





What led to WhatsApp valuation of USD 17 billion?
Year 2013
Active Users: 450 million
Revenue: USD 10 mn
Loss: USD 138 mn
Valuation : USD 1.8 bn
Goodwill: USD 17.2 bn






An entity shall be considered as a Startup:
• Up to 10 years from incorporation
• Private company or Partnership or LLP
• Turnover less than INR 100 crore (in any year)
• Working towards innovation, development or improvement of products or processes or services, or
• a scalable business model with a high potential of employment generation or wealth creation.


Ministry of commerce and industry (Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion)
SEBI has adopted the same definition under AIF regulations
Income Tax Department is using the same definition for tax breaks


That’s only legal definition for getting tax breaks.
Anycompanythat’sconstantlyinnovating/pivotingis practicallyastart-up



…notjustanynewcompanythat’sdoingsomethingdifferent

Stageinlifecycle:youngandlessmature,feweremployees, lowerassets,minimalcapital
Size:Smallersize;higherlevelsofrisk;limitedaccesstocapital markets
[callsforasmallsizediscount(premiumwhilecalculatingdiscount rate)whencomparedwithpubliccompanies]
Overlapinshareholderandmanagement:Shareholders arethemanagement;lessagencyproblem
Qualityoffinancialinformation:lackofreliabledata;lower history;discretionaryspends;questionablefinancialreporting;focuson reducingtaxes;


Acompanyintheearlieststagesofdevelopmentshouldbevaluedusingthe asset-basedapproachasfuturecashflowsmightbetoounpredictableandthereis noguaranteethatthecompanywillbeabletooperateasagoingconcernforthe foreseeablefuture.
Acompanythathassuccessfullynegotiatedtheearlydevelopmentstageandis witnessinghighgrowthshouldbevaluedusingtheincomeapproach.
Maturedstartups
Astable,relativelymaturecompanyshouldbevaluedusingthemarketapproachor
Incomeapproach

Poor corporate governance



Underestimating competition


Not adaptable to market needs

Lack of Persistence
Quitting too early

Running out of money or resources
Too slow on pick up, Late execution
Fear of taking risks

Get a Story and estimate the climax
Everyvaluationisbasedonastory.Don’tfallforVFXs Don’thidebehindmanagementforecasts.Youstillownthevalueyoureport.

May not survive in long run
Applyprobabilityof default
Will survive and scale despite competition
Will scale on its own
Applyperpetualcash flowsinTV
Will get acquired by competition
ApplyExitmultiplein TV


Expense History Limited Substantive Substantive Substantive Established history Established history
Profitability Loss Loss Loss Loss Breakeven / profitable Established history
Financing Sources Angels / Early VC VC VC / Strategic Mez fin / strategics Strategics / IPO Self Funding / Debt + Equity






Sustainable differentiation

TAM
Crowded space = market erosion
Size & growth
Macro trends and timing
Measure of consumer intent

Product Scalability, Competitiveness
Business Model
Recurring revenue, shorter sales cycle, large value proposition

Traction
Financials
Growth, Customer engagement, customer retention
Burn and use of funds, positive contribution, previous rounds, past valuation, dilution
New, Experienced, Potential, Tech, Co-founders


Most investors bet on the founders and their business story. No one knows the future and thus, valuation is often difficult and always wrong
During early stages, funds are raised based on negotiation [the early stage version of demand and supply] and thus, startups are “priced” not “valued”.

Is it solving any major problem?
No
Is there huge scaling opportunity?
No major Premium Valuation
- Cost Approach
- Income Approach (High Probability of default)

Major Valuation Premium
- Using Benchmark multiples (value available)
- Lower Discount Rate (with lower probability of default)
Yes
Are there existing player?
Can it sustain the cash flows and high margins?

Step 1: Estimate the expected earnings or revenues in a future year.

Step 2: Multiply the earnings in the future year by the multiples of earnings.
Step 3: The estimated value is discounted back at the target rate of return.


• Market Approach
• Multiples
• Industry valuation benchmarks - useful as a sanity check of values
• Available market prices
• Income Approach
• Discounted Cash Flow Method
• Replacement Cost Approach
• Net Assets


• The rates of return expected by Venture Capitalists for companies in different stages of financing as described in the two publications identified in the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA)
1.Plummer,JamesL.,QEDReportonVentureCapitalFinancialAnalysis
2.Scherlis,DanielR.andWilliamA.Sahlman,“AMethodforValuingHigh,Risk,LongTerm,Investments:TheVentureCapitalMethod,”Harvard BusinessSchool


A young EdTech company Om Ltd is expected to go public in 10 years from now. The valuer expects that the net profits of the company 10 years from now will be INR 95 crores.
Average PE Multiple of publicly traded EdTech companies is 20. Om Ltd is evaluating fund raising from investors. Investors are expecting 45 percent from the investment until the company goes public.
Solution:
Exit Value = 95 x 20 = INR 1900 Crore
Value of the company today = 1900 / 1.45^10 = INR 46.25 Cr

Key success factors
Sound Idea (basic value)
Prototype (reducing technology risk)
Quality Management team (reducing execution risk)
Strategic Relationships (reducing market risk)
Product Rollout

Add to company value up to:
USD ½ million
USD ½ million
USD ½ million
USD ½ million
USD ½ million

• Projectingfuturecashflows:
• ProjectingTerminalValue:
• Discounting back future cash flows and terminal value:
• Calculatingpresentvalueofthefirm:


Valuing Flipkart
Amazon = Market Capitalisation
Number of Users on Amazon.
Value Driver: Value per user (ValuePU) = Market Cap / No. of users.

Flipkart Value = Number of users (given by Flipkart) x ValuePU
Adjustment for:
• Marketability [Listed vs Unlisted]
• Country specific growth factors – US Growth vs India growth
• Global presence
• Product diversification
• Currency differences
Alternatively, Ecommerce companies were valued based GMV Multiple.



Numbers





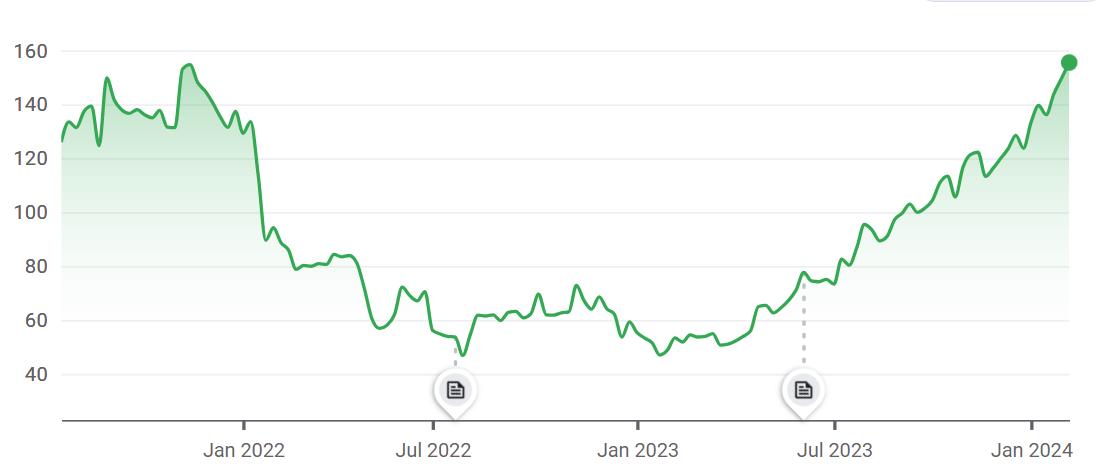






Key Business and Revenue Model
Food Delivery (Transaction based advertising)
Revenue Drivers and Cost drivers
Dining (Advertising)
Hyperpure (Transaction based)
Zomato pro (Subscription)
Key performance indicators No.
No. of Monthly transacting users
Order frequency
Commission Rates restaurant partners
Delivery Ads from Restaurant partners
Key Costs: Delivery Cost, Discounts and marketing spends
No. of Monthly Average Users
Delivery Ads from Restaurant partners
Key Costs: Sales team
No. of Restaurant partners
Order Frequency
Value of supplies per order
Key Costs: Cost of goods sold
Membership Fees
No. of pro members
Key Costs: Marketing




