Design Survival Handbook
Tools to help people working in design survive in an AI-driven creative industry.
Who needs to see it?
Fresh newcomers to the creative design field.
Practitioners who need to collaborate with AI in creative fields.
People who are worried about being replaced by AI in creativity.
What will you learn?
Principles of how to work with AI.
How to delegate and use AI in different roles.
How to define your role when compared to AI.
Produced by Yutong Wang from RCA DP (DF)
1
2
Vision: Maintain and develop the value of design.
1. Future scenarios of AI-driven industry.
2. Dilemmas faced by creative practitioners.
3. Interventions to preserve the value of designers.
Principles: You need to follow when using AI.
1. Think before using AI
2. Aligned your thoughts to AI
3. Divide results with AI
Methodology: Develop the usability of AI tools.
1. Understand how AI thinks and learns
2. Accurately translate perceptions to AI
3. Personalize teaching and delegate task to AI
Assessment: Criteria for assessing your output value.
1. Individual experience
2. Ability to work with unknown
3. Experience-based judgement
Survival: What is the future role of designer?
1. Creator (Leader)
2. Mediator (Specialist)
3. Operator (Worker)
1
Content
Vision 1. Future scenarios of AI-driven industry.
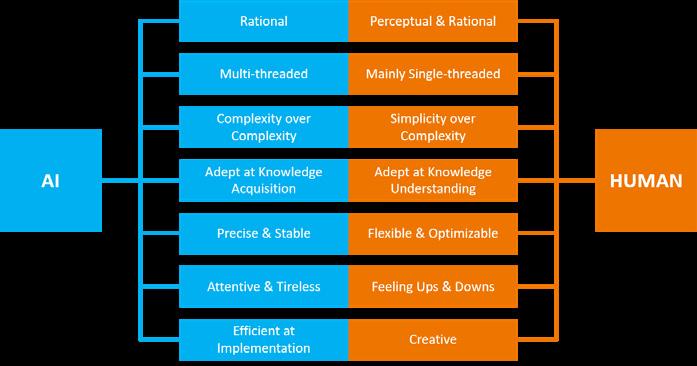
The future of AI continues to outpace humans in many ways, leading to faster efficiencies and the creation of new types of jobs and processes. But AI is a double-edged sword. While humans enjoy the fruits of the revolution brought about by AI technology, they also face a constant threat to the unique value of humanity. The risk of becoming obsolete by AI technology or by those who use it.
Where
do you want to be in the future job pyramid in the era of AI?
The long-standing human work pyramid structure is not necessarily collapsing, but more likely to be self-adjusting on the basis of the existing foundation. Even in the middle or top of the pyramid, will face the impact of artificial intelligence technology, they also need to re-adapt.
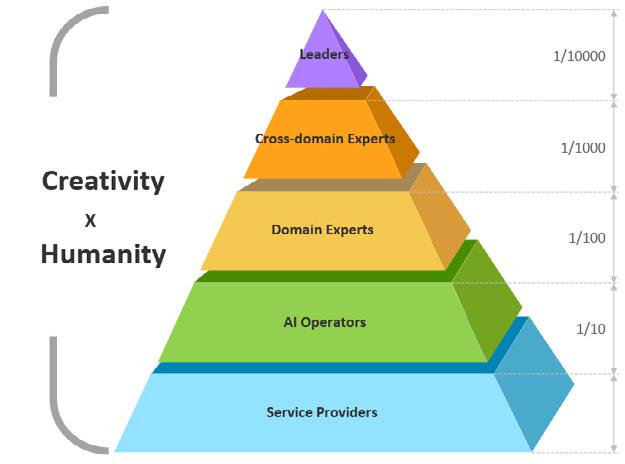
2
Kai-Fu Lee & Mr.HOW. The Human Job Pyramid in the Era of AI (2019)
Vision 2. Dilemmas faced by creative practitioners.

In the AI-driven society of the future, human designers face a variety of dilemmas.
• Several aspects of creative work will be replaced by AI.
• Inability to collaborate well with AI will make them less competitive.
• Overuse of AI will cause designers to lose their core competencies, allowing AI to take control of humanity and creativity.
What attitudes designers use to adapt the changes brought by AI in the industry?
AI already influences future employment standards

AI tech continues to catch up with human capabilities.
AI robs accomplishment of human's sense of results.
• OxfordUniversity. The Future of Employment: How susceptible are jobs to computerisation (2013) https://www.oxfordmartin.ox.ac.uk/publications/the-future-of-employment/
• OpenAI.GPT-4 Technical Report (2023) https://cdn.openai.com/papers/gpt-4.pdf
• An A.I.-Generated Picture Won an Art Prize. Artists Aren’t Happy.(2022) https://www.nytimes.com/2022/09/02/technology/ai-artificial-intelligence-artists.html
3
use AI Lose human core value Replace tasks in workflow
Overtaken by who
Deny AI Use AI
Vision
3.
to preserve the value of designers.
To find principles and methods of using AI that preserve human values and apply them to education and industry. This handbook specifically explores how future designers can harness the benefits of AI while better protecting and developing the core competencies of individual creativity. Be the one to dominate AI and avoid becoming obsolete.
What kind of intervention strategies are used in the era of AI to protect the value of designers?
4
Interventions
1. AI principles in design process.
2. Application testing in Workshop
Optimise Optimise Optimise Optimise Feedback Feedback Feedback
4. Extension to the wider design industry
3. Intervention Design Course
Design Survival Handbook New Education Subjects New design evaluation New design workflow New design tools AI
AI
Creative Workshop
Co-Design Course
Principles
1. Think before using AI
Any time you need to start using AI before you need to think about your current goals and corresponding actions on your own. This is reflected in the design of the plan, the design framework, the requirements, the problem.
Why should you think before you use AI?
Addiction - thinking becomes lazy
Fast and straightforward outputs deprive humans of the motivation to be more perfect, making them too lazy to think and be creative.
Lost - Disconnected from results
Missing human awareness of the output process, alienation from the content of the output, lack of recognition and sense of achievement.
Limitation - Exploration no longer important
A plethora of generic content and frameworks that limit the human experience of exploration and lack the random leaps of thought
5
Before AI (Human) Using AI (Huaman+AI) Future AI (Human+AI +Principle) Innovation Known
2. Aligned your thoughts to AI



Synchronise contextually relevant information in a way that the AI understands well enough. This aligns AI thinking and output content with humans in real time, allowing AI to efficiently produce content that is centred on goals and thinking that designers control. Relationship between text and sensory information


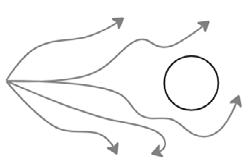
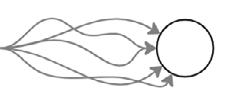
What do you need to align with AI in your design industry workflow?

6
Principles
Design Thinking Human moral standards Aligned Misaligned Goal Goal AI AI AI AI AI AI AI AI AI
Abstract definition of textual meaning
Principles
3. Divide results with AI
When do designers need to demonstrate the value of human output in the results?
Lack of identification with output




Lack of sense of accomplishment in process
If AI responds to human thinking and the output influences human decision making, then there needs to be a delineation of the value of humans and AI. There needs to be specific criteria to analyse the proportion of AI that contributes to the end result, rather than just judging it on the basis of the amount of content used. Prove
7
the value and reward as a human designer Need clear understanding of the output process
Methodology
1. Understand how AI thinks and learns
Clearly show the information that AI tools have been trained and learned, and understand how the AI learns. This helps humans to align values during collaboration with AI, or to distinguish between human and AI values when commissioning and training AI.For example showing the connection between keywords and the database of images and presenting it visually.
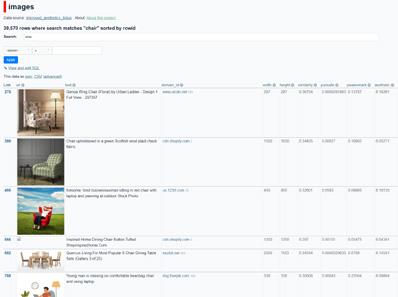
I want to design a chair, how can you help me?
Stable Diffusion is an artificial intelligence for image generation, allow me to introduce myself. Here are my designed vision and rules in the early days. The training mechanism system for my model. The data I used during training.
Copyright (c) 2022 Robin Rombach and Patrick Esser and contributors https://huggingface.co/spaces/CompVis/stable-diffusion-license



8
What content behind AI do designers need to understand clearly and intuitively in advance?
Methodology
2. Accurately translate perceptions to AI
Enables humans to talk to the AI in an intuitive interactive way. Make it easier for humans to translate their thoughts into logic that the AI can understand through framing and classification options. For example when an image needs to be described in abstract terms, the AI needs to be made to understand the visual elements that need to be included in the image.
How does accurate communication and interaction make using AI less silly?
I want to change the color to bright yellow.




How do you define bright yellow?




Fuzzy Natural Language Interaction
Natural language combined with traditional interaction (NLP+GUI)
Color
Material Style Background


Semantic training
#FFDD32
9
Methodology
3. Personalize teaching and delegate task to AI
Humans can train the AI's capabilities to suit their needs and have them operate automatically and appropriately within the workflow. For example, the AI can learn personal drawing styles and design concepts, and can be commissioned to act as a design assistant to collect references and generate sketches.
What types of roles in the design workflow does AI fit better in?
AI surpasses or equals human capabilities
1. Learning and integration of a large amount of information
2. Generate based on cognition of information
3. Repetitive enumeration and derivation
Delegated tasks in AI design
1. Integrate information templates (research, analysis, information visualization)
2. Content generation (copywriting, 2D images, 3D models, media)
3. Deduce the unknown (big data calculation, information retrieval, case enumeration)
10
Mr.HOW. Comparison of Human and AI’s Capabilities (2020) https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-78462-1_13
Assessment
1. Ability to work with unknown
How can human and AI creativity be defined in generalized forms?

Multiple new things beyond cognition

Innovate in different ways by exploring the unknown beyond what is known in different fields. Innovations can be divided into three categories, combinations of plural unknowns, unknowns plus known things, and unknown combinations of known things. New
Known things, plus a few new things
New combinations of known things

11
Product
Product
New Form
technology + New experience + New business + New culture Old product + New technology + New solution Old
+ Old
+
Assessment






2. Personality Traits
A unique personal experience and personality that allows for an independent critical perspective. A deep understanding of human nature and the abaility to use empathy in different situations to identify and gain insight into underlying needs.
What special make you different from other people or AI?
12
Human creativity AI creativity Human unique AI unique Collaboration Generate Cognition Refactor Analysis Intake Information Environment Knowledge Sense Facts Ideology Experience
Assessment
3. Experience-based judgement
Can form their own judgement criteria and intuition based on previous professional experience, can articulate the basis for their decisions and take responsibility for their choices. Can distinguish between the individual's and the AI's respective contributions in decision-making, is not completely guided by the AI's ideas, and has confidence and assertiveness in personal decision-making.
What areas does it still make sense for a designer to have specialist knowledge in?
Areas that humans need to be good at:
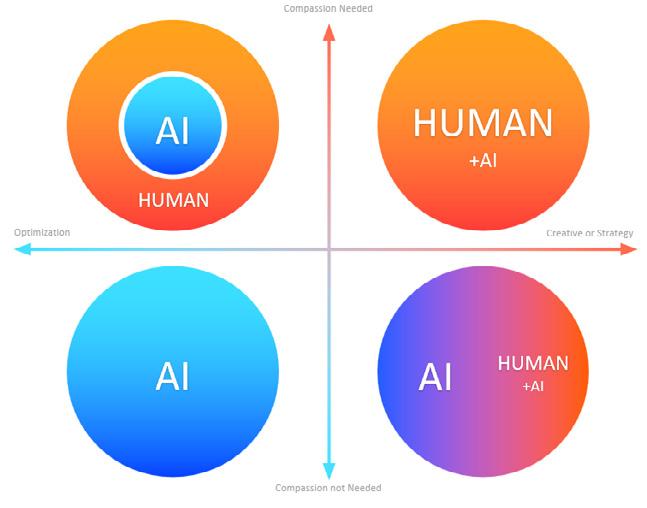
• Requires empathy + creativity and strategy
• Human nature + abstraction
13
Kai-Fu Lee. How AI Can Save Our Humanity: Blueprint of Human-AI Collaboration (2018) https://www.ted.com/talks/kai_fu_lee_how_ai_can_save_our_humanity
Survival
Visionary with a flair for exploring the unknown, setting trends and rewriting new ideas through personal charisma. Able to set goals and ideas that have never been set before, providing a visionary model for quantifying and training AI.
Translates visions and ideas to AI in a professional manner, ensuring that the algorithms that train AI and the content that is produced is accurate and efficient. Expertise in one or more areas, with extensive practical experience and judgement in the use of specialist skills and tools.
Train AI cognition in a prescriptive way, using existing programs and prescribed functions and paths in a repetitive manner. Assist the AI with complex and repetitive tasks that cannot be replaced by today's technology. Examples include the need for manual production, testing, etc., as humans that the AI controls and employs in the real world.
What does the design industry's job pyramid look like in the future era of AI?
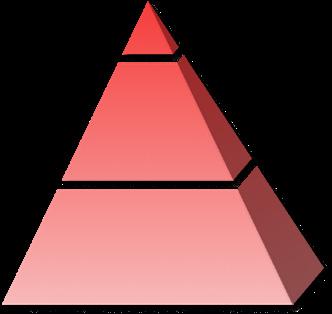
14
1. Creator. (Leader)
2. Mediator (Specialist)
3. Operator (Worker)
≈1%
70-80%
1. Creator (Leader)
20-30%
2. Mediator (Specialist)
3. Operator (Worker)
Survival
Our vision: Designers in the future can actively adapt and optimise to the upper job types.
With the advent of the AI era, there will inevitably be humans or jobs that will be eliminated. Our education and industry systems need to follow up and optimize the operating system to provide direction for the young and confused people in the future.
What we do is to hope that more creative design practitioners can improve their competitiveness and transform into upper-level occupations. Fewer and fewer people are eliminated by artificial intelligence technology, or eliminated by people using AI technology.
At which level in the pyramid of the design industry do we intervene?

The initial goal of our "Design Survival Handbook" should be: to transform more operators into creators or intermediaries, to enhance the core value of human designers, and to have the competitiveness in the industry that will not be eliminated by AI or humans.
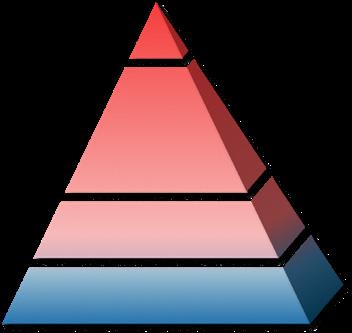
15
Without intervention Intervention worked
Be eliminated Be eliminated Enhanced
Operator
Creator Creator Mediator Mediator Operator
Survival
How might Design Survival Handbook actively intervene in the structure of the design industry?
This design survival guide will be practiced and optimized throughout the industry, and the experience will be refined into methods to guide the survival of human design creativity and dedicate it to future creative practitioners.
First of all, the principles, methods and evaluation of AI applied in design will be used in the following aspects: education, work process, industry rules and laws.
Educational curriculum
• Changing the training standards for students
• Optimize and delete existing courses
• New Disciplines and Curriculum System
• Create new forms of teaching content
Professional workflow
• Vocational training for new and existing employees
• Optimize and delete existing processes
• Create new jobs and links
• Re-evaluation of employee values
Design Tools
• Features combined with the latest AI technology
• Explore new forms of AI interaction
• Optimize traditional design tools
• Enhance the fluidity of the collaboration experience
Certification Standards
• Design Course Teaching Assessment
• Design competition award rules
• Design project results review
• AI product use design specification
16
Author:
Yutong Wang.
MA Student, Product Design (Design Futures), Royal College of Art
Tutor:
Dr. Alex Williams, Senior Tutor on Design Products, Royal College of Art
Acknowledgement of expert:
Prof. Zhuohao Wu, Communication University of China
Dr. Anders Sandberg, Future of Humanity Institute, University of Oxford
17
18







































