





Academic Authors: Ankita Yadav, Yuvraj, Urmi Maitra, Kashika Parnami, Chandani Goyal, Anuj Gupta, Simran Singh
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Sanjay Kumar Goel, Vishesh Agarwal
Project Lead: Sneha Sharma
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First impression 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Quest Social Science 3
ISBN: 978-81-979482-2-0
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
Welcome to the exciting world of social science through Quest, a textbook that has been thoughtfully designed to nurture an understanding of people, places, communities, and how society works.
In today’s rapidly evolving world, a solid foundation in understanding the social surroundings and human society from an early age is more crucial than ever. Social science education lays the groundwork for rational thinking, critical outlook, humane values, and the ability to make informed choices. These skills are not just academic: they are essential life skills that empower young minds to understand and interact with the world around them in a rational and meaningful way. At UOLO, we believe that every child deserves to learn these skills with the best resources available.
In this pursuit, Quest is uniquely crafted to provide a comprehensive and contemporary learning experience, meticulously aligned with the recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023. The book incorporates the curricular goals and competencies outlined in the NCF 2023, ensuring that every chapter, exercise, and feature reflects these foundational principles.
This textbook transcends traditional teaching methods by adopting a competency-based approach, recommended by both NEP 2020 and NCF 2023, that emphasises not just conceptual understanding and critical thinking, but also application of key concepts, and problem-solving. It is designed to make learning both meaningful and relevant, equipping students with the tools they need to thrive in the 21st century.
Carefully curated content, NEP-specific tags, and a diverse array of elements have been seamlessly integrated throughout the book to nurture essential skills, values, and dispositions outlined in the NEP. Competency-based projects and assessments are strategically placed to help students master key concepts and develop higher-order thinking skills.
The book has the unique feature of being complemented by a graphic novella. Each unit of the book begins with an episode of the gripping sci-fi tale, which not only captivates the students’ interest and promotes reading, but also ingeniously connects with some of the core concepts that will be taught in the respective units.
Each chapter is also enriched with vibrant illustrations, relatable examples, and interactive activities to engage our young learners. Observations, inquiries and community-based learning experiences have been embedded throughout the book to develop an analytical mindset and make learning a relatable and enjoyable journey for them. Moreover, assessments ‘of, as, and for learning,’ as envisioned by the NEP and NCF, have been interwoven throughout the curriculum, providing continuous evaluation and meaningful feedback to students to support their growth and success.
The Quest product bundle offers a comprehensive social science kit which includes a textbook that has relevant and up-to-date content, concept building opportunities, projects, and assessments; a teacher manual offering extensive teaching support; technology-powered features that includes engaging videos and interactive exercises for students; and digital lesson plans and an assessment generator for teachers.
In conclusion, Quest is designed to fascinate students towards social science, both as a subject and as a practical experience in their everyday lives, while also making them well-rounded individuals.
We invite educators, parents, and students to embrace Quest and join us in nurturing the next generation of rational thinkers, responsible citizens, and problem-solvers. Embark on this exciting journey with us and let Quest be a valuable resource in your educational adventure.


Welcome to the Quest journey.
The program is carefully designed to elevate the experience of learning social science through an NCF-based, age-appropriate, pedagogically-sound, and engaging content. Teachers will be supported with a manual that offers comprehensive guidance to optimise classroom instruction. Furthermore, various assessment mechanisms have been built in to the program.
Engaging Textbooks
Comic Stories
Teacher Manual
Competency-based Model Assessments
Applied Social Science Projects
Question-paper Generator
Student and Teacher Apps
Learning Videos
Interactive Tasks & Exercises
Byte-size Lesson Modules
The Quest program is also augmented by a digital learning platform that offers powerful educational videos and interactive exercises to help children master concepts and skills in a joyful and fear-free manner.

The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, introduced by the Government of India, represents a transformative shift in the country’s education system. It aims to create a more holistic, dynamic and multidisciplinary approach to education. NEP 2020 focuses on fostering conceptual understanding, skills, values, and competencies that align with the demands of the 21st century, while also preserving India’s rich cultural heritage. UOLO is fully committed to actualising the vision of NEP 2020 by meticulously adhering to its outlined recommendations.









1. Focus on conceptual understanding
2. 21st century skills, values, and dispositions
3. Critical thinking and problem solving
4. Application in real life
5. Holistic and integrated learning
6. Experiential learning
7. Enjoyable and engaging
8. Discussion-based approach
9. Technology-based solutions
10. Knowledge of India

Competency-based Education
NEP Pages 12, 17, and 22
Teaching and Learning Pedagogy
NEP Pages 3, 11, 12, and 27
National Pride
NEP Pages 15, 16, and 43
11. Assessment of core concepts and application skills Assessments
NEP Pages 12, 18, and 22


Applied
Engaging hands-on projects blending social sciences, mathematics, arts, and technology to understand the world around them
Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and application of skills
Story-based Approach
Enchanting comic stories that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure
Explore More
Curated videos to find out more about key concepts
Multidisciplinary, holistic, and fun-filled activities to internalise the concept better
Engaging with community members to make text-to-self connections and develop appreciation for diverse contexts and cultures

Concise snippets of information designed to caution against potential misconceptions
Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical, and evaluative thought processes
Digital worksheets on key concepts to supplement textbook exercises
Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage, designed to ignite a profound sense of pride and love for the nation
Picture-based Questions Questions featuring visual stimuli to elevate comprehension, interpretation, and critical thinking
Simple activities and tips to develop a diverse set of essential skills for living well


The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 outlines essential skills, values, dispositions, and learning approaches necessary for students to thrive in the 21st century. This textbook identifies and incorporates these elements throughout its content, activities, and exercises. Referred to as “NEP Tags”, they are defined as follows:



INTEGRATED
Bringing creativity and fun into learning by combining music, drama, and art with other subjects
Sports Integration
Using physical activities, sports, and games to make learning active and engaging
Cross-curricular and skill linkages to make the learning experience more holistic, joyful and meaningful
THINK RATIONAL
Using facts, logic and reasoning to understand problems and make smart decisions

Teamwork
TEAMWORK

SDG
Embracing the spirit of mutual collaboration and cooperation while working together to solve problems
Unwavering commitment to create a green, peaceful, prosperous, and equitable and inclusive world

SEL Social Emotional Learning
Developing the skills to understand and manage emotions, build positive relationships with others, and make responsible choices

The National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF), released in 2023, is developed based on the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. Its purpose is to enable the implementation of the NEP. The NCF provides guidelines for designing school syllabi and textbooks in India. It aims to improve the quality of education by making it more relevant, engaging, inclusive, and learner-centric. To achieve this, the NCF has articulated precise Learning Standards through well-defined Curricular Goals and Competency statements. These statements serve to harmonise the syllabus, content, pedagogical practices, and assessment culture, ensuring a cohesive and comprehensive educational experience.
Curricular Goals: Curricular Goals are statements that give directions to curriculum development and implementation. They are derived from Aims and are specific to a Stage in education.
Competencies: Competencies are learning achievements that are observable and can be assessed systematically. These Competencies are derived from the Curricular Goals and are expected to be attained by the end of a Stage.
NCF Page 59
CG-1
Explores the natural and social environment in their surroundings
CG-2
Understands the interdependence in their environment through observation and experiences
C-1.1 Observes and identifies the natural (insects, plants, birds, animals, geographical features, sun and moon, soil) and social (houses, relationships) components in their immediate environment
C-1.2 Describes structures, relationships, and traditions in the family and community
C-1.3 Asks questions and makes predictions about simple patterns (season change, food chain, rituals, celebrations) observed in the immediate environment
C-1.4 Explains the functioning of local institutions (family, school, bank/ post office, market, and panchayat) in different forms (story, drawing, tabulating data, noting discussion), and analyses their role
C-1.5 Creates simple objects (family tree, envelopes, origami animals) on their own using local materials
C-2.1 Identifies natural and humanmade systems that support their lives (water supply, water cycle, river flow system, life cycle of plants and animals, food, household items, transport, communication, electricity in the home)
C-2.2 Describes the relationship between the natural environment and cultural practices in their immediate environment (nature of work, food, traditions)
C-2.3 Expresses the changes in the lives of their family and community as communicated by elders and through local stories (changes in occupation, food habits, resources, celebrations, communication)
The above is a snapshot of the curricular goals and competencies relationship in EVS for the Preparatory Stage (NCF 2023, pages 340–341). The next section shows the coverage of all these competencies across the chapters.

Ch 17 Ch 18 Ch 19 Ch 20
Ch 16
Ch 15
Ch 14
Ch 13
Ch 12
Ch 11
8 Ch 9 Ch 10
7
Ch 5 Ch 6
Ch 4
Ch 3
Ch 2
Ch 1
































Competencies
C-1.1 Observes and identifies the natural (insects, plants, birds, animals, geographical features, sun and moon, soil) and social (houses, relationships) components in their immediate environment
Curricular Goals
CG-1
Explores the natural and social environment in their surroundings
C-1.2 Describes structures, relationships, and traditions in the family and community




C-1.3 Asks questions and makes predictions about simple patterns (season change, food chain, rituals, celebrations) observed in the immediate environment
C-1.4 Explains the functioning of local institutions (family, school, bank/post office, market, and panchayat) in different forms (story, drawing, tabulating data, noting discussion), and analyses their role
C-1.5 Creates simple objects (family tree, envelopes, origami animals) on their own using local materials
C-2.1 Identifies natural and humanmade systems that support their lives (water supply, water cycle, river flow system, life cycle of plants and animals, food, household items, transport, communication, electricity in the home)
C-2.2 Describes the relationship between the natural environment and cultural practices in their immediate environment (nature of work, food, traditions)
CG-2
Understands the interdependence in their environment through observation and experiences






































C-2.3 Expresses the changes in the lives of their family and community as communicated by elders and through local stories (changes in occupation, food habits, resources, celebrations, communication)
C-3.1 Describes the basic safety needs and protection (health and hygiene, food, water, shelter, precautions, awareness of emergency situations) of humans, birds, and animals
CG-3 Explains how to ensure the safety of self and others in different situations
C-3.3 Develops simple labels, slogans, and participates in roleplay on safety and protection in the local environment to be displayed/done in school and locality
C-4.2 Observes and describes cultural diversity in their immediate environment (food, clothing, games, different seasons, festivals related to harvest and sowing)
CG-4 Develops sensitivity towards social and natural environment
C-4.3 Observes and describes natural resources in their immediate environment, and their use
C-5.1 Explains a mental map of their school, village, and ward
CG-5 Develops the ability to read and interpret simple maps
C-5.2 Reads simple maps of city, State, and country to identify natural and humanmade features (well, lake, post office, school, hospital, etc.) with reference to symbols and directions
C-5.3 Draws a sketch of their school, village and ward using symbols and directions





C-6.2 Presents observations and findings through different creative modes (drawing, diagram, poem, play, skit, through oral and written expression)
CG-6 Uses data and information from various sources to investigate questions related to their immediate environment


are a part of the universe is a huge endless space which has stars, planets, It also has dust, gases, and big pieces of rocks that float in The Earth seems quite big to us but it is quite tiny in the universe.



Comic Story: Exciting story built through out the book, contains hooks to topics in a unit















We can see the stars in the sky at night. Stars look tiny to us but in reality they are big, bright balls of hot gas that shine in the sky. They are far away from us that is why they look like tiny lights.
Chapter Overview: Outline of the key concepts covered in the chapter





Did You Know?
Stars are there during the day are not visible bright light of




If we look carefully, we can make patterns of the stars in the patterns are called constellations. People have given these different names based on what they look like. They are usually animals or myths. For example, Ursa Major or Big Dipper spoon in the sky, Leo looks like a lion, Hydra looks like a water snake, and Orion looks like a hunter. The Ursa Major is called Saptarishi in India.
Get Set: A short and fun activity to get learners excited about the new topic
Did You Know: Interesting facts related to the topic
Understanding Our Universe
Revolution of the Earth

sunset, the Sun does not move. It is the Earth that moves, which causes sunset.
When we look up at the sky during the day and at night, does it look the same? During the day we can see a bright blue sky and a bright sun. At night, we can see the moon
and the stars. All these heavenly bodies are a part of the universe. The universe is a huge endless space which has stars, planets, sun, and moon. It also has dust, gases, and big pieces of rocks that float in the vast space. The Earth seems quite big to us but it is quite tiny in the universe.
We can see the stars in the sky at night. Stars look tiny to us but in reality they are big, bright balls of hot gas that shine in the sky. They are far away from us that is why they look like tiny lights.
Revolution of the Earth
The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an orbit is called revolution. The Earth moves around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit. The Earth completes one revolution in one year. The revolution of the Earth around the Sun and its tilted axis causes different seasons in different parts of the Earth.
Vocabulary: Meanings of difficult words

Earth

The Earth is the only planet in

Did You Know?
We have all seen the Sun in the sky. The Sun rises in the East West. It is also a star. It is a huge ball of very hot gas that makes give out light and heat. This heat and light makes life possible There are eight planets that revolve around the Sun. They Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The with all these planets that revolve around it together form
The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an orbit is called revolution. The Earth moves around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit. The Earth completes one revolution in one year. The revolution of the Earth around the Sun and its tilted axis causes different seasons in different parts of the Earth.

1 2 3 4 5
Stars are there in the sky during the day too but they are not visible to us due to the bright light of the Sun.
There are only five oceans Pacific Ocean is written Error Alert!





myths: oral stories that have been told over hundreds of years which not be true revolve: to go around or travel around something







Error Alert: Caution against misconceptions
During sunset, the Sun does not move. It is the Earth that moves, which causes sunset.

The Earth is the only planet in our solar system that can support life. This is possible because the Earth has water, air and sunlight. Living beings cannot survive without air or water. There is no other planet like the Earth. The Earth is our home, and it is precious. We should make sure that our actions do not harm the earth in any way. For example, we must not waste water.








Revolution of the Earth
Wonders of Bharat
Jantar Mantar is a monument in New Delhi. It was built by Maharaja Jai Singh almost 300 years ago! It was built to predict the movements of the sun, the moon and the planets. It also told time based on the shadow caused by the sun.









Ursa Major Leo Hydra

If we look carefully, we can make patterns of the stars in the sky. These patterns are called . People have given these star patterns different names based on what they look like. They are usually named after animals or myths. For example, Ursa Major or Big Dipper looks like a big spoon in the sky, Leo looks like a lion, Hydra looks like a water snake, and Orion looks like a hunter. The Ursa Major is called Saptarishi in India.
Wonders of Bharat: Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage
The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an orbit is called . The Earth moves around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit. The Earth completes one revolution in one year. The revolution of the Earth around the Sun and its tilted axis causes different seasons in different parts of the Earth.

Oceans are very important. animals. People can also oceans through ships. industry.


Explore More: Short videos to find out more about the topic
We have all seen the Sun in the sky. The Sun rises in the East and sets in the West. It is also a star. It is a huge ball of very hot gas that makes it glow and give out light and heat. This heat and light makes life possible on Earth. There are eight planets that revolve around the Sun. They are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The Sun along with all these planets that revolve around it together form the Solar System.


myths: oral stories that have been told over hundreds of years which may or may not be true revolve: to go around or travel around something
NEP Tags: To show alignment with NEP skills and values
The Earth is the only planet in our solar system that can support life. This is possible because the Earth has water, air and sunlight. Living beings cannot survive without air or water. There is no other planet like the Earth. The Earth is our home, and it is precious. We should make sure that our actions do not harm the earth in any way. For example, we must not waste water.
Wonders of Bharat
Do and Learn: Multidisciplinary, holistic, and fun activities to understand the concept better




also support the fishing industry

The Earth’s continents and oceans each has its own unique features, cultures, and wildlife. We must not pollute the water in the oceans so that we don’t harm the aquatic plants and animals.

The Earth’s continents has its own unique features, wildlife. We must not oceans so that we don’t plants and animals.
Jantar Mantar is a monument in New Delhi. It was built by Maharaja Jai Singh almost 300 years ago! It was built to predict the movements of the sun, the moon and the planets. It also told time based on the shadow caused by the sun. Jantar Mantar, New








on the map. The student with the maximum correct markings wins.






4. Directions can be found using a compass.
and Learn
Make two teams and hide small objects like toys, stones, sketch pens etc. at different places in a playground. Then make a map of the playground, marking the spots where you have hidden the objects. Now exchange your maps and use them to find the hidden objects of the other team.


Coastal Plains Islands learn more about them.


Himalayan Mountains lie in the part of India. They are highest mountain ranges in the row of mountains is called mountain range. The weather in region is cold and it is difficult crops here. The highest mountain in the world, Mount Everest, lies Himalayas. Other famous mountains Himalayas include Kanchenjunga, Parbat and Nanda Devi. Many rivers the Ganga, the Yamuna and the Brahmaputra originate in the Himalayas. formed by the melting ice.
Know?
Pause and Answer: Short exercises between the chapter to pause and assess comprehension
Tick (✓) the correct statements.
The team that finds all the objects first, wins.
1. Maps are flattened representations of the earth.
2. A physical map shows countries and boundaries.
Think and Tell
3. North is located to the opposite of South.


C Define universe.
D. How is the Sun similar or different to the Moon?
4. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
If you had to find out the names of all states in India, which type of map will you use?
4. Directions can be found using a compass.
GAMES Do and Learn
Think and Tell / Discuss: Analysis, reflection, and text-to-self connection-based prompts for discussion in class
Wonders of Bharat
A What is shown in this picture?
B Label the parts marked in the picture.
Make two teams and hide small objects like toys, stones, sketch pens etc. at different places in a playground. Then make a map of the playground, marking the spots where you have hidden the objects. Now exchange your maps and use them to find the hidden objects of the other team.
India is located in Asia and is the seventh largest country in the world by land area.

The team that finds all the objects first, wins.
Ancient Indian scholars such as Aryabhata had inspired Greeks and Romans about making maps. His famous work includes describing the shape of the Earth as round.
Think and Tell

Remember: Recall of previous knowledge relevant to the topic

C Define universe.




If you had to find out the names of all states in India, which type of map will you use?
Picture-based Questions: Special questions featuring visual stimuli to foster comprehension, interpretation, and critical thinking
Wonders of Bharat
Ancient Indian scholars such as Aryabhata had inspired Greeks and Romans about making maps. His famous work includes describing the shape of









D How is the Sun similar or different to the Moon?

4. Picture-based questions.


Life Skills: Simple activities and tips to develop a diverse set of essential skills for living well
Error Alert!
Pause and Answer USS25CBG3.indb
Learn more about how globes were made in olden times.
A What is shown in this picture?

Label the parts marked in the picture.


Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.


What would happen if the Sun stops giving heat and light?
Learn more about how globes were made in olden times.
Snow-covered Himalayas
The Mount Everest is not located in India. It lies in China and Nepal. The highest mountain peak in India is Kanchenjunga.
Word Splash
Word Splash






Skills




Create a colorful poster about our universe and include the sun, the moon, stars, and constellations in it. Give a title to your poster. Share the completed poster with your class.

rotation: movement of the earth on its axis revolution: movement of the earth around the sun orbit: a fixed path in which the earth moves around the sun








Word Splash: Recall of key terms and concepts in the chapter
rotation: movement of the earth on its axis revolution: movement of the earth around the sun orbit: a fixed path in which the earth moves around the sun
Points to Remember
to Remember
What would happen if the Sun stops giving heat and light?
Life Skills
• The Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system.
Points to Remember: Summary of the chapter

The Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system.
• The Earth moves in two ways: rotation and revolution.
Norgay and Sir Edmund Hillary were the first men to reach the peak of Everest in 1953.
• The Earth moves in two ways: rotation and revolution.
Create a colorful poster about our universe and include the sun, the moon, stars, and constellations in it. Give a title to your poster. Share the completed poster with your class.
• The rotation of the Earth causes day and night, while the revolution causes seasons.
• The rotation of the Earth causes day and night, while the revolution causes seasons.
Northern Plains
Northern Plains are flat lands to the the Himalayas. They are also known Indo-Gangetic Plains. Rivers like the and the Yamuna that originate in the Himalayas flow through these plains. This the soil fertile and suitable for farming.
originate: start or begin soil that is good for growing plants
1. Tick the correct answer.
HOTS: Intellectually stimulating

the correct answer.
A The only planet that has life on it:

Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
A The only planet that has life on it:
a Jupiter b. Neptune
a Jupiter b. Neptune c. Earth d. Saturn
B The number of hours the Earth takes to complete one rotation is: a 36 b. 24 c. 10 d. 25
c. Earth d. Saturn


B The number of hours the Earth takes to complete one rotation is:
C The sailor who proved that the Earth is round was:
a. 36 b. 24


a Vasco Da Gama b. Christopher Columbus c Ferdinand Magellan d. Maharaja Jai Singh
c. 10 d. 25
C The sailor who proved that the Earth is round was:
a Vasco Da Gama
Which states in India share a capital, and who governs that capital?
2. Fill in the blanks. orbit axis rotation round
A farmer in his wheat fields in Northern Plains
c Ferdinand Magellan
2. Fill in the blanks.
B The Earth is in shape.
Community Connect: Engagement with the community members to make text-to-self connections and develop appreciation for

Which states in India share a capital, and who governs that capital?
b. Christopher Columbus
d. Maharaja Jai Singh
A The of the Earth is an imaginary line.

D The movement of the Earth on its own axis is called Chapter
Community Connect
C The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an is called revolution.

A The of the Earth is an imaginary line.
B. The Earth is in shape.
India has changed a lot over the last 20 years. Speak to the elderly people around you and ask them what changes do they see around them in India. Ask about changes in dressing styles, ways of communication, ways of living, facilities and so on.

C The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an is called revolution.
9/17/2024 6:31:30 PM
Community Connect
India has changed a lot over the last 20 years. Speak to the elderly people around you and ask them what changes do they see around them in India. Ask about changes in dressing styles, ways of communication, ways of living, facilities and so on.
D The movement of the Earth on its own axis is called























The Sun and the Solar System The Moon The Universe Understanding Our Universe Stars and Constellations The Planets

Get Set

Look at the pictures and tell the difference between them.


When we look up at the sky during the day and at night, does it look the same? During the day we can see a bright blue sky and the bright Sun. At night, we can see the Moon and The Universe


the stars. All these heavenly bodies are a part of the universe. The universe is a huge endless space which has stars, planets, the Sun, and the Moon. It also has dust, gases, and big pieces of rocks that float in the empty space. The Earth seems quite big to us but it is quite tiny in the universe.
We can see stars in the sky at night. Stars look tiny to us but in reality they are big, bright balls of hot gas. They are far away from us that is why they look like tiny dots of light.
Stars are there in the sky even during the day but they are not visible to us due to the bright light of the Sun.
If we look carefully, we can make patterns in the stars in the sky. These patterns are called constellations. People have named these constellations different names based on what they look like. They are usually named after animals or myths. For example, the Big Dipper looks like a big spoon in the sky, Leo looks like a lion, and Orion looks like a hunter. The Big Dipper is called Saptarishi in India.






















































































































myths: stories that have been told over hundreds of years and which may or may not be true revolve: to go around or travel around something


The Sun rises in the East and sets in the West. It is also a star. It is a huge ball of very hot gas that makes it glow and give out light and heat. This heat and light makes life possible on Earth.


There are eight planets that revolve around the Sun. They are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The Sun along with all these planets that revolve around it together form the Solar System.































Tick (✓) the correct statements.






The solar system does not have nine planets. Pluto was removed from the list of planets in 2006. Error Alert!
1. The Sun rises in the West and sets in the East.
2. The Solar System has 8 planets.
3. The Big Dipper looks like a big spoon.
4. The Sun does not have light of its own.
The Moon is a big, round heavenly body that revolves around the Earth. It is much smaller than the Earth and the Sun. It is closest to the Earth in the solar system, that is why it appears as big as the Sun.
The Moon does not have any light of its own but still shines brightly at night. That is because it reflects the light from the Sun.




































































































Planets are heavenly bodies that revolve around a star. They can be made of rocks or gases. All the planets in our Solar System are different from each other. Some are hot, some are cold, and some have many moons. These planets get their heat and light from the Sun.
We live on the Earth. It is the third planet from the Sun. It is the only planet in the solar system that has life on it. So, it is important to make sure that our actions do not harm life on Earth. It is the only place for us to live, in the Universe.

The Earth has one moon. Jupiter has 95 moons! Saturn has 146 moons! Did You Know?
The Earth is the only planet in the Solar System that has life on it. What are some ways in which we can keep the Earth clean?
Chandrayaan-1 was India's first spacecraft (special vehicle that travels in space) to the Moon. It discovered tiny particles of water and large caves on the Moon's surface.

An Indian spacecraft
heavenly bodies: objects in space such as the Sun, the Moon, planets, and stars the universe: a huge endless space which has stars, planets, the Sun, the Moon, dust, gases, and big pieces of rocks floating in it stars: big, bright balls of hot gas constellations: patterns formed by the stars in the sky

Scan the QR code to learn more about the Solar System.


• The universe is a huge endless space which has stars, planets, the Sun, and the Moon.
• The Sun is the only source of heat and light in the Solar System.
• The Solar System consists of 8 planets.
• The Earth is the third planet from the Sun.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these has its own light?
a. Sun
b. Earth
B. Which of the following terms defines the Sun?
a. Star
b. Planet
C. Which is the farthest planet from the Sun?
a. Mercury
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Venus
c. Moon
c. Moon
c. Neptune
Moon hunter Leo Big Dipper
A. The revolves around the Earth.
B. The constellation looks like a lion.
C. Orion looks like a .
D. The is called Saptarishi in India.
3. Answer the following questions.
A. How does the Moon shine when it does not have its own light?
B. Which constellation looks like a hunter?


C. Define the universe.
D. How is the Sun similar or different to the Moon?
4. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.



















A. What is shown in this picture?











B. Label the planets marked in the picture.



What would happen if the Sun stopped giving heat and light?
Create a colorful poster about our universe and include the Sun, the Moon, stars, and constellations in it. Give a title to your poster. Share the completed poster with your class.



Chapter Overview

Shape of the Earth Movement of the Earth The Earth—Our Home
What Makes the Earth Unique


Solve the riddle given below.
I rise in the morning, bright and high. I give light to the Earth and the sky.
I am round and hot, glowing all day.
What am I? Can you say?
We all walk on flat land, so the Earth appears flat to us. Some people earlier believed the Earth to be flat. Around 500 years ago, a Portuguese sailor named Ferdinand Magellan set sail from Spain. He kept sailing in a single direction. After 3 years, he arrived back at the place from where he had started. This showed that the Earth is not flat but round in shape.

Shape of the Earth


Over time, photographs of Earth taken from outer space proved that Earth is round and slightly flat at the top and bottom, just like an orange.

In our day-to-day lives, it feels like the Earth is stationary. In reality, the Earth is constantly moving. We do not feel this movement because we are also moving with it. There are two types of movements of the Earth. These are rotation and revolution. Let us explore these, one by one.
Try to spin a bangle on a flat table. Can you see a vertical line in the spinning bangle? This line is not present in reality but appears to be present there. Such an imaginary line is called axis. Just like the bangle, the Earth also spins on its axis. The axis of the Earth is slightly tilted to one side. Movement of the Earth on its own axis is called rotation. The Earth rotates from West to East and takes 24 hours to complete one rotation. The rotation of the Earth causes day and night.

of the Earth causes day and night Sunlight
At a particular time, half of the Earth’s side faces the Sun and has day. The other half of the Earth has night.
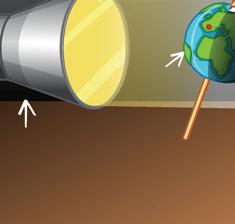
Take a blue or green sponge ball. Insert a wooden stick through its centre. The ball represents the Earth, and the stick is its axis. Now, place it in front of a torch. The torch is the Sun here. Now, the bright part of the ball is part of the Earth that has day, and the dark part has night. Now rotate the ball slowly to create day on the other side of the ball.
stationary: not moving axis: an imaginary line that goes through the centre







The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an orbit is called revolution. The Earth moves around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit. The Earth completes one revolution in one year. The revolution of the Earth around the Sun and its tilted axis causes different seasons in different parts of the Earth.
Revolution of the Earth around the Sun in an orbit
The Earth is the only planet in our solar system that can support life. This is possible because the Earth is at right distance from the Sun and it has water and air. Living beings cannot survive without air or water. There is no other planet like the Earth. The Earth is our home, and it is precious. We should make sure that our actions do not harm life on Earth in any way. For example, we must not waste water.


Jantar Mantar is a monument in New Delhi. It was built by Maharaja Jai Singh almost 300 years ago! It was built to predict the movements of the Sun, the Moon and the planets. It also works like a sundial. Jantar Mantar, New Delhi
rotation: movement of the earth on its axis
revolution: movement of the earth around the sun
orbit: a fixed path in which the earth moves around the sun


Scan the QR code to know more about the movements of the Earth.

• The Earth is the third planet from the Sun.
• The Earth moves in two ways: rotation and revolution.
• The rotation of the Earth causes day and night, while the revolution causes seasons.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. The only planet that has life on it.
a. Jupiter b. Neptune c. Earth d. Saturn
B. The number of hours the Earth takes to complete one rotation is:
a. 36 b. 24 c. 10 d. 25
C. The sailor who proved that the Earth is round was:
a. Vasco Da Gama b. Christopher Columbus
c. Ferdinand Magellan d. Maharaja Jai Singh
2. Fill in the blanks. orbit axis rotation round
A. The of the Earth is an imaginary line.
B. The Earth is in shape.
C. The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an is called revolution.
D. The movement of the Earth on its own axis is called .
3. Write True or False.
A. Earth is the only planet in our solar system that can support life.
B. Days and nights occur due to the revolution of the Earth.
C. The axis of the Earth is tilted.


4. Match the following.
A. Day and Night i. One year
B. Seasons ii. One day
C. The time taken for one rotation iii. Revolution
D. The time taken for one revolution iv. Rotation
5. Answer the following questions.
A. How does Earth support life on it?
B. Why do we not feel the rotation of the Earth?
C. How is rotation different from revolution?
D. How do sunrise and sunset happen?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Which part of the Earth has night?
B. Which movement of the Earth is shown here?














































1. What would happen if the Earth stopped revolving around the Sun?
2. What would happen if the Earth took twice as long to complete one rotation?

Speak to any two of your family members and ask them about their favourite time of the day and why do they like it.







Along with your classmates, read aloud the poem given below.
Our Earth is a place so bright, With mountains high and seas so wide Green forests dance under the sky, With colourful flowers, and birds that fly. Let’s care for it with love so deep, That its beauty we can forever keep.

As you have learnt in the previous chapter, we live on a beautiful planet called Earth. Our planet has seven large landmasses called continents. landmass: a large piece of land


The names of these continents, from the largest to the smallest, are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe and Australia.
Continents and oceans in the world
Continents are very large. Antarctica is the coldest continent. Continents are further divided into smaller parts called countries. For example, Asia is a continent and India is a country in Asia.
Did You Know?
One third of the Earth’s surface is covered by land, and the rest of it is covered by water. Therefore, it is known as the ‘blue planet’.
Look at the world map given above once more. The blue-coloured areas that you can see are the oceans. Oceans are very large and very deep water bodies.
They are much bigger and deeper than the seas. The bottom of the ocean is called the ocean floor. Ocean floors are not always flat. There can be mountains or trenches on the ocean floors.

There are five oceans on the Earth. The names of the oceans, from the largest to the smallest are: the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean and the Arctic Ocean. The Arctic Ocean is mostly frozen. The Southern Ocean is also called the Antarctic Ocean.
trench: steep and narrow deep points in the ocean



There are only five oceans on the Earth, not six. Since the Earth is round, the Pacific Ocean is written twice on the map.
Oceans are very important. They are home to many aquatic plants and animals. People can also travel from one continent to another by crossing oceans through ships. Oceans also support the fishing industry.
Each continent and ocean has its unique features and wildlife. We must not pollute the oceans so that we don’t harm the aquatic plants and animals.


With the help of your teacher, draw the world map on the ground. The teacher will then call out the name of a continent or ocean and you will take turns to go and run towards the correct location on the map. Whoever gets the maximum correct markings wins.

The Indian Ocean is the third largest ocean in the world. It is named after our country, India.

continent: a large mass of land on the surface of the Earth
ocean: a very large and deep water body on the surface of the Earth
aquatic: growing or living in water industry: business



Scan the QR code to learn more about life in the oceans.
• The large landmasses on the surface of the Earth are called continents.
• There are seven continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe and Australia.
• The large and deep water bodies separating the continents are called oceans.
• There are five oceans—the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean and the Arctic Ocean.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which is the largest continent in the world?
a. Asia
b. Australia c. Antarctica
B. Which is the coldest continent?
a. Antarctica
b. North America c. Europe
C. Which ocean is mostly frozen?
a. Indian Ocean
b. Atlantic Ocean c. Arctic Ocean
2. Fill in the blanks. oceans Australia Indian Southern Ocean
A. is the smallest continent.
B. The Ocean is located to the south of Asia.
C. Very large and deep water bodies are called .
D. The fourth-largest ocean is the .

3. Write True or False.
A. Continents cover two-thirds of the Earth’s surface.
B. Each continent is divided into smaller parts called countries.
C. Europe is closest to Australia.
D. India is a part of Asia.
4. Match the following.
A. Pacific Ocean
i. Around Antarctica
B. India Ocean ii. Between Asia and North America
C. Southern Ocean
D. Atlantic Ocean
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Name the five oceans.
B. Name the seven continents.
C. In which continent do you live?
iii. Between Africa, Asia and Australia
iv. Between North America, South America and Africa
D. Which continents share land boundary with each other?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Which ocean lies close to Japan?
B. Which ocean is close to Africa and Asia?
C. Which two oceans are close to Russia?



Jacob is a sailor. He plans to sail from India to North America. Which oceans and continents will he cross on his journey? Compare the size of these oceans and mention which one might take the longest to cross.
There are a lot of aquatic plants and animals in the oceans. Collect a few pictures of these colorful plants and animals and make a scrapbook. You can take the help of your parents in finding these pictures. Label the pictures.





Globes and Maps
Types of Maps Get Set
Directions


In the maze give below, draw the path that Sakshi and Vishesh should take to reach the waterfall.










A globe is a small model of the whole Earth. A globe shows the location of continents, countries, oceans and seas as they are on the Earth. The globe is slightly tilted to one side, just like the Earth is titled on its axis.
Maps are also representations of the Earth but on a flat surface. They can represent the whole Earth or a part of it.
A map kept on a table Globes
Maps can tell us about a specific feature of a place on the Earth. Maps also tell us about different places on the Earth. For that, we have different types of maps. A collection of different kinds of maps in a book is called an atlas.


Maps are mainly of three types: political maps, physical maps and thematic maps.
A political map shows the boundaries of countries, states, cities, towns and villages.
A physical map shows natural features like mountains, rivers, oceans, seas and more.
A thematic map gives specific information about a place, such as population, rainfall, temperature, etc.
axis: a straight line around which an object rotates representation: the way something is shown

There are 4 main directions: North (N), South (S), East (E) and West (W). If we stand facing a map, the top part of the map would be North. The bottom part would be South. The part to your right would be East. The part to your left would be West.
There are four more directions that lie between the four main directions. They are: North-east, North-west, South-east and South-west.
If you had to find out where is North in a playground without using a map, can you guess how we can do that?
In such cases, we can use a compass . A compass is a device that is used to find directions. The needle of a compass always points towards the North.



Tick (✓) the correct statements.
1. Maps are flattened representations of the Earth.
2. A physical map shows countries and boundaries.
3. North is located to the opposite of South.
4. Directions can be found using a compass.
Make two teams and hide small objects like toys, stones, sketch pens, etc. at different places in a playground. Then, make a map of the playground, marking the spots where you have hidden the objects. Now, exchange your maps and use them to find the hidden objects of the other team.
The team that finds all the objects first, wins.
If you had to find out the names of all states in India, which type of map will you use?

Aryabhata was a famous Indian mathematician and astronomer. He said that the Earth was round.


globe: a small model of the whole Earth
map: a flattened representation of the Earth
atlas: a collection of different kinds of maps in a book
political map: a map that shows the boundaries of countries, states, cities, towns and villages
physical map: a map that shows natural features like mountains, rivers, valleys, oceans and more
thematic map: a map that shows specific features of a place like population, temperature and rainfall
compass: a device that is used to find directions

Scan the QR code to learn more about how globes were made in olden times.
• A globe is a small model of the whole Earth.
• Maps are representations of the Earth but on a flat surface.
• There are 4 main directions: North, South, East and West.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What kind of map shows the boundaries of countries and states?
a. Political
b. Physical
c. Thematic
B. Towards what direction does the needle of a compass always point?
a. South
b. West
c. North


C. What is the shape of the globe?
a. Round
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Flat c. Triangle
A. A map shows natural features like mountains.
B. direction is on the opposite side of North.
C. A collection of different kinds of maps in a book is called an .
D. is on the opposite side of East.
3. Write True or False.
A. A globe is flat.
B. Thematic maps show states of a country.
C. North-east direction lies between North and East.
D. South-west direction lies between East and West.
4. Match the following.
A. Political map i. Mountains
B. Compass ii. Countries
C. Thematic map iii. Directions
D. Physical map iv. Rainfall
5. Answer the following questions.
A. What is a globe?
B. List 3 things that political maps can tell us.
C. Is it easier to find directions using a map instead of a globe?
D. Why do we need maps? Give two reasons.


6. Picture-based questions. Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. What kind of map is this?
B. Which water body is located to the east of India?
C. Which water body is located to the west of India?

1. Write one difference between physical and political maps.
2. Imagine you visited a city. To roam around there, what kind of a map would you use—physical or political?
Draw a map to show the route from your school to your house. Remember to show all the important places on the way and the directions.







Read the story with your partner.
Asha lived in a small city. She loved playing in the park close to her home. One day, the park started looking empty because many trees had been cut down. Asha felt sad and wanted to make a difference. She asked her friends to help her plant new trees. Together, they dug holes, planted seeds and small plants, and watered them every day. As the plants grew, the park became lively again. Birds sang on the trees and the trees gave shade for everyone to enjoy. Asha and her friends made the park beautiful again.


The environment is everything around us— air, water, trees, plants, animals and even the land. It includes non-living things too like roads, buildings, etc.
All natural things such as plants, soil, etc. are a part of natural environment and all human-made things such as buildings and roads are a part of human-made environment.

Living and non-living things are both part of the environment.
Pollution occurs when harmful things like smoke, trash, or chemicals make the air, water, or land dirty and unsafe. It can harm plants, animals and people. It is usually a result of human actions.
There are three main types of pollution: air pollution, water pollution and land pollution.
Air Pollution
Air pollution happens when harmful gases are released into the air, making it dirty and unsafe to breathe.
Some causes of air pollution are:
• Release of smoke by different vehicles and factories into the air.
• Burning of wood and garbage.
• Bursting crackers.
• Deforestation, which means cutting trees on a large scale.
Some ways to reduce air pollution are:
• Walk or ride a bicycle instead of using cars for short trips.

A factory chimney releasing smoke into the air
World Environment Day is celebrated every year on 5 June. Did You Know?

• Plant more trees to help clean the air.
• Avoid burning trash, as it creates harmful smoke.
Water pollution occurs when harmful things like chemicals, oil and garbage are let into rivers, lakes and oceans. These things can make the water dirty and unsafe for plants, animals and people.
Some causes of water pollution are:
• Garbage and plastic thrown into rivers, lakes and oceans.
• Chemicals from factories flowing into rivers.



Dirty water being released into a river
• Dirty water from homes and farms released into rivers.
Some ways to reduce water pollution are:
• Always throw trash in bins, not in rivers or lakes.
• Reduce the use of plastic.
• Don't pour chemicals or oils in the kitchen drain.
Why is clean water important for humans and animals?
When harmful waste or chemicals make the land dirty and unhealthy, it is called land pollution. It also includes heaps of garbage lying around and making the land unusable.
Some causes of land pollution are:
• Dumping garbage in huge amounts at various places.
• Using too much plastic.

• Pesticides and chemical fertilizers from farms leaking into the soil.
pesticides: chemicals sprayed on plants and crops to kill insects that damage the crops in the fields
chemical fertilizers: chemicals used to grow the plants quickly and make them healthy



Some ways to reduce land pollution are:
• Throw garbage in bins, not on the ground.
• Recycle paper, plastic and glass instead of throwing them away.
• Avoid using single-use plastic bags and bottles.
• Use natural fertilizers like compost.
• Participate in community clean-up activities.
Plant a small garden with your friends using compost. To do this, get seeds and compost, with help from an adult. Then, with your friends, choose a garden spot. Remove rocks and stones from the soil and mix compost in it. Now, sow the seeds and cover them lightly with the soil and sprinkle a little water. Over the next few weeks, watch the plants grow, and write about their changes. Remember to water them regularly, when the soil becomes dry. See how compost helps them stay strong and healthy.
Saving the environment helps keep our air, water and land clean so that plants, animals and people can live healthy and happy lives.

Some ways to save the environment are:
• Put paper, plastic, and glass in recycling bins so that they can be recycled into something else.
• Turn off the tap while brushing your teeth to save water.
• Planting trees helps clean the air and makes our world a better place for everyone.
Suggest some other ways to save the environment.
• Use reusable bags and bottles to cut down on trash.
compost: a mixture prepared from leaves, food scraps, vegetable peels, etc. used for making plants strong and healthy


• Turn off lights and electronics when not in use to save power.
• Paper is made from trees. Do not waste paper. You can also use recycled paper.
• Plastic harms our environment in many ways. We should not use plastic bags or things made of plastic.
The Chipko Movement took place in the forests of Uttarakhand. Villagers, especially women, hugged trees to stop them from being cut down. They wanted to protect the forests, which are important for clean air, water and the environment.

People hugging trees in the Chipko Movement
environment: all living and non-living things around us
natural environment: all the natural things like plants, soil, etc.
human-made environment: all human-made things like chairs, swings, etc. pollution: addition of harmful substances to the environment

Scan the QR code to learn about ways to recycle.
• The environment is everything around us.
• Environment pollution is of three types: air, water and land pollution.
• Saving the environment helps keep our air, water and land clean so that plants, animals, and people can live healthy and happy lives.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these is a source of water pollution?
a. Planting trees
c. Saving water
b. Chemicals from factories
B. Which of these helps reduce air pollution?
a. Burning leaves
c. Using plastic bags
b. Using public transport
C. Which of these helps reduce land pollution?
a. Chemical fertilizers
c. Use of compost
b. Use of pesticides
2. Fill in the blanks. trees pollution chemicals deforestation
A. is the introduction of harmful substances into the environment.
B. Planting helps reduce air pollution.
C. is the process of cutting trees on a large scale.
D. Using in farming can cause land pollution.
3. Write True or False.
A. Air pollution can cause breathing problems.
B. Water pollution does not affect animals and plants.
C. Recycling paper can help save the environment.
D. Chemical fertilizers cause land pollution.


4. Match the following.
A. Turn off lights when not in use i. Saves trees
B. Use reusable cloth bags ii. Saves power
C. Turn off tap while brushing iii. Saves water
D. Recycling paper iv. Reduces waste
5. Answer the following questions.
A. What is land pollution?
B. Write three ways to reduce water pollution.
C. Explain how factories can lead to all three types of environmental pollution.
D. What are three things you can do to help reduce air pollution?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the picture of a polluted river given here and answer the questions.
A. What are some things in the picture that are polluting the river?
B. What could people do to help clean this river?


1. What would happen if we do not reduce land pollution?
2. How does air pollution affect our health?
Make a poster on saving water. Suggest three ways in which we can save water in our daily lives. Give pictures, as well. Give your poster a title. Display the poster in the school corridor.


Objective: Students will create a 3D model of the Earth, showing its continents and oceans.
Materials Needed: A large ball, blue and green paint, paintbrushes, a black marker, a small piece of paper, a globe or a world map for reference.

Step 1: Prepare the Base: Use the large ball as the base for your model Earth. It can be a football or basketball.
Step 2: Paint the Oceans: Paint the entire surface of the ball with blue paint to represent the oceans. Let it dry.
Step 3: Paint the Continents: Draw the outlines of the continents. Use green paint to paint the continents.
Tip: You can use a world map or a globe when painting the continents to draw them correctly.
Step 4: Label the Continents and Oceans: Label all the continents and oceans using the black marker.
Step 5: Add directions: Draw a small compass rose on a piece of paper and stick it near the base of your model to indicate directions (North, South, East, and West). Again, refer to the globe to paste the rose correctly.
Project Output: Now you have your own small model of our beautiful Earth! Present it to your class.
Final Outcome: This project will help you understand the shape of the Earth and where the different continents and oceans are.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.


Read this article. Answer the questions given below.
The Yamuna river has serious pollution problems. Factories nearby dump harmful chemicals into the river, making the water poisonous. The river bank is also choked with plastic bags and trash. These things harm the fish, and make the river dirty, smelly, and unsafe for drinking or swimming. Many people who use the river for washing or drinking become sick because of this. Saving the river is very important for keeping our environment healthy.

1. What type of waste do factories dump into the Yamuna?
a. Paper waste
b. Food waste
c. Chemical waste
2. The water in the Yamuna River is unsafe because
a. The river has a large variety of fish.
b. It is filled with plastic and toxic waste.
c. Lots of people swim in the river.
3. The Yamuna river is an important source of water for Delhi and Uttar Pradesh. If pollution in the Yamuna River continues to get worse, how do you think would it affect the future of the people who depend on the river? Mention any 2 points.
4. Suggest two steps that can be taken to reduce pollution level in rivers.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.












Chapter Overview

Size and Neighbours


Solve the riddle given below. I am the largest continent, With many countries, big and small. Where India and China are found, Can you guess my name at all?
Parul: Maa, what makes India so special?
Mother: India is a vast and beautiful country, dear. Many different kinds of people live here.
Parul: Really? Are all of them like us?
Mother: No, that’s what’s interesting! People here speak many different languages, like Hindi, Tamil, Bengali, Marathi and many more. And they also follow different religions and celebrate many festivals.
Parul: That sounds fun! Is it okay that everyone is so different?
Mother: Absolutely! That is what makes India beautiful. We should respect everyone’s differences because that’s what helps us live happily together.

India is the seventh largest country in the world by land area. It is the largest country in the world by population.
India has the Arabian Sea in the west, the Indian Ocean in the south, and the Bay of Bengal in the east.
India shares its borders with many countries. They are our neighbouring countries. They are Pakistan, Afghanistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, China and Bangladesh. Sri Lanka and Maldives are India’s neighbours in the Indian Ocean.
Bangladesh was created in 1971. Before that, it was called East Pakistan and was a part of Pakistan itself.
India and its neighbours
In India, we have two main levels of government: the Central Government and the State Government. Both the governments are elected by the citizens of India through elections. All citizens who are 18 or above can vote in these elections.
population: the number of people living in a place election: process of choosing the government through voting vote: express one's choice


The central government makes decisions that apply to the whole country. Its offices are located in New Delhi, which is the capital of India.
Why do most members of the central government live and work in the capital?
Since India is a very large country, it is difficult for the central government to help all the people directly. So state governments govern specific states.

of India
Some parts of India are called Union Territories and are not included in the 28 states of India. They are governed directly by the central government. India has 8 union territories.
Each state and union territory in India has a capital. The capitals of all the states and union territories of India are given in the following tables.
Jammu and Kashmir has two capitals. Srinagar is the capital during the summer months but in winters, it becomes very cold and it is difficult to work from there. So, in winters the capital is Jammu.
Table 1: States and their capitals
Sl. No. State Capital
1. Andhra Pradesh Amaravati
2. Arunachal Pradesh Itanagar
3. Assam Dispur
4. Bihar Patna
5. Chhattisgarh Raipur
6. Goa Panaji
7. Gujarat Gandhinagar
8. Haryana Chandigarh
govern: rule

Sl. No. State Capital
9. Himachal Pradesh Shimla
10. Jharkhand Ranchi
11. Karnataka Bengaluru
12. Kerala Thiruvananthapuram
13. Madhya Pradesh Bhopal
14. Maharashtra Mumbai
15. Manipur Imphal
16. Meghalaya Shillong
17. Mizoram Aizawl
18. Nagaland Kohima
19. Odisha Bhubaneswar
20. Punjab Chandigarh
21. Rajasthan Jaipur
22. Sikkim Gangtok
23. Tamil Nadu Chennai
24. Telangana Hyderabad
25. Tripura Agartala
26. Uttar Pradesh Lucknow
27. Uttarakhand Dehra Dun
28. West Bengal Kolkata
Table 2: Union Territories and their capitals
Sl. No. Union Territory Capital
1. Andaman and Nicobar Islands Port Blair
2. Chandigarh Chandigarh
3. Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu Daman
4. Lakshadweep Kavaratti
5. Puducherry Puducherry
6. National Capital Territory New Delhi
7. Jammu and Kashmir Srinagar (summer), Jammu (winter)
8. Ladakh Leh


Have a quiz in the class on the capitals of the states and union territories of India.
Divide the class into two teams. The teacher will say the names of the states or union territories and the teams will tell the capital. Each team gets 2 marks for a correct answer and –1 for a wrong answer. Raise your hands to answer. Do not answer unless the teacher asks you to. Don’t look at the textbook while the quiz is going on.

The President of India lives in the Rashtrapati Bhavan in New Delhi. The Rashtrapati Bhavan is the second largest residence of a head of a country in the world. It has 340 rooms.

neighbouring countries: countries that share a border or are located close to each other across a sea or ocean
central government: governs the entire country
state government: governs specific states
union territory: it is not a state and is directly governed by the central government

Scan the QR code to learn more about the Rashtrapati Bhavan.


• India is the seventh largest country in the world by land area and the largest by population.
• India has 28 states and 8 union territories.
• India has two levels of government: Central government and State government.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these is NOT a neighbouring country of India?
a. Myanmar b. Japan
c. Sri Lanka
B. At what age can Indians begin voting in elections?
a. 25 years b. 40 years
C. Which of these is the capital of India?
a. New Delhi b. Mumbai
2. Fill in the blanks.
c. 18 years
c. Chennai
population Ladakh Arabian Union Territories
A. The Sea is on the west of India.
B. India is the largest country in the world by .
C. Parts of India that are governed directly by the central government are called .
D. Jammu and Kashmir and are Union Territories.


3. Match the following.
A. Ladakh i. Bengaluru
B. Karnataka ii. Hyderabad
C. Gujarat iii. Leh
D. Telangana iv. Gandhinagar
4. Answer the following questions.
A. What are state governments?
B. Name two countries that are India’s neighbours across the Indian Ocean.
C. What are those parts of India that have only one level of government called?
D. India has several neighbours. Should India have good relations with its neighbours? Give 2 reasons.
5. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Name the Indian states and union territories that are closest to Sri Lanka.
B. Name the Indian states and union territories that share border with Pakistan.
C. Name the Indian states and union territories that share border with Nepal.


Which states in India share a capital, and who governs that capital?

India has changed a lot over the last 20 years. Speak to the elderly people around you and ask them what changes do they see around them in India. Ask about changes in dressing styles, ways of communication, ways of living, facilities and so on.





The Himalayan Mountains
The Great Indian Desert
The Northern Plains Physical Features of India
The Southern Plateau The Coastal Plains
The Islands

Get Set

Rearrange the letters correctly. (Hint: These are names of countries.)
1. NIDAI
2. LNAKA RSI
3. IHCNA
India is a beautiful country. It has many mountains, rivers, deserts and plains. These are called landforms. A landform is a natural physical feature formed on the Earth.
There are six main physical features of India:
1. The Himalayan Mountains
2. The Northern Plains
3. The Great Indian Desert
4. The Southern Plateau
Six main physical features of India

5. The Coastal Plains
6. The Islands
Let us learn more about them.
The Himalayan Mountains lie in the northern part of India. They are the highest mountain ranges in the world. A row of mountains is called a mountain range. The weather in this region is cold and it is difficult to grow crops here. The highest mountain in the world, Mount Everest, lies in the Himalayas. Other famous mountains in the Himalayas include Kanchenjunga, Nanga Parbat and Nanda Devi. Many rivers such as the Ganga, the Yamuna and the Brahmaputra originate in the Himalayas. They are formed by the melting ice.
Remember!
India is located in Asia. It is the seventh largest country in the world by land area.

Snow-covered Himalayas
Error Alert!
Mount Everest is not located in India. It lies in China and Nepal. The highest mountain peak in India is Kanchenjunga.
The Northern Plains are flat lands to the south of the Himalayas. They are also known as the Indo-Gangetic Plains. Rivers like the Ganga and the Yamuna, that originate in the Himalayas, flow through these plains. This makes the plains fertile and suitable for farming.
Tenzing Norgay and Sir Edmund Hillary were the first men to reach the peak of Mount Everest in 1953. Did You Know? originate: start or begin fertile: soil that is good for growing plants

A farmer in his wheat fields in the Northern Plains


The weather here is hot during summers, cold in winters and receives rainfall in monsoons. The Northern Plains are densely populated. Many famous cities and towns such as New Delhi, Varanasi, Amritsar and Agra lie in these plains.
A desert is a large area of land which is covered with sand. Towards the northwestern part of India, lies the Great Indian Desert or the Thar Desert. Very few plants grow in it. It also has very, very little water. Life is difficult in deserts so they are not very populated. Camels are the most common form of transportation in the desert. Thus, they are called the ‘ship of the desert’.

What would you do if you had to spend a day living in the desert?
The Southern Plateau lies to the south of the Northern Plains. A plateau is higher than its surroundings and is flat at the top. It has steep sides. The Southern Plateau has a rocky, uneven surface and is less fertile than the Plains. Parts of the Southern Plateau have thick forests, and black soil, which is good for growing crops such as cotton. Many rivers such as Godavari, Krishna and Narmada flow through this region. The Southern Plateau is also called the Peninsular Plateau. densely: thickly

A plateau


Write whether the following statements are true or false.
1. The Great Indian Desert lies in the eastern part of India.
2. The Southern Plateau has black soil which is good for growing cotton.
3. The Ganga flows through the Northern Plains.
The narrow strips of flat land along the eastern and western sea coasts of India are called the Coastal Plains. The eastern and western coastal plains of India meet at Kanyakumari.

The coastal plains receive heavy rainfall, which is good for growing crops such as rice and maize. The weather is hot and humid. Many important ports of India are present here in cities such as Mumbai, Kolkata and Chennai. Coastal area humid: damp or moist port: a place where ships can load or unload goods

A beach in Lakshadweep Islands
A piece of land that is surrounded by water on all sides is called an island. India has two main groups of islands: the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal; and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea. Islands have moderate climate throughout the year. Many tribal groups also live on these islands. They have different ways of living than we do but they are an important part of our country. We must respect their different ways of life. All these physical features together make India a beautiful and unique country.



Divide into groups of six, each representing one physical feature. Find out how human activities are damaging that physical feature and what can be done to protect it.
Srinagar, located in the Himalayan region of India, is known for its ‘floating markets’ in the Dal Lake. There the shopkeepers sell items of daily use in long boats called shikaras.


landforms: natural physical features on the earth mountain range: a row of mountains desert: a large area of land covered with sand plateau: it is higher than its surroundings, flat at the top and has steep sides islands: a land surrounded by water on all sides

Scan the QR code to learn more about the beauty of the Himalayas.
• The Himalayas are in the northern part of India.
• The Northern Plains are fertile and suitable for agriculture.
• The Coastal Plains meet at Kanyakumari.
• India has two main island groups: the Andaman and Nicobar Islands; and the Lakshadweep Islands.

1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which is the highest peak in India?
a. Mt Everest
b. K2
B. Which animal is called the ‘ship of the desertʹ?
a. Camel
c. Kanchenjunga
b. Elephant c. Horse
C. What is the other name for the Northern Plains?
a. Indo-Gangetic Plains
c. Yamuna-Ganga Plains
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Indus Plains
Northern Plains seventh agriculture Lakshadweep
A. India is the largest country in the world in terms of area.
B. is the main occupation of most of the people living in the Northern Plains.
C. Amritsar is an important city in the .
D. The islands lie in the Arabian Sea.
3. Match the following.
A. Andaman and Nicobar i. Northern Plains
B. Mumbai ii. Islands
C. Delhi iii. Coastal Plains
D. Nanda Devi iv. Himalayas
4. Answer the following questions.
A. Name the six main physical features of India.
B. Where do the eastern and western coastal plains meet?


C. Describe the coastal plains of India.
D. Write two things that are special about the landform that lies to the south of the Himalayas?
5. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Name the physical feature shown here.
B. Where is it present in India?
C. Name any two rivers that flow in this region in India.



Jeetu’s uncle is a farmer. He wants to buy land to grow different crops. Name the part of India where he should buy land. Give 2–3 reasons to explain your choice.
Find out about people from India who have climbed the peak of Mt Everest. Learn about their challenges and how they overcame them.




Get Set

Look at this map of a neighbourhood. Find and circle the hospital, the train station, the bus stand and the sports stadium.

Civic amenities are also called public facilities. They are provided to all the people of the country to ensure their welfare. Things like roads, streetlights, parks, government hospitals, transport, garbage collection, supply of clean drinking water, electricity, etc. are examples of civic amenities. The local government bodies provide these civic amenities in villages, towns and cities.
In villages, the local government body is the Gram Panchayat. The members of the Gram Panchayat are elected by the Gram Sabha. The Gram Sabha consists of all the villagers who are 18 years or above.


The head of the Gram Panchayat is known as the Pradhan or Sarpanch. The Sarpanch is chosen from among the members of the Gram Panchayat. In India, every Gram Panchayat needs to have at least one third or more women members.
A Gram Panchayat office
Did You Know?
Chhavi Rajawat was the first woman sarpanch in India. She became the sarpanch of Soda village in Rajasthan in 2010.
The Gram Panchayat meets regularly to discuss the problems and needs of the villagers. Some of the responsibilities of the Gram Panchayat are:
• To keep the village clean.
• To build and maintain village roads and streetlights.
• To provide clean and safe drinking water.
• To provide education to children and adults.
welfare: good health and happiness elect: to choose someone for a position



• To provide and run health centres.
• To solve problems and small disputes among villagers.
• To provide support to farmers and small industries in the village.



Clean drinking water in a village A health checkup camp in a village Children studying in a village school
Tick (✓) the correct statements.
1. Civic amenities are only for the rich.
2. The Gram Panchayat solves disputes among villagers.
3. The Gram Panchayat consists of only men.
4. Clean drinking water is a civic amenity.
Do
Along with your teacher and classmates, identify ways to make improvements in your classroom. Do at least three things to improve your classroom.
Local government bodies provide public facilities in towns and cities. A Municipal Council provides public facilities in towns. The members of the Municipal Council are known as Municipal Councillors. The head of the Municipal Council is the Chairperson.
disputes: arguments


A Municipal Corporation provides public facilities in cities. The head of a Municipal Corporation is called the Mayor. People vote and elect the members of the Municipal Council and the Municipal Corporation. Everyone who is 18 years of age or above can vote in these elections.
Some of the main functions of the Municipal Corporation and the Municipal Council are:
Why is it important for the Municipal Corporation to keep the parks and streets clean? How do you think this helps people?
• To keep the city clean by collecting and disposing of garbage, and providing clean and usable public toilets.
• To provide clean and safe drinking water.
• To provide medical centres and hospitals.
• To provide free and compulsory education for children up to the age of 14.
• To construct and repair roads, footpaths and streetlights.
• To organise literacy programs for adults.
• To keep records of births and deaths, and issue birth and death certificates.
As responsible citizens, it is our duty not to damage parks, streetlights and other facilities provided by the government.

Road construction in a city

A government hospital in Delhi
If you were the mayor or chairperson of your city or town, what would be three new public amenities that you would introduce to improve the lives of your citizens?
We have learnt how the Gram Panchayat, the Municipal Council and Municipal Corporation perform so many functions. But all of these activities need money. Where does that money come from?
literacy programs: programs to teach how to read and write



They receive money from the government to perform these functions. Apart from that, they also use the tax money. The government collects money from the people according to their income to provide various public services. This money is called tax. People pay different taxes, such as road tax, property tax and so on.
The Greater Mumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC) is the largest municipal corporation in India and Asia. It is also the richest municipal corporation in India.

civic amenities: services that are provided to the people by the government gram panchayat: elected members of gram sabha gram sabha: all the villagers who are 18 years or above pradhan or sarpanch: head of the gram panchayat municipal council: provides public facilities in towns municipal corporation: provides public facilities in cities mayor: the head of a municipal corporation of the city tax: money collected by the government from the people according to their income

• In villages, a Gram Panchayat looks after the welfare of people by providing civic amenities.
• A Municipal Council provides civic amenities in towns.
• A Municipal Corporation provides civic amenities in cities.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What are the members of the Municipal Corporation called?
a. Sarpanch
c. Gram Sabha
b. Municipal Councillors
B. Who is the head of a Gram Panchayat?
a. Mayor b. Sarpanch
c. Principal
C. What is the local government body of a town called?
a. Municipal Council
c. Gram Sabha
b. Gram Panchayat
2. Fill in the blanks. mayor sarpanch chairperson tax
A. The is the head of the Municipal Corporation.
B. The money collected from people by government to provide various public facilities is called .
C. The head of a Municipal Council is called the .
D. The head of a Gram Panchayat is called the .
3. Write True or False.
A. The Gram Panchayat is responsible for maintaining roads and streetlights in villages.
B. The chairperson is the head of a municipal corporation.
C. The Gram Panchayat provides clean drinking water in large cities.
D. Municipal Corporations get money from the government.

4. Answer the following questions.
A. Write any three functions of the Gram Panchayat.
B. Who elects the members of the Municipal Corporation?
C. Write any three functions of the Municipal Council.
D. Where do local government bodies get their funding from?
5. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given pictures and answer the following questions.



A. Identify the pictures which show the functions performed by the Municipal Corporation?
B. From where would the Municipal Corporation get funds to perform these functions?

Radha lives in a village while her cousin lives in Delhi.
1. What would be the difference in the local government bodies of their places?
2. Write three similarities in the roles of the local government bodies in their places.

With the help of your parents, visit the office of the local government or talk to someone who works there. Ask them how they help keep your neighbourhood clean and safe. Can you think of one way you and your family can support their efforts in your community? Share that information with your class.



Chapter Overview

National Symbols
Great Leaders

Get Set

You must have seen the Indian flag being hoisted in your school or nearby places. Colour the Indian flag given below.
National symbols represent a nation’s culture and values and work as its identity. Let us learn about the national symbols of India.
identity: who someone or something is


The National Flag of India is rectangular and is a tricolour, meaning it has three colours. It has three equal-sized bands of saffron, white and green. The saffron band at the top represents strength and courage. The white band in the middle stands for truth and peace. The green band at the bottom stands for growth and prosperity. The white band has the navy blue Ashok Chakra in the centre. The Chakra has 24 spokes.
To respect our national flag, we must make sure that:
• It is never kept on the ground.
• There should be no other flag above it.
• The saffron band should be at the top.
• The flag should be carried over our right shoulder.
• It should be held in the front of a gathering.
• We should never hoist a torn or a dirty flag.

The Indian National Flag The National Flag of India was designed by Pingali Venkayya in 1921. Did You Know?
The National Emblem is used as a seal by the government of India. It can be seen on coins and currency notes. It can be seen on government documents and letters too. The seal has four lions that face the four directions. At a time, only three are visible at once. The base of the emblem has a horse, a bull, an elephant and a lion. Each are separated by a wheel. At the bottom, the words 'Satyameva Jayate' are written. It means 'truth always wins'.
prosperity: a condition in which people are happy spokes: rods in a wheel connecting the outer circle to the centre

The National Emblem of India


Our National Anthem is Jana-Gana-Mana. It was written by the famous poet Rabindranath Tagore. The song talks about the beauty and diversity of India. When it is played, everyone should stand in attention to show respect and love for our country.
Error Alert!
Jana-Gana-Mana is not our National Song. It is our National Anthem. The national song of our country is Vande Mataram. It was written by Bankim Chandra Chatterjee.
Our National Animal is the Royal Bengal Tiger. It is the symbol of strength, power and grace. The Royal Bengal Tiger is protected in national parks because it is an endangered animal. India gives importance to protecting its wildlife.


The Indian Government started Project Tiger in 1973. It aimed at protecting tigers and increasing their population. Did You Know?
Our National Bird is the peacock. It stands for beauty and grace. It is found across India and has an important place in Indian art and culture.

diversity: having many different people, cultures, languages, etc. national park: a forest area protected by the government endangered: a category of animals or birds which is at risk of dying out


Our National Flower is the lotus. It is also an important part of Indian art and culture. It represents truth, knowledge and wealth.


Find out the names of any three national parks in India and the states in which they are located.
India has had some great leaders who inspire us. Leaders like Mahatma Gandhi, Mother Teresa and Jawaharlal Nehru lived their lives serving the people. We can learn many important lessons and values from their lives.
Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi is also known as the Father of the Nation. He was born on 2nd October 1869 in Porbandar, Gujarat. His complete name was Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi. Rabindranath Tagore gave him the title of Mahatma. He studied law in London and later went to South Africa to work as a lawyer. He soon returned to India and helped India become free from the British rule.

He believed in non-violence, truth and simple living. From his life, we can learn the importance of honesty, kindness and standing up for what is right without hurting others. Gandhi’s values continue to guide and inspire us even today. He passed away on 30 January 1948.
inspire: to motivate someone to do something non-violence: not harming others


Jawaharlal Nehru
Jawaharlal Nehru was the first prime minister of our country. He was born on 14th November 1889 in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh. He studied law and worked as a lawyer for many years. He played an important role in our freedom struggle against the British. He was very fond of children and every year his birthday is celebrated as Children’s Day. He passed away on 27 May 1964.
Mother Teresa
Mother Teresa was born on 26 August 1910 in North Macedonia in Europe. At the age of 19, she moved to India as a nun.


She started a group called the Missionaries of Charity in 1950. Here, she and the other nuns worked hard to feed the hungry, take care of the sick, and provide shelter to the homeless. She passed away on 5 September 1997. She is remembered for her kindness. She was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize in 1979 for the work she did to help people in need.
The Ashoka Chakra is named after Emperor Ashoka who ruled India long ago. The Ashoka Chakra reminds us of his message that true strength comes from peace and living with good values.

national symbol: something that represents a nation’s culture and values, and works as its identity
national emblem: a symbol of the nation which is used for official work
nun: a religious woman who spends her life in service of the poor and needy



Scan the QR code to learn more about the national song of India.
• The National Flag of India has three colours: saffron, white and green.
• Mahatma Gandhi is known as the Father of the Nation.
• Mother Teresa cared for the poor, sick and needy.
• Jawaharlal Nehru was the first prime minister of India.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Whose birthday is celebrated as Children’s Day in India?
a. Mahatma Gandhi
c. Jawaharlal Nehru
b. Mother Teresa
B. What does our national flower stand for?
a. Knowledge
c. Beauty
b. Power
C. Which is the national animal of our country?
a. Lion
c. Horse
2. Write True or False.
A. Jana-Gana-Mana is our national song.
b. The Royal Bengal Tiger
B. Mahatma Gandhi was the first prime minister of India.
C. Mother Teresa was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for helping the needy.
D. The National Emblem has a peacock at the top.


3. Match the following.
A. National Anthem i. Mahatma Gandhi
B. National Song ii. Jana-Gana-Mana
C. First prime minister iii. Vande Mataram
D. Father of the Nation iv. Jawaharlal Nehru
4. Answer the following questions.
A. What are some rules we must follow to respect our National Flag?
B. What is the meaning of words ‘Satyameva Jayate’?
C. Where can we see the national emblem being used?
D. Which prize was Mother Teresa awarded for the work she did?
E. ‘At the top there are four lions, at the base it has a horse, a bull, an elephant, and a lion.’ What is being described here?
5. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Name the animal shown in the picture.
B. Why is this animal important to India?


If you had to create a new national symbol for India, what would it be and how would it represent important values or features of our country?
Make a scrapbook titled ‘Great Leaders of India’. Paste pictures of three leaders from our country; write their names under their pictures and any two values that they stood for. Make sure not to choose the leaders about whom you have just learnt. Share the scrapbook with your class and talk about the leader and the values that inspire you the most.















Look at the pictures. Follow the given hints and write the correct names of the monuments.

(Hint: It is a monument in the memory of Indian soldiers.)

(Hint: The Prime Minister of India hoists the National Flag here on Independence day.)
Delhi is the capital of India. It is also known as the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). It is in the northern part of India. It is bordered by Uttar Pradesh and Haryana. The Yamuna river flows through the city. Delhi is located in the

Northern Plains. So it gets very hot in summers and becomes very cold during winters. Delhi receives good rainfall during the monsoons in July and August.
Since New Delhi is the capital of our country, all important government offices are located here such as the Rashtrapati Bhavan, the Parliament and the Prime Minister's Office (PMO). The President of India lives in the Rashtrapati Bhavan. The Prime Minister’s office is in the South Block. The Parliament, the High Commissions and Embassies of other countries are also in Delhi.
Delhi is a union territory. Even though union territories don’t have a chief minister, Delhi has one. It is because it’s a very big and important city where many people live and work. The chief minister helps take care of the city to make sure everything runs smoothly.
Delhi has many transport options like taxis, buses and the metro rail. The Delhi Metro Rail connects Delhi with neighbouring cities like Noida, Gurugram, Ghaziabad, etc.
The city bus service, called the DTC (Delhi Transport Corporation), connects different parts of the city.

Delhi Metro is India’s busiest and largest metro rail network. It runs both above and underground. It was started in 2002.
The Indira Gandhi International Airport in Delhi connects it with major cities of India and the world. The Old Delhi Railway Station and the New Delhi


Railway Station are two major railway stations. Delhi has a wide network of roads too.



With the help of your partner, find the map of the Delhi Metro on the internet. Learn about the metro routes for some important places like Chandni Chowk, Red Fort, New Delhi Railway Station and India Gate.
Delhi is famous for its street food like chaat, chole kulche, etc.
People living in Delhi celebrate many festivals like Holi, Diwali, Eid, Onam, Durga Puja, Christmas, etc. Delhi is the main centre for Independence Day and Republic Day celebrations as well.
Hindi is spoken by most of the people of Delhi. Other languages like English, Urdu and Punjabi are also spoken in the city.
People mostly wear light cotton clothes in the summer and woollens in the winters. All kinds of traditional and modern clothing, from sarees and salwar kameez to jeans and T-shirts, can be found here.





Circle the correct word.
1. Delhi is situated on the banks of river Yamuna/Ganga.
2. Indira Gandhi International Airport/India Gate International Airport is in Delhi.
3. Delhi Transport Corporation runs the local trains/buses of Delhi.
Delhi has many famous places that attract tourists from India and abroad. The Red Fort in Delhi is of great significance for India. Every year on Independence Day, the prime minister of India hoists the National Flag here. Jama Masjid is another popular monument visited by tourists from all over the world.



Other famous places to visit in Delhi are the Qutub Minar, Jantar Mantar, the Nehru Planetarium, the Lodhi Garden, India Gate, Raj Ghat, Humanyun’s Tomb, Lotus Temple and Akshardham. Whenever we visit these places, we must obey the rules of that place and not harm the buildings in any way.
Khari Baoli is a street in Old Delhi which is Asia’s largest spice market. It sells a variety of spices, nuts, herbs, rice and tea.

A view of the Khari Baoli market
tourist: a person who travels to different places when they are on holiday significance: importance hoist: raise something high using ropes


metro rail: an electric railway system within a city which can be underground, on the surface, or raised on pillars

Scan the QR code to learn more about famous places in Delhi.
• Delhi is situated on the banks of Yamuna.
• New Delhi is the capital of India.
• Delhi is very hot in the summer and very cold in the winter.
• There are many famous tourist places in Delhi like the India Gate, the Lotus Temple and the Jama Masjid.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Delhi shares its boundary with
a. Uttar Pradesh and Punjab
c. Haryana and Uttar Pradesh
B. What is Delhi known as?
a. The National Capital
Territory of Delhi
c. The National Coastal Territory
b. Haryana and Punjab
b. The Royal City of India
C. Which of these is a famous tourist attraction in Delhi?
a. Taj Mahal
c. Red Fort
b. Konark Temple

2. Fill in the blanks.
Jama Masjid Qutub Minar Red Fort South Block
A. The Prime Minister of India hoists the national flag at the on Independence Day.
B. The Prime Minister’s Office is located in the .
C. is a famous mosque in Delhi.
D. is a famous tower in Delhi.
3. Write True or False.
A. The President of India's office is in the South Block in Delhi.
B. Delhi is located in the Great Indian Desert.
C. The Gateway of India is a famous place in Delhi.
4. Match the following.
A. Khari Baoli i. President of India
B. South Block ii. Prime Minister's Office
C. Rashtrapati Bhavan iii. Largest spice market in Asia
5. Answer the following questions.
A. What type of climate does Delhi have?
B. Name any two types of local transport in Delhi.
C. Which languages are spoken in Delhi?
D. Can cotton clothes be worn year round in Delhi? Why or why not?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Which place is this?
B. Why is this place important?




Delhi has people from different states living together. How do you think this mix of cultures influences the food, festivals and languages spoken in the city?
Collect pictures of famous tourist places of Delhi. Look for pictures in newspapers, magazines, and on the internet. If you have visited Delhi, then you can use pictures from your trip as well. Make a collage of all the collected pictures. Give your collage a creative title. Display the collage in your class.






All of us like watching films. Can you guess which city of India is famous for making films?

















financial: relating to money
























Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra. It is situated on the western coast of India, near the Arabian Sea.
Mumbai was earlier known as Bombay. Since it is the capital of the state, all the important state government offices of Maharashtra are located here. The chief minister, the governor and other ministers of the state also live in Mumbai. Mumbai is called the ‘Financial Capital of India’.


Mumbai is made up of seven islands. The British joined these seven islands through bridges to make one island. Did You Know?
Mumbai has a moderate climate. It is located near the sea so it is neither too hot nor too cold throughout the year. Mumbai receives heavy rainfall during monsoons.
Look at the politcal map of India in an atlas and make a list of the states neighbouring Maharashtra.
on the map of India
Mumbai has a wide network of public transport for travelling within the city. It includes local trains, metro, auto rickshaws and buses. Local trains connect different areas within Mumbai and the surrounding areas. Flights, ships and trains also connect Mumbai to other places across India and the world. The Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport in Mumbai is the second busiest airport in India. It connects Mumbai with major cities across the world. Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus, earlier known as Victoria Terminus, is an important railway station of Mumbai. Mumbai is also an important port city on the western coast of India. The Jawaharlal Nehru Port, also known as the Nhava Sheva Port, is a famous port in Mumbai.
moderate: medium


People waiting to board a local train in Mumbai.


Nhava Sheva Port

The British had started building Victoria Terminus in 1878. It took them 10 years to complete it.
Many important industries are located in Mumbai like cotton, electronic goods, textiles, medicines, oils and chemicals.
Bombay High, in the Arabian Sea, is an important oilfield in India.
The Hindi films industry is also located in Mumbai. It is known as Bollywood.
Tick ( ) the correct option.
The film industry in Mumbai has helped create many jobs for the people living there. Do you agree? Discuss with your friends.
1. Bombay High is in the Arabian Sea/Bay of Bengal.
2. The film industry in Mumbai is called Bollywood/Hollywood.
3. Mumbai is on the western/eastern coast of India.
The Nauvari saree is a traditional dress worn by most women in Mumbai. It is longer than other sarees. The traditional dress for men is a dhoti with a shirt or kurta. Both men and women also wear a turban known as pheta.

oilfield: an area under the sea where oil is found


Marathi is the main language spoken by people in Mumbai. Other languages, such as Gujarati, Hindi and English, are also spoken here. Vada pao, pao bhaji, ragda pattice, bhelpuri and poha are some of the famous street food in Mumbai. Shrikhand is a popular sweet dish that people eat there.


Ganesh Chaturthi is the most important festival of Mumbai. It is celebrated for many days across the city. At the end of the festival, idols of Lord Ganesh are immersed in the sea.


Nowadays, people have begun using Ganesh idols made of eco-friendly material and even immerse them in large tubs of water outside their homes so that the sea does not get polluted. Other major festivals like Diwali, Holi, Eid and Christmas are also celebrated in Mumbai.
Mumbai is a popular tourist destination for both Indians and foreigners. The Gateway of India is a famous tourist spot of Mumbai.
Since Mumbai is located close to the sea, it has many beaches such as Chowpatty, Versova, Marve and Juhu. People enjoy spending time at these beaches.
A long road along the seacoast, known as the Marine Drive, is another beautiful tourist attraction.
immerse: to put something in water completely eco-friendly: something that does not harm the environment





Other famous places are the Elephanta caves, the Hanging Gardens, Jehangir Art Gallery, Taraporewala Aquarium, Haji Ali and the Siddhivinayak Temple.
The dabbawalas of Mumbai are amazing delivery people who bring fresh, home-cooked lunch to thousands of office workers every day. They use bicycles, buses and trains to deliver lunchboxes. The dabbawalas are experts and they do not make any mistakes.


Mumbai dabbawallas carrying lunchboxes
local trains: trains that connects different places Bollywood: the Hindi film industry located in Mumbai nauvari: a traditional saree worn by women in Maharashtra pheta: a traditional Marathi turban worn by men and women

Scan the QR code to learn more about life in Mumbai.
• Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra.
• It is situated on the western coast of India, near the Arabian Sea.
• Ganesh Chaturthi is the most important festival of Mumbai.
• Marathi is the main language spoken in Mumbai.
• The main traditional dresses worn in Mumbai are the nauvari saree, and dhoti-kurta.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What was the old name of Mumbai?
a. Bombay b. Maharashtra c. City of Dreams
B. What type of climate does Mumbai have?
a. Hot
b. Moderate c. Cold
C. Mumbai is located near which water body?
a. Arabian Sea b. Bay of Bengal c. Indian Ocean
D. What is the traditional dress of women in Mumbai?
a. Salwar-kameez b. Skirt and blouse c. Nauvari sari
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. is the most important festival celebrated in Mumbai.
B. and are popular street food of Mumbai.
C. is the main language spoken by the people of Mumbai.
D. Mumbai is the capital of .
3. Write True or False.
A. The Hindi film industry is situated in Mumbai.
B. Mumbai is a port city.
C. Marine Drive is a famous tourist attraction in Mumbai.
D. People in Mumbai wear only saris and dhotis.

4. Match the following.
A. Pheta i. Oil field
B. Chowpatty ii. Famous food
C. Bombay High iii. Traditional clothing
D. Vada Pao iv. Beach
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Where is Mumbai located?
B. Name three famous tourist places in Mumbai.
C. Will it be correct to say that Mumbai is one of the most important cities of India? Give two reasons.
D. What is Bombay High?
E. Name the most important festival celebrated in Mumbai.
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Name the place shown in the picture.
B. Which sea is it located next to?
C. Is there any port in this city? If yes, name it.


Mumbai is one of the busiest cities in India. How do you think the city's location on the coast helps it to be an important centre for trade and industry?




Many people shift from their city to Mumbai in search of work and to make their lives better. Discuss with your parents or elders some of the challenges people might face while adjusting to a new city or state.
Use the internet to research some famous street food of Mumbai. Try to make any one of them at home, with your parents' help. Tell your classmates how you liked that dish.




Chennai
Location and Climate Culture Transport and Industries
Famous Places


Cricket is a popular sport for many of us. Can you identify the cricket team icon shown in the given picture?
(Hint: It is named after a famous city in southern part of India.)

In the previous chapters, we learnt about Delhi and Mumbai. Let us now learn about another important city of India, Chennai. Chennai is the capital city of Tamil Nadu. It was earlier known as Madras.

Chennai is located on the southeastern coast of India, facing the Bay of Bengal. Chennai has a hot and humid climate throughout the year. It receives rain mainly from October to December.
Since it is the capital of the state, the governor, chief minister and other important ministers work here. All the important government offices of the state are also situated here.
Chennai is known as ‘India’s health capital’ as it has some of the best hospitals and medical services in India.
Chennai on the map of India
Chennai is well connected to other cities in India and abroad. The Chennai International Airport connects the city with major cities of India and the world. The M.G. Ramachandran Central Railway Station, earlier known as Madras Central, is the main railway station of Chennai. Within the city, one can travel via the metro, local city buses, taxis and auto-rickshaws. The Chennai Metro was started in 2015.
Chennai is a port city as well. The Chennai Port is a very busy port. Ships carry goods to other countries from here. Goods from other countries are also brought to India from this port.


Chennai port

port city: a city located close to the sea and built around a port

Some important industries in Chennai are information technology (IT), cotton textiles, leather, and oil refineries. There are many factories in Chennai that make cycles, railway coaches, trucks and cars. There is a tank manufacturing industry at Avadi in Chennai. Chennai is also famous for its film industry, which is also called Kollywood.

Kanjeevaram sarees are worn by most women in Chennai. Kanjeevaram saree
People in Chennai mostly speak Tamil. Bharatnatyam is a famous dance form and Carnatic music is the most popular type of music here. Both men and women perform Bharatnatyam.
All major festivals of India are celebrated in Chennai. Pongal, which is the harvest festival, is the most important festival in Chennai. It is celebrated with great joy for four days. Karthigai Deepam is another important festival.

Food items of Chennai

People in Chennai eat rice with sambar, rasam, poriyal and curd. Rice is the staple diet here. Dosa, idli, upma, and vada are some of the important dishes of Chennai. Kesari is a famous sweet dish of Chennai.
As the weather of Chennai is hot and humid all year round, people wear cotton clothes. Traditional clothes of men are veshti and shirt. Women wear cotton sarees and blouses. Girls can be seen wearing pavadai.
Do people need woollens in Chennai?
textiles: relating to garments harvest: when crops are ready to be cut and collected from the fields veshti: white unstitched cloth wraps for the lower body pavadai: a long skirt in a cone shape that is tied around the waist


Famous chess player and Olympic gold medalist, Vishwanathan Anand, is from Chennai. Sports keep us healthy and fit. So, we must always play some kind of sport.
Tenzin lives in Leh. He visits Chennai during the winter vacations. Discuss how different the weather of Chennai would be for him.
Circle the correct word.
1. Tamil/Telugu is the language spoken in Chennai.
2. Pongal/Ugadi is the festival celebrated in Chennai.
3. Hindustani/Carnatic music is a popular form of music in Chennai.
Chennai is a famous tourist destination and several Indian and foreign tourists visit it every year. There are many famous temples in Chennai like the Kapaleeswarar temple, the Parthasarathy temple and the Sri Vadapalani Andavar temple.
Fort St George, the Golden Beach, St Thomas Church, the Snake Park, the Gandhi Mandapam, and Guindy National Park are some other famous places in Chennai. The Marina Beach in Chennai is the longest beach in India. Blackbuck, jackal, spotted deer, snake, and tortoise are some animals protected in the Guindy National Park.





The Government Museum, or the Madras Museum, is the second oldest museum of India and it is located in Chennai. It was started in 1851. It is owned by the Government of India. It has the largest collection of Roman antiquities (objects from ancient times) outside Europe.
kanjeevaram: special silk sarees worn in Chennai staple: a food item which is eaten almost daily Word Splash


The Government Museum, Chennai
Scan the QR code to learn more about the famous Marina Beach of Chennai.
• Chennai is the capital of Tamil Nadu.
• The climate of Chennai is hot and humid.
• Bharatnatyam is the famous dance form of Chennai. Carnatic music is a popular type of music in Chennai.
• People mostly speak Tamil in Chennai.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer. A. Chennai was earlier known as a. Madras b. Madurai c. Coimbatore


B. Which of these is a famous place in Chennai?
a. St James Church b. St Thomas Church
c. St Thomas Cathedral
C. Chennai is situated facing the a. Bay of Bengal b. Arabian sea c. Caspian Sea
D. The famous dance form of Chennai is a. Kathak b. Kuchipudi c. Bharatnatyam
2. Fill in the blanks.
pavadai Avadi Guindy Marina Beach
A. Tanks are manufactured in in Chennai.
B. National Park is situated in Chennai.
C. is the longest beach in India.
D. Young girls in Chennai wear .
3. Write True or False.
A. Chennai is located on the southwestern coast of India.
B. Metro rail was started in 2015 in Chennai.
C. Chennai has a cold winter season.
D. Chennai does not have a port.
4. Match the following.
A. Kesari i. Form of music
B. Veshti
C. Carnatic
D. Pongal
ii. Celebrated for four days
iii. Men’s clothing
iv. Sweet Dish

5. Answer the following questions.
A. What are some of the major industries of Chennai?
B. Name any three famous tourist places in Chennai.
C. What kind of clothes are worn by the people of Chennai? Give examples.
D. How is the weather in Chennai different from Delhi?
E. Which are the popular dance and music forms of Chennai?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the questions.
A. Which famous clothing item is shown in the picture?
B. Which state of India does it belong to?


Chennai and Mumbai are both located near the sea. What are some of the similarities and differences between the two cities?

Pongal is the harvest festival celebrated in Chennai. Find out why is it celebrated and when is it celebrated? You can research on the internet under your parent’s guidance. Discuss whether your family also celebrates a harvest festival or not.



Chapter Overview

Location and Climate Culture Transport and Industries
Famous Places

Get Set

Read the poem given below with your partner.
Kolkata’s streets are full of cheer, With trams and buses far and near.
The Howrah Bridge stands tall and wide, Over the river, boats gently glide.
In Kolkata, smiles are always bright, Like the city’s glowing light.

Kolkata is the capital of West Bengal. Since it is the capital of the state, all important government offices are situated here. The governor and the chief minister of the state also live here.

Kolkata is located on the banks of the Hooghly river. It is also an important port city
As you can see on the map, Kolkata is located near the sea. So, it is neither too hot in summers nor too cold in winters. It receives heavy rainfall in monsoons.
Kolkata’s old name was Calcutta. This name was given by the British. It was the capital of the British Empire in India till 1911. After that, New Delhi became the capital of India.
Kolkata on the map of India
Hooghly and Ganga are not different rivers, as many people may think. Hooghly is the name given to the Ganga river when it enters West Bengal. Error Alert!
Kolkata’s transport system is very interesting. It is a mix of the old and the new. It has trams, which are not there in any other city in India. On the other hand, it has the modern underground metro as well. A part of this metro also runs underwater.

port city: a city built around a port



It has an airport called the Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport. Kolkata also has a port named the Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port. It is the oldest operating port in India. Kolkata has two main railway stations: The Howrah Station and the Sealdah Station.

Howrah and Kolkata are known as twin cities. Howrah lies on the western bank of the Hooghly River. Kolkata lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River. They are connected to each other by the Rabindra Setu (the Howrah Bridge) and the Vidyasagar Setu.
There are several industries in Kolkata such as jute, rice, rubber, textiles, paper and chemicals.
India’s first metro rail was started in Kolkata in the year 1984. India’s first underwater metro rail is also in Kolkata. It started in 2024.
Tick (✓) the statements that are correct.
1. Kolkata’s old name was Calcutta.
2. Kolkata has jute industry.
3. Kolkata is close to the Arabian Sea.
4. Howrah is the twin city of Kolkata.
5. Kolkata's airport is known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee airport.
twin cities: two cities that are similar in size, culture and activities that happen there


Kolkata is an important centre of Indian art and culture. Many great Indian writers, artists and musicians have come from Kolkata. The main language spoken in Kolkata is Bengali.
Rabindranath Tagore was the first Indian and Asian to receive a Nobel Prize in literature for his famous work Geetanjali. He also wrote our national anthem.
Most people in Kolkata eat food such as rice and fish. Sweets such as roshogolla, sandesh and mishti doi are very popular in Kolkata.

Rabindranath Tagore


The main festivals celebrated in Kolkata are Durga Puja and Kali Puja. Big idols of goddesses are specially made for Durga Puja and large pandals (tents) are put up across the city. People celebrate this festival with great joy, and in large numbers, for five days.

People in Kolkata mostly wear pants, shirts and sarees. Traditional clothes like dhuti and panjabi are worn in ceremonies or festivals.
Find out the names of five famous people from Kolkata. They can be writers, artists, musicians, politicians or sports persons.


Kolkata has many famous tourist attractions.
The Howrah bridge is built on the Hooghly river. It is one of the most famous tourist attractions. The Howrah bridge was renamed as Rabindra Setu in the year 1965. Another famous bridge, called the Vidyasagar Setu, has also been built on the Hooghly river.

The Victoria Memorial is another popular tourist attraction. Other famous places to visit are Fort William, the Alipore Zoo, the Botanical Gardens, the Birla Planetarium, the Rabindra Sarovar, the Belur Math, and the Indian Museum (the oldest and the largest museum of India). The famous cricket ground Eden Gardens is also in Kolkata. These are important places. We must not damage these places while visiting them.



College Street in Kolkata is the largest book market in India and Asia. It is also the world’s largest market to buy used books.

tram: a vehicle that runs on tracks that are laid out on the street
metro: a railway that is used to travel within a city; and which runs on electricity
museum: a place where interesting objects are kept for people to see



Scan the QR code to know more about Kolkata.
• Kolkata is the capital city of West Bengal.
• Bengali is the main language spoken in Kolkata.
• It has many industries like jute, paper, textiles, chemical and rice.
• The main festivals of Kolkata are Kali Puja and Durga Puja.
• Some of the famous tourists attractions are Fort William, the Alipore Zoo, the Botanical Gardens, the Birla Planetarium, the Rabindra Sarovar, and the Belur Math.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Kolkata is the capital of which state?
a. Bihar
b. Maharashtra c. West Bengal
B. Kolkata is located on the banks of which river?
a. Yamuna
b. Hooghly c. Godavari
C. Which is the most important festival of Kolkata?
a. Durga Puja
b. Ganesh Chaturthi c. Onam
D. What is the main language of the people of Kolkata?
a. Tamil
b. Bengali
c. Odia


2. Fill in the blanks.
Sandesh Eden Gardens Rabindranath Tagore Rabindra Setu
A. is a famous sweet of Kolkata.
B. is a famous cricket ground in Kolkata.
C. was a famous poet who wrote our national anthem.
D. The new name of the Howrah Bridge is the .
3. Write True or False.
A. The Vidyasagar Setu has been built on the Hooghly river.
B. Kolkata has an underwater metro rail.
C. Rice and fish are the staple food of Kolkata.
D. Kolkata has one main railway station.
4. Answer the following questions.
A. Name any two tourist attractions of Kolkata.
B. Name any two important industries of Kolkata.
C. What are the different forms of transport that can be found in Kolkata?
D. Which are the main festivals of Kolkata and how are they celebrated?
5. Picture-based questions.
A. Look at the map. Which water body is near Kolkata?
B. Why do you think fish is a popular food item there?
C. Kolkata is located near the sea. Describe its climate.



How do you think is Kolkata different from Delhi? How is it similar?

Durga Puja is a famous festival. It is celebrated with a lot of enthusiasm in Kolkata. With the help of your parents or elders, find out how is it celebrated in your city? Write 3 points about it.
Imagine that you are visiting Kolkata with your family for a holiday. Discuss with your family and plan your travel, as follows:
Dates:
Mode of travel:
Clothes you will pack:
Places you will visit:
Food you will eat:


Objective: Make a travel planner for a visit to a city.
Materials Needed: pens and pencils, online research tools like the internet
Step 1: Get Ready: Choose a city and the month in which you plan to travel.
Step 2: Research: Use the internet or the journals to know about the weather, famous tourist spots, food and culture of the city.
Step 3: Create the Travel Plan: Create a fun travel plan and fill in the table below!
Day
1 City I will travel to: What will I pack: Mode of travel:
Tourist attractions and famous dishes
Days 2 and 3 Key places I will visit: Food I will try:
Travel back home Day 4
One fun thing I will do before I leave: Things that I may buy:
Project Output: You now have a beautiful 4-day travel planner for a visit to the city of your choice.
Final Outcome: This project will help you develop your ability to research and plan. It also promotes awareness and appreciation for different regions in India.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.

Read the report. Answer the questions given below. Floods in Barabanki
Barabanki is a city in North India. During monsoons, the city gets flooded. It happens because of the poor drainage system as rainwater gets collected in many areas and does not flow away. It makes life difficult for people. Many houses and shops also get damaged due to floods. The rainwater mixes with garbage and sewage water. That leads to the spread of diseases. It also attracts mosquitoes that leads to diseases caused by mosquito bite, such as dengue and malaria. People don’t know how to solve this annual problem of flooding. These challenges make life hard for people during and after heavy rains.

1. Which diseases are caused due to mosquito bite?
a. Cold and cough
b. Dengue and malaria
c. Fever and vomiting
2. Which government body is responsible for cleaning the city and making sure that heaps of garbage don’t lie around?
a. the Panchayat
b. the Municipal Corporation
c. the Police
3. Write two problems that people face due to poor drainage system.
4. If you were a member of the local government, write three things that you would do to maintain cleanliness in your city.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.












The Food We Eat Grains and Pulses
Oilseeds and Spices
Fruits and Vegetables
Transportation of Food Sweets
The Indian Way of Cooking


In the previous chapters, we have learnt about food items from different cities in India. Which food item is shown here? Which state or city is it from? Speak five lines about it in your class.

Ravi asked his father, “Papa, why does mummy make bajra khichdi so often?”
His father replied, “India is a big country, Ravi. Different foods are popular in different states. We live in Rajasthan where it is hot and dry. Bajra and jowar grow well here so they have become our staple food.”
“Oh! Like how people near the sea eat more fish?” Ravi smiled.


”Exactly, son. We must respect different eating habits of people.”
Any food item that is most commonly eaten by people in a region is known as the staple food of that region.
Grains are the most important part of our meals. Rice is the staple food in the eastern and southern parts of India. People in northern states, such as Punjab, Uttar Pradesh and Haryana, generally eat wheat. In western Indian states like Rajasthan, Gujarat and Maharashtra people eat more of jowar and bajra.
India also produces a wide variety of pulses like moong, masoor, rajma (kidney beans), arhar, soya bean and kabuli chana (chickpeas). They may have different names in different regions.




Fruit and vegetables are an important part of our diet. In summer, we get mangoes, litchees, watermelons, musk melons and cherries. In winter, grapes and oranges are commonly available. Vegetables like pumpkins, brinjals and beans are available in summers. Carrots, cauliflowers, capsicum and peas are available in winters. These fruit and vegetables are seasonal in nature. Onions, garlic and potatoes are some vegetables that are available all the year round. Fruits like bananas are available all the year round.
Many of these fruits and vegetables grow in specific states. For example, apples are grown in Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh, coconuts in Kerala, and oranges in Nagpur.
seasonal: available only in a particular season


Write whether these statements are true or false.
1. Kashmir is famous for its apples.
2. Rice is the staple food of North India.
3. Jowar is a type of a grain.
The oil that we use for cooking comes from oilseeds. Common oilseeds in India are mustard, groundnut, sesame, sunflower and coconut.
India is known for its spices worldwide. Spices make food tasty by adding colour and flavour to it. Some common spices are chillies, cardamom, coriander, cumin, turmeric, cloves and pepper.
Do and Learn


Ask your parents to show you the spices that are used in your kitchen. Write down their names in English and in your mother tongue.
India has a wide variety of sweets such as gulab jamun, roshogolla, laddoo, barfi, Mysore pak and different types of halwa. Some sweets are made specially for festivals or special celebrations. Almost all Indian states have their special sweets.
Remember!

Shrikhand is a popular sweet of Maharashtra. Sandesh and roshogolla are popular sweets of West Bengal.


Food is our source of nutrition. We must eat a balanced diet to stay healthy. Indian food lays emphasis on nutritious and healthy food. So, a lot of different types of oils, spices, dairy products, fruits, vegetables and pulses are a part of the dietary habits of the people of India. Additionally, Indian food is prepared in different ways. It is boiled, fried, steamed, baked or roasted.
Depending on the food people eat, it can be divided into three types: vegetarian, non-vegetarian and vegan.
Vegetarian: A vegetarian diet does not include any kind of meat. It may or may not include eggs. The diet mainly consists of grains, pulses, dairy, nuts, fruit and vegetables.
Non-Vegetarian: A non-vegetarian diet consists of different kinds of meat along with eggs, dairy, grains, pulses, nuts, fruit and vegetables.
Vegan: A vegan diet does not include meat, eggs or dairy. It consists of grains, pulses, nuts, fruit and vegetables. Sometimes, even honey is excluded from use in this diet.
In this chapter, we came to know how different food items are grown in different parts of India. So how do they reach the rest of the country?
Farmers grow crops in their farms and then take the harvest to wholesale markets.
Shopkeepers buy food items from these wholesale markets and bring them to the local neighbourhood shops. People then buy from these local shops and bring them home for cooking.

Truck transporting bananas
steamed: food cooked by putting it over boiling water and letting it cook in that steam baked: food cooked in an oven roasted: food cooked over a fire or in an oven until it gets brown and crispy wholesale markets: large markets where farmers sell their harvest to shopkeepers



Fruits that are grown in different states are packed and transported to the rest of the country through trucks, trains and even aeroplanes.
India is the largest producer of mangoes in the world. Indian mango varieties such as Alphonso and Dasehri are famous all over the world. Alphonso manges are grown in Maharashtra and Dasehri mangoes are grown in Uttar Pradesh. Alphonso mangoes

staple food: any food item that is most commonly eaten by people in a region oilseeds: seeds from which we get oil used for cooking non-vegetarian: a diet that consists of meat and eggs vegetarian: a diet that excludes meat
vegan: a diet that excludes meat, eggs, dairy and sometimes even honey

Scan the QR code to learn more about the different types of fruits available in India.
• Indian food lays a lot of emphasis on making the food nutritious and healthy.
• India produces a wide variety of grains and pulses like wheat, rice, rajma, soya bean, etc.
• Spices make food tasty by adding colour and flavour to it.
• Depending on the food people eat, it can be divided into three types: vegetarian, non-vegetarian and vegan.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What is the staple food in eastern India?
a. Jowar b. Rice c. Ragi d. Wheat
B. Nagpur is famous for which of these fruits?
a. Orange b. Watermelon c. Mango d. Banana
C. Which of the following is a spice?
a. Tomato b. Turmeric c. Sunflower d. Potato
D. Where do farmers sell their harvest?
a. Wholesale market
c. Grocery stores
b. Grain market
d. Shopping malls
2. Fill in the blanks. western spice oilseeds pulses
A. Moong and arhar are .
B. Bajra is commonly eaten in the part of India.
C. We get oil from .
D. Turmeric is a kind of a .
3. Write True or False.
A. Mysore Pak is a spice.
B. A vegetarian diet does not include nuts and seeds.
C. Coconuts are grown in Kashmir.
D. Chickpeas and arhar are pulses.


4. Match the following.
Food types
Examples
A. Grains i. Turmeric
B. Pulses ii. Mustard
C. Oilseeds iii. Wheat
D. Spices iv. Moong
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Which state is famous for apples?
B. Name any two fruits found in summers.
C. Distinguish between vegetarian and non-vegetarian diet.
D. What would happen if food that was grown in one state could not be transported to other states? How would it affect our diet?
6. Picture-based question.
Look at the pictures and write S if it is seasonal or A if it is available throughout the year.




























1. What problems do you think farmers can face while transporting fruits and vegetables from their fields to wholesale markets?
2. Can vegan food items be included in a vegetarian diet? Explain why or why not.
With the help of your parents, learn to make a fruit raita (curd mixed with fruits) with at least 3 types of fruits and some spices that you like.







Every day you wear your school uniform while going to school. Name any four items that are part of your school uniform.
(Hint: shirt, belt)
The clothes people wear in a place depends on that place's climate, culture and the materials available. Since India has a diverse range of climate and culture, the clothes worn by Indians are quite diverse as well.
Some clothes, such as sarees, kurta–pyjama, salwar–kameez, shirts, trousers and T-shirts, are worn commonly across India. In this chapter, we will learn about the different kinds of traditional clothes that are worn in the different parts of our country.

Shirts, trousers and t-shirts are the most commonly worn clothes by men all over the country. Kurtas are commonly worn by men in many states. Traditional clothes are worn by people living in a region.

In Rajasthan and Gujarat, men wear an upper garment called an angrakha. It is a frock-like shirt that is worn with a pyjama or dhoti. In the southern states, men wear a lungi with a kurta or a shirt. Lungi is a long cloth that is tied around the waist.
In Kerala, the lungi is called mundu. In Tamil Nadu, it is called veshti.


Lungi with shirt Mundu Gujarati
In Kashmir, long woollen kurtas called phiran are worn. In many states, men wear turbans to cover their heads. Turbans can be worn in different ways.




Women in India wear various kinds of clothes like sarees, salwar–kameez and others. Sarees are worn in different ways in different states. The design and weave of the saree also differ from state to state.
Different states have their own traditional dresses for women. Ghagara–choli and odhni are worn by women in Rajasthan. In Kashmir, women wear phiran with salwar. In Assam, women wear mekhela–chador. Women in Himachal Pradesh wear pattu. Punjabi women wear salwar-kameez with dupatta, and in Haryana they wear ghagara–kurta.




Remember!
Women in Maharashtra wear saree in a special way called Nauvari saree.
Make a chart on the traditional clothes of India. Paste pictures of the traditional clothes of different Indian states. Write down the names of the clothes under their pictures. You can look for the pictures in your local stationery shops, newspapers, magazines, and even take printouts from the internet.
Many states in India have their own special dresses for occasions like weddings and festivals. In the north-eastern states, people wear different types of headdresses for festivals and ceremonies. They also wear colourful shawls and dresses with various patterns.
weave: the pattern of threads in the cloth
headdress: a decorative covering worn on the head ceremony: a special formal event




A traditional dress worn by a woman in Mizoram
Some Indian dresses are associated with the places where they come from. Puanchei is from Mizoram, Banarasi sarees from Varanasi, and Chikankari dresses from Lucknow in Uttar Pradesh, Pashmina shawls from Kashmir, and Kanjeevaram sarees from Tamil Nadu are a few examples of this. They are famous all over the world.

What kind of special dress do you wear during festivals?
The Pashmina shawl is made from the wool of a goat found in Kashmir.
Wonders of Bharat
Chikankari dresses are bought by people from around the world for its beautiful embroidery work.

traditional clothes: clothes that are worn to represent a region, culture or a ceremony
angrakha: frock-like shirt which is worn with a pyjama or dhoti
lungi: a long piece of cloth that is wrapped around the waist
phiran: long woollen kurta

Explore More!
Scan the QR code to learn more about the traditional dresses of different states in India.


• The clothes people wear in a place depends on that place's climate, culture and the materials available.
• Traditional clothes are worn by people living in a region.
• Some traditional clothes for men are angrakha, mundu and veshti.
• Traditional clothes of women include ghagara–choli, phiran and mekhela–chador.
• People in some states in India wear headdresses for festivals and ceremonies.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What do men wear in Kashmir?
a. Veshti
b. Chadar c. Phiran
B. Pattu is the traditional dress of the women of which state?
a. Himachal Pradesh b. Odisha c. Telangana
C. What is the most common clothing of Indian women?
a. Saree b. Ghagara–choli
c. Mekhala-chador
2. Fill in the blanks. Angrakha Mundu Punjab
A. In Kerala, the lungi is called .
B. is a short, frock-like shirt worn by men in Rajasthan.
C. Salwar-kameez is the traditional dress for the women of

3. Write True or False.
A. Phiran is the traditional dress of Maharashtra.
B. Mundu is the traditional clothing of men in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
C. Banarasi sarees are from Varanasi.
4. Match the following.
A. Mekhela–chador i. Tamil Nadu
B. Puanchei ii. Assam
C. Veshti iii. Mizoram
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Which state is famous for Kanjeevaram sarees?
B. Which state is famous for Pashmina shawls?
C. What are traditional clothes? Give 2 examples.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What is the dress shown in the picture called?
B. In which state do women generally wear this dress?


In June, Shikha will be travelling from Lucknow to Kashmir to attend a wedding in her family. On the way, she will spend 3 days in Delhi as well.
1. What kind of clothes should she pack for her stay in Delhi?
2. She wants to wear something traditional at the wedding to represent her city, Lucknow. What do you think she could wear?



Lets recycle old socks and turn them into puppets.
Materials: Old socks, glue, buttons, markers, cotton.
Steps:
1. Fill the sock with cotton to create a soft toy shape.
2. Seal the open end with glue.
3. Use markers to draw eyes and a smile.
4. Glue buttons for eyes or decorations.
5. Your fun sock toy is ready!




National Festivals
Religious Festivals

Our Festivals Get Set

Harvest Festivals
Birthdays
Read the hints to correctly write the names of these festivals.
1. We light diyas to decorate our houses.
2. We celebrate India’s freedom on this day.
3. We play with colours on this day.
Festivals are special times when people come together to celebrate something important.
Some festivals are celebrated by the whole country, while other festivals are celebrated only in certain parts of the country or by the people who follow a religion. Let us learn about them.


National festivals are celebrated all over the country. In India, there are three national festivals: Independence Day, Republic Day and Gandhi Jayanti.
Independence Day
India got its independence from the British rule on 15 August 1947. We celebrate Independence Day on 15 August each year. On this day, the prime minister of India hoists the National Flag at the Red Fort in New Delhi and gives a speech from there. On this day, we also remember the freedom fighters who gave up their lives for India's independence.
Republic Day
Republic Day is celebrated on 26th January every year. The President of India unfurls the national flag on the Republic Day. Then, a special parade is held at the Kartavya Path in New Delhi. The armed forces (army, navy and air force), the police, and school children participate in the parade. The parade also has colourful tableaux of different states of India. Many children, who have been awarded for bravery, are also a part of the parade. Such parades also take place in the capital cities of different states of the country.
Gandhi Jayanti


The Kartavya Path was earlier known as Raj Path. The name was changed in 2022. Did You Know?
Gandhi Jayanti is celebrated on 2nd October every year to mark Mahatma Gandhi’s birthday. He is also known as the Father of the Nation and ‘bapu’.
hoist: to raise high using a rope unfurl: to open something that is rolled up and tied tableaux: a scene displayed on a big stage on wheels


He played an important role in India’s independence from the British rule. Every year a function is held at Raj Ghat in New Delhi. Mahatma Gandhi’s ashes are kept at Raj Ghat.
Fill in the blanks.

1. Republic Day is celebrated on . (15 August/26 January)
2. Mahatma Gandhi’s ashes are kept at . (Red Fort/Raj Ghat)
3. India got independence from the British in the year . (1947/1974)
Festivals that are celebrated to mark an important day for a religion are called religious festivals. It is important that all religions and religious festivals are respected.
India has different religions, which is why Indians celebrate a number of religious festivals together. Let us learn about some of them.
Diwali is also known as the ‘Festival of Lights’. On this day, people wear new clothes, decorate their homes with flowers, diyas, lights, candles and draw rangoli.
Holi is known as the ‘Festival of Colours’. It is a popular festival in north India. People celebrate by playing with coloured powder known as gulal.




Dussehra celebrates the victory of good over evil. Devotees believe that on this day, Lord Rama killed Ravana, the demon king with ten heads. A dance drama called Ramlila is organised in different parts of the country. Big effigies of Ravana are burnt to celebrate Dussehra. Large fairs are organised across India.

Effigy of Ravana
Durga Puja is one of the main festivals in West Bengal.
Gurupurab is celebrated in honour of the first Sikh guru, Guru Nanak. On this day, people go to the Gurudwara to pray. Langars are held and large processions are taken out in honour of Guru Nanak. Special decoration is done at all gurudwaras and a big celebration is held at the Golden Temple in Amritsar.
Eid-ul-Fitr is an important festival celebrated in India. It marks the end of a month-long period of fasting known as Ramzan. People offer special namaz at different mosques all over the country. They wear new clothes and prepare special dishes. They greet each other with ‘Eid Mubarak’, which means “Blessed Festival”. A sweet dish called sewaiyan is prepared specially on Eid.
Christmas is celebrated with joy all over India. It is celebrated every year on 25th December to celebrate the birth of Jesus Christ. Churches all over the country are decorated and prayers are held.
devotees: people who believe in a religion effigy: a model
langar: free food served to people at a gurudwara
namaz: prayers offered by Muslims

Eid celebrations at Jama

A family putting up a Christmas tree at home.

People put up Christmas trees and bake plum cakes. People exchange gifts on this day.
Navroz is the celebration of the Parsi new year. It is celebrated between 19th to 22nd March every year. It marks the end of winter and the beginning of spring.
Harvest is when the crops that were sown earlier are ready to be cut and collected from the fields. Harvest is celebrated in many Indian states as a festival.
Bihu
Bihu is Assam’s harvest festival. It is celebrated three times in a year. Women perform a special dance called the Bihu dance. They also wear their traditional dress called mekhela–chador.
Pongal is Tamil Nadu’s harvest festival. It is celebrated for four days. A dish called ‘sweet pongal’ is made by cooking rice in milk and jaggery. People decorate their houses by drawing patterns, known as ‘kolam’, on the ground. They also worship cows during the four days.

Onam is Kerala’s harvest festival. It is also known as the ‘festival of flowers’. A special meal called the Onam Sadya is served on banana leaves. One of the main events of Onam are the boat races, which are held at various places in Kerala.

Baisakhi is a harvest festival celebrated in North India, especially in Punjab. Men perform Bhangra and women perform Gidda. These are accompanied with the rhythms of the dhol.
Though harvest festivals are named differently in different parts of India, they are celebrated in almost all the parts of India. Why do you think this is the case?
Sara is preparing a dance for Teacher’s Day celebration at her school. She is excited to perform for her teachers and is practising a lot to put up a great show.
Teacher's Day is celebrated every year on 5th September which is the birthday of Dr S. Radhakrishnan. Jawaharlal Nehru’s birthday on 14th November is celebrated as Children’s Day.

Dr S. Radhakrishnan who was the 2nd President of India was a highly respected teacher. Did You Know?
Uttarayana or Makar Sankranti is also known as the ‘Kite Festival’ in Gujarat. People of all ages compete kite flying on this day. The festival is so popular that people from all over the world travel to see it.
festival: special days when people celebrate something

A girl ready to launch her kite into the sky
ramzan: a month-long period of fasting followed by Muslims
bhangra: a special type of dance performed by men in Punjab
gidda: a special type of dance performed by women in Punjab
dhol: a kind of double-sided drum



Scan the QR code to learn more about our harvest festivals.
• National festivals are celebrated all over India.
• Religious festivals are associated with different religions of India. They are celebrated all over the country.
• Harvest festivals are celebrated at the time of harvest.
• The birthdays of some important people are celebrated as festivals.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What is the month-long period of fasting for Muslims called?
a. Navroz
b. Ramzan c. Gidda
B. Gautama Buddha’s birthday is celebrated as which festival?
a. Buddha Purnima
b. Children’s Day c. Gurupurab
C. Pongal is a festival of which state?
a. West Bengal
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Gujarat c. Tamil Nadu
A. Boat races take place during .
B. People draw on the floor of their homes during Pongal.
C. People visit on the Gurupurab to pray.


3. Match the following.
A. Navroz i. 2nd October
B. Children’s Day ii. Between 19th to 22nd March
C. Gandhi Jayanti iii. 14th November
4. Answer the following questions.
A. Name any 2 harvest festivals and the states in which they are celebrated.
B. How do national festivals like Gandhi Jayanti remind us of important leaders and the lessons they taught?
C. How is Eid celebrated?
D. How is Gurupurab celebrated?
5. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the questions.
A. Which festival is being celebrated here?
B. Where is it celebrated in New Delhi?
C. Who all participate in the parade?


1. Why does India have so many harvest festivals?
2. How is the harvest festival of Kerala different from that of Tamil Nadu?
We decorate our homes during festivals. Decoration items are thrown away after the festival is over leads to wastage.
Create decoration items for an upcoming festival by reusing old material like old clothes, old newspapers, etc. You can also use natural materials like jute, clay, etc. Paint them in bright colours and use them to decorate your home.






Solve the following jumbled words.
1. REMAFR
2. OCODRT
(Hint: This person grows our food.)
(Hint: Who treats the sick person.)
Meena's mother is a doctor. Every day, she helps many people get well. Meena also wants to become a doctor like her mother when she grows up, and help people.
The work that people do to earn money is called an occupation. Everyone can take up an occupation

A doctor


depending on what they know, their needs, and the opportunities they have. Farmers, doctors, teachers, carpenters and police are some examples of occupation. Some people also run businesses to earn money. Based on their occupation, people work in different places like offices, hospitals, schools, farms and so on. Do you think all the people in a region can have the same occupation?
Let us learn more about different types of occupations.
Farming is the practice of growing crops. Farmers grow food grains, fruits and vegetables, pulses, tea, cotton, jute, oilseeds, sugarcane, spices among other things.
Some farmers also rear animals on their farms. This practice is called animal rearing. For example, sheep are reared by many people for wool. When animals like cows, goats and buffaloes are reared for milk, it is known as dairy farming. It is a popular occupation in India. Milk products like curd and cheese are also produced in dairy farming.
When animals such as hens, ducks and geese are reared for eggs and meat, it is called poultry farming.
Error Alert!
Cows, buffaloes and goats are not the only animals from which we get milk. We also get milk from sheep, horses and camels.



A poultry farm
Silk worms are reared to produce silk. It is called Sericulture. Did You Know?

Mining is the process of digging up minerals from the Earth. We get minerals like iron, mica, manganese and coal through mining. These minerals are then processed to make objects like utensils, cars, tools, etc. Mining is an important occupation in some states of India that are rich in minerals, like Jharkhand, Odisha and Karnataka.
Many people work in forests as well. They collect materials like wood, gum, honey and herbs from trees in the forests to make various items. For example, latex is collected from rubber trees to make rubber.
Fishing is the main occupation of people living in coastal areas. Sometimes, fish are reared in ponds or big tanks. This is called pisciculture. Fish are reared for meat and fish oil.
Many people work in factories that use crops and minerals to make them into other useful products. For example, cotton is used to make cloth, jute is used to make bags and ropes, tea leaves are used to make tea powder, seeds are used to make oils, and sugarcane is used to make jaggery and sugar.




mineral: a substance that is naturally formed in the Earth coastal: near the sea factories: places where things are made

Services are jobs that people do for others.
For example, wholesalers buy goods from factories and supply to shopkeepers in markets around us. They take help of people in the transport services to move the goods.
We also need other services in our daily lives that are not related to buying or selling of goods, such as postal services, entertainment, doctors, teachers, police, and mechanics.


Discuss with your friend some other services which we use daily and without which our lives will be difficult.
India is the largest milk producer in the world today. This was made possible due to the ‘White Revolution’, or ‘Operation Flood’, that was started in year 1970 by Dr Verghese Kurien. It built many milk plants to make products like cheese and curd and also created a big network to collect and deliver milk all over India.
Dr Verghese Kurien is known as the ‘father of the White Revolution’ in India.

occupation: the work done by people to earn money dairy farming: rearing animals to get milk from them poultry farming: rearing hens, ducks and geese for eggs and meat mining: digging up minerals from below the earth’s surface latex: a white liquid produced by rubber trees that is used to make rubber services: jobs people do for others
wholesalers: they buy goods in large quantities from factories and sell them to shopkeepers


Scan the QR code to learn more about the journey of the dairy industry in India.
• The work done by people to earn money is called an occupation.
• Farming also provides material to several other industries.
• We get minerals like iron, mica, manganese and coal through mining.
• Fishing is the main occupation of people living in coastal areas.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these items is obtained through mining?
a. Minerals
b. Plants c. Wood d. Spices
B. Rubber is made from which one of these materials?
a. Gum
b. Latex c. Fish d. Cotton
C. What do we get from dairy farming?
a. Meat
b. Milk c. Eggs d. Honey
2. Fill in the blanks. factories pisciculture metals
A. We get from minerals.
B. Goods are made in .
C. Rearing fish in ponds or big tanks is called .


3. Write True or False.
A. Rearing of cows is called poultry farming.
B. Fish farming can be done in ponds.
C. Rearing of silk worms is called sericulture.
4. Match the following.
A. Seeds i. Oils
B. Wood ii. Ropes
C. Jute iii. Paper
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Define occupation.
B. Why are forest-related occupations important?
C. What do you think will happen if all the people working in the transport services stop their work for one week?
D. What is meant by mining?
E. Explain dairy farming.
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the pictures and answer the following questions.
A. Name the occupations shown in the images.
B. Which of these occupations gives us milk?
C. Which of these occupations gives us iron and coal?



There is a new amusement park being built in a city. What kind of jobs will people need to do to build the park and make it a fun-filled place for everyone?
We just read that we get paper from trees. Follow these easy steps to recycle paper at home.
1. Tear old newspapers into small pieces and soak them in water for a few hours.
2. Mash the soaked paper into a pulp with your hands.
3. Spread the pulp onto a flat tray, press it and remove excess water.
4. Let it dry completely, then peel off your new recycled paper sheet.
You now have your own homemade recycled paper!



























Get Set

Answer the questions by choosing from the pictures of different vehicles given below.
1. Which is your favourite way to travel to your friend’s house?
2. How do you travel to your cousin’s house who lives in different city?



The different ways in which people or goods are moved from one place to another are known as means of transport. People choose the means of transport based on how far they have to travel, how much time they have or how much money they can spend.
Means of transport can be broadly divided into land, air and water transport.


Land transport is the most common means of transport for people and goods both. Means of transport that move only on land are called land transport, such as cars, metro, buses, trains, tractors, and so on. Bullock carts and tongas are the most common means of land transport in villages. Many people use cycles to travel in their neighbouhood or to visit the nearby markets. Using cycles is good for our health and the environment both. It helps us exercise, keeps us healthy and does not pollute the environment.



Did You Know?
The first train journey in India was in 1853. The train carried 400 passengers between Mumbai and Thane in Maharashtra. Today, the Vande Bharat and Gatimaan Express are the fastest trains in India.
Means of transport that move only in the air are called air transport, such as helicopters and aeroplanes. Aeroplanes cover longer distances and helicopters cover shorter distances. Air transport is very fast, but it is a costly means of transport. Aeroplanes use airports for landing and take off. Airports are located in many cities across India and the world.

The first aeroplane was built by two brothers, Wilbur and Orville Wright, in 1903. Did You Know?
bullock cart: a cart with two or four wheels drawn by oxen tonga: a cart with two or four wheels drawn by horses


Priya loves to make paper boats and sail them in a tub of water. Last year, she sailed in a boat for the first time when she visited Nainital with her family. Nainital has a big lake in which people can go around on boats. Means of transport that moves only in water is called water transport. Water transport is the cheapest mode of transportation, but it is also the slowest. Ships, steamers and boats are all types of water transport. Ships can carry huge amounts of cargo over long distances. There are many ports in India from where ships operate.



Find out the names of any three airports and ports in India and the cities in which they are located.
Write whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Steamers and boats are types of water transport.
2. Trains are a type of air transport.
3. Tongas and bullock carts are the most commonly used transport in villages.
cargo: goods carried over long distances by ships, aeroplanes or big trucks



We use roads almost daily. It is important to follow road safety rules. Some of them are:
• Never cross roads on your own. Take your parents’ or any adults’ help to do it.
• Always walk on the footpath or on the side of the road if there is no footpath.

• Only cross the road using zebra crossings, overhead bridges or subways. If you are using a zebra crossing, wait for the cars to stop before you cross the road.
• Before you cross the road, look to your left, then to your right and to your left again. Make sure that no vehicles are coming from either side.
• Never play, or ride your bicycle on the road.
• A place where a road crosses railway tracks is known as a level crossing. Do not try to cross it when its gates are closed.
India has a wide network of roads. The longest highway in India connects Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir to Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu. This highway is 3,745 kilometres long. It is called NH-44 or National Highway-44.


means of transport: the different ways in which people or goods are moved from one place to another land transport: means of transport that can move only on land air transport: means of transport that can move only in the air water transport: means of transport that can move only in water
subway: an underground passage meant for crossing roads level crossing: a place where a road crosses railway tracks



Scan the QR code to learn more about the history of ships.
• The different ways in which people or goods are moved from one place to another are known as means of transport.
• Cars, trains, metro, buses, bullock carts, bicycles and tongas are some examples of land transport.
• Boats, ships and steamers are some examples of water transport.
• Aeroplanes and helicopters are some examples of air transport.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which is the most common means of transport?
a. Air
b. Land c. Water
B. Which of these is a type of water transport?
a. Helicopter
b. Steamer c. Tonga
C. What is the place where a road crosses railway tracks called?
a. Level crossing b. Zebra crossing c. Subway
D. Where does an aeroplane land and take off from?
a. Airport
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Port c. Railway station
A. transport is the cheapest means of transport.
B. can carry huge amounts of cargo over long distances.

C. Apart from aeroplanes, are another means of air transport.
D. While walking on the road, we should always walk on the .
3. Write True or False.
A. We should cross roads using zebra crossings, overhead bridges or subways.
B. Bullock carts and tongas are the most common means of land transport in villages.
C. Metro is a means of land transport.
D. Level crossing is a means of air transport.
4. Match the following.
A. Boat
B. Train
C. Helicopter
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Define means of transport.
i. Land transport
ii. Water transport
iii. Air transport
B. If you need to walk on a road but it does not have a footpath, what will you do?
C. List any 3 road safety rules that we should follow.
D. What are the differences between water transport and air transport?
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What vehicle can you see in the given picture?
B. Which means of transport is being shown here?
C. Name two other vehicles which are of the same means of transport.




Gaurav has to travel from Delhi to his village which is 300 kms away. Which modes of transport can he use and why?


Ask some elderly people around you about the means of transport that were available when they were children. Make a list of those.
With the help of your parents, travel in the local bus, metro, or autorickshaw in your city.
Before travelling, revise the safety rules you must follow while using that means of transport. Follow these rules while you travel.



Means of Communication
Mass Communication Internet and Email Need for Communication
Postal System, Telephone, Fax

Get Set

Read the poem aloud.
We talk on the phone and write an email, We send our messages without fail. With calls, texts and letters too, We share our news with friends like you!








The different methods that we use to communicate with people are called means of communication. In ancient times, people used trained birds to send messages or people carried letters on foot. Now, we have modern, fast, and reliable ways to communicate. Let us learn about some of them.
communicate: to talk or share ideas, thoughts and feelings with someone


Letters and parcels can be sent to people all over the world through the postal system. In India, it is run by the government and is called the India Post.
The modern postal system was started for the public in India in 1774 by the British.
We can write our message on an inland letter, a postcard, or on plain paper and put it in a stamped envelope. All of these can be bought from any post office.
Letters are put in a postbox and a postman collects them from there. These letters are then carried by different means of transport like road, air and water to their destination.

Each letter or parcel should have the address and the pin code clearly mentioned on it so that it reaches the correct destination. Pin code stands for Postal Index Number code. It is a special 6-digit number for each area that helps the post reach the right place.

Urgent letters and parcels can be sent through services such as Speed Post or by courier. The Indian Postal Department provides the Speed Post service for the fast delivery of letters or parcels. Courier services are provided by private companies.
Write a letter to your friend. With the help of your parents, post the letter at your nearest post office. Remember to add your friend's address and pin code so that it reaches the correct address.
inland letter: a specific size of paper used for letters within India only postcard: a rectangular card used for writing short messages stamped: with a postage stamp destination: the ending point of a journey



A telephone is one of the fastest means of communication. Using telephones, we can talk to people in different cities and countries. They are available at home or at public places where anyone can pay and use them.
A fax machine is connected to a telephone line. It is used to instantly send written messages, documents and photographs. Fax machines are present in most offices.



Write whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Telephone services were started in 1774 by the British.
2. Fax machines are present in most offices.
3. Speed Post is a service which is offered by private companies.
Today, one of the easiest and fastest ways of communicating with people is through the internet. While using the internet, always ask an adult before sharing any information. Keeping oursleves safe online is as important as keeping ourselves safe in real life.
Email, or electronic mail, refers to messages that are sent and received using the internet.
The internet can also be used to read the news, find out any information, watch films, listen to music and do many more things. We can do all of this on laptops and smartphones.
Smartphones are a combination of telephones and computers. To keep our eyes healthy we must spend less time on smartphones or laptops and more time playing outside.

How can you use the internet to study? Discuss with your partner.
When information has to be delivered to a large number of people at the same time, it is done through newspapers, radio, television, satellites and the internet. They help us communicate with a large number of people at the same time. So, they are known as means of mass communication or mass media.

Reena loves sports and has been watching the 2024 Olympics taking place in Paris live on her television at home. Do you know how we are able to watch something at the same time when it is happening in a different part of the world? We are able to do that because of satellites.
Newspapers do not have news of the same day. They are printed at the end of the day and delivered to us the next morning. So, they contain news about what happened yesterday.
Satellites are artificial objects launched into space. They send signals to television, radio and internet. Satellites enable us to watch or hear events like sports or news live from our homes.


live: to watch something at the same time as it is happening in some other part of the city or the world



In India, satellites are launched by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). With Chandrayaan-3, India made history by becoming the first nation to successfully land a spacecraft near the South Pole of the Moon.

A model of Chandrayaan-3
means of communication: different ways that we use to talk to other people or send messages to them
pin code: a special 6-digit number that helps the post reach the right place mass communication: communicating with many people at the same time satellites: artificial objects launched into space that send signals to television, radio and internet

Scan the QR code to learn more about the history of communication.
• The process of sending and receiving messages and information is called communication.
• The internet has made communication faster than ever before.
• When information is delivered to a large number of people at the same time, it is called mass communication.
• Newspapers, television, radio and internet are means of mass communication


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these can we use to send parcels faster than the normal way?
a. Fax machine
b. Radio c. Speed Post
B. Which of the following is NOT a means of mass communication?
a. Letters
b. Radio c. Newspaper
C. Which of these can we use to instantly send written documents between offices?
a. Postal system
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Fax machine
c. Television
electronic mail postbox speed post
A. Email stands for .
B. Letters have to be put in a to be posted.
C. Parcels are sent to people through .
3. Write True or False.
A. We need internet to send an email.
B. Smartphones combine the features of telephones and computers.
C. The internet is the slowest means of communication.
4. Match the following.
A. Pin code
B. Radio
C. Fax machine
i. Offices
ii. Mass communication
iii. Letters


5. Answer the following questions.
A. If you had to find out news about something that happened in the world an hour ago, which means of communication will you use?
B. What is the use of satellites?
C. List any two means of mass communication.
D. What is an email? Have you ever received an email?
E. What are some differences in the ways of communication between ancient times and today?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Name the device shown in the picture.
B. Is it a means of personal communication or mass communication?






We get news from both newspapers and the television. How are these two means of mass communication similar and different?
Skills
Do you know who to call in case of emergencies? Ask your parents or elders or use the internet to find out the contact numbers of the following emergency services: • Police:
Only call these numbers if there is an emergency. Do not call them otherwise.


Objective: Students will design and create a miniature traditional dress that is from a region in India.
Materials Needed: Markers, colour pencils, fabric scraps, access to the internet or the library, craft materials (glue, scissors, decorative items), chart paper
Step 1: Research

Research the traditional dresses worn in India. Find out the names of the materials used to make these dresses, such as silk, cotton, wool, etc.
Step 2: Study Design
Study the unique design, patterns, and colours used in traditional dresses. For example, look at the designs on a Banarasi saree or the embroidery on a Chikankari saree or a Punjabi suit or salwar kameez.
Step 3: Create a Visual Representation
Create your own design for a traditional dress, inspired by traditional patterns, on a chart paper. You can sketch, colour, or even stick fabric scraps to make your design.
Step 4: Write About the Dress
Label the dress and add the name of the fabric used to make it. Write why the dress is special and where is it worn.
Step 5: Present It to the class
Share your designed dress with the class. Tell three important things about the dress.
Project Output: Now you have your own unique design for a traditional dress. Take turns to present your dress design in front of the class.
Final Outcome: This project will help you understand the diversity of traditional dresses in India. It also promotes research skills, creativity, cultural awareness, and an appreciation for the rich heritage of India.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.

Read this story. Answer the questions given below.
Anika in Samaspur
Anika lives with her family in Samaspur. Every morning, Anika’s mother, Mrs Sharma, takes the metro to her office because it is fast and doesn’t get stuck in traffic. Anika rides her bicycle to school. She loves this because it keeps her active and she can see the beautiful parks on the way to her school.
Anika’s father, Mr Sharma, works from home, so he uses his computer and smartphone to communicate with his colleagues. He often sends emails to his team and makes video calls to discuss important work matters. Anika’s grandparents live far away. Anika talks to them using a video chat app, where they share stories and laugh together.
Questions:
1. How does Anika’s father communicate with his colleagues?
a. He posts a telegram.
b. He writes letters and sends fax.
c. He uses a computer and a smartphone.
2. Why does Anika’s mother prefer taking the metro to work?
a. It is fast and avoids traffic.
b. It is cheaper than other transport.
c. She enjoys meeting people on the metro.
3. If Anika’s grandparents don’t have a video chat app, how can she stay in touch with them? Mention any two ways.
4. Write two ways in which we can reduce the pollution caused by vehicles.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.














Chapter Overview

Shelter, Clothing and Tools
Discovery of Fire

Early Man
Beginning of Farming
Domestication of Animals
Discovery of Metals
Changes in Transportation

Get Set

Find the following words in the given word grid and circle them.
1. HUNTER
2. JUNGLE 3. STONE
Early humans are said to have lived in jungles and caves. They used to cover themselves with animal skins and leaves. They were called hunter–gatherers because they either hunted for food or gathered food from trees. They usually ate fruits, roots, leaves and hunted wild animals,


birds and fish. They did not know how to cook nor did they know how to light a fire so they ate their hunted animal raw.

Tools used by early humans
Early humans made tools from stones, bones, and wood. These tools were used for hunting and digging. Animal bones, horns and sharp wooden sticks were also used as tools by them. At times, they used to tie sharp stones to wooden sticks and used it as spear for hunting animals. Use of spears helped them to hunt animals without going near them.
Get some modelling clay. Try to shape the clay into the kinds of tools made by early humans as shown in the above image.
Early humans discovered fire by accident. One day, they noticed that sparks could be created when they struck stones together or when lightning hit dry trees, causing them to catch fire. At first, they were scared, but soon they realized that fire could be useful. They learnt to use it for warmth, cooking food, and protecting themselves from wild animals. Over time, they found ways to keep the fire going by adding dry leaves, wood and sticks. This discovery changed their lives, making it easier to survive and grow as a community.
Discuss!
Discuss with your friend how life would be, if fire had not been discovered.

Early humans using fire to keep themselves warm in a cave
spear: a weapon with a long shaft and a pointed tip discovery: to find or learn something for the first time

Early humans noticed that where they dropped seeds, new plants grew in that spot. So, instead of moving around to find food, they started planting seeds where they lived. They grew crops like wheat and barley. This was the beginning of farming. With farming, they began to settle down at one place. They also understood that seeds needed good soil and water to grow. So, they began settling near rivers.
Early humans noticed that certain animals, like horses, cows, bullocks, dogs and sheep, were helpful. For example, dogs could protect them and sheep provided wool and milk. So, they began keeping these animals close, feeding and caring for them. This was the start of domestication.

Just like how we care for our pets at home, early humans learnt that taking care of animals brought safety and companionship to their lives.
Dogs were one of the first animals to be domesticated by humans. They used to accompany humans during hunting.
Tick (✓) the correct statements.

on
1. Early humans used animal bones as tools for hunting.
2. Early humans discovered fire.
3. Cow was the first animal to be domesticated.
companionship: having someone with you


Early humans used to walk and carry what they needed. But it was difficult to carry heavy things like hunted dead animals. So, they made a few things to make travel easy. Near rivers, they used rafts made of logs tied together to float across water. To make things easier on the ground, they invented sledges. These were simple platforms of wood that could be dragged over the ground. Soon, they found that it was difficult to drag them on uneven land. So, they began putting logs of wood under these sledges and began rolling the sledges over these logs. As time passed, this led to the invention of the wheel.


They also noticed that animals like horses could also help carry heavy loads, which led to the making of carts and wagons, making travel faster and more efficient. With sledges, rafts, and wheeled carts, early humans could explore new lands, trade with others, and build larger communities, changing how they lived and connected with the world.
Early humans discovered metals like copper and gold while searching for stones. They found that these shiny materials could be shaped into tools and ornaments. By heating metals, they learnt to create stronger tools for farming and hunting. This discovery made their lives easier and marked the beginning of a new era of progress.
invention: a thing that has been made or designed by somebody for the first time era: an important period of time in history


Bhimbetka rock shelters in Madhya Pradesh are rock shelters or caves that are famous worldwide. There are paintings on the walls of these caves by early humans. They are more than 30,000 years old. They show us how the life of early humans as hunters and gatherers was. Bhimbetka rock shelters

hunter–gatherers: people who either hunted for food or gathererd what they could find rafts: flat platforms made of logs tied together to float across water sledges: simple platforms of wood that could be dragged over the ground

Scan the QR code to learn more about the cave paintings of early humans.
• Early humans lived in caves and under trees.
• They were hunter–gatherers.
• Early humans discovered fire by accident by striking two stones together.
• The invention of wheel made transport easier for them.
• They discovered metals like copper and gold while searching for stones.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these materials did early humans make tools from?
a. Stone
b. Steel c. Copper
B. What did early humans eat?
a. Fruits
b. Bread c. Rice
C. Which animal accompanied early humans during hunting?
a. Cow
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Dog c. Horse
A. Early humans were and gatherers before they learnt to farm.
B. Early humans tied logs together to make a .
C. They tied sharp stones to wooden sticks to make
3. Write True or False.
A. A gas stove helped early humans to cook food and stay warm.
B. Early humans were the first to plant crops and start farming.
C. Early humans grew crops like wheat and barley.
4. Match the following.
A. Animal skins i. Tools
B. Caves and trees ii. Shelters
C. Bones iii. Clothes


5. Answer the following questions.
A. How did the invention of the wheel change the life of early humans?
B. How did the domestication of animals help early humans?
C. Why do you think early humans decided to settle down and farm instead of continuing to hunt and gather food?
D. How was the first raft made by early humans and how did they use it?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the questions.
A. Who do you see in the picture?
B. What do you think they are trying to do here?
C. How will that help them?

If early humans had not invented the wheel, how do you think our lives would have been?

The way we live changes with time. With the help of your elders, find out about some changes that have happened in your locality or city in the last ten to fifteen years. Discuss how these changes have made life better or more comfortable.













Introducing Quest, a thoughtfully designed Social Science book to nurture an understanding of people, places, social surroundings, communities, and human society. In keeping with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020’s focus on competency-based education, Quest provides opportunities for learners to master key concepts, hone their critical thinking, develop humane values alongside 21st century skills, and be able to make informed choices in their day-to-day lives.
Quest is designed to galvanise students’ interest in Social Sciences, both as a subject and as a practical experience, while also making them well-rounded individuals who interact with the world around them in a rational and meaningful way.
Product Package
• Coursebook
• Uolo App
• Teacher’s Guide
• Applied Social Science Projects: Engaging, hands-on projects blending social sciences, mathematics, arts, and technology to understand the world around them
• Competency-based Assessments: Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and application of skills
• Story-based Approach: Enchanting comic stories that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure
• Picture-based Questions: Questions featuring visual stimuli to elevate comprehension, interpretation and critical thinking
• Community Connect: Engaging with community members to make text-to-self connections and develop appreciation for diverse contexts and cultures
• Wonders of Bharat: Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage, designed to ignite a profound sense of pride and love for the nation
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, South East Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-979482-2-0
