4 minute read
02 Light-Kit House
Computational Prefabrication | Housing
The Light-Kit House redefines sustainable living in the UAE with its innovative design strategies. Featuring a lightweight floor structure, carbon-absorbing concrete, and advanced manufacturing techniques to minimize waste, this modular home offers versatility through configurable parts. Its design prioritizes energy efficiency through thermal mass utilization and electrified systems, while also incorporating an energy production strategy to sustain the house’s needs and provide surplus energy for community water solutions.
Dubai, United Arab Emirates
SU 2023 | Polyhedral Structures Lab
Team Work
Arches have been a fundamental element of architecture for centuries, and they long to be recognized as both structural integrity and aesthetically pleasing. Research has shown that funicular floor system can minimize concrete use with similar structural strength. This project combines both as the basic architecture language, and proposed a high-performance, prefabricated, funicular floor structure.
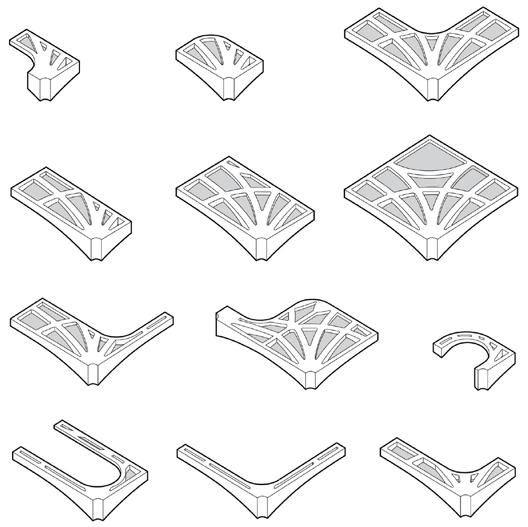

Kit of parts in 2.5x2.5m units
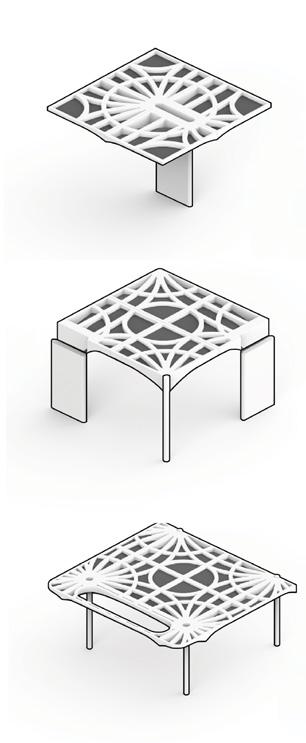
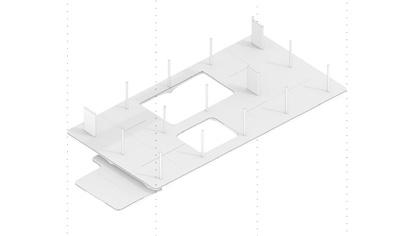
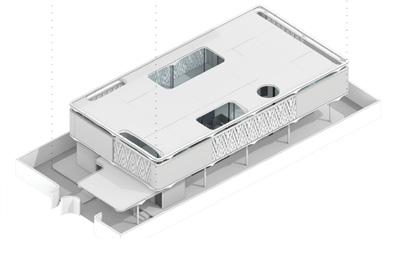
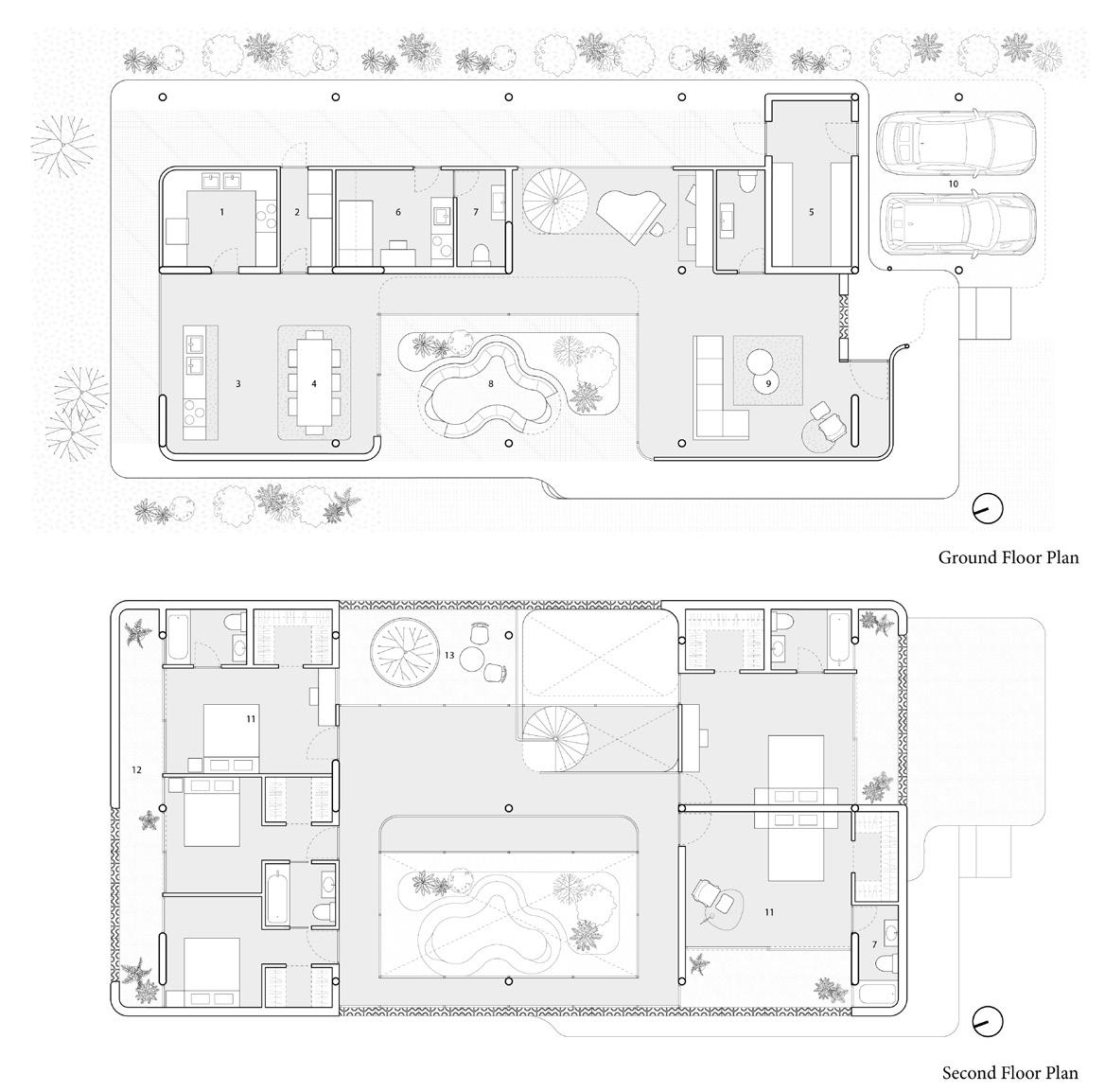
The building structure consists of prefabricated floors and column systems. The floor modules are designed to have compression-dominant structural behavior, similar to vaulted geometries of domes and ancient Middle Eastern designs. The compression-dominant floor can reduce construction materials by 50% and thus significantly minimize carbon emissions and embodied energy of the building. The structure follows a 5x5m grid that can be stacked into two or three stories and take different configurations on the plan to accommodate various performance and roof with multiple courtyards open 2nd floor with perforated walls open plan with column and walls enclosed ground floor wall orientation determined by program complete model
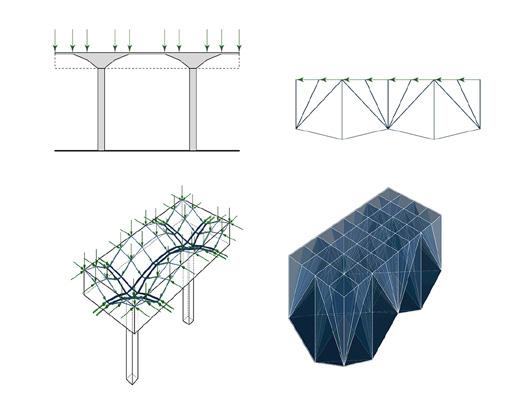
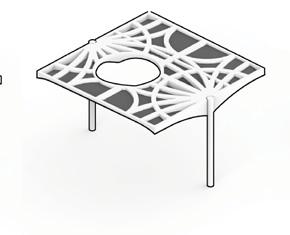

The floor elements are mainly 2.5x2.5m prefabricated units assembled on either columns or structural walls. The structural walls are designed to resist the horizontal forces in the building and to transfer mechanical, electrical, and plumbing from higher floors to lower floors. The prefabricated structural floor is architecturally exposed.
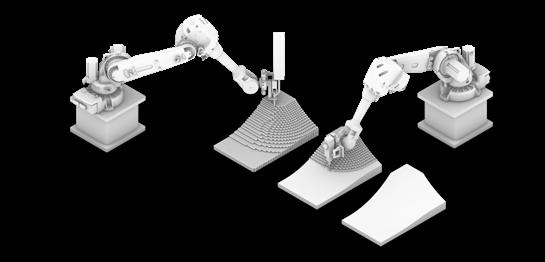
By optimizing the design, mass savings are propagated to all the lateral and foundation systems of the structure, further minimizing the emissions and realizing dramatic savings compared to traditional processes. These elements are fabricated using 3D printing technologies in prefabricated settings to eliminate the need for formwork, a significant contributor to construction waste and inefficiency. To achieve a higher level of precision, the printed samples will be numerically machined immediately after robotically printed to produce smooth surfaces and precise connection points for assembly. This process, called the additive-subtractive process, minimizes the waste and the need for formwork for prefabricated parts.

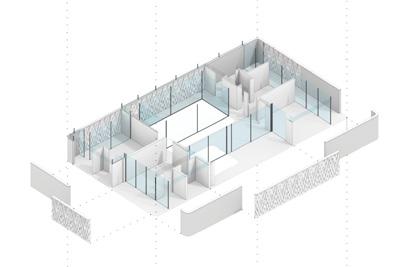
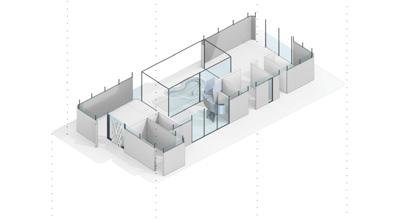
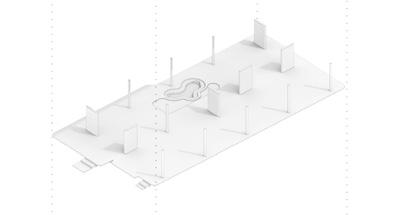
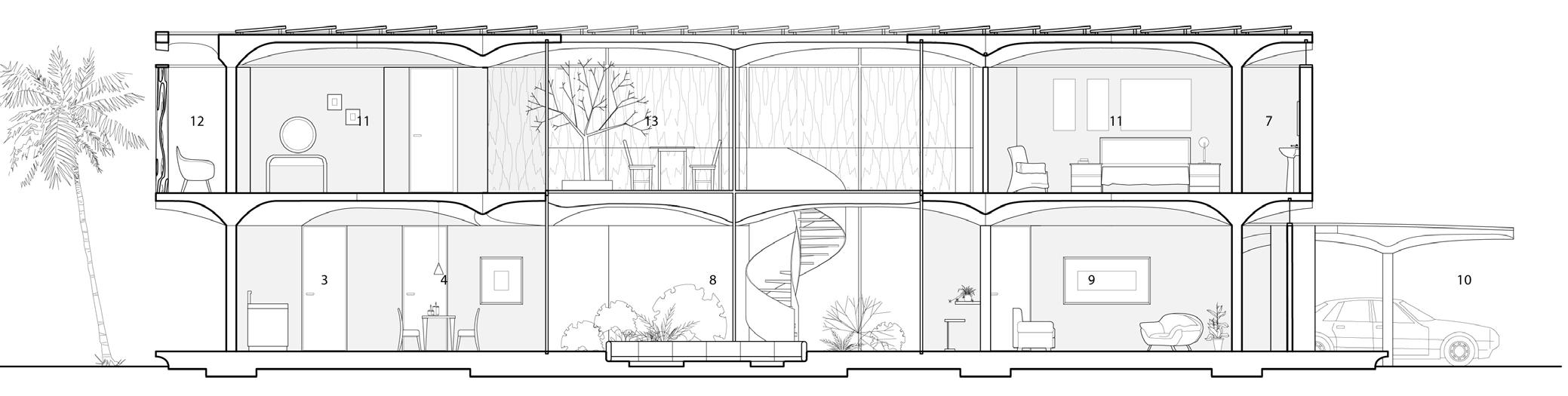
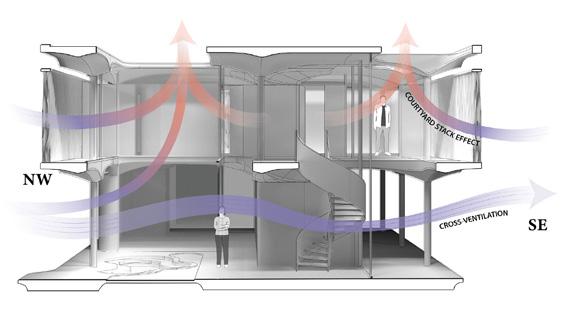
The first floor’s openness facilitates the cross-ventilation, which allows residents to enjoy the sea breeze coming from the north-west direction. Moreover, the second floor’s 3D-printed lattice screens accept the wind and reject the warmed air through open roofs. This buoyancy-driven ventilation draws fresh air from outside while refusing warm indoor air.


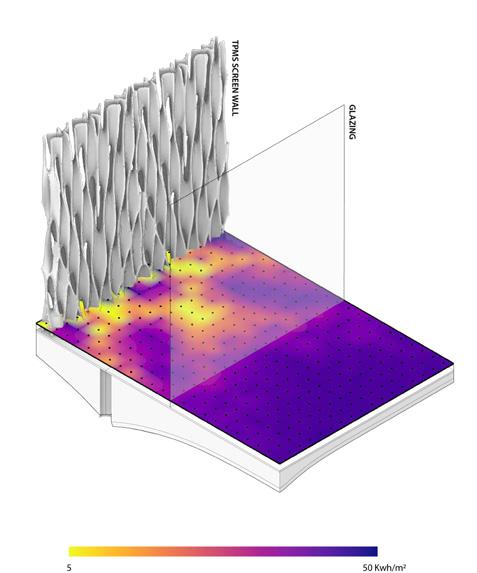
The concrete 3D-printed TPMS screen facades allow the air to penetrate through its perforated geometry. The CFD analysis validates its air permeability. Moreover, the speed of air gets faster when it passes the narrow pores due to the funnel effect. The lattice facade with optimized pore size not only allows natural ventilation but also provides residents with private living environments.