





Academic Authors: Ankita Yadav, Yuvraj, Urmi Maitra, Kashika Parnami, Chandani Goyal, Anuj Gupta, Simran Singh
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Sanjay Kumar Goel, Vishesh Agarwal
Project Lead: Sneha Sharma
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First impression 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Quest Social Science 5
ISBN: 978-81-979689-7-6
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
Welcome to the exciting world of social science through Quest, a textbook that has been thoughtfully designed to nurture an understanding of people, places, communities, and how society works.
In today’s rapidly evolving world, a solid foundation in understanding the social surroundings and human society from an early age is more crucial than ever. Social science education lays the groundwork for rational thinking, critical outlook, humane values, and the ability to make informed choices. These skills are not just academic: they are essential life skills that empower young minds to understand and interact with the world around them in a rational and meaningful way. At UOLO, we believe that every child deserves to learn these skills with the best resources available.
In this pursuit, Quest is uniquely crafted to provide a comprehensive and contemporary learning experience, meticulously aligned with the recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023. The book incorporates the curricular goals and competencies outlined in the NCF 2023, ensuring that every chapter, exercise, and feature reflects these foundational principles.
This textbook transcends traditional teaching methods by adopting a competency-based approach, recommended by both NEP 2020 and NCF 2023, that emphasises not just conceptual understanding and critical thinking, but also application of key concepts, and problem-solving. It is designed to make learning both meaningful and relevant, equipping students with the tools they need to thrive in the 21st century.
Carefully curated content, NEP-specific tags, and a diverse array of elements have been seamlessly integrated throughout the book to nurture essential skills, values, and dispositions outlined in the NEP. Competency-based projects and assessments are strategically placed to help students master key concepts and develop higher-order thinking skills.
The book has the unique feature of being complemented by a graphic novella. Each unit of the book begins with an episode of the gripping sci-fi tale, which not only captivates the students’ interest and promotes reading, but also ingeniously connects with some of the core concepts that will be taught in the respective units.
Each chapter is also enriched with vibrant illustrations, relatable examples, and interactive activities to engage our young learners. Observations, inquiries and community-based learning experiences have been embedded throughout the book to develop an analytical mindset and make learning a relatable and enjoyable journey for them. Moreover, assessments ‘of, as, and for learning,’ as envisioned by the NEP and NCF, have been interwoven throughout the curriculum, providing continuous evaluation and meaningful feedback to students to support their growth and success.
The Quest product bundle offers a comprehensive social science kit which includes a textbook that has relevant and up-to-date content, concept building opportunities, projects, and assessments; a teacher manual offering extensive teaching support; technology-powered features that includes engaging videos and interactive exercises for students; and digital lesson plans and an assessment generator for teachers.
In conclusion, Quest is designed to fascinate students towards social science, both as a subject and as a practical experience in their everyday lives, while also making them well-rounded individuals.
We invite educators, parents, and students to embrace Quest and join us in nurturing the next generation of rational thinkers, responsible citizens, and problem-solvers. Embark on this exciting journey with us and let Quest be a valuable resource in your educational adventure.


Welcome to the Quest journey.
The program is carefully designed to elevate the experience of learning social science through an NCF-based, age-appropriate, pedagogically-sound, and engaging content. Teachers will be supported with a manual that offers comprehensive guidance to optimise classroom instruction. Furthermore, various assessment mechanisms have been built in to the program.
Engaging Textbooks
Comic Stories
Teacher Manual
Competency-based Model Assessments
Applied Social Science Projects
Question-paper Generator
Student and Teacher Apps
Learning Videos
Interactive Tasks & Exercises
Byte-size Lesson Modules
The Quest program is also augmented by a digital learning platform that offers powerful educational videos and interactive exercises to help children master concepts and skills in a joyful and fear-free manner.

The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, introduced by the Government of India, represents a transformative shift in the country’s education system. It aims to create a more holistic, dynamic and multidisciplinary approach to education. NEP 2020 focuses on fostering conceptual understanding, skills, values, and competencies that align with the demands of the 21st century, while also preserving India’s rich cultural heritage. UOLO is fully committed to actualising the vision of NEP 2020 by meticulously adhering to its outlined recommendations.









1. Focus on conceptual understanding
2. 21st century skills, values, and dispositions
3. Critical thinking and problem solving
4. Application in real life
5. Holistic and integrated learning
6. Experiential learning
7. Enjoyable and engaging
8. Discussion-based approach
9. Technology-based solutions
10. Knowledge of India

Competency-based Education
NEP Pages 12, 17, and 22
Teaching and Learning Pedagogy
NEP Pages 3, 11, 12, and 27
National Pride
NEP Pages 15, 16, and 43
11. Assessment of core concepts and application skills Assessments
NEP Pages 12, 18, and 22


Engaging hands-on projects blending social sciences, mathematics, arts, and technology to understand the world around them
Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and application of skills
Enchanting comic stories that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure
Curated videos to find out more about key concepts
Multidisciplinary, holistic, and fun-filled activities to internalise the concept better
Engaging with community members to make text-to-self connections and develop appreciation for diverse contexts and cultures

Error Alert
Concise snippets of information designed to caution against potential misconceptions
Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical, and evaluative thought processes
Digital worksheets on key concepts to supplement textbook exercises
Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage, designed to ignite a profound sense of pride and love for the nation
Picture-based Questions Questions featuring visual stimuli to elevate comprehension, interpretation, and critical thinking
Simple activities and tips to develop a diverse set of essential skills for living well


The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 outlines essential skills, values, dispositions, and learning approaches necessary for students to thrive in the 21st century. This textbook identifies and incorporates these elements throughout its content, activities, and exercises. Referred to as “NEP Tags”, they are defined as follows:



INTEGRATED
Art Integration
Bringing creativity and fun into learning by combining music, drama, and art with other subjects
Sports Integration
Using physical activities, sports, and games to make learning active and engaging
THINK RATIONAL
Holistic & Integrated Learning
Cross-curricular and skill linkages to make the learning experience more holistic, joyful and meaningful
Rational Thinking
Using facts, logic and reasoning to understand problems and make smart decisions

Teamwork
TEAMWORK

SDG
Embracing the spirit of mutual collaboration and cooperation while working together to solve problems
Sustainable Development Goals
Unwavering commitment to create a green, peaceful, prosperous, and equitable and inclusive world

SEL Social Emotional Learning
Developing the skills to understand and manage emotions, build positive relationships with others, and make responsible choices

The National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF), released in 2023, is developed based on the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. Its purpose is to enable the implementation of the NEP. The NCF provides guidelines for designing school syllabi and textbooks in India. It aims to improve the quality of education by making it more relevant, engaging, inclusive, and learner-centric. To achieve this, the NCF has articulated precise Learning Standards through well-defined Curricular Goals and Competency statements. These statements serve to harmonise the syllabus, content, pedagogical practices, and assessment culture, ensuring a cohesive and comprehensive educational experience.
Curricular Goals: Curricular Goals are statements that give directions to curriculum development and implementation. They are derived from Aims and are specific to a Stage in education.
Competencies: Competencies are learning achievements that are observable and can be assessed systematically. These Competencies are derived from the Curricular Goals and are expected to be attained by the end of a Stage.
NCF Page 59
CG-1
Explores the natural and social environment in their surroundings
CG-2
Understands the interdependence in their environment through observation and experiences
C-1.1 Observes and identifies the natural (insects, plants, birds, animals, geographical features, sun and moon, soil) and social (houses, relationships) components in their immediate environment
C-1.2 Describes structures, relationships, and traditions in the family and community
C-1.3 Asks questions and makes predictions about simple patterns (season change, food chain, rituals, celebrations) observed in the immediate environment
C-1.4 Explains the functioning of local institutions (family, school, bank/ post office, market, and panchayat) in different forms (story, drawing, tabulating data, noting discussion), and analyses their role
C-1.5 Creates simple objects (family tree, envelopes, origami animals) on their own using local materials
C-2.1 Identifies natural and humanmade systems that support their lives (water supply, water cycle, river flow system, life cycle of plants and animals, food, household items, transport, communication, electricity in the home)
C-2.2 Describes the relationship between the natural environment and cultural practices in their immediate environment (nature of work, food, traditions)
C-2.3 Expresses the changes in the lives of their family and community as communicated by elders and through local stories (changes in occupation, food habits, resources, celebrations, communication)
The above is a snapshot of the curricular goals and competencies relationship in EVS for the Preparatory Stage (NCF 2023, pages 340–341). The next section shows the coverage of all these competencies across the chapters.

18
17
16
15
14
12 Ch 13
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
Ch 3
Ch 2
Ch 1














Competencies
C-1.1 Observes and identifies the natural (insects, plants, birds, animals, geographical features, sun and moon, soil) and social (houses, relationships) components in their immediate environment
Curricular Goals
CG-1
Explores the natural and social environment in their surroundings
C-1.2 Describes structures, relationships, and traditions in the family and community
C-1.3 Asks questions and makes predictions about simple patterns (season change, food chain, rituals, celebrations) observed in the immediate environment
C-1.4 Explains the functioning of local institutions (family, school, bank/post office, market, and panchayat) in different forms (story, drawing, tabulating data, noting discussion), and analyses their role





C-1.5 Creates simple objects (family tree, envelopes, origami animals) on their own using local materials
C-2.1 Identifies natural and humanmade systems that support their lives (water supply, water cycle, river flow system, life cycle of plants and animals, food, household items, transport, communication, electricity in the home)





C-2.2 Describes the relationship between the natural environment and cultural practices in their immediate environment (nature of work, food, traditions)
C-2.3 Expresses the changes in the lives of their family and community as communicated by elders and through local stories (changes in occupation, food habits, resources, celebrations, communication)
CG-2
Understands the interdependence in their environment through observation and experiences


















C-3.1 Describes the basic safety needs and protection (health and hygiene, food, water, shelter, precautions, awareness of emergency situations) of humans, birds, and animal
CG-3 Explains how to ensure the safety of self and others in different situations
C-3.2 Discusses how to prepare for emergency situations (pandemic, floods, landslide, unseasonal rains) based on discussions with family and community, or personal experiences
C-3.3 Develops simple labels, slogans, and participates in roleplay on safety and protection in the local environment to be displayed/done in school and locality
C-4.2 Observes and describes cultural diversity in their immediate environment (food, clothing, games, different seasons, festivals related to harvest and sowing)
CG-4 Develops sensitivity towards social and natural environment
C-5.1 Explains a mental map of their school, village, and ward
CG-5 Develops the ability to read and interpret simple maps














C-5.2 Reads simple maps of city, State, and country to identify natural and humanmade features (well, lake, post office, school, hospital, etc.) with reference to symbols and directions




C-5.3 Draws a sketch of their school, village and ward using symbols and directions
C-6.1 Performs simple investigations related to specific questions independently or in groups
C-6.2 Presents observations and findings through different creative modes (drawing, diagram, poem, play, skit, through oral and written expression)
CG-6 Uses data and information from various sources to investigate questions related to their immediate environment











universe is a huge endless space which has stars, planets, It also has dust, gases, and big pieces of rocks that float in The Earth seems quite big to us but it is quite tiny in the universe.

Comic Story: Exciting story built through out the book, contains hooks to topics in a unit
We can see the stars in the sky at night. Stars look tiny to us but in reality they are big, bright balls of hot gas that shine in the sky. They are far away from us that is why they look like tiny lights.
Chapter Overview: Outline of the key concepts covered in the chapter





Stars are there during the day are not visible bright light of











Get Set: A short and fun activity to get learners excited about the new topic
and the stars. All these heavenly bodies are a part of the universe. The universe is a huge endless space which has stars, planets, sun, and moon. It also has dust, gases, and big pieces of rocks that float in the vast space. The Earth seems quite big to us but it is quite tiny in the universe.
Did You Know: Interesting facts related to the topic
Understanding Our Universe
Revolution of the Earth
When we look up at the sky during the day and at night, does it look the same? During the day we can see a bright blue sky and a bright sun. At night, we can see the moon
Revolution of the Earth
The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an orbit is called revolution. The Earth moves around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit. The Earth completes one revolution in one year. The revolution of the Earth around the Sun and its tilted axis causes different seasons in different parts of the Earth.
Vocabulary: Meanings of difficult words



The Earth is the only planet in our solar system that can support
This is possible because the Earth has water,
and sunlight. Living beings cannot survive without air or water. There is no other planet like the Earth. The Earth is our

If we look carefully, we can make patterns of the stars in the patterns are called constellations. People have given these different names based on what they look like. They are usually animals or myths. For example, Ursa Major or Big Dipper spoon in the sky, Leo looks like a lion, Hydra looks like a water snake, and Orion looks like a hunter. The Ursa Major is called Saptarishi in India.
Did You Know?

3 4 5


The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an orbit is called revolution. The Earth moves around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit. The Earth completes one revolution in one year. The revolution of the Earth around the Sun and its tilted axis causes different seasons in different parts of the Earth.


We have all seen the Sun in the sky. The Sun rises in the East West. It is also a star. It is a huge ball of very hot gas that makes give out light and heat. This heat and light makes life possible There are eight planets that revolve around the Sun. They Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The with all these planets that revolve around it together form
Stars are there in the sky during the day too but they are not visible to us due to the bright light of the Sun.
There are only five oceans Pacific Ocean is written Error Alert!





Chapter 1 • The Universe are a part of
myths: oral stories that have been told over hundreds of years which not be true revolve: to go around or travel around something

Error Alert: Caution against misconceptions
During sunset, the Sun does not move. It is the Earth that moves, which causes sunset.

The Earth is the only planet in our solar system that can support life. This is possible because the Earth has water, air and sunlight. Living beings cannot survive without air or water. There is no other planet like the Earth. The Earth is our home, and it is precious. We should make sure that our actions do not harm the earth in any way. For example, we must not waste water.








Revolution of the Earth

Wonders of Bharat
and it is precious. We should make sure that our actions do not harm the earth in any way. For example, we must not waste water. Wonders of Bharat Jantar Mantar is a monument in New Delhi. It was built by Maharaja Jai Singh almost 300 years ago! It was built to predict the movements of the sun, the moon and the planets. It also told time based on the shadow caused by the sun. Jantar Mantar, New

Jantar Mantar is a monument in New Delhi. It was built by Maharaja Jai Singh almost 300 years ago! It was built to predict the movements of the sun, the moon and the planets. It also told time based on the shadow caused by the sun.









Ursa Major Leo Hydra

We can see the stars in the sky at night. Stars look tiny to us but in reality they are big, bright balls of hot gas that shine in the sky. They are far away from us that is why they look like tiny lights. If we look carefully, we can make patterns of the stars in the sky. These patterns are called . People have given these star patterns different names based on what they look like. They are usually named after animals or myths. For example, Ursa Major or Big Dipper looks like a big spoon in the sky, Leo looks like a lion, Hydra looks like a water snake, and Orion looks like a hunter. The Ursa Major is called Saptarishi in India.
Wonders of Bharat: Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage
The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an orbit is called . The Earth moves around the Sun in a fixed path called an orbit. The Earth completes one revolution in one year. The revolution of the Earth around the Sun and its tilted axis causes different seasons in different parts of the Earth.

Oceans are very important. animals. People can also oceans through ships. industry.


Explore More: Short videos to find out more about the topic
We have all seen the Sun in the sky. The Sun rises in the East and sets in the West. It is also a star. It is a huge ball of very hot gas that makes it glow and give out light and heat. This heat and light makes life possible on Earth. There are eight planets that revolve around the Sun. They are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. The Sun along with all these planets that revolve around it together form the Solar System.


myths: oral stories that have been told over hundreds of years which may or may not be true revolve: to go around or travel around something
NEP Tags: To show alignment with NEP skills and values
The Earth is the only planet in our solar system that can support life. This is possible because the Earth has water, air and sunlight. Living beings cannot survive without air or water. There is no other planet like the Earth. The Earth is our home, and it is precious. We should make sure that our actions do not harm the earth in any way. For example, we must not waste water.
Wonders of Bharat
USS25CBG3.indb
Do and Learn: Multidisciplinary, holistic, and fun activities to understand the concept better

Jantar Mantar is a monument in New Delhi. It was built by Maharaja Jai Singh almost 300 years ago! It was built to predict the movements of the sun, the moon and the planets. It also told time based on the shadow caused by the sun.







Oceans are very important. They are home to many plants and animals. People can also travel from one continent to another by crossing oceans through ships. Oceans also support the fishing industry

The Earth’s continents and oceans each has its own unique features, cultures, and wildlife. We must not pollute the water in the oceans so that we don’t harm the aquatic plants and animals.

The Earth’s continents has its own unique features, wildlife. We must not oceans so that we don’t plants and animals.





the map. The student with the maximum correct markings wins.




Coastal Plains Islands


4. Directions can be found using a compass.
Pause and Answer
Make two teams and hide small objects like toys, stones, sketch pens etc. at different places in a playground. Then make a map of the playground, marking the spots where you have hidden the objects. Now exchange your maps and use them to find the hidden objects of the other team.
Pause and Answer: Short exercises between the chapter to pause and assess comprehension
Tick (✓) the correct statements.
The team that finds all the objects first, wins.
1. Maps are flattened representations of the earth.
2. A physical map shows countries and boundaries.
Think and Tell
3. North is located to the opposite of South.


learn more about them.



C Define universe.
D. How is the Sun similar or different to the Moon?
4. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
If you had to find out the names of all states in India, which type of map will you use?
4. Directions can be found using a compass.
Think and Tell / Discuss: Analysis, reflection, and text-to-self connection-based prompts for discussion in class
Wonders of Bharat
The team that finds all the objects first, wins. GAMES Do and Learn
A. What is shown in this picture?
B Label the parts marked in the picture.
Make two teams and hide small objects like toys, stones, sketch pens etc. at different places in a playground. Then make a map of the playground, marking the spots where you have hidden the objects. Now exchange your maps and use them to find the hidden objects of the other team.
India is located in Asia and is the seventh largest country in the world by land area.
Ancient Indian scholars such as Aryabhata had inspired Greeks and Romans about making maps. His famous work includes describing the shape of the Earth as round.
Remember: Recall of previous knowledge relevant to the topic

Think and Tell

Himalayan Mountains lie in the part of India. They are highest mountain ranges in the row of mountains is called mountain range. The weather in region is cold and it is difficult crops here. The highest mountain in the world, Mount Everest, lies Himalayas. Other famous mountains Himalayas include Kanchenjunga, Parbat and Nanda Devi. Many rivers the Ganga, the Yamuna and the Brahmaputra originate in the Himalayas. formed by the melting ice.
Know?


Wonders of Bharat
Picture-based Questions: Special questions featuring visual stimuli to foster comprehension, interpretation, and critical thinking
Ancient Indian scholars such as Aryabhata had inspired Greeks and Romans about making maps. His famous work includes describing the shape of

C Define universe.
D


If you had to find out the names of all states in India, which type of map will you use?



Life Skills: Simple activities and tips to develop a diverse set of essential skills for living well
Error Alert!


Aryabhata


4. Picture-based questions.








Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
Learn more about how globes were made in olden times.
A What is shown in this picture?

Label the parts marked in the picture.
What would happen if the Sun stops giving heat and light?


Life Skills
Learn more about how globes were made in olden times.
Snow-covered Himalayas
The Mount Everest is not located in India. It lies in China and Nepal. The highest mountain peak in India is Kanchenjunga.
Word Splash
Word Splash









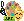
Create a colorful poster about our universe and include the sun, the moon, stars, and constellations in it. Give a title to your poster. Share the completed poster with your class.

rotation: movement of the earth on its axis revolution: movement of the earth around the sun orbit: a fixed path in which the earth moves around the sun








Word Splash: Recall of key terms and concepts in the chapter
What would happen if the Sun stops giving heat and light?
rotation: movement of the earth on its axis revolution: movement of the earth around the sun orbit: a fixed path in which the earth moves around the sun
Points to Remember
Points to Remember
Life Skills
• The Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system.
Points to Remember: Summary of the chapter

• The Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system.
• The Earth moves in two ways: rotation and revolution.
Create a colorful poster about our universe and include the sun, the moon, stars, and constellations in it. Give a title to your poster. Share the completed poster with your class.
Norgay and Sir Edmund Hillary were the first men to reach the peak of Everest in 1953.
The Earth moves in two ways: rotation and revolution.
• The rotation of the Earth causes day and night, while the revolution causes seasons.
• The rotation of the Earth causes day and night, while the revolution causes seasons.
Northern Plains
Northern Plains are flat lands to the the Himalayas. They are also known Indo-Gangetic Plains. Rivers like the and the Yamuna that originate in the Himalayas flow through these plains. This the soil fertile and suitable for farming.
originate: start or begin
soil that is good for growing plants
and
1. Tick the correct answer.

the correct answer.
A The only planet that has life on it:
Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy

A The only planet that has life on it:
a Jupiter b. Neptune c. Earth d. Saturn
a Jupiter b. Neptune
B The number of hours the Earth takes to complete one rotation is:
c. Earth d. Saturn
a 36 b. 24 c. 10 d. 25
HOTS: Intellectually stimulating questions designed for


C The sailor who proved that the Earth is round was:
B The number of hours the Earth takes to complete one rotation is:


a Vasco Da Gama b. Christopher Columbus
a. 36 b. 24 c. 10 d. 25
c Ferdinand Magellan d. Maharaja Jai Singh
2. Fill in the blanks.
C The sailor who proved that the Earth is round was:
Which states in India share a capital, and who governs that capital?
Which states in India share a capital, and who governs that capital?
a Vasco Da Gama b. Christopher Columbus
c Ferdinand Magellan
A farmer in his wheat fields in Northern Plains 9/17/2024 6:31:30 PM
orbit axis rotation round
A The of the Earth is an imaginary line.
2. Fill in the blanks.
B The Earth is in shape.
Community Connect: Engagement with the community members to make text-to-self connections and develop appreciation for diverse cultures


D The movement of the Earth on its own axis is called Chapter
d. Maharaja Jai Singh
Community Connect
C The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an is called revolution.

A The of the Earth is an imaginary line.
B The Earth is in shape.
India has changed a lot over the last 20 years. Speak to the elderly people around you and ask them what changes do they see around them in India. Ask about changes in dressing styles, ways of communication, ways of living, facilities and so on.

C The movement of the Earth around the Sun in an is called revolution.
Community Connect
India has changed a lot over the last 20 years. Speak to the elderly people around you and ask them what changes do they see around them in India. Ask about changes in dressing styles, ways of communication, ways of living, facilities and so on.
D. The movement of the Earth on its own axis is called .





















Chapter Overview

Shape of the Earth


The Globe
Poles and Hemispheres
Latitudes, Longitudes and Grids


Read the poem given below aloud along with your classmates.
The Earth is round, like a big blue ball, It spins and spins, never will it fall.
From space, it looks so small and bright, A circle of wonder, day and night.
Though it seems flat below our feet, It is round and whole, a special feat.
From oceans deep to mountains high, The Earth’s a circle, under the sky.

In this chapter, we will learn more about our planet, Earth, and what the vertical and horizontal lines on the globe and maps mean.

We have already studied that the Earth is round. In ancient times, people used to believe that the Earth is flat. They believed that if a person will walk towards the end of the Earth and keep walking, then the person will fall off the edge of the Earth. From where we stand, the Earth looks flat because our eyes can only see a small part of it. The Earth is so vast that we cannot see its shape from the ground. Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese navigator, sailed around the Earth and proved it is round. You can only see the Earth’s curve from space.
Studying the whole of Earth is not easy because it is so large. To make it easier, geographers use different methods to represent the Earth on a smaller scale. Two essential tools for this are maps and globes.


Chandani has always wondered what the Earth would look like. One day she asked her teacher, “Ma’am how does the Earth look?” Her teacher showed her a globe kept in the school library. She told her that a globe is a model of the Earth. Chandani was excited to see the globe and wanted to know more about it.
The globe is a small model of the Earth. It shows how oceans, continents and seas are spread across the Earth. We can see the location of countries on a globe. It helps us see the shape of countries, and some cities. We can only see one half of the globe at a time. To view the other half of the globe, we must rotate it. The globe can be turned around, just like the Earth turns around an imaginary line which passes through it. This line is called the axis. The axis is not straight. It is tilted at an angle of 23½°.
Even though a globe is a representation of the Earth, we cannot always use it due to the following reasons:
• It is big and difficult to carry around.
• It can only show a part of the Earth at once.
edge: the boundary line of a surface or an area vast: very large essential: very important



• It cannot show all the specific details about a place and its people.
• Globes lack the detail needed for complete understanding.
• Globes cannot be folded and included in books for easy access.
Circle the correct word.
1. People in ancient times believed the Earth was round/flat.
2. Geographers/Philosophers use different methods to study Earth’s features.
3. The axis/equator is an imaginary line passing through the centre of the Earth.
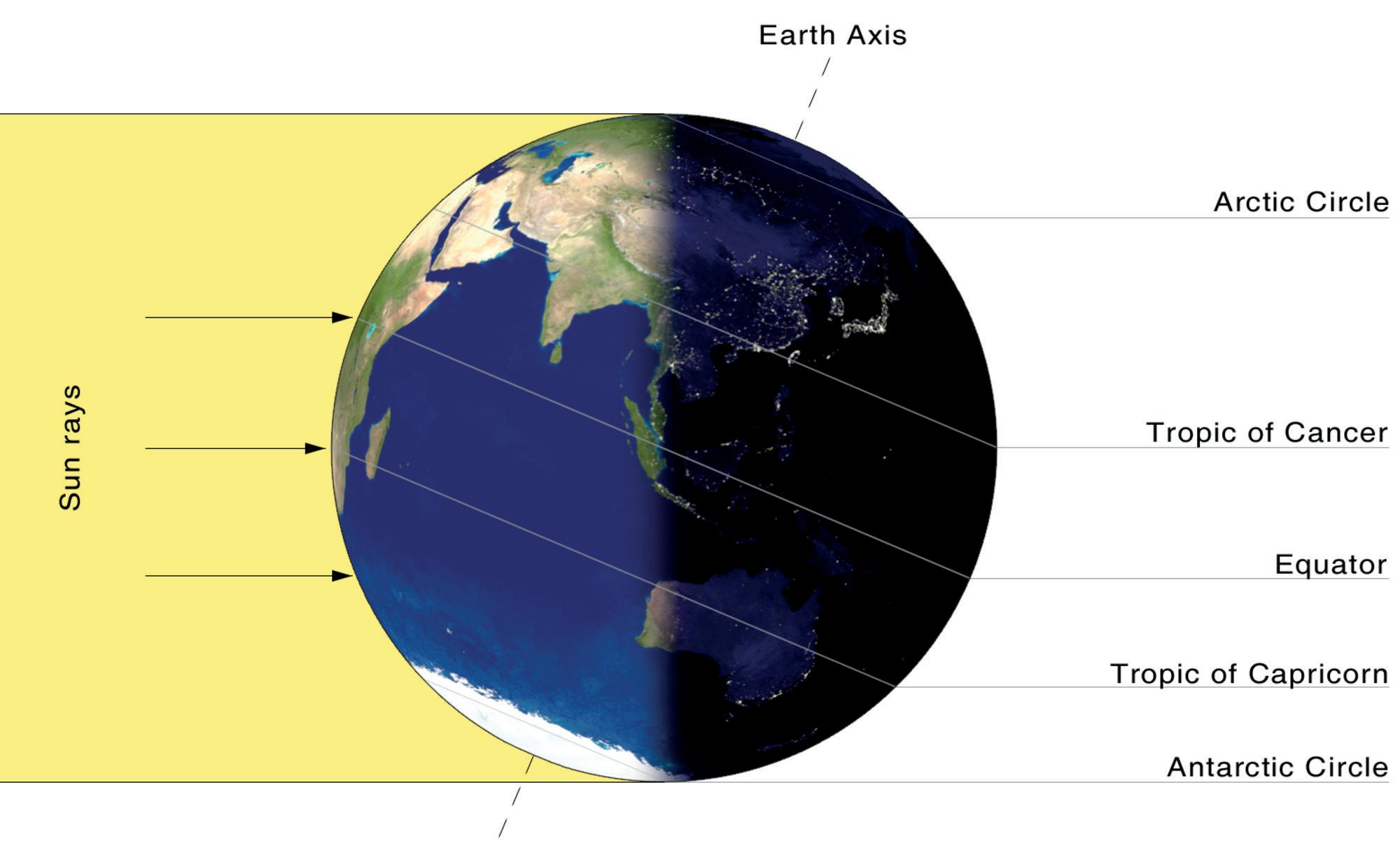
The axis of rotation has two end points called the poles. They are the North Pole and the South Pole. These poles are at the very top and bottom of the planet. The North Pole is in the middle of the Arctic Ocean and is covered by ice. The South Pole is in the middle of the coldest continent, called Antarctica, which is also covered by ice.




























and Hemispheres
At the centre, between the two poles there runs an imaginary line that circles the planet. It is called the Equator. It divides the Earth into two equal halves. These halves are called hemispheres. Towards the north is the Northern hemisphere and towards the south is the Southern hemisphere.
On the globe, horizontal and vertical lines are drawn for the ease of locating places. The imaginary horizontal lines that run from east to west on the globe are called Latitudes. The Equator is one of them. The latitudes are also called lines of latitude or parallels of latitude as they all run parallel to each other. There are 180-degree latitudes in total. The units degree (°) and minutes (`) are used to measure the latitudes. Sixty minutes (60`) are equal to one degree (1°).


The Equator lies at the 0°. At the 90° north, there is the North Pole. At 90° south, we have the South Pole. Therefore, with the help of latitudes, we can know the distance we have travelled towards north or south. For example, a place which is located 45° south, lies between the Equator and the South Pole. Similarly, 60° south will be nearer to the South Pole.
Important latitudes on the Earth:
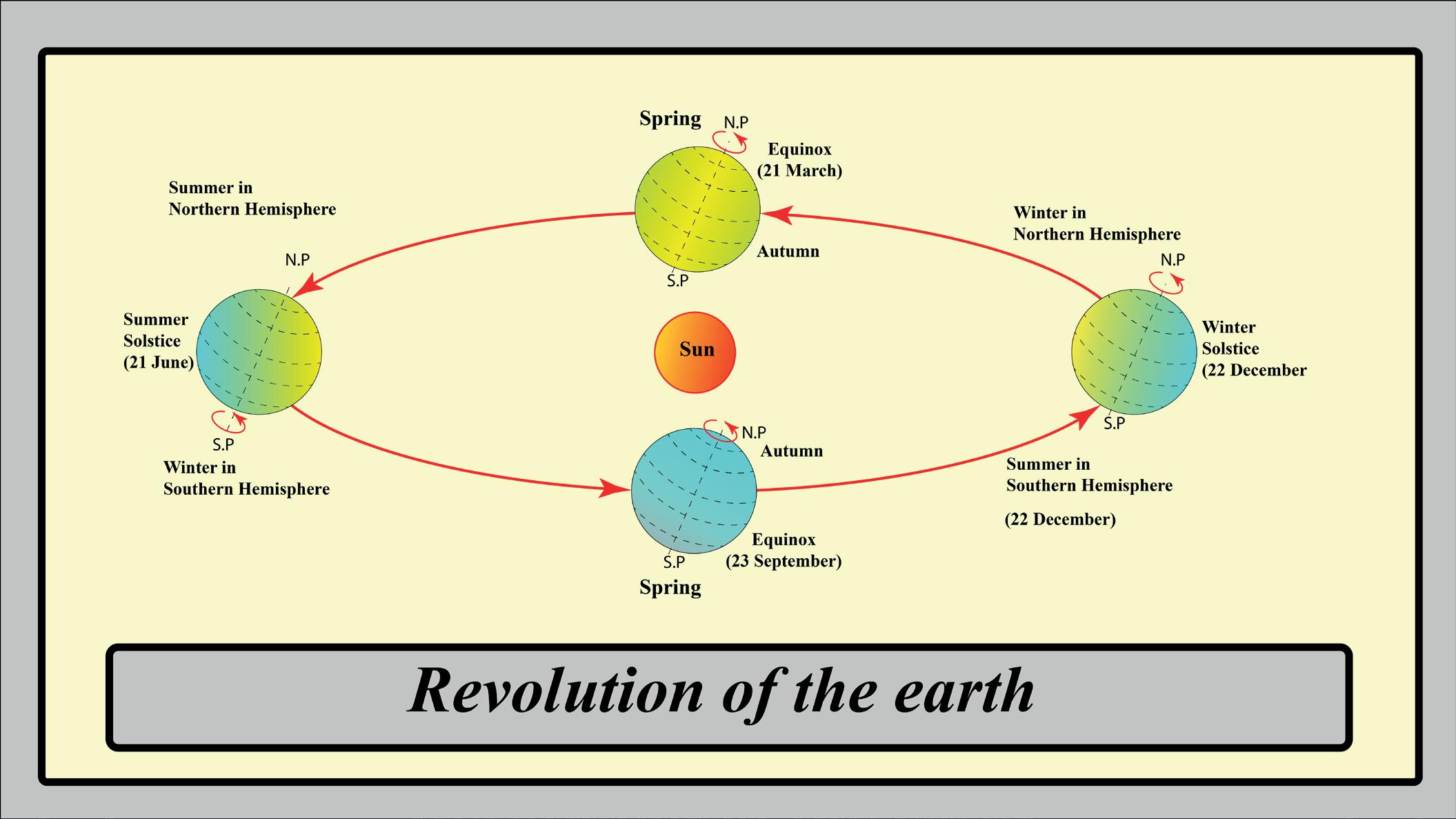
• At 23½°N, we have the Tropic of Cancer.
• At 66½°N, we have the Arctic Circle.
• At 23½°S, we have the Tropic of Capricorn.
• At 66½°S, we have the Antarctic Circle.
Properties of Latitudes
• The parallel lines are at an equal distance from each other, and they do not meet.
• The Equator is the longest latitude and other latitudes become smaller when moving towards the poles.
• The North Pole and South Pole are just points. There are no lines there.
• Latitude affects climate, with locations near the Equator being warmer and locations near the poles being colder.
With the help of the internet, look for five countries from the Northern hemisphere and five countries from the Southern hemisphere.
The vertical, imaginary lines drawn from the North Pole to the South Pole are called Longitudes. The longitude that runs through Greenwich near London is at 0°. It is called the Prime Meridian. As this meridian passes through the observatory at Greenwich in London, United Kingdom, it is also called the Greenwich Meridian.

Meridian line at Greenwich
There are 360° of longitude: 180° towards the east of the Prime Meridian and 180° towards the west of the Prime Meridian. The longitude divides the Earth into Eastern hemisphere
observatory: a place with special equipment like telescopes, where scientists watch and study the stars, planets, and weather


and the Western hemisphere. The 180th degree of the Eastern and Western hemisphere meet at a single line. It is called as International Date line or the 180° longitude.
In total, there are 360 longitudes: the Prime Meridian at 0°, the International Date line at 180°, 179 meridians in the Eastern hemisphere and 179 meridians in the Western hemisphere. The longitudes, therefore, tell us how far east and west we have travelled.
• These lines are semi-circles that run from the North Pole to the South Pole.
• The lengths of the meridians are the same.
• The distance between the lines is broader at the centre and lesser at the poles.

Distance between the lines is less at the poles.
The International Date Line is not a straight line. It is drawn as a zig-zag line to maintain a consistent time zone in the countries and islands that it passes near.
Latitudes and longitudes intersect each other at right angles, forming a network of lines called grids. By knowing the degrees of latitude and longitude, we can pinpoint the exact location of a place. The point where the latitude and longitude intersect marks the location of a place.

Latitudes and longitudes forming a grid
Norway experiences the longest night or darkness of the year in its northern regions during the winter, a phenomenon known as “polar night.”
The time at the point of the Prime Meridian, or the Greenwich Meridian, is considered as the mean time and called as the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The countries on the eastern side of this meridian get to see the sunrise earlier than the countries on the western side of the meridian. The local time of a particular place is calculated based on the distance from Greenwich and the time at Greenwich.


Every country has a particular longitude fixed to calculate the time of that country. Many longitudes pass through one single country. To avoid confusion, one longitude is chosen. In India, 82½°E longitude is chosen to calculate the time. It almost divides India into two equal parts. This longitude passes through Mirzapur, Uttar Pradesh. This standard time is called the Indian Standard Time (IST). By calculating its distance from Greenwich and the time at Greenwich, Indian Standard Time is 5½ hours ahead of the Greenwich Mean Time.
Do and Learn
Find out the current time in India and in Greenwich. Write them in your notebook.

How would the lives of people of India be different if India had different time zones? Discuss with your friends.
Jantar Mantar in Jaipur, built in the 18th century, is a place with special instruments used to measure time, predict eclipses, and observe stars and planets. It is famous for its role in advancing ancient Indian astronomy and science. It is also a UNESCO World Heritage site.

geographer: a person who studies the Earth’s features axis: an imaginary line around which the Earth spins poles: the points on the Earth’s surface where the axis ends latitude: horizontal lines drawn around the globe longitude: vertical lines drawn around the globe

Scan the QR code to learn more about how to find the location of a place using latitudes and longitudes.


• Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese explorer, sailed around the Earth and proved that it was round.
• Latitudes are the imaginary horizontal lines and longitudes are the imaginary vertical lines which help to find the location of a place.
• The important latitudes are the Equator, Tropic of Cancer, Tropic of Capricorn, Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle; and the important longitudes are the Prime Meridian and International Date Line.
• Indian Standard Time (IST) is 5½ hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. The axis of the Earth is titled at which angle?
a. 66½°
B. The 0° Longitude is called
b. 23½°
c. 90°
a. Greenwich Meridian b. International Date Line c. Equator
C. The total number of longitudes are
a. 180
b. 181
D. The total number of latitudes are
a. 90
b. 181
2. Fill in the blanks. east to west north to south poles grids
c. 360
c. 180
A. The latitudes and longitudes intersect and form a network of lines called .
B. Latitudes run from .
C. Longitudes run from .
D. The points on top and bottom of the Earth are called .

3. Write True or False.
A. Longitudes affect the climate in both hemispheres.
B. The 23½°S latitude is called the Tropic of Cancer.
C. Latitudes are also called parallels.
D. The Equator is also called the Prime Meridian.
4. Match the following.
A. Latitude
B. Longitude
C. 23½°
D. 66½°N
5. Short answer questions.
A. Define latitudes and longitudes.
i. Arctic Circle
ii. Axis of rotation
iii. Prime Meridian
iv. Equator
B. What is a globe? Write one advantage and one disadvantage.
C. What is the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)?
D. What are grids? How are they useful?
6. Long answer questions.
A. What are the properties of latitudes?
B. What are the properties of longitudes?
C. What is Indian Standard Time? How is it calculated?
7. Picture-based questions.
A. Name any one continent the Equator is passing through.
B. Which line divides the Earth into the Eastern hemisphere and the Western hemisphere?



1. If you travel directly from the Equator to the North Pole, how will the environment around you change? Describe what you might observe about the climate, daylight and landscapes as you move from 0° to 90°N latitude.
2. India has only one time zone, the Indian Standard Time (IST), which is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time. Considering the vast geographical spread of India, what could be some advantages and disadvantages of having a single time zone for the entire country?

Connect to a friend/relative who is living in a different country and find out the difference in time, weather, food and culture. Present the details to your class.




Maps and Directions
Globes and Maps
Types of Maps
Directions and Sub-directions

Reading a Map


Shreyas is new to his school. At lunch time, he asks his classmate Mahima to tell where the school canteen is. Mahima gives him the directions to these. She tell him to first go to the north block of the school, and then take a left from there. The canteen would be on his right.
Do you also give directions to others to help them reach a particular place?
In this chapter, we will learn about maps and directions.
In the previous chapter, we have learnt that a globe is a miniature model of the Earth. It accurately represents the shape, size and location of places. It helps us study the distribution of water and land on the Earth’s surface.
miniature: very small


However, globes have some limitations:
• Large globes are hard to carry around.
• You can only see one-half of the Earth at a time.
• They don’t show all the details of the Earth.
What are some ways in which maps can be more convenient than globes? Discuss with your partner.
• Making a large, detailed globe is difficult. To overcome these issues, we use maps. A map is a flat representation of the Earth’s surface, usually on paper. Since the Earth is curved, it is impossible to flatten it perfectly on paper. This leads to some inaccuracies in the shapes and sizes of landmasses on maps. Mapmakers work to reduce these inaccuracies. Maps may have distortions, but they can still show small areas precisely. This makes them useful for studying the Earth. However, maps can be outdated and need to be updated from time to time.
Maps can show the entire world or specific areas like continents, countries, cities or neighbourhoods. They come in various sizes. Larger maps, such as those of the world, tend to have more errors due to the broad area they cover. In contrast, smaller maps, like those of a neighbourhood, can provide more accurate details. A wall map of the world may be large because it includes many details, but it can be rolled up or folded for easy transport. There are various types of maps:
• Political maps: They show the boundaries of continents, countries, states and cities.
Why do you think we use different maps for a place or region instead of including all details on a single map?
During the 16th century, Gerardus Mercator, a map-maker, was the first to compile and publish a collection of maps in the form of a book.
• Physical maps: They highlight natural features such as rivers, plateaus, mountains and plains.
limitations: restrictions inaccuracies: errors or mistakes distortions: changes that make something unclear or wrong precisely: exactly or accurately contrast: comparison

• Climatic maps: They display information on rainfall and climate across different places.
• Thematic maps: They include details on railways, roads and airline routes.
• Resource maps: They show industries, crops, minerals, soils, wildlife, forests and natural resources. A book of maps is called an atlas.
Underline the correct answer.
1. A map/globe is a small model of the Earth.
2. Maps that show the boundaries of continents or countries are known as physical/ political maps.
3. Using maps, we can see the whole/half world at once.
To use any map, it is important to follow a set of directions. A direction is an indication leading towards a place. There are four major directions: North, South, East and West. These are known as cardinal directions. On a map, the top usually represents the North, the bottom represents the South, the right side represents the East, and the


left side represents the West. Often on a map, an arrow pointing to the North is marked with the letter ‘N,’ which helps you identify the other directions.
In addition to the cardinal directions, there are also intermediate directions that provide more precise guidance.
The area between North and East is called Northeast, and the area between North and West is called Northwest. Similarly, the area between South and East is called Southeast, and the area between South and West is called Southwest.
The directions
Maps provide us with detailed information about the world, a country, or a specific place. However, to effectively read a map, we need to understand certain features that guide us. These features are known as the elements of a map. Here are some basic elements:
Maps convey information about mountains, rivers, dams, lakes, bridges, landforms, airports, railway tracks and much more. Since everything cannot be written out on a map, symbols are used to represent these features. For example, cities are often marked by small circles and mountain peaks by triangles. These symbols make it easier to understand the information being given by the map.
In early maps, symbols were often more artistic with detailed drawings representing cities or mountains. Did You Know?
Map symbols


A map condenses a large area, such as the entire world, a country or a state, into a much smaller size. It is not feasible to draw a map of the same size as the actual place.
To address this, scales are introduced. A scale helps compare the actual size of an area to a smaller representation on the map.
For instance, a scale might show that 1 cm on the map equals 200 km in reality. This ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground is called the scale.

Create a map showing the route from your school to your home. Mark landmarks like libraries, hospitals, parks, etc. with your own symbols and use blue for any water bodies along the way.
Different colours are used on maps to represent various features, and most maps follow similar colour patterns. For example, generally on a physical map, mountains are shown in shades of brown, yellow represents plateaus, and green represents plains. Water bodies are shown in shades of blue, with light blue representing shallow waters and dark blue indicating deeper waters. Typically, a key is provided in the upper or lower right corner of the map. This key helps us understand what the different colours on the map represent.
Climatic regions of the world
condenses: makes something smaller or compact feasible: possible or practical to do


Indore celebrated India’s 75th Independence Day in a unique way. Over 5,000 people, including students and social workers, came together to form a giant human chain shaped like India’s map. This incredible achievement earned them a spot in the World Book of Records for creating the largest human chain forming a geographical shape. The participants carefully created the outline of the map, including the tricolor flag and the Ashok Chakra emblem in the centre.
map: a flat representation of the Earth’s surface, usually on paper atlas: a collection of maps, typically bound together in a book direction: an indication that leads to a particular point cardinal directions: the four main directions—north, south, east and west intermediate directions: the directions in between the cardinal directions elements: the features used on a map that guide you to read the map easily symbols: small pictures or icons that represent different features and landmarks scale: ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground

Scan the QR code to learn more about the symbols and colours used on maps.
• Maps may be distorted since the curved Earth cannot be represented perfectly on flat paper.
• Smaller maps show details more accurately, while larger maps may be less precise.
• An atlas contains different types of maps, such as political, physical, climatic, thematic and resource maps, each serving a specific purpose.
• There are four directions and four intermediate directions that help us to locate places on the map.
• The basic elements used on a map include symbols, scales and colours.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. A collection of maps is called
a. a map book b. a globe
c. an atlas
B. Political maps show information about a. states and cities b. rivers and plateaus c. temperature
C. Landmarks are represented on maps by a. colours b. symbols c. scales
D. The directions between the cardinal directions are called directions.
a. in-between
b. medium
c. intermediate
E. Plateaus are shown on maps in a. brown b. green c. yellow
2. Fill in the blanks.
intermediate directions resource maps thematic maps globe scale
A. shows the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground.
B. give the details of minerals, crops, industries and soil.
C. is a miniature model of the Earth.
D. give details on railway, roads and airline routes.
E. Northeast, Northwest, Southeast and Southwest are called .
3. Write True or False.
A. Water bodies are always represented in shades of green.
B. There are four cardinal directions and four intermediate directions used in a map.
C. Physical map gives information on rivers, plateaus, etc.
D. Plains are represented in shades of light green and dark green.
E. Large maps are easy to handle and read.


4. Match the following.
A. States and continents i. Climate map
B. Rivers and plateaus ii. Physical map
C. Railway and airports iii. Political map
D. Rainfall iv. Resource map
E. Crops and minerals v. Thematic map
5. Short answer questions.
A. What are the uses of maps?
B. What are symbols? Why are they used on a map?
C. What are the different elements used on a map?
D. How is the scale used on a map?
E. What does a colour key on a map mean?
6. Long answer questions.
A. What are cardinal directions and intermediate directions? Explain.
B. Name three different types of maps and describe what they represent.
7. Picture-based questions.
A. What type of map is this?
B. What does this type of map tell us?
C. What information do you get from the key of this map?




Why do you think it is important to know which direction is north, south, east or west while reading a map? Support your reason with examples.
Two friends are lost in the woods and need to find their way back to the camp! Start at the ‘START’ and follow the arrows to reach the ‘FINISH’. There might be different paths, but try to find the quickest one. Write the directions in the empty circles to guide the campers.



Rotation of the Earth
Revolution of the Earth Equinox and Solstice




Solve the riddles related to the seasons given below.
I am hot, full of sunlight, ice cream, pools and lots of fun. Who am I?
Snow games and cold winds blow, cozy sweaters and ice that glows. Who am I?
Flowers bloom and birds take flight, nature wakes, fresh and bright. Who am I?



We know that the Earth spins around its own axis. We also know that it moves around the Sun. In this chapter, we will learn more about how these movements cause day and night; and different seasons.
In ancient times, there was a belief that the Earth was flat. However, an Indian astronomer, Aryabhata, was among the first to propose that the Earth is spherical and propose: to suggest an idea, plan or action

rotates on its axis. People did not believe it until astronomers like Nicolaus Copernicus and navigators like Ferdinand Magellan provided evidence to support their findings. Today, satellite images of the Earth clearly show that it is spherical in shape.
You can learn more about the Earth and its features using a globe.
The Earth is spherical but slightly flattened at the poles and slightly bulging at the equator. As a result, gravity is stronger at the poles than at the equator.
The Earth rotates on its axis. It takes about 24 hours to complete one full rotation. The rotation of the Earth is responsible for causing day and night. As the Earth rotates from west to east, we see the Sun rising in the east and setting in the west.
To understand how day and night happens in a better way, try this activity: Take a globe and shine a flashlight on it. You will observe that light shines on only one-half of the globe, leaving the other half in darkness. This is similar to what happens on the Earth. Because the Earth is spherical, when the Sun's rays shine on one side, that side experiences day. The opposite side remains dark because the Sun's rays do not reach there, creating night. This cycle repeats regularly, creating our daily cycle of day and night.
A globe is a small model of the Earth.
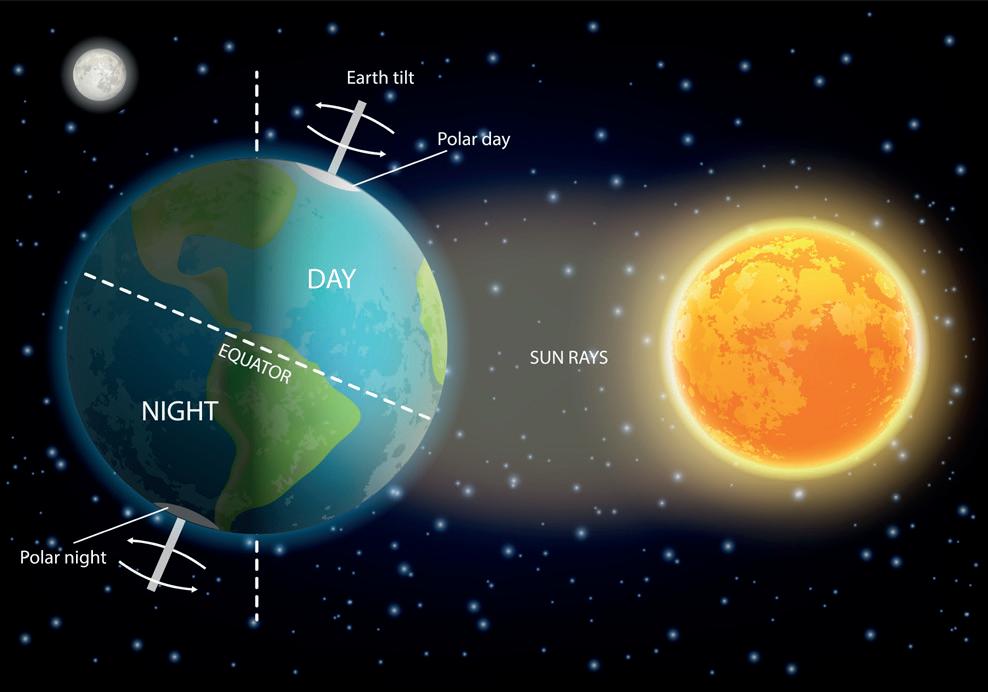
The Earth moves around the Sun in an oval-shaped path called an orbit. This movement of the Earth around the Sun, in a fixed path, is called revolution. It takes about 365¼ days for the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun. The 1/4 day
evidence: facts, information or objects that help prove whether something is true or false


adds to one full day every fourth year. To keep our calendar accurate, we add this extra day to February of that fourth year. This creates a leap year with 366 days.
As the Earth revolves around the Sun, different parts of the Earth get varying amounts of sunlight. This causes the seasons: summer, winter, spring and autumn. Because the Earth’s axis is tilted, the part that gets more direct sunlight experiences summer, while Southern Hemisphere is titled away from the Sun. So, that part of the Earth experiences winter, with shorter days and longer nights. From October to February, this is reversed the Southern Hemisphere experiences summer, while the Northern Hemisphere experiences winter. Can you guess what season does Australia have in the month of June?
Error Alert!
Although it looks like the Sun moves around the Earth, it is actually the other way round: it is the Earth that moves around the Sun.
Underline the correct answer.
1. A leap year occurs every 6/4 years.
2. Camera/Satellite images of the Earth confirm that it is a sphere.
3. The Earth takes 40/24 hours to complete one rotation.
reverse: opposite

Equinox and solstice are important positions in Earth’s revolution around the Sun. These times of the year help us note the change of seasons.
An equinox is a time of the year when the length of day and night are nearly equal. This happens twice a year: on 21 March and 23 September.
In an equinox, the axis of the Earth is neither tilted towards the Sun nor away from the Sun.
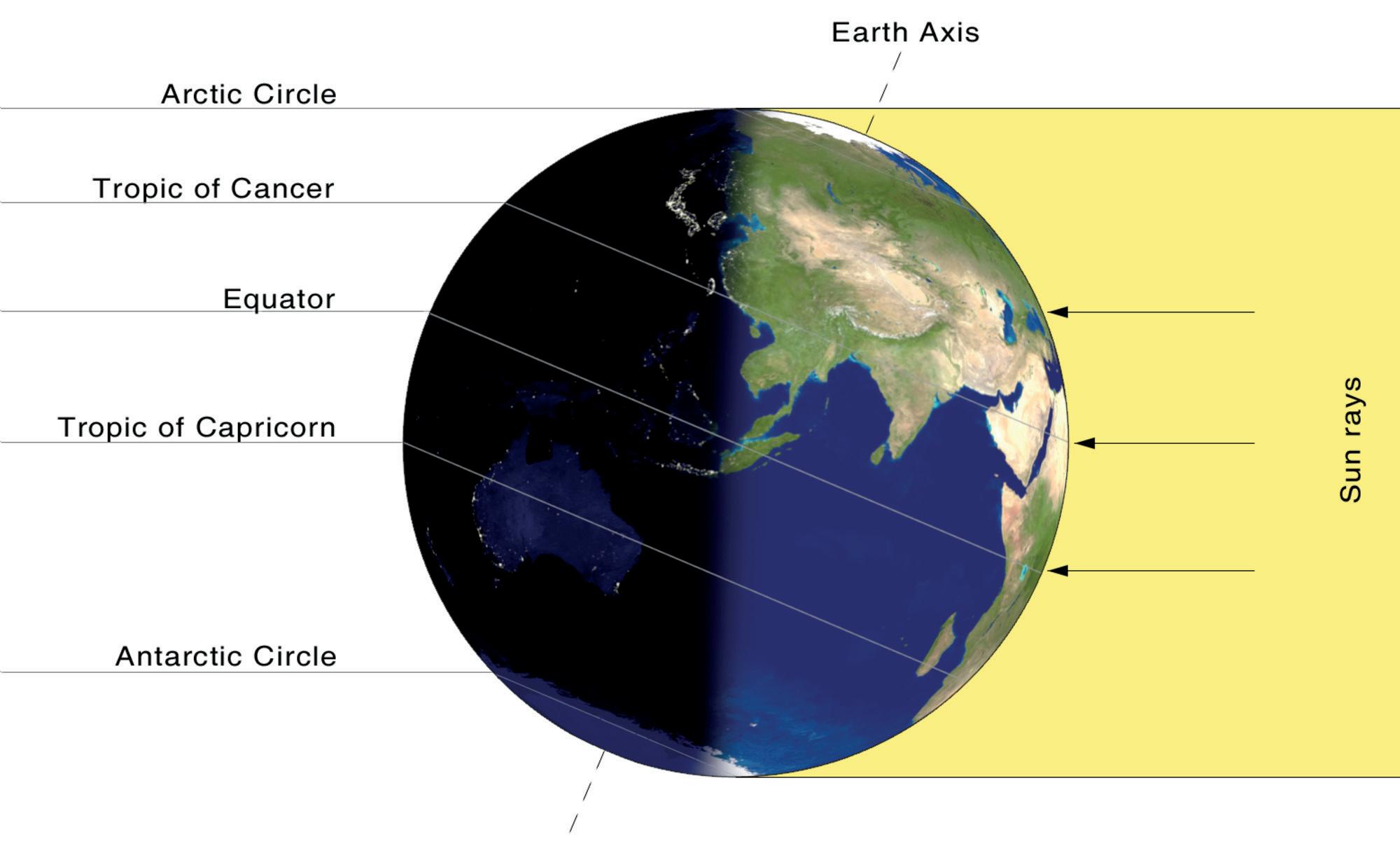
21
On December 22, the Sun's rays fall directly on the Tropic of Capricorn. So, in the Northern Hemisphere, it is the shortest day and is called the winter solstice. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is the longest day and is called the summer solstice.
Solstices are two days in a year when the Sun shines directly on one of the two tropics.
On June 21, the Sun’s rays fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer. So, in the Northern Hemisphere, it is the longest day and is called the summer solstice. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is the shortest day and is called the winter solstice.
– December 22
At the poles during the solstices, the Sun does not set or rise for extended periods. For instance, in the Arctic Circle, on the summer solstice, the Sun remains above the horizon for 24 hours. This creates a unique phenomenon known as the “midnight sun,” where the Sun is visible even at night.

On Sunday morning, when Shreya was playing outside with her brother, she noticed that it was turning dark. They quickly went inside, and Shreya asked her mother, “Why is it turning dark now? It is 11’o clock in the morning.” Shreya's mother replied, “It is because there is a solar eclipse today.”
Eclipses occur when the Earth or the Moon fall into the shadow of each other. This happens because the Earth revolves around the Sun, and the Moon revolves around the Earth. During an eclipse, the Sun, Earth and Moon are aligned in a straight line.
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, partially or completely blocking the Sun’s rays over an area on the Earth. This event can only happen on a new moon day. Because the Sun’s rays are blocked, this phenomenon is called a solar eclipse. We should not look directly at the Sun during a solar eclipse, as it can be harmful for our eyes.
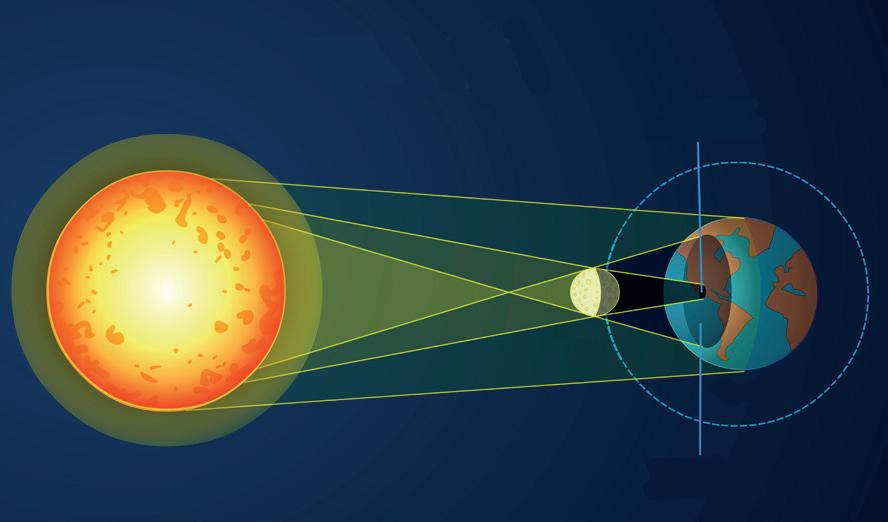
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, partially or completely covering the Moon in its shadow. This is also known as lunar eclipse. It happens on full moon nights. Since the Moon does not produce its own light, it is safe to look at it during a lunar eclipse. During a lunar eclipse, the Moon often appears reddish and generally lasts for a few hours.



Create a simple model using two balls of different sizes to represent the Moon and the Earth. Use a torch to represent sunlight. Arrange the balls in a straight line. First, shine the torchlight with the smaller ball in front of the bigger ball to understand solar eclipse. Then, exchange their places to understand lunar eclipse.
The Nehru Planetarium in Bangalore is one place where you can look at creative models of the Earth’s rotation and revolution to understand things like the axis, the Earth’s tilt, day and night, seasons, equinoxes and solstices, and eclipses.



astronomers: people who study space, including stars, planets and other objects in the universe
rotation: the spinning of the Earth on its axis which is an imaginary line that runs from the north pole to the south pole
orbit: the curved path that one celestial object takes around another celestial object
revolution: the movement of the Earth around the Sun
leap year: the year with 366 days instead of 3651/4
equinox: a time of the year when the day and the night are the same length everywhere on the Earth
solstice: the time of year when the Sun shines directly on one of the tropics

Scan the QR code to learn more about eclipses.
• The Earth takes 24 hours to complete one rotation. The rotation of the Earth causes day and night.
• The Earth moves around the Sun in an oval-shaped orbit and takes 365¼ days to complete one revolution. The revolution of the Earth causes seasons.
• Equinoxes are times in a year when the day and the night are almost equal. It happens twice a year: 21 March and 23 September.
• Solstices are times in a year when the Sun shines directly on one of the tropics. It happens twice a year: 21 June and 22 December.
• During a solar eclipse, the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth.
• A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon. This causes the Earth’s shadow to fall on the Moon.
• Solar eclipses happen on new moon days. Lunar eclipses happen on full moon nights.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. How many hours does the Earth take to complete one rotation?
a. 23 hours
b. 24 hours
c. 30 hours
B. What is the pathway along which the Earth revolves around the Sun called?
a. Orbit
b. Axis
c. Equator
C. On which of these days does the Summer Solstice occur in the Northern Hemisphere?
a. June 21
b. March 21
c. December 22
D. During which event does the Moon pass between the Sun and the Earth?
a. Solar Eclipse
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Lunar Eclipse
c. Solstice
winter solstice solar eclipse axis leap year
A. When the Sun’s rays fall on the Tropic of Capricorn, it is known as in the Northern hemisphere.
B. The Earth rotates on an imaginary tilted line called .
C. A occurs once every four years.
D. It is harmful for our eyes if we look directly at the Sun during a
3. Write True or False.
A. The Earth moves around the Sun in an oval-shaped orbit.
B. During a lunar eclipse, the Moon comes in between the Sun and the Earth.
C. During an equinox, the Sun’s rays shine directly on the tropics.
D. The seasons are caused due to the revolution of the Earth.

4. Match the following.
A. Equinox i. Axis
B. Solstice ii. 366 days
C. Imaginary line iii. March 21
D. Leap year iv. June 21
5. Short answer questions.
A. What causes day and night?
B. How are seasons caused?
C. What is an equinox?
D. What is a solstice?
6. Long answer questions.
A. Differentiate between solar eclipse and lunar eclipse.
B. Differentiate between summer solstice and winter solstice.
7. Picture-based questions.
A. What does this image show?
B. What is the cause of this eclipse?


What do you think would happen if the Earth’s axis was not tilted?

Talk to an elder in your family or your community. Ask them about any folktales or stories related to eclipses.




Weather and Climate
The Atmosphere
Weather and Seasons
Climate and the Factors Influencing It
Climatic Zones


Look at the pictures and think about the type of weather these places would have. Write it in the space given below the pictures.


In this chapter, we will learn more about weather and climate.
The atmosphere is the layer of air that surrounds the Earth, and supports life by providing oxygen and protecting us from harmful rays of the Sun.
The atmosphere has several layers. The temperature changes in each layer depending on how much heat from the Sun is absorbed.

Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time. Has it ever happened that you were out and it was dark and cloudy, but suddenly it became bright and sunny? This happens because weather can quickly change from day to day and hour to hour. Weather can be hot, cold, windy, dry or humid.
Different seasons occur because of changes in weather patterns. In India, we have three main seasons: summer, monsoon and winter. These seasons affect the food we eat and grow, what we wear, our daily activities and the kinds of houses we build.



Climate is the weather pattern of a specific place for a longer period of time. We know that the climate of hilly areas is generally cold and chilly, while deserts have a hot and dry climate. Climate affects things like transportation, food and housing. Scientists who study the climate are called climatologists.
Have you ever wondered why different places have different climates?
Did You Know?
The coldest place where people live is Oymyakon, a remote village in Siberia, Russia. During winter, temperatures here can drop below –50°C.
For example, if you compare the climate of Mumbai and Leh, you will note that Mumbai is warm and humid, while Leh is cold and dry, even though they are both in the same country. Several factors influence the climate of a place. Let us learn about them.
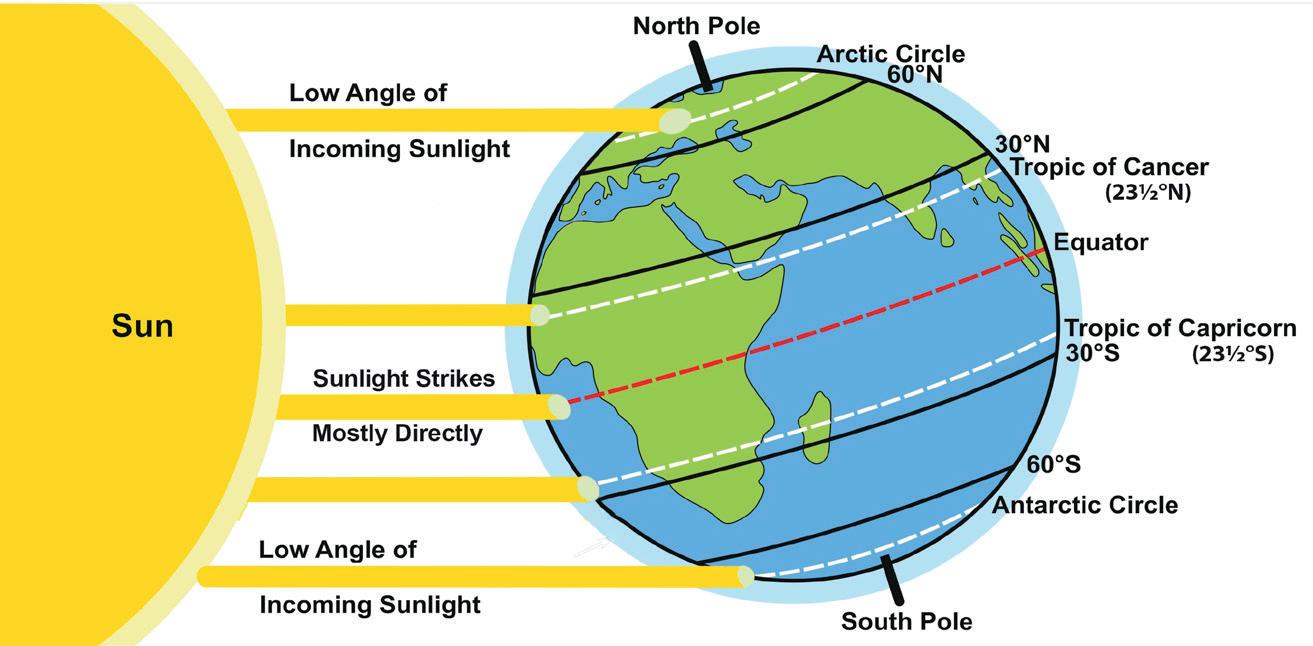
Latitude is the distance of a place from the equator. The Earth is spherical, with the equator as an imaginary line around its middle. The equator receives direct sunlight. In contrast, the North and South Poles receive sunlight at an angle. That is why, the
contrast: to show how two or more things are different from each other


Sun's rays have to travel a longer distance through the atmosphere to reach the Earth's surface around poles. As a result, the rays lose much of their heat by the time they get there. This is why regions near the equator are warmer, while areas near the poles are colder.
Altitude means the height of a place when measured from the sea. Since the sea level is the same everywhere on Earth, so it is used as a reference point for measuring altitude. The climate of a place is significantly affected by its altitude. The layer of air near the Earth's surface is thicker and can absorb and retain more heat. Therefore, areas at lower altitudes tend to be warmer. However, as altitude increases, the air becomes thinner and absorbs less heat. This is why mountain regions are colder, even in the summer, and often have freezing temperatures in winter.


The distance from the sea significantly impacts a region's climate. Coastal areas, like Mumbai, experience a moderate climate due to the sea’s influence. Seas get heated up and cooled down at a slower rate compared to land. That is why coastal areas are cooler in summer than areas which are far from the sea. Similarly, coastal areas are warmer in winters than other areas.

Places that are far from the sea, like Delhi, face extreme temperatures. Without the sea’s moderating effect, these areas experience very hot summers and very cold winters.
in Chile is one of the driest places on Earth, with less than 0.04 inches of rain per year.

Winds are the horizontal movements of air. They play a significant role in influencing the climate of a place. Hot winds can increase the temperature of an area, while cold winds can lower it. Winds also help bring rainfall to certain regions. When winds blow from the sea to the land, they are called sea breezes. These winds carry moisture, making the area humid and warm, and they often bring rainfall. On the other hand, when winds blow from the land toward the sea, they are called land breezes. These winds are dry and do not significantly affect the temperature of the area. In India, the south west monsoon wind brings rainfall from June to September.
Humidity is the amount of water vapour in the air. The heat of the Sun causes faster evaporation in the regions around the equator, which leads to heavy rains in those areas. In regions with less evaporation of water, there is little humidity, leading to dry land and very little rain throughout the year.

Humidity Meter
How is the climate in Shimla different from the climate of the Thar Desert? Discuss with your partner and think of any 2 differences.
Fill in the blanks.
1. The south west monsoon winds bring to India.
2. is the distance of a place from the equator.
3. areas experience moderate climate due to the sea’s influence.
The world is divided into three climatic, or heat, zones. These three zones are the Torrid Zone, the Temperate Zone and the Frigid Zone.
The Torrid Zone lies between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. It receives direct rays from the Sun, resulting in high temperatures and heavy rainfall. It is typically hot and humid throughout the year. This zone generally receives a lot of rainfall.


The Temperate Zone is located between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle in the Northern Hemisphere, and between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle in the Southern Hemisphere. These regions receive slanting rays from the Sun, so the climate is neither too hot nor too cold.
The Frigid Zone is found near the poles, between the Arctic Circle and the North Pole in the Northern Hemisphere, and between the Antarctic Circle and the South Pole in the Southern Hemisphere. It is very far from the equator and receives very slanted rays of the Sun. This zone remains frozen for most of the year. Due to global warming, the ice caps in the polar regions are melting. We must play our part in reducing air pollution and protecting environment so that we can stop global warming.
Polar regions are not always cold and dry. Coastal areas in Antarctica can be humid, and some Arctic regions of Alaska and Canada experience significant snowfall and milder temperatures at certain times during the year.

Gulmarg in Jammu and Kashmir is the ultimate snowy paradise in India. With its breathtaking snow-covered landscapes, fantastic skiing opportunities, and some of the heaviest snowfall in the country, it is the perfect destination for snow enthusiasts.

atmosphere: the layer of air surrounding the Earth temperature: a measure of how hot or cold something is weather: the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time climate: the average weather conditions over a long period climatologists: scientists who study climate and weather patterns latitude: distance from the equator altitude: height of a place above the sea level humidity: the amount of moisture in the air



Scan the QR code to learn more about factors that are affecting climate change.
• The atmosphere is the layer of air that surrounds the Earth.
• The local weather and climate significantly influence people's lifestyles, including their clothing, food and housing.
• Climate is the weather pattern of a place for a longer duration of time.
• The main factors affecting climate include latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, direction of winds and humidity.
• The world is divided into three climatic zones, which are the Torrid Zone, the Temperate Zone and the Frigid Zone.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. The atmosphere is a layer of air that surrounds the
a. Mountains
b. Earth
B. Altitude is the height of a place above the
a. Ground level
b. Sea level
C. The imaginary line that circles the middle of the Earth is
a. Axis
b. Equator
D. How many climatic zones is the Earth divided into?
a. 3
b. 5
c. Water bodies
c. Mountain level
c. Orbit
c. 4


2. Fill in the blanks.
moisture sea breezes climatologists Tropic of Capricorn
A. The people who study the climate are called .
B. Humidity is the measure of present in the air.
C. The Torrid Zone is located between the Tropic of Cancer and the .
D. blow from the sea to the land, bringing moisture, warmth and often rainfall.
3. Write True or False.
A. The atmosphere consists of several layers.
B. Winds blowing from the sea toward the land are called land breezes.
C. The Torrid Zone is situated between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle.
D. The Frigid Zone is far from the equator and remains cold for most of the year.
4. Match the following.
A. Distance from the equator i. Atmosphere
B. Height above sea level ii. Poles
C. Layer of air around Earth iii. Latitude
D. Frigid zone iv. Altitude
5. Short answer questions.
A. Name the factors that influence the climate.
B. What is humidity and how does it affect the climate?
C. Differentiate between sea breeze and land breeze.
D. Differentiate between latitude and altitude.
6. Long answer questions.
A. How does the distance from the equator and the sea affect the climate of a place?
B. Describe the three climatic zones of the Earth.

7. Picture-based questions.
A. What kind of place is this?
B. What will be the climate of this place?
C. What type of clothes should people wear in this place?



What role do trees and forests play in affecting the climate of a place? Mention any two points.

Talk to your grandparents or some older neighbours from your community. Ask them about how weather patterns have changed over the years. Here are some questions you can ask:
1. What was the weather usually like when you were my age?
2. Have you noticed any changes in the weather patterns from the time of your childhood till the present day?














Name the situations the given pictures are telling about. Use can take help from the hints given along with the pictures.


(Hint: When there are
(Hint: When the Earth shakes continuous rains.) and shocks are felt.) Help During Disasters
The pictures above are of natural disasters. A natural disaster is a crisis or a calamity caused by nature. These disasters occur without warning and can cause a lot of damage. They even harm people, animals and the environment. Earthquakes, floods, droughts and cyclones are some of the different kinds of natural disasters. In this chapter, we are going to learn about them.


An earthquake is the sudden shaking of the ground. One of the major reasons for an earthquake is movements under the surface of the Earth. These movements cause sudden tremors on the Earth’s surface.
The intensity of an earthquake is measured on a scale called the Richter scale. A value of 1–2 on the Richter scale indicates mild earthquakes, while that of 6 or above is considered extremely powerful. A machine that records and measures how strong an earthquake is is called a seismograph. The point from where an earthquake originates is called the focus. The place directly above the focus on the Earth’s surface is called the epicentre of the earthquake. The effects of the earthquake are maximum at the epicentre.

The Himalayas and its surrounding areas experience frequent earthquakes. They are also frequent in Japan, the Philippines and on the edges of the Pacific Ocean.
Safety tips to follow during an earthquake:
• Drop to the ground, take cover under a sturdy table or desk and hold on until the shaking stops.
• Move away from windows, glass objects and anything that could fall, like bookshelves or heavy pictures.
• If you are inside, stay there until the shaking stops. Do not use lifts; use stairs instead.
On 26 January 2001, Gujarat was struck by a violent earthquake that recorded 7.7 intensity in the Richter scale. It caused a huge loss of life and property.
Have you ever noticed how the roads in your city sometimes become waterlogged? Sometimes, when the rain is too much for the drains to handle, water starts to collect and cannot flow away easily. This waterlogging is like a small version of what happens during a flood. Floods happen when a lot of water covers the land due to water logging or overflowing of water bodies.
tremors: the shaking or vibration of the Earth's surface sturdy: something that is strong and solid or thick

Floods are often caused by heavy rainfall, cloudbursts and melting snow. Sometimes, when a dam breaks or gets damaged because of heavy rains; all the stored water can rush out quickly and flood the areas downstream of the dam. During floods, buildings are destroyed because of water filling inside them, thereby causing them to collapse. There is so much build up of water that it covers roads, enters homes, and can even sweep away everything in its path. There is loss of crops as floods can wash away crops too. Floods also cause loss of lives of animals. There is a rise in epidemics, like malaria and diarrhoea, after flooding. Assam, West Bengal, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh are frequently affected by floods.
Safety tips to follow during floods:

• Go to a high place like a rooftop or a hill where the water cannot reach you.
• Help in rescuing older people, children and pets who are caught in the water.
• Try to swim away from electronic appliances or heavy furniture.
• If the flow of water is too strong, try to swim to a sturdy pole or a tree, and hold on to it.
• Always listen to the instructions given by rescue officers.
Do and Learn
With the help of internet, prepare an evacuation plan for your family in case of floods. Include the steps to take before, during and after the floods. Share your plan with your friends as well.
Write True or False.
1. Roads become filled with water when floods occur.
2. Earthquakes are measured using the Doppler scale.
3. The breaking of dams can cause floods.
cloudburst: sudden violent rainstorm epidemics: when a large number of people in a specific area get sick from the same disease at the same time


Cyclones are violent storms that form over seas and oceans. They cause great damage when they reach the shore. During cyclones, there is heavy rainfall, and strong winds. In India, the states of Odisha, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu are frequently hit by cyclones.
Safety tips to follow during cyclones:
• Do not go close to the sea or the ocean. If you are out in the open, take shelter immediately. Avoid sheltering beneath trees.

• Stay indoors if you live in apartments or other kinds of pucca houses.
• Stay away from electrical appliances.
Another natural disaster near the coastal regions is a tsunami. They are huge ocean waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions. Large waves come rushing towards the land and cause flooding in minutes. The height of the waves can vary between 10 feet to 100 feet. Tsunamis can flood coastal areas and destroy homes, buildings and roads. The sudden impact of a tsunami can cause numerous people to lose their lives and others to get injured. The salty sea water brought in by the tsunami can make the soil less fertile, affecting farming and plant growth.
Safety tips to follow during a tsunami:

• If you hear a tsunami warning, quickly move to higher ground.
• Pay attention to emergency alerts and warnings from local authorities.
• Do not go to the beach to watch the waves.
• Use evacuation routes to reach safer areas.
numerous: too many
evacuation: safe escape


A drought occurs when there is not enough rain for a long time. This causes a shortage of water for plants, animals, and people. As the underground water levels reduce, availability of water for drinking and other daily purposes becomes scarce. The geographical location of a place plays an important role in determining places affected by droughts. Deforestation, caused due to overgrazing and excessive cutting of trees is also a factor that causes droughts. During a drought, streams, lakes and wells may dry up, leading to a shortage of clean water for families. This makes it hard to cook, drink and wash properly. Farmers are most affected by droughts. Crops dry up and die, which makes it difficult for farmers to grow food. This results in famine and starvation. Animals also struggle because there is not enough water to drink.
Some ways to stop the spreading of droughts are:

• The best way to tackle droughts is by planting more trees. This is known as afforestation. For example, Rajasthan has suffered less droughts after planting more trees.
• Rainwater harvesting techniques should be implemented.
• Water conservation projects should be implemented in states that are prone to droughts.
It is believed that droughts can only happen in very hot places. But that is not true. Droughts can occur in various climates, including temperate and even cold regions, when there is a prolonged lack of rain or snowfall.
A natural disaster can occur anytime. We must be trained and ready to keep ourselves and our family and friends safe if any natural disaster occurs. We must follow these steps in the event of a natural disaster.
• Remain calm and listen to instructions from adults or authorities.
• Move to a safe place away from danger, such as staying indoors during cyclones or going to higher grounds during tsunamis or floods.
scarce: so less in quantity that almost nothing is left famine: extreme scarcity of food


• Organise help and rescue operations.
• Stay updated through radio, TV or official announcements about what is happening and when it is safe to return to normal activities.
• Help people who are affected by natural calamities by donating clothes, money, food and medicines to help them rebuild their lives.

Rescue efforts at an earthquake site
The government also provides help during natural disasters. It invests in advanced technologies to detect natural disasters early. In India, the NDMA (National Disaster Management Authority) lays down policies for effective disaster management. Sometimes, the army is also involved to move people to safer places.
During natural calamities, apart from the government, some other organizations and agencies also help the affected people. Let us talk about some of them.
1. Red Cross Society: Their symbol is a huge red cross on a white background, which is visible on all its vehicles, equipment and clothing worn by its volunteers. The Red Cross provides medical relief to the victims and helps in rehabilitating them.
2. WHO (World Health Organisation): The WHO helps during natural disasters by giving medical care and making sure people have clean water, food and healthcare. This organisation also prevents the spreading of diseases and helps communities get their health services back quickly.
3. UNICEF (The United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund): UNICEF provides financial assistance and essential items, particularly to children. It also ensures that orphans and people with disabilities receive care and support after a natural disaster.


The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) is an Indian force dedicated to helping and rescuing people during natural disasters. It is made up of 16 battalions, each consisting of about 1,149 personnel. The NDRF's rapid and effective response to major disasters has been possible due to its extensive training and the use of advanced technology. NDRF rescuing people during floods
rescue: save from a difficult situation rehabilitating: restoring someone to normal life


natural disaster: a crisis or a calamity caused by nature earthquake: sudden shaking of the ground seismograph: a machine used to record and measure an earthquake flood: a lot of water on land which also enters homes, etc. cyclones: violent storms that form over the sea or the ocean tsunami: a huge ocean wave caused by an underwater earthquake or volcanic erruption drought: when there is not enough rain for a long time

Scan the QR code to learn more about flood prevention management.
• Natural disasters are sudden events that cause widespread death, destruction and damage.
• Earthquake, volcano, flood, tsunami and drought are some examples of natural disasters.
• The government and some other agencies provide rescue and relief support to people affected by natural disasters.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of the following is a natural disaster?
a. Afforestation
b. Tsunami
c. Deforestation
B. Which instrument measures the intensity of an earthquake?
a. Seismograph
b. Thermometer
c. Barometer


C. Which organisation provides relief, particularly for children?
a. WHO
b. UNICEF c. Red Cross
D. A drought occurs when there is .
a. Less rainfall
b. Thunderstorm c. Flooding
2. Fill in the blanks. famine coastal floods cyclone
A. Cyclones and Tsunamis occur in regions.
B. A is always accompanied by heavy rainfall and strong winds.
C. Epidemics, such as malaria and diarrhoea, are common after .
D. A drought can result in a .
3. Write True or False.
A. Drought-hit areas experience heavy rainfall.
B. The army does not play any role during natural disasters.
C. Weather updates over the radio can help during natural disasters.
D. WHO provides relief during natural disasters.
4. Match the following.
A. Drought
B. Tsunami
C. Earthquake
D. Flood
5. Short answer questions.
i. Ground shakes violently
ii. Extreme scarcity of rain
iii. Overflowing of water everywhere
iv. Huge ocean wave formed due to underwater earthquake
A. How can you identify whether the earthquake is mild or severe?
B. How does a drought occur?
C. How does a tsunami affect people?
D. Name any two organizations that provide help during a natural calamity.

6. Long answer questions.
A. Write two measures each to prevent floods and droughts.
B. What are the effects of a cyclone? How can we be safe during a cyclone?
C. What is NDMA? What does it do?
7. Picture-based questions.
A. Identify the natural calamity shown in the image.
B. What are the two after effects of this calamity?

C. Give two safety measures to be followed during this calamity.


Imagine a drought occurs in the Northern Plains of India. What do you think could happen as a result, and how would it affect the country?

Natural disasters, like floods, earthquakes and cyclones, can have a huge impact on the people and the environment. Talk to your parents, neighbours or elders and ask them if they have ever experienced a natural disaster. Find out what happened, how they prepared for it and how they stayed safe. Share the learnings with your classmates.

With the help of your teachers and friends, present a short skit on how to stay safe during an earthquake. You pretend that an earthquake happens while you are at school. Talk about what you would do to keep yourself and your friends safe during the earthquake. Then, present the skit.






Look at the pictures. Put a tick () against the images that are good for the environment.



The environment is made up of all living and non-living things around us. It also includes human-made things. We create human-made things to make our lives easier. These include vehicles, houses, electrical appliances, roads, etc. However, human-made things have also damaged the environment in many ways, like the release of smoke into the air from factories. The damage caused to the environment results in pollution.

Pollution is the introduction of harmful substances in our environment (air, water, land). These harmful substances are called pollutants. Pollution is caused by things like factories and vehicles releasing smoke into the air and the act of littering. There are three main types of pollution—air pollution, water pollution and land pollution. Let us learn about each of them.
When harmful gases, toxic particles, or a lot of dust are released into the air, they cause air pollution. Air pollution is caused when factories, power plants and vehicles release harmful gases and smoke into the air. Burning fossil fuels, like petrol releases a lot of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Also, various natural phenomena such as volcanic eruptions, forest fires and dust storms cause air pollution.

Release of smoke from a factory

from cars

• Gases like carbon dioxide and methane trap the sun’s heat and increase the temperature of the Earth. This leads to global warming, which is the increase in the Earth’s temperature by these gases (especially carbon dioxide).
• The ozone layer is a layer in the atmosphere that protects us from the harmful rays of the sun. But certain gases damage this layer, thereby exposing us to the sun's harmful rays.
• When various harmful gases rise and combine with water vapour in the atmosphere, it results in acid rain. Acid rain damages buildings and forests and is harmful for living beings as well.
• Air pollution causes several diseases such as asthma, lung cancer and bronchitis.

People get diseases due to air pollution.
littering: throwing of waste on the ground or in a public place global warming: the increase in the temperature of the Earth due to the trapping of the sun's heat by gases such as carbon dioxide


Pollution is not something that happens outside only. Indoor air pollution is as harmful as outdoor air pollution. Major pollutants of indoor pollution include vapours from paints, and dust from tiles and cement.
• Encourage afforestation or the planting of trees and plants.
• Use public transport for travelling. Try carpooling with your friends and family rather than using private vehicles. Try to walk wherever possible.
• Recycle garbage instead of burning them.
• Reduce the use of things that use up or burn fossil fuels. For example, electricity comes from burning huge amounts of coal. Switching off lights and fans when not using them reduces the use of electricity, thereby reducing the amount of coal used.
Have you ever seen people throwing garbage into rivers or washing their clothes on the river bank? What do you think happens to the river water due to this?
When things like chemicals, garbage and sewage are dumped into our water bodies, they cause water pollution. Water pollution severely affects aquatic plants and animals and cause a lot of diseases in us.
Many things cause water pollution. Some of them are:
• Domestic chores, like bathing and washing clothes in rivers, ponds or lakes.
• Dumping untreated waste from homes and factories or immersing idols in rivers, ponds or lakes.
• Oil spills caused from oil tankers or oil mining sites pollute the ocean, severely harming marine life. It takes a very long time for the ocean waters to be clean again.


• The consumption of dirty and polluted water causes several diseases like jaundice, cholera, typhoid and dysentery.
• Oil spills make a layer of oil on the surface of the water that reduces the amount of oxygen dissolving in the water. This causes marine plants and animals to choke and die due to lack of oxygen.



• Never throw garbage near or in water bodies such as rivers, lakes or ponds.
• Reuse water to prevent dirty water to be drained into rivers. For example, reuse kitchen water for cleaning your car and watering your plants.
• Use more eco-friendly products so that there is less chemical waste released from your homes.
• Use reusable items instead of items that are thrown away after being used once. For example, reusing glass bottles instead of using and throwing away a plastic bottle.
• Join cleaning drives to voluntarily clean local water bodies like ponds and streams.
Urmi and her father went to the park one evening for a walk. They noticed a garbage dump in a corner. It caused the park to smell, attracted flies, and spoilt the way the park looked. Her father told her that the dumping of waste materials on land is a cause of land pollution.

Land pollution happens when land or soil gets contaminated by harmful substances such as solid waste, garbage, and harmful chemicals. Another cause of land pollution is deforestation. The roots of the trees hold the soil firmly. But when trees are cut down, the fertile soil gets washed away due to running water and strong winds, thereby causing its erosion.
Dumping of non-recyclable waste such as polythene bags, plastic bottles, chemical waste and e-waste (old laptops, mobile phones, televisions and computers) on land causes pollution. Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides for agricultural purposes, and animal and human waste also cause land pollution.

• Most plants need soil to grow. We get our food from plants. Plants grown in polluted soil may contain harmful substances that reach us through the food we eat. This can cause several diseases.
• Some animals and plants die due to soil contamination and hence, the food chain gets disturbed.
• Chemicals in the soil also leak into the ground water or get washed into rivers during rains. This contaminates the water we use for our domestic purposes, and cause diseases.
pesticides: chemical sprays used to kill insects on crops


• Create less waste. For example, carry your water bottle instead of purchasing a new one, each time you go out.
• Plant more trees and use organic manure for agricultural purposes.
• Dispose of waste properly. Throw biodegradable wastes into green bins and non-biodegradable wastes into blue bins.

Complete the following sentences.
1. The increase in the Earth’s temperature is called .
2. Oil spills in oceans reduce the supply of dissolved .
3. One of the main causes of land pollution is . Pause and Answer
Materials that are no longer useful to people are called waste. It is important to dispose of waste properly. Otherwise, it can lead to pollution and the spreading of germs and diseases. Waste is sorted into two types:
• The waste that can be broken down by worms and bacteria when mixed with the soil is called biodegradable waste. Fruit and vegetable peels, paper and leaves are some examples of biodegradable waste. It is useful for the environment. It can be converted into manure, which can be used to improve the fertility of the soil. This is done through a process called composting. In this process, biodegradable waste is buried in the soil for around two months.

Use separate bins for different types of wastes
• Waste that cannot be broken down by worms and bacteria when mixed with the soil is called non-biodegradable waste. Plastic items, metal cans, glass bottles, etc. are examples of non-biodegradable waste.
During waste disposal, biodegradable waste should be thrown in green-coloured dustbins while non-biodegradable waste should be thrown in blue-coloured dustbins.
What are the benefits of using separate dustbins for different types of waste? Is it necessary to do so? Discuss with your classmates.



We should follow the policy of the 3Rs to protect our environment. The 3Rs are: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle.
Reduce: Reduce your usage of things that generates more non-biodegradable waste. We should reduce our usage of plastic since it cannot be broken down in the soil and it creates waste. We should only buy as much as we need so that excess items do not have to be thrown away.

Reuse: Some items can be used again and again. We can reuse plastic bottles to store water instead of throwing them away. We can reuse cloth bags to carry grocery instead of plastic bags. Plastic containers can be used to store things around the house.
Recycle: Items that cannot be reused can be made into other useful items. This process is called recycling. Old newspapers can be used to make paper bags. Waste objects made of metal are melted in factories to make other items. Even water can be recycled. The water that we use to cook food can be used to water plants.
Following the policy of the 3Rs in our daily lives will help us protect our environment and keep it clean and green.
Gather old newspapers, magazines, empty plastic bottles, cardboard boxes and other unusable items from your home. Use your creativity to make new items such as a flower vase, pot holders, pen stands, etc., from these materials. Decorate your new item with the materials of your choice.

The Bishnoi community in Rajasthan is known for their deep respect for nature and wildlife. The Bishnoi people are popularly known for their efforts to save trees from being cut down.



afforestation: planting of trees and plants
deforestation: cutting down trees and forests over a large area of land biodegradable waste: waste from natural materials that can be broken down non-biodegradable waste: waste that cannot be broken down

Scan the QR code to know more about air pollution.
• Pollution is the introduction of harmful substances into the environment.
• There are three major types of pollution—air pollution, water pollution and land pollution.
• When harmful gases or toxic particles are released into the air, they cause air pollution.
• When land or soil gets contaminated by harmful substances such as solid waste, garbage, and metal containers, it causes land pollution.
• When chemicals, wastes and sewage are added into water bodies, these pollute water and cause water pollution.
• Waste can be sorted into two types: biodegradable and non-biodegradable.
• The policy of Reduce, Reuse, Recycle can help us protect our environment.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. One cause of air pollution is a. burning of fossil fuels. b. sounds from factories. c. sewage.
B. Water pollution causes diseases like a. cholera. b. asthma.
c. high blood pressure.

C. We can tackle land pollution by a. recycling. b. throwing garbage in the open.
c. cutting down trees.
D. The 3Rs stand for
a. Reject, Redeem, Repurpose
c. Refuse, Redo, Remember
b. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
2. Fill in the blanks. pollution acid afforestation biodegradable
A. is the introduction of harmful substances into our environment.
B. rain has harmful effects on buildings and living beings.
C. We should throw waste into green dustbins.
D. Planting of trees is called .
3. Write True or False.
A. Air pollution can cause respiratory problems.
B. Water pollution does not affect aquatic life.
C. Planting trees helps reduce air pollution.
D. Recycling means creating new things out of old objects.
4. Match the following.
A. Air pollution
B. Land pollution
C. Water pollution
D. Biodegradable waste
5. Short answer questions.
A. Define pollution and pollutants.
i. Soil-borne diseases, skin allergies
ii. Cholera, typhoid, dysentery
iii. Asthma, lung cancer, bronchitis
iv. Generated from natural things
B. Mention one harmful effect of land pollution on humans.
C. What is global warming?
D. What are the 3Rs about protecting the environment?

6. Long answer questions.
A. Write a note on the causes and ways to control air pollution.
B. What are the two types of waste? How are they different?
C. In what can we apply the 3Rs in our lives to prevent environmental pollution? Give any three ways.
7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Which type of pollution is shown in the given image?
B. How will this type of pollution affect the plants and animals that depend on water?

C. Write two ways that we can use to reduce this type of pollution.


1. A forested area was cleared to build a highway. How do you think this will affect the environment?
2. What would happen if we keep polluting our environment? How do you think it will affect our future generations? Explain in 2 points.

Ask your family and neighbours about how they recycle things at home. Then, discuss with them about more ways of reusing and recycling things that would further reduce the amount of waste produced at home and in your neighbourhood.

With your parents and neighbours, organise a cleanliness drive for a nearby water body. Collect and separate waste into different coloured garbage bags. You can use green colour bags for biodegradable waste and blue/black bags for non-biodegradable waste. Make a note of 5 items you put in each bag.


Objectives: Students will understand the importance of reusing and recycling materials to protect the environment.
Materials Needed: Used plastic bottles, cans, cardboard, scissors, glue, tape, paint or markers, paper, pencils
Step 1: Learn About Reuse and Recycle

Study the basics of Reuse and Recycle, as concepts, from textbooks or online resources. Understand their importance and how they impact the environment.
Step 2: Collect Reusable Items
Gather items from home that are usually thrown away—plastic bottles, cardboard and aluminium cans.
Step 3: Sort the Items
Sort the collected items based on whether they can be reused or recycled.
Step 4: Reuse
Use the sorted items to create something useful, such as turning plastic bottles into plant pots or aluminium cans into pencil holders.
Step 5: Recycle
Work together with your friends or classmates to collect all the recyclable items, like glass and paper. You can then give it away to a scrap dealer for recycling.
Project Output: Now you have created useful items from waste, and contributed to recycling of materials. Share your experience in the class.
Final Outcome: This hands-on project will help you understand the importance of reusing and recycling materials; and how they can positively impact the environment by reducing waste output. To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.


Read this news article. Answer the questions given below.
On Monday, a powerful cyclone named Cyclone Vara hit the coastal city of Vardhanpur, causing heavy rain and strong winds. The cyclone warning was issued two days before the storm, giving the local government time to prepare. Early preparations included evacuating people from low-lying areas and closing schools and offices. Emergency shelters were set up, and rescue teams were kept on standby. Despite these efforts, the cyclone damaged many homes, uprooted trees, and disrupted electricity supply across the city. The local hospital reported a few injuries but, fortunately, no loss of life.

After the cyclone passed, the government quickly began the repair work. Workers cleared fallen trees and restored power lines. Roads were repaired, and relief camps provided food and water to those whose homes were destroyed. The city’s mayor praised the efforts of the citizens and emergency workers in their timely response to the crisis. Although Vardhanpur is recovering, it will take time for the city to return to normal.
1. What was the name of the cyclone that hit Vardhanpur?
a. Cyclone Vara
c. Cyclone Titli
b. Cyclone Vayu
d. Cyclone Phailin
2. Why were people evacuated from low-lying areas before the cyclone?
a. To protect buildings
c. To ensure safety from flooding
3. How did the cyclone harm the city?
b. To prevent waterlogging
d. To stop traffic jams
4. Imagine you are the mayor of Vardhanpur. What additional steps would you take to make sure the city is better prepared for future cyclones? Write any two steps.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.












Location
Chapter Overview Get Set

Industries,



Read the poem given below. It is about a beautiful country, the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
In Congo’s heart, the rivers flow, Through forests deep where wild things grow. With mountain peaks that kiss the sky, And vibrant sunsets waving goodbye. From Kinshasa’s streets to jungle’s call, The spirit of Congo unites us all.
A land of beauty, rich and wide, Here culture and nature, side by side.

of the Congo Lifestyle

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is located in central Africa. The Equator passes through the northern part of the country. It is the second largest country in Africa. The capital of the DRC is Kinshasa. Its neighbouring countries are the Central African Republic, South Sudan, Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, Tanzania, Angola and Zambia.
The DRC was ruled by Belgium until 1960.
The Congo is the main river in the DRC. The Congo basin is huge and covers almost the entire country. The southern part of the DRC has plateaus. High mountains are present in the east.
Since the DRC is near the Equator, the climate is hot and humid all year round. The north of the DRC receives heavy rainfall in the afternoon almost every day. Due to this, it is one of the wettest regions in the world. The southern part of the DRC is drier and has less rainfall.

What are some ways in which the Congo River might be important to the people of the DRC? Discuss with your classmates.
Most of the DRC is covered in dense vegetation. The hot and humid climate is suitable for the growth of tropical rainforests. These are evergreen forests. The trees here are very tall and closely
The Congo rainforest is the second largest rainforest in the world. It is also called the ‘Lungs of Africa’.
basin: the area of land around a large river from which smaller rivers and streams run down to it


packed together. Their branches get tangled with each other and form a canopy of leaves at the top. This canopy prevents sunlight from reaching the ground.
Evergreen forests have trees that remain green throughout the year since they lose old leaves and grow new leaves continuously.
In the south, the climate is not as hot and wet as in the north. So instead of dense forests, there are grasslands like the savanna. The forests and savannas of the DRC are very rich in wildlife. Animals such as chimpanzees, baboons, elephants, buffaloes, rhinoceroses and hippopotamuses are commonly found in the forests. Lions, leopards, zebras, giraffes and wolves can be found in the savannas. Crocodiles are present in large numbers in the rivers. Many kinds of birds, insects and snakes can also be found in the forests.


Find pictures of 2 plants and 5 animals found in the DRC, other than the ones shown in this chapter. Paste them in your scrapbook and write their names next to their pictures.
Write True or False.
1. The Congo is the longest river in Africa.
2. The equator passes through the DRC.
3. The DRC experiences heavy rainfall in the afternoon every day.
4. The DRC has deciduous forests.
canopy: the uppermost branches of the trees in a forest, forming a continuous layer of leaves



In the DRC, the main industries are mining and agriculture. The country is rich in minerals like cobalt, which is used in batteries, and diamonds, which are precious gems. The country also has gold, which is used for making jewellery, and electronics and coltan, which is used in phones and computers. These industries help support the DRC’s economy.
Agriculture is also important, with people growing crops like cassava, rice, maize, coffee, cocoa, rubber and cotton. Most of these are exported as well. Dams have been built on rivers in DRC, providing hydroelectricity.
Water transport is the major means of transport in the DRC. Railways and road networks connect different cities.


The DRC has a significant population, but much of it is rural, with many people living in villages. They live in huts which are built on raised platforms to protect them from the heavy rainfall. They grow crops like cassava and plantains.
The DRC is home to different tribes with unique customs and traditions. For example, the Bambuti people, also known as Pygmies, live in the rainforest and have a special bond with the forest. They are known for their small size and they use traditional hunting skills to find food. The Twa people also live in the forest and have similar customs.
The Babinga people live in the southern part of the country and are known for their colourful clothes and intricate beadwork.
People in the DRC often wear bright, patterned clothing made from local fabrics. Customs and festivals are an important part of life. For example, people celebrate with dances, music, and traditional ceremonies that have been passed down through generations. Life in the DRC is rich in culture and sense of community.



India has supported various UN peacekeeping missions in the DRC to maintain stability and support the local population. These initiatives reflect India’s commitment to international cooperation and its role in global affairs.

A UN peacekeeper soldier
tropical rainforest: dense and warm rainforests with high rainfall usually found between 10° north and south of the equator
savanna: grassy plains in tropical and sub-tropical regions
tribes: a group of people who have the same language, customs and live in their separate society

Scan the QR code to learn more about the Congo River of the DRC.
• The Congo is the main river in the DRC.
• The DRC is rich in minerals like cobalt, used in batteries, and diamonds, which are precious gems.
• Lions, leopards, zebras, giraffes and wolves can be found in the savannas.
• People in the DRC often wear bright, patterned clothing made from local fabrics.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which is the main river in the DRC?


B. Which of the following tribes live in the rainforest of the DRC?
a. Bambuti b. Banjaras c. Inuits
C. Which of these crops are grown in the DRC?
a. Wheat
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Millets c. Rubber
Babinga Coltan Savanna Canopy
A. The tribe in the DRC is known for its beadwork.
B. The tall trees in the forests of the DRC form a which prevents sunlight from reaching the forest floor.
C. is used in phones and is found in the DRC.
D. In the south of the DRC, there are grasslands called the .
3. Write True or False.
A. The DRC has tropical rainforests.
B. The DRC is the second largest country of Africa.
C. Republic of the Congo is the capital of the DRC.
D. The southern part of the DRC has plateaus.
4. Match the following.
A. Savanna i. Batteries
B. Kinshasa ii. Giraffes
C. Cobalt iii. Gold
D. Jewellery iv. Capital of the DRC
5. Short answer questions.
A. Why does it rain every day in the DRC?
B. Name any three crops grown in the DRC.
C. Name any two neighbouring countries of the DRC.


6. Long answer questions.
A. What kind of lifestyle do the people of the DRC have?
B. Describe the wildlife of the DRC in the north.
C. What type of climate does the DRC have?
7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the questions that follow.
CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC
CAMEROON
EQUATORIAL GUINEA
REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
SOUTH SUDAN
ATLANTIC OCEAN
A. Which countries border the DRC in the north and in the west?
B. Which ocean is closest to the DRC?

Compare the climate of the Democratic Republic of Congo with the climate in your state. How are they similar or different? Write any 3 points.
The Congo Rainforest are called the ‘Lungs of Africa’. With the help of the internet, research on the Congo Rainforest. Then, write 5 points on how it helps the environment of the DRC and of Africa. You may make this as a poster. Share your findings with your class.





Greenland: The Land of Ice and Snow
Location and Climate
Vegetation and Wildlife Occupations and Transport
Lifestyle


Which of the following places will be the coldest? Put a tick (✓) against it.



Greenland is located in the Atlantic Ocean, to the northeast of North America. It is a territory of Denmark. Its capital is Nuuk. Sisimiut is another important town.
The North Pole and the South Pole are located at 90-degree north and 90-degree south latitudes, respectively.


Greenland is the largest island in the world. The Arctic Circle passes through the southern part of Greenland. It lies in the frigid zone, which means it experiences very cold temperatures throughout the year.
The climate of Greenland is extremely cold, with long, icy winters and short, cool summers. Temperatures can drop below –30°C in winter and rise only slightly above the freezing point in summer. Most of this island is covered in ice.

GREENLAND (DENMARK)
Upernavik
Ittoqqortoormiit (Scoresbysund)
Sisimiut (Holsteinsborg)
Nuuk (Godthab)
The southwestern part of Greenland is warmer, and hence, most people live in this part.
Most of the plants grow in the tundra region, towards the coast and away from the ice sheets in central and north Greenland. Low-growing plants like dwarf birch and whortleberry, as well as mosses and lichens, can be found in this region.
Animals, like the polar bear, reindeer, seal, wolf, arctic fox and musk ox, are found here. All these animals are able to withstand extreme cold.

Many kinds of fish and birds, like the white-tailed eagle, are also found here. Seals and walruses are some of the large marine animals found in this region. Many species of whales, such as fin, minke, humpback, narwhal, beluga (white whale) and blue whale are found in Greenland.
A walrus and her pup
lichens: a group of tiny plants that grow on rocks, walls and trees



Animals are very important to people in the tundra region. Their meat, bones, skin and milk are used by the people for food, clothing and shelter.
Polar bears are the largest carnivorous land mammals on Earth. They are also very strong swimmers. They can swim continuously for many days.
Write True or False.
1. Greenland is very fertile with lots of vegetation.
2. The Antarctic region is situated between 66.5°S and 90°S.
3. Seals, whales and walruses are found in Greenland.
The most important occupations in Greenland are hunting and fishing. Sheep are also reared in small numbers in the southwestern part of the country. Vegetables, such as potatoes, are grown in the southwest part of Greenland.
Since most of Greenland is always covered with ice, it is not possible to build roads and railways throughout the island. People travel by sledges, which are drawn by reindeers or dogs found there. A sledge is a vehicle that has blades instead of wheels and is used in places that are covered with snow. People also go out into the sea in small boats called kayaks and umiaks. Kayaks are narrow boats that can carry one or two people. Umiaks are larger open boats, made of animal skin stretched over a wooden frame and can carry ten or more people at a time.



carnivorous: an organism that eats flesh of other animals mammals: animals that give birth to babies instead of laying eggs and feed the babies milk from their own bodies


Most people in Greenland are Inuits who have lived there for thousands of years. The Inuit people are known for their special skills in surviving in freezing temperatures. Many people in Greenland live in small towns or villages along the coast. The houses are made of strong materials, like wood, stones, or even concrete, with thick walls, to keep out the cold. Central heating is also common in modern homes.
What are the different ways in which the lives of the people of Greenland are influenced by its environment?

In the past, the Inuit people led a nomadic life, which means they did not settle at one place and kept moving from one place to another. They lived in igloos during the winter and in tent-houses made of leather during the summer. Igloos are dome-shaped houses made from blocks of snow. An igloo
Make a chart about the Inuit people of Greenland. Paste pictures and write about their food habits, clothing, occupations, modes of transport and festivals. Give the chart a creative title. Do and Learn
People in Greenland eat food that comes from the sea, like fish, seals and whales. Earlier people used harpoons to hunt, but now they use guns. They also eat reindeer, birds and imported foods from other countries. Hunting and fishing are still important activities in their culture, helping them survive the cold environment.
People here mostly wear clothes made of animal skin and fur to keep themselves warm. A jacket with hoods and lined with animal fur is quite popular here. It is called parka. They wear long boots made of seal skin, which makes it easy to walk in snow and keep their feet warm.
Most people live in the southwestern part since it is less cold there. Modern facilities, like schools, hospitals, permanent homes, electricity, etc., are present in these areas.

harpoon: a spear-like instrument that is attached to a long rope and thrown by hand



The Siachen glacier is one of the longest glaciers outside the polar regions. It is located in Ladakh, India.

sledge: a vehicle without wheels that is used to travel in snow kayak: a small, narrow boat with a small opening at the top for a person to sit in umiak: an open boat made of animal skin stretched over a wooden frame igloo: a dome-shaped house made of snow parka: a jacket with a hood and lined with animal fur

Scan the QR code to learn more about life in Greenland.
• Greenland is the largest island in the world.
• The Arctic Circle passes through the southern part of Greenland.
• The most important occupations in Greenland are hunting and fishing.
• Since Greenland is mostly covered in ice, plants like mosses and lichens grow here.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. In which region is Greenland located?
a. The Torrid
b. The Temperate c. The Polar
B. What are the native people of Greenland called?
a. Inuits
b. Babingas c. Bengalis


C. In the past, what did people use for hunting?
a. Hooks
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Harpoons c. Crossbows
A. Greenland is a territory of .
B. is the capital of Greenland.
C. is an important town in Greenland.
D. Inuits live in in winters.
3. Write True or False.
A. Most of Greenland is permanently covered with ice.
B. Greenland has a large network of railways.
C. Lots of vegetation is found in Greenland.
D. Greenland is located in the Atlantic Ocean.
4. Match the following.
A. Umiak i. A jacket with hood, lined with animal fur
B. Sledge ii. A boat that can carry many people
C. Parka iii. A boat meant for one person
D. Kayak iv. A vehicle without wheels
5. Short answer questions.
A. What are some of the occupations of the people of Greenland?
B. Name any three species of whales found in Greenland.
6. Long answer questions.
A. How is the climate of The Democratic Republic of the Congo different from that of Greenland?
B. How does the location of Greenland influence the life of the people there? Mention any three points.
C. What kind of clothes do people wear in Greenland?

7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. What is the boat in the picture called?
B. Do you think roads and railways can be used in the place shown in the picture? Why or why not?


Imagine you had to live in Greenland for a month. Write about the following:
1. Two things you would eat.
2. Two things you would wear.
3. Two ways in which you will travel around.
4. Two things you will do there.

Houses are built depending on the weather and the climate of the area in which they are built. With the help of your parents or elders, understand how the houses in your region are designed to suit the climate there.



Chapter Overview

Cities and Some Places of Interest

Get Set

We know that deserts have extreme climatic conditions. Name two plants that grow in deserts.


Major desert regions of the world
Saudi Arabia is a country in the western part of Asia. It is located in the Arabian Peninsula. A peninsula is a land which is surrounded by water on its three sides. Saudi Arabia has the Red Sea on the west and the Persian Gulf on the east. Riyadh is the capital of Saudi Arabia. Some of its neighbouring countries are Jordan and Iraq to the north; Kuwait to the northeast; Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; and Oman and Yemen to the south. It is the largest country in West Asia.
map of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia has the world’s largest continuous stretch of desert land. Deserts and plateaus cover the central and eastern parts of the country. The desert region is covered with hills of sand called sand dunes. The western part of Saudi Arabia is mountainous. Saudi Arabia does not have any



lakes or perennial rivers. Streams called wadis are occasionally formed after rainfall, but they disappear quickly. Due to this, Saudi Arabia has very little freshwater. In some places in deserts, underground bodies of water rise to the surface. These are called oases.

Do you think wadis and oases are important for the animals which live in the desert? Discuss with your classmates.
The Tropic of Cancer passes through Saudi Arabia, dividing the country into two halves. During summers, it has extremely hot weather with temperatures above 50° C at times. In the desert, the temperature varies greatly from day to night as well. It is very hot during the day and cold at night. The climate throughout the year is extremely dry as Saudi Arabia receives very little rainfall.
The plants that grow here have adapted to the hot and dry climate. They mostly have very long roots that go deep into the earth in search of water. They have thick, fleshy stems which can store water. Many of them have spines instead of leaves in order to minimise water loss. Some of the plants that can be found here are cacti, thorny bushes and shrubs. Trees like date palms grow in and around the oases.

How does having spines instead of leaves help trees in minimising water loss?


Deserts have very harsh climatic conditions. All the animals that live in the desert have to adapt to conditions like the shortage of food and water, and extreme heat to survive. A wide variety of animals are found in Saudi Arabia. Horses from Arabia are known all over the world for their speed. Other fast animals like gazelles, foxes and jackals can also be found in the Saudi Arabian desert. They can move across the desert very quickly in order to find food. Small animals like scorpions and snakes burrow into the sand during the day to escape the extreme heat. They come out at night to hunt for food.
We have previously learnt that the camel is known as the ‘ship of the desert.’ Camels have special adaptations that enable them to survive in the desert. They can store water in their bodies for many days. The food that they eat is stored in their hump. This allows them to survive without food or water for many days. Camels also have thick eyelids and nostrils which prevent sand from entering them. They can eat the thorny vegetation that is found in the deserts since they have rough tongues. They have wide, padded feet that do not sink into the sand. So, they can travel across the desert easily.
Bustards, pigeons, and quails are some of the birds that can be found in the desert. They are usually found around the oases.
In the mountainous regions of Saudi Arabia, animals like ibex, wolves, hyenas and wild cats are found. The coastal areas of the country are rich in marine life. Sea birds like pelicans are found here.



Write whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Riyadh is the capital of Saudi Arabia.
2. The Tropic of Capricorn passes through Saudi Arabia.
3. Arabian horses are called the ship of the desert.
adaptations: changes through which living beings become better suited to their environment


The discovery of oil in Saudi Arabia in 1937 transformed the country and the lifestyle of the people greatly. Saudi Arabia’s main industry is oil. Saudi Arabia is one of the largest producers of petroleum in the world. It exports petroleum to different countries all over the world.
Iron and steel, cement and construction are also important industries in the country. It is very difficult to carry out agricultural activities in Saudi Arabia due to the harsh environment. Only a small part of the country is suitable for growing crops. Crops such as wheat, rice and alfalfa are grown. The water required for irrigation is obtained through the desalination of seawater.
The export of petroleum has made Saudi Arabia a wealthy country. This has contributed to its rapid development. It has modern cities which have very good infrastructure. The standard of living of the people who live in the cities is very high. Saudi Arabia has a traditional society. Women generally wear abaya. Abaya is a robe worn over clothes which covers from head to toe. Men wear loose-fitting white robes called thobe. Their heads are covered with a chequered cloth called keffiyeh.
Saudi Arabia is a monarchy, which means it is ruled by a king. Arabic is the main language spoken by the people. How do you think the ruler in a monarchy is chosen?
One of the native Arab tribes in Saudi Arabia are the Bedouins. They are nomadic people. They travel on camels in groups known as caravans. They rear camels, goats, sheep and horses.
alfalfa: a kind of legume infrastructure: the systems and facilities available in a place robe: a long, flowing outer garment nomadic: living by travelling from place to place




The animals are very important to the Bedouin. They provide them with milk, meat and animal hide. During summers, they camp in and around oases where their animals can graze. In winter, they travel along those desert routes where water can be found.

Make a chart about the Bedouin people. Paste pictures and write about their clothes, food habits and houses. Give a title to your chart and display it in the class.
The capital of Saudi Arabia is Riyadh. Most of the government ministries and public service headquarters are located here. It is full of skyscrapers, parks, hospitals, educational institutions and markets.
Jeddah is a port city. It is a very important centre of trade and manufacturing. It is also known as the commercial capital of Saudi Arabia.
Mecca is the most important site of pilgrimage for Muslims in the whole world. Medina is another city of great religious importance. Both these cities are located in Saudi Arabia.



The Thar Desert in India is home to many different species of birds and animals. It is the native place of the Great Indian Bustard, which is at a great risk of dying out. In 2013, the government of Rajasthan launched Project Great Indian Bustard for the conservation of this species.
animal hide: animal skin that can be used to make tents or clothes skyscrapers: a very tall building in a city



wadis: temporary streams formed after rainfall in the desert
oases: underground bodies of water in deserts that rise to the surface
desalination: a process through which salt is removed from seawater
monarchy: a type of government where the king is the ruler of the country
Bedouin: one of the native Arab tribes with a nomadic lifestyle caravan: a group of people travelling together in a desert

Scan the QR code to learn more about Saudi Arabia.
• A desert is a large area of land which receives very little rainfall and has little to no vegetation.
• Saudi Arabia has the world’s largest continuous stretch of desert land. The capital of Saudi Arabia is Riyadh.
• Saudi Arabia has extremely hot and dry weather conditions. It is hot during the day and cold during the night.
• Camels have special adaptations that enable them to survive in the desert.
• Saudi Arabia is one of the largest producers of petroleum in the world.
• Saudi Arabia is a monarchy.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer:
A. What is the capital of Saudi Arabia?
a. Jeddah
b. Riyadh
B. What kind of government is in Saudi Arabia?
a. Republic
b. Democracy
c. Medina
c. Monarchy

C. Which animal is called the ship of the desert?
a. Camel
b. Ibex
c. Hyena
D. Which of the following is a neighbouring country of Saudi Arabia?
a. Afghanistan
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Syria
c. Oman
Bedouin Jeddah oil date palms
A. Saudi Arabia is one of the largest producers of in the world.
B. are trees that grow in and around oases.
C. is known as the commercial capital of Saudi Arabia.
D. The are a nomadic Arab tribe in Saudi Arabia.
3. Write True or False.
A. Mecca is the most important pilgrimage site for Muslims.
B. The Bedouin people do not have permanent homes.
C. The main language spoken by the people of Saudi Arabia is Arabic.
D. Desert plants have big leaves from which a lot of water can evaporate.
4. Match the following.
A. Bedouin
B. Monarchy
C. Camel
D. Wadis
5. Short answer questions.
A. Where is Saudi Arabia located?
i. Temporary streams
ii. Nomadic herders
iii. Ruled by kings
iv. Ship of the Desert
B. What is the main industry in Saudi Arabia?
C. What is an oasis?
D. How is water obtained for irrigation in Saudi Arabia?
E. Name the types of clothes worn by the people in Saudi Arabia.


6. Long answer questions.
A. What are some of the adaptations that camels have that make them suited to the desert climate?
B. What is the lifestyle of the Bedouin people like?
7. Picture-based questions.

A. Which physical feature is seen in the above image?
B. How is this feature formed?
C. Name one tree that grows in and around this feature.

In what ways do you think the discovery of oil in Saudi Arabia played an important role in the growth of the country and the changing lifestyle of the people of Saudi Arabia?

Saudi Arabia is the world’s largest producer of petroleum. Petroleum is a fossil fuel, and the burning of fossil fuels is harmful to the environment. Make a poster to show why fossil fuels are harmful for the environment. Paste pictures and cutouts of newspaper headlines. Give the poster a title.



Prairies: Temperate Grasslands
Meaning and Types
Location and Climate
Vegetation and Wildlife Economy
Lifestyle and People

Get Set

Find and circle the given words in this word search puzzle.
1. OATS
2. BARLEY
3. WHEAT
4. MAIZE
All of these can be found in North American grasslands called Prairies. In this chapter, we will learn more about them.


Grasslands are vast areas of flat land where the main vegetation is different kinds of grasses. In some places, grasslands are located between forests and deserts. There are two kinds of grasslands: tropical and temperate. Tropical grasslands are located between 0 degree and 23.5 degree latitudes in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres.
Temperate grasslands are located between 23.5 degree and 66.5 degree latitudes in the Northern and Southern hemispheres. The climate is hot during summer and cold during winter.
Temperate grasslands are called by different names in different regions. They are called prairies in North America, pampas in South America, steppes in Europe and Asia, downs in Australia and velds in South Africa.
Let us learn more about the prairies.
Grasslands are not just flat lands with grass. Grasslands can have rolling hills, and plants such as wildflowers and shrubs.
The prairies are in North America. They cover parts of Canada, the USA and Mexico. Like other temperate grasslands, the prairies experience hot weather during summer and cold weather during winter. There is moderate rainfall during the summer.


There are many different types of grasses and shrubs that grow in the prairies. The soil is very fertile due to the presence of humus, making it one of the largest farming areas in the world. The green grass turns brown in the autumn. There are not many trees, but a few can be found along the rivers.
Wildlife
Long ago, the prairies were grazing grounds for large herds of bison. However, due to the clearing of land for agriculture, there are fewer bison than before. Coyotes, prairie dogs, hawks and prairie chickens are commonly found in this region.
Make a poster on prairie wildlife. You may use the internet for your research. Find out how they are adapted to their environment and how they interact with other animals and plants.

Bison in the prairies
The prairies are also very important for migratory birds. Many migratory birds stop there for food and rest during their long journey between their summer and winter habitats.


Write whether the following statements are true or false.
1. The prairies are in South America.
2. The prairies are one of the largest farming areas in the world.
3. Large herds of bison used to graze on the prairies.
The main occupation in the prairies is farming. The land was converted into farmlands by the settlers who arrived from Europe. Wheat is the main crop that is grown there. Maize is also grown there apart from wheat. Other crops that are grown here include oats, rye, barley and beans. The prairies are known as the ‘wheat basket of the world’. The USA is one of the largest exporters of wheat.
In the western region of the prairies, cattle are reared on large farms called ranches for meat and dairy products.
The prairies are also rich in minerals. There are large deposits of coal, petroleum and natural gas. Other minerals like gold, silver and potash are also mined here.


It is important to remember that the prairies are home to many different species of animals. Human activities should not be allowed to affect the animals or the environment of the prairies.
The prairies have large grasslands where many animals live. What do you think would happen if more and more land is used for farming and animals are not allowed to graze there?
The prairies are thinly populated. Farmers and their families, as well as workers, live on very large farms. Almost all farmwork, such as ploughing, sowing, threshing, harvesting and winnowing, is done by machines.
ploughing: turning the soil before sowing seeds threshing: thrashing the grain to separate the edible part from the inedible part winnowing: blowing air through the grain to remove the husk



The Gir Forest National Park in Gujarat contains tropical grasslands as well as dry deciduous forests. It is famous all over the world as the only natural habitat where Asiatic Lions still live in the wild.

grasslands: vast areas of flat land where the main vegetation is different kinds of grasses prairies: temperate grasslands in North America ranches: large farms where cattle are reared

Scan the QR code to learn more about the prairies.
• Grasslands are vast areas of flat land where the main vegetation is different kinds of grasses.
• The prairies are located in North America. It is one of the largest farming areas in the world today.
• Cattle are reared on large farms called ranches.
• The farms in the prairies are very large. Almost all farm work is done by machines.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What are the temperate grasslands in South Africa called?
a. Prairies
b. Velds
c. Steppes
B. What substance does the soil in the prairies contain that makes it fertile?
a. Humus
b. Sand
c. Clay


C. What is the main crop cultivated in the prairies?
a. Maize b. Barley c. Wheat
D. Which type of grasslands are located between 0 degree and 23.5 degree?
a. Tropical b. Temperate c. Polar
2. Fill in the blanks.
grass ranches wheat basket bison
A. Cattle are reared on large farms called .
B. The prairies used to be the grazing grounds for large herds of .
C. The main vegetation on the prairies is .
D. The prairies are called the of the world as a large amount of wheat is cultivated here.
3. Write True or False.
A. The temperate grasslands in Australia are called downs.
B. Rice is the main crop cultivated on the prairies.
C. Mining is the main occupation on the prairies.
D. Almost all farm work on the farms of the prairies is done by machines.
4. Match the following.
A. South America i. Pampas
B. Eurasia ii. Downs
C. Australia iii. Velds
D. South Africa iv. Steppes
5. Short answer questions.
A. What are temperate grasslands?
B. What are ranches?
C. Name 2 minerals that are found in the prairies.
6. Long answer questions.
A. What are the 2 types of grasslands and where are they found?
B. Explain the climate of the prairies.
C. Why do you think the prairies are thinly populated? Give two reasons.


7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the picture and answer the following questions.
A. Identify the animal in the picture.
B. Where is this animal found?
C. Name any two other animals found in this region.


Why do you think machines are needed in to do different kinds of farm work on the prairies? Give two reasons.
The prairies are known for their wide-open spaces, where there is plenty of sunlight and wind. These natural resources can be used to generate clean energy, like wind energy and solar energy. Work with a friend and find out three ways in which farms and homes on the prairies can produce their own energy. You can take help of your elders, books from the library or the internet. Share your findings with the class.























Steam Engine and Modern Means of Transport Land Transport Airways
Waterways


Traffic and Pollution


Imagine that you need to visit your friends in your city, in another city and in another country. Draw pictures of the different types of transport you will use to visit each.
In your city
In another city In another country
Salina lived in New Delhi with her parents. One day, they had to travel to Bengaluru for a wedding. Salina and her parents first travelled to the airport using the metro rail. Then, they travelled in an aeroplane to reach Bengaluru. Salina was amazed by how she reached the other side of the country in just a few hours.
Travelling long distances in earlier times was difficult and took a lot of time. People usually walked from one place to another and used animals to carry their goods.


Transport refers to the ways people or goods move from one place to another. Bicycles, scooters, cars, rickshaws, buses, ships, trains and aeroplanes are different means of transport. Choosing any means of transport depends on the distance to be travelled, the money to be spent and the time available.

After the invention of the wheel, the most important invention was the steam engine. The first steam engine was built by Thomas Newcomen in 1712. In 1765, James Watt improved the design. A steam engine is a type of heat engine used to perform mechanical work using steam. Earlier steam engines were built to run railway engines and trains. After some time, ships were made that used steam engines. Now, steam engines have been replaced by engines that use diesel and electricity. This has helped trains to run faster and carry more goods and passengers.
Earlier, people found it difficult to travel from one place to another. But today, modern means of transport have made it easier for people to reach distant places. The three modern means of transport are land transport, water transport and air transport.
With the help of the internet, do research and create a visual timeline showing the evolution of different modes of transportation—from ancient modes (walking, horse-drawn carts, etc.) to modern modes (cars, aeroplanes, electric scooters, etc.).
The movement of goods and passengers on land is known as land transport. This is the mode of transport we use most. People and goods can travel through roadways


and railways from one part of the country to another. Land transport is also cost-effective. Land transport can be divided into roadways and railways.
Vehicles such as cars, buses, tractors, etc., are driven on roads, which are built on the surface of the land. After independence, many efforts were made to develop the roadways. India has one of the largest road networks in the world. Many countries have networks of wide, paved roads called highways. Highways connect different cities within a country. They are long, mostly straight roads which do not have sharp curves, turns and roundabouts. This enables people to drive on these roads at speed for long distances. They can reach places faster. In India, national highways, state highways, district roads and village roads have been built to make transportation easier.
A part of India’s highway network is called the Golden Quadrilateral network. It consists of highways that connect four important cities of India—Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata.
Trains are an important means of transport in many countries. They can transport people and goods over long distances. Railway tracks are built and connected to each other to form a railway network. In India, the first train journey took place between Mumbai and Thane in 1853. Today, India has thousands of trains. The introduction of superfast trains has made movement faster and cheaper than before. The Gatimaan Express and the Vande Bharat Express are the two of the superfast trains in India.
Metros are trains that run within cities. They run on tracks that are built either underground or on bridges in the city. Metro rail networks were developed to improve the public transportation
NH 44 is the longest national highway of India. It runs from Sri Nagar to Kanyakumari, covering 4112 km.


cost-effective: of good value as per the amount of money spent network: a system of intersecting roads or railway tracks

system in urban areas. They help people move from one place to another without worrying about the traffic. The first city in India to have the metro rail was Kolkata. Now, many cities such as Delhi NCR, Mumbai, Chennai and Bengaluru also have metro rail networks.
What are the benefits of using local transport while travelling within the city? Discuss two reasons with your friend.
The Kanyakumari–Dibrugarh Vivek Superfast Express is a special train that travels all the way from Dibrugarh in Assam to Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu. It is the longest train route in India, taking about 74 hours 35 minutes to cover 4218.6 km.
Since the early days, waterways have been used for transportation. The movement of goods and passengers on water is known as water transport. It is the cheapest means of transport. Heavy goods are carried over long distances on boats and ships. Local water transport such as ferries are used to carry people and goods across rivers and lakes. Water transport can be divided into two types—inland water transport and shipping.
Inland waterways consist of rivers, canals and backwaters. Inland waterways in India have been used for transportation since ancient times.
India has a very long coastline. It has thirteen important ports. Ships are used to transport goods from one port to the other. Goods are also exported and imported to India on ships. This is known as overseas shipping.


backwaters: part of a river or sea where the water remains still


Name the following.
1. He built the first steam engine in 1712.
2. The network of wide, paved roads in many countries.
3. Local water transport which carries people and goods across rivers and lakes.
Air transport is the fastest mode of transport. It enables the movement of goods and people over long distances by means of helicopters and aeroplanes. It is also the most expensive means of transport due to the high cost of fuel. Aeroplanes take off from airports. Most big cities have airports. Airways can be used to travel to the most distant and remote areas especially where there are no roadways or railways. During natural disasters like floods and landslides, airways can be used for rescuing people and distributing food, water and medicines. There are many popular airlines in India such as Air India, Indigo, Spice Jet, Go Air, etc. They run many domestic and international flights.

Why do you think airways are particularly helpful during natural disasters like floods and landslides?


Aeroplane Helicopter
Transport is essential for human survival as it saves time and energy while moving from one place to another. At the same time, the vehicles we use can also harm the environment. Vehicles emit harmful gases which pollute the air. These gases damage the environment and contribute to global warming. To prevent this, electric buses, trains, and cars have been introduced. The number of vehicles in each household is increasing and our roads cannot carry so many vehicles. This leads to major traffic

issues, especially in big cities. One way to prevent this is to improve public transport. Good quality public transport will ensure that fewer people will use their private vehicles. Spreading greater awareness about using public transport and carpools can help save the environment.

The world’s highest motorable road is called Umling La. It is located in Ladakh. It is at a height of 19,024 feet.

transport: the ways in which people, animals or goods move from one place to another steam engine: a type of heat engine used to perform mechanical work using steam highways: long roads that connect different cities in a country superfast trains: a passenger train that travels very fast overseas shipping: import and export of goods through ships global warming: increase in the temperature of the earth’s surface due to gases such as carbon dioxide

Scan the QR code to learn more about means of transport.
• The three modes of transport are land transport, water transport and air transport.
• National highways, state highways, district roads and village roads are a part of our road network.
• Water transport can be divided into two groups—inland water transport and shipping.
• Airways are the fastest mode of travel and are also used during natural calamities to rescue people.
• Vehicles cause air and noise pollution.
• An important way to reduce traffic congestion and pollution is to develop the public transport system.


1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these is the cheapest means of transport?
a. Train
b. Aeroplane c. Ship
B. Which of these is the fastest mode of transport?
a. Ship
b. Train c. Aeroplane
C. Which is the best mode of transport for sending relief supplies to areas affected by natural disasters?
a. Train
b. Bus c. Helicopter
D. Where was the first metro rail built?
a. Delhi
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Mumbai c. Kolkata
railways aeroplane wheel James Watt
A. The discovery of the made travelling easier.
B. improved the design of the steam engine in 1765.
C. transport many people and goods across long distances on land.
D. An is the fastest means of transport.
3. Write True or False.
A. Inland waterways have been used in India since ancient times.
B. Transporting goods by train is cheaper than ships.
C. The metro rail is the fastest train in India.
D. Steam engines have been replaced by engines that use diesel and electricity.
4. Match the following.
A. Important public transport i. Ship
B. Means of transport in water ii. Aeroplane
C. Fastest means of transport iii. Vande Bharat
D. Superfast train iv. Metro rail


5. Short answer questions.
A. What are the three modes of transport?
B. Why is road transport considered to be the most convenient?
C. When and where was the first railway line built in India?
D. What is overseas shipping?
6. Long answer questions.
A. What are two advantages of air transport over the other means of transport?
B. What are the two types of waterways? How are they different?
C. How do you think metro rails have helped reduce pollution in big cities like Delhi and Kolkata? Give two reasons.
7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the picture and answer the following questions.
A. What do you observe in the image?
B. How does this impact people’s health?
C. What steps should be taken to protect the environment? Give any two.


1. Why do you think waterways are still a preferred means of transport for goods in some parts of the world despite the advancements in land and air transport? Write any two points.
2. Highways are generally long, straight roads which do not have sharp curves, turns and roundabouts. Why do you think highways are built this way? Explain in two points.
Transportation is one of the biggest contributors to pollution due to the smoke from cars, planes and other vehicles. Make a poster to spread awareness about pollution from vehicles and to encourage the use of public transport as a means to control pollution. Give your poster a title. Display it in your class.







We all use communication in our daily lives. Here are some fun riddles about communication. See if you can crack them!
1. I can carry a message across the world, from the comfort of your home. With just a few clicks, you can send letters, pictures and more. What am I?
2. I’m a box that speaks without a mouth and listens without ears. I can share news and music with people far and near. What am I?
3. I orbit around the Earth and help you see sports and news from distant lands. Without me, long-distance signals would be a challenge. What am I?
Communication is the way people share ideas, thoughts, feelings or information. This can occur through various methods, such as telephone calls, face-to-face conversations, text messages or television. Communication can be spoken, such as in a conversation, or written, such as in an email or letter.


All living beings communicate with each other, even without language. For example, a dog barks at strangers, a baby cries when it needs something, and so on. In ancient times, people communicated using gestures and signs. As they grew smarter, they created languages. In the past, messages were sent over long distances using pigeons and horses. This process became easier with the introduction of postal services.

Pigeon carrying a message
We frequently communicate with our family and friends through various methods. In the nineteenth and twentieth centuries, more reliable and faster means of communication were developed. Let’s explore the different methods of personal communication.
Letters are sent through the postal system . India Post is the largest postal network in the world with 154,965 post offices. We can send letters, parcels, postcards and money orders by post. Additionally, post offices provide a service called Speed Post , which ensures the fast delivery of letters or parcels to any city in India. Private companies also provide courier services.

Telephones that are used at home and at work are a convenient and fast way to communicate. Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone in 1876. STD (Subscriber Trunk Dialing), lets us call people in other cities in India, and ISD (International Subscriber Dialing) lets us call people in other countries.

gestures: body signals reliable: dependable


Faxing is used to send pictures or written messages instantly. It sends documents over the telephone, and the fax machine prints a copy of the document. The machine is connected to the phone line.

Today, email, or electronic mail, is a fast and convenient way to send messages instantly. To send or receive emails, you need an email account. Emails are sent through computers or laptops connected to the internet. With advancements in technology, you can now also send emails using smartphones or tablets with internet access.
The first email was sent by Ray Tomlinson in 1971, and it was a test message.
When we send a text message or an email, it does not go directly to the receiver. It goes through a network of satellites and servers that eventually deliver the message to the receiver. Error Alert!
Cell phones and smartphones have made communication even easier as they can be taken anywhere. Smartphones allow us to share pictures and music files, make phone calls and send and receive emails. We can also send text messages using SMS (Short Messaging Service) on our mobile phones.
Sunita lives in Faridabad, while her cousins live in Pune. Once a week, she talks to them on a video call. Video calls enable people to see each other while talking. One popular and free service for video chatting is Skype.

Create a chart with four sections, each representing a different communication method. Add pictures for each type and write one sentence on the impact they have. Do and Learn
enable: allow or activate

Choose the correct answer.
1. In ancient times, people used pigeons/postcards to communicate over long distances.
2. Bharat/India Post is the name of India’s postal system.
3. Telephones/Smartphones let us send pictures and make voice calls.
Mass communication involves sharing information with many people at the same time. For example, magazines, books and newspapers convey ideas to a wide audience simultaneously. The invention of cinema, television and radio has transformed mass communication. Let us learn more about some methods of mass communication.
Johannes Gutenberg from Germany invented the printing press. The first printed newspaper was released in Germany around 1605. Magazines and newspapers provide information and news about developments around the world. Today, e-newspapers, or digital versions of newspapers are available and can be read on tablets, laptops and smartphones.
Radio was invented by the Italian scientist, Guglielmo Marconi. Jagadish Chandra Bose demonstrated that radio signals could be transmitted over long distances without
simultaneously: at the same time demonstrated: shown or proven transmitted: sent or conveyed




wires. Radio stations broadcast educational programs, news and entertainment from around the world. It is the cheapest means of communication that reaches even remote areas.
Television was invented by the Scottish inventor John Logie Baird in 1926. It is more popular than radio because it lets viewers see the various programs instead of just hearing them. Television channels broadcast news, and show entertainment and educational programs. They also provide live coverage of cultural events and sports.

Today, the internet keeps us informed about events happening around the world. It is a powerful and efficient means of mass communication. It provides a vast amount of information on any topic. For these reasons, it is often referred to as the Information Superhighway.
We have all seen films. Did you know that films are also a means of communication? The first film was shown in 1895. It did not have any dialogues. Talking films were introduced about 25 years later. Today, cinema is a major form of entertainment and also spreads social messages. Documentary films provide detailed information and are used for educational purposes.
Social networking is a modern way to communicate over the internet. It allows individuals to connect with friends and family through services, such as Facebook, Instagram and WhatsApp. Users can send videos, pictures and messages to their contacts. Anyone who is 18 years and above can join these platforms. Social networking is also valuable for accessing and sharing information during emergencies and disasters. Social media must be used with caution and care. A lot of unlawful activities happen on social media. We must stay safe from such activities.
efficient: productive with optimal use of resources disasters: terrible events causing great damage




Sending television and radio signals to far off places was difficult due to the curved surface of the Earth and buildings, which can interfere with signals. This issue was solved with satellite communication. Satellites are electronic devices launched into space by rockets, where they orbit around the Earth. Signals are sent from the Earth to the satellites, which then send them back to cover a larger area. Due to satellites, we can watch football and cricket matches from different countries. Satellites also help transmit computer and telephone signals to and from other countries.
ISRO has significantly advanced satellite communications in India through its INSAT and GSAT series. These satellites have enhanced telecommunication, broadcasting and internet services, boosted connectivity and enabled remote education, telemedicine and efficient disaster management.


An ISRO exhibition
postal system: the network of post offices for sending and receiving letters, parcels, etc.
India post: India’s national postal service
speed post: express mail service
STD: used for calling people in other cities within India
ISD: used for international phone calls
SMS: text message sent using mobile phones
information superhighway: vast and fast information network documentary films: films meant to educate or spread awareness

Scan the QR code to learn more about means of communication.


• Communication is the way people exchange ideas and information through talking, texting or watching television.
• Mass communication spreads information to large audiences through various methods, including newspapers, radio, television and the internet.
• Cinema and social networking have changed how we share news and connect with people worldwide.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these was a means of communication used in earlier times?
a. Carrier Pigeons b. Postal System c. Radio
B. What is the internet also known as?
a. Educational Path
c. Information Superhighway
C. Satellites are launched into the space using
b. Knowledge Network
a. Rockets b. Airplanes c. Satellite launcher
D. Radio was invented by the Italian scientist
a. Galileo
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Graham Bell c. Marconi
telephone mass communication documentary communication
A. The way people share ideas, thoughts and feelings is called .
B. Graham Bell invented the in 1876.
C. Sharing information with many people at the same time is called .
D. The type of film that provides detailed information for educational purposes is called a .

3. Write True or False.
A. A newspaper is a form of social networking.
B. Johannes Gutenberg from Germany invented printing.
C. STD is used to call people in other countries.
D. Skype helps to send and receive text messages.
4. Match the following.
A. John Logie Baird i. Printing
B. Guglielmo Marconi ii. Radio
C. Johannes Gutenberg iii. Television
D. STD iv. Other Indian cities
5. Short answer questions.
A. What is meant by mass communication?
B. What is a fax machine? Why is it used?
C. What is Speed Post?
D. What is a documentary film?
6. Long answer questions.
A. What is satellite communication? What are its advantages?
B. How has the invention of the internet transformed communication?
7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the pictures and answer the following questions.


A. Which of the two will deliver the news faster?
B. Which of the two needs a satellite to work?

Name a situation where the written form of communication, like a letter or an email, would be more suitable than a verbal or face-to-face form of communication, like phone calls or Skype. Justify your answer.




With your parents, visit the post office nearest to where you live. Talk to a postal worker in the post office. Ask them about the different stages in the journey of a letter. Ask them how technology has helped the postal system.
Write an email to your friend, telling them about your favourite film. You can add a description of the film, telling him/her about what all you liked about the movie, like the story, the conclusion, your favourite scene, etc.




Discovery of Metals
Mass Production and the Industrial Revolution
Discovery of Electricity


How old were you when you learnt how to ride a bicycle? How did you learn? Talk to your partner and share any one interesting experience from that time.

Bicycles are also machines. Let us learn about machines in this chapter.
Machines are tools that help to make our work easier. They come in many types, from simple ones, like scissors and bicycles, to more complex ones, such as computers and robots. Today, we live in the ‘Age of Machines’ because they are a big part of our daily lives. They help us travel, communicate, build, and solve problems. From the washing machine in our homes to the satellites in space, machines have transformed how we live and work. A robot

transformed: changed something to a state which is very different from its original one


List any 10 machines that you use at your home. How do these machines help you? Share with the class.
Early humans lived in jungles. They used simple stones or tools made from stones to hunt animals. With time, humans discovered metals and began using them to make better tools. The first metal discovered by humans was copper. It is believed that copper was discovered more than 10,000 years ago with its earliest use seen in Iraq. Then, around 6000 years ago, humans discovered bronze by mixing copper and tin. It was stronger than copper.

Stone tools of early humans
After bronze, humans discovered iron. It was stronger than copper and bronze and so it was used to make even better tools and weapons. Iron tools could be used to cut trees and clear the land for farming and hunt more easily than with either copper or bronze tools. The discovery of iron helped humans to progress in several ways.
As humans progressed, they invented the wheel. Once the wheel was invented, carts pulled by humans and animals followed. This continued until about 300 years ago when the steam engine was invented.
With the steam engine, humans could replace animal and human effort with machines. The steam engine could transport larger quantities of goods and a greater number of people over longer distances in less time.

Steam was used to run other big machines too. This helped produce more goods of higher quality at a lower cost than handmade goods. With better quality and cheaper prices, the demand for the goods started to increase. This was the beginning of the factory system. A factory is a place where large amounts of goods are produced quickly using big machines. Factories were set up in cities. Many people from the rural areas travelled to cities to work in factories. Slowly the cities grew bigger and the number of factories increased.


The advancement from handmade goods to machine-made goods is called the Industrial Revolution. The Industrial Revolution began in Britain in the 18th century. It is called a revolution because it brought about large-scale changes in society and the life of people.

John Lombe’s silk mill is considered to be the first factory in Britain. It was built between 1718 and 1721.
Tick (✓) the correct statements.
1. Copper was discovered around 5,000 years ago in different parts of Africa.
2. Humans used bronze tools for farming and ploughing the fields.
3. Steam engines helped to run big machines.
4. The first factory was established in Germany.
We have learnt about steam engines. How did they produce steam? Coal was burnt in the steam engines as fuel to produce steam. Coal is an important source of energy. Large amounts of coal are also used to produce electricity in power plants.
Coal is available in mines but it takes millions of years to form. Therefore, there are limited quantities of coal. Another source of energy is petroleum which is also called 'oil from the Earth'. Like coal, it is limited in quantity.
An alternative to these was found around 200 years ago by Alessandro Volta who used a small battery to produce an electric current in a wire. Over time, different types of generators were made, to produce electricity. However, these generators use coal, diesel and petrol. Burning these to generate electricity leads to pollution.
fuel: a substance which is used to provide heat or power


Today, several alternate sources of energy are being used that do not cause pollution. The heat and light of the sun is harnessed with solar panels to produce solar energy. This is then used to generate electricity. Windmills are used to produce wind energy. Hydroelectricity is electricity produced using the flowing water of rivers. It is produced using dams.




Solar panels for generating solar energy
With your partner, find out the names of any five dams in India. Also, find out the names of the rivers they are built on.

The Darjeeling Himalayan Railway in West Bengal has a train that still runs using a steam engine. It is called a ‘toy train’ because it is smaller than the usual trains.
machine: tools that makes our work easier

factory: a place where large number of goods are produced quickly using big machines
industrial revolution: the advancement from hand-made goods to machine-made goods
solar energy: use of the heat and light of the sun to generate electricity hydroelectricity: the electricity produced from flowing water of rivers

Scan the QR code to learn more about the history of machines.
dams: walls which are built across rivers to control their flow and collect the water


• Machines make our work faster and easier.
• The first metal discovered by humans was copper.
• Coal was burnt in steam engines as fuel to produce steam.
• Alternative sources of energy are solar energy, wind energy and hydroelectricity.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of the following was the first metal discovered by humans?
a. Iron
b. Bronze
c. Copper d. Gold
B. Which metal helped in the growth of agriculture?
a. Bronze
b. Iron
c. Copper d. Silver
C. Which of these is a non-polluting source of electricity?
a. Wind
b. Diesel
c. Petrol d. Coal
D. In which of these countries did the Industrial Revolution begin?
a. France
b. Britain
c. Germany d. India
2. Fill in the blanks. cheaper stone factories hydroelectricity
A. Initially, humans used tools.
B. were established where steam-driven machines were used.
C. Electricity produced by the force of flowing water is known as
D. During the Industrial Revolution, goods became and the demand increased.
3. Write True or False.
A. Tools made of iron were stronger than tools made of copper and bronze.

B. The steam engine was discovered after the Industrial Revolution.
C. The Industrial Revolution brought changes in the culture, lifestyle and economic lives of the people.
D. Bronze was the second metal to be discovered.
4. Short answer questions.
A. Define the term machines.
B. How was bronze made?
C. What is a dam?
D. What was steam engine used for?
5. Long answer questions.
A. Write a short note on the Industrial Revolution.
B. Why do we need alternate sources of energy? Give two examples of alternate sources of energy.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What is shown in the image?
B. How does it produce energy?

C. Does it cause pollution? Why or why not?


John was a weaver in eighteenth-century Britain. He made items at home which he sold in his village. He then got a new job in a factory that had recently been set up in a city.
Write about any two changes he would have experienced between his way of working in his village and in the factory?

With the help of your parents or elders at home, learn to use one machine safely. It can be anything like a microwave, a juicer, an electric kettle, a camera or a washing machine. Once you have learnt how to use it, help your parents with household work using that machine.



Objective: Students will create a visual timeline to explore the evolution of communication methods over the last 25 years in India.
Materials Needed: A chart paper for the timeline; printed or hand-drawn images of various communication methods; markers, coloured pencils, glue and scissors
Step 1: Research Phase
Do a research about the different methods of communication used in the last 25 years in India and what impact they had on the lives of people. You can use the internet or speak to your elders. Some of the examples are radio, letters, fax, social media, emails etc.
Step 2: Create the Timeline
Draw a large timeline for the last 25 years on the chart paper. Mark the years clearly on the timeline.
Step 3: Describe the Evolution
On the timeline, paste the images of modes of communication in the chronological order. Write their names too. Alongside the images, write short descriptions explaining the importance of each communication method and how it affected society. You can also write about the advantages and disadvantages of each method.
Project Output: Now you have your own timeline for the evolution of modes of communication. Present it to the class. Share some interesting insights.
Learning Outcome: This hands-on project will help you understand the progress of communication methods in India, and their significance in shaping our lives.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.


Read this article. Answer the questions given below.
The world was glued to their television screens as the Olympic Games in Paris was broadcast live to millions of homes across the globe.

Thanks to satellite communication, people from different countries can watch in real time any event that happens in any corner of the world. Viewers in India, the United States, Japan, and even remote regions enjoy the coverage of sports such as swimming, gymnastics and athletics. This incredible broadcast is made possible through satellites that orbit the Earth. These satellites send signals to television stations and devices, allowing for live coverage within seconds. The use of satellite technology has made the world smaller by connecting people through shared events like the Olympics. Before satellites, it would have been impossible to watch events happening far away in real-time.
1. What makes it possible for people around the world to watch the Olympic Games live?
a. Telephone lines
c. Postal service
2. What is not true for satellite communication?
a. It is the fastest mode of communication.
b. It allows for live coverage of events.
c. It can be used for global broadcasts.
d. It reduces the number of TV channels.
b. Satellite communication
d. Newspapers
3. Name three modes of communication where satellites play an important role.
4. Inventions are happening every day. What do you think can be the future of satellite communication? Explain your viewpoint in a few lines.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.











Chapter Overview

The First War of Independence
India as a Trade Centre
Formation of the East India Company
Discontent Among Indians
The Revolt of 1857


Every year on 15 August, we celebrate Independence Day. We also celebrate the contributions of our freedom fighters on this day. Can you name any two freedom fighters of India?
Since ancient times, India has attracted many traders. Arabs and Europeans traded with India for spices, gold, pearls and silk. India was a very prosperous country at that time. India also traded with other countries, such as Greece, Rome, Arabia, Persia, Egypt and Sumatra.
In 1498, Vasco da Gama, a Portuguese explorer, sailed around Africa and discovered a new sea route from Europe to India. He arrived in Calicut, Kerala.

The Portuguese mainly traded in spices and items like cotton, textiles and other valuable goods. After the Portuguese, the Dutch, the French and the English traders arrived. They made trading centres along the entire coastline of India which they called factories. They built them like strong forts to protect them from attack. Since so many countries wanted to trade with India, they soon began fighting to gain control of the trade.
The British established the East India Company in the year 1600 to trade in India. At that time, their aim was only trading, especially in spices and textiles.
Circle the correct word.
1. Vasco da Gama arrived in Kochi/Calicut.

2. The Europeans established factories that were built like forts/markets.
3. The British established the East India Company in the year 1700/1600.
After gaining control of the trade, the British made a lot of profit and used this money to develop industries in Britain. This helped in the Industrial Revolution in Britain. They made clothes, tools and other things much faster and in bigger amounts. Because of this, the British needed a lot of raw materials and a market to sell the huge amounts of goods they were making. They thought India could provide them with both.
To succeed in this plan, they began to gain more control over India. They started taking advantage of the weakening of the Mughal Empire and the constant fighting between different regional kingdoms. In 1757, the British, led by commander Robert Clive, defeated Siraj-ud-Daulah, the Nawab of Bengal, in the Battle of Plassey. With this, they became very powerful in Bengal, and from then on, they began expanding their control over India.
weakening: to become weaker regional: belonging to a particular region




By 1800, the East India Company had its own army, which was more than twice the strength of the British army at that time.
What do you think would have happened to the East India Company had the Mughal Empire not become weak and there was no fighting between the regional kingdoms in India?
The British made many rules that helped them at the cost of Indians. They used unfair means to become rich, such as by exploiting farmers. The British made Indian farmers grow special crops like indigo and cotton. These crops were very important for British factories in England. But, the British paid the farmers very little for their hard work. In addition, they sold the finished products back to the people in India for a lot of money! This made the farmers poor and unhappy. Indians were also taxed very heavily.
The British also sold clothes made in their factories. These clothes were of better quality and cheaper than the clothes made by the local Indian weavers. Because of this, many Indian factories closed, and many workers lost their jobs. Indian traders, who bought and sold things, also suffered because of the unfair British trade rules.

The British not only took over the economy, but also made new rules to take control of the Indian kingdoms. One of these rules said that if a king died without a child, the kingdom would be taken over by the British. Many Indian kingdoms came under British rule in this way which made the Indian rulers very angry.
All of this led to growing discontent against the British. People started to forget their fears and rise up against them.
discontent: feeling of dissatisfaction or unhappiness with a situation

Tick (✓) the correct statements.
1. Farmers were happy with the British.
2. Clothes made in British factories were cheaper.
3. Robert Clive defeated Siraj-ud-Daula.
4. The Battle of Plassey took place in 1787.
The British had introduced a new kind of rifle in their army. To load these rifles, the soldiers had to bite the ends of the cartridges. These cartridges were greased, and the soldiers believed that they were greased with cow fat and pig fat. For Indian soldiers in the army, this was a matter of great concern. Hindus considered cows sacred, and Muslims considered pigs unclean. So biting something covered in the fat of these animals angered both.
Due to growing anger among Indian soldiers, an Indian soldier named Mangal Pandey attacked a British officer near Calcutta (now called Kolkata) on 29 March 1857. As punishment, the British hanged Mangal Pandey on 8 April 1857. This angered the Indian soldiers even more, and on 10 May 1857, Indian soldiers shot British officers in Meerut and took control. Then, they marched to Delhi and convinced Bahadur Shah Zafar, the last Mughal emperor, to join their revolt against the British. This was the beginning of the First War of Independence. It is also known as the Revolt of 1857 or the Sepoy Mutiny.





Mangal Pandey Tantya Tope Nana Sahib Begum Hazrat Mahal Rani Lakshmi Bai
The news of the revolt quickly spread and more leaders joined it from different parts of India. Nana Sahib and Tantia Tope in Kanpur, Begum Hazrat Mahal in Awadh, and Rani Lakshmi Bai in Jhansi all became a part of it. Rani Lakshmi Bai died fighting a battle at the age of 29 years in Gwalior.


With their larger armies and modern weapons, the British eventually suppressed the revolt. Unfortunately, many Indians supported the British to end the revolt. Mughal Emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar was sent into exile in Burma where he died in 1862.
The British were alarmed by this revolt, and the British government under Queen Victoria took direct control of India in 1858. This ended the rule of the East India Company. Queen Victoria declared herself as the Empress of India and appointed a Viceroy to govern India on her behalf.

The revolt of 1857 ended, but it taught Indians the importance of unity. They understood that if they were united, they could defeat the British and gain independence.
The Mutiny Memorial in New Delhi was initially built in 1863 to honour those who fought on the British side during the Revolt of 1857. In 1972, it was re-dedicated to the memory of those Indians who lost their lives fighting the British.

Scan the QR code to know more about what happened during Sepoy Mutiny.

industrial revolution: time when people started using machines to make things instead of making them by hand.
taxes: money that people pay to the government economy: system of a country which people follow to buy and sell goods and services to earn money cartridges: a metal or cardboard tube that contains a bullet revolt: a fight against those in power
suppressed: stop or control something forcefully exile: forced to stay out of one’s country


• Arabs and Europeans traded with India for spices, gold, pearls and silk.
• India also traded with other countries, such as Greece, Rome, Arabia, Persia, Egypt and Sumatra.
• In 1498, Vasco da Gama discovered a new sea route from Europe to India.
• The Indian soldiers opposed the use of cartridges that were greased with the fat of cows and pigs.
• The Revolt of 1857 is also called the First War of Independence.
• The rule of the East India Company came to an end in 1858, and the British government took direct control of India.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Who was the last Mughal emperor to fight against the British in Delhi?
a. Bahadur Shah Zafar
b. Begum Hazrat Mahal
B. The East India Company was formed in the year
a. 1498
C. The Revolt of 1857 started in
a. Meerut
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. 1757
b. Awadh
c. Nana Sahib
c. 1600
c. Jhansi
viceroy the First War of Independence indigo and cotton Awadh
A. The revolt of 1857 is also known as .
B. The British forced Indian farmers to grow crops like .
C. Begum Hazrath Mahal led the revolt of 1857 in .
D. Queen Victoria appointed a on her behalf to govern India.
3. Write True or False.
A. The Dutch were the first group of traders to reach India by sea.
B. Mangal Pandey attacked a British soldier in Calicut.
C. Indians were forced to pay high taxes to the British.


D. The revolt of 1857 was a huge success.
E. The rule of East India Company came to an end in 1858.
4. Match the following.
A. Rani Lakshmi Bai i. Kanpur
B. Bahadur Shah Zafar ii. Delhi
C. Tantia Tope iii. Awadh
D. Begum Hazrath Mahal iv. Jhansi
5. Short answer questions.
A. Name any two countries that traded with India in ancient times.
B. Name any three things for which the Arabs and Europeans traded with India.
C. Who fought the Battle of Plassey against the East India Company?
D. What happened to Mangal Pandey after he started the revolt?
6. Long answer questions.
A. Why did the soldiers protest against the use of greased cartridges?
B. Why did the British government take control of India from the East India Company?
7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the picture and answer the following questions.
A. What is the name of this famous freedom fighter?
B. Where did she die?
C. How old was she when she died fighting against the British?


Do you consider the revolt of 1857 a success or a failure? Give reasons for your answer.
Choose one freedom fighter of India who inspires you the most. Collect information about them and share that with your class in the form of a poster or a speech.




Struggle For Independence Social Reformers
Civil Disobedience Movement
The Rise of Indian Nationalism Jallianwala Bagh Quit India Movement
Partition of Bengal and Swadeshi Movement Non-cooperation Movement
Mahatma Gandhi Joins the Struggle Simon Commission
Indian National Army
India Becomes Free

Get Set

Look at the picture. Write the names of these famous Indian leaders.
Let us learn more about the Indian struggle for independence.


Raja Ram Mohan Roy is known as the “Father of Modern India” because of his efforts to bring about positive changes in Indian society.
We learnt about the Revolt of 1857 in the previous chapter. Indian society had several evil practices at that time, for example, sati, child marriage, the caste system and killing of female newborn babies. Many educated Indians wanted to change the society to end these practices. These people were social reformers, like Swami Dayanand Saraswati, Raja Ram Mohan Roy, Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, Sir Syed Ahmed Khan and Savitribai Phule.



After the Revolt of 1857, the people of India realised that the British did not care for them, and they understood the value of their freedom. They were upset with unfair taxes, bad treatment, and laws that favoured the British.
Why is it important to remove evil practices from a society?

To address this, the Indian National Congress (INC) was formed in 1885 by leaders like A. O. Hume, Dadabhai Naoroji and W. C. Bonnerjee. The INC aimed to bring Indians together.
The INC had two groups: Moderates and Extremists. The Moderates, like Dadabhai Naoroji and Gopal Krishna Gokhale, wanted slow change through peaceful talks with the British. The Extremists, like Bal Gangadhar Tilak, Bipin Chandra Pal and Lala Lajpat Rai, wanted quicker action and used protests to push for change.
caste system: a system of discrimination in the Hindu society based on people’s birth





Bal Gangadhar Tilak raised the famous slogan, “Freedom is my birthright, and I shall have it.” He also started a newspaper called Kesari and wrote against British rule in India to arouse a feeling of nationalism among the people.
The growing nationalism among Indians made the British worried. They realised that if Indians united, they could put an end to British rule. To stop the Indians from standing together, the British came up with the idea of dividing Indians based on religion. During that time, the Bengal region had the strongest feeling of nationalism. In 1905, the British divided Bengal into two different parts on the basis of religion—one part belonged to the Hindus and the other to the Muslims.
The partition of Bengal caused anger among the Indians and protests started against the British. This led to the rise of the Swadeshi Movement. ‘Swadeshi’ means 'one's own country'. In this movement, people boycotted the products that were produced by the British and started using the products that were produced in India. There was mass participation of women and students, and goods that were produced by the British, mainly clothes, were burnt publicly. The movement started in Bengal and slowly spread throughout the country.
The British tried to end the movement using force, beating people mercilessly, and imposing fines on them. The movement against the division of Bengal was successful, and the British were forced to unite Bengal again.
After the partition of Bengal, many young Indians began taking more severe steps to fight against the British. They were ready to lay down their lives for the nation. They were called revolutionaries. Some important revolutionaries of India were Bhagat Singh, Chandrashekhar Azad, Khudiram Bose, Raj Guru, Sukhdev and Udham Singh.

Statues of Bhagat Singh, Raj Guru and Sukhdev in New Delhi
protests: actions that show that you do not like or approve of something boycott: to refuse to take part in something that you strongly disapprove nationalism: feeling of love and a sense of attachment to one’s country


Find out about the life of Bhagat Singh using the internet or library books. Write 5 lines about his life in your notebook.
Circle the correct word.
1. Educated Indians/Uneducated Indians were aware of the unfair practices and customs.
2. Bal Gangadhar Tilak was a famous leader from the extremist/moderate group of INC.
3. The founder of the Indian National Congress was A. O. Hume/Bipin Chandra Pal.
After World War I, Indian soldiers who had fought on behalf of the British got no recognition and British rule became even harsher. After Mahatma Gandhi returned to India from South Africa in 1915, he visited several parts of the country. He wanted to learn more about Indians and their situation. Mahatma Gandhi noticed that the people of India were living in poor conditions and that the caste system had divided people. He noticed that some people were considered untouchables and were treated badly. This shocked him. He realised that Indians needed to treat each other equally and with respect. Towards this aim, he travelled around the country and spoke against the practice of untouchability. This won him the support and respect of the common people.


In 1919, the British passed a law called the Rowlatt Act. This law allowed them to arrest and jail people without a trial if they thought they were planning to protest. Many Indians felt this law was unfair and protested against it. One terrible event during this time was the Jallianwala Bagh massacre. On April 13, 1919, a large crowd gathered peacefully in Jallianwala Bagh in Amritsar to protest against the Rowlatt Act. A British
untouchables: group of people who were considered low and polluting by other groups massacre: killing lot of people without any fault of theirs

officer, General Dyer, ordered his soldiers to fire on the crowd. Hundreds of people were killed, and this made many Indians angry. In response to these unfair actions, Mahatma Gandhi started the Satyagraha Movement. Satyagraha means “holding fast to the truth.” Gandhi encouraged people to protest peacefully by refusing to follow unfair laws, but without using violence. This movement helped to unite Indians in their fight for freedom.

Bullet marks at Jallianwala Bagh
The incident at Jallianwala Bagh convinced Mahatma Gandhi and the people of India that India should be free from British rule. Gandhiji then launched the Non-cooperation Movement. People of India were asked not to cooperate with the British. The Indians working in the British government resigned, lawyers boycotted courts and students boycotted the schools. The movement spread throughout India, and everyone participated. Gandhiji was arrested by the British but was later released. Due to Gandhiji’s arrest, a police station was set on fire by the people at Chauri Chaura. It killed many policemen. Gandhiji regarded this incident a failure of the movement, and he called it off.
The Non-cooperation Movement was joined by many young leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru, Subash Chandra Bose and Abul Kalam Azad. They participated actively in the movement.
In 1928, the British Government decided to make some changes in the governance of India. They appointed the Simon Commission under Sir John Simon to suggest changes. The commission did not have any Indian members. This angered the people and the commission was opposed. Indians protested and used the slogan ‘Simon Go Back’.



At this time, the Indian National Congress decided to demand Purna Swaraj or complete independence for India.
cooperate: to work with someone to achieve something


The Civil Disobedience Movement was started by Mahatma Gandhi in 1930 to fight against British rule in India. Gandhiji asked Indians not to pay British taxes, especially the tax on salt.
As a protest against the salt tax, he began his peaceful march from Sabarmati Ashram, Ahmedabad, to Dandi. Gandhiji’s followers and many others joined the march. This march is also known as the Dandi March. Gandhiji and his followers broke the Salt Law, which did not allow Indians to make their own salt. Gandhiji and his followers made salt in Dandi, which led to his arrest.

The movement spread across the country, and many people joined the movement to show the British that India wanted freedom. Even though many were arrested, the Civil Disobedience Movement brought Indians together in their fight for independence.
Tick (✓) the correct statements.
1. The Dandi March broke the Salt Law.
2. Maulana Abul Kalam Azad participated in the Non-cooperation Movement.
3. The Rowlatt Act was passed in 1919.
World War II (1939–1945) was a global war involving many countries, including Britain, Germany, Japan, and the United States. During this war, India was still under British rule. The British involved India in the war without asking the Indian leaders, which made many Indians unhappy.
In 1942, during the World War II, Mahatma Gandhi launched the Quit India Movement. This movement demanded that the British leave India immediately.

If you could ask one question from a freedom fighter, what would it be?
The slogan “Do or Die” was used, encouraging people to fight for freedom peacefully but firmly. Many leaders, including Gandhi, were arrested, and protests took place all over the country. Even though the British did not leave right away, the Quit India Movement brought India closer to independence by showing the strong desire for freedom. Eventually, after the war ended in 1945, the British realised they could no longer control India, and India gained independence in 1947.
Subhash Chandra Bose was a brave leader in India’s freedom struggle. Unlike others who wanted peaceful protests, Bose believed in fighting the British with force.
In 1943, the Indian National Army (INA), or the Azad Hind Fauj, was formed to fight for India’s independence.
Subhash Chandra Bose led the INA in battles against the British, hoping to free India. Although the INA didn’t fully succeed, Bose’s efforts inspired many Indians. He is remembered as a brave leader who played an important role in India’s journey to independence. Bose’s famous slogan was “Give me blood, and I will give you freedom.”

Did the INA play an important role in India’s freedom struggle?
After the end of the Second World War, the British decided to end their rule in India and leave. The Quit India Movement and the courage of the Indian National Army had shaken them.
However, their Divide and Rule Policy was successful in dividing Hindus and Muslims in India. The Muslim League, under Mohammed Ali Jinnah, demanded a separate nation for Muslims. Mahatma Gandhi tried to prevent this division but did not succeed.
On 15th August 1947, India became free, and two nations were formed: India and Pakistan.
Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru was elected as the first Prime Minister of India, and Dr Rajendra Prasad became the first President of India. With this, a new era in the history of India began.
divide and rule policy: a strategy of the British to divide the people of India


The Sabarmati Ashram was Mahatma Gandhi’s home from 1917 to 1930, and thus, it is an important place in the Indian struggle for freedom. It is situated on the banks of the Sabarmati river in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Today, people from all over the world visit the ashram to pay their respect to Mahatma Gandhi.


Ashram
social reformers: people who try to improve the society by removing evil practices from it moderates: a group of leaders in the INC who wanted slow change through peaceful talks with the British extremists: a group of leaders in the INC who wanted quicker action and used protests to push for change

Scan the QR code to learn more about the Quit India Movement.
• The Civil Disobedience Movement was started by Mahatma Gandhi in 1930.
• The Non-cooperation Movement was joined by many young leaders, like Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru, Netaji Subash Chandra Bose, etc.
• In 1942, during the World War II, Mahatma Gandhi launched the Quit India Movement.
• On 15th August 1947, India became free and two nations were formed: India and Pakistan.

1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Who formed the Indian National Army?
a. Subhash Chandra Bose b. Mahatma Gandhi
c. A. O. Hume d. Gopal Krishna Gokhale
B. When was the Indian National Congress formed?
a. 1857 b. 1885 c. 1895
C. Who was a social reformer in India?
a. Bhagat Singh b. Raja Ram Mohan Roy c. Raj Guru
2. Fill in the blanks.
Divide and Rule Subash Chandra Bose Dadabhai Naoroji Raj Guru
A. used the slogan “Give me blood, and I will give you freedom.”
B. The Policy was used to divide the Hindus and Muslims in India.
C. was a revolutionary.
D. was a moderate leader in the INC.
3. Write True or False.
A. The Jallianwala Bagh Massacre was ordered by General Dyre.
B. The Extremists believed in peaceful talks with the British government.
C. The Kesari newspaper was started by Bipin Chandra Pal.
D. Dr Rajendra Prasad was the first Prime Minister of India.
4. Match the following.
A. Bhagat Singh i. Revolutionary
B. A. O. Hume ii. Dandi March
C. Civil Disobedience Movement iii. Do or Die
D. Quit India Movement iv. Formation of INC


5. Short answer questions.
A. Name any two social reformers of India.
B. What is the meaning of Purna Swaraj that was demanded by the INC?
C. Name the main leader of the Muslim League.
6. Long answer questions.
A. Write one difference between the Moderates and Extremists of the INC.
B. Explain the Quit India Movement.
C. Give one reason why Indians protested against the Simon Commission.
7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the picture and answer the following questions.
A. Where is it located?
B. How is this place related to India’s struggle for freedom?



Which movement was of the greatest impact against the British, in your opinion? Give reasons to support your answer.
Make a poster about India’s freedom struggle. You can paste pictures of freedom fighters, mention the important movements, the year in which they took place, etc. Give your poster a title. Display your poster in class.






Read this verse from the poem, “Where the Mind is Without Fear” by Rabindranath Tagore.
“Where the clear stream of reason
Has not lost its way into the dreary desert sand of dead habit.
Where the mid is led forward by thee Into ever-widening thought and action.
Into that heaven of freedom
My father, let my country awake.”

Rabindranath Tagore was not only a great poet but he also played an important role in bringing about changes that made Indian society better. In this chapter, we will learn more about some great people who have made a difference in the Indian society and in our lives.


Throughout India’s rich history, many remarkable individuals have shaped our nation. They have contributed to our nation’s progress and unity. These leaders came from different backgrounds but worked towards making India a better place.
Dr Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar was a great leader who fought for fairness and equality for everyone in India. He was a lawyer and scholar who believed that education could make everyone equal. Dr Ambedkar fought against the unfair treatment and discrimination faced by people. He became the Law Minister of India in 1947 and helped write the Constitution of India. He made sure the Constitution included rules to protect everyone’s rights, no matter who they were. We should respect people and treat every person equally, irrespective of their caste, gender or religion.
Sarojini Naidu was a brave woman who fought for the freedom of India and for women’s rights. She was the first Indian woman to become the president of the Indian National Congress. She was also appointed as the governor of Uttar Pradesh. She was sent to prison three times because she opposed the British. She also accompanied Mahatma Gandhi to London for the Round Table Conference. She was a scholar of literature and a poet. She was called the “Nightingale of India”.




With the help of the internet, find out about another famous female Indian leader from the Indian Independence Movement. Say two things about her in your class.
remarkable: special, amazing and outstanding discrimination: treating people unfairly because of who they are based on their gender, age or race literature: writings, such as story, poem or play, which are considered artistic and valuable

Many leaders joined Mahatma Gandhi in the fight against the British. Vallabhbhai Patel, also known as Sardar Patel, was one of these leaders. He was a lawyer and one of the significant leaders in the Indian National Congress. He led a successful protest against increased taxation in the town of Bardoli, which earned him the title “Sardar,” meaning leader. After joining Gandhi, he used non-violent methods to fight for freedom. After independence, he played an important role in uniting almost 500 princely states into India. For his determination and strength, he was also called the “Iron Man of India”.

Circle the correct answer.
1. B. R. Ambedkar/Sarojini Naidu fought for equal rights for everyone.
2. Sardar Patel/Sarojini Naidu joined Mahatma Gandhi in the Round Table Conference held in London.
3. B. R. Ambedkar/Sardar Patel was called as the “Iron Man of India”.
Curiosity and knowledge have improved our daily lives through great discoveries. From studying stars to finding new medicines and creating technology, scientists have made important contributions.
Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose was a famous scientist. He was known for his work in the fields of plant physiology and physics. He did amazing experiments with plants and showed that they can feel things just like animals do. He also worked with radio waves and invented an instrument similar to a radio detector, which helped the field of physiology in later years.

curiosity: wanting to know or learn about something physiology: a branch of science that deals with the functions and activities of living organisms


Homi Jehangir Bhabha was another great Indian scientist. He developed India’s important science programs which helped in the industrial growth of India. He also founded important research institutes like the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research to help other scientists in their studies.

C. V. Raman was an Indian scholar who received the Nobel Prize in physics. He made important discoveries in light, showing that when light passes through a clear material, it changes slightly. His study was later called the Raman Effect. He was also awarded the Bharat Ratna in 1954. C. V. Raman founded the Indian Academy of Sciences and was an inspiration to many young scientists.
28 February is celebrated as National Science Day in India every year.

Since ancient times, India has seen many undesirable practices among its people. Young girls were often married early. Widows were often treated badly by their families. They were expected to burn themselves after their husband’s death in a practice known as sati. Child marriage, illiteracy and the caste system were some common issues. Brave people who come forward to fight against evil social practices to make things better for the people are known as social reformers.
Rabindranath Tagore believed strongly in education. He started a school called Shantiniketan where children learnt from books, nature and art. He also spoke out against old customs like idol worship and sati, which he thought were harmful.
inspiration: strong motivation to do something because of another person illiteracy: not being able to read or write



We all know that the National anthem of India was written by Rabindranath Tagore. The National anthem of Bangladesh was also written by Tagore. He has also set the tune for the Sri Lankan national anthem.
Swami Vivekananda shared Tagore’s passion for education. He joined a group called the Brahmo Samaj, which aimed to end child marriage and ensure that everyone could read and write. He helped develop the Ramakrishna Mission to teach people and improve their lives. Vivekananda believed that women were crucial for society’s progress and encouraged them to take part in everything. His ideas about education and treating everyone fairly still inspire people around the world today.
Annie Besant was originally from Britain, but later she became an Indian citizen. She worked hard to make India better in many ways. She strongly believed in education for all, establishing schools and colleges to spread modern learning. She also helped people in need and supported the fight for India’s independence from British rule. In 1916, she started the Indian Home Rule League to push for Indians to govern themselves. She was the only British woman to lead the Indian National Congress, where she played a significant role in India’s journey to freedom.


Education was an important issue that was taken up by many social reformers. Why do you think education is important?
Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) in Mumbai is a centre for scientific research and education. It highlights Homi Bhabha’s groundbreaking work in physics and nuclear science.



leader: a person who inspires others to follow them
Constitution of India: a document that explains how India’s government works and the rights and duties of its people
governor: a person who represents the government in a state or territory and oversees its administration
scientist: a person who studies science
social reformer: a person who works to improve society

Scan the QR code to learn more about many other leaders of India.
• Leaders like Dr Ambedkar, a lawyer and scholar, fought for justice and equality.
• Sarojini Naidu also known as the “Nightingale of India” was the first Indian woman to lead the Indian National Congress and serve as a state governor.
• Sardar Patel, a lawyer and important leader in India’s freedom struggle, united princely states after independence and was known as the “Iron Man of India”.
• Sir Jagadish Chandra Bose showed that plants can feel and invented a radio detector.
• C. V. Raman, India’s first Nobel laureate in science, discovered the Raman Effect.
• Social reformers like Tagore and Swami Vivekananda aimed to change old customs, promote education and fair treatment, while Annie Besant’s work in education and the fight for India’s freedom greatly improved the country.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Who helped write the Constitution of India?
a. Rabindranath Tagore
b. Dr Ambedkar
B. Who was called the “Iron Man of India”?
a. Sardar Patel
c. C. V. Raman
b. Swami Vivekananda
c. J. C. Bose

C. Who was the first Indian female leader of the Indian National Congress?
a. Annie Besant b. Sarojini Naidu c. Indira Gandhi
D. The Ramakrishna mission was developed by a. Swami Vivekananda b. Sardar Patel
c. Rabindranath Tagore
2. Fill in the blanks.
J. C. Bose Shantiniketan Homi Bhabha Annie Besant
A. Tagore built a school called .
B. Tata Institute of Fundamental Research was founded by .
C. proved that plants can also feel things like animals.
D. started the Indian Home Rule League to push Indians in governing themselves.
3. Write True or False.
A. Rabindranath Tagore became the leader of the Indian National Congress.
B. JC Bose worked on radio waves and found a radio detector like instrument.
C. Sarojini Naidu was called the “Nightingale of India”.
D. Swami Vivekananda was the founder of the Ramakrishna Mission.
4. Match the following.
A. Sardar Patel i. Shantiniketan
B. Sarojini Naidu ii. Nightingale of India
C. Rabindranath Tagore iii. Iron Man of India
D. Homi Bhabha iv. Nuclear energy
5. Short answer questions.
A. Why was Sardar Patel given the title ‘Sardar’?
B. What C. V. Raman discover?
C. What is Homi Bhabha’s contribution to India?
D. Write any two contributions of Annie Besant.


6. Long answer questions.
A. What was the role of Rabindranath Tagore and Swami Vivekananda in the field of education?
B. What steps did Dr Ambedkar take to bring equality among the people of India?
7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the picture and answer the following questions.
A. What is the name of this freedom fighter?
B. What was her role in the Indian National Congress?
C. Which title was she given?



In what ways do you think the role of social reformers was equally important as freedom fighters in India’s freedom struggle? Give two reasons.

Along with your parents and neighbours, organise a session by elders of your area/society/neighbourhood about the contributions of our leaders and reformers during India’s freedom struggle.
Find out the names of five Indian scientists apart from the ones you have studied in this chapter with the help of the internet. Find out about their inventions and contributions towards India’s development and society. Make a note of your findings and share them with your friends.















The Birth of the UN World Wars
Formation of the UN Objectives of the UN
Structure of the UN

Get Set

Read this passage.
Aarav and Ria were playing a game at school when a disagreement arose between them about the rules for winning. Both of them argued, and neither of them wanted to back down. Their teacher listened to both sides and asked them to play another match. This time, their teacher made clear rules for both of them.

Do you think the teacher played an important role here? Share your thoughts with your class.
Just like the teacher resolved the fight between Aarav and Ria, the United Nations, an organisation, also solves disputes between countries around the world. Many times, disputes can turn into war. The United Nations works to prevent these wars and maintain peace in the world.
World War I (1914–1918) and World War II (1939–1945) were two major wars that involved many countries. In both wars, people fought because they wanted more


power and control over the world. The wars caused a lot of damage, destroying cities and leaving millions homeless. Thousands of soldiers and civilians lost their lives.
During World War II, something very tragic happened in two Japanese cities, Hiroshima and Nagasaki. To end the war, the United States dropped two atomic bombs on these cities in 1945. The explosions were so destructive that they destroyed most city and killed nearly everyone who lived there. Even those who survived were badly injured, and the effects lasted for years.
Both world wars showed how terrible wars can be. The wars ended, but the destruction left a deep mark on those who lived through it.
After World War II, countries around the world agreed that they needed to work together to stop wars from happening again. This is why the United Nations (UN) was created—to help countries solve problems peacefully and avoid the suffering caused by the world wars.

In 1945, leaders from 50 countries met at San Fransisco, USA, and signed an important document called the UN Charter. This document outlined the goals and rules for United Nations (UN). Four months later, the UN came into existence on 24 October 1945. Its headquarters are in New York, USA.
The main goal of the UN is to maintain peace in the world and help countries solve problems without going into war.
The UN Charter guides the actions of all member countries, encouraging them to cooperate, be fair and find peaceful solutions to conflicts.
The UN also helps people in need by providing, provides food, medicine and education, and works to protect human rights. Human rights are basic rights that every person has, regardless of their country or religion.


Thanks to the UN, countries can come together to discuss their problems and work towards making the world safer for everyone.



The main objectives of the United Nations are:
1. The UN works to stop wars and help countries settle their differences peacefully.
2. The UN ensures that everyone is treated fairly and that their basic human rights are respected.
3. The UN helps people in need by giving food, water and medical care during emergencies.
4. The UN helps countries develop in ways that protect the Earth and fight climate change.
5. The UN ensures countries follow agreed-upon rules to keep things fair and peaceful.

The United Nations was not the first organisation that was formed to prevent wars. After World War I, the League of Nations was formed to promote peace between nations, but it failed as the World War II broke out.
The UN is divided into six main organs, each with different functions.
1. The General Assembly: The General Assembly is where all member countries meet to discuss world issues. Every country has one vote, regardless of its geographical area. They discuss important topics, like peace, health and human rights. While they cannot force countries to follow their decisions, they make suggestions to improve the world.
2. The Security Council: The Security Council is the most important organ of the UN. It is responsible for maintaining peace and security. Its meetings take place whenever there is a possibility of war. Nations can raise complaints against each other in the Security Council. All members are required to follow its decisions. There are 15 members in total: five permanent members (the USA, the UK, France,



Russia and China) and ten non-permanent members who are elected for two years. Permanent members have veto power, which means they can overrule or reject a decision made by the majority.
3. The International Court of Justice: The International Court of Justice is the UN’s court. It is located in The Hague, Netherlands. It helps settle disputes between countries over issues like land or resources. The court listens to both sides and makes fair decisions on international law. Judges from different countries work in the court to ensure justice for all.


With the help of the internet, make a list of Indians who have served as judges in the International Court of Justice.
4. Secretariat: The Secretariat is like the UN’s office. It helps with all the administrative work, such as planning and organising. They handle paperwork, organise meetings and carry out decisions made by the UN. They also research important global issues, like climate change or education. The Secretary-General leads this organ, making sure everything runs smoothly. António Guterres is the Secretary-General of the UN at present.

5. Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC): The Economic and Social Council helps countries improve their economies and take care of their people. It focuses on promoting international cooperation on issues like education, healthcare and clean water.
6. Trusteeship Council: The Trusteeship Council helps areas called “trust territories” become independent countries. Now that all trust territories are independent, it no longer meets regularly but is still there, if needed.

India Gate in New Delhi was built in the memory of soldiers who sacrificed their lives in World War I.



UN charter: a document that guides all UN member countries human rights: basic rights for all people as humans, no matter which country they belong to or the religion they follow veto power: power to refuse a decision or to stop an action

Scan the QR code to learn more about the UN headquarters.
• The United Nations came into existence on 24 October 1945.
• The UN has six main organs, which have different functions and responsibilities.
• The UN Charter guides the actions of all member countries, encouraging them to cooperate, be fair and find peaceful solutions to conflicts.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. In which of these cities did the USA drop an atomic bomb ?
a. Tokyo
b. Osaka
c. Hiroshima
B. Which of the following is the primary objective of the Security Council?
a. To prevent war and maintain peace
b. To help the poor countries by giving them money
c. To protect the rights of the people living in different nations
C. Which of the following country is not a permanent member of the Security Council?
a. Brazil
b. China
c. France


2. Fill in the blanks.
The Hague New York Secretary General
A. The UN Headquarter is in .
B. The leads the UN Secretariat.
C. The International Court of Justice is located at .
3. Write True or False.
A. All members have veto power in the General Assembly.
B. 30 nations adopted and signed the UN charter.
C. The Trusteeship Council does not meet anymore.
D. ECOSOC works with other organisations to improve the quality of life for people around the world.
4. Match the following.
A. The International Court of i. Permanent members of the Justice Security Council
B. The General Assembly ii. Administrative work of the UN
C. The Secretariat iii. Court of the UN
D. Veto iv. Where all countries meet in the UN
5. Short answer questions.
A. Name the five permanent members of the Security Council.
B. What is the work of the Secretariat?
C. What does the International Court of Justice do?
6. Long answer questions.
A. How did the UN come into existence?
B. What are the objectives of the UN?
C. How has the presence of the UN helped the world?


7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the picture and answer the following questions.

A. How many members does this organ of the UN have?
B. What is the special power that some members have in this organ?

Imagine you are a representative of a small country in the United Nations. You have an important issue that you want the UN to address, such as promoting education for all children. Which organ of the United Nations would you approach first, and why?
Use the internet or the library to find out the meanings of different objects and colours in the UN flag. Then, draw the UN flag on a chart paper and label what each part means. Display your poster in the class.



Chapter Overview

The Working of the UN
Special Agencies Achievements

India and UN


Can you solve the riddle given below? It is about an organ of the UN.
I help keep peace when fights break out, With 15 members, there’s no doubt. Five have a special “veto” say, To stop the danger, keep war away.
In the previous chapter, we studied about the formation of the UN, its objectives and its structure. In this chapter, we will learn about some special agencies that help the UN carry out various activities, such as healthcare, education, agriculture and nutrition.
The United Nations (UN) has special groups called agencies that help make the world a better place. Each agency focuses on different problems, like helping people get

enough food, providing education or protecting the environment. These agencies work together to solve global issues and improve lives everywhere.
UNICEF helps children around the world. It provides food, clean water, education and healthcare to children in need, especially during emergencies. UNICEF also works to protect children’s rights and ensure they grow up safe, healthy and happy.
Why is it important to provide food, clean water and education to children in need, especially during emergencies like earthquakes or floods.

UNESCO helps countries improve education, protect cultural and historical sites, and encourage science and learning. It promotes peace by bringing people from different cultures together to understand each other better. The UNESCO World Heritage Site is a special place, like a building or natural area, that is important to all people because of its history, culture or beauty.

With the help of the internet or the library, find the names, pictures and the location of any three UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India.
WHO works to improve health worldwide. It helps countries fight diseases, provides vaccines and promotes healthy living. WHO also works to ensure everyone has access to clean water, safe food and good healthcare, especially in times of crisis.


The WHO was founded on April 7, 1948. World Health Day is celebrated every year on this day.


FAO helps fight hunger by improving farming and food production. It teaches farmers how to grow more crops, protect the environment and share food fairly. It also works to ensure everyone has enough nutritious food to eat.
ILO focuses on improving working conditions for people around the world. It helps ensure workers have safe jobs, fair wages and good rights. The ILO also works to stop child labour and ensures that all workers are treated fairly and equally.
The United Nations has achieved many things, like helping to end wars and maintaining peace in many countries.
It provides food, clean water and medicine to people in need. The UN also provides food and clean water to people during emergencies, like natural disasters.
The UN protects children’s rights, fights diseases and works to improve education and the environment worldwide. Through UNICEF, the UN helps children get education and vaccination. The World Health Organisation (WHO), another UN agency, helped fight diseases like smallpox and continues to work on improving global health.

Why is it important to ensure peace in the world?
However, not everyone agrees that the UN is a successful organisation. It is because the UN was unable to stop the invasion of Iraq, the conflict in Syria or the Rwandan genocide. Some developing countries feel that the UN is less concerned about their growth compared to more developed nations. The dominance of the permanent members in the Security Council and their veto power have also been questioned many times by other countries.
invasion: when one country’s army enters another to take over that country by force genocide: large-scale killing of a particular group of people



State True or False.
1. UNICEF was established in 1949.
2. WHO was established before World War I.
3. The main objective of FAO is freedom from hunger.
4. The Security Council is a special agency of the UN.
India became a member of the UN in 1945. India has helped the UN maintain world peace on many occasions. Some contributions of India to the UN are:
• India has been a part of the UN peacekeeping forces in Sudan and the Middle East.
• India has served as a non-permanent member of the UN Security Council many times. India is demanding a permanent membership along with other nations to make the UN more democratic.
• As a developing country, India has raised issues concerning developing countries at multiple forums within the UN.
• India has supported the freedom struggle of other countries and raised their issues at the UN. For example, it opposed apartheid in South Africa and raised this issue multiple times at the UN.
• Many Indians have served in important positions in the UN. India, along with special agencies of the UN, works tirelessly for human development.
Elephant Caves, near Mumbai, were declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987. They are a collection of cave temples dedicated to Lord Shiva.
peacekeeping: to ensure peace in the world
Do you think India will be able to contribute more to the UN if it is made a permanent member of the UN Security Council?

democratic: people having a say in the governing of an organisation or a country


UNESCO World Heritage Site: a special place, like a monument or natural area, that is important to all people because of its history, culture or beauty
apartheid: a discriminatory practice that treats one group of people as socially and legally inferior to the another group

Scan the QR code to learn more about how UNICEF helps children.
• The UN protects children’s rights, fights diseases and works to improve education and the environment worldwide.
• UNICEF helps children around the world.
• India has supported the freedom struggle in other countries and raised their issues at the UN.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which UN agency works to educate children?
a. UNICEF
b. FAO
B. Which UN agency declares the World Heritage Sites?
a. UNESCO
b. ILO
C. Which UN agency helps workers?
a. FAO
b. ILO
c. UNESCO
c. FAO
c. WHO

2. Fill in the blanks.
A. teaches farmers how to grow more crops.
B. is a specialised agency of the UN that works for the development of the working class.
C. helps nations preserve their culture.
D. helps countries fight diseases, provides vaccines and promotes healthy living.
3. Write True or False.
A. India is a permanent member of the UN Security Council.
B. The UN has always failed to prevent a war.
C. World Health Day is celebrated every year on 17 April.
D. India opposed apartheid in South Africa.
4. Short answer questions.
A. Why was UNICEF established?
B. What is the work of the ILO?
C. What is the purpose of FAO?
5. Long answer questions.
A. Write a short note on UNESCO.
B. What are some of the failures of the UN? Explain using two examples.
C. What is the contribution of India to the UN? Give any four points.
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the picture and answer the following questions.
A. What is the full form of this agency?

B. List a few ways in which this agency helps in making the world a better place.




Imagine a nation is facing a shortage of food because of no rainfall. The production of food has also decreased due to the lack of irrigation. Which UN agency can support the nation? What are the two ways in which the UN agency can help the nation?


The World Health Organization celebrates World Health Day every year on a particular theme. Find out the theme for this year and make a scrapbook on this theme. Display your scrapbook in the class.

Objective: To help students learn about the life and contributions of an important figure from Indian history, such as a freedom fighter, scientist, or social reformer, by creating a biographical booklet.

Materials Needed: Sheets of coloured and white paper, scissors and glue, colourful markers, pencils, pens, craft materials (stickers, glitter, etc.), access to research materials (books, internet), ruler, photos or drawings of the chosen personality, cardboard or thick paper for the booklet cover, art supplies for decoration
Step 1. Choose any one famous persom from Indian history: a freedom fighter, scientist, or social reformer. Use the internet or books to gather information about the person’s life, work and impact on India. Collect images, quotes and other relevant information to include in the booklet.
Step 2. Plan what your booklet will look like by deciding how to organise the content (e.g., introduction, timeline, achievements, images). Create a timeline of important events in the person’s life. Your booklet should have at least 2 pages.
Step 3. Design the cover of the booklet with creative patterns or the person’s portrait. Decorate the pages with drawings, images, and visual representations of the person’s work (e.g., rockets for Dr Kalam or spinning wheels for Gandhi).
Step 4. Write short paragraphs on the achievements, important events and personal milestones of the person you are writing about. Include famous quotes made by that person. Ensure the booklet looks beautiful and is rich in information.
Project Outcome: You now have a well-designed booklet. Display your booklet in the class.
Final Outcome: This project will help you understand the life and contributions of an important figure in Indian history. You will develop skills in research, design, creativity and communication.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.


Read this article. Answer the questions given below.
The United Nations (UN) is helping war-torn regions in Northland and Southland. Northland and Southland have been in a war for two months. Many people have lost their homes, and food and medicines are running low in supply. The UN Security Council worked quickly to bring both sides together for peace talks, which helped stop the fighting temporarily. Meanwhile, the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) sent teams to provide food, clean water and medicine to children and families affected by the conflict. The World Health Organization (WHO) set up emergency clinics to treat the injured. Thanks to these efforts, normalcy and peace was slowly, but surely, restored. The UN continues to work on long-term plans to bring peace and stability to Northland and Southland.

1. Which UN organ helped to bring both sides together for peace talks in Northland and Southland?
a. UNICEF
c. United Nations Security Council
b. World Health Organization
d. World Food Programme
2. Why did the UN send teams to Northland and Southland?
a. To fight in the war
b. To provide food, water and medical supplies
c. To build new houses
d. To organise sports events
3. Imagine you are a leader in Northland. Give two ways in which you would talk to other leaders about the importance of peace and working together after the fighting?
4. Describe two other ways in which the UN could help support the children of these countries.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.













Introducing Quest, a thoughtfully designed Social Science book to nurture an understanding of people, places, social surroundings, communities, and human society. In keeping with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020’s focus on competency-based education, Quest provides opportunities for learners to master key concepts, hone their critical thinking, develop humane values alongside 21st century skills, and be able to make informed choices in their day-to-day lives.
Quest is designed to galvanise students’ interest in Social Sciences, both as a subject and as a practical experience, while also making them well-rounded individuals who interact with the world around them in a rational and meaningful way.
Product Package
• Coursebook
• Uolo App
• Teacher’s Guide
• Applied Social Science Projects: Engaging, hands-on projects blending social sciences, mathematics, arts, and technology to understand the world around them
• Competency-based Assessments: Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and application of skills
• Story-based Approach: Enchanting comic stories that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure
• Picture-based Questions: Questions featuring visual stimuli to elevate comprehension, interpretation and critical thinking
• Community Connect: Engaging with community members to make text-to-self connections and develop appreciation for diverse contexts and cultures
• Wonders of Bharat: Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage, designed to ignite a profound sense of pride and love for the nation
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, South East Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-979689-7-6
