmethodology:
3.1 Site Assessment and Data Collection
Objective: To analyse the current condition of the target lake(s) regarding water quality, biodiversity, sediment levels,andsurroundinglanduse.
MethodConductwaterqualityassessments,includingtests forpH,dissolvedoxygen,nutrientlevels(likenitrogenand phosphorus),andcontaminantpresence.
Gather historical climate and rainfall data to understand factorsaffectingthelake’sseasonalhealth.

Fig-2. Watersamplecollection

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Objective:Toevaluateandcomparevariouslakerestoration techniques in terms of their effectiveness, cost, sustainability,andimpactonbiodiversity.
MethodComparetechniquessuchasbioremediation(using plants or microbes to reduce pollutants), dredging (removing accumulated sediments), aeration (improving dissolved oxygen levels), and shoreline restoration (preventingerosion).
Assesseachtechnique’ssuccessbasedondatafromsimilar restorationprojectsandecologicalmodelling.
3.3 Design of Restoration and Beautification Plan
To create a comprehensive plan that integrates ecological restorationwithaestheticimprovementsforthelake.
Method: Develop an action plan for physical restoration activities (e.g., erosion control, native vegetation planting, sedimentremoval).
Designlandscapingandbeautificationelementsthat
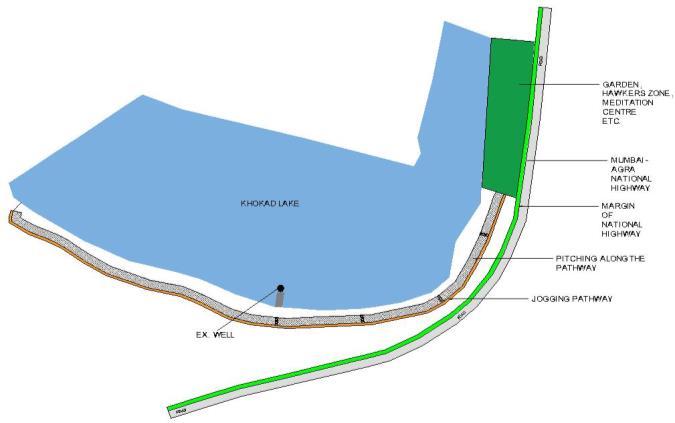
Fig- 3: Beautificationplanoflake
complementnaturalecology,suchaswalkingtrails,native plantgardens,andeco-friendlyrecreationalspaces.
Ensure sustainability by incorporating low-maintenance vegetation,raingardens,andpollutantfiltrationzone
3.4 Implementation and Pilot Testing
Objective:Toinitiatetherestorationandbeautificationplan onasmallscalebeforefull-scaleimplementation. 1.pHTest 2. TurbidityTest3.TDSTest 4.BODtest5.CODtest



-6:TurbidityTest
3.5 Monitoring and Adaptive Management
To ensure the lake’s restored environment remains
sustainableandresilienttofuturechallenges.
3.6 Impact Assessment and Reporting
Toevaluatethesuccessoftheprojectintermsofecological health,communitysatisfaction,andaestheticenhancement.
4. CONCLUSION:
The environmental restoration, rejuvenation, and beautificationofKhokadLakearecriticalforimprovingthe

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 12 Issue: 01 | Jan 2025 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ecological balance, enhancingbiodiversity, and promoting sustainable community development. The plan laid out in this proposal is a holistic approach, combining scientific, technical, and community-driven strategies to restore the health of the lake, improve water quality, and create a vibrant, aesthetically pleasing environment for all stakeholders.
Theproposedinterventions,includinghabitatrestoration, water quality improvement, waste management, and the developmentofrecreationalspaces,willnotonlyrevivethe ecological health of Khokad Lake but also foster social cohesion,supportlocaleconomiesthrougheco-tourism,and createeducationalopportunitiesforfuturegenerations.
As the plan progresses, monitoring and adaptive management will be integral to identifying challenges, measuring success, and making necessary adjustments to maintain and improve the condition of the lake. Collaborative efforts from all involved parties, including government agencies, environmental NGOs, local communities,andprivatesectorpartners,willbecrucialfor achievingtheambitiousgoalssetforthinthisplan.
Ultimately, the restoration of Khokad Lake will serve as a modelforotherwaterbodiesfacingsimilarchallengesand contribute to the broader vision of creating sustainable, resilient,andbeautifulurbanandrurallandscapes.
1.Tourbier, J.T., & Piovar, R.A “Managing Urban Runoff: Urban Land Institute Handbook. Urban Land Institute” (1984).
2.Ostrom,E.“GoverningtheCommons:TheEvolutionof Institutions for Collective Action. Cambridge University Press.”(1990).
3.Pretty,J.“SocialCapitalandtheCollectiveManagement ofResources.Science,302(5652),”(2003).
4. Pretty “Sustainability and Long-Term Management” (2003)
5. Louv, “Urban Green Spaces and Health: A Review of Evidence”(2008),
6. John Wiley & Sons, W.J., & Gosselink, J.G. “Mitsch Wetlands”.2015
7. “Maharashtra Pollution Control Board Nashik and MunicipalCorporationChandwaddistrictNashik”
8.“LakesandReservoirManagement”(NALMS)Technical ManualsandHandbook