
7 minute read
8.4 The ouTComes of The ComparaTive analysis: publiC survey and user perspeCTive
8.4 The outcomes of the comparative analysis: Public survey and user perspective
The research phase helped us understand the importance of the presence and utilisation of public spaces towards the branding of a city and its popularity amongst the people. Our previous analyses demonstrated the presence and underutilisation of the said public spaces which is scarce. Since it was possible to visit our primary case, Dubai and observe the users presence, it was necessary for us to conduct an online survey to collect similar user data for our secondary cases, Singapore and Kuala Lumpur. In October 2021 we created an online form and circulated it through social media, friends and acquaintances to about 40-45 responses for each of the three cities. The responses included city residents as well as frequent flyers.
Advertisement
The online form was structured in a simple and easy to answer format with multiple choices for the subjects to choose from. The first couple of questions determined the age and the city experienced by the subject and they were redirected to relevant questions about the selected city. The next part consisted of three sections, the first part focused questions on the public spaces mentioned in this research and their popularity among our subjects. The second part focused on the accessibility to these spaces and the mode of transportation used. The final part consisted of space for suggestions and improvements the subjects would like to see in the near future.
This research was conducted to verify and analyse if the public had similar opinions as us. We found them to run almost parallel with our thoughts as an urban designer and planner. For example, the mode of transportation most utilised by our subjects in Dubai was private vehicles whereas in Singapore and Kuala Lumpur it was distinctly public transportation and slow mobility which was almost absent in Dubai.
*Find graphical representation of the results from the survey in annex
Diagram methodology for the online survey conducted by the authors (Source: Author, Mariette Robin)
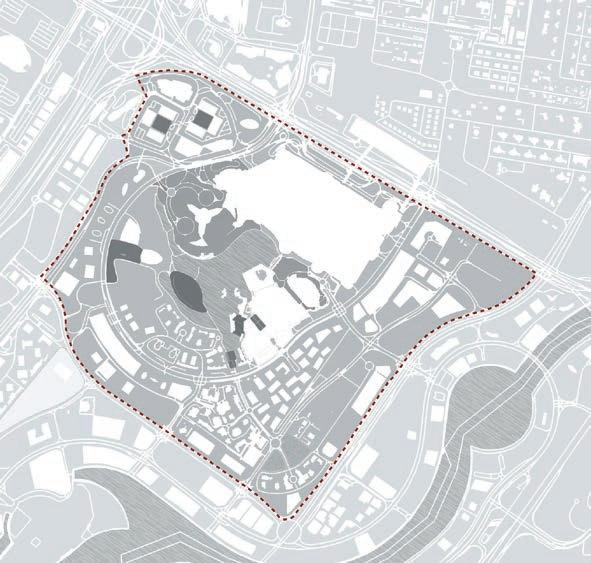
User-experience in Downtown, City Walk and Boxpark
To understand the evolution of public spaces from Dubai downtown to City Walk and Boxpark, a social gravity indication is provided to understand the frequency and popularity of use of the public spaces in these 3 developments. While in the case of Dubai downtown, the indoor spaces such as shopping malls and Opera experiences heavy influx of visitors and tourists throughout the year in comparison to the dedicated public plazas in Dubai downtown and City Walk. City Walk is an experiential development encouraging pedestrian and cycling activities with various types of public spaces. Whereas Boxpark is an entire stretch of public realm that has been gaining popularity among visitors. Public



spaces have been indicated on the maps based on a public opinion poll conducted on site and based on our personal experience of visiting the three sites of study. The enriched analysis has enabled to indicate a popularity of each public space among Dubai residents and tourists.



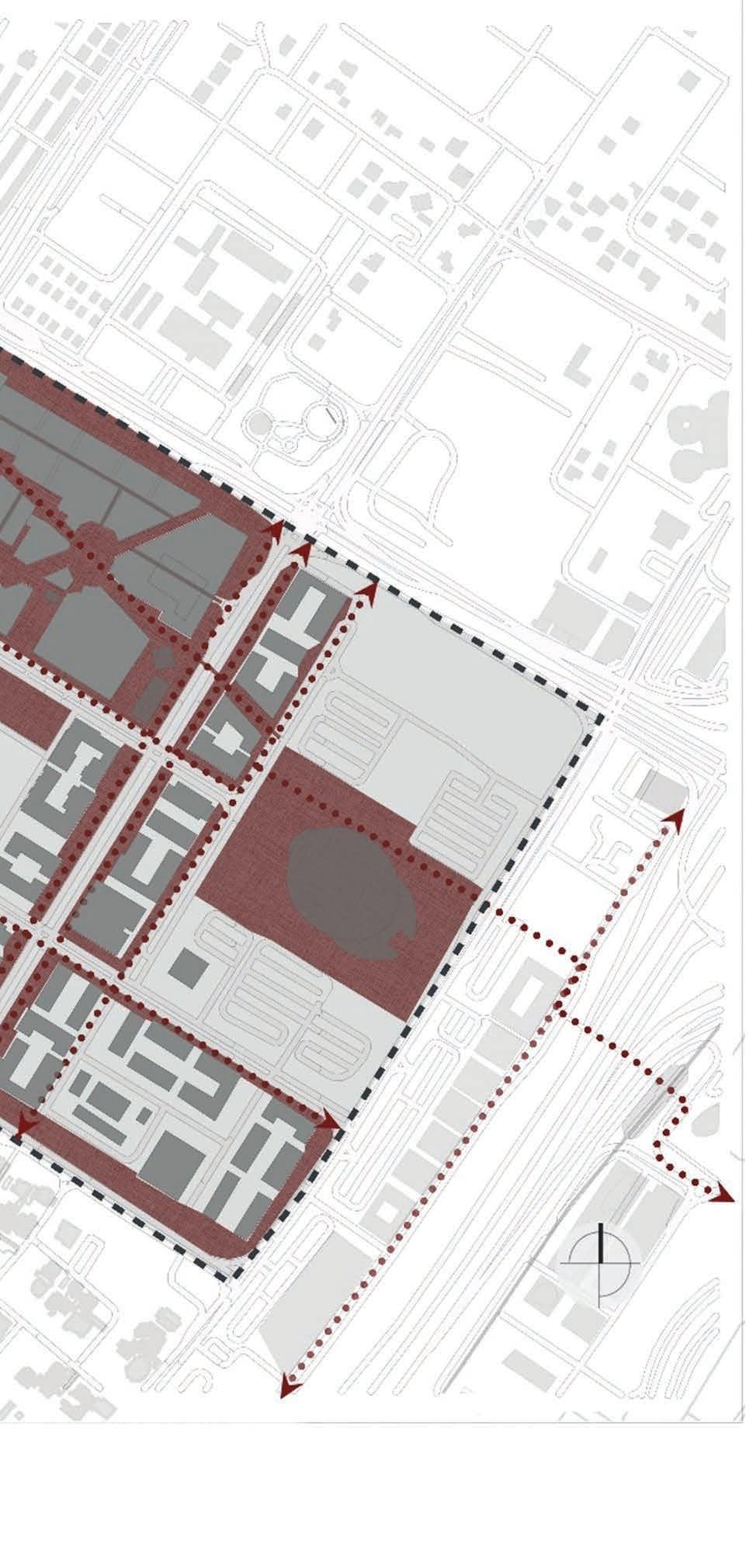
Walkability in Dubai downtown, City Walk and Boxpark
Though dedicated walkways are present in all three cases, the comfort level varies considering the arid environment. Walking is made more experiential in City Walk as it is pleasant all year round. In downtown, the disconnected pathways with scarce urban furniture has a scope for improvement. In the case of Boxpark which functions as an independent unit, the absence of viable walkways from City Walk and Downtown plays an important role in its low number of users.







Public spaces in Dubai downtown, City Walk and Boxpark




Area: 11000 sq.m Type: Open plaza No artificial shade or natural vegetation
Presence of waterbody:
Around the plaza Location: Central plaza with view of Burj khalifa, fountain, Dubai mall & Souq al bahar Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways Area: 4800 sq.m Type: Open plaza Partially shaded by artificial roof
Presence of waterbody:
Central fountain Location: Central plaza with quadratic axes connecting major locations of City Walk. Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways Area: 800 sq.m Type: Open plaza No artificial shade or natural vegetation
Presence of waterbody:
None Location: On the edge of the street Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways


Public spaces in Dubai downtown, City Walk and Boxpark



Area: 3800 sq.m Type: Open plaza Existing natural vegetation doesn’t provide shade from sun
Presence of waterbody:
None Location: Entrance plaza known as Burj Plaza Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways Area: 2200 sq.m Type: Shaded plaza Partially shaded by artificial roof
Presence of waterbody:
None Location: Entrance plaza with grand roofing Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways Area: 560 sq.m Type: Open plaza No artificial shade or natural vegetation
Presence of waterbody:
None Location: On the edge of the street Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways




Walkability in Dubai downtown, City Walk and Boxpark



Type: Open pathways No artificial shade or natural vegetation Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways Type: Shaded pathways Shaded by artificial roof Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways



(Source: Author, Sneha S Kumar)



Type: Shaded pathways Shaded by artificial roof Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways
Walkability in Dubai downtown, City Walk and Boxpark





Type: Open pathways with ample urban furnitures. Unshaded by existing vegetation Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways Type: Open pathways with ample urban furnitures. Unshaded by existing vegetation Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways Type: Open pathways with ample urban furnitures. Unshaded by existing vegetation Access: By pedestrian and cycling pathways


(Source: Author, Sneha S Kumar)













