





Academic Authors: Jatinder Kaur, Ayushi Jain, Chandani Goyal, Kashika Parnami, Anuj Gupta, Simran Singh
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Rakesh Kumar Singh, Sanjay Kumar Goel
Project Lead: Jatinder Kaur
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First impression 2023
Second impression 2024
Third impression 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Tekie ICSE Computer Science 5
ISBN: 978-81-981442-7-0
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
Standing at the forefront of the digital and AI revolution, the importance of coding and computational skills has reached unprecedented heights. In today’s professional landscape, whether it is in the fields of medicine, space exploration, education, science, or business, no sector remains untouched by this transformative wave. To thrive in the 21st century, basic computer literacy is no longer sufficient. Learners must evolve into ‘digital natives’ who can fluently read, write, and communicate in the languages that machines and AI comprehend.
Recognising this imperative, the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 has strongly recommended the integration of coding skills, computational thinking, critical analysis, and problem-solving abilities into the curriculum. Moreover, forward-looking subjects like AI, Data Science, Computer Applications, and IT have been introduced as elective subjects from grade 9 onwards. It wouldn’t be surprising if further transformative measures are taken even at the elementary education level.
Uolo has introduced an innovative 360-degree program for a coding-focused computer science curriculum, known as Tekie, spanning grades 1 to 8. Tekie is a significant stride towards STEM education that aims at making learners future-ready—enabling them with skills needed in the ever-changing, technology-driven, and dynamic 21st-century world.
Tekie adopts a captivating and engaging approach to learning, in line with the recommendations of the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023 and NEP 2020. The curriculum is ingeniously woven into the thrilling adventures of Mel and Conji, fictional characters from the enchanting land of Avora. The Mel and Conji series epitomises a modern method of acquiring computer science knowledge and honing computational thinking skills. The program includes chapters that provide a deeper immersion in computer science that both learners and teachers may find interesting.
Tekie is a technology-empowered curriculum that encompasses the following components:
• Main Content Books: These introduce learners to the theory of computer science and computer tools. Topics in AI are also covered, along with experiential and project-based learning resources.
• Coding Books: Specifically designed to nurture coding skills, this booklet aligns with the experiential and contextual learning approach of the coding curriculum, fostering critical thinking and problemsolving abilities.
• Animated Learning Videos: The program is powered by high-quality animation-based learning videos that deliver learning in an engaging manner.
• Teacher Manual: This valuable resource supports classroom instruction, ensuring that educators effectively deliver the curriculum.
Welcome to the captivating realm of Tekie! We hope you relish this educational journey as it equips you with the tools you need to thrive in the exciting and ever-changing world of the 21st century.
Tekie is an interactive, engaging, and experiential computer science program. It enables learners to attain mastery in computer science theory, new-age computer tools and coding. These are delivered through a storytelling-based coursebook and an experiential learningoriented coding book.
The learning experience is augmented by a digital platform that gives learners access to learning videos and experiential activities and projects that are rooted in the curriculum.
Engaging Textbooks
Comic Stories
Teacher Manual
Test Papers
Additional Projects
Test-paper Generator




Student and Teacher Platform
Learning Videos
Interactive Classroom and Homework Assignments
Byte-size Lesson Modules
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, introduced by the Government of India, represents a transformative shift in the country’s education system. It aims to create a more holistic, dynamic and multidisciplinary approach to education. The NEP highlights the need for early development of computational thinking, coding, and digital literacy as vital skills for students’ holistic growth. UOLO is fully committed to actualising the vision of NEP 2020 by meticulously adhering to its outlined recommendations.











1. Focus on conceptual understanding
2. 21st century skills, values, and dispositions
3. Computational and critical thinking
4. Application in real life
5. Holistic and integrated learning
6. Experiential learning
7. Enjoyable and engaging
8. Artificial intelligence and coding concepts
9. Digital literacy and emerging technologies
10. Factoids on India
Competency-based Education
NEP Pages 12, 17 and 22
Teaching and Learning Pedagogy
NEP Pages 3, 5, 11, 12 and 56
National Pride
NEP Pages 15, 16 and 43
11. Assessment of core concepts and application skills Assessments
NEP Pages 12, 18 and 22
Project-based Learning
Engaging hands-on projects encouraging practical application of computer science and coding
Story-based Approach
Enchanting tales that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure 5 7
Equipping the students with future-ready skills through exposure to the latest tools and technologies
Engaging chapters to deepen students’ understanding and engagement with AI concepts
Test papers designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills 3 4 11
Projects on the digital platform to deepen understanding and develop essential practical skills
Invites learners to discuss in small groups and present different perspectives
Story-style learning videos that deliver concepts to students.
Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical, and evaluative thought process
Interactive quizzes that reinforce learning and assess students’ understanding
Think It Through
Probing question related to the concept that arouses curiosity
Tool to create customised assessments that align with the curriculum and help evaluate students’ progress effectively.
Factoids on India
Assessment of core concepts and application skills
The curriculum is thoughtfully mapped to introduce tools and technologies at each grade level, ensuring a smooth and progressive learning experience for students. Beginning with basic concepts in junior grades, the curriculum gradually incorporates more advanced tools and concepts in higher grades. This structured approach enables students to build on their knowledge each year, equipping them with essential skills in computer science and technology as they progress from grade 1 through grade 8. By the time they reach the higher grades, students are well-equipped to tackle complex projects, think critically, and apply their skills in real-world scenarios. The curriculum not only fosters technical proficiency but also encourages creativity, problem-solving, and a deeper understanding of the digital world.

Advantages
Theme
the chapters covered under a unit


Comic Story: To introduce key concepts in a fun way
Discuss: A multi-faceted probing question related to the concept that arouses curiosity






Did You Know: Interesting facts related to the topic

c
Computers are very useful but they also have some disadvantages. Some of them are:


Explore More: Short videos to find out more about the topic






Do It Yourself:











Project-based Learning: A project-based learning approach employed to foster an engaging and interactive learning experience
Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Apply Your Learning: Intellectually stimulating questions designed for higher-order thinking and analysis

Points to Remember: Summary of the chapter
E. Answer the Following. What is MS Paint? How do you start MS Paint? What are the parts of the MS Paint
















Artificial Intelligence: Chapters on Artificial Intelligence to explore the fundamentals of AI, including its principles and applications in various fields
Test Papers: Designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills
A. Fill in the blanks.
Test Paper 1 (Based on Chapters 1 to 3)
1 Things that are present in nature are called things.
2 Some machines need to work.
3 Computers are used in to keep information of patients.
4 At restaurants, computers are used to order and pay for B. Tick () the correct answer.
1 Which of the following is a human-made thing? a Mountains b Trees c Cars d Animals 2




•
• Introduction to Presentations
• Creating a Presentation Using Google Slides
• Applying and Modifying Themes
• Inserting Tables, Charts, and Diagrams
• Working With Master Slide
•
• Requirements for Connecting to the
• Browsing the Internet
• Services on the Internet
• Threats on the Internet
• Netiquette
• Applying Animations
• Applying Transition
• Adding Audio and Video
• Fonts
• Text Alignment
• Line and Paragraph Spacing
• Hyperlinks
• Indenting Text
• Using Tab Stops
• Drawing
• Adding Shapes
• Adding Text Boxes
• Adding Images
* This chapter is not a part of the prescribed ICSE curriculum. It has been added after consideration of the latest trends in the computer science field. Teaching this chapter or including it in the assessment process is entirely at the discretion of the school and the subject teacher.



Computers have become an integral part of our lives. They help us in almost every sphere of life these days. We cannot even imagine a world without computers. Have you ever wondered how people were managing without computers before their invention?
Let us learn about the history of computers and how they evolved from slow, bulky, and room-sized machines to fast, smart, and sleek gadgets.
1. Abacus:
a. Abacus is one of the earliest counting devices.
b. It is a wooden frame that is divided into two parts.
c. Both the parts have rods on which the beads can move and are used for basic mathematical calculations.
2. Napier’s Bones:
a. It is a manually-operated calculating device developed by John Napier in 1617.
b. In this calculating tool, he used nine different ivory strips or bones marked with numbers to multiply and divide.
3. Pascaline:
a. Pascaline, also called the Arithmetic Machine or Adding Machine, is the first mechanical and automatic calculator.
b. It was invented between 1642 and 1644 by the French mathematician and philosopher, Blaise Pascal.
c. It can be used to perform only addition and subtraction.
4. Stepped Reckoner or Leibniz Wheel:
a. Leibniz, a German mathematician and philosopher, created Stepped Reckoner in 1673, improving upon earlier mechanical calculators.




b. It is a digital mechanical calculator that uses fluted drums to represent numbers.
c. Leibniz’s machine helped us see that machines could do maths automatically, which eventually led to today’s computers.
5. Difference Engine and Analytical Engine:
a. Charles Babbage designed both engines and is also known as the ‘Father of Modern Computers’.
b. The Difference Engine performs simple calculations, whereas the Analytical Engine uses punch cards for input. A punch card is a piece of card that stores digital data using punched holes.
6. Tabulating Machine:


a. It was invented by an American statistician Herman Hollerith in 1890.
b. This electromechanical machine was developed to help in processing data stored on punch cards.
7. Differential Analyzer:
a. It is the first electronic computer invented in the United States in 1930.
b. This analogue device, invented by Vannevar Bush, could perform 25 calculations in a few minutes.
8. Mark I:
a. In 1937, Howard Aiken thought of the idea of a machine to handle large-scale calculations.
b. In 1944, IBM and Harvard collaborated to build the Mark I computer.
9. ENIAC:
a. Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC) was one of the first programmable, general-purpose, electronic digital computers. It was built in 1945 by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert.
b. It was massive and superfast for its time, like a giant calculator, with lots of tubes and wires.
c. It helped with important tasks like performing calculations for the military, predicting the weather, and studying science.




d. ENIAC started the era of modern computers, demonstrating their ability and inspiring the development of smaller and more efficient machines.
10. UNIVAC:

a. After ENIAC, John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert developed the Universal Automatic Computer (UNIVAC) and delivered it to the Census Bureau on 31 March 1951. This computer is one of the earliest commercial computers.
b. It replaced the punch card accounting machines. It was the fastest machine developed in its time.
ENIAC weighed more than 27 tons and took up 1,800 square feet space. Did You Know?

c. It helped with research-level calculation in universities and helped make office calculations automatic.
Generations of computers means the various stages of advancement in computer technology. These generations are usually categorised into five main phases:
1. First generation computers (1946–59):
a. These early computers used vacuum tubes, which consisted of thin filaments. This filament caused the computers to heat up a lot.
b. They had less memory, so they could not store much information.

c. These computers were huge, costly, slow, and not so reliable. They required a lot of maintenance.
d. The famous first generation computers include ENIAC and UNIVAC.
2. Second generation computers (1959–65):
a. Compared to first generation computers, these computers were relatively smaller because they used tiny transistors instead of bulky vacuum tubes.
b. These computers were faster and cheaper, making them more efficient.
c. They stored information using magnetic core memory.
d. People used punched cards for input and got results on paper or magnetic tapes.
e. These computers used assembly languages for programming and could work on data in organised batches.
f. Famous computers from this time were the CDC 3600 and IBM 7090.
3. Third generation computers (1965–71):
a. The third generation computers used integrated circuits (ICs). They are also known as silicon chips or microchips. They were used widely. ICs are the circuits of many electronic components together on a chip. This significantly reduced the size of computers.


b. The ICs in this generation used the small scale integration (SSI) and medium scale integration (MSI) technologies.
c. They used better memory called the core memory, which was faster and more reliable than the older magnetic drum memory.
d. Keyboards and friendlier interfaces were introduced for users which helped them interact with the computers.
e. Programming languages like Common Business-Oriented Language (COBOL), Formula Translation (FORTRAN), and Beginner’s All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code (BASIC) made it easier to write software for these machines.
f. These computers were smaller but still expensive. IBM’s System/360 and DEC’s PDP-11 were popular models during this time.
4. Fourth generation computers (1971–80):
a. Fourth generation computers used integrated circuits with VLSI technology. VLSI stands for very-large-scale integration, which means almost up to 1,00,000 electronic components on a single small chip. This chip is also known as a microprocessor.

b. They use the faster and more reliable Random Access Memory (RAM) instead of the older magnetic core memory.
c. Input devices like keyboards and mouses are used to interact with these computers. For output, they have monitors and printers.
d. High-level programming languages like C, Pascal, and FORTRAN are used to write software for these computers.
e. Fourth-generation computers are faster, smaller, and cheaper than their predecessors. Some popular names from this era include IBM PC, HP 9000 Series, and DEC 10.
5. Fifth generation computers (1980–current):
a. Fifth generation computers use artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) as their main technologies.
b. They have advanced memory to store and handle large amounts of data effectively.
c. Input and output methods include voice recognition, gesture control, augmented reality, virtual reality, and brain-computer interfaces.
d. Popular programming languages like Python, R, and Julia are used to create AI and ML programs.



Learn more about ENIAC, the first programmable, electronic, generalpurpose digital computer.
Even though the first modern computer was huge, it could perform only four tasks: addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Did You Know?

Match the following.





Match the generation of computers with their technology.
First generation computers Integrated circuits (SSI, MSI)
Second generation computers Integrated circuits (VLSI)
Third generation computers Artificial intelligence
Fourth generation computers Transistors
Fifth generation computers Vacuum tubes
Computers have some special qualities that make them amazing:
1. Speed: Computers are super-fast at doing things. They can do lots of calculations and tasks in just a fraction of a second, way faster than humans can.
2. Accuracy: Computers are good at being accurate. They do not make mistakes like human beings may sometimes do.
3. Storage: A computer has a large memory. It can be used to store pictures, document, videos, and more.
4. Automatic: Computers can perform tasks on their own, following the instructions that they are given.
5. Multitasking: Computers can work on various tasks at the same time. Just like you can read a book while listening to music, a computer can run a game while also making calculations.
6. Communication: With the help of computers, you can communicate with other people using the internet.


Using the latest technology, you can make and receive phone calls by connecting your phone to a computer.
What are some basic things that you see on a computer screen? Think and Tell

Computers are incredibly powerful and versatile machines, but they also have several limitations. Here are some of the key limitations of computers:
1. Computers cannot think like humans: Computers are designed and controlled by humans. Even when they seem to operate independently, it is because humans have programmed them to do so.
2. Maintenance: A computer needs regular maintenance and timely updates for its proper working.
3. Lack of emotional intelligence: While you experience a range of emotions like happiness, sadness, and excitement, computers lack emotional intelligence and empathy. This limits their applications in fields that require emotional understanding, such as counselling and therapy.
T for True and F for False.

What tasks can be done using a computer?
1 Computers are faster than humans at performing calculations and tasks.
2 Communication with other people using the internet cannot be done through computers.
3 Computers can work on multiple tasks simultaneously.
4 Computers can experience and express human emotions like happiness and sadness.
The history of computing devices began with the invention of the abacus around 4,000 years ago in China.
Charles Babbage’s designs, the difference engine, and the analytical engine laid the foundation for modern computers.
The ENIAC, built in 1945, was the first electronic and programmable computer.
First generation computers (1946–59) used vacuum tubes, and were large and unreliable.
Second generation computers (1959–65) introduced transistors, magnetic core memory, and punch cards. These computers were more reliable than the first-generation computers.
Third generation computers (1965–71) brought integrated circuits, core memory, and userfriendly interfaces. The use of ICs significantly reduced the size of computers.
Fourth generation computers (1971–80) featured microprocessors, RAM, and advanced input/ output devices.
Fifth generation computers (1980–to date) use AI and ML technologies, advanced memory, and innovative input/output methods.
Computers are known for their speed and can perform complex calculations in a fraction of a second.
They possess memory to store vast amounts of information, ensuring quick access.
Computers are highly accurate and precise, minimising errors in calculations and tasks. They have storage capacity to hold various types of data, such as documents, images, and videos.
Computers can do tasks on their own, following the instructions that they have been given. They can multitask, working simultaneously on multiple processes.
Computers let us communicate through the internet, letting us connect globally.
Computers lack independent thinking, emotions, and empathy. They rely on precise instructions and require regular maintenance.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
The ancient Chinese invented the approximately 4,000 years ago, which is considered the first calculating device.
The first programmable electronic digital computer, often considered the beginning of modern computing, was called
The first generation of computers, from 1946 to 1959, used
The third generation of computers introduced , which significantly reduced the size of computers.
Fifth-generation computers use and have advanced memory for handling large data sets.
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
What type of memory did second generation computers use for storage?
a Magnetic core memory
c Magnetic drum memory
b RAM
d Punch cards
In which generation of computers were integrated circuits (ICs) introduced instead of transistors?
a Second generation
c Fourth generation
b Third generation
d Fifth generation
Which programming language is NOT associated with the third generation of computers?
a Python
c FORTRAN
b COBOL
d BASIC
Which computer inventor is often referred to as the ‘Father of Modern Computers’?
a Charles Babbage b John Napier
c
Which characteristic of computers allows them to perform multiple tasks simultaneously? a
C. Who Am I?
I am the one who designed two significant machines, the Difference Engine and the Analytical Engine, during the early nineteenth century.
I am the generation of computers characterised by large size, slow speed, and use of vacuum tubes for computation.
I am a machine that was invented between 1642 and 1644 by Blaise Pascal, and am capable of performing addition and subtraction operations.
I am a German mathematician known for inventing Leibniz Wheel, a digital mechanical calculator.
I am one of the first electronic computers ever made in 1945, and I helped with important tasks like performing calculations for the military, weather prediction, and scientific research.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
The Tabulating machine was invented by American statistician Herman Hollerith.
A punched card is a piece of card stock that stores digital data, using punched holes.
Fifth generation computers use AI.
E. Answer the Following.
and updates to ensure that they function properly.
Apply Your Learning.
Sree lived a long time ago, way before computers were invented. Name some devices that he could have used for faster calculations.
Raj found something to help him with multiplication and division. This device is not a modern calculator, and it has ‘bones’. What do you think it can be?
Tanya had a wooden rack, which had metal rods with beads mounted on them. Tell Tanya the name of the inventor of this wooden rack and what it is called.
Archi discovered that computers have a big closet where all their important data can be kept. Can you let Archi know what this closet is called?
Ram thought about a computer that could do many things at once. It is like a clever friend who can solve maths problems while also having fun playing a game. What do you call this characteristic of a computer?





We all have played with a remote-controlled toy car in our childhood. If we press the forward button on the remote, the car moves in the forward direction. If we press the left button, the car moves left, and so on. So, just like the remote control guides the toy car to perform various actions, the software gives instructions to computer hardware to perform various tasks.
A computer is a machine that cannot think on its own. To make it do anything, we have to give it instructions, which we call programs. These instructions are written in computer languages.
Software is a set of programs that is installed and run on computer hardware that helps users to interact with the computer. Software is an intangible part of a computer, which means that it cannot be touched.
Software started to be marketed on floppy disks in the 1980s, and then on CDs and DVDs. Most software is now bought and downloaded from the internet.

There are two types of software: system software and application software. Let us learn about both of these software in detail.
System software is responsible for managing and controlling the overall functioning of a computer system. This software provides essential services and functionalities to allow application software to run efficiently. System software reads data from the input devices and transfers processed information to the output devices. There are three types of system software: Operating system, utility software, and language processor.
An operating system is the initial system software that loads on to computer memory when you turn on a computer. An operating system acts as an interface between a user and a computer system and is, therefore, a crucial requirement for a computer to function.
Some examples of operating systems include Microsoft Windows, macOS, Android, Linux, and Unix.

An operating system carries out various important functions that help in the smooth running of a computer. Here are a few functions of an operating system:
An operating system manages everything on the computer. This program makes sure that all the games, apps, programs, applications, and files work together.
It allocates and deallocates memory space to running processes, ensuring efficient use of RAM.
It is easy to use. You can click icons and buttons because the operating system provides you a friendly way to talk to the computer.
An operating system protects a computer from viruses and hackers. This software also checks who is allowed to use which resources on the computer.
An operating system detects and handles errors or crashes, preventing a single application or hardware issue from crashing the entire system.


Utility software is a type of system software that provides essential tools and functionalities to maintain, optimise, or troubleshoot a computer system. These tools are intended to improve the overall performance and security of a computer system. Users often install these tools alongside their primary applications to ensure that their systems run efficiently and securely.
Some common examples of utility software include antivirus software, disk cleanup and defragmentation tools, backup and recovery software, file compression software, and firewalls.
File Manager: File manager helps users organise, navigate, and manage files and folders on their computer hard drives, external drives, etc. File Explorer of Windows is the most commonly used file management utility software.
Disk Management: Disk management is the software tool or utility that is used to manage data storage devices by performing various operations like managing drives, formatting disks, verifying the integrity of disks, and partitioning drives.
Backup Utility: Backup software is used to create duplicates of important files and data stored on a computer. These duplicate copies, known as backups, are typically stored in secure locations such as cloud storage or external hard drives. The primary purpose of backup software is to safeguard your data against potential loss resulting from hardware failures, human errors, or other unforeseen circumstances.
Compression: Compression refers to the process of reducing the size of data. This technique helps decrease the number of bits and bytes required to represent information in a file. Compression serves several purposes, including conserving storage capacity, speeding file transfers, and lowering the costs associated with data storage.
One common usage of compression is to archive several files into a single compressed folder using ZIP files.
Time Machine (for Mac) and Windows Backup (for Windows) are popular backup software.

Name any one utility software that you commonly use.

Computers can only understand and execute programs written in machine language, which consists of binary code made up of strings of 0’s and 1’s. A language processor is used for translating high-level programming languages, which are human-readable and easier for programmers to work with, into machine language.
Without language processors, programmers would have to build applications directly in machine code, which is difficult and prone to mistakes.
There are three types of language translators: assembler, interpreter, and compiler.
Assembler: An assembler is a translator that converts the code written in assembly language into machine language.
Interpreter: Interpreters work sequentially, reading one line of source code at a time and executing it immediately. If an interpreter finds a mistake, it stops and when you fix the mistake, it moves on to the next part of the program, repeating the same process.
Compiler: A compiler is a type of a language processor that takes the entire source code of a high-level programming language and translates it into machine code or an intermediate code in a single step. A compiler generates the object code for the program along with the list of errors. The code cannot be executed until these errors are fixed.
State T for true and F for false.
1 Several files can be compressed into a single folder using ZIP files.
2 File Explorer is a backup utility.
3 Software is a tangible part of a computer.
4 Operating System allocates and deallocates memory space to running processes.
Application software is a type of computer software designed to perform specific tasks, such as word processing, creating presentations, web browsing, email communication, doing calculations, and editing images.
There are two types of application software: General purpose application software and special purpose application software.
General-purpose application software is made to carry out several jobs and activities on a computer. This software can be used for many tasks and is not restricted to a single one. Word processors, spreadsheets, and presentation software are a few examples of general-purpose application software.
General-purpose application software may include:
Word processing software: Word processing software is a type of application software to create, edit, and format text documents.
Examples include Google Docs, Microsoft Word, OpenOffice Writer, and WordPad, which are used to type essays, letters, assignments, or simple reports.


Spreadsheet software: Spreadsheet software is used to create, manipulate, and manage tabular data in a grid of rows and columns. This software is designed to perform mathematical calculations on numerical data using formulas and functions, analyse data using charts and graphs, etc.
Examples include Microsoft Excel, OpenOffice Calc, and Google Sheets.

Presentation software: Presentation software is computer graphics software that is used to create visual presentations to convey ideas, information, and messages to a large group of audience in a lively manner. This software allows users to create slides or pages that contain content in the form of text, images, charts, audio, video, etc.
Examples include Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, and OpenOffice Impress.
Graphics software: Graphics software applications are used to create a range of visual designs, including interactive and static content, such as images, flyers, brochures, banners, logos, cartoons, etc.
Some examples are Paint, Adobe Photoshop, and AutoCad.




Multimedia software: Multimedia software helps create, edit, and manipulate multimedia content. It is used to create videos, animation, sound, graphics, and text with a high degree of interaction.
Examples include Windows Media Player, Adobe Animate, Windows Movie Maker, and Adobe Flash.

Special-purpose application software performs specific, narrowly defined tasks or functions. Unlike general-purpose software, which is designed for a wide range of applications and users, special-purpose software is tailored to meet specific needs of any user.
Examples include library management system, hotel management system, and Point of Sale (POS) system.



Match the following.
1 Multimedia software Microsoft PowerPoint
2 Spreadsheet software Paint
3 Presentation software Google Sheets
4 Graphics software Windows Media Player
1 Software is a set of programs that are installed and executed on computer hardware, facilitating user interaction with the computer.
2 System software is responsible for managing and controlling the overall functioning of a computer system. This software provides essential services and functionalities to allow application software to run efficiently.
3 Types of system software include operating system, utility software, and language processor.
4 When you turn on a computer, the operating system is the initial program that loads into its memory, setting the stage for all other operations.
5 Utility software is a type of system software that provides essential tools and functionalities to maintain, optimise, or troubleshoot a computer system.
6 A language processor is used for translating high-level programming languages, which are human-readable and easier for programmers to work with, into machine language.
7 Application software is a type of computer software designed to perform specific tasks, such as word processing, creating presentations, web browsing, email communication, doing calculations, editing images, and more.
8 There are two types of application software: General-purpose application software and special-purpose application software.
9 Word processors, spreadsheets, and presentation software are a few examples of generalpurpose application software.
10 Examples of special-purpose application software include library management system, hotel management system, Point of Sale (POS) system, etc.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
Hints assembler operating system compression system spreadsheet
1 software provides essential services and functionalities to allow application software to run efficiently.
2 software is used to create, manipulate, and manage tabular data in a grid of rows and columns.
3 A/An is a translator that converts the code written in assembly language into machine language.
4 refers to the process of reducing the size of data.
5 Microsoft Windows, macOS, Linux, and Unix are all examples of .
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1 Which of the following is not word processing software?
a Microsoft Word b OpenOffice Writer
c Microsoft Excel
d Google Docs
2 Which of the following language processors takes the entire source code of a high-level programming language and translates it into machine code in one step?
a Compiler b Interpreter
c Assembler
d File manager
3 software is used to create duplicates of important files and data stored on a computer.
a Compressor
c Backup
b File manager
d Assembler
4 When you turn on a computer, the is the initial program that loads into its memory.
a File Explorer
c Multimedia software
b Operating system
d Language processor
5 is a type of system software that provides essential tools to maintain, optimise, or troubleshoot a computer system.
a Utility software
c Language processor
b Operating system
d Application software
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Interpreters read one line of source code at a time.
2 Windows Media Player is multimedia software.
3 An operating system protects a computer from viruses and hackers.
4 High-level languages consist of strings of 0’s and 1’s.
5 A library management system is general purpose application software.
D. Answer the Following.
1 Write any two functions of operating systems.
2 Differentiate between an interpreter and a compiler.
3 What do you mean by backup?
4 Explain application software. Give examples.
5 What is the need of a language processor?
E. Apply Your Learning.
1 Surbhi is asked to give a presentation on the topic ‘Waste Management’ in the school auditorium. Name a presentation software application that she can use for the same.
2 Mohit is experiencing slow file transfer speed while sending school picnic pictures via email, even with a fast internet connection. What can be the reason and how should he resolve this issue?
3 Swati is working with a large numerical dataset. She wants to perform calculations and analyse the data using charts and graphs. What software should she use for the same?
4 Maira accidentally lost all her important data on her computer due to a hardware failure. How can she avoid a similar situation in the future?





You can talk to your friends over a phone, send and receive messages, and share pictures and a lot of other information. Have you ever wondered how all of this is possible?
Well, This is possible because of the internet.
The internet is a huge network of millions of computers connected worldwide. The internet allows communication and the sharing of

The early foundations of the internet were laid in the 1960s with the creation of Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, or ARPANET.
Some of the important uses of the internet are:
1. Online shopping: You can buy toys, clothes, and many other things online, all from the comfort of your home. Apps like Amazon, Flipkart, and Myntra make it easy to buy things with just a click.
2. Cashless payment: You can use apps like Paytm, Google Pay, or credit and debit cards to make online payments for your online purchases. These transactions known as cashless payments are becoming increasingly popular.
3. Online learning: The internet allows you to discover new information from all over the world, making it possible to learn about a wide range of topics anytime and anywhere.
4. Online communication: Using the internet, you can talk to your friends, see their pictures and videos, and share a lot of data with them. There are some applications like Facebook, Instagram, and more that make this possible.
5. Entertainment: The internet offers you plenty of entertainment options. You can enjoy videos, play games, and listen to your favourite songs. Additionally, you can download films, games, and music. Apps like Netflix, Hotstar, and YouTube provide access to a wide range of video content as well.

The first website on the internet was created in 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee. Did You Know?

To get on the internet, you need a few things. Let us learn about what you need:
1. Internet service provider (ISP): An ISP is a company that provides you with access to the internet, often for a fee. ISPs use cables, satellites, or other technologies to connect you to the internet. There are various ISPs, and they offer many speed and price options. Examples are BSNL, Airtel, Jio, etc.

2. Device: You need a device that can access the internet, such as a computer, smartphone, tablet, or smart TV. These devices should have specific features that enable you to connect to the internet, like Ethernet ports for an internet cable or a Wi-Fi functionality.
3. Modem: A modem is a device that carries out the processes of both modulating and demodulating electrical signals. It ensures a constant connection between the internet and a home or office network.
4. Network cable (for wired connections): A network cable is a type of cable that is used to connect devices on the internet. This cable is a physical connection that allows devices to communicate with each other. Network cables are typically used in offices, homes, and schools.

5. Web browser: A web browser is an application that allows you to visit websites on the internet. It lets you see various web pages and access information that are available.
The availability of the methods to connect to the internet may depend on your location. Here are some common methods:
1. Wired connection (using cables): This connection uses copper or fibre optic cables to transmit data. Wired connections are known for their reliability and speed. They are often used in homes and businesses where stable and high-speed internet access is required. They are also known as broadband connections.

2. Wireless connection (using signals): Wireless connections use radio waves to transmit data between devices and a router. This method is highly convenient as it eliminates the need for physical cables. Wi-Fi is one of the most commonly used wireless connections.
3. Cellular connection: Cellular connections use mobile networks and cell towers to provide internet access. They are widely used for mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. These devices have data limitations and varying speeds based on their network coverage.
4. Satellite: Satellite internet relies on communication satellites in orbits to provide internet access to remote or rural areas where other forms of internet connectivity may not be readily available. This method can show a slightly longer delay compared to other methods.
5. Dial-Up: Dial-up is an old and slow way to connect to the internet. A dial-up connection uses a regular phone line. But it is not good for today’s internet because it is too slow and cannot handle modern internet speed. Most people now use faster internet connections like broadband.

From the word grid, find the given words related to the internet.
DEVICE BROWSER WIFI SATELLITE ISP MODEM
Browsing the internet refers to using a web browser to search for and access information on the World Wide Web (WWW), which is a part of the internet.
There are various web browsers, but some of the most common ones include Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, Safari, and Mozilla Firefox.


You can also check your browsing history on a Wi-Fi connection.


The internet is so vast that no one knows exactly how many websites are on it. It is like having a library with more books than you can ever read in a lifetime.

Internet services refer to the various applications, resources, and functionalities available to users on the internet.
The internet offers a wide range of services and applications that have become an important part of our daily lives. Here is a list of some of the key services provided by the internet:
1. Email: Email, which means electronic mail, allows users to send and receive messages, files, audio, links, images, etc., over the internet. For example, Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, and so on.
2. Search engines: This program enables users to search for information, websites, and multimedia content on the internet. For example, Google, Bing, and so on.
3. File sharing: The file sharing services help facilitate the storing and sharing of files and documents online. For example, Dropbox and Google Drive.
4. Streaming media: These allow users to stream and consume various forms of digital media, including videos, music, and podcasts. For example, Netflix (for movies and TV shows), YouTube (for user-generated videos), and Spotify (for music streaming).
5. Social media platforms: These platforms enable users to connect, communicate, and share content with friends, family, and colleagues. For example, Meta, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn.
6. E-commerce: These applications provide a platform for buying and selling products and services online. For example, Amazon, eBay, Myntra, etc.


7. Maps and navigation: These applications offer navigation, directions, and locationbased information. For example, Google Maps, Apple Maps, Waze, and so on.
Raymond Samuel Tomlinson was the first person to send an email in 1971.

Complete the following words.
a S REA I G ED A
b FI E H RI G
c EM I
d S CI L E D A
Match the following.

The internet has so many benefits and opportunities, but it also comes with many threats and risks. Some of the risks are:
1. Malware: Malware, short for ‘malicious software’, refers to any software designed to harm, exploit, or compromise computer system, network, or user privacy. Various types of malware include:
a. Virus: A virus is a small program designed to damage your computer by gaining access to it. A virus can copy your personal data or slow down your computer.

b. Worms: A computer worm is a stand-alone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers.
c. Trojan horse (Trojan): A Trojan horse is a type of malware that disguises itself with a false or fake name to mislead users. This malware downloads on a computer, pretending to be a genuine program.
d. Ransomware: It is a mean computer trick. It locks up your important applications and asks for money to unlock them. This can cause lots of problems, like not being able to use your computer.
2. Phishing happens when online tricksters pretend to be nice but want your important information, like passwords and where you live. They send fake messages that seem real to fool you, so never share important things with anyone unknown.
3. Cyberbullying happens when people use social media platforms to be mean and hurtful to others. This can make people feel really sad and scared.
4. Privacy invasion means doing things that break the rules and make people feel uncomfortable or unsafe when they use the internet. This can include entering someone’s private information, watching what they do online without their permission, or sharing their personal data without asking.


It is important to create a strong password to keep your online resources safe from cyberbullies.
Netiquette, shortform for internet etiquette, refers to a set of guidelines and rules for polite and respectful behaviour when communicating online. Practising good netiquette is essential for a positive and productive online environment.
Here are some important netiquette principles for internet users:
1. Be kind and respectful: Treat others on the internet the way you want to be treated. Don’t say bad things or be a bully.
2. Use good language: Don’t use bad words or rude language when you are chatting or leaving comments. Use words that are nice and friendly.
3. Don’t share personal information: Never give out your full name, address, phone number, or other private details online. Keep your personal information safe.
4. Be careful with what you post: Think before you post pictures, videos, or messages. Make sure that they are safe and don’t hurt anyone’s feelings.
5. Respect other people’s privacy: Do not go through someone’s personal content or spill others’ secrets.
6. Be careful while using emojis: Emojis are a fun and expressive way to communicate, but it is important to use them carefully and considerately. Emojis may be appropriate in casual conversations with friends but should not be used in formal emails.
7. Do not spam: Spamming means sending the same message repeatedly. It is annoying. Hence, do not do it.
8. Do not shout: Writing in all capital letters is like shouting when talking to someone online. Use small letters most of the time.


The internet is a vast computer network for communication and information sharing.
Key uses of the internet are: online shopping, cashless payments, online learning, communicating with friends, and entertainment.
Requirements for connecting to the internet are: ISP, device, modem, network cable, and internet browser.
Common ways to connect to the internet are: wired, wireless, cellular, Wi-Fi, satellite, and dial-up.
Browsing the internet involves using web browsers like Edge, Chrome, Safari, and Firefox to search for information.
Internet services include email, search engines, file sharing, streaming content, social media, e-commerce, and maps/navigation apps.
Internet threats include malware, phishing, cyberbullying, and privacy invasions.
Practising netiquette is essential for polite and respectful online communication.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
A/An is a company that provides access to the internet.
A is a device that carries out the processes of both modulating and demodulating electrical signals.
Browsing the internet refers to using a web browser to search for and access information on the . is a type of malware that can lock up your important things and ask for money to unlock them. Using
B. Tick () the Correct Option. What
Internet services have become an important part of our daily lives. What does the term ‘internet services’ refer to?
a Physical devices used to access the internet.
b Websites that provide information about the internet.
c Various applications, resources, and functionalities available on the internet to users.
d Virtual reality games that are available on the internet.
Which type of malware disguises itself with a fake name to mislead users?
a Virus
c Trojan Horse
Which is not an example of a web browser?
a Google Chrome
c YouTube
b Worm
d Ransomware
b Safari
d Firefox
Which term is used for using social media to be mean and hurtful to others?
a Privacy invasion
c Cyberbullying
b Malware
d Phishing
I am a type of cable that is used to connect devices to the internet.
I am a service on the internet that facilitates the sharing and storage of files and documents online.
I am a way of connecting to the internet without using wires that uses radio waves to send and receive data.
I am the platform where you can connect and share content with your friends.
I am a stand-alone malware computer program that replicates itself in order to spread to other computers.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
Malwares are used to search and obtain information from the internet.
Wired internet connections are known for their reliability and speed.
Email is a way to send and receive messages using the internet.
Phishing is when people use computers and phones to be kind online.
Netiquette is a set of guidelines for polite and respectful behaviour when communicating online.
E. Answer the Following.
What is the internet?
What are internet services, and why do we use them?
Explain the concept of privacy invasion. Give an example.
Write down any one netiquette for ensuring safety while using the internet.
is cyberbullying?
F. Apply Your Learning.
Sree wants to buy a new book, but she is too busy to visit a physical store. Which internet service should she use to buy the book from the comfort of her home?
Raj, a school student who likes using social media to connect with friends and share his thoughts, recently experienced cyberbullying. What netiquette should he follow to keep things positive online?
Archi is going to her grandmother’s home by car. She is using an app that shows her directions to the desired location. Which internet service is she using?
Aanchal wants to learn about elephants by using the internet. She searches for information online. What application is she using for her internet search?
Tanya is chatting with her friend online. She is replying to her friend in capital letters. Is it correct to use capital letters online? Why/Why not?





Google Docs comes with various types of fonts, which help you improve the readability of the text and make your document visually appealing. In this chapter, you will learn how to add more fonts in Google Docs.
To add new fonts:
1. In the toolbar, open the Font drop-down menu and click the More fonts option. A Fonts dialog box with many available fonts appears on the screen.
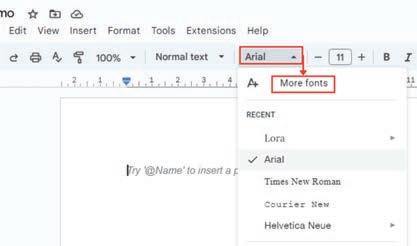

2. Use the search and filtering options at the top of the Fonts dialog box window to narrow your search. In our example, we are selecting the Display option from the Show: All fonts drop-down menu.

3. Select a font to add it to your font list. The selected font appears under My fonts on the right side of the window. You can add as many fonts as you want.

4. After adding the required fonts, click the OK button. The fonts are added to the Font drop-down menu.

In Google Docs, text alignment refers to the positioning of the text according to the edges of the pages. There are four alignment options in Google Docs:
1. Left Align: It places the selected text in line with the left margin.

2. Center Align: It places the selected text at an equal distance from both the left and right margins.

3. Right Align: It places the selected text in line with the the right margin.

4. Justify: It distributes the selected text evenly between the left and right margins.
To change the alignment:
1. Select the text that you want to align.
Google Docs can translate your document into 100 languages?

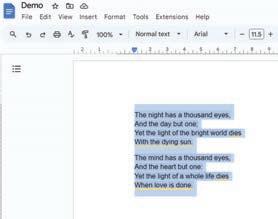
2. Click one of the alignment options in the toolbar. The text is aligned accordingly.
Line spacing is the vertical space between the lines of text in a document. For example, when the text is double-spaced, the space between the lines is two lines high. You can reduce the line spacing to adjust more lines on the page.
To format line spacing:
1. Select the text you want to format.

2. Click the Line & paragraph spacing button, then select the line spacing option from the drop-down menu. You can also click Custom spacing to change the spacing, as shown below.

3. The line spacing automatically adjusts in the document.

Paragraph spacing is the vertical spacing between paragraphs in a document. In Google Docs, you can choose the spacing between paragraphs to improve the readability of your document. Here are a few steps to format the paragraph spacing: To format paragraph spacing:
1. Select the text you want to format, as shown below.
2. Click the Line & paragraph spacing button and then select the Add space before paragraph or Add space after paragraph option from the drop-down menu.

3. The paragraph spacing adjusts in the document.

Google Docs has a built-in dictionary and spell checker tool as well.

A hyperlink is a link to a web address. If you want to add a web address to your Google Docs, you can add it as a hyperlink for someone to click it.
To insert a hyperlink:
1. Select the text for which you want to make a hyperlink, as shown below.

2. Click the Insert menu, and then select the Link option. Or alternately, click the Insert link button on the toolbar, as shown below.
3. The text you selected will now be a hyperlink.

It is the process of setting the beginning of a line of text slightly to the right of the left margin. You can also move a complete paragraph to a specific position using indentation options. Indentation helps structure the content of a document to make it easier for readers to identify paragraphs. There are two ways to implement it:
To indent the text using the tab key:
1. Place the insertion point at the start of the paragraph you want to indent.

2. Press the Tab key on the keyboard. The text in the first line moves to the right, as shown below.
To indent the text using the increase indent or decrease indent buttons:
1. Select the text you want to indent.

2. Click the Increase indent button to increase the indent by half-inch, as shown below.

3. All the lines of the paragraph are indented.

You can use the three indent markers and the ruler to create custom indents. When you move the indent markers, the ruler provides a blue-tipped guideline to help you see where the indent will appear.
There are three types of indents:
1. First-line indent: Adjust the first-line indent of the paragraph.
2. Left indent: Adjust all the lines of the paragraph at the same time from the left margin.
3. Right indent: Adjust all the lines of the paragraph at the same time from the right margin.
To customise indents:
1. Select the paragraph you want to indent.

2. Click and drag the desired indent marker. As the marker moves, the blue guide line extends from the ruler, as shown below.

3. Release the mouse at the desired location. The text is automatically indented.

Tab stops allow you to determine where words are located better. With every press of the Tab key, the insertion point automatically moves 0.5 inch to the right. You can increase the size of the tabs by adding some of the tab stops on the ruler. You can also add more than one tab stop on a line.
There are three types of tab stops in Google Docs: Left Tab Stop: Left aligns text at the tab stop. Center Tab Stop: Centres text at the tab stop.
Right Tab Stop: Right aligns text at the tab stop.
Think and Tell
What is the major difference between the left tab stop and the right tab stop?

To add tab stops:
1. Select the paragraph where you want to add tab stops.

2. Click the location on the ruler where you want your text to appear. A drop-down menu of tab-stop selections appears.
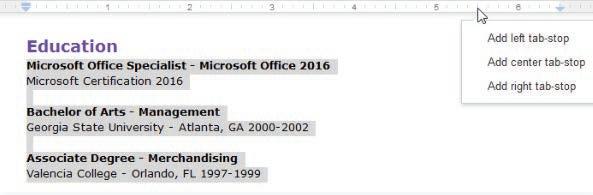
3. Select the tab-stop you want to insert in your document.

4. Place the insertion point at the location where you want to add the tab-stop, as shown below.

5. On the keyboard, press the Tab key. The text jumps to the location of the next tab stop.


Create a document about your favourite animal. Use the More fonts tool and text alignment in Google Docs to make your document look visually appealing. Also, add links to your document to make it more informative and engaging.
1 Google Docs has various types of fonts, which improve the readability of the text and makes the document visually appealing.
2 Text alignment refers to the positioning of the text according to the edges of the pages.
3 Line spacing is the vertical space between the lines of text in a document.
4 Paragraph spacing is the vertical spacing between the paragraphs in a document.
5 A hyperlink is a link to a web address. To add a web address in your Google Docs, you can add it as a hyperlink for someone to click it.
6 Indentation is the process of setting the beginning of a line of text slightly to the right of the left margin. You can also move a complete paragraph to a specific position using indentation.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
Hints left indent alignment hyperlink tab line & paragraph spacing
1 To change the space between the lines in Google Docs, select the text and then click the button in the toolbar.
2 A is a link to a web address.
3 refers to the positioning of the text according to the edges of the pages.
4 adjust all the lines of the paragraph at the same time from the left margin.
5 You can indent the text using the key.
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1 How many types of tab stops are there in Google Docs?
a Five
c Three
b Six
d One
2 Which of the following is not an option for line spacing in Google Docs?
a Double b 1.5
c Single d Triple
3 Using indents in Google Docs makes a document . a easy to read
b difficult to understand
c difficult to edit d more complex
4 To add more fonts to Google Docs, you can:
a Click the Font drop-down arrow in the toolbar and then select More fonts.
b Click Tools > Fonts.
c Click the “Font” button in the toolbar and select Manage fonts.
d All of the above.
5 How many types of indents are there in Google Docs?
a Three b Six
c Two d Five
C. Who Am I?
1 I am used to placing the selected text towards the right margin.
2 I am used to adding web addresses to documents.
3 I am used to setting the alignment to the left margin of Google Docs.
4 I am used to adding the tab stop in the centre.
5 I am used to changing the space between the lines.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Line spacing is the horizontal space between the lines of text in a document.
2 Indents can be customised in Google Docs.
3 Line and paragraph spacing can be customised in Google Docs.
4 Justify is a type of alignment.
5 Tab stops cannot be added in Google Docs.
E. Answer the Following.
1 What are hyperlinks?
2 Explain the three types of tab stops in Google Docs.
3 What is the use of
4 What is line spacing?
5 Differentiate between centre alignment and justify alignment.
F. Apply Your Learning.
1 Shreya wants to add a hyperlink in the Google Docs. What does she need to do?
2 Abhay has written three paragraphs on his favourite historical monument. But he finds that the lines of text in his document seem very congested due to lack of spacing between them. What will you suggest to him?
3 Nancy wants to place the text of her document evenly between the left and right margins. What should she do?
4 Agniv has to submit his holiday homework. He is using Google Docs for the same. Suggest him any two features that can help him make his document visually appealing.





Google Docs includes a simple drawing tool that you can use to create and insert basic shapes, text, and images in your documents. Drawing is a virtual board that allows users to create flowcharts, diagrams, concept maps, visual storyboards, original art, and more. This board allows you to create and edit digital images.
To use the Google Docs drawing tool:
1. Click in Google Docs document where you want to insert your drawing.
2. Select Insert > Drawing > New.

3. The Drawing dialog box appears with drawing toolbar.
4. To draw a line, click the Select line drop-down from the toolbar and then select the type of line you want to draw. Drag the line on the drawing canvas.


5. After you are finished drawing, click to insert your drawing into your document.
The Google Docs drawing tool is a versatile tool that can be used to create a variety of educational materials.
Did You Know?
The computer drawing tool, which was similar to Google Docs, was introduced in 1985 when Microsoft Paint was released as a part of Windows 1.0. This tool started with basic shapes and colours. Over time, it improved and some new features like layers and images got added. Today, it is easy to use, allowing people to draw and share their ideas online, making art and creativity accessible to all.

Google Docs is a useful tool for writing and editing documents, but it can also be used to create diagrams and other visual aids. One way to do this is to add shapes to your document.
To add a shape to your Google Docs document:

2. The Drawing dialog box appears.

3. Click the Shape tool from the drawing toolbar and then select the shape from the drop-down that you want to add to your document. Here, we have selected Arrows.
4. Drag on the drawing canvas to draw the desired shape. To change the size of a shape, you can click and drag the resizing handle.
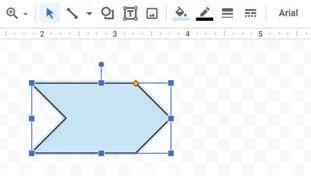
5. Release the mouse button.
6. If you want, you can add more shapes.
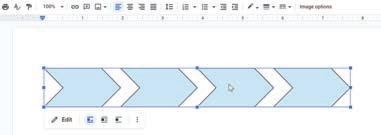

7. When you are done adding shapes, click . The shapes are added to your document at the point where your cursor was when you clicked Save and Close. You can then move and resize the shapes, as needed.
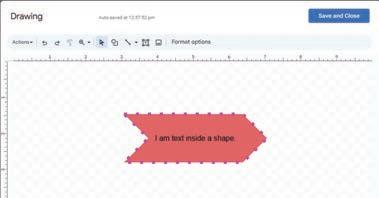
Let us now learn how to write text in a shape.
1. Double-click the shape in the Drawing dialog box. A text box appears.
2. Type your text in the text box.

3. When you stop typing, click outside the text box. The text is added to the shape.
Shapes can be a great way to make your Google Docs documents more visually appealing and informative.
Create a diagram to show the various parts of a plant or an animal.
Create a flowchart to show the steps in a process.
Create a Venn diagram to compare and contrast two things.
Create a timeline to show the order of events.
Create callouts to write dialogues for comic characters.
Explain the various parts of a plant using Google Docs.
To do this, first insert a drawing in your Google Docs document. Then, select the shape that you want to use for each part of the plant. You can use a rectangle for the stem, a triangle for the leaves, and a circle for the flowers and fruit.
After adding the shapes to your drawing, you can move and resize them as needed. You can also add text to the shapes to label them.
After completing, rename the document and then close the drawing.
After you add a shape to your document, you can format it in a variety of ways, such as changing the Border color, Fill color, Border weight, or Border dash. You can also change the font and font size of the text in the shape.
A text box is a container that can be used to hold text. Text boxes can be used in many ways. For example, you can use text boxes to:
Add definitions to key terms.
Provide additional information about a topic.
Create sidebars with activities or quizzes.
Add captions to images or diagrams.
Create callouts to highlight important information.
To add a text box in Google Docs:
1. Select Insert > Drawing > New.
2. In the Drawing toolbar, click the Text box icon.
3. Click and drag the icon in the document to create a new text box.
4. Type your text in the text box.
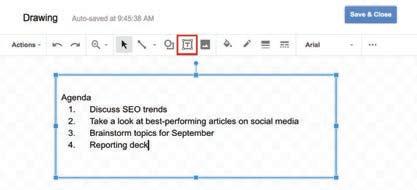


5. Click to save and exit the drawing editor.
After adding a text box to your document, you can format it in a variety of ways, such as changing the Border color, Fill color, Border weight, and Border dash. You can also change the font and font size of the text in the text box. You can choose these options from the drawing toolbar.

Did You Know?
The history of adding text boxes to computers, like Google Docs, began in the early 20th century, when typewriters allowed users to type text in organised boxes. As technology evolved, software like Google Docs introduced digital text boxes in the 21st century, making it easier to insert and format text within documents.

You can also insert an image in the Drawing tool of the Google Docs. Follow the given steps to insert an image in the drawing canvas.
1. To add an image, click the Image tool. The Insert image dialog box appears on the screen.

2. You can choose to insert images by selecting any of the following tabs:
• Upload: You can drag an image from your computer to the drawing canvas or click the Choose an image to upload button to select an image. Thereafter, click the Open button to insert an image from the drives on your system.
• By URL: You can copy the link or URL of an image and paste the URL in the bar. If your URL is correct, you will see an image preview here. Click the Select button to insert the image in the drawing canvas.

• Google Drive: You can insert an uploaded image from Google Drive. If an image is not uploaded, upload the image first.
• Search: Click this tab and write the keywords for the image you want to insert, and then click the Search icon. Choose an image of your choice, and then click the Select button.

3. When you are done, click the Save and Close button.
Did You Know?
Customising text boxes and shapes on the computer, like Google Docs, has evolved over time. In the early days, it was basic and had limited options. But as technology advanced, so did customisation. Now, we can change colours, sizes, and fonts easily and make our documents look exactly the way we want them to!

Objects such as text boxes and shapes are a great way to add visual interest to your Google Docs documents. But if you have multiple text boxes or shapes overlapping, you may want to change the order in which they appear. This is easy and can make a big difference in the overall look of your document.
Follow the given steps to change the order of text boxes or shapes:
1. Click the text box or shape that you want to move. Right-click and then select the Order option.
Choose the option you want, like:
Bring to Front: Moves the text box or shape in front of all other objects in your document.
Bring Forward: Moves the text box or shape one level forward in the order of objects.
Send Backward: Moves the text box or shape one level backward in the order of objects.
Send to Back: Moves the text box or shape to the back of all other objects in your document.
Example:
You have a Google Docs document with a shape and a text box. The text box overlaps the shape, and you want the shape to be in front of the text box.

2. Click the text box.
3. Right-click and then select Order.
4. Select Send to back.


Try the following on the Drawing canvas of Google Docs.
1 Draw various shapes and then add text boxes to the digital canvas.
2 Now, change the order of these shapes and text boxes.
3 Do experiment with the ‘Bring to front,’, ‘Bring forward’, ‘Send to back’, and ‘Send backward’ options.
Think and Tell
What did you learn about changing the order of shapes and text boxes in Google Drawings? How did rearranging them help you make your artwork more appealing?

Changing the order of text boxes or shapes on the computer, like in Google Docs, has evolved over time. Initially, it was challenging, but modern software has made it easier. In the past, it required complex commands, but now, you can choose suitable options to simplify your work. Did You Know?

1 Google Docs includes a simple drawing tool that you can use to create and insert basic shapes, text, and images in your documents.
2 Drawing is a virtual board that allows users to create flowcharts, diagrams, concept maps, visual storyboards, original art, and more.
3 A text box is a container that can be used to hold the text. Text boxes can be used to add text to a document in many ways.
4 You can use shapes in Google Docs to create a diagram, flowchart, Venn diagram, etc.
5 Objects such as text boxes and shapes are a great way to add visual interest to your Google Docs documents.
6 If you have multiple text boxes or shapes overlapping, select the object whose order you want to change and then right-click and select the Order option.
A. Fill in the Blanks. Hints
1 is a virtual board that allows users to create flowcharts, diagrams, concept maps, visual storyboards, etc.
2 To change the size of a shape in your drawing, you can click and drag the handle.
3 You can add a text to your drawing project by selecting the tool.
4 To create diagrams in your drawing, you can add to your document.
5 After you are done drawing, click the button to insert your drawing into your document.
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1 What is the primary purpose of the Drawing tool of Google Docs?
a Sending and receiving emails
c Creating visual content like diagrams and charts
b Creating and editing spreadsheets
d Updating information
2 A is a container that can be used to hold the text.
a Line tool
c Fill color
b Text box
d Lasso tool
3 Which of the following is the correct method to open the drawing tool of Google Docs?
a Click Insert > Drawing > New
c Click Insert > New
b Click File > New
d Click Insert > Drawing
4 While inserting an image into the drawing canvas, which of the following is not a tab in the Insert image dialog box?
a By URL
c Search
b Upload
d Insert
5 Which of the following orders cannot be used to arrange the order of multiple overlapping objects in a drawing?
a Bring to front
c Send backward
C. Write T for True and F for False.
b Hide behind
d Send to back
1 The Drawing tool on Google Docs is word processing software.
2 You can insert an uploaded image on the drawing canvas from Google Drive.
3 You can add shapes, text, and images to create visuals using the Drawing tool.
4 If you have multiple text boxes or shapes overlapping, then right-click the object and then select the Arrange option to change the order in which they appear.
5 You cannot add text to a shape.
D. Answer the Following.
1 Explain the Drawing tool of Google Docs. What can you create using this tool?
2 How can you add a new text box to your Google Docs drawing project?
3 What is the purpose of the Shape tools? How can you insert text in the shape?
4 Name any two tools of the drawing toolbar that can be used to format a text box.
5 Explain the By URL method to insert an image in Google Docs.
1 Amita wants to create callouts for comic characters. Name the tool on the drawing toolbar that she can use to create the same.
2 Vansh wants to draw a diagram for his school project. Which popular online platform can he use as a drawing tool?
3 Shaurya has drawn various shapes on the drawing canvas. Which option should he use to fill colour in the shapes?





When you share an idea or a thought with an audience, a visual representation—with pictures, words, videos, and sound—makes this task much easier. This helps to get the message across to the audience. Such sharing also helps the audience to visualise the idea and makes them interested in what you’re saying.
Now, imagine that you are standing in front of your class, showing them a beautiful presentation while explaining your science project!

A presentation is a way to share information, ideas, or stories using a combination of pictures, text, and sometimes even audio or video.
How do you think presentations can help your teacher during a class?
We can create presentations on various applications like PowerPoint, Canva, Google Slides, etc. In this chapter, we will learn to create beautiful presentations on Google Slides. Google Slides is one of Google’s apps that is used to create presentations online.
Let us learn how to create a new presentation on Google Slides:
1. Open the Google Chrome browser and go to the link: https://docs.google.com/presentation/
2. Click the plus + sign to open a blank presentation.

We have learnt to create a new presentation on Google Slides. Now, let us learn about the various parts of the presentation window.
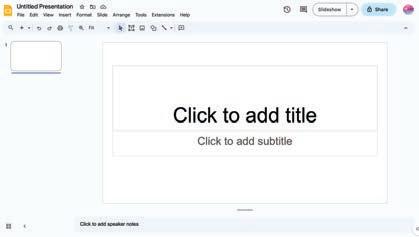
Purpose
1.Presentation Title It shows the name of a presentation.
2. Menu Bar It contains various menus like File, Edit, and View. Each menu offers different options.
3. Toolbar It contains tools for quick and easy access.
4. Slide Workspace The area where you add items such as text, images, and videos for a slide.
5. Slide Navigation Pane Space where you can see thumbnails or miniature images of all the slides of your presentation.
6. Speaker Notes The area where you can add notes for the speaker to remember important points during a presentation.
7. Slideshow Button Turns the slides into the presenter mode to showcase the slides in the full-screen mode.
Did You Know?
Ancient Egyptians used papyrus scrolls to record information in the same way as we use digital documents and presentations nowadays.

Now, let us learn how to choose themes that suit our presentation. Let us also learn to use various layouts to organise our slides.
Themes are like special designs for your slides. They make the presentation look colourful and interesting, just like wearing clothes for different occasions.
When you start making a presentation in Google Slides, you can choose various themes.
Imagine that you are creating a presentation about Seven Sister States of India. To apply themes to this presentation, open Google Slides and follow the given steps:
1. Click on the presentation title bar in the newly created presentation.
2. Enter the title Seven Sister States of India in the title bar.
3. Click the Slide menu in the menu bar.
4. Select the Change theme option. The Themes pane opens on the right side. This pane will contains various themes that are available.
5. Check out the various themes for your slide and click a theme of your choice. The selected theme is applied to all the slides.

Think and Tell
If you were making a presentation on forests, which colour theme would you choose?

Sometimes, we might like a theme, but we still want to make certain changes in it. To do that, we can use various colours, fonts, effects, and background styles.
Modifying themes in a presentation is important because it allows you to make the presentation look exactly the way you want it to. It is like deciding upon and changing the colours and decorations for your room to match your idea of decorating it.
Let us learn how to give your presentation a personal touch.
To add new colours to the background of your slides:
1. Select the slide in the Slide Navigation Pane.
2. Click the Slide menu in the menu bar.
3. Select the Change background option from the drop-down menu.

4. The Background pane appears. Select the colour of your choice from the Color drop-down list.
5. Click the Done button. Colours can make people feel emotions. For example, blue may make you feel calm and yellow might make you feel happy.


Layouts determine how your content, such as titles, text, and images, is organised on the slide.
You can choose a different layout for each selected slide. Let us learn how to add different layouts to different slides:
1. Select the slide in the Slide Navigation pane.
2. Click the Slide menu from the menu bar.
3. Select the Apply layout option
4. You will see various layout options; choose the one you like the most.
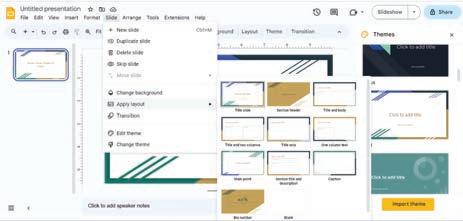
Your slide will change to that layout and have a whole new look!

Similarly, you can use a Title and Body layout to talk about each of the seven state’s cultures.
Assam is famous for its tea gardens and the mighty Brahmaputra River. It is home to the one-horned rhinoceros too!


Arunachal Pradesh is a land of beautiful mountains and green forests. ‘It’s the place where the sun rises first in India, making it really special.
Manipur is famous for its special dance called Manipuri dance, and it is a land of colourful owers and traditional crafts.


Meghalaya means abode of clouds. This is a place with lots of rain, amazing waterfalls, and a living root bridge that is made naturally.
Mizoram is a place of hills and valleys, and it is known for its unique bamboo houses and the colourful festival called Chapchar Kut.


Nagaland is a land of many tribes, each with its own special traditions. It is also known for the Hornbill Festival, a big celebration of cultures.

Nestled among hills, Tripura is a land of splendid palaces and temples, where stories of the past come to life in its every corner.
1 Choose the correct answer and fill in the blanks.
a The shows the name of a presentation.
i Presentation title
iii Speaker notes
ii Toolbar
iv Slide workspace
b An area where you add items such as text, images, and videos for a slide is called the .
i Menu bar
iii Speaker notes
ii Toolbar
iv Slide workspace
c The holds tools for quick and easy access.
i Presentation title
iii Slides panel
2 Match the following.
Theme
Layout
Slide → Change background
Google Slides
ii Toolbar
iv Themes section
It is used to change the background of the slides.
It is like a special design for your slide.
It is an online presentation-making app.
It determines how your content is organised on the slide.
Tables are used to organise information neatly and in an easy-to-understand manner. They help you put information clearly in rows and columns.
Let us say we want to show the capital cities of each state. We can use a table in Google Slides.
To insert a table:
1. Click the Insert menu in the menu bar.
2. Select the Table option from the drop-down list.
3. Select the number of rows and columns required from the grid that appears. The table will appear on the slide.

4. Type the states in one column and their capitals in the next column. You can adjust the size of the table and add colours using the Fill color tool to make it look beautiful.

The Fill color tool is used to fill colour in a table cell, row, or column, or a complete table. This tool appears on the toolbar when you click the table cell.

State
Assam
Arunachal Pradesh
Nagaland
Manipur
Meghalaya
Tripura
Mizoram
Capital
Dispur
Itanagar
Kohima
Imphal
Shillong
Agartala
Aizawl
Charts are graphics or visual representations that are used to display and compare data easily. Charts make your information more interesting and easier to understand. There are different kinds of charts in Google Slides, such as:
• Bar chart: A bar chart represents data using bars of different lengths, which are arranged sideways.
• Column chart: A column chart represents data using bars of different heights, which are arranged like columns.
• Line chart: A line chart represents data using a series of points, which are connected by a line.
• Pie chart: A pie chart represents data using ‘slices’ of a whole circle. The size of each ‘slice’ shows how much value that specific ‘slice’ holds.



Suppose in our presentation, we want to show the number of elephants in four different North-Eastern states. We can use a column chart to represent this data.
To insert a chart:
1. Click the Insert menu from the menu bar.
2. Select the Chart option.
3. Select the type of chart. Let us select the Column chart.
4. The Column chart is inserted on the slide. Now, click the three dots in the right-hand corner and then select Open source.
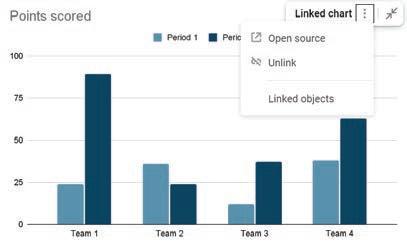
A new Google Sheet opens, containing a table. This is where we will add the data, that is, the number of elephants in the four states. Google Sheets is another app by Google which is used to record and work with numbers, words, formulas, etc. You will learn more about it in the next chapters. For now, we will write the number of elephants for each state in this table. This data will be reflected directly on the chart.

Now, let us enter the data.
a. Enter the name of the states in the first column. Enter the number of elephants in the second column. Remember to rename the columns to State and Number of Elephants.
b. Delete the third column as we don’t need it. You can click the column and press the Backspace key on the keyboard to do so.

5. After you enter your data, return to your slide and then click the Update button.

Your column chart appears on the slide. Each state will have its own colourful columns.

The taller the column, the more animals there are. Looking at the chart shown above, we can easily say that Assam has the highest population of elephants and Nagaland has the least. This way, we can easily compare the elephant population in different states.
Diagrams are colourful pictures that help you show how things are connected, explain processes, or display information in a clear and organised way.

























































In our project about the seven sister states of India, we can use diagrams to show the folk dances of some states. Let us follow the steps given below:
1. Click the Insert menu in the menu bar.
2. Select the Diagram option. We will see various types of diagrams you can use like Grid, Hierarchy, and more.
3. As we are showing the folk dances of different states, a cycle might be a good choice. Select the Cycle option.

4. The Cycle pane appears on the right side. Customise your diagram by adding more shapes and labels. The maximum number of Steps in a cycle is 5. You can also select suitable colours and styles of diagram based on your project requirements.
5. You can also customise the diagram by using the Fill color tool to colour the various components of the diagram.
The style and colour that you select will apply to the diagram.


The Master Slide is like the main slide. Think of it as a slide that allows you to change the appearance of your entire presentation all at once. Suppose, we want the image of our national flag on all of our slides. What would we do? We could add the image in each of the slides, resizing and placing it how we want it to be. But if you have 15 slides, would it not be easier if we could make the changes in one slide and it could reflect on all the slides? Here, the master slide comes into play.
In Google Slides, we have the Edit theme option of the Slide menu, which helps us reflect one change in all the slides. When you use a theme, it changes the colours, fonts, and background designs of all your slides. Let us understand by following the steps given below:
1. Click the Slide menu in the menu bar.
2. Select the Edit theme option from the drop-down list.
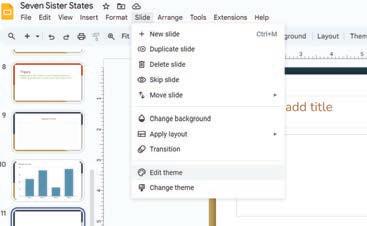
3. A pane appears with lots of colourful slides as options.


4. Copy the image you want to add and paste it here on the slide.

5. Resize the image according to your choice and place it anywhere that you want it to appear.
6. You will notice that the image has been added to all the slides.

Similarly, you can add titles, change the font, or add more images and visuals, to the main slide and it will reflect on all the slides of your presentation.
Changing the order of the slides means to rearrange the slides in the desired order. Suppose you want to change the existing order of the slides. You can click and drag the slides in the sidebar to arrange them in the order that you want.




Learn to draw a cartoon character in Google Slides!
1 Fill in the blanks.
a displays data across rows and columns.
b are graphics that are used to display and compare data easily.
c A column chart represents data using bars of different heights.
d The is a slide that allows you to change the appearance of your entire presentation all at once.
2 Write the correct order of steps (1 to 4) to add changes to all the slides using the Master Slide:
a Select Edit theme from the drop-down.
b Click Slide from the menu bar.
c Add the changes in selected master slide.
d A pane will appear.
1 A presentation is a way to share information, ideas, or stories using a combination of visuals, text, and sometimes even audio.
2 Google Slides is one of Google’s apps that is used to create presentations online.
3 Themes are special designs for your slides. They make your presentation look colourful and interesting.
4 Layouts determine how your content is organised on the slide, such as titles, text, and images.
5 Tables are used to organise information neatly and in an easy-to-understand manner.
6 Charts are visual representations or graphics that are used to display and compare data easily.
7 Diagrams are colourful pictures that help you show how things are connected, explain processes, or display information in a clear and organised way.
8 The master slide is similar to the main slide and allows you to change the look of your entire presentation faster.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
Hints columns themes menu master apply layout
1 bar holds various menus like File, Edit, View, etc.
2 are like special designs for your slides.
3 To apply a layout on a slide, select Slide > option.
4 Tables consist of rows and .
5 The slide allows you to change the appearance of your entire presentation all at once.
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1 Which component of Google Slides allows you to add notes for the speaker during a presentation?
a Slide Workspace
b Slides Panel
c Speaker Notes d Toolbar
2 What is the purpose of a theme in Google Slides?
a To change the design of the presentation.
b To change the font style.
c To change the layout of the presentation. d To insert charts and tables.
3 Which menu will you use to change the background colour of a theme in Google Slides?
a Insert menu
b Slide menu
c View menu d File menu
4 What are tables used for in Google Slides?
a Creating diagrams.
b Displaying information neatly in rows and columns.
c Applying themes.
d Changing slide backgrounds.
5 Which chart is used to represent data using horizontal bars of different lengths?
a Bar chart
c Line chart
Who Am I?
b Column chart
d Pie chart
1 I am a component in Google Slides window that turns the slides into the presenter mode to showcase the slides in full-screen mode.
2 I am a pane in Google Slides that contains different themes for your presentation.
3 I am a menu that allows you to add a table into your presentation.
4 I am a set of colourful pictures that helps you show how things are connected and explain processes.
5 I am a type of chart in Google Slides that represents data with a series of data points connected by a line.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Google Slides is a tool for creating and sharing documents.
2 Themes in Google Slides only change the background colours of your slides.
3 A column chart is a circular graph, which uses slices to represent the relative size of data.
4 Changing slide order in Google Slides means deleting some slides.
5 Diagrams in Google Slides are used mainly for creating mathematical charts.
E. Answer the Following.
1 Write the names of any three presentation applications.
2 What is the Slide Navigation
3 What is the difference between themes and layouts?
4 In which menu is the Edit theme option present?
5 What is a pie chart?
F. Apply Your Learning.
1 Imagine that Shaina is making a presentation on her favourite book. What features would she use to make it look good?
2 Himank is preparing a presentation on various animals found in a zoo. He wants to organise information about the animals’ names, habitats, and diets in rows and columns. Which feature should he use?
3 Vamika wants to showcase pictures of various sports for her school’s annual sports day in full-screen mode. Name the component of the Google Slides window that can help her achieve this.
4 Suppose Komal is giving a presentation on the solar system. Which option should she use to ensure that a specific image, such as a planet, appears consistently on all the slides?
5 Saharsh has created a presentation on famous monuments around the world. He realises that he wants to change the order in which the slides were arranged. Which feature of Google Slides will help him achieve this?




In our previous chapter, we explored how to create effective presentations. However, the presentation did not have anything that moved and was animated in any way. So, is there a way that you can make those additions to your slides? Of course, you can! You can do it by using animation. Now, let us understand what animation is.
Animation is a process through which you can bring still objects, such as text, shapes, images, charts, and logos, ‘to life’ by making them move. Animation is a great tool with which you can make your presentation lively and engaging. You can add one animation effect to multiple objects or add more than one animation effect to a single object. It enables you to control the flow of information presented or convey processes and alterations with greater efficiency. It also helps you connect with your audience in a better way. But applying too many animations distracts the audience from the actual content. So let us start with how to add animation to your slides. We will use the same project that you created in the last chapter.
The word “Animation” comes from the Latin word “Anima”, which means “soul”. So, the process of animation refers to making characters come to life.

Let us learn how to add animation to our presentation. Open the presentation on “Seven Sister States of India” in Google Slides. Follow the steps given below to add animation to different objects on a slide:
1. Select an object on a slide that you want to animate.
2. Click the Insert menu in the menu bar.
3. Select the Animation option from the drop-down list. The Motion pane will open on the right side.
4. In the Motion pane, go to the Object Animations section.
Here, the first option is Animation type. Click this option and select an animation from the drop-down list.
5. The next option is the Start condition. Select one of the following options from the dropdown list:
On click: Animation starts when you click your mouse.


After previous: Animation starts after the previous animation ends. With previous: Animation starts with the previous animation.
6. If the object is a placeholder or text box, the By paragraph check box is displayed. If this check box is checked, each paragraph of text in the box is displayed one by one. Otherwise, the entire box will be displayed at once.
7. If you want to add more animations, you can select an object and click the Add animation option.
8. Click the Play button to check how that animation effect works on the selected object.




A slide transition provides a visual effect that takes place when one slide changes to another during a presentation. You can control its speed, add sound, and personalise the appearance of these transition effects.
To add a transition effect to your presentation:
1. Select the slide to which you want to apply the transition effect.
2. Click the Slide menu from the menu bar.
3. Select the Transition option from the drop-down list.
Alternatively, you can right-click the selected slide from the Slide Navigation pane and click the Transition option.

4. The Motion pane will appear on the righthand side. In the Motion pane, go to the Slide Transition section.
Select the Transition type from the dropdown list.
5. Set the transition Duration by dragging the slider. This slider will only appear once you have selected the Transition type
6. Click the Apply to all slides button to apply this transition effect to all the slides.
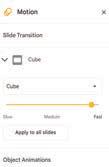
If you do not click this button, the transition will be applied to the current slide only.
7. Click the Play button to view the transition effect.



1 Read the following statements and place a tick mark beside the correct statements.
a Animation can be added to every object on the slide.
b When we select the starting condition as “After previous”, the animation starts once the previous animation ends.
c Applying too many animations distracts the audience from the actual content.
d The speed of a transition can be controlled.
e A Cube is a type of transition.
2 Raju has to revise the concepts he has learnt. But he is confused about how to add a transition. He has written the steps in an incorrect order. Help him by numbering the steps (a. to e.) in the correct order.
Select the Transition option from the drop-down list.
Click the Slide menu from the menu bar.
Set the transition’s Duration.
Click the Play button.
Select the Transition type from the Motion pane.
Why are transitions important?

Adding audio and video elements to your presentation can add a new dimension to it. Using audio or sound, you can include background music and narrate key points. Using videos, you can showcase the video content in your presentation. Your presentation can become more engaging and informative using audio and videos. The most commonly used audio format is .mp3, while the most popular video format is .mp4.
In this section, we will learn the steps to add audio and video elements that can enhance the effectiveness of your presentation.
Let us add music to your presentation. To insert any audio file in your presentation, you need to first upload an audio file to Google Drive.
1. Open drive.google.com.
2. Click the New button.
3. Select the File upload option from the drop-down list.
4. The Open dialog box will open. Select the audio file you want to upload.
5. Click the Open button.
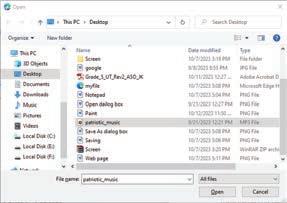
6. Wait for the file to upload. Once the file is uploaded, proceed with the next step.
Once you have uploaded the audio file, you can add the audio file to the presentation. To add an audio file in the presentation:
1. Go on your presentation again.
2. Click on the Insert menu.
3. Select the Audio option from the drop-down menu.
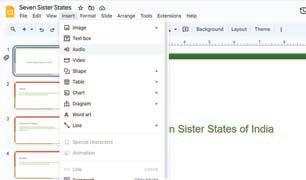
4. The Insert audio window will open. Select the audio file that you want to add.
5. Click the Insert button.

6. The speaker icon on the slide indicates that the audio file is attached to your presentation. You can play it by using the Play button.


Are different types of background sounds important in presentations?
You have learnt how to add audio to your presentation in the last section. In this section, you will learn how to add a video file to your presentation. You can add videos to your presentations in two different ways:
A. From YouTube: You can add videos from YouTube. Let us learn how to add videos using YouTube: 1. Click the Insert menu.
2. Select the Video option from the drop-down list.

3. The Insert video window will open. Here, click the YouTube tab.
4. To search for a video, enter the video name in the search bar and press the Enter key.

5. A list of videos will appear. Select a video and click the Insert button that appears when you click the video.

6. You can see the inserted video on the slide. Click the Play button.
B. From Google Drive: Like the audio file, you need to first upload the video to Google Drive. After uploading the video, you can add it to your presentation by following the steps given below:
1. Click the Insert menu.
2. Select the Video option.
3. The Insert video window will open. In this window, click the Google Drive tab.
4. Click the video to be added to the presentation.
5. Click the Insert button.
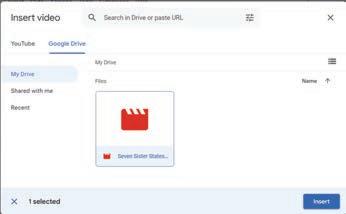

1 Match the following.
Terms Meaning
YouTube tab
.mp4
Play button
.mp3
Allows to play audio/video on the slide
Audio format
Video format
Used to add videos from YouTube
2 Rearrange the steps of adding a YouTube video to a slide.
Select the Video option from the drop-down list.
Search for the video you want to add.
Select a video and click the Insert button.
Click the Insert menu.
In the Insert video window, select the YouTube tab.
1 With the animations, you can make objects like text, images, and shapes move on your slides.
2 A single object can have multiple animation effects applied to it. But too many animations can cause distraction.
3 Transitions are visual effects that can be applied to slides when one slide changes to another.
4 The speed of transitions can be changed, and the same transition effect can be applied to all the slides or any individual slide.
5 The most commonly used audio format is .mp3, while the most popular video format is .mp4
6 Audios can be added as background music, voice narration, or sound effects to your presentation.
7 Any video from Google Drive or YouTube can be inserted in a presentation.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
Hints on click animation audios slide
1 In a presentation, animations can be applied on .
2 To add an animation effect to a presentation, go to the Insert menu and choose the option.
3 A provides a visual effect that takes place when one slide changes to another during a presentation.
4 With the option, animation starts when you click your mouse.
5 and make the presentation more engaging and informative.
B. Tick () the Correct Option.
1 Which menu do you use to smoothly move from one slide to the next?
a File b Slide
c Insert d View
2 What does this button signify?
a A picture is inserted into the presentation b Sound is attached to the presentation
c Text is inserted into the presentation d Shape is inserted into the presentation
3 Which option would you choose if you want to make an object move on a slide?
a Click Insert → Animation b Click Insert → Image
c Click Insert → Audio d Click Slide → Transition
4 How do you insert an audio file into your slide?
a Click Insert → Audio b Click Insert → Video
c Click Insert → Picture d Click Insert → Table
5 Press this button to…

a Upload an audio file to Google Drive
b Add an audio to a presentation
c Add a video to a presentation d Add animation in a presentation
C. Who Am I?
1 I am a feature that makes objects move on slides and makes the presentation more engaging.
2 I am a visual effect that makes your slides change smoothly during a presentation.
3 I am the option that adds sound to your presentations. It can be background music, voice narration, or even special sound effects.
4 I am an option in the Motion pane that helps you change the speed of a transition effect.
5 I am a button that helps you reuse the same transition for all the slides.
D. Write T for True and F for False.
1 Animations can only be added to text in a presentation.
2 In a presentation, videos can only be added from YouTube.
3 Sound cannot be added to a presentation.
4 Sounds, videos, animations, and transitions make a presentation more engaging.
5 Animations and transitions are the same thing, and you can use them interchangeably.
E. Answer the Following.
1 What is the purpose of animations in a presentation?
2 Can you add animations to both text and objects in a presentation?
3 Define slide transition. Name the button used to view the transition effect.
4 Write down the two ways in which you can add a video to your presentation.
5 What is the purpose of adding a video to a presentation?
1 Siya has made a presentation. She wants to show some movement of objects in her presentation. What should she use to add movement?
2 Rita has to present her project for which she has prepared multiple slides. She wants smooth movement from one slide to another during her presentation. Which feature should she use?
3 Raju has used a transition effect in his presentation. But when he started the presentation, the slides were moving slowly. Which option should he use to increase the speed of the slides?
4 Suman watched a video on YouTube that suits her presentation for the science fair perfectly. Can she add this video to her presentation?
5 Preeti has created a presentation that she wants to make more engaging. She has added transition effects to one slide. What can she do to apply transition effects to all the slides?


Have you ever heard of Amazon’s Alexa or Apple’s Siri?
All these technologies have something in common: they use Artificial Intelligence, or AI.
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is the ability of a computer to think and learn.
With AI, computers can perform tasks that are generally done by people, like recognising voice, problem-solving, and learning.
AI is all around us, and whether or not you realise it, we use it every single day.
Let us discuss some applications of artificial intelligence.
These are the various ways in which we can use AI:
• AI-powered robots are used to perform surgery with greater precision and accuracy than human surgeons.
• AI is being used to develop new drugs and treat critical diseases.
• AI is being used to diagnose diseases by analysing medical records and images of patients.

Did You Know?
AI can read medical images, like X-rays and MRIs; and in some cases, it can detect diseases.

AI-powered personalised learning programs are helping students learn at their own pace. Students can customise these programs in the way that best suits their learning styles and needs.
• Google and Tesla are developing AI-powered self-driving cars.
• AI is being used to analyse traffic flow and improve safety by predicting congestion and suggesting alternative routes.
• AI-powered robots are being used to perform tasks automatically in factories, enhancing productivity.
• AI is being used to improve quality by identifying defects in products.
AI-powered chatbots are being used to answer customer questions and provide 24/7 support.
AI-powered security systems are used to identify suspicious people and prevent crime.
AI is being used to:
• Develop realistic video game characters and generate creative content.
• Recommend personalised options on video-streaming platforms, like Netflix and social media platforms like Facebook.
• Develop new forms of entertainment, such as virtual reality and augmented reality experiences.




Machine learning is a domain of Artificial Intelligence because of which machines learn from data and become intelligent.
We humans learn from our experiences. In the same way, machine learning makes the computers learn from data and improve their performance over time.
Machine learning provides the power to computers to become intelligent. Every field of artificial intelligence uses machine learning at its core.
Look at the following figure to understand machine learning in a better way.
In this picture, a number of pictures of cats and dogs are fed into the machine learning model. The features of cats and dogs are also provided to the system. Over a period of time and with the help of data, the machine learning model becomes self-sufficient in differentiating between cats and dogs.
This is how machine learning systems learn.
One of the most useful applications of machine learning systems is computer vision. Let us learn about it.
Computer vision is a way for computers to ‘see’ and ‘understand’ the world around them. This is How It Works:
1. Computers use cameras to take pictures or videos of the world around them.
2. Software is used to analyse the images or videos to identify objects and patterns.
3. AI is used to make sense of the data collected and understand the information that the computer is ‘seeing’.
There is a popular application called Google Lens that uses computer vision. Let us learn about Google Lens.
Google Lens is a visual search tool developed by Google that uses AI and machine learning to recognise and provide information about objects, images, and text captured through a camera.

Did You Know?
Google Lens can recognise over 1 billion objects, including plants, animals, landmarks, and products.

These are the various applications of Google Lens:
Text Translation
Text translation in Google Lens is a feature that allows you to translate text from one language to another using your phone camera.
To use the text translation feature in Google Lens:
1. Open the Google on your device.
3. Point your camera at the text you want to translate.

5. Tap the Translate button at the bottom of the screen.


2. Tap the Google Lens icon in the search bar.

4. Select the language you want to translate the text to.

6. Google Lens will translate the text and display it on your screen.

Smart text selection in Google Lens is a feature that uses AI to recognise and understand text within images or documents.
To use the smart text selection feature in Google Lens:
1. Open the Google app on your device.
2. Tap the Google Lens icon in the search bar.
3. Point your camera at the text you want to select and tap the Google Lens button.
4. Google Lens will automatically select the text.
5. Tap the text selection bar to see options for copying, listening, translating, or searching the text.


Rearrange the following steps in the correct order to use Google Lens for translating text. Write down the correct step number in the given box.
Select the language into which the text is to be translated.
Tap the Google Lens icon.
Open the Google app on your device.
Tap the Translate button.
Point your camera at the text.
Write T for True and F for False.
a Google Lens is a popular application that uses computer vision.
b AI-powered facial recognition systems are used to identify people.
c Computer vision is a way for computers to recognise voices in their surroundings.
Artificial intelligence, or AI, is the ability of a computer to think and learn.
AI-powered robots are being used to perform surgery with greater precision and accuracy than human surgeons.
AI-powered personalised learning programs are helping students learn at their own pace and in the way that best suits their learning styles and needs.
AI-powered self-driving cars are being developed by companies like Google and Tesla.
AI-powered facial recognition systems are used to identify people and prevent crime.
Machine learning is a domain of Artificial Intelligence due to which machines learn from data and become intelligent.
Computer vision is a way for computers to see and understand the world around them.
Google Lens is a visual search tool developed by Google.
Text translation in Google Lens is a feature that allows you to translate text from one language to another using your phone camera.
Smart text selection in Google Lens is a feature that uses artificial intelligence to recognise and understand text within images or documents.
A. Fill in the Blanks.
Computers use to take pictures or videos of the world around them. is like teaching computers to learn from examples.
AI-powered are being used to answer customer questions and provide
is the ability of a computer to think and learn.
B. Tick () the Correct Option. What does AI stand for?
a
c
What
b
c
Which companies are developing self-driving cars with AI?
a Apple and Amazon
c Google and Tesla
What is computer vision?
a A type of eyeglasses
b The ability to hear sounds
b Facebook and Twitter
d Netflix and Hulu
c The ability for computers to see and understand the world around them
d A type of video game
C. Match the Following.
AI is being used to develop new drugs
Self-driving cars

Chatbots
AI-powered security systems
D. Answer the Following.
E. Apply Your Learning.
Shamak is visiting a foreign country, and he sees signs written in a language he does not know. Which application can he use to help him understand the meaning of those signs?
Kanika loves watching films on video-streaming platforms. She is getting suggestions on films based on what she has already watched. Which technology is used behind this?
Deeksha is shopping online and has a question about a product she wants to buy. Which AI-based technology can provide her with answers immediately?
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 is considered one of the first mechanical and automatic calculator.
2 An acts as an interface between a user and a computer system.
3 A is an application that allows you to visit websites on the internet.
4 spacing is the vertical spacing between paragraphs in a document.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Which of the following is a manually-operated calculating device developed by John Napier?
a Abacus
c Leibniz wheel
2 Which type of connection is used by mobile phones?
a Dial-up
c Wired
b Pascaline
d Napier’s bones
b Cellular
d Satellite
3 What do we call a set of programs that is installed and run on computer hardware?
a Programs
c Games
b Software
d Utilities
4 Text refers to the positioning of the text according to the edges of the pages.
a Spacing
c Alignment
C. Write T for True and F for False.
b Style
d Size
1 The second-generation computers used integrated circuits (ICs).
2 The operating system allocates and deallocates memory space for running processes.
3 Wired connection is highly convenient as it eliminates the need for physical cables.
4 You cannot insert a hyperlink in a Google Docs document.
D. Answer the following questions.
1 What do you know about UNIVAC?
2 Differentiate between a virus and a worm.
3 What is the use of general-purpose application software?
4 How does indentation help in structuring the content of a document?
E. Apply your learning.
1 Arushi is using the voice command application in her computer. In which generation of computers is this possible?
2 Neetu’s mother is not familiar with the apps used on the internet for entertainment. Could you suggest some apps she can use to watch films?
3 Rama is designing a card for his classmates. He wants to write his friends’ names in different fonts, but he does not know how to add fonts in a Google Docs document. Help him with adding fonts to a Google Docs document.
A. Fill in the blanks.
1 is the option that starts the animation when you click your mouse.
2 The Google Docs tool is a virtual board that allows users to create flowcharts, diagrams, and more.
3 are like special designs for your slides.
4 gives machines the ability to think smartly.
B. Tick () the correct option.
1 Which of the following is the most commonly used audio format?
a .mp1
c .mp3
b .mp2
d .mp4
2 The determine how your content, such as titles, text, and images, is organised on the slide.
a Themes b Layouts
c Transitions d Animations
3 Which of the following is a domain of AI?
a Machine learning
c Programming
b Robotics
d Google Slides
4 Which of the following is not a method to insert images in a Google Docs document?
a By URL
c Download from your
b Upload from your computer
d Using Google Drive computer
C. Write T for True and F for False.
1 You can only add those videos in the presentation that are stored on your computer.
2 Google Slides automatically saves your work.
3 Tables help you organise information clearly in rows and columns.
4 Google and Tesla are developing AI-powered self-driving cars.
D. Answer the following questions.
1 Differentiate between the Bring Forward and Send Backward options of images in Google Docs.
2 What is the use of the master slide in a presentation?
3 What is the difference between transitions and animations in a presentation?
4 Describe two uses of the Google Lens application.
E. Apply your learning.
1 Ayushi has created a document using Google Docs, in which she wants to insert images. How can she do that?
2 Mayra wants to use a presentation application, but she does not want to pay any licence fee. Which application of Google will be the most suitable for her?
3 Neha’s brother is working in a manufacturing company. How can AI help enhance productivity in the manufacturing industry?
4 Happy wants to add visual effects to elements on his slides to make them more engaging. Which feature in Google Slides should he use?
This book embodies the principles outlined in the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) and the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. It unveils the world of computer science through a unique and captivating pedagogical approach— seamlessly integrating curriculum content into the mesmerising adventures of Mel and Conji, fictional figures hailing from the enchanting world of Avora. Our aim is to prepare learners for the dynamic and technology-driven landscape of the 21st century, equipping them with the essential skills they need to thrive in an ever-evolving world.

• Explore More: QR codes to explore an exciting application of the concept.
• Discuss: Questions to trigger engaging group discussions in the classroom.
• Think and Tell: Probing questions to stimulate thinking at an individual level.
• Did You Know? Interesting facts related to the application of a concept.
• Do It Yourself: Milestone exercises to practice specific concepts.
• Chapter Checkup: A pool of questions catering to all topics and skills covered in the chapter.
• Test Papers: Designed to evaluate understanding of core concepts and application of skills.
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-981442-7-0
