1 minute read
Transmission lines parameters
TRANSMISSION SYSTEM
1.0 INTRODUCTION
Advertisement
Power system engineering is that branch of Electrical Engineering which concerns itself with the technology of generation, transmission and distribution of electrical energy. The power system growing into a vast and complex system represents one of the most vital systems in every modern nation.
Fig. 1: Power System from Generation to End-user via Transmission
From figure 1.0, we can see that electrical energy, after being produced at generating stations is transmitted to the consumers for utilization. This is due to the fact that generating stations are usually situated away from the load centers. The network that transmits and delivers power from the producers to the consumers is called the transmission system. This energy can be transmitted in AC or DC form. Traditionally, AC has been used for years now, but HVDC (High Voltage DC) is rapidly gaining popularity.
1
The term transmission lines broadly refer to overhead transmission lines and underground cables. The key function of a transmission line is to transfer bulk power from generating plant sources and load centres which ultimately supplies the load. Transmission lines, when interconnected, become the transmission networks, typically referred to as the power grid. Transmission line also interconnects neighboring power utilities which allows not only economic dispatch of electrical power within regions during normal conditions, but also transfer the power between regions during emergencies.
1.1 Main Components
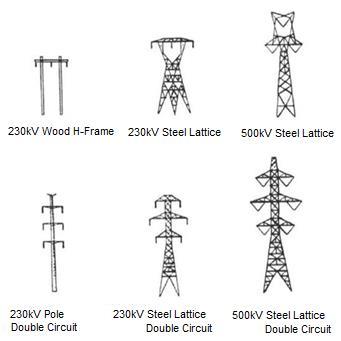
Transmission lines are made up of various components namely towers, poles, lattice structures, conductors, cables, insulators, foundations and earthing systems. The successful transmission of power relies on the effectiveness of these components.
The main components of High-Voltage (HV) electric transmission lines include: 1.1.1 Tower 1.1.2 Conductor 1.1.3 Insulator
Fig. 1.1: Transmission Line

2