Correlation Between Brand Reputation Damage & Hotline Reports
 Kyle Welch, Professor | George Washington University School of Business
Kyle Welch, Professor | George Washington University School of Business

 Kyle Welch, Professor | George Washington University School of Business
Kyle Welch, Professor | George Washington University School of Business
Kyle Welch Professor / George Washington University School of Business

Previous Professional Experience:
• The Stanford Management Company – institutional investor for the Stanford University Endowment


• Standard & Poor’s – valuation consultant
Education:
• Harvard Business School – Doctorate
• Brigham Young University – Undergraduate
• Overview of Key Findings
• Initial Correlations: Part I


• 2019 Findings: Part II • Implications




There is a significant difference between the types of firms that have a high level of usage of their hotline reporting system vs. those with low usage.
1. Power Users: More profitable firms (ROA), large firms, and firms with higher quality governance

2. Limited Users: Less profitable, smaller firms, and firms with lower quality governance



More active, robust hotline reporting & incident management usage is associated with:
1. Greater firm productivity as measured by return on assets (ROA)
2. Fewer material lawsuits & lower settlement costs
3. Fewer external regulatory agency inquiries & lower fine amounts
4. Fewer negative news stories in the business/financial media



• Seeking improved processes for discovering and managing problems in firms
• Lack of empirical research on the topic of internal reporting systems (hotlines) linked directly to business performance


• Believed there could be predictive value in this data


Love for my own kids
Production Issues
Aggressive Accounting
Accounting Performance Metrics

God
Minor HR Related Issues
Minor OSHA / EPA Violations
Asset Theft
Macro
Economic Trends
Major HR Related Issues
Kick Backs
The meaning of life

The Cockroach Theory
“There’s never just one cockroach in the kitchen” — Warren Buffett
• Internal WB reports are the tip of the iceberg of potential undiscovered problems
• Firms with more reports have more problems
• The quality of the firm and leadership is reflected in the number of reports that show up in the system
The Cutting Wood Theory
“When you cut wood, you get sawdust”
• Internal WB reports reflect the discovery of unknown problems common to every firm
• Firms with more reports know more about unobservable problems than firms with fewer reports
• The number of reports is unrelated to the overall quality of the firm
• Firms that proactively solicit reporting are able to get ahead of problems before they become worse

There is a significant difference between the types of firms that have a high level of usage of their hotline reporting system and a low level of usage.
1. Power Users: More profitable firms (ROA), large firms, and firms with higher quality governance
2. Limited Users: Less profitable, smaller firms, and firms with lower quality governance
Firms that have more active hotline reporting systems have…


1. Fewer material lawsuits filed against the organization
2. Lower amounts paid in litigation settlements
3. Lower levels of discretionary accruals


• Ex-ante, the results are not obvious
• Increased usage could have indicated more problems and litigation; it did not
• Firms with increased administration of reports (i.e., accessing reports, gathering additional detail) have even fewer lawsuits
• Increased usage does not indicate increased problems; rather, higher engagement suggests a healthier culture with fewer problems

• Material Lawsuits decline as hotline usage increases


• Larger firms benefit more from becoming a “power user” of their hotline
• A one standard deviation increase in the use of an internal WB system is associated with 6.9% fewer material pending lawsuits and 20.4% less in aggregate settlement amounts
• Material Lawsuits decline as hotline usage increases

• Larger firms benefit more from becoming a “power user” of their hotline
• A one standard deviation increase in the use of an internal WB system is associated with 6.9% fewer material

Fits into “Plausible Causal Inference”


• Doll and Peto [1976] studied mortality rates of male doctors between 1951 and 1971 and found “a striking correlation between smoking and lung cancer”
• Gillies [2011] argues that “this correlation was accepted at the time by most researchers (if not quite all!) as establishing a causal link between smoking and lung cancer”
• Thus, through a process involving multiple studies over two decades, a plausible set of causal mechanisms between smoking and atherosclerosis was established



• Human capital is the most important corporate asset, and a window into the health & performance potential of the organization

• Existing “whistleblower” research is based on externally reported events that make it into the media or court room (frequently both)
• Research shows that one bad public event tends to presage more
• We wanted to see what was happening inside of firms, before events are “public”


• Internal hotline reporting data, and the processes used for incident management, is instructive about workplace culture

• The data are likely indicative – and potentially predictive – of business results




Conflicting perceptions on internal whistleblowing activity:
• Should management strive for fewer reports? No reports?
• Should management strive for more reports?
• Is there such a thing as too many reports?



More active, robust hotline reporting & incident management usage is associated with:
1. Greater firm productivity as measured by return on assets (ROA)
2. Fewer material lawsuits & lower settlement costs
3. Fewer external regulatory agency inquiries & lower fine amounts
4. Fewer negative news stories in the business / financial media
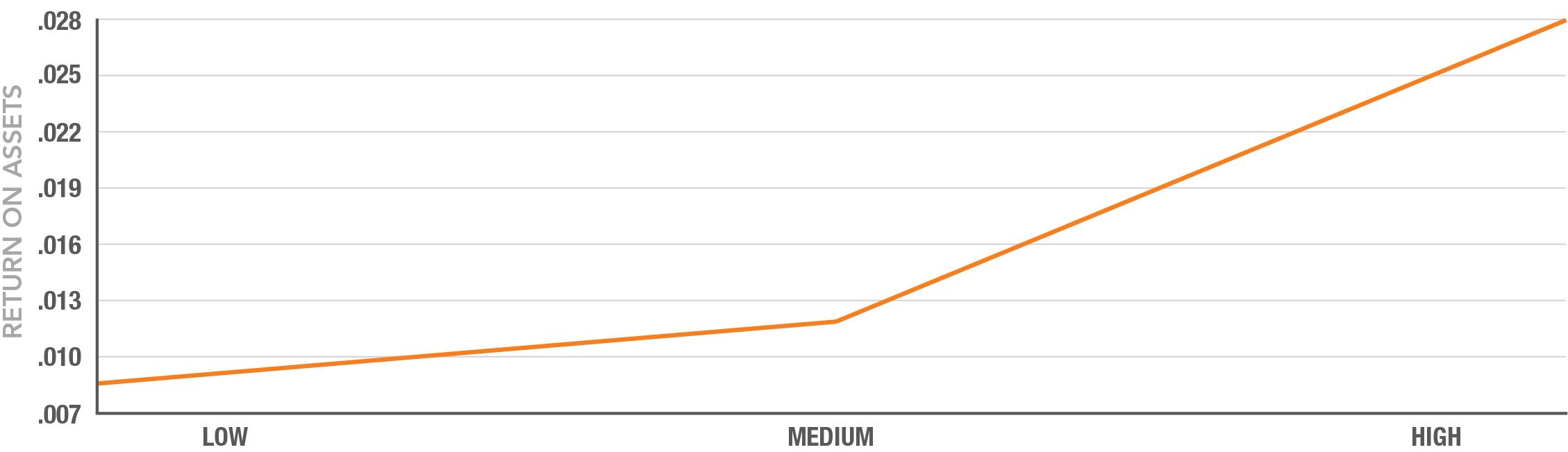
* Evaluates efficient use of resources: Net Income / Assets Used






Corporate fines and penalties obtained data from Violation Tracker

• Maintained by Good Jobs first
• Monitors regulatory fines imposed by more than 40 federal agencies and all divisions of the Justice Department
• Dataset goes back to 2000, and includes 368,000 civil and criminal cases with total penalties of more than $464 billion




• Firms with more internal WB reports tend to face fewer and smaller aggregate amounts of fines

• A 10% increase in WB reports is associated with a 2.0% decrease in the dollar amount of government fines received in subsequent years
• Reports of misuse of corporate assets and workplace safety concerns are associated with a lower amount of aggregate government fines










• The average report is reviewed 9.1 times before being closed in 43.7 days
• Reports are reviewed more frequently and take longer to close when they:
• Relate to accounting issues
• Contain more information about the alleged activity
• Are made by business partners rather than employees
• Allege retaliation by management
• Allege management involvement
• Allege activity over a longer period of time
• Anonymous reports contain more information, but also are less likely to be substantiated
• Firms that advertise their systems as “helplines” receive significantly more reports…

• However, these firms tend to receive reports with less actionable information

Firms with higher levels of hotline reports are not lower quality firms with worse protocols and compliance. Instead …


• This analysis suggests the number of reports received (normalized for company size) is a good proxy of compliance health
• Firms actively using internal whistleblowing systems are able to get ahead of problems before they become lawsuits
• Firms with lower quality governance, with entrenched management, are less likely to use the whistleblowing system
• Audit committees should consider the monitoring of whistleblowing systems management and frequency of reports as key parts of evaluating financial reporting
• How can firms increase their volume of hotline usage?


• What was the methodology behind your research?
• How will you investigate the research next?


