
COMPUTER SCIENCE

JOURNEY TO THE MINISTRY OF HAPPINESS

Evolution of Computers
Story Time
Note: Use the following points to prepare for the session beforehand. Avoid reading the points in the class.
In the Previous Grade…
● Conji helped Mel recover her memory.
● There was a change in all the robots and machines due to an anomaly in Avora’s timeline.
● Mel and Conji’s arrival in Nexus caused an interchange in the meaning of binary digits.
● With Conji by Mel’s side, the duo once again become a ray of hope for Avora to fix the timeline.
In this Chapter…
● Conji recalls how he and Mel overcame all the challenges thrown by Lord Ero.
● Mel disguises herself as a dragon to prank Conji.
● To make up for the prank, Mel agrees to teach Conji about computers.
● Eva joins them on their journey of learning about computers.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standards
● 1B-CS–01 Computing Systems
This chapter is divided into the following classroom sessions
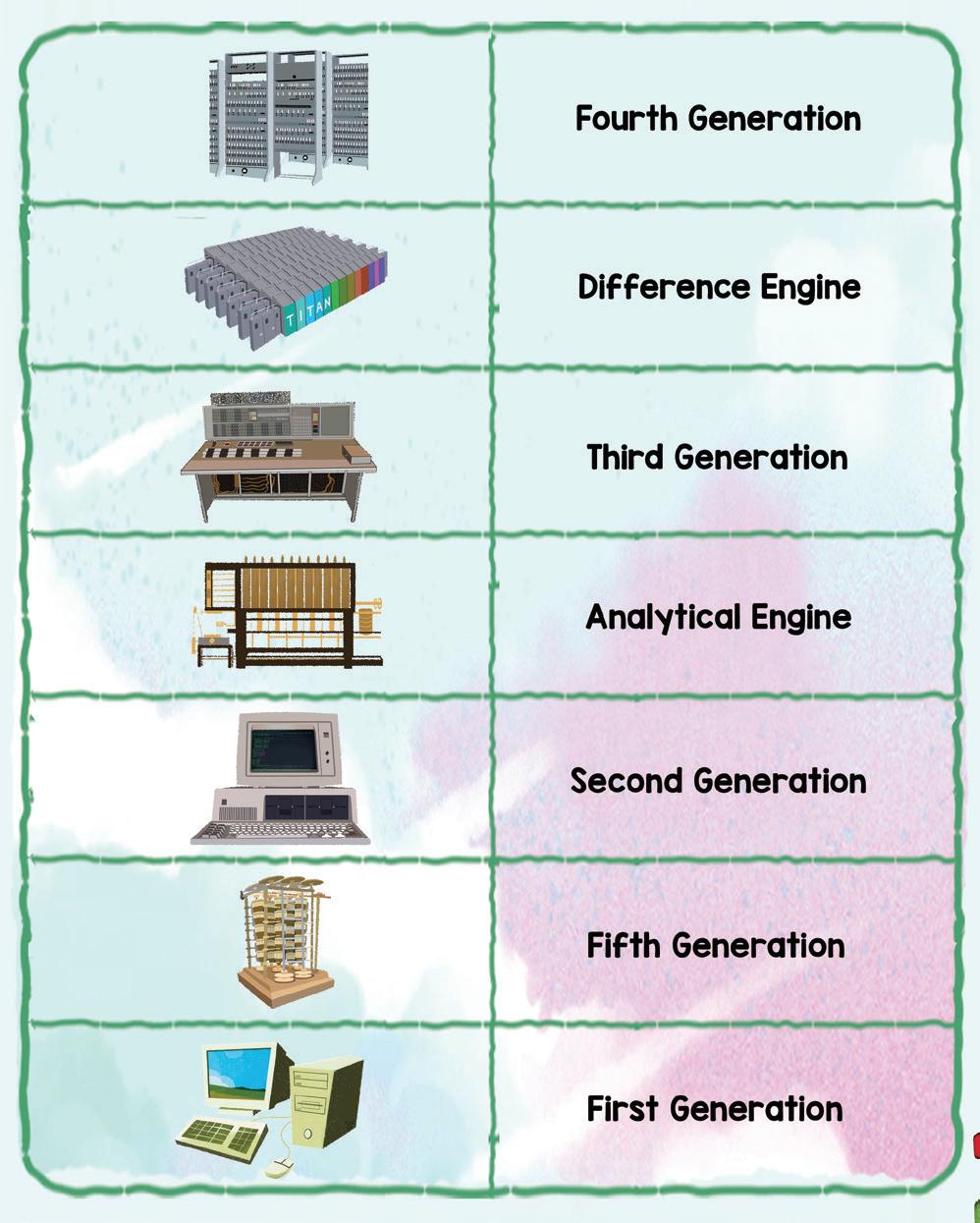
1. Difference and Analytical Engines
2. Generations of Computers I
3. Generations of Computers II
1. Difference and Analytical Engines
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
● Computers
● Analytical Engine
● Difference Engine
Keywords
● Storage: A process by which digital data is stored in a storage device by a computer
● Calculator: A small electronic device used for doing mathematical calculations

WEBS at a Glance
Brief the story of the previous grade
Read or invite the students to read the story aloud
Discuss computers, analytical engine and difference engine
Fill Up – Q1, 2 Find the Truth – Q1, Q2 Answer in Short - Q1
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Recap the story covered in the previous grade.
● Read or Invite two students to read the story aloud from Page 2 to 4 up to Mel’s words “You know….., right?”
● Say: Let’s learn about computers, the first computer ever made: The Analytical Engine; and a device with storage capacity: The Difference Engine.
CS Concepts
Computer
Analytical Engine
Difference Engine
As given in Panel 1 on Page 5
As given in Panel 3 on Page 5
As given in Panel 1 on Page 6
● Present the scenario: Consider your father has asked you to help him in calculating monthly expenses.
● Discuss:
■ Which device will you use to perform calculations?
Possible Responses: Calculator; Computer; Analytical Engine.
■ Which device lets you store the answer to your calculations?
Possible Responses: Computer; Difference Engine; Storage device.
■ What challenges do you think you would face if the computers we see today were as big as the first generation computers?
Possible Responses: They would need huge spaces to store them; they would be expensive; they would be immovable.
■ Why do you think the machine to solve maths problems was called a Difference Engine?
Possible Responses: They could do calculations; they could find the difference between two numbers.
Note
● lf time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill Up section at page 13:
■ Say: Avorians are at war against hostile powers. Let’s help Mel and Conji fill in the blanks to prepare themselves.
■ Read Q1 and 2 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 13:
■ Say: Let’s practise more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1 and 2 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Write answers in your books.
● Conduct Answer in Short on Page 14:
■ Say: Let’s test our learnings to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Write answers in your books.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the section Answer in Short - Q2 or, assign it as the homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about the first computers ever made: Analytical Engines and Difference Engines.
● Ask the following probing questions:
● When do you think you would need computers to perform calculations?
Possible Responses: to solve math problems; to add or subtract large numbers; to do 10-digit multiplication
● What do you think the Analytical Engine could do?
Possible Responses: Solve math problems; Add; Subtract; Multiply; Divide
● Assign Q2 from Answer in Short as homework.
2. Generations of Computers I
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –

● Generations of computers
● Details of the first four generations of computers
Keywords
● Generation of computers: Indicates the change in the technology of computers that were in use
● GUI: Graphical User Interface is a way to communicate with a computer using interactive icons
WEBS at a Glance
Revise the story of the previous session
Recall the concepts of Analytical engine and Difference engine
Discuss the first four generations of computer
Inform that we are in the fifth generation of computers
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Instruct: Let’s recall the concepts learned so far.
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Invite some students to recall and share the concepts aligned with the chapter story.
● Say: Currently, we are in the fifth generation of computers. Let’s learn about the first four generations of computers.
CS Concepts Explain
Hint about the current generation of computers
As given in Panel 2 on Page 6
As given in Panel 2 on Page 50
First four generations of computers
As given in Panel 2 on Page 6, Page 7, and Page 8
● Present the scenario: Consider you are building a computer.
● Discuss:
■ If you are in the 1940s, which areas will your computer be used in?
Possible Responses: Military; Industries; Scientists.
■ Why can only these areas use your computer?
Possible Responses: The computers are expensive; Use a lot of electricity; Very advanced computers of their time.
■ You build a PC. Which generation does it NOT belong to?
Possible Responses: First-generation computers, Second-generation computers, Thirdgeneration computers, Fifth-generation computers.
■ What are the features of the PC you have made?
Possible Responses: generates less heat; is faster; has a mouse; has GUI; can be used by anyone.
Note
● If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 13:
■ Read Q3 and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 13:
■ Say: Let’s practice more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q3 and 4 aloud, one by one. After each sentence, ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Write answers in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 14:
■ Say: Let’s test our learnings to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q4 and 5 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share their responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the section Answer in Short - Q3 or, assign it as the homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about the first four generations of computers. We also learned about the generation of computers we are in.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Why could people not build small and fast computers in the 1950s?
Possible responses: they did not have the knowledge; technology was not advanced enough; there was no need.
■ Name computers you see in your daily life.
Possible Responses: smartwatch; phone; laptop; calculator.
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Answer in Short – Q3
■ DIY – Fun time Q1 – 3
3. Generations of Computers II
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –

● Fifth-generation computers
● Supercomputers
Keywords
● Artificial Intelligence: The ability of computers to perform tasks which previously required human intelligence
● Weather forecasting: Prediction of weather conditions in a certain place
WEBS at a Glance
Revise the story of the previous session
Read the story aloud/ask the students to read the story aloud
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Say: There is a new character in this chapter.
● Introduce Eva to the students.

● Instruct: Let’s learn how the story moves ahead. We will read from page 9.
● Say: Let’s learn about the fifth generation of computers, and the most powerful computers: the supercomputers.
CS Concepts
Fifth Generation of Computers As given from Panel 1 on Page 9
Supercomputers
From web as given in Panel 2 on Page 50
As given from Panel 1 on Page 10
● Present the scenario: Consider you want to plan a trip to the mountains. And, before you plan, you first want to check the weather conditions in the area.
● Discuss:
■ Which type of computer can you use for weather forecasting?
Possible Responses: Supercomputers; very powerful computers
■ Which generation computer cannot be used here?
Possible Responses: First-generation computers; Second-generation computers; Thirdgeneration computers; Fourth-generation computers; Fifth-generation computers
■ Name the generation if the device you used is your phone to check the weather in the mountains.
Possible Responses: Fifth-generation computers; Fourth-generation computers; Current generation of computers
■ Why do you think we need fifth-generation computers in this situation?
Possible Responses: to save time; to make the computers less expensive; to make the computers widely available; to save space; to make the computers available for everybody
● If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill-Up on Page 13:
■ Read Q4 aloud.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Find the Truth on Page 13:
■ Say: Let’s practice more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q5 aloud. Ask if it is true or false.
■ Invite some students to share responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answer in your books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 14:
■ Say: Let’s test our learnings to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1, 2, and 3 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share responses.
■ Discuss and validate the answers with the whole class.
■ Instruct: Fill in the final answers in your books.
● If time permits, discuss the section Answer in Short - Q4, 5 or, assign it as the homework.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about the fifth generation of computers and supercomputers.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ List some features of Fifth-generation computers.
Possible responses: faster; easier; cheaper to use; take less space; widely available; based on AI
■ Name computers you see in your daily life.
Possible Responses: Smartwatch; Phone; Laptop; Calculator.
● Assign the following as homework:
■ Answer in Short - Q4, and 5
■ Match Me
■ DIY – Fun time Q4 - 5
Types of Software
Story Time
Note: Use the following points to prepare for the session beforehand. Avoid reading the points in the class.
In the Previous Chapter…
● Conji recalled how he and Mel overcame all the challenges thrown by Lord Ero.
● Mel disguised herself as a dragon to prank Conji.
● To make up for the prank, Mel agreed to teach Conji about computers.
● Eva joined them on their journey of learning about computers.
In this Chapter…
● Conji is curious about how machines work.
● So, Mel takes Conji on an excursion to a Robot Workshop.
● Conji is excited to look around the museum and learn new things.
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-CS–02 Hardware & Software
This chapter is divided into the following classroom sessions
1. System Software I
2. System Software II
3. Application Software
1. System Software I
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
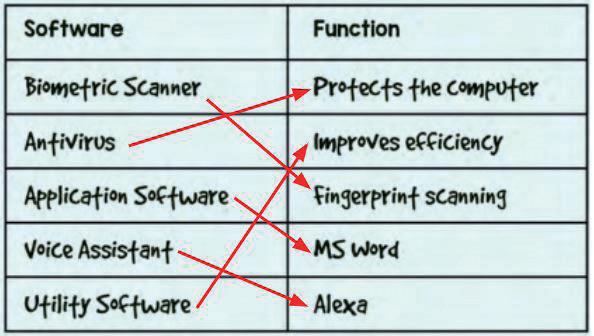
● System Software
● Operating Software

Keywords
● Software: A set of instructions that tells the computer what to do and how to do it
● System Software: Any program that controls internal computer operations
● Operating Software: A system software that controls the overall activities of a computer and acts as a link between user and hardware
WEBS at a Glance
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Instruct: Let’s recall the concepts learned so far.
● Read the story aloud from Page 18 to Panel 3 on Page 19 up to Conji’s words “What do you mean?”.
● Say: Let me explain about types of software: CS Concept Explain
Software As given in Panel 1 on Page 20
Software As given in Panel 2 on Page 20
● Present the scenario: Consider your school wants to build the software of a computer from scratch.
● Discuss:
■ What elements will you require?
Possible Responses: system software; operating software; application software
■ Name the operating system you would like to install.
Possible Responses: MacOS; Windows; Linux
■ What will the operating system do?
Possible Responses: Controls the overall activities; Acts as a link between user and hardware
Note
● If time allows, discuss all three questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 28:
■ Say: Let’s practise to revise what we have learned today.
■ Read Q1, 2 and 4 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct students to write the final answers in their book.
● Conduct Answer in Short on Page 30:
■ Say: Let’s test our learnings of today.
■ Read Q2 and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers.
■ Discuss and Validate their answers.
■ Instruct students to write the final answers in their book.
Note
● If time permits, conduct Fill Up – Q1 from DIY or assign it as homework.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Name the operating software you have used.
Possible Responses: MacOS, Windows, Linux
■ What are the categories of System Software?
Possible Responses: Operating Software; Utility Software; Device Drivers; Firmware; Language Translator
● Assign Q1 of Fill UP from DIY as homework.
2. System Software II
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
● Utility Software

● Utility Programs
■ Scanning
■ Backup
■ Defragmentation
Keywords
● Utility Software: System software that helps to maintain the proper and smooth functioning of a computer system
● Scanning: A process of using an anti-virus software to scan and identify viruses in a computing device
● Backup: The process of creating a copy of the data on your system that you can then use for recovery in case your original data gets lost or corrupted
● Defragmentation: The process of rearranging the data so that the disks and drives can work more efficiently
Discuss utility software and utility programs, i.e. scanning, backup, and
Tick the Correct Answer – Q1, 2, 3 Answer in Short – Q3
Conclude the session Assign the homework
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Instruct: Let’s recall the concepts learned so far.
● Read the story aloud from Page 21 to Panel 3 on Page 23 up to Conji’s words “...types of system software later ”
● Say: Let me explain utility software and the types of utility programs.
CS Concept Explain
Utility Software As given in Panel 3 on Page 20
Scanning As given in Panel 2 on Page 21
Backup As given in Panel 1 on Page 22
Defragmentation As given in Panel 2 on Page 23
● Present the scenario: Consider you are doing your holiday homework.
● Discuss:
■ How will you start the research on your homework?
Possible Responses: By scanning the internet; By asking elders; By scanning previous years’ papers.
■ How will you ensure you have a copy of your submitted homework?
Possible Responses: By keeping a backup; By taking a xerox copy; By keeping a saved file on the computer.
■ What will you do to organise all the data in your report?
Possible Responses: rearranging the data in the correct format.
Note
● If time allows, discuss all three questions, or discuss the first two.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 29:
■ Say: Help Mel and Conji give the correct answers.
■ Read Q1, 2 and 3 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct students to mark the final answers in their books.
● Conduct Answer in Short on Page 30:
■ Say: Let’s test what we have learned today.
■ Read Q3 aloud
■ Invite some students to share their answers.
■ Discuss and Validate their answers.
■ Instruct students to write the final answers in their books.
Note
● If time permits, conduct Find the Truth – Q1 and 4, or assign it as homework.
min
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Name a few utility operations you have used.
Possible Responses: Scanning, Backup, Defragmentation
■ What are some anti-virus programs you have used?
Possible Responses: Norton, McAfee, Kaspersky
● Assign the following questions from Brain Teasers as homework:
■ Find the Truth – Q1, 4
■ Match Me – Q5
3. Application Software
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
● Application Software

● Voice Recognition
● Cloud Storage
Keywords
● Cloud Storage: It allows us to access our files on any device we want, as long as it is connected to the internet
● Biometric Software: Software that helps us identify people based on their unique characteristics like fingerprint, face, retina, etc.
WEBS at a Glance
Recap the story and the concepts covered in the previous session
Read the story to be covered in the current session aloud
● Recap the story covered in the previous session.
● Instruct: Let’s recall the concepts learned so far.
● Read the story aloud from Panel 3 on Page 23 to Panel 4 on Page 26 up to the words “…the Robot Workshop”
● Say: Let’s learn about the second type of software, application software.
CS Concept Explain
Application Software As given in Panel 3 on Page 23
Voice Recognition As given in Panel 2 on Page 24
Cloud Storage
As given in Panel 3 on Page 25
● Present the scenario: Consider you are playing on your dad’s mobile phone.
● Discuss:
■ Whom will you ask to do the operations on the phone?
Possible Responses: Siri; Google Assistant; Alexa; Cortana.
■ How will you unlock the phone?
Possible Responses: Faceid; Fingerprint; Iris recognition
■ What will you do if you want to edit a text?
Possible Responses: Use general-purpose editors like MS Word; Google Doc; Pages.
■ What will you do if you want to edit pictures and videos specifically?
Possible Responses: Use Adobe Photoshop; iMovie; etc.
Note
● If time allows, discuss all four questions, or discuss the first two.
Build
● Conduct Fill Up on Page 28:
■ Say: Let’s test what we have learned to revise it.
■ Read Q3 and 5 aloud, one by one.
10 min
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct students to write the final answers in their book.
● Conduct Find The Truth on Page 28:
■ Say: Let’s help Conji evaluate the given statements as true or false.
■ Read Q2, 3, and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers.
■ Discuss and Validate their answers.
■ Instruct students to mark the final answers in their books.
● Conduct Tick the Correct Answer on Page 29:
■ Say: Help Mel and Conji give the correct answers.
■ Read Q4 and 5 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers and others to validate their peers’ answers.
■ Instruct students to mark the final answers in their book.
● If time permits, conduct Answer in Short on Page 30:
■ Say: Let’s practise some more to revise what we have learned.
■ Read Q1 and 4 aloud, one by one.
■ Invite some students to share their answers.
■ Discuss and Validate their answers.
■ Instruct students to write the final answers in their books.
● Ask the following probing questions:
■ Name a few voice assistants you know.
Possible Responses: Alexa; Siri; Google Assistant; Cortana
■ What can you store in cloud storage?
Possible Responses: Pictures; Videos; Documents; Folders
● Assign the following questions as homework:
■ Brain Teasers: Match Me – Q1, 2, 3, 4
■ DIY: Fill Up – Q2, 3, 4, 5
Chapter
1. Analytical Engine is a machine that could solve math problems. It was created by English mathematician Charles Babbage.
2. Difference engine is a device created by Charles Babbage that could read numbers and print mathematical tables. It also had storage.
3. GUI stands for Graphical User Interface. It allows us to interact with computers using icons instead of just text.
4. First Generation computers were very expensive, used a lot of electricity and produced a huge amount of heat. Whereas Fifth generation computers are less expensive, compact, use less electricity and are faster than first generation computers.
5. Supercomputers are extremely powerful and fast computers. They are mostly used for engineering and scientific work that needs high speed calculations like weather forecasting.
Chapter 2
Brain Teasers
2. System software controls the internal workings of computers.
3. Defragmentation is the process of rearranging the data so that disks and drives can work more efficiently.
4. Biometric software helps us identify people based on their unique physical characteristics, like fingerprints, faces, retinas, and so on.
5. General-purpose software helps us perform a variety of tasks.


Introduction to Blockly
The content covered in this chapter is aligned with the following CSTA Standard
● 1B-AP–09 Variables
● 1B-AP–10 Control
This chapter is divided into the following lab sessions
1. Print Statement
2. Operations
3. Variables
4. Comparison Operators
5. Logical Operators
6. Conditions
1. Print Statement
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
● Programming
● Basic blocks in Blockly – Print, number, text
Keywords
● Programming: A set of instructions given to the computer to perform a particular task
● Coding: A term for computer programming
● Programming Language: A language which can be used to give instructions to the computer
● Block-based Coding: Instructions are given to the computer using programming blocks
WEBS at a Glance
Discuss the word “coding” with students

Show the video “Meet Koi and Newt” in the panel
● Say: Today, the session topic is “Print Statement”. What does the word “coding” mean?
● Invite 1 or 2 responses from the students, but don’t give the correct answer yet.
● Say: Let’s watch a video together and come up with a definition of “coding” afterwards.
● Show the video “Meet Koi and Newt” in the panel.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -
As given on Page 1
Block-based Coding As given on Page 1
Text, Number Block
given on Page 1
● Show slides one by one and discuss the blocks shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
● If time permits, present the scenario:
Let’s assume that I (the teacher) am a computer. Consider you want me to give you a pencil. What should your instructions be? The instructions should be in English for now.
■ To conduct this activity smoothly, consider picking one student at a time.
■ Whenever the students give you an instruction, think if it is a clear instruction or not. If not, come up with a counter-question.
■ Let the students think. Do not give away the answer. Here are some possible responses
■ Students: Please, give me a pencil.
■ Teacher: But I (the computer) don’t know where the pencil is.
■ Students: On the table, there is a pencil box. Look inside the pencil box. Locate a pencil and pick up the pencil.
■ Teacher: With what should I pick up the pencil?
■ Students: With your hand
■ Teacher: Yes, but I have two hands. Which one should I use?
■ Students: Use your right hand to pick up the pencil from the pencil box on your table.
■ Teacher: *picks up the chalk and stands still*
■ Students: Now, give it to me.
(Teacher keeps this conversation going until students come up with a clear set of sequential instructions.)
When the students come up with a clear set of instructions, ask them to draw conclusions from this activity.
Here are the conclusions:
1. A computer needs clear instructions to complete a task.
2. The instructions should be in the proper order.
3. The instructions should be given in a language that the computer understands.
4. When you write instructions for the computer, you are coding/programming.
● Conclude: Today, we learned about coding. We were introduced to block-based coding named Blockly.
● Ask the following probing questions: (Conduct the activities only if the time permits)
■ When you are giving instructions to the computer, is it important to write the instruction in a certain order?
Explanation: Yes. If the instructions are not in order, the computer will not be able to perform a task properly. Let’s say we want to add two numbers and print the result. If we give the print command first and the addition command after that, the program will not work.
■ Do you think the computer would understand my instructions if I give instructions in Spanish?
Explanation: No. The computer only understands computer languages. Spanish is a human language which the computer doesn’t understand.
2. Operations
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
● Operators
● Maths blocks
Keywords
● Math Block: All the operator blocks available under Math Block in Blockly
WEBS at a Glance
Revise the concepts from the previous coding class
Show the video “The Zombie Game”
Discuss operators and maths blocks
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the concepts learned in the previous class.
● Show the video, “The Zombie Game” on the panel.
Conclude the concepts Assign homework
● Discuss the concepts shown in the video
● Say: We can perform various mathematical functions using blocks under the Math Block in Blockly.

● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -
CS Concepts
Operator Block
Even/Odd Block
Positive/Negative Block
Prime Numbers
As given on Page 2
As given on Page 4
As given on Page 4
As given on Page 5
● Ask the students to open the Maths with Blockly section.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the Worksheet Solving - Operations activity and complete it in class. Otherwise, assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we have learned Operations. Additionally, we have learned about the various mathematical operators present in the math operator block.
● Assign the following as homework -
■ Complete the Worksheet Solving – Operations at home.
3. Variables
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
● Variables
● Data Types
Keywords
● Variable: A memory location to store a value in a computer
● Data Types: Types of data a variable can hold
WEBS at a Glance
Revise the concepts from the previous coding class
Show the video “Horror Movie” in the panel
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Discuss the homework from the previous session.
● Play the video “Horror Movies” on the panel. Let the student watch the complete video.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -

CS Concepts Explain
Introduction to Variables
Naming a Variable
Updating Values of a Variable
Data Types
As given on Page 5
As given on Page 6
As given on Page 9
As given on Page 11
min
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the activities mentioned under the homework section and complete it in class. Otherwise, assign it as homework.
2 min
Sum-Up
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about variables.
● Assign the following as homework –
1. Create a variable named num1 and store the value 5 in it. Create another variable named num2 and store the value 26 in it. Add both numbers using an operator block and print it.
2. Assign the Q2 from Practice Questions (Page 23, Coding booklet).
4. Comparison Operators
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
● Comparison Operators
Keywords
● Comparison Operators: Compare two values of the same data type, i.e., either numbers or strings
WEBS at a Glance
Revise the learnings from the previous class
Show the video “Super Speed: Fastest Car Mission” in the panel
Discuss comparison operators like - equal, not equal, greater than, less than, etc.
Attempt the activities related to comparison operators
Conclude the concepts
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the Variables learned in the previous class.
● Play the video “Super Speed: Fastest Car Mission” in the panel. Let the student watch the complete video.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -

Equal (=)
Not Equal (≠)
Less than (<)
Less than or equal to (<=)
Greater than (>)
Greater than or equal to (>=)
As given on Page 12
As given on Page 12
As given on Page 12
As given on Page 12
As given on Page 12
As given on Page 13
min
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Coding Assignment
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the activities mentioned under the homework section and complete it in class. Otherwise, assign it as homework.
2 min
Sum-Up
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about Comparison Operators.
● Assign the following as homework –
■ Create two variables, num1 and num2, with values of your choice and check whether the result of their multiplication is greater than 500 or not.
5. Logical Operators
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –
● Logical Operators
Keywords
● Logical Operators: Used to compare two or more conditions, which are formed using the comparison operator
WEBS at a Glance
Revise the learnings from the previous class
Show the video “Logical Operators” in the panel
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the Comparison Operators learned in the previous class.
● Play the video “Logical Operators” on the panel. Let the student watch the complete video.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding booklet -

CS Concepts
AND Operator
OR Operator
NOT Operator
As given on Page 14
As given on Page 15
As given on Page 17
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide in the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment or give it as homework.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
2 min
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about Logical Operators.
● Assign the following as homework –
■ Practise the truth tables at home.
6. Conditions
Objectives
In this session, students will learn about –

● Conditions
Keywords
● Conditions: Used to make decisions
WEBS at a Glance
Revise
● Say: Do you remember what we learned in the previous session?
● Invite responses from some students.
● Revise the Logical Operators learned in the previous class.
● Play the video “Conditions” in the panel. Let the students watch the complete video.
● Explain the following concepts from the coding bookletCS Concepts
If-else Statement
If-do Block
Else-if Block
As given on Page 17
As given on Page 18
As given on Page 19
● Show slides one by one and discuss the concepts shown on the slide on the panel.
● Discuss the Quiz questions given in the Panel.
● Invite answers from as many students as possible.
● Ask the students to complete the Assignment or give it as homework.
● Walk around in the classroom and observe the activity done by the students.
Note
● If time permits, discuss the Q1 from Practice Questions (Page 23, Coding booklet) and complete it in class. Otherwise, assign it as homework.
● Conclude: Today, we have learned about Conditions.
● Assign the following as homework -
1. Assign the Q1 from Practice Questions (Page 23, Coding booklet)
About this teacher manual
This Teacher Manual has been designed to implement Tekie, the storytelling-based Coding and Computer Science program. The manual consists of lesson plans within each chapter that teachers transact within classrooms and computer labs. Each lesson is based on a research-based ‘WEBS’ framework that simplifies pedagogical practices for teachers and enables them to deliver effectively.

‘WEBS’ Framework
W E B S Warm-Up Engage Build Sum-up
Special features
• Sharp Lesson Planning: Each lesson plan focuses on specific sub-learning outcomes within a chapter and are designed for delivery within the stipulated class or lab time.
• Real-life and Application-based Questions: Additional questions that link Computer Science to real-life contexts and assist teachers to develop learners’ conceptual understanding and application skills.
• Support and Detailed Solutions: In-depth solutions for in-class and post-class activities to reinforce learning.

About Uolo
Uolo partners with K12 schools to bring technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 8,000 schools with more than 3 million learners across India, South East Asia, and the Middle East.
