





Academic Authors: Jatinder Kaur, Ayushi Jain, Anuj Gupta, Simran Singh
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh, Sakshi Gupta
Project Lead: Jatinder Kaur
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First published 2023
Second published 2024
Third published 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Tekie Computer Science Python II Web Development II
ISBN: 978-81-979364-7-0
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
Standing at the forefront of the digital and AI revolution, the importance of coding and computational skills has reached unprecedented heights. In today’s professional landscape, whether it is in the fields of medicine, space exploration, education, science, or business, no sector remains untouched by this transformative wave. To thrive in the 21st century, basic computer literacy is no longer sufficient. Learners must evolve into “digital natives” who can fluently read, write, and communicate in the languages that machines and AI comprehend. Recognising this imperative, the National Education Policy of 2020 (NEP 2020) has strongly recommended the integration of coding skills, computational thinking, critical analysis, and problem-solving abilities into the curriculum. Moreover, forward-looking subjects like AI, Data Science, Computer Applications, and IT have been introduced as elective subjects from grade 9 onwards. It would not be surprising if further transformative measures are taken even at the elementary education level.
Inspired by these insights, Uolo has introduced an innovative 360-degree program for a codingfocused computer science curriculum, known as Tekie, spanning grades 1 to 8. The program provides an experiential learning approach, going beyond theoretical knowledge. It not only covers theoretical aspects of computer science and coding, but includes hands-on activities and technology-based projects that enable students to experience computer science first hand. The program includes chapters that provide a deeper immersion in computer science that both learners and teachers may find interesting.
This coding book is a part of the larger Tekie program that also includes a main computer science textbook, covering the basics of computing, the latest technologies, and essential computer tools.
In addition to the textbooks, we provide a digital platform where students can actively engage in practical activities and hands-on learning projects. This platform is designed to enhance the learning process by allowing students to experiment and apply their knowledge in a real-world context.
We have meticulously aligned our activities with the guidelines of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, which emphasises a holistic approach to learning. This approach is aimed at developing critical thinking, logical reasoning, and practical skills among students. By integrating these elements into our coding program, we aim to prepare students for the future, equipping them with the necessary skills to navigate and excel in the ever-evolving world of technology.
Our mission is to cultivate a passion for coding and computer science among young learners, making the learning process enjoyable and impactful. We are confident that this series will not only help students grasp the fundamentals of coding but also inspire them to explore the endless possibilities that technology offers.
We invite you to embark on this exciting journey of learning and discovery. Let’s empower the next generation with the skills and knowledge they need to thrive in a digital world.
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 outlines essential skills, values, dispositions, and learning approaches necessary for students to thrive in the 21st century. This textbook identifies and incorporates these elements throughout its content, activities, and exercises, ensuring students develop coding skills and essential life skills. Referred to as “NEP Tags”, they are defined as follows:



INTEGRATED



CRITICAL THINKING

Art Integration
Bringing creativity and fun into learning by integrating art with computer science and coding
Sports Integration
Using games and sports in daily life to enrich computer-related activities
Holistic & Integrated Learning
Cross-curricular linkages to make learning-experiences more holistic and joyful and meaningful
Critical Thinking
Coding opportunities to apply higher-order skills like algorithmic and computational thinking and problem-solving
HANDS-ON

SDG
Hands-on Activity
Coding opportunities that enable learners to put theoretical knowledge into practice
Sustainable Development Goals
Coding opportunities related to real-world issues and sustainable development

SEL Social Emotional Learning
Developing emotional intelligence and collaboration skills through coding exercises



hands with soap keeps germs away, wearing clean clothes is another way to stay clean. Dirty clothes can collect sweat and germs, so washing them regularly helps keep our skin free of germs and itch.
1 Gather all the clothes you want to wash.
Here are the steps to wash clothes:
2 Sort your clothes by colour. Keep dark-coloured clothes in one pile and white or light-coloured clothes in another pile.
1 Gather all the clothes you want to wash.
3 Check the pockets for tissues, candy wrappers, and other items, and take them out.
2 Sort your clothes by colour. Keep dark-coloured clothes in one pile and white or light-coloured clothes in another pile.
4 Put your clothes in the washing machine, one pile at a time.
3 Check the pockets for tissues, candy wrappers, and other items, and take them out.
Discuss What is the difference between the stage and the backdrop?
4 Put your clothes in the washing machine, one pile at a time.
Discuss What is the difference between the stage and the backdrop?

Discuss: A multi-faceted probing question related to the concept that arouses curiosity
We will be using block-based coding to make computers do things for us.
We will be using block-based coding to make computers do things for us.
Block-based coding is the language in which we use colourful code blocks to tell computers what to do
You must have drawn things on a computer earlier, right?
Block-based coding is the language in which we use colourful code blocks to tell computers what to do
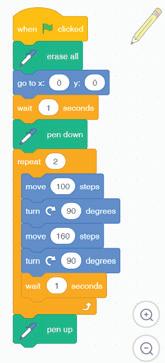
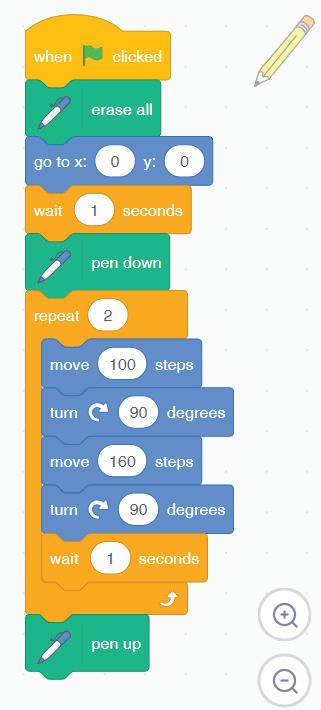
We are going to use a block-based coding platform called Scratch 3.0 to create code for drawing and shapes.
Did You Know: Interesting facts related to the topic
What happens when you run your project?
You must have drawn things on a computer earlier, right?
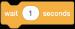
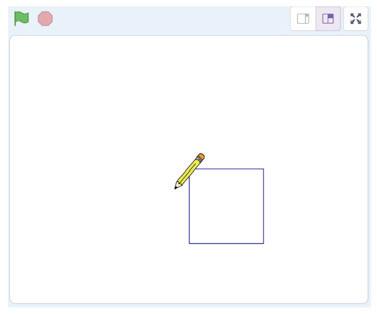
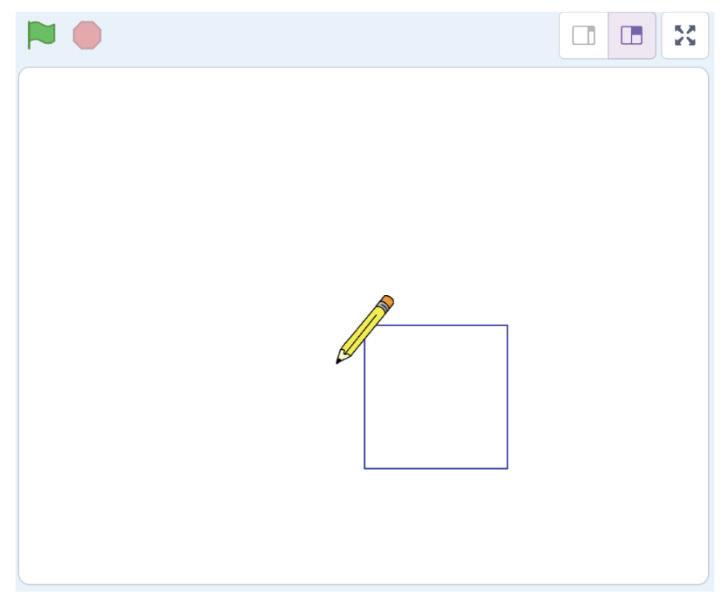
The Pencil sprite moves quickly and draws the rectangle. Steps to add a delay of 1 second:
Identify and label the components based on the clues given below.
1 Click Control category in the blocks panel.
We are going to use a block-based coding platform called drawing and shapes.
Chapter Checkup
Code Snippets: Complete code for each activity with output facilitating hands-on learning and immediate feedback
A Fill in the blanks.
NEP Tags: To show alignment with NEP skills and values
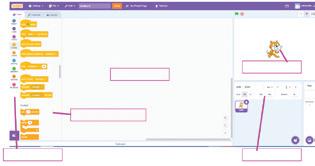

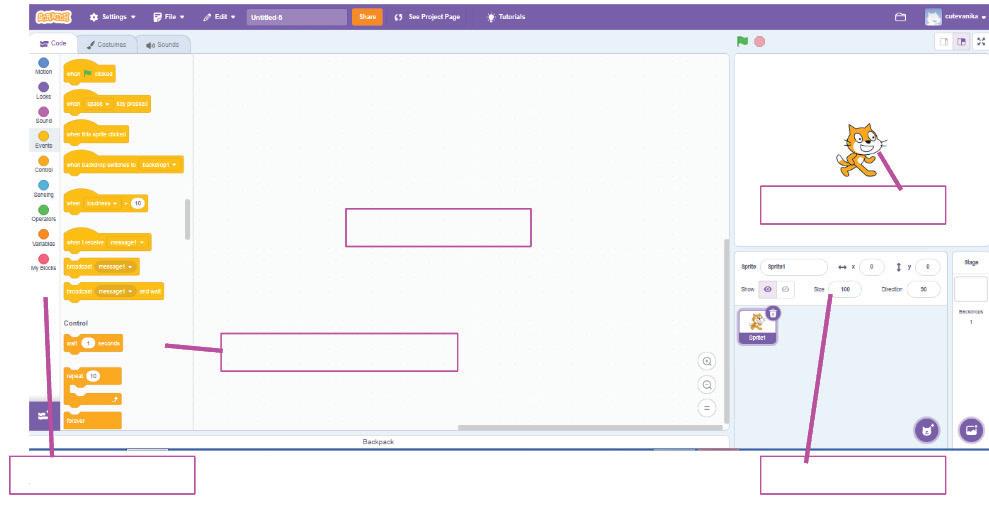
a I am a character in your project.
d I am the area where you drag and join the blocks. Do It Yourself 1A
2 Drag the inside the repeat block.
e I hold all the blocks for a block category.

b I show you the options to change the name, size, and location of a character.
c I hold colour-coded categories of blocks.
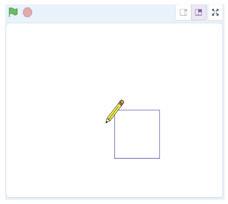

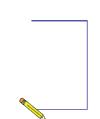
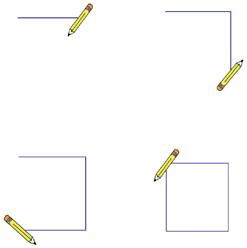


We have completed the script to draw a rectangle. Save this project with the name 'Drawing a Rectangle'.
Challenge
Open Scratch.
2 Drag the block to after the repeat block. Code Click the Go button We have completed the script to draw a rectangle. 'Drawing a Rectangle'.

Hints menu bar untitled backdrop blocks create
Short exercises between the chapter to pause and assess comprehension
1 In Scratch, we use colourful to create our own games, stories, and drawing.
Identify and label the components based on the clues given below.
Go to the Backdrops pane. Click on Choose a Backdrop option and select Blue Sky.
Now, go to the sprites pane. Click on Choose a Sprite option and select the Amon sprite.
2 To create a project in Scratch, you need to click
Coding Challenge
The stage will look like the figure below.

3 By default, the name of the Scratch project is .
Hands-on challenges to encourage and actively engage with the concepts learnt throughout the chapter
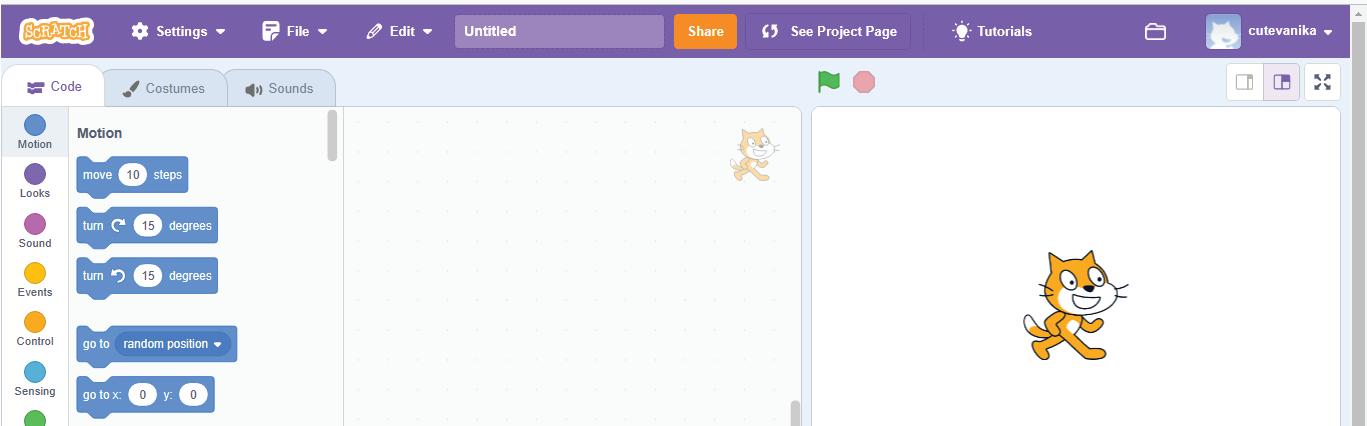
Identify and label the components based on the clues given

4 The purple bar at the top of the Scratch editor is called the .
5 The background of the stage is called the

F Apply your learning.
Chapter Checkup
What are the other platforms you know of that assist in block-based coding? Think and Tell
Think and Tell: Analysis, reflection, and text-to-self connection-based prompts for discussion in class
e I hold all the blocks for a block category. A Fill in the blanks.
show you the options to change the name, size, and location of a character. c I hold colour-coded categories of blocks. d I am the area where you drag and join the blocks.
1 Nia is making a Scratch project where she needs to move the dog from left to right. Which block should she use?
Hints menu bar untitled backdrop blocks create
Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Coding Challenge
Open Scratch.
Apply your learning: Intellectually stimulating questions designed for higher-order thinking and analysis
Test Papers: Designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 In Scratch, we use colourful to create our own games, stories, and drawing.
2 To create a project in Scratch, you need to click
e I hold all the blocks for a block category. A Fill in the blanks.
3 By default, the name of the Scratch project is
4 The purple bar at the top of the Scratch editor is called the

Hints menu bar untitled backdrop blocks create
5 The background of the stage is called the F Apply your learning.
1 In Scratch, we use colourful to create our own games, stories, and drawing.
2 To create a project in Scratch, you need to click
3 By default, the name of the Scratch project is
4 The purple bar at the top of the Scratch editor is called the

1 Nia is making a Scratch project where she needs to move the dog from left to right. Which block should she use?

Test Paper (Based on Chapters 1 to 4)
5 The background of the stage is called the F Apply your learning.
1 Nia is making a Scratch project where she needs to move the dog from left to right. Which block should she use? Chapter Checkup
Test Paper (Based on Chapters 1 to 4)

1 In Scratch, the blocks you put together in the script area are called a
A. Fill in the blanks.

1 In Scratch, the blocks you put together in the script area are called a
2 The is the background of the stage.
2 The is the background of the stage.
1 Basics of Python
• Programming Languages
• Introduction to Python
• Data Types
• Variables
• Simple Calculator
• Dynamic Typing
• Typecasting
• Arithmetic Operators
1
3 Introduction to Web Development ��������������������������������� 31
• Web Development
• HTML
• Basic Structure of an HTML Document
• Basic HTML Terminologies
• CSS
4 Images and Hyperlinks in HTML ����44
• Adding Images
2 Control Statements in Python ����� 16
• Control Statements
• Conditional Statements
• Types of Conditional Statements
• Logical Operators
• Loops
• Jump Statements
• Infinite Loop
• Styling Images
• Flexbox
• Hyperlinks
5 Lists and Tables in HTML �������������� 61
• Adding Lists
• Styling Lists
• Tables Test Paper

Have you ever wondered how the computer games you play or the websites you explore actually work? Well, to design these, we need programming languages. As a computer is an electronic device, it does not understand the language that we speak. To communicate with the computer, we need to create programs in its language, which is known as a programming language.
A computer program is basically a set of instructions given to a computer to perform a task. We need a programming language to write these programs.
Programming languages are classified into two main categories:
Low-level Languages
Low-level languages (LLLs) are machine-friendly languages that are understandable for the machines and harder for humans to understand. They are used to control the hardware of the computer.
Machine language and assembly language are examples of low-level languages. These languages communicate with the computer directly, so no language translation is required. The instructions in the machine language are written using 0s and 1s, which are known as binary digits. On the other hand, symbolic names, also known as mnemonics, are used in assembly language for writing programs.
High-level languages (HLLs) are user-friendly and easier to use than low-level languages. They are used for various tasks like making games, websites, and analysing data.
HLLs make programming simpler because they use words that are human readable like English language words, instead of the hard-toremember 0s and 1s of machine language.
But, before a computer can run an high-level language program, it needs to be translated into low-level language program.








Some common examples of high-level languages are C, C++, Java, and Python. In this book, we will learn Python, which is a very popular programming language these days.
Python is a high-level programming language that is easy to learn and simple to use. It comes with a lot of pre-installed features. This makes it simple to start programming without having to learn a lot of complicated material. It was created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991.
Here are some of the features of Python:
1 Easy to read: Python code is easy to read, just like English.
2 Quick to learn: Python has few keywords, a simple structure, and a clearly defined syntax. This makes it easier to learn and understand, even for beginners.
3 Easy to maintain: Python source code is easy to maintain and update.
4 Interactive execution mode: Python offers script and interactive modes for running programs. The code can be interactively tested and debugged in the interactive mode.
A three-step loop process defines how Python is run in the interactive window:
• The Python interpreter first reads the code entered at the prompt.
• Then it evaluates the code.
• Finally, it prints the outcome and awaits new input.
Python is named after a famous British comedy group called Monty Python.
5 Dynamic typing: Python defines data type dynamically for the objects according to the value assigned. It also supports dynamic data type checking.
6 Portable: Python is a portable language because it can be used on a variety of hardware platforms.
7 Large database support: Python provides interfaces to all major commercial databases.
8 GUI application creation: Python also supports the creation of Graphical User Interface (GUI) applications.
9 Scalable: Python provides better structure and support for larger programs than shell scripting. This makes it scalable.
Like any language, programming languages have their own sets of rules for writing programs. These rules, called syntax rules, tell us how to write programs in that language.
Python is not different; it has its own rules that we must follow when writing code.
If we don’t follow the naming conventions or any syntax of a language, we may get syntax errors when executing our code.

Syntax errors are mistakes that happen when we don’t write our code correctly, such as using incorrect function names or missing quotes and brackets.
In Python, there are numerous built-in functions readily available. A function is a block of code used to perform a specific task. Built-in functions are functions predefined in the Python programming language. These functions can be used without the need to define them yourself.
One of the built-in functions is the print() function.
The print() function displays a value or information in the output.
Syntax: print(“value“)
print("Hello kitty!") Hello kitty!
print(25) 25
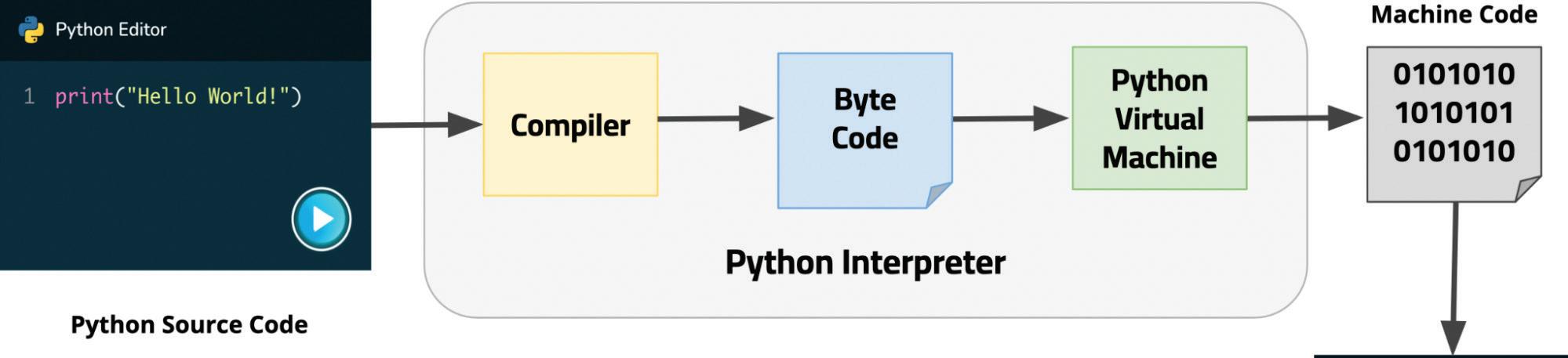
But how does a Python code get executed?
The Python interpreter reads and executes the code line by line. If there are any results (output) for a particular line, it displays them. During execution, the interpreter compiles the code into bytecode, an intermediate language that the Python virtual machine understands. This bytecode is then executed directly, without needing a separate conversion to machine code. If errors occurs during execution, the process stops.
In Python, every value has a data type. Data types define the type of data that a variable can store. There are two categories of data types in Python: Immutable and Mutable.
• Immutable data types are those whose values cannot be changed once declared.
• Mutable data types are those whose values can be changed at any time.


4, 7, 10.5


7, 10

(True, False)

Tuples (4,3.5, ‘b’)


Lists [4, ‘b’, 6.5]
Dictionaries {1: ‘a’, 2: ‘b’}
Sets {2, 5, 7}
Look at the table. It shows the different data types and their descriptions.
Name Type
Integer int
Floating point float
String str
List list
Dictionary dict
Tuple tuple
Set set
Boolean bool
Description
Whole numbers, like 15, 200, and 275.
Numbers with a decimal point, like 4.3, 7.6, and 340.0.
Ordered sequences of characters, like "Python", "hello", "1495", and "SV".
Ordered sequences of objects, like ["hello123", 40, 107.5].
Unordered key-value pairs, like {"key": "value", "language": "Python"}.
Ordered immutable sequences of objects, like (50, "python", 208.7).
Unordered collections of unique objects, like {"apple", "bird"}.
Logical value indicating True or False.
A variable is a reference name given to a location in the computer’s memory. It allows you to store a value in that location and refer to it as needed. Variables can be used to store numbers, strings, lists, and other data types. They are just like a label that can be changed.
5 num

Imagine a memory location as a box and a variable name as a label for that box. You can store a number in the box and label it as “num”. Whenever you need to use the number, you can easily find it by the label on the box. You can even remove the label and put it on another box, or you can replace the number in the box as needed.
In Python, unlike some other programming languages, variable declaration and initialisation occur in a single step. You can simply assign a value to a variable’s name, and it will be automatically created.
Syntax: variable_name = value
Assignment operator (=) is used to assign a value to a variable.
word = "Hi"
number = 5
print(word, number)
5
We can also initialise multiple variables in one line.
Syntax: var1, var2 = value1, value2
word, number = "Hi", 5
print(word, number)
5
There are certain rules we need to follow while naming a variable.
Some rules are:
1 Instead of using spaces, you should use the underscore (_) symbol when naming variables.
and Tell
Will a syntax error prevent the program from running?
2 A variable name must start with a letter or the underscore character.
greeting_message = "Good Evening!"
_number_ = 205
print(greeting_message)
print(_number_)
greeting%message = "Good day!"
print(greeting%message)
SyntaxError: cannot assign to expression here
3 Python is a case-sensitive language, so the variable names are also case-sensitive. Example: num, Num, and NUM are three different variables.
num = 25
Num = 30
print(Num) print(NUM)
4 A variable name can have numbers within it but cannot begin with a number
num_1 = 430 _num2 = 250 print(num_1) print(_num2)
1num = 100 print(1num)
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
As we have case styles for words in English, we have some case styles for naming variables. Below are the case styles you can follow to name variables in Python:
Camel Case
• The first letter of the variable is lowercase.
• Each subsequent word’s first letter is capitalised.
• No spaces or underscores.
• Often used for variable and function names.
Example: “Nameofthecompany” can be written as “nameOfTheCompany”.

As this represents the camel’s hump we call it Camel-Case.
camelCaseExample = "Hello Camel"
print(camelCaseExample)
Snake Case
• All letters are lowercase.
• Words are separated by underscores (_).
• Often used for variable and function names.
Example: "name of the company" in snake-case is written as "name_of_ the_company".
snake_case_example = "Hello Python" print(snake_case_example)
In Python, we can even create a variable with user input. To do so, we use a built-in function named input().
The input() Function
The input() function in Python is used to allow input from the user. It is a built-in function.
Syntax: name = input(“<message to be displayed>“) Code
user_input = input("Enter your favourite colour: ") Enter your favourite colour: blue
Solved Examples
Example 1.1
The side of a square is 80. Use camel case to name a variable for area of the square. Calculate the area. Print the result.
Answer:
side = 80
areaOfSquare = side * side print("The area is: ", areaOfSquare)
Example 1.2
The area is: 6400
Given is the average temperatures of different places. Store them in different variables. The temperature has increased by 0.5 in the afternoon. Display the updated temperature of all the places.
Place
Zo Hills
Met Town Bay Area Temperature 20 25 26
Answer:
Zo_Hills=20
Met_Town=25
Bay_Area=26
print("Place","Updated Temperature")
print("Zo Hills", Zo_Hills+0.5)
print("Met Town",Met_Town+0.5)
print("Bay Area",Bay_Area+0.5)

Let’s build a simple calculator project while learning the concepts in the chapter. We will be building this project by dividing it into various sub-tasks.
Task 1: Take two numbers and an operator as input from the user.
Let’s create three variables and use the input() function to allow input from the user.
Code
num1 = input("Enter first number: ")
operator = input("Enter operator (+, -, *, /): ")
num2 = input("Enter second number: ")
Now, before we execute the project, do you remember what Dynamic Typing is?
Dynamic typing is a feature of Python where the data type of a variable is not determined until runtime. This means that you can assign a variable to a value of any type, and the variable will automatically take on that type.
The type() Function
In Python, we use the type() function to check the dynamic data type assigned to a variable. It is a built-in function that returns the type of an object. The object can be a variable, a value, or an expression.
Syntax: type(object_name)

Simple Calculator
Task 2: Check the data type of user input.
num1 = input("Enter first number: ")
operator = input("Enter operator (+, -, *, /): ")
num2 = input("Enter second number: ")
print(type(num1))
print(type(num2))
print(type(operator))
Output
Enter first number: 4
Enter operator (+, -, *, /): +
Enter second number: 6
<class ‘str’>
<class ‘str’>
<class ‘str’>
The input() function always returns a string value, even if it takes a number, operator, or any other value as input. Since we have created variables with user input, all three variables are of string type.
1 Use camel case and snake case to name a variable to represent the scores of a match. Camel case: Snake case:
2 What will be the output of the given code? Code Output
a = 7
print(type(a))
b = 3.0
print(type(b))
c = a + b
print(c)
print(type(c))
Typecasting is conversion of the data type of a value into another data type.
We can typecast a data type using typecasting functions: 1 int() 2 float() 3 string() 4 bool()
The int() Function
The int() function is used to typecast the value of a variable into an integer.
It converts the following data type into an integer:
1 Float by removing the decimal point and everything after it.
2 String only if string represents a number.
3 Boolean by converting True to 1 and False to 0.
Syntax: int(variable_name) Code
str_to_int = int("8")
bool_to_int = int(True)
print(str_to_int, type(str_to_int))
print(bool_to_int, type(bool_to_int))
number=int("Hello")
The float() Function
If you try to convert a string type variable to int type, you will get an error.
ValueError: invalid literal for int() with base 10: ‘Hello’
The float() function is used to typecast the value of a variable into float.
It converts the following data type into float:
1 Integer by adding a decimal followed by a zero.
2 String only if the string represents a float or an integer.
Syntax: float(variable_name)
a=float(10)
b=float("10.2")
c=float("Hello")
The str() Function
ValueError: could not convert string to float: ‘Hello’
The str() function is used to typecast the value of a variable into a string. It converts all the data types including float, integer, and boolean into a string.
Syntax: str(variable_name)

num_1 = str(5)
num_2 = str(7.2)
print(num_1 , type(num_1))
print(num_2, type(num_2))
The bool() Function
5 <class ‘str’>
7.2 <class ‘str’>
The bool() function is used to typecast the value of a variable into boolean. It converts the following data type into boolean:
1 Integer and prints False if the value of the variable is 0, otherwise prints True
2 String and prints False if the string is empty, otherwise prints True.
Syntax: bool(variable_name) Code
a=bool(0)
b=bool(1)
c=bool("")
d=bool("Python")
print(a,b,c,d)
Simple Calculator
Task 3: Typecast the numbers that the user inputs into floats.
num1 = float(input("Enter first number: "))
num2 = float(input("Enter second number: "))
Next, we need to learn about operators we can use for various mathematical operations on numbers that the user inputs.
Arithmetic operators are the operators used with the integer or float values to perform mathematical operations on them.
There are 7 arithmetic operators in Python:
Write a program to get the right answers to the questions given below.
a = 23 b = 13
a. Addition of a and b.
b. Multiplication of a and b.
c. Division of a and b.
d. Base a to the power b.
e. Modulus of a%b
Answer:
a,b=23,13
Think and Tell
Can we multiply a string by a float value in Python?
Code Output
Addition of a and b is: 36
print("Addition of a and b is:",a+b)
print("Multiplication of a and b is:",a*b)
print("a divided by b is:",a/b)
print("Base a to the power b is:",a**b)
print("Remainder, when a is divided by b, is:",a%b)
Python follows the PEDMAS rule, which stands for:
1 Parentheses (P)
3 Division (D)
5 Addition (A)
Multiplication of a and b is: 299
a divided by b is: 1.7692307692307692
Base a to the power b is: 504036361936467383
Remainder, when a is divided by b, is: 10
2 Exponents (E)
4 Multiplication (M)
6 Subtraction (S)
This rule tells us the order in which operations are performed in an expression.
Operations within parentheses are performed first, followed by exponents, multiplication and division from left to right, and finally addition and subtraction from left to right.
Example:
9 + 7 * (8 - 4) / 2 - 3**2 (First, the brackets are solved.)
= 9 + 7 * 4 / 2 - 3**2 (Then, the exponent is solved.)
= 9 + 7 * 4 / 2 - 9 (Then, multiplication is solved.)
= 9 + 28 / 2 - 9 (Then, division is solved.)
= 9 + 14 - 9 (Then, addition is solved.)
= 23 - 9 (Finally, subtraction is solved.)
= 14

Simple Calculator
Task 4: Apply all four basic arithmetic operations ( +, - , *, / ) to the numbers the user inputs.
num1 = float(input("Enter first number: "))
num2 = float(input("Enter second number: "))
add = num1+num2
sub = num1-num2
mul = num1*num2
div = num1/num2
print("Addition: ", add)
print("Subtraction: ", sub)
print("Multiplication: ", mul)
print("Division: ", div)
1 Write the output of the following expressions:
Enter first number: 6
Enter second number: 8
Addition: 14.0
Subtraction: -2.0
Multiplication: 48.0
Division: 0.75
2 Write the output of the following code: value = True + False + True print(value)
A Fill in the blanks.
1 A allows you to store a value on that location and refer to it as needed.
2 A variable name must start with a or the character.
3 are mistakes in following rules to write the code.
4 means we can assign a variable to a value of any type, and the variable will automatically take on that type.
5 functions are the predefined functions in the Python programming language.
B Tick () the correct option.
1 Python is a language because it can be used on a variety of hardware platforms.
a Usable b Scalable c Portable d Changeable
2 Which of the following data types in Python is mutable?
a String b Integer c List d Tuple
3 Which operator is used to assign a value to a variable?
a Logical b Assignment c Arithmetic d Comparison
4 Which of the following is a valid variable name?
a Hello_Name b %Name-Hello c Hello%Name d Hello-Name
5 The function in Python is used to allow input from the user. a print() b input() c type() d int()
C Who am I?
1 I am a type of data that can be changed after being created.
2 I am a variable naming style where words are separated by underscores.
3 I am the process of converting one data type into another.
4 I am an acronym that represents the order of operations in mathematical expressions in Python.
5 I am the function used for converting a value into a floating-point number.
D Write T for True and F for False.
1 The exponentiation operator has the highest precedence in any expression.
2 Arithmetic operators can perform operations on the integer type of data only.
3 Variable names in Python are case-sensitive.
4 Dynamic typing is a feature of Python where the data type of a variable is determined at compile time.
5 The type() function returns the data type of a variable.
E Answer the following questions.
1 What are the two main categories of data types in Python?
2 Write the output of the following code in the given space.
x = 5.7
y = int(x) print(y)

3 What is the difference between mutable and immutable data types in Python?
4 What is the full form of PEDMAS?
5 In Python, what does the input() function return after reading user input from the console?
F Apply your learning.
1 Write a Python program that takes two numbers as input from the user and displays their average.
2 Write a program to keep track of a user’s expenses. Choose appropriate variable names to store the user’s name, total expenses, and the category of expenses (e.g., “Food,” “Transportation”).
Display a message like “Jia spent `50 on Food.”
3 Write a Python program to calculate the area of a circle.
4 Write a program to find the total expenditure on the stationery you purchased from a shop:
5 Write a program to take a temperature in Fahrenheit as input from a user and convert it to Celsius. Then print the result.
Control statements in Python are used to control the flow of execution of the program. They allow you to make decisions, repeat code, and skip code.
There are three main types of control statements in Python:
• Conditional Statements
• Loops
• Jump Statements
Let us learn about these statements in detail.
Suppose you are going on a 3-day, 2-night class trip to Shimla during your summer holiday. What type of clothes will you pack?
You will check the weather in Shimla and pack your clothes accordingly. Since you are visiting Shimla during the summer, you should pack light woollen clothes, as it will be pleasant during the day and a little cold at night.
Similarly, we often find ourselves in situations where we need to make some decisions according to the given conditions. This skill we have is called decision-making ability
However, computers are machines. They cannot make decisions on their own. We need to make programs for them so that they can give the appropriate results according to the given condition. This can be achieved with the help of conditional statements in Python.
Conditional statements allow us to instruct the computer to check for a specific situation and make it do something if that situation occurs.
A condition is set to establish criteria that require some form of comparison to be performed. Therefore, to define a condition, one must also understand the comparison operators.
Comparison operators are the symbols or expressions that allow us to compare two values or variables. They compare the value on the left-hand side with the value on the right-hand side and return either ‘True’ or ‘False’ as the result of the comparison.
These operators are also known as Relational Operators.




Below are the six comparison operators in Python.
Operator Name
== Equal to Returns True if both operands are equal
!= Not Equal to Returns True if operands are not equal
> Greater than Returns True if the left operand is greater than the right
< Less than Returns True if the left operand is less than the right
>= Greater than or equal to Returns True if the left operand is greater than or equal to the right
<= Less than or equal to Returns True if the left operand is less than or equal to the right
Let us look at the following example to understand the usage of comparison operators.
Johnny needs to determine whether the number of balls in box A is equal to, less than, or greater than the number of balls in box B. Box A contains 453 balls, and box B contains 454 balls. Using comparison operators, print whether the situations are ‘True’ or ‘False’.
Answer: Code
box_A=453
box_B=454
cond1=box_A==box_B
print("Are balls in box A equal to box B? ", cond1)
cond2=box_A<box_B
print("Are balls in box A less than box B? ", cond2)
cond3=box_A>box_B
print("Are balls in box A more than box B?", cond3)

What is the difference between the greater than operator (>) and the greater than or equal to operator (>=)? Think and Tell
Are balls in box A equal to box B? False
Are balls in box A less than box B? True
Are balls in box A more than box B? False
Joe always likes to help his parents with the household chores. His mother has given him ` 350 to buy some groceries from a nearby shop. He plans to purchase tomatoes for ` 50, onions for ` 60, and a jar of peanut butter for ` 100.
1 Using comparison operators, print ‘True’ or ‘False’ to help him determine whether the money his mother gave him will be enough to buy the planned items or not.
2 Joe intends to buy 2 more jars of peanut butter with the remaining money. Assist him in deciding if he has enough money to do so.
Indentation refers to a fixed number of spaces (or sometimes tabs) added at the beginning of each line of code. These spaces create a visual hierarchy in your program, just like paragraphs in a story or chapters in a book. Indentation helps Python understand which lines of code belong together and should be executed as a single unit.
Interpreter view of Code
Code block 1 begins
Statement 1
Code block 2 begins
Statement 2
Statement 3
Code block 2 ends
Code block 1 ends
What happens if you don’t indent your code properly?
In Python, we have three types of conditional statements that allow us to make decisions in our programs. These include:
• if Statement
• if… else Statement
• if… elif… else Ladder
The if Statement
The ‘if’ statement is used to check a specific condition. If the condition following the ‘if’ keyword evaluates to True, the code block after the ‘if’ condition will be executed; otherwise, the code block will be skipped.
Syntax: if condition1:
# Statement to execute if condition1 is true
The colon (:) sign is used after the condition with the if statement. The statements inside the if statement should be properly indented.
age = 21
if age >= 18: print("Eligible to vote.")
The if… else Statement
Eligible to vote.
Flowchart
The ‘if… else’ statement checks a condition, allowing us to instruct the computer on what to do in both cases, whether the statement is true or false.
If the condition following the ‘if’ keyword evaluates to True, the code block after the if condition will be executed; otherwise, the code block after the ‘else’ keyword will be executed.

Syntax: if condition_1:
#Statements to execute if condition_1 is True else:
#Statements to execute if condition_1 is False
Flowchart
age = 21 if age >= 18:
print("Eligible to vote.") else:
print("Too young to vote!") Eligible to vote.
Sometimes, we need to evaluate multiple conditions. In such cases, we use the ‘elif’ statement, which stands for ‘else if’. It allows us to check multiple conditions in sequence, and Python checks each condition until one of them is True.
Syntax: if condition_1:
Statement_1 if condition1 is True elif condition_2:
Statement_2 if condition2 is True .. .. else:
Final_Statement if no condition is True
print("x is positive") elif x == 0:
print("x is zero") else:
print("x is negative") x is positive
If condition_1 becomes True, Statement_1 will be executed, otherwise, the interpreter moves on to condition_2 and if it becomes true then it will execute Statement_2.
This process continues until a True condition is found, otherwise the Final_Statement inside ‘else’ statement will be executed if none of the conditions are True. Code Output x = 10 if x > 0:
Let us update the project we created in the previous chapter using comparison operators and conditionals.
Simple Calculator
num1 = float(input("Enter first number: "))
operator = input("Enter operator (+, -, *, /): ")
num2 = float(input("Enter second number: ")) if operator == "+":
result = num1 + num2
elif operator == "-":
result = num1 - num2 elif operator == "*":
result = num1 * num2
elif operator == "/": if num2 == 0:
result = "Division by zero is not allowed." else:
result = num1 / num2 else:
result = "Invalid operator." print("Result:",result)
Enter first number: 6
Enter operator (+, -, *, /): /
Enter second number: 8
Result: 0.75
1 Write a program to check if a number is greater than 100 or not.
2 Write a program to print the largest number among three inputs.
Logical operators allow us to combine multiple conditions in one. There are three important logical operators in Python: ‘and’, ‘or’ and ‘not.’

The ‘and’ operator allows us to combine two conditional statements and returns True only if both statements are true.
In all other cases, it returns False. If Statement 1 is True and Statement 2 is True, then the result is True. If either Statement 1 or Statement 2 (or both) is False, then the result is False.
Syntax: Statement 1 and Statement 2
Following is the truth table for the and operator:
print(3<7 and 8==8)
print(6>2 and 9==8)
The ‘or’ operator allows us to combine two conditional statements and returns True if either of the statements is true.
It returns False only if both statements are false. If Statement 1 is True or Statement 2 is True (or both), then the result is True. If both Statement 1 and Statement 2 are False, then the result is False.
Syntax: Statement 1 or Statement 2
Following is the truth table for the or operator:
print(4+5>8 or 9!=7) print(6>7 or 8==9.0)
What is the difference between the ‘and’ and the ‘or’ operator?
In Python, we have the flexibility to create complex conditional statements by using multiple ‘and’ and ‘or’ operators. When dealing with multiple conditional statements involving both ‘and’ and ‘or’, it is important to know that ‘and’ takes precedence over ‘or’.
This means that conditions with ‘and’ are evaluated first, followed by the conditions with ‘or’.
Statement 1 or Statement 2 and Statement 3
#First we solve the ‘and’ operator, and then the ‘or’
print(2>3 or 3==3 and 1>0) True
Let us look at how we got the output for the given code:
2 > 3 or 3 == 3 and 1 > 0
False or True and True #Solve and first
False or True #Solve or True
Solved Example
Write a program to help David pick students for his project.
He has two rules:
1 Students must have at least 60% in their school grades.
2 They need a score of at least 7 in their analytical tests.
Run the program to check if Ray and Joe meet David’s conditions.
Ray has 65% in school and 8.5 in tests.
Joe has 55% in school and 8 in tests.
Answer:
Code
ray_academics=65
ray_analytical=8.5
print("Ray’s scores:")
print("Academics:", ray_academics)
print("Analytical test:", ray_analytical)
ray_condition = ray_academics>=60 and ray_analytical>=7
print("Does Ray meet David’s criteria?-", ray_condition)
joe_academics=55
joe_analytical=8
print("Joe’s scores:")
print("Academics:", joe_academics)
print("Analytical test:", joe_analytical)
joe_condition = joe_academics>=60 and joe_analytical>=7
print("Does Joe meet David’s criteria?-", joe_condition)
Output
Ray’s scores:
Academics: 65%
Analytical test: 8.5
Does Ray meet David’s criteria?- True Joe’s scores: Academics: 55%
Analytical test: 8
Does Joe meet David’s criteria?- False

The not operator reverses the result of the condition. True will be reversed to False, and vice versa. For example, not (True) will return False.
When we write computer programs, there are times when we need to execute the same piece of code again and again. In that case, we have to write the same code again and again.
This is not an efficient way of programming. This can be improved by using ‘loops’.
Loops allow us to execute a set of instructions as long as a certain condition is True. Once that condition becomes False, the loop stops. This process is also known as iteration.
Python provides mainly two types of loops, the while loop and the for loop.
A ‘for’ loop is a way of telling a computer to do something over and over again. It can be used to repeat a block of code a certain number of times, or to go through a list of things one by one.
A ‘for’ loop is also known as a counting loop. We use a variable to create the ‘for’ loop called the loop variable.
Syntax: for variable in sequence: # Statements to be executed
Flowchart
If no more item to iterate for item in sequence:
item in sequence?
Next item from sequence
Code to be executed
There are two ways to create a ‘for’ loop:
1 Using the range() function.
2 Using the in operator.
Using range() Function
The range() function in Python returns a sequence of numbers, starting from 0 by default, and increments by 1 by default, and stops before a specified number.
The range() function can be used in a ‘for’ loop to iterate over a sequence of numbers.
Syntax: for loop_variable in range(start, stop, step):
<statements>
#the loop runs from start to stop-1 where:
start is the starting number (optional, default is 0) stop is the ending number (not inclusive) step is the increment (optional, default is 1)
for num in range(0, 5):
Here, the ‘for’ loop starts at 0 and counts up to 4, increasing by 1 each time. Note that if the increment is by 1, there is no need to specify it.
The ‘in’ operator is a membership operator that checks if an item is a member of a sequence or not. It can be used in a ‘for’ loop to iterate over the items of a string, list, tuple, or dictionary.
Syntax: for loop_variable in string_variable: <statements>
word = ‘bumfuzzle’ for letter in word: print(letter)
Here, the loop iterates over the letters of the string word, starting with the first letter ‘b’ and ending with the last letter ‘e’.
The ‘while’ loop repeats a set of instructions as long as a condition is True. It is also known as a conditional loop. It verifies the condition before executing the loop.

Flowchart
Statement 1
Statement 2 Increment/decrement loop variable
Here, the ‘while’ loop starts with the value of i being 1. As long as i is less than 6, the loop will continue. In each iteration of the loop, the value of i is printed and then incremented by 1. The loop will stop when i is equal to 6.
for versus while Loop
The ‘for’ loop and the ‘while’ loop are both control flow statements in Python that are used to repeat a block of code. However, they have different usage scenarios.
The ‘for’ loop is used to iterate over a sequence of items, such as a list, tuple, or string, when the number of times you want to iterate is known.
The ‘while’ loop is used to repeat a block of code when the number of times you want to iterate is not known or when the number of iterations depends on the results of the loop.
Loops run the same set of code for a defined number of times or until the test condition becomes False. However, sometimes we might wish to stop the loop even before the test condition becomes False or skip an iteration.
This is where we need Jump statements.
Jump statements allow you to skip code or terminate a loop. We have two jump statements in Python:
• break statement
• continue statement
The break Statement
The ‘break’ statement is used to terminate the loop.
Syntax: while expression: if condition: break
#breaks out of the loop
#executes statement outside the loop
word = input(‘Enter a word: ‘) for letter in word: if letter in ‘aeiou’: print(‘Vowel found!’) break
Enter a word: apple Vowel found!
Here, the loop checks for all the letters in the word entered by a user for vowels. If the letter is a vowel, the ‘break’ statement will run, and the loop will terminate. Otherwise, the loop will continue to run until it reaches the end of the word.
The continue Statement
The ‘continue’ statement skips the current iteration of the loop and continues with the next iteration.
Syntax: while expression:
Statement_1 if condition: continue
#skips next set of statements and starts with next loop iteration Statement_2
for num in range(1, 11): if num == 4 or num== 6 or num==8: #when num = 5, it is False
Here, the loop starts counting from 1 and increments the value of num by 1 in each iteration. When the value of num is equal to 4, 6, or 8, the ‘continue’ statement is executed, which skips the printing of the number and goes to the next iteration of the loop.
In a program, if a loop is executed over and over again without stopping, it is called an ‘infinite’ loop. This can happen if the condition that controls the loop is always true, or if the loop is never terminated by a ‘break’ statement.
Code
while True: print("This is an infinite loop!")
Here, the loop will print the message “This is an infinite loop!” repeatedly, until the program is terminated by the user. An ‘infinite’ loop can lead to the program becoming unresponsive.
Infinite loops can be useful when you want to create a program that runs continuously, such as a server or a chatbot.

To prevent an ‘infinite’ loop, it is important to carefully consider the condition that controls the loop. Make sure that the condition is only true under the circumstances you want. You should also use ‘break’ statements to terminate loops when you no longer need them to run.
counter = 0
while counter < 5: # This loop will run 5 times.
print("Loop iteration:", counter)
counter += 1
Output
Loop iteration: 0
Loop iteration: 1
Loop iteration: 2
Loop iteration: 3
Loop iteration: 4
Here, the loop will run five times because the counter variable starts at 0 and increments by 1 each time the loop runs. The loop will continue as long as the counter is less than or equal to 5. Once the counter reaches 5, the condition is no longer true, and the loop exits.
1 Write a program to generate and display the first 10 numbers of the Fibonacci sequence.
The Fibonacci sequence is a series of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers. If the sequence starts with 0 and 1, and the first 10 numbers will be:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55
2 Write a program to calculate the sum of the digits of a given number. Take the number from the user as input. For example, if the input number is 4453, the sum of the digits will be 4 + 4 + 5 + 3 = 16
FizzBuzz
Write a program that prints the numbers from 1 to 100. However, for multiples of 3, the program should print “Fizz” instead of the number. For multiples of 5, the program should print “Buzz” instead of the number. For numbers that are multiples of both 3 and 5, the program should print “FizzBuzz” instead of the number.
A Fill in the blanks.
1 In programming, statements are used to execute different blocks of code based on specific conditions.
2 operators are used to compare two values or expressions and return a Boolean result.
3 The operator checks if two values are equal.
4 A statement is used to specify a code block that executes when none of the preceding conditions in the ‘if’ and ‘elif’ statements are True.
5 In a program, if a loop is executed over and over again without stopping, it is called an loop.
B Tick () the correct option.
1 What is the output of the given code?
x = 5
if x > 10:
print("x is greater than 10") elif x == 10:
print("x is equal to 10") else:
print("x is less than 10")
a x is greater than 10
c x is less than 10
2 What is the output of the given code? i = 1 while i <= 5: print(i) i += 1
b x is equal to 10
d An error occurs
of the above

3 What is the output of the given code? for i in range(1, 6): if i == 3: continue print(i)
a 1 2 3 4 5
c 1 2 4
4 What is the output of the given code? while True: print("Infinite Loop") break
a Infinite Loop
b 1 2 4 5
d None of the above
b No output
c An error occurs d Loop runs infinitely
C Who am I?
1 I am a type of operator that allows you to compare two values or variables.
2 There is no effect of indentation on the statements inside the if statement.
3 I am a type of statement that allows you to skip code or terminate a loop.
4 I can combine two conditions together to test.
5 I repeat a block of code as long as a certain condition is true.
D Write T for True and F for False.
1 The ‘for’ loop is used to iterate over a sequence of elements.
2 The logical operator ‘and’ returns True if at least one of the conditions it combines is True.
3 The ‘continue’ statement in Python skips the current iteration of a loop and continues with the next iteration.
4 An infinite loop is formed if the condition that controls the loop is always true.
E Answer the following questions.
1 What is the purpose of the ‘elif’ statement in Python’s conditional statements? Give an example.
2 Define the ‘and’ and ‘or’ logical operators and give an example of how they can be used in a conditional statement.
3 How does a ‘for’ loop differ from a ‘while’ loop in Python? Provide an example of when you might use a ‘for’ loop.
4 Write the syntax of the while loop.
F Apply your learning.
1 Write a program to display a multiplication table for a number the user inputs. Ask the user for the number of terms to display and print the result.
2 Write a program check if a number is prime or not.
3 Create a program that calculates the factorial of a positive integer entered by the user using a loop. A factorial of a number ‘n’ is the product of all positive integers from 1 to ‘n’.
4 Write a program to implement a word guessing game where players guess one letter at a time until they solve the word or run out of attempts.

5 Ben, the school’s football team captain, wants to find players who are tall and strong for the defenders, and short and nippy for the attackers. He needs defenders to be over 6 foot tall and weighing over 68 kilos. For attackers, he wants players under 5 foot tall and weighing less than 57 kilos. Write a program to help Ben find the right players.


Do you explore the internet for various tasks, like searching for information, doing online shopping, playing online games, and so on? Which websites do you visit often, and how do you think these websites are created?
Let us understand this with the help of an example.
Imagine you are creating a flyer for a school event. The flyer needs a title, some text to describe the event, and maybe a picture. You also need to decide where to place the title, text, and picture on the flyer. After that, you may think of giving some style to these objects as well.
This is similar to designing a web page. The process of creating web pages and then linking them together to form a website is called web development Web development involves multiple tasks, such as:
• Designing the layout and appearance of the website
• Writing the code that makes the website work
• Adding content to the website, such as text, images, and videos
There are two main types of programming languages used in web development:
HTML (HyperText Markup Language): HTML is the markup language used for creating websites. It is also used to structure the content of a website. For example, HTML tags can be used to tell the computer whether a piece of text is a heading, a paragraph, or a list.
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): CSS is used to style the content of a website. For example, CSS can be used to change the font size, colour, and alignment of text.
The first website, CERN, was created in 1989 and is still alive today.
HTML stands for ‘HyperText Markup Language’. It is used to develop web applications. It tells a web browser how to display content on a website. In HTML, ‘Hypertext’ means the text that is more than static text. It can be interactive and linked to other pages or resources.
Markup are the tags we use in HTML to structure and format the text on a web page. These tags are the instructions that tell the browser how and where to display the content on a page.
Some common features of HTML are:
1 Easy to learn: HTML is an easy language to learn, even for beginners. It is made up of tags that tell the browser what to do.
2 Platform independent: HTML is platform independent, which means that it can be used to create web pages that can be viewed on any device, regardless of the operating system or web browser.
3 Media support: HTML can be used to display images, videos, and audio on web pages.
HTML is a markup language. It defines the structure and content of a web page but does not involve complex calculations or logic like programming languages such as Python and Java.
4 Hypertext: HTML supports hypertext, which means that text on a web page can be linked to other web pages or resources.
5 Semantic structure: HTML5 introduced many new semantic elements, which can be used to improve the accessibility of web pages.
6 Case insensitive: HTML elements and attribute names are generally case-insensitive.
An HTML document is structured into two main parts: the head and the body. The head contains information about the document, such as the title.
The body contains the content of the web page, such as text, images, and videos. The body is displayed in the browser window.
The basic structure of an HTML document looks like this:
1 The <!DOCTYPE html> declaration is part of HTML5 and is used to indicate that you are using the HTML5 standard.
2 The <html> and </html> tags enclose the entire document.
3 The <head> and </head> tags enclose the head section of the document.
4 The <title> and </title> tags enclose the title of the document.
5 The <body> and </body> tags enclose the body section of the document.
A web browser is a software application that allows you to access and view web pages.
There are many web browsers available, such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, and Apple Safari. All web browsers work in a similar way, but they may have different features and user interfaces.
HTML Document Basic Structure
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head>
<title> Document Title</title> </head> <body> <!-- Content goes here --> </body> </html>

They allow us to browse websites, watch videos, listen to music, and play games.
Some of the basic components of a web browser are as follows:
• Address bar: The address bar is where you type the URL of the website you want to visit.
• Navigation buttons: The navigation buttons allow you to move forward, back, and refresh the current web page.
• Tabs: Tabs allow you to have multiple web pages open at the same time.
Tabs Address bar
Navigation buttons Bookmarks icon
• Bookmarks: Bookmarks allow you to save the URLs of your favourite websites so that you can easily access them later.
• History: The history feature allows you to view a list of the websites you have recently visited.
A tag tells the browser how to display the content that follows it. Tags are enclosed in angle brackets (< and >).
For example, <h1> is the opening tag for heading and </h1> is the closing tag for heading.
To create an HTML document, we have the following tags:
<!----> Used to insert comments in the HTML code. <!--comment–->
<p> It is used as the paragraph tag that is used to add a paragraph.
Heading tags HTML heading tags are used to add headings and sub-headings to the content you want to display on a web page. HTML has six levels of heading from <h1> to <h6>.
<div> This tag is used in HTML to make divisions of content in the web page such as text, images, and header.
<p>content</p>
<h1>Most important heading</h1> <h2>content</h2> <h3>content</h3> <h4>content</h4> <h5>content</h5> <h6>Least important heading</h6>
<div>content</div>
<br> Inserts a single line break Should be added where the line break is needed.
<b> Converts the text into bold <b>text</b>
<i> Converts the text into italics <i>text</i>
<u> Underlines the text <u>text</u>
<hr> Inserts a horizontal line. <hr> <em> Emphasises text and displays it in italics. <em>text</em> <strong> Represents strongly emphasised text and displays it in bold. <strong>text</strong>
<sub> Represents text as a subscript. <sub>text</sub> <sup> Represents text as a superscript. <sup>text</sup> <section> Defines the grouping of content in a document. <section>text</section>
<article> Represents a self-contained composition. <article>text</article>
An element is a combination of a tag and its content. For example, the <h1> element is a heading element.
There are mainly two types of HTML elements:
1 Container elements: Container elements are HTML elements that can contain other elements or text within them. They have both an opening tag and a closing tag to enclose their content.
Opening Tag Content
<h1> This is my first HTML document. </h1> Element Closing Tag
Examples: <html></html>, <head></head>, <body></body>.
2 Empty elements: Empty elements, also known as void elements or self-closing elements, do not contain any content between opening and closing tags. They are self-contained and do not require a closing tag.
Examples: <br>, <hr>, <img>.
It is used to define the characteristic of an HTML element. An attribute is always placed in the opening tag of an element and generally provides additional styling (an attribute) to the element.

Project: Saving Endangered Species
<h1> <font color= ''red''> This is my first HTML document. </font> </h1>
Attribute
Let us build a simple web page project on the topic “Saving Endangered Species” while learning the concepts in the chapter.
We will be building this project by dividing it into several tasks.
Task 1: Create a web page and name it ‘Saving Endangered Species’. Add the heading ‘Saving Endangered Species’ and then add an introduction for it.

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Saving Endangered Species</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Saving Endangered Species</h1>
<div>
<p>From majestic animals to tiny insects, every creature plays a vital role in the ecosystem. Thus, protecting these creatures helps preserve biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem flexibility. <br><br>It is also crucial for maintaining the <i><b> balance in nature. </b></i> <br><br> Conservation efforts, such as <u>habitat preservation,</u><u> anti-poaching measures,</u> and <u>breeding programs </u>are vital for protecting endangered species. <br> <br>By saving them, we will ensure that future generations benefit from a rich and diverse ecosystem.</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
From majestic animals to tiny insects, every creature plays a vital role in the ecosystem. Thus, protecting these creatures helps preserve biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem flexibility.
It is also crucial for maintaining the balance in nature.
Conservation efforts, such as habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and breeding programs are vital for protecting endangered species.
By saving them, we will ensure that future generations benefit from a rich and diverse ecosystem.
1 Match the following terms with their descriptions.
Column A Column B
<h1> Is a language for structuring web content.
<!-- --> Converts the text into bold.
<div> Is used for inserting comments in HTML code.
HTML Is used to create a division within a web page.
<b> Defines the main heading of a web page.
2 Identify the error in the following element examples:
a <titl>My Web Page</title>
b <h1>Welcome to My Page<h1>
c <p>This is a paragraph</h>
d Plants give us O<sub> 2 </sup>.
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is a language used to style HTML elements. CSS can be used to change the appearance of HTML elements, such as their font, colour, and size.
Some key features of CSS include:
1 Selectivity: CSS can be used to select specific HTML elements to style such as changing colours, styling fonts, spacing elements, and resizing them.
2 Consistency: You can use the same styles for many pages on a website to make them look similar.
3 Cascading: CSS styles are applied in cascading order. This means that the most specific style will be applied to an element, even if there are other styles that are more general.
4 Responsive design: CSS can be used to create responsive web pages that work on all devices, from desktop computers to smartphones.
5 Animations and transitions: CSS can be used to add animations and transitions to web pages, which can make them more visually appealing and engaging.
There are three ways to add style to an HTML document:
1 Inline CSS: Inline CSS is used to style a single HTML element. To add inline CSS, you use the style attribute. For example, the following code will make the <h1> element red and 20 pixels in size:
<h1 style="color: red; font-size: 20px;">This is a heading</h1> This is a heading.
2 Internal CSS: Internal CSS is used to style all the elements on a single HTML page. To add internal CSS, you use the <style> tag. The <style> tag should be placed in the <head> section of your HTML document. For example, the following code will make all <h1> elements on the page red and 20 pixels in size:

<html> <head> <style> h1 { color: red; font-size: 20px; }
</style> </head> <body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<h1>This is another heading</h1> </body> </html>
This is a heading.
3 External CSS: External CSS is used to style all the elements on all of the pages of a website. To add external CSS, you use the <link> tag. The <link> tag should be placed in the <head> section of your HTML document. For example, the following code will link to an external CSS file called style.css:
<html> <head> <link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css"> </head> <body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1> </body> </html>
This is a heading.
The rel attribute specifies that the linked file is a CSS stylesheet and the href attribute specifies the path of the stylesheet file. The style.css file would contain the following CSS:
Code
h1 { color: red; font-size: 20px; }
If you only need to style a single element, then use inline CSS.
Which method of CSS will you use to style a web page?
If you need to style all the elements on a single page, then use internal CSS.
If you need to style all the elements on all the pages in a website, then use external CSS.
CSS classes are a way to group similar HTML elements together so that you can style them all at once. This can save you a lot of time and effort, especially if you have a lot of similar elements on your page.
To create a CSS class, you add the class attribute to an HTML element and assign it a unique name.
For example, the following code would create a CSS class called my-class: <p class="my-class">This is a paragraph</p>
Once you have created a CSS class, you can style it using the . (dot) character and the class name. For example, the following CSS code will make all paragraphs with the my-class text red and 20 pixels in size: .my-class { color: red; font-size: 20px; }
Selectors are used to select the HTML elements that you want to style, and properties are used to define the styles that you want to apply to those elements.
Some of the most common selectors in HTML include:
1 Element selectors: Select elements by their tag name, such as h1, p, or img.
2 Class selectors: Select elements by their CSS class.
3 ID selectors: Select elements by their ID.
4 Combination selectors: Combine multiple selectors to target specific elements.
There are many CSS properties, including:
CSS Property Purpose Syntax
color Sets the colour of the text.
font-family Sets the font family of the text.
color:blue
font-family:cambria font-size Sets the size of the text.
font-size:x-small
Note: x-small, small, medium, large, x-large, xx-large can also be used as values.
font-weight Sets the weight or thickness of the text.
font-weight: bold
Note: lighter, or any number can also be used
text-decoration Formats the text.
text-align Aligns the text.
text-decoration: underline
Note: line-through, overline can be used.
text-align: left
Note: right, center, justify can be used.
background-color Sets the background colour of the element. background-color:red background-image Sets background images for an element, you can set one or more images. background-image:url("https://example. com/image.png")
border To set the border around the element. border: solid
border-color Sets the colour of the border of an element. border-color:blue

CSS Property Purpose
border-radius Round the corners of the outer border edges of an element.
padding To set the space around the content of the element.
border-radius:30px
padding:40px
Note: Any number can be added according to the use.
margin To set the space around the element itself. margin:20px
Note: Any number can be added according to the use.
You can also use multiple attributes of a property in one declaration. For example, you can use the background property to set the background colour, image, size, and position of a div element all at once.
Here is an example: div { background: blue url(‘image.jpg’) no-repeat center/cover; }
In this example:
• blue sets the background colour to blue.
What are the benefits of having classes in an HTML document?
• url(‘image.jpg’) sets the background image to the image named image.jpg.
• no-repeat prevents the image from repeating.
• center/cover positions and sizes the image so that it covers the entire div element.
How are selectors and properties different?
You can apply the background property to any HTML element, not just to div elements. For example, you can apply it to the <body> element to set the background of your entire web page.
Project: Saving Endangered Species
Task 2: Use internal CSS to make the project colourful and attractive.
1 Inside the head element, create a style element and:
a Add a style for body element.
b Create a content class for styling internal content.
Code
<html> <head> <title>Saving Endangered Species</title> <style> body { background-color: peachpuff;

color: black; text-align: center; } .content{ color: darkred; text-align: left; } </style> </head>
2 Update the body element by applying the content style in content div.
Code
<body> <h1>Saving Endangered Species</h1>
<div class=content>
<p>From majestic animals to tiny insects, every creature plays a vital role in the ecosystem. Thus, protecting these creatures helps preserve biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem flexibility. <br><br>It is also crucial for maintaining the <i><b> balance in nature. </b></i> <br><br> Conservation efforts, such as <u>habitat preservation,</u><u> anti-poaching measures,</u> and <u>breeding programs </u>are vital for protecting endangered species. <br> <br>By saving them, we will ensure that future generations benefit from a rich and diverse ecosystem. </p> </div> </body> </html>

1 Create a web page with the following content:
a. A title: My Dream Vacation
b. A paragraph describing my dream vacation
c. Set the font and background colour.

1 Fill in the blanks.
a If you want to style all elements on a single HTML page, you can use CSS.
b CSS classes are used to group HTML elements together.
c The shorthand for setting multiple background-related properties in one declaration is the property.
d To set the background colour of an element, you can use the property.
e External stylesheets are linked to HTML documents using the element.
2 Write T for true and F for false.
a Internal CSS is added to the <body> section of an HTML document.
b You can create a CSS class by adding the class attribute to an HTML element.
c The no-repeat property of CSS prevents the image from repeating.
d External stylesheets are included directly within an HTML document, using the <style> element.
e CSS can be used to change the colour and size of HTML elements.
A Fill in the blanks. Hints head web applications angle body external
1 Web development involves designing, building, and maintaining
2 The basic structure of an HTML document consists of the and the .
3 HTML tags are enclosed in brackets.
4 You can apply CSS using three main methods: inline styles, internal stylesheets, and stylesheets.
B Tick () the correct option.
1 Which type of CSS would you suggest to style a single HTML element?
a Internal CSS
c Inline CSS
2 Which HTML tag is used to create a single line break?
b External CSS
d Outline CSS
a <newline> b <line-break>
3 Which of the following is an example of a CSS class?
a .my-class
c <class="my-class">
b my-class
d my.class
4 Which of the following HTML elements is used to create a link to the stylesheets?
a <p>
c <h1>
b <img>
d <link>
5 Which of the following CSS properties is used to set the colour of the border of an element?
a border-color b color
c bordercolor d border
C Who am I?
1 I define the characteristics of an HTML element and am placed in the opening tag.
2 I make divisions of content on a web page, like sections of text, images, headers, and more.
3 I am a CSS property to set the space around the element itself.
4 I convert text into an italic format in HTML.
5 I am a CSS property used to set the background of an element.
D Write T for True or F for False.
1 A web browser is a software application that allows you to access and view web pages.
2 CSS-created web pages don’t work on all devices.
3 You can use the . (dot) character and the class name to style a CSS class.
4 Element selectors select elements by their tag name, such as h1, p, or img.
5 Class Selectors select elements using their ID.
E Answer the following questions.
1 What is web development? Name two programming languages used to develop and style web pages.

2 What is the basic structure of an HTML document?
3 What is CSS, and what are some of its features?
4 What are CSS classes? Give an example.
5 What are selectors and properties in CSS? Provide examples of each.
F Apply your learning.
1 In CSS, how would you make all paragraphs with the class “my-class” blue in colour and 30 pixels in size?
2 When you use the HTML tag <div>, what purpose does it serve?
3 You have a paragraph of text that you want to make bold. How would you do this using HTML tags?
4 Create a CSS class named “highlight” that changes the text colour to yellow and applies the ‘back.png’ images as background of the web page.

Just like pictures make a book more interesting, images make websites more exciting and interesting. Images are used for many purposes, such as providing visual support to written content, conveying feelings, telling stories, providing clarity of purpose, and making the content easy to remember.
Climate change is making the protection of endangered species increasingly challenging The best way to protect endangered species is to prevent their decline and deterioration
LEARN MORE .
Let us learn to add and style images.
In an HTML document, you can add images using the following methods:
1 Using the <img> element: The most common way to add images is by using the <img> element. You need to specify the source (URL) of the image, using the 'src' attribute.
Here is an example:
<img src="image.jpg" alt="A beautiful landscape">
In this example, ‘image.jpg’ is the source file for the image, and “A beautiful landscape” is the alternative text (alt text) that appears if the image cannot be displayed.
2 Using background images: You can set background images for HTML elements (like <div> or the entire <body>), using CSS.
Note the following points while adding images in a web page:
1 You can acquire the image to be inserted into the web page from any resource. It can be a file downloaded and saved on your computer, or you can provide a direct link to an online resource.
2 If the image is on your computer, both the image and your web page should be saved in the same folder or location. In this case, you can reference the image file like this:
<img src="image.jpg">
3 If the image and the HTML file are in different folders, then you should give the full path or relative path to the image in the code. The corrected example should look like this:
<img src="C:\images\image.jpg"> or using a relative path like: <img src="../images/image.jpg">.
4 You can provide the URL of the image directly if it is hosted on the internet: <img src="https://www.example.com/image.jpg">.
5 In case you are using the Tekie platform for developing your project, then you will get the required resources for the respective projects on the platform.
Here is an example of setting a background image for a <div> element:
<style> .my-div { background-image: url(‘background.jpg’); background-size: cover; /* Adjust the size as needed */ } </style>
<div class="my-div"> <!-- Content of the div goes here --> </div>
You can include comments in HTML documents using <!--text--> and in CSS documents using /*--text--*/ tags.
In this example, ‘background.jpg’ is the source file for the background image and ‘background-size: cover;’ ensures that the image covers the entire div.
In the last chapter, we created a project called Saving Endangered Species. In this chapter, we will add an image of wild animals to the project.
Task 3: Adding an image of wild animals
Continue adding the code in your main HTML document at the respective places.
<body>
<h1>Saving Endangered Species</h1> <img src="wild_animals.jpg" alt="wild animals" width="100" height="100"> <div class=content>

Task 4: Adding a background image and changing the text colour Code
<html> <head>
<title>Saving Endangered Species</title> <style> body { background-image: url("forest_background.jpg"); color: white; text-align: center; } .content{ text-align: left; } </style> </head>
The remaining code will remain same as given in the <body> part in the last chapter.


We can style an image in two ways:
1 Using a style attribute: To use a style attribute, specify the CSS properties you want to apply to the image, separated by semicolons.
For example, the following code makes the image 100% wide and auto height: <img src="https://example.com/image.jpg" style="width: 100%; height: auto;">
2 Using a class: To use CSS to style an image, you can either create a CSS class or ID and apply it to the image using the class or id attribute, or you can use an inline CSS block.
Here is an example of how to use a CSS class to style an image: <img src="https://example.com/image.jpg" class="image-style"> .image-style { width: 100%; height: auto; margin: 10px; }
You can use CSS to style images in many ways.
Here are some of the most common CSS properties used to style images:
• width: Specifies the width of the image.
• height: Specifies the height of the image.
• margin: Specifies the amount of space around the image.
• padding: Specifies the amount of space between the border of the image and its contents.
• border: Specifies the border around the image.
• border-radius: Specifies the radius of the corners of the image border.
• box-shadow: Specifies a shadow around the image.
• opacity: Specifies the transparency of the image.
• filter: Specifies a filter to apply to the image.
Project: Saving Endangered Species
Task 5: Adding an image and styling it using a class Code
<html> <head>
<title>Saving Endangered Species</title> <style>
body { background-image: url("wild_background.jpg"); color: white; text-align: center; } .img-style{ border: 5px solid orangered; border-radius: 15px; width: 120px; height: 80px; margin: 10px; } .content{ text-align: left; margin: 10px; }
</style> </head> <body>
<h1>Saving Endangered Species</h1> <img src="wild_animals.png" align="left" class="img-style">
<img src="birds.jpg" align=left class="img-style"> <!-- The remaining code will be same-->
Output


1 Match the columns.
Column A Column B
It is an attribute for specifying the source of an image Used to provide alternative text for images
It is an HTML element for adding images Using a class It is a purpose of the alt attribute margin
It is a way to apply CSS styles directly to an HTML element src It specifies the amount of space around the image <img>
2 Fill in the blanks.
a In an HTML document, you can add images using the element.
b The attribute of an <img> tag is used to style an image using a class.
c The property specifies the height of the image.
d To set background images for HTML elements, you use the property.
e The property can make the corners of an image round.
Imagine that a container element is like a box and the flex items are like the objects inside the box.
A flexbox is a CSS layout module that allows you to easily create flexible and responsive layouts by arranging the objects inside the box in a flexible and responsive way.
You can line up the objects in a row or a column, and you can control how much space each object takes up. You can also control how the objects are aligned inside the box, such as horizontally centred or vertically centred.
Items
A flexbox works by dividing a container element into flex items. These items can be any type of an HTML element, such as divs, spans, and images. Flex items can be resized and rearranged to fit the available space in the container. Here is a simple example of how to use a flexbox:
<div class="container">
<div class="item">Item 1</div>
<div class="item">Item 2</div>
<div class="item">Item 3</div> </div>
.container { display: flex; }
.item { flex: 1; }
Share some of the applications or websites where you notice the use of flexboxes.
This code creates a container element with three flex items. The flex items are arranged horizontally and take up equal amounts of space.
You can also use a flexbox to control the alignment of flex items.
For example, the following code vertically aligns the flex items in the centre of the container: .container { display: flex; align-items: center;
}
You can also use a flexbox to control the direction of flex items.
For example, the following code arranges the flex items vertically instead of horizontally: .container { display: flex; flex-direction: column;
} Properties of a Parent (Flex Container)
display: flex Makes the parent container flexible.
flex-direction: row | column Allows flex items of the container to be displayed row-wise or column-wise.
flex-wrap: wrap | nowrap Allows flex items to wrap onto more than one line.
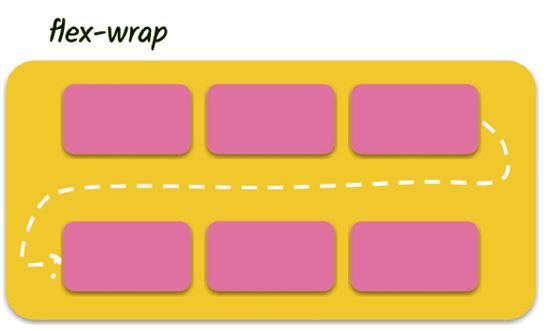
justify-content: centre | flex-start | flex-end Allows items to align along the main axis.
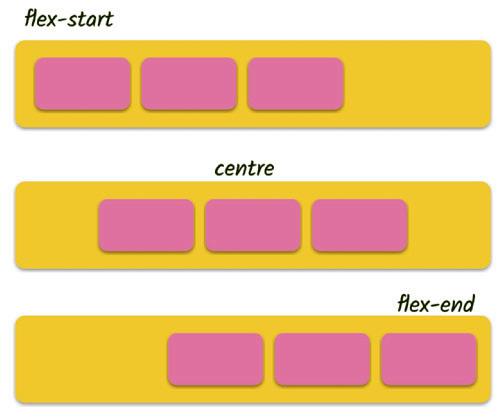

Property Purpose
align-items: centre | flex-start | flex-end Allows multiple lines of items to align along the cross axis.
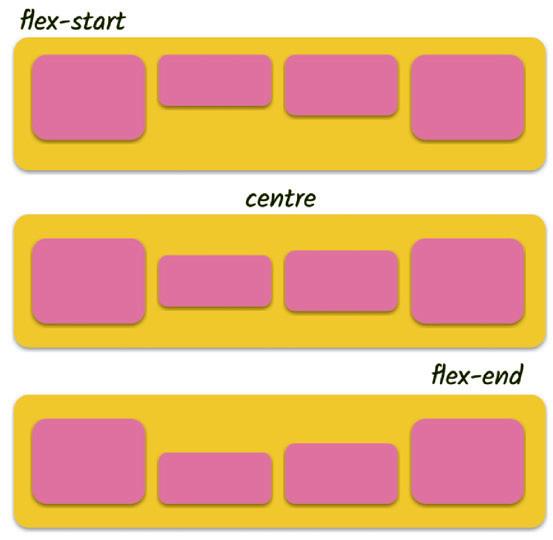
align-content: centre | flex-start | flex-end Allows items to align along the cross axis in a single line.

Properties of a Child (Flex Item)
Property Purpose
order allows the change in order of items without altering the source order.
flex-grow allows an item to fill up the available free space.
flex-shrink allows an item to shrink if there is not enough free space available.
flex-basis defines the size of an item before space is distributed. flex shorthand for flex-grow + flex-shrink + flex-basis. flex-self can align a single item within the flex container.
Project: Saving Endangered Species
Task 6: Use a flexbox to place items within a web page.
1 Replace the body element with the header class and update as shown to add a flex container for the header part of your web page.
2 Update the content class by adding a flex container.
Code <html> <head> <title>Saving Endangered Species</title> <style> .header{ display: flex; background-image: url"(wild_background.jpg");
justify-content: center; color: white; border-radius: 5px; width: 100%; } .content{ display:flex; text-align: left; margin: 10px; }
3 Add the new classes for cards.
a .card-holder – a flex container for flex items
b .cards – flex items
c .cards-img – for images in flex items
d .cards:hover – to add a hover feature
Code
.card-holder { display: flex; justify-content: space-around; flex-wrap: wrap; } .cards { width: 16%; color: white; background-color: #2c3350; padding: 10px; border-radius: 5px; margin: 0.35%; font-size: 14px; text-align: center; } .cards-img { position: relative; width: 90px; height: 65px; border-radius: 5px; } .cards:hover { background-color: #646f9a; box-shadow: 5px 5px 5px 5px #d3d3d3; } </style> </head>

4 Add the header division.
<body>
<div class=header>
<h1>Saving Endangered Species</h1>
<img src="wild_animal.png" alt="rocket" width="100" height="100"> </div>
5 Add a sub-heading for the article cards.
<div class=content>
<p>From majestic animals to tiny insects, every creature plays a vital role in the ecosystem. Thus, protecting these creatures helps preserve biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem flexibility. <br><br>It is also crucial for maintaining the <i><b> balance in nature. </b></i> <br><br> Conservation efforts, such as <u>habitat preservation,</u><u> anti-poaching measures,</u> and <u>breeding programs </u>are vital for protecting endangered species. <br> <br>By saving them, we will ensure that future generations benefit from a rich and diverse ecosystem. </p>
</div>
<h3> Links of articles on some endangered species in India:</h3>
6 Add the card-holder and cards div tags.
7 Add the image and text for the first article card.
<div class=card-holder>
<div class=cards>
<img src="tiger.jpg" class=cards-img>
<p>The Bengal Tiger</p> </div>
8 Duplicate the cards div of the first card.
9 Change the details of the second card.
<div class=cards>
<img src="lion.jpg" class=cards-img>
<p>Asiatic Lion</p> </div>
10 Repeat the process to create remaining cards.
<div class=cards>
<img src="bustard.jpg" class=cards-img>
<p>Great Indian Bustard</p> </div>
<div class=cards>
<img src="heron.jpg" class=cards-img>
<p>White-bellied Heron</p>
</div> </div> </body> </html>
When done, run your code to test it.
Output

Hyperlinks, also known as links, allow users to navigate from one web page to another by clicking a text or an image link.
To create a hyperlink in HTML, use the <a> tag. The <a> tag has the required href attribute, which specifies the URL of the linked page. The text or the image that you want to be the link should be between the opening and closing <a> tags.

For example, the following HTML code creates a hyperlink to the Uolo home page:
Code
<a href="https://www.uolo.com">Uolo</a>
Uolo
Output
When a user clicks the word "Uolo", the web browser opens the Uolo home page.
You can also use the <a> tag to create links to other resources, such as images, PDFs, and other types of files.
Let us hyperlink the article cards for the Saving Endangered Species project.
Project: Saving Endangered Species
Task 7: Hyperlink the card images.
Use an anchor tag to add a link to the card image. Don’t forget to close the tag.
Code
<div class=cards>
<a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bengal_tiger"
<img src="tiger.jpg" class=cards-img>
</a>
<div class=cards>
Code
<a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Asiatic_lion">
<img src="lion.jpg" class=cards-img>
</a>
Repeat the process for the remaining cards.
<div class=cards>
<a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Indian_bustard">
<img src="bustard.jpg" class=cards-img>
</a>
<p>Great Indian Bustard</p>
</div>
<div class=cards>
<a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/White-bellied_heron">
<img src="heron.jpg" class=cards-img>
</a>
<p>White-bellied Heron</p>
</div>
</div> </body> </html> Output



Click a card to check if the link is opening or not.
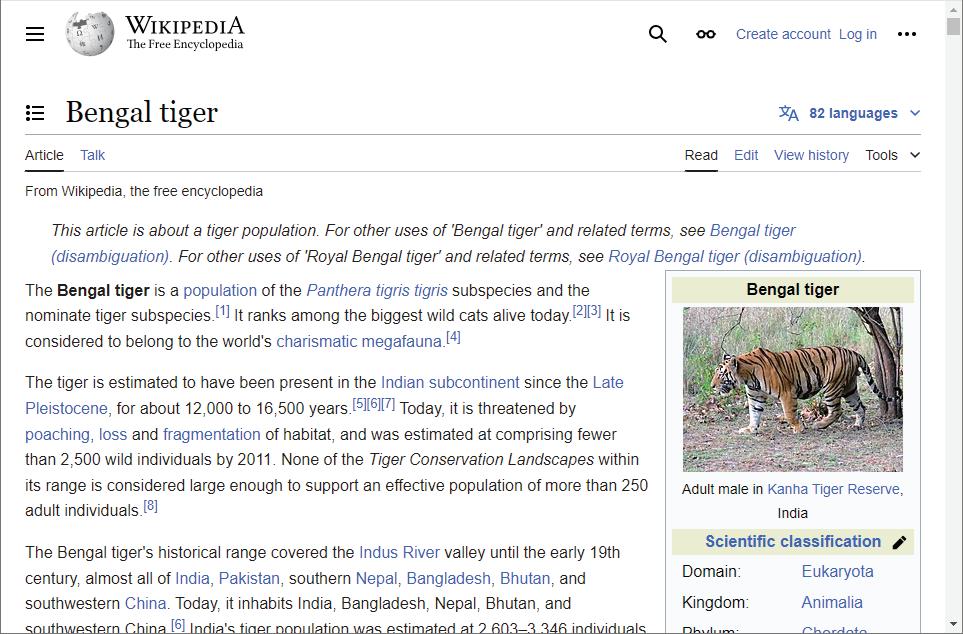
Consider any four famous personalities who have made significant contribution in the field of space. Make a web page about them using flexboxes. Include a picture of them, a short story about their lives, and a link to another web page with more information about them.
A Fill in the blanks.
1 The attribute is used to display the alternative text describing the image, if the image does not load on the web page.
2 The property allows flex items to wrap onto more than one line.
3 The tag is used to create a hyperlink.
4 The property allows multiple lines of items to align along the cross axis.
5 The flex container can change the width, height, and order of the elements.
B Tick () the correct option.
1 How do you create a hyperlink to an external website, using the <a> tag in HTML?
a <a href="#external-website">External Website</a>
b <a href="http://www.example.com">Visit Website</a>
c <a src="http://www.example.com">Open Link</a>
d <a link="http://www.example.com">Go There</a>
2 Which CSS property is used to create rounded images?
a border-radius
c round-image
b image-shape
d Image-border
3 What is the main purpose of flexboxes in web development?
a To add images to a web page
c To change the font style on a web page
b To create flexible layouts and arrange elements flexibly
d To add animations to web pages
4 How can you set a background image for an HTML <div> element, using CSS?
a Using the <background> element
c Using the src attribute
b Using the background-image property
d Using the alt attribute
5 Which CSS property is used to make a parent container flexible in flexbox?
a display: flex b flex-grow
c flex-direction d align-items
C Who am I?
1 I have attributes like ‘src’ and ‘alt’ to specify the image source and the alternative text.
2 I ensure that a background image covers the entire HTML element.
3 I create a shadow around an image, using CSS.

4 I am a CSS property to specify a filter to apply to the image.
5 I control the alignment of items in a flex container.
D Write T for True and F for False.
1 In CSS, the ‘border-radius’ property is used to make images transparent.
2 You can style images using CSS in two ways—using the style attribute and using classes.
3 Hyperlinks can be created using text only, and images cannot be linked to other web pages.
4 The ‘margin’ property in CSS determines the space around an image.
5 The ‘flex-direction’ property determines whether flex items are arranged horizontally or vertically.
E Answer the following questions.
1 Identify and correct the error in the following HTML code for inserting an image: </img src="image.jpg" alt="A beautiful landscape">
2 Which CSS property is used to specify the amount of space between the border of the image and its contents?
3 Correct the CSS code that sets the background image for a <div> with class "my-div" and ensures that it covers the entire div: .my-div { background: url(‘background.jpg’); background-size: cover; }
4 Find the error in the following CSS code that arranges the flex items vertically in a flexbox: .container { display: flex; flex-direction: row; }
5 Explain the purpose of the ‘flex-grow’ property in a CSS flexbox.
F Apply your learning.
1 Given the following HTML and CSS code, what will be the background colour of the div when you hover over it?
<div class="hover-button">Hover Me</div> .hover-button:hover { background-color: yellow; }
2 If you have a web page with three images styled using the class ‘image-style’ and the following CSS code, what will be the output?
<img src="image1.jpg" class="image-style">
<img src="image2.jpg" class="image-style">
<img src="image3.jpg" class="image-style">
.image-style { width: 80%; margin: 10px; }
3 What is the output of the following HTML code?
<img src="https://example.com/image.png" alt="Image of my cat">
What error will you get if you try to display an image that is not found?
What error will you get if you forget to add the alt attribute to an image tag?
4 Consider the following HTML code:
<div class="flex-container">
<img src="https://example.com/image.png" alt="Image of my cat"> <a href="https://example.com/cat-breeds">Read more about cat breeds</a> </div>
What output will you get if you try to display the above HTML code without using a flexbox?

Lists in HTML are similar to a shopping list or a to-do list. They help us organise items in a neat and easy-to-read way on a webpage.
In this chapter, we will learn about lists and tables in HTML.
In HTML, we can create three types of lists:
• Ordered (numbered)
• Unordered (bulleted)
• Description
Ordered Lists
Ordered lists, also known as numbered lists, are used to list items in a specific order. They are defined using the <ol> tag.
Each list item in an ordered list is defined using the <li> tag.
Here is an example of an ordered list:
<ol>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ol>
Item 1
Item 2
Item 3
You can use the type attribute to specify the type of numbering for your ordered list. The default numbering type is numbers, but you can also use uppercase letters, lowercase letters, or Roman numerals.
<ol type="I">
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ol>
Item 1
Item 2
Item 3
Here are some examples of different numbering schemes:
type=" 1"
type=" A"
type=" a"
The list items will be numbered with numbers (default).
The list items will be numbered with uppercase letters.
The list items will be numbered with lowercase letters. type=" I"
The list items will be numbered with uppercase Roman numbers. type=" i"
The list items will be numbered with lowercase Roman numbers.
Unordered lists, also known as bulleted lists, are used to list items in no particular order. They are defined using the <ul> tag.
Each list item on an unordered list is defined using the <li> tag.
Here is an example of an unordered list:
<ul>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
Item 1
Item 2
Item 3
You can use the style attribute to specify the bullet style for your unordered list. The default bullet style is a disc, but you can also use squares, circles, or other symbols. Code
<ul style="list-style-type: square;">
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
Item 1
Item 2
Item 3
Here are some examples of different bullet point styles:
Bullet Style Description
disc
Change the list item marker to a bullet. circle
Change the list item marker to a circle. square
Change the list item marker to a square. none
No list item marker will be displayed
Description lists are used to display a list of terms and their definitions. They are defined using the <dl> tag.

Each term in a description list is defined using the <dt> tag, and each definition is defined using the <dd> tag. Here is an example of a description list:
<dl>
<dt>Term 1</dt>
<dd>Definition 1</dd>
<dt>Term 2</dt>
<dd>Definition 2</dd>
<dt>Term 3</dt>
<dd>Definition 3</dd>
</dl>
Term 1
Definition 1
Term 2
Definition 2
Term 3
Definition 3
Styling lists means improving the appearance of the list items, such as the bullet style, numbering, padding, and margin. There are two main ways to style HTML lists:
1 Using the style attribute
2 Using CSS classes
The style attribute can be used to specify the appearance of individual list items or entire lists.
To use the style attribute, simply add it to the opening tag of the list or list item and specify the desired CSS properties.
Styling a List Item: We can style a list item in a list using the style attribute.
For example, the following HTML code styles a list item to have grey background colour:
<ul>
<li style="background-color: #ccc;">Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul> Item 1 Item 2 Item 3
Styling a List: We can also use the style attribute to style entire lists.
For example, the following HTML code defines an unordered list with square bullet points and 10px padding and margin:
<ul style="list-style-type: square; padding:10px; margin:10px;">
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
Item 2
Item 3
</ul> Item 1
Here are some of the most common CSS properties that can be used to style lists:
• List-style-type: Specifies the style of the bullet points or numbers in a list.
• List-style-position: Specifies whether the bullet points or numbers are placed inside or outside of the list items.
• List-style-image: Specifies an image to use as the bullet points in a list.
• Padding: Specifies the amount of padding around the list items.
• Margin: Specifies the amount of margin around the list items.
• Font-size: Specifies the font size of the text in the list items.
• Font-colour: Specifies the font colour of the text in the list items.
• Border: Specifies a border around the list items.
CSS classes can be used to style lists in a more reusable way.
To use a CSS class to style a list, simply add the class name to the opening tag of the list or list item.
For example, the following HTML code adds the CSS class list-style-square to an unordered list:
<ul class="list-style-square">
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
Then, you can use CSS to style the list items with the list-style-square class.
For example, the following CSS will give all list items with the list-style-square class square bullet points and 10px padding and margin:
.list-style-square { list-style-type: square; padding: 10px; margin: 10px;
}
How are the list style and type different?
If you need to style only a few individual list items or lists, then using the style attribute is fine.
However, if you need to style a lot of lists or you need to reuse the same list style throughout your webpage, then it is better to use CSS classes.
Task 8: Create and style an unordered list of fun facts about wild animals.
To do so, we first need to identify where the list will appear and what flex container do we need.
We need four flex containers to place our content on the webpage as shown.


1
Create an unordered list of fun facts about wild animals in sub-holder2 after the cards’ code.
<div class=sub-holder2>
<div>
<h3> Facts About Wild Animals </h3>
<ul>
<li>Snow leopards are rarely seen due to their excellent camouflage and elusive nature.</li>
<li>Hawksbill turtles are critically endangered sea turtles which are vital for coral reef health.</li>
<li>Mountain gorillas share 98% of their DNA with humans and exhibit complex social behaviours.</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
2 Update and add div for containers for header, holder and sub-holder1.
<body>
<div class=header>
<h1>Saving Endangered Species </h1>
<img src="wild_animals.jpg" alt="wild animals" width="100" height="100"> </div>
<div class=holder>
<div class=sub-holder1>
<div>
<p>From majestic animals to tiny insects, every creature plays a vital role in the ecosystem. Thus, protecting these creatures helps preserve biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem flexibility. <br><br>It is also crucial for maintaining the <i><b> balance in nature. </b></i> <br><br> Conservation efforts, such as <u>habitat preservation,</u><u> anti-poaching measures,</u> and <u>breeding programs </u>are vital for protecting endangered species. <br> <br>By saving them, we will ensure that future generations benefit from a rich and diverse ecosystem.
</p>
</div>
3 Create style classes for containers and the list inside the style tag.
.holder { display: flex; justify-content: space-around;
}
.sub-holder1 { width: 65%;
box-shadow: 0 0 20px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.15); padding: 5px;
} .sub-holder2 { width: 25%; } ul{
box-shadow: 0 0 20px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.15);
} </style>


Just like the bookmarks we use in our books to quickly jump to a specific page, HTML bookmarks help us jump to a specific part of a webpage on the internet.
To add a bookmark in an HTML document, follow these steps:
1 Choose the element you want to bookmark. This could be a heading, a paragraph, an image, or any other HTML element.
2 Add an id attribute to the element. The id attribute must be unique on the page.
<h2 id="mybookmark">This is my bookmark</h2>
3 Create a link to the bookmark. To do this, use the <a> element and the 'href' attribute. The href attribute should point to the id of the element you want to bookmark.
<a href="#mybookmark">Click here to go to my bookmark</a>
Project: Saving Endangered Species
Task 9: Add bookmarks
1 Add information about Documentaries on endangered species after the cards’ details.
<h3>Documentaries on the endangered species in India: </h3>
<p><b>Tiger - Spy in the Jungle (2008):</b> This award-winning documentary uses innovative spy cameras to capture the secretive lives of Bengal tigers in India's Bandhavgarh National Park.<br><br>
<b>The Lions of Gir (2001):</b> This documentary examines the struggles of the Asiatic lion population after being hunted nearly to extinction. India's Gir National Park is the last home of these majestic creatures.<br><br>
<b>In Search of Godawan (2018):</b> This Indian documentary, though not solely focused on the Great Indian Bustard, features them as one of the many endangered species struggling in the Godavari River basin. It might offer valuable insights into the challenges faced by the Great Indian Bustard and other wildlife in the region.<br><br>
<b> My Garden of a Thousand Birds (2020):</b> This captivating documentary tells the story of a man in India who creates a haven for endangered birds in his urban garden. It shows the power of individual action in making a positive impact on conservation.<br><br>
<b>Ocean Giants (2014):</b> This stunning documentary takes viewers on a breathtaking journey into the lives of whales, sharks, and other magnificent creatures of the deep. It shows the vital role these animals play in the marine ecosystem and the threats they face from human activities.<br><br><br></p>
2 Add an id attribute to the elements you want to bookmark:
a The h3 element for the articles section.
<h3 id=b1> Links of interesting articles about wild animals:</h3>
b The h3 element for the documentaries section.
<h3 id=b2>Documentaries on the endangered species in India: </h3>
c The h3 element for Fun facts.
<h3 id=b3> Fun Facts About Wild Animals </h3>
3 Create link to the bookmarks.
<div class=holder> <div class=sub-holder1> <div>
<p><a href="#b1">Interesting Articles</a></p>
Code
<p><a href="#b2">Documentaries on the endangered species</a></p> <p><a href="#b3">Fun Facts about Wild Animals</a></p>
<p>From majestic animals to tiny insects, every creature plays a vital role in the ecosystem. Thus, protecting these creatures helps preserve biodiversity, which is essential for ecosystem flexibility. <br><br>It is also crucial for maintaining the <i><b> balance in nature. </b></i> <br><br> Conservation efforts, such as <u>habitat preservation,</u><u> anti-poaching measures,</u> and <u>breeding programs </u>are vital for protecting endangered species. <br> <br>By saving them, we will ensure that future generations benefit from a rich and diverse ecosystem.
</p>

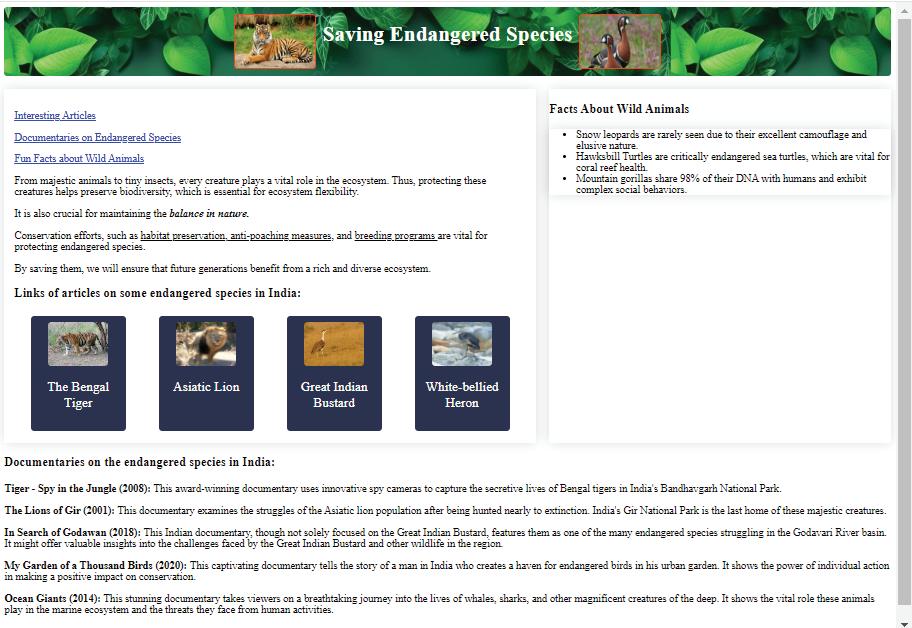
1 Read the statements and solve the puzzle.
Across
a CSS property can be used to add space around list items.
b The HTML tag used to create an unordered list.
c This HTML tag is used to create an ordered list.
Down
d A type of HTML list that doesn’t have any specific order.
e The HTML tag is used for individual list items.
2 Match the following.
Column A Column B
HTML tag used for ordered lists disc
The default bullet style for an unordered list <ol>
CSS property used to specify the style of bullet points or numbers in a list style an individual list item using HTML attributes
Using the style attribute list-style-type
Imagine you have a list of your favourite video games. You want to write down the name of each game, the genre, and the release date. You could write this information in a list, but it would be difficult to read and understand. A better way to organise this information is to use a table.
A table is a grid of rows and columns. Each row represents one item on your list, and each column represents a different piece of information about that item.
To create a table in HTML, we use the following tags:
Web designers choose colours for websites based on colour psychology. Like blue is often used for trustworthiness, while red can create a sense of urgency.
<table></table> This tag is used to create a table. <th></th> This tag is used to add table headers. The headings are bold and centred by default. <tr></tr> This tag is used to create table rows. <td></td> This tag is used to create a data cell and add data to the cell. The data in a cell is left-aligned by default.
<caption></caption> This tag is used to add captions to a table. It must be added right after the <table> tag. A table caption will be centred above a table by default.
<thead></thead> This stands for ‘table header’ and is used to group the header content in your table. <tbody></tbody> This stands for ‘table body’ and contains the main content of your table, such as data rows with <td> (table data) elements. <tfoot></tfoot> This stands for ‘table footer’ and is used for any footer content in your table.
Here is an example of a simple HTML table:
<table> <caption>Favourite Video Games</caption> <thead> <tr> <th>Video Game</th> <th>Genre</th> <th>Release Date</th> </tr> </thead>
Code
<tbody> <tr> <td>Minecraft</td> <td>Sandbox</td> <td>2011</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Fortnite</td> <td>Battle Royale</td> <td>2017</td> </tr> </tbody>
<tfoot> <tr> <td>
Total Games: 2 </td> </tr> </tfoot> </table>

Favourite Video Games
Video Game Genre
Release Date
Minecraft Sandbox 2011
Fortnite Battle Royale 2017
Total Games: 2
To style tables in HTML, you can use CSS. CSS is a language that allows you to control the appearance of HTML elements.
Here are some basic CSS properties that you can use to style tables:
• Border: This property controls the border of the table. You can specify the border thickness, style, and colour.
• Border-collapse: This property controls the collapse of table borders. By default, the borders of adjacent table cells will touch each other. You can use the border-collapse property to collapse the borders of adjacent table cells into a single border.
• Margin: This property controls the margin around the table. The margin is the space between the table and the other elements on the webpage.
• Padding: This property controls the padding inside the table. The padding is the space between the border of the table and the content of the table cells.
• Width: This property controls the width of the table.
• Height: This property controls the height of the table.
You can also use CSS to style the individual elements of a table, such as the table header cells, table data cells, and table caption.
Here is an example of how to use CSS to style a table:
Code
<html> <head> <style> table { border: 1px solid black; border-collapse: collapse; margin: 0 auto; padding: 10px; width: 400px; } th { background-color: #ab2f; text-align: center; } td { text-align: center; } </style> </head>
<body> <table> <tr>
<th>Video Game</th> <th>Genre</th> <th>Release Date</th> </tr> <tr>
<td>Minecraft</td> <td>Sandbox</td> <td>2011</td> </tr>
<tr> <td>Fortnite</td> <td>Battle Royale</td> <td>2017</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Among Us</td> <td>Social Deduction</td> <td>2018</td> </tr> </table> </body> </html>
Task 10: Add a table and style it.
1 Add the table on the number of endangered species left in India in sub-holder2 before Facts.
<div class=sub-holder2> <div>
<h3 id=b3>Number of Endangered Species Left in India</h3> <table> <tr>
<th>Name of the Species</th> <th>Number</th> </tr>
<tr>
<td>The Bengal Tiger</td> <td>2967</td> </tr>
<tr>
<td>Asiatic Lion</td> <td>600</td> </tr>
<tr>
<td>Great Indian bustard</td> <td>150</td> </tr>
<tr>
<td>White-bellied Heron</td> <td>300</td> </tr> </table> </div>
<div>
<h3 id=b4>Fun Facts About Wild Animals</h3>
2 Style the table by adding shadow.
table { box-shadow: 0 0 20px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.15); } </style>
Code


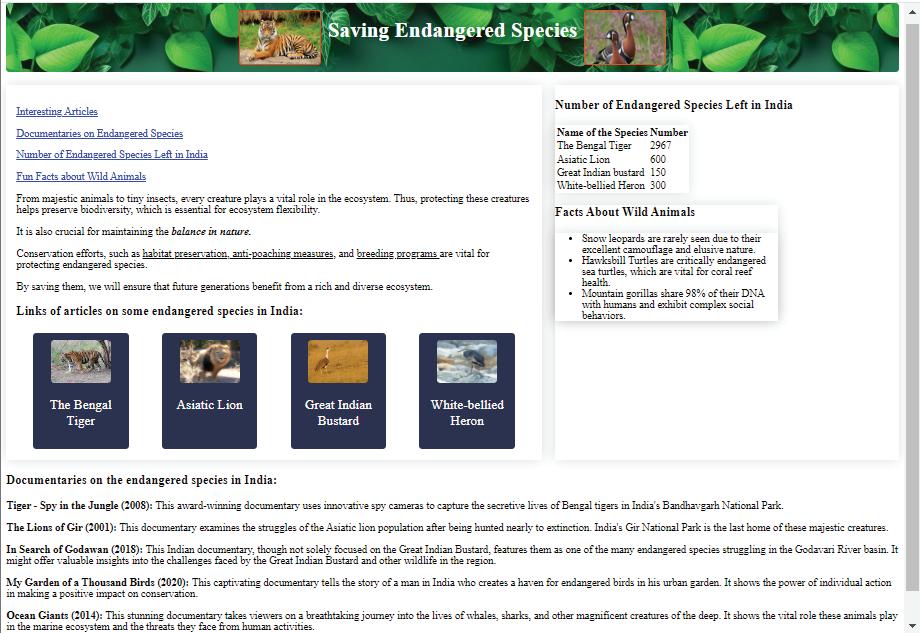
1 Create a webpage for your travel bucket list.
2 Create a webpage about your favourite book. Add bookmarks to different sections of the book, such as chapters or characters, and create links to jump to those bookmarks.
A Fill in the blanks.
1 Ordered lists are also known as lists and are used to list items in a specific order.
2 You can change the style of unordered list items using the property.
3 To style an individual list item using HTML attributes, we can use the attribute.
4 You can change the type of numbering in ordered lists using the attribute.
5 The HTML tag used to contain the main content of your table, such as data rows with <td> (table data) elements is tag.
B Tick () the correct option.
1 Which CSS property specifies an image to use as the bullet points in a list?
a List-style-image
c List-style-type
2 Which tag is used to define a term in a description list?
a <dd>
c <dl>
3 What property is used to add a border to a table in CSS?
a Border-style
c Border-collapse
4 The data in a table's cell is:
a Left-aligned by default.
c Centre-aligned by default.
C Who am I?
b Padding
d None of these
b <dt>
d <li>
b Border
d Table-border-style
b Right-aligned by default.
d Top Left-aligned by default.
1 I am an attribute to specify the type of numbering for your ordered list.
2 I am an HTML tag used to create a table header. I am commonly found inside the <thead> element.
3 I am a CSS property that helps you set the background colour for table cells. I can make your tables visually distinct.
4 I am centred above the table by default.
5 I am used to mark a specific spot on a webpage to quickly jump back to it when needed.

D Write T for True and F for False.
1 Each list item in an unordered list is defined using the <li> tag.
2 <style> table,th,td{ margin:2px; border-collapse: collapse; } </style> In the code snippet other than ‘solid’, you can use any other style.
3 <th> tag does not have a closing tag.
4 <td> tag is used to create a row in a table.
5 <a href="#bookmark"> is a valid way to create a link to a bookmark within the same HTML document.
E Answer the following questions.
1 What happens when you click on a link with the following HTML code? <a href="#myBookmark">Jump to Important Information</a>
2 Write the code to change the bullet style of the list to squares.
3 How would you change the text colour of all the list items to blue?
4 What is the purpose of using the id attribute when creating bookmarks?
5 Identify the error in this CSS code and provide the corrected version: body { background-color: #f0f0f0; font:size: 14px; font-color: #333; margin 15px; padding: 10px; }
1 Make an ordered list of your hobbies and number the list with lowercase letters.




2 Identify the error in the following HTML code snippets: a <ol>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</ol>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ol>
b <table>
<caption>Table of Products</capiton>
<tr>
<th>Product</th>
<th>Price</th>
<tr>
</table>
3 What’s the mistake in this code for creating a bookmark link? <a href="section2">Jump to Section 2</a>

4 Write a program that creates a table of the planets in the solar system, including their names, distances from the sun, and number of moons.

5 Write a program that creates a table of the scores for a soccer game, including the team names, goals scored, and yellow and red cards received.

A. Fill in the blanks.
1 Python is a language because it can be used on a variety of hardware platforms.
2 The rules tell us how to write programs in a coding language.
3 The comparison operators are also known as operators.
4 The body part of an HTML document contains the of the web page.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 What is the meaning of typecasting in a coding language?
a Conversion of one statement to another
b Conversion of one data type into another
c Casting of one data type into another statement
d Casting of one variable into another
2 In which of the following cases does the ‘and’ operator gives a True value?
a True and True b True and False
c False and True d False and False
3 Where will you type the URL of the website you want to visit?
a Navigation button b Bookmarks tab
c Address bar d Tabs
4 How can you style an image in an HTML document?
a Using a style attribute b Using a class
c Both a and b d None of these Test Paper (Based on Chapters 1 to 5)
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Python source code is easy to maintain and update.
2 Indentation is optional in Python.
3 HTML tells a web browser how to display content on a website.
4 CSS cannot be used to style images.
D. Answer the following questions.
1 Write the rules for naming a variable in Python.
2 What are control statements in Python?
3 How can you style an image using a style attribute?
E. Apply your learning.
1 What will be the result of the following expression: (((3 * 2) + 4) % 7) * (8 - (10 / 2))
2 Imagine you are designing a smart home system that controls the heating and cooling of a house. The system needs to decide whether to turn on the heating or cooling based on the following conditions:
• Turn on the heating if the current temperature inside is less than the desired temperature, and it is not too hot outside.
• Turn on the cooling if the current temperature inside is greater than the desired temperature, and it is not too cold outside.
Write a Python program that uses logical operators to decide whether to turn on the heating or cooling system.
3 Reema has created a web page but she is not satisfied with the look of it. How can she style the web page to make it look interactive?

This coding book is supplementary to the main “Mel and Conji” content book. This book represents a 21st-century approach to learning coding concepts and developing computational thinking and problem-solving skills. To prepare students for the digital age, the curriculum is interwoven with well-thought-out concept progression, real-life examples, and practice problems.

• Project-based learning: Engaging hands-on projects encouraging practical application of computer science and coding.
• NEP Tags: To showcase alignment with NEP skills and values.
• Code snippets: Complete code for each activity with output facilitating hands-on learning and immediate feedback.
• Coding challenges: Includes projects through which learners can demonstrate their learning outcomes in coding and computer science.
• Test Papers: Designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills.
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-979364-7-0
