ENDPOINT ASSESSMENT (EPA)
DOMESTIC RETROFIT


● UK’s aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to net zero by 2050 is possible by prioritizing the energy
efficiency of the new & old Buildings
● A whole house retrofit is fundamental to the UK's aim to retrofit all homes to an Energy Performance
Certificate (EPC) band C standard by 2035.
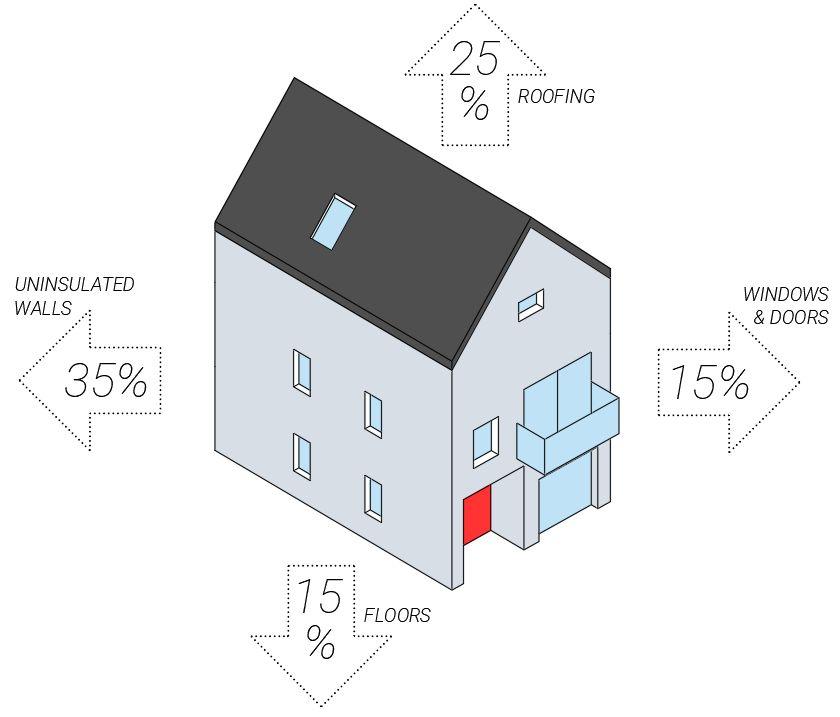
● 35% Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are from domestic households - central issue of the Climate Change Act 2008
● There are 29 million households in UK and 80% will exist by 2050
● 13.4% of the UK homes are in fuel poverty = 3.26 million homes
● The UK retrofit market is worth an estimated £3.5 – £6.5 billion per year
= JOBS + FUEL/ ENERGY / MONEY SAVING + LESS CO2 EMISSIONS
Domestic households (old buildings with solid stone walls/ void cavity walls) need retrofitting measures to
create an airtight, heat retaining efficient home with increased comfort. Improving energy efficiency will reduce energy expenses, carbon emissions, reliance on fossil fuels, AND SAVES ON ENERGY BILLS!
Retrofitting will stop climate change/ global warming, making it imperative to the UK's net-zero targets.
1. INSULATION / BUILDING FABRIC
2. SPACE & WATER HEATING / -UPGRADING & REPAIRS
3. HEATING CONTROLS
4. VENTILATION / COOLING SYSTEMS
5. RENEWABLE ENERGY SOURCE
6. EFFICIENT LIGHTING / ELECTRIC APPLIANCES

WARM HOMES
HEALTH WELLBEING
DIRECT BENEFITS
STOPS GLOBAL WARMING REDUCES CO2
COST / FUEL SAVING
BARRIERS
- Cost - Time, labour, and planning
- irrelevant + expensive
- Social Norms
- Lack of Incentive
- Lack of Knowledge /Understanding of technical issues
INCREASED PROPERTY VALUE
BENEFITS OF RETROFIT
DIRECT BENEFITS OF RETROFIT
STOPS CLIMATE CHANGE INCREASED COMFORT
ENERGY EFFICIENCY
- Low Importance of energy efficiency
- Inadequate number of companies and tradespeople
- Other Priorities
- Circumstances e.g. renting
- Lack of Faith / trust in workers, companies or products
- People don’t like change
- Aesthetics (it may not look great)
1.INCEPTIONRequirement Budgeting
2. RISK ASSESSMENTEvaluate risks to plan for project development
3. ASSESSMENTSite visit and collect information about present conditions
4. STRATEGYUse the collected data and project a 30 year plan
5. DESIGNEnsure project schedule, identify contractors, costs and contracting
6. INSTALLATION & HANDOVERSupport installation team and the customer
7. MONITORING & EVALUATIONEnsure project effectiveness and share/ collect feedbacks
1. CLIENT Property owner, householder, landlord and/or tenant
2. RETROFIT COORDINATOR The Retrofit Coordinator is the lead character
2. RETROFIT ADVISOR/ SUSTAINABILITY OFFICER Liaison bet. customers & Company/ Advice & solutions.
3. RETROFIT ASSESSOR Involved in the Risk and Dwelling Assessment stages 4. RETROFIT DESIGNER
The Retrofit Designers main role is in the design stage
5. RETROFIT INSTALLER Person or organization undertaking the physical placement of EEM(s)
6. RETROFIT EVALUATOR Monitors and evaluates after project completion
● Tariffs - Energy plan (Cost of charges gas and electricity) / Today’s Competitive market = new + many marketing strategies
1. The Standard (Variable) Tariff - Default tariff, No fixed term & exit fee/ most expensive of the tariffs.
2. Off-peak tariffs - Designed for electric storage heating, with cheaper electricity at off-peak times / Economy 7 & Economy 10
3. Fixed tariffs - Guaranteed standing charges and unit rates, no price fluctuations
4. Online tariffs - Customer manage account via the internet + discounts
5. Dual fuel tariffs - Provides gas and electricity from the same energy supplier +discounts
6. Green tariffs - Energy generation from renewable sources of energy + Contribute towards environmental schemes.
7. Prepayment tariffs - For people with prepayment meters = pay in advance by 'topping-up' their meter using prepay tokens, cards, or a key.
8. Social tariffs - Special social tariffs for customers who had difficulty paying their bills
9. Feed in tariffs (FITs) - Contracts where an energy supplier pays the customer to generate electricity at home

INFORMATION ON EACH BILL:
- Npam (Account) number
- Name of the person
- Period of the BIll
- Name of the Tariff
- Product Type
- Payment method
- Unit rate
- Standing charge
- Estimates annual usage
- Readings of Electricity or Gas
- 5% Vat Information
- Conversion of Gas to Kwh

● ENERGY USE / COST IS HIGHER FOR LARGER HOUSEHOLDS WITH MORE OCCUPANTS
● MAXIMUM % OF ENERGY IS USED FOR HEATING - 79%
● LIGHTING & APPLIANCES 14%, COOKING 6%
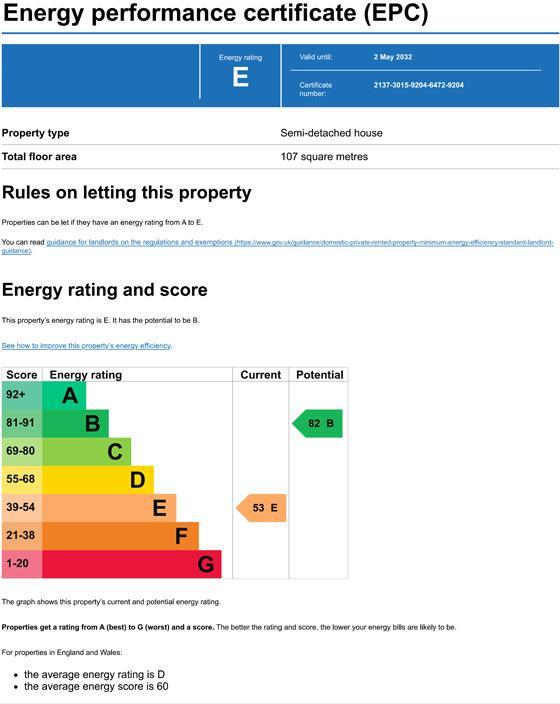
● The Energy Performance Certificate (EPC) - 10-year valid document - energy ratings for domestic homes. / A (most efficient) to G (least efficient) rating.
● EPC CONTENTS :
- Address, Energy rating, Valid date, Certification number
- Property type, Total floor area / Rules on letting this property,
- Energy rating and score
- Break down of property energy performance (Features in this property, Primary energy use)
- How this affects your energy bills (Heating this property)
- Impact on the environment (Carbon emissions)
- Changes you could make (List of measures)
- Who to contact about this certificate, Other certificates for this property
● A legal requirement by the HM Government, after construction, sale or rental. / The property owner / agent must provide the EPC to all buyers/ renters.
● Essential for budgeting and building rental or purchase.
● Compares current ratings of properties - how to save energy / money by installing improvement measures.
● Minimum Energy Efficiency Standards (MEES), or Minimum Energy Performance Standards (MEPS) are building regulations that set a minimum requirement for the Energy Performance Certificate
● Introducing new materials, products, and technologies into an existing building to reduce energy consumption & CO2 emissions. Conducted under regulation standards like PAS 2030-35, Enerphit, Trustmark, MCS, HES.
● (PAS) 2035 is a British specification - framework for designing / installing energy efficiency measures (EEMs) - advocates the "fabric first" - improving the building envelope as the 1st step
● PROCESS: Assessment of dwellings for retrofit / energy performance certifications + Identification and evaluation of improvement options (energy-efficiency measures, or EEMs) + Design and specification of EEMs + Monitoring, Installation and evaluation
● EEMS- Insulating floors, walls, and roofs + installing high-quality windows and doors to reduce draughts and thermal bypasses + Heating system / Controls + Ventilation
● A whole house retrofit is integral to the UK's aim to retrofit all homes to an Energy PerformanceCertificate(EPC)bandCstandardby2035.

FUEL POVERTY = 10% OR MORE OF NET HOUSEHOLD
INCOME IS SPENT ON ENERGY BILLS
LEADING CAUSES
● Household’s Low income
● High energy prices and Higher tariffs
● Low-volume users
● Unable to pay via direct debit
● Poor energy efficiency
- inadequate insulation / old heating systems
● Under-occupied larger-than-average homes
EFFECT OF FUEL POVERTY
● Physical and psychological health of the public
● Economic burdens on healthcare systems
● Hampering of society's well-being and education
● Cold and damp homes - that are below 18-21 degrees
IMPACT ON HEALTH AND WELLBEING
● Health issues - respiratory diseases, heart diseases, circulatory diseases, and mental health problems
● Increased winter deaths/ repeated visits to GPs
● Late discharge/ increasing annual spending.
● Loss of dexterity and accidents

● The healthy levels of CO2 in the air = 400 -600 parts/million & relative humidity = 40 to 65%
● Condensation = warm air is in contact with cold surfaces
- CAUSES : Excess water vapour, gases and odours due to cooking, washing, use of hot water, Breathing / The lack of ventilation in air-tight spaces = interstitial condensation
- EFFECTS : Mould and dry/ wet rots, Respiratory diseases, Bad air quality, destruction to property
- SOLUTION : Well heated homes/ insulation/ natural + mechanical ventilation/ above 18 C temp
● Ventilation = fresh air + reduces overheating by solar gains, body heat, electrical appliances + necessary for combustion devices + vent
indoor pollutants (vapour, CO2, CO, NO2, VOC- volatile organic compounds and dust mites)
● Ventilation = 1. background ventilation, 2. Purge (Rapid)/ Mechanical , 3. Infiltration (uncontrolled Ventilation).
● Typical room req background ventilation of 15-25 sq inches -> ‘trickle’ window vents & door undercuts
● Purge/ Rapid Mechanical Ventilation ventilates - kitchens and bathrooms (high level of moisture & impurities in the air)
● The building regulation approved document part F details the requirements for proper ventilation per space volume, building occupancy, and other variables.


● Provide information about the product's energy efficiency, consumption, and usage features. It uses colour banding and QR codes similar to the EPC labels.
● It is a system created by the EU in the 1900s - covers a range of appliances like lighting, heating, fridges, freezers, televisions, fuel boilers and air conditioners.
● Electrical appliances have power and energy rating labels for electrical safety and information on energy consumption.
● Power rating is measured in Watts (W) or kilowatts (1000W) per Hour (h)
● Energy Labels helps us use/ choose the most efficient appliances = cost & energy savings + reduced CO2 emissions + various other benefits like time/ resources/ comfort levels
● ErP, SEDBUK are the systems that give energy efficiency ratings.
● ErP (energy-related products) energy label - European energy label introduced in September 2015; it has a rating from most efficient of A to least efficient rating of G.
● SEDBUK stands for ‘seasonal efficiency of a domestic boiler in the UK,’ the latest SEDBUK provides a rating in terms of a percentage score
● Insulation and airtightness
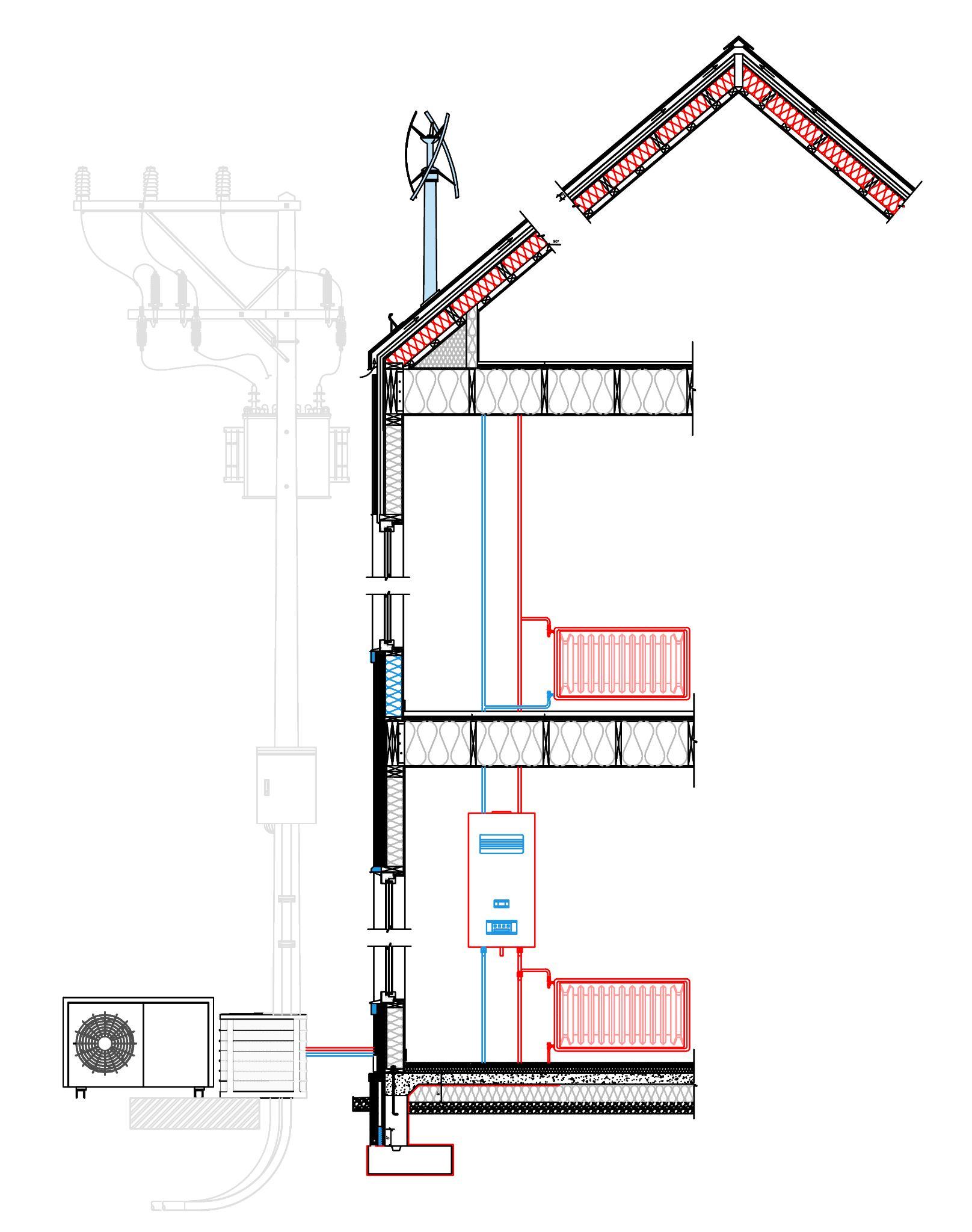
● Upgraded heating systems - combi boilers/CHP/ heat pumps/ storage heaters
● Heating controls - thermostatic radiator valve (TRV) / Programmers / Timers
● Microgeneration - solar photovoltaic panels (pv), solar thermal panels, ground and air source heat pumps, wind turbines, hydro, heat and power (chp) units fuel cells, biomass and anaerobic digestion.
● Use energy labels to use appliance that are energy efficient
● Use compact fluorescent light bulbs and led light bulbs
● One less laundry per week
● Powerdowns- switch off standby - £55 / year
● 4 min shower - save £65 / year
● Turn off lights - £20 / year
● Fill kettle with only what you need - £11 / year
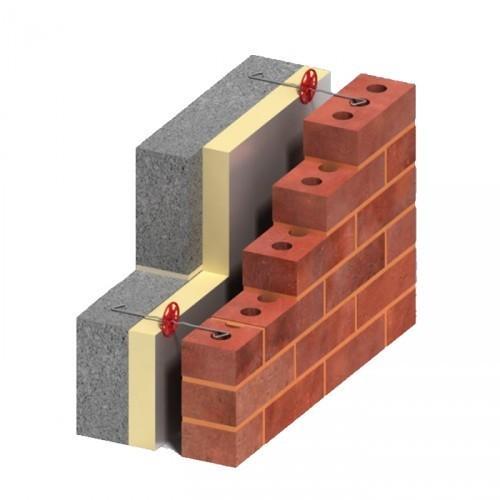
● INSULATION - Cavity walls (£24/msq.)/ Solid walls - external (£120/msq.)/ and internal insulation(£100/msq.)/ / Loft spaces
(£25/msq.)/ Roofs - warm or cold roof insulations / Floors (£95/msq.)/- rigid board insulations with floating floors, suspended timber and a solid concrete floor insulation system.
- Insulating materials like Mineral glass or rock wool, hemp/ Wood fibre, Cellulose fibre, Rigid Board insulation (polyisocyanurate or PIR, PF, polyisocyanurate or PUR, thermoplastic or EPS), Polyurethane PU sprayed or injected and Extruded polystyrene (XPS) are the best solutions for all domestic or non-domestic building insulation.
● Space and water heating system improvements - upgrading boiler systems + control systems.
-Combi and condensing boilers, heat pumps, and Combined heat and power (CHP) systems
● Prioritising thermostats, digital and mechanical Programming, and Thermostatic valves
● Use of Secondary glazing, Double or triple glazed windows
● Ventilation - Using trickle vents / background ventilation / Mechanical ventilation - Intermittent extract ventilation (IEV), Single room heat recovery ventilators (SRHRVs), Passive stack ventilation (PSV), Mechanical extract ventilation (MEV), Mechanical Ventilation with Heat Recovery and Positive input ventilation (PIV).
● Microgeneration - Microgeneration (also known as renewables) - Solar photovoltaic (solar PV), Wind (micro wind turbines), Micro combined heat and power (micro-CHP), Hydro (water turbines), Air source (ASHP)/ Ground source (GSHP) heat pumps.




● Warm home Discount scheme (WHD) - financial support (A)
● Winter Fuel Payment / Cold Weather Payment- financial support
- gov.uk/winter-fuel-payment ‘or’ /cold-weather-payment
● Fuel supplier’s trusts and hardships - grants for vulnerable customers
● Priority Service Register (fuel suppliers and distributors) - offer special services to customers who are in vulnerable situations.
● Energy Company Obligation (ECO) - assists households in fuel poverty, low income and struggling with heating costs. (B, D)
● Great British Insulation Scheme – (runs from 2023 to March 2026) -provides installation of energy efficiency measures to a wide range of households.
● Home Upgrade Grant (HUG) -Funds to improve low-income homes (offf gas network)- 100% subsidy
● Smart Export Guarantee - Payment for energy export to grid
● Boiler Upgrade Scheme - Grants for Heat pump / Biomass
● Renewable Heat Incentive (RHI) - financial support (C)
● Nest Scheme (Available to Wales)- (A,B,C,D,E)
● Home Energy Efficiency Programmes for Scotland (HEEPS)energy efficiency and fuel poverty scheme funded by the Scottish Government
& FUNDS:
British Gas (British Gas Energy Trust)
EDF Energy (EDF Energy Customer Support Fund)
E.ON (Energy Fund)
E.ON Next (Energy Fund)
SEE (Priority Assistance Fund) 6. Octo Assist Fund 7. Scottish Power (Hardship Fund)
(Energy Fund) 9. Let’s Talk Energy Fund 10. Charis Grant / 11. Turn to US
PROPERTY & CUSTOMER DETAILS:
● Four bedroomed detached property / Fifties built - cavity walls made of brick and concrete panels.
● 2 employed adults and three children. - Income possibly above £31,000
● Boiler, heating and hot water system has been in over 20 years (no evidence of any service and maintenance history) - This will keep the Energy Performance Certificate ratings of E-F with potential of B.
REQUIREMENT:
● Upgrade the heating and hot water system
- New gas combi boiler and system - £4,750 to £6,750 / Average - £5,750
- New gas combi boiler and radiators £8,420 to £11,820 / Average - £10,120
- New electric central heating system £3,810 to £4,930 / Average - £4,370
● Install renewables as a further OPTION.
- Solar water heating/cost - £4,000 - £6,000
- Solar photovoltaic panels, 2.5 kWp/ cosy £3,500 - £5,500- Typical yearly saving £356
POSSIBLE GRANTS AND FUNDING SUPPORT:
1. Boiler Upgrade Scheme - (2022 to 2025)
- £7,500 towards an air source heat pump
- £7,500 towards a ground source heat pump (including water source heat pumps and those on shared ground loops)
- £5,000 towards a biomass boiler
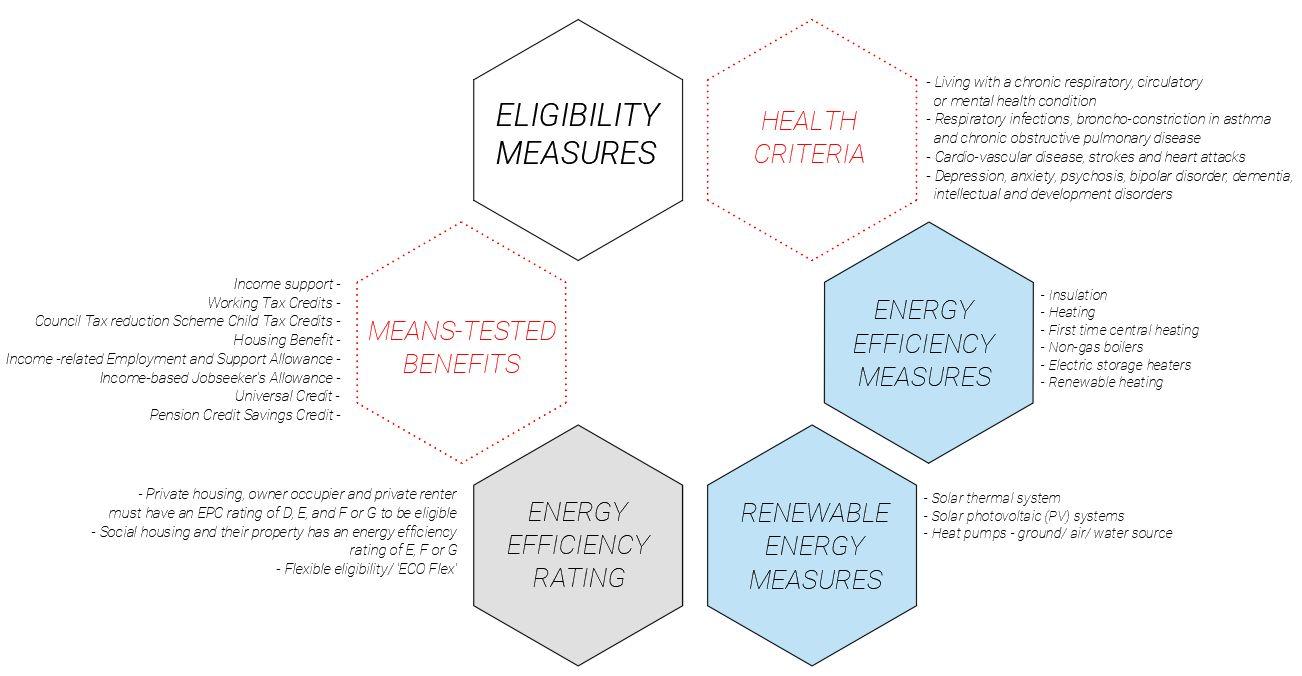
Eligibility:
- Property owner (business, a second home, rent out property)
- Be replacing fossil fuel heating systems - (POSSIBLE AS THE SYSTEM IS 20 YRS OLD - NEED PROPER ASSESSMENT)
2. Energy Company Obligation (ECO) (Valid till March 2026) - assists households in fuel poverty (MAY BE PRESENT DUE TO OLD HEATING SYSTEM EFFICIENCY), low income and struggling with heating costs.
Eligibility
- Live in private housing, owner occupier and private renter and in receipt of specific benefits.
- EPC rating of D, E, and F or G to be eligible.
Measures :
- Heating
- First time central heating
- Non-gas boilers
- Electric storage heaters
- Renewable heating
Biomass boilers (NOT ELIGIBLE - NOT OFF THE GRID / NOT NEW BUILD Home Upgrade Grant - (NOT ELIGIBLE - GROSS ANNUAL INCOME ABOVE £31,000)
POSSIBLE MEASURES TO INSTALL:
- New gas combi boiler and system - £4,750 to £6,750 / Average - £5,750 - 90-94% efficient
- New gas combi boiler and radiators - £8,420 to £11,820 / Average - £10,120
- New electric central heating system - £3,810 to £4,930 / Average - £4,370
- Air source heat pumps (ASHPs) / Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs) / Water source heat pumps (WSHPs)
- 2.5kW of heat for each 1kW of electricity used, i.e. it is 250% efficient.
- Underfloor heating / radiator system
- Air-source heat pump - $4,000 to $8,000
- Geothermal heat pump - $15,000 to $35,000