





Academic Authors: Jatinder Kaur, Ayushi Jain, Anuj Gupta, Simran Singh
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh, Sakshi Gupta
Project Lead: Jatinder Kaur
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First published 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Hexa Computer Science 2
ISBN: 978-81-979297-4-8
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, computer science has become an essential field of study, shaping the world around us in countless ways. From the smartphones in our pockets to the vast networks that connect people across the globe, computer science drives innovation and progress in nearly every aspect of modern life. In today’s fast-paced digital world, understanding the basics of computer science is as important as learning to read, write, or solve maths problems.
Recognising this imperative, the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has strongly recommended the integration of coding skills, computational thinking, critical analysis, and problem-solving abilities into the curriculum.
Inspired by these insights, Uolo has introduced a comprehensive program, Hexa, for grades 1 to 8, to empower young minds with the knowledge and skills they need to thrive in the digital age. From the basics of how computers function to the tools that shape our digital landscape, this series opens the door to a world of endless possibilities. This series will build a strong foundation, helping shape the next generation of digital citizens and innovators. It aims to demystify the world of computer science, making it accessible and engaging for young learners, while preparing them for future academic and professional pursuits in the field.
We believe that learning computer science should be an engaging and accessible experience for all children. This series takes a project-based approach, allowing students to learn by way of concurrently applying acquired knowledge and skills. As they progress through the course, they will build strong foundations in computational thinking, coding basics, and digital literacy. Our program focuses on three key areas:
1. Computer Science Fundamentals: Core concepts are introduced step by step, ensuring a solid grasp of how computers function, and how information is processed and stored.
2. Latest Computer Tools: Various computer tools relevant to today’s world are included, equipping students with the confidence to thrive in the digital age.
3. Introduction to Coding: The series offers an introductory look into coding, preparing students for more advanced learning in the future.
To broaden the learning process, we have included informational annexures on Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its related fields, offering students an early insight into the groundbreaking technologies that are shaping our world. These sections aim to inspire curiosity and encourage a deeper exploration of computer science.
Our mission is to make computer science approachable and exciting for young learners. By providing early exposure, we aim not only to teach about computers but also to cultivate skills that will benefit students in their future endeavours.
We invite you to embark on this exciting journey with us through the world of computer science. Let us empower the next generation with the skills and the knowledge they need to thrive in a digital world.
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 outlines essential skills, values, dispositions, and learning approaches necessary for students to thrive in the 21st century. This textbook identifies and incorporates these elements throughout its content, activities, and exercises. Referred to as “NEP Tags”, they are defined as follows:


GAMES

INTEGRATED



CRITICAL THINKING

Art Integration
Bringing creativity and fun into learning by combining music, drama, and art with other subjects
Sports Integration
Using games and sports in daily life to enrich computer-related activities
Cross-curricular linkages to make the learning experience more holistic, joyful and meaningful
Critical Thinking
Coding opportunities to apply higher-order skills like algorithmic and computational thinking, and problem-solving

SDG
Hands-on Activity
Step-by-step activities to enable learners put theoretical knowledge into practice
Applied computer science activities related to real-world issues and sustainable development

SEL Social Emotional Learning
Developing the skills to understand and manage emotions, build positive relationships with others and make responsible choices

An Internet Service Provider, or ISP, is a company that provides you access to the internet, often for a fees. Some examples of ISPs are BSNL, Airtel, Jio, and Excitel.
To draw a circle, press and hold down Did You Know?




Communication media helps us connect to the internet. Let us see some of their types. 1.
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. It is a type of communication media that uses your telephone line to transmit data.
Project-based Learning: A project-based learning approach employed to foster an engaging and interactive learning experience




Cable is a type of communication media that uses the existing cable television wires to connect your computer to the internet.

NEP Tags: To show alignment with NEP skills and values
Fibre optic cable is a type of communication media that uses light rays to connect your computer to the internet. Fibre optic cables are much faster than copper or cable wires. In fibre cables, the data travels in the form of light. Nothing in the universe travels faster than light. So, the internet through fibre optic cables is often the fastest type of internet connection available.

Chapter Checkup
Discuss: A multi-faceted probing question, related to the concept, that arouses curiosity


Now think of the fan speed knob, or regulator, on the switchboard. It changes the speed at which the fan spins, instead of just switching it on or off. We can have the fan spin at the fastest speed, reduce it to a slower speed, then much slower, and finally switch it off. We can do more things with the regulator than the switch. That is how analog signal works.
Find out which type of internet connection your house or school has.
3. After selecting it, go to the main drawing area.
e I hold all the blocks for a block category.
A Fill in the blanks.
Did You Know: Interesting facts related to the topic
3
Did You Know?
India has the second-largest internet user base in the world, with over 70 crore users.
Think and Tell
Can you think of more examples of analog and digital signals?
Hints menu bar untitled backdrop blocks create
ISP
1 In Scratch, we use colourful to create our own games, stories, and drawing.
An Internet Service Provider, or ISP, is a company that provides you access to the internet, often for a fees. Some examples of ISPs are BSNL, Airtel, Jio, and Excitel.
Do It Yourself: Short exercises between the chapter to pause and assess comprehension

2 To create a project in Scratch, you need to click .
4. Hold the left mouse button, move the pointer and then release the button. You will see that a triangle has been drawn. In the same way, we can draw many shapes in Paint.
3 By default, the name of the Scratch project is
Communication media helps us connect to the internet. Let us see some of their types.
1. DSL
Think and Tell: Analysis, reflection, and text-to-self connection based prompts for discussion in class
DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. It is a type of communication media that uses your telephone line to transmit data.
4 The purple bar at the top of the Scratch editor is called the .

2. Cable
5 The background of the stage is called the
F Apply your learning.
AI Annexures: To offer a basic understanding of specific domains of Artificial Intelligence
Chapter Checkup
Cable is a type of communication media that uses the existing cable television wires to connect your computer to the internet.
e I hold all the blocks for a block category.
3. Fibre
A Fill in the blanks.
Hints menu bar untitled backdrop blocks create

1 Nia is making a Scratch project where she needs to move the dog from left to right. Which block should she use?
Intelligence, or AI, helps computers think. It can learn like people do.It learns new things all the time. AI is very smart. It will keep changing and
Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Apply Your Learning: Intellectually stimulating questions designed for higher order thinking and analysis
AI
Test Papers: Designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 In Scratch, we use colourful to create our own games, stories, and drawing.
Chapter Checkup
Fibre optic cable is a type of communication media that uses light rays to connect your computer to the internet. Fibre optic cables are much faster than copper or cable wires. In fibre cables, the data travels in the form of light. Nothing in the universe travels faster than light. So, the internet through fibre optic cables is often the fastest type of internet connection available.
2 To create a project in Scratch, you need to click
3 By default, the name of the Scratch project is
e I hold all the blocks for a block category. A Fill in the blanks.
4 The purple bar at the top of the Scratch editor is called the
Hints menu bar untitled backdrop blocks create
Find out which type of internet connection your house or school has.
5 The background of the stage is called the
F Apply your learning.
Chapter 4 • Browsing the Internet
1 In Scratch, we use colourful to create our own games, stories, and drawing.


1 Nia is making a Scratch project where she needs to move the dog from left to right. Which block should she use?
2 To create a project in Scratch, you need to click
3 By default, the name of the Scratch project is
4 The purple bar at the top of the Scratch editor is called the
5 The background of the stage is called the F Apply your learning.
Test Paper (Based on Chapters 1 to 4)
1 Nia is making a Scratch project where she needs to move the dog from left to right. Which block should she use?
Test Paper (Based on Chapters 1 to 4)

1 In Scratch, the blocks you put together in the script area are called a
A. Fill in the blanks.

1 In Scratch, the blocks you put together in the script area are called a
2 The is the background of the stage.
2 The is the background of the stage.


Colour the given picture and write the name of this device in the given space.
Devices are things that help us to do specific tasks. For example, a phone is a device to talk to others.
An electronic device is a device that works on electricity.
A computer is an electronic device that helps us do many things.
A computer is used for:
Charles Babbage is known as “the Father of Computers.” Did You Know?








A computer can do many things for us. Some advantages of computers are:
Storage 1

It can store a large amount of data like pictures, music, videos, and games.
Calculation 4
Connectivity 2

We can share information and talk to each other using a computer.
Information 3
Computers have calculators in them that can help us do additions and subtractions.
Computers can help us to know about new things and subjects.
Entertainment 5

We can watch cartoons and films on a computer. We can also play games on it.
Computers are very useful but they also have some disadvantages. Some of them are:
Think and Tell
Is doing many things on a computer at the same time an advantage?
Using a computer for a long time can make your eyes and head hurt.
Criminals can use the internet to steal our private information stored on our computer.



Computer parts like batteries are harmful for nature. Not recycling them, and throwing them in the garbage harms the soil. This pollutes the environment.
Do It Yourself 1A



In today’s world, computers are used everywhere. They are used:
Banks 1





• To let us take money out from our account.
• To tell us how much money we have left in our account.
• To help us send money to other accounts.
Schools 2
• To help us learn new things.
• To help teachers to make time tables and report cards.
• To help in collecting schools fees.
Hospitals 3
Airports and Stations 4

• To tell us about the timings of the flight, train or bus.
• To help us in booking tickets.
• To keep a record of all the passengers.
• To keep records of all the patients in a hospital.
• To help run big machines like X-ray machine.
• To prepare and print medical reports.

• To keep a record of the number of items in shops.
• To create and print orders and bills.
• To keep a record of people who work in the shops and offices.
How can computers help us in doing homework and creating projects?

Which other places use a computer? Scan the QR code to know more.










Press the ON button on the monitor.
Wait for the computer to start. Once your computer is ‘awake’, you can use it.
To shut down your computer means to turn it off. Always shut down the computer when it is not in use.
A computer can be shut down by following these steps:
1. Click Start to open the menu.
2. Then, click on the Power icon.
3. Click on the Shut down option from the second menu. The computer will start shutting down. Start

Scan this QR code to learn other quick ways to turn off a computer.




You need to start your computer. Number the images in the correct order.



A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints: main power schools security problems entertainment shutdown
We can use computers for and having fun! Computers are used in to manage fees.
To start a computer, first switch on the button.
To your computer means to turn it off.
disadvantages of computers.
B. Tick () the correct option. Which button is used to start the computer? 1























C. Who am I?
I am an electronic device that helps you do many things. I can help you play games, draw pictures, and find information on the internet.
I am the place where computers are used to keep records of all the patients.
I am the place where computers are used to withdraw money.
I am the button that helps you shut your computer down.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
A computer is an electronic device. Hospitals use computers to keep records of patients.
Computers are only used for cooking food.
Computers help us to play music, videos, and games.

To start a computer, you need to press the button on the monitor first.
E. Answer the
F. Apply your learning.
Pranav wants to book a train ticket. Can you suggest what he should do?
Tanya wants to know where computers are used. She also wants to know how they are used there. Can you help her?

Do you know about the friendship between cats and humans?
Cats and humans are friends. Humans take care of cats by giving them food and lots of love. In return, cats become their friends and help keep homes safe from mice. This special bond brings joy and warmth to both of them.
Look at the image of the cat and label its body parts. Just as the cat has different body parts, similarly, a computer also has different parts.
A computer has three types of parts. These are input devices, output devices, and storage devices.
Input devices help us to tell a computer what to do. Input devices provide ways to ‘talk’ to the computer. There are many input devices. Let us learn about them.
Keyboard
A computer keyboard is a board with buttons on it. These buttons are called keys. Each key on the keyboard does one type of thing only. Using the keyboard, we can type on the computer.



Typing words, sentences, and numbers.
Using key combinations to perform specific actions
Mouse
A standard keyboard has 104 keys. Some keyboards have more keys for playing audios and videos. Did You Know?
A computer mouse is a small input device. It is used to move the pointer around the computer screen and click on files or icons to use them. It has two buttons and a wheel between them.
• Pointing at things on the computer screen.
• Moving pages on the computer screen up and down.
• Selecting items.
• Clicking on items to open them.

The first mouse was made up of wood and had two wheels underneath it. It was invented by Douglas Engelbart. Did You Know?
A microphone is an input device that lets us use our voice to tell the computer what to do. Microphones these days are fitted into the computer itself. We can also buy microphones that can be plugged into the computer.
• Recording our voice.
• Talking to other people while online.
• Giving voice commands to the computer to play music, search for a file, or open it.
The microphone helps us to use our voice to tell the computer what to do.
The keyboard helps us to type on the computer.
The mouse has only one button.
We learnt that input devices help us tell the computer what we need. But how does the computer show us the results of our commands? It does so by using output devices.
Output devices show the results of what we want from the computer. Let us see some output devices.
A monitor is the screen of your computer. It shows you the result of your input.
• Helps us to see what we are doing on the computer, like typing or moving the mouse.
• Lets us watch videos or films.


Do you want to know what is inside a monitor? See here!
A printer is used to print text or pictures on paper. The printout is called a hard copy.
• Lets us get a printout of text or pictures.
Speakers and headphones help us hear sounds that a computer creates as outputs.

Speakers are different from headphones.
Speakers are used when more than one person wants to hear the sounds and music.
Headphones are worn over the ears. They are meant for only one person to listen to sounds and music, without disturbing others.
• Help in listening to music or sounds in a computer.
• Help in listening to the voice of the person who we have called using the internet.
Did You Know?
Speakers use magnets to create sounds.
We can do many things on a computer. We can listen to music, watch a video, and even get printouts.
We can also store information in the computer, like our favourite songs, our school projects, films, and games. This is called data.
In the computer, data is stored in storage devices. Let us learn about them.
A hard disk is like a box that stores all the data in the computer. Every computer needs a hard disk to store things.
• Keeps important things on the computer safe.
• Stores all that we have on the computer—including our favourite games, music, films, and projects.
CDs and DVDs are both storage devices. They are used by putting them in the CD/DVD Drive.
Both the CD and the DVD are round in shape and look similar, but they are different in functioning. Let us see how!

CD stands for Compact Disc. DVD stands for Digital Versatile Disc.
A CD holds less amount of data. A DVD holds a large amount of data.
of
• These help us in storing things like music, films, and homework.
• These can be carried around easily.
Pen Drives
A pen drive is a small stick-like device in which you can store files. You can also transfer these files to another computer easily. It is also called a flash drive. It is smaller than CDs and DVDs.
• They can be used to easily transfer files from one computer to another.
• These are used to store a greater amount of data than CDs or DVDs.
• These, like CDs and DVDs, can be carried around easily.
Did You Know?
Cloud storage allows you to save your pictures, games, and school projects on the internet so you can access them from any device, like a computer, tablet, or smartphone, anywhere you go.

Label the parts of the computer in the given image.

















































Computers work in a similar way. Let us see how.
Input: What we give to the computer.
Process: What the computer does with the input.
Output: What the computer gives us back.












































Have you ever seen a plant grow? You water the plant. The plant also breathes in air. It also takes in sunlight. It takes in all these things and uses them to give us flowers and fruits!
This is called the Input, Process, and Output cycle or simply the IPO cycle. The IPO cycle tells us how a device works.
Let us see another example. This time, of a washing machine.
Can you think of another example for the IPO cycle?
Input We put dirty clothes in the washing machine.
Process The washing machine washes the clothes.

Output We get clean clothes.
Write I for Input, P for Process, and O for Output.
Alarm Clock
a You set the alarm on the clock.
b The clock runs and keeps a track of the time.
c When the time matches, the alarm rings.
Refrigerator
a The food is cold.
b The food is hot.
c The
from the food.
A. Fill in the blanks.
help you listen to music.
A mouse is an device.
A is a screen that looks like a TV. A is a small storage device that can be carried around easily. We type on a computer using a .
B. Tick () the correct option.
Which device allows you to type letters, numbers, and special signs on a computer?
Which of the following is a
Which device do we use to get a printed copy of a picture from the computer?
Which storage device is like a small stick?
Which device helps you move items on the computer screen?
C. Who am I?
I let you listen to music without disturbing others.
I am round in shape and shiny. You can store things in me. I cost more than a CD.
If you use me, everyone can hear the sound given by me.
I keep all your favourite games and pictures safe in the computer.
When you type something on the keyboard, the numbers and the alphabets are seen on me.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
We give instructions to the computer using input devices.
A computer mouse helps you click on the computer.
A keyboard is small and round like a shiny plate.
A microphone is used to record sounds.
A mouse is a box that stores pictures in the computer.
E. Answer the following questions.
What is an input device?
What is an output device?
Why do we need storage devices?
F. Apply your learning.
On a family vacation, Aman took many photos. Now, he wants to save them on a storage device that he can carry around with him. It would be great if the device can be carried safely in his pocket. Which device should he choose and why?
Riya wants to type a letter on the computer. Which devices will she use?
Aarav is watching a film on his computer. Which devices is he using?




Tina was hungry. Her mother made her a sandwich using a toaster, bread, and cheese. Is this an IPO cycle? If so, correctly identify the input, process, and output.
Sagar loves drinking cold water. He keeps a glass of water in the refrigerator to make it cold. Explain the input, process, and output for this.
Look at these pictures and write their names.




Have you noticed one common thing in all these pictures?
Each picture shows keys used for playing the piano, playing a video game, and switching channels on TV. Similarly, keys on the keyboards are used for typing on a computer.
The keyboard is an input device. It has lots of buttons, called keys, on it. It helps us type letters, numbers, and symbols on the computer.
Let us learn about these keys.
The alphabet keys are the keys with letters on them.

The computer keyboard is also called the QWERTY keyboard. It is based on the first six letters on the keyboard. Did You Know?

INTEGRATED
There are 26 alphabet keys, one for each letter in the English language. We use the alphabet keys to type words and sentences on a computer. The keys are arranged in such a way that they make typing letters easier.
The number keys are the keys with numbers on them. There are 10 number keys, from 0 to 9.
These keys help us to type numbers on a computer. Some keyboards have number keys on the righthand side also. This is known as the numeric keypad.
Colour the vowels. 1

Can you use the computer keyboard to write in another language? Find out!

) the correct type for the given keys.
Number Key Alphabet Key




There are many special keys on a keyboard. These keys are used to do particular tasks.
Let us learn about them.
Sometimes, while typing, we make mistakes. We can correct them by erasing them.
The backspace key helps us remove the text or objects before the cursor (the blinking line).
Imagine we have typed ‘computerr’ by mistake instead of ‘computer’.
To fix this:
1. First, check if the cursor is at the right place. It should be after the letter to be erased, as shown.
2. Then, press the Backspace key.
Think and Tell
Which item in your pencil box works like the backspace key?
The Delete key also helps us remove text or objects but when they are after the cursor.
Imagine we have typed ‘machinee’. We can correct this mistake by clicking before the extra ‘e’ and pressing the Delete key.
To fix this:
1. Check if the cursor is before the extra ‘e’.
2. Press the Delete key.

Punctuation keys are used to add punctuation symbols. These symbols are the question mark (?), exclamation mark (!), full stop (.), comma (,), semi-colon (;), and colon (:).
The Spacebar is also called the Space key. The spacebar is the largest key on the keyboard. It adds a space between two words. Imagine we have typed ‘Ahorse’.
To fix this:
1. Check if the cursor is where we want to add space.
2. Press the Space key.






Caps Lock key is used to type letters in capital or uppercase. If you press this key once, your letters will be in capital when you type. To write in small letters or lowercase again, press the Caps Lock key again.

Think and Tell
Just like Caps Lock, is there a key on the keyboard that helps us to type capital letters?
The Enter key is used to move the cursor to a new line while typing.
For example, imagine we have typed ‘I am a student. I study in grade 2’. To move the second sentence to the next line:
1. First, check if the cursor is before the sentence.
2. Then, press the Enter key.

I am a student. I study in grade 2.
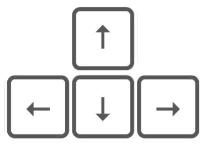
The arrow keys are four keys with arrows pointing in different directions.
They are used to move the cursor in the direction of the arrow. I am a student. I study in grade 2.
A combination is when two or more things are done together. So, a combination on a keyboard happens when we press two or more keys together. Let us learn these keyboard combinations.
Some keys have two things printed on them. They can help us type both the things, if we know how to use them. For example, look at the number keys. They have symbols written above the numbers.
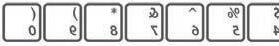
We can type these symbols by pressing and holding the Shift key and then that number key.
For example, we want to type ‘Hello!’. Let us first type the word ‘Hello’.

Then, to add the exclamation mark (!), we will press and 1 together.

Yourself 3B

Colour the key that:
b Adds space between two words. 1
a Turns the lowercase letters to uppercase letters.
Which key helps us type the symbol on the top of a key? a Caps Lock b Shift c Backspace d Delete
Tick () Yes if the symbol can be used as combination key only. Tick () No if the symbol can be used without combination.
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints: uppercase numbers line backspace alphabet
The keys are used to type letters, words, and sentences.
The number keys are used to type .
The key on the keyboard is like an eraser for your words.
Caps Lock key is used to write the letters in .
The Enter key is used to move to a new when typing.
B. Tick () the correct option.
What is the use of alphabet keys?
a Typing numbers b Typing special or punctuation symbols
c Typing words d Adding spaces between words
Which is the largest key on the keyboard? It also adds a space between two words. a Backspace key
Lock
What are the arrow keys used for on the keyboard?
a Typing letters, words, and sentences
c Entering symbols and punctuation
b Moving the cursor in different directions
d Adding spaces between words
Which key is used along with other keys as a combination?
a Enter key
c Arrow keys
b Backspace key
d Shift key
How can you type the symbol above a number key?
a Press the Shift key and that number key together.
b Press the Caps Lock key and that number key together.
c Press the Enter key and that number key together.
d Press the Spacebar key and that number key together.
C. Who am I?
I help to move the cursor to the next line.
If you have typed something wrong, I help you go back and remove it.
I make the letters capital when you type.
I add a space between two words.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
A keyboard is used to type letters, numbers, and symbols.
The alphabet keys on the keyboard are arranged as A, B, C, and so on.
The number keys are used to type letters, words, and symbols.
Some keyboards have number keys on the right-hand side also.
E. Answer the following questions.
What is a Spacebar used for?
words.
F. Apply your learning.
Riya wants to type her name in capital letters. Which key should she use?
Raja wants to type an exclamation mark at the end of a sentence. Which keys should he use?
Aarav wants to add a question mark to the end of a sentence. Which keys should he use?




Maya is wondering why the letters on the keyboard are in a different order than the book. What do you think is the reason?
Naina is playing a game on the computer. She needs to move the character on the screen. Which keys could help her?
Look at the given picture.
In the given picture, the teacher is pointing at the question and asking the students for answers. Similarly, a computer mouse is used to point at things on the computer screen.
A mouse is a pointing device. It helps to draw and colour pictures. When you move the mouse, an arrow also moves on the computer screen. This arrow is called the pointer.

Think and Tell
Is mouse an input device?
A mouse has three parts—a left button, a right button, and a scroll wheel.
Scroll Wheel
Left Button

Right Button
But how do these parts help us?
The mouse was invented by Douglas Engelbart in the 1960s. Did You Know?
• Left Button: helps you click on things you want to open or use on the computer.
• Right Button: opens up additional options.
• Scroll Wheel: helps you move a page that is open on the computer screen up and down.
Now, let us learn how to hold the mouse properly. To hold a mouse properly, put your hand on top of it in such a way that:
1. Your index finger should be on the left button.
2. Your middle finger should be on the right button.
3. Your thumb and the other two fingers should be on the sides of the mouse.
Index Finger
Left Button
Thumb
Right Button
Middle Finger
Other Two Fingers
Discuss!
Does the mouse work when it is in the air? Why or why not?
Now, move the mouse on the table. See how the pointer on the monitor also moves.
Do It Yourself 4A

Colour the parts of the mouse with these colours: left mouse button in orange, right mouse button in blue, the scroll wheel in red, and the body of the mouse in green.
The mouse pointer is the little arrow on the monitor that moves when we move the mouse. It helps you to point at, select, and click on many things that you see on the monitor.
At first, the mouse pointer is simply a white arrow with a black border.
What if we don’t like this arrow? Can we change it? Yes, we can!
There are many other types of mouse pointers. Let us look at some of them.

Find out how your mouse pointer can be changed.
We have learnt what a mouse is and how to hold it. Now, let us learn how to use it.
Pressing a mouse button is called clicking. We hear a soft clicking sound when we press the mouse buttons.

Clicking with the left button is called a left-click. With one left-click, we can select an item. This PC click

Clicking the left button two times, very quickly, is called a double-click. When we double-click the left mouse button, it will open the selected item. This PC click click


Clicking with the right mouse button is called a right-click. When we right-click, we get a list of choices that we can select.
Rolling the scroll wheel up and down using your index finger is called scrolling. Scrolling moves the page that is opened on the monitor up and down.
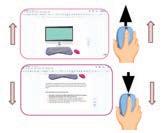
Moving the mouse without leaving the left mouse button is called dragging.
1. Select an icon by left-clicking on it.
2. Then hold the left mouse button and move the mouse without leaving it.
3. When you release the left button, you will see the icon is placed where the pointer is.
4. This way of moving the icon is called drag and drop.
Left-click
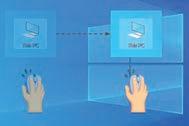
Drag Open a list of options. Drop Select an item. Match the following. 1
Hold the left button to do this.
Right-click Place an object at a new place on the monitor.
Write T for True and F for False.
a Right-click is used to select an item.
b Drag is used to move an object.
c The default mouse pointer is a white arrow with a black border.
A. Fill in the blanks.
Hints: scroll wheel right button left button mouse pointer
A is an input device that helps control the pointer on the monitor.
The is the little arrow that appears on the monitor when you move the mouse.
The is used to select an item on the computer monitor.
The is used to see more options for a selected item.
The is used to scroll up and down on a page or a document.
B. Tick () the correct option.
Which part of the mouse is used to select an object on the computer monitor? 1
To open an item on the computer, we should the item.
When we want to move up and down on the page opened on the monitor, we should on the page.
Which finger is used to click the left button?
C. Who am I?
I am a computer device. I have the name of a small animal.
I move on your monitor when you move your mouse.
You roll me up and down on the mouse.
I help you go up and down on a page.
I am the button on the mouse that you use to open a list of choices.
I am the button on the mouse that you use to select an item.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
We cannot move the pointer on a computer monitor.
The mouse is an input device.
The computer mouse is an animal.
We can move an object from one place to another on a computer monitor using a mouse.
You can select a particular item by left-clicking on it.
E. Answer the following questions.
What are any two uses of the mouse?
What is single-click and double-click?
What can you do with a left-click?
F. Apply your learning.
Aarna wants to move an item on the desktop from one place to another. What should she use?
Tiya sees an arrow on the monitor that moves when she moves the mouse, but she doesn’t know what it is. Can you tell her what it is?
Ravi is reading a story on the computer. He wants to move to the lower part of the page. Which part of the mouse can help him?
Eva is new to computers. She doesn’t know how to open an item. Which button on the mouse can help her?
Conji has clicked a mouse button which opens a list of options. Which button did he click?

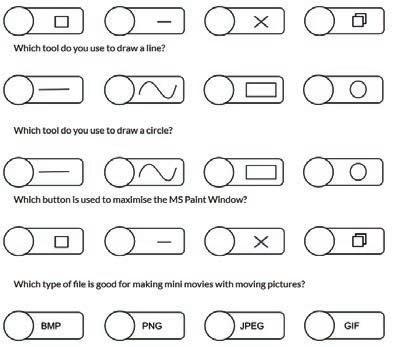
Match the shape with its correct shadow.
Do you know you can also draw these shapes on the computer using MS Paint?
MS Paint lets us draw and colour on the computer.
To open MS Paint, follow these steps:
1. Click on the Search bar. Search Bar

Type “paint”
2. Type “paint ”. Click here
3. Click on the Paint app.

The Paint window has the following parts:
Group Tabs
Area
Title Bar: Shows the name of your MS Paint file.
Tabs: This is where you can use different types of tabs like File, Home, and View.
Ribbon: Group of tools to help you draw.
Drawing Area: Space to draw.
Colors: Colour choices to choose colour from.
Shapes Group: Contains various shape tools using which we draw many shapes in Paint.
Tools Group: Contains various tools used in creating drawings.
Fill in the boxes. 1
Hints: title bar ribbon tabs colors drawing area

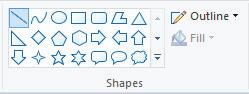
A shape is a figure that is made of lines or curves. There are many shapes like squares, circles, and triangles. In MS Paint, we have Shapes group, which contains many shape tools. They help us to draw shapes easily.
Let us learn how to draw some shapes in MS Paint.
Steps to draw a line:
1. Choose the Line tool from Shapes.

2. Press and hold the left mouse button where you want to start drawing the line.
3. Move the mouse to where you want to end drawing the line.
End Point
4. Leave the left mouse button when you are done. Your line is drawn.

Steps to draw a curve:
1. Choose the Curve tool from Shapes.
Curve Tool

2. Press and hold the left mouse button.
3. Move the mouse to an end point and then leave it.
End Point
4. Press the left mouse button from where you want to make it curved and then move it.
5. Leave the left mouse button when you are done. The curved line is drawn.

Steps to draw a rectangle:
1. Choose the Rectangle tool from Shapes. Rectangle Tool

2. Press and hold the left mouse button where you want to start drawing the rectangle.
3. Move the mouse to where you want to end drawing the rectangle.
End Point
4. Leave the left mouse button when you are done. The rectangle is drawn.

Steps to draw a circle:
1. Choose the Oval tool from Shapes. Oval Tool
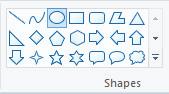
2. Press and hold the Shift key. Also press and hold the left mouse button where you want to start drawing the circle.
3. Move the mouse to where you want to end drawing the circle.
End Point
4. Leave the left mouse button when you are done. The circle is drawn.
A polygon is a shape with many sides. A triangle is a polygon with three sides. A square is a polygon with four sides. We can draw any shape with the Polygon tool in MS Paint.
Steps to draw a polygon:
1. Choose the Polygon tool from Shapes. Polygon Tool

2. Press and hold the left mouse button where you want to start drawing the polygon.
3. Move the mouse where you want the next point of polygon.
4. Continue moving and pressing the left mouse button to add points.
5. Connect the last point added to the start point to complete the polygon.
6. Leave the left mouse button when you are done. The polygon is drawn.

What things can you draw using the shapes we learnt?
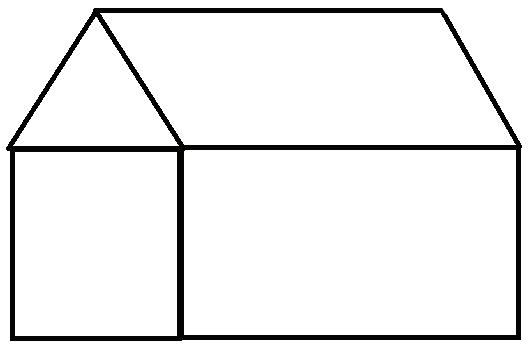
Now that we have learnt how to draw different shapes, let us draw a hut using the Shapes tools.
1. Select the Rectangle tool from the Shapes section.
2. Draw a large rectangle in the drawing area to form the base of the house.
3. Draw another rectangle beside the first one.
4. Select the Triangle tool from the Shapes group.
5. Draw a triangle on top of the second rectangle to form the roof.


6. Select the Line tool and draw the slanting lines on the other two sides of the house.
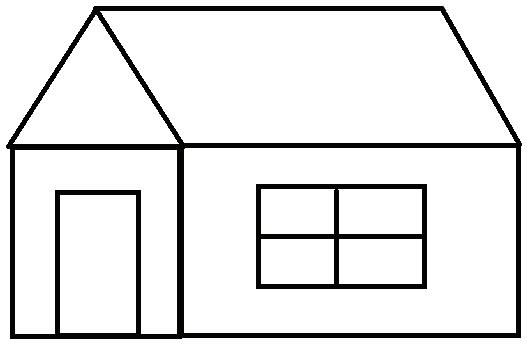
7. Draw a smaller rectangle inside the large rectangle to represent the window.
8. Use the Line tool again to draw cross lines inside the smaller rectangle.

9. Draw a smaller rectangle in the left-base rectangle to represent the door.
10. Select the Circle tool and draw a circle inside the triangle. The house should look like this.
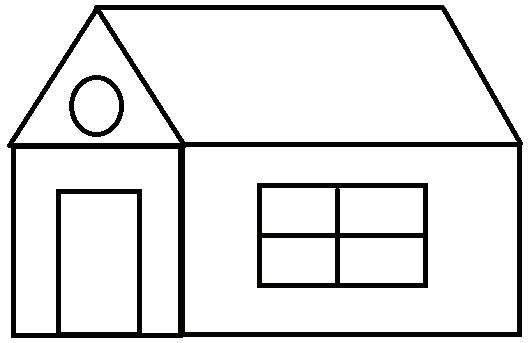
a Drawing
When you have finished drawing on MS Paint, you need to save it so that you can always see it again later. Let us see how we can do that.
Steps to save your MS Paint file:
1. Click on the File tab.
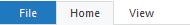
2. A menu will open up.
3. Click on the Save as option.
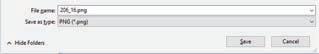
4. Another window will open which will allow you to save your file.
5. Type a name for your drawing in the File name box.
6. Click on the Save button.


Would you like to know what else can be drawn on MS Paint? See this video!
Let us now learn how to open a previously saved file.
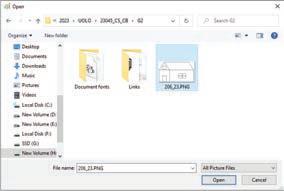
Steps to open a drawing file:
1. Click on the File tab.
2. Click on the Open option.
3. Find the drawing file you want to open.

4. Select the file and click on the Open button.



A. Fill in the blanks.
C. Who am I?



D. Write T for True and F for False.

Triangles, squares, and rectangles are types of polygons.



If we want to see our work again after closing MS Paint, we should save our file before closing it.
In MS Paint, we can draw only one shape.
You can see your drawing only once after you save the file.
You can only use four colours to colour your drawings in MS Paint.
E. Answer the following questions.
F. Apply your learning.
Manisha wants to draw a car. Which app can she use?
Sara wants to make a beautiful flower in Paint. What tools can Sara use?
Tanya wants to keep her drawing so that she can work on it later. What should she do?

Imagine that you speak only in English. For your summer holiday, you have gone to Japan. You see that nearly everyone speaks Japanese over there.
Will you be able to talk to them? Will you be able to ask for things like directions, food, etc? No, right? You need to know their language to talk to them.
Similarly, computers cannot understand what we want them to do unless we ‘speak’ to them in a way that they understand. We need to learn ‘their language’. That is what coding is.
Coding is a language that is used to talk to a computer.
The coding language that uses blocks to give instructions is called block-based coding.
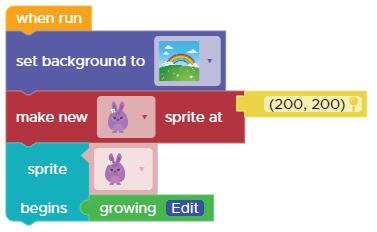
Code.org is a fun coding platform where you can learn to use colourful blocks to make characters move, play games, and even tell stories.
Look at the given picture.
What is the instruction here?
You are correct! The instruction is to jump. For computers, an instruction is called a command. A command is an instruction that tells a computer what to do.
In block-based programming, we use code blocks to give commands to a computer.

Block to make a character move up
In block-based coding, the blocks can be of different colours. Did You Know?
We all follow a routine in our daily lives. The pictures below show the steps to get ready for school in an order.
Just like this, we do a lot of tasks in our daily lives.
A task is a piece of work that needs to be done.
It can be as simple as brushing our teeth or as fun as playing with our toys. We follow a particular sequence to do a task.
A sequence is when we do things step by step in an order.
A sequence can be a:
Fixed sequence : There is only one way to do the task.
Making your bed! Is it a fixed sequence or a flexible sequence?
Flexible sequence : There can be more than one way to do the task.
Observe the given picture and tick () the correct type of sequence. Do It Yourself 6A

A problem is like a puzzle that needs to be solved. There can be more than one way to solve a problem. Each way has some steps to be followed to solve it.
The set of steps in an order to solve a problem is called an Algorithm.
In the example given in the previous section, getting ready for school is the problem. The steps given in order are the solution for this.
Think and Tell
Can we have more than one way to solve a problem?
Some algorithms have fun names, like Hummingbird, Bat, Firefly, and Grey Wolf. You can give your algorithm a name too. Did You Know?
Sometimes problems can be too big to solve. But we can break them down into smaller steps to solve them easily. Let us talk about drawing a cat.
Drawing a cat may seem like a big problem. But we can solve it easily by breaking it into smaller steps.

Let us draw a cute cat step by step:
In a similar way, we can solve many problems in coding by putting the code blocks in a sequence.
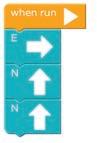
Now, look at the given picture. We need to help the bird reach the pig. We can do this by putting direction code blocks below each other in an order.
These blocks are called direction blocks as they are named after the four main directions: North, South, East, and West. These blocks can be used to move the sprite up, down, right, or left.
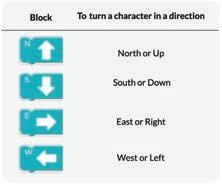
Let us see how we can make the bird reach the pig. The W block will make the bird move one step left.
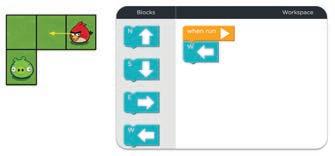
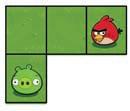
Think and Tell
If we put the blocks in a different order, will the bird do something else?
Now, we need to give two W blocks to make the bird move in the left direction.
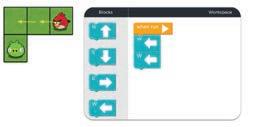

Finally, the S block will make the bird move one step down and reach the pig.


Think of the story of a thirsty crow.
Then, number the given pictures in the correct sequence.


2 Look at the given pattern and select what will be next.
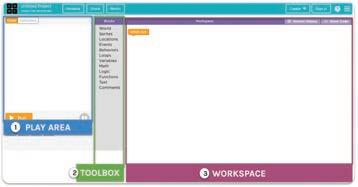
The Puzzle Code Studio on Code.org is the playground where we code to solve the given puzzles.
There are four important parts:
Play Area: The area where we can see things happening.
Instructions: The hints that help us know what to do next.
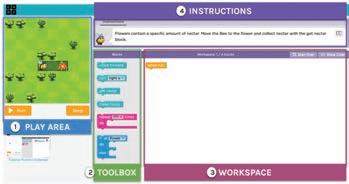
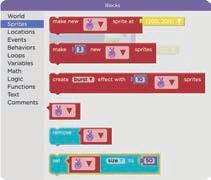
Toolbox: The area that holds all the code blocks which we can use to give commands.
Workspace: The area where we can drag and attach the blocks together to make things happen.
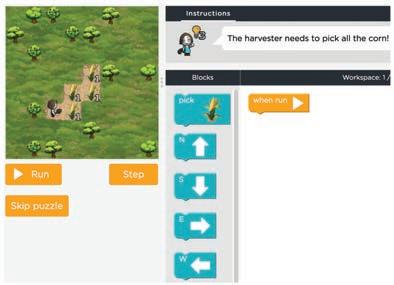
Create a code to help the harvester get all the corns. Scan the QR Code to open the activity. A Fill in the blanks.

1 is the language used to talk to a computer.
2 We can give a to a computer to do a task.
3 A is when we do things step-by-step in an order.
4 In a sequence, we can do a task in more than one way.
5 The is the area where we can see things happening.
B Tick () the correct option.
1 holds all the code blocks which we can use to give commands.
a Play Area
b Toolbox
c Workspace
d Instruction
2 The set of steps in order to solve a problem is called a/an .
a Sequence
c Algorithm
b Command
d All of these
3 Identify the section shown in the given picture.
a Toolbox
b Workspace
c Play Area
d Instruction
4 Which block can help us move a character up?



5 Which of the following codes will make the bird reach the pig?






Move the character downward Sequence
Move the character to the right Coding
An ordered group of commands
A coloured picture that tells the computer what to do


A language that helps you talk to a computer Code block
D Write T for True and F for False.
1 Using coding, we cannot talk to a computer.
2 A sequence is an instruction.
3 There is a sequence to everything happening around us.
4 In a fixed sequence, we can do the task in more than one way.
5 The toolbox has all the blocks we need for coding.
E Answer the following questions.
1 What is a command?
2 Name the two types of sequences.


Number the pictures in the correct sequence to complete the story.
4 Label the parts of the screen.




5 Find out where the cat will reach if it follows the given commands.
F Apply your learning.
Write down the commands in the given spaces to help the squirrel reach the nut.
Just like the one you see here.



when run
when run when run
We all enjoy listening to stories. But do you know how stories are created? A story is made up of four elements, such as:
1. Characters : People, animals, or things in the story
2. Problem : Something that needs to be done or solved
3. Setting : The place where the story happens
4. Events : When and what happens

We can use block-based coding to make stories. Let us make a story about an astronaut going on a space adventure.
An astronaut is a person who travels in space to do experiments and explore space.
But before we begin, we should find out the elements of our story.
Who will be the main character in the story?
Correct! The astronaut will be the main character in our story.
A character in coding is called a Sprite.
So, the astronaut will be the main sprite in the story. Now, what does an astronaut need to travel in space?
Yes! An astronaut needs a rocket to travel. In coding, any other character or thing in the story is also called a sprite.
So the rocket will be another sprite in our story. Where should the journey of the astronaut begin? From the Earth, Right! And where is the astronaut travelling to? Mars, the red planet!

Write down the number of sprites shown in the given pictures.

Now, let us learn about the tool from code.org that we will use to make our project. It is called Sprite Lab.
A Sprite Lab is where we can create our own stories and games. The Sprite Lab has three parts:
Play Area: The area where we can see things happening.
Toolbox: The area that holds all the code blocks and which we can use to give commands
Workspace: The area where we can drag and attach the blocks together to make things happen.
It is time to make scenes for the exciting journey of the astronaut in Sprite Lab.
We will have two scenes: one for the start of the story and another for reaching Mars.
Let us begin with the first scene.
Who will be the characters? Where will the scene happen?
Characters: Sprites Setting: Background

Now, let us find the steps to create the first scene in the Sprite Lab.
Algorithm to setup the first scene

1 Set the background to a park. 2 Add the astronaut sprite.

3 Set the size of the astronaut sprite. 4 Add the rocket as the second sprite.
5 Set the size of the rocket sprite.

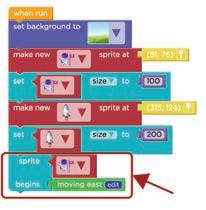
Now, let us follow the algorithm to code the first scene.
Steps to code the first scene:
1 Set the background to a park. Go to the World section. a Find the “set background to“ block. b


1. Drag the set background to block.
2. Drop it under the when run code block in Workspace. Set the background.

Add the park background. e
1. Click the plus sign.
2. Scroll down to choose the park background.
3. Click the Done button.
1. Click the drop-down button.
2. Select Backgrounds. Select the background.


2 Add the astronaut sprite.
Go to the Sprites section. a
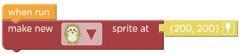
Find the “make new sprite at” code block. b
1. Click and drag the make new sprite at code block.

1. Click the drop-down button in the make new sprite at code block.
2. Click the Costumes button to add the astronaut sprite to your library.


1. Click New Costume. Add a new costume. d

2. Click the Done button. Select the astronaut sprite.
1. Select the astronaut sprite.
Move to the Code window. g
1. Click the Code tab.
Position the astronaut.
1. Click the astronaut sprite. Select the sprite. h

1. Click the location icon to change the position of the astronaut.

2. Move cursor in the Play Area.
3. Click where you want to place the astronaut.

3 Set the size of the astronaut sprite.
Go to the Sprites section. a

1. Go to the Sprites section in Toolbox. 2. Click and drag the set size to code block. Find the “set size to“ code block. b
1. Click the drop-down in the set size to block.
2. Select the astronaut sprite.
3. Change the value of size to 100. Set the size of the astronaut sprite.

4 Add the rocket sprite.
2. Click and drag the make new sprite at code block. Get another “make new sprite at“ code block. a
1. Go to the Sprites section in the Toolbox.

2. Select rocket from the list of sprites. Place the rocket where you want it. Add rocket sprite. b
1. Click the drop-down in the make new sprite at code block.

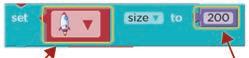
2. Change the value of the size to 200. Set the size of the rocket sprite. a
1. Go to the Sprites section in the Toolbox.
2. Click and drag the set size to code block. Find the “set size to“ code block. c

1. Click the drop-down and select rocket sprite.
Our first scene setup is done.
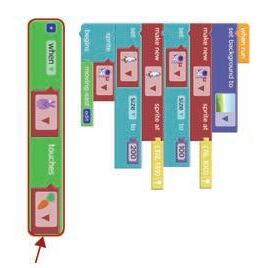
Now, we will add the moving behaviour of the astronaut.
Adding Behavior means telling our sprites what to do when we press the Run button.
Here, we need to make our astronaut sprite move to the right to reach the rocket. Go to the Behaviors section in the Toolbox.
Find the “sprite begins“ code block. 1
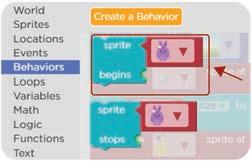
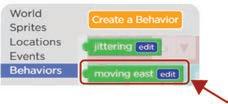
2. Scroll down and look for the moving east code block. Find the “moving east“ code block. 3
1. Go to the Behaviors section.
1. Drag the sprite begins code block.
3. Select the astronaut sprite. Set the “sprite begins“ code block. 2
2. Attach it below the size block of the rocket sprite.
Drag the moving east code block next to begins. Attach the “moving east“ code block. 4
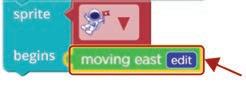
Click the Run button in the Play Area.

A Fill in the blanks.
Hints location sprite behavior size four
1 There are main elements that make up a story.
2 A character in coding is known as a .
3 You can change the of a sprite to place it anywhere in the Play Area.
4 You can change the of a sprite to make it big or small.
5 You can add and control the of a sprite.
B Tick () the correct option.
1 How many sprites are there in the picture given below? a 1 b 2 c 0 d 3 Chapter Checkup








2 Which block can be used to change the costume of a sprite?


3 Sprites can be created with the help of which block?


4 Which block can change the size of a sprite?








5 is the area that holds all the code blocks, which we can use to give commands.
a Play Area
c Workspace
C Who am I?
b Toolbox
d None of these
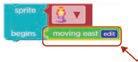
Identify and name the highlighted parts in the given pictures.





D Write T for True and F for False.
1 We need to set the location of a sprite before we make it.
2 You can change the outfit of a sprite.
3 Sprites can touch each other.
4 You cannot add multiple sprites to a scene.
5 You cannot change the size of a sprite.
E Answer the following questions.
1 What is a sprite?
2 What does this button do?

3 Which of the following options will show this sprite in the Play Area?

4 Which of the following options will be shown for the given code?

5 To what side will the sprite move with the given code?

Right
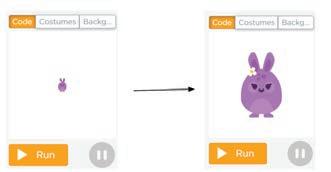
1 Name the blocks in the given space to see this in the Play Area.

2 Observe the Play Area. Name the missing block in the given code.

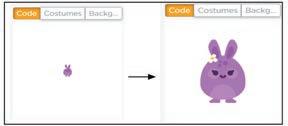
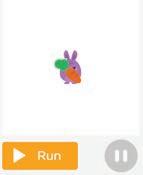
3 Name the missing part in the set block to get the change shown in the purple rabbit.
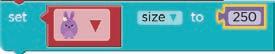
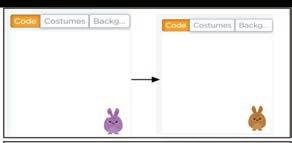
4 What will the given code do to the purple rabbit?



When you complete your work on time, you get good grades. Right?
Here, completing your work is an event and getting good grades is an action.
An event tells you when an action will happen.

What will you do when your hands are dirty? You will wash your hands. Right?
Here, having dirty hands is an event and washing them is an action.
Events are important in coding too!
In a car racing game, we can make the car go left or right, using arrows.
Clicking the arrows is the event. The car moving to the left or right is the action that happens!
Think and Tell
Are mouse clicks and keypress events too?
Now it is time to complete our astronaut story.
Do you remember what the astronaut wants?
The astronaut wants to go to the planet Mars for space exploration.
We had set up our first scene in the previous chapter.
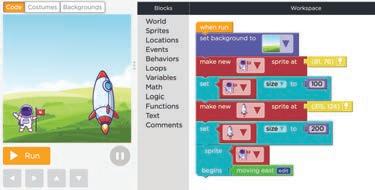
Now, we need to add code for the second scene.
The second scene is where the astronaut will reach the planet Mars. When will the astronaut reach the planet Mars?
The astronaut will reach the planet Mars when it touches the rocket.
Here, touching the rocket is the event.
The astronaut reaching the planet Mars is the action.
We can even change the costume of the astronaut into another to show the victory. A costume sets the appearance of a sprite.
1 Match the correct event and action pairs.
Let us define the event to set up the second scene.
1 Set the event—when the astronaut touches the rocket. Find the “when touches” block. b Go to Events. a


Add it to Workspace. c
Drag and drop the when touches event block below the code we made last time.

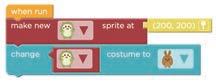
2 Change the costume of the sprite.
2. Scroll down to find the change costume to block. Find the “change costume to“ block. a
1. Go to the Sprites section.

2. Change the carrot sprite to the rocket. Change the sprites. d
1. Change the rabbit sprite to the astronaut.

Attach it to the “when touches” block. b
Drag and drop it below the when touches block.
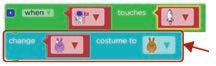
2. Change the brown rabbit to the second costume of the astronaut. Set the costume. c
1. Change the purple rabbit to the first costume of the astronaut.

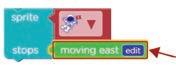
3 Stop moving the astronaut when it touches the rocket.
3. Drop it below the change costume to block. Add the “sprite stops” code block. a
1. Go to Behaviors.
2. Drag the sprite stops block.

1. Scroll down and look for moving east block.

Drag and drop it to the stops section of the sprite stops block. Set the “moving east” block.

A Fill in the blanks.
Hints when touches change costume to costume action event
1 Clicking the Run button to try the game is an .
2 Laughing is an for the tickling event.
3 The block is used to add the event for sprites when sprites bump into each other.
4 A sets the appearance of a sprite.
5 The block will change the costume of a sprite.
B Tick () the correct option.
1 Which of the following statements is true about events and actions?
a An event tells you when an action will happen.
b An action tells you when an event will happen.
c Both actions and events will happen at the same time.
d Actions and events are both independent.
2 Choose the correct action for the given event.
Event: You have an exam tomorrow.
Actions:
a Watch a movie
c Prepare for exam
b Go to a party
d Play a game
3 If you press the ON button on the TV remote, what will be the action of this event?
a Your TV will turn on.
c It will change the channel.
b Your TV will not turn on.
d It will increase the volume.
4 Choose the correct action for the given event.
Event: You spilled your drink.
Actions:
a Mop the floor
c Put on a jacket
b Leave it as it is
d Turn on the TV
5 When will the background change in the story?
a At the start
c Not at all
C Match the following.




b At anytime
d When the astronaut touches the rocket



3 The ringing of a doorbell is an action.
4 Opening the door when a doorbell rings is an example of an action.
5 The “moving east” block stops the behaviour of a sprite.
E Answer the following questions.
1 What is an event?
2 What is an action?
3 What will happen if you use this block?



4 What will you see in the Play Area if you run the given code?

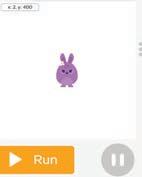
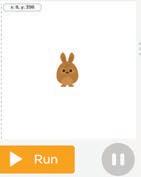
5 What will happen if you run the given code?

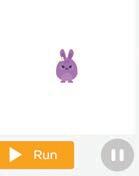
1 Observe the code and the Play Area. Circle the missing sprite in the given code.
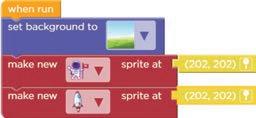



2 Observe the given code. Identify and circle the missing sprite in the given code.

3 Name the missing part of the given code.

4 Write down E for event and A for action in the given boxes.


5 Your room is very untidy. Your mother has asked you and your sister to clean it up. Look at the following pictures and name them as Events or Actions.
























A. Fill in the blanks.
1 is an electronic device that helps us do many things.
2 A lets us use our voice to tell the computer what to do.
3 A is a small stick-like device in which you can store files.
4 The mouse is the little arrow on the monitor that moves when we move the mouse.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Which device helps us print text or pictures on paper?
a Mouse b Monitor
c Printer d Keyboard
2 Which key on the keyboard makes all letters uppercase when you hold it down?
a Shift key b Arrow key
c Enter key d Spacebar key
3 Which button is used to switch off the computer?
a Shut Down b On button
c Switch off d Power off
4 Which button on the mouse is used for opening more options?
a Left button b Scroll wheel
c Right button d Middle button
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Using computers for a long time can harm our eyes.
2 We can use computers to talk to our friends who are far away.
3 The scroll wheel on a mouse can only move in one direction.
4 Numeric keys are used to type letters.
D. Answer the following questions.
1 Write one use of a computer mouse.
2 How are computers useful for teachers?
3 What are punctuation keys?
E. Apply your learning.
1 Ayush wants to type his name in capital letters on the computer. Which key should he use?
2 Aditi was thirsty. Her mother made her juice using an orange and a juicer. Is this an IPO cycle? If so, correctly identify the input, process, and output.
3 Prashant wants to send money to his friend who lives in a far away city. Can you suggest which feature of computer he can use?
4 Pihu is new to computers. She doesn’t know how to open an item. Which button on the mouse can help her?
A. Fill in the blanks.
Test Paper 2 (Based on Chapters 5 to 8)
1 language is used to talk to a computer.
2 A sequence is when we do things step by step in an .
3 A sets the appearance of a sprite.
4 A is a group of tools to help you draw.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Where do you find the ‘when touches’ block?
a Sprites section b Events section
c Behaviors section d Sounds section
2 What is an event in coding?
a Eating food b Clicking a mouse
c Writing with a pen d Sleeping
3 What is Sprite Lab used for?
a Creating stories and games b Editing photos
c Writing documents d Watching videos
4 Which tool in MS Paint would you use to draw a straight line?
a Brush tool b Eraser tool
c Line tool d Text tool
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 An algorithm refers to a set of steps in order to solve a problem.
2 Event and action are both independent of each other.
3 The ‘sprite stops’ block is found in the Behaviors section.
4 A polygon is a shape with many sides.
D. Answer the following questions.
1 Give a real-life example of an event and action.
2 Define a shape.
3 What is an algorithm?
E. Apply your learning.

1 Recall the story of ‘The Hare and the Tortoise‘ and number the pictures in the correct sequence.
2 Write down (E) for event and (A) for action in the given boxes.

3 Mahi wants to draw a picture of a traffic signal. Which tools can she use?
Robots are machines that can do things for us. They can move, think, and even talk. Some robots look like people or animals, while others look like big machines or tiny helpers. People use robots to make work easier and to do things we can’t do by ourselves. Robots use Artificial Intelligence to work.
Robots at Home
• Robots can clean floors for us.
• Some robots can also cook.
• They can help carry things.
• Some robots can water plants.








Robots at Hospitals
• In hospitals, robots help doctors by treating the sick people.
• Robots can help people by reminding them to take medicine.














Robots at Factories
• In factories, robots help make things like cars and toys.
• They can lift heavy things.
• They work fast and don’t get tired.


Robots in Exploration


• Robots can explore outer space, like the ones on Mars.
• Robots can explore deep oceans where it is too dark and deep for humans.



• Robots on farms help plant seeds and pick crops to make food.
• Robots help in watering the crops.
• Robots can cook and bake delicious food in kitchens.
• Some robots work as waiters in restaurants and serve food.
• Firefighter robots help by going into burning buildings and rescue people.
• Police robots help people who are in danger and catch bad people.
• In schools, robots help kids learn to code and build things.
• Some robots can read stories to us and answer our questions.
• Robots can defuse bombs and scout.
• Some robots can even fight.
Uolo has introduced a comprehensive program, Hexa, for grades 1 to 8, to empower young minds with the knowledge and the skills they need to thrive in the digital age. From the basics of how computers function to the tools that shape our digital landscape, this series opens the door to a world of endless possibilities. This series will build a strong foundation, helping shape the next generation of digital citizens and innovators. It aims to demystify the world of computer science, making it accessible and engaging for young learners, while preparing them for future academic and professional pursuits in the field.
• AI Annexures: To offer a basic understanding of specific domains of Artificial Intelligence.
• Discuss: A multi-faceted probing question, related to the concept, that arouses curiosity.
• Think and Tell: Analysis, reflection, and text-to-self connection based prompts for discussion in class.
• Did You Know? Interesting facts related to the application of a concept.
• Do It Yourself: Short exercises between the chapter to pause and assess comprehension.
• Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom's Taxonomy.
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to bring technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, South East Asia, and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-979297-4-8
