2 minute read
2.8 Using Delay Function
2.8 Using Delay function
A time delay is something that is very important when working with embedded applications,
Advertisement
because there are times you want a delay before something is begun.
Time delays can also be used for breaks between processes. For example, a time delay in
between an LED can make the LED blink on and off, on and off, repeatedly. So time delays can
be very useful and important for embedded applications.
A __delay_ms() is not a real function, it is a macro which will expand into in-line assembly
instructions or a nested loop of instructions which will consume the specified number of time.
So the delay argument must be a constant and can't be changed during runtime. This function
is known as the compiler’s in-built delay function.
If you want a real function with a parameter, you had to write it on your own as shown in
Figure 2.14.
void delay_ms (unsigned int x) {
for(; x>0; x--) __delay_ms(1); //delay 1ms
Figure 2.14: User defined delay function
If an accurate delay is required, or if there are other tasks that can be performed during the
delay, then using a timer to generate an interrupt is the best way to proceed. The timer
module of PIC will be discussed in the next chapter.
Example 2.8
Refer Figure 2.12, write a program to blink the LED which is connected to pin RD0 of PIC18.
The LED will turn ON for 500 ms and turn OFF for 500 ms.
Solution:
#include <xc.h> #define _XTAL_FREQ 20000000 #define LED RD0 void delay_ms (unsigned int x);
void main(void) {
TRISD0 = 0; while(1) {
LED =1; //turn on LED delay_ms (500); //delay 500ms LED =0; //turn off LED delay_ms (500); //delay 500ms
} void delay_ms (unsigned int x) {
for(; x>0; x--) __delay_ms(1); //delay 1ms
Example 2.9
By referring to Figure 2.13, LED1 is connected to RD0 and LED2 is connected to RD7. Write a
program to make LED1 and LED2 blink alternately for each 2s continuously.
Solution:
#include <xc.h> #define _XTAL_FREQ 20000000 #define LED1 RD0 #define LED2 RD7
void delay_ms (unsigned int x); void main(void) {
TRISB = 0b00000000; //RD0 and RD7 as output pin while(1) {
LED1 =1; //turn on LED1 LED2 =0; //turn off LED2 delay_ms (2000); //delay 2s LED1 =0; //turn off LED1 LED2 =1; //turn on LED2 delay_ms (2000); //delay 2s
} void delay_ms (unsigned int x) {
for(; x>0; x--) __delay_ms(1); //delay 1ms
Example 2.10
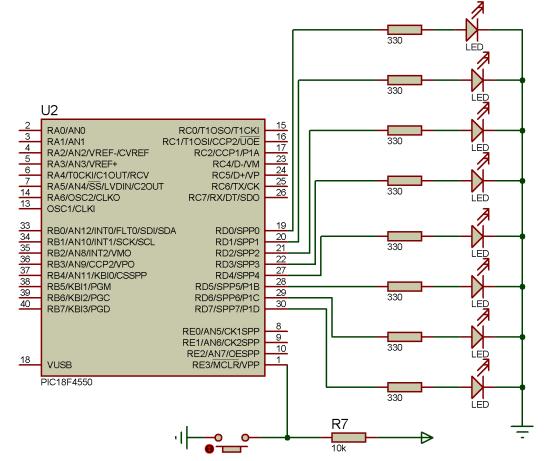
You are assigned to design a running light using 8 LEDs. Assumed the LED is connected to
PORTD as shown in Figure 2.15, write a complete program to make the LEDs turn on and off
as below:
Use byte addressable format for data.
11000000 delay 1s 00110000 delay 1s 00001100 delay 1s 00000011 delay 1s
Figure 2.15