5 minute read
131
by 5rXobdlLrFp
GIGA - Interdisciplinary Research Institute in Biomedical Sciences of the University of Liège Cutting-edge technological platforms at the service of the biomedical sector
The aim of GIGA’s technological platforms is to meet the needs of the biomedical sector by providing high quality technological support and cutting-edge expertise in research and industrial and academic innovation (from fundamental to preclinical and clinical).
Advertisement
The ability to explore the genome (DNA), transcriptome (RNA) and proteome (proteins) of different organisms, analyse the data generated through systematic analysis thanks to bioinformatics and replace it in a cellular or organismic context seems indispensable for all research projects or businesses active in the field of biopharmaceuticals or biotechnologies. This is also true of research conducted in the food industry and materials sector.
Access to exceptional technological equipment for research and innovation is becoming difficult - especially for SMEs - due to the implementation cost and increasing levels of expertise they require. The GIGA's technological platforms group together cutting-edge technologies and top-of-the-range skills. They can be accessed by researchers in all sectors (both academic and private).
Daily interaction with the research units makes it possible to adapt the services on offer to the demands of researchers and to keep pace with scientific and technical progress. The advantages of this approach are many. It guarantees equipment that is always at the cutting edge of technology, it offers a local, accessible service to the academic world and local businesses at an optimal cost and provides analyses carried out by experts in the field.
The GIGA's technological platforms
The GIGA provides services in the following fields: - Genomics - In vitro Imaging (via Cell Imaging and Flow Cytometry) - In vivo Imaging (via the Cyclotron CRC platform) - Immunohistology - Viral Vectors - Proteomics - Animal Facilities (Mouse and Zebrafish).
Exceptional equipment
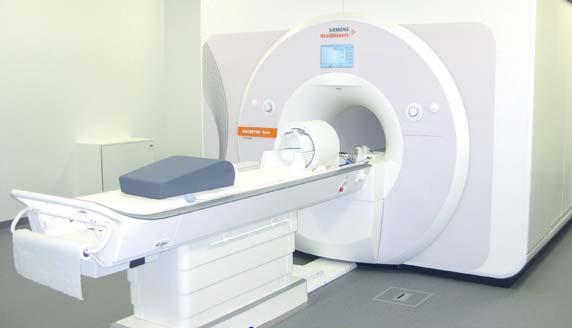
The 7 Tesla MRI Among the exceptional equipment that the GIGA has, we should mention the first 7 Tesla MRI scanner operational in Belgium. This ultra-high magnetic field imaging device has been installed at the Cyclotron-In Vivo Imaging GIGA Research Centre at the University of Liège since September. Thanks to this state-of-the-art technology, researchers will be better able to understand the cerebral physiology and pathology of neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s, epilepsy, Parkinson's and multiple sclerosis.
The first operational 7 Tesla MRI scanner in Belgium, an ultra-high magnetic field imaging device, was installed at the Cyclotron-In Vivo Imaging GIGA Research Centre at the University of Liège in September 2019.
The new 7 Tesla MRI scanner will initially be dedicated to neuroimaging research. The level of infra-millimetric resolution of the brain structure and the ability to detect with incredible precision the variations in the brain’s activity will allow several of the GIGA’s scientific teams to continue their work in the field of neuroscience and neurodegenerative diseases.
“In order to gain more in-depth knowledge of brain physiology and pathologies and further develop our research on cognitive neuroscience, we need to be able to study increasingly small structures and nerve cells”, explains Dr Éric Salmon, director of the Cyclotron-In Vivo Imaging GIGA Research Centre.
The 7 Tesla MRI MAGNETOM Terra, developed by Siemens Healthineers, is able to produce images of the living human brain at a very high isotropic spatial resolution up to 0.2 mm. This MRI scanner will first and foremost help researchers to more quickly identify new neurodegenerative pathology biomarkers, achieve a better understanding of sleep, list the metabolic processes of the brain and visualise neurodegenerative diseases.
The NovaSeq6000 sequencer In genomics, the platform now has a new generation sequencer, the NovaSeq 6000 Illumina, which it purchased this year with ERDF funding.
The NovaSeq6000 is a cutting-edge, ultra-high-speed sequencer with the necessary capacity to routinely sequence entire (human) genomes. It is possible to analyse 48 human genomes in two days, which allows for accurate and personalised medicine.
Thanks to this exceptional technology, applications that require a large amount of data such as sequencing of the entire human genome, exome sequencing at great depth and personalised tumour profiling can be carried out much more quicker and accurately. This sequencer is also fully compatible with projects that require less speed, but also has the advantage of a reagent cost that is lower than that of other sequencers.

Lightsheet Zeiss Z1 microscope The Cell Imaging platform has a whole range of state-of-the-art microscopes. Among those, we would like to tell you about the Lightsheet microscope. Zebrafish: a model for medical research The GIGA zebrafish aquarium houses around 15,000 fish.
The zebrafish has multiple advantages as a model for medical research. In addition to its high level of homology with humans (75% of the genome), they also have the advantage of very fast embryo development, i.e. 3 days. What is more, the embryos are transparent, which facilitates imaging. The reproduction time is also very short. These fish reach sexual maturity in 3-4 months and a female lays on average 150 eggs a week, which is a much higher fertility rate than in other species.
Zebrafish can be used in a large number of scientific fields, whether for developmental processes, the discovery and screening of new molecules, in neuroscience, in the cardiovascular field, to study organ regeneration processes or to monitor host-microbe interactions in immunology, behavioural genetics and (eco)toxicology.
Embedded in the heart of the GIGA institute, the Cell Imaging Core Facility specializes in advanced light microscopy. Our goal is to help researchers to use these systems to answer their research questions.
© GIGA
LIGHT-SHEET MICROSCOPES illuminate samples with a thin sheet of light, and the emitted fluorescence is then collected at 90° by a wide-field detection system. Moving the sample through the sheet of light enables rapid acquisition of 2D optical sections, which can be combined to generate a 3D image of the sample.
Our Lightsheet Zeiss Z1 proposes long-term live imaging of semi-transparent model systems such as zebrafish and drosophila embryos and imaging of fixed, cleared tissues such as mouse embryos, tissues and organs up to 5mm thickness, cellular aggregates and spheroids.
The MS Quanta platform This year, Wallonia and the ERDF European funds invested over 2 million euros in MS-QUANTA, a platform dedicated to the validation of new biomarkers. This new academic structure installed at ULiège (GIGA Proteomics) and at UMONS has given Wallonia considerable analysis capacities in a promising field given the role biomarkers play in the development of personalised medicine, industrial microbiology and food safety. Within MSQUANTA, the role played by ULiège and the GIGA will focus more specifically on proteomics guided by mass spectrometry imaging, a high-performance instrument for identifying and quantifying biomarkers.
A unique structure in Belgium, MS-QUANTA will strengthen the analytical capacity of all health academic and industrial stakeholders in Wallonia, enabling them to benefit from recent technological developments in the field of biomarker validation. The analytical platform will also be useful for other fast-growing scientific and economic sectors, in particular the agri-food (food safety), environment and industrial microbiology sectors.











