












AsthetheColdWarendedandenvironmentalawarenessgrew,the needtocleanupthenuclearweaponscomplexandmilitarybases acrossthenationprovidedthefoundationfora newapproachto environmentalsecurity.
❏ Nuclear facilities and military bases needed to comply with safety & environmental laws and regulations.
❏ Goodman drafted legislation to create new oversight for nuclear facilities as a staffer on the Senate Armed Services Committee.
❏ Growing environmental awareness in the 1990s combined with enforcement of environmental laws led to clean up efforts across the country at military installations.


In1993,Goodmanwasappointedthefirstdeputyundersecretaryofdefense (environmentalsecurity). Amajormilestone inherowncareer,itmarkeda turning pointforourmilitary’s environmentaljourney.

❏ Goodman led efforts to clean up military bases and hundreds of superfund sites around the nation.
❏ DoD launched efforts to conserve natural resources on military bases which have a high density of endangered species.
❏ Engaging with militaries around the world to improve environmental practices helped support America’s national security strategy of promoting democracy and global cooperation on strategic issues.
The 1990’s markeda collaborativechapterinUSRussia relationsintheshared Arctic Region.
❏ The US, Russia, and Norway worked together in the 1990s to reduce the risks of liquid waste from sunken Russian submarines which could contaminate Norwegian fishing areas.
❏ The Arctic Military Environmental Cooperation (AMEC) succeeded in developing a cask (pictured here) to safely offload radioactive and hazardous waste from sunken submarines.
❏ The two nations shared satellite imagery of US & Russian bases to reveal areas of contamination.

In2007,SherriGoodmanconvenedthefirstgroupsofAdmiralsandGeneralsto assess thenationalsecurity implications of climatechange.Intheirinauguralreport, theCNAMilitary Advisory Boardlabeledclimate change a “threatmultiplier.”

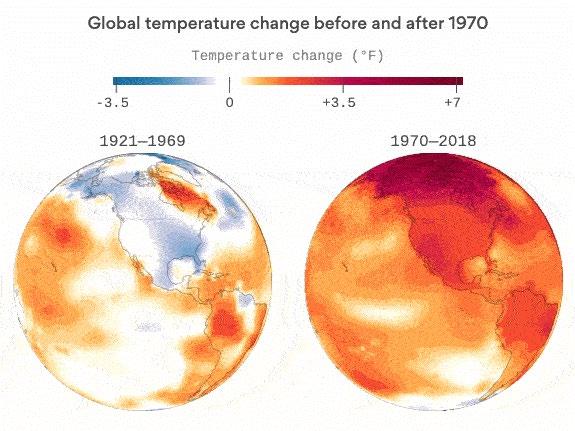










❏ In the Arctic, temperatures are rising four times faster than the global average, resulting in permafrost collapsing and sea ice retreating.
❏ A region once characterized by cooperation is increasingly a zone of competition as a resources become accessible and sea lanes increasingly navigable.
❏ Russia seeks to convert its long northern sea route into a toll road for transportation from ports in Asia to Europe.
❏ China eyes the Arctic as offering shorter global shipping routes, energy resources, and future fishing grounds.


❏ Increasing conflicts between farmers and herders for scarce water resources creates a petri dish for terrorsim, particularly when strong governance is absent.
❏ Terrorist organization, such as ISIS, have weaponized water as a means to take advantage of vulnerable populations and recruit new members to its forces.
❏ As General Tom Middendorp (photo) and others have found, shared water resources also present opportunities for peacebuilding as cross-border communities must work together to manage precious sources of water.
❏ The increasing strength of storms threaten megacities across the region, such as Mumbai, Dhaka, Ho Chi Minh City, and more.
❏ Small island nations face existential risk from sea level rise and loss of fresh water.
❏ U.S. forces prepare to both deter chinese aggression and respond to increased needs for humanitarian assistance and disaster response.


❏ Stronger storms, prolonged drought, and warming oceans imperil South America.
❏ Climate hazards impair sustainable economic growth and fuel migration towards the North bringing both human and narcotics trafficking to the US.
❏ Increasing loss of the Amazon rainforest could lead to a global climate tipping point.
❏ Climate-security cooperation together with supporting economic development can strengthen our regional allies and partners.



❏ Preparing our military for the climate era requires climateproofing installations.
❏ As climate change worsens, bases must be able to withstand stronger storms, higher winds, more frequent floods, and more.
❏ Each base requires a unique climate adaptation plan to ensure it is capable of enduring regional climate changes.
❏ In some cases, climate changes are so profound, the DoD must determine if the base’s mission is worth the financial investment.


❏ DoD is the nation’s single largest energy user.
❏ Disentangling our military’s tether to liquid fuel reduces the logistical burden of constantly moving fuel, protecting the lives of troops charged with this dangerous route.
❏ Today, being mission-ready demands moving away from a fossil-fuel powered force towards one powered by renewables.
❏ Each branch of the service has its own ambitious clean energy transition plan.




(1) Awareness: Improve climate predictions & integrate these forecasts into all aspects of military planning & operations.

(3) Mitigation: Decarbonizing defense improves the military’s readiness by increasing energy security and reducing fuel tethers .

(2) Adaptation: We must harden our military & civilian infrastructure for the worsening climate conditions on our horizon.

(4) Alliances: Climate security & environmental peacebuilding offer opportunities to strengthen our global partnerships as well as chart new pathways towards peace.
“A must read for everyone who wants to understand why climate imperatives aren't just for environmentalists.”
John Kerry



