




- By end of the Spring term I can
Write expanded noun phrases for description and specification (Y2)
Use prepositions to express time, place and cause Group related ideas into paragraphs
Use inverted commas to punctuate direct speech Use conjunctions and adverbs to express time, place and cause use a or an correctly create settings, characters and plot indicate possession by using the possessive apostophe with singular nouns Use present and past tenses correctly and consistently including the progressive form and the present perfect form group related ideas into paragraphs use inverted commas to punctuate direct speech (using dialogue to show relationship between characters)
Build an increasing range of sentence structures use adverbs to express time, place and cause choose nouns or pronouns appropriately for clarity and cohesion to avoid repetition use inverted commas to punctuate direct speech
- By end of the Spring term I can
Expand noun phrases by the addition of modifying adjectives, nouns and prepositional phrases
choose nouns or pronouns appropriately for clarity and cohesion and to avoid repetition use fronted adverbials organise paragraphs around a theme use commas after fronted adverbials
Use Standard English forms for verb inflections
Extend the range of sentences with more than one clause by using a wider range of conjunctions including when, if, because, although Build a varied and rich vocabulary Indicate possession by using the possessive apostrophe with plural nouns Recognise the difference between plural and possessive ‘s’
Variety of verb forms used correctly and consistently including the progressive and thepresent perfect forms
Use Standard English for verb inflections
Organise paragraphs around a theme (using fronted adverbials to introduce or connect paragraphs)
Use and punctuate direct speech (using dialogue to show the relationship between characters)
Build an increasing range of sentence structures
Expand noun phrases by the addition of modifying adjectives, nouns and prepositional phrases choose nouns or pronouns appropriately for clarity and cohesion to avoid repetition Use and punctuate direct speech Use commas after fronted adverbials
6 Green Forms recognisable lower-case letters, most of which are correctly formed. Uses the Tree Symbol to learn and practise letter formation, orientation and placement Understands which letters belong to which handwriting families (Jumper, Abracadabra, Window Cleaner, Special Squirter, Fisher and Slider)
7 Orange Forms recognisable lower-case letters, starting and finishing at the right place Forms capital letters correctly, Forms digits 0-9 correctly, Writing sits on the line.
8 Turquoise Forms lower-case letters and capital letters correctly, starting and finishing at the right place. Lower-case and capital letter sizing may not yet be consistent. Uses spaces between words that reflects the size of the letters
9 Purple Forms lower-case letters and capital letters of the correct size relative to one another All letters are written in the correct orientation, and relationship to one another, in preparation for joining. Uses adequate and consistent spaces between words
10 Gold Begins to use some of the diagonal and horizontal strokes needed to join letters Starts to understand which letters when adjacent to another are best left unjoined.
11 White More consistently uses the diagonal and horizontal strokes needed to join letters. More consistently leaves the appropriate adjacent letters unjoined Spaces between words continue to be consistent
12 Lime Writes with increasing legibility, consistency and quality. Ensures that the downstrokes of letters are parallel and equidistant. Ensures that ascenders and descenders of letters do not touch
13 Brown Writes legibly, fluently and in a consistently joined way (may show an individual style). Writes with increasing speed

- By end of the Spring term I can spell the following words:
accident actual address appear believe build busy caught circle complete consider decide different early earth eight enough experiment
extreme February forward fruit grammar group heard heart important interest island learn length material minute natural occasion
- By end of the Spring term I can spell the following words: accidentally actually answer arrive breath breathe business bicycle centre century certain continue calendar describe difficult disappear notice
eighth exercise experience famous favourite guard guide height history imagine increase knowledge library medicine mention naughty occasionally opposite
Preposition: Links a
noun, pronoun or noun phrase to another word.
Often a location, direction or relation of time: The dog ran to her. Put it in the box. I haven’t seen him since yesterday.
Conjunction: Links words or phrases.
Co-ordinating conjunction - links equal words or phrases: Bring your bucket and spade.
Subordinating conjunctionintroduces a subordinate clause: He put on his coat because it was forecast to rain.
Determiner: Specifies a noun.
Definite article: the Indefinite article: a, an Demonstratives: this, those Possessives: e.g. my, your Quantifiers: e.g. some, every

Pronoun: Used in place of a noun or noun phrase:
Mark smiled at Laura. He smiled at her.
Shall I take the cakes? Shall I take those?
Possessive pronoun
Used in place of a noun or noun phrase:
Ahmed’s bag
His bag
It was the girls’ turn. It was their turn







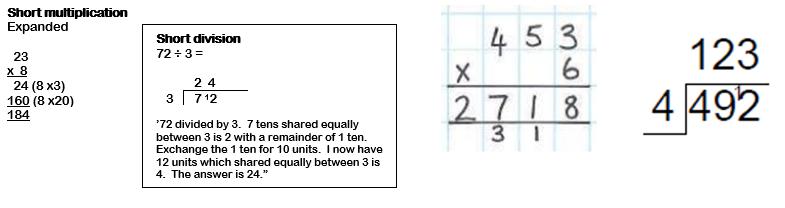
Knows the relative position of numbers.
Knows zero as a place holder in three-digit numbers. Knows the rules of rounding
Knows efficient mental strategies including partitioning and adjusting for addition and subtraction.
Knows how to calculate with columnar methods regrouping the tens and exchanging in subtraction
Multiplication & Division Measure
Knows the 2, 3, 4- and 8-times tables and the doubling patterns, odds and evens.
Knows how to multiply using partitioning. Knows how to find corresponding division facts Knows how to partition numbers when multiplying in a grid/short method.
Knows how divide and record remainders.
Knows how to recognise multiples of a divisor.
Knows how to measure accurately reading the marked divisions in the appropriate units
Geometry
Know and recognise right angles in 2d shapes.
Knows acute and obtuse in relation to right angles Knows how to describe lines using mathematical terms
Calculations:
Knows the correct notation and strategies for calculating with money
Knows how to select and efficient method when calculating with all four operations
Knows how to add and subtract within the same denominator.
Knows that tenths occur when an object or number is divided into 10 equal parts
Statistics:
Knows how to interpret and analyse data
Knows the relative position of numbers.
Knows zero as a place holder in three-digit numbers. Knows the rules of rounding
Knows efficient mental strategies including partitioning and adjusting for addition and subtraction.
Knows how to calculate with columnar methods regrouping the tens and exchanging in subtraction
Multiplication & Division Measure
Knows the 2, 3, 4- and 8-times tables and the doubling patterns, odds and evens.
Knows how to multiply using partitioning. Knows how to find corresponding division facts Knows how to partition numbers when multiplying in a grid/short method.
Knows how divide and record remainders.
Knows how to recognise multiples of a divisor.
Knows how to measure accurately reading the marked divisions in the appropriate units
Geometry
Know and recognise right angles in 2d shapes.
Knows acute and obtuse in relation to right angles Knows how to describe lines using mathematical terms
Calculations:
Knows the correct notation and strategies for calculating with money
Knows how to select and efficient method when calculating with all four operations
Knows how to add and subtract within the same denominator.
Knows that tenths occur when an object or number is divided into 10 equal parts
Statistics:
Knows how to interpret and analyse data




























By end of the Spring term all children should be able to:
locate the world’s countries, using maps to focus on Europe (including the location of Russia) and North and South America, concentrating on their environmental regions, key physical and human characteristics, countries, and major cities
Year 3 Checklist:
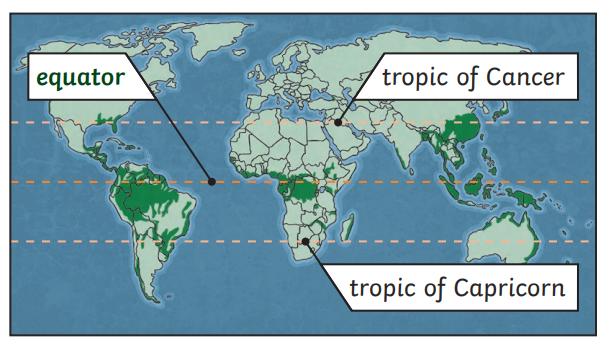
I can describe the climate(s) surrounding the equator.
I can state which photographs were taken close to the Equator and further away
I can use an atlas to build knowledge of the wider world.
I can use symbols and a key on maps and O.S. maps to build knowledge of the wider world.
I can use symbols and a key to build knowledge the wider world
Year 4 Checklist
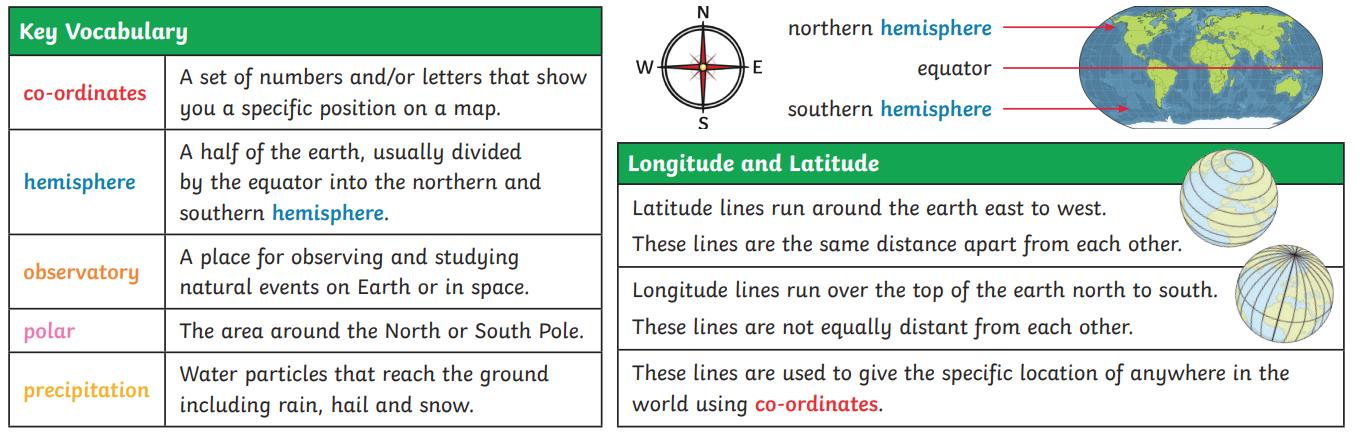
I can use 4 figure grid references to build knowledge of the wider world I can name some countries in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres and close to the Equator.
I can identify the position of Prime/Greenwich Meridian.
I can identify different time zones.
I can explain the significance of longitude and latitude
I can explain the significance of the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
I can use eight points of a compass to build knowledge of the wider world
I can use 6 figure grid references to build knowledge of the wider world

The Arctic region is home to the North Pole.

The Arctic polar region consists of the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas, parts of Alaska, Canada, Finland, Greenland, Iceland, Noway, Russia and Sweden.

The Arctic region is found in the northernmost part of Earth.
Indigenous people who live in the Arctic have adapted to the cold weather and harsh environmental conditions.
The coldest recorded temperature in the Arctic is around −68 °C (−90 °F).

Over recent years, the Arctic region has shrunk due to global warming.
Small shrubs can grow in warmer parts of the Arctic, as well as various herbs, mosses and lichens.
A number of different types of animals make their home in the arctic, including polar bears, wolverines, squirrels, birds, walrus and seals.



The Arctic has a number of natural resources, including fish, oil, gas and various minerals.

Antarctica is the southernmost continent on Earth.

The South Pole is found in Antarctica.
Antarctica is surrounded by the Southern Ocean.
Antarctica is bigger than Europe and almost double the size of Australia. Most of Antarctica is covered in ice over 1.6 kilometres thick (1 mile).
Because it experiences such little rain, Antarctica is considered a desert.
The coldest recorded temperature on Earth occurred in 1983 at Vostok Station, Antarctica, measuring a rather chilly −89.2 °C (−128.6 °F).
While humans don’t permanently reside in Antarctica, several thousand people live and work at various research facilities found on the continent.
While Antarctica features harsh living conditions, a number of plants and animals have adapted to survive and call the icy continent home.

Well known animals that live in Antarctica include penguins and seals.


Around 90% of the ice on Earth is found in Antarctica.
Sea levels would rise around 60m (200ft) if all
Head to the opposite end of the globe and check out our fun Arctic facts.

Year 3
Can use words which mark the passing of time e.g. moving from simple ‘before and after’ to use words such as during or while Children make simple deductions about what text means based on what is included e.g., the teacher in the photograph of Victorian school is holding a cane, they must be strict. Can identify differences between versions of the same event e.g. the video gives a different view to what we have just read.
Year 4
Can talk about three periods of time Begins to think of reasons why a source might be unreliable e.g., view of the Vikings may be partial because the evidence we have was written by people who suffered most at the hands of these raiders Can understand that people create different versions of the past for different audiences and therefore might give a different emphasis

Chieftain – The leader of a village or small group of people
Danelaw – The area of England ruled by the Vikings Freeman – A person who is not a slave and free to choose who he or she worked for Longship – A Viking ship with a sail and oars, also called a dragon ship
Monastery – The building where monks live
Pagan – A person who believed in many gods
Runes – The name given to the Viking alphabet
Thatched – A roof covered in straw
Trader – A person who sells good
The Vikings came from the modern Scandinavian countries of Denmark, Norway and Sweden. They travelled in boats called longships and first arrived in Britain around AD 787.

The Vikings raided places such as monasteries and pillaged expensive items to trade They were looking for valuable goods like gold and jewels, imported foods and other useful materials
The Vikings also wanted to claim land and tried to take over much of Britain. They invaded and settled in Scotland before heading south to places such as York By AD 878 the Vikings had settled permanently in Britain
The kings of Anglo-Saxon Britain each ruled their own kingdom and the people in it They fought to defend their kingdom or take control of other kingdoms When the Anglo-Saxons first settled in Britain, there were seven kingdoms, but by AD 878 there was just one kingdom left (Wessex) as the others had been overrun by the Vikings. Many Anglo-Saxon kings tried to resist the Vikings and fought hard to keep control of their land King Alfred the Great was the best known Anglo-Saxon king and the first to defeat the Vikings in battle.

AD 1042 – Edward the Confessor became King He was known as ‘the Confessor’ because he led a very religious life and was very kind and thoughtful.
AD 1066 – Harold II tried to stop Harald of Norway from invading England and killed him in the Battle of Stamford Bridge William, the Duke of Normandy, thought he should be king so came to fight Harold in the Battle of Hastings (AD 1066).
Harold was shot through the eye with an arrow and died in the battle William of Normandy, who became known as William the Conqueror, became King, bringing the Viking and Anglo-Saxon age to an end in AD 1066.

Farms - Vikings lived on farms and kept cows, pigs and sheep for milk, wool and meat.
Houses - Walls made of stone or wood A straw roof Wattle and daub (sticks and mud/dung) for the inside of the walls.
Jewellery - Worn to show off how rich a person was Pagans - Vikings arrived as pagans but eventually converted to Christianity.
Sagas - Vikings used rhyme to tell stories about adventures and battles against monsters
Science- Animals including humans
In the Spring term I will learn to:
Year 3
Identify that animals, including humans, need the right types and amount of nutrition, and that they cannot make their own food; they get nutrition from what they eat.
Identify that humans and some other animals have skeletons and muscles for support, protection and movement.
Year 4
Recognise that living things can be grouped in a variety of ways.
Explore and use classification keys to help group, identify and name a variety of living things in their local and wider environment.
Recognise that environments can change and that this can sometimes pose dangers to living things.
Describe the simple functions of the basic parts of the digestive system in humans.
Identify the different types of teeth in humans and their simple functions.
Construct and interpret a variety of food chains, identifying producers, predators and prey.



To
herbivore An animal that eats plants
carnivore An animal that feeds on other animals
omnivore An animal that eats plants and animals.



producer An organism, such as a plant, that produces its own food.

predator An animal that hunts and eats other animals.
prey An animal that gets hunted and eaten by another animal.