2 minute read
Research Update from VT
Empowering Turfgrass Management: The Impact of Automated Machine Learning on Dollar Spot Control
By Elisabeth Kitchin, Masters of Science in Plant Pathology, Physiology, and Weed Science Virginia Tech School of Plant and Environmental Science
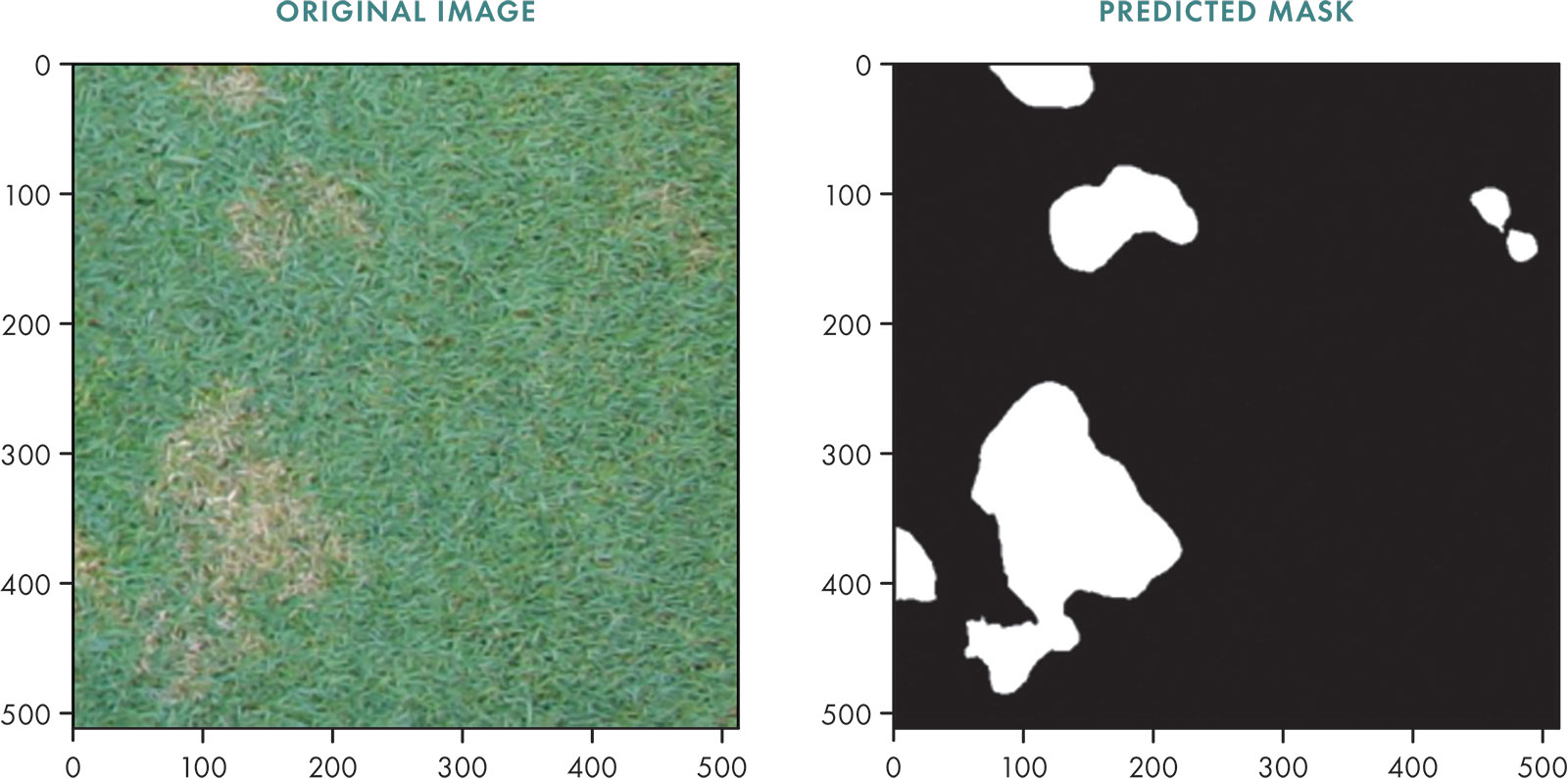
In turfgrass management, dollar spot disease demands precise strategies. This article introduces an advanced machine-learning model for professionals, transforming disease identification and quantification. This research focuses on refining a machine-learning algorithm through extensive training, achieving exceptional accuracy (93%) and precision (76%) in various conditions. This technology streamlines identification, precisely mapping disease spots in turfgrass images.
The automated model is significant for the turfgrass industry, reducing time and human bias in disease quantification by eliminating labor-intensive manual assessments. This shift establishes a standardized methodology, ensuring consistent and reliable disease assessment practices for turfgrass managers.
So, what does this mean for the turfgrass industry?
1. Efficiency Gains: The automation of disease quantification translates to time and resource savings for turfgrass professionals. Managers can promptly implement targeted disease control measures with quicker and more accurate assessments.
2. Consistency Across the Board: Standardized disease quantification ensures consistency in turfgrass management practices. This consistency is pivotal for making informed decisions on disease control strategies, optimizing resource allocation, and promoting overall turf health.
3. Reduced Human Bias: The reliance on automated assessments mitigates the subjectivity of manual evaluations. This reduction in observer bias leads to more reliable and impartial disease quantification, allowing for objective decision-making in disease control and turfgrass maintenance.
4. Enhanced Decision-Making: Armed with accurate and consistent disease data, turfgrass managers can make well-informed decisions regarding disease control measures and overall turfgrass maintenance. This empowers professionals to manage disease outbreaks and optimize turf health proactively.
In conclusion, the implications of this technology are far-reaching, promising a more resilient and sustainable approach to tackling the challenges posed by dollar spot disease. Ongoing efforts are underway to enhance its accuracy further and expand its applicability under diverse conditions. With continued development and validation, this innovative tool will hopefully become accessible to the broader turfgrass community, offering an invaluable resource for industry professionals in their ongoing quest for efficient and precise disease control strategies.