





Academic Authors: Latika Uppal, Cherry Chadha, Akanksha Singh, Kashika Parnami, Chandani Goyal, Anuj Gupta, Simran Singh
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Sanjay Kumar Goel, Vishesh Agarwal
Project Lead: Sneha Sharma
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First impression 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Reflection Science 4
ISBN: 978-81-979832-0-7
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address:
85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
Welcome to the exciting world of science through Reflection, a textbook that has been thoughtfully designed to ignite curiosity, and nurture a love for evidence-based thinking in young minds.
In today’s rapidly evolving world, a solid foundation in science from an early age is more crucial than ever. Science education lays the groundwork for critical thinking, problem-solving, and the ability to make informed choices. These skills are not just academic: they are essential life skills that empower young minds to understand and interact with the world around them in a rational and meaningful way. At UOLO, we believe that every child deserves to learn these skills with the best resources available.
In this pursuit, Reflection is uniquely crafted to provide a comprehensive and contemporary learning experience, meticulously aligned with the recommendations of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 and the National Curriculum Framework (NCF) 2023. The book incorporates the curricular goals and competencies outlined in the NCF 2023, ensuring that every chapter, exercise, and feature reflects these foundational principles.
This textbook transcends traditional teaching methods by adopting a competency-based approach, recommended by both NEP 2020 and NCF 2023, that emphasises not just conceptual understanding and critical thinking, but also application of scientific concepts, and problem-solving. It is designed to make learning both meaningful and relevant, equipping students with the tools they need to thrive in the 21st century.
Carefully curated content, NEP-specific tags, and a diverse array of elements have been seamlessly integrated throughout the book to nurture essential skills, values, and dispositions outlined in the NEP. Competency-based projects and assessments are strategically placed to help students master key concepts and develop higher-order thinking skills.
The book has the unique feature of being complemented by a graphic novella. Each unit of the book begins with an episode of the gripping sci-fi tale, which not only captivates the students’ interest and promotes reading, but also ingeniously connects with some of the core concepts that will be taught in the respective units.
Each chapter is also enriched with vibrant illustrations, relatable examples, and interactive activities to engage our young learners. Hands-on experiments and inquiry-based learning experiences have been embedded throughout the book to instil a scientific temper among students and make learning an enjoyable journey for them. Moreover, assessments ‘of, as, and for learning,’ as envisioned by the NEP and NCF, have been interwoven throughout the curriculum, providing continuous evaluation and meaningful feedback to students to support their growth and success.
The Reflection product bundle offers a comprehensive science kit which includes a textbook that has relevant and up-to-date content, concept building opportunities, projects, and assessments; a teacher manual offering extensive teaching support; technology-powered features that includes engaging videos and interactive exercises for students; and digital lesson plans and an assessment generator for teachers.
In conclusion, Reflection is designed to fascinate students towards science, both as a subject and as a practical experience in their everyday lives, while also making them well-rounded individuals. We invite educators, parents, and students to embrace Reflection and join us in nurturing the next generation of thinkers, innovators, and problem-solvers. Embark on this exciting journey with us and let Reflection be a valuable resource in your educational adventure.


Welcome to the Reflection journey.
The program is carefully designed to elevate the experience of learning science through an NCF-based, age-appropriate, pedagogically-sound, and engaging content. Teachers will be supported with a manual that offers comprehensive guidance to optimise classroom instruction. Furthermore, various assessment mechanisms have been built in to the program.
Engaging Textbooks
Comic Stories
Teacher Manual
Competency-based Model Assessments
STEAM Projects
Question-paper Generator
Student and Teacher Apps
Learning Videos
Interactive Tasks & Exercises
Byte-size Lesson Modules
The Reflection program is also augmented by a digital learning platform that offers powerful educational videos and interactive exercises to help children master concepts and skills in a joyful and fear-free manner.

The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, introduced by the Government of India, represents a transformative shift in the country’s education system. It aims to create a more holistic, dynamic and multidisciplinary approach to education. NEP 2020 focuses on fostering conceptual understanding, skills, values, and competencies that align with the demands of the 21st century, while also preserving India’s rich cultural heritage. UOLO is fully committed to actualising the vision of NEP 2020 by meticulously adhering to its outlined recommendations.









1. Focus on conceptual understanding
2. 21st century skills, values, and dispositions
3. Critical thinking and problem solving
4. Application in real life
5. Holistic and integrated learning
6. Experiential learning
7. Enjoyable and engaging
8. Scientific-inquiry and discovery-based approach
9. Technology-based solutions
10. Knowledge of India

Competency-based Education
NEP Pages 12, 17, and 22
Teaching and Learning Pedagogy
NEP Pages 3, 11, 12, and 27
National Pride
NEP Pages 15, 16, and 43
11. Assessment of core concepts and application skills Assessments
NEP Pages 12, 18, and 22


Engaging hands-on projects blending Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Maths (STEAM) to inspire young minds
Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and application of skills
Enchanting comic stories that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure
Curated videos to find out more about key concepts
Multidisciplinary, holistic, and fun-filled activities to internalise the concept better

Hands-on experiments to foster the spirit of scientific inquiry and evidence-based thinking

Error Alert
Concise snippets of information designed to caution against potential misconceptions
Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical, and evaluative thought processes
Interactive
Digital worksheets on key concepts to supplement textbook exercises
Wonders of Bharat
Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage, designed to ignite a profound sense of pride and love for the nation
Picture-based Questions
featuring visual stimuli to elevate comprehension, interpretation, and critical thinking
Simple activities and tips to develop a diverse set of essential skills for living well


The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 outlines essential skills, values, dispositions, and learning approaches necessary for students to thrive in the 21st century. This textbook identifies and incorporates these elements throughout its content, activities, and exercises. Referred to as “NEP Tags”, they are defined as follows:



INTEGRATED
Bringing creativity and fun into learning by combining music, drama, and art with other subjects
Sports Integration
Using physical activities, sports, and games to make learning active and engaging
Cross-curricular and skill linkages to make the learning experience more holistic, joyful and meaningful
SCIENTIFIC TEMPER
Scientific Temper
A mindset rooted in curiosity, critical thinking, problem-solving, and evidence-based reasoning

Teamwork
TEAMWORK

SDG
Embracing the spirit of mutual collaboration and cooperation while working together to solve problems
Unwavering commitment to create a green, peaceful, prosperous, and equitable and inclusive world

SEL
Developing the skills to understand and manage emotions, build positive relationships with others, and make responsible choices

The National Curriculum Framework for School Education (NCF), released in 2023, is developed based on the vision of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. Its purpose is to enable the implementation of the NEP. The NCF provides guidelines for designing school syllabi and textbooks in India. It aims to improve the quality of education by making it more relevant, engaging, inclusive, and learner-centric. To achieve this, the NCF has articulated precise Learning Standards through well-defined Curricular Goals and Competency statements. These statements serve to harmonise the syllabus, content, pedagogical practices, and assessment culture, ensuring a cohesive and comprehensive educational experience.
Curricular Goals: Curricular Goals are statements that give directions to curriculum development and implementation. They are derived from Aims and are specific to a Stage in education.
Competencies: Competencies are learning achievements that are observable and can be assessed systematically. These Competencies are derived from the Curricular Goals and are expected to be attained by the end of a Stage.
NCF Page 59
CG-1
Explores the natural and social environment in their surroundings
CG-2
Understands the interdependence in their environment through observation and experiences
C-1.1 Observes and identifies the natural (insects, plants, birds, animals, geographical features, sun and moon, soil) and social (houses, relationships) components in their immediate environment
C-1.2 Describes structures, relationships, and traditions in the family and community
C-1.3 Asks questions and makes predictions about simple patterns (season change, food chain, rituals, celebrations) observed in the immediate environment
C-1.4 Explains the functioning of local institutions (family, school, bank/ post office, market, and panchayat) in different forms (story, drawing, tabulating data, noting discussion), and analyses their role
C-1.5 Creates simple objects (family tree, envelopes, origami) on their own using local materials
C-2.1 Identifies natural and humanmade systems that support their lives (water supply, water cycle, river flow system, life cycle of plants and animals, food, household items, transport, communication, electricity in the home)
C-2.2 Describes the relationship between the natural environment and cultural practices in their immediate environment (nature of work, food, traditions)
C-2.3 Expresses the changes in the lives of their family and community as communicated by elders and through local stories (changes in occupation, food habits, resources, celebrations, communication)
The above is a snapshot of the curricular goals and competencies relationship in EVS for the Preparatory Stage (NCF 2023, pages 340–341). The next section shows the coverage of all these competencies across the chapters.


















C-1.1 Observes and identifies the natural (insects, plants, birds, animals, geographical features, sun and moon, soil) and social (houses, relationships) components in their immediate environment
C-1.3 Asks questions and makes predictions about simple patterns (season change, food chain, rituals, celebrations) observed in the immediate environment



CG-1
Explores the natural and social environment in their surroundings
C-1.5 Creates simple objects (family tree, envelopes, origami animals) on their own using local materials

C-2.1 Identifies natural and humanmade systems that support their lives (water supply, water cycle, river flow system, life cycle of plants and animals, food, household items, transport, communication, electricity in the home)
CG-2 Understands the interdependence in their environment through observation and experiences

C-3.1 Describes the basic safety needs and protection (health and hygiene, food, water, shelter, precautions, awareness of emergency situations) of humans, birds, and animals



CG-3
Explains how to ensure the safety of self and others in different situations
C-3.3 Develops simple labels, slogans, and participates in roleplay on safety and protection in the local environment to be displayed/done in school and locality






















C-4.1 Observes and describes diversity among plants, birds, and animals in their immediate environment (shape, sounds, food habits, growth, habitat)
CG-4 Develops sensitivity towards social and natural environment
C-4.2 Observes and describes cultural diversity in their immediate environment (food, clothing, games, different seasons, festivals related to harvest and sowing)
C-4.3 Observes and describes natural resources in their immediate environment, and their use
C-4.4 Discusses how natural resources can be shared and maintained (growing vegetables in flowerpots/kitchen gardens, use of rainwater)
C-4.5 Identifies needs of plants, birds, and animals, and how they can be supported (water, soil, food, care)








C-6.1 Performs simple investigations related to specific questions independently or in groups

C-6.2 Presents observations and findings through different creative modes (drawing, diagram, poem, play, skit, through oral and written expression)
CG-6 Uses data and information from various sources to investigate questions related to their immediate environment






































Comic Story: Exciting story built through out the book, contains hooks to topics in a unit

Chapter Overview: Outline of the key concepts covered in the chapter





































Get Set: A short and fun activity to get learners excited about the new topic
You know about different parts of a plant. Solve the crossword puzzle as quickly as you can!










Did You Know: Interesting facts related to the topic











Vocabulary: Meanings of difficult words



Error Alert: Caution against misconceptions



Investigate and Discover: Hands-on experiments to nurture the spirit of curiosity, inquiry and evidence-based thinking
Pause and Answer: Short exercises between the chapter to pause and assess comprehension
NEP Tags: To show alignment with NEP skills and values

Do and Learn: Multidisciplinary, holistic, and fun activities to understand the concept better







Think and Tell / Discuss: Analysis, reflection, and text-to-self connection-based prompts for discussion in class
Remember: Recall of previous knowledge relevant to the topic
Wonders of Bharat: Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage

Word Splash: Recall of key terms and concepts in the chapter






Explore More: Short videos to find out more about the topic
Points to Remember: Summary of the chapter
Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Picture-based Questions: Special questions featuring visual stimuli to foster comprehension, interpretation, and critical thinking
HOTS: Intellectually stimulating questions designed for higher order thinking and analysis
Life Skills: Simple activities and tips to develop a diverse set of essential skills for living well

























Nutrients from Food
Food and Digestion Preserving Food Cooking Food Balanced Diet Digestion of Food


Get Set

Food is important for us. Give examples of the following food types.
1. Energy-giving food
2. Body-building food
3. Protective food

After getting ready for school, Reyansh asks his mother, “Mumma, what is for breakfast today?” His mother gives him bread and jam for breakfast. The next day, Reyansh asks his mother about breakfast again. She replies, “Today, we have paneer paratha!” Reyansh feels sad and asks for bread and jam only. His mother then explains to him that he needs to have a variety of food to get different nutrients. Reyansh then asks his mother about the nutrients and their types. Let us learn about them.

Food is one of the necessities of life. When we eat food, our body absorbs useful substances called nutrients from it.
Nutrients give us the energy to do various activities, such as playing, running and studying. They help in the growth and repair of our body. They also protect our body against diseases and keep us healthy. So, in order to fulfil our body needs, we need to eat a variety of food in our meals.
Food can be divided into three food groups: energy-giving food, bodybuilding food and protective food.
The food we eat contains different types of nutrients along with roughage and water. The five main types of nutrients in our food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. Let us learn about each type of nutrient.
Carbohydrates play an important role in our diet. They are the nutrients that give us energy to do work. Carbohydrates are of two types—sugar and starch.
Foods such as rice, chapati, bread, corn, potato, sugar and honey are rich in carbohydrates.
People who do more physical work like sportspersons, labourers and farmers should include more carbohydrate-rich food in their meals as they need more energy.
Like carbohydrates, fats also provide energy to the body. They help to keep our bodies warm.
Foods such as butter, ghee, oil and dry fruits are rich in fat.
We require fats in very small amounts in our bodies. The extra fat we eat gets stored in our body for later use.
Food rich in carbohydrates and fats are called energy-giving food.













Some people think that eating more fatty foods gives them more energy. But fats are difficult to digest and get stored in our body. Too much fat can cause health problems. Error Alert!

Protein helps in the growth and repair of our body. Have you ever got a cut? What happens to the wound after some time? After some time, our injuries heal. It is the protein that helps our body to recover from an injury by generating new cells. This is why growing children and sick people should include more protein-rich food in their meals.
Foods like milk, eggs, meat, fish, beans and pulses are rich in proteins. Food rich in proteins is called body-building food.
Vitamins help our body fight against infections. They help to heal wounds and keep our bones and gums strong. They are required in small amounts but are important for the body.
Minerals keep us fit and healthy. These are required for the smooth functioning of our body. They help in the formation of blood, teeth and bones.
Some important minerals are sodium, potassium, calcium, iodine and iron. Fresh fruits, leafy vegetables, milk, meat and fish are good sources of vitamins and minerals.
Food rich in vitamins and minerals is called protective food.









Besides nutrients, our body also needs water and roughage. Water and roughage do not provide any nutrients but they are important for the proper functioning of body.
• Water helps to digest food.
• It helps to remove waste from the body in the form of urine and sweat.
• It also regulates our body temperature.
Fruits, vegetables and grains contain fibres that cannot be digested by the human body. They are called roughage.
Roughage does not contain any nutrients but it is important for digestion. It adds bulk to the food and helps to get rid of the undigested food from the body. It helps in digestion and prevents constipation.
regulate: to control



Given below are some food items. Sort them and fill in the table below based on the nutrients present in them.
Meat, chapati, fish, milk, fresh fruits and vegetables, bread, honey, spinach, dry fruits, ghee, oil, pulses, beans, eggs, potatoes
Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Vitamins
Minerals
Nutrients such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals are essential components of a balanced diet. A balanced diet should also include roughage (fibre) and water. So, we can say a diet that has all the essential nutrients in the right amounts, as required by the body, is called a balanced diet. We must eat a balanced diet to lower the risk of diseases and stay healthy.

A balanced diet is not the same for everyone. It can be different for people based on their age, job and health needs. Error Alert!
Pause and Answer
Tick ( ) the correct statements about a balanced diet.
Think and Tell
How many glasses of water and milk do you drink daily?
1. A balanced diet should contain all the nutrients in the right amount.
2. A balanced diet should not include water and roughage.
3. A balanced diet is the same for everyone.
4. A balanced diet keeps us healthy.
5. A balanced diet lowers the risk of diseases.


Most food items are consumed only after cooking. Cooking kills germs present in the food. It makes the food tasty. But overcooking destroys the nutritional value of the food.

While steaming, the food is cooked using steam or water vapours. Foods such as idlis and dumplings are cooked by steaming.

While boiling, the food is cooked in hot water. Foods such as pulses and eggs are boiled before eating.

In roasting, the food is cooked in dry heat on stove. Foods such as brinjal and meat can be roasted before eating.

In frying, the food is cooked in hot oil or ghee. Foods like puris and fritters (pakoras) are cooked by frying.

In baking, the food is cooked in dry heat in a closed space like an oven. Foods such as cakes and cookies are cooked by baking.
Do you have food left over after your meals at home? If so, how do you store them? We mostly store cooked food in our refrigerator for a few hours to a few days. There are some food items which can be stored for months. Some food items get spoiled easily while some do not spoil for a long time. Food gets spoiled due to germs. If we eat this spoiled food, we can fall sick. We can prevent the spoilage of food through preservation. The process in which food is treated and stored to prevent spoilage is called food preservation. Some methods for food preservation are:
• Drying: It is one of the oldest methods of preservation. In this method, the food is dried under the sun. Drying removes the moisture from the food and stops germs from growing. Drying is used to preserve food like potato chips, mangoes and dry fruits.
dumplings: a small piece of dough filled with spiced vegetables or meat prevent: to stop spoilage: getting wasted

Potatoes need to be dried to make chips.

• Freezing or Refrigeration: In this method, food items are stored at low temperatures to preserve their taste and nutrients. Peas and meat are preserved by freezing.
• Sweetening: When excess sugar is added to food, it kills germs and protects the food from getting spoiled. Sugar also adds a sweet taste to the food. We preserve jams and jellies by sweetening.
• Salting: In this method, salt is used to preserve the food. Salting removes moisture from the food. Fish is preserved by salting.
• Boiling: Have you ever wondered why your mother boils milk? She does this to prevent the milk from spoiling. Boiling is used to preserve food items only for a short time.
• Canning: It is the method in which food is stored in airtight jars called cans. Fruits, vegetables and meat can be preserved by canning.



Look into the kitchen. Make a list of different food items that are preserved in the kitchen. You can ask an adult for help. Also, write down the name of the preservation method used for each food item. Record your observations in a table as shown below.
Method of Preservation


Read the sentences given below. Write the name of the preservation method. Also, give an example of a food item preserved in this way.
1. This method removes moisture from the food and stops germs from growing.
2. This method is used to preserve food items for a short time.
3. This method uses salt for food preservation.
4. This method freezes the food items to preserve their taste and nutrients.
5. This method uses sugar to preserve food items.
Our body cannot directly absorb nutrients from the food we eat. The food we eat needs to be broken down into simpler forms so that it can be easily absorbed by our bodies. This process of breaking down food into simpler forms is called digestion. The group of organs that help in the digestion of food in our body makes up our digestive system. The main parts of the body that are involved in digestion are the mouth, food pipe (oesophagus), stomach, liver, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine and anus.
1. Mouth: The process of digestion begins in the mouth. The food is first broken down by biting and chewing. This food is then mixed with saliva, a watery substance present in the mouth. Saliva helps in food digestion.
4. Small intestine: After passing through the stomach, the food reaches the small intestine. In this organ, all the nutrients from the food is absorbed, and then supplied by the blood to other body parts.
5. Liver: It produces a juice that breaks down fats into tiny droplets.
Pancreas: It produces a juice that also helps in digestion.
2. Oesophagus: This is also called the food pipe, and it is a thin, long tube. After the mouth, the food goes through the food pipe and reaches the stomach.
3. Stomach: This is a saclike or J-shaped organ. This organ acts like a mixer and mixes all the food particles to form a fine paste.
6. Large intestine: The large intestine absorbs water from the undigested food, and the remaining food is formed into a waste called faeces.
7. Anus: The faeces produced in the large intestine get removed from the body through the anus.



Aim: To understand the process of digestion in the mouth
Materials Needed: A zip lock bag, two slices of bread and water
Method:
Step 1: Take a zip lock bag and place the slices of bread inside.
Step 2: Add a small amount of water to the bag.
Step 3: Seal the bag tightly and mash it gently with your hands for some time.
Step 4: Observe what happens to the bread.
Findings: The bread slices will get crushed and mix well with the water, similar to how food is broken down and mixed with saliva in the mouth.
Conclusion: This is how food gets mixed with saliva in the mouth during the process of digestion.
India has a variety of fermented foods such as idli and dosa that promote gut health. These are made from fermented rice and lentil batter making them easier to digest and enhancing the nutrient content in them.


nutrients: components in food that help our bodies to grow and stay healthy constipation: a condition where undigested food (stool) becomes hard and painful to pass balanced diet: a diet that has all the essential nutrients in the right amount as required by the body food preservation: the process in which food is treated and stored to prevent spoilage digestion: the process of breaking down food into simpler forms digestive system: group of organs that help in the digestion of food in our body

Scan the QR code to know more about food.
• There are five types of nutrients namely carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals.
• We must eat a balanced diet to stay fit and healthy.


• Cooking food makes it tasty but overcooking destroys its nutritional value.
• Food needs to be preserved to prevent it from spoilage.
• Digestion is important to absorb all the nutrients from the food we eat.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which nutrient gives us the energy to do work? Carbohydrates Proteins Minerals Vitamins
B. Which food items are cooked by steaming? Cakes Idlis Cookies Pulses
C. Which preservation method is used for jams and jellies? Drying Salting Boiling Sweetening
D. In which part of the digestive system does the food enter first? Anus Mouth Stomach Food pipe
E. Which method is commonly used to preserve food only for short interval of time? Drying Boiling Salting Canning
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. help in the formation of teeth, bones and blood.
B. help us fight infections and heal wounds.
C. help with the growth and repair of our body.
D. Foods rich in and are called energy-giving foods.
E. Foods rich in vitamins and minerals are called foods.
3. Write True or False.
A. Roughage is an example of a nutrient.
B. We should not overcook our food.
C. Canning, salting and refrigeration are methods of food preservation.
D. The digestion of food starts in the food pipe.
E. Cakes and cookies are cooked by frying.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. Give two examples of foods rich in vitamins and minerals.
B. Why do we need to cook food?


C. Which two food items are cooked by baking?
D. Name two food items that are preserved by sweetening.
E. What is digestion?
F. What is the function of liver and pancreas?
5. Long-answer questions.
A. What are nutrients? Name the different types of nutrients with one example of each.
B. Explain any 3 methods of cooking. Give examples of food items cooked by each method.
C. What is food preservation? Write one line about each of the different methods of preserving food.
D. Explain digestion with the help of a well-labelled diagram.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. Look at the image. Label it.
B. Write the function of the organ mentioned in label 6.


Heena often falls sick. She is also constipated. What kind of diet would you suggest to her to help her get well?

Food is a basic requirement for all living beings. We should not waste food. With the help of your parents and neighbours, collaborate with the nearby restaurants to collect the extra or leftover food they have, and donate it to needy people.




Teeth and Microbes

Importance of Teeth
Types of Permanent Teeth
Structure of a Tooth
Care for Teeth
What Are Microbes?

Get Set

Read the story given below.
While eating her breakfast, Rani felt one of her front tooth shake, and then it gently fell out. She showed it to her grandmother, who said, “Ah, one of your milk tooth fell out, did it? Don’t worry! A stronger tooth will grow in its place soon.”
Teeth are very important for our digestive system. They help break down food by crushing or cutting it before we swallow it and digest it further. Most humans have 32 teeth.

Teeth are important because they help us bite and chew our food. When we bite and chew, it makes the food smaller and easier for our stomach to digest. They also help us speak clearly, and they are an important part of our smile.
Human beings have two sets of teeth: temporary and permanent.
This first set of teeth is called temporary teeth or milk teeth. The first tooth appears when a baby is seven or eight months old. By the age of three years, a baby has 20 teeth.
When a child is around six years old, the milk teeth begin to fall out. A new set of teeth grows in place of the milk teeth. These are called permanent teeth. An adult human has 32 permanent teeth.

Permanent Teeth
Teeth are used for tearing, biting and grinding food. There are four main types of teeth, each with a different shape and function to perform these tasks.
These are eight teeth located at the front part of the mouth, with four in the lower and four in the upper jaw. These are usually the first permanent teeth that a child gets. They generally grow between the ages of six and eight. Incisors are the teeth we use to bite or cut our food.

Neha got all her new teeth in place of the ones which fell out when she was six years old. However, her grandfather, who has lost all his teeth, does not grow new teeth. Why?
Incisor Premolar Canine Molar Types of Permanent Teeth
Incisors
Canines
Premolars
Molars
Types of Teeth
There are four canines—two in the upper and two in the lower jaw. These are next to the incisors. Canines are our sharpest teeth and help us tear food apart.


There are eight premolars in your mouth—two on each side of the upper and the lower jaws. These teeth help tear and crush food.
Molars are your largest teeth, twelve in total, and at the back of your mouth. Like premolars, they help grind, tear and crush food. Their large, flat surface makes them perfect for this job.
Name the following.
1. The teeth used for tearing and crushing food
2. The teeth with a large flat biting surface
Herbivores, like cows, horses, rabbits and deer, generally do not have canines. But some, like hippopotamus, have them to defend themselves.
We have learnt about different types of teeth. Each tooth has three main parts.
Crown: The crown is the part of the tooth that can be seen in our mouth. It is the part we use to chew our food. Different types of teeth have different shapes of crowns. For example, incisors have flat, sharp edges for cutting, while molars have large and flat surface for grinding.
Neck: The neck of the tooth is where the crown meets the gumline. It is the middle part of the tooth and it holds the tooth in place.
Root: The root is the part of the tooth that is hidden under your gums and anchored into the jawbone. It keeps the tooth stable and strong.
The internal structure of a tooth consists of three main layers:
Enamel: The enamel is the outermost white layer of the crown. It is the hardest part of our body and it protects the tooth from damage.
Dentine: Underneath the enamel is the dentine. It is not as hard as enamel but still protects the pulp of the tooth. Dentine is yellowish and makes up most of the tooth.
Pulp: The pulp is the soft, inner part of the tooth. It has blood vessels and nerves. The pulp keeps your tooth alive and healthy.
edges: sharp or flat sides of an object anchored: to be held firmly in one place


Take a small mirror. Now, look at your teeth in the mirror and find the different types. First, find the incisors at the front and count their number. Next, look for the canines on either side of the incisors. Finally, locate the premolars and molars at the back of your mouth. Now, count the number of each type of teeth in the mouth.
Label the different parts of the tooth.
Did You Know?
your tooth, called
A tooth cavity is a small hole or opening that forms on the surface of a tooth. It happens when the hard outer layer of the tooth, called enamel, gets damaged or worn away by bacteria and acids from leftover food in our mouth. Cavities can cause tooth pain and lead to problems if proper care is not taken.


Taking good care of your teeth by brushing, and visiting the dentist can help prevent cavities.
Here are some simple tips for taking care of your teeth (oral hygiene):
• Brush Twice a Day: Brush your teeth in the morning and evening using a toothbrush and toothpaste. This helps to remove food and plaque, keeping your teeth clean and healthy.
• Floss Daily: Flossing helps clean between your teeth where your toothbrush cannot reach. Do this once a day to keep your gums healthy.
acids: liquids that can wear away or break down materials plaque: a harmful substance that forms on your teeth


• Eat Healthy Foods: Eat lots of fruits and vegetables, and avoid too many sugary snacks and drinks. Too much sweet food can cause cavities.
• Rinse After Eating: If you cannot brush your teeth after a meal, rinse your mouth with water to help remove food particles.
• Visit the Dentist: Go to the dentist regularly for oral check-ups.

Brush twice Floss daily. Eat healthy foods. Rinse after eating. Visit the dentist. a day.

Aim: To show that fizzy drinks harm our teeth
Materials Needed: a hard-boiled egg (with the shell), a cup of fizzy drink, a clear jar or a glass
Method:
Step 1. Pour a cup of fizzy drink into the jar.
Step 2. Add the hard-boiled egg into the jar.
Step 3. Leave the egg in the fizzy drink for a day.
Step 4. Remove the egg the next day and feel its shell.
Findings: You will observe that the egg shell has become yellow and soft due to the action of fizzy drink on the egg shell.
Conclusion: This proves that our teeth are harmed by fizzy drinks as our teeth are also made of the same substance as the egg shell.
Fill in the blanks.
1. rich foods are good for your teeth.
2. Brush your teeth a day.
3. drinks are not good for teeth.
What is the right way to brush one’s teeth? Name at least two ways.

Microbes are tiny living things that are too small to see with our naked eyes. We need a microscope to see them. They are found all around us as they live in water, soil and air. The human body is home to millions of these microbes. Some common types of microbes are bacteria, algae, fungi and protozoa. Some of these microbes make us ill while some are important for us.

Different Types of Microbes

Harmful microbes can make us sick. They can cause illnesses like colds, flu and stomach bugs. These microbes can spread from one person to another through coughing, sneezing or touching dirty surfaces.
• Bacteria can cause common illnesses like sore throat, ear infections and food poisoning.
• Viruses can cause illnesses such as the common cold, flu and chickenpox.
• Some fungi can cause infections like athlete’s foot, ringworm and yeast infections.
• Malaria is a common illness caused by protozoa, which can cause a high fever and make us feel very weak.
Not all microbes are bad. Microbes help us in many ways.
• They are used to make food such as curd, yoghurt, cheese and bread.
• They help in digestion of food.
• Scientists use microbes to make medicines like antibiotics.
• Microbes also help break down dead plants and animals into nutrients that growing plants can use.
• They even help in cleaning up the environment. These tiny microbes play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of our world.


Fastminar is a 40-foot structure made with approximately 80,000 toothbrushes. It is located at Terna Dental College in Navi Mumbai, India. The monument has been certified by Guinness World Records as the largest toothbrush sculpture of a body part in the world.
gumline: where your teeth and gums meet jawbone: the hard, bony part of the mouth that holds teeth cavity: a small hole or opening that forms on the surface of a tooth antibiotics: medicines that fight infections microbes: tiny living things that are too small to see with our naked eyes

Scan the QR code to know more about teeth and microbes.
• Human beings have two sets of teeth: temporary and permanent.
• Teeth are of different types: Incisors, Canines, Premolars and Molars.
• There are 3 main parts of a tooth: crown, neck and root.
• Microbes are tiny living things that are found all around us.
• The conversion of milk into curd occurs due to the presence of bacteria.
• Microbes can be useful or harmful.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of the following is NOT true regarding the care of teeth?
Teeth get damaged by chewing food.
We should not eat too many sweets. We should brush our teeth twice a day. We should eat raw fruits and vegetables.


B. The number of molars in each jaw is four two one six
C. Which of the following is not a microbe? Bacteria Fungi Plaque Protozoa
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. A tooth has a , a neck and a .
B. Eating too many causes cavities.
C. are tiny living things that are too small to see with our naked eyes.
D. Medicines such as are prepared with the help of microbes.
E. teeth begin to fall off at the age of six.
3. Write True or False.
A. Microbes are organisms which are not visible to human eyes.
B. The crown is the top most part of your tooth.
C. The first tooth appears when a child is around seven to eight months old.
D. A new born baby has only two teeth.
4. Match the following.
A. Incisors
i. Grinding
B. Canines ii. Crushing
C. Premolars iii. Cutting
D. Molars
5. Short-answer questions.
A. How many types of teeth do we have?
B. How can we avoid cavities?
C. What are temporary teeth?

iv. Tearing
D. Draw and label the different parts of a tooth.
E. List two uses of microbes.
6. Long-answer questions.
A. How does flossing help to keep your teeth healthy?
B. What can happen if you don’t take care of your teeth properly?
C. What is the effect of fizzy drinks on your teeth?
D. Explain why visiting the dentist regularly is important for dental health.
E. Which type of tooth (incisor, canine, premolar, molar) do you think is most important for chewing food? Justify your answer.
F. What happens to your teeth when you eat too much sugar?


7. Picture-based questions.
A. Name the type of teeth numbered 32, 24, 11 and 9 in the given image.

B. Write the number of the teeth that are used to bite food.


Predict what might happen if you do not brush your teeth for two weeks. What changes would you notice?
It is really important to take care of our teeth. Here are some easy tips that we can share with our family and friends:
• Brush your teeth twice a day for 2 minutes with a soft toothbrush and toothpaste.
• Floss every day to clean between your teeth where the toothbrush can’t reach.

• Rinse your mouth with water after meals to help remove food bits.
• Eat healthy snacks like fruits, and vegetables instead of sugary treats.
• Drink plenty of water to keep your mouth hydrated and help wash away food.
• Visit the dentist every six months for check-ups to keep your teeth strong and your smile bright.
Let us spread the word so everyone can have healthy teeth and happy smiles.











Clothes We Wear
Need for Clothes What Makes Clothes?
Different Clothes

Caring for Clothes




Complete the crossword puzzle with the help of the hints given below.
Across
1. We wear this to protect ourselves from getting wet in the rain.
2. We wear these boots in the rainy season.
Down
3. We wear these types of clothes in summer.
4. We wear these types of clothes in winter.
You are going to picnic with your friends. You see that the weather outside is sunny and breezy. What clothes would you choose for yourself and why? Would you have chosen the same kinds of clothes if:

• the sky outside was covered in dark, heavy clouds?
• if it was cold outside?
Clothes are one of the basic needs of human beings. We wear clothes to protect us from dust, germs and different weather conditions (heat, cold, wind and rain). We look smart when we wear clean and good clothes.
Tick ( ) all the correct statements.
1. Clothes are the basic needs of human beings.
2. We wear dirty clothes to look smart.
3. Clothes do not protect us from heat and cold.
4. Clothes protect us from dust and germs.
We wear different types of clothes. These clothes are made from different fabrics. Fabrics are the materials that are obtained from fibres. Fibres are long thread-like materials that are used to make clothes.
Depending on the source, fibres can be of two types—natural and synthetic.
Natural fibres: These are obtained from natural sources such as plants and animals.
Natural fibres, such as cotton, jute and linen, are obtained from plants. Fibres obtained from plants are called plant fibres.
Cotton is obtained from cotton plants. Cotton clothes absorb sweat, and are useful in summer.
We get jute from the jute plant. It is used to make sacks and ropes.




materials: substances that are used to make something


Linen is obtained from flax plants. It is used to make clothes and bedsheets.
Natural fibres such as wool and silk are obtained from animals. These are also called animal fibres. Wool is obtained from the hair or fur of animals like camels, goats and sheep. We get silk from the cocoons of silkworms.


from the hair of sheep.


Mulberry silk is the best quality of silk produced in India. It is also known as Bombyx silk.


Synthetic fibres: These are artificially prepared fibres and are not found in nature. Such fibres are also called human-made fibres. Some examples of synthetic fibres are nylon, rayon and polyester.
Synthetic fibres are durable, stretchable and wrinkle-free. These fibres can be washed easily and dried quickly. But clothes made from these fibres can catch fire easily. So, never wear these clothes while lighting diyas or playing with firecrackers.



These clothes do not absorb sweat, so they are not suitable for hot and humid climates.
Name the following.
1. We get this fibre from the cotton plant.
2. We obtain this fibre from the flax plant.
3. We obtain this fibre from the hair of camels or goats.
4. We obtain this fibre from the cocoons of silkworms.
5. We get this fibre from the jute plant.
artificially: made by humans durable: that can exist for a long time without loss in quality stretchable: that can be pulled or stretched and will go back to its original shape after you let go wrinkle-free: smooth



Nowadays, we wear different types of clothes. The choice of clothes depends on the person. Our style of clothing depends on certain other factors as well. Let us learn about them.
In India, each state has its traditional dress for men and women. Collect pictures of the traditional dresses of any five states. Paste them in your scrapbook. Write the names of each dress and the state to which it belongs. Decorate your scrapbook to make it look colourful and attractive.
We know different seasons have different weather conditions. So, we need different types of clothes for different seasons. In summers, we wear clothes that absorb sweat and keep us cool. Cotton and light-coloured clothes are preferred during the hot summer season.
In winter, we wear clothes that protect us from the cold and keep us warm. Woollen clothes protect us from the cold and chilly weather. During extreme winters, we wear layers of woollen clothes which trap the warm air inside them and keep us warm. Dark-coloured clothes also absorb heat and keep us warm. So, woollen and darkcoloured clothes are preferred during winter season.
In the rainy season, we wear raincoats and gumboots. Raincoats are made up of waterproof materials that keep us dry and comfortable.
Depending on the occasion, we wear different types of clothes. We wear loosefitted and comfortable clothes when we are at home. We should wear clean and comfortable clothes for bedtime. We wear fancy and stylish clothes for formal events such as weddings, parties and festivals.
fancy: special







Some people wear special clothes for specific work. These clothes are called uniforms. Uniforms show a sense of equality among different members of the team.
Students of a specific school, soldiers, doctors, police officers and firefighters wear uniforms. Soldiers work in extremely rough conditions. So, they wear uniforms made up of tough fibres.
Doctors wear white coats as uniforms. Firefighters wear safety suits that are made up of heat- and fireresistant materials which protect them from heat and fire. It also protects their skin from getting burnt. Factory workers wear overalls that cover their whole bodies. They also wear helmets to protect their heads from any serious injuries at work.
Circle the incorrect option.


People wearing uniforms.

Do you think people living in different countries wear the same type of clothes? Discuss with your classmates.

1. Summer Light-coloured clothes Cotton clothes Raincoats
2. Winter Woollen socks Woollen clothes Raincoat
3. Monsoon Raincoat Fancy clothes Gumboots
4. Parties Stylish clothes Raincoats Fancy clothes
Clothes are an important part of our everyday lives. We should take good care of our clothes so that they last longer and look good.
• Our clothes become dirty due to dirt, sweat and stains. We should wash our clothes regularly in clean water with detergent.
How would you take care of your school uniforms?
• White and coloured clothes should be washed separately and carefully.
• Clothes should be washed properly so that no soap or detergent remains on them.
• After washing, clothes should be dried in sunlight to kill germs and bacteria.
equality: when all persons are treated in the same manner tough: strong


• Once the clothes are completely dried, we should iron them properly. Ironed clothes make us look good and tidy.
• We should wash silk and woollen clothes gently using a mild soap or detergent.
Coloured clothes should not be dried in direct sunlight for a very long time, as their colour may fade.
• Some insects, such as moths and silverfish, can eat silk and woollen clothes. Therefore, these clothes need to be stored with extra care. These clothes should be stored in a safe and dry place. We should keep dried neem leaves or naphthalene balls between the folds of clothes while storing them.

Wash your clothes regularly.

Dry your clothes in the sunlight.

Keep naphthalene balls while storing clothes.
Write ‘T’ for true and ‘F’ for false.
1. We should wash our clothes regularly.
2. We should wash white and coloured clothes together.
3. We should iron our clothes after drying them.
4. Woollen and silk clothes should be washed using strong detergents.
5. We should place naphthalene balls with our silk clothes to protect them from insects.
Rajasthan is the largest producer of wool in India. This state has eight different sheep breeds well-known for producing carpet wool.



fabrics: clothing materials that are obtained from fibres fibres: long thread-like materials that are used to make clothes cocoon: a covering of silky threads to protect insects like silkworms uniform: special clothes worn for specific work overalls: clothes that cover the body completely

Scan the QR code to know more about clothes.
• Clothes protect us from dust, germs and different weather conditions.
• Fibres are of two types: natural and synthetic.
• Natural fibres, like cotton, jute and wool are obtained from plants and animals.
• Synthetic fibres, like nylon and polyester, are also called human-made fibres.
• We wear different types of clothes depending on seasons, occasions and profession.
• We should take good care of our clothes to make them last longer.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of the following is a natural fibre?
Jute Rayon Nylon Polyester
B. Which of the following is a synthetic fibre?
Linen Nylon Wool Silk
C. Why do firefighters wear safety suits?
To look different
To stay dry
To protect themselves from heat and fire To carry heavy equipment


2. Fill in the blanks.
A. Jute is an example of fibre.
B. is an example of synthetic fibre.
C. We wear clothes in summer.
D. are special clothes worn by some people for specific work.
E. We should keep balls between the clothes to protect them from insects.
3. Match the following.
A. Soldier i.

B. Doctor ii.

C. Police officer
D. Firefighter
E. Student
4. Short-answer questions.
A. Why do we wear cotton clothes in summer?
B. Which types of clothes are worn in winter?
C. Why do we wear raincoats in the rainy season?
D. Why do firefighters wear safety suits?




E. What kind of clothes do you like to wear on festivals?
F. Why do silk and woollen clothes need extra care?
5. Long-answer questions.
A. What is the difference between natural and synthetic fibres? Give examples.
B. What is a uniform? Name some people who wear uniforms.
C. List three ways to take care of our clothes.



Synthetic fibres are often used in the production of sportswear. Why do you think sportspersons mostly wear synthetic clothes?
There are many people who do not have enough clothes to wear or cannot buy them. We should help such people. Instead of throwing away clothes that don’t fit you, you can wash and pack them neatly, and give them to someone who needs it more than you.





Safety First
Safety Rules First Aid


Look at the following images and tick ( ) the ones that are safe and cross ( ) out the ones that are unsafe. Get Set



Accidents can occur at any time and cause harm to life and damage to property. We can prevent accidents by being more careful, alert and following safety rules at home, at school, on the playground and on the road. Let us learn about some of the common safety rules.
accidents: unplanned events that cause harm to people or damage to property prevent: to stop something from happening


We may get hurt at home if we are not careful. Common causes of injuries at home include touching a switch board with wet hands, carelessly using knives or forks, not using things like matchsticks safely, keeping things lying around on the floor. Let us learn about some important safety measures at home.
To be safe at home, you need to follow some safety rules.
• Always use electrical appliances with dry hands. Touching plugs or switches with wet hands can result in electric shocks.
• Always use knives or other sharp tools under adult supervision.
• Always keep things in their proper places otherwise you may trip and fall.
• Never take medicines without consulting a doctor. Some medicines that are safe for adults can be harmful for children.
• Keep bathroom floors dry and clean to not slip and fall.





Schools are places for learning and fun, but they can also pose risks if safety rules are not followed. We should follow some safety rules to avoid injuries at school too.
• Do not run or play inside the classroom.
• Avoid fighting, hitting or pushing your classmates. Never throw things at others.
• Avoid climbing on desks and chairs in the classroom.
• Do not run or push others while climbing up or down the stairs.
• Always walk in a queue in corridors and while boarding or getting off the bus.






Being outdoors can be fun, but it is important to stay safe. Let us now learn some of the basic rules that we should follow when we are outside.
injuries: harm or damage to someone supervision: the act of watching over someone carefully


By following these simple rules, you can stay safe on the roads and avoid accidents.
• Never run or play on the road. Roads are meant for vehicles, not for playing or running around. It can result in accidents.
• Always walk on the footpath, or, if there is none, walk on the left side of the road facing the traffic.
• Always cross the road at the zebra crossing. Before crossing the road, first look to your right, then to your left, and only cross when it is clear.
• Follow the traffic lights and signals. Cross the road only when the pedestrian light is green.
• Never put your head or hands out of a moving vehicle.
• Do not get on or off a moving bus. Wait for it to stop completely.

On the playground, we enjoy playing games with our friends. To make sure you or your friends do not get hurt while playing, it is important to remember and follow these safety rules.


Always cross the road at the zebra crossing.


Never take your hand or head out of a moving car.
The zebra crossing is named after the black and white stripes on a zebra. It is used by pedestrians to cross roads safely.
• Always wear shoes while playing to protect your feet.
• Always wait for your turn on the swings and slides.
• Never fight with or hit others while playing.
• Each game has its own set of rules. Make sure to follow them to play safely and fairly.


Wait for your turn on the swings.
It is important to keep yourself safe from people you do not know. Follow these simple rules to stay safe:
• Never open doors for any strangers, especially when you are alone at home.
• Never give your name, address or any other personal details to strangers, especially those who call you on the phone.
pedestrians: persons walking on the roads or streets


• If a stranger offers you something or tries to talk to you, say ‘No’ and run to an adult who you trust.
• If someone makes you feel scared or uncomfortable, don’t hesitate to run away and tell your parents about it.
Tick ( ) the safe actions and cross out ( ) the unsafe ones.
1. We should use sharp tools only under adult supervision.
2. We should hit or push our classmates.
3. We should wait for our turns on swings and slides.
4. We should give our personal details to a stranger.
When someone gets hurt, we need to help them right away. Stay calm, and do not crowd around the injured person.
The quick help given to the patient before the doctor arrives is called first aid. A box with first-aid items is called a first-aid box. It has things like cotton, bandages, gauze, scissors, antiseptic lotion, cream and Band-aids. India has a universal emergency number, 112, that can be dialled for any kind of emergency. You can call the police, the fire station and the ambulance service. This number can be dialled from any phone for free. Did You Know?
Create your own first-aid box at home. Keep items like cotton, Band-aid strips, antiseptic lotion and a small pair of scissors in it.
Let us now learn about first aid for injuries such as burns, cuts and wounds, sprains, nosebleeds, dehydration, and animal bites.
Fire, hot liquids or steam can cause burns.
• Wash the burnt area with cool, running water until the pain or burning stops.
• Apply antiseptic cream or lotion on the burn.
• If the pain continues, seek medical help. Applying antiseptic cream on a burn.


• Clean the injured area with clean water to remove dirt or dust from it.
• Apply antiseptic cream or lotion on the wound to kill germs.
• For minor cuts, use a Band-aid. For deep cuts, apply pressure with a clean cloth and cover with a bandage.
• If the bleeding does not stop, go to a doctor.
Sprains happen when you twist your ankle or pull a muscle, often while playing. Sprains cause swelling and pain.
• Put an ice pack on the sprain (do not put ice directly on the skin).
• Wrap the injured part with a bandage. Do not move or apply pressure on the injured part.
• Visit a doctor if the pain or swelling persists.
• Make the person sit with their head tilted slightly forward. Do not make the person lie down or lean backward.
• Pinch the soft part of the nose with your index finger and thumb, and hold it for about 10 to 15 minutes.
Using bandage for cuts and wounds.
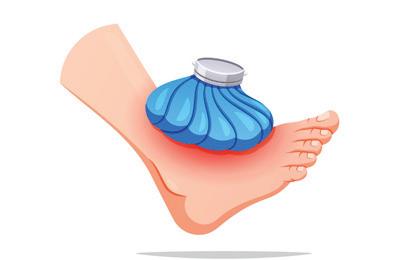
Applying ice pack on the sprain.

• If the bleeding does not stop, go to the hospital or to the nearest doctor.
Dehydration happens when the body loses more water than it takes in, often due to sweating, heat or illness.
• Encourage the person to drink plenty of fluids, like water or oral rehydration solutions (ORS).

Pinching the nose to stop the nosebleed. Drinking water to prevent dehydration.
• If the person cannot drink, or shows severe symptoms, seek medical help right away.
Animal bites can bring harmful bacteria into the body, causing infections.
• Put a cool cloth or ice pack on the bite to reduce pain and swelling.
• Apply antiseptic ointment to the bite.
• Visit a doctor for vaccination against tetanus and rabies.
Applying antiseptic on the animal bite.
Knowing basic first aid helps us give timely attention to someone who is hurt and can even save their lives.


Every year, from January 11 to 17, India observes National Road Safety Week. This week helps teach people about safe driving and the importance of following traffic rules. Schools also organise special activities and workshops to help students learn about road safety.
first aid: immediate help given to an injured person before a doctor arrives sprain: an injury caused by twisting a joint or pulling a muscle dehydration: a condition in which the body loses more water than it takes in antiseptic: a substance that stops or slows down the growth of harmful microbes

Scan the QR code to know more about first aid.
• We should follow safety rules while staying indoors. This prevents accidents at school and at home.
• Following safety rules while outside helps us prevent accidents on the roads and playgrounds.
• We should not give personal any information or talk to any stranger.
• First aid is the quick help given to the patient before the doctor arrives.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. How should you handle electrical appliances?
Touch them with wet hands Put your finger inside the electric sockets
Touch them with dry hands Always play with them


B. Where should you cross the road to stay safe?
Between parked cars
Anywhere you like
C. Who should you let into your home?
Anyone who knocks
At the zebra crossing
Close to a turning
Delivery people only
People you know and trust Strangers with badges
D. What should you do if you get dehydrated?
Drink less water
Drink water or ORS
Sleep well
Wait until you feel better
E. What should you apply to an animal bite?
Cold cream
Hot water
2. Fill in the blanks.
Antiseptic ointment
Sunscreen lotion
A. Keep bathroom floors to prevent slipping.
B. Always wear while playing in the playground.
C. Consult a doctor before taking any .
D. To prevent infection, apply cream to wounds.
E. If the bleeding from a nose doesn’t stop, seek help.
3. Write True or False.
A. Running in the classroom is safe.
B. It is safe to get on or off a moving bus.
C. You should always let strangers into your home.
D. First aid is the quick help given to an injured person.
E. You should put an ice pack on the sprain.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. How can you safely cross a road?
B. Why should you not touch plugs and switches with wet hands?

C. What will you do if a stranger knocks on your door when you are alone?
D. What is the first-aid box used for?
E. What should be done immediately if someone gets a nosebleed?

5. Long-answer questions.
A. Why is it important to follow safety rules at school?

B. List two safety rules to follow on the playground to avoid injuries.
C. Write the first aid for each.
a. Cuts and wounds b. Burns c. Sprain d. Dehydration
D. What first aid will you give for an animal bite? Explain the steps.

E. Imagine you are alone at home and smell something burning in the kitchen. What steps would you take to ensure your safety before seeking help?
6. Picture-based questions.
A. Which of the given images ensures safety at school? Why so?
B. Which of the given images is not safe for students at school? Why so?




What would you do if a stranger asks for help, like finding their lost pet? Why?
Do you know that medicines have an expiry date after which they don’t remain effective in treatment? With the help of an adult, find out the expiry dates of various medicines that are at your home. Throw away all the medicines that have crossed their expiry dates. Also, encourage your friends and family not to keep any expired medicines.



































Plants are living things that make, or produce, their own food. That is why plants are also called producers. Let us understand with the help of a simple example.
We cook food in our kitchen using raw materials such as vegetables and spices. Just like us, plants also make their food using some raw materials. Plants need air (carbon dioxide), water and sunlight to make their food. The process by which plants make their food is called photosynthesis. Plants make food in the leaves. That is why leaves are also called the ʻkitchen of the plantsʹ.
Various parts of plants work together to make food.
Roots: Absorb water and minerals from the soil.
Stem: Transports water from roots to leaves.
Leaves: Take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen produced during photosynthesis. It also helps to trap sunlight.
In the word photosynthesis, ‘photo’ means ‘light’ and ‘synthesis’ means ‘to make’. As plants make food with the help of sunlight, this process is called photosynthesis.
In the leaves, carbon dioxide and water combine to form a sugar called glucose, which serves as the plant's food. The stem then transports this food to all parts of the plant. During this process, the plant also produces oxygen, which we breathe in.
Sunlight
We often think that plants do not give out carbon dioxide. That's not true. Like other living things, plants also breathe in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide. But while making their food, plants take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen. The oxygen given out by plants is more than the carbon dioxide released by them.
absorb: to take in combine: mix or join


Aim: Prove that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis
Materials Needed: Potted plant with wide leaves, thick black paper, tape or clip
Method
Step 1: Take a potted plant with wide leaves.
Step 2: Cover a part of a leaf with a strip of thick black paper or tape.
Step 3: Keep the plant in sunlight and water it regularly.
Step 4: After a few days, remove the strip of black paper or tape.
Findings: The part of the leaf covered with the strip of black paper is discoloured.
Conclusion: The covered part of the leaf became discoloured because it did not receive the sunlight required to make food. This proves that sunlight is essential for photosynthesis.
Name the following.
1. The process by which plants make food.
2. The part of the plant where its food is made.
3. The part of the plant that absorbs water from the soil.
4. The part of the plant that carries food to the other parts.
Deepak went to a nursery to buy some indoor plants. He was amazed to see big and small plants with differently shaped leaves. He noticed that most leaves were shades of green. Have you ever thought why most leaves are green? What gives them their green colour?
Leaves have a special substance called chlorophyll in them. Chlorophyll is a pigment that gives leaves their green colour. It is the chlorophyll that helps to absorb sunlight during photosynthesis.
pigment: a substance that gives colour


The leaves of certain plants, like Croton and Rhoeo, are colourful but that does not mean that they do not have chlorophyll. They do, but the colourful pigment hides the green chlorophyll.
Leaves of different plants have different shape and size. Some parts are common in all the leaves. The main parts of a leaf are the stalk, mid vein (midrib), side veins and leaf blade (lamina). Leaves also have special pores called stomata. These tiny pores help in exchange of gases in the leaves and also helps in the loss of water by the process called transpiration.
Side veins
They are thin, side lines that arise from the mid vein.
Mid vein (Midrib)
It is the central, thick line that runs through the leaf.



Plant Croton Plant
Cactus is a plant in which the leaves have changed to spines. So, it is the green stem of the cactus plant that has stomata and chlorophyll to do photosynthesis and store food in it.

Stomata
Leaf blade (Lamina)
It is the flat, green and broad part of the leaf. It bears mid vein and side veins.
Stalk
It is the part that joins the leaf to the branch.
Aim: Observe the structure of stomata under a microscope
Materials Needed: Microscope, prepared slide of a leaf showing stomata
Method:





Step 1: Fix the prepared slide of leaf stomata under the microscope.














Step 2: Observe the structure of stomata through the microscopic lens.
Step 3: Carefully note its structure and draw the same in your notebook.
Findings: You will see tiny structures with holes or pores. These are stomata.
Conclusion: Stomata are small pores found on the surface of the leaf. Under the microscope, they appear as tiny openings that allow the plant to exchange gases, such as taking in carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. These pores play a vital role in photosynthesis.
Tip: Take help from the diagram of stomata shown in your book.


Match the part of the leaf.
1. Thick line in the centre
2. Thin side lines
3. Flat part of the leaf
4. Part joined to the branch
5. Tiny pores on the leaf
i. Stalk
ii. Stomata
iii. Lamina
iv. Mid vein
v. Side veins
We know that plants make food in their leaves. The stem carries this food to different parts of the plant. How is this food useful for the plants?
Plants use the food they make to get energy and grow. Any leftover food is turned into starch and stored in different parts of the plant, like fruits, leaves, stems, roots and flowers. We eat these parts of the plant that have the stored food.
Food Stored in Roots






We eat root part of radish and carrot plants.
Food Stored in Leaves
We eat the leaves of spinach and cabbage plants.
We eat raw and cooked food. Name some foods that can be eaten raw and those that need to be cooked? Share with others.
starch: reserve food stored in plants
Food Stored in Stem
We eat the stem part of potato and sugarcane plants.
Food Stored in Flowers
We eat the flowers of cauliflower and broccoli plants.
Fruits, vegetables, cereals, pulses, oils, tea, coffee and spices are some examples of food we get from the plants.


Aim: Prove that a leaf contains starch
Materials Needed: a green leaf, water, ethanol (a chemical), iodine solution, a beaker, a test tube, a dropper, a burner
Method:
Step 1: Boil the leaf in water for a minute.
Step 2: Take out the leaf and put it in the beaker containing ethanol.
Step 3: Place this beaker in hot water.
Step 4: Wait until the leaf loses its green colour. Take the leaf out and let it cool.
Step 5: Add iodine solution on the leaf using a dropper. Note the change in the colour of the leaf.
Findings: The colour of the leaf changes to blue-black.
Conclusion: When iodine is added to starch, it turns blue-black. This colour change proves that leaves contain starch.
Identify the part of the plant where food is stored for each of the following.
1. Potato, sugarcane:
2. Cabbage, spinach:
3. Carrot, beetroot:
4. Cauliflower, broccoli:

Look at the picture. What do you notice?
You can see thin, yellow, thread-like stems growing all over the tree leaves. These yellow, thread-like plants are dodder plants. They have no leaves to perform photosynthesis. So, they depend on other green plants for food. They slowly take away all the nutrition and may harm the plants on which they grow.
Some plants grow in soil that does not have the nitrogen needed for the plants to grow. Although these plants can do photosynthesis to make their food, but they still lack nitrogen. So, they eat insects to get the nitrogen they require for healthy growth. Such plants are called insect-eating plants. The pitcher plant and Venus flytrap are insect-eating plants.
The pitcher plant has special cup-like structures with lids. When an insect sits on them, the lid closes to trap the insects.
The venus flytrap has special flap-like leaves. When an insect sits on these leaves, the flaps shut to trap the insect between them.

are not plants. They are non-green living things (called fungus) that feed on dead matter from the soil.



plants found in Mount
the Philippines) are so large that they can trap even rats and frogs.
Tick ( ) the options that are true for insect-eating plants.
1. They cannot do photosynthesis.
2. They get nitrogen by eating insects.
3. Venus flytrap is an insect-eating plant.
4. They depend on other green plants for food.
nutrition: getting nutrients from food




Can you think of a world without plants in it? Can animals live without plants? Humans and animals depend on plants in a number of ways.
Some ways in which animals depend on plants are:
For food: Plants are the main source of food for all living beings. Animals depend on plants for their food. This creates a food chain in nature, which shows who eats whom. Let us look at an example of a food chain on land. Grass
For shelter: Plants provide a safe space for animals to live. Birds build nests in the trees. Squirrels hide in the tree trunk and branches.
For oxygen: Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis. Animals and humans use this oxygen to breathe. It is like a gift from plants to other living beings. That is why planting more trees is important. Trees make the air clean and fresh by adding oxygen to it.
Plants also depend on animals for their needs. Some ways in which plants depend on animals are:
For carbon dioxide: When animals breathe out, they release carbon dioxide. Plants use this carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
For spreading plant seeds: When animals eat fruits, they consume the seeds inside as well. Some seeds stick to the animals' fur or get carried in their beaks. As the animals move around, they drop the seeds in different places. This helps the plants find new places to grow.


So, we can say that plants and animals depend on each other. We must take care of both plants and animals in order to maintain the balance in nature. They are our friends.
Visit a park or garden. Collect leaves of different plants that may have fallen to the ground. Take an A4 sheet and arrange the leaves in patterns so that they look like different animals, as shown. You may try different patterns. Share your sheet with the class.






The Great Banyan Tree in Howrah is one of the largest banyan tree in the world. It is about 250 years old and covers about 14,500 square metres (3.5 acres) of land. From a distance, the tree gives the appearance of a forest instead of a tree.

photosynthesis: the process by which plants make their food chlorophyll: a pigment that gives green colour to the leaves and helps to absorb sunlight stalk: the part that joins the leaf to the branch mid vein (midrib): the central, thick line that runs through the leaf side veins: thin, side lines that arise from the mid vein that carries water and food through the leaf leaf blade (lamina): the flat, green and broad part of the leaf that bears the mid vein and the side veins stomata: special tiny pores present in leaves that help in exchange of gases

Scan the QR code to know more about the process of photosynthesis.
• Plants need carbon dioxide, water and sunlight for photosynthesis.
• Stomata helps in the exchange of gases in plants.
• Plants make food in the form of glucose and store extra food in the form of starch.
• Plants store extra food in their fruits, flowers, leaves, stems and roots.
• Some plants eat insects to get essential nitrogen from them.
• Plants and animals depend on each other and help to maintain balance in nature.


1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Where does photosynthesis mostly occur?
Roots
Leaves
Flowers
Branches
B. What is formed during photosynthesis?
Glucose, oxygen and water
Starch, carbon dioxide and water
Oxygen, carbon dioxide and water
Glucose, oxygen and carbon dioxide
C. Which of these plants stores extra food in their leaves?
Spinach and cabbage
Cauliflower and onion
Potato and sugarcane
Beetroot and turnip
D. Which of the following statements about plants is incorrect?
Green plants make their own food.
Some plants are insect-eating plants.
Plants depend for food on other animals.
Plants store extra food in the form of starch.
E. Which of these plants is an insect-eating plant?
Cactus Venus flytrap
Dodder plant
2. Fill in the blanks.
Banyan
A. Plants produce which animals breathe in.
B. is the process by which plants make their food.
C. Plants like radishes and carrots store food in their .
D. The flat part of the leaf is called .


3. Write True or False.
A. Plants provide shelter for animals like birds.
B. Animals provide oxygen to plants.
C. Plants make food in the form of glucose.
D. Animals help to spread the plant seeds.
4. Match the following.
A. Pitcher plant
B. Dodder plant
C. Potato plant
D. Cauliflower plant
E. Spinach
5. Short-answer questions.
i. Stores food in its stem
ii. Stores food in its leaves
iii. Stores food in its flower
iv. A non-green plant
v. An insect-eating plant
A. Name the things plants need for photosynthesis.
B. Why are leaves called the kitchen of the plants?
C. Dodder, a yellow plant, does not have chlorophyll to make food. How does it manage to stay alive?
D. What is the role of stomata in leaves?
E. Write an example of a food chain on land.
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Draw a labelled diagram of a leaf and explain its parts.
B. How do plants and animals depend on each other? Explain with two examples of each.
C. Plants store food in their parts.
a. Why do plants need to store food in their parts?
b. How is this stored food useful for us? Support your answer with examples.
D. Explain the process of photosynthesis. Write the equation too.
E. Venus flytrap and the pitcher plant are both insect-eating plants. How are they able to trap the insects?


7. Picture-based questions.
A. Name the process shown in the image.
B. Label 1, 2, 3 and 4 marked in the image.
C. Why is this process important for plants?



A forest area was cleared to build a highway. How will this create an imbalance in nature?

Carry out a tree plantation drive in your surroundings. Involve your friends and family. Follow these steps to make your drive successful.
• Find out about plants that are easy to grow and survive without much care.
• Find places where plants need to be grown.
• Gather plantlets.

• Dig holes in the ground where the plantlets can be planted.
• Keep watering your plant from time to time and see it growing!


Objective: Students will investigate the difference between natural and synthetic fibres.
Materials Needed: Small pieces of different fabrics (cotton, wool, polyester, nylon), a magnifying glass (optional), water in a spray bottle, paper and pencil for recording observations
Step 1: Collect different kinds of fabric
Gather small pieces of fabric of different kinds as listed above. Ensure there is a mix of natural fibres (like cotton and wool) and synthetic ones (like polyester and nylon).
Step 2: Observe, touch and look

Feel each fabric and look at it closely, with or without a magnifying glass. Describe how each one feels—soft, rough, stretchy or smooth.
Step 3: Test for absorption of water
Spray a little water on each fabric sample and observe how they absorb water. Which fibres absorb water quickly? Which fibres absorb water slowly or do not absorb at all?
Step 4: Record your observations
Note down your findings in a simple chart. Write Yes or No at the correct places.
Fibre Type (natural/ Synthetic) Absorbs water quickly Absorbs water slowly Does not absorb water
Nylon
Polyester
Step 5: Think and Reflect
Discuss why certain clothes are made from natural fibres and others from synthetic ones. For example, cotton is great for hot weather because it absorbs sweat, while synthetic fibres might be better for raincoats and sportswear because they repel water.
Project Output: Now you have a chart that helps you understand the difference between different kinds of fibres. Share and discuss it with the class.
Final Outcome: This project will help you understand about the special qualities and utility of different cloth fibres.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.

Navya was excited to learn that plants use a process called photosynthesis, where they need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make their own food. Plants use the food they make to get energy and grow. Any leftover food is turned into starch and stored in different parts of the plant, like fruits, leaves, stems, roots and flowers.
Navya has a small kitchen garden outside her home. She has plants like coriander, brinjal, lemon, tomato, pumpkin and ladies' finger. She has decided to take extra care of these plants so that they grow well, and she can enjoy these homegrown vegetables.
1. What are the three main things plants need for photosynthesis?
A. Sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide
B. Sunlight, soil, and rain
C. Water, sunlight and oxygen
2. What is photosynthesis?
A. The process of giving sunlight by plants
B. The process of making food by plants
C. The process of producing carbon dioxide
3. Plants make their own food. What happens to the extra food made by the plants?
4. Name any three plant parts that we eat for food. Give two examples of each.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.




Adaptation in Plants
Habitat and Adaptation
Terrestrial Plants
Aquatic Plants


Given below are some images of plants. Tick ( ) the ones that you like.




Have you noticed that the place where you live provides you everything you need? For example, you have a house that provides you shelter. You also have markets from where you can buy food.
Similarly, in nature, such a place where animals and plants normally live and grow is called their habitat.

Plants of one habitat generally do not survive in a different habitat. For example, a mango tree would wither and die if it was grown in a desert.
The living and non-living things around us make our environment.
In a new habitat, only those plants can survive that develop some new features suitable to that habitat. For example, the cactus does not die in the desert because it has adapted to that environment. Therefore, the special features that a plant develops to survive in a new habitat are called adaptations.
Plants that grow on land are called terrestrial plants. Terrestrial plants are of different types depending on their habitats.
Mountains have a very cold climate. In winters, they receive heavy snowfall. Therefore, trees that grow here are tall, straight and have sloping shapes to make the snow fall off easily. They are usually flowerless and have cones with seeds inside them. Such trees are called coniferous trees. The leaves are needlelike with a waxy coating to avoid water loss. For example, fir, deodar, pine and cedar.
Small flowerless plants like ferns, lichens and mosses are also found in the mountains.

Plains are the flat regions with a warmer climate than mountains. Some trees like peepal, neem, gulmohar and apple are found in the plains. These trees have flat leaves and spreading branches. Most of these trees shed all their leaves once a year to reduce water loss. Such trees are called deciduous trees.
Some trees like tamarind, mango and rubber are green throughout the year. Therefore, these are called evergreen trees.




The desert is a place with hot weather, very little water and scanty rainfall. Plants growing in deserts need less water to grow. Plants like cactus, babool and date palms are found in deserts.
Some unique features of cactus are:
• Its leaves are modified into spines to avoid the loss of water from the surface of the leaves.
• It has thick, green and fleshy stem that is capable of photosynthesis.
• It has thin roots that spread around and absorb rainwater from below the ground before it evaporates.

Areas with clayey and sticky soil and an abundance of water are called marshy areas. Trees like mangroves are found in these areas. Since the soil in marshy areas have too much water, the roots of the mangroves have adapted to extend above the soil and take in air directly.
What kinds of plants do you see around your home and school? Observe them and discuss their special features in your class.
The areas between the land and the sea are called coastal areas. These areas have sandy soil and strong winds. So, the trees that grow here have long and widespread roots that help hold them strongly to the sandy soil. They are also very tall and have flexible trunks with large leaves that are cut in strips. This helps them against the strong winds. Coconut trees are an example of the trees that grow in coastal areas.


scanty: in small quantity spines: needle-like sharp points (for example, those found in cactus) abundance: excess trunk: the central part of the tree from where branches grow

Visit a nursery or a garden and take a look at the plants there. Choose any five plants and write their names in your notebook. Observe the shape and texture of the leaves of these plants. Record your observations in the table below.
Name one plant found in each of the following areas.
1. Mountains
2. Plains
3. Marshy areas
4. Deserts
Aquatic plants are the plants that grow in water. They can grow in ponds, lakes, rivers or seas. Aquatic plants are further divided into three types. Let us learn about them.
As is evident from the name, these plants float on the water surface. These plants do not have fixed roots, due to which they float freely in the water. Their leaves have stomata only on the upper side. They have light and spongy stems with air pockets in them, helping them to keep floating on the water surface. Some examples of floating plants are duckweed, water lettuce and water hyacinth.


These plants have roots fixed to the soil at the bottom of the ponds or lakes. They have thin, long, hollow and very flexible stems. These plants have broad and flat, plate-like leaves with waxy coatings on the surface. Some fixed aquatic plants are lotus and water lily.

These plants grow completely under the water surface. Therefore, they are also called submerged plants. The leaves of these plants are long, narrow and look like ribbons. The stems of these plants are flexible. Some examples of submerged plants are hydrilla, tape grass and pondweed.
The seeds of the lotus plant can survive in dry conditions for many years. But they germinate only in water.


Submerged aquatic plants do not have stomata. They absorb nutrients and gases, that are dissolved in water, directly.
The AJC Bose Indian Botanic Garden, in Howrah, West Bengal, is the largest garden in India. It is also home to the Great Banyan Tree, which is around 250 years old and is nearly twice the size of a cricket field.

habitat: the natural environment where a living thing lives adaptations: the special features that help a living thing to survive in its habitat coniferous trees: trees that produce cones instead of flowers deciduous trees: trees that shed all their leaves once a year to reduce water loss evergreen trees: trees that are green throughout the year submerged plants: plants that grow completely under the water surface



Scan the QR code to know more about plant adaptations.
• Plants have some unique features that help them survive in their habitats. These features are called adaptations.
• Plants that grow on land are called terrestrial plants, while those that live in water are called aquatic plants.
• Terrestrial plants can be found on mountains, plains, deserts, marshy and coastal areas.
• Aquatic plants are categorised into three groups: floating, fixed and underwater plants.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of the following is not a terrestrial plant?
Pine tree Mango tree Lotus Mangrove
B. Which of these is not an aquatic plant?
Duckweed Hydrilla
C. Which is an example of a floating plant?
Water hyacinth
Water lettuce Coconut tree
Tape grass Pondweed Water lily
D. Which of these is an example of a fixed plant?
Water lily
Water lettuce
Water hyacinth Hydrilla
E. Which of these is an example of a submerged plant?
Tape grass
2. Fill in the blanks.
Lotus
Water lettuce Duckweed
A. Terrestrial plants grow on .
B. Trees that shed their all leaves once a year are called .
C. Trees that do not shed all their leaves in any season are called .


D. Coconut trees are found in areas.
E. Aquatic plants grow in .
3. Write True or False.
A. Deciduous trees have flexible trunks.
B. Fir, pine, ferns and mosses are found in plains.
C. Cactus is found in marshy areas.
D. Duckweed is an aquatic plant.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. Why do plants need to adapt?
B. Why do coniferous trees have needle-like leaves?
C. Write one special feature of mangroves.
D. Why do cactus have spines instead of leaves?
E. Why do coconut trees have flexible trunks?
F. How do underwater plants breathe?
G. What helps floating plants to float on water?
5. Long-answer questions.
A. How are terrestrial plants different from aquatic plants? Explain with examples.
B. Differentiate between deciduous and evergreen trees with examples.
C. Describe some unique features of a cactus plant that help it to survive in deserts.
D. Differentiate between floating, fixed and submerged plants. Give examples for each.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. Which type of tree is this?
B. How did you identify it?
C. Where do these plants grow?


Which one of these should be kept inside an aquarium—water hyacinth, duckweed or tape grass? Give reasons for your answer.


Chapter Overview

Animals and Their Young Ones
Reproduction
Animals that Give Birth to Young Ones
Animals that Lay Eggs
Life Cycles of Egg-laying Animals
Life Cycles of Insects

Get Set

Sort the following animals based on where they live.
Fish, deer, elephant, bat, sparrow, pigeon, dog, shark, dolphin
Creatures Living on Land Creatures Living in Water Creatures Flying in Air
Rahul was looking through his family album. He saw pictures of his grandparents, uncles, aunts and cousins. He wondered how much his father resembles his grandfather, and how he resembles his father. Have you also wondered why you resemble your parents or grandparents? This is due to a process called reproduction.


Reproduction is a natural process by which living beings produce new ones of their own kind.
Animals can reproduce in two ways—by giving birth to young ones and by laying eggs.
Some animals carry their babies inside their bodies until they are ready to be born. After giving birth, these animals feed, care for and protect their young ones. These animals are called mammals. The bodies of mammals are typically covered with hair.
Most mammals, such as cats, dogs, lions and humans, live on land and are known as terrestrial animals. However, some mammals, like dolphins and whales, live in water and are known as aquatic animals.



Some mammals, such as kangaroos and koalas, have a pouch attached to their bodies. They carry their young ones in these pouches. Such animals are known as marsupials.

Bats are the only mammals that can fly.
Give any two examples of the following:
1. Terrestrial mammals
2. Aquatic mammals
3. Marsupials
pouch: pocket on the lower part of the body in which young ones are protected after they are born

There are some animals that lay eggs from which their young ones are born. The young ones develop inside the eggs, which the mother lays.
Many birds build a nest to lay their eggs. They sit on the eggs to protect them and keep them warm. After some time, the eggs hatch and the young ones come out. Birds, most insects (such as butterflies and cockroaches) and reptiles (snakes and crocodiles) lay eggs.
Have you ever wondered how an egg looks from inside? Let us look at the structure of an egg.

The egg is covered with a hard covering called a shell. This safeguards the egg and keeps it moist. Inside the shell, there is a soft, white jelly-like substance called albumin. It provides water and protein to the young one that will grow inside. It also protects it.
At the centre of the egg, there is a round, yellow-coloured yolk . The young one develops inside the yolk. It contains important nutrients such as fats, vitamins and minerals. The yolk consists of the embryo , which later develops into the young one. The yolk provides the required food to the embryo for its healthy development.
Every living thing goes through different stages as it grows up. This series of changes is called a life cycle. Let us learn more about it.
Once the eggs are laid, the mother hen sits on them to provide warmth and protection, for about 21 days. This is called the incubation period.
embryo: the unborn animal or human in very early stages of its development

Once the embryo is completely developed, it will crack open the egg shell and come out. This process is called the hatching of the egg.
Hatchlings are the young ones that emerge from eggs. The chicks then grow into adult hens.
Some animals undergo significant changes in their form and structure as they grow. This process is called metamorphosis. Let us look at the life cycle of a frog to understand this.
The mother frog lays many eggs in water. After some days, young frogs emerge from the eggs. They are called tadpoles. At this stage, it resembles a fish as it has gills and a long tail so that it can swim in the water.
As the tadpole develops, its tail shortens. The hind legs develop first, followed by the front legs. The tadpole’s lungs start to develop, and its gills begin to disappear. This stage is called a froglet.
The froglet then transforms into an adult frog, which can hop and jump. The adult frog no longer has a tail but has fully developed legs, allowing it to live both on land and in water.
Animals that can live on land and in water are called amphibians.
A frog can lay up to three thousand eggs at a time!
The female fish lays many eggs in water. The fish embryos start developing their organs and tail while still inside the egg. After they hatch from the eggs, the young fish are called larva. The larva has an attached yolk sac, which provides all the nutrients needed for growth.
Life Cycle of a Fish


Once the larvae develop further, they become fry. At this stage, they are small but will grow stronger and larger as they start eating. As the fry continue to grow, they become fingerlings. Eventually, as they mature, they develop into adult fish.
Circle the correct option.
1. It takes about 11 / 21 / 31 days for the chick to come out of the egg.
2. The stage between an adult fish and a fry is called eggs / fingerling / embryo.
3. The process of changing into a very different form when growing into an adult is called life cycle / embryo / metamorphosis.
Just like fish and frogs, many insects also hatch from eggs and grow into adults.
A butterfly also undergoes metamorphosis, just like the frog. The female butterfly lays eggs. A small, worm-like creature, called a caterpillar (larva), hatches from the egg. The caterpillar feeds on leaves and increases in size. It then builds a cocoon around itself to form a chrysalis (pupa). When the pupa grows into a butterfly, it breaks out from its cocoon.
There are three stages in the life cycle of a cockroach. The mother cockroach lays eggs. After the eggs hatch, a small creature called a nymph emerges. At the initial stage, the nymph does not have wings but looks like a cockroach. As it grows, it sheds its old skin to become an adult. This process is called moulting.
Eggs
Caterpillar (larva)
Butterfly
Life Cycle of a Butterfly
Chrysalis (pupa)
Eggs
Adult Nymph
Life Cycle of a Cockroach


India is home to unique megafauna (large animals) like the Asiatic elephant, the one-horned rhino and the Royal Bengal tiger.

reproduction: a process through which living beings can give birth to new beings of their own kind life cycle: a series of stages that a young one goes through before developing into an adult metamorphosis: when an animal or insect develops and changes into something completely different
larva: a small, worm-like creature that hatches from the egg nymph: the young one of a cockroach that does not have wings at the initial stage

Scan the QR code to know more about reproduction in animals.
• Living beings produce new beings of their own kind by a process called reproduction.
• Animals can reproduce by giving birth to their young ones or by laying eggs.
• Animals that give birth to young ones are called mammals.
• Animals like frogs and butterflies undergo metamorphosis before they develop into adults.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of the following is a mammal?
Fish Cockroach Cat Frog
B. Which of the following animals reproduce by laying eggs?
Whales

Bats
Elephants Butterfly

C. What is the jelly-like substance found inside the eggshell? Nymph Tadpole Albumin Cocoon
D. Which process provides warmth to the embryo? Hatching Incubation Moulting Metamorphosis
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. The hard covering of an egg is called the .
B. The soft and white jelly-like substance present inside the egg shell is called .
C. The provides food to the embryo for its development.
D. The stage of fish between the larva and the fingerling is called
3. Write True or False.
A. Dolphins and whales are mammals.
B. The egg shell fulfils the food requirements of the yolk.
C. When the fish eggs are ready to hatch, it is called pupa.
D. Mammals do not lay eggs.
4. Match the following.
A. Young one of a hen i. Tadpole
B. Young one of a butterfly ii. Nymph
C. Young one of a frog iii. Caterpillar
D. Young one of a cockroach iv. Chick
5. Short-answer questions.
A. How do birds reproduce?
B. What is meant by incubation?
C. Describe the importance of the yolk in an egg.
D. How does a tadpole become a frog?
6. Long-answer questions.
A. What is reproduction? Mention the two ways in which animals reproduce. Give examples of each.

B. Draw the structure of an egg. Name and explain its different parts.
C. Explain the lifecycle of the following:
a. Cockroach
b. Fish


7. Picture-based questions.
A. What process is shown in the given image?
B. Identify and label 1, 2, 3 and 4 in the given image.
C. Describe the transformation of stage 2 into stage 3.

Think about the life cycle of a chicken and a frog. Write one similarity and one difference.
Have you heard about dinosaurs? They no longer exist now, and hence, are called extinct. Try to find out the reasons behind the extinction of these animals. Also, try to find out about three other animals that have become extinct or are about to be extinct.





Adaptation for Habitat
Adaptation for Food
Adaptation for Survival


Write the names of two animals that:
1. Eat only plants
2. Eat only animals
3. Eat both plants and animals
Different types of animals are found in different places, ranging from forests, hot deserts, oceans and very cold regions. The natural place where an animal lives and grows is called its habitat. Different animals have different features that help them to survive and grow in their habitats. These features are called adaptations.
There are four main types of habitats where animals can live—forest, desert, aquatic and polar. Let us learn about the various adaptations animals acquire in these habitats.

Animals that live in forests have four strong legs that help them to run fast. They breathe with their lungs. They have a good sense of smell, sight and hearing which helps them in hunting for food and protecting themselves. Tigers, zebras and monkeys are some examples of animals that live in forests.

Deserts are hot and dry regions where water is scarce. It also gets quite cold at night. Deserts have sandy soil. Animals such as camels, snakes, kangaroos and lizards are well adapted to live in these conditions. The camel is popularly known as the ‘ship of the desert’. Let us learn about some adaptations of camel.
Fat is stored in the camel’s hump, which allows it to survive many days without food and water.
The thick and less hairy skin protects it from both hot and cold weather conditions.
The thick and padded feet help it walk easily on sand.

Animals that live in freshwater or seawater are called aquatic animals. Crabs, fish, alligators and turtles are some examples of aquatic animals. The aquatic animals have the following features:
scarce: not easy to find

Why do you think the camel is called the ship of the desert?
A camel can close its nostrils to avoid sand.
Its long eyelashes and double eyelids protect its eyes from sand.
The long neck helps them reach high branches of trees.
Long legs keep its body away from the hot sand and also help cover long distances in search of food and water.
An octopus has three hearts and blue blood! Two hearts pump blood to its gills, and one pumps blood to the rest of its body.


• Most aquatic animals breathe through gills, for example, fish.
• Fish have fins and turtles have paddles to move easily in water.
Fish breathe through gills.
• Some aquatic animals, such as whales and dolphins, breathe through lungs.
• Most aquatic animals have a streamlined body that helps them swim easily.
Whales and dolphins don't have noses. They have blowholes at the top of their heads.

The North and the South Poles of the Earth remain covered with snow throughout the year. The weather conditions are cold and harsh. Animals like polar bears and penguins are found in these regions. To adapt to this kind of a habitat, these animals have the following features:
• Polar bears have a thick layer of fur on their bodies that protects them from extreme cold.
• Both penguins and polar bears have a thick layer of fat under their skin called blubber to keep them warm.
• They have broad and furry feet that help them walk easily in the snow.
In the polar regions, there are times when the sun does not rise for months (polar night), and other times when the sun never sets for months (polar day)!





Animals eat different types of food. Their teeth and other body parts are adapted to the types of food they eat. Depending on their food habits, animals can be herbivores, carnivores, omnivores or scavengers.
Animals that only eat plants are called herbivores. These animals have strong and sharp front teeth which allow them to easily cut leaves and grass. At the back, they have flat and strong teeth. These teeth help them grind food. Cows, elephants, deer, rabbits and giraffes are some examples of herbivores.


An adult human has 32 teeth. The front teeth that are used for cutting are called incisors. The long, sharp teeth that are used for tearing are called canines. The teeth that are at the back and are used for grinding are called premolars and molars.
Animals that eat the flesh of other animals are called carnivores. These animals have long and sharp teeth that help them tear the flesh of their prey. Tigers, lions and foxes are some examples of carnivores. Birds like eagles and owls also eat flesh with the help of their hooked beaks.
Animals that eat both plants and the flesh of other animals are called omnivores. They have sharp front teeth for tearing flesh and flat, strong grinding teeth that help them chew plant food. Humans, bears and crows are examples of omnivorous animals.
prey: animals that are hunted for food





Scavengers feed on the flesh of animals that are already dead. They have sharp beaks or teeth to tear flesh. Examples of scavengers include vultures, jackals and hyenas.


Lice, ticks and fleas are parasites. They live on the body of another living being, and suck their blood for their food.
Write one word for the following.
1. Animals that eat only plants.
2. Animals that eat both plants and meat.
3. Animals that eat the flesh of other animals.
4. Animals that eat the flesh of animals that are already dead.
5. Animals that depend on hosts for their food.
Animals have special adaptations to help them survive. Some animals have adaptations for hunting, like sharp claws or good eyesight. Other animals have adaptations to stay safe, like blending in with their surroundings or having tough shells. Let us learn about some of these amazing adaptations and how they help animals survive.
Camouflage
Many animals have adapted themselves well to the environment or to protect themselves from predators.
Some animals have specific colours or markings on their body. These features help them blend well into their surroundings through camouflage. Some examples of camouflage are as follows:
• Chameleons change their body colour according to their surroundings.


• The fur of the arctic fox is grey and brown in summer to camouflage with rocks and dry plants. In winter, its fur turns white to match the colour of snow, helping it to escape from its predators.
• A stick insect looks like a stick or a twig, making it difficult to spot when it is sitting on a tree branch.



Birds use their beaks to catch and eat food. Different birds have different types of beaks.
• The strong and sharp beak of the eagle helps it tear the flesh of its prey.
• The sharp, strong and curved beak of the parrot helps it break nuts and fruits. It also helps them to climb trees.
• The duck’s broad and flat beak helps it catch fish and insects. While catching fish, the holes present on its beak drain out the water.
• The short and thick beak of the sparrow helps it pick up small grains and seeds.

Strong and sharp beak of an eagle

Sharp and curved beak of a parrot

Broad and flat beak of a

Short and thick beak of a sparrow
Birds have different types of claws at the end of their toes, which help them to jump, pick up food, and move around.
• Eagles, vultures and hawks have four sharp and hooked claws. These claws help them to catch other animals.
• Woodpeckers and cuckoos have long curved claws that help them to climb trees.

Sharp and hooked claw of an eagle

Long curved claws of a woodpecker

Monkeys have long limbs to swing from one branch to another. The long tail of the monkey helps in balancing its body while swinging on tree branches. Animals, such as zebras and deer have strong legs that help them to run fast in times of danger.

Behavioural adaptations refer to the actions that animals take to survive. Let us learn more about this.
When animals move from one place to another in search of food, to reproduce and to protect themselves from harsh climate, it is called migration.
For example, Siberian cranes migrate from Siberia to Bharatpur in Rajasthan, India in winters. Siberia is located near the poles and it is extremely cold during winter. Therefore, Siberian cranes are unable to survive the extreme cold in their normal habitat, which is why they migrate to warmer places like India.

Similarly, wildebeest migrate to search for food. They live in southwestern Africa, where food becomes scarce by the end of the summer. So, they follow the rain to get fresh food and water.
Some animals like bears, lizards and bats sleep throughout the winter to protect themselves from extremely cold and harsh conditions. This is called hibernation. During hibernation, the animal’s body temperature drops, and their breathing slows down, thereby reducing their energy usage. These animals eat extra food in summer and store it as fat, which they use as energy while they are in a state of hibernation.
Bears can lose about one-third of their body weight during hibernation! So a 210 kg-bear could lose around 70 kg of its weight!
Some animals such as buffalo, elephants, fish and birds live in groups to protect their young ones.



Elephants live in groups.


Jim Corbett National Park is located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand, India. This park is home to many different animals, including Bengal tigers, elephants, deer and leopards. It helps protect these animals and their natural habitat.
habitat: the natural place where an animal lives and grows adaptations: features that help animals survive in their habitat
aquatic animals: animals that live in freshwater or seawater
predators: animals that hunt other animals for food

camouflage: the ability of animals to blend in with their surroundings
migration: mass movement of fish, bird and animals from one place to another hibernation: a long winter sleep

Scan the QR code to know more about adaptation in animals.
• The natural place where an animal lives and grows is called its habitat.
• The features that help animals survive in their habitat are called adaptations.
• There are four main habitats of animals—forests, deserts, aquatic and polar regions.
• Animals are grouped based on their eating habits—herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and scavengers.
• Animals have different adaptations in their bodies and vary in their behaviour to protect themselves from their enemies.


1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. The features that help animals to survive and grow are called Habitat Adaptation Environment Climate
B. Which organ helps terrestrial animals breathe?
Lungs Gills Air holes Stomata
C. When a chameleon sits on a branch of a tree, which of the following colours will be suitable to hide from its predators?
Yellow Red Brown Blue
D. Which of the following animals undergo hibernation?
Humans Crows Elephant Bear
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. Animals that eat only plants are called .
B. Hyenas and vultures are examples of .
C. The long winter sleep of animals is called .
D. Lice is a .
3. Write True or False.
A. Omnivores depend on hosts for their food.
B. Animals live in groups to protect their young ones.
C. Migration helps animals hide from predators.
D. The long tail of the monkey helps in balancing the body.
4. Match the following.
A. Stick insect i. hibernation
B. Siberian cranes ii. scavenger
C. Jackal iii. migration
D. Bear iv. camouflage

5. Short-answer questions.
A. Why do birds have different types of beaks?
B. Mention two adaptations that you see in animals living in polar regions.
C. How are omnivores different from scavengers?
D. Why do animals migrate?
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Explain different characteristic features of a camel that help it survive in deserts.
B. Define camouflage. Explain with the help of 2 examples.
C. Differentiate between herbivores, carnivores and omnivores with examples of each.
7. Picture-based question.
A. Look at the bird’s beak carefully. Guess what kind of food does it eat?
B. Can you name the bird?



1. What would happen if polar bears were left in the desert?
2. In the food chain, which type of animals—herbivores, carnivores, omnivores or scavengers, according to you, are the most important? Justify your answer.













Our Environment Waste Management Green Surroundings Pollution





Let us recite a poem together!
The sun that shines, the rain that falls, The whispers of the wind that calls. Every creature, big and small, A part of nature, loved by all.
Let's protect this earth we share, Show we truly, deeply care. For clean air and water pure, A healthy world, let's ensure.

Shashi goes to picnic at the park with her family. After reaching the park, Shashi tells her mother, “Mumma, this place is so beautiful! I wish it always remains like this.” To this, her mother replies, “Yes, you are right. It is beautiful. And it is our responsibility to keep it like this forever. For this, we need to protect our environment.”


Our environment includes everything around us. It consists of both living and nonliving things. We depend on our environment for many things.
• We get food, water and air from the environment.
• We also get medicines, gum, paper and other useful things from it.
But humans have become greedy and caused harm to the environment to get more of everything that it offers. The forests have been cut down to make houses, malls, roads and buildings. Animals are being slaughtered for their fur, leather, teeth and horns.
The environment includes the air we breathe, the water we drink and the land on which we live.
Pollution is caused by the addition of unwanted and harmful substances to our environment. These substances affect air, water and soil, making them unsafe for living things. These unwanted substances are called pollutants. Let us learn about the different types of pollution.
When harmful substances like smoke and chemicals are released into the air, making the air dirty and unfit for breathing, it is called air pollution.
Causes of air pollution:
• Burning of fuels such as petrol, diesel and coal.
• Emission of smoke and other harmful gases from factories and automobiles.
• Burning waste in open areas.

Air pollution can cause serious health problems to humans, and harm animals and plants as well. When harmful gases in the air mix with rain, it results in acid rain. This rain damages buildings, and harms plants and animals as well.
Steps to control air pollution:
• Use more public transport like buses and trains.
• Use vehicles that run on green fuels like CNG.
• Plant more trees.
emission: the release of something as gas or particles in air or water slaughtered: killed in a way that is cruel and unnecessary



Aim: To understand how air pollution affects cotton balls kept in different locations
Materials Needed: 2 cotton balls, 2 transparent jars or containers
Method:
Step 1: Place one cotton ball in a jar and keep it in a room. Place the second cotton ball in another jar and leave it outside your home at a place facing a busy road with traffic. Do not close the lid of the jar.
Step 2: After a few days, take out both the cotton balls and compare them.
Step 3: Note the differences in the appearance of the cotton balls.
Findings: We will see that the cotton ball that was kept outside turned more grey or brown in colour.
Conclusion: Air outside is polluted. This is proved on comparing the two cotton balls.
When harmful substances get into rivers, lakes, oceans and other water bodies, making it dirty and unsafe for living things, it is called water pollution.
Causes of water pollution:
• Human activities such as dumping waste and washing clothes in rivers and ponds.

• Factories and industries often release harmful chemicals and untreated waste into rivers, lakes and oceans. All of this makes the water unfit for human consumption and causes diseases like typhoid, cholera and dysentery. It also harms the plants and animals that live in or depend on that water body.
• Avoid disposing of waste and untreated chemicals into water bodies.
• Ensure dirty or waste water is properly treated before releasing it into rivers, lakes or oceans.

The River Ganga is one of the most polluted rivers in the world due to industrial waste and sewage. In 2014, the Government of India started a special program called the Namami Gange project. This project aims to clean the river and make its water safe again.
• Use fewer chemicals like pesticides and fertilisers, as these can seep into water sources and pollute them.


The addition of harmful substances into soil is called land or soil pollution.
Causes of land pollution:
• Throwing wastes like food waste, plastics and glass in open areas.
• Improper discarding of electronic wastes like old computers, phones and batteries.
• Discarding chemical waste from factories in agricultural fields. Chemicals spoil the quality of the soil and pollute it.
As the soil gets damaged due to land pollution, it affects the growth of trees, plants and crops.
Steps to control land pollution:

• Sort household waste as wet waste and dry waste for proper disposal.
• Dump wastes like fruit and vegetable peels into pits to turn into manure.
• Use manures instead of fertilisers and pesticides in farms.
Write the type of pollution caused by the following.
1. Smoke from factories and vehicles.
2. Dumping garbage in a river.
3. Throwing plastic bottles in an open ground.
Wastes can be of two types: biodegradable and non-biodegradable.
• Biodegradable wastes are the wastes that easily decompose and mix with the soil. For example, fruit and vegetable peels, leftover foods, paper, plant leaves and eggshells. We can throw biodegradable waste into soil pits where it can change into manure. These pits are called compost pits. Biodegradable Wastes

discarding: throwing away fertilisers: chemicals added to fields to help plants grow pesticides: chemicals added to fields to kill animals and insects that eat away crops

• Non-biodegradable wastes are the wastes that do not decompose and mix with the soil. Examples of non-biodegradable wastes are plastic, glass and metals.
Imagine you are on a picnic and you have leftovers, a plastic bottle and some paper napkins. Which items would you throw in a compost pit?



Non-biodegradable Wastes
One day, Riya found an old pickle jar in the kitchen. Instead of throwing it away, she cleaned it, and turned it into a beautiful pencil holder. She showed it to her teacher the next day. The teacher was really happy. She explained to the class, “The way Riya recycled the old jar into a pencil holder, in the same way, we can also reuse and recycle things to reduce wastage, and help save the environment.”
Let us learn about some important ways to save our planet.
It means to decrease the use of things that release harmful substances in the environment. By reducing waste, we keep our environment clean and save our natural resources. For example:
• Use cloth or jute bags instead of plastic bags.
• Use metal spoons and straws instead of plastic ones.
It means finding new ways to use old items instead of throwing them away. This helps save our money and resources. For example:
• Use glass jars to store food.
• Reuse old boxes to store things.


Paper, plastic, glass and metal wastes should be sold to the scrap dealer and sent for recycling. In recycling units, they are turned into new products. This saves money, water and other resources that go into making new items. Recycling reduces pollution in the environment. For example:
• Paper is recycled into tissue paper or handmade paper.
• Tin cans are recycled to make new cans.
scrap dealer: a person who buys and sells old things



Write ‘B’ for biodegradable wastes and ‘N’ for non-biodegradable wastes.



Trees play a key role in keeping the environment clean and green. They keep the air fresh by adding oxygen to it. They also keep the surroundings cool as they release water vapours through leaves. Trees also hold the soil tightly and stop soil erosion.
However, we cut down trees to get paper, rubber and wood. The large scale cutting down of trees is called deforestation. Deforestation harms our surroundings and destroys the natural habitat of animals.



It takes an entire tree to create just 3 to 4 textbooks.
To save our environment, we need to plant more trees than we cut down. Planting trees in large numbers is called afforestation.
In India, Van Mahotsav is celebrated for a week every year in July. During these seven days, millions of trees are planted across the country, promoting afforestation and environmental awareness.
We should also use paper wisely because a lot of trees are cut down to make paper. Reusing and recycling paper saves a lot of trees.
The Rock Garden is a sculpture garden located in Chandigarh. This garden is based on the concept of ‘best out of waste’. It is made up of household and industrial wastes. The Rock Garden
erosion: (here) removal of the topmost, fertile layer of soil habitat: natural home of a living organism



pollution: the addition of unwanted or harmful substances in the environment
pollutants: unwanted substances that affect the environment
acid rain: when harmful gases in the air mix with rain
compost pits: pits or holes in the soil where biodegradable wastes are collected to turn them into manure
deforestation: large scale cutting down of trees
afforestation: planting trees in large numbers

Scan the QR code to know more about pollution.
• Our environment consists of living and non-living things around us.
• There are three main types of pollution—air, water and land pollution.
• Pollution damages the environment and harms living things.
• Waste management helps to dispose of our waste in an efficient manner.
• Reduce, reuse and recycle are the three main ways of waste management.
• To save our environment, we need to plant more trees than we cut down.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of the following harms the environment?
B. What happens when harmful gases mix with rain?
It becomes hot water. It turns into acid rain.
It makes the air fresh.
It helps plants grow.

C. Which of the following items can be recycled?
Food waste Paper
Potato peels
D. Which of the following causes land pollution?
Water
Planting vegetables Throwing waste in open areas
Using soil for farming Watering plants regularly
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. Fruit and vegetable peels are waste.
B. wastes do not decompose.
C. rain is rain mixed with harmful chemicals.
D. Trees prevent soil .
3. Write True or False.
A. Burning of fuels causes air pollution.
B. Water pollution leads to diseases like typhoid and cholera.
C. Land pollution is good for the soil.
D. We must follow the 3Rs for waste management.
E. Afforestation is harmful to our environment.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. Write two human actions that harm the environment.
B. Why is acid rain harmful?
C. Suggest two ways to control land pollution.
D. What is soil erosion?
E. What is the importance of Van Mahotsav?
5. Long-answer questions.
A. What are the causes of air pollution? How can we prevent it?
B. How are biodegradable wastes different from non-biodegradable wastes? Give examples of each.
C. Explain the 3Rs of waste management.
D. How are trees important for humans? Write any three ways.

E. Write 3 things you can do to save the environment?


6. Picture-based questions.
A. What are the cows eating?
B. Is it safe for them to eat? Why or why not?
C. How would it affect our health?


1. Rahul visits Mumbai. He sees the seashore littered with plastic bags, bottles, batteries and other types of wastes. How does this affect the animals living in and near the sea? Mention any two ways.

2. Out of paper, plastic and glass which material do you think is most important to recycle and why?

Imagine you see someone throwing garbage on the ground in your school playground.
• How would you respond to this situation?
• Explain why it is important to take responsibility for keeping our environment clean.





What is Weather?
Factors Affecting Weather
The Role of the Sun
Circulation of Air
Circulation of Water

Get Set

Identify the weather and write it in the blanks given below each card.

Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time. Has it ever happened that you were out and it was dark and cloudy, but suddenly it became bright and sunny? This happens because weather can quickly change from day to day and hour to hour. Weather can be hot, cold, windy, dry or humid.


It is always useful to know the weather beforehand so that you can plan your day better. If you know it is going to rain, you will take an umbrella with you. Scientists who study, observe and forecast the weather are known as meteorologists.
Climate is the weather pattern of a specific place for a longer period of time. We know that the climate of hilly areas is generally cold and chilly, while deserts have a hot and dry climate.
Crickets chirp more frequently as the temperature rises. That is why we can hear more crickets chirping in summer evenings.


Ravi lives in Chennai. He was playing outside in the sun when he got a call from his cousin Tara, who lives in Kashmir. Tara excitedly told Ravi that it was snowing in Kashmir. Ravi wondered why the weather was so different at these two places at the same time.
The weather of a place depends upon different factors. Let us know about some of them.
• Distance from the sea: Seas get heated up and cooled down at a slower rate compared to land. That is why coastal areas are cooler in summer than areas which are far from the sea. Similarly, coastal areas are warmer in winters than other areas.
• Sunlight: It heats up the Earth, making its surface and the surrounding atmosphere warmer. This, in turn, affects the weather of a place.
• Humidity: It is the amount of water vapour present in the air. Generally, the areas with high humidity are warmer, while those with low humidity are cooler.
• Clouds: Clouds can block the heat and light from the Sun reaching the Earth’s surface, making that area cooler.
• Wind: Fast moving air is called wind. Depending on the direction the wind blows, it brings hot or cool air. This, in turn, affects the weather of a place.
beforehand: in advance forecast: predict meteorologist: a scientist who studies the Earth’s atmosphere and the weather


Name the following.
1. The condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time.
2. Scientists who study, observe and forecast the weather.
3. The weather pattern of a specific place for a longer period of time.
4. The amount of water vapour present in air.
The Sun plays an important role in causing weather changes. At noon, it is directly overhead, making the weather hotter. Conversely, during the morning and evening, the sunrays strike the Earth at a slant. As a result, the Earth’s surface does not heat up as much. Therefore, afternoons are generally hotter than mornings and evenings.

The positions of the Sun during the day.
The Sun is not the only factor that determines the weather of a place. Other factors, like cloud cover and green cover, can also affect the weather.


When the sun shines brightly, it not only heats up the land but also the air above that area of land. When air heats up, it becomes lighter and rises above. Heavier and cooler air rushes in to take its place. This movement of air causes the winds to blow.
Breeze: Gentle wind is known as a breeze.
Gale: Strong wind is known as a gale.
Storms: Very strong winds are known as storms.
When a lighted matchstick is blown out, the smoke rises upwards. Why?
During the day, the sun heats up the land and also the air above it. Since land heats up faster than water, the air above the land becomes warm and rises up. As a result, the cool air from the sea rushes towards the land. This movement of air from the sea to the land is called sea breeze.
During the night, the land cools down faster than the sea. This makes the air above the land cooler, while the air above the sea stays warmer. As a result, the cool air from the land rushes towards the sea. This movement of air from the land to the sea is called land breeze.

Complete the following table.
Type of breeze Direction Time
Land Breeze
Sea Breeze
Water is an important part of our everyday lives. It exists in three major states: solid (ice), liquid (water) and gas (steam or water vapour).
The water cycle is the continuous movement of water from the earth’s surface to the sky and back again. There are four stages involved in the water cycle: evaporation, condensation, precipitation and collection. Let us learn about them.
• Water in different water bodies gets heated up by sunlight and changes into water vapour. This process is called evaporation.
• When water vapour moves up in the atmosphere, it cools down into water droplets, which combine to form clouds. This process is called condensation.
• When clouds become heavy with water droplets, the water falls back to the earth in the form of rain or snow. This process is called precipitation.
• The water falling on the ground flows into different water bodies like rivers, oceans, lakes and ponds. This process is called collection. The entire process of the water cycle is repeated again.
Water Cycle
More than two-thirds of the Earth’s surface is covered with water.


Take a transparent glass or jar. With the help of an adult, pour a little bit of boiling water in the glass or jar. What do you observe? Do you see steam rising from the water?
Cover the glass or jar with a plate and wait for a few minutes. Observe the bottom of the plate. Do you see water drops forming at the bottom of the plate?
Describe to your friends the various stages of water cycle with the help of this experiment.

Aim: To demonstrate the process of evaporation
Materials Needed: A plastic container, water and marker
Method:
Step 1: Fill the container with water. Use a marker to mark the water level on the container.
Step 2: Place the container in the sun and leave it undisturbed for a few hours.

Evaporation of Water
Step 3: Observe the water level in the container after a few hours.
Findings: The water level in the container goes down. The water gets heated up due to the sun’s heat and eventually evaporates.
Conclusion: The above experiment shows how water evaporates due to the heat of the sun.
When water falls on the ground in any form, it is called precipitation. Let us learn about its types.
• Rain: It is the liquid form of precipitation. When clouds become heavy, water falls down in the form of rain.


• Snowflakes: At low temperatures, the water vapours in the clouds suddenly cool down and form tiny white crystals called snowflakes.

• Hail: When water falling down as rain passes through the cold regions of the atmosphere, it freezes to form small ice balls called hail.


• Dew: After a cold night, we see tiny drops of water on leaves in the early morning. These water drops are called dew.
• Frost: At low temperatures, the dew freezes into tiny white crystals called frost.



• Fog or mist: Fog forms when water vapour condenses into tiny droplets around dust particles in the air, reducing visibility. Thin fog is called mist.
Heavy rains and snowfalls are common in the northern and far-eastern parts of India. The central part and the Thar regions receive scanty to no rainfall. The coast and the regions near it receive a healthy amount of rainfall. The heaviest rainfall in the world is in Mawsynram in Meghalaya. This shows that India has a unique mix of weather and climatic conditions.
weather: the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time climate: the weather condition of a place for a longer duration of time breeze: gentle wind gale: strong wind storms: very strong winds
sea breeze: the movement of air from the sea to the land land breeze: the movement of air from the land to the sea water cycle: the continuous movement of water from the earth’s surface to the sky and back again precipitation: when water falls on the ground in any form



• Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time.
• Sunlight, humidity, wind, clouds and distance from the sea are some factors affecting weather.
• The continuous movement of water from the earth’s surface to the sky and back again is called the water cycle.
• There are four stages in a water cycle: evaporation, condensation, precipitation and collection.
• There are six types of precipitation: rain, snowflakes, hail, dew, frost, fog or mist.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What is the time and direction of the flow of the land breeze?
Sea to land during the day Sea to land at night
Land to sea during the day Land to sea at night
B. What is the main source of energy that drives the water cycle?
Wind Sun Moon Stars
C. Which of the following is NOT a type of precipitation?
Gale Hail Dew Frost
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. is the liquid form of precipitation.
B. Thin fog is called .
C. breeze is during the night.
D. breeze is during the day.
3. Write True or False.
A. At night, the land cools down much faster than the sea.
B. Breeze is a strong wind.
C. Storm is a gentle wind.
D. Hail is thin fog.

4. Circle the odd one out.
A. Storm Dew Breeze Gale
B. Wind Frost Rain Hail
C. Condensation Collection Water cycle Water purification
5. Short-answer questions.
A. How is weather different from climate?
B. Name some factors affecting the weather of a place.
C. Why are mornings and evenings cooler than afternoons?
D. How does the wind blow?
E. Name different types of precipitation.
6. Long-answer questions.
A. How is sea breeze different from land breeze?
B. Explain the role of the sun in changing weather.

C. Draw a well-labelled diagram of the water cycle. Explain the different steps involved in it.
7. Picture-based questions.
A. What do you think this chart shows?
B. Which days are the hottest?
C. What kind of clothes would you wear on those days?
D. Looking at the chart, can you guess the climate of this place?
TODAY 10/9 34O 22O 10-DAY WEATHER FORECAST
Hazy sun Night: Clear THU 10/10 35O 22O Hazy sun Clear Hazy sun Clear Hazy sunshine Clear Hazy sunshine Clear
Hazy sunshine Clear
Hazy sunshine and hot Clear
Hazy with plenty of sun Clear Hazy with plenty of sun Clear Plenty of sunshine Clear FRI 10/11 34O 21O SAT 10/12 35O 20O SUN 10/13 34O 20O MON 10/14 34O 20O TUE 10/15 37O 21O WED 10/16 38O 21O THU 10/17 38O 21O
10/18 34O 20O


Imagine you are planning a picnic. How would you use the weather information to decide if it is a good day for a picnic or not? What kind of weather would you avoid?


It is important to be active and play sports. On regular days, we can play outdoor games like cricket, tennis, badminton and football. However, on rainy or very hot days, we can play indoor games like Ludo, snakes and ladders, carrom, and Scrabble. Indoor games are also good for our mental development. Have a good time playing these games!


Objectives: Students will understand the concept of reusing and recycling materials to protect the environment.
Materials Needed: Used plastic bottles, cans, cardboard, scissors, glue, tape, paint or markers, a small compost bin, paper, pencils, a box or bin
Step 1: Learn About Reuse and Recycle
Study the basics of Reuse and Recycle, as concepts, from textbooks or online resources. Understand their importance and how they impact the environment.
Step 2: Collect Reusable Items




Gather items from home that are usually thrown away—plastic bottles, cardboard and aluminium cans.
Step 3: Sort the Items
Sort the collected items based on whether they can be reused or recycled.
Step 4: Reuse

Use the sorted items to create something useful, such as turning plastic bottles into plant pots or aluminium cans into pencil holders.
Step 5: Recycle
Work together with your friends or classmates to collect all the recyclable items together. You can then give it away to a scrap dealer for recycling.
Step 6: Make a Compost Bin
Set up a compost bin for organic waste. Collect and throw organic wastes like leftover or stale food, fruit and vegetable peels, and things like eggshells. This can be turned to manure and used for gardening.
Project Output: Now you have created useful items from waste. Share your experience in the class.
Final Outcome: This hands-on project will help you understand the importance of reusing and recycling materials; and how they can positively impact the environment by reducing waste output.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.


Maya saw a beautiful butterfly flying from flower to flower. Later, when she read about butterflies, she learnt that butterflies start their life as an egg on a leaf. After a few days, the egg hatches into a small caterpillar that eats leaves and grows bigger. Then, the caterpillar forms a cocoon called pupa, where it rests and changes its form. Maya was amazed to find out that after some time, the pupa changes completely to a butterfly! The cycle then starts again when the butterfly lays new eggs. Maya looked at the butterfly in her garden and thought how amazing its life story is.
1. What are the four stages of a butterfly’s life cycle?
A. Egg, tadpole, frog, adult frog
B. Seed, sapling, tree, fruit
C. Egg, caterpillar, pupa, butterfly
2. What happens at the pupa stage?
A. The butterfly lays eggs.
B. The caterpillar starts changing into a butterfly.
C. The caterpillar goes for a long sleep.
3. Why do you think butterflies lay their eggs on leaves? What might happen if the eggs were laid somewhere else, like on the ground?
4. The changing of the caterpillar to a butterfly is called metamorphosis. Can you name another animal that goes through metamorphosis in its life cycle? Describe its stages.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.












Matter and Its States

What is Matter?
Different States of Matter Soluble and Insoluble Substances Change of States

Get Set

Find out the following words from the given word search.
1. Matter
2. Mass
3. Solid
4. Liquid
5. Gas
Matter is all around us. Everything you can see, touch, or feel is made of matter, including the air we breathe, the water we drink and the food we eat. Thus, matter is anything that has mass and occupies some space. The mass of an object tells us about the amount of matter present in it. We can feel the mass of an object as its weight when we carry it.

For example, tables, chairs, your school bag, water bottle, and air flowing in your classroom are all examples of matter. They all occupy space and have mass.
Physical properties are the characteristics of matter that we can observe or measure without changing the substance itself. Some physical properties are mentioned below.

The tables and chairs have mass and take up space.
All living and non-living things are made of matter.
• Colour: It is a property of matter that can be seen. For example, the red colour of apples and the blue colour of the sky.
• Size: It tells us how big or small an object is. For example, a basketball is big while a tennis ball is small.
• Shape: It tells us about the form of an object. For example, a round ball or a rectangular sheet of paper.
• Texture: It tells us how an object appears on touching. For example, silk is smooth while sand paper is rough.
• Volume: It tells us about the space that an object takes up. For example, a full cup of water and a half cup of milk.
• State: It tells us the form in which matter is. For example, a table is solid, milk is liquid, and oxygen is gas.
Matter is made of tiny particles called molecules. On the basis of the arrangement of molecules, matter can be classified into three different states: solid, liquid and gas. Let us learn about these states, one by one.
Try to press the chair you are sitting on. Can you change its shape? No, you cannot. That means the chair has a fixed shape. This state of matter is called a solid.
Some properties of solids are:
• The molecules in solids are tightly packed. Due to this, they cannot move. Therefore, solids have a definite shape that cannot be changed unless we cut or break them.
characteristics: qualities that help identify and describe something observe: look at carefully definite: fixed

Molecules in Solids

• They have a fixed volume.
• They cannot flow.

• Most solids are hard and cannot be pressed. Some, like clay and dough, can be pressed easily and moulded into different shapes. This is because their molecules are less tightly packed as compared to other solids.
• Some examples of solids are table, chair, door, book and jar.

Try pouring some water from a bottle into a glass. What do you notice? The water will take the shape of the glass. Now, pour the same water into a bowl. It will take the shape of the bowl. This means that water does not have a fixed shape. Instead, it takes the shape of the container in which it is placed. But, the volume of water in the glass and in the bowl will remain the same. This state of matter, that does not have a fixed shape but has a fixed volume, is called a liquid.
Some properties of liquids are:
• The molecules in liquids are not as tightly packed as they are in solids. Due to this, the molecules can move. Therefore, liquids do not have a fixed shape.
• They have a fixed volume.
• They can flow and hence are also called fluids.
• Some examples of liquids are juice, milk, water and oil.


Let us take a balloon and fill it up with air. What happens? The air fills up as much space as it can inside the balloon. If you let the air out, it spreads out into the room. This shows that gases spread out to fill any space available to them. Thus, the state of matter that does not have a fixed shape or volume is called a gas.
Some of the properties of gases are:
• The molecules in gases are very loosely packed. Due to this, they can move freely. Therefore, gases do not have a fixed shape.
• They also do not have a fixed volume.
• They can flow, like liquids, and hence are also called fluids.
• Some examples of gases are air, gas filled in hot air balloons and footballs, and water vapour (steam) rising from boiling water.
fluids: substances that can flow






Pair with your partner. Move your body to represent the states of matter. For instance, act like a solid (still), a liquid (flowing) and a gas (moving quickly).
Observe different things in your surroundings. Classify them as solid, liquid and gas. Record your observation in the form of a table as shown below.
Write one word for the following.
1. This state of matter has a fixed shape and volume.
2. The particles in this state of matter are very loosely packed.
3. This state of matter takes up the shape of the container in which it is placed.
4. A term used for substances that can flow.
Certain things, when heated or cooled, can change their forms from one state to another. Let us learn about the different ways in which these changes of state can occur.

Mohit was making lemonade for himself. He took out the ice tray from the freezer and added some ice cubes to his lemonade. Then, he sat down to enjoy his lemonade. Meanwhile, he forgot to put the ice tray back in the freezer. After some time, he returned to the kitchen and observed that the ice cubes in the ice tray had turned into water. Do you know why that happened? It happened due to melting.

Melting of Ice
When a solid is heated, its temperature rises. The molecules inside absorb heat and begin to move more freely. This causes the solid to change into a liquid. This process is called melting. Here, ice turned into water by absorbing the heat from the surroundings.

What would happen if you fill an empty ice tray with water and keep it in the freezer for some time? The water will change to ice. This happens due to freezing. When liquid (like water) is cooled, its temperature drops. The molecules lose heat and come closer together. This process, of a liquid becoming a solid when cooled, is called freezing.


Rehaan was helping his mother hang wet clothes to dry in the sun. He asked her, “Why do clothes dry when we hang them in the sun, after washing?” She explained that due to the sun’s heat, the water from the wet clothes evaporate. That is why they dry. When a liquid is heated, its temperature rises, and the molecules move farther apart. This allows the liquid to change into gas. This process of liquid becoming gas when heated is called evaporation.
Roshni put some water to boil in a pot and covered it with a glass lid. After some time, she removed the lid and saw tiny water droplets on the inner surface of the lid. This happened because when water vapour from the boiling water touched the cold surface of the lid, it condensed to form water droplets. Thus, when a gas is cooled, its temperature decreases and its molecules come closer together, turning the gas back to liquid. This process of a gas becoming a liquid when cooled is called condensation.
When a solid converts directly into gas on heating, without turning into liquid first, it is called sublimation. For example, when naphthalene balls are left in the open, they become smaller and smaller. This is because the solid naphthalene balls are evaporating directly instead of melting.
Do you know why we use naphthalene balls?





Deposition is the reverse of sublimation. In deposition, the gas directly converts directly into solid without turning into liquid first. For example, when it is very cold outside, frost (a thin layer of ice) begins to form on the glass windows or grass, especially during the night. This happens because water vapour in the air turns directly into ice, without turning into water first.

Not all materials change states at the same temperature. Different things change their state at different temperatures. For example, water boils at a higher temperature than some other liquids, like alcohol.

Interconversion of States of Matter
Aim: To demonstrate the process of melting and freezing.
Materials Needed: Two ice cubes, a candle, small bowls and an ice tray
Method:
Step 1: Place two ice cubes in a small bowl.
Step 2: Light a candle and carefully heat the bottom of the bowl with ice cubes. You can take the help of an adult for this step.
Step 3: Observe what happens to the ice.
Step 4: Now, remove the candle and pour the water in an ice tray. Place it in the freezer for some hours.
Step 5: Take out the ice tray and observe what has happened to the water.
Findings: Ice melts to form water upon heating. Water becomes ice on cooling.
Conclusion: The process of melting and freezing can be easily observed in a liquid like water. Water freezes to form ice and ice melts to form water.


Match the following.
1. Melting i. Solid to gas
2. Freezing ii. Gas to Liquid
3. Evaporation
4. Condensation
5. Sublimation
6. Deposition
iii. Liquid to gas
iv. Solid to liquid
v. Liquid to solid
vi. Gas to solid
What happens when you add a teaspoon of salt to a glass of water? Can you see the salt and water separately? Or do they both mix together completely? When we add salt to the glass of water, at first we can see them separately. Gradually, it dissolves completely and we cannot see the salt separately anymore.
But what happens when we add sand to water? Even after a lot of mixing, the sand and the water can be seen as different layers. Gradually, the sand settles at the bottom of the glass but still does not dissolve in it. This means that the sand does not dissolve in water.
Based on their ability to dissolve, substances can be classified as soluble or insoluble. Let us learn about them.
Salt is soluble in water.
Soluble substances are things that can dissolve in a liquid, especially water. Salt and sugar are soluble substances.
Insoluble substances are things that do not dissolve in a liquid. No matter how much you stir, these substances will not mix with the liquid. Sand and chalk powder are insoluble substances.
When we dissolve a soluble substance in a liquid, we form a solution. The substance that is dissolved is called a solute. The substance in which the solute is dissolved is called a solvent. In a solution, the solute is evenly distributed in the solvent.
Water is a universal solvent as most substances dissolve in water.





Stirring
When we mix a spoon of salt in a glass of water, we get a salt solution. Here, salt is the solute and water is the solvent. But have you ever wondered where the salt goes when mixed with water? We have already learnt that liquid molecules are loosely packed. They have spaces between them. So, the salt molecules fit into these spaces.
Particles
Chilika Lake in Odisha, India, is Asia’s largest brackish water lagoon. The lake’s high salt content and the unique climatic conditions allow for natural salt production through evaporation.
condensation: the change of state from gas to liquid on cooling deposition: the change of state from solid directly to gas on cooling evaporation: the change of state from liquid to gas on heating freezing: the change of state from liquid to solid on cooling liquid: the state of matter with no fixed shape but has a fixed volume and can flow matter: anything that has mass and occupies space melting: the change of state from a solid to liquid on heating solid: the state of matter with fixed shape and volume solute: the substance that dissolves in another substance solution: when two substances are mixed together and they get evenly distributed, it forms a solution brackish water: water that is a mix of fresh water and salt water sublimation: the change of state from gas directly to solid

Scan the QR code to know more about the different states of matter. Particles


• Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass.
• Matter exists in three states: solid, liquid and gas.
• The states of matter can be changed from one form into another.
• Solutions are formed by adding a solute to the solvent.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What happens when naphthalene balls are left in the open?
They change to a liquid. They don’t change. They change to a gas. They become powdery.
B. What happens when a liquid is poured into a container? It keeps its shape. It takes the shape of the container. It turns into a solid. It turns into gas.
C. Which of the following is soluble in water?
D. Which of the following is insoluble in water?
2. Fill in the Blanks.
A. Molecules are very tightly packed in .
B. Liquids and gases are also called .
C. In , the particles are very loosely packed.
D. take the shape of the container in which they are placed.
3. Write True or False.
A. Solids have a definite shape and volume.
B. In deposition, a liquid changes into a solid.
C. Gases have no definite shape or volume.
D. Sublimation changes a solid directly into a gas.


4. Short-answer questions.
A. What are the three states of matter?
B. How is sublimation different from deposition?
C. What are soluble and insoluble substances?
D. Define condensation and evaporation.
5. Long-answer questions.
A. Explain the different states of matter with an example of each. Also, draw diagrams to show the arrangement of molecules in the different states of matter.
B. Define the following:
6. Picture-based questions.
A. Label the processes 1, 2, 3 and 4.
B. Give one example each of all the four processes.

1. Why do you think water changes into ice in the freezer, but not in the fridge?
2. If you had two different liquids as solvents, how would you test which one dissolves more solute?
Our lives are full of examples of changes in states of matter. For instance, evaporation (liquid to gas) takes place while drying clothes in the sunlight. Find out three other examples from your daily life where changes in states of matter take place. Share them with your friends and family.





Look at the picture. Write PUSH or PULL according to the force applied. Force

Get Set


Force is a push or a pull applied on an object. We use force to do many things. Here are some effects of force:
• Force can move objects: When you kick a football, it moves.

• Force can stop moving objects: A fielder uses force to catch and stop a moving ball.
• Force can change the direction of moving objects: A batsman changes the ball’s direction by hitting it with his bat.



• Force can change the shape of objects: Pressing dough changes its shape. Similarly, when we squeeze a toothpaste tube, its shape changes.
Discuss with your classmates two effects of force that you experience in your daily life.
Forces are of many types, such as muscular force, gravitational force, magnetic force and frictional force. Let us now learn about them.
Muscular force is the force applied by the muscles of our body. Whenever we move our body parts, like our arms or legs, we use muscular force. For example, a rickshaw puller uses muscular force to pedal and move the rickshaw forward. We walk, run, jump, bend and lift using our muscular force. Animals like bulls and horses also use muscular force to pull carts.

Rickshaw puller uses muscular force to pull the rickshaw.
Have you ever wondered why a ball thrown upwards comes back to us? It is because of gravity. Gravitational force, or gravity, is the force that pulls everything towards the

Earth. Every object on Earth experiences this force. It is for the same reason that fruits fall to the ground instead of floating away when falling from a tree. Gravitational force also attracts all objects in space towards each other.
Error Alert!
Gravitational force does not act only on falling objects. It acts on everything present on Earth, including you and everything around you, keeping them grounded.

gravity.
What would happen if there was no gravity on Earth?
Magnetic force is the force exerted by a magnet on another magnet or on magnetic materials like iron. For example, when you bring a magnet close to iron nails, the nails stick to the magnet because of magnetic force.

Friction is the force that opposes movement between two surfaces in contact. It slows down moving objects and finally stops them. For example, when you slide a toy car on the floor, it gradually slows down and then stops because of the friction between the car’s wheels and the floor.
Frictional force is important in our daily lives. It helps us to walk and run. We can hold things due to friction. If there were no friction, a moving object would never stop by itself.


Choose any sport like football, cricket or basketball and note how force helps you play them. For example, kicking a ball moves it (muscular force), and gravity pulls the ball down when it is in the air (gravitational force).
Try this: kick a ball and watch how it moves, changes direction or stops when someone catches it. Then, discuss with your classmates how forces like friction, gravity and muscular force are at play during the game. You’ll discover that sports are a fun way to see forces in action.
opposes: to act against gradually: slowly over a period of time



Aim: To prove that rough surfaces cause more friction than smooth surfaces.
Materials Needed: One ball, chalk / marker, a measuring tape or a ruler
Method:
Step 1: Mark a starting line on your classroom floor. Roll the ball on the floor by lightly pushing it forward. Use the measuring tape to note the distance it covers on the floor before it stops.
Step 2: Now, roll the ball again but this time on the grass in your school field, using equal amount of force. Compare the distance covered by the ball on the floor and on the grass.

Findings: The ball rolls farther on the classroom floor than on the grassy field.
Conclusion: Smooth surfaces have less friction, making it easier for objects to move over them. Rough surfaces like grass cause more friction, making it harder for objects to move over them.
Name the forces.
1. The force applied by the muscles of our body.
2. The force that pulls everything down towards the Earth.
3. The force exerted by magnets.
4. The force that opposes movement of objects.
Energy is the ability to do work. There are different forms of energy. We also use fuels such as coal, petrol, diesel, natural gas, kerosene and wood to get energy.
Energy is exists in many forms. Let us learn more about them.

Solar energy comes from the Sun, which is the ultimate source of energy on Earth. It gives us heat and light. Plants use sunlight to make food, which we eat to get energy. We also use the Sun’s energy directly in solar cookers and solar heaters. Solar panels are used to generate electricity from solar energy.


Many villages in India use electric stoves that run on electricity generated by solar energy, thereby reducing the need for firewood and promoting the use of clean energy.
Fast-moving winds can be used to generate energy in the form of electricity. They are used to spins the blades of a windmill, which then turns machines called turbines to produce electricity.
Fast-moving water in rivers contains a lot of energy. To use this energy, dams are built across rivers. These dams store water, which is then released from a height, directing it into turbines. The turbines spin due to the water's force, generating electricity. This type of energy, gained from the flow of water or from water falling from a height, is known as water energy or hydro energy.
Electric Energy


Electric energy is either produced in power plants by burning coal and natural gas, or through solar, wind and hydro energy. It is used to run electrical appliances and devices such as fans, lights, TVs and computers.
We get heat energy by burning fuels. Coal, petroleum and wood are examples of fuels. This energy is then used to run vehicles, cook food, and to generate electricity. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. It can only be changed from one form to another. For example, in electric bulbs, electric energy is converted into light energy. In electric irons, electric energy is converted into heat energy.
turbines: a machine that has a wheel with blades






India is the third largest producer of solar energy, globally.
force: a push or a pull on an object
energy: the ability to do work

Scan the QR code to know more about force.
• A force can move objects, stop objects, change their direction and shape.
• There are four main types of forces—muscular force, gravitational force, magnetic force and frictional force.
• The Sun is the ultimate source of energy on Earth.
• Solar energy, wind energy, hydro energy, electrical energy and heat energy are some common forms of energy.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of these actions uses muscular force?
Riding a bicycle Apple falling down
Boiling water in a pan
B. What does gravitational force do?
Dreaming in one’s sleep
Pushes objects away Keeps objects in the air
Pulls objects towards itself
Throws objects to the sky
C. Which of these materials gets attracted to magnetic force?
Iron nail Plastic cup
Clay ball
Rubber tyre


D. Which force makes a ball stop rolling on the ground by itself?
Magnetic force
Gravitational force
Frictional force
Muscular force
E. Which of these is the ultimate source of energy on Earth?
Sun Moon Mars Stars
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. slows moving objects.
B. is the ability to do work.
C. Flowing water’s energy is used to produce .
D. Solar energy comes from the .
E. energy is released by burning fuels.
3. Write True or False.
A. Force is a push or pull.
B. Gravity pushes everything away from the Earth.
C. Magnetic force can pull iron objects.
D. Hydro energy comes from flowing water.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. How does gravity affect objects on Earth?
B. What effect of force is observed when you press dough with your hands?
C. What is the effect of friction on moving objects?
D. Mention any one use of solar energy.
E. Write two uses of fuels in our daily life.
5. Long-answer questions.
A. Explain the effects of force with examples.
B. Define force. Name and explain any two types of forces.
C. Energy can be converted from one form to another. Justify this statement with the help of examples.
D. List the various forms of energy and write one use of each.


6. Picture-based questions.
A. Name the type of force applied by the man.
B. Name the type of force that opposes the movement of the box on the floor.
C. How is the direction of both forces related to each other?


1. How do frictional forces benefit us and cause problems in our everyday activities? Give one example for each.
2. You are using a magnet to pick up metal paper clips from a table. What do you think will happen if you place a thick book between the magnet and the paper clips? Why?
Energy is very important for our daily lives. So, we need to be careful while using it so that it is not wasted. Saving energy helps the environment and can also lower the costs of electricity. Let us think of five easy ways to save energy at home. For example, you can turn off the lights when you leave a room, or use appliances that are energyefficient.
Write down these points on a chart paper and display them at school, in your neighbourhood or at home. Make your chart or poster attractive by decorating it. Encourage the people around you to follow these suggestions to save energy.
Small changes can make a big difference.




Machines for Us
What is a Machine?
Making Machines Efficient Types of Machines


Look at the images given below. In the space provided, write the names of different things that are being used. Get Set



Do these things make our work easier?
Can you cut a piece of wood with your hands? Can you open the sealed lid of a glass bottle without a bottle opener? The answer to these questions is no. We need different machines to do these tasks. We need a saw to cut wood and a bottle opener to open a bottle.

A simple machine is a device that makes our work simple, easier and faster.
Have you ever observed an adult chop vegetables? They may use a knife or a chopper. These are machines. They chop the vegetables more easily by using force.
Simple machines can be used to change the direction of the force or make the force stronger. They also make our work easier in the following ways.
• Machines reduce the amount of force we need to apply to complete a task.
• Machines help us perform tasks more quickly.

A force is a pull or push applied on an object.
• Machines allow us to complete tasks more efficiently, saving our time and energy.
There are six types of simple machines. Let us learn about them, one by one.
An inclined plane is a surface whose one end is raised to some angle while the other end stays on the ground. It requires a lot of effort to lift something straight. But it is easier to push or roll it up an inclined plane. This makes tasks like loading or unloading heavy goods from trucks much easier. Some examples of inclined planes are ramps, slides and sloped roads.
Can you think of two places where an inclined plane helps?

This simple machine has a circular part called the wheel attached to a smaller rod called an axle. The axle is attached to the centre of the wheel. When the axle moves, the wheel turns around it. We can easily move heavy objects using this arrangement. Some examples of wheel and axle are the steering wheel of a car, bicycle pedals and roller skates.
A pulley is a simple machine made up of a grooved wheel with a rope around it. The heavy objects are attached at one end of the rope, while we pull the other end of the rope. It is used to lift or lower heavy objects like drawing water from wells, hoisting flags, and pulling window blinds up.
A wedge is a simple machine made up of two inclined planes joined back-to-back, forming a sharp edge. It is used to cut or split objects. Some common examples of wedges are knives, axes and nails.
A screw is an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder. It is used to hold objects tightly together. Some examples of screws are bottle caps, jackscrews, nuts and bolts.






















































A clock contains many simple machines like wheels and axles, levers, pulleys and wedges.
grooved: with narrow cuts on the surface split: to divide into parts



Aim: To show that a screw has an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder.
Materials Needed: A sheet of paper, a pencil and a pair of scissors
Method:
Step 1: Take a sheet of paper and cut out a right-angled triangle.
Step 2: Colour the edge opposite to the right angle.
Step 3: Wrap the edge around a pencil. Observe what happens.
Findings: The coloured edge forms a spiral, resembling the threads of a screw.
Conclusion: The above experiment proves that a screw is an inclined plane wrapped around a wedge.
A lever is a straight rod that rests on a fixed point and can be turned around that point. That fixed point is called the fulcrum. The force applied on a lever is called effort. The object that is moved by a lever is called the load. For example, a metal spoon used to open a tin lid acts as a lever. Some other examples of levers are scissors, bottle openers, pliers, tongs and a see-saw.
Look around and observe what devices and tools are being used in your daily life. For example, your mother using a knife to cut vegetables is an example of a lever being used. Write the type of simple machines for each of the devices.


Give two examples for each of the following.
1. Lever
2. Inclined plane
3. Wheel and axle
4. Pulley
5. Wedge
6. Screw
Machines help us do work more easily and quickly. But, to get the best results, it is important to keep them working efficiently. Here are some simple ways to make machines more efficient:
• Cleaning: Remove dust and dirt from machines to keep them running smoothly.
• Lubricating: Apply oil or grease to moving parts to reduce friction and wear-and-tear.
• Tightening: Check and tighten any loose bolts or screws to keep the parts of a machine in place.
• Follow Instructions: Always read and follow the instructions for using a machine.
• Avoid Overloading: do not use a machine to do more work than it is designed for. For example, do not carry too much weight in a wheelbarrow.
• Use the Right Tool: Make sure to use the correct machine or tool for the job. For example, use a knife to cut vegetables and not a screwdriver. By taking care of machines and using them properly, we can ensure they help us do our work efficiently and last longer. This not only saves time and effort but also helps in conserving resources.
Imagine if we didn’t have any simple machines to help us with our daily tasks. Discuss with your friends how our lives would be different without these simple machines.
wheelbarrow: a small vehicle with a single wheel in front, used to carry small loads



India has one of the biggest train networks in the world. The Chittaranjan Locomotive Works in West Bengal is one of the oldest places in India that makes electric train engines. These engines help move lots of trains all over the country every day.

effort: the force applied on the lever fulcrum: a fixed point around which a lever can be turned inclined plane: a surface whose one end is raised at an angle while the other end stays on the ground lever: a straight rod that rests on a fixed point and can be turned around that point load: the object that is moved by a lever machine: a device that makes our work simple and faster pulley: a grooved wheel with a rope around it wedge: it is made up of two inclined planes joined back-to-back, forming a sharp edge screw: an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder wheel and axle: it consists of a circular part called the wheel which is attached to a rod called an axle

Scan the QR code to know more about machines.
• A machine is a device that simplifies our work and makes it faster.
• Simple machines are simple tools that we use in our daily lives to make our work easier.
• There are six types of simple machines: inclined planes, wheel and axle, pulleys, wedges, screws and levers.
• Proper maintenance and usage of machines make them last longer and work efficiently.


1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of these is an example of an inclined plane? Hammer Ladder Wedge Ramp
B. A lever rests on a: Fulcrum Pulley Load Effort
C. Pulleys are used to:
Cut objects Lift objects Hold things together Increase size
D. A wedge is used to:
Cut objects Lift objects Move objects Rotate objects
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. A is a device that simplifies our work.
B. A is made up of two inclined planes joined back-to-back to form a sharp edge.
C. A screw is an inclined plane wrapped around a .
D. A is a grooved wheel with a rope around it.
3. Write True or False.
A. Roller skates are an example of wheel and axle.
B. An inclined plane helps move heavy objects with less effort.
C. Using the wrong tool for a job can damage the machine.
D. Overloading machines makes them more efficient.
4. Name the following.
A. A device that simplifies our work and makes it faster. M H I
B. A fixed point on which a lever rests. L U
C. An object moved by the lever. O
D. The force applied on a lever. E O T
5. Short-answer questions.
A. Why do we need machines?
B. Give an example of an inclined plane.
C. What is the function of a pulley?


D. How is a wedge formed?
E. Why is regular maintenance of machines important?
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Name the six types of simple machines. Give examples of each.
B. How do inclined planes help in reducing effort?
C. List any three ways by which we can make machines more efficient.


Picture-based questions.



Name the devices and machines used in each image.


You need to move a heavy box from the ground to the top of a platform. You have a pulley, an inclined plane and a lever. Which machine would you use and why?
How often do you clean your bicycle? It is very important to take care of your bicycle. Cleaning it helps it last longer, and looks nice and shiny. You should clean/wash your bicycle after each ride, check the tyres and make sure the chain is working well. By doing these simple things, you can make your bicycle safe to ride and also use it for many years.






Importance of Measurement
Measurement and Estimation


Measuring Time
Measuring Temperature


One Sunday, Aisha decided to bake a cake.
“I want to make the tastiest cake ever!” Aisha exclaimed. She mixed one cup each of flour, sugar, baking powder and butter.
Her mom smiled and said, “Aisha, we need to measure our ingredients correctly. Let me help you.”

Aisha was puzzled—why did it matter? Mom explained that measuring the ingredients carefully helps the cake rise and be fluffy. With a measuring cup in hand, Aisha learned that the secret to a great cake is all about the right measurements.
Have you ever noticed what a fruit seller does when you go to buy some fruits? They measure the weight of fruits using a weighing balance. Similarly, the milkman measures the quantity of milk before selling it. You wake up at a fixed time to reach the school on time. We measure so many things in our daily life. Measurement plays an important part in our everyday lives.


In ancient times, different body parts were used to measure different things. We know different persons have different sizes of the same body parts. Therefore, the older units gave different measurements for the same things and could not be used reliably.
To avoid the difference in the measurements, standard units were introduced. These units give the same results for all the measurements. The value of the standard unit is fixed and does not vary from person to person.
The standard unit for measuring length is metre (m), for measuring weight is kilogram (kg) and for measuring volume or capacity is litre (L).
The metric system is a system of measurement that measures length in metres, weight in grams and volume in litres.
A unit is a fixed quantity that is used as a standard of measurement.
Measurement refers to the action of measuring the amount, duration and size of something. But sometimes, we just guess the value of a measurement, without actually measuring it. This thoughtful guess about the value of something is called estimation. By estimating, we only get a rough idea about a measurement.
Estimation is useful in many ways in our daily lives. Have you ever seen your mother cooking food in the kitchen? Does she use any measuring instrument while adding salt to the food? No, right! She adds salt by estimation only. On the other hand, if you were experimenting in the science lab and added a chemical with estimation only, do you think you will get the correct results? No. While experimenting, we need to have exact measurements of the materials used. Otherwise, we will get incorrect results.
Can you give any two examples where you estimate measurement in your daily life?

Estimating the amount of spices required
reliably: doing something in a way that can be trusted to work well every time thoughtful guess: a guess made on a topic after having studied it very well


Time is a measure of the duration of an event. It is used to determine the beginning and ending of something. It also tells us for how long an event occurs.
The basic unit of measuring time is seconds. Some other units of time are minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years. The unit of time changes with the type of activity involved. For example, if you are going out for a film, you will measure time in hours. If you are participating in a 100-metre race with your friends, you will measure time in minutes.
Can you think of some more examples where you measure time in your daily life?
We use clocks to measure time. A clock has two major hands—an hour hand and a minute hand. Some clocks have a second hand as well. The hour hand is shorter than the minute hand.
It takes the second hand 1 minute to complete one round of the clock. Similarly, it takes the minute hand 1 hour to complete one round of the clock. Lastly, it takes the hour hand half a day to complete one round of the clock.

A clock has the numbers 1 to 12 on it. These numbers tell us the hours of the day. When an hour is complete, the hour hand moves from one number to the next. The clock shows a total of 12 hours at a time. The hour hands needs to go around the clock twice to show one day.
A clock also has five little dashes (') between every two numbers. These dashes represent minutes or seconds, depending on which hand is on them. There are 60 dashes in total to show that there are 60 seconds in a minute, and 60 minutes in an hour.
However, just by looking at the clock we cannot say if it is morning or evening. To determine that, we use a.m. and p.m. along with the time value. The period from midnight till noon is indicated by adding a.m. with the time. The period from noon till midnight is represented by adding p.m. with the time. For example, 11 a.m. (in the morning) and 11 p.m. (at night).


Make a list of some activities that you do daily like having breakfast, lunch and dinner, going to school, doing your homework, playing and sleeping. Now, mention the time of each activity. Make sure to write a.m. or p.m. with the time value.
There are two major types of clocks—analog and digital. A digital clock shows numbers to indicate the time. It does not have hour and minute hands. Sometimes, we use a stopwatch to measure very short time intervals. It is a hand-held watch with a start and a stop button.
In earlier times, a sundial was used to measure time. A sundial had two parts, a circular dial with 12 marks, and a stick in the centre.
Complete the following.



1. The instrument with an hour and a minute hand.
2. The instrument that shows only numbers to depict time.
3. The instrument is used to measure very short intervals of time. S
Have you ever touched something cold, like ice or a glass of cold water? When you touch it, you feel the cold on your skin. Now, think about touching something hot, like a hot pan on the stove. The moment you touch it, your skin feels the heat, and you quickly pull away. These experiences help us understand temperature, which measures how hot or cold something is.
A thermometer is a device that is used to measure temperature. A thermometer has three main parts: a glass outer tube, a thin inner tube, and a small bulb filled with a liquid. There are markings on the inside to measure how hot or cold something is.


When we use a thermometer, the liquid in the bulb moves up the tube to a specific marking, which tells us the temperature of the particular thing.

We measure the temperature in different units like degrees Celsius (˚C) and degrees Fahrenheit (˚F). Usually, we use degrees Celsius to measure the temperature of objects. We usually measure the temperature of animals and humans in degree Fahrenheit.

Aim: To prove that a thermometer can measure different temperatures accurately
Materials Needed: Thermometer (digital or mercury), a glass of hot water, a glass of cold water, a glass of water in room temperature, a notepad and a pencil
Method:
Step 1: Measure the temperature of hot water with the thermometer and record it.
Step 2: Measure the temperature of cold water with the thermometer and record it.
Step 3: Measure the temperature of water that is in room temperature with the thermometer and record it.
Findings: The recorded temperatures will show that hot water has the highest temperature, cold water has the lowest, and water in room temperature is in between.
Conclusion: A thermometer can measure different temperatures accurately, demonstrating its usefulness for determining the temperatures of various things.
The Jantar Mantar in Delhi is made of several structures, or jantars, used to calculate time. These structures estimate time using the movements of different celestial bodies like planets, the Moon and the Sun.



standard units: units that give the same results for all measurements
estimation: a thoughtful guess about the value of something time: the measure of the duration of an event
temperature: the measurement of the hotness and coldness of a particular thing

Scan the QR code to know more about temperature and its measurements.
• The value of standard unit is fixed and does not vary from person to person.
• Time is a measure of the duration of an event.
• Time can be measured in seconds, minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years.
• Temperature measures the hotness and coldness of a substance.
• Temperature can be measured in degrees Celsius (˚C) and degrees Fahrenheit (˚F).
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which instrument is used to measure time?
Ruler
Thermometer Weighing balance Clock
B. Which of the following instruments shows only numbers to represent time?
Thermometer Stopwatch Analog clock Digital clock
C. Which of the following instruments is used to measure very short intervals of time?
Stopwatch
Thermometer Analog clock Digital clock
D. Which of the following instruments is used to measure temperature?
Stopwatch Analog clock Thermometer Digital clock


2. Fill in the blanks.
A. is a guess about the value of something.
B. The basic unit of time is .
C. An clock has numbers from 1 to 12.
D. A thermometer is used to measure the of a thing.
3. Write True or False.
A. The standard units have a fixed value.
B. The exact value of something is called estimation.
C. The hour hand of a clock is longer than the minute hand.
D. A digital watch measures very short intervals of time.
4. Match the following.
A. An analog clock
i. very short time intervals
B. A digital clock ii. two major hands
C. Evening time iii. shows only numbers
D. A stopwatch iv. adding a.m. with time
E. Morning time v. adding p.m. with time
5. Short-answer questions.
A. Why do we need standard units of measurement?
B. Give any two examples of estimation from daily life.
C. Name the standard units used for measuring weight and volume of a substance.
D. Name three instruments used to measure time.
E. How do we determine morning and evening using time?
6. Long-answer questions.
A. What is the difference between measurement and estimation?
B. What do we use to measure time? Describe that device and its types.
C. What does a thermometer do? Describe how it functions.

7. Picture-based questions.
A. Label the minute, second and hour hands in the image shown below.

B. Name the type of the clock.
C. Name another instrument to measure time.


You are planning a party and need to set up tables for 30 guests. Each table seats 6 people.
A. How many tables do you need?
B. Why is it important to measure and calculate correctly in this situation?













The Earth and the Solar System
The Solar System
The Earth Satellites


Let us recite the poem together!
The Sun shines bright with golden rays, Warming Earth throughout the days. Earth spins round, both night and day, Bringing light in a wondrous way. Life on Earth, the Sun sustains, Together they, in harmony, remain.

We all live on the planet Earth. The Earth revolves around the Sun. Likewise, there are seven more planets that move around the Sun. Do you think people live on these planets as well? What is the position of planets around the Sun? Let us find out. The natural objects that appear in the sky are called celestial or heavenly bodies. Some examples of celestial bodies are the Sun, the stars and the Moon. Earth



The Sun and the planets, and other heavenly bodies that revolve around them, are together called the solar system. The Sun is at the centre of the solar system. All the planets and the other celestial bodies revolve around it in an elliptical path called an orbit.
Sun
The Sun is a star. Stars are celestial bodies that are huge balls of gases and have their own heat and light. So, the Sun also releases heat and light. The Sun is the nearest star to the Earth. This is why it looks bigger than other stars.
The Sun is the ultimate source of energy on the Earth.
Planets

Planets are the celestial bodies that move around the Sun. All planets move in their respective orbits around the Sun. The gravitational force of the Sun keeps the planets in their place in the solar system. They do not have their own light; instead, they reflect the Sun’s light.




































“Many Very Elderly Men Just Snooze Under Newspapers”
Many—Mercury
Very—Venus
Elderly—Earth
Men—Mars
Just- Jupiter
Snooze- Saturn
Under- Uranus
















Let us recall the names of eight planets with the help of a mnemonic.




Newspapers- Neptune
elliptical: a shape that is oval or an elongated circle mnemonic: a special trick or rhyme that helps you remember something more easily










The planets in our solar system are divided into two groups.
Inner Planets: These planets are nearest to the Sun. These are rocky planets. The names of the inner planets are Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
What other name would you like to give to planet Earth? Why?
Outer Planets: These planets are also called gas giants. They are made of gases and ice. The names of the outer planets are Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Some unique features of the planets of our solar system are as follows:
Mercury
Features
It is the smallest planet. It is the planet closest to the Sun. It does not have any atmosphere or moon. It becomes very hot during the day and very cold during the night.
Venus It is the brightest planet. It is also called the Morning and the Evening Star as it is visible just before sunrise or just after sunset. It is the hottest planet.
Earth It is also called the ‘Blue Planet’. It has air and water. It is known to be the only planet that supports life. It has one moon.
Mars It is also called the ‘Red Planet’ since the red soil and rocks on its surface makes it appear reddish in colour when seen from the Earth. It is the only planet with a surface similar to that of the Earth. It has two moons.
Jupiter It is the fifth and the largest planet. It has more than 80 moons.
Saturn It is the second largest planet. It has the maximum number of moons (>140). It also has giant rings around it.
Uranus It is as an ice giant. It appears light blue. It has 27 moons. Its poles are tilted on its side.
Neptune
It is also an ice giant. It is the farthest and the windiest planet. It has 14 moons.
Images









Match the following.
1. The nearest planet to the Sun
2. Blue Planet
3. A planet with the maximum number of moons
4. The largest planet
i. Earth
ii. Jupiter
iii. Mercury
iv. Saturn
We all live on the surface of the Earth. But have you ever wondered what is the Earth made up of? Let us learn about this in detail.
The Earth is made up of three main layers—crust, mantle and core.
Crust/Surface: It is the outermost layer of the Earth. It forms the surface on which we live. It is hard and cool.
Mantle: It is present between the crust and the core. It is made up of rocks, minerals and metals. This is a solid layer of the Earth.
Core: It is the innermost layer of the Earth. It is very hot. It is made of metals, minerals and gases. The core is further divided into two parts—the outer core and the inner core. The outer core is liquid. The inner core is solid.
Imagine you are riding on a merry-go-round at the playground. As it turns around, you see different parts of the playground because it moves in a circle. This is how a merry-go-round moves around a central point.
The Earth is also like a huge merry-go-round. It has an imaginary line that passes through its centre between the North and South poles. This imaginary line is called an axis. The axis is not a straight
imaginary: unreal


line. It is slightly tilted. The North Pole is the point at the top of the axis. The South Pole is the point at the bottom of the axis.
The equator is an imaginary line that divides the Earth into two halves. The upper half is the Northern Hemisphere. The lower half is the Southern Hemisphere.
The Earth performs two types of movements, rotation and revolution. Let us learn about them.


















































Have you ever seen a top spinning on the ground? It spins on its axis. Similarly, the Earth also moves around its axis. This movement is called rotation. The Earth takes 24 hours to complete one rotation.
The rotation of the Earth on its axis causes the formation of day and night. During rotation, the part of the Earth that faces the Sun experiences day. The other part of the Earth that does not receive sunlight experiences night.


Revolution
It is the movement of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun. When the Earth completes one round along its orbit, it is called a revolution. The time taken to complete one revolution is one year.
The Earth’s revolution causes different seasons. You know that the Earth’s axis is tilted. This
tilted: leaning to one side







makes one pole of the Earth closer to the Sun at a particular time of the year. Thus, that hemisphere receives more sunlight and experiences summer. At the same time, the other hemisphere that is tilted away from the Sun experiences the winter season.
Revolution changes the position of the poles tilted towards the Sun. For about six months in a year, the North Pole is tilted towards the Sun while for the rest of the year, the South Pole is tilted towards the Sun. This cycle of tilt and revolution causes the seasons to change throughout the year.

Here, it is important to note that the equator always receives direct sunrays. So, it always remains hot. On the other hand, the North and South poles always remain cold.

Aim: To study the formation of day and night.
Materials Needed: A clay ball (representing the Earth), a wooden stick and a torch
Method:
Step 1: Take the clay ball and insert a wooden stick in it. Make sure the stick is slightly tilted. This will represent the Earth’s axis.
Step 2: Throw light on the clay ball using a torch. Observe what happens.






Findings: The part of the ball that receives direct torchlight indicates day. On the other hand, the opposite dark part represents night.
Conclusion: The Earth’s rotation is responsible for the formation of days and nights.





Cross ( ) out the statement that is not true about the rotation of the Earth.
1. It is the Earth’s movement on its own.
2. It causes the formation of seasons.
3. One rotation is completed in 24 hours.
4. It takes place around an imaginary line.
Do you know that the Moon revolves around the Earth? A heavenly body that revolves around a planet is called a satellite.
Therefore, the Moon is the natural satellite of the Earth. The Moon does not have air or water to support life. The surface of the Moon that we see from the Earth is called its face. The surface of the Moon is not smooth. Instead, has craters on it.

The Earth is also surrounded by several man-made objects known as artificial satellites, which orbit the planet. These satellites are launched into space using rockets. The first artificial satellite sent into space by humans was Sputnik 1. Artificial satellites play important roles, such as weather forecasting, providing communication services, and studying the solar system and the universe.
Did You Know?
The Moon appears as a beautiful shiny object from the Earth. However, it does not have its own light. The Moon shines when it reflects the Sun’s light.
The Birla Planetarium in Kolkata is the largest planetarium in Asia. This planetarium uses advanced projection systems to represent the solar system and different celestial bodies. It also conducts educational shows about space exploration.
India’s first artificial satellite, Aryabhata, was launched into space in the year 1975.

craters: large holes


celestial bodies: the objects present in the space planets: the celestial bodies that revolve around the Sun
revolution: the movement of the Earth around the Sun in an orbit rotation: the movement of the Earth around its own axis satellites: the objects that revolve around a planet

Scan the QR code to know more about the solar system.
• The Sun is at the center of the solar system.
• There are eight planets in the solar system—Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
• There are three main layers of the Earth—crust, mantle and core.
• Satellites are the heavenly bodies that revolve around the planets.
• The rotation of the Earth causes the formation of days and nights.
• The revolution of the Earth causes different seasons.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. The celestial objects that have their own heat and light are called . Stars Planets Satellites Moon
B. The number of planets in our solar system is

C. The path in which the planets move around the Sun is called Satellite Orbit Crust Space
D. The revolution of the Earth is responsible for
The change of seasons
Formation of solar system
2. Fill in the blanks.
The formation of days and nights
Change in the order of planets
A. is the innermost layer of the Earth.
B. is present between the crust and core.
C. The of the Earth causes different seasons.
D. of the Earth causes and night.
3. Write True or False.
A. Earth is the only planet with a natural satellite.
B. The equator always receives direct sunrays.
C. All the planets of our solar system have air and water.
D. The Moon is the nearest star to the Earth.
4. Circle the correct option in each of the following.
A. Inner / Outer planets are also called gas giants.
B. Neptune / Jupiter is the windiest planet in our solar system.
C. Uranus / Mars is also an ice giant.
D. Venus / Mars is called the morning star as well as the evening star.
5. Short-answer questions.
A. Name the planets that form the solar system.
B. How are the inner planets different from the outer planets? Give examples of each.
C. What features of the Earth make it suitable to support life?
D. Define axis and equator.
E. How many layers does the Earth have? Name them.

6. Long-answer questions.


A. Explain the different layers of the Earth with the help of a well-labelled diagram.
B. Why do seasons change on Earth? Explain with the help of a diagram.
C. Explain the formation of day and night.
7. Picture-based questions.
A. What does the given image represent?
B. Label the 1, 2, 3 and 4 marked in the image.
C. Write one sentence about each of them.


1. Stars have their own light and heat. Yet, we do not feel the heat of the stars visible at night. Why?
2. What might happen if the planets in our solar system do not revolve in their orbits around the Sun?
The world’s population is increasing at an alarming rate. Do you think humans can live on other planets? With the help of your friends, find out the following:
• What are the conditions required for the presence of life on a planet? Is there any other planet, that has all these conditions?

• Mention any one habit that you would change to protect our planet Earth.


Objective: Students will explore how the slope of an inclined plane affects the speed of an object that is moving down the inclined plane.
Materials Needed:
Wooden plank or piece of cardboard (2–3 feet long), stack of books (to create different slopes), toy car or small rolling object, ruler or measuring tape, stopwatch, notebook and pencil (to record results)
Step 1: Learn about Simple Machines
Revise about the different types of simple machines given in the textbook. Focus on how an inclined plane makes our work easier.
Step 2: Create the Inclined Plane
Place one end of the wooden plank or cardboard on a stack of 2–3 books to create a low slope. Measure the height of the slope from the ground using the ruler or measuring tape. Record this height in your notebook.
Step 3: Measure Speed Down the Inclined Plane
Place the toy car at the top of the slope and let it roll down. Use the stopwatch to measure the time it takes for the car to reach the bottom of the slope. Record the time in seconds. Repeat this step three times to get an average time for the low slope. Record all results.
Step 4: Repeat for Different Slopes
Increase the height of the inclined plane by adding more books (4–5 books for a medium slope, 6–7 books for a high slope). Repeat Step 3 for each new slope, measuring the time taken for the car to reach the bottom three times and calculating the average time.
Step 5: Compare the Results
Create a table to compare the height of the slope and the average time taken for the car to reach the bottom.
Project Output: You have learnt that the time taken for the car to reach the bottom, changes with different slopes. The higher slopes result in shorter times, meaning the car moves faster. Present your findings to your class.
Final Outcome: This hands-on project will help you understand how an inclined plane works and how it reduces human effort to make tasks easier by allowing objects to move smoothly and quickly.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.


In India, solar energy has made a big difference by providing many real-life benefits. For example, in small villages, solar panels on rooftops provide enough energy to light up homes, run fans and charge mobile phones. Large solar parks in Gujarat and Rajasthan produce a lot of electricity for the country. Solar energy works by capturing sunlight with panels and turning it into electricity. This helps reduce pollution and cuts down on electricity bills. The Indian government’s National Solar Mission also supports putting solar panels on government buildings and schools, encouraging more people to use this clean energy source. By using solar energy, we can help protect the environment and make sure there is enough power for everyone.
1. Which energy comes from the sun?

A. Solar energy B. Hydro energy
2. Why is solar energy good for the environment?
A. Electricity made from solar energy has no cost.
B. It helps reduce pollution and keeps the air clean.
C. It makes the sun shine brighter.
C. Electric energy
3. Apart from solar energy, name any three other forms of energy.
4. Which kind of energy sources should we use to help fight climate change? Why?
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.









Introducing Reflection, a thoughtfully crafted Science book that ignites curiosity, and nurtures a love for enquiry and evidence-based thinking, in young minds. In keeping with National Education Policy (NEP) 2020’s focus on competency-based education, Reflection provides opportunities for learners to master core scientific concepts, develop a scientific temper, hone their critical thinking, and apply 21st century skills in their day-to-day lives. Reflection is designed to fascinate students towards science, both as a subject and as a practical experience, while also making them well-rounded individuals.
• Coursebook
• Uolo App
• Teacher’s Guide
• STEAM Projects: Engaging, hands-on projects blending Science, Technology, Engineering, Art and Maths (STEAM) to inspire young minds
• Competency-based Assessments: Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and application of skills
• Story-based Approach: Enchanting comic stories that bring learning themes to life, making education a captivating adventure
• Investigate and Discover: Hands-on experiments to foster the spirit of scientific enquiry and evidence-based thinking
• Picture-based Questions: Questions featuring visual stimuli to elevate comprehension, interpretation and critical thinking
• Wonders of Bharat: Fascinating insights into India’s rich culture and heritage, designed to ignite a profound sense of pride and love for the nation
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-based learning programs. We believe pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, South East Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-979832-0-7
