CompaCt City
masterplan Framework For underutilised deFenCe land Priyadarshini Jain | PUD21264


masterplan Framework For underutilised deFenCe land Priyadarshini Jain | PUD21264

I would like to earnestly acknowledge the sincere efforts and valuable time given by Prof. Brijesh Bhatha, Prof. Vanishree Helkar, and teaching assistant Jugal Bhatt. Their valuable guidance and feedback has helped me in developing basic understanding of master planning framework.
Also, I would like to mention the support of my unit mates because of them site study was a fun and learning experience.
A special thanks to my parents, friends and classmates who contributed in one way or the other for accomplishing the project.
“The information presented in this portfolio has been studied and collected by author as a part of Masterplan Studio, Faculty of Planning, CEPT University. Any omissions and errors are deeply regretted.”
The studio focuses on the master planning and design of single-ownership large Greenfield developments/ cleared brownfield development with a key emphasis on the design of livable neighborhoods.
In the past few years, there has been increasing attention to redeveloping vacant and inefficiently used public land within cities to add much-needed housing, amenities, and an accessible and inclusive public realm.
The Ministry of Defense is the largest land-owning public authority in the country, with 17.3 Lakh acres of land under its ownership. The studio unit makes a case for opening up part of the under-utilized defense land along the Sabarmati River in Ahmedabad for redevelopment. This is aligned to the new National Defense Land Policy currently under consideration that encourages the development of surplus defense lands outside Cantonments for public infrastructure and improvements.
The strategic location of the Ahmedabad Cantonment site close to the airport and abutting the riverfront phase 2 provides a unique opportunity to imagine future waterfront developments and to trigger further investments in the area.
The focus of the design exercise is to imagine and envision the future of the cities. In order to understand the existing brownfield site of Defence land, site study was done as a group of 11 students. The study focused on how defence land policy came into being and how it could be utilised in Ahmedabad’s context. Along with this, a comprehensive site analysis was done to detail out threats and opportunities that site possess.
62
Notified Cantonment
1.63 Lac acres Cantonment Area
15.95 Lac acres Outside Cantt
Defence cantonments when planned, were on the outskirts of cities, but with growing urbanisation, these areas have now become part of the cities. The Ministry of Defence also owns land around und these cantonments not used for military uses. This underutilized land in midst of the city offers an opportunity for development and cater to the rising housing demand along with providing much needed social and recreational public amenities for the city.
Proximity Map Land Value Map
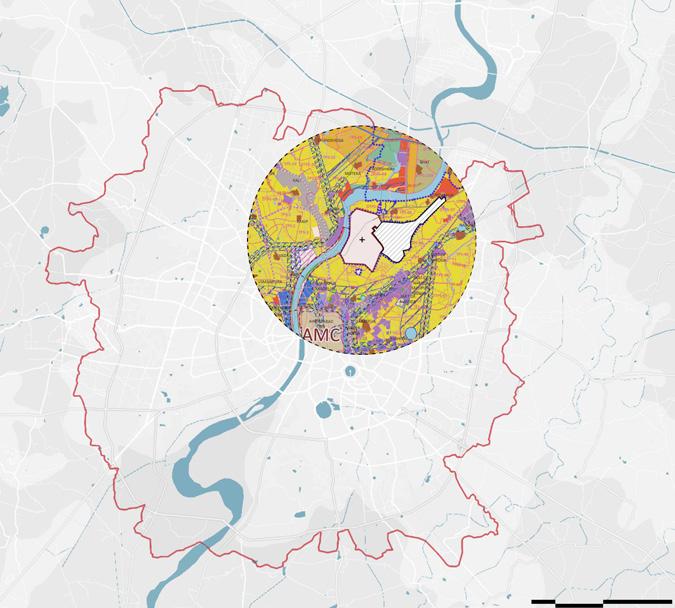

Defence land lies within close proximity of intermodal and intramodal transit options thereby increasing its connectivity with city
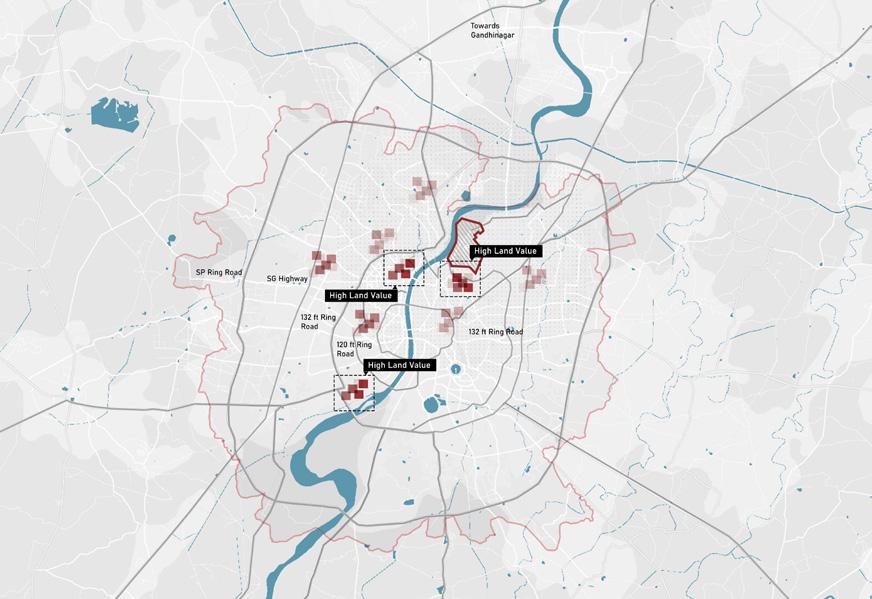
After Riverfront Phase 2 development the property price especially around riverfront by 22% thereby rendering the land as high value
Due to the restrictions imposed on defence land the high priced land sits as a void amidst the development plan
Note. Analysis and Presentation done as a group work
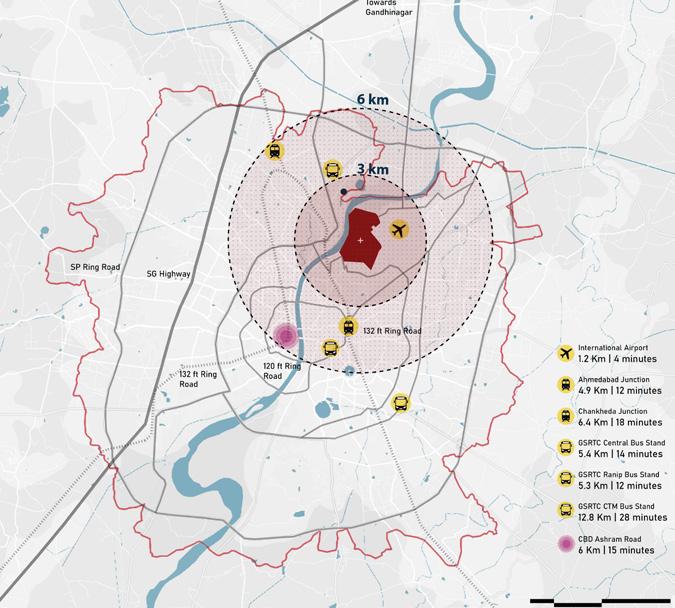
In Ahmedabad Defence land lies within close proximity to airport along the high valued riverfront land . Along with this it also is in 3kms radius of Multi Modal transit stops. Thereby increasing its potential for development.

There are five categories of Defence land where A1 is primarily army land an in active use by unit, A2 is reserved for defence estates, B1 reserved for central government, B2 by State Goverment, B3 B4 and C are occupied by cantonment but can be leased out
In Ahmedabad Defence land is spread across 1000 acres. Out of which only 450 acres is primarliy under active army use rest is either laying vacant or is leased out.
4 sqkm Defence Land
0.95 sqkm Site Area
Note. Analysis and Presentation done as a group work




On the northern side the site is lower but with the riverfront Phase 2 development the site is being levelled
North side of the site is prone to heavy water flow during rainfall creating catchment areas
43% of the site is filled by wild vegetation Most of them is of no economic or ecological value to the area.

Site abutting the riverfront phase 2 which is currently under development and site is being levelled for the same

Airport road is the major thoroughfare that connects site to the rest of city

The present buildings on the site are in dilapidated condition. The land is leased out by defence to these developments.

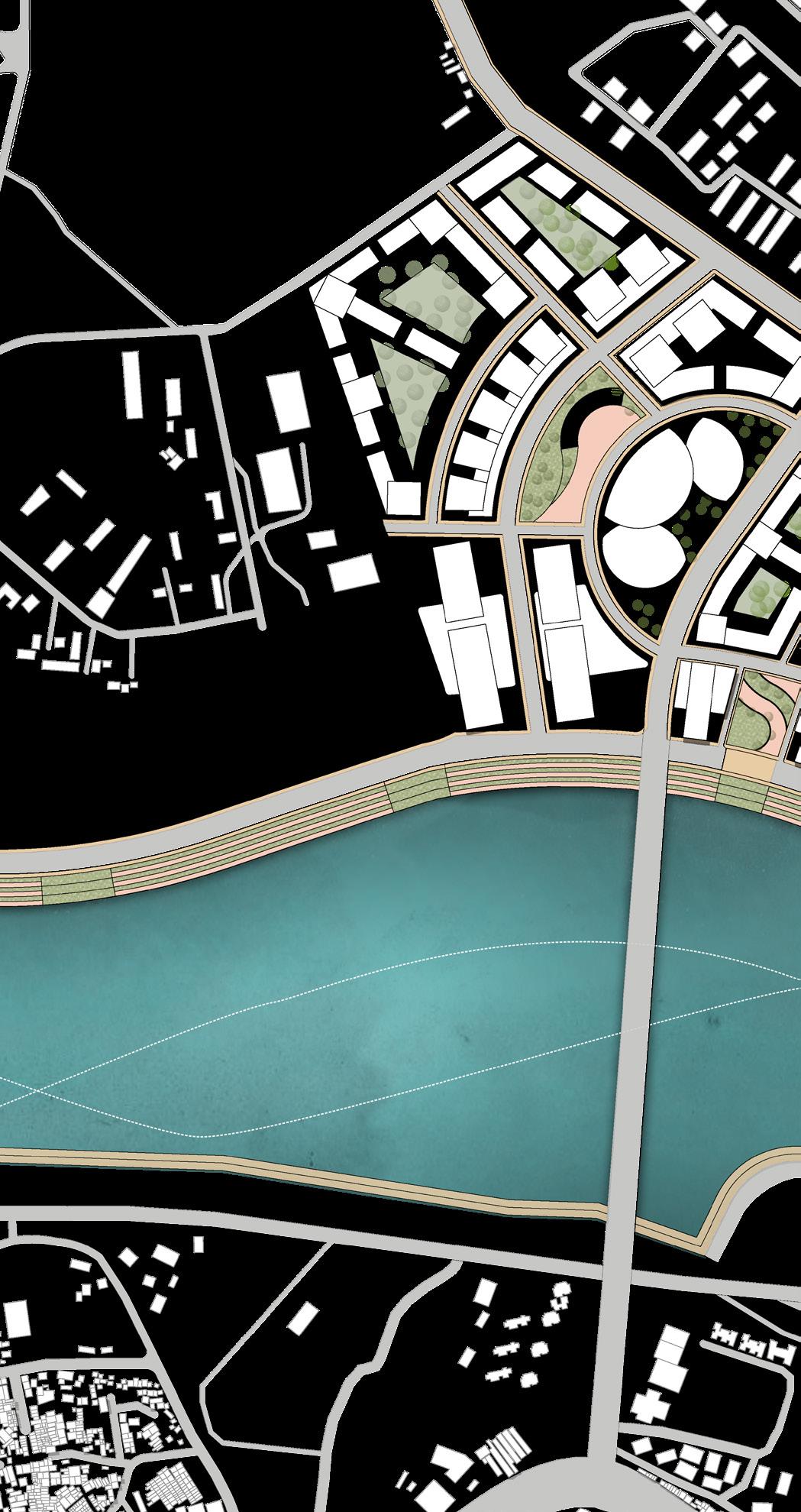
1.6km long, 60m Wide riverfront phase 2 promenade is integrated with site . Riverfront Phase II emphasizes on greener development having stepped green multi layered Promenades, excellent Road network, active green Parks, Children’s Play area, Food Plaza, Amphitheatres etc.
Note. Analysis and Presentation done as a group work
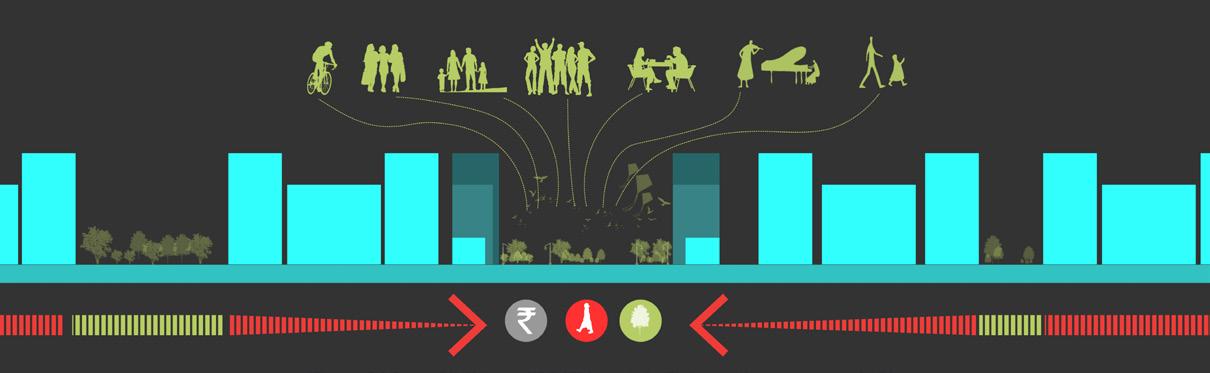
Convergence of open spaces into urban Densities
In order to conceptualise the master plan existing trends in urban peripheries and overall city were researched through various primary and secondary sources.
In addition to that conceptual theories and ideas revolving around how cities are growing and how they can evolve were analysed.
The study indicates that newer eastern as well as western suburbs have low walkabiliy due to footpath unavaibility and and lower connected node ratios. Parallety it can be observed that in western side large chunks of vacant land be observed but there are no usable public open and green spaces present for the residents (Adapted From “Understanding the City studio” (Unpublished portfolio from Master’s of Urban Design) by P. Jain, 2021, CEPT University. Copyright 2021 by P. Jain.







Larger block sizes
Larger block sizes




600m – 700m
600m – 700m
600m-700m
Block Perimeter
Block Perimeter
Block Perimeter
Larger blocks tend to have fewer intersections and access points, which can make it difficult for people to easily move around
Less Walkability Only 15% Out of total road length have footpath
Less Walkability Only 15% Out of total road length have footpath
Only 15% Footpath out of total road network
The lack of footpaths can is contributing to traffic problems and pollution. In addition to this available footpath is encroached by on street parking
High Land Wastage
High Land Wastage
Only 18.36%
Only 18.36%
Only 18.36%
Lack of absorptive landscape 55%
Lack of absorptive landscape 55%
Land under Public open space
Land under Public open space
Land under public Domain
Public open spaces are wasted in setbacks and underutlised land.
Lack of per capita green open space in the city
Western Ahmedabad prone to urban Flood
Western Ahmedabad prone to urban Flood
55% of Western Ahmedabad prone to urban Floods
Concretisation or urban landscape has resulted in city being prone to flood like situation even after a smallest downpour

A compact city is a type of urban development that is characterized by high-density development and a mix of land uses. In a compact city, buildings are generally built close together, and residential, commercial, and institutional areas are all located within close proximity to one another. This type of development is designed to be more sustainable and efficient than traditional suburban development, which tends to be more dispersed and low-density. Compact cities are typically designed to be more walkable and bikeable, and to have a strong public transit system. Compact neighborhoods are characterized by higher population densities and a more efficient use of land. This can have a number of benefits, including reducing the need for people to travel long distances, reducing traffic congestion, and making it easier for people to access various amenities and services within the neighborhood. Compact neighborhoods can also help to promote a sense of community and social interaction, as people are more likely to encounter each other in a dense, urban environment. Overall, a compact neighborhood is a type of urban development that is characterized by high population density and efficient land use.




A comprehensive master plan is designed understanding the need of the city as well as the national and international trends.
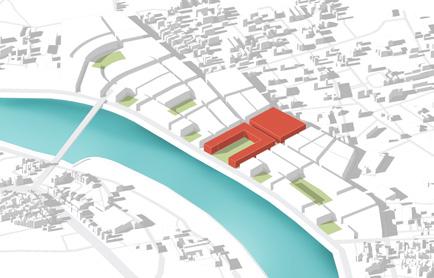
To create Dense mixed use building systems along the riverfront that promotes active and healthy lifestyle, increase walkability and offers high quality living experience.


As per compact neighbourhood formulating districs that are smaller in size have less block perimeter so as to promote walking. Within 5 min of walking distance all amenties are availaible
To bring in and connect with the existing riverfront a central promenade which is can act as economical, ecological and visual catalyst for the development.
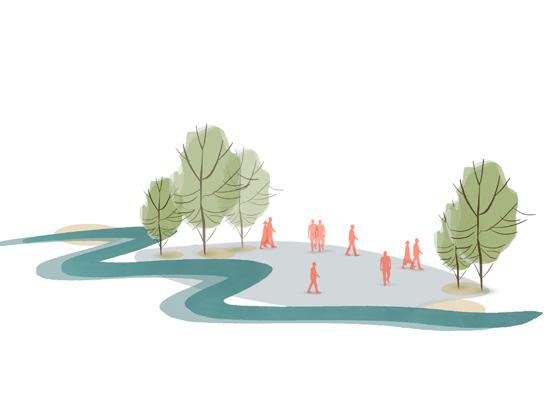
Creating Mixed use development across the site as it lies within close proximity of multi modal transit stops
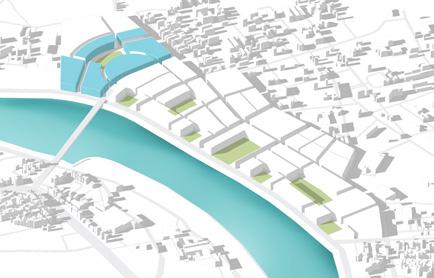
Formulating urban greens such that there is open space within 5 min walking distance of every unit at different levels
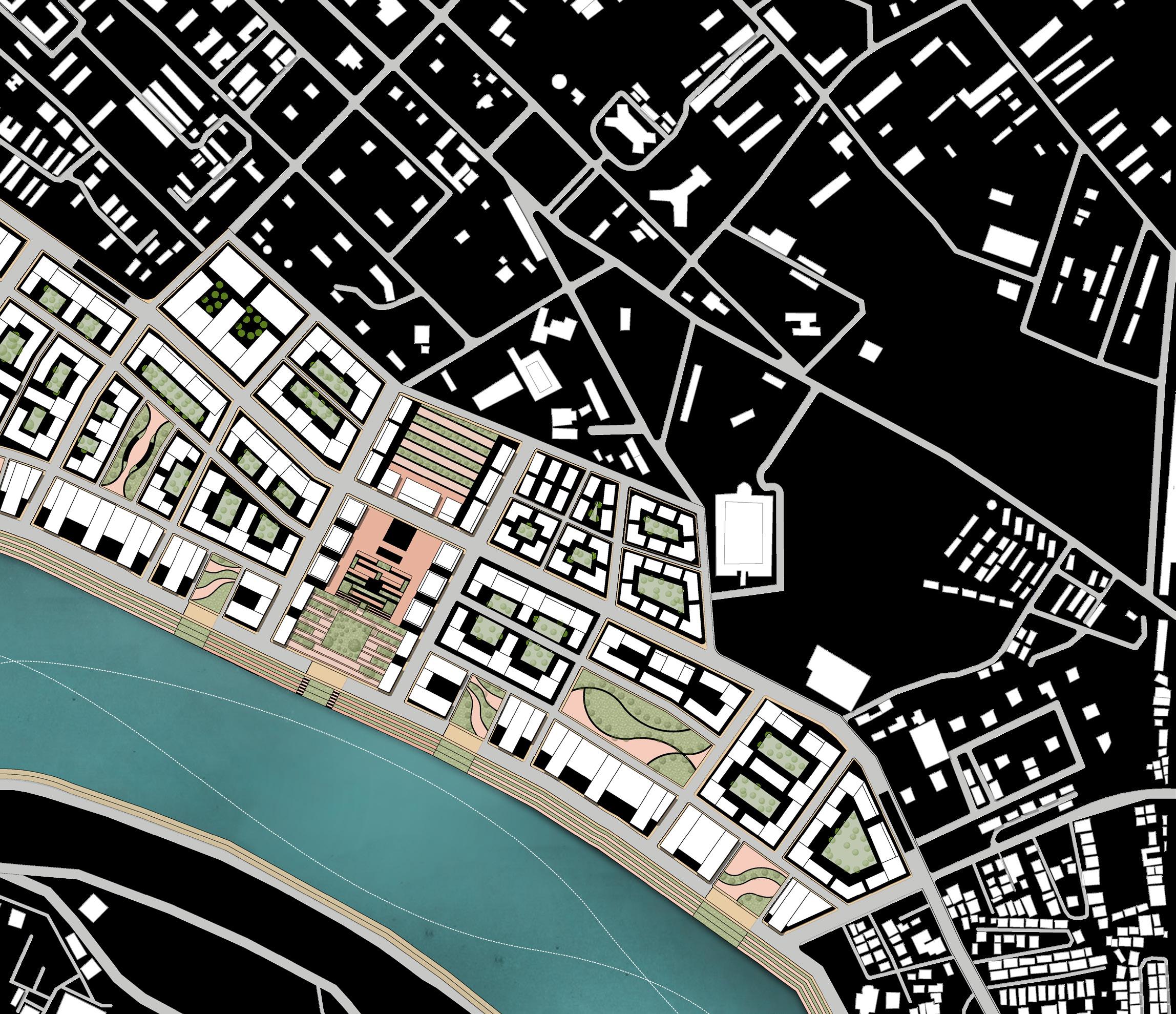
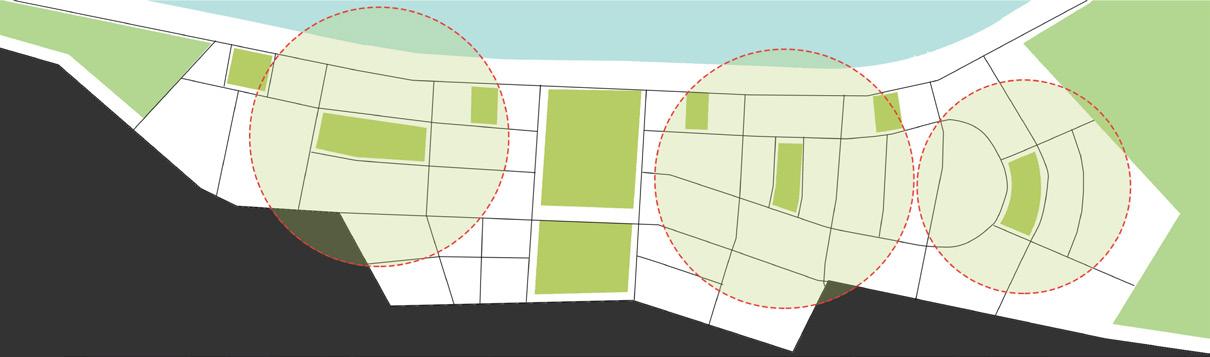
Site is divided via road network so as to create smaller walkable and compact parcels. With parcels along the riverfront being narrow and more oriented towards the river


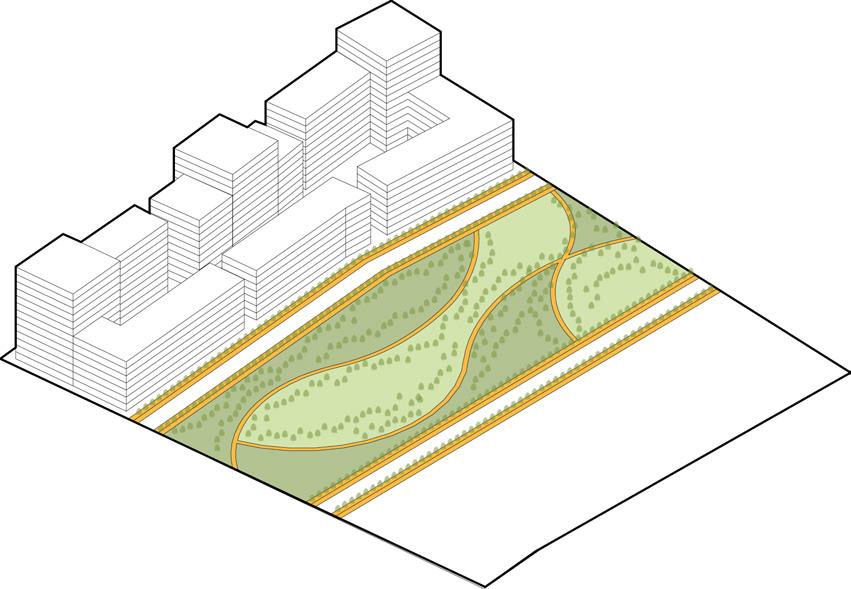
One major central open space that will act as catalyst for the city as well as this development and multiple smaller open spaces across 1.6km stretch to cater to spillover from riverfront
Green spaces places in such a combination that every unit, every person has individual as well as public open space available within 5 min walking distance
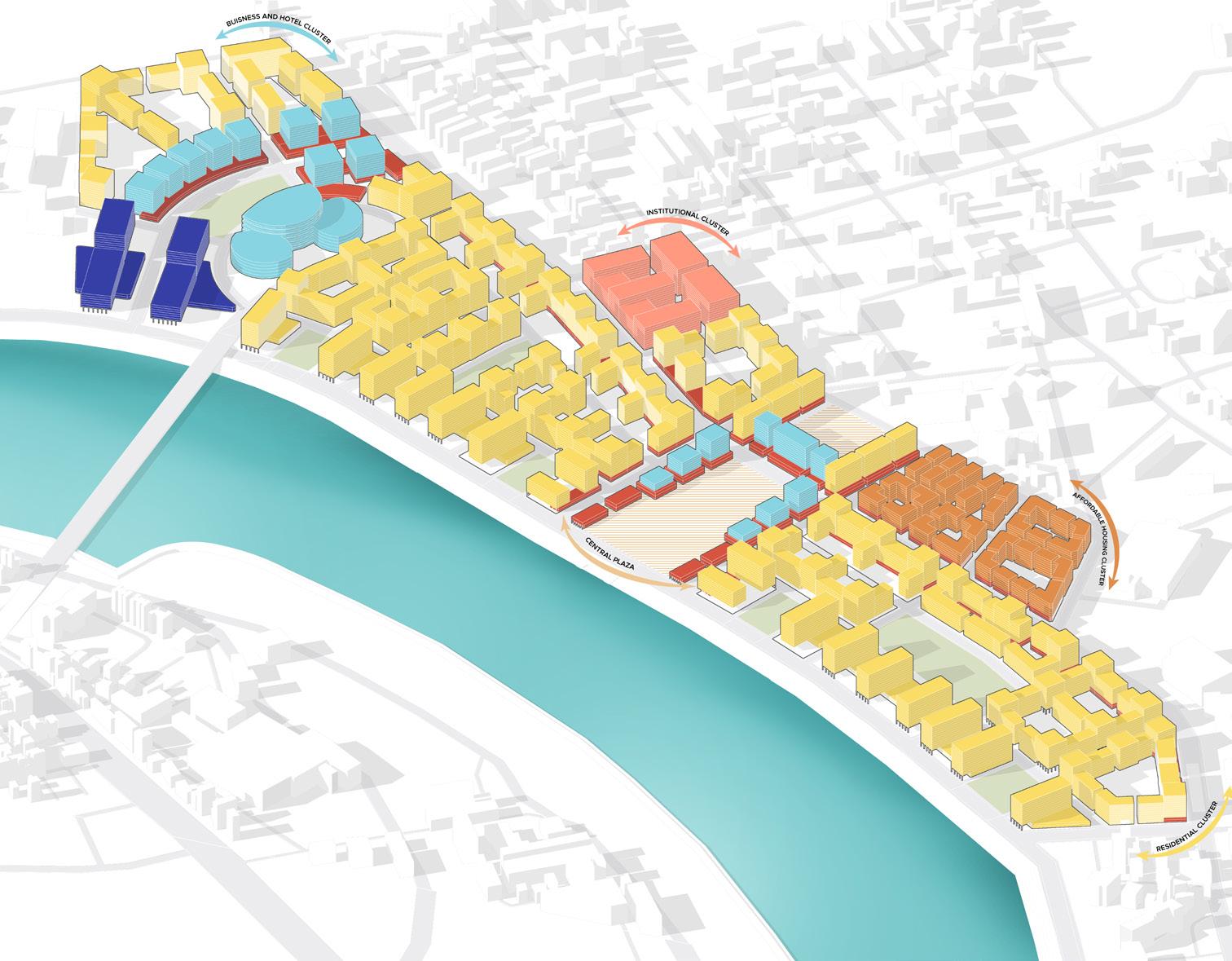
Affordable housing district placed in the inner side of the site as land value just adjancent to rivefront is higher.

Institution is placed along the area which already comprised of a school facility and will cater to neigh bouring developments also
Due to the airport in close proximity commercial district is placed along this side which will act as a image for the city as well as cater to the aiport needs
To fullfill the rising housing demand most of the site is utlised for residential district for middle income groups
Open space that can cater too spillover from river front and be utilised as retail, shopping, food and activities plaza


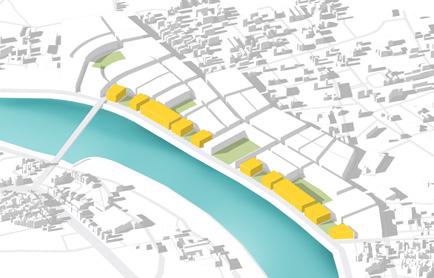
These are high end residential district that will cater to the economical value of the land as well as im prove the imageability of the riverfront promenade
With an intent to formulate smaller parcels a robust street network system is designed where Street density is higher to disperse the traffic and have high connected node ratio and multiple avenues to reach riverfront promenade which is currently absent 23% Area under roads Street Density Connected Node Ratio



The aiport road is vertically divided such as underpass caters to thoroughfare traffic for airport and upper street acts as commercial boulevard and shared street.
0.98 13Km/sqkm Commercial Lane Commercial Lane 3.5m 5m 5m
2m 2m 2m Footpath Footpath Footpath
3.5m 2m 2.4m 2.4m
Cycle Lane MUZ MUZ 7.5m Carriageway 7m Carriageway
Underpass 7.5m Carriageway
Footpath Cycle Lane Cycle Lane Cycle Lane
7.5m Carriageway
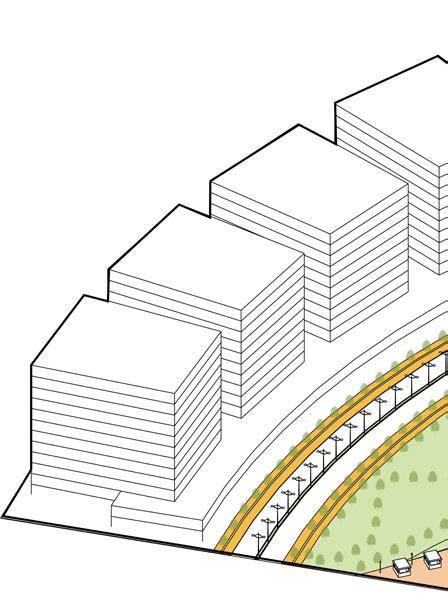
24m wide riveFront ConneCtors
MUZ zone is created along 24m road such as there are parking bays and bus drop off zones availaible so as to cater to multi-modal as well as slow moving traffic.
18m wide internal streets

These are internal connector streets hence developed as shared streets with no on street parking because it will be utilised by residents for entering there respective apartments


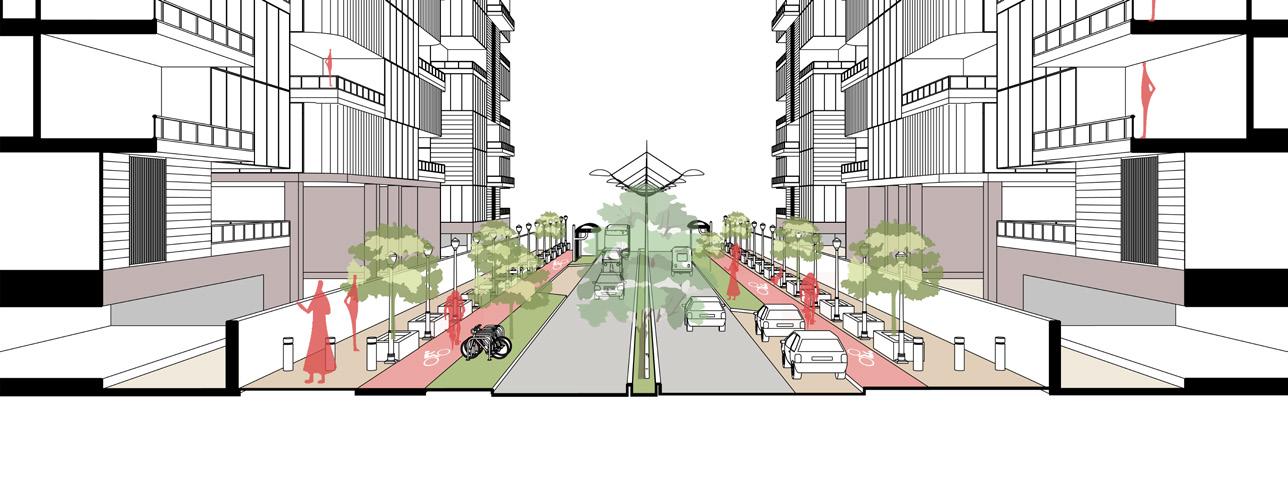

15m wide pedestrian priority streets
These are pedestrian priority streets that connects entire site to riverfront which are cyclable as well as walkable.
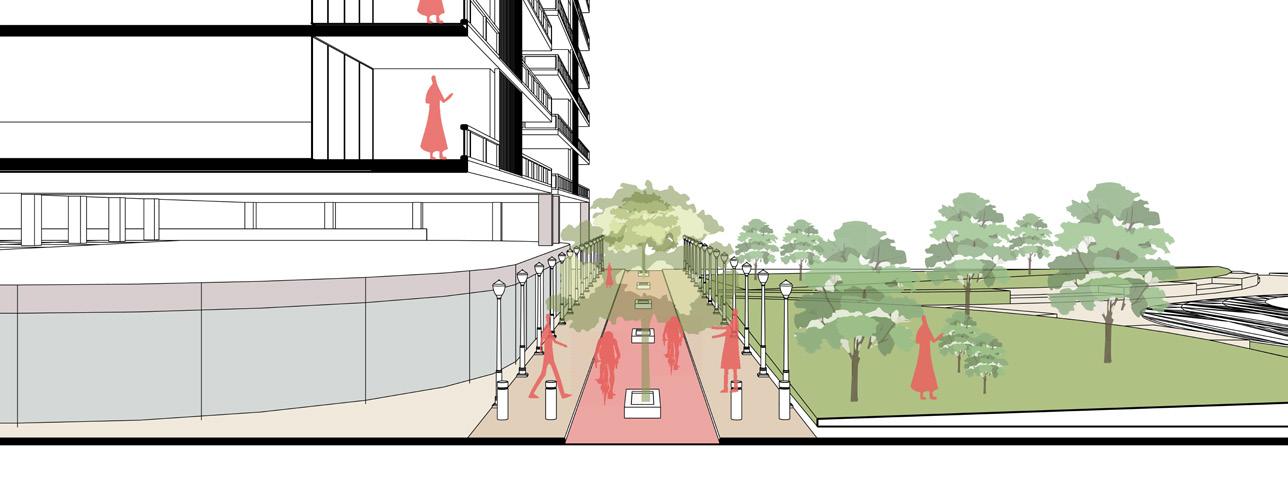
Open space are designed in such a way that within 5 min walking distance there is public area available that will cater to all the residents. The central open space or the hub is formulated as plaza so as to act as catalyst for the development Out of 6% hardscape area only 1% area is lined with non porous material which has some structure beneath it rest 17% of land on ground is porous. In addition to this there are multiple open spaces at various levels which act as green roofs so as to increase overall absorption capacity of the area.






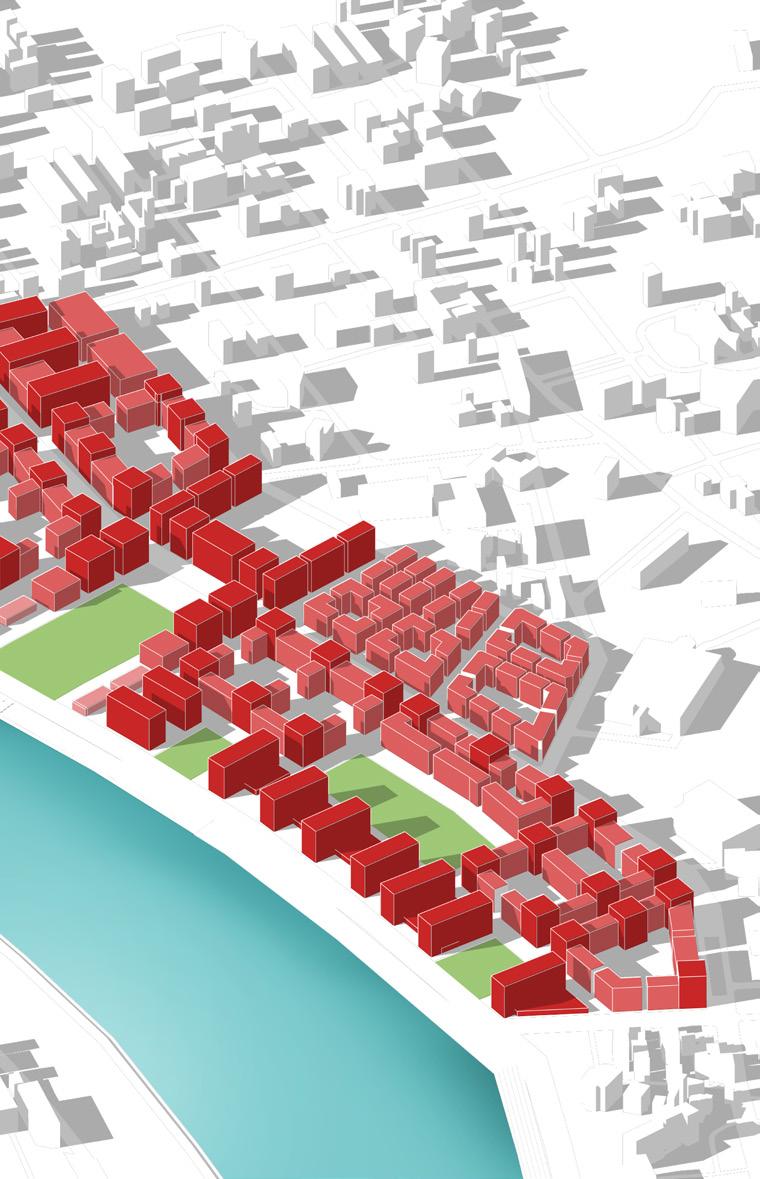
Creating High density built forms as it allows for the efficient use of this limited space by allowing for a larger number of buildings and residents to be accommodated in a smaller area. This can help to reduce urban sprawl and the associated environmental impacts, such as air and water pollution and habitat

In order to achieve Gross FSI of 2.4 and G+11 structures are proposed.



Built form interior blocks
Perimeter blocks are designed for the internal areas so as to maintain constant urban street wall. In addition with this to provide private multi functional open spaces
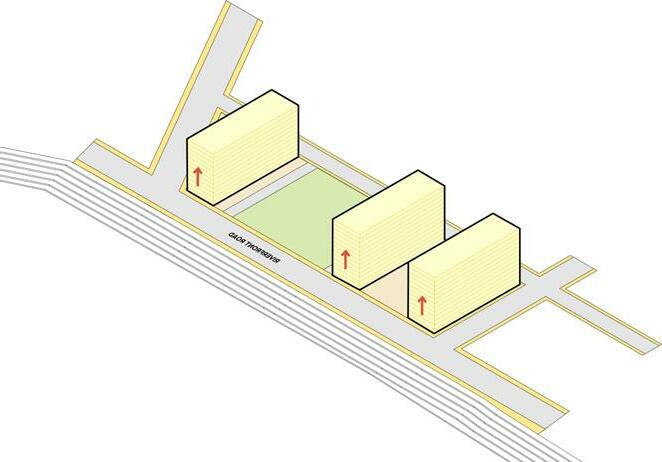
To utilised the demand and land value generated by riverfront point towers are created such that even innermost unit gets a riverview.




The character image illustrats on how people can uti lised the riverfront park and with the proposed guide lines how urban form can be shaped

A view of private open space from upper level of the high end tower which can act as gathering space as well as viewing deck for them.


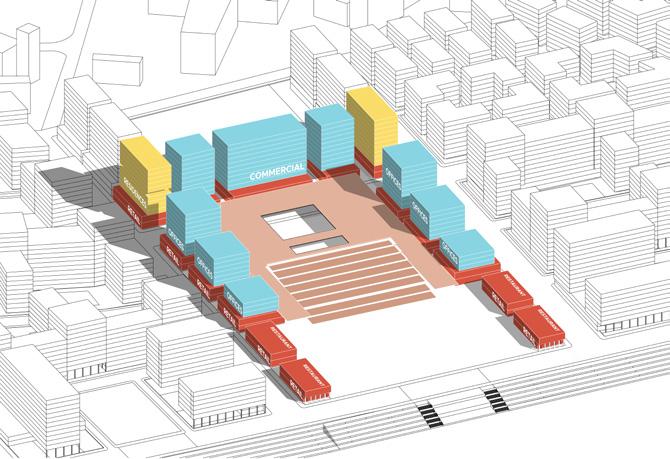



Creating lower levels as retail only and upper level as com mercial including offices to ca ter to central hub
Connecting offices and upper retail via upper promenade that will act as shopping and gath ering area
Steps that will act as seating and viewing decks for the river viewing
Lower promenade that caters to spillover activities like vending, exhibitions, High street shopping, Sankrant Functions, etc.


view oF Central huB From riverFront road
View of central hub from riverfront road that shows how outdoor eating vending and seating areas can be designed along this



Lower promenade can act as a hub for variety of activities like vending, exhibitions, High street shopping, Sankrant Functions, etc.

In Phase 1 its proposed to develop first half of the central hub that will act as catalyst and landmark to the overall development financially as well as visually. Along with a test fit of residential development cluster in order to understand public response to the project. This residential cluster consists of all three major typologies

In Phase 2 its proposed to develop the Shahibaugh side residential cluster and affordable housing cluster. The affordable housing cluster land lies under the cantonment boundary which will be acquried in phases. Along with this present residents on the north side can be accomodated when their lease is over.

The land that will be developed in phase 3 is occupied by existing buildings whose lease will be over and residents can be accomodated in the affordable housing or other clusters thereby this land opens up. The commercial hub will act as another landmark for this development.

Finally as cantonment area opens up to further development phase 4 cluster can be developed opening up new avenues for further development

A set of urban design guidelines is formulated in order to achieve a coherent builform as site is developed in different phases spread across years
To maintain a contiguos urban edge along the riverfront road and to achieve multiple level of open spaces
1a: Along riverfront blocks arcade typology to be followed. Therefore upto the height of 7m or 2 floors minimum 9m setback to be followed.
1b: After 7m to create arcade Built to edge must be followed
1c: Minimum 40m of Distance to be achieved between consecutive towers to achieve upper level viewing decks
To maintain constant urban street wall perimeter block placement must be followed in the inner parcels which are larger in size
2a: Built to line must be followed for plots abutting the 18m and 24m wide roads
2b: Corner buildings must achieve the height of 42m or G+11 in order to maintain urban density.
2c: Stilt to be provided in the corner blocks to create a contiguos ground connectivity but only upto the height of 7m
2d: For the median buildings those connect the corner towers a minimum height of G+4 or a maximum of G+7 must be achieved to maintain the urban density

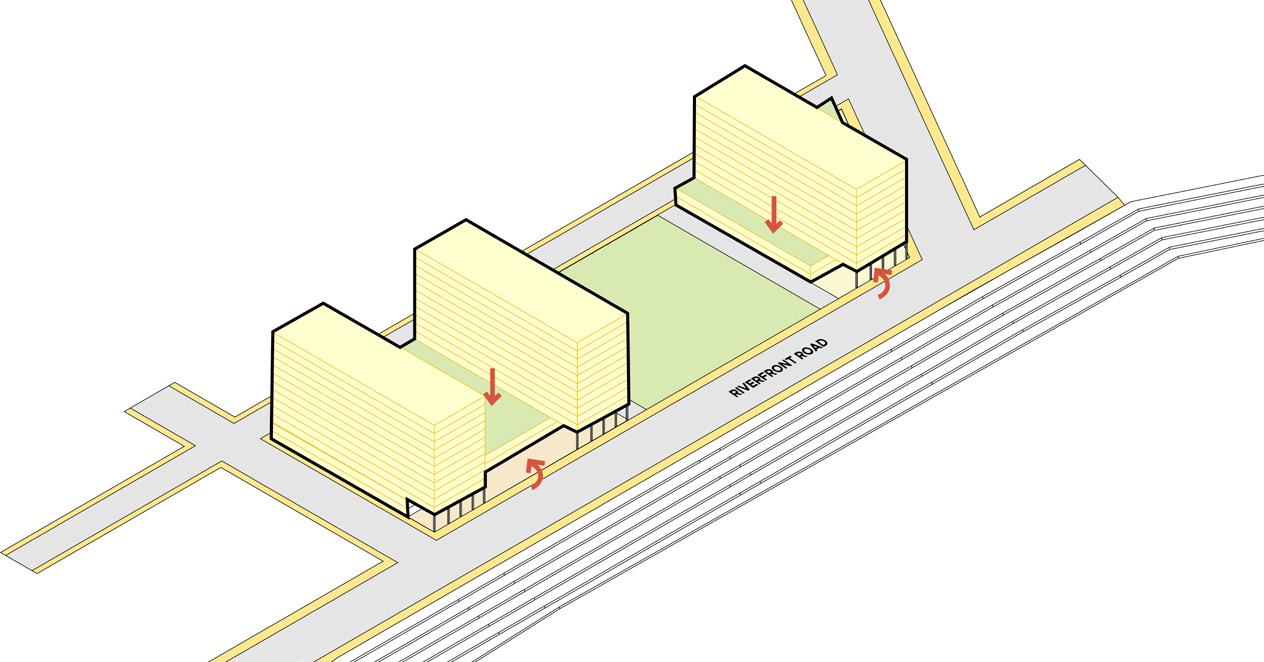
3. along aiport road and CommerCial Boulevard
To create interactive retail commercial street along airport and commercial roads
Block placement guidelines are same as 2a.

3a: To create a retail interactive urban wall built to line is followed which will allow spillover spaces in the parcel itself
3b: After 7m or 2floors a minimum step back of 5m to be achieved to create lower level as podium.
4. open spaCes and parking guidelines
To have minimum on street and surface parking
4a: For internal parking either it should be done in corner stilts or basement and ramps should be provided along 24m Wide Street and 18m Wide street.
4b: The central open space can be utlised for on street parking or private open green space as per developer

Master plan studio imparted the ability to understand and comprehend large scale urban design projects. In addition to this it provided with an understanding of how to identify need for such projects. Especially dealing with brownfield site that sits among the bounds of city. The smaller ideas of how people will live, navigate and process the area was a major learning.
As cities are growing and demand increasing its evident there is a need to create dense urban enviroments that can cater to them. This studio was an eye opener on envisioning the future of the cities which is dense yet livable.
Adhvaryu, B. (2011). Analysing evolution of urban spatial structure: a case study of Ahmedabad, India. Environment and Planning B: Planning and Design, 38, 850-863. https://doi.org/10.1068/b36088
Ahmedabad Urban Development Authority. (2021). Urban planning and development practices of Ahmedabad Urban Development Authority. https://www.auda.org.in/uploads/Urban-Planning-andDevelopment-Practices-of-AUDA.pdf
Brody, S. (2013) The Characteristics, Causes, and Consequences of Sprawling Development Patterns in the United States. Nature Education Knowledge 4(5):2
Models of Urban Growth. (2021, February 20). https://socialsci.libretexts.org/@go/page/8500
Molaei, P., Tang, L., Hardie, M. (2021) Measuring Walkability with Street Connectivity and Physical Activity: A Case Study in Iran. World 2021, 49–61. https://doi.org/ 10.3390/world2010004
Parekh, V., & Makwana, H. (2020). Transformation of Urban Structure and Emergence of HigherOrder Commercial Areas: Case of Ahmedabad, India. ICCAUA2020 , 189-199. https://doi.org/10.38027/N182020ICCAUA316369
Simon Elias Bibri, J. K. (2020). Compact city planning and development: Emerging practices and strategies. Developments in the Built Environment. Retrieved from www.editorialmanager.com/ dibe/default.aspx
TNN. (2020, January 4). City’s emerging realty hub. Times of India. https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/ahmedabad/citys-emerging-realty-hub/ articleshow/73091927.cms

Envisioning future of cities where open space and urban densities converge to create a liveable community “ “