




English Mathematics
General Knowledge Science
Social Science

Academic Authors: Melanie Grobler, Chandani Goyal, Neena Aul, Animesh Mittal, Muskan Panjwani, Sneha Sharma, Anuj Gupta
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Sanjay Kumar Goel, Tauheed Danish, Amisha Gupta
Project Lead: Chandani Goyal
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First impression 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Wisdom 3 Semester 2
ISBN: 978-81-980880-5-5
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address: 85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.


Author/
Invitation
Interview
Listen and choose the correct answer
Simple present tense Present continuous tense
Collocations
Prefixes and suffixes
Chwords with sounds /ch/ and /k/–chain, chaos
Factual questions Ordering Contextual meaning Making connections
Biographical story
Write a story
Picture talk
Listen and mark true or false
Phrasal verbs Verb forms in the simple past tense
Contractions
Factual questions Identifying problems and solutions Making predictions Making observations silent letters–k, b, w, l, t–thum b , k nife, ca t ch, ta l k, w rite
Homophones
8. Protecting Animals Carpet Sahib
Dialogue writing
Roleplay
Listen and fill in the key details
Punctuation
Simple future tense
Similes
Homographs
Fable
Joseph Jacobs
9. Nature The Magpie’s Nest
Factual questions Making observations Poetry appreciation– identifying setting Visualisation
Poem
10. Nature Wind on the Hill A A Milne
Debate Paragraph composition
Listen and fill in a chart
Adverbs
Compound words Anagrams
Syllables– break words into syllables
Factual questions Summarising Identifying key events Identifying problems and solutions Making inferences Making comparisons
Factual questions Identifying characters’ actions Identifying problems and solutions Retelling the main events Analysing characters Making connections
Rhyming words
Writing instructions
Share a Story
Listen and answer the riddles
Conjunctions
Idioms
Different spellings of the long I sound–pie, pine, shy, high
Retelling the main events
Factual questions Making connections Poetry appreciation– imagery
Factual questions Ordering Analysing characters and their actions Identifying cause and effect Making connections
Graphic story
Folktale
Poem
Folktale
Project 3: Plant a Sapling
11. Imagination and Fantasy Alice in Wonderland
12. Humour The Pot Face
13. Humour I Woke Up This Morning Kenn Nesbitt
Project 4: Spreading Laughter
14. World Story Momotaro, the Peach Boy




Discuss your ideas in class. Get Set
There are many animals that live in the wild. What can we do to see that these animals are safe? 1.




Many years ago, in a small village, a man-eating tiger started attacking humans. The villagers were helpless and needed someone to protect them. They went to Carpet Sahib for help. Who was Carpet Sahib? What did he do to help the villagers? Let us read the story to find out.



The moon shone brightly over the thick jungle of Nainital as Jim Corbett moved quietly through the bushes. The night was silent, and every sound made Jim’s heart beat faster.
‘Please, Carpet Sahib, you must help us,’ the villagers had begged him earlier that day. ‘The leopard is attacking our people. We are too scared to go outside.’ The villagers trusted Jim and called him Carpet Sahib because they could not say his surname. He knew that a leopard could be dangerous and that he had to help his friends.


Jim Corbett was a hunter, but he did a lot to protect wildlife in India. He was also a good photographer. He took beautiful photos of wild animals and used them to talk to people about how to care for animals and nature.
begged: asked for something again and again protect: look after and keep safe photographer: person who takes photos
Think and Tell Why did Jim’s heart beat faster?
Jim entered the forest with a guard or two and waited patiently at the spot where the cat was last seen. The thick trees did not let any moonlight through, making it very difficult to see in the darkness. Suddenly, Jim heard it—a low growl that made his heart race. The leopard was close.
Jim and his guards held their guns tightly, listening very carefully. There, in the distance, he saw two glowing eyes. The leopard was watching him. It moved with a limp—the leopard had been hurt. Jim felt sad for the leopard. He realised it might be attacking people because it was very hungry and humans were easy prey.
Jim decided to set a trap to capture the leopard without hurting it. He found a safe spot and put food for the cat inside a cage. Then, he waited again, his heart pounding. The jungle was silent except for the rustle of leaves. Minutes felt like hours. Finally, the leopard came out of the shadows, drawn in by the smell of the food. It walked slowly at first, and then, with a quick move, entered the cage. The door closed behind it.
Jim walked slowly to the cage. ‘It’s okay, my friend,’ he whispered. ‘I am here to help.’
Jim called for the village doctor, and together, they treated the leopard’s injured leg. The villagers watched as Jim gently cared for the big cat. Over time, the leopard got stronger and healthier. When the leopard was well enough, Jim and the villagers released it back into the wild. The leopard looked at Jim one last time, as if saying thank you, before disappearing into the jungle. The villagers were safe again.
growl: a low, angry sound made by an animal made his heart race: made him very excited and scared prey: a person or animal being hunted capture: catch

What was the leopard feeling when it looked at Jim for one last time?
his heart pounding: his heart beating very fast
rustle: a soft sound of something moving treated: gave care and help injured: hurt released: to let something go free

Jim then spent even more time in the village teaching the villagers about animals and helping them understand the jungle and its creatures. Jim showed them how to stay safe and live peacefully with the wildlife around them.
To keep the villagers and animals safe, he built a high wall around the village of Chhoti Haldwani. This wall kept the tigers and leopards away from the village. The wall is still there today.
Wherever he went, Jim taught children why it is important to protect nature and wild animals. His good work led to the creation of India’s first national park, now called the Jim Corbett National Park. This park is home to many tigers and other animals that now live safely in the jungle. Through his actions and teachings, Jim Corbett showed that the villagers and wild animals could live together in peace.


peacefully: without trouble
wildlife: animals living in nature
creation: making or building
National Park: an area that a country sets aside to protect nature and wildlife




The Jim Corbett National Park is in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It was opened in 1936 and is the oldest national park in India.
Listen to all the keywords here.


Read and Respond

1. Fill in the blanks with the words in the box.
Hint Box: leopard trap protect injured wall
a Jim Corbett went into the jungle to the villagers.
b Jim set up a with food inside to capture the leopard.
c The had a hurt leg.
d Jim and the village doctor treated the leopard’s leg.
e Jim built a high around the village to keep the leopards away.
2. Number the events of the story, 1–5, in the correct order.
a They treat the leopard and look after it until it is well.
b Jim and his helpers find the leopard and see it is hurt.
c They set the leopard free in the forest.
d The villagers ask for help, as a leopard is attacking people.
e Jim decides to set a trap for the leopard.
3. Answer the questions in one or two sentences.
a Why did the villagers call Jim Corbett ‘Carpet Sahib’?
b How did Jim and the guards know that the leopard was close?
c Why did the leopard start catching people instead of animals?
d Why did Jim spend more time in the village after they released the leopard?
e What was India’s first national park called? Why was it created?






Answer the questions.
a Find another expression in the text that means almost the same as, ‘Jim’s heart beat faster’.
b Choose one sentence that shows that Jim really cares about the leopard.
c Write the words from the passage that show that the leopard did not get better quickly.
d How would you describe the look that the leopard gives Jim when they release it?
It gave Jim a look.


In India, there are more than three hundred types of animals that are endangered. As a student, write what can you do at your school and at home to protect these animals?
Some of India’s endangered animals:




Pronounce Well

Read these words aloud.
ch words with a /ch/ sound
chop chip chain chest cheese lunch
Listen to the words here.
ch words with a /k/ sound
ache chorus echo stomach school character
Look at the ch-words in the sentences. Write ch or k based on the sound. Then, read the sentences aloud.
a The baby birds chirp loudly when their stomachs are empty.
b There is chaos when this angry elephant charges through the forest.
c Our school wins every choir competition.
d Your chest aches when you have a cough.
e The ship’s anchor was tied to a chain.



1. There are some words that usually go together. Match these pairs and then say them aloud.
endangered tricks
animal fire
national animals
monkey pond
duck kingdom
forest park
In your notebook, make three sentences with any of the word pairs you matched.
2. Look at the pictures. Fill in the prefixes re- or un- to complete the words. Make sentences with each word in your notebook.
Remember!
A prefix is a group of letters added to the beginning of a word to change its meaning. For example: tidy- untidy; use-reuse



3. Complete the sentences by adding a suffix from the box to the words in brackets.
Hint Box: -ess -ful -less -ness -ly -ers
a Rangers are the of animals. (protect)
b Rangers can give people information. (help)
c The actions of people can harm animals. (care)
d The zookeeper handles the animals . (safe)
e A female lion is called a . (lion)
f We should show to animals. (kind)


The Simple Present Tense
• We use the simple present tense to talk about things that happen every day. These can be habits. For example: The rangers pump water every morning.
We use different forms of doing words (verbs) to show the time things happen.
• There are also things that are true all the time. In such sentences, we always use the simple form of the doing word (verb). For example: Cows are mammals.
Don’t forget that the simple form of the verb may need -s or -es.
Action done by
He (Ankit)
She (Anu)
Form of doing word (verb)
It (The moon) is -s or -es form of the verb
Ankit is a boy. Anju is a girl. The moon shines at night. Remember!
Examples of facts that are always true

Action done by
You (One or more)
We (Anu and I)
Form of doing word (verb)
They (Reptiles) are simple form of the verb
I am am simple verb
Examples of facts that are always true
You are from India. (one) You are all from India. Anu and I are from Raipur. Frogs and crocodiles are reptiles. Reptiles have scales.
Owls catch their prey at night.
I am a girl. I belong to the human race.
The Present Continuous Tense
• The present continuous tense is used to show that actions are happening or continue at the time of speaking.
Here, is, are and am are helping verbs. The main verb takes -ing. Look, the bird is building a nest!
We use the is/are/am + ing form of the verb.
For example:
The rangers are busy pumping water for the animals.
1. A. Underline the verbs in the sentences to see how they are different. Write (SP) if the sentence is in the simple present and (PC) if the sentence is in the present continuous tense.
a The sun usually shines during the day. The sun is shining at the moment.
b Is the earth moving around the sun now?
The earth moves around the sun.
c There are rules in the Jim Corbett National Park. The people in that car are breaking the rules!
d Metu, why aren’t you reading the rules?
I always study the rules given at the park gate.
B. Write what you noticed about the verbs in each tense. How are they different?
2. Look at the picture and fill in the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
a The jaguar (watch) its prey.
b Look, it (sit) very still.
c Jaguars (be) the third biggest cat after tigers and lions.
d You (see) them mostly in the Amazon jungle.
e Their numbers (decrease) because people keep on (cut) down trees in the forest.


Listen Well
Listen to the text here.
Listen to the passage carefully. Tick () the correct answers.
a Where did the sea turtles lay their eggs?
i In the ocean ii On the beach iii In the forest
b What problem did the turtles face?
i There were too many people on the beach.
ii There was a lot of garbage on the beach.
iii There were many birds on the beach.
c Who decided to help the turtles?
i The parents ii The children iii The fishermen
d What did the children do to help the turtles?
i They built nests for the turtles.
ii They cleaned up the beach.
iii They moved the eggs to a different place.

e How did the children’s efforts help the turtles?
i The turtles could lay their eggs safely.
ii The turtles found new homes.
iii The baby turtles stayed out of the sea.




Practise speaking here.
Interview a person in your community, like a vet, a farmer, or someone who knows a lot about or helps birds and other animals.
• Step 1: Decide who you will talk to.
• Step 2: Write down the questions you will ask. Some ideas have been given below.
• Step 3: Remember to introduce yourself at the start and thank the person at the end.
• Step 4: You can record the interview so that you can play it to your classmates. Remember to first ask the person you interview for their permission to record what is said.
Some interview questions:
When did your interest in animals start?
What is the most interesting thing you have done? How long have you been ….?


We write an invitation to ask someone to come to an event. An invitation has five sections.
Model Answer
Date: Saturday, 15 July 2025
Time: 2–4 p.m.
Where: Central School Hall
Location
Join us for a talk by Dr Rambani of the Wildlife Society to learn more about this interesting topic.
Date and Time

Invite friends and their parents to a tree-planting event in a nearby park. Give your invitation a heading and use the correct format.




Get Set

Match the information about the birds and their pictures.
Name and Description
A magpie is a black, white and blue bird with a long tail.
A thrush is a brown bird with spots on its chest.
A blackbird is an all-black bird with a bright yellow beak.
A turtle dove is a small bird with a reddish-brown feathers.
A starling is a dark, shiny bird with spotted feathers.

The birds decided they needed nests, but they didn’t know how to build them. They went to Magpie for help. Let us read the story to find out how Magpie helped the birds.

Let’s Read

Once upon a time, all the birds wanted to learn how to build nests. They went to the cleverest bird, the magpie, and asked her to teach them. The magpie agreed and gathered all the birds around her.
First, the magpie took some mud and made a round shape with it.
‘Oh, so that’s how it’s done!’ said the thrush. The thrush flew away and that’s how thrushes build their nests now.
Next, the magpie added some twigs around the mud.

cleverest: the smartest gathered: called or collected

‘Now I know how to do it,’ said the blackbird, and off he went. Blackbirds have been building their nests this way ever since.
Then, the magpie put another layer of mud over the twigs.
‘Oh, that’s easy!’ said the wise owl, and away he flew. Since then, owls have been making their nests this way.
After that, the magpie wrapped twigs around the outside of the nest.
‘That’s perfect!’ said the sparrow, and off he flew. Sparrows make rather messy twig nests, but this is how they still do it.
Finally, the magpie added some feathers and soft material inside the nest to make it comfortable.
‘That’s just right for me,’ said the starling, and off he flew. Starlings have cosy nests because of this.


Magpies are called ‘clever’ because they can solve puzzles, use tools and understand other magpies. They are very smart birds!
What kind of nests do owls make?
layer: a thin covering of something that is spread over something else wrapped: covered something by putting something around it
material: what you use to make something with comfortable: nice and cosy cosy: soft and warm
One by one, each bird learned a little bit and then flew away. No bird stayed until the end to see the whole process. Only the turtle-dove remained, but she was not paying attention. She kept repeating her silly cry, ‘Take two, Taffy, take two-o-o-o.’
The magpie was busy and heard this just as she was adding a last twig to the nest. She said, ‘One’s enough.’
But the turtle-dove kept saying, ‘Take two, Taffy, take two-o-o-o.’
The magpie was annoyed and said, ‘One’s enough, I tell you! There isn’t place for more.’
Still, the turtle-dove kept repeating, ‘Take two, Taffy, take two-o-o-o.’
Finally, the magpie looked up and saw that all the other birds, except the silly turtle dove, had flown away. She got very angry and flew away too, refusing to teach the birds any more.
And that is why different birds build their nests in different ways.

process: the steps to make or do something cry: a sound of a bird enough: as much as needed annoyed: upset or irritated except: not counting something as a part of group or team refusing: saying no to someone
Why did the magpie refuse to teach the birds any more?
Listen to all the keywords here.




1. Match the birds and how the story says they build their nests.
Birds Nests
Thrush feathers and soft things inside
Blackbird messy twig nests
Starling mud and twig nests
Sparrow mud nests
2. Fill in the blanks.
Hint Box:
a The magpie agreed to teach the birds how to build .
b They asked the magpie because they thought she was .
c The flew away and was the first to go and build a nest.
d The said that building a nest was easy.
e It is the materials inside a nest that make it comfortable.
3. Answer the questions in one to two sentences.
a Give three facts that show that magpies are smart birds.
b What problem did the birds face? How did they solve it?
c Why do starlings have cosy nests?
d What did the magpie think ‘Take two, Taffy, take two-o-o-o’ meant?
e Name two things that made the magpie angry.



What do you think would have happened if the birds had all stayed for the Magpie’s full lesson?
a What would the nests have looked like?
b Would this have been a good thing or a bad thing? Give two reasons for your answer.




The magpie is a very interesting bird! Watch the birds near your house and fill in this information sheet about one bird.

The bird is called .
The bird’s feathers are colour.
Draw what its beak looks like.
The bird’s eyes are . (colour)
The bird lives in .
The bird eats . I saw it do these interesting things: 1. 2. 3.


Draw and colour in the bird.
Listen to the words here.
Read the words aloud without saying the underlined letters.
know write climb talk listen knit wrong bomb walk catch knock wrap lamb calf watch knot wriggle thumb half match kneel wrist crumb yolk often

2. Fill in the blanks with the correct letters. Then, read the sentences aloud.
a The yo of the egg feeds the chick as it grows in the egg.
b The bird flew to ca ch a worm.
c The bird ate the bread cru .
d The woodpecker ocks on the tree trunk.
e The worm iggled when the bird picked it up.


Vocabulary

We can use an apostrophe (‘) to make shortened forms of words. These are called contractions.
Look at how the apostrophe is used in the place of the letters and spaces that are left out.
For example:
• I do not see a bird, do you? • You are not even looking. I don’t see the bird, do you? You aren’t even looking.
1. Write the words these contractions are made of.
a isn’t b there’s
c didn’t d you’re
e can’t f they’re
g musn’t h we’ll
i wasn’t j I’ll
2. Fill in the blanks with the correct contractions.
a The magpie said, ‘ teach you how to make a nest.’
b ‘ hard to build a nest,’ she said.
c The birds stay for the whole lesson.
d It long before the birds were all building their own nests.
e ‘ a silly bird,’ said the magpie to the dove.


Phrases are groups of words that do not make complete sense. gather around The birds gathered around the magpie.
This does not make complete sense. This makes complete sense.
Verbs (doing words) can combine with other words like prepositions (position words). We call these phrasal verbs. For example: Let’s gather around the table. Here, gather is a verb and around is a preposition. It means to come together.
1. Underline the phrasal verbs in the sentences. Then, match the phrasal verbs and their meanings.
a The magpie looked for twigs for her nest. relied on
b The birds set up a meeting with the magpie. understood
c Each bird must look after its own nest. searched
d The owl figured out how to build a nest. arranged
e The birds counted on the magpie for help. take care of

When verbs take -ed at the end to show an action in the past we call them regular verbs.
For example:
Remember!
Verbs (doing words or action verbs) show us when an action happens.
The birds ask the magpie to help them. (Simple present)
The birds asked the magpie to help them. (Simple past)
Here ask + ed shows that the action was done in the past.
Irregular verbs change completely in the past tense.
For example:
The birds go to the magpie for help. (Simple present)
The birds went to the magpie for help. (Simple past)
Can you find more irregular verbs in the story?
2. Write the past tense form of the underlined verbs. Use a dictionary to check your spelling.
Present tense verbs Past tense verbs
a The bird taps against the window.
b I wrap the little bird in a soft cloth.
c It dips its beak in the water.
d I hum to myself.
e The bird flaps its wings.
What did you notice about the spelling?
3. Fill in the past tense forms of the verbs. Write ‘R’ for regular verbs and ‘IR’ for irregular verbs.
a All the birds (hope) the magpie would help them.
b They (feel) she was the right one to ask.
c When she (begin) the lesson they listened carefully.
d The birds (form) a circle around the magpie.
e The magpie was cross when she (find) that they had left.
4. Rewrite the sentences using the past tense forms of the verbs.
a No bird stays till the end.
b Only the turtle-dove remains.
c Why does the turtle dove repeat the same silly call?
d The birds dream of having their own nests.
e The magpie feels angry.


Listen Well

Listen to the text here.
Listen to the text Interesting Facts About Birds carefully and write if the sentences are True or False.
a Penguins can fly very high in the sky.
b Eagles have excellent eyesight.
c Parrots are known for their dull colours.
d Hummingbirds can hover in one place by flapping their wings very quickly.
e Birds use their feet to eat different kinds of food, like seeds, insects and nectar.
f Each bird has its own special song that it uses to communicate with others.



Imagine that you and your class visited the Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary. Work in a group and take turns to describe what you saw and what you did there.
Practise speaking here.



Use expressive words like curious, delighted and gigantic to make your description interesting.

Sit in a group of five. Read the information about what makes a good story. Then, work together and plan your story. Write your story in your notebook.
Setting: The setting is where and when the story takes place.
Characters: The characters are the people or animals in the story.
Beginning: The beginning of the story tells us where, when and who. It introduces the characters and the setting.
Middle: The main events form the middle of the story. The characters face problems or go on adventures. What is the problem in this story?
End: The end is how the story finishes. It tells us how the characters solve the problem or what happens after the adventure.

Get Set 10 . Wind on the Hill —A A Milne

List five things that you see moving when a strong wind blows. Share your list in class.
We all love the wind because it cools us down. When the wind blows, there is a feeling of excitement in the air. But where does the wind go? Let’s read the poem to find out.


Let’s Read

No one can tell me, Nobody knows, Where the wind comes from, Where the wind goes.
It’s flying from somewhere As fast as it can, I couldn’t keep up with it, Not if I ran.
But if I stopped holding The string of my kite, It would blow with the wind For a day and a night.
And then when I found it, Wherever it blew, I should know that the wind Had been going there too. So then I could tell them Where the wind goes...
But where the wind comes from Nobody knows.
Think and Tell Who is ‘I’ in the poem?

keep up with: (here) try to match the speed of the wind
Think and Tell
Where do you think the wind comes from?
Listen to all the keywords here.



1. Tick () the correct answers.
a Where does the wind come from?
i We don’t know where. ii The mountains
iii The ocean
b How fast does the wind blow?
i Slowly ii Not too fast iii As fast as it can
c What will happen if the speaker lets go of the kite string?
i The wind will stop blowing.
ii The kite will fly away.
iii The kite will come down.
d How long will the kite fly if the poet lets it go?
i For a few minutes.
ii For a whole day and night.
iii It won’t fly at all.
2. Write True or False.
a The poem says that nobody knows where the wind goes.
b The speaker can keep up with the wind by running.
c The kite will blow away if the speaker lets go of the string.
d The wind has gone wherever the kite blew.
3. Answer the questions in two to three sentences.
a Which lines tell us that the speaker has asked people where the wind comes from and where it goes?
b What would happen to the kite if the wind stopped blowing?
c What do you think will happen if there are very strong winds?
d How does the speaker think he can find out where the wind goes?




Keep track of the wind for a day. Fill in this table after observing the wind carefully.
Time of Day Morning Afternoon Evening
Wind strength (circle)
Ways in which the wind helps me and my family
Ways in which the wind troubles me and my family

Vocabulary

• No wind
• A little windy
• Very windy
• No wind
• A little windy
• Very windy
• No wind
• A little windy
• Very windy
There are many words that sound the same but mean different things. These words are called homophones.
1. Look at the pictures and circle the correct spelling of the word shown in the picture.


2. Choose the correct homophones to complete the sentences.
a The river flows down to the . (see/sea)
b The hopped quickly across the meadow. (hare/hair)
c We found a small in the ground where the rats might be hiding. (hole/whole)
d The cat is over , near the tree. (there/their)
e The wind very strongly. (blue/blew)



Poems and stories have a setting. A setting is where the events take place.
1. Describe the setting of the poem.

2. Close your eyes. Ask your partner to read the poem to you. What do you see? Describe what you imagine in three to four sentences.





You are going to plant a sapling at home in a small pot and create a picture guide to show how you did it. Your guidebook will include step-by-step instructions with pictures on how to plant a sapling and how to take care of it.
Materials Needed:
• A small pot
• A sapling
• Your English notebook
• Glue or tape
Instructions to plant the sapling
• Potting soil
• A watering can or a cup

• Markers, crayons or coloured pencils
• A camera or a phone (to take pictures)
• Take an empty pot. It should have a small hole at the bottom.
• Fill the pot halfway with soil.
• Place the sapling in the centre of the soil and cover the roots with more soil.
• Sprinkle water on the soil to make it damp. Take care not to make it too wet. Plants need water to grow, but too much water can spoil the roots.
• Place your sapling in a sunny and airy spot.
• Water your plant whenever the soil feels dry.
• Watch your plant grow and take care of it every day. Take pictures of each step.



• In your notebook, give a heading, ‘How to Plant and Care for a Sapling’ and your name. You can draw or add a picture of your plant.
• Use the pictures you took of each step. Paste them in your notebook.

• Write short and simple instructions next to each picture, explaining what to do in that step.
• Decorate your guide with drawings, stickers, or any other decorations you like.






Get Set

We have all read stories about magic places. Close your eyes and think about a magical place you would like to be. What will it look like? Who will be there and what will you see?
Draw/write about your magic place.
(Draw/write here)
Alice sees a talking rabbit and follows it into a new world full of adventures. Does such a world really exist or is it her imagination? Let us read to find out.



boring: not interesting
Think and Tell
If you were Alice, what would you do after falling down the tunnel?


Think and Tell
Why does Alice decide to drink the liquid in the bottle?
made it: reached somewhere here goes nothing: something you can say when you try something without being sure what will happen
Who did not want Alice at the tea party? Why?

no room: not enough space squeeze in: try to fit in a small place strangest: very odd and surprising in a way we may find hard to understand field: a large, open, grassy piece of land croquet: a field game where players use sticks called mallets to hit balls through small metal hoops stuck in the grass chop off: to cut something off using a sharp tool

Why was the Queen of Hearts angry with Alice?
Listen to all the keywords here.




1. Complete the summary of the story with the words in the box.
Hint Box: hole wonderland sister tea party Queen of Hearts talking rabbit
Alice saw a . She followed it into the rabbit . She drank something from a bottle and became smaller. She went through the small door and into a . She attended a and met the . It was all a dream and she was woken up by her .
2. Rewrite one main event that happened at the beginning, middle and end of the story.
a Beginning . b Middle .
c End .
3. Answer the questions in two to three sentences.
a What does the talking rabbit say while running past Alice?
b Why do you think Alice decided to follow the white rabbit down the rabbit hole?
c How do you think Alice felt when she realised she had grown smaller after drinking from the bottle?
d Do you think Alice enjoyed the tea party with the Mad Hatter and the March Hare? How do you know?
e At what part of the dream did Alice finally wake up?



Complete the table with the solutions to the problems in the story.
Alice found a door that she was too small to pass through.
Alice became too small and wanted to become bigger.
The Mad Hatter told Alice there was no place for her at the table.


When we use our imagination, we can think of wonderful things that may or may not exist in the real world. Fill in this table with three things that are both in the real world and in Wonderland, and three things that are only in Wonderland.
What is in both the real world and in Wonderland?
What is only in Wonderland?



Similes compare two different things using ‘like’ or ‘as.’ They help make descriptions more interesting.
For example: The cat was as quiet as a mouse.
1. Underline the simile in each sentence. Circle the person or thing the simile describes.
a Alice felt as light as a feather as she floated down.
b The dormouse snored like a bear.
c The rabbit ran as fast as the wind.
d The Cheshire’s cat was as big as a pumpkin.
e The tea at the Mad Hatter ’s party was like honey.
Homographs are words that are spelled the same but have different meanings and are sometimes even said differently.
For example:
Homograph
Meanings Rose a flower the past tense of ‘rise’

























2. Match the homographs, in the middle column, with both its meanings. a character in the alphabet a device to tell time right moving water on the sea a message written to someone on paper bat something that is correct a flying mammal wave


Capitalisation









Punctuation marks are symbols we use in writing to make the meaning clear and show how to read sentences.
Capitalisation is the use of a big letter (capital letter) at the beginning of a word.




A stick used to hit a ball a direction watch to look at something to move your hand back and forth letter



First word in a sentence. This is a cat.
Names of people, places and specific things. Riya, Sam, India, Taj Mahal
Days of the week and months of the year Monday, January
The word ‘I’ My friend and I will have fun.
Titles of books, movies, and songs
Full Stop (.)
It is used at the end of sentences. For example: Alice had a dream.
Question mark (?)
It is used at the end of a question. For example: Where is the rabbit going?
Exclamation mark (!)
It is used to show strong feelings. For example: Wow! This place is beautiful.
Comma (,)
The Lion King

It is used to list more than one of something in a sentence. For example: I have apples, mangoes, oranges and bananas.
1. Rewrite the sentences using the correct punctuation marks and capital letters.
a Alice saw a white rabbit It was wearing a coat
b ‘I’m late I’m late’ exclaimed the rabbit
c Alice met the caterpillar the march hare the mad hatter and the queen of hearts.
d ‘Wait Where are you going’ Alice asked the rabbit
e The queen of hearts was playing croquet with a flamingo and a hedgehog
We use the simple future tense to talk about an action that will happen in the future (tomorrow, next week, next month, next year).
We add will before the verb to talk about actions that have not happened yet.
For example:
The drink will help me fit through the door.
(Here, the drink is not helping Alice right now, but it will help her later.)
2. Fill in the blanks with simple future forms of verbs.
a I (go) where the rabbit goes.
b Alice (drink) from this bottle.
c A bite from the other side (make) you smaller.
d The Queen (have) some tea.
e You (let) the Queen win.
3. Correct and rewrite the sentences to describe actions that will happen in the future.
a Everyone will enjoys the tea party.
b The flamingo will spoiling Alice’s game.
c Alice will misses a shot.
d Alice will passing through a tiny door.



e The Dormouse will sleeps till tea.


Listen to the text here.
Listen carefully to the text and fill in the blanks with the words in the box.
Hint Box:
a Jack lived with his .
b Jack exchanged the cow for five magic .
c A giant grew outside Jack’s house.
d Jack climbed the beanstalk and saw a .
e Jack took a golden and a that laid golden eggs.
f Jack cut down the beanstalk with an . Practise speaking here.


Sit in a group of four. Perform a role play.
Step 1: Choose a story that your group likes.
Step 2: Decide on a scene from the story that your group likes.
Step 3: Write what each character says (dialogue).
Step 4: Learn your lines and practise together.
Step 5: Enact the scene.



Speak clearly, so everyone can hear you.
You should change your voice to match what you are saying.
Let your group members finish their lines before you speak.

A dialogue is when characters in a story talk to each other. It’s the words they say.
To write a dialogue, we need to remember four things:
1. Speaker Tags: Write the name of the character/speaker.
2. Natural Speech: Write dialogue that sounds like speech and not written language.
3. Characterisation: In brackets, write how the words should be spoken. For example: Queen of Hearts (angrily): Off with her head!
Paul and Amala have found a magic key in their garden. Write the dialogue between them.
Paul: (shouts) Hey Amala, come here. Look what I found.
Amala: (whispers) It looks like a .
Paul: Let’s
Amala: (excited)


Paul: Amala: (nervous)







1. Think about a time when you were upset with someone. What did you do in this situation?
2. Sometimes our actions upset other people and make them angry. Think about a time when that happened. How did you calm that person down?
Discuss in pairs and share your thoughts with your classmates.
Tenali Ramakrishna is loved by everyone in King Krishnadevaraya’s court.
But, one day, King Krishnadevaraya becomes upset with Tenali. What did he do to upset the king? Does Tenali find his way back to the king’s court?
Let us read the story to find out.



Once upon a time in the kingdom of Vijayanagara, there lived a clever and funny poet named Tenali Ramakrishna. King Sri Krishnadevaraya and his courtiers respected him for his smart thinking.
Most people loved Tenali, but there was a chief priest who did not like him at all. He was jealous of Tenali and would look for reasons to belittle Tenali. One day, he hatched a plan to make Tenali Ramakrishna look bad in front of the king. He went to the palace to talk to the king.
Why do you think the chief priest was jealous of Tenali Ramakrishna?
courtiers: people who help and work with a king or queen chief priest: the head of a religious group jealous: being upset because someone else has something that we want but do not have belittle: to make someone feel they are not important hatched a plan: made a plan

Chief Priest: Your Majesty, I have terrible news! Tenali Ramakrishna has been telling everyone that you have a secret collection of pink elephants and you sleep with a garland of flowers around your neck!
King: (angrily) What? How dare he! Bring him to me at once!
Tenali Ramakrishna is brought to the court.
King: (shouting) Never show me your face again, or I will lock you up in prison!
Tenali: (shocked) But, your majesty, what did I…?
King: Enough! I do not want to listen to anything you have to say. You must follow my orders.
Tenali tried to explain, but the king was too angry to listen. Sad and confused, Rama left the court.
Days passed, and the court felt dull without Tenali’s jokes and wisdom. The courtiers missed his clever remarks. One day, as they were discussing something important, they saw someone with a pot on his head sneaking around the palace gardens.
Minister 1: Who is that? Is that Tenali?
Minister 2: Impossible! He would not dare.
They tried to catch this mysterious person, but he was too quick and was
garland: a string of flowers how dare he: an expression of anger at something someone has done dull: boring wisdom: the ability to make good and smart decisions

remarks: things that someone says sneaking: moving quietly so that nobody can see or hear impossible: something that cannot happen mysterious: something strange and unknown which makes one curious
gone before they could reach him. The ministers were left confused and a little amused.
Another day, the king himself saw the person with a pot on his head while taking a walk in the royal gardens.
King: Who is that? Why is there someone with a pot on their head in my garden?
The guards tried hard to catch the man, but they failed every time. They realised the man was really clever.
A few days later, the courtiers found out that the chief priest had lied to the king. They hurried to inform him.
King: ( looking guilty ) What have I done? ( talking to the guards )
Bring Tenali Ramakrishna back at once!
Think and Tell Who do you think this mysterious person could be?
Tenali Rama was a real person who lived several hundred years ago. He did not go to school as a child, but he learnt from a wise teacher who taught him stories and wisdom.
To the king’s surprise, Tenali Rama entered the court with a large pot covering his head. The courtiers giggled.
King: Why have you covered your face with a pot, Rama?
Tenali: (voice echoing from inside the pot) Your majesty, as a loyal citizen of Vijayanagara, it is my duty to follow your orders. You asked me never to show my face, but I could not stay away from my royal duties. So, I used this pot to hide my face from you but still do my work.
amused: feeling entertained and happy because something is funny
hurried: rushed or ran quickly
guilty: feeling bad knowing that one is wrong
echoing: a sound that repeats itself
loyal: being a good friend or member of a group
royal: something to do with a king

King: (laughing) Only you, Tenali, could come up with something so clever! Remove the pot, my friend.
Tenali removed the pot, smiling. The king hugged him warmly.
King: I am sorry I was unfair. I should have listened to you.
Tenali: Your majesty, all is forgiven. After all, it is not every day that I get to see the king make such a grand mistake!
And so, Tenali Ramakrishna was back at court, and the chief priest never tried to trick the king again.

forgiven: not being angry about what someone has done grand: something big that can not be missed
Listen to all the keywords here.


Read and Respond

1. Match the characters and their actions in the story.
Character Action
The chief priest The King
The ministers
Tenali Ramakrishna discussed important matters. wore a pot on his head.
2. Tick () the correct answers.
shouted at Tenali.
lied to the king.
a Who was the clever poet in Vijayanagara?
i The Chief Priest ii Tenali Ramakrishna iii The King
b Why was the chief priest unhappy?
i He was jealous of Tenali.
ii He did not like the king.
iii He wanted to be a poet.
c What did the king order Tenali Ramakrishna to do?
i He asked Tenali Rama to leave the kingdom.
ii He asked him never to show his face again.
iii He told him to write a poem.
d How did Tenali Ramakrishna solve the problem of not showing his face?
i He wore a mask.
ii He covered his head with a pot.
iii He stayed at home.
3. Answer the questions in two to three sentences.
a What did the priest tell the king? How did the king react?
b How did Tenali follow the king’s orders but still do his work?
c Why was the court dull without Tenali?

d Why did people laugh when they saw Tenali with a pot on his head?
e How did the king feel at the beginning of the story? How did he feel when he knew the truth?



1. Retell the story ‘The Pot Face’ in your own words. What did he do? The priest was jealous so he
Next, The king
Then, Tenali
But, The courtiers
Finally, The king
2. Compare Tenali and the priest. Write their actions and what each action tells us about them. You can use some of the words in the box.

Who is a better person, Tanali or the priest?
I say so because


Tenali solves many problems in the kingdom. Do you think there are problems around us that also have to be solved? Think about your home, your community, or your school. Complete the table with a problem and solution.
Problem 1
Problem sentence No street lights.
Where is it happening? My community.
Who does it affect?
What is the solution?

Problem 2
People living in the area.
People who live there should complain to the local authorities.

Pronounce Well Listen to the words here.
We can break words into small parts called syllables. A syllable usually has one vowel (a, e, i, o, u) sound.
(here, ‘ly’ ends with an ‘i’ sound)

Say the words aloud. Write the number of syllables in each word.
Word Number of syllables
Word Number of syllables
man elephant
garland ministers
wisdom garden

Vocabulary

Compound words are words that are formed by combining two simpler words to create a new word with a specific meaning. For example: sun + set = sunset
1. Look at the pictures and write the compound words.





























An anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of another word or phrase. The new word must use each letter only once. For example: listen silent
2. Rearrange the letters to write a new word. The picture will give you a clue.
a post b save c earth e danger d hear

















Words that tell us more about actions (verbs) are called adverbs.
They tell us how the action is being done. We add -ly at the end of a word to make an adverb.
For example:
The courtiers laughed loudly. How did the courtiers laugh? loudly (loudly tells us about the verb ‘laugh’)
The king hugged him warmly. How did the king hug him? warmly (warmly tells us about the verb ‘hug’)
Sometimes, we remove or change the last letter before adding -ly.
• If the word ends with -y, we change it to i and then add -ly.
For example: happy – The children were playing happily.
• If the word ends with -le, we remove -le and add -ly.
For example: horrible – I am horribly dirty.
• The last letter can also double up.
For example: final – He finally came home.
1. Change the underlined words to adverbs.
a Tenali spoke clever.
b He looked at the priest cunning.
c Tenali left the palace sad.
d He thought of an idea quick.
e The king spoke angry.
2. Fill in the blanks with the -ly forms of the word.
a The chief priest behaved (bad).
b The king was treated (royal).
c Tenali moved around (mysterious) in the garden.
d The guards left (immediate).
e (surprising), the king asked Tenali to leave his court.


Listen to the text and fill in the table.
Who are the main characters?
Where does the story take place?
What do the characters try to find?
Listen to the text here.
Do they succeed? How do you know?



Practise speaking here.
In a debate, two or more people talk about a topic. They say if they agree or disagree with a topic and give reasons.
Sit in pairs. Choose one of the topics given below. Discuss with your partner whether you agree or disagree with the topic.
• Maths is the most important subject in school.
• Each student should do at least two kinds of sport.

• Art and music should be given more time in school.

You can use the following sentence starters:
• I agree because...
• Yes, I think that...
• I feel the same way because...
• That’s a good idea because...
• You are right because...

• I disagree because...
• No, I don’t think that...
• I see it differently because...
• I don’t agree because...
• I think you are wrong because...


Don’t interrupt when someone else is speaking. Give reasons why you agree or disagree. It is good to give examples as well.

A paragraph has the following parts:
• Topic Sentence: Here we introduce the main idea of the paragraph.
• Supporting Details: These sentences provide details and examples that support the topic sentence.
• Concluding Sentence: This is the last sentence that gives a final thought or summary.
Model Answer
My Favourite Animal
I think dogs make the best pets.
Dogs are very friendly and loyal. They have soft fur that makes them nice to cuddle. Dogs also have a good sense of smell that helps them find things.
I love dogs because they are playful and fun. Dogs are amazing pets!
Write a paragraph on ‘My Favourite Comedy Show.’
Topic sentence
Supporting details
Concluding lines Topic





In class, share what happened one morning when you were late for school. Give the reason why you were late. Get Set
Imagine a morning where everything seems to go wrong. The poem tells the story of a girl who wakes up late and rushes to school, only to be surprised. What could have happened? Let us read to find out.


Let’s Read

I woke up this morning, I climbed out of bed. I put on my clothes and a hat on my head.
I went to the kitchen to look for some food. I let out a yawn, then I sleepily chewed.
I picked up my books and my lunch and a snack and managed to stuff it all into my pack.
I walked out the front door and wandered to school, and, wow, did I feel like the world’s biggest fool.
The lights were all off and the doors were all locked, and I was embarrassed; a little bit shocked.
I looked at my watch and, indeed, it was eight. But I’d overslept. I was twelve hours late.
How did the girl feel while eating breakfast?

stuff: to push and fit into a small space wandered: walked in a very relaxed way embarrassed: felt shy or ashamed
Think and Tell
Why was the girl embarrassed?
Listen to all the keywords here.


Read and Respond

1. Write True or False.
a The girl put on a hat after getting dressed.
b The girl packed her books, lunch and a snack into her pack.
c The girl felt very confident and happy while walking to school.
d When the girl reached her school, the lights were on and the doors were open.
e The girl looked at her watch and realised she was twelve hours late.
2. Imagine you are the girl in the poem. Complete the sentences with the words from the poem to retell what happened.
I woke up this morning and got out of bed. I put on my and a hat on my head. I went to the to look for some food and yawned. I managed to stuff all my things into my . I left home and wandered to . When I arrived, the were all off and the doors were locked! I must say, I was embarrassed and a little bit shocked. I looked at my and realised it was eight o’clock. I’d and was twelve hours late.
3. Answer the questions in one to two sentences.
a What items did the girl stuff into her pack?
b Use your own words to describe how the girl walked to school.
c Why did the girl feel like ‘the world’s biggest fool’?
d What did she realise after looking at her watch?



Big Idea

Everyone makes silly mistakes from time to time, and it’s okay. It could be something as silly as forgetting to wear the correct uniform or mixing up school days.
Share a funny or silly mistake you made recently. You may use one of the ideas below or think of your own.
1. Have you ever put something in the wrong place and had a difficult time finding it?
2. Can you think of a time when you made a mistake that made everyone laugh?
3. What silly thing have you done that you still remember?
Then in class, discuss how making mistakes is a normal part of life and how everyone learns from them.


1. Read the words from the poem. Match the words that rhyme. bed chewed food shocked locked snack eight head pack late
2. Read the poem. Then, use rhyming words to add your own lines to the poem.
Squeaky the squirrel loved to play, He danced and pranced every day. He wore a hat that was too big, And tried to dance a silly jig.
Squeaky’s hat was so big, . He loved to dance, to move and sway. .
3. Match the words and their meanings. to giggle a statement or story meant to make people laugh a fool a trick played on someone a joke to act in a playful or stupid way be silly to laugh quietly and often uncontrollably a prank a person who acts in a way that will make people laugh



Imagery is when words are used to create pictures in your mind. It helps you imagine what things look like, smell like, sound like, taste like or feel like.

Sit in pairs. Read the poem I Woke Up This Morning to each other. Close your eyes and visualise the poem. Complete the table.




Let’s create a class joke book filled with laughter! Your funny jokes will make everyone smile and brighten up the classroom.
Materials Needed:
• A small notebook or a diary
• Markers, crayons, or coloured pencils
• Stickers, doodles or other kinds of decoration
Steps
• Think of a theme for your jokes. It could be about animals, school, food, or anything that makes you laugh!
• Write three to five jokes for your book. You can think of a guiding question to create a joke or a funny event in your life. For example:
• Q: Why did the student eat his homework?
A: Because the teacher said it was a piece of cake!
• Q: What do you call a bear with no teeth?
A: A gummy bear!
• As a class, divide the roles of who will be compiling all the jokes in the book, who will decorate the joke book, who will design the front and back cover of the book.
• Add drawings, funny pictures, or decorations to your joke book.
• Make a cover page with the title ‘My Joke Book’ and your class.
Keep the joke book on your class’s bookshelf/teacher desk. You may read it to your friends when they are sad or distressed.

You may ask for help from your teachers or elders.

Work on the joke book as a team. You may decide on a date when you will show the book to your teachers.






How would you help people if you found a large amount of treasure? Get Set
Get ready for an exciting adventure with Momotaro, the Peach Boy! This story from Japan is full of magic, bravery, and fun. Let us read and find out what amazing things happen in the story.



A long time ago, there lived an old man and an old woman. One day, the old man went to the mountains to cut grass. The old woman went to the stream to wash clothes. While she was washing, something big came tumbling down the stream. The old woman was very curious. She pulled it out of the water with a piece of bamboo.

When she looked closely, she saw that it was a very large peach. She quickly finished her washing and went home. She planned to share the peach with her husband.
When she cut the peach in half, a child came out of the large seed! The old couple were overjoyed. They named the child Momotaro, which means Little Peach Boy. They took good care of him, and he grew up to be strong and adventurous.

Every summer in Japan, people celebrate the Momotaro festival. Sometimes people also dress up as Momotaro.
tumbling: falling and rolling around curious: wanting to know more about something overjoyed: very happy
Why did the old man and woman name the baby Momotaro?
adventurous: used to describe someone who likes exploring unknown places and trying new things
As Momotaro grew up, he heard many stories about a faraway island where scary giants lived. These giants had stolen many treasures and kept them on their island. Momotaro wanted to help the people who had lost their treasures. He decided to go to the island of the giants, and bring the stolen treasures back home. He talked to his parents about his plan. The parents were surprised, but they were also very proud of Momotaro for wanting to help other people. They made him some dumplings for his journey. Momotaro put the dumplings in his pouch and set out.
When he started his journey, a dog came up to him and asked, ‘Momotaro, what do you have hanging from your belt?’ Momotaro replied, ‘I have some of the best Japanese millet dumplings here.’

‘Give me one, and I will go with you,’ said the dog. So, Momotaro gave the dog a dumpling. Then a monkey came and got a dumpling in the same way. A pheasant also flew by and said, ‘Give me a dumpling too, and I will go with you.’ So, all three animals went along with him. Soon, they arrived at the island of the giants.

In a lot of cultures, dumplings are considered a symbol of wealth and luck because of their shape.
treasures: valuable and special items dumplings: small balls of dough filled with vegetables or meat and steamed
Which three animals did Momotaro meet on his way to the island?
set out: to leave on a journey millet: a type of grain that is used to make porridge and bread


They broke through the front gate, with Momotaro leading and his three friends following. They met many giants who tried to stop them, but Momotaro and his friends fought their way to the chief of the giants, Akandoji. Akandoji was tough but they fought until Momotaro defeated Akandoji. Akandoji agreed to give up all his treasures. After gathering a huge pile of precious things, Momotaro loaded them up and set off for home. He was happy and proud of his success and thanked his three friends.
How would you feel if you had to fight Akandoji? Would you like to be alone or have some friends with you during the fight?
The old man and the old woman were overjoyed when Momotaro returned. They had a big feast. Momataro shared stories of his adventures, and showed everyone the treasures. And so, the Little Peach Boy became a very important and respected man. defeated: beaten by someone precious: very special and valuable
How did Momotaro’s parents feel when he came back? Why?
Listen to all the keywords here.


Read and Respond

1. Fill in the blanks with the correct answers.
Hint Box: pheasant Akandoji peach giants Momotaro
a The old woman found a large in the stream.
b The child who came out of the peach was named .
c Momotaro decided to go to the island of the .
d Momotaro’s three friends were a dog, a monkey, and a .
e The chief of the giants was called .
2. Number the events, 1 to 6, in the order they happened in the story.
a Momotaro fights Akandoji.
b She takes the peach home, and finds a boy inside it.
c Momotaro returns home with the treasures.
d Momotaro sets off to find the treasure.
e An old woman finds a peach in the stream.
f Momotaro meets a dog, a monkey and a pheasant.
3. Answer the questions in one to two sentences.
a What are the places where the events of the story happen?
b How did Momotaro learn about the island of the giants? What did he learn?
c How did Momotaro’s parents feel about his plan to go to the island of the giants?
d Describe the actions that took place on the island of giants.
e How did the family celebrate Momataro’s return?




1. What do the events tell you about the characters? Tick () the correct option.
Event
The old woman pulls the large peach out of the stream.
The giants stole the treasures and kept them on their island.
Momotaro decides to go to the island of the giants to get back the stolen treasures.
What it tells me about the character
This shows that the old woman is .
a hungry
b curious
c kind
This shows that the giants are .
a greedy and terrifying
b kind and powerful
c protective and caring
This shows that Momotaro is .
a lazy and selfish
b brave and selfless
c selfish and courageous
2. Match the events that happened in the story and their effect.
Event Effect
The old woman finds a large peach in the stream.
Momotaro shares his decision to go to the island of giants.
Momotaro gives a millet dumpling each to a dog, a monkey and a pheasant.
Momotaro fights the chief of the giants, Akandoji, and defeats him.
Momotaro brings the stolen treasures home.
Momotaro gets loyal friends and helpers.
The family found a child, and named him Momotaro.
The family is worried, but they support Momotaro’s good cause.


Think of a story that you have read where one of the characters is a giant/a beast. For example: Beauty and the Beast
Complete the table.
Name the story: .
Name the main characters: .
List the things that are similar or different in your story and Momotaro, the Peach Boy. . . . .



When talking about the similarities and differences, you can talk about the place, the problem, and the nature/behaviour of the characters.

Pronounce Well
Listen to the words here.
Read the words aloud. Different spellings of the long ‘I’ sound
pie flies pine ride shy reply high fright
lie cried fine kite why July sigh sight
tie dried nine shine fly cycle fight bright

Fill in the blanks with the correct words. Then, read the sentences aloud.
a Momotaro found a magic .
(clue: it flies in the sky and rhymes with ‘site’)
b Momotaro likes to eat dumplings made of .
(clue: it rhymes with ‘nice’)
c Together, they crossed a river.
(clue: opposite of narrow and rhymes with ‘side’)
d Momotaro and his friends got home at .
(clue: rhymes with ‘sight’)
e Momotaro’s parents were scared that he might .
(clue: an end of line and rhymes with ‘lie’)

Vocabulary

Idioms are phrases that mean something different from what the words actually say. We use them to express ideas in a colourful way.
For example:
Momotaro has the heart of a lion.
Literal meaning
Meaning of the idiom
Momotaro’s heart is the same as a lion’s heart. Momotaro is brave.
1. Match the idioms and their meanings. Then, complete the sentences with the correct idiom. on top of the world something amazing or wonderful out of this world feeling very happy carry the world on very different from each other one’s shoulder the world is your oyster to carry a lot of responsibility worlds apart you can do anything you want
a Momotaro seems to ; he has taken the responsibility to bring back the treasures.
b After winning the battle, Momotaro felt .
c Momotaro’s parents told him that he could be anything he wanted to be! Remember, .
d The treasures on the island of giants were .
e Although Momotaro and the animals were friends, they were in how they looked.
2. In your notebook, write the sentences where the words have been used in the story. Then, write your own sentences using the words.
a overjoyed
c treasures


b adventurous
d defeated
Conjunctions are joining words. We use conjunctions like and, or, but and so to join two sentences. and It is used to join two words or two sentences.
Momotaro was brave and courageous. Momotaro fought the giant and defeated it. or It is used to give a choice. Will Momotaro go in a boat or swim to the island of giants? but It is used to join sentences with opposite meanings.
Momotaro's parents were afraid but they agreed to let him go. so It is used when one thing is the reason for the other.
The old woman wanted to wash the clothes, so she went to the stream.

1. Fill in the blanks with the joining words and/but/so/or.
a The old woman was very curious, she pulled the big peach out of the water.
b She quickly finished her washing went home.
c Momotaro was very strong, he was not arrogant.
d Momotaro wanted to help the people, he went to the island of the giants.
e He could ask the dog monkey to help.
2. Join the sentences using or, and, so or but.
a Momotaro can eat dumplings. Momotaro can eat peaches.
b They met many of the giants’ helpers. They were looking for Akandoji.
c Momotaro fought for the treasures. Momotaro took them home.
d Momotaro gave the dog a dumpling. The dog went with him.
e Akandoji attacked Momotaro with an iron club. Momotaro dodged him.


Listen Well
Listen to the text here.
Listen carefully to the riddles and write the correct answers.


Try to connect the riddle with an object around you.
You may ask the teacher to repeat the riddles and pause between riddles for you to think.


Speak Well
Practise speaking here.
Sit in pairs. Think of a story and narrate it to your partner.



• Remember to include characters, setting, beginning, middle (problem or adventure) and end in your story.
• Narrate your story using gestures.
Speak clearly so that your partner can hear you.
Maintain eye contact when you narrate the story.
Speak slowly and don't rush. Take your time to tell your story.

Write Well
Instructions are a set of steps or directions that tell someone how to do something or how to complete a task.

Model Answer
Materials Needed
• 1 sheet of paper (any colour)
Steps:
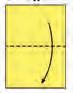
• First, fold the paper in half.
• Then, fold the top corners down to meet the centre fold. This will form a triangle at the top of the paper with a rectangle at the bottom.
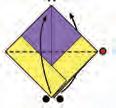
• Next, pull the sides out and press them flat.
• Now, fold the front and back up.
• After that, pull the two sides apart gently to open up the paper.
Topic
Pictures or diagram


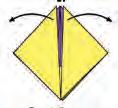
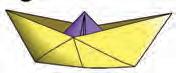
• Next, adjust the folds and shape of the boat to make sure it looks like a boat and has good balance.
• Finally, place your paper boat on the water and watch it float!
Warning: Be careful not to tear the paper.
Tips or Warnings
Write the instructions on ‘How to Make an Ice-cream Sundae’.


You may follow the steps with an adult at home. Take pictures of all the materials and steps to make your instructions visually appealing.
1. Write the correct doing words to complete the sentences about what happens in a camp every morning.
Hint Box: start wake up drink go get
a We all very early.
b One person a fire.
c Someone else to fetch water for coffee.
d The rest of us our things to get ready for the trek.
e We all coffee before we leave.
2. Fill in the doing words to make sentences about what is happening in the jungle right now.
Hint Box: swing read carry fly walk
a The explorers through the jungle.
b They bags on their backs.
c One explorer a map.
d A monkey from the branches.
e The butterflies around.

3. Make sentences in the simple present and in the present continuous tense. Use the verb and the time words given.
a Shine Always: Right now:
b Look Always: Right now:
c Care Always: Right now:
d Feed Always: Right now:
1. Fill in the blanks with the correct phrases to complete the sentences.
scaled back – reduced the amount of something use up – finish the quantity of something throw away – dispose of the rubbish wiped out – destroyed something die out – stop existing
a The flood the entire village.
b People have on the use of fuels.
c We should not reusable items.
d Bengal tigers may .
e I am worried we will the world’s natural resources.
2. Underline the simple past form of verbs in the sentences below.
a The magpie knew the owl.
b The magpie put another layer of mud over the twigs.
c The turtle-dove sang a silly song.
d At last, the magpie heard it.
e She flew away too.

3. Fill in the blanks with the -ed forms of the animal sounds.
Hint Box: neigh quack croak bark roar
a The horses .
b The dogs .
c The frog .
d The lions .
e The duck .
4. Look at the picture. Make sentences to describe it using the given words.

a visited:
b watched:
c walked:
d smelled:
e enjoyed:
1. Rewrite the story using the correct punctuation marks. once upon a time, a tiny dragon named puff met a magical fairy ‘can you help me fly higher’ puff asked. The fairy smiled She gave puff some pixie dust a wand and a cloak. she exclaimed, ‘Now you can soar to the stars’ puff flew up, up, and away He shouted, ‘Thank you, fairy!’
2. Write ‘P’ for sentences that talk about the present and ‘F’ for sentences that talk about the future.
When we talk about something that happens every day or regularly, we use the simple present tense.
a I will tell you a story.
b The knight fights a dragon.
c He will rescue the princess.
d The princess keeps her promise.
e They will live happily ever after.

3. Rewrite the sentences in the simple future tense.
a Reva enters an enchanted forest.
Tomorrow, .
b She meets the King of Hearts. .
c He tells her about the lion’s birthday. .
d They surprise the lion with a party. .
e The elephant and giraffe join in.
1. Fill in the missing words. Adjectives
2. Tick () the correct adverb. Then, rewrite the sentence.
a She writes …
• slowly • bravely
• neatly
b The tortoise moves … • brightly
quickly
slowly
c She fights …
slowly
bravely • neatly

d The sun shines …
• brightly
quietly
slowly
e I read … • brightly
quietly
slowly
3. Fill in the blanks with the -ly form of words in the box.
Hint Box: graceful honest polite tight eager
a We speak to our teachers .
b He does his duties .
c The Queen dances .
d Children wait to see the king.
e He ties the knot .
1. Join the sentences using the words in brackets.
a Do you want to read a fairy tale? Do you want to read an adventure story? (or)
b I would like to read together. It is getting late. (but)
c It ’s getting dark. We can read stories some other time. (so)
d I like adventure stories. I like fairy tales. (and)
e Rohan wants to read an adventure story. I want to read a fairy tale. (but)
2. Tick () the correct option.
a Martial arts started long ago, and people all over the world started practising them.
Martial arts started long ago, but people all over the world started practising them.
b Did kung fu start in China so India? Did kung fu start in China or India?
c She practises kung fu every day but she is strong. She practises kung fu every day, so she is strong.

d Some martial arts use weapons, but others use only hands and feet.
Some martial arts use weapons, or others use only hands and feet.
e Taekwondo comes from Korea or it uses a lot of kicks.
Taekwondo comes from Korea and it uses a lot of kicks.
3. Add in the joining words (and, but, or, so) correctly.
There was a woman who was old very active. She grew her own tea leaves brewed the best tea.
One day a traveller passed by asked, “Do you have coffee tea?” The old woman said, “I only have tea.” He loved the tea she served.
The wise old woman shared her recipe the traveller could teach others to make the wonderful tea.
Name of the Student:
Class: 3
Roll Number:
Section:
Date:
Section – A (Reading and Vocabulary — 20 marks)
Read the story and answer the questions.
Amit and his elder sister, Anaya loved visiting the jungle near their village. One day, while exploring the jungle, they heard a loud noise coming from a cave. Inside they found a tiger cub stuck in a trap! The cub’s mother roared outside, worried and anxious.
Amit and Anaya knew they had to help. They ran to the village to ask for help. A group of villagers came back with them. First, they lured the tigress into a cage. Then, they carefully used a stick to unlock the trap and set the tiger cub free. The relieved tigress nuzzled her cub with love and affection. Just then, the forest ranger arrived and promised to remove all the dangerous traps from the forest to keep the animals safe.
The villagers were delighted to see the tigress and her cub walk away. They patted Amit and Anaya on their backs for their bravery and kindness. The two children were proud. They had saved the baby tiger and helped protect their jungle friends.
1. Match the characters and their actions. (5 marks)
Characters
Actions
The cub used a stick to unlock the trap
Amit and Anaya nuzzled her cub in affection
The villagers ran to get help
The tigress promised to remove dangerous traps
The forest ranger was caught in a trap

2. Answer the following questions in one sentence. (5 marks)
a How did Amit and Anaya know there was something in the cave?
b How did Amit and Anaya help the tiger cub?
c How did the villagers help?
d What did the forest ranger promise to do?
e Why did the villagers pat Amit and Anaya on their backs?
3. Use the suffix in the box to complete the sentences. (2 marks)
Hint Box: -ess -ful -less -ness -ly -ers
a The children showed (kind) by helping the tiger’s cub.
b The forest ranger promised to make the jungle (harm) by removing the traps.
c The villagers were (care) not to hurt the cub.
d The villagers rescued the tiger cub (courageous).
Read the following poem and answer the questions given below.
In the jungle bright and green, Lives a tiger, strong and keen. We must protect and keep them clear From hidden traps, dangers near,
With gentle hands and hearts kind, We help the animals we find. A monkey swings from tree to tree, While birds sing songs so wild and free.
Keep them safe in every way, In the jungle, every day. So let’s be heroes, young and true, And guard the wildlife, me and you!
4. Write True or False. (5 marks)
a The poem is about protecting animals in the zoo.
b A tiger needs protection from hidden traps.
c The poem encourages us to be heroes and save wildlife.
d The birds are scared and are hiding in the trees.
e A monkey swings from tree to tree.
5. Answer the questions in one sentence. (3 marks)
a According to the poem, how should we help animals?
b Why does the poet use the word ‘heroes’ for the children?
c What is the main message of the poem?
Section – B (Grammar — 8 marks)
6. Rewrite the sentence with the past tense form of the underlined verbs. (3 marks)
a The cat jumps over the fence. .

b The dog runs in the park.
c The tiger roars for help.
7. Rewrite the simple present sentence to present continuous tense. (3 marks)
a Nisha goes to the animal shelter every day. Right now, .
b Naman bathes his pet and brushes his teeth. At the moment, .
c Mother treats the injured animal. Look, .
8. Underline the verbs that show that the actions will happen in the future. (2 marks)
a The cat will play with a toy.
b Bruno will bark as the postman comes closer.
c We will visit the zoo next weekend.
d The parrot will fly to the top of the cage.
9. Complete the conversation between Riya and Arjun. (4 marks)
Riya: Hey Arjun, did you know that many animals are in danger because of ?
I think we can . (reason for danger) (action to help)
Arjun: Yes, I heard about that. We should do something to help them.
Riya: We can start by and telling others about it. Every little bit helps!
(activity) (additional action)
Arjun: Great idea! I’ll also and encourage my friends to join us.
10. Write an invitation to your classmates asking them to join you in taking care of the animals at the local animal shelter. (8 marks)
Hint Box:
Include the name of the event, date, time, place and other details like what they could bring with them for the animals at the shelter.
Date: Time: Where: We will . (draw here) (Event name)

Name of the Student:
Class: 3
Roll Number:
Section:
Date:
Section – A (Reading and Vocabulary — 20 marks)
Read the story and answer the questions.
Bala and the Magical Lantern
In the enchanted village of Shanti, Bala found an old map in her grandmother’s attic. It led to a hidden cave deep in the forest. Eager for adventure, Bala followed the map, crossing a shaky bridge and walking through thorny bushes. Finally, she reached the cave, but it was guarded by a mischievous witch.
The witch challenged her with a riddle: ‘What flies without wings and can be lost or found?’ Bala thought carefully and answered, ‘A dream!’ The witch was impressed and let her enter the cave.
Inside, Bala discovered a magical lantern that could grant wishes. She wished for peace and happiness for her family and her village. The lantern glowed, and soon her village was filled with joy.
Bala returned home as a hero, and the villagers celebrated her bravery. From that day on, Bala was known as the ‘girl who brought peace to Shanti’.
1. Answer the following questions. (4 marks)
a Where did Bala find the mysterious map?
b What riddle did the witch ask Bala?
c What did Bala discover in the cave?
d What was Bala’s wish?
2. Rewrite one main event that happened at the beginning, middle and end of the story. (3 marks)
a Beginning .
b Middle .
c End .
3. Fill in the blanks with the correct word from the text. (3 marks)
a The journey through the forest was not easy because Bala had to cross a bridge and walk through bushes.
b We know that the lantern granted Bala’s wish because it started .
4. Write the opposite of the underlined words from the story. (2 marks)
a Bala lost an old map.
Opposite:
b The cave was guarded by the well-behaved witch.
Opposite:
Read the poem and answer the questions.
A sky ship sails on a cloud so high, With dragon wings in a starry sky. The captain is a friendly cat, Wearing a hat that’s blue and flat.

The moon whispers secrets in a glow, As the ship glides where moonflowers grow. It visit planets made of candy bright, And returns home with the dawn’s first light.
So dream of adventures and magical sights, On the magic sky ship that flies through the night!
5. Answer the questions. (4 marks)
a What kind of a ship sails on clouds, in the poem?
b Who is the captain of the magical sky ship?
c Who whispers a secret?
d Where does the ship go at night?
6. Use the words to form sentences of your own. (4 marks)
a captain:
b dragon:
c planet:
d magic:
Section – B (Grammar — 8 marks)
7. Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the adverbs. (4 mark)
a Bala answered the riddle , (wise) impressing the witch.
b The lantern glowed (gentle) when Bala touched it.
c The villagers cheered (happy) when peace came to the village.
d Bala ran (quick) through the forest to follow the map.
8. Fill in the blanks correctly with the conjunctions ‘and’, ‘but’, ‘so’, and ‘because’. (4 marks)
a The prince was brave, he was afraid of the dark forest.
b The fairy waved her wand, a rainbow appeared in the sky.
c The knight wanted to save the kingdom he set out on his quest.
d The dragon was fierce, it was also kind to those who respected it.
Section – C (Writing — 12 marks)
9. Think of a story idea. Fill in the following information in the blanks. (12 marks)
Setting:
Characters:
Beginning (how the story starts):
Middle (a problem or an adventure):

End (how the problem is solved or what happens in the end):
Finally, write the story below.























































Mohit’s class is playing a ‘shape hunt’ game in the classroom. The teacher asks the students to find objects that have the same shape and raise their hands to answer.
Mohit: I can see rectangles on the noticeboard and in my notebook.
Teacher: Very good, Mohit!
Sujata looks out of the window and says, “I see circles in the sun and the wall clock.”
Teacher: Excellent, Sujata!
The students continue discussing objects with similar shapes.
There are four basic shapes that we can see in objects around us—square, circle, triangle and rectangle.
Basic shapes are also called 2-dimensional or 2-D shapes. They are flat and have no height. So, a 2-D shape has only length and width, or breadth. There are 2 more features of 2-D shapes—sides and corners.
Sides: The line segments that form the shape are called sides.
Corners: A corner is a point where two sides meet.
Let us check the number of sides and corners in the 4 basic 2-D shapes.
Corners = 4; Sides = 4 Corners = 4; Sides = 4 Corners = 3; Sides = 3 Corners = 0; Sides = 0 Opposite sides are equal. All sides are equal. Sides may or may not be equal. Round in shape.
Let us learn about another feature of a circle.
The distance between the centre and the edge of the circle is always the same.
This is called the radius of the circle.
We can draw 2-D shapes on dot paper by joining the dots. Let us see how.
Think and Tell
How many sides and corners does this shape have? Are the sides in the shape straight?

Example 1: Look at the picture. Count the shapes and fill in the table.
Example 2: Write True or False.
a A rectangle has 4 sides and 4 corners.
b Only the opposite sides are equal in a square.
c Any circle has a centre. True False True

















What is the shape of these objects?

Colour the squares red, circles orange, rectangles pink and triangles brown, in the given picture.
Count and write the number of shapes in the figure.
Write True or False.
a A triangle has 3 curved sides.
b The opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length.
c An oval has 0 sides and 0 corners.
d The 4 sides of a square are straight sides.
Create a figure using these shapes. You can use them any number of times.
Symmetry and Maps
Mohit and Sujata enjoyed learning about 2-D shapes in their maths classroom. The art teacher gives them square sheets of paper.
Teacher: Fold the paper in half. Then, open it and draw dotted lines on the fold.
Sujata: Mohit, look! I got two similar rectangles when I drew a line on the fold.
Mohit: But I got two equal triangles! How does this happen?
Let us help Sujata and Mohit understand this!
Symmetry
The two same rectangles or triangles are because of symmetry in a square! A shape is symmetrical if it can be divided in such a way that the two halves are exact copies of each other.
Many figures and shapes around us show symmetry. They are called symmetrical. Look at these examples:

A line that divides the shape into equal halves is called the line of symmetry. It can be a standing, sleeping or slanting line. Let us look at the line of symmetry in 2-D shapes.

Standing lines of symmetry:
Sleeping lines of symmetry: Slanting lines of symmetry:
Some shapes can have more than one line of symmetry. For example, a square can be divided into equal halves by standing, sleeping or two slanting lines. It has 4 lines of symmetry.
Similarly, a rectangle has 2 lines of symmetry. It has a standing and a sleeping line of symmetry.
In a circle, the number of lines of symmetry cannot be counted. It has infinite lines of symmetry.
Example 3: Which of these shapes do not show symmetry along the dotted line?
The jug does not show symmetry along the dotted line. The leaf, smiley face and butterfly show symmetry. So they are symmetrical.
Look at the girl standing in front of the mirror. What do you notice?
The girl can see her mirror image.
Look at some more examples of mirror images.








The line between the object and its mirror image is called the mirror line.
Example 4: Draw the mirror image of the given grid.
A mirror image is reversed and is the same distance away from the mirror line as the object is.
1 2
Sujata�s family plans to visit her grandparent�s village. They want to find out the places they can visit. Father suggests they use a map of the village. A map is a drawing that shows an area. It shows large areas on a small sheet of paper. It helps us to locate a place and find the route to go there. For example, from the park the pond is two steps up and 1 step to the left.







Example 5:
1 Use the above map to fill in the blanks with left, right, up and down.
a To reach the fire station from the shop, take two steps left.
b To reach the fair from the school, take two steps up.

2 Write a route from the pond to the shop. Take one step up and 3 steps left to reach the shop from the pond.

















Which of these shapes show symmetry along the dotted line?
Draw a line of symmetry on these figures.
Draw the mirror image of these figures along the mirror line.
Colour the other grid such that it is the mirror image of the coloured grid given.
Use the map showing Sujata�s grandparents� village. Answer the questions.
c Write a way to the park from the fire station such that the hospital doesn't come in between. 5
a Go 4 steps up from the house and then 1 step to left then you will reach the .
b Go 2 steps up and 2 steps right from the school and you will reach the .
Colour the grid in yellow and blue such that one side is the mirror image of the other.
In the evening, Mohit went to the park with his father and sister Tina. They saw an ice-cream cart and asked their father to buy them an ice cream each.
Mohit: I want this triangular one, with three circles on the top.
Tina: I don’t want ice cream. I want a can of juice.
Mohit saw the shape of his sister’s can. He wondered what he should call this shape. Let us help Mohit learn more about shapes!
Look at the shapes of different objects given below. These everyday objects have the following shapes—cube, cuboid, cylinder, cone and sphere. These shapes are called solid shapes or 3-D shapes.







We can measure the length, width and height of a 3-D shape.
Each 3-D shape has faces, edges and corners.
• The surface of a 3-D shape is its face. The face can be flat or curved.
• Two faces meet at an edge. The edge can also be straight or curved.
• Two or more edges meet at a corner.
corner plane faces
edge
face
curved edge
curved face
curved edge
Let us look at the number of sides, corners and edges in each solid shape.
6 plane faces
12 straight edges
8 corners
6 plane faces
12 straight edges
8 corners
2 plane faces and 1 curved face
2 curved edges
No corners
1 plane face and 1 curved face
1 curved edge
1 corner or vertex
We can use toothpicks and clay to make a 3-D shape, such that toothpicks become the edges and balls of clay become the corners of it.
1 curved face
No edges
No corners

We can use everyday objects like cans, matchboxes and cardboard boxes to trace 3-D shapes. Tracing 3-D shapes will give us flat shapes or 2-D shapes.
Example 6: Name the 3-D shape of the given objects. Also, name the 2-D shape you get on tracing them.
1 Speaker 2 Cap 3 Box

2-D Shape Circle Circle Square
















Name the solid shapes of the objects.
a b c d

Match the descriptions with the solid shapes.
a 6 plane rectangular faces Cube
b Only 1 curved face Cone
c 1 plane and 1 curved face Cylinder
d 6 plane square faces Cuboid
e 2 plane faces and 1 curved face Sphere
Ramya made 3-D shapes using toothpicks and clay. She used 8 clay balls and 12 toothpicks of the same size. Which 3-D shape did she make? Find out by drawing the shape in your notebooks.
Name 3 solid objects that, when traced, give rectangles. Trace one of them.
Every night, after dinner, Mohit sits down with his sister Tina to draw. Today, they are drawing a cup-and-plate set.
Tina’s drawing looks like this: Mohit’s drawing looks like this:

Why do these drawings of the same thing look different?
Tina looked at the cup-and-plate set from the top. Mohit looked at the cup-and-plate set from the side. This is why their drawings look different.
3-D objects look different when we view them from the top, sides or front. Let us look at some more examples:
The top and side view of an umbrella and the front and side view of a scooter can be given as:
Now, let us use paper folding to make some 3-D shapes. The 2-D shapes that can be folded to make 3-D shapes are called nets.
Net of a Cylinder Net of a Cone Net of a Cube Net of a Cuboid
Example 7: Ritik is riding a bicycle. Which pictures show him from the sides?
Pictures A, C and E show Ritik from the sides. Picture B shows him from the front. Picture D shows the back view.

















Which view shows these objects from the side?


Draw the front and side views of these objects.



Look at the pictures. Draw the top view of these objects.



























Draw your maths textbook from the top and any one side. What shapes do you get in each drawing? Draw the net of the 3-D shape that the textbook looks like.





















Sujata’s mother got a new saree.
Sujata: Maa, your saree is beautiful! Oh, the border has red and yellow rectangles one after another.
Mother: Yes, Sujata! It is a pattern!
Sujata: A pattern? On a saree border?

The shapes that repeat one after another make patterns. Patterns can be seen everywhere around us. Some examples of patterns in our day-to-day lives are given below.



Patterns follow a rule. Let us look at a few patterns to understand some rules.
Patterns repeat a unit. A repeating unit could be one or many lines, shapes, colours, numbers, letters, or objects.
repeating unit
Here, the shapes that are being repeated are squares and triangles.
repeating unit
Here, the colours of the balls are repeated as yellow, red and green.
The unit changes direction with each next step in a rotating pattern.
In this pattern, the arrow changes direction clockwise as up, right, down, left and up.
In this pattern, the rectangle is rotated with each step as up, right, up and right.
One or many lines, shapes, colours, numbers, letters or objects are added to every next unit to grow the pattern. Thus, the pattern increases in number or size.
In this pattern, 1 triangle and 1 star are added to the next unit.
In this pattern, 1 triangle is added to the next unit.
These patterns are made of numbers. They also follow the same rule of repeating a unit.
Sometimes, the unit of the pattern has a pattern within itself. The pattern is made of a combination of patterns.

Do not add random parts to the pattern. It can disrupt the overall flow of the pattern. Error Alert!
Secret Message
A secret message is a fun way of writing a message using patterns. Let us try to read a secret message: 5H5O5W 5A5R5E 5Y5O5U5?
Here, the number 5 is repeated after each letter of the alphabet. Highlight the alphabet letters and see the message: 5H5O5W 5A5R5E 5Y5O5U5?
The message is: HOW ARE YOU?
Tiling Patterns
Have you ever noticed how the tiles are arranged on a footpath?
When a floor or wall is completely covered with tiles that are arranged without any gap in between, it is called tiling. It follows a pattern too!
Let us have a look at these tiling patterns:

Hawa Mahal in Jaipur has a huge number of patterns in it. The jharokhas (windows) of the palace display a honeycomb-like pattern.

Example 8: What would be the next two units in the pattern? Label the repeating unit.
Example 9: Which of these shapes can be used in tiling patterns? Both the shapes can be used in tiling patterns, as shown here:

















Underline the repeating units in the pattern. a b
c d
Colour the units to complete the pattern.
Extend the pattern by drawing the next 3 figures.
e 28, 32, 36, 40, , ,
95, 85, 75, 65, , ,


Create a Figure with Shapes!
Materials Required: 1 tangram set of shape cutouts.
Prepare Material: You may do it at home or in class. Take a white square sheet of paper. Draw the shapes on it, as shown in the picture here. You may colour each shape as shown. Then cut along the lines to get 1 set of shapes.
What to Do?
• In class, with your partner, point to any one figure made with tangramshaped cutouts.
• Remember the figure and the placement of the shapes. Arrange the shapes to create the figure in 5 minutes. The pair that makes the figures first, wins the round.
• Continue playing the game till you have created all the figures.

Integration
Integration
1 a Write the number of shapes in the given figure.
b Colour the squares pink, circles red, triangles green and rectangles blue.
Square = Rectangle = Triangle = Circle =
2 Draw one line of symmetry on each figure. a b c d
3 Name the 3-D shape of the given objects.





4 Draw a net of the cardboard boxes used for packing cake.
5 Draw a mirror image of the given picture.
6 Complete the patterns.
7 Complete the number patterns.
a 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, , ,
c 32, 37, 42, 47, , ,
8 Colour to complete the tiling patterns.
a
b 48, 56, 64, 72, , ,
d 29, 32, 35, 38, , ,
9 Draw and write the shape of a table when seen from the side and the top.

10 a Make a tiling pattern of your own choice by colouring the shapes.
b Draw another tiling pattern using triangles, rectangles and squares. Colour it.

Anaya places 3 cubes next to each other in different ways. In how many ways can she do it? What possible shapes will she get by joining 3 cubes?
How many different triangles can be made using the dots on this circle?




Sara and her friends are planning a swim party at her place after the football match. Sara draws a map to explain the path. Read the map to answer following questions.








1 Which place does the �+� sign show?
2 Circle the picture on the map that shows the football ground.
3 Which place does the (H) sign show?
a Hospital b Hotel
c Guesthouse

d Sara�s house
4 Find the way from the football ground to Sara�s house.
5 Which view (top/front/side) is given for the parking area?

























































John wanted to buy a string of lights to decorate his house. He went to a light shop for it.
Sure! Here are some strings. I want a string of lights, please.

The shopkeeper showed him different lengths of string. John picked the suitable length of string and went home.
We saw that the shopkeeper showed different lengths of string lights. Length refers to how long or tall an object is from one end to another. It is also the distance between two places. The length of objects and the distance between places are measured using standard units.
We can use different units based on the type of length to be measured.
Type of lengths Units
Short length Centimetres cm Nail, safety pin
Long length Metres m Cloth, wire
Examples



Short distance Metres m
Long distance Kilometres km
Height Centimetres, Metres cm, m
Distance from bedroom to kitchen
Distance from home to hospital
Height of a tower
To identify the correct unit when measuring length, first identify the type of length and then choose the unit to be used.
A ruler is a tool used to measure the length of small objects.
A ruler with short and long lines on it is shown below. The longer lines that have a number written on them are centimetre lines. The distance between two centimetre lines is 1 centimetre.
1 cm
Short line
Long line
Burj Khalifa is the tallest building in the world. Its height is 828 m.
To measure an object using a ruler, place the ruler against the object. Make sure that one end of the object is at 0 cm.
Remember!

Another name for a ruler is a ‘scale’.
Let us measure the length of a crayon!












This crayon is 6 cm long.


We have learnt that metre and centimetre are two units of length. Did you know there is a relationship between centimetres and metres?
1 metre = 100 centimetres
Do you remember John who wanted to buy a string of lights? John asked for a 2 m long string but the shopkeeper is used to measuring the string in centimetres. Let us help the shopkeeper to convert m into cm.
We know that, 1 m = 100 cm.
2 m = 2 × 100 = 200 cm
Therefore, the shopkeeper will give John a string of 200 cm.
What if John wanted a 2 m 50 cm string?
We have already found that 2 m = 200 cm
2 m 50 cm = 200 cm + 50 cm = 250 cm
We can also convert cm to m.
Let us convert 300 cm into m.
300 cm = 100 cm + 100 cm + 100 cm = 1 m + 1 m + 1 m (as 1 m = 100 cm) = 3 m
Therefore, 300 cm = 3 m.
Example 1: Convert:
1 8 m to cm
1 m = 100 cm
8 m = 8 × 100 cm = 800 cm

Do not forget to add the length given in cm after converting m to cm.
3 m 45 cm = 3 × 100 cm = 300 cm 3 m 45 cm = 3 × 100 + 45 cm = 300 cm + 45 cm = 345 cm
Remember!

The unit ‘metre’ is longer than the unit ‘centimetre’. The unit km is the longest.
2 400 cm to m.
100 cm = 1 m
Then, 400 cm = 100 cm + 100 cm + 100 cm + 100 cm
= 1 m + 1 m + 1 m + 1 m = 4 m

The next day, John went to buy two ropes. He wanted one rope of length 38 cm and another of 52 cm. Let us find the total length of rope that John bought.

Length of the first rope = 38 cm
Length of the second rope = 52 cm
As we need to find the total length, we will add the lengths given.
38 cm + 52 cm = 90 cm
Therefore, the total length of the two ropes is 90 cm.
Example 2: Chintu’s height is 125 cm, and Neelu’s height is 132 cm. How much taller is Neelu than Chintu?
Chintu’s height = 125 cm
Neelu’s height = 132 cm
To find out how much taller Neelu is than Chintu, subtract Chintu’s height from Neelu’s height.
132 cm – 125 cm = 7 cm
Therefore, Neelu is 7 cm taller than Chintu.

















1 Write the suitable unit to measure the following.
a The distance between two cities b A pipe




















































c A phone








d The length of hands of a person
2 Measure and write the length of the following objects.


3 Convert the following into cm.
a 6 m b 8 m




c 9 m 9 cm d 4 m 15 cm
e 7 m 26 cm f 2 m 52 cm
4 Convert the following into m.
a 700 cm b 600 cm
c 400 cm
e 500 cm
800 cm
900 cm
5 A mobile tower is communication equipment installed to support better phone networks. A mobile tower with a height of 14 m is mounted on top of a building which is 22 m high. What is the total height of the tower from the ground?
6 The length of a monitor lizard is about 2 m, and the length of a python is about 6 m. Which is longer and by how much in cm?
Naveen went to the doctor's clinic as he wasn't feeling well. The doctor asked him to step on a weighing scale. Naveen saw the numbers move on the weighing scale. Dr Smith wrote down the measurement.

Weight is the measurement of the heaviness of an object.
We saw that Dr Singh used a weighing scale to measure Naveen’s weight. Can a fruit vendor use the same weighing scale to weigh fruit?
No! The weighing scale for measuring human weight is different from the weighing machine used for fruit and vegetables.
Different types of weighing machines are shown below.
The weight of an elephant is around 3500 kg.
Weighing machine to measure body weight
We have learnt that we measure the weight of an object in grams or kilograms.
Grams to measure lighter weights
Kilograms to measure heavier weights
Some of the common weights used with weighing scales are:

There are some items which can be measured both in grams and kilograms, like a packet of sugar!
The relationship between grams and kilograms can be given as:
1 kilogram = 1000 grams
Let us find out how many grams are there in 2 kg.
We know that, 1 kg = 1000 g.
Therefore, 2 kg = 2 × 1000 g = 2000 g
Alert!
Multiply the kg by 1000 to convert it into g.

5 kg = 5 × 100 g = 500 g 5 kg = 5 × 1000 g = 5000 g
Example 3: Uma has luggage weighing 7 kilograms and 300 grams. How many grams of weight does she have?
Weight of Uma’s luggage = 7 kg and 300 g
We know that, 1 kg = 1000 g.
7 kg = 7 × 1000 g = 7000 g
7 kg 300 gm = 7000 g + 300 g = 7300 g
Therefore, the total weight of Uma’s luggage is 7300 g.
Do you remember Naveen who went to the doctor? The doctor found his weight to be 25 kg. The doctor saw that Naveen’s weight was 23 kg at the last visit. Let us find the increase in Naveen’s weight.
Naveen’s current weight = 25 kg
Naveen’s previous weight = 23 kg
Increase in weight = current weight – previous weight = 25 kg – 23 kg = 2 kg
Therefore, Naveen’s weight has increased by 2 kg.
















Do It Yourself 9B

1 Write the correct unit to measure the weight of the given objects.

2 Convert kg into g.
a 8 kg b 9 kg c 1 kg 500 g
d 4 kg 200 g e 3 kg 300 g f 7 kg 750 g
3 Farah has a pet cat which weighs 3 kg and 600 g. How much does the pet weight in grams?
4 A wholesale vegetable market is called a sabzi mandi in Hindi. Shalu went to the sabzi mandi and bought 4 kg of vegetables and 5 kg of fruit. How much more fruit did she buy than vegetables?
5 The weight of a watermelon is 5 kg. Seema cuts it into two pieces. The weight of one of the pieces is 2 kg. What is the weight of the other piece?

6 A scrap dealer is a person who buys scrap (old newspaper, plastics, etc.) materials at a very low cost. Rohit sold 4 kg and 200 g of newspapers and 700 g of magazines to the scrap dealer. Find the total weight of articles sold.
Asha’s family and friends are going on a picnic. Asha is helping her mom to make orange juice.
Asha: How much juice should we take with us, Mom?
Mom: There will be 8 members at the picnic. 2 bottles of juice will be sufficient.
Asha pours the juice into the bottles and puts them inside the basket.
In the case of liquids like water, milk and juice, we need to find the capacity. Capacity is defined as the maximum quantity a container can hold when it is full.
Given below are some containers with different capacities.
As different containers have different capacities, we use different standard units to measure the capacity. Millilitre (mL) and litre (L) are the units used for measuring capacity.
Millilitre to measure small capacities
Litre to measure large capacities
Water bottles, cans and jars are usually measured in litres.
Measuring cups, syringes and measuring spoons are measured in mL.
Let us now understand how the units of capacity are related to each other.
1 litre = 1000 mL
Asha’s mom made a 2 L jug of juice for the picnic. Let us find out the capacity of the jug in mL.
We know that, 1 L = 1000 mL.
Then, 2 L = 2 × 1000 mL = 2000 mL
What if they need 4 L 250 mL of juice?
Then, 4 L = 4 × 1000 mL = 4000 mL
4 L 250 mL = 4000 mL + 250 mL = 4250 mL
So, the quantity of juice in mL is 4250 mL.
Is 2 L of juice sufficient for a group of 30 people?
Asha had 2 L of orange juice. Her mother made 5 L of mango juice. Let us find out the total amount of juice that Asha was taking to the picnic.
Amount of orange juice = 2 L
Amount of mango juice = 5 L
Total amount of juice = 2 L + 5 L = 7 L
Therefore, the total amount of juice is 7 L.

Example 4: Rima opened a 900 mL bottle of milk. She filled a 250 mL glass with it. How much milk is left in the bottle?
Total amount of milk in the bottle = 900 mL
Amount of milk filled in the glass = 250 mL
Amount of milk left in the bottle = 900 mL – 250 mL = 650 mL

















Circle the items that are measured in mL.
Items
a Cough syrup
b Syringe
c Tub of water
d Bucket of water
e Hand sanitizer
2 Convert the following into mL.
a 2 L
d 4 L 500 mL
b 6 L
e 9 L 200 mL
f Barrel of water
c 9 L
f 5 L 850 mL
3 Lemonade is a drink made with lemon, water and sugar. It is an easy way to get a dose of Vitamin C. Rohan wants to make lemonade for his friends. He needs 3 litres of water for the recipe. How many millilitres of water does he need?
4 Taking care of plants by watering them is a good habit. Mohan filled a 500 mL water bottle three times to water his plants. How much water did he use in total?
5 Raju poured 4 L of water into a jug and then transferred 750 mL of the water into a glass. How much water is left in the jug?
6 Mohit bought a car with a fuel tank of capacity 38 L, while Soham bought a car with a fuel tank of capacity 45 L. What is the total capacity of both tanks?
Setting: In groups of 5

Materials Required: Measuring tape
Method:


1 Do this activity on your school playground.
2 One child from the group will guess the length to which he/she can jump.
3 He/she will then take three tries to jump.
4 Select the best jump and measure it using measuring tape.
5 Write it down in a notebook.

6 All the members of the group will repeat the same activity.
7 Add the lengths of the jumps of the whole group.
8 Compare it with other groups. The group with the highest total will win. Collaboration & Experiential Learning


1 Circle the object whose capacity is measured in litres (L).
a Tank of water b Spoonful of oil c Cough syrup
d A jug of lemonade e Petrol tank f Glass of juice
2 Circle the object which is measured in metres (m).
a The length of a spoon b The height of a tree
c The width of a book
d The length of a swimming pool
e The height of a house f The length of a room

3 Circle the object which is measured in kilograms (kg).
a An empty box b A banana c A cylinder
d A lollipop e A bag of flour f Two apples
4 Find the length in cm.
a b c d
5 Convert the lengths into centimetres (cm).
a 5 m
2 m
6 Convert the lengths into metres (m).
a 200 cm
d 1100 cm
300 cm
1200 cm
7 Convert the weight into grams (g).
a 8 kg
d 2 kg 999 g
9 m
1000 cm
1300 cm
9 kg c 7 kg 450 g
3 kg 760 g
8 Change litres (L) into millilitres (mL). a 2 L
7 L
5 L 800 mL
4 L
9 A fully growth goliath frog found in central Africa weighs 3 kg 250 g. How much does the frog weigh in grams?
10 When Ahana brushes her teeth, she leaves the tap running. She uses 5 L 500 mL of water. Sameer only turns on the tap when he rinses his mouth after brushing his teeth. He uses 1 L 200 mL of water. How much water does Sameer save?

1 A ribbon of length 1 metre is cut into 4 equal pieces. How many cuts were made?
2 In Hina�s house there are six trees growing in a line at intervals of 3 metres. Can you tell the distance between the two trees at either end?



Fruit smoothies are a mixture of fruits, milk and sometime nuts. Yash is free, as his school summer break is going on. He helps his father in the kitchen to make fruit smoothies for his family. He uses 225 mL of milk, 2 bananas and 50 g of sugar for a banana smoothie. He also makes a mango smoothie and uses 225 mL of milk, 1 mango, 20 g of sugar, 10 g of nuts and some ice cubes. Read and answer the questions.











2 How much milk does he use in both smoothies?


1 What quantity of nuts does he use in a mango smoothie? a 10 g b 10 mg c 10 kg d 10 m
3 If he has 1 kg of sugar, how much will be left with him after he makes both the smoothies?
4 Do you help your parents with house chores? How?





























































Sonu and Tina are playing during lunchtime. The teacher said, ʻʻKids, lunchtime will be over at 1 o’ clock. After that, we will go to the art class. So, hurry up!ˮ
Tina: I want to play some more! But I do not want to miss the art class either.
Sonu: Let me check the time. It is quarter to 1 now. We have 15 minutes more to play.
Tina: Thanks, Sonu! I wish I could read the clock too!
Remember!

The minute hand is always longer than the hour hand.
To read time, we look at the minute hand and the hour hand. The longer hand is the minute hand, and the shorter hand is the hour hand. We see numbers 1 to 12 on the clock. The face of a clock is called the dial.
Both the hour and the minute hands always move towards increasing numbers. The direction in which they move is called the clockwise direction.
Hour time: The hour hand on the number shows the hour time. When the time is to the hour, the minute hand is on 12, and the hour hand tells us the hour. It is read as o’ clock.
For example, if the hour hand is on 1 and the minute hand is on 12, the time is 1 o’ clock. Notice the change in the hour hand from one clock to the next.
Remember!

It is 0 minutes when the minute hand is on 12. So, the minute hand is always on 12 when it is a full hour.
Minute Time
There are 60 minutes in an hour. When the minute hand moves from one number to another, 5 minutes have passed. We keep adding 5 more minutes as the minute hand keeps moving to the next number. Look at the clocks given.
The term �past� is used when the minute hand is on the right side of the clock face, from 12 up to 6.
The term �to� is used when the minute hand is on the left side of the clock face, from 6 up to 12.
Now look at the time on these 2 clocks.

Think and Tell
How many times does the hour hand point to a number in one day?
5:15 five fifteen 8:55 eight fifty-five
The minute hand has moved 3 places, so, the total number of minutes = 5 + 5 + 5 = 15 minutes.
The hour hand is between 5 and 6. So, the hour hand shows 5. Thus, the time is 5:15.
The first clock shows 15 minutes past 5.
Similarly, the time on the second clock is 8:45 or quarter to 9.
Let us read time by the minutes on the clock. 8:00 8 o’ clock
15 minutes past 8 or quarter past 8
Time as a.m. and p.m.
30 minutes past 8 or half past 8 8:45 15 minutes to 9 or quarter to 9
One day has 24 hours. On the clock, we have numbers only from 1 to 12. When the hour hand of the clock goes around once, it completes 12 hours. In a day, the hour hand goes around the clock twice to complete 24 hours.
A new day begins at 12 o’ clock midnight. From 12 o’ clock midnight until 12 o’ clock noon is a.m.
The next 12 hours, from 12 o’ clock noon until 12 o’ clock midnight, are p.m.
This type of clock displays the time in a digital format using numbers, rather than traditional clock hands. These clocks are found in mobile phones, cars, etc.
Example 1: Every morning, Tara gets on her school bus at 8 o’ clock. What time is it—8:00 a.m. or 8:00 p.m.?

It is a.m. from midnight 12 o’ clock to noon 12 o’ clock. 8 o’ clock in the morning is before noon. So, Tara gets on the bus at 8:00 a.m.
















What do A and B show on the clock?
2 Look at the minute and hour hands. What time is it? a b c d
3 Read the time of Sai’s daily activities. Fill in the blanks with a.m. or p.m.
a Sai wakes up at 7 in the morning.
b He reaches school by 9 in the morning.
c Sai comes back from school at 1 after noon.
d He goes to play with his friends at 6 in the evening.
4 Draw the hour hand and the minute hand to show the time on the given clocks. a 5 minutes past 2 b 40 minutes to 3 c Half past 10 d Quarter past 1
5 The August Kranti Rajdhani Express runs between Delhi and Mumbai at 5:30 p.m. every day. It reaches Mumbai Central the next day at half past 10 in the morning. Write the times in a.m. and p.m.

Tina: Thanks, Sonu! Now I can tell time too!
Sonu: You are welcome, Tina!
Just then the bell rings and their teacher comes over.
Teacher: Remember, the art class is 60 minutes long. Be back on time.
Tina: Sonu, why did the teacher say 60 minutes? I thought the art class was for 1 hour.
Sonu: Tina, one hour is the same as 60 minutes. Let us see how.
Here, we can see that the time now on the clock is 1 o’ clock. When the hour hand reaches 2, the time will be 2 o’ clock, thus 1 hour will have passed.
How many hours do you spend at your school every day? Think and Tell
We know that the hour and minute hands move around the clock. When the hour hand moves from one number to another, the minute hand moves around the clock. When the minute hand moves from one number to another, 5 minutes will have passed.
So, 1 hour = 60 minutes.
Example 2: Write the number of minutes that have passed by looking at the movement of the minute and hour hands.
Time Taken: The minute hand moves from 2 to 3. So, the time taken is 5 minutes. The hour hand remains on 8.
Time Taken: The hour hand takes a complete round. So, the time taken is 1 hour = 60 minutes.
Different activities take different amounts of time. Some activities take less than a minute, such as sneezing, snapping fingers or clapping hands. Some activities take a few minutes and some even take hours to complete. For example:
Brushing teeth Packing the school bag Time in school Stitching a shirt Take minutes Take hours
So, different activities take different times to complete. Guessing which activity will take how much time to complete is called estimating time. By doing this, we can plan our activities and day better.
Example 3: Look at some of Mia’s activities. Which activities will take her minutes, an hour and more than an hour to complete?
Waking up Getting dressed Dance class Sleeping at night Minutes Minutes Hour More than an hour

















Fill in the blanks.
a The minute hand of a clock completes one round in minutes.
b The hour hand of a clock completes one round in hours.
2 How many hours/minutes have passed between the times given? a 3:00 to 4:00 b 4:00 to 7:00 c 11:45 to 12:00 d 3:30 to 5:45

3 Write whether the activity will take minutes or hours to complete.
a Filling a glass of milk b Watering a plant
c Eating a banana d Washing, ironing and folding some clothes
4 A marathon is 26.2 miles long. Eliud Kipchoge also completed a marathon in around 2 hours at the Berlin Marathon on September 25, 2022. In how many minutes did he complete the marathon?
5 The Shatabdi Express is a day train that runs between Delhi and Meerut. Vibu started at 6:45 a.m. from Delhi and reached Meerut at 8:00 a.m. How many minutes did the train take?
Mia’s school has a new rule. Students can wear dresses of their choice every second Friday of the month. Mia is getting ready for school this morning.
Mia: Mummy! I don’t want to wear my uniform today! Can I wear my new dress? I know it is 4th August. Is it the second Friday of the month? Does the rule apply today?
A calendar can help Mia with what she wants to know. A calendar tells us which day of the week, month and year it is today. For example, 4 August 2023 is a Friday. It is the first Friday of the month.
Days of the week
Units of Time on a Calendar
Days of the week, months and a year are the units of time on a calendar.
Days of the Week: A day is the smallest unit of time on a calendar. There are 7 days in a week.
Months and Year: A month is longer than a week. There are 12 months in a year.
Remember the new dress rule in Mia’s school, starting from the second Friday of August. Mia was not sure if she could wear her new dress on 4 August. Let us read a calendar to help her!
The second Friday will be on 11 August. Mia can wear her dress then, but not today!
Reading a calendar is fun! It helps us know the day and dates for special events and count the number of days left before the event. 1st Friday 2nd Friday

Some months have 30 days, while others have 31. February is special, as it has either 28 or 29 days.
A year has 365 days. If February has 29 days, the year is called a leap year. A leap year has one extra day, making it 366 days.

A leap year comes after every 4 years.
The year 2024 was a leap year. It has 29 days in February. In total, there are 366 days in 2024.
We also find dates on a calendar which can be written in different ways. We usually write dates as: date/month/year. For example, in 11/09/2024, 11 is the date, 09 is the month and 2024 is the year. We can also write the date as Date Month Year, which is 11 September 2024.
Example 4: Rehan’s birthday is on 10 July and Muskaan’s birthday is on 15 July. Use the 2024 calendar above to answer.
1 On what days are their birthdays?
Rehan’s birthday is on Wednesday. Muskaan’s birthday is on Monday.
2 How many days will be left to celebrate Muskaan’s birthday after Rehan’s birthday? 5 days

















Match the units of time on a calendar.
a 2024 Day of the week
b January Month
c 26th Year
d Friday Date of the month
2 Write True or False.
a Sunday is a month.
b December is a month.
c May is the first day of the week.
d A leap year has 29 days in February.
3 Read the calendar. Fill in the blanks.
a There are (5/4) Sundays in this month.
b The month starts from (Monday/Tuesday).
c On 25 May, the day is (Tuesday/Thursday).
d 2 May is a Tuesday. The next Tuesday will be on __________ May.














e In this month, Saturdays are on the dates 6, , and .

4 Anand has been practising for a dance performance for two weeks now. How many days has he practised?
5 Look at the May 2034 calendar in Q3 and create a calendar for the month of June 2034. Use colours to decorate it.
6 26 January—Republic Day is a national holiday in India. The Constitution of India was adopted by the Constituent Assembly on 26 November, 1949 but was implemented on 26 January, 1950. How many months did it take to implement the Constitution?
On a timeline, the years, months or days of the events are always written in the order in which they come first.
A timeline helps us to show the journey over the year, in a year or in a month. We mark special years, months, days and dates on a timeline. We can show the special years of our life events on a timeline. Look at the timeline of special school events in Mia’s life.
We can also show the months and dates of special events and festivals on a year timeline. Look at this timeline showing some celebrations and festivals in a year.






Example 5: Birthdays of 4 friends born in the same year are given in the table. Show them on a timeline.
Anu 21 August
Samira 12 April
Danny 10 November
Raj 7 May
12 April
Samira’s birthday

On a timeline, we always mark events in the order in which they come first. So, we will mark birthdays in the order of the months as they come in a year.
7 May Raj’s birthday
21 August Anu’s birthday
10 November Danny’s birthday
A birth certificate gives details of where and when you were born, along with the details about your parents, and it is made after you are born. It also shows if the baby born is a boy or a girl, the place of birth, parents’ names and the registration number. You write dates every day in your notebook. Dates can be seen on many other papers. Let us take a look at this birth certificate: Ria was born on 14 July in the year 2016. These dates can help us to know how much time has passed since she was born.
Example 6: Look at Ria’s birth certificate. Answer the questions.
1 What is Ria’s place of birth?
Ria’s place of birth is New Delhi.
2 How old would Ria would have been on 14 July 2020?
There are four years up to 2020. So, Ria would have been 4 years old on 14 July 2020.
3 In what year will Ria be 15 years old?
Add 15 to the year 2016: 2016 + 15 = 2031. So, Ria will be 15 years old in the year 2031.

How many years old were you last year? In which year would you be 10 years old?

















e are 5 festivals in the month of October and November. The table shows the festivals in a particular year. Draw them on a timeline.
Navratri Starts Diwali Dusshera Bhai Dooj Guru Nanak Jayanti
3 October 1 November 12 October 3 November 27 November
2 The table shows the months in which the school is planning sports events in the year 2024. Draw this sports schedule on a timeline.
Cricket match
February November December October August
3 Read the timeline. Answer the questions.
Rina was born Rina went to school Rina's baby sister was born Rina won a dance competition Rina went to college Rina got a job
a In which year was Rina born?
b How old was Rina when her sister was born?
c How old was she when she won the dance competition?
d How old will Rina be in 2034?
4 Tinu was born on 31 July 2015. His friend Mitu was born on 31 July 2021. Who is older? By how many years?


Preparation at Home: Ask for help from your parents to fill in the birth certificate given on the right side.

Discussion: Exchange your birth certificate with your partner. Look at the birth dates on the certificates. Determine how old your partner is currently or will be this year. This activity will help children to look at dates and understand the concept of a calendar.



Form Number
Government of ____________ BIRTH CERTIFICATE
This is to certify that this information is taken from the original record of birth which is in the register for the year __________
Name:
Sex:
Date of Birth:
Place of Birth:
Name of Father:
Name of Mother:
Date of Registration:
Registration Number: Date: Signature of issuing authority
1 Look at the minute and hour hands. What time is it?
2 Draw a clock to show the times given.
a 10 minutes past 12
b Half past 1 c Quarter to 7
3 How many hours have passed between the times given?
a 5:20 to 7:20
4 Write the time using a.m. or p.m.
a 7:30 in the morning
c 5 minutes to 12 midnight
b 9:15 to 11:15 c 2:10 to 4:10
b 6:15 in the evening
d 5 minutes after 12 midnight
5 Write if the following activities would take less than a minute, some minutes or hours to complete.
a Making tea b Washing a shirt
c Blinking your eyes 5 times d A picnic day

6 Fill in the blanks.
a The date on the last day of the year is always December.
b If today is 30 April 2023, the date tomorrow will be .
c If today is 12 June 2023, yesterday’s date was .
d If today is Monday, 1 June 2023, the date after a week will be .
7 Draw a timeline with the following events in Virat Kohli�s life.
July 2006 April 2011 5 November 1988 March 2008 October 2002
8 Draw a calendar for the month of July. The month starts on a Sunday. Then, answer the questions.
a How many Sundays are there in the month?
b What is the date on the 2nd Saturday?
c Write the dates of all Mondays.
9 Rama woke up at 7 o’ clock in the morning and went to bed at 9 o’ clock that night. Write the time she woke up and went to bed, using a.m. and p.m.
10 Aditi turned 7 years old on 28 August 2007. In which year will she be 14 years old?

1 Today is Monday, 17 April 2023. Arun’s uncle is coming to stay with them after 5 days. On what day and date will Arun’s uncle come?
2 How many times between 3 p.m. and 6 p.m. do the hour hand and the minute hand coincide? Justify your answer.



Priya is travelling to Indore for her cousin�s wedding. She went to the railway station to board a train. Outside the railway station she saw a clock showing 3:00 p.m. Priya knew that there were still 50 minutes for her train to leave. The train was late and finally arrived 50 minutes after the actual departure time. Read the questions and answer them.



1 The train was delayed by minutes.
2 What was the actual time of Priya’s train?
a 3:50 a.m.
c 3:00 p.m.

3 At what time did the train finally arrive?
4 Was the train delayed by an hour?
5 A sweeper cleaned the platform for an hour. How many minutes did he clean the platform for? How do you help in keeping the platforms clean? Cross Curricular & Value


b 3:50 p.m.
d 4:05 p.m.























































Grandfather: Mohit, let us go and buy bread from the shop.
Mohit: Of course, grandfather!
They went to the store. The shopkeeper gave the packet of bread and charged them ₹21.50.
Grandfather made the payment and they both returned home.
We have already learnt about the types of coins, that is rupee coins and paise coins. Let us learn to write the rupees and paise together.
Grandfather paid ₹21.50 for the packet of bread.
₹21.50
Each Indian banknote has its value written in the script of 17 languages.
The number on the left of the dot shows rupees. The number on the right of the dot shows paise.
The dot separates the rupees and paise.
The amount ₹21.50 can be read as “twenty-one rupees fifty paise”.
On the way home, Mohit asked his grandfather to buy a pack of pencils. The shopkeeper said that the pack costs ₹19.05.
Let us see how to read this amount.
rupees
₹19.05 paise
The amount ₹19.05 can be read as nineteen rupees five paise.
Example 1: Write ₹52.50 in words.
rupees
₹52.50 paise
₹52.50 = fifty-two rupees fifty paise.
Remember!

If the paise amount is less than 10, write a 0 after the dot.
Example 2: Write thirty-eight rupees seven paise in figures.
Thirty-eight rupees = ₹38
Seven paise = 07
Thirty-eight rupees seven paise = ₹38.07
Do you remember Mohit and his grandfather, who went to buy the packet of bread? When the shopkeeper asked him to pay ₹21.50, Mohit helped his grandfather to count the notes and coins shown below.




Is the number of notes and coins counted by Mohit correct? Let us find out.
Step 1
Add the rupee notes and coins.
Two ₹10 notes = ₹10 + ₹10 = ₹20
₹20 and one ₹1 coin = ₹20 + ₹1 = ₹21
Step 2
Think and Tell
Is there any other way to make up the amount of ₹21.50?
Write the paise amount separated by a dot, along with the total rupee amount.
₹21 and one 50 paise coin = ₹21.50.
Two ₹10 notes, one ₹1 coin and one 50 paise coin = ₹21.50. The amount taken out by Mohit is correct.

We can convert rupees into paise using some simple steps. Let us convert ₹23.25 into paise.
Step 1
Step 2
Remove the dot and ₹ sign. Write paise with the number.
₹23.25 = 2325 Therefore, ₹23.25 = 2325 paise.
₹15.36 = ₹1536 paise ₹15.36 = 1536 paise Error Alert!
Remove the ₹ sign before writing paise with the number.

Example 3: How will you convert ₹93 into paise?
Here, we see only money in rupees.
Step 1
Step 2
Remove the �₹� sign and Write paise with the number. add 2 zeroes after the number. Therefore, ₹93 = 9300 paise.
₹93 = 9300
Converting Paise into Rupees
We can also convert paise into rupees using some simple steps. Let us convert 5212 paise into rupees.
Step 1
Step 2
Remove the word ‘paise’ and Put the sign of �₹� before the number. put a dot after counting 2 numbers Therefore, 5212 paise = ₹52.12. from the right of the given number.
5212 paise = 52.12 2 places from the right
Example 4: Convert 8400 paise to rupees.
Remove the word ‘paise’ and put a dot after counting 2 numbers from the right of the given number.
8400 paise = 84.00
Put the sign of �₹� before the number.
Therefore, 8400 paise = ₹84.00
₹84.00 can also be written as ₹84.


Do not write paise after the dot.

2356 = ₹23.56 2356 = ₹23.56 paise















Write the amount in words.
Write the amount in numerals.
a fifty-six rupees seventy paise b twenty-nine rupees eighty-eight paise
c thirty-five rupees fifty-seven paise d sixty-eight rupees fifty paise
e seventy-three rupees twenty-two paise f fifteen rupees sixty-six paise
Count the money and write the amount in figures.
Notes and Coins Amount in figures

















Fill in the blanks. a ₹25.36 = paise b 802 paise = ₹ c 2125 paise = ₹ d ₹125.36 = paise e 36125 paise = ₹ f ₹358.80 = paise

The price of petrol in Mumbai as of July 2024 was ₹103.44. Write the amount in words.
Mahi feels bad that she has more money in her gullak than her younger sister Meher. How much money should she transfer from her gullak to Meher's gullak so that they have the same amount of money?
Mahi�s Gullak: One note of ₹50, one note of ₹20, coins of ₹10, ₹5 and ₹5
Meher�s Gullak: Three notes of ₹20 and one coin of ₹10
The next day, Mohit and his grandfather went to the market. They bought a packet of tea for ₹52.50 and a packet of biscuits for ₹40.00. Let us find out how much money they spent in total.
Step 1
Write the information given in the question.
Cost of tea = ₹52.50; Cost of biscuits = ₹40.00.
Step 2
Choose the correct operation.
Remember!

0 after the dot means 0 paise. Therefore, ₹40.00 = ₹40
We need to find the total amount spent; hence we will add the costs.
Step 3
Add the paise amounts. Then, add the rupee amounts. Both amounts have to be added separately.
Therefore, Mohit and his grandfather spent ₹92.50 in total.
Example 5: Neeraj had ₹175.50 with him. He spent ₹53.00 on buying coloured pencils. How much money does Neeraj have left?
Money Neeraj had = ₹175.50
Money spent on coloured pencils = ₹53.00
We need to find the amount Neeraj has left. Hence, we will subtract the given amounts.
Amount left with Neeraj = ₹122.50.

















The price of a lunch box is ₹85.50, but Priya only has ₹72. How much more money does she need, to buy the lunch box?
Vaibhav saved his pocket money to buy a football for ₹50.50. He then shared the idea of saving money with Neeraj who saved ₹75.00. How much money did they save together?
The price of a cricket bat is ₹235.50, and a ball costs ₹45.00. What is the total price of the bat and the ball?
Snake plants and money plants can purify the air and are easy to care for. Divya spent ₹238 on the snake plant and ₹125.50 on the money plant. How much did she spend in total?
John and Maria have ₹284.50 and ₹156.00, respectively. Richa has an amount equal to the difference between the amounts John and Maria have. What amount does Richa have?
John went to the nearby stationery shop to buy some items. He saw that one pencil costs ₹5.00, one eraser costs ₹6.50, one notebook costs ₹15.00 and one sharpener costs ₹12.00. He bought 3 pencils, 1 eraser, 2 notebooks and 1 sharpener.
The shopkeeper gave him a bill.
A bill shows the details of how much we are paying for each item bought from the shop. It also tells us the total amount we have to pay for the items we bought.
Let us learn how to make a bill.
Step 1
Make a table as shown. Write the names of the items bought and the quantity of each item.

Stationery Shop
Amount = Quantity × Rate Cost of each item
Step 2
Find the amount of each item.
Amount = Quantity × Rate per item
Step 3
Find the total by adding the money in the amount column. Remember!
Stationery Shop
If John buys 6 pencils and 1 notebook, will his bill be the same? How? Think and Tell

Quantity = Number of items bought

















Vipin went to a nearby store to buy the following items. What total amount does he need to pay?
Manya went to buy some items from the nearby store. The shopkeeper gave her the following bill. Is the bill correct? If not, prepare the correct bill for her.
Total ₹245.50
Sam purchased the following items from the nearby supermarket:
Two ice creams for ₹20.00 each. Three packets of cookies for ₹15.00 each. One packet of chips for ₹24.50. Two bottles of juice for ₹26.00 each.
Prepare a bill and find the amount paid by Sam.
A supermarket is a self-service shop. It is big and has a variety of products. Ravi, Joe and Tanya went shopping to a supermarket. Look at the items and their prices. Fill in the table.













Ravi buys Joe buys Tanya buys
a 2 bananas for ₹ 1 banana for ₹ 5 bananas for ₹
b 1 teddy for ₹ 1 teddy for ₹ 1 teddy for ₹
c 5 toffees for ₹ 2 toffees for ₹ 4 toffees for ₹
Amount paid = ₹
Setting: In groups of 5.
Amount paid = ₹
Amount paid = ₹
Materials Required: Price tags with various items and their cost in rupees and paise.
Play money in the form of rupees and paise.
Pen and paper.
Method: Display the items along with their price tags.
1 The teams select the items they want to purchase and write the quantity on the paper.
2 The teams find the total amount they need to pay.
3 The teams use the play money for their purchases.
4 The team with the correct amount and money in hand wins!
1 Write the amount in words.
a ₹52.36 b ₹65.14 c ₹71.05
2 Write the amount as numerals.
a thirty-eight rupees sixty-five paise b twenty-nine rupees fifty-five paise
3 Convert the amount given in rupees to paise.
4 Write the amount in rupees.
a 3256 paise b 15236 paise c 52364 paise
5 Match the amounts in rupees and paise. In rupees In paise
a
b
c
d
paise
paise
paise
paise
6 Look at the bills and correct them if you find a mistake.
7 Divya purchased some items from the nearby store. Prepare a bill and find the amount paid by Divya.
Three packets of rice for ₹45.00 each.
Two packets of chips for ₹18.00 each.
One packet of milk for ₹17.50.
8 Baking is a way of cooking by using heat in an oven. Seema is a baker who makes cupcakes. A pack of cupcakes costs her ₹136.50 to make. Each pack uses ₹55 worth of sugar. How much money does she spend on the other ingredients?
9 Reena has to pay school fees of ₹535.50 but she has only ₹425.00 with her. How much more money does she need?
10 Shyam donates some part of his salary to the poor and needy. He donated ₹152.00 at a mall and ₹58.50 to the poor sitting outside a temple. How much money did he donate in all? Have you seen donation boxes in markets or malls?

1 2

Raman made a bill for 5 packets of biscuits, each costing ₹12.00, and 2 cans of juice, each costing ₹35.00. The customer gave him a ₹200 note. How much change will Raman return to the customer?
Who has more money, and by how much?










Ajay had these coins in his pocket. Rahul had these coins in his pocket.



Long before the use of metal coins, people in our country used kauris (sea shells) as money. Sheena and her friends were playing with the kauris to buy things. They decided that 1 paisa = 10 kauris and 1 rupee = 100 paisa. Read the questions and answer them.
1 How many kauris will make one rupee?
a 10
b 100
c 500
d 1000




2 If a toy costs 10 paisa, how much will it cost in kauris?

3 Convert 5 rupees into paisa.
4 If you want to choose something for your own currency (like the rupee and paisa in India), what will that thing be and why?

























































Ravi and Manya are feeling hungry. Mother bakes a pizza for them.
Ravi: Wow! The pizza looks yummy. I can’t wait to eat it.
Manya: Yes, Ravi! Let me cut the pizza into equal parts first. Manya cuts the pizza into equal parts and they both enjoy their meal.
Fraction: Fractions are equal parts of a whole. Let us learn how to divide a whole object into equal parts!
A full or complete object or collection of objects is a whole. Whole means 1.
When a whole is divided into two equal parts, then each part is called half of the whole. It is written as 1 2 , half, or one-half.
A whole pizza half or 1 2
When a whole is divided into three equal parts, then each part is called onethird of the whole. It is written as 1 3 . 1 3

One-fourth
When a whole is divided into four equal parts, then each part is called one-fourth of the whole. It is written as 1 4 .
When a whole is divided into three equal parts, and 2 out of 3 parts are shaded or used, it is called two-thirds or 2 3 .
Three-fourths
Three out of four equal parts is called three fourths. It is written as 3 4 . 3 4
Brahmagupta (598-668 CE), an Indian mathematician, provided rules for fractions in his book ��Brahmasphutasiddhanta.��
Can we divide the given pizza into 5 equal parts? What would each piece be called?
Example 1: What fraction of the shape is shaded?
Total number of equal parts = 4
Number of parts shaded = 1
1 out of 4 equal parts is shaded; hence, 1 4 fraction is shaded.
Example 2: Which shape is not divided into equal parts?
Divided into 2 equal parts
Divided into 4 equal parts
Not divided into equal parts
Divided into 3 equal parts

















1 Write the fraction for the shaded portion in each figure.
a b c
2 Colour each shape to represent the given fraction.
a half or 1 2 b Three-fourths or 3 4 c one-third or 1 3
d one-fourth or 1 4 e two-thirds or 2 3 f Three-fourths or 3 4
3 Match the shaded figures to the fractions they represent. a Half b One-fourth c Three-fourths
4 Shade one-third or 1 3 of each shape.
5 Evaporation is the process by which water turns into water vapour. 4 cups of water was boiled and 2 cups of water evaporated. What fraction of the water turned into water vapour?

We already know that fractions are equal parts of a whole. We also know that:
1
2 means 1 part out of 2 equal parts.
1
3 means 1 part out of 3 equal parts.
1
4 means 1 part out of 4 equal parts.
The above facts can be used to shade or find the fractional part of a collection or group of objects.
Half of a collection of objects:
Let us find and shade 1 2 of a collection of 12 bananas.
Divide the number of bananas into two equal groups, as shown below:
Clearly 1 2 of the collection of 12 bananas = 12 ÷ 2 = 6 bananas in each group.
Shading 1 2 of the collection of bananas can be shown as:
The number of shaded bananas is half of all the bananas, and all the bananas are double the number of shaded bananas.
One-third of a collection of objects:
Let us now find and shade 1 3 of a collection of 12 bananas.
Clearly 1 3 of the collection of 12 bananas = 12 ÷ 3 = 4 bananas in each group.
Shading 1 3 of the collection of bananas can be shown as:
One-fourth of a collection of objects:
Let us now find and shade 1 4 of a collection of 12 bananas.
Clearly 1 4 of the collection of 12 bananas = 12 ÷ 4 = 3 bananas in each group.
Shading 1 4 of the collection of bananas can be shown as:
From the above discussion; we can say that:
• To find 1 2 of a collection, we divide the number of objects by 2.
• To find 1 3 of a collection, we divide the number of objects by 3.
• To find 1 4 of a collection, we divide the number of objects by 4.
Example 3: Colour one-third of the collection of crayons.
Total number of crayons = 15
Collection of crayons we want to colour = 1 3
1 3 of a collection of 15 is 5. Hence 5 crayons can be coloured as:
Example 4: Find.
1 1 2 of 20 apples
– Divide 20 apples into 2 equal parts.
– Count the number of apples in 1 part.
2 1 3 of 24 trees
– Divide 24 trees into 3 equal parts.
– Count the number of trees in 1 part.
10
24 = 8


















Colour to show the given fraction of the collection. 1 Art Integration b 1 2 a 1 2 c 1 3
Write True or False.
a 1 4 of 16 apples is 4 apples. b 1 2 of 10 pears is 2 pears.
c 1 3 of 6 mangoes is 6 mangoes. d 2 3 of 18 grapes is 6 grapes.
a 1 2 of 18 b 1 3 of 9 c 1 3 of 21 d 1 4 of 12
Ramya had 12 plants. She put 1 3 of the plants in her living room. How many plants did she put in her living room? 4 Draw a shape or figure and divide it into parts and shade parts to show any fraction.
We learnt what fractions as parts of a whole look like. Let us now learn how to write a fraction numerically.
a
Remember, we divided the pizza into two, three and four equal parts. We also learnt that:
half = 1 2 ; one-third = 1 3 and one-fourth = 1 4
Let us see how a fraction is written.
(Number of parts chosen)
(Total number of equal parts) Numerator

0 can never be the denominator. This is because we never divide a number by 0.
Let us now learn how to write other fractions.
Find the fraction of the blue parts in the given figure.
Fraction of the blue parts = Number of parts chosen Total number of parts = 5 8
Error Alert!
Always write the total number of parts in the denominator. For instance, the fraction of 2 slices of cake out of 7 slices will be given as:
Example 5: What fraction of the given figure is coloured pink?
Number of parts coloured pink = 7
Total number of parts = 12
The fraction of pink parts = Number of parts coloured pink Total number of parts = 7 12
Example 6: What fraction of the balls are
a Red? b Green?
a Number of red balls = 8
Total number of balls = 11
Fraction of red balls = Number of red balls
Total number of balls = 8 11
b Number of green balls = 3
Total number of balls = 11
Fraction of green balls = Number of green balls
Total number of balls = 3 11


Now, let us learn how to solve word problems on fractions. Manya cut the pizza into 8 equal parts. She ate 3 slices and Ravi ate the remaining 5. What fraction of the pizza was eaten by Manya?
We know that,
Fraction = Number of parts chosen
Total number of parts or Number of objects chosen
Total number of objects
To solve a word problem on fractions:
Step 1: Find the total number of parts / objects chosen. In the above case, number of parts chosen = number of slices eaten by Manya = 3
Step 2: Find the total number of parts / objects.
Here, the total number of slices of pizza = 8
Step 3: Write the given information in the form of fractions.
The fraction of pizza eaten by Manya = Number of slices eaten by Manya Total number of slices = 3 8
Manya ate 3 8 of the pizza.
Example 7: Wasim ordered a pizza. The pizza was divided into 6 slices. If he ate 1 3 of the pizza then how many slices did he eat?







3 of 6 slices = 2
Total number of slices = 6
1 3 of a collection is 1 part out of 3 equal parts. Each equal part has 2 slices.
Slices eaten by Wasim = 1 3 of 6 = 2 slices. Wasim ate 2 slices of the pizza.
About 1 3 of the earth’s surface is covered with land.
Example 8: Ranu bought a packet of bread which had 12 slices. She gave 1 2 of the packet to a street dog. How many slices of bread did she give to the dog?
Total number of slices of bread = 12
Fraction of bread given to the dog = 1 2
12 slices split into 2 equal parts gives 6 slices in each part. (12 ÷ 2 = 6)
So, the number of slices given to the dog = 6 slices.

















1 What fraction of the given figures is shaded?
2 Colour to show the given fraction.
3 Write the fractions for the coloured and uncoloured parts of the collections.
4 Kavya places 17 roses in a beautiful vase. It holds 8 red roses and 9 pink roses. What fraction of the roses are red?
5 The students of Class 3 collected 24 waste bottles for a recycling project. One-half of the bottles were plastic. How many bottles were plastic?

6 Vishal has 12 shirts. 1 4 of his shirts are blue. How many shirts are blue?
7 There are 25 building blocks in a bag. Ravi uses 16 blocks to build a house. What fraction of the building blocks remain unused?
8 Rani has 27 books. She donates 1 3 of the books. How many books does Rani have left? Do you donate your old books?
Math Lab
Let’s Find the Fraction! Collaboration & Experiential Learning
Setting: In groups of 2.
Materials Required: A small bag, 30 marbles of two colours, paper and pen.
Method:
1 Put the marbles into the bag and give it a good shake.
2 Each student in the group takes a handful of marbles.
3 They record the fraction of each colour on the paper.
4 The student who writes the fractions first is the winner!
1 Write the fractions.
a Half = b One-third =
c Three-fourths = d Numerator: 5; Denominator: 8 =
e One-fourth = f Numerator: 7; Denominator: 12 =
2 Write the fraction of the given collections.
Green capsicums = Yellow capsicums = Pink stars = Blue stars =
3 Colour as per the fractions given.
b
of the kites
d 4 Solve. a 1 2 of 12 b 1 3 of 15
3 of the balls
1 4 of 4 d 1 2 of 8
5 Tim has a cake. He wants to share it equally among him and his 4 friends. If the cake is divided into 5 equal parts, what fraction of the cake does each friend get? Do you share things with your friends?
6 Meena bought 9 flowers from the market, of which 1 3 were tulips. How many of the flowers were tulips?

7 Manya planted 6 plants in her garden, of which 2 were rose plants. What fraction of the plants were rose plants?
8 There are 24 apples in a basket. If 1 4 of the apples are rotten, how many apples are still good?
9 Raj wanted to celebrate his housekeeper's birthday. He sent invitations to 18 friends for the birthday party, but 3 of them were unable to attend. What fraction of the friends attended the party?
Critical Thinking & Art Integration
1 Use the clue to find the correct fraction from the given possibilities of images.
Clue: I am less than 2 and a half wholes. I am more than a whole. You can make me out of 4 halves. What am I?
2 Show and colour halves in 4 different ways in the given figure.

A balanced diet is very important for our body. It includes a variety of food groups, such as fruits, vegetables, grains and proteins. Each food group should make up a certain portion of our daily intake. Riya’s parents give her a balanced meal, this is what her plate looks like.

1 What fraction of a healthy plate is filled with fruits and vegetables?
a 2 8 b 1 8 c 3 8 d 5 8


2 The fraction of proteins in the plate is .
3 Write if True or False.
a Grains cover 2 8 of the plate.
b 3 4 of the plate is proteins.

4 What fraction of the plate is not proteins?
5 Do you eat healthy food?

























































Yash’s school organised a cricket tournament. He helped with scorekeeping in each match. He noted down the number of wickets taken by each player.
Amir took 8 wickets, Vihan took 7, Avyaan took 8, Deepak took 9, Prabhakar took 6, and Shreshth took 7 wickets.









Can Yash put this data together in a better form? Are there any details that he can draw from this data?
To better understand the data, let us try to put it in a table.
Data is a collection of numbers or values that we can sort and use to understand things.
Step 1
Make a table with 2 rows and label them.
Remember!

Arranging data into meaningful chunks that can be easily understood is called data handling.
Step 2
Write the names of the players.
Player Amir Vihan Avyaan Deepak Prabhakar Shreshth
Wickets Taken 8 7 8 9 6 7
Step 3
Write the wickets taken by each player.
What if Yash wanted to identify the player who took the highest number of wickets?
We can see in the table that Deepak took the most wickets, which is 9.
We can re-order the data table in descending order, so that bowlers with a higher number of wickets appear first.

A list helps organise information about things.
Player Deepak Amir Avyaan Shreshth Vihan Prabhakar
So, now we know that Deepak, Amir, and Avyaan were the top 3 bowlers in the tournament.
Example 1: A car seller collects the following data on sales of cars from his shop.
1 Which colour has the most number of cars sold? Black
2 What is the total number of cars sold?
Total number of cars sold = 15 + 20 + 17 + 12 + 6 = 70

















Write True or False.
a Raw data is an organised form of data.
b Writing the numbers in ascending or descending order makes it easier to find the greatest or smallest from the data.
c Collecting data makes it easy to understand.
d The data collected from surveys is called raw data.

Organise the raw data of marks obtained in maths out of 100, from the highest to the lowest.
65, 70, 78, 58, 80, 98, 45, 77, 99, 83, 89.
Fruits are very good for you because they have fiber, which helps your stomach and intestines work well and stay healthy. The choices of fruit of 28 students in a class are given below. Draw a table to show the data.
Apple, Orange, Banana, Mango, Apple, Grapes, Banana, Grapes, Apple, Grapes, Banana, Mango, Apple, Grapes, Mango, Apple, Banana, Grapes, Mango, Banana, Apple, Orange, Mango, Orange, Grapes, Banana, Orange, Mango.
Grains are the harvested seeds of grasses. They are common staple foods. They are also called cereals. Given below is the data showing the grain that some people eat. Read the data and fill in the blanks.
Rice Wheat Maize Barley Ragi
a The number of people who eat barley is .
b The number of people who eat ragi is ___________ (more/less) than those who eat rice.
c The most people eat as their main food.
Pictograph
Do you remember Yash who noted down the wickets taken by the players in a data table? The table helped us to compare the wickets taken by each player.
What if Yash wanted to represent the data in an interesting way using pictures?
Drawing a Pictograph
When we use pictures or symbols to show data, it is called a pictorial representation or pictograph.
The same data of the players can be represented in a pictograph.
Players Wickets Taken
Amir
Vihan
Avyaan
Deepak
Prabhakar
Shreshth
Key: = 1 wicket
The key tells us the meaning and value of the picture or symbol.
In the above chart, so many symbols have to be entered! This can get very tiresome. Is there a quicker way to represent the data?
What if each was 2 wickets instead of 1?
The chart would then become:
Player Wickets Taken
Amir
Vihan
Avyaan
Deepak
Prabhakar
Shreshth
Key: = 2 wickets

The symbols that are drawn in a pictograph should be of the same size. Error Alert!








Half a symbol can be used to show that it has half of the value of the whole symbol.
In this key, stands for 2 wickets, so stands for 1 wicket.
Why is it important to select a key in a pictograph? Think and Tell

Example 2: Draw a pictograph for the data shown in the table. Take the key as, = 5 balls bowled.
Bowler Balls Bowled Jasprit
Jaidev 20
Key: = 5 balls bowled
Bowlers with the number of balls bowled. (Key: = 5 balls bowled)
Bowlers Balls Bowled
Jasprit
Bhuvneshwar
Shami
Mukesh
Jaidev
Reading a Pictograph
Let us look at a weather data pictograph! The pictograph shows the rainfall received by a city in different months.
Month Rainfall
June
July
August
September
Key: = 5 cm
What if we wanted to know the rainfall in the month of July?
There are 5 symbols in July. As per the key, each symbol equals 5 cm of rain.
Indian mathematicians, P.C. Mahalanobis and C. R. Rao have played a major role in the field of statistics. Statistics is all about collecting, organising and understanding data.
13 • Data Handling
5 10 15 20 25
What if we want to find the month with the least rainfall?
We can see that September has the least number of symbols. There are 2 symbols. So, each symbol = 5 cm.
Therefore, 2 × 5 = 10 cm of rain was received in September.


Will it be easier or more difficult to make the same pictograph if the key is = 1 cm?















Write True or False.
a A pictograph represents data using pictures and objects.
b In a pictograph, more pictures mean a bigger number.
c Pictographs help us understand and interpret the data.
Draw the symbols to complete the pictograph for the data. = 2 children













The pictograph shows the number of books borrowed from the library on different days of the week. Read the pictograph and answer the questions. = 2 books
Days Books Borrowed
Monday
Tuesday
Wednesday
Thursday
Friday
a How many books were borrowed on Wednesday?
b On which day was the highest number of books borrowed and how many?
c What is the difference in the number of books borrowed on Tuesday and Thursday?
Draw a pictograph for the given data. Key: = 1 ice cream
Ice
Segregating waste makes it easier to recycle materials. The pictograph shows the number of households that segregate different types of waste. Read the graph and answer the following questions.
a How many more households segregate wet waste compared to e-waste?
b If 3 more households start segregating wet waste, how many will there be in total?
c Do you or your family practice waste segregation at home? If so, how do you do it? If not, why not?
Create a new question on the pictograph shown in Q5.
We learnt about representing data pictorially. Are there other ways to represent data?
Let us look at Yash’s data table again. The table shows wickets taken by the players in the tournament. Players Amir Vihan Avyaan Deepak Prabhakar Shreshth
A bar graph is a chart that uses bars to show comparisons between categories of data. It has a horizontal axis (x–axis), and a vertical axis (y–axis). The horizontal axis shows what is being measured and the vertical axis shows the number for the categories being measured.
Let us learn how to draw a bar graph. We will use Yash’s data above.
Step 1
Draw the x-axis and y-axis and label them.
Step 4
Write the names of the players on the x-axis, and the number of wickets taken on the y-axis.
Step 2
Write the title of the graph.
Example 3: Draw a bar graph for the following data.
Step 3 Write the scale.
Step 5
Draw the rectangular bars for the number of wickets taken by each player.

Interpreting a Bar Graph
Now that we have learnt to draw bar graphs, can we read and interpret them? Let us read the given graph and answer some questions.
1 Which students scored 8 marks?
Both Alex and Anaisha scored 8 marks.
2 Who got more marks—Ann or Piya? How many more?
Ann scored 7 marks and Piya scored 6 marks.
Ann scored 1 more mark than Piya.
Example 4: The bar graph shows the number of buckets of water filled by the members of the family in a week. Who filled the most number of buckets and how many?
Tallest bar is for the father = 8 divisions 1 division = 1 bucket
Thus, the father filled the most buckets, which is 8.

















It Yourself 13C
he data shows the number of people who use different modes of transport. Draw a bar graph to show the data.
The data shows the number of states in 4 countries. Draw a bar graph for the data given in the table.

Drinking the right amount of water is important because it helps your body work properly. The bar graph shows the number of glasses of water that 5 students drink in a day. Read the bar graph and answer the questions.
a Who drank the most and least number of glasses?
b How many more glasses did Nimisha drink than Rajat?
c How many fewer glasses did Raghav drink than Shoaib? 4 a How many children like sports?
Read the bar graph showing the favourite TV channels of children in a class. Answer the questions.
b Which channel is the most popular and how many children like it?
c What is the difference of the number of children who like sports and the number of children who like adventure?
d On how many children was the survey conducted?
Create a question on the bar graph given in Q4.
Experiential Learning & Art Integration
Objective: To record and represent the data in a bar graph.
Material required: Sheet of paper and pencil, colourful origami sheets.
Method:
1 Ask all the students in the class the mode of transport they use to come to school.
2 Note down the information in a table.
3 Ask the students to take squared paper and draw horizontal and vertical lines on it.
They will mark all the modes of transportation on the horizontal axis and the number of students on the vertical axis.
Finally, they will strips from the origami sheet of appropriate heights and paste on the grid to represent the number of students taking the different modes of transportation. 4 5
1 The data given below shows the favourite colour of the students in a class. Organise the data in a table.
Orange, Pink, Blue, Yellow, Black, Black, Black, Orange, Orange, Pink, Blue, Yellow, Yellow, Pink, Pink, Pink, Blue, Blue, Pink, Pink, Orange, Black, Black, Orange, Orange, Pink, Blue, Blue, Blue, Black, Pink, Yellow, Yellow, Pink, Blue, Orange, Orange, Pink, Black, Black, Yellow, Yellow, Pink, Yellow, Blue, Black
2 Favourite hobbies of 40 students of a class were noted. Create a pictograph for the given data. Use = 1 student.
Singing, Dancing, Sports, Watching TV, Reading, Dancing, Singing, Singing, Sports, Sports, Watching TV, Watching TV, Watching TV, Dancing, Sports, Sports, Sports, Watching TV, Dancing, Dancing, Singing, Reading, Reading, Singing, Watching TV, Sports, Dancing, Dancing, Watching TV, Watching TV, Sports, Dancing, Singing, Reading, Reading, Watching TV, Singing, Dancing, Sports, Sports
3 A film is like a story that you can watch on a big screen, like at the cinema or on a TV. Some children were asked about their favourite genre of films—comedy, musical, or action. Study the pictograph and answer the questions that follow.
Key:
= 2 students
a How many children like musical films?
b Which type of film is liked by the least number of children?
c How many more children like musical films than action films?

4 The bar graph shows the runs in the first 10 overs of a cricket match. Study the bar graph and answer the questions that follow.
a How many runs were scored in the 5th over?
b In which over were the most runs scored?
c How many runs were scored in all the overs?
5 The table shows the household size in a country. Draw a bar graph to show this data.
1 Meher records the number of squirrels that visit her garden each day. She makes a pictograph, with one showing 2 squirrels. She records the squirrels that visited on Sunday as . How many squirrels visited her garden on Sunday?
2 The pictograph shows the number of tomatoes used by 3 cooks for a dish. Read the pictograph and answer the questions.
Name
Ramesh Suresh
Tarachand
Key: = 2 tomatoes
Number of Tomatoes
a If you remove 2 pictures of tomatoes from Suresh's row, how many tomatoes did he use?
b If the key changes to 1 picture = 4 tomatoes, how many pictures should be drawn for Tarachand?

Rainfall charts are used for showing the amount of rain measured for various months. We measure rainfall to know about the climate and its changes. Look at the bar graph and answer.




1 Which month shows the highest rainfall? a January b March c February d June
2 shows the lowest rainfall.
3 Which month shows the second highest rainfall?
4 Can you think of any other real life usage of a bar graph? Give an example.



Name of the Student:
Time: 1 Hour
Total Marks: 50
1 Which shape is divided into equal parts? (2 marks)
2 Fill in the blanks. (5 marks)
A A square has ________ sides.
B A cuboid has ________ edges.
C The 3-D shape that has 1 edge is a ____________.
D A circle has ________ corners and ________ sides.
3 Write the time shown on the clocks in 2 different ways. (4 marks)
4 Count and write the amounts in figures. (2 marks)









5 Complete the number pattern by writing the next 2 numbers. (4 marks)
A 1, 7, 13, 19, 25, 31, ____, ____
B 1, 2, 4, 7, 11, 16, ____, ____
6 Convert as directed. (6 marks)
A 6 m into cm
C 4200 g into kg and g
B 4 m 5 cm into cm
D 2566 mL into L and mL
7 Read the calendar and answer the questions. (4 marks)
A How many Sundays are there in the month of August?
B What is the day of the week on August 12?
8 Tara bought the given items from a grocery store. Make a bill to find the amount Tara paid. (5 marks)
1 kg rice for ₹120; 5 packets of biscuits each costing ₹25; 2 bottles of juice for ₹45 each
9 Find. (4 marks)
A 2 3 of 12 apples
B 1 4 of 24 pears
10 If = 10 books, how many circles will you draw to show: (4 marks)
A 40 books
B 65 books
11 These toys belong to Anuj. Write the fraction of the given toys. (4 marks)





A Cars
































B Teddy bears
12 The data shows the number of items sold by Mira at a Diwali Mela. Draw a bar graph to show the data. (6 marks) Candle Boxes = 20, Chocolate Boxes = 65, Wooden toys = 30

8
Do It Yourself 8A
1. a. Square b. Circle c. Rectangle
Do It Yourself 8E 1. a.
3. Square = 2, Rectangle = 2, Triangle = 1, Circle = 6
4. a. False b. True c. True d. True
5. Answers may vary.
Do It Yourself 8B
1. b and d
2. a. b. c. d. 3. a. b. c.
5. a. park b. hospital c. 5 steps to the right, 1 step up
6.
Do It Yourself 8C
1. a. Cube b. Cylinder c. Sphere d. Cone
2. a. Cuboid b. Sphere c. Cone d. Cube e. Cylinder 3. Cube 4. box, book, eraser
Do It Yourself 8D
1. a. View B b. View B
2. Drawings may vary a. , b. , c. ,
3. Drawings may vary.
a. b.
4. Drawings may vary. , Rectangle
e. 44, 48, 52 f. 55, 45, 35 4. d
5. a. THE CAR IS RED b. I LIKE DOSA
6. Figures may vary. Sample figure.
1. a. Square = 1, Rectangle = 7, Triangle = 2, Circle = 5 b.
2. a. b. c. d.
3. a. cone b. cube c. cylinder d. cuboid 4.
5.
6. a. b. c.
7. a. 32, 36, 40 b. 80, 88, 96 c. 52, 57, 62 d. 41, 44, 47
8. a. b.
9. Side: Rectangle Top: Circle
10. a. Colouring may vary. b. Answers may vary.
Challenge 1. She can do it in 4 different ways. She will get only a cuboid.
2. 4 triangles can be made but 8 triangles can be seen.
Real-Life Maths
1. Hospital 2. Circle football ground. 3. b. hotel
4. Step on MG Road, turn to the right and walk straight. The house is on the left. 5. top
Do It Yourself 9A
1. a. Kilometres b. Metres c. Centimetres d. Centimetres
2. a. 8 cm b. 11 cm c. 10 cm d. 15 cm
3. a. 600 cm b. 800 cm c. 909 cm d. 415 cm
e. 726 cm f. 252 cm 4. a. 7 m b. 6 m c. 4 m
d. 8 m e. 5 m f. 9 m 5. 36 m
6. The python is longer by 400 cm.
Do It Yourself 9B
1. a. grams b. kilogram c. grams d. kilogram e. grams
f. kilogram 2. a. 8000 g b. 9000 g c. 1500 g
d. 4200 g e. 3300 g f. 7750 g 3. 3600 g
4. 1 kg 5. 3 kg 6. 4 kg 900 g
Do It Yourself 9C
1. a, b, e 2. a. 2000 mL b. 6000 mL c. 9000 mL
d. 4500 mL e. 9200 mL f. 5850 mL
3. 3000 mL 4. 1 L 500 mL 5. 3 L 250 mL 6. 83 L
Chapter Checkup
1. a. ; d. ; e. 2. b, d, e, f 3. c. ; e
4. a. 12 cm b. 4 cm c. 7 cm d. 8 cm
5. a. 500 cm b. 200 cm c. 900 cm d. 850 cm
e. 1300 cm f. 1490 cm 6. a. 2 m b. 3 m c. 10 m
d. 11 m e. 12 m f. 13 m 7. a. 8000 g b. 9000 g
c. 7450 g d. 2999 g e. 3760 g f. 4640 g
8. a. 2000 mL b. 7000 mL c. 4000 mL d. 5800 mL
e. 6550 mL f. 8900 mL 9. 3250 g 10. 4 L 300 mL
Challenge 1. 3 cuts 2. 15 m
Real-Life Maths
1. a. 10 g 2. 450 mL 3. 930 g 4. Answers may vary.
Chapter 10
Do It Yourself 10A
1. A. Hour hand B. Minute hand
2. a. 12:00 or 12 o’ clock b. 10:15 or Quarter past 10
c. 2:30 or Half past 2 d. 12:20 or 20 minutes past 12
3. a. a.m. b. a.m. c. p.m. d. p.m.
4. a. b. c. d.
5. Train starting time: 5:30 p.m., Train End time: 10:30 a.m.
Do It Yourself 10B
1. a. 60 b. 12
2. a. 1 hour b. 3 hours c. 15 minutes d. 2 hours 15 minutes
3. a. Minutes b. Minutes c. Minutes d. Hours
4. 120 minutes 5. 75 minutes
Do It Yourself 10C
1. a. Year b. Month c. Date of the Month d. Day of the week
2. a. False b. True c. False d. True
3. a. 4 b. Monday c. Thursday d. 9 e. 13, 20, 27
4. 14 days
5. 6. 2 months
Do It Yourself 10D
1. Navratri
Starts Dusshera Diwali Bhai Dooj Guru Nanak Jayanti
3 October 12 October 1 November 3 November 27 November
2. Cricket match Basketball match Tug-of-war match Football match Kho-Kho match February August October November December
3. a. 2000 b. 7 years c. 15 years d. 34 years
4. Tinu; 6 years
Chapter Checkup
1. a. 1:50 or 10 minutes to 2 b. 1:30 or half past 1
c. 10:45 or quarter to 11
2. a. b. c.
3. a. 2 hours b. 2 hours c. 2 hours
4. a. 7:30 a.m. b. 6:15 p.m. c. 11:55 p.m. d. 12:05 a.m.
5. a. Some minutes b. Some minutes c. Less than a minute
d. hours 6. a. 31 b. 1 May, 2023 c. 11 June, 2023
d. Monday, 8 June 2023
7. Born in Delhi Played for Delhi U-15 U-19 England Tour Won U-19 World Cup Won ODI World Cup 5 November 1988 October 2002 July 2006 March 2008 April 2011

a. 5 Sundays b. 14 July c. 2, 9, 16, 23 and 30
9. Woke up at 7 a.m.; Slept at 9 p.m. 10. 2014 Challenge 1. Saturday, 22 April 2023 2. 3 times.
Real-Life Maths
1. 50 minutes 2. b. 3:50 p.m. 3. 4:40 p.m.
4. No 5. 60 minutes, Answers may vary.
Do It Yourself 11A
1. a. Twenty-eight rupees fifty paise b. Thirty-six rupees twentyfive paise c. Forty-nine rupees seventy paise d. Fifty-seven rupees thirty-five paise e. Sixty-five rupees thirtyseven paise f. Seventy-one rupees seventy-five paise
g. Eighty-eight rupees sixty-two paise
h. Ninety-two rupees forty-eight paise
2. a. ₹56.70 b. ₹29.88 c. ₹35.57 d. ₹68.50 e. ₹73.22
f. ₹15.66 3. a. ₹32.50 b. ₹45.25 c. ₹160.50 d. ₹252.50
4. a. 2536 paise b. ₹8.02 c. ₹21.25 d. 12536 paise
e. ₹361.25 f. 35880 paise
5. One hundred three rupees forty-four paise.
6. Mahi should transfer 2 coins of ₹5.
Do It Yourself 11B
1. ₹13.50 2. ₹125.50 3. ₹280.50
4 ₹363.50 5. ₹128.50
Do It Yourself 11C
1. ₹96.50
2. No, the bill is not correct.
New Era Store
Toy car 1 ₹85.00
3. Sam paid ₹233.00
4. Ravi buys: a. ₹10.00 b. ₹75.50 c. ₹10.00
Amount Paid = ₹95.50
Joe buys: a. ₹5.00 b. ₹75.50 c. ₹4.00
Amount Paid = ₹84.50
Tanya buys: a. ₹25.00 b. ₹75.50 c. ₹8.00
Amount Paid = ₹108.50
Chapter Checkup
1. a. Fifty-two rupees thirty-six paise
b. Sixty-five rupees fourteen paise
c. Seventy-one rupees five paise
2. a. ₹38.65 b. ₹29.55 3. a. 2515 paise
b. 5225 paise c. 23548 paise 4. a. ₹32.56
b. ₹152.36 c. ₹523.64 5. a. 235 paise
b. 348 paise c. 2356 paise d. 3480 paise
6.
All in one mart
Item Quantity Rate per item Amount
Pen 5 ₹12.00 ₹60.00
Marker 2 ₹55.00 ₹110.00
Ruler 1 ₹11.50 ₹11.50
Pencil box 3 ₹65.00 ₹195.00 Total ₹376.50 All in one mart
Item Quantity Rate per item Amount
Sugar 1 ₹39.50 ₹39.50 Marker 3 ₹45.00 ₹135.00
7. Store
₹388.50
Item Quantity Rate per item Amount
Rice 3 packets ₹45.00 ₹135.00
Chips 2 packets ₹18.00 ₹36.00
Milk 1 packet ₹17.50 ₹17.50 Total ₹188.50
Divya has to pay ₹188.50. 8. ₹81 .50 9. ₹110.50 10. ₹210.5
Challenge 1. ₹70 2. Rahul has one rupee more than Ajay.
Real-Life Maths
1. d 2. 100 kauris 3. 500 paisa 4. Answers may vary.
Chapter 12
Do It Yourself 12A
1. a. 1 2 b. 1 3 c. 1 4 2. Sample answers: a. b. c.
d. e. f.
3. a. One-fourth b. Three-fourths c. Half
4. Sample answers: a. b. c.
5. 2 4
Do It Yourself 12B
1. a. 8 pumpkins b. 7 bats c. 6 mangoes d. 4 apples
2. a. True b. False c. False d. True
3. a. 9 b. 3 c. 7 d. 3 4. 4 plants
5. Answer may vary.
Do It Yourself 12C
1. a. 4 8 b. 5 9 c. 4 9 d. 7 16
2. Sample answers:
a. b. c. 6 trees b. 5 tomatoes
3. a. 4 9, 5 9 b. 3 9, 6 9 c. 6 11, 5 11 d. 6 13 , 7 13
4. 8 17 5. 12 plastic bottles 6. 3 blue shirts
7. 9 25 8. 18 books
Chapter Checkup
1. a. 1 2 b. 1 3 c. 3 4 d. 5 8 e. 1 4 f. 7 12
2. a. 5 12 , 7 12 b. 9 17, 8 17
3. Sample answers: a. b. c. 9 kites d. 7 balls
4. a. 6 b. 5 c. 1 d. 4
5. 1 5 6. 3 flowers 7. 2 6 8. 18 apples 9. 15 18
Challenge 1. A
2. Answer may vary. Sample answer.
Real-Life Maths
1. c. 3 8 2. 3 8 3. a. True b. False 4. 5 8
5. Answer may vary.
Do It Yourself 13A
1. a. False b. True c. False d. True
2. 99, 98, 89, 83, 80, 78, 77, 70, 65, 58, 45
3. Fruit Number of Students
Apple 6
Banana 6
Grapes 6
Mango 6 Orange 4
4. a. 3 b. less c. rice
Do It Yourself 13B
1. a. True b. True c. True
2. Favourite Swing
3. a. 8 books b. Friday, 11 books c. 1 book
4. Drawings may vary. Sample answer: Flavour Number of Ice Creams
Vanilla Strawberry Chocolate Mango
5. a. 1 household b. 8 households c. Answers may vary.
6. Answers may vary. Do It Yourself 13C 1. 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Number of People
Different Modes of Transport used by People Scale: 1 Division = 1 People
Bus Train Bicycle Bike Auto
Mode of Transport

3. a. Most = Nimisha; Least = Raghav and Eric b. 1 glass
c. 1 glass 4. a. 4 children b. Cartoon, 9 children
c. 1 child d. 26 children 5. Answer will vary






Hold a balloon and blow into it.
A. What gets filled in the balloon?
B. Tick ( ) the things that changed in the balloon due to blowing. Its s
C. Write more things that can be filled in the balloon for the same change(s) to occur. Get Set Chapter Overview
One day, Riya asks her mother, “What is air?” Her mother asks her in return, “Do you feel anything on you when you sit under the fan?” Riya thought for a moment and said, “Yes, I feel something blowing across my body.”
Her mother nodded and said, “Yes, that is the moving air that you feel.” Riya’s eyes widened with understanding.
The air forms a protective layer around the Earth. This layer of air is called the atmosphere. The air in our surroundings is a mixture of gases. It contains 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and rest 1% argon, carbon dioxide water vapour and other gases. Air also contains dust.
The heat of the sun warms up the air in our surroundings. The warm air, being lighter, rises up. This creates an empty space. The heavier cooler air from the sides moves in to fill this space. This moving air is called wind.

Air also contains germs and harmful substances that can make us sick.
What would you do when there is a strong wind outside?
Aim: To show that warm air rises up
Materials Needed: 2 paper bags, a thin stick, a lighted candle, a string of thread to tie

Method:
Step 1: Take two empty paper bags of the same size. Use threads to tie them upside down on the ends of a thin, wooden stick.
Step 2: Now, tie a piece of thread in the middle of the stick and let it hang freely.
Step 3: Place a burning candle below the open mouth of the paper bag hung on the left side. Observe the wooden stick after some time.
Finding: You will observe that the bag above the candle goes up.
Conclusion: This is because the air above the candle becomes warm and rises, which pushes the bag up.
Number the steps in the correct order to explain the formation of winds. An empty space is created
Cool air from the sides moves in to fill this space.
The sun’s heat warms the air in the surroundings. This moving air results in the formation of wind.
The warm air moves up.
• All living things need air to survive. We breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide.
• Plants use carbon dioxide from the air to make their own food through photosynthesis .
photosynthesis: a process by which plants make their food
Air is used for breathing.
• Air is pumped into the tyres of cars, bicycles and other vehicles to make them move smoothly on the road.
• Air is necessary for burning.
• Air helps to dry our clothes. When we hang wet clothes, the air dries them by taking away the moisture.

Air is pumped into tyres. Air helps in burning.
Can you imagine a day without water? No, right! Even though 70% of the Earth’s surface is covered with water, only a small portion of this water is usable. So, we should use water wisely.
Rain is the major source of water on the Earth. The water that falls on Earth gets collected in the form of surface water and groundwater.
Surface Water: The rainwater falls on the land and is collected in water bodies. The water collected in the water bodies formed on the surface of the Earth is called surface water. Surface water also comes from melting of ice. Ponds, lakes, rivers, sea and oceans are the sources of surface water for us.



Groundwater: Groundwater comes from the rainwater that seeps into the ground and gets collected in the soil and rocks below the ground. Wells, tubewells and handpumps are the sources of groundwater on Earth.
consumption: the using up of a resource
Although seas and oceans are also sources of surface water, the water in these sources is salty. As a result, it is not fit for human consumption.




Well Tubewell Handpump
• We need water for everyday activities like drinking, cooking food, bathing, brushing and washing clothes.
• Farmers use water for irrigation. W e also water the plants at our home.
Can you name some of your daily activities that will be affected if we have a shortage of water?


Water is used for irrigation.
Classify the following sources of water as surface water sources and ground water sources.
pond lake well handpump sea ocean river tubewells
Surface Water Sources
Ground Water Sources
Water can be found in three forms in nature.
• Water in the solid form is found as snow on mountains. Water is also frozen as ice in glaciers and icebergs, in nature. Ice is also the solid form of water. We can get ice by freezing water. Glacier

irrigation: watering land to grow crops; glaciers: large sheets of ice formed in nature icebergs: pieces of ice that have broken off from glaciers and float in the sea

• Water in the liquid form is collected in the water bodies. Snow in the mountains melts to form water. Ice also melts to form water.
• Water in the gaseous form is found in the atmosphere as water vapour. Water in our surroundings evaporates to form vapour. Water from the wet floor or clothes also evaporates into the atmosphere.

When the sun heats up water in different water bodies, this heated water turns into vapour which then rises in the air. This process is called evaporation. As the vapour rises, it cools down and forms clouds. This process is called condensation. When these clouds become heavy with water, they release it as rain, snow or hail. This process is called precipitation. Some of the rainwater is collected in the water bodies while some of it seeps into the ground to become groundwater. The collected water is again heated by the sun, evaporates again and the cycle starts over. This continuous process is called the water cycle.
The water on the Earth today is the same as the water that was here when the Earth was formed and when the dinosaurs lived. We keep using the same water again and again. Did You Know?
Bawaris or baolis are step wells found in Gujarat and Rajasthan. These wells have steps that go down to a large natural or artificial water body. They are very effective in collecting rainwater and keeping a steady water supply all year round.


atmosphere: the layer of air surrounding the Earth

Scan the QR code to know more about water cycle.
• Air is a mixture of gases.
• The sun’s heat makes the air move which results in the wind.
• Water can be a solid (ice), liquid (water) or gas (water vapour).
• Water can change from one state to another.
• Evaporated water keeps on coming back in the form of rain due to the water cycle.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What is air made up of?
Only oxygen
A mixture of gases
Only carbon dioxide
Only nitrogen
B. Which of these shows that air is all around us?
We can see it. We can touch it.
We can feel it. We can drink it.
C. Which of these is a source of groundwater?
Lakes Rivers Wells Ponds
D. Where is water found in solid form in nature?
Lakes and ponds
Rivers and streams
Glaciers and icebergs Clouds
E. How can we get water from ice?
By melting it. By freezing it. By boiling it. By evaporating it.
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. air rises up when it is heated.
B. is the major source of water on the Earth.
C. Water evaporates to turn into .
D. We can get ice by water.
E. in its solid state is called snow.
3. Write ‘T’ for true and ‘F’ for false.
A. We can see air around us.
B. Air contains only oxygen.
C. Water does not change its form.
D. The liquid form of water is called ice.
4. Picture-based question.
Ice Water Water Vapour
A. Name the three forms of water. Solid:
B. How do we get one form of water from another?


5. Short-answer questions.
A. Why is air important for us?
B. List four uses of water in our daily life.
C. Where does the water in the wells come from?
D. Why is water important for farmers?
E. Name three processes that take place in the water cycle.
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Explain the composition of air with the help of a diagram.
B. Write any three uses of air.
C. Explain the various sources of water.
D. In how many forms does water exist in nature? Explain with examples of each form.

E. Explain water cycle with the help of a labelled diagram.


1. If you live in a village with no river nearby, where would you get water from?
2. Suggest two ways in which you can save water.

Life Skills
You can save freshwater by collecting rainwater. Use this water for various purposes like watering your plants or cleaning. Encourage your family and friends to collect rainwater and save as much fresh water as they can.

Chapter Overview

Weather
Weather and Seasons Seasons
Clothes Worn in Different Seasons

Solve the riddles. Get Set


You can feel me but you cannot touch or see me.
I am birds’ favourite; I fill up all the space.
Who am I?

I am found in a lake and in a stream. When frozen, I turn into ice. When boiled, I turn to steam. Who am I?

Weather is the day-to-day condition of our atmosphere at a given place and time. The weather of a place does not remain the same. It may change any time.
Atmosphere is the layer of air around the Earth.
The factors that affect the weather are the sun, winds, clouds and rain. Let us discuss these factors, one by one, in detail.
The sun is the main source of heat and light on the Earth. At noon, the sun’s rays fall in a straight line on Earth. That is why noon becomes the hottest time of the day. The mornings and evenings are cooler as the rays of the Sun are slanting.
At noon, sun rays fall straight on the Earth.
The sun’s rays heat up the land and the air above it. The warm air rises. The cool air from the sides then takes the place of the warm air. This causes the blowing of wind.
When the wind blows gently, it is called a breeze.
The sun heats up water in rivers, lakes, and seas, causing it to turn into water vapour. These vapours rise into the atmosphere, where they mix with dust particles and form clouds.
Clouds cause rain. They can also block the sunlight when they pass above us during the day.
slanting: at an angle
Only some of the heat reaches the Earth
Clouds block the path of sun rays.

When clouds become dark and heavy, they can burst to cause rainfall. Rain makes the weather cool and pleasant.
What would happen if it never rains? Would we be able to survive then? Why?
Rainfall is important for crops. We must collect and store rainwater for later use. We can use this water for cleaning and gardening.

Aim: To prove that warm air rises upwards
Materials Needed: Candle, a piece of paper cut in a circle, a pair of scissors, a wooden stick, clay, matchbox/lighter
Method:
Step 1: Take the piece of paper and ask your parents or an older person to cut it in a spiral.
Step 2: Take the wooden stick and attach it on the clay.
Step 3: Stick one end of the spiral on the wooden stick and let the other end hang freely.
Step 4: After that, light the candle at the bottom of the spiral and observe what happens.
Findings: We will see that the spiral begins to spin.
Conclusion: This happens because warm air rises upwards and cool air from sides blow towards the empty space. This creates wind and makes the paper spin.
Weather is of different types.
1. Sunny
In this weather, the sun shines brightly in the clear sky. The days are hot.
pleasant: nice and likable

When it rains, the weather is called rainy. The weather become cool and pleasant after the rain.
Rainy Weather
When there are a lot of clouds in the sky, it is called cloudy weather. Sometimes, a cloudy sky can block out the sun.





Cloudy Weather




























Snowy Weather
In winters or in cold places, the water drops in the clouds freeze and fall as snow. Such kind of weather is called snowy.
Look at the pictures and name the weather. Pause and Answer
Seasons
Seasons are the conditions of our atmosphere for longer durations. Unlike the weather, seasons remain the same for several months and they follow a cycle.
freeze: turning into ice duration: time during which something continues
There are five main seasons in a year: summer, monsoon, autumn, winter and spring.
1. Summer
It is the hottest season of the year. The days are longer, and nights are shorter during summers. We like to have cool drinks like juices and shakes. We also enjoy fruits, such as mango, muskmelon, watermelon and litchi in summers.
2. Monsoon
It is also known as the rainy season. Monsoon season is from July to September. It comes after the summer season. In this season, we see clouds and rain. Sometimes, we also see a rainbow in the sky.
3. Autumn
The autumn season is from October to November. It is after the monsoon season. The days and nights are of nearly equal duration.
4. Winter
The winter season is from December to February. It comes after the autumn season. In this season, the days are shorter, and the nights are longer. The weather becomes colder. People wear woollen clothes to keep the cold away.
5. Spring
Spring comes after the winter season. In this season, days and nights are of nearly equal duration. During this season, a lot of flowers bloom. People enjoy staying outdoors due to the pleasant weather.


• Take a paper plate and draw lines to divide it into five equal parts.
• Colour each part to represent one of the five seasons: monsoon, spring, summer, autumn, and winter.
• Paste pictures in each section that show things related to that season, like:
⸰ Clothes people wear ⸰ Activities people do
⸰ Months when the season happens
• Show your Wheel of Seasons to your classmates and explain what each season is like.
Do you think all parts of India experience the same conditions during different seasons? Discuss with your classmates.
Countries like the Philippines, Kenya, Singapore and the Maldives have similar weather conditions even during different seasons.
People wear different clothes in different seasons.
Clothes for Summers: In summers, we wear light, cotton clothes. Cotton clothes absorb sweat and keep us cool.
Clothes such as shorts, skirts and half-sleeved T-shirts are worn in this season.

Clothes for Summers
Things like hats, sunglasses and umbrellas are also used during summers to stay away from direct rays of the sun.
Clothes for Monsoon: To protect ourselves from rain, we wear raincoats and gumboots. We also use umbrellas.
Raincoats are made up of waterproof fabric that keeps us dry. Sometimes, getting wet in the rain can make us fall sick.
for Monsoon
Clothes for Winters: We wear woollen clothes, such as sweaters, jackets and coats, in this season. We also use caps, mufflers, gloves and socks to keep us warm.

Clothes for Winters
Woollen clothes trap the body heat and keep us warm. We also wear thick and dark-coloured clothes to stay warm in winters.
Mawsynram, a place in Meghalaya, is known as the wettest place on Earth. This place gets the heaviest rainfall in the world.

weather: it is the day-to-day conditions of our atmosphere at a given place and time atmosphere: it is the layer of air around the Earth breeze: the gentle blowing wind is called breeze

Explore More!
Scan the QR code to know more about seasons.
• The weather of a place changes due to the sun, the clouds, the rain and the wind.
• The weather can be sunny, rainy, cloudy or snowy.
• Seasons remain the same for several months.
• Seasons occur in a cycle throughout the year.
• We wear different types of clothes in different seasons.

1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which factor affects the weather?
Sun Soil Clothes Month
B. What causes air to rise up?
the heat of the sun the clouds in the sky the cool winds the rainwater
C. Which season comes after the summer season?
Fall season Winter season
Autumn season Monsoon season
D. What type of clothes should be worn in the winter season?
Cotton clothes Raincoats and gumboots
Woollen clothes
2. Fill in the blanks.
Waterproof clothes
A. is the hottest season of the year.
B. We experience heavy rains in the season.
C. The winter season has days and nights.
D. is the season when flowers bloom.
3. Write ‘T’ for true and ‘F’ for false.
A. The weather can change during a season.
B. There are two types of seasons in a year.
C. Most of the trees shed their leaves during spring.
D. Summers have longer days and shorter nights.
4. Picture-based question.
Look at the picture and answer:
A. What is the weather shown in the picture?
B. Write any two activities that you like to do in the weather shown in the picture.
5. Short-answer questions.
A. Name the different types of weather.
B. Which is the hottest part of the day? Why?
C. Why should we avoid getting wet in the rains?
D. Why do we wear woollen clothes in the winter?
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Name the different types of weather. How is the weather today?
B. How are weather and seasons different? Explain with examples.
C. Which season is your favourite? Why?


Rainwater is freshwater that can be collected for later use. Suggest a way in which you can collect rainwater.


Winters can be harsh for people who do not have enough clothes or the money to buy them. People who can afford extra clothes should donate them to the needy. Take the help of your family, friends and neighbours to organise a donation drive where you collect woollen clothes and donate them in an orphanage or to the needy.



How is Soil Formed?
Get Set Chapter Overview
What is Soil Made Of ? Types of Soil Uses of Soil


Reema has brought a plant from a nursery.
A. Write the things this plant would need to grow healthily.
1. A
2. S L
3. W T
4. S L
B. Suggest one thing she should do to take care of the plant.

Soil is the topmost layer of the earth. It consists of minerals, rock particles, and dead and decaying remains of plants and animals. It also contains air and water. The soil is home to many animals.


What happens when we crush a piece of chalk? It breaks into small pieces. If we crush it further, it will turn into chalk powder. Like chalk powder, soil is formed by crushing or breaking down of big rocks due to the action of the sun, rain and wind. This is called the weathering of rocks.

Step 1: The sun heats up the large rocks. The wind and the rain cool down these heated rocks. This continuous heating and cooling forms cracks in the rocks. As the cracks get bigger, the rocks break down into small pieces.
Step 2: Over time, the rock pieces break into even smaller pieces to form soil. Small plants begin to grow in them.


Step 3: Dead plants and animals mix with water and small particles to form humus.
minerals: substances naturally formed in the Earth decaying: breaking down of substances burrow: a tunnel or a hole in the ground humus: the part of soil made from dead plants and animals

The formation of soil is a slow and continuous process. It takes millions of years to form a thin layer of soil. So, we should not pollute the soil and try to conserve it.
A handful of soil contains about seven billion microorganisms, small living beings which we cannot see with the naked eyes.
We know that the soil is made up of broken pieces of rocks and humus. Along with rocks and humus, soil also contains air and water.

Investigate and Discover
Aim: To prove that soil contains air and water in it
Materials needed: A glass jar, a vessel with a cover, a stove, some water and some soil
Method: Put some soil in a glass jar and pour water over it. Notice what is formed in the water. Now take a vessel with a lid and put some soil in it. Close the lid and heat the vessel for some time. Open the lid carefully and notice what is formed on the lid.
Result: In the first setup, air bubbles form in the glass jar. In the second setup, on heating the soil, small droplets of water appear in the inner side of the vessel and the lid.
Air Bubbles
Soil Contains Air
Water Droplets Drops of water are formed inside of the lid
Soil Contains Water
Conclusion: The formation of air bubbles on pouring water into the soil proves that the soil contains air. The formation of water droplets on heating the soil proves that the soil contains water.

When you dig the soil to make a pit, you will see different layers of the soil. The four main layers of soil are topsoil, subsoil, parent rock and bedrock.
Nature takes 500 years to create one inch of topsoil. Did You Know?
Topsoil: The outermost layer of the soil is called topsoil. It is 2 to 8 inches thick. It also contains humus which makes it fertile. The roots of all plants grow in the topsoil.
Subsoil: The layer below the topsoil is called subsoil. It is a mixture of sand, clay and broken rocks.
Parent Rock: This is the layer below the subsoil and contains big solid rocks that can be broken down further into pieces.
Bedrock: The layer of soil made up of rocks is called bedrock. Water cannot pass through this layer and gathers over the bedrock to form the water table.
Take a transparent plastic jar and display different soil layers.
Gather pebbles, gravel, sand mixed with small pebbles, and garden soil. Using this diagram as a reference, layer the largest pebbles at the bottom, followed by gravel, then the sand and small pebbles mixture and finally the garden soil on top. Enhance the model with dried leaves and twigs and label each soil layer on the jar for clarity. Your soil layers model is now complete!
Name the following layers of soil.
1. A layer through which water cannot pass
fertile: rich in minerals required for plant growth gravel: collection of small, loose pieces of rock and stone
2. The most fertile layer that consists of humus
3. A layer made of sand, clay and small rocks
Shalu went on a desert safari with her parents. She noticed that the soil there was dry and powdery and quite different from the soil in her garden. She asked her parents why it was so. Her parents replied that there could be many types of soil. The type of soil depends on the size of its particles. Based on the particle size, soil is of three types—sandy soil, clayey soil and loamy soil.
Sandy soil is dry and light and contains large sand particles. It does not hold much water due to the large air spaces between the particles. Plants like cacti and coconuts grow well in sandy soil.
When we dissolve sand in water, after some time the sand settles down. Think and tell what this tells us about the sand?
Clayey soil contains very fine particles and holds water well. It becomes sticky when mixed with water. However, it is not ideal for most plants because it lacks air due to the small spaces between the particles.
Loamy soil has medium-sized particles. It is a mix of sand and clay. It is good for plant growth because it has enough air, water and humus. Adding manure and fertilisers can make it even more fertile.



particles: very small pieces of anything manure: a natural substance which helps in the growth of the plants fertilisers: chemical-based minerals added to the soil


Soil is useful in many ways:
1. Soil provides water and minerals for the crops and plants.
2. It is the home of animals such as earthworms, ants, rats, rabbits and snakes.
3. Soil allows rainwater to seep in and prevent floods.

Soil used to make pots.
4. Soil (clayey soil) is used to make pots, diyas, bricks and kutcha houses.
The top layer of soil gets washed away due to wind and rain. This washing away of topsoil is called soil erosion. Since soil formation is a slow and continuous process, we must protect the soil. The practice of protecting soil from erosion and other damage is called soil conservation. Planting trees can prevent soil erosion.




Rajkumari Ratnavati Girls’ School, in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, is built from yellow sandstone, which comes from local sand. The school is designed in an oval shape to stay cool even in very high temperatures. The school does not use air conditioners.

weathering: breaking down of huge rocks due to the action of sun, rain and wind humus: the layer of topsoil made up of dead plants and animals
soil erosion: washing away of topsoil due to wind and rain
soil conservation: taking care of the soil and preventing its erosion

Scan the QR code to know more about soil.
• Soil is made up of rocks and humus. It also has air and water in it.
• Soil is formed by the weathering of rocks.
• Soil has the following layers—topsoil, subsoil, parent rock and bedrock.
• There are three types of soil—clayey, sandy and loamy.
• Soil is very important to all living beings.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Plants grow well in this layer of soil. Which layer of soil could this be?
top soil bedrock subsoil parent rock
B. Which of the following is made from decaying plants and animals? rocks humus gravels clay
C. Which layer of soil is made of large rocks and through which water does not seep?
topsoil subsoil bedrock parent rock
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. is the topmost layer of the Earth.
B. Along with rocks and humus, soil also contains and .
C. Topsoil gets eroded by the action of and rain.
3. Write ‘T’ for true and ‘F’ for false.
A. Clayey soil has fine soil particles.
B. Bedrock is the top layer of soil.
C. Loamy soil is a mixture of clay and sand.



4. Picture-based question.
Label the layers of soil and answer the question.
Which layer is the most fertile? Why?
5. Short-answer questions.
A. List the factors that cause the weathering of rocks.
B. How is humus useful to plants?
C. What is meant by soil conservation? Why is it important?
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Write the steps involved in the formation of soil.
B. Draw a diagram showing the layers of soil and explain each layer in brief.
C. What is the difference between clayey and sandy soils?
D. What are the different uses of soil in our daily life?

1. If you wanted to grow a garden, which type of soil would you choose—sandy, clayey, or loamy? Explain your choice.
2. If there were no soil on earth, how do you think it would affect the environment and living beings?

Take some clay and sieve it with a fine cotton cloth. Add some water to it and make a soft and smooth dough. Use the dough to make toys, animals, pots or other decorative items. Keep them in the sun to dry. Now paint them with different colours. Your clay gift items are ready. You can gift them to your friends and relatives.



Unscramble the words to name the things numbered in the picture. Also, write if they occupy space and have weight. Get Set Chapter Overview


Name of things Do they occupy space and have weight? (Yes/No)

We see a lot of things around us, such as plants, animals, buildings parks and mountains. All these things are called matter. Matter is anything that takes up space and has weight.

Steam is a gas.
Tea is a liquid.
Cup is a solid.
Matter can exist in three forms. They are solids, liquids and gases. The different forms are also called the different states of matter. Everything around us exists in these three states of matter.
Ananya was playing with the Rubik’s cube and trying to arrange all the colours together. She tried to fold the cube to bring similar blocks together but could not. She wondered why she could not change the shape of the cube. This is because the cube is a solid.
A ball, a brick, a pencil and a cup are some examples of solids.


Solids have fixed shape and size. They do not change their shape and size on their own unless you break, cut, squeeze or crush them. For example, a paper changes shape when we cut, tear or crush it.



Solids do not flow from one place to another. However, if a solid is crushed into a powder, it can be poured and formed into a pile.
Write one example of each.
1. A solid that is red in colour:
2. A solid that is hard to break:
3. A solid we can break easily:
List examples of solids that can change their shape and size. Also, tell the conditions in which they change their shape or size.
Oil, milk, paint and juice are some examples of liquids. Water is also a liquid.
Liquids do not have a fixed shape and size. They take the shape of the container they are put in.




Liquids can flow and be poured easily. When you pour a liquid from one container to another, the quantity of liquid doesn’t change, even if it looks different. For example, if you pour water from a jug into a glass, the water takes the shape of the glass but its quantity remains the same.
Icebergs are giant pieces of ice floating in the ocean. They are solid forms of water.
Can you see the air? Can you feel it?
Where is air found? We can’t see air, but we can feel it on our skin. Air is all around us and takes up all the space. Air is a mixture of gases. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are some of the gases in the air.
Steam, smoke, cooking gas and water vapour are also examples of gases.
Like liquids, gases do not have a fixed shape or size. They spread out to fill all the space in a container.

Water takes the shape of the container

Remember!
Plants, animals and humans take in oxygen gas and give out carbon dioxide gas.




Unlike liquids, gases do not settle at the bottom of the container. Gases can flow freely from one place to another, within the container.
Look around and list different solids, liquids and gases in your house. Sort them into groups and talk about the different properties of solids, liquids and gases that they show.
Kavita was watching her mother fill an ice tray and then keep it in the refrigerator. After some time, when her mother took out the ice tray, Kavita was surprised to see ice instead of water. She wondered if water and ice are the same. Let us learn more about how matter changes its state.
Water (Liquid) to Ice (Solid): On cooling, water can turn into ice. This process is called freezing.

Ice changes to water on melting.


Water changes to ice on freezing.
Ice (Solid) to Water (Liquid): When ice gains heat from the surroundings, it turns back into liquid water. This process is called melting.
Water (Liquid) to Water Vapour (Gas): When a liquid, like water, changes into a gas, like water vapour, and goes up into the air, it is called evaporation.
Water evaporates into water vapour.
Water Vapour (Gas) to Water (Liquid): When steam or water vapour are cooled down, they turn back into liquid water. This process is called condensation
Ice cools down the water vapour.
Water vapour cools to change into water.
Vapour changes to water on condensation.

Changes in the state of water
Aim: To observe the change in state of water
Materials Needed: Few ice cubes, a pan, a burner, a glass lid and a spoon
Method:
Step 1: Take a few ice cubes and put them on a pan. Leave it for some time and note the changes in the ice.
Step 2: After some time, heat the pan on a burner. Note the changes that happen on heating the pan.
Step3: Next, cover the pan with a glass lid and turn off the burner. Note the changes on the glass lid after some time.



Step 4: Take the glass lid off the pan. Keep it upside-down on a table for sometime. Note the changes you see on the lid.
Findings: Ice cubes melt to form water in some time. On boiling, water changes into steam. When the lid was covered, steam cooled down to turn back into water drops. The wet glass lid also dried after some time as the water from the lid has evaporated.
Conclusion: Water can change its state on heating or cooling.



The Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC) is a state of matter other than solid, liquid and gases. The matter that is in this state is formed at very low temperatures. This idea of Bose-Einstein Condensate state of matter was first given by a famous Indian scientist, Dr Satyendra Nath Bose.

matter: anything that takes up space and has weight freezing: the process in which a liquid changes into a solid melting: the process in which a solid changes into a liquid evaporation: the process in which a liquid changes into vapour condensation: the process in which a gas changes into a liquid

Scan the QR code to learn more about the process of change in the state of matter.
• Matter is anything that occupies space and has weight.
• Matter exists in three forms—solid, liquid and gas.
• Solids have fixed shape and size unless we cut or break them.
• Liquids and gases do not have any fixed shape and size.
• Heating and cooling can result in the change in state of matter.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of the following is a solid?
Ice Oxygen Juice Carbon dioxide
B. Which of the following is a liquid?
Bottle Soil Juice Air
C. What state of matter fills up the entire space available to them?
Solid Liquid Gas
2. Fill in the blanks.
None of these
A. is the state of matter that can flow and be poured easily.
B. Liquids take the of the container they are put in.
C. Smoke and vapour are examples of .
3. Write ‘T’ for true and ‘F’ for false.
A. Paints change their shape when we pour them on a plate.
B. A pen changes its shape when we put it in a pen stand.
C. Water vapour condenses to form water drops.
D. Gases collect at the bottom of a container.
4. Picture-based question.
Look at the picture. Write the names of the processes in the boxes. Then, answer the questions.
A. What causes water to change from solid to liquid and liquid to gas.
B. What causes water to change from gas to liquid and liquid to solid.
5. Short-answer questions.
A. Will water change its shape when poured from a bottle into a glass? What shape will water take?


B. Write one example of a solid, a liquid and a gas present in your classroom.
C. Write the difference between melting and freezing.
D. How can we change the state of matter from one form to another?
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Explain the process of condensation with the help of a diagram.
B. What happens to water when you a. heat it for a long time? Why? b. put it in the freezer? Why?

1. Why does ice melt faster on a hot day compared to a cold day?
2. Can you change the shape of a solid without turning it into a liquid? How? Give an example.

To explore the change in the state of matter, prepare home-made ice cream and share the learning with your friends and family.
First, mix 1 cup milk, 1 cup heavy cream, 1/2 cup sugar, and 1 teaspoon vanilla extract in a small ziplock bag and seal it tightly. Fill a larger ziplock bag halfway with ice and add 1/3 cup of salt. Place the small bag inside the large one, seal it, and shake it vigorously for 5–10 minutes, using a towel or gloves to protect your hands. The ice absorbs heat from the mixture, causing it to freeze. Take out the small bag and you will see that the liquid mixture has turned into ice cream, demonstrating the change in the state of matter. Enjoy your ice cream with friends.


Chapter Overview

Measuring Things


Need to Measure Things
Measuring Things in Olden Times
Measuring Things in Today’s Time

Get Set

Look at the pictures and write the correct options in the box.

Tall and Short Light and Heavy

Measurement is an important part of our day-to-day lives. For example, when we go to buy clothes, we measure our size according to our height, chest and waist. The milkman also measures the milk when we buy it. The action


of measuring the amount, duration and size of something is called measurement.
Do measurements have an important role in our lives? Why or why not? Discuss with your classmates.
In earlier times, people used to measure things by comparing them with their body parts. Measures such as handspan, cubit, foot and stride were used in olden times.
Handspan: It was the unit measured by the length of the palm.
Cubit: It was the unit measured by the length of arm up to elbow.
Foot: It was the unit measured by the length of the foot.
Stride: It was measured by the distance covered by a single step of a person.
But body parts of different people have different sizes. So, these units can give different measurements for the same things.
Take a book and measure its length using your handspan. Now ask your younger brother or sister and an adult to measure the length of the same book using their own handspans. Note each of the measurements in your notebook. Are all measurements the same or different?
You will observe that the length of the same book comes out to be different in each case. This shows that handspan is not a standard unit for measuring lengths.
duration: for how long something lasts
Pause and Answer
Match the following.
1. Handspan
2. Cubit
3. Foot
4. Stride
i. Length of arm up to elbow
ii. Length of foot
iii. Length of palm
iv. Length covered by one step
We have learnt that the units used in olden times gave different measurements for the same thing. Such units are not the standard units for measurements. Therefore, we need some standard units for measuring different things. These units give the same results for all the measurements. A unit is a fixed quantity that is used as a standard of measurement.
Length tells us how long an object is. Nowadays, the standard unit of measuring lengths is metre. It is written as ‘m’. Longer lengths, such as the length of the clothes and height of the tower, are measured in metres. Smaller lengths, such as the height of a flowerpot or length of crayon, can be measured in centimetres. It is written as ‘cm’.
Why do we need standard units to measure things?

Ruler

Measuring Tape
Measuring tape, ruler and metre rod are some tools that measure lengths. For example, the length of the room is measured using a measuring tape. But the length of your pencil can be measured easily using a ruler.
Have you ever gone to buy a piece of cloth with your mother? The shopkeeper uses the measuring rod to measure the length of the clothes.

Only same kind of measurements are added or subtracted. For example, weight can be added to weight only and not to length.
The weight tells us how heavy or light an object is. The standard unit of measuring weights is kilograms. It is written as ‘kg’. Heavier objects are measured in kilograms (kg). Lighter objects can be measured in grams. It is written as ‘g’. A scale or a balance is a tool used to measure the weight of an object. Weighing machines like electronic balance and beam balance are used to measure weights.



Aim: To compare the weight of different objects and balance them. Materials needed: Two paper cups, two strings of equal lengths, a coat hanger and some small objects (like an eraser, a sharpener, a ruler, pencils, crayons and marbles)
Method:
Step 1: Hang the coat hanger at a place. Now, attach each string to one corner of the hanger.
Step 2: Tie one paper cup to each string.
Step 3: Now add different things in both the cups and try to balance both cups. Keep adding or removing things from the cups to balance them.
Step 4: The things that maintain the balance of the cup have the same weights.
Tie with Strings
Step 5: Repeat the procedure by changing things in both the cups and observe what happens.
Findings: We can balance the cups on the weighing scale only when the objects with the same weight are put into the cups.
On the way back to their home, Rahul’s father stops the car at the petrol pump. He then asks the attendant to fill 12 litres of petrol in his car. Rahul gets confused and asks his father, “Why do you ask for 12 litres of petrol and not 12 kg of it?” His father tells him that only weight is measured in kg. The capacity of liquids is not measured in kilograms or grams. Let us also learn about capacity and its units.
The amount of liquid that a container can hold is called its capacity. The standard unit of measuring capacity is litres. It is written as ‘L’.

The capacity of a container determines the volume of a liquid. Measuring cylinders are used to measure the volume of liquids. These cylinders come in different capacities.
Larger amounts of liquids, such as milk and water, are measured in litres (L). Smaller amounts of liquids, such as cough syrups and sanitizers, are measured in millilitres. It is written as ‘mL’.
Liquids take the shape of the vessel in which they are kept.
Have you ever noticed what your parents do when you have a fever? They use a thermometer to measure the temperature of your body.
Temperature tells us how hot or cold an object is. The units to measure temperature are degrees Celsius or degrees Fahrenheit. Degree Celsius is written as ‘˚C’ and degree Fahrenheit is written as ‘F’. The normal temperature of the human body is 37˚C or 98.6F.

Thermometer is used to measure body temperature.





The standard unit to measure time is seconds. It is written as ‘s’ and used to measure smaller intervals of time. Other units of time are minutes, hours, days, weeks, months and years. A clock or watch is used to measure time. Nowadays, digital clocks are also used to measure time.



A regular year has 365 days. But a leap year has 366 days. It comes every 4 years. Did You Know?
Different units of time are related to each other as follows:
The Konark Temple in Odisha has 12 pairs of wheels that represent the wheels of Lord Surya’s chariot. These wheels indicate the months of a year. Each wheel has 8 wider and 8 inner spokes. These spokes signify 8 prahars or time divisions of the day.

handspan: the unit measured by the length of the palm cubit: the unit measured by the length of arm up to elbow foot: the unit measured by the length of the sole of a foot stride: it was measured by the distance covered by a single step of a person unit: a fixed quantity that is used as a standard of measurement
chariot: a vehicle used in olden times that was pulled by horses and had two wheels spokes: rods that connect the centre of the wheel to its edges

Scan the QR code to know more about measurements.
• Older units, such as handspan, cubit, foot and stride, are used to give different measurements for the same object.
• A metre rod, measuring tape and ruler are used to measure length.
• Electronic balance and beam balance are used to measure weight.
• Measuring cylinders are used to measure the volume of liquids.
• A thermometer is used to measure the temperature of our body.
• A clock or watch is used to measure time.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of the following is used to measure length?
Ruler
Thermometer
Weighing balance
Watch
B. Which of the following was a unit used in olden days to measure length?
Litre Handspan Kilogram Second
C. Which unit is appropriate to measure the length of a room?
Metre Degree Celsius Centimetre Kilogram
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. is the unit measured by the length of the sole.
B. We can measure the length of a pencil in .

C. Liquids, such as water and milk, are measured in .
D. We use a to measure the temperature.
3. Write ‘T’ for true and ‘F’ for false.
A. Stride is the unit to measure length.
B. Temperature is measured in seconds.
C. A measuring cylinder is used to measure capacity.
4. Picture-based question.
A. Look at the given images. Name the tools shown in each image.



B. Write one use of the tool shown in picture 3.
5. Short-answer questions.
A. Why do we need standard units of measurement?
B. Name three tools used to measure length.
C. What does a measuring cylinder do?
D. Name a device used to check body temperature.


E. Name two tools that were used to measure length in olden days.
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Explain the problems caused by the units of measurement used in olden times.
B. We use different units based on the length of the object. Justify with the help of examples.


Why is it important to measure time in our daily lives? Support your answer with two examples.
Time is very important. Make a time table for yourself to make the best use of your time. You may decorate your time table with colours and designs of your choice.
Activity Time
Wake up
Get ready
Go to school
Come home
Have lunch
Study
Play
Have dinner
Hobby time
Sleep



Light, Sound and Force Sound Force Chapter Overview

Solve the riddles. Get Set

I am yellow, I am hot. I shine brightly in the sky. I am visible only during the day.
Who am I?
Who am I? Light
I can be half, I can be full. Many shapes I have. I am visible during the night.
Light is what helps us to see. An object is visible when light falls on it. Otherwise, everything is dark.
Anything that gives out light is called a source of light. Based on the source of light, objects can be luminous or nonluminous.
Electric bulbs, torches, candles and matchsticks are some sources of light that are made by humans. They are also considered luminous objects.
Luminous Objects: The objects that give out light of their own are called luminous objects. The Sun and the stars are examples of luminous objects found in nature. Fireflies are also luminous as their bodies glow.


Luminous Objects
Non-luminous Objects: The objects that do not have light of their own are called non-luminous objects. Some examples of non-luminous objects are chairs, tables, walls and the Moon.
Remember!
The Sun is the ultimate source of light on Earth.


Non-luminous Objects

The Moon shines very brightly, but it does not have its own light. It is the light of the Sun that bounces off the surface of the Moon. Error Alert!
You must have seen sunrays, beams of light from a car headlight or from a torch. You will notice that light rays always travel in a straight path.
Light travels in a straight path.

A shadow is formed when an object blocks the path of light. We see the shadow as a dark patch formed on the opposite side of the light source. A shadow may be bigger or smaller than the object itself.
Object blocking the path of light
Shadow of the object
The source of light
Formation of a Shadow
Take a pencil and stand it upright on a piece of cardboard using clay. Place it outside where it gets sunlight all day. At different times (morning, noon, and afternoon), measure the pencil's shadow with a ruler. You will see the shadow is longer in the morning and afternoon, and shortest at noon. This shows shadows change size depending on the sun’s position.
Have you ever wondered how we talk to each other? We make sound from our throat and hear them with our ears. We hear different types of sounds every day. Sounds can be pleasant or unpleasant.
Pleasant Sound: A sound that is nice to hear and makes us feel good is called a pleasant sound. Some examples of pleasant sounds are chirping of birds, soft music and tinkling windchimes.

Did You Know?
Animals like dogs can hear sounds that are too faint for the human ear.
Which other sounds do you find pleasant?

Unpleasant Sound: A sound that is loud and harsh is called an unpleasant sound. Our ears don’t feel good after hearing such sounds. Some examples of unpleasant sounds are loud sirens, honking of horns and bursting of firecrackers.

Unpleasant sound that disturbs others is also called noise . It is harmful for our ears. So, we should take care of the following things to avoid noise.
• Speak softly with everyone.
• Play television and music at lower volumes.
• Avoid honking of horns.
• Do not burst firecrackers.
Why should you never talk loudly with other people?
harsh: unpleasant sirens: devices that make a loud sound as a warning honking: to make a short and loud noise from vehicle horns



Aim: To understand how sound travels
Materials Needed: Two empty paper cups, a pair of scissors and a string
Method: Follow the steps to make paper cup telephone and understand how sound travels
Step 1: Take two empty paper cups and make a hole on the bottom of each.
Step 2: Take the string and pass one end of it through the hole of one cup. Tie a knot in the part of the string that is inside the hole to secure it. Repeat it with the other end of the string and the other cup.
Step 3: Give one cup to your friend and ask him/her to take it as far as the string will go.
Step 4: Speak into the cup that you are holding. Ask your friend to hold the cup near their ear and listen carefully.
Finding: When you speak into one cup, your friend can hear it softly from the other cup.
Conclusion: Sound travels from one cup to the other through the length of the string.
A force is a push or a pull. We apply force to do work. We use our muscles to apply force. People also use animals to generate force to do their work. We must treat animals properly when using them for work. Nowadays, we mostly use machines to apply force.

Force can help us do many things.






Force can move objects.
Force can stop moving objects.
Force can change the direction of moving objects.
What happens when you push a toy car on the floor? The toy car slows down and stops after some time. Have you wondered what stopped the car? The toy car is stopped by a force from the floor. This force is called friction. Friction is a force that stops moving objects. We walk on the floor without slipping because of the friction between our shoes and the floor.
Force can change the shape of objects.
Friction helps us to walk on the floor without slipping.
Discuss how our lives would be different if there was no friction in nature.
Varanasi is popularly known as the ‘city of lights’. In ancient India, this city was called ‘Kashi’, which means ‘to shine’.


luminous objects: the objects that give out light of their own non-luminous objects: the objects that do not give out light of their own shadow: a dark patch formed on the opposite side of the light source when the path of light is blocked by an object noise: the unpleasant sound that disturbs others
force: a push or a pull
friction: a force that stops moving objects

Scan the QR code to know more about light and shadow.
• Luminous objects, such as the Sun and the stars, give out light.
• Non-luminous objects, such as table and chair, do not give out light.
• A shadow is always formed on the opposite side of the source of light.
• Sound can be pleasant or unpleasant.
• A force is a push or a pull.
• Friction is a force that stops moving objects.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What helps us to see things around us?
Light Sound Force Shadow
B. Which of these is a luminous object?
Moon Chair Sun Table
C. Which of these is a non-luminous object?
Sun Star Moon Firefly
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. We make from our throat.
B. Soft music is an example of sound.
C. A push or a pull is called .
D. is a force that stops moving objects.
3. Match the following.
A. Non-luminous objects
B. Pleasant sound
C. Unpleasant sound
4. Picture-based question.
i. loud honking
ii. pencil
iii. tinkling windchime
Given below are some objects. Write L for luminous objects and N for non-luminous objects.


5. Short-answer questions.
A. Why can we not see things in a dark room?
B. Name any three sources of light that are found in nature.
C. How are shadows formed?
D. What is force?
E. Write one use of friction in our life.


6. Long-answer questions.
A. Write the difference between luminous and non-luminous objects, with examples.
B. What are the different types of sound? Explain them with examples.
C. Write any three uses of force in your daily life.
D. Explain the formation of a shadow with the help of a diagram.

Imagine you are in a dark room. What are two different sources of light that you could use to brighten the room? How would each source of light affect the room differently?

Your neighbours play very loud music. Which of the following sentences will you use to politely tell them to lower the volume?
• Could you please lower the volume?
• Switch off the music right now!
• Do you mind turning down the volume, please?
• Do you want me to call the police?



Get Set

Look at the pictures of some objects seen in the sky and fill in the table.
What is it called?
When do you mostly see it?
(Day Sky/Night Sky)
Does it change its shape?















When we look at the sky, we see objects like the Moon, the Sun and the stars. The objects that we see in the sky are called celestial objects.

Manish went to a planetarium with his father. There he saw a few balls hanging around a bright yellow ball. Each ball had a name written on it.
Manish: Dad, what are the names written on these balls? What do these balls represent?

Dad: Son, the yellow ball at the centre represents the Sun. All the balls around the Sun are the planets, including our own planet the Earth. Planets are celestial objects that move around the Sun. The Sun, the Moon and the planets make our solar system. The Sun is at the centre of the solar system.
Manish: How many planets are there in our solar system?
Dad: There are 8 planets in the solar system. They are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Mercury is the smallest planet. It is the closest planet to the Sun. The biggest planet is Jupiter. All the planets receive heat and light from the Sun.
Read the hints and write the names.
1. The celestial object at the centre of the solar system.
2. The planet farthest from the Sun.
3. The smallest planet in the solar system.
4. The biggest planet in the solar system.
The Sun is a huge ball of burning gases. It is the brightest object in the sky. It is a star closest to the Earth. The Sun gives us heat and light.
The Sun is very important to us because:

• The heat of the Sun helps maintain the temperature on the Earth.
• The light from the Sun helps us see things around us.
• Sunlight is also used by plants to make their food.
We say that the Sun rises in the East and sets in the West. Actually, it is the Earth that moves and not the Sun. The Earth spins from West to East.
What might happen if heat and light from the Sun do not reach the Earth?
We live on the Earth. It is the third planet in our solar system. Life exists on Earth because the Earth is at the right distance from the Sun. The Earth is spherical in shape. It looks flat to us as it is huge, and we only see a very small part of it.

Nearly 70% of the Earth is covered with water and only 30% is land. Earth is also called the ‘Blue Planet’ because a large part of it is covered with water. Earth also has an atmosphere. Let us learn about it in detail.
The protective layer of gases around the Earth is called the atmosphere. Gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide are found in the atmosphere.
The atmosphere is important because:
• It traps the heat of the Sun and keeps the Earth warm. spherical: ball-like shape traps: to hold something

• It stops the harmful rays of the Sun from reaching the Earth.
• It supports life on Earth. Living beings use oxygen for breathing.
The harmful rays from the Sun are called UV rays. The atmosphere has a protective layer called the ozone layer that stops these UV rays from reaching the Earth.
The Earth is not still at its place. It is moving all the time. Earth shows two types of movements: Rotation and Revolution.
The Earth shows a movement in which it spins around a fixed, imaginary line called the axis. This movement of the Earth is called rotation.
The rotation of the Earth causes day and night. The side of the Earth that faces the Sun has day while the side away from the Sun has night. Earth takes 24 hours (1 day) to complete a rotation.
We also know that the Earth moves around the Sun. The path along which the Earth moves around the Sun is called its orbit. The movement of the Earth around the Sun is called revolution.
The Earth takes around 365 days (1 year) to complete one revolution. The revolution of Earth causes seasons. The side of the Earth that is tilted towards the Sun experiences the summer season and the side away from the Sun experiences the winter season.
Take a soft ball and insert a pencil or a thin stick through it. Use a marker to write the letters A and B on the ball such that they are on the opposite sides. Take a torch and place it at a distance from the ball. Hold the pencil in such a way that the letter A is in front of the torch. Now, turn the torch on and slowly rotate the pencil from right to left till the letter B is facing the torch. Observe the side of the ball where the letter A is present now. Is it brighter or darker than the side with the letter B? What does each side represent? Which side shows day and which side shows night?

Fill in the table.
Movement of the Earth on its Movement of the Earth around the
1 rotation equals 1 revolution equals It results in It results in
What is the bright white object in the night sky? It is the Moon. It is the Earth’s nearest neighbour. The Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth as it revolves around the Earth on a fixed orbit.
When we look at the Moon, we see black spots on it. These spots are actually craters. Unlike the Earth, the Moon does not have air and water on it. That’s why there is no life on the Moon.

satellite: an object moving around a larger object in space

The Moon does not have light of its own. Just like in a mirror, the light of the Sun reflects on the surface of the Moon and reaches the Earth.
The Moon completes one revolution around the Earth in about 29 days. The phases of the Moon are the new moon, the crescent moon, the half-moon, the gibbous moon and the full moon.

Aim: To observe and record the shape of the Moon over a period of 10 days.
Materials Required: a notebook, pen or pencil, a window with a clear view of the night sky, a clock
Method:
Step 1: Choose a fixed time each night for observing the Moon from your house’s window.
Step 2: For 10 consecutive days, go to the window at the chosen time and look at the Moon.
Step 3: Draw the visible shape of the Moon in your notebook each night.
Step 4: At the end of 10 days, review your drawings to observe the changes in the Moon’s shape.
Findings: Upon reviewing the drawings of the Moon over the 10-day period, it is observed that the Moon appears to change its shape.
Conclusion: The Moon appears to change its shape. However, the Moon does not actually change its shape. The different shapes of the Moon are due to the changing amount of the Moon’s sunlit portion visible from the Earth as the Moon orbits the Earth.
Look at the pictures. Name the shapes of the Moon.
Stars are huge balls of fire that give out light. We do not see stars during the day due to the bright light of the Sun. Sometimes, a group of stars appear in a particular shape. The shape made by a group of stars is called a constellation.
Some of the constellations seen in the night sky are:




The big The little Orion the Cassiopeia dipper dipper hunter

The Sun is also a star. It does not appear to be twinkling as the other stars in the night sky, because it is very close to the Earth. All other stars are very far from the Earth.
The Jantar Mantar is a monument located in New Delhi, India. It functions as a time-telling device during the day. A central pillar casts a shadow, which moves along the large curved arms of the structure, indicating the time.

celestial objects: the objects that we see in the sky atmosphere: the protective layer of air around the Earth orbit: the path along which the Earth moves around the Sun constellations: groups of stars forming particular shapes craters (Moon): Big holes on the surface of the Moon, made when rocks from space hit it


Scan the QR code to know more about phases of the Moon.
• The Sun is at the centre of the solar system with planets moving around it on their orbits.
• The eight planets in the solar system are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
• The Earth has the right conditions of atmosphere, sunlight and heat for life to exist.
• The Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth.
• Stars appear to make pattern in groups, called constellations.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What is at the centre of our solar system? the Earth the Moon the Sun Mars
B. What is the Earth’s natural satellite?
Star the Sun the Moon Planet
C. What are the different shapes of the Moon called? Phases Patterns Constellations Orbits
D. In which phase does the Moon look completely round and bright?
New Moon Full Moon Crescent Moon Half Moon
E. What is the layer of air that surrounds the Earth called?
Ocean Atmosphere Space Cloud
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. The Earth takes days to complete one revolution.
B. A group of stars that form a pattern is called a .


C. The planet that is closest to the Sun is .
D. The gives light and heat to the Earth.
E. Earth’s revolution causes different .
3. Write ‘T’ for true and ‘F’ for false.
A. The Sun moves from north to south in the sky.
B. The Earth rotates on its axis from east to west.
C. The Moon is the closest planet to the Sun.
D. Stars are planets that twinkle in the night sky.
E. The Moon glows due to the sunlight it reflects.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. What are celestial objects?
B. Why is the Sun important to us?
C. Name the planets in the solar system.
D. Draw any one constellation and write its name.
5. Long-answer questions.
A. Draw a diagram of the solar system.
B. What is the atmosphere and why is it important?
C. Explain how the rotation of the Earth causes day and night.
D. Explain how the revolution of the Earth causes seasons to change.
E. What are constellations? Explain with examples.
6. Picture-based question.
Look at the picture and answer the questions.


A. How many planets are there in the solar system?
B. Name the smallest and the biggest planet in the solar system.
C. Name the sixth planet from the Sun.

1. How would life on the Earth be different without the Sun?
2. If the Earth stops rotating, what changes will you expect to see in day and night?
The Earth is the only known planet with life on it. Spread awareness about the need to take care of our planet Earth by making a poster. Share the poster with your friends and family.

Objective: To observe and record daily weather conditions.
Materials Needed: chart, sheets of paper, markers, colours, glue or tape, a pair of scissors
Steps:
Step 1: Learn about weather
Learn about the different types of weather (sunny, rainy, cloudy, snowy, stormy, windy) using your school textbook or the internet.
Step 2: Prepare a weather chart
On a big chart paper, create a weather chart as given below. SUNMONTUEWEDTHUFRI
Snowy
Windy
Stormy
Step 3: Create weather symbols
Using some papers, draw weather symbols, such as the sun for sunny days, clouds for cloudy days, raindrops for rainy days, and snowflakes for snowy days. You can choose your own designs too. Make a few copies of each weather symbol. Colour them in and cut them out.
Step 4: Track the weather and fill in the weather chart
Each day for a week, choose the weather symbol that best matches the day’s weather and paste it in the appropriate column for that day.
Step 5: Present your weather chart
Present your weather chart to the class. Pay attention to the charts that will be presented by your classmates.
Project Output: You have created a weather chart which shows the weather conditions for a week.
Final Outcome: This project will help you understand the different types of weather and understand how weather is not the same, but changes over short periods of time.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.


Read this article. Answer the questions given below.
Soil erosion is when the top layer of the soil is washed or blown away by wind and water. In India, soil erosion is a big problem in several states. For example, in places such as in Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh, heavy rains and deforestation have caused the top layer of soil to wash away, making it hard for plants to grow and leading to more landslides.
In the Deccan Plateau, which includes parts of Karnataka and Maharashtra, overgrazing by animals and poor farming practices have led to soil erosion. The soil has become dry and less fertile, making it difficult for crops to grow.

To stop soil erosion, people can plant trees, use smart farming methods, and build barriers to protect the soil. This is called soil conservation. It helps keep the soil healthy, so plants can grow well and the environment stays balanced.
1. What is soil erosion?
A. Adding nutrients to the soil and making it fertile
B. When the top layer of soil is washed or blown away
C. The excess layers of soil on the ground
2. Why is soil conservation important?
A. To avoid the earthquakes
B. To increase the amount of sand
C. To balance the environment
3. Imagine you are a farmer and you are facing the problem of soil erosion due to heavy rain. What soil conservation methods could you use to protect your soil? Suggest any two.
4. What will happen if we are not able to stop soil erosion?
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.
Name of the Student:
Time: 1 Hour
Total Marks: 30
1 Tick () the correct answer. (1 × 4 marks)
A Which one affects the weather?
a Sun b Soil c Moon d Stars
B In which level of soil will plants grow well?
a Bedrock b Subsoil
c Parent rock
d Topsoil
C What state of matter fills up the whole space available?
a Solid b Liquid c Gas d BEC
D Which of these is a non-luminous object?
a Sun b Moon c Star d Firefly
2 Fill in the blanks. (1 × 4 marks) liquids thermometer freezing constellation
A A group of stars that form a pattern is called a .
B take the shape of the container they are put in.
C We use a to measure temperature.
D We get ice by water.
3 Write ONE word for the following. (1 × 4 marks)
A The protective layer of air around the Earth.
B A force that stops moving objects.

C Anything that takes up space and has weight.
D The mass movement of birds from colder places to warmer places.
4 Write True or False. (1 × 4 marks)
A Loamy soil is a mixture of clay and sand.
B Stars are planets that twinkle in the night sky.
C The Earth rotates on its axis from east to west.
D Water vapour condenses to form water drops.
5 Picture-based questions. (1 × 3 + 1 marks)
Look at the pictures and answer the questions. Ice Water Water Vapour
A Name the three forms of water.
B How do we get one form of water from another?
6 Answer the following questions. (2 × 5 marks)
A What is the difference between weather and seasons?
B What is meant by soil conservation? Why is it important?
C Why do we need standard units of measurement?
D Write any two uses of force in your daily life.
E Why is the atmosphere important?





All of us like watching films. Can you guess which city of India is famous for making films?












financial: relating to money
















Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra. It is situated on the western coast of India, near the Arabian Sea.
Mumbai was earlier known as Bombay. Since it is the capital of the state, all the important state government offices of Maharashtra are located here. The chief minister, the governor and other ministers of the state also live in Mumbai. Mumbai is called the ‘Financial Capital of India’.

Mumbai is made up of seven islands. The British joined these seven islands through bridges to make one island. Did You Know?
Mumbai has a moderate climate. It is located near the sea so it is neither too hot nor too cold throughout the year. Mumbai receives heavy rainfall during monsoons.
Look at the politcal map of India in an atlas and make a list of the states neighbouring Maharashtra.
Mumbai has a wide network of public transport for travelling within the city. It includes local trains, metro, auto rickshaws and buses. Local trains connect different areas within Mumbai and the surrounding areas. Flights, ships and trains also connect Mumbai to other places across India and the world. The Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport in Mumbai is the second busiest airport in India. It connects Mumbai with major cities across the world. Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus, earlier known as Victoria Terminus, is an important railway station of Mumbai. Mumbai is also an important port city on the western coast of India. The Jawaharlal Nehru Port, also known as the Nhava Sheva Port, is a famous port in Mumbai.
moderate: medium

People waiting to board a local train in Mumbai.


Nhava Sheva Port

The British had started building Victoria Terminus in 1878. It took them 10 years to complete it.
Many important industries are located in Mumbai like cotton, electronic goods, textiles, medicines, oils and chemicals.
Bombay High, in the Arabian Sea, is an important oilfield in India.
The Hindi films industry is also located in Mumbai. It is known as Bollywood.
Tick ( ) the correct option.
The film industry in Mumbai has helped create many jobs for the people living there. Do you agree? Discuss with your friends.
1. Bombay High is in the Arabian Sea/Bay of Bengal.
2. The film industry in Mumbai is called Bollywood/Hollywood.
3. Mumbai is on the western/eastern coast of India.
The Nauvari saree is a traditional dress worn by most women in Mumbai. It is longer than other sarees. The traditional dress for men is a dhoti with a shirt or kurta. Both men and women also wear a turban known as pheta.

oilfield: an area under the sea where oil is found

Marathi is the main language spoken by people in Mumbai. Other languages, such as Gujarati, Hindi and English, are also spoken here. Vada pao, pao bhaji, ragda pattice, bhelpuri and poha are some of the famous street food in Mumbai. Shrikhand is a popular sweet dish that people eat there.


Ganesh Chaturthi is the most important festival of Mumbai. It is celebrated for many days across the city. At the end of the festival, idols of Lord Ganesh are immersed in the sea.


Nowadays, people have begun using Ganesh idols made of eco-friendly material and even immerse them in large tubs of water outside their homes so that the sea does not get polluted. Other major festivals like Diwali, Holi, Eid and Christmas are also celebrated in Mumbai.
Mumbai is a popular tourist destination for both Indians and foreigners. The Gateway of India is a famous tourist spot of Mumbai.
Since Mumbai is located close to the sea, it has many beaches such as Chowpatty, Versova, Marve and Juhu. People enjoy spending time at these beaches. A long road along the seacoast, known as the Marine Drive, is another beautiful tourist attraction.
immerse: to put something in water completely eco-friendly: something that does not harm the environment




Other famous places are the Elephanta caves, the Hanging Gardens, Jehangir Art Gallery, Taraporewala Aquarium, Haji Ali and the Siddhivinayak Temple.
The dabbawalas of Mumbai are amazing delivery people who bring fresh, home-cooked lunch to thousands of office workers every day. They use bicycles, buses and trains to deliver lunchboxes. The dabbawalas are experts and they do not make any mistakes.


Mumbai dabbawallas carrying lunchboxes
local trains: trains that connects different places Bollywood: the Hindi film industry located in Mumbai nauvari: a traditional saree worn by women in Maharashtra pheta: a traditional Marathi turban worn by men and women

Scan the QR code to learn more about life in Mumbai.
• Mumbai is the capital of Maharashtra.
• It is situated on the western coast of India, near the Arabian Sea.
• Ganesh Chaturthi is the most important festival of Mumbai.
• Marathi is the main language spoken in Mumbai.
• The main traditional dresses worn in Mumbai are the nauvari saree, and dhoti-kurta.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What was the old name of Mumbai?
a. Bombay b. Maharashtra c. City of Dreams
B. What type of climate does Mumbai have?
a. Hot
b. Moderate c. Cold
C. Mumbai is located near which water body?
a. Arabian Sea
b. Bay of Bengal c. Indian Ocean
D. What is the traditional dress of women in Mumbai?
a. Salwar-kameez b. Skirt and blouse c. Nauvari sari
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. is the most important festival celebrated in Mumbai.
B. and are popular street food of Mumbai.
C. is the main language spoken by the people of Mumbai.
D. Mumbai is the capital of .
3. Write True or False.
A. The Hindi film industry is situated in Mumbai.
B. Mumbai is a port city.
C. Marine Drive is a famous tourist attraction in Mumbai.
D. People in Mumbai wear only saris and dhotis.

4. Match the following.
A. Pheta i. Oil field
B. Chowpatty ii. Famous food
C. Bombay High iii. Traditional clothing
D. Vada Pao iv. Beach
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Where is Mumbai located?
B. Name three famous tourist places in Mumbai.
C. Will it be correct to say that Mumbai is one of the most important cities of India? Give two reasons.
D. What is Bombay High?
E. Name the most important festival celebrated in Mumbai.
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Name the place shown in the picture.
B. Which sea is it located next to?
C. Is there any port in this city? If yes, name it.


Mumbai is one of the busiest cities in India. How do you think the city's location on the coast helps it to be an important centre for trade and industry?


Many people shift from their city to Mumbai in search of work and to make their lives better. Discuss with your parents or elders some of the challenges people might face while adjusting to a new city or state.
Use the internet to research some famous street food of Mumbai. Try to make any one of them at home, with your parents' help. Tell your classmates how you liked that dish.




Chennai
Location and Climate Culture Transport and Industries
Famous Places


Cricket is a popular sport for many of us. Can you identify the cricket team icon shown in the given picture?
(Hint: It is named after a famous city in southern part of India.)

In the previous chapters, we learnt about Delhi and Mumbai. Let us now learn about another important city of India, Chennai. Chennai is the capital city of Tamil Nadu. It was earlier known as Madras.
Chennai is located on the southeastern coast of India, facing the Bay of Bengal. Chennai has a hot and humid climate throughout the year. It receives rain mainly from October to December.
Since it is the capital of the state, the governor, chief minister and other important ministers work here. All the important government offices of the state are also situated here.
Chennai is known as ‘India’s health capital’ as it has some of the best hospitals and medical services in India.
Chennai on the map of India
Chennai is well connected to other cities in India and abroad. The Chennai International Airport connects the city with major cities of India and the world. The M.G. Ramachandran Central Railway Station, earlier known as Madras Central, is the main railway station of Chennai. Within the city, one can travel via the metro, local city buses, taxis and auto-rickshaws. The Chennai Metro was started in 2015.
Chennai is a port city as well. The Chennai Port is a very busy port. Ships carry goods to other countries from here. Goods from other countries are also brought to India from this port.


Chennai port
port city: a city located close to the sea and built around a port

Some important industries in Chennai are information technology (IT), cotton textiles, leather, and oil refineries. There are many factories in Chennai that make cycles, railway coaches, trucks and cars. There is a tank manufacturing industry at Avadi in Chennai. Chennai is also famous for its film industry, which is also called Kollywood.

Kanjeevaram sarees are worn by most women in Chennai. Kanjeevaram saree
People in Chennai mostly speak Tamil. Bharatnatyam is a famous dance form and Carnatic music is the most popular type of music here. Both men and women perform Bharatnatyam.
All major festivals of India are celebrated in Chennai. Pongal, which is the harvest festival, is the most important festival in Chennai. It is celebrated with great joy for four days. Karthigai Deepam is another important festival.

Food items of Chennai

People in Chennai eat rice with sambar, rasam, poriyal and curd. Rice is the staple diet here. Dosa, idli, upma, and vada are some of the important dishes of Chennai. Kesari is a famous sweet dish of Chennai.
As the weather of Chennai is hot and humid all year round, people wear cotton clothes. Traditional clothes of men are veshti and shirt. Women wear cotton sarees and blouses. Girls can be seen wearing pavadai.
Think and Tell
Do people need woollens in Chennai?
textiles: relating to garments harvest: when crops are ready to be cut and collected from the fields veshti: white unstitched cloth wraps for the lower body pavadai: a long skirt in a cone shape that is tied around the waist

Famous chess player and Olympic gold medalist, Vishwanathan Anand, is from Chennai. Sports keep us healthy and fit. So, we must always play some kind of sport.
Tenzin lives in Leh. He visits Chennai during the winter vacations. Discuss how different the weather of Chennai would be for him.
Circle the correct word.
1. Tamil/Telugu is the language spoken in Chennai.
2. Pongal/Ugadi is the festival celebrated in Chennai.
3. Hindustani/Carnatic music is a popular form of music in Chennai.
Chennai is a famous tourist destination and several Indian and foreign tourists visit it every year. There are many famous temples in Chennai like the Kapaleeswarar temple, the Parthasarathy temple and the Sri Vadapalani Andavar temple.
Fort St George, the Golden Beach, St Thomas Church, the Snake Park, the Gandhi Mandapam, and Guindy National Park are some other famous places in Chennai. The Marina Beach in Chennai is the longest beach in India. Blackbuck, jackal, spotted deer, snake, and tortoise are some animals protected in the Guindy National Park.




The Government Museum, or the Madras Museum, is the second oldest museum of India and it is located in Chennai. It was started in 1851. It is owned by the Government of India. It has the largest collection of Roman antiquities (objects from ancient times) outside Europe.
kanjeevaram: special silk sarees worn in Chennai staple: a food item which is eaten almost daily Word Splash


The Government Museum, Chennai
Scan the QR code to learn more about the famous Marina Beach of Chennai.
• Chennai is the capital of Tamil Nadu.
• The climate of Chennai is hot and humid.
• Bharatnatyam is the famous dance form of Chennai. Carnatic music is a popular type of music in Chennai.
• People mostly speak Tamil in Chennai.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer. A. Chennai was earlier known as a. Madras b. Madurai c. Coimbatore
B. Which of these is a famous place in Chennai?
a. St James Church b. St Thomas Church
c. St Thomas Cathedral
C. Chennai is situated facing the a. Bay of Bengal b. Arabian sea c. Caspian Sea
D. The famous dance form of Chennai is a. Kathak b. Kuchipudi c. Bharatnatyam
2. Fill in the blanks.
pavadai Avadi Guindy Marina Beach
A. Tanks are manufactured in in Chennai.
B. National Park is situated in Chennai.
C. is the longest beach in India.
D. Young girls in Chennai wear .
3. Write True or False.
A. Chennai is located on the southwestern coast of India.
B. Metro rail was started in 2015 in Chennai.
C. Chennai has a cold winter season.
D. Chennai does not have a port.
4. Match the following.
A. Kesari i. Form of music
B. Veshti
C. Carnatic
ii. Celebrated for four days
iii. Men’s clothing
D. Pongal iv. Sweet Dish

5. Answer the following questions.
A. What are some of the major industries of Chennai?
B. Name any three famous tourist places in Chennai.
C. What kind of clothes are worn by the people of Chennai? Give examples.
D. How is the weather in Chennai different from Delhi?
E. Which are the popular dance and music forms of Chennai?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the questions.
A. Which famous clothing item is shown in the picture?
B. Which state of India does it belong to?


Chennai and Mumbai are both located near the sea. What are some of the similarities and differences between the two cities?

Pongal is the harvest festival celebrated in Chennai. Find out why is it celebrated and when is it celebrated? You can research on the internet under your parent’s guidance. Discuss whether your family also celebrates a harvest festival or not.

Chapter Overview

Transport and Industries
Location and Climate Culture
Famous Places

Get Set

Read the poem given below with your partner.
Kolkata’s streets are full of cheer, With trams and buses far and near.
The Howrah Bridge stands tall and wide, Over the river, boats gently glide.
In Kolkata, smiles are always bright, Like the city’s glowing light.

Kolkata is the capital of West Bengal. Since it is the capital of the state, all important government offices are situated here. The governor and the chief minister of the state also live here.

Kolkata is located on the banks of the Hooghly river. It is also an important port city
As you can see on the map, Kolkata is located near the sea. So, it is neither too hot in summers nor too cold in winters. It receives heavy rainfall in monsoons.
Kolkata’s old name was Calcutta. This name was given by the British. It was the capital of the British Empire in India till 1911. After that, New Delhi became the capital of India.
on the map of India
Hooghly and Ganga are not different rivers, as many people may think. Hooghly is the name given to the Ganga river when it enters West Bengal. Error Alert!
Kolkata’s transport system is very interesting. It is a mix of the old and the new. It has trams, which are not there in any other city in India. On the other hand, it has the modern underground metro as well. A part of this metro also runs underwater.


port city: a city built around a port
It has an airport called the Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport. Kolkata also has a port named the Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port. It is the oldest operating port in India. Kolkata has two main railway stations: The Howrah Station and the Sealdah Station.

Howrah and Kolkata are known as twin cities. Howrah lies on the western bank of the Hooghly River. Kolkata lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River. They are connected to each other by the Rabindra Setu (the Howrah Bridge) and the Vidyasagar Setu.
There are several industries in Kolkata such as jute, rice, rubber, textiles, paper and chemicals.
India’s first metro rail was started in Kolkata in the year 1984. India’s first underwater metro rail is also in Kolkata. It started in 2024.
Tick (✓) the statements that are correct.
1. Kolkata’s old name was Calcutta.
2. Kolkata has jute industry.
3. Kolkata is close to the Arabian Sea.
4. Howrah is the twin city of Kolkata.
5. Kolkata's airport is known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee airport.
twin cities: two cities that are similar in size, culture and activities that happen there


Kolkata is an important centre of Indian art and culture. Many great Indian writers, artists and musicians have come from Kolkata. The main language spoken in Kolkata is Bengali.
Rabindranath Tagore was the first Indian and Asian to receive a Nobel Prize in literature for his famous work Geetanjali. He also wrote our national anthem.
Most people in Kolkata eat food such as rice and fish. Sweets such as roshogolla, sandesh and mishti doi are very popular in Kolkata.

Rabindranath Tagore


The main festivals celebrated in Kolkata are Durga Puja and Kali Puja. Big idols of goddesses are specially made for Durga Puja and large pandals (tents) are put up across the city. People celebrate this festival with great joy, and in large numbers, for five days.

People in Kolkata mostly wear pants, shirts and sarees. Traditional clothes like dhuti and panjabi are worn in ceremonies or festivals.
Find out the names of five famous people from Kolkata. They can be writers, artists, musicians, politicians or sports persons.

Kolkata has many famous tourist attractions.
The Howrah bridge is built on the Hooghly river. It is one of the most famous tourist attractions. The Howrah bridge was renamed as Rabindra Setu in the year 1965. Another famous bridge, called the Vidyasagar Setu, has also been built on the Hooghly river.

The Victoria Memorial is another popular tourist attraction. Other famous places to visit are Fort William, the Alipore Zoo, the Botanical Gardens, the Birla Planetarium, the Rabindra Sarovar, the Belur Math, and the Indian Museum (the oldest and the largest museum of India). The famous cricket ground Eden Gardens is also in Kolkata. These are important places. We must not damage these places while visiting them.



College Street in Kolkata is the largest book market in India and Asia. It is also the world’s largest market to buy used books.

tram: a vehicle that runs on tracks that are laid out on the street
metro: a railway that is used to travel within a city; and which runs on electricity
museum: a place where interesting objects are kept for people to see


Scan the QR code to know more about Kolkata.
• Kolkata is the capital city of West Bengal.
• Bengali is the main language spoken in Kolkata.
• It has many industries like jute, paper, textiles, chemical and rice.
• The main festivals of Kolkata are Kali Puja and Durga Puja.
• Some of the famous tourists attractions are Fort William, the Alipore Zoo, the Botanical Gardens, the Birla Planetarium, the Rabindra Sarovar, and the Belur Math.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Kolkata is the capital of which state?
a. Bihar
b. Maharashtra c. West Bengal
B. Kolkata is located on the banks of which river?
a. Yamuna
b. Hooghly c. Godavari
C. Which is the most important festival of Kolkata?
a. Durga Puja
b. Ganesh Chaturthi c. Onam
D. What is the main language of the people of Kolkata?
a. Tamil
b. Bengali c. Odia
2. Fill in the blanks.
Sandesh Eden Gardens Rabindranath Tagore Rabindra Setu
A. is a famous sweet of Kolkata.
B. is a famous cricket ground in Kolkata.
C. was a famous poet who wrote our national anthem.
D. The new name of the Howrah Bridge is the .
3. Write True or False.
A. The Vidyasagar Setu has been built on the Hooghly river.
B. Kolkata has an underwater metro rail.
C. Rice and fish are the staple food of Kolkata.
D. Kolkata has one main railway station.
4. Answer the following questions.
A. Name any two tourist attractions of Kolkata.
B. Name any two important industries of Kolkata.
C. What are the different forms of transport that can be found in Kolkata?
D. Which are the main festivals of Kolkata and how are they celebrated?
5. Picture-based questions.
A. Look at the map. Which water body is near Kolkata?
B. Why do you think fish is a popular food item there?
C. Kolkata is located near the sea. Describe its climate.



How do you think is Kolkata different from Delhi? How is it similar?

Durga Puja is a famous festival. It is celebrated with a lot of enthusiasm in Kolkata. With the help of your parents or elders, find out how is it celebrated in your city? Write 3 points about it.
Imagine that you are visiting Kolkata with your family for a holiday. Discuss with your family and plan your travel, as follows:
Dates:
Mode of travel:
Clothes you will pack:
Places you will visit:
Food you will eat:


Grains and Pulses
Oilseeds and Spices
The Food We Eat
Sweets The Indian Way of Cooking
Fruits and Vegetables
Transportation of Food


In the previous chapters, we have learnt about food items from different cities in India. Which food item is shown here? Which state or city is it from? Speak five lines about it in your class.

Ravi asked his father, “Papa, why does mummy make bajra khichdi so often?”
His father replied, “India is a big country, Ravi. Different foods are popular in different states. We live in Rajasthan where it is hot and dry. Bajra and jowar grow well here so they have become our staple food.”
“Oh! Like how people near the sea eat more fish?” Ravi smiled.


”Exactly, son. We must respect different eating habits of people.”
Any food item that is most commonly eaten by people in a region is known as the staple food of that region.
Grains are the most important part of our meals. Rice is the staple food in the eastern and southern parts of India. People in northern states, such as Punjab, Uttar Pradesh and Haryana, generally eat wheat. In western Indian states like Rajasthan, Gujarat and Maharashtra people eat more of jowar and bajra.
India also produces a wide variety of pulses like moong, masoor, rajma (kidney beans), arhar, soya bean and kabuli chana (chickpeas). They may have different names in different regions.



Fruit and vegetables are an important part of our diet. In summer, we get mangoes, litchees, watermelons, musk melons and cherries. In winter, grapes and oranges are commonly available. Vegetables like pumpkins, brinjals and beans are available in summers. Carrots, cauliflowers, capsicum and peas are available in winters. These fruit and vegetables are seasonal in nature. Onions, garlic and potatoes are some vegetables that are available all the year round. Fruits like bananas are available all the year round.

Many of these fruits and vegetables grow in specific states. For example, apples are grown in Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh, coconuts in Kerala, and oranges in Nagpur.
seasonal: available only in a particular season
Write whether these statements are true or false.
1. Kashmir is famous for its apples.
2. Rice is the staple food of North India.
3. Jowar is a type of a grain.
The oil that we use for cooking comes from oilseeds. Common oilseeds in India are mustard, groundnut, sesame, sunflower and coconut.
India is known for its spices worldwide. Spices make food tasty by adding colour and flavour to it. Some common spices are chillies, cardamom, coriander, cumin, turmeric, cloves and pepper.
Do and Learn


A spice box
Ask your parents to show you the spices that are used in your kitchen. Write down their names in English and in your mother tongue.
India has a wide variety of sweets such as gulab jamun, roshogolla, laddoo, barfi, Mysore pak and different types of halwa. Some sweets are made specially for festivals or special celebrations. Almost all Indian states have their special sweets.
Remember!

Shrikhand is a popular sweet of Maharashtra. Sandesh and roshogolla are popular sweets of West Bengal.


Food is our source of nutrition. We must eat a balanced diet to stay healthy. Indian food lays emphasis on nutritious and healthy food. So, a lot of different types of oils, spices, dairy products, fruits, vegetables and pulses are a part of the dietary habits of the people of India. Additionally, Indian food is prepared in different ways. It is boiled, fried, steamed, baked or roasted. Depending on the food people eat, it can be divided into three types: vegetarian, non-vegetarian and vegan.
Vegetarian: A vegetarian diet does not include any kind of meat. It may or may not include eggs. The diet mainly consists of grains, pulses, dairy, nuts, fruit and vegetables.
Non-Vegetarian: A non-vegetarian diet consists of different kinds of meat along with eggs, dairy, grains, pulses, nuts, fruit and vegetables.
Vegan: A vegan diet does not include meat, eggs or dairy. It consists of grains, pulses, nuts, fruit and vegetables. Sometimes, even honey is excluded from use in this diet.
In this chapter, we came to know how different food items are grown in different parts of India. So how do they reach the rest of the country?
Farmers grow crops in their farms and then take the harvest to wholesale markets.
Shopkeepers buy food items from these wholesale markets and bring them to the local neighbourhood shops. People then buy from these local shops and bring them home for cooking.

Truck transporting bananas
steamed: food cooked by putting it over boiling water and letting it cook in that steam baked: food cooked in an oven roasted: food cooked over a fire or in an oven until it gets brown and crispy wholesale markets: large markets where farmers sell their harvest to shopkeepers
Fruits that are grown in different states are packed and transported to the rest of the country through trucks, trains and even aeroplanes.


India is the largest producer of mangoes in the world. Indian mango varieties such as Alphonso and Dasehri are famous all over the world. Alphonso manges are grown in Maharashtra and Dasehri mangoes are grown in Uttar Pradesh. Alphonso mangoes
staple food: any food item that is most commonly eaten by people in a region oilseeds: seeds from which we get oil used for cooking non-vegetarian: a diet that consists of meat and eggs vegetarian: a diet that excludes meat vegan: a diet that excludes meat, eggs, dairy and sometimes even honey

Scan the QR code to learn more about the different types of fruits available in India.
• Indian food lays a lot of emphasis on making the food nutritious and healthy.
• India produces a wide variety of grains and pulses like wheat, rice, rajma, soya bean, etc.
• Spices make food tasty by adding colour and flavour to it.
• Depending on the food people eat, it can be divided into three types: vegetarian, non-vegetarian and vegan.

1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What is the staple food in eastern India?
a. Jowar b. Rice c. Ragi d. Wheat
B. Nagpur is famous for which of these fruits?
a. Orange b. Watermelon c. Mango d. Banana
C. Which of the following is a spice?
a. Tomato b. Turmeric c. Sunflower d. Potato
D. Where do farmers sell their harvest?
a. Wholesale market
c. Grocery stores
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Grain market
d. Shopping malls
western spice oilseeds pulses
A. Moong and arhar are .
B. Bajra is commonly eaten in the part of India.
C. We get oil from .
D. Turmeric is a kind of a .
3. Write True or False.
A. Mysore Pak is a spice.
B. A vegetarian diet does not include nuts and seeds.
C. Coconuts are grown in Kashmir.
D. Chickpeas and arhar are pulses.

4. Match the following.
Food types
Examples
A. Grains i. Turmeric
B. Pulses ii. Mustard
C. Oilseeds iii. Wheat
D. Spices iv. Moong
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Which state is famous for apples?
B. Name any two fruits found in summers.
C. Distinguish between vegetarian and non-vegetarian diet.
D. What would happen if food that was grown in one state could not be transported to other states? How would it affect our diet?
6. Picture-based question.
Look at the pictures and write S if it is seasonal or A if it is available throughout the year.


















1. What problems do you think farmers can face while transporting fruits and vegetables from their fields to wholesale markets?
2. Can vegan food items be included in a vegetarian diet? Explain why or why not.
With the help of your parents, learn to make a fruit raita (curd mixed with fruits) with at least 3 types of fruits and some spices that you like.






Every day you wear your school uniform while going to school. Name any four items that are part of your school uniform. (Hint: shirt, belt)
The clothes people wear in a place depends on that place's climate, culture and the materials available. Since India has a diverse range of climate and culture, the clothes worn by Indians are quite diverse as well.
Some clothes, such as sarees, kurta–pyjama, salwar–kameez, shirts, trousers and T-shirts, are worn commonly across India. In this chapter, we will learn about the different kinds of traditional clothes that are worn in the different parts of our country.
Shirts, trousers and t-shirts are the most commonly worn clothes by men all over the country. Kurtas are commonly worn by men in many states. Traditional clothes are worn by people living in a region.

Gujarati boys wearing angrakha
In Rajasthan and Gujarat, men wear an upper garment called an angrakha. It is a frock-like shirt that is worn with a pyjama or dhoti. In the southern states, men wear a lungi with a kurta or a shirt. Lungi is a long cloth that is tied around the waist. In Kerala, the lungi is called mundu. In Tamil Nadu, it is called veshti.


Lungi with shirt Mundu
In Kashmir, long woollen kurtas called phiran are worn. In many states, men wear turbans to cover their heads. Turbans can be worn in different ways.




Women in India wear various kinds of clothes like sarees, salwar–kameez and others. Sarees are worn in different ways in different states. The design and weave of the saree also differ from state to state.
Different states have their own traditional dresses for women. Ghagara–choli and odhni are worn by women in Rajasthan. In Kashmir, women wear phiran with salwar. In Assam, women wear mekhela–chador. Women in Himachal Pradesh wear pattu. Punjabi women wear salwar-kameez with dupatta, and in Haryana they wear ghagara–kurta.




Remember!
Women in Maharashtra wear saree in a special way called Nauvari saree.
Make a chart on the traditional clothes of India. Paste pictures of the traditional clothes of different Indian states. Write down the names of the clothes under their pictures. You can look for the pictures in your local stationery shops, newspapers, magazines, and even take printouts from the internet.
Many states in India have their own special dresses for occasions like weddings and festivals. In the north-eastern states, people wear different types of headdresses for festivals and ceremonies. They also wear colourful shawls and dresses with various patterns.
weave: the pattern of threads in the cloth headdress: a decorative covering worn on the head ceremony: a special formal event


A traditional dress worn by a woman in Mizoram
Some Indian dresses are associated with the places where they come from. Puanchei is from Mizoram, Banarasi sarees from Varanasi, and Chikankari dresses from Lucknow in Uttar Pradesh, Pashmina shawls from Kashmir, and Kanjeevaram sarees from Tamil Nadu are a few examples of this. They are famous all over the world.

What kind of special dress do you wear during festivals?
The Pashmina shawl is made from the wool of a goat found in Kashmir.
Chikankari dresses are bought by people from around the world for its beautiful embroidery work.

traditional clothes: clothes that are worn to represent a region, culture or a ceremony
angrakha: frock-like shirt which is worn with a pyjama or dhoti
lungi: a long piece of cloth that is wrapped around the waist
phiran: long woollen kurta

Scan the QR code to learn more about the traditional dresses of different states in India.

• The clothes people wear in a place depends on that place's climate, culture and the materials available.
• Traditional clothes are worn by people living in a region.
• Some traditional clothes for men are angrakha, mundu and veshti.
• Traditional clothes of women include ghagara–choli, phiran and mekhela–chador.
• People in some states in India wear headdresses for festivals and ceremonies.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What do men wear in Kashmir?
a. Veshti
b. Chadar c. Phiran
B. Pattu is the traditional dress of the women of which state?
a. Himachal Pradesh b. Odisha c. Telangana
C. What is the most common clothing of Indian women?
a. Saree
c. Mekhala-chador
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Ghagara–choli
Angrakha Mundu Punjab
A. In Kerala, the lungi is called .
B. is a short, frock-like shirt worn by men in Rajasthan.
C. Salwar-kameez is the traditional dress for the women of .
3. Write True or False.
A. Phiran is the traditional dress of Maharashtra.
B. Mundu is the traditional clothing of men in Rajasthan and Gujarat.
C. Banarasi sarees are from Varanasi.
4. Match the following.
A. Mekhela–chador i. Tamil Nadu
B. Puanchei ii. Assam
C. Veshti iii. Mizoram
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Which state is famous for Kanjeevaram sarees?
B. Which state is famous for Pashmina shawls?
C. What are traditional clothes? Give 2 examples.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What is the dress shown in the picture called?
B. In which state do women generally wear this dress?


In June, Shikha will be travelling from Lucknow to Kashmir to attend a wedding in her family. On the way, she will spend 3 days in Delhi as well.
1. What kind of clothes should she pack for her stay in Delhi?
2. She wants to wear something traditional at the wedding to represent her city, Lucknow. What do you think she could wear?


Lets recycle old socks and turn them into puppets.
Materials: Old socks, glue, buttons, markers, cotton.
Steps:
1. Fill the sock with cotton to create a soft toy shape.
2. Seal the open end with glue.
3. Use markers to draw eyes and a smile.
4. Glue buttons for eyes or decorations.
5. Your fun sock toy is ready!


Chapter Overview

Our Festivals
National Festivals Religious Festivals
Harvest Festivals
Birthdays


Read the hints to correctly write the names of these festivals.
1. We light diyas to decorate our houses.
2. We celebrate India’s freedom on this day.
3. We play with colours on this day.
Festivals are special times when people come together to celebrate something important.
Some festivals are celebrated by the whole country, while other festivals are celebrated only in certain parts of the country or by the people who follow a religion. Let us learn about them.

National festivals are celebrated all over the country. In India, there are three national festivals: Independence Day, Republic Day and Gandhi Jayanti.
India got its independence from the British rule on 15 August 1947. We celebrate Independence Day on 15 August each year. On this day, the prime minister of India hoists the National Flag at the Red Fort in New Delhi and gives a speech from there. On this day, we also remember the freedom fighters who gave up their lives for India's independence.
Republic Day is celebrated on 26th January every year. The President of India unfurls the national flag on the Republic Day. Then, a special parade is held at the Kartavya Path in New Delhi. The armed forces (army, navy and air force), the police, and school children participate in the parade. The parade also has colourful tableaux of different states of India. Many children, who have been awarded for bravery, are also a part of the parade. Such parades also take place in the capital cities of different states of the country.

Independence Day celebrations at Red Fort, New Delhi

Republic Day parade in New Delhi
The Kartavya Path was earlier known as Raj Path. The name was changed in 2022. Did You Know?
Gandhi Jayanti is celebrated on 2nd October every year to mark Mahatma Gandhi’s birthday. He is also known as the Father of the Nation and ‘bapu’.
hoist: to raise high using a rope unfurl: to open something that is rolled up and tied tableaux: a scene displayed on a big stage on wheels

He played an important role in India’s independence from the British rule. Every year a function is held at Raj Ghat in New Delhi. Mahatma Gandhi’s ashes are kept at Raj Ghat.
Fill in the blanks.

1. Republic Day is celebrated on . (15 August/26 January)
2. Mahatma Gandhi’s ashes are kept at . (Red Fort/Raj Ghat)
3. India got independence from the British in the year . (1947/1974)
Festivals that are celebrated to mark an important day for a religion are called religious festivals. It is important that all religions and religious festivals are respected.
India has different religions, which is why Indians celebrate a number of religious festivals together. Let us learn about some of them.
Diwali is also known as the ‘Festival of Lights’. On this day, people wear new clothes, decorate their homes with flowers, diyas, lights, candles and draw rangoli.
Holi is known as the ‘Festival of Colours’. It is a popular festival in north India. People celebrate by playing with coloured powder known as gulal.



Dussehra celebrates the victory of good over evil. Devotees believe that on this day, Lord Rama killed Ravana, the demon king with ten heads. A dance drama called Ramlila is organised in different parts of the country. Big effigies of Ravana are burnt to celebrate Dussehra. Large fairs are organised across India.

Effigy of Ravana
Durga Puja is one of the main festivals in West Bengal.
Gurupurab is celebrated in honour of the first Sikh guru, Guru Nanak. On this day, people go to the Gurudwara to pray. Langars are held and large processions are taken out in honour of Guru Nanak. Special decoration is done at all gurudwaras and a big celebration is held at the Golden Temple in Amritsar.
Eid-ul-Fitr is an important festival celebrated in India. It marks the end of a month-long period of fasting known as Ramzan. People offer special namaz at different mosques all over the country. They wear new clothes and prepare special dishes. They greet each other with ‘Eid Mubarak’, which means “Blessed Festival”. A sweet dish called sewaiyan is prepared specially on Eid.
Christmas is celebrated with joy all over India. It is celebrated every year on 25th December to celebrate the birth of Jesus Christ. Churches all over the country are decorated and prayers are held.
devotees: people who believe in a religion effigy: a model
langar: free food served to people at a gurudwara
namaz: prayers offered by Muslims


A family putting up a Christmas tree at home.
People put up Christmas trees and bake plum cakes. People exchange gifts on this day.
Navroz is the celebration of the Parsi new year. It is celebrated between 19th to 22nd March every year. It marks the end of winter and the beginning of spring.
Harvest is when the crops that were sown earlier are ready to be cut and collected from the fields. Harvest is celebrated in many Indian states as a festival.
Bihu is Assam’s harvest festival. It is celebrated three times in a year. Women perform a special dance called the Bihu dance. They also wear their traditional dress called mekhela–chador.
Pongal is Tamil Nadu’s harvest festival. It is celebrated for four days. A dish called ‘sweet pongal’ is made by cooking rice in milk and jaggery. People decorate their houses by drawing patterns, known as ‘kolam’, on the ground. They also worship cows during the four days.

Onam is Kerala’s harvest festival. It is also known as the ‘festival of flowers’. A special meal called the Onam Sadya is served on banana leaves. One of the main events of Onam are the boat races, which are held at various places in Kerala.

Baisakhi is a harvest festival celebrated in North India, especially in Punjab. Men perform Bhangra and women perform Gidda. These are accompanied with the rhythms of the dhol.
Though harvest festivals are named differently in different parts of India, they are celebrated in almost all the parts of India. Why do you think this is the case?
Sara is preparing a dance for Teacher’s Day celebration at her school. She is excited to perform for her teachers and is practising a lot to put up a great show.
Teacher's Day is celebrated every year on 5th September which is the birthday of Dr S. Radhakrishnan. Jawaharlal Nehru’s birthday on 14th November is celebrated as Children’s Day.

Dr S. Radhakrishnan who was the 2nd President of India was a highly respected teacher. Did You Know?
Uttarayana or Makar Sankranti is also known as the ‘Kite Festival’ in Gujarat. People of all ages compete kite flying on this day. The festival is so popular that people from all over the world travel to see it.
festival: special days when people celebrate something

A girl ready to launch her kite into the sky
ramzan: a month-long period of fasting followed by Muslims
bhangra: a special type of dance performed by men in Punjab
gidda: a special type of dance performed by women in Punjab
dhol: a kind of double-sided drum

Scan the QR code to learn more about our harvest festivals.
• National festivals are celebrated all over India.
• Religious festivals are associated with different religions of India. They are celebrated all over the country.
• Harvest festivals are celebrated at the time of harvest.
• The birthdays of some important people are celebrated as festivals.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. What is the month-long period of fasting for Muslims called?
a. Navroz
b. Ramzan c. Gidda
B. Gautama Buddha’s birthday is celebrated as which festival?
a. Buddha Purnima b. Children’s Day c. Gurupurab
C. Pongal is a festival of which state?
a. West Bengal b. Gujarat c. Tamil Nadu
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. Boat races take place during .
B. People draw on the floor of their homes during Pongal.
C. People visit on the Gurupurab to pray.


3. Match the following.
A. Navroz i. 2nd October
B. Children’s Day ii. Between 19th to 22nd March
C. Gandhi Jayanti iii. 14th November
4. Answer the following questions.
A. Name any 2 harvest festivals and the states in which they are celebrated.
B. How do national festivals like Gandhi Jayanti remind us of important leaders and the lessons they taught?
C. How is Eid celebrated?
D. How is Gurupurab celebrated?
5. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the questions.
A. Which festival is being celebrated here?
B. Where is it celebrated in New Delhi?
C. Who all participate in the parade?


1. Why does India have so many harvest festivals?
2. How is the harvest festival of Kerala different from that of Tamil Nadu?
We decorate our homes during festivals. Decoration items are thrown away after the festival is over leads to wastage.
Create decoration items for an upcoming festival by reusing old material like old clothes, old newspapers, etc. You can also use natural materials like jute, clay, etc. Paint them in bright colours and use them to decorate your home.




Solve the following jumbled words.
1. REMAFR
2. OCODRT
(Hint: This person grows our food.)
(Hint: Who treats the sick person.)
Meena's mother is a doctor. Every day, she helps many people get well. Meena also wants to become a doctor like her mother when she grows up, and help people.
The work that people do to earn money is called an occupation. Everyone can take up an occupation

A doctor

depending on what they know, their needs, and the opportunities they have. Farmers, doctors, teachers, carpenters and police are some examples of occupation. Some people also run businesses to earn money. Based on their occupation, people work in different places like offices, hospitals, schools, farms and so on. Do you think all the people in a region can have the same occupation?
Let us learn more about different types of occupations.
Farming is the practice of growing crops. Farmers grow food grains, fruits and vegetables, pulses, tea, cotton, jute, oilseeds, sugarcane, spices among other things.
Some farmers also rear animals on their farms. This practice is called animal rearing. For example, sheep are reared by many people for wool. When animals like cows, goats and buffaloes are reared for milk, it is known as dairy farming. It is a popular occupation in India. Milk products like curd and cheese are also produced in dairy farming. When animals such as hens, ducks and geese are reared for eggs and meat, it is called poultry farming.
Cows, buffaloes and goats are not the only animals from which we get milk. We also get milk from sheep, horses and camels. Error Alert!



A poultry farm
Silk worms are reared to produce silk. It is called Sericulture. Did You Know?
Mining is the process of digging up minerals from the Earth. We get minerals like iron, mica, manganese and coal through mining. These minerals are then processed to make objects like utensils, cars, tools, etc. Mining is an important occupation in some states of India that are rich in minerals, like Jharkhand, Odisha and Karnataka.
Many people work in forests as well. They collect materials like wood, gum, honey and herbs from trees in the forests to make various items. For example, latex is collected from rubber trees to make rubber.
Fishing is the main occupation of people living in coastal areas. Sometimes, fish are reared in ponds or big tanks. This is called pisciculture. Fish are reared for meat and fish oil.
Many people work in factories that use crops and minerals to make them into other useful products. For example, cotton is used to make cloth, jute is used to make bags and ropes, tea leaves are used to make tea powder, seeds are used to make oils, and sugarcane is used to make jaggery and sugar.




mineral: a substance that is naturally formed in the Earth coastal: near the sea factories: places where things are made

Services are jobs that people do for others.
For example, wholesalers buy goods from factories and supply to shopkeepers in markets around us. They take help of people in the transport services to move the goods.
We also need other services in our daily lives that are not related to buying or selling of goods, such as postal services, entertainment, doctors, teachers, police, and mechanics.

Discuss with your friend some other services which we use daily and without which our lives will be difficult.
India is the largest milk producer in the world today. This was made possible due to the ‘White Revolution’, or ‘Operation Flood’, that was started in year 1970 by Dr Verghese Kurien. It built many milk plants to make products like cheese and curd and also created a big network to collect and deliver milk all over India.
Dr Verghese Kurien is known as the ‘father of the White Revolution’ in India.
occupation: the work done by people to earn money

dairy farming: rearing animals to get milk from them poultry farming: rearing hens, ducks and geese for eggs and meat mining: digging up minerals from below the earth’s surface latex: a white liquid produced by rubber trees that is used to make rubber services: jobs people do for others
wholesalers: they buy goods in large quantities from factories and sell them to shopkeepers

Scan the QR code to learn more about the journey of the dairy industry in India.
• The work done by people to earn money is called an occupation.
• Farming also provides material to several other industries.
• We get minerals like iron, mica, manganese and coal through mining.
• Fishing is the main occupation of people living in coastal areas.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these items is obtained through mining?
a. Minerals
b. Plants c. Wood d. Spices
B. Rubber is made from which one of these materials?
a. Gum
b. Latex c. Fish d. Cotton
C. What do we get from dairy farming?
a. Meat
b. Milk c. Eggs d. Honey
2. Fill in the blanks. factories pisciculture metals
A. We get from minerals.
B. Goods are made in .
C. Rearing fish in ponds or big tanks is called .

3. Write True or False.
A. Rearing of cows is called poultry farming.
B. Fish farming can be done in ponds.
C. Rearing of silk worms is called sericulture.
4. Match the following.
A. Seeds i. Oils
B. Wood ii. Ropes
C. Jute iii. Paper
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Define occupation.
B. Why are forest-related occupations important?
C. What do you think will happen if all the people working in the transport services stop their work for one week?
D. What is meant by mining?
E. Explain dairy farming.
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the pictures and answer the following questions.
A. Name the occupations shown in the images.
B. Which of these occupations gives us milk?
C. Which of these occupations gives us iron and coal?


There is a new amusement park being built in a city. What kind of jobs will people need to do to build the park and make it a fun-filled place for everyone?
We just read that we get paper from trees. Follow these easy steps to recycle paper at home.
1. Tear old newspapers into small pieces and soak them in water for a few hours.
2. Mash the soaked paper into a pulp with your hands.
3. Spread the pulp onto a flat tray, press it and remove excess water.
4. Let it dry completely, then peel off your new recycled paper sheet.
You now have your own homemade recycled paper!















Answer the questions by choosing from the pictures of different vehicles given below.
1. Which is your favourite way to travel to your friend’s house?
2. How do you travel to your cousin’s house who lives in different city?



The different ways in which people or goods are moved from one place to another are known as means of transport. People choose the means of transport based on how far they have to travel, how much time they have or how much money they can spend.
Means of transport can be broadly divided into land, air and water transport.

Land transport is the most common means of transport for people and goods both. Means of transport that move only on land are called land transport, such as cars, metro, buses, trains, tractors, and so on. Bullock carts and tongas are the most common means of land transport in villages. Many people use cycles to travel in their neighbouhood or to visit the nearby markets. Using cycles is good for our health and the environment both. It helps us exercise, keeps us healthy and does not pollute the environment.



Did You Know?
The first train journey in India was in 1853. The train carried 400 passengers between Mumbai and Thane in Maharashtra. Today, the Vande Bharat and Gatimaan Express are the fastest trains in India.
Means of transport that move only in the air are called air transport, such as helicopters and aeroplanes. Aeroplanes cover longer distances and helicopters cover shorter distances. Air transport is very fast, but it is a costly means of transport. Aeroplanes use airports for landing and take off. Airports are located in many cities across India and the world.
Did You Know?

The first aeroplane was built by two brothers, Wilbur and Orville Wright, in 1903.
bullock cart: a cart with two or four wheels drawn by oxen tonga: a cart with two or four wheels drawn by horses


Priya loves to make paper boats and sail them in a tub of water. Last year, she sailed in a boat for the first time when she visited Nainital with her family. Nainital has a big lake in which people can go around on boats. Means of transport that moves only in water is called water transport. Water transport is the cheapest mode of transportation, but it is also the slowest. Ships, steamers and boats are all types of water transport. Ships can carry huge amounts of cargo over long distances. There are many ports in India from where ships operate.



Find out the names of any three airports and ports in India and the cities in which they are located.
Write whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Steamers and boats are types of water transport.
2. Trains are a type of air transport.
3. Tongas and bullock carts are the most commonly used transport in villages.
cargo: goods carried over long distances by ships, aeroplanes or big trucks

We use roads almost daily. It is important to follow road safety rules. Some of them are:
• Never cross roads on your own. Take your parents’ or any adults’ help to do it.
• Always walk on the footpath or on the side of the road if there is no footpath.

• Only cross the road using zebra crossings, overhead bridges or subways. If you are using a zebra crossing, wait for the cars to stop before you cross the road.
• Before you cross the road, look to your left, then to your right and to your left again. Make sure that no vehicles are coming from either side.
• Never play, or ride your bicycle on the road.
• A place where a road crosses railway tracks is known as a level crossing. Do not try to cross it when its gates are closed.
India has a wide network of roads. The longest highway in India connects Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir to Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu. This highway is 3,745 kilometres long. It is called NH-44 or National Highway-44.


means of transport: the different ways in which people or goods are moved from one place to another land transport: means of transport that can move only on land air transport: means of transport that can move only in the air water transport: means of transport that can move only in water
subway: an underground passage meant for crossing roads
level crossing: a place where a road crosses railway tracks


Scan the QR code to learn more about the history of ships.
• The different ways in which people or goods are moved from one place to another are known as means of transport.
• Cars, trains, metro, buses, bullock carts, bicycles and tongas are some examples of land transport.
• Boats, ships and steamers are some examples of water transport.
• Aeroplanes and helicopters are some examples of air transport.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which is the most common means of transport?
a. Air
b. Land c. Water
B. Which of these is a type of water transport?
a. Helicopter b. Steamer c. Tonga
C. What is the place where a road crosses railway tracks called?
a. Level crossing b. Zebra crossing c. Subway
D. Where does an aeroplane land and take off from?
a. Airport b. Port c. Railway station
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. transport is the cheapest means of transport.
B. can carry huge amounts of cargo over long distances.
C. Apart from aeroplanes, are another means of air transport.
D. While walking on the road, we should always walk on the .
3. Write True or False.
A. We should cross roads using zebra crossings, overhead bridges or subways.
B. Bullock carts and tongas are the most common means of land transport in villages.
C. Metro is a means of land transport.
D. Level crossing is a means of air transport.
4. Match the following.
A. Boat i. Land transport
B. Train ii. Water transport
C. Helicopter iii. Air transport
5. Answer the following questions.
A. Define means of transport.
B. If you need to walk on a road but it does not have a footpath, what will you do?
C. List any 3 road safety rules that we should follow.
D. What are the differences between water transport and air transport?
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What vehicle can you see in the given picture?
B. Which means of transport is being shown here?
C. Name two other vehicles which are of the same means of transport.




Gaurav has to travel from Delhi to his village which is 300 kms away. Which modes of transport can he use and why?

Ask some elderly people around you about the means of transport that were available when they were children. Make a list of those.
With the help of your parents, travel in the local bus, metro, or autorickshaw in your city.
Before travelling, revise the safety rules you must follow while using that means of transport. Follow these rules while you travel.

Chapter Overview

Need for Communication Postal System, Telephone, Fax
Internet and Email
Mass Communication

Get Set

Read the poem aloud.
We talk on the phone and write an email, We send our messages without fail.
With calls, texts and letters too, We share our news with friends like you!







The different methods that we use to communicate with people are called means of communication. In ancient times, people used trained birds to send messages or people carried letters on foot. Now, we have modern, fast, and reliable ways to communicate. Let us learn about some of them.
communicate: to talk or share ideas, thoughts and feelings with someone


Letters and parcels can be sent to people all over the world through the postal system. In India, it is run by the government and is called the India Post.
The modern postal system was started for the public in India in 1774 by the British.
We can write our message on an inland letter, a postcard, or on plain paper and put it in a stamped envelope. All of these can be bought from any post office.
Letters are put in a postbox and a postman collects them from there. These letters are then carried by different means of transport like road, air and water to their destination.

Each letter or parcel should have the address and the pin code clearly mentioned on it so that it reaches the correct destination. Pin code stands for Postal Index Number code. It is a special 6-digit number for each area that helps the post reach the right place.

Urgent letters and parcels can be sent through services such as Speed Post or by courier. The Indian Postal Department provides the Speed Post service for the fast delivery of letters or parcels. Courier services are provided by private companies.
Write a letter to your friend. With the help of your parents, post the letter at your nearest post office. Remember to add your friend's address and pin code so that it reaches the correct address.
inland letter: a specific size of paper used for letters within India only postcard: a rectangular card used for writing short messages stamped: with a postage stamp destination: the ending point of a journey

A telephone is one of the fastest means of communication. Using telephones, we can talk to people in different cities and countries. They are available at home or at public places where anyone can pay and use them.
A fax machine is connected to a telephone line. It is used to instantly send written messages, documents and photographs. Fax machines are present in most offices.



Write whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Telephone services were started in 1774 by the British.
2. Fax machines are present in most offices.
3. Speed Post is a service which is offered by private companies.
Today, one of the easiest and fastest ways of communicating with people is through the internet. While using the internet, always ask an adult before sharing any information. Keeping oursleves safe online is as important as keeping ourselves safe in real life.
Email, or electronic mail, refers to messages that are sent and received using the internet.
The internet can also be used to read the news, find out any information, watch films, listen to music and do many more things. We can do all of this on laptops and smartphones.
Smartphones are a combination of telephones and computers. To keep our eyes healthy we must spend less time on smartphones or laptops and more time playing outside.
A smartphone

How can you use the internet to study? Discuss with your partner.
When information has to be delivered to a large number of people at the same time, it is done through newspapers, radio, television, satellites and the internet. They help us communicate with a large number of people at the same time. So, they are known as means of mass communication or mass media.

Reena loves sports and has been watching the 2024 Olympics taking place in Paris live on her television at home. Do you know how we are able to watch something at the same time when it is happening in a different part of the world? We are able to do that because of satellites.
Newspapers do not have news of the same day. They are printed at the end of the day and delivered to us the next morning. So, they contain news about what happened yesterday.
Satellites are artificial objects launched into space. They send signals to television, radio and internet. Satellites enable us to watch or hear events like sports or news live from our homes.


live: to watch something at the same time as it is happening in some other part of the city or the world

In India, satellites are launched by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). With Chandrayaan-3, India made history by becoming the first nation to successfully land a spacecraft near the South Pole of the Moon.

A model of Chandrayaan-3
means of communication: different ways that we use to talk to other people or send messages to them
pin code: a special 6-digit number that helps the post reach the right place mass communication: communicating with many people at the same time satellites: artificial objects launched into space that send signals to television, radio and internet

Scan the QR code to learn more about the history of communication.
• The process of sending and receiving messages and information is called communication.
• The internet has made communication faster than ever before.
• When information is delivered to a large number of people at the same time, it is called mass communication.
• Newspapers, television, radio and internet are means of mass communication

1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these can we use to send parcels faster than the normal way?
a. Fax machine
b. Radio c. Speed Post
B. Which of the following is NOT a means of mass communication?
a. Letters
b. Radio c. Newspaper
C. Which of these can we use to instantly send written documents between offices?
a. Postal system
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Fax machine c. Television
electronic mail postbox speed post
A. Email stands for .
B. Letters have to be put in a to be posted.
C. Parcels are sent to people through .
3. Write True or False.
A. We need internet to send an email.
B. Smartphones combine the features of telephones and computers.
C. The internet is the slowest means of communication.
4. Match the following.
A. Pin code i. Offices
B. Radio ii. Mass communication
C. Fax machine iii. Letters

5. Answer the following questions.
A. If you had to find out news about something that happened in the world an hour ago, which means of communication will you use?
B. What is the use of satellites?
C. List any two means of mass communication.
D. What is an email? Have you ever received an email?
E. What are some differences in the ways of communication between ancient times and today?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Name the device shown in the picture.
B. Is it a means of personal communication or mass communication?




We get news from both newspapers and the television. How are these two means of mass communication similar and different?
Do you know who to call in case of emergencies? Ask your parents or elders or use the internet to find out the contact numbers of the following emergency services:
• Police:
• Fire:
• Ambulance:
Only call these numbers if there is an emergency. Do not call them otherwise.




Chapter Overview

Shelter, Clothing and Tools Early Man
Discovery of Metals
Beginning of Farming
Domestication of Animals
Discovery of Fire Changes in Transportation

Get Set

Find the following words in the given word grid and circle them.
1. HUNTER
2. JUNGLE
3. STONE
Early humans are said to have lived in jungles and caves. They used to cover themselves with animal skins and leaves. They were called hunter–gatherers because they either hunted for food or gathered food from trees. They usually ate fruits, roots, leaves and hunted wild animals,

birds and fish. They did not know how to cook nor did they know how to light a fire so they ate their hunted animal raw.

used by early humans
Early humans made tools from stones, bones, and wood. These tools were used for hunting and digging. Animal bones, horns and sharp wooden sticks were also used as tools by them. At times, they used to tie sharp stones to wooden sticks and used it as spear for hunting animals. Use of spears helped them to hunt animals without going near them.
Get some modelling clay. Try to shape the clay into the kinds of tools made by early humans as shown in the above image.
Early humans discovered fire by accident. One day, they noticed that sparks could be created when they struck stones together or when lightning hit dry trees, causing them to catch fire. At first, they were scared, but soon they realized that fire could be useful. They learnt to use it for warmth, cooking food, and protecting themselves from wild animals. Over time, they found ways to keep the fire going by adding dry leaves, wood and sticks. This discovery changed their lives, making it easier to survive and grow as a community.
Discuss!
Discuss with your friend how life would be, if fire had not been discovered.

Early humans using fire to keep themselves warm in a cave
spear: a weapon with a long shaft and a pointed tip discovery: to find or learn something for the first time

Early humans noticed that where they dropped seeds, new plants grew in that spot. So, instead of moving around to find food, they started planting seeds where they lived. They grew crops like wheat and barley. This was the beginning of farming. With farming, they began to settle down at one place. They also understood that seeds needed good soil and water to grow. So, they began settling near rivers.
Early humans noticed that certain animals, like horses, cows, bullocks, dogs and sheep, were helpful. For example, dogs could protect them and sheep provided wool and milk. So, they began keeping these animals close, feeding and caring for them. This was the start of domestication.

Just like how we care for our pets at home, early humans learnt that taking care of animals brought safety and companionship to their lives.
Dogs were one of the first animals to be domesticated by humans. They used to accompany humans during hunting.
Tick (✓) the correct statements.

1. Early humans used animal bones as tools for hunting.
2. Early humans discovered fire.
3. Cow was the first animal to be domesticated.
companionship: having someone with you
Early humans used to walk and carry what they needed. But it was difficult to carry heavy things like hunted dead animals. So, they made a few things to make travel easy. Near rivers, they used rafts made of logs tied together to float across water. To make things easier on the ground, they invented sledges. These were simple platforms of wood that could be dragged over the ground. Soon, they found that it was difficult to drag them on uneven land. So, they began putting logs of wood under these sledges and began rolling the sledges over these logs. As time passed, this led to the invention of the wheel.

A raft

Stone wheel of early humans
They also noticed that animals like horses could also help carry heavy loads, which led to the making of carts and wagons, making travel faster and more efficient. With sledges, rafts, and wheeled carts, early humans could explore new lands, trade with others, and build larger communities, changing how they lived and connected with the world.
Early humans discovered metals like copper and gold while searching for stones. They found that these shiny materials could be shaped into tools and ornaments. By heating metals, they learnt to create stronger tools for farming and hunting. This discovery made their lives easier and marked the beginning of a new era of progress.
invention: a thing that has been made or designed by somebody for the first time era: an important period of time in history


Bhimbetka rock shelters in Madhya Pradesh are rock shelters or caves that are famous worldwide. There are paintings on the walls of these caves by early humans. They are more than 30,000 years old. They show us how the life of early humans as hunters and gatherers was. Bhimbetka rock shelters

hunter–gatherers: people who either hunted for food or gathererd what they could find rafts: flat platforms made of logs tied together to float across water sledges: simple platforms of wood that could be dragged over the ground

Scan the QR code to learn more about the cave paintings of early humans.
• Early humans lived in caves and under trees.
• They were hunter–gatherers.
• Early humans discovered fire by accident by striking two stones together.
• The invention of wheel made transport easier for them.
• They discovered metals like copper and gold while searching for stones.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of these materials did early humans make tools from?
a. Stone
b. Steel c. Copper
B. What did early humans eat?
a. Fruits
b. Bread c. Rice
C. Which animal accompanied early humans during hunting?
a. Cow
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Dog c. Horse
A. Early humans were and gatherers before they learnt to farm.
B. Early humans tied logs together to make a .
C. They tied sharp stones to wooden sticks to make
3. Write True or False.
A. A gas stove helped early humans to cook food and stay warm.
B. Early humans were the first to plant crops and start farming.
C. Early humans grew crops like wheat and barley.
4. Match the following.
A. Animal skins i. Tools
B. Caves and trees ii. Shelters
C. Bones iii. Clothes

5. Answer the following questions.
A. How did the invention of the wheel change the life of early humans?
B. How did the domestication of animals help early humans?
C. Why do you think early humans decided to settle down and farm instead of continuing to hunt and gather food?
D. How was the first raft made by early humans and how did they use it?
6. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the questions.
A. Who do you see in the picture?
B. What do you think they are trying to do here?
C. How will that help them?

If early humans had not invented the wheel, how do you think our lives would have been?

The way we live changes with time. With the help of your elders, find out about some changes that have happened in your locality or city in the last ten to fifteen years. Discuss how these changes have made life better or more comfortable.
Objective: Students will design and create a miniature traditional dress that is from a region in India.
Materials Needed: Markers, colour pencils, fabric scraps, access to the internet or the library, craft materials (glue, scissors, decorative items), chart paper
Step 1: Research

Research the traditional dresses worn in India. Find out the names of the materials used to make these dresses, such as silk, cotton, wool, etc.
Step 2: Study Design
Study the unique design, patterns, and colours used in traditional dresses. For example, look at the designs on a Banarasi saree or the embroidery on a Chikankari saree or a Punjabi suit or salwar kameez.
Step 3: Create a Visual Representation
Create your own design for a traditional dress, inspired by traditional patterns, on a chart paper. You can sketch, colour, or even stick fabric scraps to make your design.
Step 4: Write About the Dress
Label the dress and add the name of the fabric used to make it. Write why the dress is special and where is it worn.
Step 5: Present It to the class
Share your designed dress with the class. Tell three important things about the dress.
Project Output: Now you have your own unique design for a traditional dress. Take turns to present your dress design in front of the class.
Final Outcome: This project will help you understand the diversity of traditional dresses in India. It also promotes research skills, creativity, cultural awareness, and an appreciation for the rich heritage of India.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.

Read this story. Answer the questions given below.
Anika in Samaspur
Anika lives with her family in Samaspur. Every morning, Anika’s mother, Mrs Sharma, takes the metro to her office because it is fast and doesn’t get stuck in traffic. Anika rides her bicycle to school. She loves this because it keeps her active and she can see the beautiful parks on the way to her school.
Anika’s father, Mr Sharma, works from home, so he uses his computer and smartphone to communicate with his colleagues. He often sends emails to his team and makes video calls to discuss important work matters. Anika’s grandparents live far away. Anika talks to them using a video chat app, where they share stories and laugh together.
1. How does Anika’s father communicate with his colleagues?
a. He posts a telegram.
b. He writes letters and sends fax.
c. He uses a computer and a smartphone.
2. Why does Anika’s mother prefer taking the metro to work?
a. It is fast and avoids traffic.
b. It is cheaper than other transport.
c. She enjoys meeting people on the metro.
3. If Anika’s grandparents don’t have a video chat app, how can she stay in touch with them? Mention any two ways.
4. Write two ways in which we can reduce the pollution caused by vehicles.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.
Name of the Student:
Time: 1 Hour
Total Marks: 30
1 Tick () the correct answer. (1 × 4 marks)
A Mumbai is located near which water body?
a Arabian Sea b Bay of Bengal c Indian Ocean
B Nagpur is famous for which fruit?
a Watermelon b Mango c Orange
C What did early humans use to make tools from?
a Copper b Steel c Stone
D Which one is a type of water transport?
a Helicopter b Steamer c Tonga
2 Fill in the blanks. (1 × 4 marks)
factories mundu spice pisciculture
A Rearing fish in ponds or big tanks is called .
B In Kerala, the lungi is called a .
C Turmeric is a kind of a .
D Goods are made in .
3 Match the following. (1 × 4 marks)
A Kesari i Form of music
B Veshti ii Celebrated for four days
C Carnatic iii Men’s clothing
D Pongal iv Sweet dish

4 Write True or False. (1 × 4 marks)
A Mumbai is a port city.
B Coconuts are grown in Kashmir.
C The rearing of silk worms is called sericulture.
D Banarasi sarees are from Varanasi.
5 Picture-based questions. (1 + 1 + 2 marks)
Look at the picture and answer the questions.

A What vehicle can you see in the picture?
B Which means of transport is shown here?
C Name two other vehicles which are of the same means of transport.
6 Answer the following questions. (2 × 5 marks)
A How did the invention of the wheel change the life of early humans?
B What is meant by mining?
C What are traditional clothes? Give an example.
D Name any 2 harvest festivals and the states in which they are celebrated.
E How do satellites help us?
Our Earth is divided into oceans and continents. Let us learn about them.
A very large mass of land is called a continent. Continents are separated from each other by water. There are seven continents in the world.
It has 23 countries. The five Great Lakes, which form the largest fresh water system, are located here.
It has 44 countries. The smallest country in the world, Vatican City, is located here.


It has 12 countries. The world’s biggest rainforest, the Amazon rainforest, is located here.
It has 54 countries. The world’s longest river, the Nile, flows through Africa.
It is the largest continent. It has 48 countries. It is home to the the world’s tallest mountain range, the Himalayas.
It is the smallest continent. It is home to unique animals like koalas and kangaroos.
It is almost completely covered in ice and snow. It is home to animals like penguins and seals.
Oceans are huge bodies of water. There are five oceans in the world:
The Pacific Ocean: It is the largest and the deepest ocean on Earth.
The Atlantic Ocean: It separates Europe and Africa from the Americas.
The Indian Ocean: It is surrounded by Asia, Africa and Australia.
The Southern Ocean: It is also called the Antarctic Ocean. It surrounds Antarctica.
The Arctic Ocean: It is the smallest ocean in the world. It surrounds the North Pole.
Use the internet to find the names of any two countries that are located on each of these continents.

Practice Time

Scan
1 Match the following.
a The Himalayas Antarctica
b Koalas and kangaroos Africa
c Penguins and seals Asia
d Nile Australia
2 Fill in the blanks.
a is almost completely covered in ice and snow.
b The Ocean surrounds the North Pole.
c in Europe is the smallest country in the world.
d is the largest continent.
e The Ocean is the deepest ocean on Earth.
f The Amazon rainforest is located in .
g The Ocean surrounds Antarctica.
3 Identify the continents on the map.

Kho Kho is a very popular game played in India. It is one of the oldest forms of outdoor sport. Let us learn more about it.
Kho Kho was first played in Maharashtra. The word ‘Kho’ in Marathi means ‘go and chase.’ It is a team game, and both men and women play it.
How to Play Kho Kho?
Number of teams: 2 teams (Chasing and Defending)
Number of players in a team: 9 players
Field: It is played on a rectangular field with a centre line and posts at each end of the line.

Chasing Team (Red): Eight players from the team sit on the central line, while one player from the same team tries to chase the runners, called the chaser. The chaser can transfer their role to other players by tapping their back and saying ‘Kho’.
Defending Team (Blue): Three players from the defending team run between the players sitting on the ground. They are called runners. They try to avoid being touched by the chasers.
Points: The chasers score points by touching the runners. And the runners score points by avoiding being touched. There are two halves in the game. The teams change roles at the end of the first half. The team with the most points wins the match.
We need strength and stamina to play Kho Kho. It helps us to stay fit and healthy.

Practice Time

Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Fill in the blanks.
a The team has eight players sitting on the field.
b The team has three players on the field.
c There are players in each Kho Kho team.
d There are posts on the Kho Kho field.
e The score points by chasing the runners.
2 Write True or False.
a Kho Kho is played on a circular field.
b Both men and women play Kho Kho.
c The word ‘Kho’ in Marathi means to go and chase.
d Kho Kho is only played in the first half.
e Kho Kho was first played in Maharashtra.
3 Label the Chaser, the Runner and the Post.

Composting is a way to turn waste food scraps and other natural things like leaves into rich soil. Compost is put into the soil to grow healthy plants. Composting can easily be done at home. Let us learn how.
STEP 1: Get a Bin
Get a composting bin or a bucket. It must have a lid to keep away the smell and insects.

STEP 2: Collect the Waste
To make a good compost mix, you must have greens—food waste and grass, and browns—garden waste and newspaper.
STEP 3: Layer the Greens and the Browns
First, place the brown waste into your bin. Then place the green waste on top. Lightly pour water on the top layer.
Composting Life Cycle
STEP 4: Keep Mixing
Turn or mix the things in your bin every time you add more waste. It helps to let air inside.
STEP 5: The Compost Is Ready
You can tell that the compost is ready once the material in the bin turns into a dark brown colour, and smells more like soil than rotten food. This takes about two to three months.

Composting helps to reduce waste. It makes the soil healthier and makes plants grow better. We should practise composting.

Practice Time

Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Tick () the waste that can be used for composting.
a Dry grass
c Plastic bags
b Orange peels
d Cardboard
e Leaves f Broken pieces of glass
2 Name any four kinds of green and four kinds of brown waste.
Waste
Waste
3 Sequence the steps (1-5) of composting in the correct order. Turn the compost mixture.
Get a bucket or bin.
Collect green and brown waste.
The ready compost can be used for plants.
Layer the green and brown waste.

It is a set of rules and laws according to which a country is governed. The document or book in which this set of rules is written is called a constitution.

The Indian Constitution was created by the Constituent Assembly of India.
Dr Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar was the chairman of the committee that was formed to write the constitution of India.
Dr BR Ambedkar is known as the Father of the Indian Constitution. He was born on 14 April 1891. Every year this day is celebrated as Ambedkar Jayanti in India.
The Constitution of India
• It was originally written in two languages—Hindi and English.
• It is the longest constitution in the world.
• It was passed on 26 November 1949, which is celebrated as National Constitution Day every year.
• The constitution came into effect on 26 January 1950, this is the day that we celebrate as Republic Day.

The constitution of India protects our rights and keeps India a peaceful country.


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Write the correct date of these events.
a The Indian Constitution was passed:
b The Indian Constitution came into effect:
c Dr BR Ambedkar was born on:
2 Fill in the blanks.
a A is a set of rules according to which a country is governed.
b The is the longest constitution in the world.
c was the chairman of the committee who wrote the Indian constitution.
d The was the government body that created the Indian Constitution.
e The Indian Constitution was originally written in and .
3 Match the following.
a National Constitution Day 14 April
b India’s First Republic Day 26 November
c Ambedkar Jayanti 26 January 1950
A passport is a document issued by a government that confirms a person’s identity and nationality (status of belonging to a nation). It is an official travel document. Let us learn more about passports.


Date of Expiry
Uses of Passports
• A passport verifies a person’s identity and nationality.
• It enables a person to travel to foreign countries.

Passport Number
Date of Issue
How to Get a Passport in India?
• The Ministry of External Affairs of India is responsible for issuing passports.
• We can apply for passport by filling in a form. We can do this online on the Passport Seva Online Portal. We can also get this form from the District Passport Cell which is a government office.
• After filling in the form, we need to visit the nearest Passport Office and submit all the required documents.
• In India, a passport is valid for a period of 5 years for children below the age of 18. For those above the age of 18, it is valid for a period of 10 years. When our passport expires, we have to apply for a new one.
Sit in groups with your classmates and talk about the different countries you would like to visit.


1 Name the following.
a The government body that is responsible for issuing passports
b The website on which we can fill in the form for a passport
c The place from where we can get the application form for a passport
d The place where we need to submit the required documents for a passport
2 Tick () the things that a passport can be used for.
a Travelling to foreign countries
b Withdrawing money from the bank
c Buying goods
d As a proof of identity
3 Write True or False.
a An Indian passport is valid for 10 years for children below the age of 18.
b A passport is issued by a bank.
c The passport form can be filled in online on Passport Seva Online Portal.
d A passport is required to travel to a foreign country.
e After our passport expires, we cannot get a new passport.
The Olympics are a multi-sport tournament that is held every four years. The 2024 Olympics were held in Paris, France. Let us learn about India’s performance at the 2024 Olympics.
117 athletes represented India at this event in 16 different sports. India won six medals—three in shooting and one each in athletics, hockey and wrestling.

Manu Bhaker won a bronze medal in the women’s 10m air pistol event. She became the first Indian woman to win a medal in shooting at the Olympics.

Swapnil Kusale won a bronze medal in the men’s 50m rifle 3 positions event. He became the first Indian to win a medal in this event.

Manu Bhaker and Sarabjot Singh won a bronze medal in the 10m air pistol mixed team event. This was India’s first-ever shooting medal in a team event.

Neeraj Chopra won a silver medal in the javelin throw. This was his second medal at the Olympics.

The Indian hockey team won a bronze medal. This is the 13th medal won by the Indian hockey team at the Olympics.

Aman Sehrawat won a bronze medal in the men’s 57kg freestyle event. He became the youngest Indian to win an individual Olympic medal.

Athletes and sportspersons stay strong with exercise and a healthy diet. To be like them, we need to stay active, eat well and stay positive.


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Match the athletes and the events in which they won the medals.
a Aman Sehrawat
b Neeraj Chopra
c Swapnil Kusale
Men’s 50m rifle 3 positions
Men’s 57 kg freestyle
Women’s 10m air pistol
d Manu Bhaker Javelin throw
2 Fill in the blanks.
a The 2024 Olympics were held in .
b athletes represented India in different sports at the 2024 Paris Olympics.
c and won a bronze medal in the 10m air pistol mixed team event.
d The Indian hockey team won a medal at the 2024 Paris Olympics.
e The Indian hockey team has won medals at the Olympics.
3 Name the Indian Athletes.
a She won two medals at the 2024 Olympics.
b He is the first Indian to win a medal in the men’s 50m rifle 3 positions shooting event.
c He became the youngest Indian to win an individual medal at the Olympics.
d They became the first Indians to win a medal in a team shooting event.
e He won a silver medal at the 2024 Olympics.

Some places on Earth have a very extreme climate where the weather is either very hot or freezing cold; very wet or very dry. Let us learn about these places on Earth.



Antarctica is the coldest place on Earth. Almost the entire continent is covered with ice and snow. Penguins, seals and humpback whales are some of the animals that live here.
The Death Valley, located in California, USA, is the hottest place on Earth. The temperature here rises to more than 56 degrees Celsius. Some animals, such as desert tortoises, bighorn sheep and various insects, are found here.
Mawsynram, located in Meghalaya, India, is the wettest place on Earth. This village experiences an average annual rainfall of over 11,000mm. With a huge amount of rainfall throughout the year, this place has many waterfalls.

The Atacama Desert, located in the northern part of Chile, is one of the driest places on Earth. It receives less than 1mm of rainfall each year. Animals like the Andean flamingo and the Atacama toad can be found here.
Use the internet or ask your parents to help you find the hottest and coldest places in India.


1 Name the places.
a The coldest continent in the world.
b The wettest place in the world.
c The hottest place on Earth.
d The driest place on Earth.
2 Name any two animals that live there.
a Antarctica: ;
b The Atacama Desert: ;
c The Death Valley: ;
3 Which place am I?
a Almost the entire continent is covered with ice and snow.
b The wettest place on Earth is located in this state of India.
c The temperature here rises to more than 56 degrees Celsius.
d The driest place on Earth is located in this country.
Diseases can make people unwell and affect how they function. They are mainly caused by tiny organisms called germs. Germs can enter our bodies in many ways. Here are some common ways that germs spread.

Water-borne diseases are caused when the water we drink becomes dirty. Sometimes, they are also caused by the water we use for other purposes. Example: Typhoid and cholera.
Food-borne diseases are caused by eating food that contains germs. These germs can be found in undercooked food or food that has not been cleaned properly. Examples: Dysentery and diarrhoea.

Air-borne diseases pass from one person to another when a sick person coughs or sneezes without covering their mouth. The germs travel through the air and get into our bodies. Examples: Common cold and the flu.
Wash your hands very well with soap and water.


Cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze.
Drink filtered or boiled water. Carry water in clean water bottles when outside.


Avoid close contact with people who are sick.

Get timely vaccinations to stay healthy and avoid diseases.
When we are unwell, we should take care of our health and the health of others by staying indoors.


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Fill in the blanks with the correct word from the box.
dirty Food-borne Germs Air-borne
a are small organisms that cause diseases.
b diseases can pass from one person to another when a sick person coughs or sneezes without covering their mouth.
c Water-borne diseases are caused by drinking water.
d diseases can be caused by eating food that’s not clean or is undercooked.
2 Write any two examples of the following types of diseases.
a Air-borne diseases ,
b Water-borne diseases ,
c Food-borne diseases ,
3 Tick () the ways to prevent the spreading of diseases.
a Cover your mouth and nose when you cough or sneeze.
b Eat fruits without washing them.
c Avoid close contact with a sick person.
d Wash your hands with soap and water.
e Drink tap water.
f Get timely vaccinations.

India has a very large film industry. Thousands of films are produced in India every year. Let us learn about some of the firsts in Indian films.

The first Indian film was ‘Raja Harishchandra.’ It was a black and white film. It was directed by Dadasaheb Phalke and released in 1913.

The first Indian coloured film was ‘Kisan Kanya.’ It was released in 1937 and was directed by Moti B. Gidwani.

The first Indian film with sound was ‘Alam Ara.’ It was directed by Ardeshir Irani and was released in 1931.

The first Indian film to be nominated for an Oscar was ‘Mother India.’ It was directed by Mehboob Khan and was released in 1957.

The first Indian 3-D film was ‘My Dear Kuttichathan.’ It was directed by Jijo Punnoose.
Teamwork is important to achieve big goals like making films. Everyone’s effort helps make something special together.

Practice Time

Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Write the year in which these films were released.
a Raja Harishchandra
b Alam Ara
c Kisan Kanya
d Mother India
2 Match the following films and their directors.
a Alam Ara Jijo Punnoose
b My Dear Kuttichathan Mehboob Khan
c Kisan Kanya Ardeshir Irani
d Raja Harishchandra Moti B. Gidwani
e Mother India Dadasaheb Phalke
3 Name the following.
a First Indian film to be nominated for an Oscar
b First Indian coloured film
c First Indian film
d First Indian film with sound
e First Indian 3-D film
The capital of a country is usually the city that has the greatest political, cultural and historical importance. Let us learn about the capitals of some countries.




Country: Bhutan Capital: Thimphu
Thimpu is the political and cultural centre of Bhutan. It houses the most important government institutions. It is also home to the Lingkana Palace, where the King of Bhutan lives.
Country: Nepal Capital: Kathmandu
Kathmandu has historical and cultural importance. It is home to a number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites such as the Durbar Square and the Pashupatinath temple.
Country: Bangladesh Capital: Dhaka
Dhaka is the largest city in Bangladesh, both in terms of population and area. It has many important landmarks, like the National Parliament House and the historic Lalbagh Fort.
Country: China Capital: Beijing
With a vast area and large population, Beijing is a centre for government institutions and international organisations. Landmarks, such as the Forbidden City and the Great Wall of China, attract millions of tourists every year.
Countries with Multiple Capitals
Some countries have more than one capital.
CountryCapitals
Sri Lanka Colombo and Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte
Netherlands Amsterdam and The Hague
BoliviaLa Paz and Sucre
South Africa is the only nation that has 3 capitals—Pretoria, Bloemfontein and Cape Town.

Countries without a Capital

Nauru is the only country in the world without an official capital. It is also the third smallest country in the world.
Why do you think some countries have more than one capital city?


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Name the capital cities of the following countries.
a Nepal:
b Bhutan:
c China:
d Bangladesh:
2 Match the places and the countries.
a Durbar Square Beijing
b Lalbagh Fort Thimphu
c Forbidden City Dhaka
d Lingkana Palace Kathmandu
3 Write the two capitals of each of the following countries.
a Sri Lanka: and
b Bolivia: and
c Netherlands: and
4 Name the country.
a It is the only country in the world with three capitals.
b It is the only nation without an official capital.

Festivals are special occasions that bring people together to celebrate their traditions, food and families.
Diwali is celebrated around October or November each year. It is also known as the Festival of Lights as people light oil lamps called diyas. Families clean and decorate their homes, exchange gifts and enjoy eating sweets.
Christmas is celebrated on 25 December. It celebrates the birth of Jesus Christ. People decorate Christmas trees with lights and stars. They exchange gifts and spend time with their families.
Eid-ul-Fitr is celebrated on the last day of Ramadan, after a month of fasting. People wear new clothes, go to the mosque for special prayers, and meet with family and friends.
The Chinese New Year, is known as the Spring Festival. It falls between 21 January and 20 February. People celebrate with colourful parades, dragon dances and fireworks. Children receive red envelopes with money as a symbol of good luck.
Gurpurab generally falls in November each year. It is a celebration of the birth of Guru Nanak, the founder of Sikhism. People light candles in their homes and in gurudwaras. Langars are served on this day.





























































































































Use the internet to find three festivals that are celebrated all over the world.

1 Fill in the blanks.

Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
a Christmas is a festival celebrated on .
b is celebrated every year in October or November.
c Eid-ul-Fitr comes after , a month of fasting.
d The Chinese New Year falls between and .
e The Chinese New Year is celebrated with festivities such as colourful parades, dances and fireworks.
f is a festival to celebrate the birth of Guru Nanak.
2 Answer the following.
a In which month is Gurpurab celebrated?
b What is the another name for the Chinese New Year?
c Where do people go for special prayers during Eid-ul-Fitr?
d What is Diwali also known as?
3 Read about the celebrations. Unjumble the name of the festivals.
a Oil lamps, called diyas, are lit to remove darkness. (IWDAIL)
b People decorate trees with lights and stars. (HSTMICRSA)
c People eat langars. (PRBGUURA)
d This holiday marks the end of a month of fasting. (IED-LU-TRIF)

When we buy and sell items, we can make a profit or a loss. Profit is when a shopkeeper gets more money when selling an item. Loss is when a shopkeeper gets less money when selling an item than what they bought it for. Let us learn more about profit and loss.
The price at which someone buys an item is called its cost price. For example: If one buys a book for ₹250, the cost price of the book is ₹250.
The price at which a person sells an item is called the selling price. For example: If one sells a book for ₹350, the selling price of the book is ₹350.
The price that is marked on an item is called its market price.
When someone sells an item for a higher price than its cost price, they make a profit.
For example: If you buy a book for ₹250 and sell it for ₹350, you make a profit of 100 rupees.
When someone sells an item for a lower price than its cost price, they make a loss.
For example: If you buy a book for ₹250 and sell it for ₹200, you make a loss of ₹50.
Ask your parents how they have made a profit or loss while buying and selling objects in daily life.

Practice Time
1 Write True or False.

Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
a The price at which an item is sold is called the cost price.
b The price marked on an item in a shop is called the market price.
c We make a profit if the selling price is higher than the cost price.
d The price at which an item is bought is called the selling price.
e We make a loss if the cost price and the selling price are the same.
2 Fill in the blanks.
a Gurpreet bought a movie ticket for ₹350. This is the ticket’s price.
b Salina sold a pair of trousers for ₹600. This is the trousers’ price.
c Aanchal sold a table for ₹800. This is the table’s price.
d The tag on a watch in a shop says ₹550. This is the watch’s price.
e Rohit bought some apples for ₹90. This is the apples’ price.
3 Write down whether the items are sold at a profit or a loss.
a Neha bought a chair for ₹600 and sold it for ₹450.
b Aditya bought a hat for ₹150 and sold it for ₹300.
c Mukul bought a toy car for ₹300 and sold it for ₹350.
d Leena bought a box of paints for ₹200 and sold it for ₹75.
13. Oceans and Continents
1. a. Asia b. Australia c. Antarctica d. Africa
2. a. Antarctica b. Arctic c. Vatican City d. Asia e. Pacific f. South America g. Southern
3. a. North America b. Asia c. Africa
14. Kho Kho
1. a. chasing b. defending c. nine d. two e. chasers
2. a. False b. True c. True d. False e. True
3. a. Runner b. Post c. Chaser
15. Composting at Home
1. a. b. c. d. e. f.
2. Green Waste: Vegetable scraps, Fruit scraps, Plant trimmings, Animal manure
Brown Waste: Leaves, Sawdust, Paper, Cardboard Pieces
3. 4,1,2,5,3
16. The Constitution of India
1. a. 26 November 1949 b. 26 January 1950
c. 14 April 1891
2. a. constitution b. Constitution of India
c. Dr BR Ambedkar d. Constituent Assembly of India e. Hindi, English
3. a. 26 November b. 26 January 1950 c. 14 April
17. Passport
1. a. The Ministry of External Affairs
b. Passport Seva Online Portal
c. District Passport Cell d. Passport Office
2. a, d
3. a. False b. False c. True d. True e. False
18. India at the Olympics, 2024
1. a. Men’s 57 kg freestyle b. Javelin throw
c. Men’s 50m rifle 3 positions
d. Women’s 10m air pistol
2. a. Paris, France b. 117, 16
c. Manu Bhaker, Sarabjot Singh d. bronze e. 13
3. a. Manu Bhaker b. Swapnil Kusale
c. Aman Sehrawat
d. Manu Bhaker and Sarabjot Singh
e. Neeraj Chopra
19. Places with Extreme Climate
1. a. Antarctica b. Mawsynram
c. The Death Valley d. The Atacama Desert
2. a. Penguins, seals
b. Andean flamingo, Atacama toad
c. Desert tortoise, bighorn sheep
3. a. ANTARCTICA b. MEGHALAYA
c. DEATH VALLEY d. CHILE
20. Diseases and the Ways to Stop Them
1. a. Germs b. Air-borne
c. dirty d. Food-borne
2. a. common cold, flu b. typhoid, cholera
c. dysentery, diarrhoea
3. a, c, d, f
21. Firsts in Indian Films
1. a. 1913 b. 1931 c. 1937 d. 1957
2. a. Ardeshir Irani b. Jijo Punnoose
c. Moti B. Gidwani d. Dadasaheb Phalke
e. Mehboob Khan
3. a. Mother India b. Kisan Kanya
c. Raja Harishchandra d. Alam Ara
e. My Dear Kuttichathan
22. Countries and Their Capitals
1. a. Kathmandu b. Thimphu
c. Beijing d. Dhaka
2. a. Kathmandu b. Dhaka
c. Beijing d. Thimphu
3. a. Colombo, Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte
b. La Paz, Sucre c. Amsterdam, The Hague
4. a. South Africa b. Nauru
23. Festivals Around the World
1. a. 25 December b. Diwali c. Ramadan
d. 21 January, 20 February e. dragon f. Gurpurab
2. a. November b. Spring Festival
c. Mosque d. Festivals of Lights
3. a. DIWALI b. CHRISTMAS
c. GURPURAB d. EID-UL-FITR
24. Profit and Loss
1. a. False b. True c. True d. False e. False
2. a. cost b. selling c. selling d. market e. cost
3. a. Loss b. Profit c. Profit d. Loss

Introducing WISDOM, a 21st-century product for the learners of grades 3 to 5. It includes all curricular areas—English, Mathematics, Science, Social Science and General Knowledge. WISDOM is aligned with the NEP 2020 in terms of its design principles, and fulfils all recommendations of the NCF 2023.
Product Package
• Semester Books
• Uolo App
• Teacher Guide
• Focus on HOTS and Critical Thinking: Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical and evaluative thought processes
• Digital Aids: Animated talking books, interactive quizzes for additional practice and curated learning videos
• Experiential and Applicative Learning: Projects and activities designed for real-life settings, like lab activities and community projects, to enable the development and practice of life skills
• Rootedness to India: Examples from India’s unique culture and history, linked to each topic, to inculcate a sense of pride and love for the nation
• Model Assessments: Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and the application of skills
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-980880-5-5
