




Quest ion:
With HAMH, FXcare and cardioversion in a critical access hospital, can we charge for MACby ED provider doing that care?What CPT ® codes or modifiers do we use, if we can?

Answ er:
First, the facility may charge a fee for moderate sedation; some facilities charge, others do not. The facility charge (under revenue code 0370 ? ANESTHESIA) represents the facility resources to provide labor and supplies necessary for the moderate sedation. The fee can be a flat rate or time based, at the facility?s discretion.
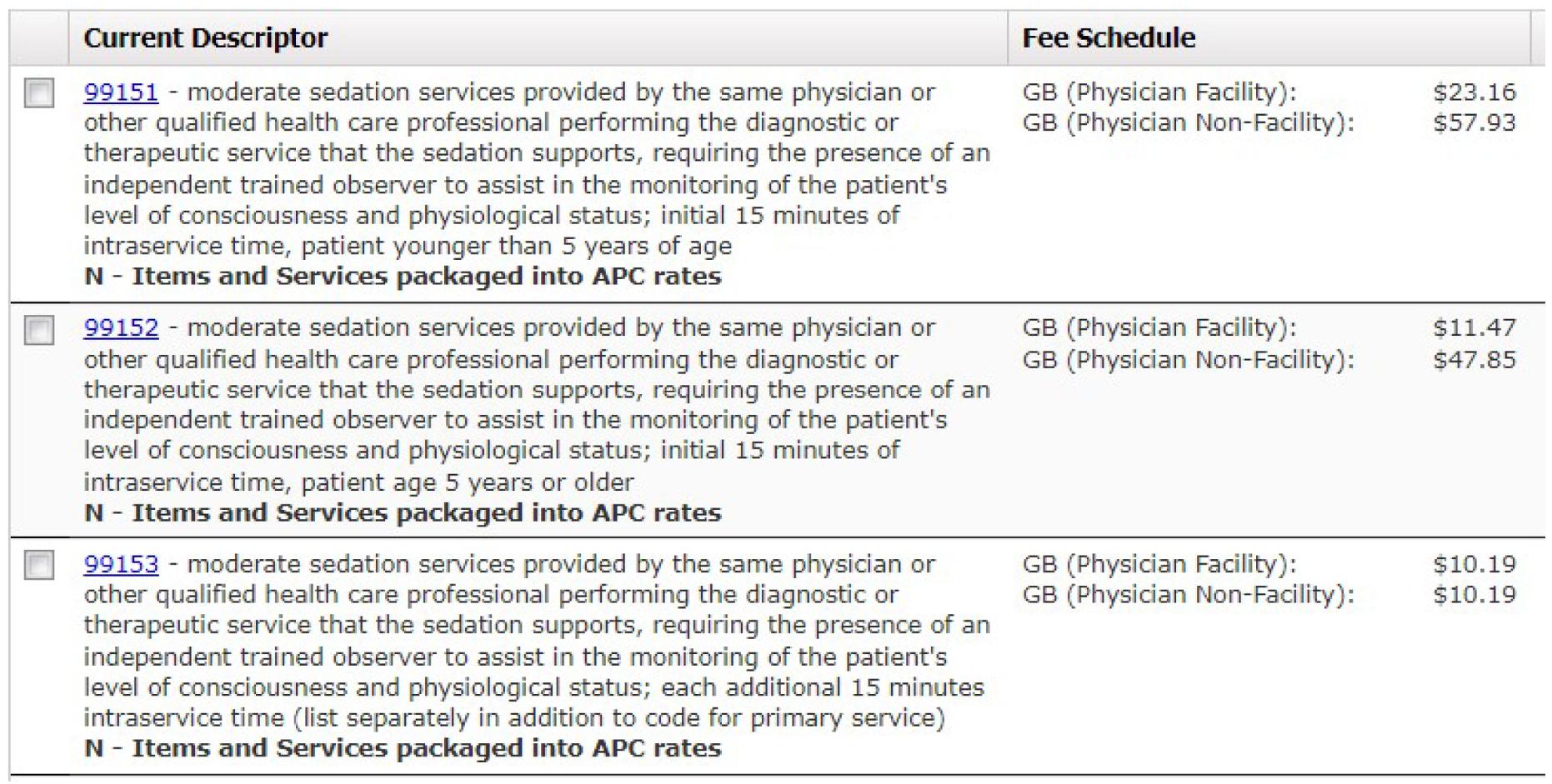
Professional Fees : An emergency department physician may report a professional fee for supervising moderate sedation with the assistance of a trained observer (such as a nurse) when necessary to perform a therapeutic or diagnostic procedure, such as fracture care CPT®s 99151-99153 should be used in that circumstance; when a Method II CAH reports professional fees on an outpatient facility claim, emergency physician fees should be reported under revenue code 0981 - EMERGENCYROOM SERVICES
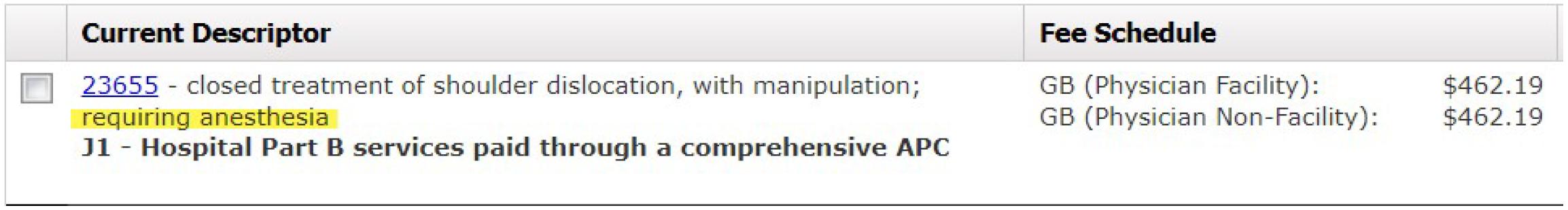
There are some procedures which include anesthesia in the description of the code in which case the provision of anesthesia as ?integral to?the procedure. Here?s an example:
The code for cardioversion does not include any reference to anesthesia, therefore anesthesia is not ?integral to?CPT® 92960
Background: Prior to 2018, the CPT® code book included a list of codes in Appendix G (CPT® Codes that Include Moderate (Conscious) Sedation?), which listed procedures for which moderate sedation supervision was considered ?integral to?the procedure.
Starting in 2018, the AMA discontinued Appendix G and instructed professionals to report the moderate sedation codes when performed, unless the CPT® descriptor specifically included anesthesia The AMA also reduced the physician work RVUs for the procedures formerly listed on Appendix G, because physicians would earn credit by separately reporting the moderate sedation codes. Consequently, physicians will be underpaid unless they report the moderate sedation codes in tandem with a procedure code that does not include anesthesia in the code description. The medical record must clearly state how long the anesthesia service was provided to support the time based codes.
Modifiers: It would not be necessary or appropriate for an emergency department physician to report modifier QS Certain modifiers are limited for use by an anesthesia professional (MD Anesthesiologist or CRNA, for example) who report anesthesia CPT®s in the 00100 ? 01999 code range.
Here?s the anesthesia modifiers section of Chapter 12 of the Medicare Claims Processing Manual ? Physicians and Non-Physician Practitioners: (See Next Page)
There are some procedures which include anesthesia in the description of the code in which case the provision of anesthesia as ?integral to?the procedure. Here?s an example:
CCI Edit s: Here?s a pertinent excerpt from Medicare?s NCCI Edit Manual, Chapter 11 ? note the different policy for ?anesthesia?vs ?moderate sedation?:

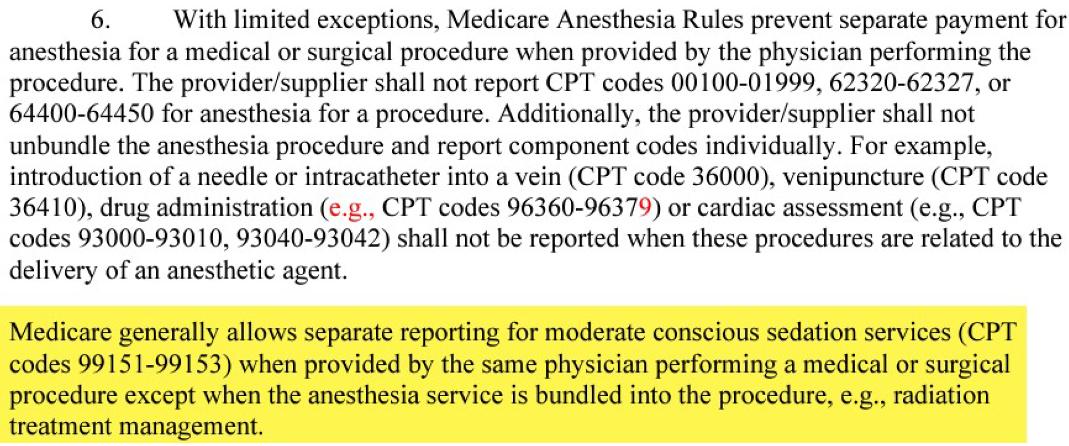
https://www.cms.gov/files/ document/medicare-nccipolicy-manual-2023chapter-11.pdf

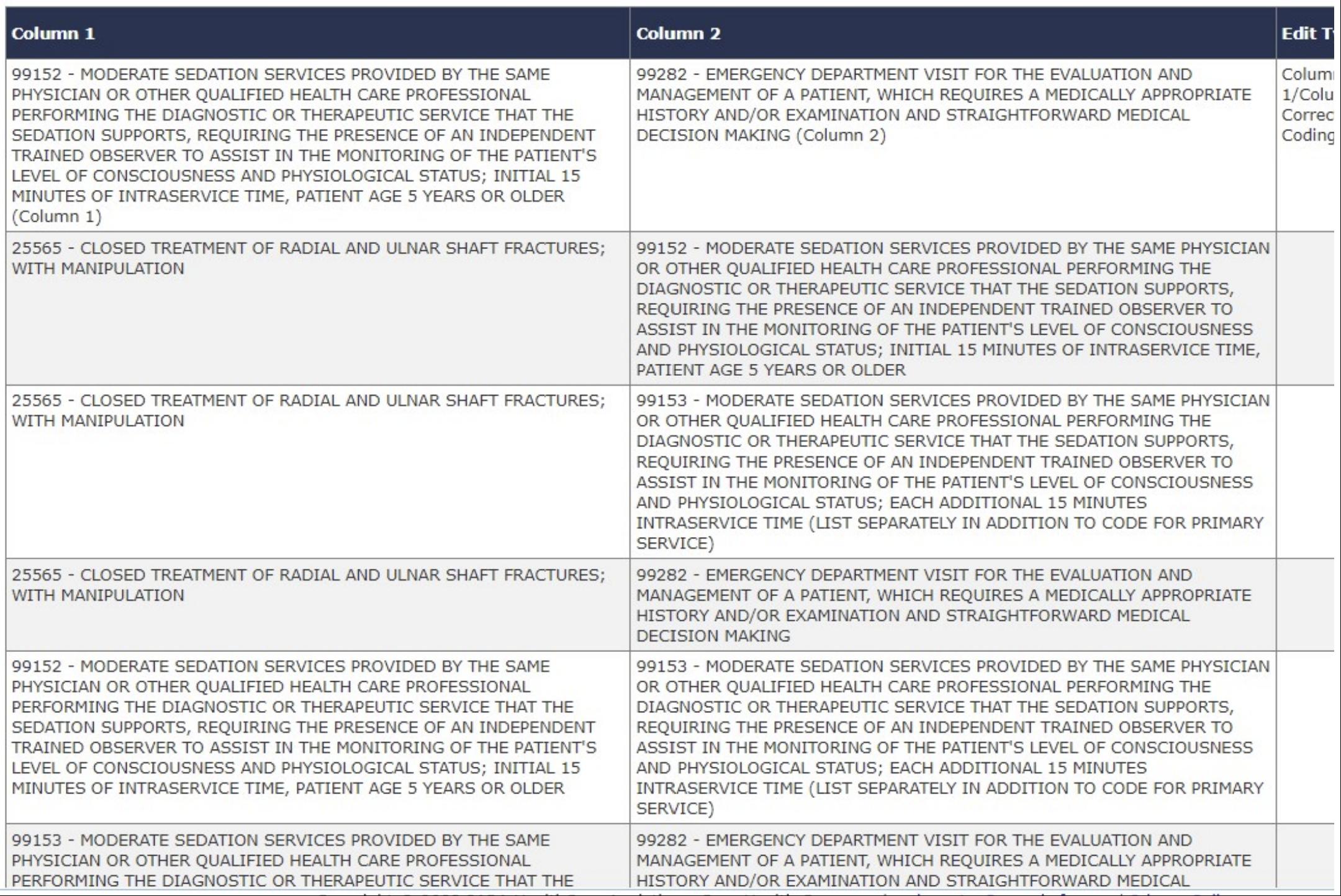
There is a CCI edit between an ED E/M code and 99152 ? as displayed on the PARA Data Editor Calculator tab; the edit may be resolved with a modifier, such as XU or 59, if the sedation is separate and distinct from the evaluation and management service
When attempting to resolve a CCI edit, the correct choice of modifier depends on the specific circumstances. Attached is a CMSfact sheet explaining the proper use of modifiers 59 and the X{EPSU} modifiers We would expect either modifier XU (unusual, non-overlapping service) or modifier 59 to be appropriate when reporting moderate sedation that is separate and distinct from the emergency department evaluation and management service.
Addressing the two specific scenarios:
- The documentation supports reporting a professional fee under revenue code 0981
(Professional Fees - Emergency Department Services) for 94 minutes of moderate sedation: CPT® Units 99152 1 99153 5
- Can we charge Anesthesia for cardioversion when done by an ED MD (facility and professional) ?
The American College of Emergency Physicians offers the following guidance in its ?ACEPNow? publication:
Anesthesia for cardioversion
CPT® 92960, for elective, external, electrical cardioversion in theemergencydepartment. There areno separatecodesor modifiersfor usingpaddlesor hands-free, and thereareno special codesor modifiersfor biphasiccardioversion. CPT® code92960 isfor electivecardioversion, not defibrillation. Thereisno separatecodefor defibrillation. Defibrillation isincorporated into CPR, which hasitsown CPT® code(92950). Therefore, it isimportant to havethe correct terminologyin thechartingto demonstratecardiovertingthepatient and not defibrillatingthe patient.
Previously, themoderate sedation codeswerenot allowed to be billed alongwith the cardioversion codes. However, in 2017, thisrestriction wasremoved, and theynowcan be billed together.
If an emergency department physician performed non-emergency cardioversion, and supervised moderate sedation, then yes, the physician could charge a professional fee for the moderate sedation along with the professional fee for 92960. The documentation supports 19 9 minutes of sedation:
CPT® Units
99152 1
99153 3
Please note that cardioversion 92960 (CARDIOVERSION, ELECTIVE, ELECTRICAL CONVERSION OFARRHYTHMIA; EXTERNAL) maynot be reported for emergency cardiopulmonary resuscitation Per the AMA publication ?CPT® Assistant?(Nov 2000) ?Code 92960 specifically describes elective (nonemergency) external electrical cardioversion. Elective cardioversion is most often used to treat atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter if antiarrhythmic drugs fail to convert the heart back to normal sinus rhythm, or if the patient is hemodynamically unstable The electric shock given in cardioversion is synchronized (ie, timed to occur during the Rwave of the electrocardiogram) The patient will have his/her heart rhythm monitored for several hours after the procedure to ensure the rhythm remains stable.?If the service rendered is defibrillation, there is no specific CPT® code, it is a component of the critical care codes 99291-99292 reported by emergency department physicians
Incidentally, Medicare?s NCCI Edit Manuals are available on the PARA Dat a Edit or Calculat or tab ? click on the ?Search CMSManuals?hyperlink in the lower left corner of the page:
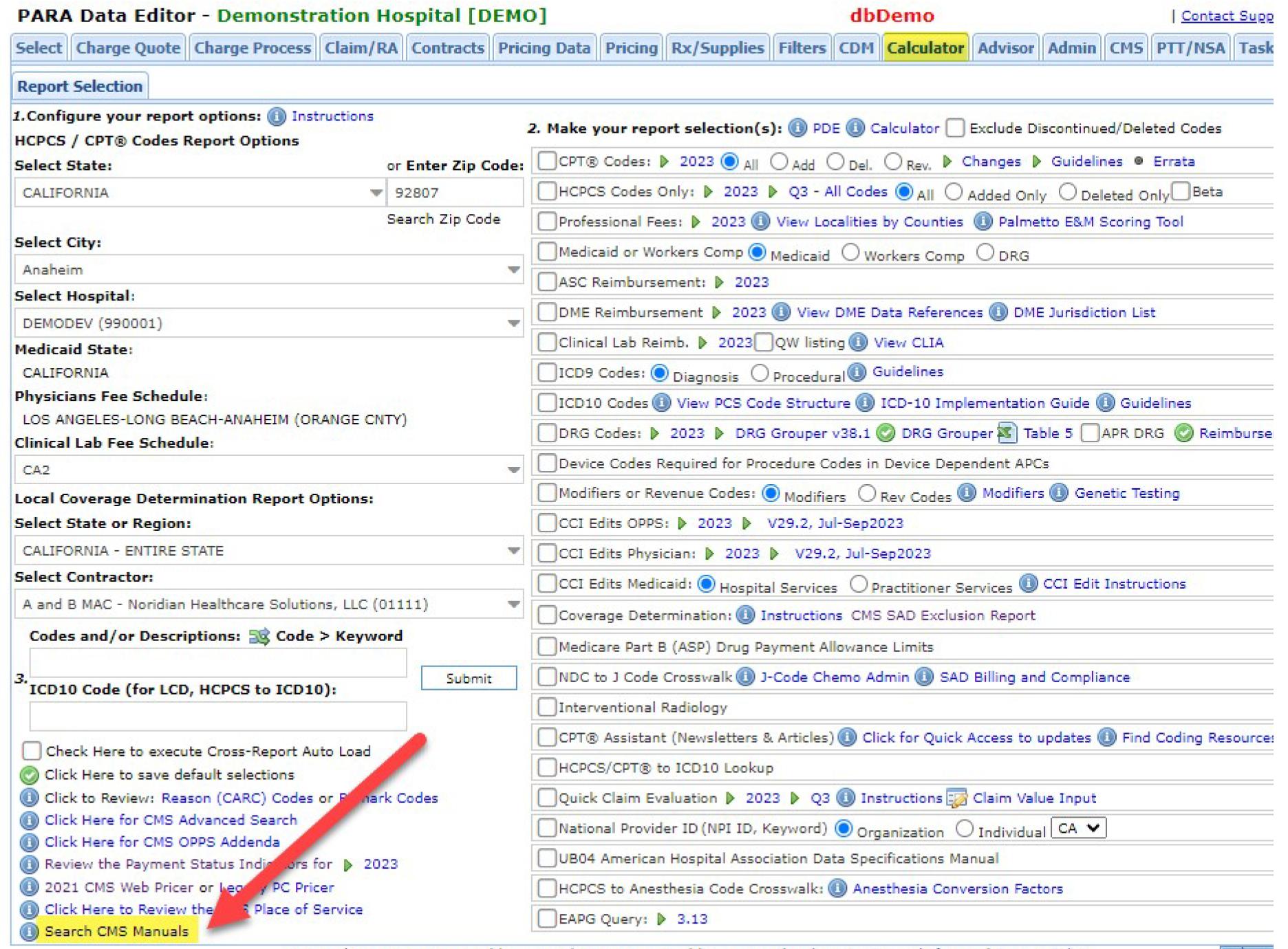
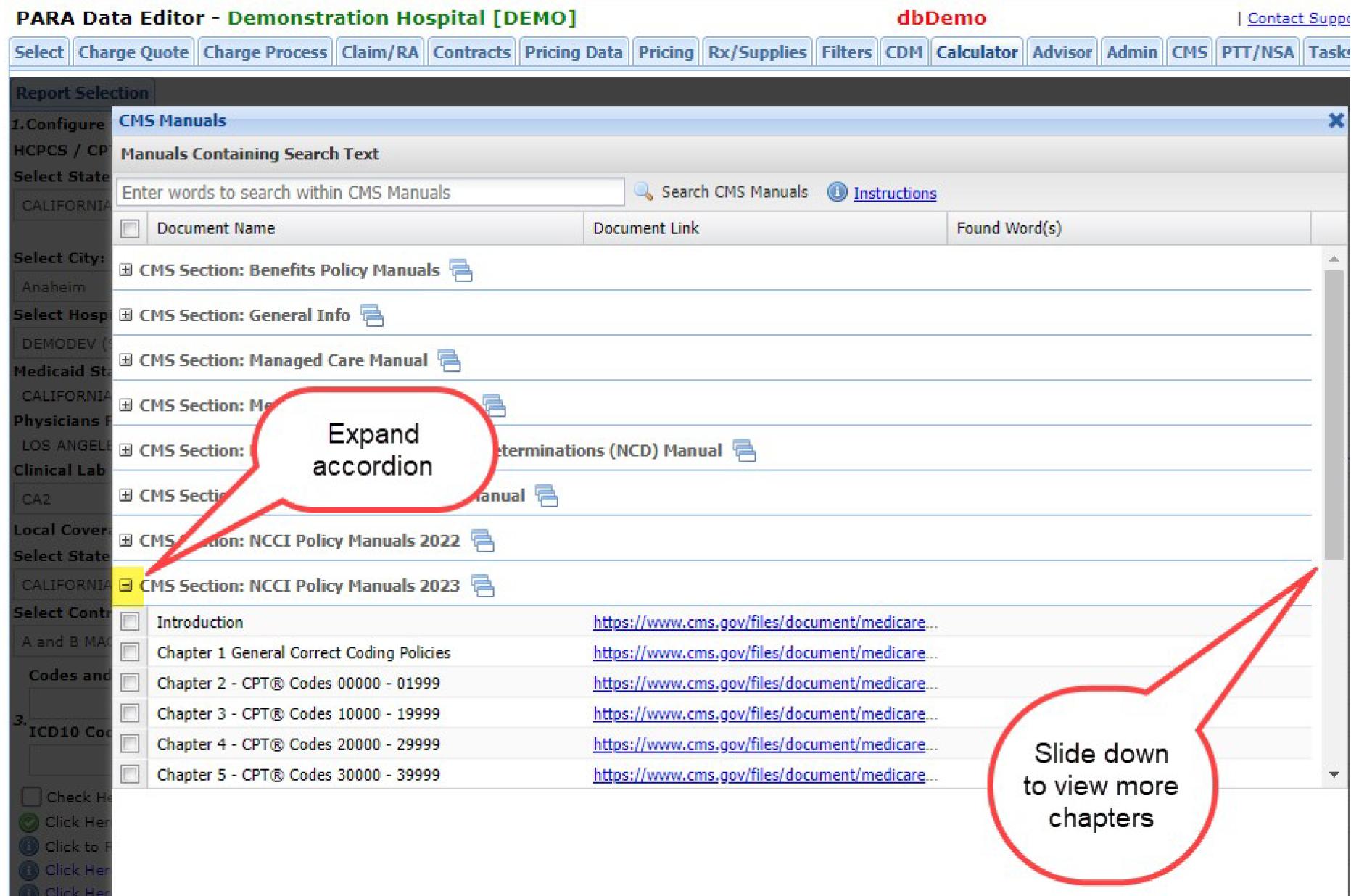
Then click on the + sign to expand the accordion for the manual set you seek:
Quest ion:
We are looking into doing spirometry in our occupational health clinic and wanted to look into the charge and procedure codes for this service We believe the proper code is 94010, but want to ensure this is correct. Can you confirm this for us?

Answ er:
The CPT® code reported for spirometry is indeed 94010. Medicare?s OPPSfacility reimbursement (for non-CAH hospitals) is $145 43 in your area Physician reimbursement in the freestanding clinic setting is $24 91, as displayed in the HCPCSreport of the PARA Data Editor:
An Occupational Health program typically provides two types of service for local employers:
- Rout ine Em ployee healt h m onit oring: particularly for employees who are exposed to hazardous substances or working conditions. Routine monitoring services are typically invoiced to the employer according to the terms of a contract with the Occupational Health provider The terms of the contract between the employer and the provider govern the level of detail required on the invoice, and might not be restricted to CPT® code reporting


For example, some occupational health contracts may include a per-period charge for monitoring the respiratory function of numerous employees, which service might consist mainly of spirometry. The invoice might read ?Quarterly Respiratory Monitoring?, or ?Spirometry?, rather than the CPT® code ? whatever level of detail that acceptable to both parties, the provider and the employer, is acceptable.
Medically necessary services t o t reat w ork-relat ed injuries: which must be billed to a worker?s compensation program. Billing for medically necessary care submitted to worker?s compensation or to a group health insurer needs to comply with standard CPT®/HCPCScoding and billing procedures.
AI continues to maintain top-of-mind presence with healthcare leaders. It has become more and more evident these tools are supportive of healthcare efforts and not human replacements.
In this issue, we take a glance at Artificial Intelligence (AI) and how it really affects healthcare in several arenas.
We wanted to provide examples of AI generated content to ensure our readers are introduced to the level of detail these tools can generate with proper prompting and inquiry
So we gave ChatGPT three different "inquiries" covering three different potential applications of A I in the healthcare space Our inquiry generated 1,000-word articles We are sharing this here in this issue
These articles should be read with the caveat in mind that they are generated by AI and not fully vetted. They are simply serving as examples of these tool?s potential.




The healthcare industry is undergoing a profound transformation fueled by technological advancements, and one area where this transformation is particularly promising is in billing and revenue collection Hospitals, traditionally burdened with the complexities of billing and revenue management, can now leverage the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to streamline processes, improve accuracy, and enhance financial sustainability In this essay, we will explore the ways hospitals can adopt AI in billing and collecting revenue, the benefits it offers, the challenges it presents, and the future potential of this technology.
Before delving into the role of AI, it is crucial to understand the existing challenges faced by hospitals in billing and revenue collection:

- Com plexit y and Errors: Hospital billing involves intricate coding systems and compliance with numerous regulations. Human error is not uncommon, leading to costly mistakes and delayed payments
- Adm inist rat ive Overhead: Hospitals employ a substantial workforce for billing and collections, which translates into high administrative costs This manual effort also results in prolonged revenue cycle times
- Revenue Leakage: Unbilled or underbilled services, denied claims, and inefficiencies in collections contribute to revenue leakage, diminishing the financial health of healthcare providers
- Evolving Regulat ions: The healthcare industry operates in a highly regulated environment. Keeping up with ever-changing rules and regulations poses a constant challenge.
Aut om at ion and Process Efficiency
- Claim s Processing: AI-powered systems can automatically process claims by analyzing patient records, medical codes, and insurance information. This reduces the time required to submit claims and minimizes errors, increasing the chances of reimbursement
- Pre-Aut horizat ion: AI algorithms can assess the eligibility of patients for specific procedures and check if they meet insurance criteria before treatment This proactive approach can prevent costly denials
- Predict ive Analyt ics: AI can predict which claims are more likely to be denied, allowing hospitals to focus on them for timely resolution and to reduce the overall denial rate
Enhanced Revenue Capt ure
- Opt im izing Pricing: AI-driven tools can analyze historical data to determine optimal pricing for services, helping hospitals maximize revenue without overcharging patients
- Ident ifying Underbilling: AI can analyze vast datasets to identify cases where services were provided but not billed. This helps hospitals recapture revenue that would otherwise be lost
- Denial Managem ent : AI can improve the accuracy of claims to reduce the likelihood of denials In cases where claims are denied, AI can assist in quickly identifying the root causes and rectifying them.
Com pliance and Regulat ion Adherence
- Real-time Updates: AI systems can continuously monitor and adapt to changes in healthcare regulations, ensuring that billing practices remain compliant
- Auditing and Documentation: AI-powered auditing tools can review billing and coding practices for compliance and accuracy, reducing the risk of regulatory penalties
Benefit s of AI Adopt ion in Hospit al Billing and Revenue Collect ion
- Im proved Accuracy: AI algorithms can significantly reduce errors in billing and coding, minimizing the risk of denied claims and costly rework
- Fast er Revenue Cycle: Automation expedites the billing process, reducing the time between service delivery and payment receipt
- Enhanced Cash Flow : Hospitals can expect a more predictable and steady cash flow with fewer billing bottlenecks and reduced revenue leakage
- Cost Savings: Automation and AI reduce the need for extensive manual labor, leading to substantial cost savings in staffing and administrative overhead
- Bet t er Resource Allocat ion: Hospitals can redirect human resources to more strategic tasks, such as patient care and experience improvement
- Predict ive Insight s: AI-generated insights can inform decision-making, helping hospitals optimize pricing, resource allocation, and overall revenue strategies
- Pat ient Experience: Faster and more accurate billing can lead to improved patient satisfaction and loyalty, positively impacting a hospital's reputation and patient retention
While the benefits of AI adoption in hospital billing and revenue collection are compelling, there are several challenges to overcome:
- Dat a Qualit y: AI relies on high-quality data Hospitals must ensure the accuracy, completeness, and security of patient and billing data
- Im plem ent at ion Cost s: Integrating AI systems can be costly, and hospitals may need to make substantial upfront investments
- Workforce Transit ion: The adoption of AI may require retraining or reassigning staff, which can be met with resistance
- Et hical and Privacy Concerns: Handling sensitive patient data in AI systems raises ethical and privacy considerations. Hospitals must maintain strict compliance with data protection regulations
- Regulat ory Com pliance: Staying updated with evolving healthcare regulations is crucial to ensure AI-driven systems remain compliant.
- Change Managem ent : Hospitals must manage the cultural shift towards AI adoption and ensure that employees understand and embrace the technology.
As AI technology continues to advance, its potential in hospital billing and revenue collection is poised to grow exponentially:
- AI-driven Revenue Cycle Managem ent (RCM) Plat form s: Comprehensive AI-powered RCM platforms will become standard in healthcare, offering end-to-end automation and optimization of billing processes
- Int eroperabilit y: AI systems will seamlessly integrate with Electronic Health Records (EHR) and other healthcare systems, creating a unified ecosystem for patient data management and billing
- Personalized Financial Guidance: AI can provide patients with personalized cost estimates and financial guidance, improving transparency and patient engagement in the billing process
- AI-Pow ered Chat bot s: Hospitals will utilize AI chatbots for patient inquiries, payment reminders, and even financial assistance, improving patient experience and reducing administrative workload
- Fraud Det ect ion: AI will play a pivotal role in detecting fraudulent claims and mitigating healthcare fraud, safeguarding hospital revenue.
The integration of artificial intelligence into hospital billing and revenue collection processes presents a transformative opportunity for healthcare providers. With the potential to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and compliance, AI can significantly improve financial sustainability and patient satisfaction
While there are challenges to overcome, the future of AI in healthcare revenue management is promising, and hospitals that embrace this technology will likely thrive in the ever-evolving healthcare landscape. As AI continues to advance, its role in healthcare finance will only become more integral, reshaping the way hospitals manage their revenue and contribute to improved patient care.

In recent years, the field of healthcare has witnessed a revolutionary transformation through the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) One of the most remarkable applications of AI in healthcare is in medical diagnoses. AI-powered diagnostic tools have the potential to enhance the accuracy, speed, and efficiency of diagnosing various medical conditions This essay explores the effectiveness of AI in medical diagnoses, examining its advantages, challenges, and the impact it has on patients and healthcare professionals.
One of the primary advantages of AI in medical diagnoses is its ability to provide highly accurate results AI systems can analyze vast amounts of medical data, including patient records, laboratory test results, and medical images, to identify patterns and anomalies that might be missed by human healthcare professionals For example, AI algorithms have shown exceptional accuracy in detecting early-stage cancers, such as breast and lung cancer, often outperforming human radiologists in identifying abnormalities in medical images like X-rays and CT scans This increased accuracy leads to earlier diagnoses and more effective treatment options, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
AI systems can process and analyze medical data at a speed that is unattainable for human healthcare professionals. This efficiency is particularly critical in emergency situations, where rapid diagnosis can make the difference between life and death. For instance, AI-powered chatbots and virtual triage systems can quickly assess a patient's symptoms and medical history to determine the severity of their condition and recommend appropriate actions, such as seeking immediate medical attention or self-care measures Such systems can alleviate the burden on healthcare facilities by efficiently managing patient influx.
Diagnostic errors are a significant concern in healthcare, with potentially serious consequences for patients AI systems can help mitigate these errors by providing a second opinion or flagging potential inconsistencies in a diagnosis. For example, AI-powered clinical decision support systems can review a physician's diagnosis and recommend additional tests or alternative treatment options based on the latest medical guidelines and research. This not only enhances the quality of care but also reduces the risk of misdiagnoses and their associated negative outcomes
The healthcare industry generates an enormous amount of data daily, making it challenging for human healthcare professionals to process and analyze effectively AI excels in handling big data by swiftly extracting relevant information and drawing insights from it. This capability is especially valuable for identifying trends and predicting disease outbreaks, as demonstrated during the COVID-19 pandemic AI-driven predictive models helped public health officials and researchers track the spread of the virus and make informed decisions about resource allocation and containment measures.
While AI holds immense promise in medical diagnoses, it also faces several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed:
- Dat a Qualit y and Bias: AI systems heavily rely on the quality and diversity of training data Biased or incomplete datasets can lead to biased AI algorithms that may not perform well across diverse patient populations
- Lack of Explainabilit y: Many AI models, such as deep learning neural networks, are often considered "black boxes" because they provide results without clear explanations. This lack of transparency can make it challenging for healthcare professionals to trust and interpret AI-generated diagnoses
- Regulat ory and Et hical Concerns: Integrating AI into healthcare raises regulatory and ethical concerns regarding patient privacy, data security, and liability in the event of AI-related errors or malfunctions
- Int egrat ion w it h Exist ing Syst em s: Healthcare institutions must invest in infrastructure and training to seamlessly integrate AI into their existing workflows and ensure healthcare professionals can effectively use AI tools
- Cost and Accessibilit y: The development and implementation of AI technologies in healthcare can be expensive, potentially limiting access for smaller healthcare facilities and underserved communities
The integration of AI in medical diagnoses has a profound impact on both patients and healthcare professionals:
- Patient-Centered Care: Patients benefit from AI's ability to provide more accurate diagnoses, reducing the chances of misdiagnosis and unnecessary treatments This leads to improved patient outcomes and overall satisfaction
- Empowering Healthcare Professionals: AI assists healthcare professionals by providing them with valuable insights and decision support It can help doctors make more informed choices, improve the accuracy of their diagnoses, and enhance the efficiency of their practices
- Reducing Healthcare Costs: By facilitating earlier and more accurate diagnoses, AI can help reduce the overall cost of healthcare. Timely intervention and prevention of complications can result in significant cost savings for both patients and healthcare systems
- Enhanced Workflows: Healthcare professionals can streamline their workflows by integrating AI into their practice AI tools can automate routine tasks, such as data entry and paperwork, allowing healthcare providers to focus more on patient care
- Improved Accessibility: Telemedicine platforms, powered by AI, enable patients to access medical consultations and diagnoses remotely, increasing healthcare accessibility for individuals in remote or underserved areas.
- IBM Wat son for Oncology: IBM Watson for Oncology is an AI-powered system that analyzes large volumes of medical literature and clinical trial data to assist oncologists in making treatment recommendations In a study conducted in India, Watson for Oncology demonstrated concordance rates of 96%for breast cancer treatment recommendations when compared to expert oncologists
- Pat hAI: PathAI is an AI platform that assists pathologists in diagnosing diseases from histopathology slides. In a study published in JAMA Oncology, PathAI's algorithms demonstrated high accuracy in detecting breast cancer metastases in lymph nodes, outperforming pathologists in some cases.
The healthcare industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by advances in technology, data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) One area where AI is making a substantial impact is the healthcare revenue cycle. The revenue cycle encompasses all administrative and clinical functions that contribute to the capture, management, and collection of patient service revenue It's a complex process that can be fraught with inefficiencies and errors AI is being leveraged to streamline and optimize various aspects of the revenue cycle, from patient billing to claims management, ultimately improving financial outcomes for healthcare providers.
Before delving into the ways AI is revolutionizing healthcare revenue cycle management, it's essential to understand the key components of this process:
- Pat ient Regist rat ion and Verificat ion: The revenue cycle begins when a patient schedules an appointment. Accurate patient data, including insurance information, is crucial for claims processing
- Charge Capt ure: This step involves recording the services provided to patients and assigning appropriate billing codes
- Claim s Subm ission: Healthcare providers submit claims to insurance companies for reimbursement. Accurate and timely submission is vital to prevent delays in payment
- Paym ent Post ing: Payments from insurance companies and patients are posted to the patient's account, and any discrepancies are resolved
- Denial Managem ent : Handling claim denials and resubmitting them for approval is a critical step in revenue cycle management
- Pat ient Billing and Collect ions: Patients are billed for their portion of the healthcare costs, and collection efforts are initiated if necessary
- Revenue Analysis and Report ing: Analyzing revenue data helps healthcare organizations identify trends and areas for improvement in the revenue cycle.
- Pat ient Regist rat ion and Verificat ion: AI can improve the accuracy of patient data by automating data entry and verification processes. Natural language processing (NLP) algorithms can extract information from documents, reducing errors caused by manual data entry AI-driven identity verification tools can also help prevent fraud and improve the accuracy of insurance information
- Charge Capt ure: AI can assist in automating charge capture by identifying billable items and suggesting appropriate billing codes based on medical records and clinical documentation. This reduces the risk of underbilling or overbilling
- Claim s Subm ission: AI-powered software can help healthcare providers submit claims more efficiently by automatically checking them for errors and inconsistencies before submission. This reduces the likelihood of claim denials due to missing or incorrect information
- Claim s Adjudicat ion: AI can accelerate the claims adjudication process by automating the review of claims for compliance with insurance policies and medical necessity Machine learning models can predict the likelihood of claim denials and prioritize follow-up efforts
- Paym ent Post ing: AI can automate payment posting by matching electronic remittance advice (ERA) with claims and patient accounts. This reduces manual data entry and errors while speeding up the reconciliation process
- Denial Managem ent : AI can assist in identifying the root causes of claim denials by analyzing historical claims data. This enables healthcare organizations to implement targeted strategies to reduce denials and improve revenue collection
- Pat ient Billing and Collect ions: AI-driven patient billing systems can personalize billing statements and payment options based on a patient's financial situation. Chatbots and virtual assistants can also provide automated support for patient inquiries and payment arrangements, improving patient satisfaction and collection rates
- Revenue Analysis and Report ing: AI-powered analytic tools can provide insights into revenue trends, patterns, and anomalies. These insights help healthcare organizations make data-driven decisions to optimize their revenue cycle processes continually
The integration of AI into the healthcare revenue cycle offers several significant benefits:
- Im proved Efficiency: AI automates time-consuming and repetitive tasks, allowing healthcare staff to focus on more strategic and patient-centered activities This leads to faster claims processing and reduced administrative burden
- Increased Accuracy: AI reduces errors caused by manual data entry and human oversight, leading to more accurate billing and claims submissions This, in turn, reduces the risk of claim denials and payment delays
- Enhanced Revenue Collect ion: AI-driven denial management and patient billing systems improve the chances of collecting the full amount owed by patients and insurance companies. This positively impacts the financial health of healthcare organizations
- Cost Savings: By automating various revenue cycle processes, healthcare providers can reduce operational costs associated with administrative tasks and manual interventions
- Dat a-Driven Insight s: AI-driven analytics provide valuable insights into revenue cycle performance, enabling healthcare organizations to identify areas for improvement and optimize their processes continually
While AI holds great promise in healthcare revenue cycle management, there are several challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Int egrat ion Com plexit y: Integrating AI systems into existing healthcare IT infrastructure can be complex and may require significant resources and expertise
- Cost of Im plem ent at ion: Implementing AI solutions can be costly, and healthcare organizations must weigh the upfront investment against the potential long-term benefits.
- Et hical Considerat ions: AI algorithms must be designed and trained ethically to avoid bias and discrimination in decision-making processes
CorroHealt h invit es you t o check out t he m lnconnect s page available from t he Cent ers For Medicare and Medicaid (CMS). It 's chock full of new s and inform at ion, t raining opport unit ies, event s and m ore! Each w eek PARA w ill bring you t he lat est new s and links t o available resources. Click each link for t he PDF!

Thursday, Sept em ber 7, 2023
New s
- New Version of CMS.gov
- HHSProposes Minimum Staffing Standards to Enhance Safety and Quality in Nursing Homes
- CMSAnnounces Resources and Flexibilities to Assist with the Public Health Emergency in the State of Florida
- Laboratory Tests for Blood Counts: Comparative Billing Report in September
- Expanded Home Health Value-Based Purchasing Model: Submit Technical Expert Panel Nominations by September 27
- Physicians & Non-Physician Practitioners: Revised Medicare Enrollment Application Required November 1
-
DMEPOS: New Benefit Category Determinations
- Short-Term Acute Care Hospitals: Program for Evaluating Payment Patterns Electronic Reports
- Healthy Aging: Recommend Services for Your Patients
MLN Mat t ers®Art icles
- Changes to the Laboratory National Coverage Determination Edit Software: January 2024
Update
- Inpatient Psychiatric Facilities Prospective Payment System: FY2024 Updates
Publicat ions
- Evaluation and Management Services Guide ? Revised
Mult im edia
- Medicare Ground Ambulance Data Collection System Video
Therew ere9new or revised Transmittalsreleased thisw eek.
To go to thefull Transmittal document simply click on thescreen shot or thelink.










Therew ereFOUR new or revised MedLearn released thisw eek. To go to thefull Transmittal document simply click on thescreen shot or thelink.





Theprecedingmaterialsare for instructional purposesonly. Theinformation ispresented "as-is"and to thebest of CorroHealth'sknowledgeisaccurateat thetimeof distribution. However, due to the ever-changinglegal/regulatory landscape, thisinformation issubject to modification asstatutes, laws, regulations, and/or other updatesbecome available. Nothingherein constitutes, isintended to constitute, or should berelied on aslegal advice. CorroHealth expresslydisclaimsanyresponsibilityfor anydirect or consequential damagesrelated in anywayto anything contained in thematerials, which areprovided on an "as-is"basisand should beindependentlyverified before beingapplied. You expresslyaccept and agree to thisabsoluteand unqualified disclaimer of liability. The information in thisdocument isconfidential and proprietaryto CorroHealth and isintended onlyfor thenamed recipient. No part of thisdocument maybereproduced or distributed without expresspermission. Permission to reproduceor transmit in anyform or byanymeanselectronicor mechanical, includingpresenting, photocopying, recording, and broadcasting, or byanyinformation storageand retrieval system must beobtained in writingfrom CorroHealth. Request for permission should bedirected to Info@Corrohealth.com.

