





Academic Authors: Melanie Grobler, Chandani Goyal, Neena Aul, Animesh Mittal, Muskan Panjwani, Sneha Sharma, Anuj Gupta
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Sanjay Kumar Goel, Tauheed Danish, Amisha Gupta
Project Lead: Chandani Goyal
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First impression 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Insights 2 Term 2
ISBN: 978-81-981053-6-3
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.

Comprehension Pronunciation
Acting out action words and framing sentences
Listen and circle
Doing words Using describing words to compare
Word formation- small words from a big word
Words with bl/fl/pl sound –pl ane, fl ag, bl ock
Factual questions Ordering Making predictions Making connections
Story
5. Nature A Suitable Shell Radha Rangarajan
Rhyme time Story writing
Listen and respond
Using a, an and the Position words–place and time
Words with similar meaning Homophones
Factual questions Making predictions
Acrostic poem 6. Nature The Golden Sun Lenore Hetrick Poem
Complete the comic strip.
My routine
Listen and fill in
Using comma to make
Lists
The simple present
The present continuous
Words related to season Project 2: Making a Thank-You Card 7. Imagination and Fantasy Roopa and the Bloop
Words with br/dr soundbr oom, dr eam
Factual questions Identifying key events Comparing and contrasting Inferring character’s thoughts
Graphic Story
Vocabulary from text
Healthy habit related vocabulary
Words with fr/gr soundfr og, gr ass
Factual questions Visualization Making predictions
Story
8. Health and Well-Being King Munch and Mr Wise





Get Set

A beach is a place near the sea. It has lots of sand! We should keep beaches clean. Draw a line to show things that you should throw into the dustbin.

Let us read a story about Mili, a hermit crab. Most crabs have their own hard shells that protect them, but hermit crabs do not have their own shells. So, they have to look for empty shells left by snails and use them as their homes.
Let us read how Mili finds a shell for herself.



Mili woke up and fell straight into the sand.
She looked up. The sun was shining, like it did every day. But today, Mili felt hotter and lighter. She wondered why.
How did Mili feel when she lost her shell?
Oh, no! Mili had lost her orange shell that fit her so well!
Mili had no time to lose. She had to find a new shell before it became too hot or a bird gobbled her up!
Mili found a black shell and tried to snuggle into it.
‘Go away!’ an angry voice said. ‘I’m in here, and I need to sleep.’
She left the snail alone and moved along the beach. Let’s Read
shell: a hard cover that animals like crabs use as their home
protect: to keep someone safe from something that can hurt them
wondered: thought about something and wanted to know more about it
gobbled up: ate up very fast
snuggle: to fit comfortably into something

Mili saw a blue shell and ran that way. But it was not a shell. It was a plastic cap, with its bottle hidden in the sand.
‘That won’t fit me!’ Mili mumbled.
What did Mili find?
Mili saw a yellow shell and ran that way. But it was not a shell. A dry lemon lay there, all the juice gone.
‘How can I live inside a lemon?’ Mili moaned.

Mili saw a white shell and ran back. But it was not a shell. It was an egg with the yellow yolk eaten.

‘This shell will just crumble!’ Mili complained.
Mili saw a purple shell and ran ahead. But it was not a shell. The chocolate had been eaten, the cover thrown away.
‘I thought it was a shiny shell.’ Mili said sadly.
mumbled: spoke very softly and not clearly moaned: made a long, low, sad sound yolk: the yellow part inside an egg crumble: to break into small pieces easily complained: said unhappily
Mili saw a pink shell and stopped. But, it was not a shell. A toe moved, followed by a foot. It was the giant leg of a man asleep on the beach!
‘I think I tickled him!’ Mili laughed.
Mili saw a brown shell and ran up to it. But it was not a shell. The groundnuts had been eaten, and the empty shells thrown around.
‘It will fly away with the wind!’ Mili grumbled.
Mili sees a broken bulb, a wafer packet, and an old button.
But they were not shells.
‘Why are there no shells for me on this beach?’ Mili cried.
Mili saw her friend Toya sliding into a new shell.
‘This new shell fits me better!’ Toya said, leaving behind her old one.
Mili tried the old green shell. It fit her just fine. A happy Mili walked away, hugging her new shell hard!

Think and Tell
Where should you put empty food packets and bottles if you are at a beach? Why?
Did You Know?
Plastic and other waste, in rivers and seas, can make fish and other water animals very sick. Water animals accidentally eat the plastic we throw in the water and this harms them.
grumbled: talked about something in a soft, unhappy voice

Hermit crabs like to live in groups, to feel safe and find food together. Did You Know?
Think and Tell
What do you think Mili should use as her new shell?

Listen to all the keywords here.



1. Write T for True and F for False.
a Mili felt hotter and lighter because she lost her shell. T
b The blue shell Mili found fitted her.
c Mili found a yellow shell that was a dry lemon.
d Mili saw a pink shell of a giant turtle.
2. Answer the questions in one to two sentences.
a Why was Mili looking for a new shell?
b What did Mili find instead of a purple shell?
c Why didn’t Mili use the brown shell?
d What did Toya say when she found a new shell?



1. Look at the pictures and write what Mili finds. Then, number the pictures, 1–6, to show the order in which she finds them.
















2. Mili finds a chocolate paper, a plastic cap, and a dried lemon on the beach. What will happen if we throw trash on the beach?



Colour in the pictures that show how we can keep our beaches clean.

Use the recycling bin.
Take our trash home. Throw peels on the beach.

Throw plastic in the sea. Do a beach clean-up. Leave our trash behind.


Pronounce Well
Listen to the words here.
Read the words aloud. flag block plug flip blanket place float blood plane flower black plant


Read the words and write them. Then, colour the matching picture.

Vocabulary

Circle all the words you can make using the letters in the big word.
Then, match the words and the pictures.

Go Grammar

1. Complete the sentences with the correct doing words in the box.
Hint Box: smiles hugs swim plays
















Remember!
Doing words tell us what someone or something is doing.
a Mili at Toya every morning.
b Mili her new shell.
c Mili with other animals.
d Mili and her friends in the sea. smiles


Describing words tell us more about naming words. They describe the shape, size, or colour of the naming word.
We can use describing words to compare. Look at how we add -er to the end of a describing word to compare Mili and Toya.
For example:
• Mili is smart. Toya is smarter than Mili.
• Toya is fast. Mili is faster than Toya.
Sometimes we repeat the last letter before adding -er.
For example:
• The beach is big. The sea is bigger than the beach.
• Mili is hot in her new shell. She was even hotter when she had no shell.
2. Match the words that compare Mili’s old shell and her new shell. Her old shell is… Her new shell is… hard lighter long brighter light harder bright longer

3. Fill in the blanks with -er form of words.
b A snake is (shorter/longer) than a worm. faster
a A cheetah is (faster/slower) than an elephant.
c A tortoise is (faster/slower) than a cat.
d An elephant is (taller/shorter) than a cheetah.


Listen Well
Listen to the text here.
Listen carefully to the text. Circle the correct doing words to complete the sentences.
The horse is running walking going
The cow is grazing lying standing
The ducks are quacking floating swimming
The cat is crawling sleeping lying
The dog is licking holding eating


Practise speaking here.
Choose four action words. Make sentences with the words. Now, act out your sentences as you share them with the class.
Actions words:
• jumping
• swimming
• sleeping
• singing
• drawing

I am jumping. I am dancing.
• running
• eating
• dancing
• laughing
• writing
You may also use other action words.



Read this poem. Crab on the beach, Red shells shining bright, Always moving sideways, Bubbles on their claws, Searching for food at night.
This is a poem about crabs, and each line starts with a letter from the word ‘CRABS!’

Write a similar poem on NATURE. Start each sentence with the given letter.



Tick () the correct pictures.
1. What do flowers do when the sun shines?
Open their petals
Sleep Wake up Get Set
2. What do owls do when the sun shines?
Fly and hunt
3. What do we do when the sun shines?














Sleep Close their petals
It is true that we see the sun every day. But do we need the sun? Let us read the poem to find out!


Let’s Read

Great, glorious, golden sun, Shine down on me today, You are the life of all this earth, You and your magic ray. You are the life of bird and plant, All must depend on you.
Shine down, great sun, the whole day long!
Shine from the sky’s blue.

glorious: (here) bright and beautiful depend: (here) to wait for the sun’s help

Rainbows are formed by the sunlight shining on water droplets after it rains.
How does the sun make you feel when it shines on you?
And I will welcome your golden rays, For you mean life to me, And you mean happiness and health, Strength and energy. Shine down, great sun, on flower and field, And never say goodbye. Forever and ever give us your light, From the wide blue sky.

Why do you think the sun is important for plants, animals and people?

forever: always
Listen to all the keywords here.





1. Complete the sentences with the words in the box.
Hint Box: Earth sky flowers happiness sun health
a The poem is about the great, glorious, golden .
b Everything on depends on the sun.
c The poet asks the sun to shine from the blue all day long.
d The sun gives us , , and strength.
e The poet wants the sun to shine on the and fields.
2. Answer the questions in one to two sentences.
a What is the colour of the sun in the poem?
b What does the poet ask the sun to do at the start of the poem?
c Why does the poet welcome the sun’s rays?
d Why does the poet think the sun is so important?


Big Idea
Imagine that the sun does not come out tomorrow! Write three sentences about how our days would look different. Then, share your sentences with your friend. sun


For example: The owls will not sleep. Everything will be dark.



1. Look at the pictures for clues. Circle the words in the puzzle that tell us something about a season.




2. We hear different sounds in nature. Match the words and the sounds.




The poet uses words like ‘great’, ‘golden’ and ‘glorious’ to describe the sun. Look at the picture and write five describing words for the sun.
Remember!
Describing words are words that tell us more about naming words.
Hint Box: You can talk about the shape, colour and size of the sun.



















































































































































































































































Let us make a special thank-you card. A thank-you card is a way to show someone you appreciate them.
What you need for this project:
One A4-size sheet of paper

A pencil


Crayons or markers
Glitter/stickers
Step 1: Take your A4 paper and fold it in half to make a card. Now you have a front side and an inside.
Step 2: Decorate the Front:
• Think what you would like to thank Mother Nature for.
• On the front of the card, draw a picture related to nature like trees, flowers, birds or the sun.
• Write “Thank You” in big, bold letters on the front.
• Use colours to make your card look pretty.
Step 3: Write Your Thank-You Note Inside:
• Open the card and write a short thank you note inside.
Example of Thank-You Note Create your own lines!
Mother Nature “Thank you, Mother Nature, for the beautiful trees and flowers. I love playing outside!”
“Thank you, Mother Nature, for and . You make the world .”
Step 4: After you finish, you can show your card in class.

You may decorate the inside of the card with drawings, stickers, or any little details you like. Make it special!







It is your birthday. How would you like to decorate the room? Imagine the things you would put in the room. Draw and colour them. Get Set
Roopa has a friend, Bloop, whom she loves a lot. What is so special about their friendship? What do they do when they are together? Let us read the story to find out.

Let’s Read


imaginary: something that you think of but is not real silly: funny and playful
Think and Tell
The Bloop is not clear. Do you think he is Roopa’s real friend or does she imagine him?


making a mess: making something very untidy
lovely: nice and beautiful
notice: see something and pay attention to it
Can Roopa’s parents also see Bloop? Why?

How do you think Roopa feels when Bloop says he is proud of her?
races: runs to see who comes first watches over: protects and keeps safe



Listen to all the keywords here.
1. Tick () the sentences that are right, and cross () the sentences that are wrong.
a Roopa is Bloop’s imaginary friend.
b Bloop helps Roopa brush her hair.
c In class, Bloop scares Roopa.
d Roopa is afraid of the dark.
2. Choose what happens next in the story.
a Roopa wakes up in the morning, and Bloop makes funny faces at her. i Roopa stays in bed. ii Roopa gets ready for school.

b Roopa and Bloop are in class, and Bloop helps Roopa. i Roopa raises her hand. ii Roopa stays quiet.
c Roopa and Bloop race to the bus. i Roopa wins. ii Bloop wins.
3. Answer the questions in one to two sentences.
a Why is Bloop special?
b How does Roopa feel in the morning when Bloop wakes her up?
c How does Bloop try to help Roopa when she is getting ready for school?
d How does Bloop help Roopa finish her fruit?



1. Bloop is Roopa’s imaginary friend.
a How do you think Bloop is the same as our human friends? You can use these words in your answer: kind, fun and play.
b How do you think Bloop is different from our human friends? You can use these words in your answer: imaginary and pretend.
2. Tick () what Roopa must be thinking.
a Bloop asks to comb Roopa’s hair.
Yes, Bloop! Please help me. Oh no! He will mess it up again.

b Bloop shares jokes with Roopa.
Oh Bloop, you are so funny!
Bloop, let me finish my food.
c Bloop says, ‘I am so proud of you, Roopa.’
I am so tired.
That is so kind of you, Bloop.


Big Idea



Imagine that you have an imaginary friend. Draw what it would look like.
What name would you give it?
What would you and your imaginary friend do?


Pronounce Well
Listen to the words here.
Read the words aloud. bring broom drum drive brick brook draw drink break brown dress dry

Read the words in the box. Fill in the blanks with the correct words in the box.
Hint Box: bread
a Roopa likes to eat bread and jam.
b Bloop says, ‘Wear your pink .’
c Roopa must her wet clothes.
d Bloop helps Roopa sweep with a .
e I my teeth twice a day.




1. Sometimes different words have similar meanings. Match the words that have almost the same meaning.































Homophones are words that have the same sound but different spelling. For example: I have one cookie. I have won the match.
2. Complete the sentences with the similar-sounding words in the box.
Hint Box: bare/bear sun/son flower/flour sea/see
a Grandmother always makes a delicious cake with . She decorates it with a beautiful .
b Nishant is Raghav’s . He likes to play in the .
c Roopa and her family are at the . Her parents can her play in the sand.
d The cupboard was , so Mama had to go and look for honey.


Go Grammar flour flower
Using A, An and The
• We use a or an before words that name one thing or person. These words do not say which exact thing.
For example:
Bloop and Roopa race to a bus. (We are not saying which bus.)
Roopa ate an ice cream. (We are not saying which ice cream.)
• We use an before words that start with the vowel sounds a, e, i, o, u.
For example: She is eating an apple.

• We use the when we know what we are talking about or when we have already used the naming word.
For example:
Bloop races her to the bus. (Here, we are saying which bus: Roopa’s school bus and not just any bus.)
Roopa ate the chocolate ice cream. (chocolate says which ice cream.) She is eating the red apple from her tiffin box. (Here, we are saying which apple.)
1. Fill in the blanks with the correct article, a or an.
a Bloop is imaginary friend.
b Roopa eats apple.
c Bloop always makes mess.
d Is Bloop elephant?
2. Roopa is telling her friend about a dream. Look at the picture and use the articles, a, an and the, in the sentences. an

I saw magical forest in my dream. There was owl in magical forest. owl was friends with elephant. elephant had long trunk. Its trunk was like magic wand.
These words tell us where something is— behind, under, above, between or in front of. For example:
Remember!
Position words help us understand where things are. They tell us the position or place.
The cat is behind the box.
The cat is above the box. The cat is under the box.
The cat is between the boxes.
The cat is in front of the box.
3. Fill in the blanks with position words of place.

a The fox is the tree.
b The fox is the two bushes. under


Hint Box: behind between in front of above





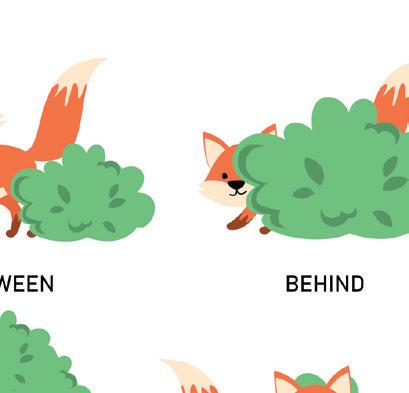




c The fox is the bush.



d The fox is jumping the bush.

e The fox is hiding the bush.




These words tell us when something happens—one, at and in.




At We use at for an exact time. Roopa goes to school at 7:30 a.m.
On We use on for days or dates. Roopa does not go to school on Sundays.

My birthday is on 7 June.
In We use in for longer periods of time, like months or years.
We also use in for broad times in a day.
Roopa is going on a school trip in May.
Bloop wakes Roopa in the morning.
4. Fill in the blanks with the correct position words of time (on/at/in).
a Roopa and Bloop decided to go for a picnic 8 May.
b They went for a picnic Saturday.
c They left home 6 a.m.
d Roopa promised Bloop to go again December. on


Listen Well
Listen to the text here.
Listen carefully to the text. Choose the correct answers.
a Who told Lily the secrets of the night sky?
i Emy ii Sparky
b What are the stars for the fairies?
i lamps ii bulbs
c When will the friends visit Sparky?
i next week ii the next day
d What does Emy want to ask a question about?
i aliens ii shooting stars



Practise speaking here.
Recite your favourite rhyme with expression and hand movements in class. Here is a list to help you.
• Twinkle, twinkle, little star…
• Baa baa black sheep…
• Humpty Dumpty sat on a wall…
• Mary had a little lamb…
• Old Mac Donald had a farm…
• Row, row, row your boat…
• Jack and Jill went up the hill…
• London Bridge is falling down…
Have fun singing!

Take your time to remember the words of the rhyme. Sing out loud and in tune.




Let us write an imaginary story!
Look at this picture and complete the story.
Who? There is a bear, some rabbits and a bird.
Where? The story is set in a forest.
What? The bear is wearing glasses and reading a book to the rabbits and the bird.














































































































Plan your story.
The names of the boy, the girl and the dragon:
Name of the place: List the things they do together:


























































Look at the picture and write your story in your notebook.






























































































Once, there was a bear named Baloo. He loved to read. Every day, he would sit under a tree and read books. The rabbits and the birds would come and listen to the stories.








Tick () your favourite sports activities that help you stay fit! Get Set





























A king who loved to eat junk food became so unhealthy that he could not even tie his shoelaces. What did he do to solve this problem? Let us read the story to find out.




Once upon a time, in a faraway kingdom, there lived a king named King Munch. King Munch loved to eat junk food. He loved burgers, fries and candy more than anything else. He ate them for breakfast, lunch and dinner. King Munch also hated exercising. Instead, he liked to sit on his throne all day, munching on snacks.
Should we eat junk food every day? Why?
One day, King Munch noticed he could no longer fit into his favourite chair. His clothes were getting tighter, and he was out of breath even when he laughed. But King Munch did not see the problem. He thought it was all just fine. His ministers and doctors were very worried. They tried to talk to him gently.
‘Your Majesty, maybe you should eat less cake and more fruit and vegetables,’ said one minister.
‘But I love cake!’ said the king, looking surprised.
‘Exercise can be fun! You can play badminton or go for a run,’ said a doctor.
But King Munch just laughed and said, ‘Why do I need to change? I am happy just the way I am!’
junk food: food that is not good for us throne: a special chair on which a king or queen sits munching: eating in small bites while making a sound
Why did the minister ask the king to eat more vegetables and less cake?
out of breath: needing to breathe deeply after exercise
worried: nervous or scared about something gently: in a kind way

help him put on his walking shoes and started his journey. The walk was tough. King Munch puffed and panted all the way up the mountain. When he finally reached Mr Wise’s house, he was very tired. ‘Welcome, King Munch,’ said Mr Wise with a smile. ‘I can help you, but I cannot leave my house and my books, so you must come here every day.’
King Munch wanted to argue, but he was too tired. So, he nodded and went back to the palace.
Soon, the king could not even tie his shoes or walk up the palace stairs. One day, his minister heard of a wise man who lived outside of town. ‘Your Majesty,’ said the Minister, ‘I know someone who can help you. His name is Mr Wise, and he lives on the other side of the mountain. But no horse cart can go there, so you must walk to his house.’ King Munch sighed but agreed. He really wanted to be able to tie his shoes again. So, he asked one of his servants to

Why didn’t King Munch argue with Mr Wise?
sighed: let out a long breath agreed: said yes to something journey: a long trip tough: hard and difficult
puffed and panted: breathed quickly and with difficulty argue: give a reason for not agreeing nodded: moved his head up and down to say yes

Every day, King Munch walked up the mountain to visit Mr Wise. At first, it was very hard, but each day it got a little easier. He started to notice something amazing. His clothes were not as tight, and he could breathe better. He even began to enjoy the fresh air and beautiful views on his walks. When he reached Mr Wise’s house, they would sit and talk about King Munch’s favourite snacks, laugh and share stories.
One day, after many walks up the mountain, King Munch looked in the mirror and saw that his clothes fit better. He could now tie his shoes, walk up the palace stairs and fit into his throne again. ‘Mr Wise, you have helped me become healthy without me even noticing it!’ King Munch said with a big smile. Mr Wise laughed, ‘Sometimes, the best way to help is to make it fun and simple.’
King Munch returned to his palace with a new habit. He still loved his snacks, but he also enjoyed fruit, vegetables and his daily walks. And so, King Munch lived happily and healthily ever after.

Walking every day keeps our heart active and strong.

amazing: something really great and surprising Listen to all the keywords here.


Read and Respond

1. Fill the blanks with words in the box.
Hint Box: fresh junk tight mountain
a King Munch ate food every day.
b King Munch’s clothes got very .
c Mr Wise lived on the other side of the .
d King Munch began to enjoy the air on his walks.
2. Tick () the correct answers.
a Why did King Munch visit Mr Wise?
i To learn how to bake a tasty cake
ii To get help with becoming healthy
b What did King Munch notice after he started walking every day?
i His clothes were getting tighter, and he could not breathe easily.
ii His clothes were getting looser, and he could breathe better.
c How did King Munch feel about exercising at the start of the story?
i He loved it.
ii He hated it.
d What did King Munch enjoy during his daily walks to Mr Wise’s house?
i The yummy snacks
ii The beautiful views
3. Answer the questions in one to two sentences.
a What did King Munch do all day at the beginning of the story?
b What did the doctor say King Munch should do?
c What did Mr Wise ask King Munch to do? Why?
d Name three things that King Munch could do when he was healthy.




1. Fill in the table.
Hint Box: calm grand beautiful royal
People Where do they live?
King Munch
Mr Wise
Give two words to describe the place
2. On the left are things that the unhealthy King Munch would do. Write what would change after the King’s habits become healthier.
Unhealthy King Munch What will a healthy King Munch do?
Gets tired and cannot walk up the mountain He will enjoy walking.
Eats only burgers, fries, and candy He will
Cannot bend to tie his shoelaces He will Always lies on his bed He will



A dietician helps people choose yummy and healthy food to keep their bodies strong. Imagine that you are King Munch’s dietician. Circle yummy and healthy food from this list.























Read the words aloud. frog fry green grow frock fruit grape group from friend grin grass

Say the name of the item in the pictures aloud. Then, write the words.










































1. Use words from the story to fill in the gaps.
Charlie Chew has eaten too much food and he is finding the race very . He has not even gone halfway, but he is already out of . Can you hear him and ? junk frock
Hint Box: breath junk puffing panting tough
2. Good habits help us stay happy and healthy. Put each habit into the right box.
Hint Box:
brushing our teeth doing yoga doing homework reading books taking a bath running and dancing
Cleanliness habits
Study habits
Exercise habits

Go Grammar

We use a comma (,) between words in a list so that the reader knows we are naming different things. We do not need a comma before and.
For example:
• King Munch eats chocolate, chips, cookies and pizza for breakfast!
Without the commas we may think the king ate chocolate chip cookies and pizza!
We use a capital letter to start a sentence. We end a sentence with a full stop and a question with a question mark.
1. Correct this conversation between the King Munch and Mr Wise by adding commas, full stops or question marks.
Mr Wise: What did you have for breakfast today
King Munch: I had brown bread egg melon and a banana
Mr Wise: I had upma poha and dhokla

The Simple Present is used to state facts.
For example:
• The sun rises in the morning.
We also use the simple present to talk about actions which happen regularly or every day. For example:
Doing words tell us what something or someone is doing. For example: The King walks up the mountain.
• The ministers help King Munch. The words rises and help are doing words. If the action is done by he, she or it, we add -s or -es after the doing word—helps, eats, grows.
We add -es to doing words that end in -ch, -o, -s, -sh, -x and -z.
I watch He watches I wash He washes We do She does We mix He mixes They miss He misses The bees buzz It buzzes
One person
More than one person I eat rice. We (Da and I) eat rice. You (one) eat rice. You eat rice.
He/She/It (Da/Ba/The bird) eats rice. They (Da and Ba) eat rice.
2. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the doing words. Hint
a King Munch on his throne every day.
b Mr Wise on the other side of the mountain.
c King Munch up the mountain every day.
d They always about their favourite snacks.
e King Munch’s clothes him well now.
The Present Continuous
We use the present continuous to talk about actions that are happening right now or at the moment of speaking.
For example:
Look, King Munch is eating healthy food!
The children are studying right now.
The present continuous is formed by adding is/am/are and -ing to doing words.
I am playing.
He/She/It is jumping.
We/They/You are dancing.
3. Choose the correct words to fill in the blanks. The actions are happening now.
a I in my book now.
i is writes ii am writing iii writed
b They around outside.
i are runs ii run iii are running
c Look, Nitesh a beautiful picture.
i is painting ii paints iii is paints
d Ria a healthy salad.
i is eat ii eats iii is eating am writing



Listen Well

Listen to the text here.
Listen carefully to the story and fill in the blanks with the correct words.
a The man asked the villagers for some to eat.
b The man decided to make .
c After the stone, the man added to the soup.
d The second villager got for the soup.
e The villagers learnt a lesson about . Practise speaking here.



Look at this picture. Take turns to tell your teacher what the boy is doing.
Sit with four friends and talk about what you do daily.
Hello friends!
I wake up at 6 o’clock in the morning. First, I get ready for school. Then, I eat my breakfast. After school, I rest for one hour. Next, I do my homework and go to the park to play with my friends. Finally, I go to bed at 9 o’ clock.



Complete the comic strip by writing the conversation between Karthik and Rohit.
Hi Rohit! Why did you not come to yesterday?
I had Doctor says it was due to germs.
Are you now?
Yes! The doctor told me, we should always our hands before .
We should also wash our before cooking.
You are, right Karthik! I will be more careful.
Take care, Rohit. Goodbye!
Karthik. I will see you in .



1. Fill in the blanks with the correct doing words in the box.
Hint Box: flow soar stop plant hunt
a People should cutting down trees.
b We should more and more trees.
c People should not animals.
d The birds high in the sky.
e The rivers through many places.
2. Fill in the blanks with the -er form of describing words.
a dense denser
b dark
c sweet
d big
e thick












3. Use the word in brackets to make sentences.
The boy is younger than the man.





































4. Complete the sentences by adding -er to the describing words.
a This river is (clean) than that one.
b A plastic bag is (thin) than a cloth bag.
c A crab is (quick) than a snail.
d The bench is nearer (near) than the dustbin. (small) (sharp)

1. Fill in the blanks with the correct articles.
Hint Box:
a Look at colourful rainbow.
b Can you spot moon?
c There is elf hiding behind the tree.
d children are dancing in the garden.
e Let us find tree for shade.
2. Look at the picture and tick () the sentence with the correct position words of place.
a
b



c







The cat is behind the table.
The cat is under the table.
The boy is in front of the balls.
The boy is between the balls.
The girl is standing in front of a box.
The girl is standing above the box.





The bird is flying between the trees.
The bird is flying above the trees.
Rohan was hiding behind the box.
Rohan was hiding in the box.
3. Fill in the blanks with the correct position words of time.
a We eat breakfast (in/on) the morning.
b It snows here (in/on) winter.
c My birthday is (at/on) the first of June.
d The party starts (at/on) 5 o’clock.
e We will have a lot of fun (at/on) that day.

1. Rewrite the following sentences using capital letters, commas and full stops.
a my kitten likes to eat fish rice and biscuits
b is this your tiffin box
c seema and ranu cook healthy food together
d i like to eat poha
e my grandmother likes coconut water mango shake and guava juice
2. Write SP for the simple present sentences and PC for the present continuous sentences.
a Rohan exercises every morning.
b Radhika is washing her hands in the bathroom.
c We play for an hour in the afternoon to stay fit.
d They are busy cleaning their room.
e We eat dinner at 7 o’clock.

3. The family cooks together every day. Write sentences about what each one does.
Hint Box: stir chop cut peel help



a Mother:
Mother stirs the
b Father:
c My brother:
d My sister:
e My brother and my sister:
4. Use the words in the box to say what is happening in the pictures right now.
Hint Box: say tell fill look cry

Raj at the salad. Mother him to eat it.

Raj loudly. c Raj his mouth with chips.
e Sorry Raj he will not be naughty again.

Name of the Student:
Class: 2
Roll Number:
Section:
Date:
Section – A (Reading and Vocabulary)
1. Read the story and answer the questions.
In a small village, there was a magical garden. This garden was full of fruit, vegetables and grains that could talk! The garden belonged to a kind old lady named Grandma Green. Three friends—Aarav, Meera, and Rohan—visited Grandma Green’s magical garden.
Annie Apple told the children how she gives vitamins, and Carl Carrot explained how he makes bones strong. Milly Millet and Rachel Rice give energy. Now, the children know that eating healthy food helps them grow strong and happy. From that day, they shared their new knowledge with others and ate healthy food.
a Choose the correct answers.
i Who owned the magical garden?
a. Grandpa Green
c. Carl Carrot
ii What did Annie Apple provide?
a. Energy
c. Strong bones
b. Grandma Green
b. Vitamins
iii Which vegetable makes bones strong?
a. Annie Apple
c. Carl Carrot
b. Milly Millet
iv What do Milly Millet and Rachel Rice give us?
a. Vitamins
c. Strong bones
b. Energy
v What important lesson do the children learn?
a. Eating healthy food helps them grow strong and happy.
b. How to take care of a garden
c. How to talk to fruit and vegetables
b Fill in the blanks with the words from the passage.
i In the magical garden, , fruit and grains could talk to the children.
ii taught the children about vitamins.
iii Carl Carrot explained how he makes strong.
iv The children get from Milly Millet and Rachel Rice.
v By visiting the garden, the children learned the importance of food.
c Write True or False.
i Grandma Green’s magical garden had talking fruit and vegetables.
ii Annie Apple said she gives vitamins.
iii Carl Carrot said he gives energy.
d Look for the words from the passage that sound the same as the words below. Use the words to write sentences of your own.
i No . ii Eight .

2. Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the doing words to show actions done daily.
a Aarav (eat) fruit every day to stay healthy.
b Every morning, Meera (brush) her teeth before breakfast.
c In the evening, Rohan (run) around the park with his friends.
3. Rewrite the sentences by using capital letters, full stops (.) and a comma (,).
a aarav now eats fruit and vegetables every day
b he washes his hands before meals
c He runs plays and studies with his friends
Section – C (Writing)
4. Complete the story by filling the blanks.
Box: junk food doctor eat healthy food strong run and play well more energy
Raman loved to eat . One day, he met a wise who taught him to . After learning this, he started to eat . Soon, he felt







very and could . Now, he always chooses healthy food and has .
5. Complete the comic strip by filling in the blanks.

Complete the comic strip by filling the blanks.
My healthy habit is
I stay healthy by eating . I always feel by eating . I stay away from to be healthy.






















































































Pooja and Rohit went to buy candies with their father.
Pooja: Father, let us buy candies for my birthday.
Father: Okay, 200 candies for your school friends and 25 candies for your park friends.
Pooja: Wow! 225 candies!
Rohit: How did you count that? Please teach me to count beyond 200.
Let us help Rohit count numbers more than 200.
We know how to count and write numbers from 0 to 100.
We can write numbers more than 200 the same way as we write numbers from 1 to 100.

Counting Forward and Backwards
Read the numbers on the grid again. Read them this way:
Counting
Counting BACKWARDS
Hundreds, Tens and Ones
We know that a 3-digit number has hundreds, tens and ones. We can show a 3-digit number using place value blocks.
We also know that 10 ones = 1 tens, and 10 tens = 1 hundreds.
Let us now see how the 225 candies are shown using place value blocks.
So, 225 candies are shown as 2 hundreds blocks, 2 tens blocks and 5 ones blocks.
Think and Tell
























The Burj Khalifa in Dubai is the tallest building in the world. It has 163 floors. Write the number as a number name.
Write the number that has:
a 4 hundreds, 6 tens and 5 ones
c 6 hundreds and 3 ones
b 7 hundreds, 7 tens and 7ones
d 5 hundreds and 5 ones
Show the given numbers using place value blocks. Use for hundreds, for tens and for ones.
We saw that Rohit and Pooja�s father bought 225 candies.
Now, let us write the number using a place value and an expanded form.
Place value is the value of a digit based on its position in a number. Each digit has a place value, such as ones, tens, hundreds and so on. The face value of a digit is the value of the digit itself.
For example, in 225, there are 2 hundreds, 2 tens and 5 ones. We can write 225 as:
Aryabhata, an Indian mathematician worked on the place value system.
So, the place value of the hundreds place is 200. The place value of the digit at tens place is 20. The place value of the digit at ones place is 5.

The place value of 0 is always 0 no matter what its position in the number is.
Example 2: Write the place value and face value of the coloured digits.
234 4 ones; 4 953 9 hundreds; 9 806 0; 0 662 6 tens; 6
Let us understand the expanded form of numbers up to 999.
Expanded form refers to writing a number as the sum of its place values. We can write the number name of a given number using its expanded form.
Expanded form of 983:
Standard Form – 983
Expanded Form – 900 + 80 + 3
Number Name – nine hundred eighty-three





















Do It Yourself 6B

Write the place value of all the digits in the given numbers. Then, write the numbers in their expanded form.
398
170
Write the number. Write its number name.
Tick () the numbers in which the place value of:
Some temples in India have steps. The Rameshwaram temple has 127 steps. Write the number name and expanded form for the given number.

Pankaj and Ria like to play with marbles.
Pankaj had 120 marbles and Ria had 69 marbles.
Pankaj: I have more marbles than you.
Ria: No, I think I have more.
Comparing Numbers
Who has more marbles?
Ria has 69 marbles.
Pankaj has 120 marbles.
It is a 2-digit number.
Remember!
It is a 3-digit number.

A number that has more digits is always greater!
So, Pankaj has more marbles than Ria as 120 > 69 (120 is more than 69).
A 3-digit number is always more than a 2-digit number.
Compare 547 and 328
Both are 3-digit numbers. We first compare the digits in the hundreds place of both the numbers.
5 is greater than 3
So, 547 > 328 (547 is greater than 328).
Now, when the number of digits is the same and the digits in the hundreds place are also the same, then, we compare the digits in the tens place to see which is greater or smaller.
For example, compare 437 and 453.
Chapter 6 • Numbers up to 999
Same digit in the hundreds place.
4 is equal to 4, 4 = 4
Since the digits in the hundreds place are the same, we compare the digits in the tens place.
3 is less than 5. So, 437 < 453.
Now, when the number of digits is the same and the digits in the hundreds and tens places are also the same, then, we compare the digits in the ones place to see which is greater or smaller.
For example, compare 847 and 849.
Same digits in the hundreds and tens places. Compare the digits in the ones place.
When both the numbers are equal, we use the equal to sign � = � . 344 = 344
7 is less than 9. So, 847 < 849.

Compare the digits in the tens and ones places ONLY if the digits in the hundreds place of the two numbers are the same!
Example 3: Compare 689 and 681.
Same digits in the hundreds and tens places. Compare the digits in the ones place.
9 is greater than 1. So, 689 > 681.
Ordering Numbers
We learnt how to compare two numbers. Let us now compare more than 2 numbers.
Let us compare 34, 871 and 679.

We know that 2-digit numbers are always smaller than 3-digit numbers. So, 34 is less than both 871 and 679. Now, let us compare 871 and 679.
So, 871 is greater than 679, or we can also say 679 is less than 871. Numbers, when written from the smallest to the largest, are arranged in increasing or ascending order.
The three numbers in this order would be: 34, 679, 871 or 34 < 679 < 871. Numbers, when written from the largest to the smallest, are arranged in decreasing or descending order.
The three numbers in this order would be: 871, 679, 34 or 871 > 679 > 34.
We can form numbers by arranging the digits in ascending or descending order. To form the greatest number, arrange the given digits in descending order. To form the smallest number, arrange the given digits in ascending order. We can form 3-digit numbers by arranging any 3 given digits.
Let us form numbers using the digits 2, 8 and 4.
Digits
Digits arranged in ascending order
Example 4: Form the greatest and smallest number using 3, 9 and 5.
Greatest number: Arrange the given digits in descending order to get 953.
Smallest number: Arrange the given digits in ascending order to get 359.






















Circle the bigger number.
Colour the box with the greatest number red and the smallest number yellow in each of the following groups.
Arrange the numbers in increasing and decreasing order. 3
Form the greatest and the smallest 3-digit number using 2, 5 and 7.
Houses are built using bricks. Bricks are used to make walls along with cement. Toni built a wall using 790 bricks. His neighbour, Ramu, also built a wall but he used 689 bricks. Who used more bricks?
Setting: In groups
Things Needed: 1 abacus, 1 pencil
Method:
1 Students are to understand how to show numbers on an abacus. Then, each group should think of two 3-digit numbers.
2 The groups take turns to show one number at a time on the abacus to the other groups, who then write the number and its number name in their notebooks.

3 The group that writes the number and number name correctly, gets a point.
4 The next group then shows their 3-digit number on the abacus and the game continues.
Chapter Checkup
Write the missing numbers.
567 b 202 c 986 2 Art Integration
Write the place value of each digit in the given numbers. Write the numbers in their expanded form. Draw place value blocks for each. Use for hundreds, for tens and for ones.
5 The group that gets the maximum points, wins the game. Write the number.
Compare the numbers using the symbols <, > or =.
Write the numbers in decreasing order.
a 559, 678, 345 b 109, 289, 678 c 345, 696, 873
a 540, 330, 257 b 678, 447, 567 c 600, 120, 499
A colony has many different houses arranged in rows on different streets. The houses in a row are usually numbered. There are four houses on a street with numbers in the order 223, 224, 225 and 226. What will be the number of the next house? 7 Cross Curricular
Choose the numbers from the balloons and fill in the boxes.
Form the greatest and smallest 3-digit number using the digits 6, 1 and 4.
Colour the boxes by following these instructions.
Colour the box green if the digit in the ones place is greater than 5.

Colour the box yellow if the digit in the tens place is greater than 5.
Colour the box pink if the digit in the hundreds place is greater than 5.






A metro train is a train that runs just in a city and connects one area to another. Jenny is visiting her cousin�s house during summer break in Delhi. She sees the Metro train for the first time. She sees the pillars and tries to read the number on each pillar. Look at the picture and answer the questions.





1 How many metro pillars are shown in the picture?

2 If the metro is moving towards the right, the pillar numbers are (increasing/decreasing)
3 Write the number name of the smallest pillar number shown in the picture.

4 Use the digits of the greatest pillar number in the picture to form the smallest number.























































































Rakesh is a fruit seller.
He bought 115 mangoes on Monday.
He bought 123 apples on Tuesday.
To find the total number of fruits, we need to add the number of fruits bought on Monday and Tuesday.
Addition without Regrouping
How many fruits are there with Rakesh? There are 115 mangoes and 123 apples.
We know that
Let us add the 2 numbers using place value blocks. = 1 hundreds (H), = 1 tens (T) and = 1 ones (O).

Thus, the sum of 115 and 123 is 238.
Now let us see if we get the same answer by adding vertically.
Step 1
Step 2
Write the numbers vertically. Add the digits in the ones place. 5 + 3 = 8 ones
Step 3
Add the digits in the tens place. 1 + 2 = 3 tens
Step 4
Add the digits in the hundreds place. 1 + 1 = 2 hundreds
We get 2 hundreds, 3 tens and 8 ones.
115 + 123 = 238 fruits
Example 1: Add 143 and 206 by using the place value blocks and writing the numbers vertically.
Use for 1 hundreds (H), for 1 tens (T) and for 1 ones (O).
Place Value Blocks
The total number of fruits Rakesh has is 238.
Now, Rakesh has bought 177 bananas.
Let us see how many fruits are there now.
Let us add the 2 numbers using place value blocks.
Remember!

When we add, the number of things becomes greater. Chapter 7 • Addition and Subtraction of 3-digit Numbers
tens = 1 hundreds
Now let us see if we get the same answer by adding vertically.
2
Add the ones.
8 ones + 7 ones = 15 ones
10 ones = 1 tens
Write 5 and move 1 tens to the tens place.
Add the tens.
3 tens + 7 tens + 1 tens = 11 tens
10 tens = 1 hundreds
Write 1 and move 1 hundreds to the hundreds place.
3
Add the hundreds.
2 hundreds + 1 hundreds + 1 hundreds = 4 hundreds
Write 4 in the hundreds place.
So, we see that we get the same answer on adding 238 and 177 using place value blocks and vertical addition.

Example 2: Add 289 and 32.
Write the numbers according to their place value.
Add 256 and 34.























Add the 3-digit numbers without regrouping.
Add the 3-digit numbers without regrouping. 2 a 347 + 2
664 + 35
Draw the place value blocks to add.
783 + 214
Use for 1 hundreds (H), for 1 tens (T) and for 1 ones (O).
123 + 543
801 + 111
Add the given 3-digit numbers vertically.
707 + 128
349 + 521
209 + 340
+ 412
Raghu had 475 fruits on Wednesday. He sold 322 fruits. How many fruits are left with him now?
453 + 212
656 + 322
549 + 144
• Addition and Subtraction of 3-digit Numbers
To find the number of fruits left, we need to subtract 322 from 475.
Let us see how we can subtract 2 numbers using place value blocks.
Step 1
Show the bigger number using place value blocks.
475
Step 2

Subtraction means taking something away from a group. We take away the smaller number from the bigger number. The number of things becomes less in subtraction.
Cross out or take away as many blocks as in the smaller number.
475 – 322
Step 3
Count the number of hundreds, tens and ones left. That will give us the answer.
475 – 322 = 153
Vertical Subtraction
Let us see how we can subtract 2 numbers by writing them vertically.
Step 1
Write the numbers vertically as per their place values.
Subtract the ones. 5 ones – 2 ones = 3 ones Write 3 in the ones place.
Step 2
Subtract the tens.
7 tens – 2 tens = 5 tens Write 5 in the tens place.
Step 3
Subtract the hundreds. 4 hundreds – 3 hundreds = 1 hundreds
Write 1 in the hundreds place.

Here, we can see that we get the same answer on subtracting 322 from 475 using place value blocks and vertical subtraction.
There are 153 fruits left with Raghu.

We subtract the smaller number from the bigger number. Write the smaller number under the bigger number.

When we subtract the same number from itself, we get 0. 9 – 9 = 0
Example 3: Subtract 23 from 138 by writing the numbers vertically and using the place value blocks and vertical subtraction.
1
(H),






















place value block and subtract. Use for 1 hundreds (H), for 1 tens (T) and for 1 ones (O).
Subtract the numbers vertically.
Shreya and her friends went to a library.
Teacher: Could you please help me arrange the books?
Shreya: Yes, ma’am.
There were 135 books on the table. The teacher gave 125 more books. Shreya and her friends arranged 100 books. How many books are left to be arranged?
Identifying the Right Operation
First, there were 135 books. Then, 125 more books were added. So, Shreya needs to add 135 and 125 to find the total number of books.
Remember!
When we have to find the total number, or how many in all, we add.

There are 260 books in all. Shreya and her friends arranged 100 books. So how many are remaining?
We have to subtract 100 from 260.
Remember!
When we have to find how many are left or remaining, we subtract.


So, we get 160 when we subtract 100 from 260. Thus, 160 books are left to arrange.
Example 3: Situation Add or Subtract?
There were 235 apples in a basket. 125 apples were sold. How many apples are left?
Subtraction
We have to find out how many are left. So, we subtract.
Word Problems on Addition and Subtraction
The Food Corporation of India stores wheat in bags in large godowns. Wheat is stored to protect it from insects. 350 bags were sold to the shopkeepers directly. 573 bags were transported to other places. What is the total number of wheat bags?
What do we know?
Wheat bags sold to shopkeepers = 350
Wheat bags transported to other places = 573
What do we find?
Total number of wheat bags. How do we find?
The keyword ‘total’ tells us that we need to add. 350 + 573
Solve to find the answer.
So, the total number of wheat bags is 923.





















2
4

Identify the correct operation and solve.
a There are 456 books on a table. The teacher keeps 198 more books on the table. How many books are there on the table?
b There were 568 toys in a toy store. 232 were sold. How many toys are left?
A farm is a place where animals are kept. Read the table, find the correct operation and solve the problems.
a What is the total number of sheep and goats on the farm?
b How many more dogs are there than sheep?
Pappad is a thin wafer or flat bread. It is made up of dried lentils. A shopkeeper had 583 packets of pappad. He sold 272 packets. How many packets are left with the shopkeeper?
Tigers are kept safely in the tiger reserves. Corbett has 260 tigers, and Kanha has 105 tigers. How many tigers are there in total at the Corbett and Kanha Tiger reserves?
Setting: In groups of 4

Collaboration & Experiential Learning
Materials Required: Number chits, pencil, operation chits, place value blocks
Method:

Make chits for numbers 0 to 9. Make 2 operation chits by writing the addition ‘+’ and subtraction ‘ –’ symbols on them.





Player 1 will pick 3 chits and form a 3-digit number.
Player 2 will again pick 3 chits and form a 3-digit number.
Player 3 will choose the operation chit: addition or subtraction.
Player 4 will solve it using place value blocks.

Repeat the cycle until everyone gets their turn to solve.


Draw place value blocks to solve.

Fill in the blanks. 456 + 456 = 9 hundreds + tens + 2 ones 763 + 234 = hundreds + 9 tens + 7 ones 435 + 546 = 9 hundreds + 8 tens + ones
a Rahul bought 345 books and arranged 115 books on the shelf. How many books are left to be arranged on the shelf?
b Mona had 123 marbles. Her friend Tina had 167 marbles. How many marbles are there in all?
A book fair is a place where many different types of books are sold. There are 568 English books and 345 Hindi books in a book fair. Which books are fewer, and by how much?
6 Cross Curricular Phool jhadu is made up of broom grass. The flower of this plant is used for cleaning. Heera makes 145 jhadus in one month and 206 jhadus in another month. How many jhadus did she make it in all?
7 Cross Curricular Rohit baked a batch of 340 biscuits for an event. He baked 105 more biscuits for the same event. He sold 130 biscuits at the event. How many biscuits does he have now?
8 Given below are place value blocks to show a number.
a What is the number shown by the place value blocks?
b What will the new number be, if Anaisha adds 145 to this number?

2
Column 1

A milkman delivers milk to different houses. Solve the riddles in Column 2 and match them to the correct house numbers in Column 1. Add or subtract to find the answers.
Column 2
a Mr Parikh�s house no. is 299. My number is 100 more than 216.
b Mr Ahmad�s house no. is 300. My number is 25 less than 267.

c Ms Shah�s house no. is 316. My number is the number before 300.

d Mrs Paul�s house no. is 242. My number is 10 less than 310.
Create a word problem on subtracting 456 from 124 and solve it.
Real-Life Maths

Cross Curricular & Value Development



Ria makes organic soap using plants, olive oil, coconut oil and water. Ria and her friends plan to put a stall in the school fair and then donate money earned for books for orphanages. They make 237 bars of soap and sell 168. Later, they made 134 more bars.
1 How many bars of soap did they make first?
a 237 b 134

c 168 d 234

2 How many soap bars were left after selling the bars the first time?
3 What is the total number of soap bars they have in the end?

4 Have you ever helped anyone in need? How?























































































Aditya is helping his mother to set the table. Some guests are coming for lunch.
Place 3 plates on the table. Bring 2 bowls for each plate.
How many bowls should I bring?
Multiplying by 3
Multiplying by 3 means counting all the groups of 3 together.
3 groups of 2 = 6 or 3 twos are 6
3 × 2 = 6 bowls
Let us count the number of bowls to build the multiplication table of 3.

Multiplication is repeated addition.

3 fours are 12 3 × 4 = 12
3 fives are 15 3 × 5 = 15
3 sixes are 18 3 × 6 = 18
3 sevens are 21 3 × 7 = 21
3 eights are 24 3 × 8 = 24
3 nines are 27 3 × 9 = 27
3 tens are 30 3 × 10 = 30
Example 1: Count the number of groups. Count the number of ducks in each group. Write the multiplied answer.







There are 3 groups.
There are 5 ducks in each group.






The multiplied answer is: 3 × 5 = 15





















Write the multiplication fact.
a b c d Do It Yourself 8A
d , 24, , 30 e 9, , , f 15, , , 2
Fill in the missing numbers using the table of 3. a 3, 6, 9, b 18, 21, , 27 c 12, , 18, 21
Chapter 8 • Multiplication Tables 3, 4 and 6
Use the table of 3 to find the answer mentally.
Fill in the blanks.
Write the multiplication statement for the following from the table of 3. Draw circles to show it.
Multiplying by 4
Aditya is helping his mother lay the table for dinner. Aditya is sitting at the table with his parents. Aditya’s sister, Mohi, walks in.
Aditya, place 1 more plate for Mohi. Place 3 cookies on each plate.
Sure Mom!
There were 3 plates. Aditya placed one more plate. There are 4 plates now. He placed 3 cookies on each plate.
4 groups of 3 = 12 4 × 3 = 12 cookies
Let us count the number of cookies to build the table of 4. 4 ones are 4 4 × 1 = 4 4 twos are 8 4 × 2 = 8 4 threes are 12 4 × 3 = 12
4 fours are 16 4 × 4 = 16
4 fives are 20 4 × 5 = 20

After lunch, everyone played a game with balloons.
Mohi, we are 6 members. We need 4 balloons for each member!
How many balloons do we need in total?
Multiplying by 6 means counting all the groups of 6 together.
So, 6 members with 4 balloons will have a total of:
6 × 4 = 24 balloons or 6 fours are 24.
Let�s count the number of balloons to build the table of 6.

Example 3: Count the number of groups. Count the number of pens in each group. Write the multiplication fact.
There are 6 groups of 7 pens.
Multiplication fact: 6 × 7 = 42






















Write the multiplication statement for the pictures.
a Do It Yourself 8C
b
c
Fill in the missing numbers using the table of 6.
Use the table of 6 and answer.
Fill in the blanks.
Meghna went to a shop to buy some eggs. In the shop, she saw eggs in trays. There were 4 trays, and each tray had 12 eggs in it. She wondered how many eggs would there be in total.
But I don’t know how to find 4 × 12.
To multiply a 2-digit number with a 1-digit number, we can use the column method.
The shopkeeper has 4 trays with 12 eggs in each tray.
We need to multiply 12 by 4.
Let us multiply 12 by 4 using the multiplication table of the smaller number 4.
Step 1
Write the 2-digit number according to its place value in the table. Write the smaller number below it.
Step 2
Multiply the smaller number with the ones of the 2-digit number.
4 × 2 = 8
Write 8 in the ones place.
Step 3
Multiply the smaller number with the tens of the 2-digit number.
4 × 1 = 4
Write 4 in the tens place.
So, 12 × 4 = 48.
Example 4: Multiply 23 × 3.
Brahmagupta, an Indian Mathematician was the first one to explain the rules of multiplication.
So, 23 × 3 = 69.























Chaach is a curd-based drink. It has a cooling, refreshing effect on the body in summer. Each jug has 3 glasses of chaach. 13 such jugs will have 13 × 3 = glasses of chaach.
Let us learn how to group ones and tens to make multiplication of larger numbers easier.
Abdul has 93 marbles in each packet. He has 4 such packets. To see how many marbles Abdul has in total, we need to multiply 93 by 4.
Look at the given steps:
Step 1
Write the 2-digit number according to its place value in the table. Write the smaller number below it.
Step 2
Multiply the smaller number with the ones digit of the 2-digit number. 4 × 3 = 12. 12 has 1 tens and 2 ones.
Write 2 in the ones place and carry over the 1 to the tens place.
8 • Multiplication Tables 3, 4 and 6
Step 3
Multiply the smaller number with the tens of the 2-digit number.
9 × 4 = 36. We carried over 1 tens.
36 + 1 = 37
Write 3 in the hundreds place and 7 in the tens place.
So, 93 × 4 = 372.
Example 5: Multiply 63 by 8.

So, 63 × 8 = 504






















× 4
× 92
× 6
Makar Sankranti is celebrated with kite flying to mark the end of winters. There are 13 types of kites available at stalls A and B.
If stall A sells 2 kites of each type, the total number sold is = 13 × 2 = 26 kites.
If stall B sells 6 kites of each type, the total number sold is = 13 × = kites.
Write True or False. By multiplying 41 by 6, we will get 7 ones. Explain your answer by showing multiplication.
How many tens will you get when you multiply 92 by 5?

Let us explore some story problems on multiplication.
Meghna went to another shop and saw 6 trays, with 30 eggs in each tray. How many eggs were there in total?
What do we know?
Total trays = 6
Eggs in each tray = 30
What do we want to know?
We need to find the total number of eggs. How do we find the answer?
Total number of eggs = Total trays × Eggs in each tray
Solve to find the answer.
= 30 × 6 = 180 eggs
So, there are 180 eggs in all.






















There are 98 packets and 5 candies in each packet. How many candies are there in total?
A bus has 46 seats, and there are 4 such buses. How many seats are there in total?
There are 6 pins in each pouch. If there are 52 such pouches, how many pins are there in total?
Bamboo is used for making garden fences. It is an eco-friendly choice. 6 bamboo poles are needed to fence a garden. Each pole costs ₹85. What is the total cost of all the bamboo poles?
Setting: Whole class

Materials Required: 150 ice-cream sticks, 6 transparent glasses Method:

1 glass and 36 ice-cream sticks.



Try solving more multiplication problems using both methods. 2 3
Make bundles of tens with the ice-cream sticks. Put the single sticks next to them. Put all of these in one glass.
Make 4 such groups of ice-cream sticks in 4 glasses.
This shows 4 groups of 36 or 4 × 36.
Put all the ice cream sticks together and find the total.
Multiply 36 by 4 using the column method.


Match your answer with the total number of ice-cream sticks. Discuss the answer in class.


Use the table of 3 and write the answer.
Solve mentally by using the table of 4.
Fill in the blanks by using the table of 6.
In cricket, a six is scored when the ball is hit over the boundary without bouncing and touches the ground outside the field of play. In a cricket match, if Rahul scored 6 runs on each of the 7 balls he played, how many runs did Rahul score?
Garba is a folk dance from Gujarat. It is done during the Navratri days. If 28 dancers are there in 4 rows, how many dancers are there in total?
There are 6 plates of dosa, and each plate costs �85. How much do all the dosas cost in

Solve the multiplication problems and complete the crossword. First, solve across, and then down.
Across Down
1. 6 × 8 2. 9 × 9
3. 8 × 9 4. 4 × 6
5. 3 × 5 6. 6 × 9
7. 8 × 8
8. 4 × 10


Write a word problem to show the multiplication of 42 by 5. 2

Value Development & Cross Curricular


We get sugarcane juice by pressing sugarcane. It refreshes us. Sonesh and his friends decided to distribute free juice during the summer to the people passing by. They have 5 jugs of juice. Each jug has 81 cups of juice. Read the questions and answer.








1 Why should we drink sugarcane juice in summer?
2 How many jugs of juice do they have?

3 How many cups of juice does each jug have?
4 How many cups of juice will they be able to distribute?
5 Which juice do you like?

Chapter 8 • Multiplication Tables 3, 4 and 6






















































































Sam has 6 chocolates.
Sam wants to share the chocolates with his friend, Ravi. Both of them should have the same number of chocolates.
How many chocolates will Sam share with Ravi?
Let us divide the 6 chocolates equally between Sam and Ravi. First, each boy takes 1 chocolate.
We strike out 2.
4 chocolates are left with Sam. Then, again they take 1 more chocolate each.
We strike out 2 more chocolates.

Now, 2 chocolates are left with Sam.
Then, they take 1 more chocolate each.
We strike out 2 chocolates.
We get 2 groups of 3 chocolates.
No more chocolates are left with Sam.
Example 1: Share 4 laddoos between Meena and Tina.






Strike out 2 laddoos. Meena and Tina get 1 laddoo each.






Strike out 2 remaining laddoos. Meena and Tina get 2 laddoos each.
Example 2: There are 10 apples. Circle to show 2 apples in each basket.

In division, an equal number of objects is kept in each group.
There are 2 apples in each basket. There are 5 groups of 2 apples.






















Circle the set of pictures that show equal sharing. One has been done for you.
b c Draw and share the objects equally.
a Share 9 carrots among 3 rabbits.
Each rabbit will get carrots.
b Share 8 biscuits between 2 friends. Each friend will get biscuits.








How many items will each child get?
a 8 bananas shared equally among 4 children.
b 12 cupcakes shared equally among 4 children.





There are 20 mangoes. Draw pictures to divide the mangoes among 5 children. How many mangoes did each child get?
Next day, 8 chocolates were divided between Sam and Ravi. They got 4 chocolates each.
Let us understand this using subtraction.
There were 8 chocolates. Sam Ravi
One chocolate was taken by each.
8 – 2 = 6. 6 chocolates are left.

One more chocolate was taken by each.
6 – 2 = 4. 4 chocolates are left
One more chocolate was taken by each.
4 – 2 = 2. 2 chocolates are left.
Again, one more chocolate was taken by each.
2 – 2 = 0. No chocolates are left.
We see that 2 is subtracted from 8 four times. This means 8 divided by 2 is equal to 4. So, division is also known as repeated subtraction.
Let us see this using a number strip.
=
The answer is 4 because we are subtracting 2 four times until we get 0.
Division Fact
Dividing 8 in equal groups of 2 can be written as 8 ÷ 2 = 4. This is the division fact. ‘÷’ is the symbol used to show division.
8 ÷ 2 = 4
Remember!

We keep subtracting from the total until the answer is 0.
8 divided into groups of 2 will give 4 equal groups.
Total number of things.
Number of things in each group.
Number of groups.
Example 3: Divide 12 pencils among a group of students such that each student gets 3 pencils. Use repeated subtraction to find the number of students.
3 is subtracted from 12 four times.
12 ÷ 3 = 4 is the division fact, so 4 students get 3 pencils each.
Example 4: Show the division fact 12 ÷ 4 using a number strip. We start going back from 12 by 4 steps.

The answer is 3 because we are subtracting 4 three times until we get 0.





















Use repeated subtraction to show the answer. How many children will get these items if:
a 18 chocolates are shared equally in groups of 6?
b 14 pens are shared equally in groups of 2?
c 8 apples are shared equally in groups of 4?
Circle the correct division fact.
2 Show the repeated subtraction by showing jumps on the number strip. a 15 ÷ 3 3
a 12 books shared in groups of 3. 3 ÷ 12 12 ÷ 3 12 ÷ 12
b 15 pencils shared in groups of 5. 15 ÷ 5 5 ÷ 15 15 ÷ 15

Write True or False.
a 15 objects in 3 equal groups, with 5 objects in each group.
b 12 objects in 4 equal groups, with 2 objects in each group.
c 20 in 4 equal groups can be written as 4 ÷ 20.
Let us see how multiplication and division are related.
Case 1: 8 chocolates are divided between Sam and Ravi. They have 4 chocolates each.
We have 2 groups of 4.
Division fact: 8 ÷ 2 = 4
How do we get this using multiplication?
Say the table of 2 until we get 8.
2 × 4 = 8. (Multiplication fact)
So, 8 ÷ 2 = 4.
Case 2: 8 chocolates are divided among 4 children. They get 2 chocolates each. We have 4 groups of 2.
Division fact: 8 ÷ 4 = 2
Say the table of 4 until we get 8.
4 × 2 = 8. (Multiplication fact)
So, 8 ÷ 4 =2.
For 1 multiplication fact, there can be 2 division facts:
Or
Error Alert!

Divide 12 in 3 equal groups is written as: 3 ÷ 12 = 4
Example 5: Write the division fact and the multiplication fact for 4 groups of 3 balloons.
We have 4 groups of 3.
Multiplication fact: 4 × 3 = 12
Division facts: 12 ÷ 4 = 3 and 12 ÷ 3 = 4






Think and Tell!
Can you divide 13 mangoes among 4 friends?
How many will each friend get?
















at the picture and write down the multiplication facts and the division fact.
Fill in the blanks to write down the division and the multiplication facts.
2 division facts for the given multiplication
Draw pictures to show the groups and write the multiplication facts. Then write one division fact for the multiplication fact.
a 4 groups with 2 in each
How to Divide
6 groups with 3 in each
Shweta has 18 roses with her. She needs to make 6 garlands with an equal number of flowers in each garland. How many roses will each garland have?



















We know 18 ÷ 6 = 3 (We say the table of 6 until we get 18, 6 × 3 = 18)
Each garland will have 3 flowers in it.
Let us understand other ways of writing and solving division.
Division
We will use the division house to divide two numbers.
18 ÷ 6 = 3 can be written as:
1. Write the bigger number inside the division house.
3. Say the table of 6 until we get 18. 6 × 3 = 18. So, 3 is the answer.
2. Write the smaller number outside the division house.
Example 6: Solve 15 ÷ 5.

We say the table of 5 until we get 15. 5 × 3 = 15. So, 3 is the answer.




















Do It Yourself 9D

Circle the sum that shows the correct answer.
Solve the given sums to find the answer.
Write down the sums and solve using the long division method.
Use the long division method to show 21 chocolates in 7 groups of 3.
We can use the CUBES method to solve story sums. In the CUBES method, we follow the 5 given steps.
Circle the numbers.
18 flowers are kept equally in 3 baskets. How many flowers are there in each basket ?
Underline the question. Box the key words.
Total number of flowers = 18
Number of baskets = 3
Flowers in each basket = 18 ÷ 3
There are 6 flowers in each basket.




C: Circle the numbers.
U: Underline the question.
B: Box the key words.
E: Evaluate/draw.
S: Solve and check!
Evaluate Solve and Check!
Check: 3 × 6 = 18. So, the answer is correct. 6 3 18


















There are 12 pencils. The pencils are kept equally in 4 pencil boxes. How many pencils are there in each box?
There are 20 cherries. The cherries are placed equally on top of the 5 cakes. How many cherries are there on each cake?
Rita has 10 apples. She wants to give an equal number of apples to 5 friends. How many apples will each friend get?
Jalebi is one of the most popular desserts in India. Nidhi has 18 jalebis and she wants to distribute them equally among 6 friends. How many jalebis will each friend get?

Setting: In groups of 4

Materials required: Buttons/rajma beans/beads, A4 size paper with pictures of 5 shirts printed on it. (Make sure the shirts do not have buttons)
Method:
Each group should get 25 buttons/beans/beads and the A4 sheet with shirts printed on it.

Two members of the group will place buttons on the shirts given, so that each shirt has an equal number of buttons.

The remaining two members will write the division fact, looking at the equal sharing.
The students will then check the division facts using long division.
Checkup
make


groups. a Make groups of 4. There are groups of 4.

b Make groups of 2. There are groups of 2.

Divide the objects using repeated subtraction.
a 12 balls in 4 boxes. b 18 pencils in 3 boxes.
c 20 marbles in 5 boxes. d 16 books on 2 shelves.
Write down the division facts for the given multiplication fact.
a 2 × 3 = 6 b 3 × 8 = 24 c 3 × 3 = 9
Solve. 3 21 a 6 48
5 45 c 2 18 d
Solve using long division.
a 25 ÷ 5 b 40 ÷ 4
c 30 ÷ 3 d 20 ÷ 2
Fill in the blanks.
a 35 ÷ 5 is . b 18 ÷ 3 is . c 28 ÷ 4 is .
Amlas or gooseberries boost appetite. They are rich in vitamins. Julia has 18 amlas. She needs to divide these equally into 6 packets. How many amlas will there be in each packet?
Jack has 20 packets of rice. He wants to give an equal number of packets to 5 families. How many packets of rice will each family get?

If 36 ÷ 6 = 6 is a divison fact, its multiplication fact with the same two numbers is 6 × 6 = 36. Find one more division fact that we get by multiplying two numbers that are the same.
I am a 1-digit number. If I am multiplied by 6, the product is 24. When I divide 36, the answer is 9. Who am I? 1 2 Challenge




Christmas Carols are performed during Christmas. Ruhaan and his class are planning to sing Christmas Carols. Look at the picture and answer the questions.

1 How many children are there? a 10 b 11 c 12 d 9
2 How many groups of 2 can they form?
3 Can they form 4 groups with 3 children in each group?

4 If not, how many more/less children do they need?
5 One of Ruhaan’s friends was feeling nervous about singing. What should Ruhaan do to encourage him?
























































































Sonu and Neha were having dinner. Only one chapati was left.
Both of them wanted to eat it.
What can they do?
Parts of Whole
Mother gave them an idea to cut the chapati into parts.
Let us us see how the chapati can be divided. These show parts of a whole. whole 2 parts 2 parts 3 parts
Fraction means part of a whole.
Equal and Unequal Parts

Whole of something means a complete thing.
Let us see, if we can divide a chapati in different ways. When something is divided into parts that are not equal, the parts are called unequal parts. Unequal parts do not fractions.
When the parts are of the same size, they are equal parts.
Think and Tell
Can we divide all things in equal parts?
Equal Parts
Unequal Parts

Shape divided into unequal parts
One half

Shape divided into equal parts One half
Example 1: Tick () the pictures that show unequal parts.
Here, the 3 parts are unequal parts. Here, the 2 parts are equal parts. Here, the 2 parts are unequal parts. Here, the 3 parts are equal parts.
Example 2: Divide the whole into equal parts.
Let us learn more about fractions. We have a whole circle.
Let us divide the circle in equal parts.
Chapter 10 • Introduction to Fractions
3 equal parts 3 equal parts one-third two-thirds
In ancient India, people knew about fractions. The fraction one-half was called ardha.
Example 3: Colour one-half of the rectangle green.

One-half means one out of two equal parts or halves.




























Let us understand how we can read and write fractions using numbers.
One-half
Top part shows the number of parts shaded.

The parts shaded in a whole make the fraction.
One out of two equal parts is shaded.
1 part out of 3 equal parts is shaded.
Think and Tell
Bottom part shows the total number of equal parts.
1 part out of 4 equal parts is shaded.
3 parts out of 4 equal parts are shaded. 2 parts out of 3 equal parts are shaded.
If we divide a cake into 5 equal parts and take 4 parts away from it, then how do we write the fraction for the remaining parts?






















Naisha and Raina order an aloo parantha and divide it into two parts. Naisha is hungry. So Raina gives her the bigger part. Has Raina done the correct thing? Is each piece called a half?
Write the fraction in numbers. Draw any shape to show the fractions.
one-third b one-half c three-fourths d two-thirds
Draw any figure or shape and divide it into equal parts. Shade a part and write its fraction.
Setting: In groups of 4

Material required: A4 size white paper, colours, pencils
Method:
Take an A4 size paper.

Fold it by bringing the opposite edges together. Unfold the paper.

Then draw a line to show that the paper is split into two equal halves.
Try to divide the sheet into three or four equal parts and show the fractions you have learnt so far.
Shade these paper

and use them to make a collage.




Choose the image which is divided into equal parts. 1
Fill in the blanks.
a 1 2 means part out of equal parts.
b 1 4 means part out of equal parts.
c 1 3 means part out of equal parts.
d 3 4 means parts out of equal parts.
e 2 3 means parts out of equal parts. 2
3
Look at the shaded part of the shape. Circle the fraction that represents the shaded portion.
Write the fraction of the coloured part in words.
Colour the shapes on each petal of the flower to match the given fraction. Colour the flowers with your own choice of colours. One has been done for you.
Apple pie is a dessert made from apples cooked under or inside the pastry. Write the fraction of one part for the given apple pie. One has been done for you.



















Write True or False.
a One-half is written in words as 1 2 .
b Two-thirds can also be written as 2 3 .
c When one out of 4 parts is shaded, the fraction is 1 4 .
d 3 4 can be shown by shading 1 out of 4 parts.

1 Neha, Shreya and Garima want to eat pizza. They ordered one pizza and came up with three different ways to cut the pizza, so that each gets an equal share. Who is correct and why?








2 Diya wants to shade 3 parts of the given flower pink. She has already shaded 1 part.


a What fraction of the flower has she already shaded?
b What fraction more of the flower does she need to shade?




Jaya is in the kitchen with her parents. She is learning to cut vegetables from her father. Look at the picture and answer the questions.








1 The tomato is cut in half. Write its fraction.


2 What is cut into unequal parts? a apple b tomato c cucumber d watermelon
3 Which vegetable or fruit is one whole?
a tomato b watermelon c apple d cucumber

4 Do you think all vegetables can be cut equally? Give an example.



Name of the Student: Time: 1 Hour
1 Write the multiplication facts for the given set of pictures.
2 Tick () the shape that shows equal parts.
3 Read the number. Write the number and number name.
Number =
Number Name =
4 Colour the shapes to show the fractions.
A one-fourth B two-thirds
5 Form the greatest 3-digit number using any 3 digits from 5, 6, 2, 0, 9.
6 Circle the correct division fact.
A 14 pencils shared equally among 7 students. i 14 ÷ 4 ii 7 ÷ 7 iii 14 ÷ 7
B 20 erasers shared equally among 5 students. i 20 ÷ 2 ii 20 ÷ 5 iii 5 ÷ 5
7 Multiply and complete the crossword puzzle. 4 × 3 =
8 Circle the pencils to make 6 groups of 2. Complete the division statement.
9 Read the rate list given below. Answer the questions.
A What is the total cost of the kitchen set and the teddy bear?
B How much more does the toy car cost than the ball?

Do It Yourself 6A
1. a. 721, 723, 724, 726, 727, 729, 730 b. 810, 812, 814, 815,817, 819, 820
2. a. 403, 404, 406, 407, 408, 409, 410, 411, 412, 413, 414, 415, 416
3. one hundred sixty-three 4. a. 465 b. 777 c. 603 d. 505
5. a.
d.
Do It Yourself 6B
1. a. 3 hundreds + 9 tens + 8 ones
398 = 300 + 90 + 8
b. 1 hundreds + 7 tens + 0 ones
170 = 100 + 70 + 0
c. 6 hundreds + 5 tens + 4 ones 654 = 600 + 50 + 4
2. a. 984, nine hundred eighty-four
b. 576, five hundred seventy-six
c. 702, seven hundred two
3. a. 701 b. 567 c. 345
4. Number name of 127 is One hundred twenty-seven expanded form: 100 + 20 + 7
Do It Yourself 6C
1. a. 879 b. 901 c. 204
2. a. Greatest = 709; Smallest = 97 b. Greatest = 783; Smallest = 446
c. Greatest = 865; Smallest = 175 d. Greatest = 538; Smallest = 159
3. Increasing order: 100, 345, 620, 789 decreasing order: 789, 620, 345, 100
4. Greatest number: 752 Smallest number: 257
5. Toni used more bricks.
Chapter Checkup
1. a. 303, 304, 305, 306, 307, 308, 310 b. 602, 603, 605, 606, 607, 608, 609
2. a. 567
b.
+
3. Before: 78, 179, 966, Between: 246, 434, 255, After: 457, 516, 699,
4. a. 345 > 232 b. 999 > 678 c. 945 = 945 d. 34 < 344 e. 123 < 856 f. 899 < 999
5. a. 678, 559, 345 b. 678, 289, 109 c. 873, 696, 345 6. a. 257, 330, 540 b. 447, 567, 678 c. 120, 499, 600 7. The next house number is 227
8. Less than 500: 123, 459, 229, 289 More than 500: 985, 769, 590, 890
9. The greatest number is 641 the smallest number is 146
Challenge
1. H T O 4 5 1
T O 8 7 9
2. There are 6, 3-digit odd numbers between 101 and 115.
Hint: Do not count 101 and 115.
Real-Life Maths
1. b. 8 2. increasing 3. five hundred seventy-six 4. 358
Do It Yourself 7A
1. a. 129 b. 661 c. 182 2. a. 349 b. 699 c. 997
3. a. 666 b. 912 c. 665 4. a. 835 b. 549 c. 978
d. 870 e. 939 f. 693
Do It Yourself 7B
1. a. 443 b. 131 c. 550
2. a. 524 b. 616 c. 820 3. a. 180
b. 000 c. 670 d. 780 e. 620 f. 234 4. 167
Do It Yourself 7C
1. a. addition, 654 b. subtraction, 336
2. a. 361 b. 55 3. 311 packets 4. 365 tigers
Chapter Checkup
1. a. 699 b. 615 c. 996 2. a. 123 b. 333 c. 423
3. a. 549 b. 1077 c. 704 d. 115 e. 350 f. 244
4. a. 1 b. 9 c. 1
5. a. Subtraction, 230 b. Addition, 290
6. Hindi, 223 7. 351 jhadus 8. 315 biscuits
9. a. 256 b. 401
Challenge
1. a. My number is before 300.
b. My number is 10 less than 310.
c. My number is 100 more than 216.
d. My number is 25 less than 267.
2. Answers may vary. Sample answer. There are 456 coconuts in a farm. 124 coconuts are sold. How many coconuts are left in the farm?
Real-Life Maths
1. a. 237 2. 69 3. 203 4. Answers may vary.
Do It Yourself 8A
1. a. 3 × 6 = 18 b. 3 × 5 = 15 c. 3 × 3 = 9 d. 3 × 9 = 27
2. a. 12 b. 24 c. 15 d. 21, 27 e. 12, 15, 18 f. 18, 21, 24
3. a. 18 b. 27 c. 15 d. 24 e. 30 f. 12
4. a. 6 b. 10 c. 2 d. 9 e. 8 f. 3
5. a. 3 × 8 = 24
b. 3 × 4 = 12
c. 3 × 10 = 30
Do It Yourself 8B
1. a. 4 × 3 = 12 b. 4 × 8 = 32 c. 4 × 2 = 8 d. 4 × 6 = 24
e. 4 × 9 = 36 f. 4 × 1 = 4 2. a. 20 b. 12 c. 40
3. a. fives b. tens c. nines d. fours e. twos f. sixes
4. a. 4 × 7 = 28
b. 4 × 9 = 36
c. 4 × 4 = 16
Do It Yourself 8C
1. a. 6 × 7 = 42 b. 6 × 5 = 30 c. 6 × 4 = 24 2. a. 36
b. 18 c. 30 3. a. 42 b. 24 c. 48 d. 60 e. 18
f. 54 4. a. 5 b. 7 c. 9 d. 2 e. 8 f. 3
Do It Yourself 8D
1. a. 6 b. 2 c. 0 2. a. 48 b. 99 c. 82 3. a. 20 × 4 = 80
b. 34 × 2 = 68 c. 44 × 2 = 88 4. 13 × 3 = 39
Do It Yourself 8E
1. a. 96 b. 96 c. 156 2. a. 72 b. 90 c. 366 d. 276
e. 295 f. 168 3. 6; 78
4. No; on multiplying 41 and 6, we will get 6 at the ones place.
5. 6 tens
Do It Yourself 8F
1. 490 candies 2. 184 seats 3. 312 pins 4. ₹510
Chapter Checkup
1. a. 24 b. 15 c. 6 d. 3 e. 9 f. 30
2. a. 36 b. 32 c. 20 d. 24 e. 28 f. 40
3. a. 7 × 6 = 6 × 7 = 42 b. 6 × 10 = 10 × 6 = 60
c. 6 × 5 = 5 × 6 = 30 4. a. 74 b. 90 c. 148 5. a. 100
b. 190 c. 282 d. 168 e. 410 f. 138
6. 42 runs 7. 112 dancers 8. 510
Challenge 1.
2. Answers may vary. Sample answer. A vegetable vendor sells 5 baskets of tomatoes, and each basket contains 42 tomatoes. How many tomatoes does he sell?
Real-Life Maths
1. Answers may vary. Sample answer: To keep ourselves cool in summer. 2. a. 5 3. 81 cups 4. 81 × 5 = 405
5. Answers may vary.
Do It Yourself 9A
1. a. b.
c. 2. a. 3 b. 4 3. a. 2 bananas b. 3 cupcakes
4. 4 mangoes
Do It Yourself 9B
1. a. 3 children b. 7 children c. 2 children
2. a. 12 ÷ 3 b. 15 ÷ 5
3. a.
5 – 5 = 0 10 – 5 = 5
4. a. True b. False c. False
Do It Yourself 9C
1. 4 × 3 = 12, 12 ÷ 4 = 3 2. a. 20, 20 b. 6 c. 28, 4
3. a. 8 ÷ 4 = 2, 8 ÷ 2 = 4 b. 12 ÷ 3 = 4. 12 ÷ 4 = 3
c. 30 ÷ 5 = 6. 30 ÷ 6 = 5
4. a. 4 × 2 = 8, 8 ÷ 4 = 2
b. 6 × 3 = 18, 18 ÷ 6 = 3
Do It Yourself 9D
1. a. 4 3 12 b. 5 4 20
2. a. 6 b. 7 c. 7 d. 2
3. a. 9 b. 4 c. 8 d. 7 e. 7 4. 21 ÷ 7 = 3
Do It Yourself 9E
1. 3 pencils 2. 4 times 3. 2 apples 4. 3 friends
Chapter Checkup
1. a. 3 b. 6 2. a. 3 balls b. 6 pencils
c. 4 marbles d. 8 books
3. a. 6 ÷ 3 = 2, 6 ÷ 2 = 3 b. 24 ÷ 3 = 8, 24 ÷ 8 = 3
c. 9 ÷ 3 = 3, 9 ÷ 3 = 3
4. a. 7 b. 8 c. 9 d. 9 5. a. 5 b. 10
c. 10 d. 10 6. a. 7 b. 6 c. 7 7. 3 amlas 8. 4 packets
Challenge 1. 9 ÷ 3 = 3 2. 4
Real-Life Maths
1. a. 10 2. 5 groups 3. No 4. They will need 2 more children 5. Answer may vary.

Chapter 10
Do It Yourself 10A
1. 2.



3. 4. (Answer may vary) (Answer may vary) Do It Yourself 10B
1. a. 2 4 b. 1 3 c. 1 2 d. 3 4
2. a. b. c. d.
3. Yes Raina has done the correct thing. No, each piece will not be called a half since they are not equal.
4. a. One-third b. One-half c. Three-fourths d. Two-thirds 1 3 1 2 3 4 2 3
Chapter Checkup 1.
5. Answers may vary. Sample answer.
5. a. One-half b. Three-fourths c. One-fourth d. One-half e. Two-thirds f. Three-fourths
6.
4. Not all vegetables can be cut equally. Vegetables like spring onions cannot be cut equally. 1 2 1 3 1 4 3 4
7. b. One-third c. One-fourth 8. a. True b. True c. True d. False
9. Figures may vary. Sample figures. a. b.
Challenge 1. Garima is correct because it shows three equal parts. 2. a. one-fourth b. two-fourths
Real-Life Maths
1. 1 2 2. c. Cucumber 3. Watermelon






Match the things given in the two rows. Get Set






We all love to play games. We play games to have fun and enjoy ourselves. Playing games is very important for our health too.
In this chapter, let us learn more about why games are so important.

Rohan is studying. His mom walks in and tells him, “Rohan, why don’t you take a break? Go outside and play for a bit.” Rohan happily goes out to play football with his friends.
Just like Rohan, we all need a break to have fun. Let us learn why we must play games every day.
• To be fit and healthy: Playing games helps our bodies stay strong and active.
• To refresh our minds: After a long day at school, games make us feel happy and energised.
• To make new friends: Playing games is a great way to meet friends and make new ones.
We should play games every day to have fun and stay healthy.
Tick ( ) the correct sentences.
1. Playing games makes us lazy.

Rohan plays football with his friends.

A few children playing a game of tag.

A few friends playing with a skip-rope.
2. Playing is a good way to make new friends.
3. We should play every day for some time.
4. We learn to fight while playing.
break: to stop working for a while refresh: to feel better and more energetic


Divya and her friends were playing football outside when it started to rain. They all quickly went inside. Divya said, “Let us wait for the rain to stop. In the meantime, let us play ludo.”
We play many types of games. We play some games inside our house and some outside in an open area. Let us read about different types of games.
Indoor games are games that can be played inside. Some indoor games are Scrabble, Uno, darts, chess, ludo, snakes and ladders, carrom, cards and video games. Games like Scrabble can help us learn new words.

Chess, ludo, snakes and ladders, and carrom are from India.


Outdoor games are the games we play outside in places like parks, playgrounds or open fields. These games are great when you want to run around and get some fresh air. Badminton, football, cricket, basketball, volleyball, kho-kho and hockey are some outdoor games. Outdoor games keep us healthy and fit.







Playing both indoor and outdoor games is important. It helps you stay healthy, learn new skills, meet friends and have fun.
Sachin Tendulkar is the only player to score more than 2,000 runs in the World Cup.

indoor games: games we play inside outdoor games: games we play in a park or a playground Word Splash

Scan the QR code to learn more about the games we play at home.

• Playing games keeps us fit and healthy.
• We should play both indoor and outdoor games.
• Chess, ludo and carrom are some examples of indoor games.
• Football, cricket and badminton are some examples of outdoor games.
1. Tick ( ) the correct picture.
A. This is an indoor game.

B. This is an outdoor game.

C. This game is called darts.




D. This picture shows a boy playing a video game.

2. Write True or False.

A. Playing games is good for our health.
B. We can play badminton in a park.
C. We should play cricket inside our house.
D. Hockey is an indoor game.




3. Fill in the blanks.
A. Playing games keeps us .
B. We make new while playing.
C. Scrabble is an game.
D. Volleyball is an game.
4. Match the following.
Chess




5. Which Game Am I?
A. Roll the dice, move your piece, Get to the end, quickly please. Snakes make you slide, Ladders help you climb, What is the game, So much fun each time?
B. You need a racket And a net. Hit the shuttle, That’s the best bet. Over the net and back again, What do you think is this game?

6. Answer the following questions.
A. Why do we play games?
B. Write one difference between indoor and outdoor games.
C. Name two indoor games.
D. Name two games you can play outside with your friends.

E. How do you feel when you win a game? How about when you lose?
7. Picture-based questions.
A. Does the picture show an indoor game or outdoor game?
B. What are the children doing?
C. Have you ever played such a game?


1. Write one new thing you learnt while playing your favourite game.
2. Tarun wants to be home all the time and just play video games. Should he do this? Give one reason for your answer.

Here is a fun and energising morning routine to help you feel great.
Let us start our day by waking up early. Stand up tall and stretch your arms as high as you can. Take a deep breath and let it out slowly. Next, jump and spread your arms and legs wide. Jump again and bring your arms and legs back together. Do this 10 times. After that, bend down and try to touch your toes. Do this 10 times. Finally, run in one spot for 30 counts. This will make you feel fresh and ready for the day.





Chapter Overview

Neighbourhood Services

Neighbours and Neighbourhoods
Keeping Our Neighbourhood Clean Important Neighbourhood Services

Get Set

Hi, I am Tanu!
I love playing with my friends. They live close to my house. Now, I am going to the park with them. Do you also have friends who live nearby? What about a park?



Neighbours are the people who live near you. They can be your friends who you can play with. We should be good and kind to our neighbours.

The houses and places around us make our neighbourhood. A neighbourhood is a place where we can find many houses, people and other buildings. Many families live here. We find shops, parks, schools and even hospitals in a neighbourhood.
How can you be a good neighbour? Talk to your partner and discuss in class.
Our neighbourhood has many special places that are useful for us. Let us know about them.
In every neighbourhood, there is a place with lots of shops. It is known as a market. These shops sell things we use daily such as milk, bread, eggs, clothes, medicines, vegetables, groceries and stationery. The person who sells us these things is called a shopkeeper.


Many people take buses to travel around. But where do we catch a bus? We wait for and catch a bus at the bus stop.
Every neighbourhood has a school where children learn, study and play. Schools also have playgrounds.
groceries: food items stationery: things such as paper, pens, pencils


Find out the names of 2 schools and 2 hospitals in your neighbourhood.
A hospital is where people go when they are sick. Many neighbourhoods have one. We see many doctors and nurses at the hospital who look after us. We also see ambulances there. Outside the hospital, there is a pharmacy where people buy their medicines.

Rahul’s grandparents live in a different city. He has written a letter to his grandmother to tell her about his new pet dog. He plans to go with his father to the post office to mail the letter.
Have you ever been to a post office? At the post office, we put our letters in a big red postbox. We can also send money and parcels to people who live far away. We can buy stamps, envelopes and postcards at the post office. The postal workers hand us our letters.


ambulances: special vehicles used to take sick or injured people to hospital pharmacy: a shop where medicines are sold parcel: a small, wrapped bundle postcard: a card that you write a message on and send to somebody postal: of or relating to the mail or the post office


Visit a post office with an elder. Buy some stamps from there. Paste them in your notebook. Show them in the class.
A police station is where police officers work. They help people in trouble, solve crimes, and catch criminals and thieves to keep everyone safe. They also help us find our stolen things.
We can dial 100 from the phone to call the police for help.
Firefighters work at a fire station. They ride in big red fire trucks to put out fires. Firefighters use a long hose to spray water and stop the fire. They also use big ladders to spray water on tall buildings.
If there is a fire, we can call 101 to ask for help from the firefighters.

A bank is a place where people can keep their money safe. We can put our money in the bank, and the bank will keep it safe for us. We can also take out our money whenever we need it.
Some people also keep valuable things, like jewellery and important papers, in a bank. We can take out cash from a machine called the ATM, which can be found inside or outside the bank.
hose: a long plastic or rubber pipe valuable: very expensive or important


We can take care of our neighbourhood by keeping it clean. We can keep it clean by doing these things.
• Do not litter.
• Pick up any waste we see on the ground and put it in a dustbin.
• Join in neighbourhood clean-up events.
• Plant trees.




Children cleaning the park.
India has the largest postal network in the world.
neighbours: people who live near our house
neighbourhood: a place where we can find many houses, people and other important buildings
market: a place with many shops
bus stop: a place where people get in or out of a bus school: where children study, learn and play
hospital: a place where people go when sick, for treatment
post office: a place from where you can post letters and parcels
police station: a special building where police officers work
fire station: a place where firefighters work a place where people can keep their money safely

Scan the QR code to know more about neighbourhood services.
litter: throw waste in a place where it does not belong

• The area around our house is our neighbourhood.
• People who live in our neighbourhood are called neighbours.
• Shops, hospitals, police stations, banks and schools are some places in our neighbourhood.
• We should take care of our neighbourhood and keep it clean.
1. Tick ( ) the correct picture.
A. This is where we go to study.


B. This is where we go when we are sick.




2. Write True or False.
A. We buy stamps from a hospital.
B. We wait for a bus at a bus stop.
C. Firefighters work in a police station.
D. We can keep our money in the bank.
3. Fill in the blanks.
postal playground pharmacy shopkeeper
A. The person who sells things in a shop is called a .
B. Schools also have a .
C. A is where people buy medicines.
D. The workers deliver our letters and parcels.
4. Help these people reach the correct places.
A. Reema is very sick. Where will she go for the treatment?
B. Mr Verma wants to buy a shirt. Where will he go?
C. Meera has to post a letter. Where will she go?
D. Pooja has to keep her gold jewellery safe. Where will she go?
5. Write the phone numbers of these places.
Police station:
Fire station:
6. Answer the following questions.
A. What is a neighbourhood?
B. Write the names of three places in your neighbourhood.
C. Write two uses of a bank.
D. Write one way in which police officers help us.



A. Name the places shown in picture 1 and picture 2.
Picture 1:
B. Name the vehicle shown in Picture 1.
C. Name the vehicle shown in Picture 2.

2:
If you could add a new place to your neighbourhood, what would it be? Why?

SEL What will you do if you get lost in a market or a shopping mall?
Step 1: Stay calm and do not walk around.
Step 2: Find a security guard, watchman or a police officer and let him know that you are lost.
Step 3: Share with them your name and your parent’s phone number.
Step 4: Stay with them till your parents come. Remember not to leave the place with anyone. ONLY go with your parents.


Our Festivals
National Festivals Harvest Festivals Religious Festivals

Get Set

Look at the pictures. Write the names of the festivals shown in the boxes.




India is a land of festivals. Festivals are special days to celebrate and have fun with family and friends. Festivals are about sharing our happiness with each other. We also give gifts to our friends and relatives. We have three types of festivals: national, religious and harvest. Let us read about them.
National festivals are special days celebrated by the whole country. Let us read about some national festivals of India.
On August 15, 1947, India got its freedom from the British rule. We celebrate it as our Independence Day. Our prime minister hoists the national flag at the Red Fort in Delhi.
On January 26, 1950, India became a republic. Every year on Republic Day, a big ceremony happens on Kartavya Path in New Delhi. Soldiers march in a grand parade there, and the national flag is raised on all government buildings and schools.

The Red Fort on Independence Day.

A Republic day parade.
celebrate: to show that a day or an event is important by doing something special hoists: to raise or pull up

We celebrate 2 October as Gandhi Jayanti. Mahatma Gandhi was born on this day. He is called the Father of the Nation. On this day, people offer prayers at his samadhi at Raj Ghat, Delhi.
When do we celebrate the following?

Independence Day: Republic Day: Gandhi Jayanti:
A festival mostly celebrated by people of a particular religion is known as a religious festival. Let us learn about some religious festivals of India.
Holi is the Festival of Colours. People throw colours or gulal at each other. They eat sweets, play with colours and have fun. We should be careful while playing with colours and not hurt anyone. If someone says ‘No’, we should not throw colours at them.
Dussehra is also known as Vijay Dashami. We celebrate the victory of good over evil. On this day, Lord Ram killed Ravan, the ten-headed king of Lanka. Ramleela is


Ramleela: performance of the Ramayana during Dussehra

performed in different parts of the country. Effigies of Ravan, Kumbhkaran and Meghnad are burnt.
Diwali is also known as the Festival of Lights. It marks Lord Ram’s return to Ayodhya after 14 years. On this day, people clean their homes and wear new clothes. They decorate their homes with diyas, candles, lights and rangolis. People make and eat different types of sweets. They worship Goddess Lakshmi and Lord Ganesha.

Eid is celebrated after a month long fasting called Ramzan. People wear new clothes. They pray at mosques. They hug and greet each other by saying “Eid Mubarak”. On this day, a special sweet dish called sewaiyan is prepared.
Christmas
Christmas celebrates the birthday of Lord Jesus Christ on 25 December. Some people decorate Christmas trees in their homes. Some people bake plum cakes and exchange gifts on this day. Special prayers are held in churches.


effigies: models of a person or character rangoli: a pattern made with colours or flowers

People celebrate Gurupurab on Guru Nanak’s birthday. On this day, people go to the gurudwaras to pray. They listen to the holy Guru Granth Sahib. Langars are organised in all the gurudwaras. Sweets are distributed. Candles are lighted.

Gurupurab celebrations
All people do not get to enjoy sweets and tasty dishes during festivals. What can you do with the extra, or leftover, food after the festival celebrations are over? We can donate the extra food to the poor people or share it with neighbours to spread joy and reduce food wastage.

Make a nice greeting card on any festival you like. Give it to your friend. Do and Learn
Think and Tell India has many religious festivals. Can you name a few more?
People celebrate harvest festivals when the crops are ready to be cut. They are celebrated by different names in different parts of the country. Let us learn about some harvest festivals.
This harvest festival is celebrated in Kerala. On this occasion, Kerala has the world-famous snake-boat races. A special dish called payasam is made on this day. People celebrate this festival for ten days.

langar: the food provided at gurudwaras as charity

It is the harvest festival of Tamil Nadu. It is celebrated for four days. The rain god, the sun god and the cow are worshiped on this day. People draw kolams to decorate their homes. Pongal, a special dish made of rice, milk and jaggery, is prepared on this day.
It is the harvest festival of Punjab. Baisakhi marks the beginning of the new year. Good food, music and dance (Bhangra and Gidda) are all part of Baisakhi celebrations.

Pongal celebrations

Festivals are a time to have fun. People forget their sorrows and differences. Festivals bring people together in a spirit of sharing and happiness.




Baisakhi celebrations
During Diwali, people in Bharat light numerous lamps. The homes and neighbourhoods look beautiful.
national festivals: celebrations that are observed and enjoyed by the whole country
religious festivals: celebrations mostly held by people of a particular religion
harvest festivals: celebrations when crops are ready to be cut
kolam: decorative designs drawn on the floor
Bhangra and Gidda: dance forms

Scan the QR code to learn more about festivals.
• On festivals, people get together to celebrate important days.
• We have three national festivals: Independence Day, Republic Day and Gandhi Jayanti.
• Holi, Dussehra, Diwali, Eid, Christmas and Gurupurab are some of our religious festivals.
• Onam, Pongal and Baisakhi are some of our harvest festivals.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. He is called the Father of the Nation.
Sardar Patel Mahatma Gandhi
Lal Bahadur Shastri
B. This sweet is especially made on the harvest festival of Tamil Nadu.
Cake Burfi Pongal
C. This sweet is especially made on Eid.
Laddoo
Sewaiyan Kheer

2. Write True or False.
A. On Independence Day, the prime minister hoists the national flag at the Red Fort.
B. We celebrate the victory of good over evil on Dussehra.
C. People throw water and gulal at each other on Diwali.
3. Fill in the blanks.
A. Eid is celebrated after a month of fasting called .
B. Diwali is also known as the Festival of .
C. is also known as the Festival of Colours.
D. Onam is the harvest festival of .
4. Match the following.
A. Baisakhi
B. Holi
C. Eid
D. Christmas
E. Pongal
5. Answer the following questions.
a. Dish made of rice, milk and jaggery
b. 25 December
c. Harvest festival of Punjab
d. Festival of Colours
e. People pray in mosques
A. Name the three national festivals of India.
B. Where does the Republic Day parade take place?
C. What do we do on Diwali?
D. What happens during Gurupurab?
E. Which harvest festival is celebrated in Kerala?
6. Picture-based questions.
A. Name the festival shown in the picture.
B. Write one special thing about this festival.
C. Write one thing that we should NOT do on this festival.


Which festival do you think has the most fun activities? What do you do on that festival?


Chapter Overview

Weather and Seasons
Weather Seasons


What kind of a day does each picture show? Write it in the boxes. Get Set



We see different kinds of weather every day. On some days, the sun may shine brightly and the very next day it may rain. Have you ever thought about how the weather changes? How is weather different from seasons? Let us learn about weather and seasons in this chapter.
Weather is how it feels at a particular time and place. It can be hot, cold, rainy, cloudy or windy. It can change from day to day and even from hour to hour.
We choose our clothes and the things we want to do, depending on the weather. For example, we like to wear light cotton clothes and play outside on sunny days. We wear warm clothes and drink hot milk or tea on colder days. We use a raincoat or umbrella to keep ourselves dry on rainy days.
When the weather remains similar for a few months, it is called a season. Each season has its own kind of weather. We have five seasons: summer, rainy (monsoon), autumn, winter and spring. Let us learn about each season.
Summer is the hottest season of the year. The days are long, and the sun shines brightly. We feel hot and thirsty. We wear light cotton clothes to stay cool. We also like to eat fruits and ice-creams. We use a fan, cooler or air conditioner to stay cool. Activities like swimming is popular in this season. We must drink lots of water in this season.

A girl drinking water on a hot day.

The rainy season brings a lot of rain. The sky is often covered with dark clouds. We need umbrellas and raincoats to stay dry in the rain. Plants and trees grow well because they get a lot of water. They also look very fresh and green! We see puddles on the roads. When it rains, we see the lightning in the sky and hear the thunder.

Kids using umbrella on a rainy day.
Do you like the rainy season? Why or why not?
Autumn comes after the rainy season. The weather is not too cold or too hot. Most trees shed their leaves. The leaves of some trees change colour to orange, yellow or red before they fall. The days get shorter in autumn, so it gets dark earlier in the evening.


Collect differently-coloured leaves and paste them on a sheet of paper to make a beautiful autumn collage.
puddles: small pools of water formed on land after rain lightning: flash of light (in a zigzag shape) that can be seen in clouds during rain thunder: the sound that comes after lightning




Winter is the coldest season of the year. The days are short, and the nights are long. We wear warm clothes like woollen sweaters, jackets, caps and gloves to keep warm. We like to drink soup, tea, coffee and hot milk.

We also use blankets or quilts and heaters to keep our bodies warm. A girl wearing woollens and drinking coffee to stay warm.
Spring season comes after winter. It is a season when the weather starts to get warmer, and flowers begin to bloom. It is a great time to go outside and play in the sunshine, fly kites and have picnics.

Varahamihira was an ancient Indian astronomer and mathematician. He taught people how to guess the weather by studying the sky and the clouds.
weather: what it feels like outside at a particular time and place season: the period of time when the weather remains similar for a few months
bloom: when flowers open up


Scan the QR code to learn more about the weather and seasons.
• Weather changes from day to day. It can be hot, cold, rainy, windy or cloudy.
• When the weather remains similar for a few months, it is a season.
• Summer is the hottest season.
• Rainy season brings lots of rain.
• Autumn is when leaves change their colour, and trees shed their leaves.
• Winter is the coldest season.
• Spring is when the weather begins to get warm and flowers bloom.
1. Tick ( ) the correct picture.
A. Which of these pictures shows summer?


B. What do we use in the rainy season to stay dry?


C. Which of these pictures shows autumn?





2. Fill in the blanks.
grow summer autumn rain
A. Monsoon brings lots of .
B. The sun shines brightly in .
C. In the season, the weather gets cooler and leaves fall from trees.
D. Rainy season helps plants .
3. Write True or False.
A. We wear warm clothes in summer.
B. Flowers bloom in spring.
C. We like to have hot soups and food in summer.
D. The days are short and the nights are long in the winter.
E. We wear cotton clothes in winter season.
4. Match the following.




5. Circle the odd one out.
A. umbrella raincoat sunglasses puddle
B. winter autumn weather spring
6. Answer the riddle.
I am the season with the most sun, where playing outside is lots of fun. Who am I?
7. Answer the following questions.
A. How was the weather today at your place?
B. Name the five different seasons.
C. Write three things we do in the summer.
D. Write one way in which rains help plants and trees.
8. Picture-based questions.
A. Which season does the picture show?
B. What is happening in this picture?
C. What can we do to stay healthy in this season?


Which is the season you like the least? Why?





Circle the things that air can move. Get Set





Have you ever blown a balloon or felt the air on your face? That is air in action! Air is all around us. We cannot see it, but we can feel it. When we breathe, we can feel air going in and out of our nose. Air is a mixture of many gases. Without air, we would not be able to breathe, plants would not grow and birds would not fly. Fast moving air is called wind.

A boy blowing air into a balloon.
Breeze: Wind that blows gently is called a breeze. It feels nice and cool. Storm: A wind that blows strongly is called a storm.
Air is useful in many ways.
• Breathing: We breathe in and breathe out air.

We breathe in air.
• Flying: Birds and aeroplanes fly in the air. People fly kites in the air.
Aeroplane flies in the air.
• Filling up: Air fills up balls, balloons and tyres.

Fans keep us cool.

Air fills up tyres.
• Cooling: Fans and air conditioners move air to cool us down on hot days.
mixture: a mix of many things

Air helps dry clothes.
• Drying: Air helps dry clothes when they are wet.
• Lighting fire: We need air to light a fire.
Astronauts carry their air in cylinders to breathe in space because there is no air there.
Pause and Answer
Write True or False.
1. We can live without air.
2. Aeroplanes do not need air to fly.
3. Air helps dry our clothes.
Air has some special properties. Let us understand them with fun activities!
Have you ever seen how a balloon gets bigger and bigger when you blow air into it? A balloon becomes bigger when we blow air into it because air fills the space inside the balloon and gives it a shape. This shows that air occupies space.



Air occupies space.
properties: qualities


Have you ever thought why a balloon filled with air is heavier than an empty balloon? Let us know about it with an activity! Air has weight.
Things needed: Two balloons, string, hanger
Steps:


• Inflate (fill in air) both the balloons so they are the same size.
• Tie each balloon to the ends of the hanger with a string.
• Balance the hanger on a table.
• Gently poke one balloon with a needle. That will burst the balloon and let the air in it out.
• Notice how the side with the balloon that has air in it goes down. This shows that air has weight.
Have you ever seen water drops outside a cold glass of water? Let us find out more with an activity!
Things needed: glass, ice cubes, water
Steps:
• Fill a glass with ice cubes and add water.
• Wait for a few minutes and look at the outside of the glass.
• Look at the water drops that form on the outer surface of the glass.
The air that touches the cold outer surface of the glass turns into drops of water (we see on the outside of the glass). This shows that air contains water.
inflate: to fill with air

Air has water.
Have you seen smoke coming out of vehicles on the road or from the chimneys of a factory? Does it make the air dirty? Yes, and this smoke causes air pollution.
Air pollution happens when the air gets dirty with harmful gases, smoke and dust. This can make it difficult for us to breathe and can harm plants and animals.

We need clean air to stay healthy. Plants clean the air by removing harmful gases. We should grow more plants to get fresh and clean air.



The International Kite Festival held in Gujarat is one of the most famous kite festivals in India. Visitors come from all over the world to participate in this festival and fly kites with unique shapes.
air: a mixture of many gases
wind: moving air

International Kite Festival, Gujarat
breathing: the way our body takes in air and lets it out air pollution: when the air gets dirty from harmful gases, smoke and dust
chimneys: pipes on buildings that help to carry smoke and gases from fireplaces out of the building


Scan the QR code to know more about air.
• Air is all around us.
• We need air to breathe.
• Air is useful for lighting fire, flying kites and drying clothes.
• Air takes up space, has weight and contains water.
• Air pollution occurs when the air gets dirty with harmful gases, dust, germs and smoke.
• We should grow more plants to keep the air fresh and clean.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What is air made of?
Rocks
Gases
B. What can help reduce air pollution?
Cutting down trees
C. Which of the following flies?
Lions
Soil
Planting trees Setting up factories
Birds
D. Which of the following can cause air pollution?
Smell from flowers
Smoke from factories
Monkeys
Sound from vehicles
2. Fill in the blanks.
harmful pollution plant weight
A. The presence of dust and smoke in the air is called air .
B. Polluted air is for plants and animals.
C. Inflated football has more than an empty football.
D. We should more trees to get fresh air.
3. Write True or False.
A. We can see air with our eyes.
B. Parrots fly in the air.
C. Air pollution is good for our health.
D. A rabbit also breathes air.
4. Match the following.
A. Breathing
B. Aeroplanes
C. Balloons
D. Plants
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Write any two uses of air.
a. Fly in the sky
b. Inflate with air
c. Clean the air
d. Taking in and letting out air
B. What happens to a balloon when you inflate it?
C. Write any two important properties of air.
D. What is air pollution? How can we reduce it?
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What is coming out from the factory chimneys in the picture?
B. Why is it harmful for us?




What will happen if there is no air?
Keeping the air clean means making sure that the air we breathe is healthy. There are two simple ways you can help keep the air clean.
• Plant more trees to help keep the air clean.
• Reduce the amount of things you use. Reuse, recycle or donate things instead of throwing them away. This will help reduce air pollution caused by factories and transport system.



Get Set

Tick ( ) the activities that need water.




Water is something we use every day. It is important for all of us. Let us know more about water and why it is so important for us.

Think about all the things you do in a day. We use water to brush our teeth, wash our hands, or drink when we are thirsty. It is important for all living things.




We use water to cook food. Plants need water to grow. Animals like fish live in water. Plants like lotus grow in water.
We get water from different sources such as rivers, streams, waterfalls and rain. Let us learn about these sources of water.
When snow melts in the mountains, the water from the melted snow flows down the mountains. Some of the water seeps into the ground while some water that flows down makes waterfalls, streams and rivers.



sources: from where something comes seeps: to flow or leak slowly through small openings
Rainwater helps fill rivers, ponds and streams.
The rainwater that seeps into the ground makes groundwater. We use wells, handpumps and tubewells to get this water. People dig deep holes called wells to reach the underground water. A hand pump helps us pump water from underground.



Seas and oceans also have lots of water. But we cannot use it for drinking, bathing, washing or cooking because it is very, very salty.
Think about a time when you saw dirty water. How did it make you feel? Would you like to drink it or swim in it?
Water pollution is the addition of harmful things like waste from factories, house waste and trash into the water. It makes the water dirty and unsafe for people, plants and animals.

Tick ( ) the activities that pollute water.


Sakshi did not come to school today. She is unwell because she drank water from outside, which was dirty. We should never drink dirty water. It can make us sick. Always drink clean water as it does not have harmful substances and germs.
Here are some ways to clean water:
Boiling: Heat the water till it bubbles. Heat it like that for 2–5 minutes. This helps to kill the germs present in water.

dirty water.

Using a water filter: A water filter can help remove dirt and germs from the water.

Have you ever faced water-shortage? How can you help save water? Water is precious, and we need to save it. Here are some ways to save water:

Turn off the tap when not in use.


Fix leaks to save water. Collect rainwater and use it for other activities.




The Ganga River is a very important river. Many festivals and important ceremonies happen along the banks of the Ganga. It shows how much people love and respect the river. The Ganga River provides water for farming for a large part of India.

rivers: large, flowing bodies of freshwater groundwater: water that is stored underground water pollution: mixing of harmful substances into water

Explore More!
Scan the QR code to know more about water.
precious: very valuable or important

• We use water for drinking, cooking, cleaning and growing plants.
• Rivers, streams, waterfalls and rain are sources of water.
• Water pollution makes water dirty and unsafe to drink.
• Boiling and filtering help clean water.
• We need to save water as there is no life without water.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What is the use of water?
Drinking Flying Digging
B. Which animal lives in water?
Rabbit
Fish Cat
C. How we can make water clean?
Filtering
D. How can we save water?
Keeping the tap open.
2. Fill in the blanks.
Boiling
Both
Using a bucket to take a bath. Playing with water.
dug drink filters sources
A. We water when we are thirsty.
B. Water is passed through to remove dirt and harmful substances.
C. Wells are often to get groundwater.
D. Rivers, lakes, rain and groundwater are of water.
3. Write True or False.
A. Water pollution harms all living things.
B. We drink water to breathe.
C. We should save rainwater and use it later.
D. We can drink water from the oceans.
4. Answer the riddle.
I help plants grow and I keep you clean. In streams and rivers, I can be seen. Who am I?
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Why can’t we drink water from the sea?
B. Why is water important for us?
C. Name some sources of water.
D. Write two ways in which water gets polluted.
6. Picture-based questions.

A. Which source of underground water do you see in the picture?
B. How does it help people?



Imagine there is a small pond in your village. Suggest one thing that can be done to keep the water clean and safe for fish and plants.
Let us read and learn the steps to wash our hands:
Step 1: Turn on the tap just enough to wet your hands and then turn it off.
Step 2: Use soap to rub your hands together and lather it well.
Step 3: Make sure to scrub all parts of your hands.

Step 4: Turn on the tap again and wash the soap off quickly.
Step 5: Turn off the tap as soon as your hands are clean.
Objective: To create a map of your neighbourhood including all the different services available
Things Needed: A large sheet of paper, pencil and erases, ruler, colours small pieces of paper, glue or tape, smileys and stickers for decoration
Step 1: Learn about Neighbourhood Services
Find out different places in your neighbourhood that help people every day, like the market, park, school, hospital and the police station. These are all neighbourhood services.
Step 2: Draw a Neighbourhood Map
On a large sheet of paper, draw your house and different neighbourhood services such as market, park, school, etc. You can show the connecting roads too. Use a ruler to draw roads and buildings.
Step 3: Label the Neighbourhood Helpers
On small pieces of paper, write the name of each place. Next to the name, write who works at that place. (For example, hospital- doctors and nurses). Paste these pieces of paper next to the drawing of each place. You can decorate these labels.
Step 4: Decorate the Map
Finally, fill colours in the map and decorate it with stickers, dried flowers/leaves and smileys. You can give a title to your map too!
Project Output: Now you have your own map of your neighbourhood. Present it to your class.
Final Outcome: This fun project will help you understand your neighbourhood better, and know about the important services that are there.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.

Read the paragraph. Look at the picture. Answer the questions below.
It is spring season and the Holi festival is here. Everyone loves Holi. We eat gujiya and play with colours and water.
Aman’s mother has made the colours for him using natural things at home. Aman is playing Holi. He is throwing colours and water at his friends. While it is fun to play Holi, it is important to remember that water is precious. We should not waste it. We can use some water for playing, but we should not waste it. By being careful of the ways we use water, we can enjoy the festival and also help save water.
1. In which of these seasons do we celebrate Holi?
A. winter
B. spring
C. summer
2. Holi is also called the festival of .
A. colours
B. dance
C. lights
3. What do people do on Holi?
4. Write two ways in which we can save water in our daily lives.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.
Name of the Student: Time: 1 Hour
1 Tick () the correct picture.
A Which of these is an indoor game?



B Which of these do we use in the rainy season to stay dry?


C In which of these places do we go to study?

2 Fill in the blanks.



A Diwali is also known as the ‘festival of .
B The presence of dust and smoke in the air is called air .
C Wells are dug to get .
3 Match the following.
A Baisakhi i Firefighters
B Fire station ii Clean the air
C Plants iii Harvest festival in Punjab

4 Write True or False.
A We drink water to breathe.
B We can play badminton in the park.
C We can see air.
5 Answer the questions.
A Write one way in which police officers help us.
B Name the three national festivals of India.
C Write two things we do in the summer.
6 Picture-based questions.

A Which source of water is shown in this picture?
B How does it help us?
Our solar system has the Sun in the centre. There are eight planets moving around the Sun.

Mercury is the smallest planet. It is closest to the Sun.

Jupiter is the biggest planet in our solar system.

Venus is the hottest planet.

Earth is the only planet with life on it. It is called the blue planet.

Saturn is a planet with wide rings.


Mars is called the red planet.


Uranus and Neptune are far from the Sun. They are made mostly of ice and gas.
The Earth has a moon. With the help of the internet, find out if other planets also have their own moons.




Practice Time
1 Match the columns.
Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
a Mars hottest planet
b Earth red Planet
c Mercury blue planet
d Venus largest planet
e Jupiter smallest planet
2 Who am I? Rearrange my name.



a I am a planet made up of gas and ice. (ETUNPEN)







I am the closest planet to the Sun. (URMERCY)
c I am the only planet that has life on it. (HARET)


d I am the planet with wide rings. (RUSNAT)
e I am the hottest planet in the solar system. (UNEVS)


3 Colour in the planets.






People from different states of India have different traditional clothes. They are mostly worn during festivals. Let us learn about some of them.
• The men wear kurta and pyjamas.
• The women wear a salwar kameez.

Maharashtra
• Men wear a dhoti and kurta. They also wear a turban called pheta.
• Women wear a long saree known as nauvari.
Tamil Nadu
• Men wear lungis and shirts.
• Women wear sarees.












• The men wear a dhoti with kurta or kediyu.
• The women wear chaniya choli.
• Men wear a dhoti and kurta.
• Women wear mekhela chador.

What is the traditional dress of your state? Find out!
West Bengal
• Men wear a kurta called panjabi with a dhoti.
• Women wear sarees. They have a different way of wearing the saree.

Practice Time

Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Sort the traditional dresses worn by men and women.
Dhoti and Kediyu Lungi Mekhela Nauvari Chaniya Choli Panjabi
Men
Women

2 Match the traditional dresses and the states they are worn in.
a Nauvari Punjab
b Chaniya Choli Maharashtra
c Panjabi Gujarat
d Salwar kameez West Bengal
3 Solve the crossword.




ACROSS
1. A long saree worn by women in Maharashtra.
2. A turban worn by men in Maharashtra.
DOWN
1. This is worn with a shirt by men in Tamil Nadu.
2. This is the traditional dress of women in states like West Bengal and Tamil Nadu.

The Indian Rupee is the form of money used in India. Its symbol is ₹.
In our country, we have paper notes. They have different values, such as 10, 20, 50, 100, 200 and 500 rupees. They are of different colours and sizes.






The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) prints the money as directed by the government.
We also have coins of 1, 2, 5, 10 and 20 rupees.













Different countries have different currencies.
This note is an American Dollar. It has a $ symbol on it.
With the help of the internet, find out the currencies of India’s neighbouring countries, Bhutan and Sri Lanka.


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Tick ( ) the correct name.
a It is different in every country.
Currency Colours
b It is the form of money used in India.
Dollar Rupee
c In India, these have different values and colours.
Paper notes Envelopes
d It prints the Indian currency.
USA RBI

2 Look at the symbols. Name the country that the notes belong to. Then, colour them in.
The house next to ours belongs to our neighbours. The countries right next to India are called our neighbouring countries. Let us learn more about these countries.
This country is China. Its capital is Beijing. This country is Pakistan. Its capital is Islamabad.
This country is called Afghanistan. Its capital is Kabul.

This country is the Maldives. Its capital is Male.







This country is Nepal. Its capital is Kathmandu.
This country is Bhutan. Its capital is Thimphu.
This country is Myanmar. Its capital is Naypyidaw.
This country is Sri Lanka. Its capital is Colombo.
This country is Bangladesh. Its capital is Dhaka.
Each country has different traditions, languages and food. We should respect the diversity of all the countries.





Practice Time

Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Solve this crossword puzzle using the hints given.
ACROSS
1. I am the capital of Nepal.
2. I am the capital of Sri Lanka.
DOWN
1. I am the capital of Afghanistan.

2. I am the capital of Bangladesh.
2 Label these three countries on the map.









Some games are played inside the house, while some are played outside. Let us learn about them.
Indoor games are games that are played inside a house.
Ludo is played by two to four players. A dice and ludo pieces are needed to play it.
Chess is played by two players. It is played using a chess board and chess pieces.
Snakes and Ladders is played by two or more players. It is played with colourful pieces and a dice.
Carrom is played by two to four players. It is played using small discs called carrom men and a striker.
Outdoor games are games that are played outside in an open space.









Badminton is played by two players or two teams (of two players). It is played using a shuttlecock and a racket.





Volleyball is a team game. Players hit the ball over the net to the other side.




Football is a team game. Players kick the ball to score a goal.
Cricket is a team game. It is played using a ball, bat and stumps.
Both indoor and outdoor games keep us healthy and happy. Which games do you like to play inside or outside your home?




Practice Time
Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Write ‘I’ for indoor games and ‘O’ for outdoor games.
a Ludo: b Football:
c Cricket: d Carrom:
e Volleyball: f Chess:
2 Match the things and the games.
a Bat and ball Ludo
b Shuttlecock Cricket
c Dice and board Carrom
d Striker Badminton
3 Circle the odd one out.




Ludo b Carrom


c Badminton d Cricket








Food is important for us. Let us learn what we can do to make sure that our food is clean.


Wash fruit and vegetables with water before using them. Always wash your hands before and after touching food.


Drink only clean water. Do not drink water directly from the tap.
Always keep cut and cooked food covered.


Use clean utensils. Wash them properly with soap and water.
Store raw vegetables and fruit in the refrigerator.
Store dry food properly in jars. They may get spoilt easily if left in the open.


We keep and prepare our food in the kitchen. We should keep our kitchen clean.
Always throw the kitchen waste in a closed dustbin.
There are many people in the world who do not get enough food to eat. We should never waste food.





Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Put a tick ( ) next to the things we should do and put a cross ( ) next to the things we should not do.



a Leave cooked food uncovered.
b Eat a washed apple.
c Drink filtered water.
d Cut vegetables without washing them.
e Wash hands with soap and water before a meal.
f Keep kitchen waste in the kitchen for many days.
2 Circle the pictures that show food that is safe to eat.

The world of Disney was created by Walt Disney. It has given us many lovable cartoon characters. Let us learn about some of them.

Mickey Mouse is a clever and friendly mouse. He is good at solving problems.

Minnie Mouse is another mouse from Disney. She has a friendly and helpful nature. She is Mickey’s friend.

Cinderella is a character from a famous story of the same name. She has a fairy godmother who turns her into a princess for one night.

Aladdin has a genie who makes his wishes come true. He also has a magical carpet that can fly.

Donald Duck is a duck who makes people laugh. He has a funny voice.


Elsa has the power to turn anything that she touches into ice. She lives in the kingdom of Arendelle with her sister Anna.
Do you know the names of any other Disney cartoon characters?
Use the internet to find out the names of five more Disney characters.

Practice Time


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Match the Disney characters and their names.
a Mickey Mouse


b Elsa

c Cinderella

d Donald Duck
2 Which Disney character am I? Unjumble the names and write them down.




a I have a magical flying carpet. (LADANID)
b I am good at solving problems. (IKCEMY SOUME)
c I can turn anything into ice with (SELA) my touch.
d I am good at making people laugh. (OADNDL KUCD)
e I have a fairy godmother who turned (ELALDRICNE) me into a princess.
f I am often seen as Mickey’s friend. (NINMEI SOUEM)
7. The Solar System
1. a. red planet b. blue planet
c. smallest planet d. hottest planet
e. largest planet
2. a. NEPTUNE b. MERCURY c. EARTH
d. SATURN e. VENUS
8. Traditional Indian Wear
1. Men Women Dhoti and Kediyu Lungi Panjabi Mekhela Nauvari Chaniya Choli
2. a. Maharashtra b. Gujarat
c. West Bengal d. Punjab
3. Across
1. NAUVARI 2. PHETA Down
1. LUNGI 2. SAREE
9. Indian Currency
1. a. Currency b. Rupee c. Paper notes
d. RBI
2. a. India b. The United States of America
10. India and its Neighbours
1. Across
1. KATHMANDU 2. COLOMBO Down
1. KABUL 2. DHAKA
2.
11. Indoor-Outdoor Games
1. a. I b. O c. O d. I e. O f. I
2. a. Cricket b. Badminton c. Ludo d. Carrom
3. a. Ludo b. Carrom


c. Badminton d. Cricket



12. Food and Hygiene
1. a. X b. c. d. X e.

e.
13. Disney World
1. a. Cinderella b. Elsa c. Mickey Mouse
d. Donald Duck
2. a. ALADDIN b. MICKEY MOUSE
c. ELSA d. DONALD DUCK
e. CINDERELLA f. MINNIE MOUSE

Introducing INSIGHTS, a 21st-century product for the learners of grades 1 and 2. It includes all curricular areas—English, Mathematics, Environmental Science and General Knowledge. INSIGHTS is aligned with the NEP 2020 in terms of its design principles, and fulfils all recommendations of the NCF 2022.
Product Package
• Semester Books
• Uolo App
• Teacher Guide
• Focus on HOTS and Critical Thinking: Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical and evaluative thought processes
• Digital Aids: Animated talking books, interactive quizzes for additional practice and curated learning videos
• Experiential and Applicative Learning: Projects and activities designed for real-life settings, like lab activities and community projects, to enable the development and practice of life skills
• Rootedness to India: Examples from India’s unique culture and history, linked to each topic, to inculcate a sense of pride and love for the nation
• Model Assessments: Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and the application of skills
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-981053-6-3
