





Academic Authors: Tarunna Mendirata, Ankita Yadav, Yuvraj, Anuj Gupta, Urmi Maitra, Rachna Bhardwaj
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Sanjay Kumar Goel, Vishesh Agarwal
Project Lead: Sneha Sharma
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First published 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Discover Environmental Science 3
ISBN: 978-81-979364-5-6
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
Welcome to the fascinating world of environmental science with Discover, a textbook that has been thoughtfully designed to spark curiosity, and nurture a love for understanding the environment in young minds.
In today’s rapidly evolving world, building a solid foundation in understanding the surroundings and environment from an early age is more crucial than ever. It lays the groundwork for observation, critical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to make informed choices about the world around us. These skills are not just academic: they are essential life skills that empower young minds to understand and interact with the world around them in a rational and meaningful way. At UOLO, we believe that every child deserves to start this journey with the best resources available.
In this pursuit, Discover is uniquely crafted to provide a comprehensive and contemporary learning experience, meticulously aligned with the recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023. The book incorporates the curricular goals and competencies outlined in the NCF 2023, ensuring that every chapter, exercise, and feature reflects these foundational principles.
This textbook transcends traditional teaching methods by adopting a competency-based approach, recommended by both NEP 2020 and NCF 2023, that emphasises not just conceptual understanding and critical thinking, but also application of key concepts, and problem-solving. It is designed to make learning both meaningful and relevant, equipping students with the tools they need to thrive in the 21st century.
Carefully curated content, NEP-specific tags, and a diverse array of elements have been seamlessly integrated throughout the book to nurture essential skills, values, and dispositions outlined in the NEP. Competency-based projects and assessments are strategically placed to help students master important concepts and develop higher-order thinking skills.
The book has the unique feature of being complemented by a graphic novella. Each unit of the book begins with an episode of the gripping sci-fi tale, which not only captivates the students’ interest and promotes reading, but also ingeniously connects with some of the core concepts that will be taught in the respective units.
Each chapter is also enriched with vibrant illustrations, relatable examples, and interactive activities to engage our young learners. Hands-on activities and real-life applications have been embedded throughout the book to instil a pragmatic mindset among students and make learning an enjoyable journey for them. Moreover, assessments ‘of, as, and for learning,’ as envisioned by the NEP and NCF, have been interwoven throughout the curriculum, providing continuous evaluation and meaningful feedback to students to support their growth and success.
The Discover product bundle offers a comprehensive EVS kit which includes a textbook that provides relevant and up-to-date content, concept building opportunities, projects, and assessments; a Teacher Manual offering extensive teaching support; technology-powered features, including engaging videos and interactive exercises for students; and digital lesson plans and an assessment generator for teachers. In conclusion, Discover is designed to fascinate students towards their environment, both as a subject and as a practical experience in their everyday lives, while also making them well-rounded individuals. We invite educators, parents, and students to embrace Discover and join us in nurturing the next generation of thinkers, innovators, and problem-solvers. Embark on this exciting journey with us and let Discover be a valuable resource in your educational adventure.


Welcome to the Discover journey.
The program is carefully designed to elevate the experience of learning EVS through an NCF-based, age-appropriate, pedagogically-sound, and engaging content. Teachers will be supported with a manual that offers comprehensive guidance to optimise classroom instruction. Furthermore, various assessment mechanisms have been built in to the program.
Engaging Textbooks
Comic Stories
Teacher Manual
Competency-based Model Assessments
STEAM Projects
Question-paper Generator
Student and Teacher Apps
Learning Videos
Interactive Tasks & Exercises
Byte-size Lesson Modules
The Discover program is also augmented by a digital learning platform that offers powerful educational videos and interactive exercises to help children master concepts and skills in a joyful and fear-free manner.

The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, introduced by the Government of India, represents a transformative shift in the country’s education system. It aims to create a more holistic, dynamic and multidisciplinary approach to education. NEP 2020 focuses on fostering conceptual understanding, skills, values, and competencies that align with the demands of the 21st century, while also preserving India’s rich cultural heritage. UOLO is fully committed to actualising the vision of NEP 2020 by meticulously adhering to its outlined recommendations.









1. Focus on conceptual understanding
2. 21st century skills, values, and dispositions
3. Critical thinking and problem solving
4. Application in real life
5. Holistic and integrated learning
6. Experiential learning
7. Enjoyable and engaging
8. Discovery-based approach
9. Technology-based solutions
10. Knowledge of India

Competency-based Education
NEP Pages 12, 17, and 22
Teaching and Learning Pedagogy
NEP Pages 3, 11, 12, and 27
National Pride
NEP Pages 15, 16, and 43
11. Assessment of core concepts and application skills Assessments
NEP Pages 12, 18, and 22


Engaging hands-on projects blending Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Maths (STEAM) to inspire young minds 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 11
Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and application of skills 1 2 3 11
Enchanting comic stories that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure
5 7
Curated videos to find out more about key concepts
7 9 1 Focus on conceptual understanding
Multidisciplinary, holistic, and fun-filled activities to internalise the concept better
21st century skills, values, and dispositions 3 Critical thinking and problem solving
Application in real life
Holistic and integrated learning
Experiential learning

Error Alert
Concise snippets of information designed to caution against potential misconceptions
Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical, and evaluative thought processes
Digital worksheets on key concepts to supplement textbook exercises
Wonders of Bharat
Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage, designed to ignite a profound sense of pride and love for the nation
Picture-based Questions
featuring visual stimuli to elevate comprehension, interpretation, and critical thinking
Simple activities and tips to develop a diverse set of essential skills for living well


The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 outlines essential skills, values, dispositions, and learning approaches necessary for students to thrive in the 21st century. This textbook identifies and incorporates these elements throughout its content, activities, and exercises. Referred to as “NEP Tags”, they are defined as follows:

Art Integration
Bringing creativity and fun into learning by combining music, drama, and art with other subjects

Sports Integration
Using physical activities, sports, and games to make learning active and engaging

INTEGRATED
Holistic & Integrated Learning
Cross-curricular and skill linkages to make the learning experience more holistic, joyful and meaningful

Teamwork
TEAMWORK
Embracing the spirit of mutual collaboration and cooperation while working together to solve problems

SDG
Sustainable Development Goals
Unwavering commitment to create a green, peaceful, prosperous, and equitable and inclusive world

SEL Social Emotional Learning
Developing the skills to understand and manage emotions, build positive relationships with others, and make responsible choices

The National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF), released in 2023, is developed based on the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. Its purpose is to enable the implementation of the NEP. The NCF provides guidelines for designing school syllabi and textbooks in India. It aims to improve the quality of education by making it more relevant, engaging, inclusive, and learner-centric. To achieve this, the NCF has articulated precise Learning Standards through well-defined Curricular Goals and Competency statements. These statements serve to harmonise the syllabus, content, pedagogical practices, and assessment culture, ensuring a cohesive and comprehensive educational experience.
Curricular Goals: Curricular Goals are statements that give directions to curriculum development and implementation. They are derived from Aims and are specific to a Stage in education.
Competencies: Competencies are learning achievements that are observable and can be assessed systematically. These Competencies are derived from the Curricular Goals and are expected to be attained by the end of a Stage.
NCF Page 59
CG-1
Explores the natural and social environment in their surroundings
CG-2
Understands the interdependence in their environment through observation and experiences
C-1.1 Observes and identifies the natural (insects, plants, birds, animals, geographical features, sun and moon, soil) and social (houses, relationships) components in their immediate environment
C-1.2 Describes structures, relationships, and traditions in the family and community
C-1.3 Asks questions and makes predictions about simple patterns (season change, food chain, rituals, celebrations) observed in the immediate environment
C-1.4 Explains the functioning of local institutions (family, school, bank/ post office, market, and panchayat) in different forms (story, drawing, tabulating data, noting discussion), and analyses their role
C-1.5 Creates simple objects (family tree, envelopes, origami) on their own using local materials
C-2.1 Identifies natural and humanmade systems that support their lives (water supply, water cycle, river flow system, life cycle of plants and animals, food, household items, transport, communication, electricity in the home)
C-2.2 Describes the relationship between the natural environment and cultural practices in their immediate environment (nature of work, food, traditions)
C-2.3 Expresses the changes in the lives of their family and community as communicated by elders and through local stories (changes in occupation, food habits, resources, celebrations, communication)
The above is a snapshot of the curricular goals and competencies relationship in EVS for the Preparatory Stage (NCF 2023, pages 340–341). The next section shows the coverage of all these competencies across the chapters.

20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
Ch 4 Ch 5
Ch 3
Ch 2
Ch 1



































Competencies


C-1.1 Observes and identifies the natural (insects, plants, birds, animals, geographical features, sun and moon, soil) and social (houses, relationships) components in their immediate environment
C-1.2 Describes structures, relationships, and traditions in the family and community
C-1.3 Asks questions and makes predictions about simple patterns (season change, food chain, rituals, celebrations) observed in the immediate environment







C-1.4 Explains the functioning of local institutions (family, school, bank/ post office, market, and panchayat) in different forms (story, drawing, tabulating data, noting discussion), and analyses their role
C-1.5 Creates simple objects (family tree, envelopes, origami animals) on their own using local materials
C-2.1 Identifies natural and humanmade systems that support their lives (water supply, water cycle, river flow system, life cycle of plants and animals, food, household items, transport, communication, electricity in the home)

Curricular Goals
CG-1
Explores the natural and social environment in their surroundings
CG-2
Understands the interdependence in their environment through observation and experiences
C-2.2 Describes the relationship between the natural environment and cultural practices in their immediate environment (nature of work, food, traditions)






















C-3.1 Describes the basic safety needs and protection (health and hygiene, food, water, shelter, precautions, awareness of emergency situations) of humans, birds, and animals
CG-3 Explains how to ensure the safety of self and others in different situations






















C-4.1 Observes and describes diversity among plants, birds, and animals in their immediate environment (shape, sounds, food habits, growth, habitat)
CG-4 Develops sensitivity towards social and natural environment
C-4.2 Observes and describes cultural diversity in their immediate environment (food, clothing, games, different seasons, festivals related to harvest and sowing)
C-4.3 Observes and describes natural resources in their immediate environment, and their use
C-4.5 Identifies needs of plants, birds, and animals, and how they can be supported (water, soil, food, care)
C-4.6 Identifies the needs of people in different situations—access to resources, equal opportunities, work distribution, shelter
C-5.1 Explains a mental map of their school, village, and ward
C-5.2 Reads simple maps of city, State, and country to identify natural and humanmade features (well, lake, post office, school, hospital, etc.) with reference to symbols and directions
CG-5 Develops the ability to read and interpret simple maps
C-6.1 Performs simple investigations related to specific questions independently or in groups
C-6.2 Presents observations and findings through different creative modes (drawing, diagram, poem, play, skit, through oral and written expression)
CG-6 Uses data and information from various sources to investigate questions related to their immediate environment

carbon dioxide. They
in the exchange of




Inhalation: When we breathe in, our lungs take in air containing oxygen. This oxygen is then transported to the different parts of our body through the blood. The lungs expand during inhalation.
Take a deep breath in and count to five. Now, breathe out slowly. Did you feel your lungs filling up with air?
Comic Story: Exciting story built throughout the book, contains hooks to topics in a unit Error Alert: Caution against misconceptions
Omnivores

Get
Chapter Overview: Outline of the key concepts covered in the chapter
Exhalation: When we breathe out, our lungs remove carbon dioxide from our body. Removing carbon dioxide is essential for our body to function properly. The lungs contract during exhalation.

Breathe out slowly and feel the air leaving your body. Can you feel it? Did

important because they provide oxygen to our body and remove carbon dioxide. They help in the exchange of gases.




Inhalation: When we breathe in, our lungs take in air containing oxygen. This oxygen is then transported to the different parts of our body through the blood. The lungs expand during inhalation.

Have you ever thought about what would happen if our hearts a bit scary to think about because we need our hearts to stay heart by eating healthy food, exercising and feeling happy helps you think feeling good and taking care of our body helps us
Take a deep breath in and count to five. Now, breathe out slowly. Did you feel your lungs filling up with air?
Exhalation: When we breathe out, our lungs remove carbon dioxide from our body. Removing carbon dioxide is essential for our body to function properly. The lungs contract
These are animals that eat only meat. They have sharp claws to catch and hold the prey and long, pointed front teeth to tear its flesh. Lion, eagle and sharks are few examples of carnivores.
Internal and External Organs

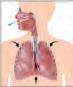
The heart is reddish brown in colour. Its size is the same as that slightly towards the left side of our chest. If you put your hand feel your heart beating.


The heart pumps blood to all body parts. This blood supplies to other body parts. It also collects carbon dioxide and other different body parts.
Did You Know: Interesting facts related to the topic
Breathe out slowly and feel the air leaving your body. Can you feel it?

Our body is like a big machine with many parts, each playing its own special role. In this chapter, let’s learn about different parts of our body and how they work.
Organs are different parts of the body that work together to help us stay healthy and perform all the activities we need to do. Organs are mainly classified into external and internal organs.
These are animals that eat both plants and meat. They have a combination of sharp and flat teeth to help them eat different types of food. Bears, pigs and humans are a few examples of omnivores.
Some animals like vultures and hyenas eat dead animals and are called scavengers






Vocabulary: Meanings of difficult words
Have you ever thought about what would happen if our hearts stopped beating? It’s a bit scary to think about because we need our hearts to stay alive. Taking care of our heart by eating healthy food, exercising and feeling happy helps keep it strong. How do you think feeling good and taking care of our body helps us stay healthy?
Organs are different parts of the body that work together to help us stay healthy and perform all the activities we need to do. Organs are mainly classified into external and internal organs.
The heart is reddish brown in colour. Its size is the same as that of a fist. The heart is slightly towards the left side of our chest. If you put your hand on your chest, you can feel your heart beating.
both
and
Chapter 1 • Parts of Our Body transport: to carry from one place to another (here, oxygen) expand: increase in size contract: decrease in size fist: tightly-closed hand with fingers pointing inwards
Pause and Answer Sort the animals into groups based on their food habits.

Pause and Answer: Short exercises between the chapter to pause and assess comprehension
Reproduction is the process by which living beings produce young ones of their own kind. Animals reproduce in two ways:
Do and Learn: Multidisciplinary, holistic, and fun activities to understand the concept better
by laying eggs • by giving birth to young ones
Let’s learn about them.
The heart pumps blood to all body parts. This blood supplies oxygen and nutrients to other body parts. It also collects carbon dioxide and other waste materials from different body parts.


NEP Tags: To show alignment with NEP skills and values















Most of the public property, such as roads, are built and maintained by the government, using money collected from the people. The collected money is known as tax







Wonders

Tell
Tell Look around your desk and in the classroom. Note down the different objects you see. Which of these objects are private property and which ones are public property?
Remember: Recall of previous knowledge relevant to the
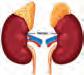
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located on either side of our spine, below the ribs and behind the belly. Each kidney is about 4–5 inches long, roughly the size of a large fist. The kidneys filter blood and remove waste from our body. The waste is collected in the urinary bladder and is then removed from the body as urine.




The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located on either side of our spine, below the ribs and behind the belly. Each kidney is about 4–5 inches long, roughly the size of a large fist. The kidneys filter blood and remove waste from our body. The waste is collected in the urinary bladder and is then removed from the body as urine.
The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located on either side of our spine, below the ribs and behind the belly. Each kidney is about 4–5 inches long, roughly the size of a large fist. The kidneys filter blood and remove waste from our body. The waste is collected in the urinary bladder and is then removed from the body as urine.


Think and Tell / Discuss: Analysis, reflection, and text-to-self connection-based prompts for discussion in class
Do and Learn

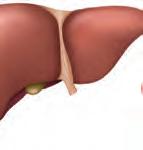
Collect pictures of different internal organs like the brain, stomach, liver, kidneys and heart. Paste them in your scrapbook. Write about the importance and functions of each organ below the respective images. Make your scrapbook look attractive. Show it to your friends.
Collect pictures of different internal organs like the brain, stomach, liver, kidneys and heart. Paste them in your scrapbook. Write about the importance and functions of each organ below the respective images. Make your scrapbook look attractive.
Show it to your friends.


Collect pictures of different internal organs like the brain, stomach, liver, kidneys and heart. Paste them in your scrapbook. Write about the importance and functions of each organ below the respective images. Make your scrapbook look attractive. Show it to your friends.
Wonders of Bharat
Wonders of Bharat

In Ayurveda, a traditional Indian system of health, the heart is thought to hold our emotions. Breathing exercises like Pranayama and simple meditation, both from India, are suggested to keep the heart healthy and lower stress. These practices also help with blood circulation and overall well-being. A girl practising

In Ayurveda, a traditional Indian system of health, the heart is thought to hold our emotions. Breathing exercises like Pranayama and simple meditation, both from India, are suggested to keep the heart healthy and lower stress. These practices also help with blood circulation and overall well-being. A girl practising Pranayama
In Ayurveda, a traditional Indian system of health, the heart is thought to hold our emotions. Breathing exercises like Pranayama and simple meditation, both from India, are suggested to keep the heart healthy and lower stress. These practices also help with blood circulation and overall well-being. A girl



organs: different parts of the body that work together skull: the part of the head that
organs: different parts of the body that work together
skull: the part of the head that protects our brain atria: the chambers located at the upper side of the heart ventricles: the chambers located at the lower side of the heart
Explore More: Short videos to find out more about the topic
Points to Remember

• The brain helps us think, learn and feel emotions.

organs: different parts of the body that work together skull: the part of the head that protects our brain atria: the chambers located at the upper side of the heart ventricles: the chambers located at the lower side of the heart
blood vessels: fine tubes that help in circulation of blood arteries: red-coloured blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all body parts
blood vessels: fine tubes that help in circulation of blood arteries: red-coloured blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all body parts veins: blue-coloured blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from all body parts oesophagus: the pipe through which food passes from mouth to stomach Word Splash
veins: blue-coloured blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from all body parts
oesophagus: the pipe through which food passes from mouth to stomach


organs.
Know more about internal organs.
We can see and touch external organs from the outside, but we can’t see or touch internal organs because they’re inside our body.
• The lungs help us breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide.
• The heart pumps blood to all parts of our body.
We can see and touch external organs from the outside, but we can’t see or touch internal organs because they’re inside our body.
• The stomach helps digest the food we eat.
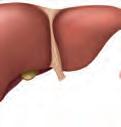
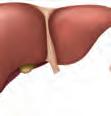
• The liver cleans our blood and helps us digest fats.
• The brain helps us think, learn and feel emotions.
• The lungs help us breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide.
• The kidneys filter waste from our blood and produce urine.
• The heart pumps blood to all parts of our body.
• The stomach helps digest the food we eat.
• The liver cleans our blood and helps us digest fats.
• The kidneys filter waste from our blood and produce urine.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
Points to Remember: Summary of the chapter Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
A. What protects the brain?
6. Long-answer questions.
6. Long-answer questions.
Skull Heart Liver
B. Which organ pumps blood throughout our body?
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.

A. Explain the journey of food from farms to our tables. List all the steps and the people involved.
Lungs Heart Kidneys
B. How do protein-rich foods help our bodies? Give two examples of protein-rich foods.
A. What protects the brain? Skull Heart Liver
C. Which organ helps us to breathe?
Picture-based Questions: Special questions featuring visual stimuli to foster comprehension, interpretation, and critical thinking
7. Picture-based questions.
B. Which organ pumps blood throughout our body?
questions.
Lungs Heart
D. Which blood vessels carry oxygenated blood to different body parts? Ventricles Arteries Veins
C. Which organ helps us to breathe?
2. Fill in the blanks.
liver atrium ventricles kidneys

D. Which blood vessels carry oxygenated blood to different body parts? Ventricles Arteries
A. The upper chambers of the heart are called
HOTS: Intellectually stimulating questions designed for higher order thinking and analysis
B. The lower chambers of the heart are called





2. Fill in the blanks. liver atrium ventricles kidneys
C. helps us in the digestion of fats.
D. filter our blood to remove waste and extra water.
A. The upper chambers of the heart are called
3. Write True or False.
B. The lower chambers of the heart are called
A. Brain and lungs are external organs.





C. helps us in the digestion of fats.
B. The heart has only two chambers.

D. filter our blood to remove waste and extra water.
3. Write True or False.
A. Brain and lungs are external organs.
B. The heart has only two chambers.



Life Skills: Simple activities and tips to develop a diverse set of essential skills for living well
You’ve


You’ve now learned the importance of a balanced diet in your life. Create a weekly meal plan after discussing it with your family. The meal plan must ensure a balanced diet on all the days.






















Chapter Overview







Our Body
External Body Parts Internal Body Parts Differently-abled People

Get Set






Read the poem and circle the names of the body parts. My body is amazing, from my head down to my toes, With eyes to see the world and a nose that smells the rose. Ears to hear the music, and a mouth to taste and talk, Legs to run and jump, and feet that help me walk!



Our body is amazing. It helps us run, jump, play and do many things. Let us learn about our body.
Look at your partnerʹs face and name some body parts you can see. We have eyes, a nose, lips and ears. These body parts are present on the outside of our bodies.

Body parts that are present on the outside of the body and can be easily seen are called external body parts. Our arms and legs are external body parts.
The external body parts can be divided into three main parts: the head, trunk and limbs. Limbs

Head: topmost part of our body
Trunk: middle part of our body
Limbs: arms and legs together
External body parts
The arms and legs of a person are called limbs. The limbs are joined to the trunk. Our limbs help us in many ways.
Our arms and hands help us to write, eat, hold, lift and catch things. We also use our arms to hug our family members and friends.
Our legs and feet help us jump, run, dance, jog and play. They help us to stay balanced and to stand upright.






A girl kicks the ball.
Sheena sat on the soft grass and looked at the beautiful flowers around her. She heard birds chirping in the trees. She smelt the sweet scent of flowers. She also picked up fallen mangoes, washed them, and tasted them.
Sheenaʹs five senses helped her to sense the different kinds of things in the garden.
Sense of touch: feeling the grass
Sense of sight: looking at the flowers
Sense of smell: smelling the flowers
Sense of hearing: hearing the chirping birds
Sense of taste: tasting the mangoes
Just like Sheena’s senses helped her to understand so much about the garden (her surroundings), our five senses help us understand the world around us.
trunk: the middle part of the body limbs: arms and legs together
upright: straight (while standing)
chirping: the sound of birds surroundings: things that are around a person or place


The body parts that help us sense and feel things around us are called our sense organs. Our eyes, nose, ears, tongue, and skin are sense organs.
Eyes
We have a pair of eyes that help us see things around us. We recognise things by their shape, size, and colours.
Ears
We have two ears on the sides of our heads. Our ears help us hear different kinds of sounds and recognise them. They help us listen to our friends and other people around us. They help us listen to songs and music. Listening also helps us learn to talk.
Nose

Some people need help to see things clearly. Spectacles make it easier to see things near or far. For people who have trouble hearing, a hearing aid helps them hear sounds around them better.
Our noses help us smell different things, like the scent of an incense stick. Our noses also help us to sense danger like smoke and gas leaks or to smell food that is spoilt. We breathe air in and out with the help of the nose.
Tongue
Taste buds are tiny little bumps on our tongue that help us taste things that are sweet, sour, umami, salty, or bitter. Our taste buds help us enjoy the flavours of the foods and drinks that we like. The tongue also helps us speak clearly. Hearing Sight Taste Smell
Have fun playing a tasting game with grown-ups! Ask your elders at home to pick three yummy foods with different flavours. Do not look at the foods they choose for the game. Close your eyes and let them feed you each food. Taste the foods and guess their names.
umami: meaty taste
bitter: sharp, unpleasant taste
flavours: taste

Think of what could happen if we did not take care of our sense organs. Discuss with your partner and present two points to your class.
Our skin helps us feel things. It is the biggest organ of our body and covers us everywhere. When we touch something, our skin tells us if it is hot or cold, rough or smooth. Our sense organs help us explore the world and keep us safe. They warn us of dangers around us.
Look at the picture. Use words from the help box to fill in the blanks. sight touch brown
1. I will use my sense of to find the colour of the teddy bear. It is in colour.
2. I will use my sense of to know if it is soft.
The body parts present inside our bodies are called our internal body parts. The heart, the brain, the lungs and the stomach are some of our internal body parts. Let us learn more about these internal body parts.
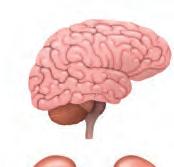
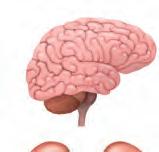
The brain is present inside the head. It is protected by a cover of hard bones called the skull. The brain helps us think, learn, understand our lessons and remember things. It also controls other body parts, telling them what to do. Brain




The heart is a reddish-brown coloured organ and is roughly the same size as a person’s fist. It is present in the middle of our chest, but a little to the left. It pumps blood to different parts of the body. Do you know that the heart beats continuously throughout our life? Try to feel your heart beat by placing your hand on the left side of your chest.
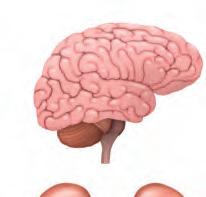
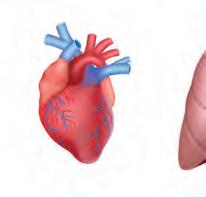



The heart beats around 72 times in a minute for a normal healthy person.

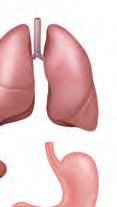
All the food we eat goes into the stomach, a small, bag-like part inside our belly. In the stomach, food is broken down or digested into simpler parts. These parts are then sent to different organs of the body to give us energy and help us grow.

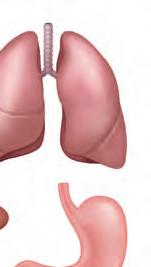



The lungs are the organs that help us breathe. We have two lungs inside our chest. They look like big balloons and are present inside the chest. The oxygen we breathe in through our nose goes to the lungs, which then pass this oxygen into the bloodstream. This oxygen-rich blood flows to the heart, which pumps it to all parts of the body.






Bones and muscles are present all over our bodies. They are important for activities like running, jumping, and even smiling.
pump: to squeeze and push breathe: the process of taking in and giving out air
Bones in our body.

Bones
Bones are the hard parts of our body.
They help us stand up straight and move around. They give shape and support our body.
They protect the soft organs like our brain, heart and lungs.
Bones cannot move on their own. Our muscles help them to move. Bones and muscles work together like a team to help us do different actions.
We use the muscles in our arms and legs to run and play.
Pause and Answer
Name the internal organ that helps...
1. to break or digest food:
2. us breathe:
3. to pump blood to different parts of the body:
Some people around us are differently-abled which means they are unable to see, hear, speak or walk like everyone else. For example, some people have weak legs and may not be able to walk. They may use a wheelchair to move instead.
Let us learn about some of the things differently-abled people use to do their activities:
People who cannot hear can use hearing aids to listen. Hearing aids are small devices that make sounds louder. Hearing aid

People who cannot speak use sign language for communication. Sign language is a way to communicate using specific hand movements.
People who cannot see can use Braille script to read and write. Braille is a system of raised dots that can be felt with the fingers. People who have difficulty walking can use crutches or a wheelchair.

A girl reading in the Braille script.
We must understand that everyone is special in their own way. We should always treat others with kindness and respect.
Braille script was invented by a Frenchman named Louis Braille when he was just 15 years old. Did You Know?

Bharat Kumar is an Indian para-swimmer. He was born without a left arm. He has won 2 international awards and more than 50 medals.
external body parts: body parts present on the outside of the body limbs: arms and legs of our body
sense organs: ways in which we feel, hear, see, smell and taste what is around us
taste buds: tiny bumps on the tongue which help us sense different tastes internal body parts: body parts present inside the body differently-abled: people who are unable to see, hear, speak or walk like everyone else hearing aids: small devices for our ears that make hearing better
script: a system of writing crutches: special sticks that help people walk



Scan the QR code to learn more about the internal parts of our body.
• Our body has both external and internal parts.
• Hands, legs, eyes, ears and feet are some external parts.
• We use our sense organs to sense the world around us.
• The heart, lungs, stomach, bones and muscles are some internal body parts.
• Differently-abled people are unable to move, think or communicate like everyone else.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. We use this to smell perfume.
eyes
nose ears
B. We use this to taste an ice cream.
tongue nose eyes
C. This is a reddish-brown coloured organ that pumps blood in our body.
D. This organ helps to break food into smaller parts. ears
stomach


2. Write True or False.
A. Our head is the middle part of our body.
B. We have two pairs of limbs.
C. The brain tells the other organs what to do.
D. The heart is an external organ of our body.
3. Fill in the blanks. bones limbs stomach lungs
A. Our arms and legs together are called .
B. helps us to breathe.
C. help us to stand up straight.
D. Our breaks down the food to smaller parts.
4. Match the following.
A. Hands a. help the bones
B. Brain b. hold things
C. Skin
c. controls the body
D. Muscles d. helps us feel
5. Who Am I?
Iʹm in the middle of your face, I can detect every smell with grace. When something is cooking, Iʹll let you know, And when thereʹs danger, Iʹll alert you, so.
Who am I?
6. Answer the following questions.
A. Write one difference between the internal and external organs of our body.


B. What is the role of taste buds in our body?
C. What are sense organs? Name them.
D. Where is the heart present in our body? What does it do in our body?
E. Explain two ways in which differently-abled people use special tools.
7. Picture-based questions.
A. Which part of the body is shown in the picture?
B. Is it an internal or an external organ?
C. Write one way in which it helps us.

1. How do your eyes and ears work together to help you understand the world around you? Can you think of an example?
2. What do you think would happen if we didnʼt have bones to protect our organs?
Skills
Let us use a checklist to take good care of some of our sense organs. Sense organs Things I will do every day
Eyes I will read and write when the light is not too dim.
Ears I will keep the volume low when listening to music or watching TV.






































Family and Family Relations Resemblance in a Family
Tree Importance of Family Types of Families


Paste in a photograph of your favourite family member in the space given.
1. How is this person related to you?
2. Why is he/she your favourite person? Get Set


A family is a group of people who love and care for each other. They can be related by birth, marriage or adoption. People who are part of a family are called family members. Family members may live in the same house or in different places.
There are different types of families, depending on the number of members in them.
A family picture.

We know that families can be small or big. Let us learn about different types of families.
Sheena lives with her parents and brother in Ajmer. Their parents love and care for them. Sheenaʼs parents work to support the family. Sheena and her brother go to school. Her family often shares household work. A family with only the parents and their children is called a nuclear family. It is a small family. During the holidays, Sheena’s family visits her grandparents and other relatives, like uncles and aunts.
A nuclear family.
related: connected adoption: when adults take a child, who was not born to them, and love and care for the child as their own


If a family consists of a husband and a wife, can we call it a nuclear family?
Vani lives with her parents, brother and grandparents. She has a big family. Such a family that has grandparents, parents and children staying together is called a joint family. In a joint family, parents, children and grandparents live together. Vani’s father goes to work every day. He earns money and takes care of the family. Vani’s mother has a tiffin service business. She earns money and helps Vani’s father to support the family. In a joint family, each member does their share of work. Every evening, Vani goes for a walk with her grandparents. Her grandparents tell Vani and her brother bedtime stories.
Yash lives next door to Vani. He lives with his parents, grandparents, uncle, aunt and cousins. His family is bigger than Vani’s family. His family is also a joint family.
Radhika lives with her father. A family with only one parent (mother or father) is called a single-parent family. Radhika also has a pet dog. Radhika goes to school. Her father works in an office. Every evening, Radhika and her father go and play in the park. Radhika’s father takes good care of her. Single-parent family
business: making and selling things to earn money cousins: children of aunts and uncles


So, we see that families might be different, but love and support bind them together.
Which type of family would you prefer to live in—a single-parent, nuclear or joint family? Why? Talk to your partner and share in the class.
Name the following.
The Narasinganavar family is a joint family with over 200 members from Lokur village in Karnataka.
1. A family with parents and their children.
2. A family with grandparents, parents and children.
3. A family with only one parent and children.
A family tree shows how family members are related to each other.
A family tree often starts with the grandparents, who form the first generation. The second generation consists of the parents, uncles and aunts. The third generation includes the children.
The parents of the mother are called maternal grandparents. Similarly, the parents of the father are called paternal grandparents. Did You Know?
generation: a group of people who are about the same age


Let us make a family tree booklet!
• Take a scrapbook.
• On the first page, write “My Family Tree Booklet”.
• On each page, paste a photograph of a family member and write a few sentences about them.
• On the last page, draw a simple family tree to show how everyone is connected.
• Share your booklet with the class.
Our family supports us and helps us learn new things in life. Let us learn why family is important.
• Our family makes us feel safe and happy.
• Our family loves and cares for us.
• When we are sad or have a problem, our family members help us feel better.
• We learn a lot from our family. Family members teach us important values like kindness, honesty and respect.
• Spending time with our family is fun. We play games, go on trips and celebrate special days together.

Remember to appreciate and spend time with your family. This is because your family members are the ones who will always be there for you. Your family is your support system.
appreciate: to be thankful



Family members resemble each other. They may share the same physical and facial features. We call this family resemblance. Children may look like their parents or grandparents. Sometimes, siblings also resemble each other.
Children born to a mother at the same time are called twins. Twins that look exactly the same are called identical twins. However, some twins can be non-identical too.
It is commonly believed that twins are similar in every way. People think that identical twins should have the same fingerprints. This is not true. Fingerprints are unique to each person. Identical twins, who look very similar, have different fingerprints.
The Kodava family has the largest family tree in Bharat. This family has over 18,000 members shown in their family tree.
family: a group of people who are related to each other family tree: a representation that shows how family members are related to each other twins: children born to a mother at the same time
resemble: means to look like or be similar to someone else in appearance facial: something related to the face, typically describing features or expressions siblings: brothers and sisters, meaning children born to the same parents



Scan the QR code to learn more about different types of families.
• A family is a group of people who are related to each other.
• Families can be nuclear, joint or single-parent families.
• A family tree shows how family members are related to each other.
• A family loves us and makes us feel safe and happy.
• Family members resemble each other.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What is a family with parents and children called?
Joint family Nuclear family
Single-parent family
B. Which generation is formed by your parents?
First generation Second generation
Third generation
C. What do we call the people who are related to us?
Neighbours Relatives
Family members


2. Fill in the blanks.
generation resemble single-parent family members
A. People who are part of a family are called .
B. A family of only one parent and children is called a family.
C. In a family tree, grandparents form the first .
D. Family members each other.
3. Write True or False.
A. Family members are only related by birth.
B. Families can be both big and small.
C. A single-parent family is bigger than a joint family.
D. Our family keeps us safe and happy.
4. Match the following.
A. Nuclear family
B. Joint family
C. Single-parent family
5. Answer the following questions.
a. family with one parent and children
b. family of parents and children
c. family of grandparents, parents, and children
A. How are family members related?
B. What is the difference between a nuclear family and a joint family?
C. How is a family tree formed? Draw your family tree.
D. Write any two ways in which family is important?
E. What do you mean when you say that a daughter resembles her father?
F. Write two ways in which you support your family.


6. Picture-based questions.
A. What types of families are shown in each picture?
B. How are these families different?

What changes will a child experience when moving from a nuclear family to a joint family? Write any two.
How do you help out at home? Write at least three ways in which you help at home. How do you feel after helping other family members in your home? Share your experience with your friends. Encourage your friends to help their family members in whatever way they can.
















Read the poem aloud and underline two ways to be safe.
Every day, safety is the key, For you and me, it is easy to see.
Look both ways before you cross the street, Wear your helmet while on your bicycle seat. Hold hands of elders, do not run too fast, Safety first, make each second last.
Safety is an important part of our lives. Safety means staying alert and away from danger. It keeps us safe from accidents and diseases. We must learn and practice safety rules at home, school, on the road and in our neighbourhood. Let us learn more about keeping safe.


Priya wanted to play with her friends outside in the road, but her mom said no. Can you guess why?
Her mom said there were cars and other vehicles on the road, and she was worried about accidents. Accidents can occur anytime, anywhere, and with anyone, but we can avoid them by following certain safety rules. Some of the rules we should follow to stay safe on the roads are:
• Never play or run in the road.
• Walk on the footpath.
• Always look right, then left, and right again, before crossing the road. Always cross the road at the zebra crossing.
What do you think will happen if there are no zebra crossings or footpaths?
• Wear a helmet when riding on a bike, scooter or skateboard to protect your head. Wear a seatbelt while travelling in a car.
• Follow traffic signs and signals. Always stop at the red light.
While travelling, look for road signs and signals. Ask an adult what they mean. Draw some of them and write their meaning.
Sharp objects like knives, scissors or blades can hurt us if we do not handle them properly. Remember a few things while using sharp objects to keep safe:
• Ask an adult for help when using sharp objects.
• Stay away from barbed wires.
footpath: a path along the side of a road for people to walk on





Handle sharp objects carefully.

• Do not play with objects made of glass as they can break easily.
• Keep sharp objects out of reach of small children.
Some common types of accidents are slipping on wet floors, tripping over toys or falling off furniture like chairs or beds. Some of the rules that we should follow to avoid falling are:
• Do not run on wet floors and stairs.
• When using stairs, hold onto the handrail.
• Make sure the floor is clear of toys, shoes and other objects that could make people trip.
• Sit properly on chairs and benches. Do not rock on them or stand on them.
Do not run on a wet floor.
• Follow playground rules. Do not push other players. Never jump off a moving swing or slide.
• Do not leave soap on the bathroom floor. Someone may accidentally step on it and fall. Also keep the floor dry.
We may get an electric shock if we do not handle electrical appliances correctly. Remember the following to stay safe from electric shocks:
• Ask an adult for help when using an electrical appliance.
• Never touch electrical appliances, sockets or wires with wet hands.
• In case someone gets a shock, do not touch the person with your bare hands. Turn off the main supply or unplug the appliance that is causing the shock.
Never touch an electrical socket with wet hands.

Burns can happen on the skin from fire, steam, or hot liquids. They often occur in the kitchen, but we can prevent serious burns by following these safety tips:
• Don’t play with matchsticks.
• Avoid wearing synthetic clothes in the kitchen; they catch fire easily.
• Use tongs or a thick cloth to hold hot utensils.
• Always turn off the gas stove and cylinder knob when done.
Do not touch hot pot on the stove.
• If there is an LPG leak, close the cylinder knob and open all windows and doors to let the gas out.
We use many chemicals at home, like paints, certain sprays, washing detergents, pesticides and medicines. Some of these chemicals can be dangerous to our health and the environment. Such chemicals are called harmful chemicals. It is important to be careful when these are used.
• Never touch or taste any chemicals without an adult present.
• Take medicine only when given by a doctor or adult.

pesticides: chemicals used to kill insects
Never take a medicine on your own.


Fill in the blanks.

1. Do not run on wet or stairs.
2. Never touch an with wet hands.
3. Always wear a when travelling in a car.
4. Take only when given by a doctor or adult.
First aid is the immediate help given to someone who is injured or suddenly becomes ill in the time before a doctor can arrive.
A first aid box or kit helps us to provide first aid. It must be kept at home, schools, offices and even in cars. It usually has cotton, common medicines, band-aids, a thermometer and an antiseptic lotion.

Here are a few things we can keep in mind while giving first aid.
• Don’t crowd around the injured person.
• Stay calm and get help by calling an adult and a doctor.
• Help the injured person sit or lie down comfortably.
• Call 102 for an ambulance or ask an adult to call for help if someone is seriously hurt or sick.
Do and Learn
Ask a parent or another adult and create a small first aid kit. Put cotton, band-aids, and an antiseptic cream in it. You may use it to help yourself or an injured friend in need.
thermometer: a tool to measure how hot or cold things are

Good health means taking care of your body and mind. We feel strong, happy and full of energy when in good health. Let us learn how to stay healthy.
Eating clean, healthy food gives our body energy and nutrients, keeping us fit and protecting us from illnesses. In contrast, junk or unclean food can cause serious health issues. To stay healthy, follow these simple tips:
• Always wash hands before and after meals.
• Use clean utensils for cooking and eating.
• Keep food covered to protect it from flies, dust, and germs; avoid eating uncovered food.
• Eat only freshly cut fruits and vegetables.
• Avoid overcooking food, as it can destroy important nutrients.












































































































Eat healthy food, avoid junk food.

We like eating packet food like chips and biscuit, but do you think it is healthy? What do you think they are made of? Discuss in your class.
• By practicing these habits, we can enjoy good health and prevent sickness.
Exercise helps keep our body fit, strong, and healthy. Activities like brisk walking, jogging, cycling, yoga, and swimming are all great forms of exercise. Regular movement improves blood circulation, strengthens muscles, and keeps us active. It helps us develop strong muscles and bones.
Did You Know?

Dancing is a good exercise.
International Day of Yoga is celebrated every year on 21 June.





Rest and sleep are very important if we want to stay healthy and strong. When we rest or sleep, our bodies get time to relax. We can also relax by reading a book, listening to a story or listening to music. A good night's sleep of around eight hours is essential for staying healthy. Sleep gives the body a chance to repair the wear and tear when we sleep.
Listening to a story helps us relax.
We should keep ourselves and our surroundings clean. Let us learn some of the ways to keep clean:
• Brush your teeth twice a day to keep them strong and healthy.
• Bath every day and wear clean clothes.
• Wash your hands after using the bathroom to keep germs away.
• Cut your nails regularly.
hands
Let us make a promise to keep ourselves safe and healthy by practicing all these good habits every day.
Yoga is believed to have started in ancient India over 5,000 years ago. We read about yoga in very old texts like the Vedas, Upanishads and the Bhagavad Gita.
zebra crossing: a marked path with white stripes where people walking can safely cross the road first aid: immediate help given to someone who is injured or suddenly becomes ill



Scan the QR code to learn more about being healthy!
• Falls, electric shocks and burns are some accidents that may happen if we are not careful.
• We need to follow safety rules at all times to stay safe and avoid accidents.
• We must keep a first aid kit ready at home, school and in vehicles.
• Healthy food, good eating habits, regular exercise and getting enough rest are important for good health.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What should we wear while sitting in a moving car?
seatbelt cap gloves helmet
B. Which of these should be kept away from small children?
toys
books knives clothes
C. Which of these is not present in a first aid box?
cotton medicines fork band-aid
2. Fill in the blanks. bath overcooking rest exercise
A. Our bodies need to have energy for the day.
B. Regular helps develop our bones and muscles.
C. Avoid food, as it can destroy important nutrients.
D. We need to every day to keep the body clean.



3. Write True or False.
A. We should never rock on our chairs.
B. We must brush our teeth four times a day.
C. We should sleep for only 4 hours a day.
D. A footpath is a safe place to walk.
4. Match the following.
A. exercise a. scissors
B. sharp object b. apples
C. healthy food c. medicines
D. first aid d. yoga
5. Answer the following questions.
A. What should we wear for safety while travelling in a car?
B. Name two objects that may cause an electrical shock.
C. Write any two practices that we should follow to stay healthy.
D. What should we do in case of an electric shock?
E. Priya is using a pair of scissors for her craft activity. Write two safety rules she should follow while handling a pair of scissors.
F. Why is exercise important for us?
G. What is first aid? Write four things that a first aid box must have.
H. There are different ways to exercise. Which way is your favourite? Write 2–3 sentences about it.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What is the girl in the picture doing?
B. Write one way in which this activity helps her body.



1. Ruhi likes eating only junk food. She also goes to bed late and rarely exercises.
A. How do you think these habits will affect Ruhi’s health?
B. Write two ways in which you can help Ruhi to stay healthy.
First-aid when a wound bleeds.
1. Press a clean cloth on the wound to stop the bleeding.
2. Wash the wound with clean water.
3. Apply an antiseptic cream.
4. Cover it with a bandage.






















































































Chapter Overview





The Food We Eat
Importance of Food Types of Food Sources of Food Cooked and Raw Food Balanced Diet Healthy Food Habits




Get Set

Think about the food you ate yesterday. Now, put a tick ( ) or a cross ( ) for the following statements.
1. I ate a fruit yesterday.
2. I ate a bowl of dal yesterday.
3. I drank a glass of milk yesterday.
4. I ate chapati/rice yesterday.
5. I ate some fresh vegetables yesterday.
It was breakfast time. Samit made a face as he did not want to eat. Samit’s sister, Amina, made him sit to have breakfast. “You must eat, Samit.”
“But why, Amina? Why do we need to eat every day?” While Samit started to eat, Amina explained why food is important to us:

• Food gives us the energy to do work. It helps us to grow.
• Food protects us against diseases.
• Food also helps repair our bodies when we get hurt. So, we need food to stay strong and healthy. All living things need food.
Have you seen people feed animals or birds? Do they also need food like us?
“But where does our food come from?” asked Samit. Amina explained: Our food comes from two main sources—plants and animals. Let us learn more about it.
We eat different parts of plants. We eat the roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits of plants. We also eat the seeds of some plants. Cereals, like rice and wheat, pulses like lentils and beans and nuts like almonds and peanuts, are all seeds.




cereals: grains like wheat, rice, maize and barley



Spices, like coriander, black pepper, cinnamon sticks and turmeric, are also obtained from different parts of plants. They add taste and aroma to food.



Spices from plants
Mushrooms look like vegetables but they are not from plants or animals. They are fungi, a different group of living beings. We use them as vegetables. Error Alert!

With the help of your parents, observe the different spices your family uses in cooking. List them in your notebook and write one special feature of each.
We get milk from buffaloes, cows and goats. Milk is used to make tea and coffee. We also make various dairy products from milk. Butter, curd, cheese, paneer and ghee are dairy products. We also get meat from goats, sheep, ducks, hens and fish. We get eggs from hens and ducks.

Dairy products: butter, curd, cheese, eggs, milk
We often use honey as a sweetener and in medicine. Do you know where it comes from? Is it from a plant or animal? Remember!
People who eat only plant and milk products are called vegetarians. People who eat plant-based foods, dairy products, eggs and meat are called non-vegetarians. spices: plant parts, used to add taste and aroma to food


Circle the correct example.
1. A plant root that we eat: spinach broccoli beetroot
2. A plant stem that we eat: tomato potato cabbage
3. A plant flower that we eat: broccoli cashews almonds
4. A food that we get from animals: egg garlic peanuts
5. A milk product: walnut butter honey

Amina is in the kitchen with her father, watching him prepare something special. He chops up different vegetables, adds a pinch of salt, a dash of pepper, and a squeeze of lime juice. To Amina's surprise, they don’t even use the stove! Yet, the simple "vegetable salad" turns out to be absolutely delicious.
A bowl of salad.
Why do you think Amina’s father has not used the stove to make a salad?
Food we eat can be raw or cooked. Some vegetables, like tomatoes and cucumbers and most fruit, can be eaten raw. We often make salads with them. Nuts, seeds, and certain milk products like curd and cheese can also be eaten raw. We do not need to cook them.
We need to cook most foods, though. Let us learn why and some ways to cook them.
Foods, like wheat, rice and pulses, cannot be eaten raw. Some vegetables, like potatoes, ladyfingers and pumpkins, also cannot be eaten raw. We cook food because:
• Cooking softens the food, so it can be eaten easily.
• Cooking makes foods, like pulses, easy to digest.
• Cooking also removes germs from the food.
• Cooking adds taste and aroma to food.


There are different ways to cook food.
1. Boiling: In this method, food is cooked in boiling water. Rice, eggs, pulses and some vegetables are boiled to make them soft and ready to eat.
2. Baking: This involves cooking food with dry heat, usually in an oven. We bake things, like bread, cakes and biscuits, using this method.
3. Frying: Food is cooked in hot oil or ghee when we fry it. We make puris, samosas and pakodas by deep-frying them.
4. Roasting: In roasting, food is cooked either in an oven or over a fire. Paneer, chicken and some vegetables can be roasted.
5. Grilling: In grilling food is cooked on a griller or tandoor, usually over direct heat. Grilling is a healthy way to cook both vegetables and meat.
6. Steaming: Foods, like vegetables, momos, idli and dhokla, are steamed. Steaming happens inside a pressure cooker or steamer, making the food soft and healthy.
Match the food with the way it is cooked.








We need to eat different types of food to stay healthy and fit. Different foods help the body in different ways. We can divide food in three ways, based on how they help our bodies.
These foods give us energy to do different activities throughout the day.
Examples: Rice, chapati, milk and bread
Body-Building Food
These foods build muscles and keep our bones healthy and strong.
Examples: Pulses, eggs, milk, meat and fish
Protective Food
These foods protect us from diseases.
Examples: Fresh fruit and vegetables; milk and milk products.







Make a list of the foods that you have eaten since yesterday. Group them into energy-giving, body-building and protective foods. Which types of foods did you eat most of? Discuss the list with your parents.
Discuss!
Labourers usually need to eat more energy-giving foods than children. Think about a reason. Then, discuss it in your group.





A balanced diet includes a mix of foods that provide energy, build and repair our body, and protect us from illness. This means eating a variety of foods in the right amounts. By following a balanced diet, we ensure that our body gets all it needs to stay strong, active, and healthy.
Milk is called a complete food. It gives us energy, builds muscles, helps us grow and protects us from diseases as well. Did You Know?
We should follow good food habits:
• Do not eat food that has been left uncovered, exposed to dust and flies.
• Always wash your hands with soap before and after every meal.
• Always wash fruit and vegetables before eating them. It removes germs, dust and other harmful things from them.
• Do not wash peeled vegetables. Wash them before peeling to avoid the loss of nutrients.

Wash fruits before eating
• Do not heat food repeatedly. It causes the loss of nutrients.
• Drink lots of water to remain healthy.
Khichdi is sometimes called the national food of India. It is a simple yet balanced meal, eaten across India in different forms. Vegetable khichdi includes rice (energy-giving food), pulses (body-building food) and vegetables (protective foods).



dairy products: milk and milk products, such as curd, cheese and ghee balanced diet: a diet that has all the required nutrients in the right amounts nutrients: substances in food that help our body grow, stay healthy, and provide energy

Scan the QR code to learn more about the importance of various types of food.
• We get energy from food.
• Food helps us grow and protects us from diseases.
• We get food from two sources—plants and animals.
• Food can be eaten raw or cooked.
• Boiling, frying, baking, grilling and roasting are some ways to cook food.
• The three main groups of foods are—energy-giving foods, body-building foods and protective foods.
• A balanced diet has all the required nutrients in the right amounts as required by the body.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What group of foods do chapati and bread belong to?
Protective foods Energy-giving foods
Body-building foods
B. From which of the following do we get spices? plants cows hens bees
C. Which of the following are protective foods?
pulses rice fruits water


D. Which of the following is not a cereal?
wheat rice peas corn
2. Fill in the blanks.
Frying Baking Grilling Boiling
A. is a method of cooking with water.
B. is a method of cooking in hot oil.
C. makes cakes and bread in the oven.
D. is cooking food over direct heat or fire.
3. Write True or False.
A. Almonds and walnuts are nuts.
B. Cheese, paneer and fish are dairy products.
C. Cereals and pulses are mostly cooked before eating.
D. Some dairy products come from plants.
4. Choose the odd one out.
A. Carrot, beetroot, potato
B. Spinach, cabbage, radish
C. Orange, apple, broccoli
D. Rice, wheat, almonds
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Complete the statement: Food is important for us because .
B. What are the two sources of food? Give one example of each.
C. Name two foods that can be eaten without cooking.
D. What is the role of body-building foods?
E. What is a balanced diet?
F. What are the methods of cooking food? Explain any two.

6. Picture-based questions.
A. Which of these foods are from plants? Which of them are from animals?
B. Name one protective food and one body-building food shown in the picture.

1. If you only ate energy-giving food, like chapati and rice, but no body-building or protective food, how would it affect your health?
2. Why do you think some foods are better when eaten raw, while others need to be cooked before we can eat them?

Life Skills
Eating a balanced diet is necessary to stay healthy. However, many people in our country do not get enough food to eat.
1. Think of some ways that help us not to waste food.
2. How would you help people who do not have enough food to eat?

Share your ideas with your family and friends. Make a poster on ‘Ways to stop food wastage,’ and with the help of an adult, put it up near a cafeteria or a restaurant.

















Solve this riddle:
I am a place you go to find peace, Where your day’s troubles can cease.
I might have a roof and a floor, And often, a family to adore.
What am I? Write here:
Richa's father comes back from the office. He is relaxing after a long day. Richa also feels good when she comes home after playing football.
We all return to our houses after studying at school. A house is a place where we live with our families. We eat, sleep and spend time together

in our homes. Our belongings are safe in our homes. A house protects us from heat, cold and rain. It also protects us from animals and thieves.
What is the address of your house? Does it have the house number, the street name, the road and the city?
Early humans lived in caves. Later they learnt to make houses using materials like straw and mud. Did You Know?
There are different types of houses. The type depends on the following:
• The climate of the place.
• The building materials that are easy to get.
• The locations such as plains, deserts, mountains or forests.
• Money a person wants to spend. Let us learn about some types of houses.
Igloos are made of snow and ice blocks. Inside the igloo, it is warmer than the cold weather outside.
A stilt house is mostly found in areas near water bodies or where there are floods. These houses are built on high platforms made of wooden or concrete poles. This protects the house from rising water levels. It also protects people from wild animals.
belongings: things like clothes and books that we own climate: weather conditions of a place


Stilt house
Inuit: people who live in the cold northern areas of the world floods: overflow of water onto dry land


Tents are made of fabric like nylon or canvas. These are not fixed but temporary houses. They are used by soldiers and campers on holiday.
Mud houses are made from mud and straw. These are found in hot places such as deserts. These houses are cool on the inside during hot summers.
A houseboat is a house that is built on a boat. Houseboats are common in places that have lakes and rivers. They are used on the Dal Lake in Kashmir where they are called shikaras . They are also common in the backwaters of Kerala.
Houseboats can move easily from one place to another.



Why are stilt houses common in Assam? Give reasons for your answer. Discuss in your class.
Caravans are houses on wheels. These can be pulled by a vehicle. They are used by people who travel a lot.
A bungalow is an independent house. It is made of materials like wood, bricks, cement, glass and iron. A bungalow has one or two floors.
backwaters: quiet areas of a river or lake where the water is still and doesnʼt flow like the rest of the water



A multi-storey building has many flats used as houses. It may also have offices and shops. These are mostly found in big cities. These buildings have stairs or lifts to reach the flats.
Name the following:
1. A house that pulled by a vehicle:
2. A house built on poles:
3. A house made of ice blocks:
4. A house made of canvas:
Houses are built with materials that are easy to find in the place. Village houses are usually built from wood, mud, stone, bamboo and dry leaves. These are called kutcha houses.
City houses are mostly built with strong materials like bricks, iron, concrete, stones and wood. These are called pucca houses.
Houses in the villages are not always kutcha. There are also strong pucca houses made of cement and bricks. Error Alert!



Jhuggis and slums are small, temporary houses often built from materials like plastic, tin, or wood. People living in these homes face many challenges, like lack of clean water and electricity. Keeping the surroundings clean helps improve their living conditions!


Our houses are places where we live and rest. We should keep our houses clean. Let us learn some ways to keep a house clean.
• Sweep and dust the house regularly.
• Keep your belongings in the proper places.
• Only throw waste in covered dustbins.
• Keep the floor dry and clean. Do not spill water and food on it.
• Open windows regularly to allow fresh air and sunlight in. Sunlight kills many germs.
• Do not allow garbage and water to collect around the house. It attracts germs, insects and mosquitoes.
Unwanted insects and animals like cockroaches, flies, mosquitoes, and rats are called pests. They spread diseases and hide in dirty places, so we must keep our homes clean and use chemicals called pesticides carefully to control them.
Write True or False.
1. We should only throw the garbage in covered bins.
2. Kutcha houses are built with mud and straw.
3. Pucca houses are stronger than kutcha houses.
4. Dirty surroundings spread germs in the air.
Apart from our houses, we should also keep our surroundings clean. It prevents the spread of diseases. Some people throw garbage anywhere they like. This pollutes the land and spreads diseases. At home, we throw



garbage in a covered dustbin. Then, the sweepers collect it and throw it in closed garbage bins. Finally, municipality trucks dispose of the garbage far away from the city.
Make a list of five activities that you would do to keep your house and surroundings clean. List them on paper and discuss them with your parents.
Rohit went to the nearby park for a walk in the evening. He saw garbage bins of different colours. Why were different coloured bins placed there? Let us help him find out.
Coloured garbage bins are used to sort different wastes. There are two types of waste—biodegradable and non-biodegradable.
Biodegradable waste includes peels of fruit and vegetables, leftover food, eggshells and other waste from the kitchen. It also includes paper and cardboard. Biodegradable waste can be broken down easily into simpler forms naturally. This type of waste is collected in green garbage bins.

Non-biodegradable wastes include glass, plastic bags, bottles, metal and tin cans. These are not easily broken down in nature. We should reuse or recycle them. This type of waste is collected in blue garbage bins.

Garbage bins of different colours help in sorting the waste.
dispose: to dump or throw away

Used plastic bottles can be reused to grow plants. What are some more ways to reuse plastic bottles? Discuss in your class.

Broken pieces of glass, bulbs, old medicines and batteries are called hazardous waste. These are collected in red garbage bins. Did You Know?




Wonders of Bharat
Houseboats in Kerala, India are called kettuvallam. It means ‘the large boat of yesteryears’. It is famous among tourists.

temporary houses: houses that are not fixed and can be moved from one place to another
kutcha houses: houses built with materials like wood, mud, stone and bamboo pucca houses: houses built with materials like bricks, concrete and iron biodegradable waste: waste that is broken down easily into simpler forms in nature
non-biodegradable waste: waste that does not break down easily in nature


More!

• A house protects us from cold, rain, heat, thieves and animals.
• Igloos, stilt houses, houseboats and tent houses are some types of houses.
• Based on the material houses are built with, there can be pucca and kutcha houses.
• We should keep our houses clean and germ-free.
• Garbage should be separated and disposed of properly.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What do we call a house built with ice blocks?
Stilt house Igloo Houseboat
B. What are tent houses made of?
Mud and straw Nylon or canvas Cement and bricks
C. Which of the following houses is common in hot areas? Igloos Mud houses Stilt houses
2. Fill in the blanks.
Caravans Stilt Tents Houseboats
A. are used by campers for a temporary stay.
B. houses are built on high platforms made of poles.
C. are also called houses on wheels.
D. are commonly found on lakes in Kashmir.
3. Write True or False.
A. Stilt houses are found in Assam.
B. Mud houses are made in hills.
C. Igloos are built in hot regions.
D. Houseboats are permanent houses for tourists.


4. Circle the odd one out.
A. mud concrete bamboo dry leaves
B. bricks cement iron straw
C. vegetable peels eggshells plastic paper
D. metal glass tin cans fruit peels
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Why do we need a house? Write two reasons.
B. Name two things we should think about before building a house.
C. Name any four materials we use to make kutcha houses.
D. Write one difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste. Also, give two examples of each type of waste.
E. Riya lives in the deserts of Rajasthan. Ranjan lives in West Bengal near a river. What would be the difference in the type of house they live in?
6. Picture-based questions.

A. What type of waste is shown in the given picture?
B. Would you collect it in the blue or green garbage bin?


1. What do you think will happen to the environment if people throw plastic and other waste on the ground instead of throwing it away properly?
2. What can happen to your health if you donʼt keep your house clean? Why is it important to keep your home clean?



Our home is where we live safely and comfortably, but it’s also important to care for the area around it. Clean surroundings help prevent diseases and create a healthy environment for everyone.
• Draw and colour in a picture of your house, showing the surroundings too.
• Find out and write the names of some diseases that spread in places that are not clean.
• List a few simple tasks you can do regularly to keep your home and neighbourhood tidy.


























Chapter Overview

Need for Clothes






Clothes We Wear
Different Clothes
Types of Fibres
Taking Care of Clothes

Get Set

Draw a picture of your favourite piece of clothing (your favourite shirt, dress or a T-shirt) in the space below and colour it in.
In this chapter, we will learn more about clothes.


We need clothes because they are one of our basic needs, just like food and shelter. Clothes protect our bodies from extreme weather conditions, such as strong winds, heat, cold and heavy rain. Wearing clothes keeps us safe, warm and comfortable. Besides this, clothes also help us express our personality and make us look good. When we wear clean, comfortable clothes, we feel happy, confident and ready for the day!
Read this poem aloud with your friends!
Clothes we wear in the sun and rain, Keep us safe from the weather’s strain. Jackets are warm in winter’s chill, Cotton is cool when summer’s still. Raincoats are bright for rainy days, Clothes protect us in many ways.
If we do not wear clothes that are right for the weather, we may fall sick. For example, if we do not use raincoats and umbrellas during the rainy season, we might get wet and catch a cold.
Clothes do more than just keep us safe. We wear different clothes for different reasons. For example: We wear warm clothes, like jackets and woolen caps in cold weather, and light clothes, like cotton dresses and shorts in hot weather, to stay comfortable. If it’s rainy, we wear raincoats and use umbrellas to stay dry.
Special clothes, called uniforms, help us know who people are and what they do. For example, we can tell if someone is a student, a firefighter, a police officer, a doctor or a nurse by looking at their uniforms. For example, a doctor wears a white coat and each school has its own uniform.
Different kinds of clothes for different seasons.


Think about the clothes someone gave you as a gift. How does it make you feel when you wear them?
Every culture has its own unique style of dressing. For example, in Maharashtra, women usually wear sarees but their style is not the same as in other parts of India. Women also wear a choli (blouse) and ghagra (skirt) in some regions. Men usually wear a dhoti and kurta. In Punjab, men wear turbans that are different from those worn in Rajasthan. Each region has its own way of dressing.
A man in turban, kurta and pajama. A woman in a saree.
We wear different clothes for different events. Bright, colourful and fancy clothes are worn for happy occasions like weddings, family gatherings, festivals and parties. For everyday activities, people usually choose simple and comfortable clothes.
Discuss!
Think about the clothes you and your family wear for different occasions. Share it with your friends!
culture: way of life of a particular society or group


The clothes that we wear are made of different fibres. Fibres are thin threads that are joined together to make a piece of cloth. There are mainly two types of fibres: natural and human-made.
Natural fibres are the ones that we get from plants and animals. Some natural fibres are:
• Wool is a natural fibre that is obtained from the fleece of sheep. The fleece or soft, fluffy wool is sheared from the sheep and then processed to make wool yarn.
⸰ Wool is a strong material that can last for a long time if taken care of properly. This makes it great for making clothes and blankets that can be used for many years.
⸰ Wool traps heat, which keeps us warm even in cold conditions.
⸰ Wool is commonly used to make cosy sweaters and warm socks, providing comfort during winter.
Wool from sheep is used to make woollen clothes.
• Cotton is a natural fibre that we get from the cotton plant. The fibres are collected and made into yarn.
⸰ Cotton is gentle on the skin and allows air to pass through, keeping us cool during the summer.
fleece: soft and fluffy wool that grows on a sheep and is used to make warm clothing
sheared: cut off or removed, referring to wool or hair being shaved from an animal like a sheep

⸰ Cotton is also easy to care for, as it can be washed and dried in a machine or in the sun.
⸰ Cotton absorbs sweat well, helping us to stay dry.
⸰ Cotton is widely used for everyday clothing, like t-shirts and sarees and bedsheets. It is comfortable and durable.
• Silk is a natural fibre produced by silkworms when they spin their cocoons.
⸰ Silk feels soft and smooth against the skin.
⸰ Silk has a natural shine. It is used to make festive clothing.
⸰ Silk is a lightweight fabric, which makes it comfortable to wear.
⸰ Silk is often used to make beautiful dresses and scarves.
Ria: Mom, can I have a silk dress for our school play?
Mother: Silk is very delicate. Your dress will get easily wrinkled or stained. How about we look for another dress that’s easier to take care of?

Ria: But silk looks so beautiful and shiny! I want to stand out on the stage.
Mother: I understand that, but I am sure we will find something pretty.
Let’s find a dress that’s comfortable, easy to move in and still looks beautiful. How about we go shopping together this weekend to find a synthetic dress for you?
Human-made fibres, also known as synthetic fibres, are made from chemicals.
Two main types of human-made fibres are nylon and rayon.
Qualities of Nylon and Rayon:
• Clothes made from these fibres are durable.
• These fibres are used to make items like shirts, suits, gowns, curtains and many kinds of clothes.
durable: the ability to last a long time
cocoon: a protective covering spun by silkworms


• They can easily catch fire and therefore, should be avoided in the kitchen.
• Nylon is used to make swimwear as it dries quickly when it gets wet.
• Rayon can be made to look like silk or cotton, so it can be used for many different types of clothing.
Solve the riddles. “What am I?”
1. I am often used to make cosy sweaters and warm socks. What am I?
2. I am gentle on the skin and allow air to pass through. What am I?
3. I feel soft and smooth against your skin and have a natural shine. What am I?
Taking care of clothes helps them last longer and stay in good condition. Here are some simple steps to follow:
• Check clothing labels for washing instructions. Sort by colour before washing.
• Use the proper amount of detergent.
• Gently dry clothes by hanging them up.
• Iron clothes at the correct temperature setting.

• Keep your clothes in the proper place. By following these steps, your clothes will stay clean, fresh and in good shape for a longer time.
detergents: cleaning agents used to wash clothes

Some people think that more detergent makes clothes cleaner, but thatʼs not true! Using too much detergent can make your clothes, feel stiff or sticky.

Surat, located in the state of Gujarat, is known for producing textiles, including silk. It is also known as the textile hub of the nation.
uniforms: special clothes that help us know who people are and what they do fibres: thin threads that are joined together to make a piece of cloth synthetic: made using chemicals, not natural

Scan the QR code to learn more about synthetic clothes.
• Clothing is essential, just like food and shelter, it protects us from harsh weather conditions.
• People wear different clothes based on the weather, the occasion, the work they do and the place where they live.
• Clothes are made from natural fibres, like wool, cotton and silk, and human-made fibres, like nylon and rayon.
• Proper washing, using the right amount of detergent, and drying and ironing clothes carefully, will help them last longer and stay in good condition.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of the following is a human-made fibre?
Rayon Silk Wool
B. Which type of clothes do we wear during winter to stay warm?
Shorts Sweaters Dresses
C. Which fibre is produced by using the fleece of sheep?
Cotton Silk Wool
2. Fill in the blanks. sweat nylon silk winter
A. fibre has a natural shine.
B. Wool traps heat, making it perfect for the season.
C. Cotton absorbs well, keeping us dry.
D. Human-made fibres, like rayon and , are durable.
3. Write True or False.
A. Silk is a synthetic fibre.
B. Cotton is obtained from a plant.
C. Using too much detergent makes clothes cleaner.
D. Raincoats are used to keep us dry in rainy weather.
4. Match the columns.
A. Silk
B. Nylon
C. Cotton
a. bedsheet
b. sweater
c. swimwear
D. Wool d. festival clothes


5. Answer the following questions.
A. What are natural fibres?
B. Give two examples of human-made fibres.
C. Why is it important for us to take care of our clothes?
D. Explain why cotton is a popular choice for summer clothing.
E. Think of a time when someone told you that they liked what you were wearing. How did it make you feel? Write a sentence to explain your feelings.
6. Picture-based question.
Write the correct weather conditions to wear these clothes.


Why might it be important for us to wear uniforms in schools?

Let us REUSE old clothes!
Cut out fabric strips from old clothes and braid or twist them to make bracelets, necklaces or headbands.
Cut out small pieces of fabric from old clothes and glue them onto pieces of cardboard to make colourful bookmarks.

Cloth bookmarks


Objective: Learn the importance of a first aid box and how to create one using items found at home.
Materials Needed: A small box (like a shoebox), band-aids, cotton balls, antiseptic liquid, a clean handkerchief, bandages
Step 1: Paint the box:
Paint your box using white paint. Let it dry. Then, paint a red cross on it. Write “First Aid” on the box.
Step 2: Prepare the contents:

Gather items like 4 band-aids, cotton balls, a clean handkerchief and antiseptic liquid. You can also add antiseptic cream and bandages. Assign a cost to each item, either by checking the prices at a store or guessing how much they cost. Write down the costs.
Step 3: Put the items in the box:
Put all the items in your box. Make sure everything is packed neatly.
Step 4: Research:
Find out why each item in the first aid kit is important and how it helps to treat injuries. Note down your findings in your notebook.
Step 5: Learn more about first-aid practices:
Explore online resources or videos with the help of your parents or elders to learn more about first aid. Share any interesting tips you find with your class.
Project Output: Now you have your own basic first aid box and you are ready to handle small injuries! Present your box to your class and say how much it cost you.
Final Outcome: This hands-on project will help you understand which items we should keep in a first aid box and why each item is important when treating small injuries.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.


Read the story and answer the questions that follow.
Priya was excited when she had to choose her own food for the first time. She wanted to make a balanced plate that would give her energy, help her grow strong, and keep her healthy. First, she chose a chapati and a bowl of rice as her energy-giving food, because she knew these would give her the energy to play and study. Then, she added a boiled egg and some dal (lentils) to build her body. Finally, Priya added a serving of vegetables and a piece of fruit to her plate. She knew these would protect her and keep her healthy. When she looked at her plate, she was proud to see a colourful and balanced meal that had everything she needed to be active, grow, and be healthy.
1. Which energy-giving food did Priya choose?
A. Boiled egg
B. Fresh vegetables
C. Chapati and a bowl of rice
2. Why did Priya include a boiled egg and dal (lentils)?
A. To give her energy for playing
B. To help her muscles grow strong
C. To make her food taste better
3. Priya included fruit and vegetables as protective foods. How will these foods help her stay healthy, and why is it important to eat such foods daily?
4. Compare Priyaʼs balanced plate with a plate that only has snacks like chips and sweets. How do you think each type of meal will affect Priyaʼs health and energy?
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.













Chapter Overview








Our Neighbourhood Services
Caring about Our Neighbourhood
Neighbourhood Services Work People Do
Child Labour


Find and circle the following words in the given box. One has been circled for you. Get Set
BOOKS
MARKET
SCHOOL

You may have people and friends living near your house. You may go to school with them or see them in the park. People who live near us are called our neighbours. The area around your house is called your neighbourhood.
Neighbourhoods are usually filled with people, houses, buildings and open spaces. Neighbourhoods also offer different services that we need. Some of these services are parks, schools, markets and shops, banks, hospitals, police stations and post offices. These are called neighbourhood services. Let us learn about some of these services.
A market is where we buy things for our daily needs like milk, bread, fruit and vegetables. Many shops in a market sell different things such as clothes, shoes, bags, medicines, utensils and furniture.












We also get groceries, like pulses, grains, bread, and milk, from the market. People who sell groceries are called grocers. Those who sell fruit and vegetables are called greengrocers.







School is a place where we study. Our teachers teach us many new things and we do many activities like sports, art, craft and music too. The principal is the head of the school. There are many other people who take care of the school.
grocers: people who sell groceries, like pulses, grains, bread, and milk
greengrocers: people who sell fruit and vegetables


A park is a green area full of different plants. People come to the park for many reasons. Children come to play, ride their bicycles and have fun on the swings. Adults usually come to walk or jog to stay fit. Many people come to park just to relax. A gardener takes care of the plants in the park and keeps it beautiful. A sweeper keeps the park clean.
People do different activities in a park.
How does a park in the neighbourhood help people stay connected and healthy? Discuss in your class.
Milk Booth
In our neighbourhood, we may also find a milk booth. A milk booth usually opens very early in the morning to provide us with fresh milk and milk products such as curd, buttermilk and paneer. We can also get bread, eggs and ice creams from the milk booth.
A police station is a place where we can file a complaint for any law-and-order problem. All the Police officers work in a police station. They help to maintain law and order. The police officers that we see around our neighbourhood keep us safe and it is our duty to support them.
A


People visit hospitals for treatment or regular check-ups. Doctors, nurses, and, hospital staff treat and help patients. Some hospitals also have rooms for patients to stay. People can also get their medicines from medicine stores that are within the hospital premise. These shops are called a chemistsʼ shop or a dispensary.
hospital
In case of emergency, dial 100 for police. In any case of medical emergencies, dial 102. Phone 108 to call an ambulance.
A bank helps us to keep our money and valuable things safe. First, we need to have an account with the bank. Workers at the bank help people to open accounts and to put in and take our money or valuables when they need to.
ATMs (automated teller machines) are also used to withdraw the money people keep in their bank accounts.
Banks provide services to keep our money safe.
Observe and list the services available in your neighbourhood. Choose any two places to visit with your parents. Speak to people who work there and learn more about their work.
patients: sick or injured people who need treatment withdraw: to take out


Name the neighbourhood place.
1. We come here to learn and study new things:
2. We buy groceries and clothes when we come here:
3. We visit this place to play, exercise and relax:
4. This place keeps our money safe:
5. People at this place help to keep us healthy:
There are many different services that our neighbourhood provides. Most of them, such as schools, milk booths, markets and banks are essential parts of our day-to-day lives. They make our lives comfortable and connect us with other people. Thus, we must respect and take care of our neighbourhood. Let us learn more about how we can do this.
• Introduce yourself to your neighbours and try to help each other as much as possible. You may exchange phone numbers to contact each other in case of an emergency.
• Never litter your neighbourhood and also stop others from doing so.




















A neighbourhood with different services
essential: necessary or important




• Grow more plants to make your neighbourhood look clean and green.
• Be polite to people who help you with different services.
• Greet people in your neighbourhood with a smile.
We need food to eat, clothes to wear and a house for shelter. All these things cost money. To earn money, our parents and other adults in the family go out to work. The work that a person does to earn money for a living is called an occupation.
Think and Tell
Do your parents or grandparents go to work? Why do you think it is important for them to work?
Online delivery services bring groceries, food, and other items straight to your home, making life easier and saving time!
People have many different occupations in villages, cities and urban areas. People go to different workplaces according to their occupation.

Doctors treat and check patients. They work in hospitals and clinics.

Nurses help doctors by treating and taking care of patients. They work in hospitals, clinics or dispensaries.

Teachers teach students many new things. They work at schools, colleges or universities.


Police officers maintain law and order. They also catch criminals like thieves or anyone who breaks the law. They work in a police station.


Potters make beautiful articles using clay. A postman delivers letters, money orders and speed post. They work in a post office.


Soldiers provide safety and security and protect us from our enemies. They work on the border of the country.

Farmers grow various grains, vegetables and fruit. They work on a farm.
There are many other occupations in our country. We should be thankful that adults work to care for us. Their hard work and support make our lives comfortable.
Match the following.
A. Teacher
B. Doctor
C. Potter
D. Postman

a. treats ill people
b. delivers letters to people
c. teaches in the school, college or university
d. makes beautiful articles using clay


We know that the adults in our family go out to work to earn a living. Sadly, some children in our society also work to earn money for food and clothes. You may have noticed them working in shops, dhabhas, factories and workshops.
These children are not as lucky as we are. In most cases, their families are too poor to send them to school. These children help their families to earn money. However, this is not right. According to law, children under the age of 14 are not allowed to work. If children below the age of 14 work, it is called child labour. It is a crime in India.
As part of the community, we should help to stop child labour. We must spread awareness about child labour so that it can be removed from our society.

Uttar Pradesh is the largest farming state in India. The farmers mostly grow crops like grains, rice, sugarcane and potato.
neighbours: people who live near our house
neighbourhood: the area around our house

neighbourhood services: services such as hospitals, banks and schools that are available in our neighbourhood
occupation: work people do to earn money
child labour: a child under 14 years of age, working to earn money

Scan the QR code to learn more about actions against child labour.


• People who live near our house are called neighbours.
• Services that we get in our neighbourhood are called neighbourhood services. Some examples are hospitals, parks, schools and banks.
• We should respect and take care of all the services and workers in our neighborhood.
• People do different kinds of work to earn money. This is called an occupation.
• Children below the age of 14 should not work, as it is called child labour, which is a crime in India.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which service do we use when we are ill?
hospitals banks schools cafes
B. Where do soldiers work?
In a police station On the borders
In a security room In the market
C. Which service do we use to keep our valuables safe?
hospitals banks schools cafes
D. If children under the age of work it is called child labour.


2. Fill in the blanks. doctor nurse principal potter farmer
A. A grows food crops for us.
B. The is the head of a school.
C. A makes things out of clay.
D. A and can help us when we are ill.
3. Write True or False.
A. A postman delivers letters, money orders and speed post.
B. A postman works in a hospital.
C. Soldiers help us by protecting our nation from enemies.
D. A milk booth usually opens at night for people to buy milk.
4. Circle the odd one out.
A. Neighbourhood services:
hospital bank police station nurse
B. Emergency contact numbers: 100 102 108 144
C. Things a postman delivers: speed post fruit letters money orders
5. Answer the following questions.
A. What does a greengrocer sell?
B. Name any five neighbourhood services.
C. How does a bank help us?
D. Write any three ways to care for your neighbourhood.
E. Name any three occupations. In one or two sentences, also explain how each one us helpful.


6. Picture-based questions.
A. Which service does this place provide to the people in the neighbourhood?
B. Name one important worker in this place and describe what they do to help people.
C. Why is it important for a neighbourhood to have this service available?

1. If you could create a new neighbourhood service that doesnʼt exist yet, what would it be, and how would it help improve the lives of people in your neighbourhood?
2. What occupation would you like to choose for yourself? Why?
Think of one neighbourhood service, like the post office, school or hospital, and a person who works there. Imagine a day without this service and write or draw what would happen. Think about how these helpers make our lives easier and why it is important to appreciate their work. Try to say “thank you” the next time you see a neighbourhood helper!













Our Festivals


Draw a picture of your favourite festival. Write two things that you like the most about this festival. Get Set


Festivals are happy times when people come together to celebrate. Festivals are enjoyed all over the world. In India, we celebrate many festivals because we have people from different communities and cultures living together.
Some festivals are celebrated by the whole country. Based on this, we can group festivals into three types:
National festivals
Harvest festivals
Religious festivals
Let us learn about them.
National festivals are important to all Indians. They are celebrated all over the country. We have three national festivals: Independence Day, Republic Day, and Gandhi Jayanti.
Independence Day
We celebrate Independence Day on 15 August each year. India got its independence from British rule on 15 August, 1947. On each Independence Day, the Prime Minister of India hoists the national flag at the Red Fort in New Delhi and speaks to the nation to give a message of peace and progress. On this day, we also remember the freedom fighters who gave their lives to win freedom for India.
hoists: to raise high using a rope

Independence Day celebrations at Red Fort, New Delhi.


Make a greeting card, wishing people a happy Independence Day.
Republic Day is celebrated on 26 January every year. The President unfurls the national flag on Republic Day and a special parade is held at the Kartavya Path in New Delhi. The parade starts at Vijay Chowk near Rashtrapati Bhavan. Different states, the armed forces (army, navy and air force), police and school children participate in the parade. People who have been awarded for bravery are also a part of the parade. The parade ends at the Red Fort. Such parades also take place in the capital cities of different states of the country.
Gandhi Jayanti is celebrated on 2 October every year in honour of Mahatma Gandhi. We celebrate Gandhi Jayanti to mark Mahatma Gandhi’s birthday. He is known as the Father of the Nation and ‘bapu’. He played an important role in India’s independence from British rule. Mahatma Gandhi’s ashes are buried at Raj Ghat. The President, the Prime Minister and other leaders pay their respects there.

Republic Day parade in New Delhi.
The Kartavya Path was earlier known as Raj Path. The name was changed in 2022.

Ghat, New Delhi
At Raj Ghat, there is a lamp that is always burning. Did You Know?


Many prayer meetings are organised by people all over the country on this day to remember the teachings and sacrifices of Mahatma Gandhi.
Error Alert!
Even though Gandhiji is known as the Father of the Nation, he did not hold any government position after Independence. Jawaharlal Nehru was the first Prime Minister of India.
Fill in the blanks.
1. Republic Day is celebrated on .
2. Mahatma Gandhi’s ashes are buried at .
3. India got independence from the British in the year .
India has people of many different religions. Festivals that are tied to a religion are called religious festivals. All religious festivals are celebrated with great enthusiasm. Let us learn about some of them.
Holi is the festival of colours. It is celebrated by both children and adults. It is a popular festival in north India. People celebrate by playing with coloured powder known as gulal.

religion: a group of people who worship the same god/gods

Navratri and Dussehra
Navratri is an important Hindu festival that celebrates the victory of good over evil. A dance drama called the Ramlila is organised in different parts of the country based on the story of Rama’s life and his battle with Ravana. The festival is celebrated over 9 days. The 10th day of Navratri is Dussehra. Devotees believe that on this day, the god Rama killed Ravana, the demon king with ten heads. Big effigies of Ravana are burned in the evening to celebrate Dussehra. Large fairs are organised in cities across India. In some states, like West Bengal and Assam, Navratri is celebrated as Durga Puja. In Gujarat, people perform dances such as Garba and Dandiya Raas during Navratri.

Dussehra celebration
Durga Puja is one of the main festivals of Kolkata.
Diwali
Diwali also known as Deepawali, is mainly a festival for Hindus.
It is celebrated twenty days after Dussehra and is known as the festival of lights. It marks the return of Lord Rama to Ayodhya after spending fourteen years in exile.

People wear new clothes and pray to Goddess Lakshmi on Diwali. People decorate their homes with flowers, diyas, lights, candles and rangoli. Rangolis are artistic patterns made at
devotees: people who deeply believe in or follow a religion or God effigy: a model of a person rangoli: patterns drawn on the floor to decorate houses


the entrance of houses using colours, flowers and diyas. Some people also burst fire crackers on Diwali.
Did You Know?
Businesspeople close their previous yearʼs accounts, celebrating Diwali eve as the ‘New Yearʼ.
Many types of special foods and sweets are prepared, and people exchange gifts with their friends and family.
Ganesh Chaturthi is one of the most important festivals in Maharashtra. During this festival, devotees worship Lord Ganesh. Huge idols of Lord Ganesh are made, and large processions take place. The idols are immersed in water at the end of the festival.
Gurpurabs are special days celebrated by Sikhs to honour their gurus’ birthdays. Sikhs have ten gurus, and these birthdays are celebrated as Gurpurabs. The first guru, Guru Nanak Dev Ji, is honoured on his birthday, known as Guru Nanak Jayanti.


On Guru Nanak Jayanti, large processions start from gurudwaras, where people gather, wear new clothes, sing hymns, and light candles. Gurudwaras are beautifully decorated, and free food, is served to everyone from langars or community kitchens.
The martyrdom days of Guru Arjun Dev, the fifth guru, and Guru Tegh Bahadur, the ninth guru, are remembered as Shahidi Diwas.


Eid-ul-Fitr is one of the most important festivals for Muslims. It marks the end of a month-long period of fasting known as Ramdan. People offer special namaz at different mosques all over the country. They wear new clothes, prepare special dishes and visit their friends and family. They greet each other with the words ‘Eid Mubarak’, which means “Blessed festival.”

A sweet dish called sewain is specially prepared on Eid. People also donate money and clothes to the poor on this day.
Christmas is an important Christian festival. It is celebrated every year on 25 December on the occasion of Jesus Christ’s birthday. Churches all over the country are specially decorated for this festival, and special prayers are held in churches at midnight. People decorate their homes, put up Christmas trees and bake plum cakes. Gifts are exchanged by family and friends. Children also receive gifts from Santa Claus on this day.

Navroz is celebrated by the Parsis. It is the celebration of the Parsi New Year. It is celebrated on 21 March every year. It marks the end of winter and the beginning of spring.


Write True or False.
1. Dussehra is celebrated as Durga Puja in West Bengal.
2. People pay to have food at a langar.
3. Sewain is prepared on the occasion of Navroz.
Harvest is when the crops sown in the fields are ready to be cut and collected from the fields. Farmers are happy because they finally see the results of their hard work. Harvest festivals celebrate the gathering of crops. During these festivals, farmers celebrate the good crops and say thank you to the people and animals who helped make the harvest successful. Some harvest festivals are:
Bihu is Assam’s harvest festival. It is celebrated three times a year. Singing, dancing, feasting, bonfires and buffalo fights are part of the celebrations. Women perform the Bihu dance and sing songs. They also wear their traditional dress called Mekhela Chador.

Pongal is Tamil Nadu’s harvest festival. It is celebrated in January. It goes on for 4 days. A dish called Pongal, made by cooking rice in milk and jaggery, is offered to the sun god. People decorate their houses by drawing patterns known as Kolam on the floor. Cows are washed, painted,

fed, and worshipped. The harvest is also celebrated in Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Karnataka. In those states, it is known as Sankranti.
Onam is Kerala’s harvest festival. It is known as the festival of flowers. A special meal called Onam Sadya is served on banana leaves. People decorate their homes with flower garlands and create pookkalam (floral rangolis). During Onam, exciting boat races called Vallamkali take place, along with the traditional Pulikkali, or tiger dance.
Baisakhi
Baisakhi is the harvest festival of north India, especially in Punjab. It is celebrated in April. It also marks the beginning of the traditional New Year in Punjab. Men perform the Bhangra and women perform the Gidda. These are accompanied by the rhythms of the dhol.


Though harvest festivals are named differently in different parts of India, they are celebrated in almost all the parts of India. Why do you think this is the case?
India is a land of many festivals. As Indians, we should respect each other’s festivals and celebrate these festivals together. dhol: a kind of double-sided drum


The Kumbh Mela is a festival and religious gathering that is held every 4 years in different cities in India. In 2019, the Kumbh Mela achieved the world record for having the largest gathering of people in the world.

festival: a day of celebration independence: freedom from control of others republic: a form of government where people choose their leaders religious: tied to a particular religion gurudwara: the place of worship of Sikhs langar: the community kitchen of a Gurudwara where free food is served Ramdan: a month-long period of fasting followed by Muslims namaz: prayers offered by Muslims harvest: the time when crops are ready to be collected from the fields bhangra: a special type of dance performed by men in Punjab gidda: a special type of dance performed by women in Punjab

Scan the QR code to learn more about our harvest festivals.
• Festivals are days of celebration.
• National festivals are celebrated all over India.
• Religious festivals are celebrated by the people of different religions.
• Harvest festivals are celebrated in different states at the time of harvest.


1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What is the month-long period of fasting for Muslims called?
Navroz Ramdan Gidda Bihu
B. In which of these states, is Pongal celebrated?
West Bengal Gujarat
Tamil Nadu Himachal Pradesh
C. Whose birthday is celebrated on 2 October?
Jawaharlal Nehru Rajendra Prasad
Dr S Radhakrishnan Mahatma Gandhi
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. Boat races take place during (Onam/Baisakhi).
B. People draw (rangoli/kolam) on the floor of their homes during Pongal.
C. Ganesh Chaturthi is the main festival of (Rajasthan/Maharashtra).
D. The Independence Day celebration is held at (Red Fort/India Gate) in New Delhi every year.
E. A dance drama called the (Ramlila/Langar) is organised during Dussehra.
3. Match the following.
A. Navroz a. 26 January
B. Independence Day b. 2 October
C. Gandhi Jayanti
D. Republic Day
E. Christmas
c. 21 March
d. 25 December
e. 15 August


4. Answer the following questions.
A. Name any two harvest festivals and the states in which they are celebrated.
B. Write three lines on Republic Day.
C. Name any two religious festivals.
D. How is Eid celebrated?
E. What are some of the things that people do on Diwali?
5. Picture-based questions.
A. Which festival is being celebrated here?
B. Where is it celebrated in New Delhi?
C. Which groups of people participate in the parade shown in the picture?


How is the Independence Day celebration in your school different or similar to the one in New Delhi?
Write a letter to your friend inviting them to celebrate a festival at your house.














Chapter Overview







Reaching Places
Directions Landmarks Maps Using Symbols on Maps

Get Set

Look at the maze and decide the path that Sakshi and Sonhan should take to reach the waterfall. Use directions like left, right and straight to describe the path you choose.



Reaching a place is easy when we have the right directions. Without directions, we could get lost. In this chapter, we will learn about directions and maps.
Directions tell us how to travel from one place to another. Directions help us save time, avoid getting lost and reach our destinations easily. We can give directions using direction words or cardinal directions.
Direction words are words that tell you how to move from one place to another. They help guide you along a path. Some common direction words are:
• Turn left
• Turn right
• Go straight
• Walk forward
• Go back
Cardinal directions help us find our way using four main directions: north, east, south and west. Instead of using direction words like “left” and “right,” which can change depending on where you are, cardinal directions always stay the same. Cardinal directions are fixed based on the position of the sun in the morning and evening. Here is a simple way to understand them:
1. East: This is where the sun rises. At sunrise, if you face the sun, you are looking towards the east.
2. West: This is where the sun sets in the evening. West lies opposite east.
3. North: If you are looking at the sunrise (east) and turn to your left, you will be facing north.
4. South: If you are looking at the sunrise (east) and turn to your right, you will be facing south.


Directions are given in the table below. Draw the shapes wherever asked, as given in the instructions.
Instructions:
1. Draw a triangle south of the circle.
2. Draw a star west of the circle.
3. Draw a circle south of the star.
4. Draw a star north of the square.
5. Draw a happy face �� in the last vacant place.
We can also find cardinal directions using a compass. A compass is a tool that helps you find north, east, south, and west. It has a magnetic needle that always points north. Once you know which way north is, you can easily find the other directions:
• North: The needle points to north.
• East: It is to the right of north.
• South: It is behind you if you are facing north.
• West: It is to the left of north.
By using a compass, you can find out where you are going and which way you need to turn. A compass
Fill in the blanks.


1. The compass needle always points to the .
2. The sun rises in the .
3. There are main cardinal directions.

A landmark is a special place or building that is easy to spot and remember. It might be famous because of its history, beauty or cultural importance. Landmarks help us know where we are and which way to go.
Landmarks are useful because they stay in the same place, so they are useful when giving or following directions. Landmarks help us navigate places in the following ways:
1. Landmarks serve as clear reference points to guide us through unfamiliar places. For example, spotting a tall clock tower or a colourful building can help you know where you are.
2. People often give directions based on landmarks. Instead of saying, “Turn left after 500 metres,” they might say, “Turn left after the big red church.” Landmarks make directions easier to follow.
Are there any landmarks that can be used to locate your school?
Landmarks can be natural, like mountains, rivers, or forests or man-made, like buildings, monuments or bridges.

Let us explore some examples of historical places which are important landmarks.
1. The Taj Mahal is beautiful white marble building in Agra. It is an important landmark in Agra.
2. The Qutub Minar is a tall tower made of red sandstone. It is an important landmark in Delhi.


navigate: to find your way from one place to another


A map is a drawing that shows what a place looks like from above. It can show different places like cities, roads, rivers, mountains and even your own neighbourhood. Maps can be small, showing just a room, or large, showing a whole country or continent.
To read a map, you should understand three important things: viewpoint, compass rose, and symbols.
• Viewpoint: Imagine looking down at the area from above, like a bird. This is what a map looks like. Maps give us a bird’s-eye view of an area.
• Compass Rose: This is a symbol on a map that shows the four main directions: north, south, east and west. It helps us know where to go.
• Symbols: Maps use small pictures or symbols to show different things. A key or a legend is usually given with a map that explains what each symbol means.
map of India
Drawing real objects can take up a lot of space, therefore, symbols are used to show objects on maps. Symbols on a map show various features, such as landmarks, roads, rivers and buildings. Always check the map key or legend (usually located in a corner). It explains what each symbol means.


Ujjain is an old city in India. A long time ago, it was very important when maps were made. People used Ujjain as the centre point for Indian maps. This is similar to how Greenwich in England is used for world maps today. The city of Ujjain

direction: the way along which someone or something moves or points map: a picture of the Earth that shows where places are destinations: places you are going to landmark: a place or building that is easy to spot and remember map key or legend: a map key that explains the meaning of symbols on a map



Scan the QR code to learn more about maps.
• Directions help us save time and avoid getting lost by guiding us from one place to another.
• The sun rises in the east and sets in the west. If you face the sunrise, you are looking towards the east, with the north to your left, the south to your right, and the west behind you.
• Combining direction words and cardinal directions can give clear instructions like “Turn right and travel north”.
• Cardinal directions are fixed based on the position of the sun in the morning and evening, making them fixed and reliable.
• Using symbols on maps helps us represent different features like roads, rivers, and landmarks, making it easier to understand the map.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these is a cardinal direction.
South Left Right
B. Which of these cannot be a landmark.
A mountain A church A car
C. A compass needle always points in which direction?
East West North
D. Which direction lies opposite north?
South East West

2. Fill in the blanks. west natural direction cardinal
A. The sun sets in the .
B. Landmarks can be or man-made.
C. A compass rose on a map show the 4 main .
D. The four main directions are called directions.
3. Write True or False.
A. A map key is also called a legend.
B. A map shows a place as if viewed from above.
C. Cardinal directions are always fixed.
D. The sun rises in the west and sets in the east.
4. Match the following.
A. North a. a man-made landmark
B. Taj Mahal b. lies to the left of east
C. South c. a tool for finding direction
D. Compass d. lies to the right of east
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Name the four cardinal directions.
B. What is a legend?
C. Name one example of a natural landmark and one example of a man-made landmark.
D. How can cardinal directions help us when we travel?


6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the image and answer the questions.
A. Find the state where you live on the image and write the states to its north and south.
B. Write the states that lie to its east and west.

Imagine you are lost in a city without a map and you can see the sun setting. How would you use your knowledge of directions, landmarks and the sun to find your way back?
Ask your parents to show you how to use the Google Maps app on their phone or tablet to reach your school or any important place from your home. Ask them to show you how to find your current location, which is marked with a blue dot. And, using the “directions” button to find the route to your school. You can choose whether to walk, drive or cycle. Follow the path on the map, and notice how Google Maps shows you the distance and time it will take to reach your school. Share the experience with your friends and family.








Size and Neighbours





Our Country India
States and Union Territories

Get Set

Read the poem given below aloud with your friends.
India is my country, big and wide, With rivers, hills and seas beside. Tigers, birds and big trees too, People live with love so true. We speak in many ways, but we are one, Under the same bright, shining sun. From north to south, and east to west, India is the place we love best.
Parul: Mother, what makes India so special?
Mother: India is a vast and beautiful country, dear. It’s so big that many different kinds of people live here.


Parul: Really? Do they all speak the same language?
Mother: No, that’s what’s interesting! People here speak many different languages like Hindi, Tamil, Bengali, Marathi and many more. And they also have different religions and celebrate many festivals.
Parul: That sounds fun! Is it okay that everyone is so different?
Mother: Absolutely! That is what makes India special. We should be proud of our country and respect everyone because that’s what helps us live happily together.
India is the seventh largest country in the world by land area. It has the largest population in the world. India has a population of more than 140 crore.
India is surrounded by water on three sides. It has the Arabian Sea in the west, the Indian Ocean in the south and the Bay of Bengal in the east.
India shares its borders with many other countries. Our neighbouring countries are Pakistan, Afghanistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, China and Bangladesh.
Political map of India
population: the number of people living in a place


Sri Lanka and Maldives are India’s neighbours in the Indian Ocean. Bangladesh was created in 1971. Before that it was part of our neighbouring nation, Pakistan. Did You Know? Pause and Answer
Write True or False.
1. The Indian Ocean is located to the east of India.
2. India is the largest country in the world by land area.
3. Nepal is one of India’s neighbouring countries.
4. China is located across the Indian Ocean.
India has some national symbols. These symbols represent the values and culture of our country. They give us a sense of pride in our identity as Indians. Let us learn about our most important national symbols.
Our national flag is a tricolour flag. It has three horizontal stripes of equal size. They are saffron, white and green. Saffron is the topmost stripe. It symbolises courage and sacrifice. The middle stripe is white. It represents truth and peace. The bottom stripe is green. It stands for the fertility and growth of the Indian land. There is a blue emblem in the middle of the white stripe. It is called the Ashoka chakra. It is a wheel with 24 spokes. It signifies the progress of the nation.

The national flag is a symbol of our freedom. It is hoisted during our national festivals and on our government buildings. We must respect our national flag.
tricolour: with three colours
courage: bravery
sacrifice: destruction or surrender of something for the sake of something else


The national anthem of India is titled Jana-Gana-Mana. It was written by the poet Rabindranath Tagore. It represents the unity and oneness of all Indians. It is sung during national occasions. We must respect our national anthem. We should stand at attention and not talk or move while the national anthem is being sung.
The National Emblem of India has four lions which stand back-to-back, facing the four directions. It has been taken from the head of a column built by Emperor Ashoka. The Ashoka Chakra is shown below the lions. On its left, there is a horse. There is a bull on its right. The words “Satyamev Jayate” are inscribed at the bottom of the emblem. This means “Truth alone triumphs.” The national emblem is used on coins, notes, envelopes and all government documents.

In India, we have two main levels of government: the Central Government and the State Government. The levels of government are elected by the citizens of India in an election. All citizens aged 18 and above can vote in these elections.
The Central Government takes care of the whole country and makes decisions that apply to the whole country. Its offices are located in New Delhi which is the capital of India. The President, the Vice President and the Prime Minister along with other ministers and officers of the Central Government work in New Delhi.


Why do most members of the central government live and work in the capital?
Since India is a very large country, it is difficult for the Central Government to help all the people directly. So, the people of each state vote to elect their own state government. The state governments govern specific states. The Governor, the Chief Minister and other ministers of the state government live and work in the capital of the state. Some parts of India are called Union Territories and are not included in the 28 states of India. They are governed directly by the Central Government. India has 8 Union Territories including the National Capital Territory of Delhi. Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh were added to the list of union territories in 2019.
Each state and union territory in India has a capital. The chief minister, governor and important people live in the capital city of the state. The capitals of all the states and union territories of India are given in the following tables.
Sl. No. State Capital
1. Andhra Pradesh Amaravati
2. Arunachal Pradesh Itanagar
3. Assam Dispur
4. Bihar Patna
5. Chhattisgarh Raipur
6. Goa Panaji
7. Gujarat Gandhinagar
8. Haryana Chandigarh
9. Himachal Pradesh Shimla
10. Jharkhand Ranchi
11. Karnataka Bengaluru
12. Kerala Thiruvananthapuram
13. Madhya Pradesh Bhopal
14. Maharashtra Mumbai
govern: rule
Sl. No. State Capital
15. Manipur Imphal
16. Meghalaya Shillong
17. Mizoram Aizawl
18. Nagaland Kohima
19. Odisha Bhubaneswar
20. Punjab Chandigarh
21. Rajasthan Jaipur
22. Sikkim Gangtok
23. Tamil Nadu Chennai
24. Telangana Hyderabad
25. Tripura Agartala
26. Uttar Pradesh Lucknow
27. Uttarakhand Dehradun
28. West Bengal Kolkata

1. Andaman and Nicobar Islands Port Blair
2. Chandigarh Chandigarh
3. Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu Daman
4. Lakshadweep Kavaratti
5. Puducherry Puducherry
6. National Capital Territory New Delhi
7. Jammu and Kashmir Srinagar (summer), Jammu (winter)
8. Ladakh Leh

Have a quiz in the class on the capitals of states and union territories of India.
Divide the class into two teams. The teacher will say the names of the states or union territories and the teams will give the capital. Each team gets 2 marks for a correct answer and –1 for a wrong answer.
Raise your hands to answer. Do not answer unless the teacher tells you to. Don’t look at the textbook while the quiz is going on.

The President of India lives in the Rashtrapati Bhavan in New Delhi. The Rashtrapati Bhavan is the second largest residence of a head of a country in the world. It has 340 rooms.

Rashtrapati Bhavan, New Delhi
neighbouring countries: countries that share a border or are located close to each other across a sea or ocean emblem: symbol
Central Government: governs the entire country
State Government: governs specific states election: the process of choosing the government



Scan the QR code to learn more about the Rashtrapati Bhavan.
• India is the seventh largest country in the world by land area and the largest by population.
• India’s neighbouring countries are Pakistan, Afghanistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, China, Sri Lanka and the Maldives.
• India’s National Flag has three colours: saffron, white and green.
• India’s National Anthem is titled Jana-Gana-Mana and was written by Rabindranath Tagore.
• India’s National Emblem has four lions which stand back-to-back, facing the four cardinal directions.
• India has 28 states and 8 union territories.
• India has two levels of government, the Central government and the State governments.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of these is NOT a neighbouring country of India?
Myanmar Japan Sri Lanka
B. What is the Indian national anthem called?
Amar Sonar Bangla Jana Gana Mana
God Save the Queen
C. Which of these is the capital of India?
New Delhi Mumbai Chennai


D. How many states does India have?
E. What is the meaning of the words “Satyamev Jayate”?
Truth alone triumphs Truth is good
India is great
2. Fill in the blanks.
population Ladakh Arabian Union Territories
A. The sea lies to the west of India.
B. India is the largest country in the world by .
C. Parts of India that are governed directly by the Central Government are called .
D. Jammu and Kashmir and were added to the Union Territories in 2019.
3. Match the following.
A. Bihar
B. Ladakh
C. Karnataka
D. Gujarat
E. Telangana
a. Bengaluru
b. Hyderabad
c. Patna
d. Leh
e. Gandhinagar
4. Answer the following questions.
A. What are state governments?
B. What is India’s national emblem?
C. List all the neighbouring countries of India.
D. India has several neighbours. Why do you think having good relations with neighbours is helpful for India? Give two reasons.


5. Picture-based questions.
Look at the image given and answer the questions.
A. Name the state or union territory which is closest to Sri Lanka.
B. Name the state or union territory that shares a border with Pakistan.
C. Name the state or union territory that shares a border with Afghanistan.

Which states in India share a capital and who governs that capital?
Use newspapers or the internet to find out the names and pictures of the President, Vice President and the Prime Minister of India and stick their pictures in a scrapbook. Write their names under their pictures. Then do the same for the Governor and Chief Minister of your state.






Chapter Overview








Land and Rivers of India

Get Set

Read the poem aloud.
India’s Natural Beauty
The Himalayas, snowy up high, A mountain range that touches the sky.
The Northern Plains, so green and wide, Where many rivers run and glide.
The Thar Desert, sandy and dry, But life there thrives as days go by.
Natural features, like mountains, plateaus and plains, are called landforms. India is a country with many natural landforms and rivers. Let us learn more about them.

India is known for its diverse landforms. Each landform has its own unique features. Look at the map that shows the different landforms and where they are located.
Northern India is home to some of the highest mountain ranges, the Himalayas, and fertile plains, the Northern Plains.
The Himalayas
A mountain is a landform that rises much higher than the land aound it. The sharp and pointed top of a mountain is called a peak. Many mountains together form a mountain range.
The Himalayas are the highest mountain ranges in the world with many peaks, such as Mount Everest, Kanchenjunga and Nanda Devi. Mount Everest is the highest peak in the world. Most of these mountains are covered with snow throughout the year. The weather in this region is cold and it is difficult to grow crops here.
Many rivers, like the Ganga, the Yamuna, and the Brahmaputra, originate from the Himalayas. They are formed when the snow on the mountain peaks melts. The melting of snow keeps these rivers full of water during the hot and dry summer months. The area on the lower slopes is covered with forests and is known as the Terai region
diverse: of many different kinds
unique: one of a kind peak: the sharp, pointed top of a mountain originate: start or begin
Terai region: the forest-covered area on the lower slopes of the Himalayas


Did You Know?
Mount Everest is not located in India. It lies in China and Nepal. The highest mountain in India is Kanchenjunga.
Tenzing Norgay and Sir Edmund Hillary were the first men to climb the peak of Mount Everest in 1953.
The Northern Plains are very fertile and are often called the “food bowl of India”. They lie to the south of the Himalayas. Rivers, like the Ganga and the Yamuna, flow through these plains, making the soil fertile. The Northern Plains are also called the IndoGangetic Plains. Many crops are grown here, providing food for the whole country. The Northern Plains stretch from the western part of Punjab and Haryana, across Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, and extend up to West Bengal in the east.

fertile: rich soil in which plants grow well


The fertile soil and abundant water in the Northern Plains make them perfect for growing wheat, rice, sugarcane and pulses. Thus, agriculture is the main occupation of the people in this region. The weather is hot during summer and cold in winter. This area is densely populated.
The southern part of India is a peninsula and a plateau.
A peninsula is a piece of land that it is surrounded by water on three sides. The Indian peninsula is surrounded by the Arabian Sea in the west, the Indian Ocean in the south and the Bay of Bengal in the east.

A plateau is a flat piece of land that is higher than the land that surrounds it. The Southern Plateau is separated from the Northern Plains by the Vindhya Mountain range. The mountains of the Southern Plateau are not high as the Himalayan Mountains. The Southern Plateau is divided into two parts: the Central Highlands and the Deccan Plateau. The land here is rocky and uneven. The Southern Plateau has many rivers, such as the Godavari, the Krishna and the Kaveri. Some parts of the plateau have dense forests. The plateau also has black soil. Although it is less fertile than the soil in the Northern Plains, yet it is very good for growing cotton.
How would living in the Southern Plateau be different from living on the Northern Plains?
abundant: a large quantity densely: thickly


A desert is a large area of land that is covered with sand. The Great Indian Desert or the Thar Desert lies in the north western part of India.
The summers are hot and dry, and winters are cold, in this region. There is very little rainfall and vegetation. Due to the extreme weather conditions, this region is thinly populated.

The camel is used for transportation in the desert. It has also been called ‘the ship of the desert’.
Fill in the blanks.
1. is the highest mountain peak in the world.
2. The Indo-Gangetic Plains is another name for the .
3. The Southern Plateau is located of the Northern Plains.
Make a scrapbook titled ‘My Beautiful Countryʹ. Paste pictures of the six physical features of India, under the correct headings. Share your scrapbook with the class.
Rivers are large, flowing bodies of fresh water that move from high places like mountains to lower places like seas or oceans. Major rivers are important



rivers which provide water for agricultural purposes like irrigation and support the daily activities of people.
India has many rivers, both large and small. A river is a flowing waterbody that eventually merges with another river or the sea. Rivers give us resources such as drinking water and transport routes. They also provide work for many people. Most major Indian cities are situated along riverbanks.

Some of the major rivers in India are the Ganga, Yamuna, Satluj, Brahmaputra, Narmada, Krishna, Kaveri, Godavari, and Mahanadi. These rivers flow across various Indian states before they drain into the Arabian Sea or the Bay of Bengal. The Ganga begins at the Gangotri glacier, while the Yamuna starts from the Yamunotri glacier. The Yamuna is the Ganga’s largest tributary.
Rivers play an important role in our lives. As they flow, they make the land fertile and provide us with fresh water. Farmers make small canals from these rivers to water their fields. Rivers also have freshwater fish, on which many people rely for food.
Rivers carry nutrients from the mountains and deposit them on the plains, making the soil rich and fertile. Additionally, we generate electricity by constructing dams on rivers.
Many rivers in India are heavily polluted. Wastewater from industries and households, and solid waste from cities, are dumped in our rivers. Our rivers are very important. They are a precious resource and we should keep them clean.


The Rann of Kutch is a vast salt desert located in the northwestern part of Gujarat. This unique landscape is a part of the Thar Desert, which stretches across several states in northwestern India. The Rann of Kutch is famous for its vibrant cultural festival, the Rann Utsav, where visitors can experience local crafts, music, dance and food.

plateau: large, flat area of land that is higher than the land around it landforms: different shapes of land, like mountains, plains, plateaus and deserts
peninsula: a piece of land that is surrounded by large bodies of water on three sides
desert: a dry area with very little rain and few plants

Scan the QR code to learn more about the Himalayas.
• India has many landforms. The major landforms of India are the Himalayas, the Northern Plains, the Southern Plateau and the Thar Desert.
• India has many rivers, including major ones like the Ganga, Yamuna, Brahmaputra, Godavari and Krishna.
• Rivers in India provide essential resources, such as fresh water, fertile soil for farming, transportation routes and electricity through dams.
• Rivers are also important for cultural and religious reasons.


1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which river meets the Ganga in Allahabad?
The Yamuna The Godavari The Brahmaputra
B. Which is the highest peak in the Himalayas?
Mount Everest K2 Kanchenjunga
C. What type of soil does the Southern Plateau have?
Red Black Brown
D. What is another name for the Northern Plains?
Indo-Gangetic Plains Indus Plains
Yamuna-Ganga Plains
2. Fill in the blanks.
landforms Thar Desert the Godavari River Bay of Bengal
A. India has many kinds of .
B. is also called the Ganga of the South.
C. The is in the north-western part of India.
D. The Ganga River flows into the .
3. Write True or False.
A. The Northern Plains are very fertile.
B. The river Ganga originates from the Yamunotri Glacier in Uttarakhand.
C. The Krishna River starts from Uttarakhand.
D. The Godavari River starts in Maharashtra.


4. Match the following.
A. Ganga a. Terai region
B. Yamuna b. Tsangpo River
C. Brahmaputra c. Thar Desert
D. Great Indian Desert d. Starts at Gangotri Glacier
E. The Himalayas e. Starts at Yamunotri Glacier
5. Short-answer questions.
A. Why are the Northern Plains called the “food bowl of India”?
B. Why are the Himalayas important for India?
C. Name any two important features of the Northern Plains.
D. Why are rivers important?
E. Why are deserts thinly populated?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the image and answer the questions that follow.

A. Name the physical feature shown here.
B. Name the two rivers that flow through this area.
C. Name one crop that is grown in this area.



Why do you think that cities and towns are often found on plains rather than on mountains? What challenges would people face if they tried to build large cities in mountainous areas?
India faces water shortages in many regions. Water is an important resource that we all need to save. Ask an adult at home to help you calculate the water usage at your home. Discuss your calculations with your classmates and write down three simple ways in which you can save water at home. Share your ideas in class.














Chapter Overview








Solve the following crossword puzzle.
1. A big boat that runs on water.
2. A vehicle that flies in the air.
3. A written message that you can send through a post office.
4. A gadget used to listen to music and news.


People move from one place to another for many reasons. They might go to work, visit new places, or take a vacation. To do this, they use different types of transport, like buses, cars or airplanes. These are called means of transport.
We also have different ways to stay in touch with our friends and family. We can call them on the phone, send emails or write letters. These are known as means of communication.
In this chapter, we will learn more about the means of transport and communication.
We use different types of transport to travel to different places. Transport helps people and goods move from one place to another.

For short distances, we may use a bicycle, car, autorickshaw or scooter.
If the destination is far, we can travel by train or airplane. The type of transport we choose depends on the distance we need to cover and the time we have for the journey.
Means of transport can be divided into land, air and water transport.
All vehicles that move only on land are called land transport. It is the most common type of transport for carrying people and goods from one place to another. Cars, metro trains, buses, trains, bicycles, autos, tractors, trucks, bullock carts and tongas are all means of land transport.





Bullock carts (a cart drawn by bullocks) and tongas (a cart drawn by horses) are common means of land transport in villages. Other animals like elephants, camels, donkeys, and ponies have also been used to transport people and goods since ancient times.
The first train journey in India took place in 1853. The train carried 400 passengers between Mumbai and Thane in Maharashtra. Today, the Vande Bharat and Gatimaan Express are the fastest trains in India.
Means of transport that move only in water are called water transport. Water transport is the oldest mode of transportation, but it is slower than land and air transport. Ships, steamers, rafts and boats are all means of water transport. Ships can carry huge amounts of cargo over long distances. Large quantities of goods are easily transported by water transport to far-off places.



Means of transport that move only in the air are called air transport, such as helicopters hot air balloons and aeroplanes. Air transport is the fastest means of transport. Many cities around the world have airports where flights go to places within the country and to other countries too. A helicopter


Write True or False.
1. Water transport is the slowest means of transport.
2. Steamers and boats are means of water transport.
3. Trains are a means of air transport.
4. Tongas and bullock carts are used in villages.
5. Air transport is the fastest means of transport.

All our friends and family members do not live together in one place. We try to meet them as much as possible. Sometimes we cannot meet them but want to know if they are well or what they are doing. For example, you cannot meet your school friends every day during school vacations. How do you talk to your friends during this time? Do you talk to them on the phone? Do you write them emails? Do you send them handwritten letters and post them? All these methods are called means of communication.
The way we send and receive messages to share information, ideas and feelings with others is called communication. Machines or tools that we use to share our thoughts or communicate are known as means of communication. Communication is very important in our everyday lives.
In ancient times, humans didn’t have languages or know how to read or write. They communicated using different sounds and movements to express their ideas.
Eventually, they began making paintings on cave and rock walls, often showing animals, people, and daily activities. Later, they used smoke signals or beat drums to warn people of danger. Over time, humans learned to write, first on clay tablets and then on paper.


People used birds to carry messages. They trained pigeons to carry letters to faraway places. Later, written messages were sent from one place to another by men who travelled on foot or on horseback. This took several days, and sometimes the letters would get lost on the way.
Pigeon trained to carry letters.
Today, technology has advanced and we have many modern means of communication that are fast and reliable.
Let us learn about some of them.
Letters and packages can be sent to people across the country through the postal system. In India, it is run by the government and is called India Post.
We can write our message on an inland letter, a postcard or on a plain sheet of paper and put it in a stamped envelope. All of these can be bought from a post office.
A letter carries messages to your friends and relatives who live far away. We can also send greeting cards for special occasions.

Let us write a letter! Choose a decorative sheet of paper, write your message, fold it, and place it in an envelope.
Now, make sure the envelope is facing the right way. It is important to know how to write the address correctly. Here is what you should include:
1. The receiver’s name
2. The house number or address
3. The name of the city, town or village
4. The state
5. The pin code
6. A postage stamp in the top-right corner

A letterbox


Once your letter is ready, take a walk to the nearest red letter box and drop it in. Your part is done. Now the postal service takes over.
The postman or postwoman will collect the letters from the box and take them to the post office. There, the staff will sort the letters based on the city, town or village they must go to. Then, these letters will be sent to their destinations by road, rail, air or water.
At the destination post office, the letters are sorted again by neighbourhood and address, using the information written on the envelope.
Finally, the postman or postwoman will deliver the letter to the correct address.
Urgent letters and parcels in India can be sent through services such as Speed Post or courier services. Speed Post is a service run by the Indian Postal Department for the fast delivery of letters and packages. Courier services are provided by private companies.
Write a letter to your friend telling them about your favourite book or cartoon. With the help of an adult, post the letter at your nearest post office.
A telephone is one of the fastest means of communication. Using telephones, we can talk to other people in different cities and countries. Telephones are available at home or in public booths where anyone can pay and use them.
Mobile phones are portable, wireless phones through which we can talk to people or send written messages called SMSs (Short Message Service). Mobile phones need to be charged from time to time.


A telephone
The first telephone was invented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876. Did You Know?

A fax machine is connected to a telephone line. It is used to instantly send written messages, documents and photographs. A fax machine sends copies of letters using a phone. It’s like sending a letter, but it travels electronically! There are fax machines in most offices.

A fax machine
These are means of communication used to share ideas with a small or large group of people. They are used to communicate with a large number of people at the same time. Newspapers give us information about events that are happening in our city, country and around the world.
Alert!
Newspapers often do not have news of events that happened on the same day. They are printed at the end of the day and delivered to us the next morning. Most newspapers have news about what happened the day before.
Do you like to watch television or listen to songs or other programmes on the radio? Radio and television help spread information to a large number of people. They have programmes for entertainment, education, news broadcasting and music.

The first television image was shown, or broadcast, on 7 September 1927. Did You Know?
Write True or False.
1. Fax machines are used in most offices.
2. Speed Post is a service which is offered by private companies.
3. A postman collects letters from people’s homes.
broadcast: transmit (a programme or some information) by radio or television

Today, one of the easiest and fastest ways to communicate with people is through the internet. We can send information from one electronic device to another using the internet.
E-mails or electronic mail, are messages that are sent and received using the internet. Ask an adult to help you write an email to your friend.
Do you use the internet? What do you use it for? Discuss with your partner.
The internet can also be used to read the news, find information, watch films, listen to music and do many more things. The internet is available on computers, laptops and smartphones.
Smartphones are new versions of mobile phones that allow us to do all the above things. They are a combination of telephones and computers.

India has a wide network of roads. The longest highway in India connects Srinagar on the northern tip of Jammu and Kashmir to Kanyakumari at the southern-most tip of India. This highway is 3,745 kilometres long. It is called NH-44 or National Highway-44.

means of transport: the different ways in which we travel from one place to another
means of communication: ways to send or receive messages land transport: means of transport that can move only on land water transport: means of transport that can move only in water


cargo: goods carried over long distances by ship, aeroplane or big trucks
air transport: means of transport that can move only in the air
postal system: a network of post offices and means of transport to help deliver letters and packages
pin code: a special 6-digit number for each area that helps the post reach the right place
mobile phones: portable telephones that we can use to communicate with people from any place
fax machine: a machine connected to a telephone line that is used to instantly send written messages, documents and photographs
internet: a global network that connects many computers and electronic devices
e-mail: electronic message sent online
smartphones: phones that combine the features of computers and telephones

Scan the QR code to learn more about transport and communication.
• The different ways in which we travel from one place to another are known as means of transport.
• Cars, trains, buses, bullock carts, bicycles, tongas, etc. are means of land transport.
• Boats, ships and steamers are means of water transport.
• Aeroplanes, spacecrafts, hot air balloons and helicopters are means of air transport.
• The process of sending and receiving messages and information is called communication.
• The internet has made communication faster than ever before.


1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which is the most common means of transport?
Air Land Water
B. Which of these can we use to instantly send written documents between offices?
Postal system Fax machine Television
C. Which of these is a means of water transport?
Helicopter Steamer Tonga
D. Which of these enables us to send urgent letters within India?
Fax machine Radio Speed Post
2. Fill in the blanks.
ships animals water mobile phones
A. transport is the oldest means of transport.
B. can carry huge amounts of cargo over long distances.
C. Portable telephones are called .
D. In ancient times, were used for transportation.
3. Write True or False.
A. An aeroplane is the fastest means of transport.
B. The internet has made communication faster than ever before.
C. Metro trains are the most common means of transport in villages.
D. The Speed Post service is used to send urgent parcels.


4. Answer the following questions.
A. Name any three means of water transport.
B. What is meant by means of communication?
C. Name the fastest means of transport.
D. How are smartphones helpful in communication?
E. What are the differences between water transport and air transport?
F. How did people send messages in ancient times?
5. Picture-based questions.
A. Identify and name the means of transport shown in the picture.
B. What type of transport is it?
C. Give two more examples of the same means of transport.


Do you think modern means of transport and communication have made our life easier? Why or why not?
Do you know who to call in case of emergencies? Talk to your parents or elders or use the internet to find the contact numbers of the following emergency services:
• Police:
• Fire:
• Ambulance:
Only call these numbers if there is an emergency. Do not call them otherwise.


Objective: To understand directions and how to use a compass by creating a simple compass and map.
Materials Needed: Paper plates, markers, scissors, glue, a straight pin, a small magnet (for magnetising the pin), a pencil
Step 1: Make the compass: Take a paper plate and draw a large circle in the centre. Mark the four main directions (north, south, east, west) around the circle.
Step 2: Make the compass needle: Rub the pin or needle with the magnet in one direction to make it a magnet. This helps the needle line up with the Earthʼs magnetic field.
Step 3: Put the compass together: Attach the compass needle to the centre of the paper plate. Ensure the needle can move freely.
Step 4: Create your map: On a separate sheet of paper, draw a simple map of your neighbourhood. Include landmarks like the market, the park and so on.
Step 5: Use your compass: Hold the compass flat and let the needle point north.
Step 6: Explore directions: On your map, practise finding directions. For example, find out in which direction the office lies from your classroom or where the north side of the playground is.
Step 7: Technology check: Use a digital map or compass app on a tablet or smartphone with the help of an adult. See if it gives you the same directions as your compass. Observe how technology can also help us find directions.
Project Output: Now you have your own homemade compass and a simple map that you can use to practise navigation present it to your class.
Final Outcome: This hands-on project will help you understand how a compass works and how to use it to find directions on a map.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.

Read this story and answer the questions given below.
In Vijaynagar Town, Smriti’s family uses various means of transport and communication to make their daily lives easier. Amit, her father, drives a car to his office in the city because it is convenient and fast. Smriti travels to school by bus. Her father uses his smartphone to stay in touch with his family and friends by calling them and sending messages. He uses email to send longer and more important messages. Smriti’s grandparents live in Ooty, which is far away from Vijaynagar. Smriti talks to them on the telephone. During the summer holidays, Smriti and her parents fly to Ooty to visit her grandparents. Smirti loves seeing all the aeroplanes at the airport.
1. How does Smriti’s father travel to his office in the city?
A. By bus
B. By car
C. By aeroplane
2. Why does Smriti’s family travel to Ooty by aeroplane?
A. It is the most expensive means of transport.
B. It is fun to travel in an aeroplane.
C. It is the fastest way to get there.
3. Smriti’s father drives to his office in his car, and Smriti takes a bus to school. Why do you think they choose different types of transport? How does each type of transport fit their needs?
4. Apart from talking to her grandparents on the telephone, what are some other ways that Smriti can communicate with her grandparents?
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.
















Chapter Overview

Living and Non-living Things







Living and Non-living Things
Characteristics of Living Things Natural and Human-made Things


Read aloud the poem given below. Get Set
In our world, both big and small, Living things grow, move, and call. Animals, plants, and you and me, We need air, water, and food to be.
Non-living things don’t grow or play, Like a rock, a book, or a toy we sway. They don’t need food, they don’t need rest, But they’re useful and help us the best.
Look around and you will see, Both living and non-living things, you and me!
In this chapter, we will learn about living and non-living things.

Aryan went for an evening walk with his grandfather. On their way, he noticed buildings, houses, plants, cars, birds, dogs and many other things. Some of these things, like plants, birds and dogs, are alive. These things are called living things. On the other hand, things, like buildings, houses and cars, do not have life in them. These things are called non-living things.


Living things


Non-living things
Think and Tell
Can you think of some non-living things in your classroom?
Classify these things as living or non-living.
Remember!
Plants and animals are an important part of our lives.
Door, rocks, books, plants, cat, dog, humans, table, chair, flowers


Sing the poem.
Living things can grow and play, Breathe and move in their own way.
Plants and animals, big and small, Living things include them all.
Non-living things like rocks and chairs, Do not breathe or have any cares.
They do not grow or eat or play, They stay the same day by day.
Living things share some common characteristics that make them different from non-living things. Let us learn about these.

All living things need food to survive. Food gives us energy to do various activities. It helps us stay healthy and strong. Green plants make their own food using air, water and sunlight. Animals and humans depend on plants or other animals for their food.


Non-living things do not

characteristics: special qualities of a person, group or thing survive: to stay alive

Some plants, like the Venus flytrap and Sundew plant, trap insects for food!

Venus flytrap eating an insect.
All living things need air to breathe. They take in oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide. Different living things use different body parts to breathe.
• Humans and many animals breathe through their noses.
• Plants have small pores on their leaves. These pores, called stomata, help plants to exchange gases.
• Animals like fish and tadpoles breathe through gills.
• Insects, like grasshoppers and cockroaches, breathe through air holes called spiracles on their bodies.
A grasshopper breathes through spiracles.
Fish breathe through their gills.
Non-living things do not breathe.
Living things can produce young ones of their own kind. We call this reproduction. Some animals, like cows, elephants and even humans, reproduce by giving birth to young ones. Birds and fishes lay eggs that hatch into young ones. Plants produce new plants with the help of seeds.
Non-living things do not reproduce.

Plants breathe through stomata.


All living things grow and change over time. For example, seeds grow into plants. Buds bloom into flowers, and flowers turn into fruits. Fruits have seeds that grow into new plants.
Similarly, baby animals grow into adults. A puppy grows into a dog, or a chick hatches from an egg and becomes a hen.


Non-living things do not grow.
Most living things move around to find food and explore their surroundings. Humans and animals use their legs to move. Birds use their wings to fly. Some animals, like snakes and earthworms, move by crawling.
Plants do not move from one place to another. However, they show movement in some other ways. For example, a sunflower turns towards the sun during day, and the leaves of the touch-me-not plant close when touched.
Non-living things cannot move by themselves.


explore: to discover or learn about something new



Circle the odd one out.
1. Birds hen fish table
2. Seed plant tree dog
3. Humans animals plants wings
4. Snakes earthworms wings birds
What happens when you touch a hot container by mistake? You immediately pull your hands away from the hot object? This happens because living things feel and respond to changes in their environment. Humans and animals feel through their sense organs. The five sense organs include the eyes, nose, tongue, ears and skin. Although plants do not have sense organs, they also respond to the changes in their surroundings. For example, sunflowers turn towards the sun. When sunlight falls on the lotus, it opens its petals.


Non-living things do not feel anything.
If you look around, you will see a variety of things in your surroundings. These things can be divided into two types: natural and human-made things. Let us learn about them.
respond: to answer or react surrounding: all the things around us


These things are found in nature. Natural things can be living or non-living. Natural things, like trees, animals and flowers, are living. On the other hand, natural things, like mountains, rivers and rocks, are non-living.
These things are not found in nature but are created by human beings. All humanmade things are non-living. We use different materials to make human-made things. For example, a table is made of wood. Some examples of human made things are buildings, cars, furniture and kitchen utensils.


Why do we need to create human-made things? Discuss about the importance of these things.
The Valley of Flowers in Uttarakhand, Bharat, has thousands of colourful wildflowers (living things), surrounded by tall and snow-capped mountains (non-living things). This place has a combination of beautiful flowers and natural beauty.

Valley of flowers
Word Splash
living things: things that have life in them non-living things: things that do not have life in them


stomata: small pores present on the leaves of plants that help in the exchange of gases
reproduction: the process by which living things produce young ones of their own kind
natural things: things that are found in nature
human-made things: things that are created by human beings

Scan the QR code to learn more about living and non-living things.
• Living things have life, while non-living things do not.
• Living things grow, reproduce, need food and water, respond to their environment and can move on their own, while non-living things do not show these features.
• Natural things are found in nature.
• Human-made things are created by people.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of the following is a living thing? Rock Car Tree Pencil
B. Which of the following is not a characteristic of living things? Breathing Growing Moving Staying the same size
C. What helps fish to breathe? Gills Stomata Noses Pores


D. Which of the following lays eggs?
2. Fill in the blanks. sense organs reproducing stomata air
A. Living things need to breathe.
B. Plants breathe air through small pores called .
C. Animals produce young ones of their own kind by .
D. Humans and animals get to know things and feel using their .
3. Write True or False.
A. All moving things are living.
B. Non-living things cannot move by themselves.
C. Rocks can grow and reproduce.
D. Human-made things are found in nature.
4. Match the following.
A. Plants a. gills
B. Fish b. nose
C. Cockroach c. stomata
D. Humans d. air holes
5. Answer the following questions.
A. How is a non-living thing different from a living thing?
B. How do plants show movement? Draw a picture to support your answer.
C. Describe some ways in which living things reproduce.
D. How do humans respond to their surroundings?
E. How are natural things different from human-made things? Give examples for each.



6. Picture-based questions.
A. What is shown in the image?
B. Is it a living or a non-living thing?
C. Does it make its own food or not?


1. Why do you think some non-living things, like cars, can move?
2. If you could create a new living thing, what would it be? Describe what it would look like and what non-living things it would need to survive.
You have a small plant that looks weak. Make a plan to help it grow by listing what it needs. Decide how often you will water it and how much sunlight it will get each day. Create a simple schedule to check on the plant regularly and see how it’s doing. Adjust your care if needed to help the plant grow strong!












Parts of Plants Uses of Plants Types of Plants How Plants Make Their Food?




Read the poem aloud. As you read, underline the names of any three parts of a plant in the poem.
In the garden, a plant does grow, Roots below, they firmly hold. Stems reach up towards the sky, Leaves relax in the sun up high. Flowers bloom in colours bright, Attracting bees in joyful flight.

In this chapter, we will learn more about plants.

We see different types of plants around us. Plants are living things that grow in our environment. All plants have two main parts: one part above the ground and the other part below the ground.
Root
The part of the plant below the ground is called the root.
Roots fix the plant in the soil, helping it to stay upright and stable.
Roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil and transport them to the rest of the plant to help it grow. Some plants store food in their roots, which they can use later. Several plants have roots are commonly eaten as food, for example, carrots, beetroots, radishes and turnips.
Talk to your elders at home and find out the names of some roots that you eat at home.
Shoot
The part of the plant above the ground is called the shoot. It includes the stem, leaves, flowers and fruit.
The stem carries other parts of a plant such as the leaves, fruit, flowers and buds. It acts like a straw and carries water and nutrients from the roots to all the other parts of the plant.
Leaves are the food factory of a plant. They use sunlight, water and air to make food for the plant. They are also called the kitchen of a plant.
nutrients: essential substances in food that help living things grow, stay healthy, and get energy


Let us create piece of art by rubbing leaves.
1. Place a leaf under a piece of white paper (the lines on the leaf must face up).
2. Use a crayon to gently rub over the paper covering the leaf, showing the leaf’s texture and shape.
3. Use different colours and types of leaves to create colourful artwork.
4. You can also cut out the leaf rubbings and glue them on coloured paper to create a collage.
Flowers are usually the bright and colourful parts of a plant. They produce fruit and help plants make seeds to grow new plants.

A fruit is the colourful and delicious food that grows on plants and trees. They are usually sweet or sometimes a little sour. They have seeds inside, which can grow into new plants when planted in the soil. A fruit with seeds.

Name the following.
1. The part of the plant that makes food for the plant .
2. The part of the plant that absorbs water and nutrients from the soil .
3. The part of the plant that includes leaves, stems, fruit and flowers .
4. The part of the plant that carries water and food to other plant parts .
There are many types of plants, from tiny grasses to giant trees. Let's learn about the different kinds of plants around us.

Trees are big, tall and strong plants with very thick stems. Banyan, mango, and neem are examples of trees.
The thick wooden stem of a tree is called the trunk.

Shrubs are medium-sized bushy plants with woody stems. These are smaller than trees and usually have many stems rising from the bottom of the plant.
Rose, hibiscus and lilac plants are shrubs.
Herbs are small plants with thin, soft and weak stems. These plants do not grow very high from the ground. For example, mint and coriander plants are herbs.
Climbers usually have flexible stems that help them to bend and twist around objects for support as they grow. Money plants and pea plants are climbers.
Creepers have long, flexible stems that can spread along the ground. For example, pumpkin and watermelon plants.
Giant Sequoias are among the largest trees in the world. Some of these trees live over 3000 years! Did You Know?
Talk in groups about the plants you see in your neighbourhood. Identify if they are trees, shrubs, herbs, climbers or creepers.




Not all plants grow upright. Some plants like creepers spread along the ground. Error Alert!
bushy: full of thick leaves and branches flexible: able to bend easily without breaking

Sahil: Mom, I have grown tall because I eat healthy food. You cook and give me food every day, but I wonder how these plants in our garden grow. Who gives them food?
Mom: Yes, Sahil you are right, just like we need food to grow and stay healthy, plants also need food to grow big and strong. Plants are amazing because they can make their own food using sunlight, air and water. Let me explain how it works.
Photosynthesis
Plants make their food through a process called photosynthesis.
They use sunlight, water and air to make their food. The leaves of a plant make food and this is the reason why leaves are called the food factory or the kitchen of a plant. Plants use only a part of the food prepared by them. The rest is stored in the roots, stem, leaves and fruit.

Ra hul bought rose plants for his balcony. He likes to decorate his house with plants that have flowers. Rahul takes care of his plants. We must take care of all living things around us. Do you have plants in your house? How do you take care of them?
Plants are important for life on earth. Plants add beauty to our surroundings such as gardens, parks and our homes. They also give us many things such as:
Fresh Air
Plants give out oxygen which we need to breathe. Plants take in carbon dioxide from the air to make their food.
Food
Many plants provide us with fruit, vegetables, grains and nuts that we eat to stay healthy and strong. We eat different parts of different plants.



For example, we eat the leaves of spinach and cabbage plants; the flowers of cauliflower and broccoli plants and the stems of sugarcane plants. We should never waste food. We can always feed needy people with leftover food instead of throwing it in a dustbin.
Plants like aloe vera, tulsi and lavender have medicinal properties and can be used to make natural medicines to cure illnesses.

We use wood from plants to make doors and windows for houses, chairs and tables. The wood of trees such as oak, sandalwood and teak are used to make furniture, cricket bats and many other useful things.
Fibre: We get fibres such as jute and cotton from plants. Fibres are used to make clothes, bags and ropes.
Complete the following.
1. Two plant roots we eat ,
2. Two leaves we eat as food ,
3. Two plants with medicinal properties ,

4. Two fibres we get from plants that are used to make clothes ,





Tulsi, also called Holy Basil, is a special plant. Tulsi is considered a holy plant in India. It is believed to be very special and is often grown in homes and temples. People believe that having a tulsi plant in their home brings positive energy and purifies the surroundings. A tulsi plant
fibre: a thread-like material found in plants that can be used to make fabric and clothes


shoot: the part of the plant above the ground
shrub: a medium-sized plant with many branches coming from the bottom of the plant
herb: a small plant with soft and weak stems
climber: a plant with a flexible stem that grows upward by using support
creeper: a plant with a long, flexible stem that spreads along the ground photosynthesis: the process by which plants make their food using sunlight, water and air
oxygen: a gas released by plants, essential for breathing carbon dioxide: a gas plants need to make their food

Scan the QR code to learn more about plants.
• All plants have two main parts: the shoot and the roots.
• There are different types of plants such as trees, shrubs, herbs, climbers and creepers.
• Plants make their food through photosynthesis using sunlight, water and air.
• Plants provide food, oxygen, wood and fibres to make clothes.
• Plants help maintain the balance in nature by giving out oxygen and taking in carbon dioxide from the air.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which part of the plant holds it in the soil? leaf root flower
B. Name the process by which plants make their food. Digestion Photosynthesis Respiration


C. Which of these plants is a creeper?
Money plant Mango tree Cactus
D. What do plants release that we need to breathe?
Carbon dioxide Oxygen Nitrogen
2. Fill in the blanks.
carbon dioxide herbs shoot leaf
A. are small plants with soft and weak stems.
B. Plants take in gas to make their food.
C. The part of the plant that is above the ground is called .
D. The is known as the food factory of the plant.
3. Write True or False.
A. Creepers grow straight up towards the sky.
B. Roots help plants to stand upright and be stable.
C. We eat the roots of the cabbage plant.
D. Plants provide us with wood to make furniture.
4. Match the following.
A. Photosynthesis a. hold the plant in soil
B. Fruits b. contain and protect seeds
C. Roots c. the process through which plants make food
D. Stem d. change into fruit
E. Flowers e. carries water and nutrients
5. Answer the following questions.
A. What are the main parts of a plant? Draw and label the parts of a plant.
B. Write three uses of plants.
C. Write one difference between a creeper and a climber.


6. Picture-based questions.
A. Name the plants shown in the pictures.
B. Which part of these plants do we eat?



1. If plants could not make their food, what would happen to life on Earth?
2. How does the stem of a plant act like a highway? What would happen if the stem is damaged?
Let us reuse plant materials.
1. Collect things like fruit peels, vegetable scraps, leaves or flowers that you no longer need.
2. Place the plant materials in a bin or pile them up. Add some soil and water to keep the pile or bin it moist.
Reuse plant materials.
3. Every few days, mix the materials with a shovel or stick. This helps the materials break down faster.
4. Let the mix sit for a few weeks to a few months. During this time, the plant materials will break down and turn into nutrient-rich compost.
5. Once the mix or soil is ready, use it in your garden or potted plants. It will help the plants grow healthy and strong.













Animal Movement Places Where Animals Live Eating Habits of Animals Food Chain

Get Set

Identify and name any four animals shown in the image given below.















































































































Animals are living things. They come in different sizes. Some animals are big, like whales and elephants. Some are small like a cat and a mouse.

Some are tiny, like an ant. Like us, they can move, need shelter, eat food and grow. In this chapter, let us learn more about animals.

Arya went on a jungle safari with her parents. She saw many animals. Monkeys were jumping from one tree to another. Flocks of birds f lew in the sky. A herd of deer ran in the open field. They even saw a lion and lioness walking slowly past their jeep. “Look at all these animals walking, jumping and running so freely!” said Arya’s Mom.

Animals move in different ways. They move from one place to another in search of food, to escape from danger and to find shelter. They can walk, run, jump, fly and swim. They use different body parts for these movements, including their legs, wings, tails, and fins. Let us learn more about how animals move.
Animals that live on land are called land animals. Most of them have legs. They use their legs to run and walk.
Examples: Deer, tiger, horse and zebra
Animals like lizards, chameleons and crocodiles crawl. They have short legs. They move by crawling on their bellies, using their legs. Their scaly skin protects them as they move.



shelter: a safe place to live scaly: covered with small, flat pieces like the skin of a snake or fish
have short legs to crawl.

Snakes slither by bending their bodies in a wavelike motion. They push against the ground with their muscles and scales to move forward. The scales on a snake’s body grip the ground and help them move.
Snakes move with the help of muscles.

Birds have wings to fly.

3 pairs of legs
Birds and insects move in the air. Birds have wings and feathers that help them fly. They flap their wings to glide through the air. Some insects, like butterflies and bees, have wings that help them fly. They also have three pairs of legs to help them move on the ground.
A pair of wings A flying bee
Error Alert!
While all birds have wings, not all of them can fly. Some birds like the ostrich, kiwi and penguin cannot fly. They use their legs to move on the ground.
Animals that live in water, like fish, octopuses and turtles, swim to move. Fish use their fins and tails to swim. Animals like ducks and frogs have webbed feet, which help them swim. Sea turtles have flippers instead of legs, which help them swim.
slither: to move the body like a wave glide: to move smoothly in the air flippers: broad, flat limb without fingers


Aquatic animals can swim.
Octopuses have eight arms that they use to move. They can change their colour to blend in with their surroundings.


Animals can be seen in different places in our surroundings. Some walk on land, others fly in the air and some even live deep under the water. Based on the places animals live, they are divided into groups:
Terrestrial Animals—Animals such as cats, dogs, lions and elephants, live on land. They can be found in places like forests, deserts and grasslands. They have special features:
• Most terrestrial animals have legs to walk, run or jump.
• Most terrestrial animals have lungs to breathe air.
• Most terrestrial animals have fur or skin to protect them from the weather and other animals.
• Some animals have paws while others have hooves to move over the ground.



Arboreal Animals—Some animals, like monkeys, tree frogs, koalas and squirrels, live in trees.
• Most arboreal animals have long limbs that help them move easily from one branch to another.
• Their feet are strong, allowing them to grip branches tightly.
• Their claws are sharp and curved, which helps them climb trees.
Some animals like monkeys have tails which they use as a support to move in trees.

have hooves.
Remember!
Animals like ants and rabbits that live underground are land animals too.

have strong limbs to grab branches.
limbs: body parts like arms and legs that are used for movement grip: hold tightly

How would the life of animals like monkeys be different if they did not have tails?
Aerial Animals—These animals spend a lot of their time in the air. Birds have light bodies, strong wings and feathers that help them fly.
Bats and insects like butterflies and bees also have wings.


Aquatic Animals—Animals such as fish, whales and octopuses, live in water. They are called aquatic animals. They have fins that help them swim in water. Most aquatic animals breathe through gills, while dolphins and whales come to the surface of the water to breathe. They have lungs instead of gills.
Animals like frogs and toads can live on both land and water. They are called amphibians. They breathe through their lungs on land, and in water, they breathe with the help of their moist skin.



Choose an animal. Find out where this animal lives. Draw or decorate the inside of a shoe box to create the features of the place where the animal lives. Use different materials like cotton, sand, wool, paper, etc.
Circle the odd one out based on the place they live.
1. butterflies bees lions bats
2. fish whale octopus dog
3. squirrels tree frogs eagles monkies


Animals need food to stay healthy and strong. They move from one place to another in search of food. Based on their eating habits, animals are divided into three groups—herbivores, carnivores and omnivores. They have body parts that are suited to their eating habits.
Animals that only eat plants are called herbivores. Cows, horses, rabbits, deer, zebras and elephants are some herbivores. They chew on grass and leaves. Herbivores such as horses, cows, and zebras have sharp, broad teeth that allow them to cut through grass and the leaves of plants. Some birds, like parrots and woodpeckers eat fruits, seeds and grain and are herbivores.

Animals that only eat the flesh of other animals are called carnivores. They hunt and kill small animals to eat them. The small animals they hunt are called prey. Carnivores have sharp teeth and claws to catch, hold and tear the flesh of other animals. Lions, tigers, eagles and wolves are carnivores.

chew: to break up food in the mouth using teeth
prey: animals that are eaten by other animals

How do the eating habits of rabbits and lions help them survive?

Some animals eat plants as well as the flesh of other animals. They are called omnivores. These animals have a combination of sharp teeth to tear meat and flat teeth to eat plants. Bears, pigs and humans are omnivores.
Birds, however, don’t have teeth. They eat using their beaks, which are adapted to suit their specific diets.
A parrot is a herbivore; its beak is designed to eat fruit and seeds.

Bears can eat plants as well as flesh of animals.
A pigeon is an omnivore; its beak helps it eat both worms and seeds.

An eagle is a carnivore; its beak is shaped to tear flesh.

Birds also use their feet and claws to find, hold and carry their food. Their feet and claws are adapted so that they can feed themselves.
Hens use their claws to search for insects and seeds to eat. Parrots hold their food with their claws.
Owls use their claws to catch, carry and eat the small animals they catch.

Look at the picture. A grasshopper eats grass, the bird eats the grasshopper and the snake eats the bird. Who eats the snake?














































This process, where a smaller animal eats plants and is then eaten by a larger animal, which in turn may be eaten by an even larger animal, is known as a food chain.
Every food chain starts with plants, meaning all animals on earth rely, either directly or indirectly, on plants for food. Birds, like animals, are also part of the food chain.
























The sun provides energy for the plants to make food. Since the food chain starts with plants, all animals directly or indirectly depend on plants for all their food.
The Royal Bengal Tiger is the national animal of India. It is a beautiful animal with an orange coat covered in black stripes and a white belly.
terrestrial animals: animals that live in land
arboreal animals: animals that live in trees

aerial animals: animals that spend most of the time in the air
aquatic animals: animals that live in water
amphibians: animals that can live both on land and in water
herbivores: animals that eat only plant-based food
carnivores: animals that eat other animals
omnivores: animals that eat both plants and animals


Scan the QR code to learn more about animals.
• Animals move in different ways. They run, walk, crawl, slither, fly and swim to move from one place to another.
• Based on where they live, animals are grouped as terrestrial, arboreal, aerial and aquatic animals. Amphibians live on the land and in water.
• Based on their eating habits, animals are grouped as herbivores, carnivores and omnivores.
• A food chain tell us who eats whom in nature. All food chains in nature begin with plants.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What helps butterflies fly? wings fins feathers a tail
B. Which of the following animals has hooves? fish eagle horse crocodile
C. Which aquatic animal breathes using lungs? shark goldfish octopus dolphin
D. What do we call animals that eat only plants? carnivores omnivores amphibians herbivores


2. Fill in the blanks.
food chain aquatic aerial carnivores amphibians
A. Animals that can live both in water and on land are called .
B. An animal like an eagle can fly high in the sky.
C. Animals that eat other animals are called .
D. Animals that live in water are called animals.
E. A always begins with a green plant.
3. Write True or False.
A. Most land animals walk or run using their legs.
B. Snakes crawl on their bellies using their legs.
C. Frogs can live on both land and water.
D. A food chain usually begins with a green plant.
4. Match the animals with the way they move.
A. Lion
B. Snake
C. Lizard
D. Eagle
E. Whale
a. crawl
b. walk and run
c. fly
d. swim
e. slither
5. Answer the following questions.
A. What are arboreal animals?
B. Leopards and tigers are carnivorous animals. Give a reason.
C. Write two differences between aquatic and aerial animals.
D. How are the eating habits of bears and humans similar?
E. What is a food chain? Explain with an example.


6. Picture-based questions.
A. Name the animal. Write how it moves from one place to another.
B. Is it a terrestrial, aquatic, aerial or arboreal animal?
C. How do you classify the animal based on its food habits?


What do you think would happen if all green plants disappeared from the earth?
Choose a pet like a dog, cat, cow, or parrot.
Describe how the pet moves (walking, running, flying, etc.).
Describe its eating habits (herbivore, carnivore, omnivore) and explain how you would provide the right food for it.
Share your ideas with your parents and family members. Discuss how to take good care of the pet.















Get Set

Join the numbers to complete the picture. Then, write the name of this bird and colour it in.
This is a .



Let us read a poem.
If I were a bird, I would have sung a song, I would fly around, the whole day long
And when the night comes, I would go to rest, Up in a tree, in my warm little nest.
Birds are animals with feathers and wings. They lay eggs, and most of them can fly. Let us learn what helps a bird fly.
• Birds have a pair of wings to fly. They flap their wings to push the air down and behind their bodies while flying.
• To stay in the air, birds keep flapping their wings or glide in the air.
• Their streamlined bodies help them move through the air easily. The bones of birds are hollow, making their bodies light. This helps birds lift off and fly easily.

All birds cannot fly. Some birds, like penguins, ostrichs and emus, cannot fly but can walk, run and jump.
Birds have special features that make them different. Birds’ bodies are covered with feathers, which help them fly, stay warm and look colourful. Birds use their beaks to catch and eat food as well as to make their nests. A bird’s feet and claws help it walk, run or jump and catch its food. Let us learn more about all these features.
flap: to move up and down or from side to side in the air streamlined: a smooth, narrow shape that allows something to move through air or water easily

Birds have three types of feathers:
• Down feathers: These are soft, small and fluffy feathers. They are found on the underside of the bird and keep it warm.
• Flight feathers: These are the longest feathers on a bird’s body. They are found on the wings and tail. They help the bird fly and change direction.
Body feathers
Down feathers

Flight feathers
Types of feathers.
• Body feathers: These feathers cover the rest of the body. They give the bird its shape and colour.
Did You Know?
A peacock’s tail feathers are long and colourful. Each feather has a hollow space at the bottom. In old times, these feathers were used as writing pens.
Birds have beaks instead of teeth. Beaks are hard and help birds pick up, hold and break their food. Birds also use their beaks to build their nests. Birds have beaks of different shapes and sizes according to the food they eat.
Hooked Beak: Birds that prey on other animals or small birds have hooked beaks. This type of beak is small, curved and sharp at the tip. Eagles, hawks and kites have this type of beak.

Straight beak
Hooked beak
Small, Straight Beak: Birds that eat fruit and grains have small, straight and smooth beaks. These birds use their beaks to pick up food like grains from the ground. Doves, pigeons and sparrows have this type of beak.
prey: an animal hunted for food


Long, Thin Beak: Birds such as hummingbirds that suck nectar from flowers have long, needle-like beaks. Birds such as woodpeckers that pull insects from the bark of trees also have thin, narrow beaks.


Short, Thick Beak: Birds like parrots and canaries that eat seeds and nuts have short, thick beaks. Such beaks are usually strong and can crack open hard foods like seeds and nuts in their shells.
Flat, Broad Beak: Birds like ducks and flamingos that eat small water animals have flat and broad beaks. Their beaks have holes on the sides, which are used to filter food from the water. These birds scoop up water and then let it drain out, keeping small fish, plants and tiny insects inside to eat.
So, next time you see a bird, carefully observe its beak.
Match the bird’s name with the type of beak it has.
Bird
A. Duck
B. Parrot
C. Pigeon
D. Eagle
Beak
a. hooked beak
b. straight beak
c. short and thick beak
d. flat and broad beak
Birds use their feet and claws to grip branches and sit without falling. Birds use their sharp claws to catch and hold onto their food. Their claws also help birds fight with their enemies.


nectar: a sweet liquid that bees and birds collect from flowers scoop up: take in quickly


Birds have different types of claws according to the food they eat and the place they live.
Perching Birds: Birds like crows, sparrows and mynahs have claws with three toes pointing forward and one toe pointing backward. This helps them to perch and hold on to branches tightly. They use their feet to sit on branches or hold food.
Claws of scratching birds.
Claws of perching birds.
Scratching Birds: Birds like chickens, turkeys and hens have strong feet with sharp claws. They use their feet to scratch in the ground and find food like seeds and insects hidden there.
Climbing Birds: Birds like parrots and woodpeckers, have claws with two toes pointing forward and two toes pointing backward. This helps them grip tree trunks tightly, making it easy to climb up and down.
Claws of flesheating birds.
Claws of climbing birds.
Flesh-Eating Birds: Birds like eagles and hawks eat the flesh of other animals. They have strong feet with sharp, curved claws called talons. Talons help them catch and hold onto their prey, such as small animals and fish. The strong grip of their talons makes it easier for them to tear apart their food.
Do you think the claws of birds are similar to our hands? What similarities do you see?
Do and Learn
Observe a bird in your surroundings. Note the shape of its beak, the type of feet and claws and the colours and design of its feathers. Draw it or write about it.
perch: sit on a branch


Birds live in nests. Birds build different kinds of nests. They lay their eggs there to keep their babies safe. Let us learn about the nests of some birds.
Weaver birds build their nests by weaving long grass and twigs. Their nests hang from tree branches and look like little bags. They have an opening at the bottom, which is covered with leaves. This keeps the eggs and baby birds safe.


The tailor bird makes its nest by stitching leaves together with its beak. The nest is lined with cotton, dried grass and wool that keeps it warm. Sparrows and pigeons make their nests with twigs, grass and feathers. They like to live close to humans, so they build their nests in safe places, like a corner of a house or building. They make their nest using broomsticks, dry grass, twigs etc.
Alert!

We often think that birds only build their nests in trees, but this is not true! Birds build their nests in many other places, such as among rocks, in caves and even on the ground.
Birds build nests to live in and lay their eggs. They sit on the eggs to keep them warm. Inside the egg, the baby bird grows and develops. The baby bird gets everything it needs from the egg. When the baby bird is ready, it starts pecking at the inside of the egg with its beak. The egg cracks open, and the baby bird slowly comes out of the egg. This is known as hatching. Hatching of an egg.
pecking: to hit something with the beak


Most newly born birds are blind and without feathers. Parents protect and feed the baby birds until they grow feathers and are ready to fly away. Did You Know?
When it gets too cold or food becomes scarce, birds fly to warmer places where food is easily available and the weather is good. When a large number of birds travel together from one place to another, the movement is called migration.
Every year, during winter, we see lots of birds migrating from cold regions to warm regions. When the weather warms up again, birds travel back to their original homes to lay eggs and raise their young ones.
birds: animals with feathers and wings
talons: sharp, curved claws of flesh-eating birds
hatching: the process of a baby bird coming out of an egg migration: movement of animals in a large number from one place to another
• Birds are animals with feathers and wings.
• Wings and a streamlined body are some features of birds that help them fly.
• Birds have different types of feathers, beaks and claws.
• Birds build different types of nests to lay eggs and stay safe.
• In winters, birds fly to warmer places. This is called migration.





Keoladeo National Park, also known as Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary, is in Rajasthan, India. It is home to many birds. In winter, many migratory birds, such as painted storks, visit there. Over 370 different types of birds can be seen there.


Scan the QR code to learn more about the migration of birds.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which body part do birds flap to fly? claws feet wings beaks
B. Which body part helps parrots crack open nuts? feathers tail beak wings
C. What do tailor birds use to build their nests? rocks mud leaves straw
2. Fill in the blanks. streamlined feathers migration hatch
A. Flight are found on the wings and tail of birds.
B. Birds have a body shape that helps them fly.
C. Baby birds from the eggs when they are ready to come out.
D. The flight of birds from colder to warmer places in search of food is called .

3. Write True or False.
A. Birds use their feet and claws to grip branches.
B. Sparrows and pigeons live only in forests.
C. Birds that suck nectar have a hook-shaped beak.
D. Body feathers give birds shape and colour.
4. Choose the correct option.
A. Bird with a hook-shaped beak: pigeon eagle dove
B. Bird with a flat, broad beak: crow parrot duck
C. Bird with a needle-like beak: hawk sparrow hummingbird
D. Bird with a small, straight beak: kite dove flamingo
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Name the types of feathers that birds have.
B. A water bird has a flat, broad beak. How does it help the bird eat?
C. Why do hens sit on their nests after laying eggs?
D. Why do birds migrate? Write two reasons.
E. Describe the nest of a tailor bird.

F. Draw the claws of climbing birds like woodpeckers. Write how these claws help the bird.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What kind of beak does this bird have?
B. What type of claws does this bird have?
C. Describe the type of nest this bird makes.

Based on what you have learnt in the chapter, what kind of beaks would birds that eat fish have?



Let us do a small activity on birds.
Activity: “Birds Need Freedom”
Materials Needed:
• Poster board or large piece of paper, markers, crayons, or colour pencils, scissors, glue, pictures of birds from magazines or printouts (optional)
Steps:
1. Talk with your friends about why birds should be free and not in cages.
2. Think of ideas and messages for your poster about letting birds fly free.
3. Write a slogan like “Birds need to fly free to be happy!” or create your own.
4. Use markers, crayons and pictures to make a bright and colourful poster.
5. Show your poster to your classmates and tell them why birds should be free.
















Chapter Overview










Let us solve a riddle:
I am felt when you blow out, but never seen. I am all around you, yet you often forget I’m there.
What am I?

Air is all around us. The Earth is surrounded by a layer of air called the atmosphere. We cannot see, smell or taste it, but we can feel it when it moves. Moving air is called wind or a breeze.
wind: moving air

Air on Earth is made up of various gases such as nitrogen, oxygen and carbon dioxide. They are present in different amounts. Air also has water vapour, dust and germs. Thus, we can say that air is a mixture of gases and other things.
If air already has germs, what can we do to stop ourselves from getting infected? Discuss with your class.
Rima was taking a walk outdoors. Suddenly, she felt a strong gust of wind. It blew away her hat! “Oh, what happened! she exclaimed. She then wondered. Where does wind come from?”
We know that moving air is called wind. Let us learn how the wind is formed. When the sun shines, it warms the air. Warm or hot air is lighter, so it goes up. As the hot air rises, it starts to cool down. Cooler air is heavier, so it sinks back down. This movement of hot air rising and cool air sinking makes the air move around. We feel it as the wind!
So, when the temperature changes, it makes the air move and forms wind.
Do and Learn





germs: tiny harmful living things gust: a sudden rush of something wondered: a feeling of shock or surprise







Take two paper bags of the same size. Hang them on the two ends of a wooden stick. Tie a piece of thread in the middle of the stick. Hold the


stick by the thread like a balance. Place a candle below one of the bags. Light it. Make sure that your bags are at a safe distance from the candle flame, but not too far away as to not feel the heat of the flame.
After a while you will notice that the bag which has the candle below it rises up a little. This is because the candle flame heats up the air inside that bag, making it warmer and lighter.
Tick ( ) the correct statements.
Warm air is heavier than the cool air.
Warm air rises and cool air sinks.
The movement of hot and cool air forms wind.
Air is very important for life on earth. Let us learn about some of its uses.
• Air contains oxygen, which is needed by all living things to breathe.
• Plants use the carbon dioxide in air to make their food.
• The oxygen in air also causes things like wood and coal to burn. Burning coal and wood are used for other things like cooking.
• Sound travels in air, which helps us to hear things.


• Moving air dries wet clothes. Moving air is also used in sports like kite flying.
• Moving air is also used to turn the blades of windmills.
• We feel balloons and tyres with air. Vehicles won’t run if their tyres don’t have air in them.
If there is no air, then we won’t be able to hear anything. That is why nothing can be heard in outer space. Did You Know?
Make a windmill with paper. Follow these steps: Do and Learn






1. Take a square piece of paper. Fold it as shown and cut it along the dotted lines.
2. Fold each corner to the centre and paste them.
3. Add a straw or a stick to its centre with a pin.
Blow on it or run with it and see it move with the wind.
Name the following.
1. The gas released by plants.
2. The gas all living things breathe in.
3. The gas plants use to make their food.
windmill: a device that works by moving air


Have you seen smoke rising when we burn things? How does it change the air around you?
Air pollution is caused when unwanted things like smoke, dust and harmful gases are added to the air. It makes the air polluted. When the air is polluted, it is hard for us to breathe and it can cause many health problems. It can also make the sky look hazy and dull. Plants, animals and even buildings can be harmed by air pollution.
Air can become polluted in the following ways:
• Smoke from factories, vehicles and houses.
• Burning garbage instead of recycling or managing them properly.
• Burning of wood and coal.



We can help to keep the air clean with the following actions:
• Plant more and more trees.
polluted: made dirty or harmful due to unwanted or dangerous substances hazy: looking dim and unclear



• Throw garbage in covered bins.
• Do not burn garbage, or burst excess firecrackers.
• Walk or cycle to places that are a short distance away. Use public transport more than private cars.


Vehicle and factory owners can help in the following ways:
• Regularly check vehicles for pollution control.
• Set up factories away from residential areas.
• Smoke from factories should be recycled instead of being let out into the air.
The biggest wind farm in Asia is in Lamba, Gujarat. Wind is a type of renewable energy, which means it can be used again and again.
Plants take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen. It helps to keep the air clean for us.

Factories have tall chimneys.

atmosphere: the layer of air that surrounds the Earth breeze: moving air that we can feel air pollution: the presence of harmful gases, dust and smoke in the air
residential areas: places where people live



Scan the QR code to learn more about air.
• Air is made up of different gases: oxygen, nitrogen and carbon dioxide.
• We need air for breathing, burning, inflating tyres and balloons and producing electricity.
• When things like smoke, dust and harmful gases enter the air, they cause air pollution.
• We can help to keep the air clean, for example, by planting more trees.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Moving air is called: wind atmosphere oxygen nitrogen
B. Which of the following gases do we breathe in?
Nitrogen Oxygen Carbon dioxide
Water vapour
C. Which of the following does not pollute the air?
Smoke Dust Harmful gases
Water vapour
2. Fill in the blanks. vapour tyres breeze carbon dioxide
A. Moving air is called a .



B. Air has water in the form of water .
C. Plants use from the air to make food.
D. The of vehicles like bicycles and cars are filled with air.
3. Write True or False.
A. We can see the air around us.
B. Plants keep the air clean.
C. Bursting firecrackers cleans the air.
D. Factories should be built away from residential areas.
4. Name the following.
A. The gas we breathe-out:
B. Layer of air that surrounds the earth:
C. Addition of unwanted things like smoke, dust and harmful gases to the air:
5. Answer the following questions.
A. What is air made up of?
B. What is air pollution?
C. Write two human activities that pollute the air.
D. List two ways to control air pollution.
E. What causes air to move? Draw a picture to explain this.
F. Write any five uses of air.
6. Picture-based questions.

Ravi is visiting a city. Look at his picture and answer the questions.
A. Why do you think he is wearing a mask?
B. Write what is making the air dirty.
C. Write one thing he can do to clean the air.



If air is required by plants, both for breathing and for photosynthesis, then what do underwater plants do?
Let’s do our bit to clean the air:
• Ask your parent or a trusted adult to take you to a plant nursery.
• Pick any plant that will grow into a tree.
• Choose a spot in your garden or neighbourhood and plant your tree. You may ask your parents or any adult to help you.
Take care of your plant regularly and watch it grow!
















Read the poem aloud. Underline three uses of water in the poem.
We drink water to stay strong, And wash our hands all day long. Plants need water to grow tall, And fish swim in rivers, big and small. For cooking, cleaning, and staying neat, It even helps to wash my feet!
So let’s keep water pure and clear, And use it wisely, year after year.
In this chapter, we will learn more about water.


Water is everywhere. About 3/4th of the Earth’s surface is covered with water. Water is an important part of our lives. Some of the uses of water are:
• We need water for drinking.
• We use water for bathing.
• We use water for cooking.
• Plants need water to grow.
• We need water for cleaning and mopping.
• Farmers use water for irrigation.
Water is found in oceans, seas, lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams. The water in oceans and seas is very salty, so cannot use it. We need fresh water. Most of the fresh water on Earth is frozen in ice caps. Only a small quantity of water is found in lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams. Lakes, ponds, rivers and streams are sources of surface water. Rain is the main source of water on the earth. It fills rivers, lakes and ponds. Rainwater also seeps into the ground and collects as groundwater. We draw groundwater through wells, tubewells and handpumps.



irrigation: watering crops by drawing water from nearby rivers surface water: water found at ground level, like rivers and seas
groundwater: water found under the ground

Write True or False.
1. Water in oceans and seas can be used for drinking.
2. Most of the freshwater on Earth is found in ice caps.
3. Rainwater fills lakes and ponds.
4. We can draw groundwater by using wells, tubewells and handpumps.
5. Oceans, seas, lakes, ponds, rivers and streams are all sources of surface water. Pause and Answer
Since most of the Earth’s surface is covered with water, Earth is also called ‘Blue Planet’.
Water is an important liquid. Let us discuss some of its unique properties.
Pure water does not have any taste, colour or smell.
Water is transparent, which means that we can see through it or see the things that are in it. Water is also colourless.
Although water is colourless, but we see the sea as blue because it reflects the colour of the sky. It is the same reason why they turn dark grey during storms. Did You Know?
properties: characteristics that describe an object or thing

Water does not have any fixed shape, so it flows. It takes the shape of the container in which it is kept.

Water takes the shape of a container
We can dissolve a lot of things in water. The substances that dissolve in water are called soluble substances, for example, common salt, sugar, milk powder and soap. Substances that do not dissolve in water are called insoluble substances, for example, stones, oil, sand and chalk powder.
Error Alert!
Although water is tasteless, the 'taste' we get in water is actually because of the minerals dissolved in it.
If water is transparent, then can we see right to the bottom of the sea or the river? Why or why not?
Tick ( ) the correct statements.
Water in oceans is fit for drinking.
Common salt is a soluble substance.
Water has a fixed shape.
Water is blue in colour.


Sugar dissolves in water.

Sand does not dissolve in water.

Water is an amazing substance that can exist in three different states: solid, liquid, and gas.
Solid water is called ice. When it is very cold, water freezes and becomes hard like the ice cubes in your freezer.

Liquid water is what we usually see and use every day. It flows and takes the shape of its container, like the water in a glass or a jug.
The gaseous form of water is called water vapour. When water is heated, it turns into an invisible gas that we can feel as steam from a hot pot or see when we breathe out on a cold day.
One form of water can be changed into another form by heating or cooling it. Melting is the changing or conversion of ice into liquid water upon heating. Freezing is the conversion of liquid water into solid ice upon cooling.
Take some ice cubes out of the refrigerator. After a while, you see that the solid ice converts into liquid water. This occurs because the outside air is warmer than the air inside a refrigerator. Now, fill an ice tray with water and keep it in the freezer for a few hours. You will see that the water inside the tray converts into ice cubes.


invisible: something that cannot be seen melting: the conversion of solid ice into liquid water upon heating




























































Due to the sun’s heat, water from the oceans, seas, and rivers forms water vapour. The conversion of water into water vapour upon heating is called evaporation. Water vapour rises in the sky and cools down into tiny water droplets. The conversion of water vapour into water droplets upon cooling is called condensation.
freezing: the conversion of liquid water into solid ice upon cooling


Water evaporates under the sunʼs heat and rises up as water vapour. As the water vapour rises higher into the atmosphere, it cools down and condenses into tiny water droplets. These droplets gather to form clouds. When the water droplets in the clouds combine and grow heavy enough, they fall back to the Earth as rain, snow, sleet or hail. Rainwater can follow different paths once it reaches the ground: It can flow over the surface as runoff into rivers and streams or it can seep into the soil to become groundwater. This movement of water between the atmosphere and the earth’s surface is called the water cycle. Let’s make a ‘Water Cycle Bracelet’. Make a simple bracelet using beads of different colours to show the different stages of the water cycle. Use blue beads for evaporation, white beads for condensation and clear beads for rain. Thread the beads with the help of an adult at home and explain each stage as you thread the beads.
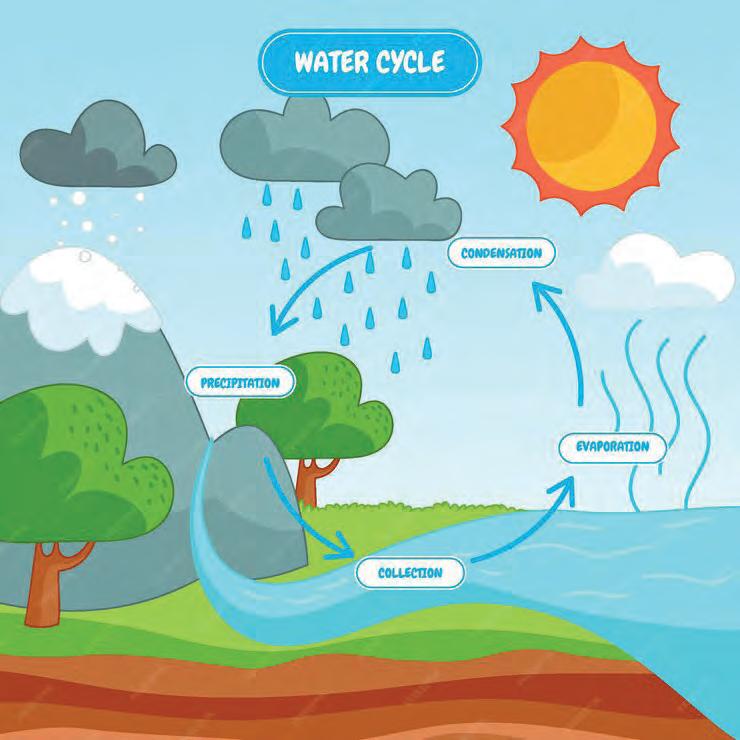

sleet: tiny, frozen ice particles
hail: larger, solid ice balls





Water pollution is when water sources become dirty because of human activities. People pollute rivers when they wash clothes near or in waterbodies, bathe animals in waterbodies, or throw trash from factories and homes in waterbodies, in the water. The harmful things that make the water dirty are called water pollutants. Drinking or using dirty water can cause diseases like cholera, diarrhoea and typhoid as polluted water contains germs.
Some of the causes of water pollution are:
• Throwing garbage into rivers or lakes
• The release of chemicals from factories or farms into the water
• Oil spills from ships
Cleaning water means making it safe to drink or use. There are different ways to clean water so that we can drink it without getting sick. We can boil it, use a water filter or add special tablets. These methods help remove dirt, germs and other pollutants that can make us sick.

When it snows in the Himalayas, the snow melts and the water runs into rivers like the Indus, Ganga and Brahmaputra. These rivers provide water to grow crops on the Indian plains.
germs: tiny living things that cause diseases



soluble substances: substances that dissolve in water insoluble substances: substances that do not dissolve in water evaporation: the conversion of water into water vapour upon heating condensation: the conversion of water vapour into water droplets upon cooling water cycle: the movement of water between the atmosphere and the earth’s surface water pollution: the addition of harmful things to water that makes it dirty pollutants: harmful substances that dirty the environment

Scan the QR code to learn more about water.
• We use water for many activities in daily life.
• A large amount of the earth's surface is covered with water.
• Ponds, lakes and rivers are sources of surface water.
• Wells, tubewells and handpumps are used to draw up the groundwater.
• The water cycle circulates water between the atmosphere and water bodies.
• The addition of harmful things to water is called water pollution.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of the following draws up the groundwater?
Tubewell Water filter Tap
B. Freshwater is NOT found in Ponds Seas Rivers
C. Which of these is a soluble substance?
Sand Pebbles Milk powder


2. Fill in the blanks.
condensation evaporation water cycle insoluble
A. Substances that do not dissolve in water are called substances.
B. The conversion of water into water vapour upon heating is called .
C. The conversion of water vapour into water droplets upon cooling is called .
D. The movement of water between the atmosphere and the earth's surface is called the .
3. Write True or False.
A. We need water for growing crops.
B. A large part of Earthʼs surface is covered with water.
C. Rivers and seas are sources of freshwater.
D. Rainwater seeps into the ground and makes surface water.
4. Match the following.
A. Melting
B. Freezing
C. Evaporation
D. Condensation
a. conversion of water into ice
b. conversion of ice into water
c. conversion of water vapour into water
d. conversion of water into water vapour
5. Answer the following questions.
A. List two causes of water pollution.
B. Mention any two properties of water.
C. What are soluble and insoluble substances? Give two examples of each.
D. Draw and label the steps of the water cycle.


6. Picture-based questions.
A. What makes the water dirty in the picture?
B. Why is it important to keep the water clean?
C. What can you do to stop water pollution?



We know that 3/4th of the Earth has water. Do you think it is still important to conserve water every day? Why or why not?
Make a poster on the topic: “Let us Use Water Wisely”.
• Choose a few actions that you can take at home or at school to use water wisely. Show these actions as drawings on the poster.
• Make an attractive poster that includes drawings and messages on ways to save water.
• Decorate the poster with colourful borders, stickers or additional drawings related to the careful use of water.
• Once the poster is complete, show it to the class.















Sing the song and underline the names of the seasons.
The sun is bright, the sky is clear, Summer fun is finally here.
Autumn leaves of red and gold, Fall to the ground as it gets cold.
Winter comes with chilly air, We put on coats and play with care.
Spring brings flowers that start to grow, Birds sing songs, making worries go.
Raindrops fall, the sky turns blue, Everything feels fresh and new.


Weather is the day-to-day condition of the atmosphere at a place on any given day, and it changes over time. It can change during the day and from day to day. We check the weather to decide what clothes to wear and what activities we can do outside.
Remember!
Weather changes from day to day and from hour to hour.
Changes in weather are caused by the sun. The sun gives us heat. Places near the equator get more heat from the Sun than places near the poles. The wind, temperature, rain and clouds also affect the weather. Land gets hot and cools down faster than water. This uneven heating and cooling of the Earth creates wind which is moving air. Winds push clouds from one place to another. Clouds carry water that falls as rain or snow. Warm air can hold more water than cool air. The weather of a place can be sunny, rainy, windy, snowy or cloudy.









Children playing in sunny weather.








Children with umbrellas in rainy weather.





Children flying kites in windy weather.
Different weather conditions
What is the weather like today?
atmosphere: the layer of air around the Earth

One hot afternoon, Rohan was sitting in the shade of a tree, feeling the warm breeze. He turned to his dad and asked, “Dad, why is it so hot? Will it always be this warm and sunny?” His dad smiled and said, “Rohan, it’s summer now. The days are longer and warmer because it’s the sunniest time of the year. Soon, the season will change.”
Curious, Rohan asked, “Dad, what are seasons?”
Seasons are different times of the year when the weather is similar for a few months at a time. There are five main seasons: summer, monsoon, autumn, winter and spring.
Let us learn about each of them.
Summer is the hottest season of the year.
During summer, people like to wear cotton clothes because they are light and absorb the sweat. Some people also wear sunglasses while going outside to protect their eyes from sun’s rays.
The days are longer than the nights during summer.

It is important to drink plenty of water in summer because our bodies lose a lot of water when we sweat.
sweat: when beads of water form on your skin due to heat


What are some fun activities you like doing in summer? How do these activities help you enjoy the warm weather or stay cool? Discuss with your partner.
Did You Know?
In some places like Norway, the sun does not set for weeks. That is why Norway is also known as the Land of the Midnight Sun.
People are very happy to welcome the rains after the hot summer months. The rainy season is also called the monsoon. The weather is cool and cloudy during season. Dark clouds and lightning can be seen in the sky. The rain cools down the air. Due to the rain, plants and trees become very green and fresh. This is a good time for farming because crops get plenty of water. Rainwater fills lakes, rivers, wells and ponds. There is enough water for our needs. When you go out in the rain you should wear a raincoat, gumboots or carry an umbrella. If you get wet in the rain, dry yourself or you may catch a cold and fall ill.
A boy uses an umbrella to stay dry in the rainy season.
A rainbow during the monsoon.
In the monsoon season, people enjoy warm and comforting foods like hot soups, and spicy snacks such as pakodas. Sometimes we see a rainbow in the sky when it is raining and the sun is shining at the same time.
The short season between the rainy and winter seasons is called autumn. The weather is neither too hot nor too cold at this time of the year. The leaves on some trees change colour to red, orange and yellow. After some time, the leaves

Children playing in a park in autumn season.

fall off the trees. Hence, this season is also known as the ‘fall’ in some parts of the world. The days get shorter, and the nights get longer. People wear long-sleeved shirts and light jackets because it gets a bit cooler.

Children wearing woollen clothes in winter.
It is the coldest season of the year. The days are shorter and the nights are longer. In some places in India, it snows during winter while in other places it is just cold. Some people light bonfires and sit around them to keep warm when it gets very cold. People also use heaters to stay warm. People wear woollen clothes such as sweaters, mufflers, caps and gloves to stay warm.
People like to eat warm meals and baked foods in winter. They also like to have hot drinks like hot chocolate, tea and coffee to stay warm.
Spring is a wonderful season that comes after winter. In spring, the weather is pleasant, flowers start to bloom and trees grow new leaves. It is a great time to play outside, fly kites and have picnics in the park. People like to spend time outside as the weather is pleasant. Bees and butterflies fly around the beautiful flowers in the garden.
Children enjoy playing in a park in spring.
Discuss with your friends what their favourite season is and why they enjoy it.

Circle the odd one out.
1. sweater gloves raincoat muffler
2. ice creams hot soups mangoes cold juice
3. light jacket long pants cotton clothes woollen cap
Clothes help us look good and feel comfortable. Clothes also keep us clean and safe from things that might hurt our skin. We wear clothes to protect our bodies from extreme weather conditions like the hot sun, cold wind and rain.
The weather is different in every state of India. So, the clothes we choose depend on the weather in that place.
For example, it is very cold in the hilly and mountain areas like Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh. So, people wear warm clothes for most of the year.
In coastal areas like Mumbai, Goa and Kerala the weather is warm for most of the year. So, people wear cotton clothes to stay comfortable.
In places such as Delhi and Punjab people wear cotton and woollen clothes according to the season.
A woman in a salwar kameez. A man in a dhoti-kurta.

A woman in a saree.
Men usually dress up in a shirt and trouser, a dhoti-kurta or a pyjama-kurta.
Women prefer to wear sarees, salwar-kameez or a blouse with a skirt or pants.
coastal: places near the sea



Cut out pictures of the different traditional clothes worn in India, such as sarees, salwar kameez, kurta-pyjama and dhotis from magazines and make a collage.




The Tulip Garden in Kashmir, India is one of the largest tulip gardens in Asia. The garden is known for its beautiful display of colourful tulips during the spring season.

weather: the day-to-day condition of the atmosphere wind: moving air seasons: different times of the year when the weather is similar for many days

Scan the QR code to learn more about weather and seasons.
• The condition of the atmosphere in a place is called the weather. The weather can change during the day and from day to day.
• People choose the clothes, the food they eat and their activities according to the weather of a place.
• Times of the year when the weather is similar for many months at a time are called seasons.
• There are five main seasons in a year: summer, monsoon, autumn, winter and spring.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. In which of these seasons do we like to eat ice cream? monsoon summer autumn
B. In which season will you see a rainbow? summer autumn monsoon
C. What should you carry during the monsoon season? scarf sunglasses umbrella
D. In which season do flowers bloom? monsoon winter spring
2. Fill in the blanks. autumn summer spring winter
A. We sweat a lot in .
B. We use heaters to stay warm in .
C. Leaves on some trees change colour during .
D. Flowers bloom in the gardens in .
3. Write True or False.
A. The weather of a place changes every year.
B. During summer, the days are usually hotter and longer.
C. In autumn, the leaves trees turn green and then fall off.
D. In the monsoon season, people use umbrellas to stay dry.
E. Winter is the hottest season of the year.
4. Match the following.
A. weather
B. winter
C. summer
D. monsoon
E. clouds
a. bring rain
b. changes from day to day
c. umbrellas and raincoats
d. hottest season
e. hot soups


5. Answer the following questions.
A. Name four things on which the weather of a place depends.
B. Why do people wear cotton clothes in summer?
C. What is the weather like in spring? Name any two activities you like to do with your friends in this season.
D. Write any four features of the winter season.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. Which season does the picture show?
B. Name one thing that helped you know which season it is.
C. Write another name for this season.


Your friend is at your house. Suddenly, the weather changes and it begins to rain. What are two things you can give your friend so that he/she can go back home safely?

Let us REUSE our clothes!
Reusing clothes means finding ways to use them again instead of throwing them away. Here are some simple ways to reuse clothes:
• Give your old clothes to someone who needs them or you can swap them with your friends or family members for something else.
• Find new ways to wear your clothes by mixing and matching them in different ways.


Use old jeans to make shorts to be worn in summer.
• Turn old clothes into something new such as cutting an old pair of jeans to make a new pair of shorts or making a cloth bag out of an old T-shirt. (Ask an adult to help you before cutting up the clothes.)










Chapter Overview The Universe The Sun The Earth The Moon The Stars





Colour in the picture given below. Get Set

Did you see in the picture you coloured in? Is it day or night?
We know that we live on Earth. When we look up at the sky during the day and at night, does it look the same? During the day, we can see a bright blue sky and a bright sun. At night, we can see the moon and the stars. All these heavenly bodies are a part of the universe. The universe is a huge, endless space that has stars, planets, the sun and the moon. It also has dust, gases and big pieces of rock that float in the vast space.
Let us learn more about the universe.
The Sun is a massive ball of fire that provides us with heat and light. On Earth we see it rise in the east and set in the west. Life on Earth would not be possible without the Sun. Positioned at the centre of the solar system, the Sun is orbited by eight planets, each following its own path.
The Sun is a star and it provides us with heat and light. Earth is about 150 million kilometres away from the Sun. This is the perfect distance to give us just the right amount of warmth and light needed for living things to grow.
The Moon also gets its light from the Sun.
There are eight planets that revolve around the Sun in fixed paths called orbits. The eight planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The Sun, along with all these planets that revolve around it, together form the Solar System. The largest planet is Jupiter. The smallest planet is Mercury. Mercury is closest to the sun, while Neptune is the farthest.
revolve: move in a circle on a central axis
















The Earth is the third planet from the Sun. Earth is the only planet in the solar system that has life on it. The Earth has plants, animals and human beings. It is special because it has air and water on it. It also receives light from the sun. These things make life on earth possible. There is a layer of air that surrounds the Earth. This layer is called the atmosphere.
The Earth is constantly moving. The Earth spins around an imaginary vertical line called an axis, which is slightly tilted. This spinning of the Earth is called rotation. Rotation causes day and night. The Earth completes one rotation in 24 hours. As the Earth rotates, one half of it faces the Sun. It is day time in the places on Earth that lie in the half that is lighted by the Sun. It is dark on the side facing


away from the Sun. As the Earth rotates, day turns to night and night turns to day, depending on which part faces the Sun.
Thus, the rotation of the Earth causes day and night. Do you think Earthʼs rotation also affects the time difference between countries around the world?
The Earth also moves around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit. This movement is called revolution. It takes one year for the Earth to complete one revolution. The Earth’s tilt and its revolution around the Sun create the different seasons we experience.
Imagine if there was only day and no night on Earth. How would our lives change? Discuss with your friends.
The Moon is a large, round satellite that revolves around the Earth. A satellite is an object in space that orbits a larger object. The Moon is smaller than both the Earth and the Sun. It is made of rocks and is the closest celestial body to the Earth in the solar system. This is why it appears almost as large as the Sun, even though the Sun is much bigger.















































































The Moon does not have any light of its own but still shines brightly at night. That is because it reflects the light from the Sun.
The moon takes 27 days to complete one revolution around the Earth.
Have you noticed how the Moon seems to change its shape each night? This happens because we can only see the part of the Moon that is lit up by the Sun. As the Moon revolves around the Earth, the sunlight falls on different parts of it, causing these changes. These changes are called the phases of the Moon.
When the Moon looks completely round in the sky, it is called a full moon.

There is no air and water on the moon. So, there is no life on it.




























The surface of the moon has big holes called craters. Phases of the Moon

In your scrapbook, draw the sun, the moon and the planets in our solar system. You can use different colours to make your drawings pretty. When you are done, share your work with everyone in your class.
Stars are big balls of hot gas that have their own light. We can see the stars in the sky at night. Stars look tiny to us but they are big, bright balls of hot gas that shine in the sky. They are far away from us, which is why they look like tiny lights.



One night, Bhawna was sitting on her terrace watching the sky with her elder brother. She looked up in the sky and said, “Look, I can see a spoon in the sky!”, Her brother smiled and explained, “Bhawna, those are patterns formed by stars. They are called constellations, and they take different shapes.” Bhawna was amazed and started searching for more patterns in the sky.
Stars are there in the sky during the day too but they are not visible to us due to the bright light of the Sun.

If we observe carefully, we can spot star patterns called constellations. People have given these star patterns different names, based on what they look like. For example, the Big Dipper looks like a spoon in the sky, Leo looks like a lion and Hydra looks like a water snake. The Ursa Major is called Saptarishi in India.







































The Indian Space Research Organisation conducts missions to explore space. In 2008, it launched Chandrayaan-1, India’s first spacecraft to the Moon. Chandrayaan-1 discovered tiny particles of water on the surface of the Moon.


















stars: big, bright balls of hot gas heavenly bodies: objects in space, such as the Sun, the Moon, the planets and the stars
the universe: a huge, endless space that has stars, planets, the Sun, the Moon, dust, gases and big pieces of rock floating in it constellations: patterns formed by the stars in the sky

Scan the QR code to learn more about the Solar System.
• The universe is a huge, endless space that has stars, planets, the Sun and the Moon.
• The Sun is Earthʼs source of energy, heat and light.
• There are 8 planets in the solar system.
• The Earth is the third planet from the Sun.
• The Moon is Earthʼs natural satellite, made of rocks, and is smaller than Earth.
• The Moon appears in different shapes because we only see the part lit by the Sun as it revolves around Earth.
• Constellations are patterns formed by stars in the sky, named after objects, animals, or figures they resemble.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these has its own light?


B. Which of the following terms defines the Sun?
Star Planet Satellite
C. Which is the farthest planet from the Sun? Mercury Venus Neptune
2. Fill in the blanks.
Major moon atmosphere Leo
A. The revolves around the Earth.
B. The constellation looks like a lion.
C. The is called Saptarishi in India.
D. The Moon is a big, round satellite that revolves around the .
E. The Earth also moves around the Sun in a fixed path called an .
F. The layer of air that surrounds the Earth is called .
3. Write True or False.
A. The Sun is the largest planet.
B. The patterns in the stars are called constellations.
C. The rotation of the Earth makes day and night possible.
4. Answer the following questions.
A. Name the planet nearest to the Sun.
B. What are constellations? Name any one constellation and draw its pattern of stars.
C. What is a moon?
D. Name the planets of the solar system.
E. Where do you think the stars go during the day?


5. Picture-based questions.









B. Which planet is the largest?








A. Name the planets that you can see in the picture.


C. What is the source of light, energy and heat on Earth?

1. Raghav and Rahul are cousins. Raghav lives in India, and Rahul lives in Canada. When Raghav is asleep, Rahul goes to school in Canada. Why do you think this happens?
2. Why do you think the revolution of Earth takes more time than the rotation of Earth?
Along with your friends, create a starry sky with the help of your friends. You will need a sheet of black-coloured chart paper, a pencil, a torch and some tape. Draw stars on the paper and carefully poke a small hole for each star. Tape the paper over the front of the torch, making sure the holes are not covered. Turn off the lights, point the torch at the ceiling and switch it on. The light will shine through the holes, creating a starry sky on the ceiling.









Objective: Students will explore different ways to filter and clean water by creating a simple water filtration system using materials available at home.
Materials Needed: A 2-litre plastic bottle (cut in half), coffee filter or clean cloth, sand, gravel, activated charcoal (optional), dirty water (mix of water with soil, small bits of dirt, etc.), recycled materials (like an old plastic bottle, recycled sand, or gravel), water collection container, notebook and pencil
Step 1: Prepare Your Materials: Collect all the materials you need. The plastic bottle must be cut in half. The top half is a funnel and the bottom half collects the water.
Step 2: Assemble the Filter Layers
o Put the coffee filter or cloth at the bottom of the funnel.
o Add a layer of activated charcoal if available (or skip if not).
o Add a layer of clean sand on top of the filter.
o Then, place a layer of gravel over the sand.
Step 3: Pour Dirty Water Through the Filter: Slowly pour the dirty water into the funnel and watch as it passes through the layers of the filter. The water should collect in the bottom part of the bottle.
Step 4: Observe and Record Results: Write down your observations in your notebook. How did the water change? Does it look cleaner? Were the bits of dirt removed?
Step 5: Improve Your Filter: After the first round, think about how you could improve your filter. Would adding more layers help? Could you use different materials, like cotton or recycled plastic, to make your filter better?
Step 6: Test and Compare Filters: Now, build a second filter using different materials (like cotton, different sizes of gravel, or more sand). Pour dirty water through it and compare the results with your first filter. Note down which one worked better and why (use your notebook and pencil).
Step 7: Present your filtered water to the class. Explain how each material helped filter the water. Also talk about the importance of clean water and how we can recycle materials to help us filter water.
Project Output: You have created your own filtered water!
Final Outcome: This hands-on project will help you understand the importance of filtering water and how it can be done using simple materials.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.


Read this story. Answer the questions given below.
In the village of Neerpur, the people rely on a nearby river for their water. They use it for drinking, farming, cooking, and bathing. However, in the past few months, the river has become dirty because of waste being thrown into it. The villagers are worried because many people are getting sick after drinking the water.
A local school teacher explains the Water Cycle to the children in the village, showing how the water evaporates from the river, forms clouds, and then falls as rain. The teacher also talks about how important it is to keep the water clean because polluted water can harm both people and animals.

The villagers decide to clean up the river and stop throwing waste into it. They also begin learning ways to use water wisely so they don’t waste it.
1. Which part of the water cycle is mentioned in the story ?
A. Evaporation
B. Digestion
C. Combustion
D. Photosynthesis
2. The villagers stopped throwing waste into the river to keep the water clean. Based on this, which of the following actions can also help reduce water pollution?
A. Throwing plastic bags into the river.
B. Washing clothes in the river.
C. Recycling waste in the village.
D. Using the river water for farming.
3. Why is it important for the villagers to keep the river clean, especially when they rely on it for drinking water?
4. What can the villagers do to make sure they don’t waste water and keep it clean for everyone?
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.













Introducing Discover, a thoughtfully crafted EVS book that builds an understanding of, and nurtures a love for, the environment in young minds. In keeping with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020’s focus on competency-based education, Discover provides opportunities for learners to master key concepts, hone their critical thinking, develop the ability to make informed choices, and apply 21st century skills in their day-to-day lives.
Discover is designed to pique the students’ interest in EVS, both as a subject and as a practical experience, while also making them well-rounded individuals who interact with the world around them in a rational and meaningful way.
Coursebook
Uolo App • Teacher’s Guide
• STEAM Projects: Engaging, hands-on projects blending Science, Technology, Engineering, Art and Maths (STEAM) to inspire young minds
• Competency-based Assessments: Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and application of skills
• Story-based Approach: Enchanting comic stories that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure
• Picture-based Questions: Questions featuring visual stimuli to elevate comprehension, interpretation and critical thinking
• Wonders of Bharat: Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage, designed to ignite a profound sense of pride and love for the nation
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, South East Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-979364-5-6
