




English Mathematics
General Knowledge Science
Social Science

Academic Authors: Melanie Grobler, Chandani Goyal, Neena Aul, Animesh Mittal, Muskan Panjwani, Sneha Sharma, Anuj Gupta
Creative Directors: Bhavna Tripathi, Mangal Singh Rana, Satish
Book Production: Sanjay Kumar Goel, Tauheed Danish, Amisha Gupta
Project Lead: Chandani Goyal
VP, Learning: Abhishek Bhatnagar
All products and brand names used in this book are trademarks, registered trademarks or trade names of their respective owners.
© Uolo EdTech Private Limited
First impression 2025
This book is sold subject to the condition that it shall not by way of trade or otherwise, be lent, resold, hired out, or otherwise circulated without the publisher’s prior written consent in any form of binding or cover other than that in which it is published and without a similar condition including this condition being imposed on the subsequent purchaser and without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the above-mentioned publisher of this book.
Book Title: Wisdom 5 Semester 1
ISBN: 978-81-980880-1-7
Published by Uolo EdTech Private Limited
Corporate Office Address: 85, Sector 44, Gurugram, Haryana 122003
CIN: U74999DL2017PTC322986
Illustrations and images: www.shutterstock.com, www.stock.adobe.com and www.freepik.com
All suggested use of the internet should be under adult supervision.
In this 21st–century world, just “knowing” is not enough. Our dynamic and ever-changing world demands “thinking” skills. Learners need to be able to not just consume knowledge but also acquire higher-order thinking skills in various domains—be it in language, mathematics or general awareness—to apply that knowledge. This is the spirit and the recommendation of the NEP (National Education Policy) 2020.
It is in this context that UOLO has designed WISDOM, a 21st–century product for primary grade learners (grades 1 to 5) that includes all curricular areas—English, Mathematics, Science, Social Science and General Knowledge. WISDOM strongly aligns with NEP 2020 in terms of its design principles and fulfils all recommendations of the NCF (National Curriculum Framework) 2022–23.
English: This section not only focuses in listening, speaking, reading, writing, grammar and vocabulary, but also hones the ability to interpret, analyse and communicate confidently. The task-based approach and frequent opportunities for collaborative learning provided in this section encourage learners to express ethical views, interact constructively, solve problems creatively, apply their knowledge in new situations, and take responsibility for their own learning.
Mathematics: This section introduces mathematical concepts through real-life situations and storytelling, connecting them to children’s experiences and transitioning smoothly from the abstract to the concrete. Clear explanations and simple steps are provided for problem-solving. This section supports learners at all learning levels. It includes extensive practice aligned to the levels in Bloom’s Taxonomy—from basic practice questions to thought-provoking and higher order thinking questions.
Science: This section focuses on conceptual understanding, critical thinking, application, and problem-solving skills, making science learning highly relevant in the context of the 21st century. Each chapter is filled with vibrant illustrations, relatable examples, interactive activities, hands-on experiments and stimulating exercises. All of these instil a scientific temper in young learners and make learning a joyous experience.
Social Science: This section is designed to fascinate students about social science, both as a subject and as a practical experience, in their everyday lives, while also making them well-rounded individuals. Observations, inquiries and community-based learning experiences have been embedded throughout the book to develop an evaluative mindset and make learning a relatable and enjoyable journey for them.
General Knowledge: This section focuses on enabling the learners to be well-informed individuals so as to navigate through the complexities of the modern existence, make informed decisions, think critically and appreciate the world’s diversity. This section is crafted in keeping with the principles of NEP 2020, emphasizing the need to develop in learners the respect towards fundamental duties and constitutional values, generating awareness on one’s roles and responsibilities in a dynamic world, and fostering a sense of national pride and global citizenship. It offers an informative and enjoyable learning experience, incorporating clear explanations, captivating visuals and abundant questions for interactive classroom engagement.
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, introduced by the Government of India, represents a transformative shift in the country’s education system. It aims to create a more holistic, dynamic and multidisciplinary approach to education. NEP 2020 focuses on fostering conceptual understanding, skills, values, and competencies that align with the demands of the 21st–century, while also preserving India’s rich cultural heritage. UOLO is fully committed to actualising the vision of NEP 2020 by meticulously adhering to its outlined recommendations.









1. Focus on conceptual understanding
2. 21st-century skills values, and dispositions
3. Critical thinking and problem-solving
4. Application in real life
5. Holistic and integrated learning
6. Experiential learning
7. Enjoyable and engaging
8. Inquiry- and discovery-based approach
9. Technology-based solutions
10. Knowledge of India

Competency-based Education
NEP Pages 12, 17, and 22
Teaching and Learning Pedagogy
NEP Pages 3, 11, 12, and 27
National Pride
NEP Pages 15, 16, and 43
11. Assessment of core concepts and application skills Assessments
NEP Pages 12, 18, and 22

Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical and evaluative thought processes
1 2 3 11
Talking books with animations, interactive quizzes for additional practice, and curated learning videos to make learning fun and engaging
1 2 3 7 9 11
Projects and activities are set in real-life context, like lab activities and community projects, to enable the development and practice of life skills 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 11
Examples from India’s unique culture and history have been linked to each topic to inculcate a sense of pride and love for the nation
5 7 10
Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and application of skills in learners
1 2 3 11
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 outlines essential skills, values, dispositions and learning approaches necessary for learners to thrive in the 21st century. Wisdom incorporates these elements throughout its content, tasks and projects. Referred to as ‘NEP Tags,’ they are defined as follows:

Bringing creativity and fun into learning by combining music, drama and art with other subjects

GAMES
Using physical activities, sports and games to make learning active and fun

INTEGRATED

BHARAT
Cross-curricular linkages to make the learning experience more holistic, joyful and meaningful
Texts and tasks are rooted in the Indian context and culture to develop a sense of national pride
Using facts, logic and reasoning to understand problems and make smart decisions THINK RATIONAL

TEAMWORK
Embracing the spirit of mutual collaboration, communication and cooperation while working together or engaging in a guided conversation

SDG
Unwavering commitment to generating awareness of a green, peaceful, prosperous, equitable and inclusive world








Developing the skills to understand and manage emotions, build positive relationships and make responsible choices
HANDS-ON
Engaging actively in hands-on tasks to acquire knowledge and skills
HOTS


Encouraging higher-order skill such as analyzing, evaluating, problem-solving and fostering deep understanding
Generating awareness of a green, peaceful and prosperous world
Developing a mindset rooted in curiosity, critical-thinking, problem-solving and evidence based-reasoning
21st SKILLS
Fostering skills and knowledge—such as critical thinking, communication, and digital literacy—that are essential for success in today’s rapidly changing world
Promoting practices that support physical, mental, and emotional well-being for a balanced and healthy lifestyle


Building a strong character, guiding towards ethical decision making, and developing respect, kindness, and a sense of responsibility




Living things grow over time. A small plant grows into a big plant. A child grows into an adult.
Non-living things do not grow.




A small plant grows


—Shweta Ganesh Kumar

Draw or paste pictures of any three things that you love sharing with your friends.
Warm Up: A short and fun activity to assess the learners’ pre-knowledge and get them excited about the new topic
Investigate and Discover
Aim: Growing plants from seeds
Materials Needed: A plastic tub, soil, seeds,
Method:
Step 1: At home, look for a plastic tub that has


Step 2: Take the help of an adult and make bottom of the tub.
Elements: Interesting elements like Did You Know, Error Alert, Remember, and Think and Tell to keep the learners hooked
Do you think sharing is important? Why? Discuss in pairs.
Plants reproduce through seeds. When you plant a seed and the seed gets air, water and minerals, it grows into a new plant. For example, a mango seed grows into a mango tree.
Some plants reproduce with their body parts such as roots, stems and leaves.

Step 3: Soak the seeds in water overnight in can germinate easily.


Step 4: Fill the tub with soil and sow the seeds.
Non-living things do not reproduce. A table cannot make another table on its own.
Vocabulary: Meanings of difficult words
Meenu is tired of eating idli-podi for lunch every day, and Kamlesh cannot eat another bite of bhakri-bhaji! What do the classmates do to solve this problem? Let us read the story to find out.
Living Things Grow
Living things grow over time. A small plant grows into a big plant. A child grows into an adult.

3
Pause and Answer
Non-living things do not grow.
6. Long-answer questions.

Tick (✓) the correct statements.
Check for Understanding: Short exercises between the
1. Maps are flattened representations of the Earth.
2. A physical map shows countries and boundaries.

3. North is located to the opposite of South.
4. Directions can be found using a compass.
Do and Learn
other team.
Investigate and Discover Chapter • germinate: to start growing
A small plant grows into a big plant. A baby grows into an adult.
A. Why do you think different birds have different types of beaks and feet?
B. Compare the nests made by a weaver bird and a tailorbird.
C. What is migration? Why do birds migrate?
Aim: Growing plants from seeds

6. Long-answer questions.
Materials Needed: A plastic tub, soil, seeds, water Method:
D. Draw a new type of bird by combining features from three different birds that you have learnt about. Write one special thing about your new bird.
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Why do you think different birds have different types of beaks and feet?
B. Compare the nests made by a weaver bird and a tailorbird.
7. Picture-based question.
A. Why do you think different birds have different types of beaks and feet?
C. What is migration? Why do birds migrate?
Step 1: At home, look for a plastic tub that has not been in use.
B. Compare the nests made by a weaver bird and a tailorbird.

The team that finds all the objects first, wins.

Aryabhata was a
C. What is migration? Why do birds migrate?
D. Draw a new type of bird by combining features from three different birds that you have learnt about. Write one special thing about your new bird.
Look at the picture of a duck and answer the questions.
Step 2: Take the help of an adult and make small holes in the bottom of the tub.

7. Picture-based question.
Visual Prompts: Special questions featuring visual stimuli to foster comprehension, interpretation and critical thinking
D. Draw a new type of bird by combining features from three different birds that you have learnt about. Write one special thing about your new bird.
A. Look at the bird’s feet. Where do you think it lives?
Step 3: Soak the seeds in water overnight in a container so that they can germinate easily.
7. Picture-based question.
Look at the picture of a duck and answer the questions.
A. Look at the bird’s feet. Where do you think it lives?
B. Look at the bird’s beak. What do you think it eats?
Look at the picture of a duck and answer the questions.
A. Look at the bird’s feet. Where do you think it lives?
B. Look at the bird’s beak. What do you think it eats?
germinate: to start growing
HOTS: Intellectually stimulating questions designed for higher order thinking and analysis


Step 4: Fill the tub with soil and sow the seeds. Water it from time to time.
B. Look at the bird’s beak. What do you think it eats?

Challenge (HOTS)
Challenge (HOTS)

Challenge (HOTS)


If a bird with webbed feet were to live in a desert, what challenges might it face?
If a bird with webbed feet were to live in a desert, what challenges might it face?
If a bird with webbed feet were to live in a desert, what challenges might it face?
Life Skills
21st–century Focus: Simple activities and tips to develop a diverse set of essential skills for living well in the 21st century
Life Skills
Life Skills
Make a bird feeder to help our feathered friends find food. Follow these simple steps to create your very own bird feeder.


• Take a toilet paper roll. Use a spoon or a butter knife to spread peanut butter all over the outside of the toilet paper roll.
Make a bird feeder to help our feathered friends find food. Follow these simple steps to create your very own bird feeder.
• Take a toilet paper roll. Use a spoon or a butter knife to spread peanut butter all over the outside of the toilet paper roll.
• Thread a piece of string or yarn through the hole in the toilet paper roll and tie the ends of the string to create a loop.
Make a bird feeder to help our feathered friends find food. Follow these simple steps to create your very own bird feeder.
• Find a tree branch or a hook outside to hang your bird feeder.
• Thread a piece of string or yarn through the hole in the toilet paper roll and tie the ends of the string to create a loop.
• Find a tree branch or a hook outside to hang your bird feeder.
• Take a toilet paper roll. Use a spoon or a butter knife to spread peanut butter all over the outside of the toilet paper roll.
• Thread a piece of string or yarn through the hole in the toilet paper roll and tie the ends of the string to create a loop.

• Find a tree branch or a hook outside to hang your bird feeder.
7


Birds migrate in search of food, water and
where they can lay eggs and raise their babies. The Siberian crane migrates to India from Russia during the winters.
Wonders of Bharat

Think and Tell Do birds migrate back to their original places? If so, when and how?

Salim Ali was a famous Indian scientist who studied birds. He was popularly called the “Birdman of India”. He wrote important books about birds, helped create safe places for birds to live, and worked hard to protect them.
Think and Tell Do birds migrate back to their original places? If so, when and how?
National



Word Splash
Wonders of Bharat
Salim Ali was a famous Indian scientist who studied birds. He was popularly called the “Birdman of India”.
pectoral muscles: strong muscles located in the chest area migration: movement of birds from colder places to warmer places

Word Splash
pectoral


Explore More!
Scan the QR code to know more about birds.

Points to Remember
Points
• Birds have wings and feathers, which are useful for flying.
are useful for flying.
• Birds use their beaks to catch and eat food.
• Birds use their beaks to catch and eat food.
• Feet and claws help birds to walk, perch, climb, and catch food.
• Feet and claws help birds to walk, perch, climb, and catch food.

There are only five oceans on the Earth, not six. Pacific Ocean is written twice on the map. Error Alert!
• Birds live in nests. They lay eggs in them and also protect themselves from predators or harsh weather. Explore More! Scan the QR code to know more about birds.

Explore More!
Scan the QR code to know more about different types of animals.
Explore More!
Scan the QR
• Birds live in nests. They lay eggs in them and also protect themselves from predators or harsh weather.
Points to Remember: Summary of the chapter
6
Points to Remember
Points to Remember

• Wild animals live by themselves in nature. They find their food and live in the natural surroundings.
• Wild animals live by themselves in nature. They find their food and live in the natural surroundings.
• Pet animals are domestic animals that are kept by human beings for companionship.
• Pet animals are domestic animals that are kept by human beings for companionship.
• Herbivores eat plants, carnivores eat the flesh of other animals, and omnivores eat both plants and other animals.
• Herbivores eat plants, carnivores eat the flesh of other animals, and omnivores eat both plants and other animals.
• A food chain shows how living things depend on each other for food
• A food chain shows how living things depend on each other for food
Chapter Checkup: Chapter-end practice exercises aligned to different levels of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Error Alert!





Chapter Checkup
Chapter Checkup
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of these eats both plants and animals?
A. Which of these eats both plants and animals?
Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore All of these
Herbivore Carnivore Omnivore All of these
B. Which of these animals is a carnivore?

Summative Assessments:
266 There are only five oceans on the Earth, not six. Since the Earth is round, the Pacific Ocean is written twice on the map.
B. Which of these animals is a carnivore?
Rabbit Deer Lion Cow
Rabbit Deer Lion Cow
C. Which animal is most likely to be found in a farm?
C. Which animal is most likely to be found in a farm?
Oceans are very important. They are home to many aquatic plants and animals. People can also travel from one continent to another by crossing oceans through ships. Oceans also support industry
Wolf Horse Elephant Shark
Wolf Horse Elephant Shark
D. What type of animal is a zebra if it eats only plants?
D. What type of animal is a zebra if it eats only plants?
Oceans are very important. They are home to animals. People can also travel from one continent oceans through ships. Oceans also support the fishing industry. Each continent and ocean has its unique features and wildlife. We must not pollute the oceans so that we don’t harm the aquatic plants and animals.
Each continent and ocean has its unique features and wildlife. We must not pollute the oceans so that we don’t harm the aquatic plants and animals.
Do and Learn
NEP Tags: To show alignment with NEP skills and values

Herbivore Carnivore and wild Omnivore and pet Omnivore and farm
Carnivore and wild Omnivore and farm
Experiential Learning: Multidisciplinary, holistic, and fun activities / projects to understand the concept better
With the help of your teacher, draw the world map on the ground. The teacher will then call out the name of a continent or ocean and you will take turns to go and run towards the correct location on the map. Whoever gets the maximum correct markings wins.

With the help of your teacher, draw the world
Wonders of Bharat
The Indian Ocean is the third largest ocean in the world. It is
Splash

The teacher will then call out the name of you will take turns to go and run towards map. Whoever gets the maximum correct
8

Name of the Student: Time: 1 Hour Total Marks: 50
1 Write True or False. (4 marks)
A The place value of 5 in 7645 is 50.
Wonders of Bharat
B The face value of 3 in 5673 is 3.
C The expanded form of the number 4190 is 4000 + 100 + 90.
D The number name for 1740 is
The Indian Ocean is the third largest ocean in the world. It is named after our country, India.


Vocabulary Grammar
Ending a story
Listen and fill in Roleplay– community workers
Types of nouns –proper, common, collective, concrete, material and abstract
Text-based vocabulary
Alphabetical order Dictionary hunt–parts of speech
Summary writing
Skit about a humourous incident
Listen and answer
Notice writing
Giving directions
Listen and follow directions
Subject-verb-object
Transitive and intransitive verbs
Subject-verb-agreement
Singular and plural Suffixes
Pronouns–personal, demonstrative, possessive, interrogative and reflexive
Collocations
Dictionary hunt Synonyms
Comprehension
Factual questions Ordering Making inferences Making connections
Type
Author/Poet
Chapter
Themes
S.No
The Shawl Fable
1. Community
Factual questions
Identifying contextual meaning Analysing character actions and traits Making connections
Realistic story
Ruskin Bond
Project 1: A Visit to the Post Office 2. Wit and Humour The Adventure of Toto
Formal letter
Persuasive speech
Listen and choose
Articles–definite and indefinite Modal verbs–can, may, should, must
Collocations Synonyms
Factual questions Identifying setting, characters, problem and solution Making inferences Identifying point of view Analysing character traits Doing research
Biography
Making connections Factual questions Making inferences Identifying contextual meaning Poetry appreciation–personification, theme, main idea
Compound adjectives
Homographs
Factual questions Identifying character actions and motivation Identifying contextual meaning of idioms Summarising Making inferences Identifying theme and symbolism Making connections
Text-based vocabulary Synonyms Mind map –Nature
Making connections Factual questions Identifying theme Making inferences Poetry appreciation–personification, rhyme, imagery, repetition and alliteration
Article writing
Narrate an anecdote
Listen and fill in a chart
Types of adverbs–manner, time, degree, frequency
Dictionary hunt Phrasal verbs
Word web
Text-based vocabulary
Making connections Ordering Summarising Factual questions Making inferences Identifying stereotypes
Making connections Identifying main idea Identifying contextual meaning Identifying assonance and onomotopoeia Poetry appreciation–imagery
3. Compassion The Life- Saving Dog
4. Compassion Kindness Edgar Albert Guest Poem
Folktale
5. Peace and Harmony Old Jaideep and the Carpenter
6. Peace and Harmony Laughing Song William Blake Poem
Project 2: Promoting Peace and Harmony
Biography
Space India’s Star in Space
7.
8. Space Speedy Rocket Joseph Coelho Poem



Think about something you loved but lost.
What did you lose?
Why was it special to you?
Did you find it again? How?
First share your story and feelings with a partner and then with the class.
Nicki’s Dadijaan gives him something very special and asks him to be careful with it. But, something unexpected happens to the gift, that neither Nicki nor his Dadijaan could have imagined. What is this unexpected event? Let’s find out.

Let’s Read

Nicki lived with his grandmother, whom he lovingly called Dadijaan, in a quaint, little village in Himachal Pradesh. Every summer, Kaku Dada brought colourful shades of wool for Dadijaan to choose from. This year was no different. Kaku Dada displayed bright red, sunny yellow, deep blue, lush green, and even some multi-coloured balls of wool. Dadijaan decided to knit a shawl for Nicki and called him over to choose a colour. But, Nicki had a different idea, ‘I want my new shawl to be as white as snow,’ he declared. Dadijaan hesitated. ‘If you drop it in the snow,’ she warned, ‘you’ll never find it.’ But Nicki was adamant. He loved the idea of a snow-white shawl, and finally, Dadijaan agreed.
What did Nicki request?
All summer long Dadijaan’s needles clicked rhythmically as she knitted the shawl. Finally, as the last leaves of autumn fell and the first snowflakes began to fall from the sky, Dadijaan finished the shawl.
Nicki wrapped himself in the warm, white shawl and gave Dadijaan a hug. He stepped outside to play when he heard Dadijaan shout, ‘When you come home, first I’ll look to see if you are safe and sound, and then I’ll look to see if you still have your snow-white shawl.’

quaint: attractive and old fashioned adamant: determined, unwilling to change her mind rhythmically: making a pattern of sound


Before long, as it sometimes happens, Nicki dropped his shawl and forgot all about it. Soon, a mole, tired from tunnelling, discovered the shawl and moved in. It was warm and cosy inside. A rabbit hopped looking for shelter and warmth. He too saw the shawl and moved in. The mole didn’t think there was any room, but when he saw how cold the rabbit was, he moved over.
Next, a porcupine came snuffling by. Having spent all day looking under wet leaves for things to eat, he crawled into the shawl to warm himself. The mole and the rabbit thought there was no room for a third one, but who could argue with someone covered with quills? Moreover, they wanted to help.
A big owl who was attracted by the commotion, swooped down. The animals thought there was no more room, but when they saw his big talons, they quickly let him in.
Up through the snow appeared a marmot. He saw the shawl and began to get in. The mole, the rabbit, the porcupine, and the owl were not too pleased. But still, they moved over.
Soon a fox was trotting by. She saw the shawl and poked in her muzzle. When the mole, the rabbit, the porcupine, the owl, and the marmot saw her shivering, they let the fox squeeze in.
tunnelling: digging any room: (here) any space
snuffling: smelling something and making a sound while doing it quills: long sharp points on the body of a porcupine
Name all the animals who got into the shawl.
commotion: a lot of noise and activity swooped: moved quickly and suddenly downwards through the air talons: hooked claws muzzle: nose and mouth
A big brown bear lumbered by. He saw the shawl and nosed his way in. The animals were packed in as tightly as could be. The shawl stretched many times its size, but Dadijaan’s knitting held fast .
Along came a meadow mouse, no bigger than an acorn. She wriggled into the one space left, on top of the big brown bear’s nose. Her whiskers tickled the bear’s nose, and he gave an enormous sneeze, ‘Aaaaaaa–aaaaa–aaaaa–Chooo!’
The force of the sneeze shot the shawl up into the sky and scattered the animals in all directions.
Is it possible for so many animals to fit into the boy’s shawl? Why do you think the author tells the tale in this way?
On his way home Nicki saw a white silhouette fly up into the sky. It was his shawl. He ran to catch it. As he drew closer to home, he saw Dadijaan’s face in the window. First, she looked to see if he was safe and sound, and then she saw that he still had his new shawl.
As for the animals, they landed safely and quickly ran to their holes.

lumbered: moved slowly and clumsily acorn: a nut of an oak tree wriggled: moved by twisting and turning enormous: very big scattered: thrown in different directions silhouette: an outline of something against a lighter background
Listen to all the keywords here.




1. Write True or False.
a Nicki’s Dadijaan was confident that a snow-white shawl was a good idea.
b The mole was the first animal to discover the shawl and decided to move in because it was warm and cosy.
c The shawl ripped apart when the bear tried to squeeze in with the other animals.
d The owl was the last animal to join the others in the shawl before it flew up into the sky.
e When Nicki saw the shawl flying into the sky, he ran to catch it.
2. Answer the questions in three to four sentences.
a Prove from the story that the wool Kaku Dada brought was ‘colourful’. Which colour did Nicki choose, and why?
b Why did Dadijaan think the colour Nicki chose for the shawl was not a good choice?
c What did Nicki do when Dadijaan had finished knitting the shawl?
d Which animals found shelter in the shawl, and in what order did they arrive?
e Describe what happened when the bear sneezed.
3. Fill in the key details using words from the story. Then, arrange the events in the correct sequence from 1–5.
a One day, Nicki his shawl while playing outside. A mole found the shawl and decided to in because it was warm and cosy.
b Finally, Nicki saw his shawl in the sky and ran to it. When he got home, Dadijaan checked to see if he was safe and and if he still had the shawl.
c Nicki, who lived with his grandmother in a small village in , asked for a white shawl even though she him it was easy to lose.

d When a small mouse’s whiskers tickled the big brown bear’s nose, the bear gave an sneeze, sending the shawl flying into the .
e As more animals looked for , the shawl stretched to fit them all, including a porcupine, a big , and even a fox.



1. Answer these questions in three to four sentences.
a ‘When you come home, first I’ll look to see if you are safe and sound, and then I’ll look to see if you still have your snow-white shawl.’
What do these lines tell us about Nicki’s Dadijaan and the relationship between Nicki and Dadijaan?

b The mole didn’t think there was any room, but when he saw how cold the rabbit was, he moved over.
How would you describe the mole’s action? Which other reasons are given for allowing more animals in?
c Considering the actions of the animals and Dadijaan’s care for Nicki, explain how the story highlights the theme of sharing and caring.
2. Read the following descriptions from the story and answer the questions.
a Nicki lived with his grandmother in a quaint village in Himachal Pradesh.
What does the word ‘quaint’ tell us about the village where Nicki lives?
b Every summer, Kaku Dada brought colourful shades of wool for Dadijaan to choose from.
What does Kaku Dada do in summer and autumn and how is this similar to what some animals do?
c Finally, as the last leaves of autumn fell and the first snowflakes began to fall from the sky, Dadijaan finished the shawl.
How do the descriptions of the seasons help you understand the time period over which the story takes place?
d Nicki wrapped himseslf in the warm, white shawl and stepped outside to play.
Based on this description, what can you infer about the weather outside when Nicki goes to play?




Think about a time when you received a special gift.
a Describe the special gift you received. What was it and why was it special to you?
b What did you do to take care of this special gift? Describe any specific actions or feelings involved.


1. Read the sentences in the table and match the bold words and their correct meaning. In which part of speech are these words used in the story?
The workers were tunnelling through the mountain to build a new railway.
Part of speech: the nose and mouth of an animal
The small cabin was warm and cosy during the winter storms.
Part of speech: shaking due to cold or fear
The girl stroked the horse’s soft muzzle.
Part of speech: warm and comfortable
We had to squeeze all our luggage into the tiny car.
Part of speech: making a hole or passage
After playing in the snow, the children came inside shivering.
Part of speech: press together tightly
2. Look up each word in the dictionary and write the part of speech next to it. Use the abbreviations (n, v, adj, adv). Then, write a sentence to illustrate the meaning of each word.
a quaint ( ):
b discovered ( ):
c rhythmically ( ):
d enormous ( ):
e trotting ( ):



• Common nouns are the general names of people, things, animals and places.
For example: boy, village, mole.
• Proper nouns are capitalised because they are the specific names of people, things, animals and places.
For example: Nicky, Himachal Pradesh
• Collective nouns are names for a group of people, things, animals, and places.
For example: a cluster of houses, a huddle of penguins (if there are just a few)
Here are some more examples of collective nouns:
A line/dynasty of kings
A panel of experts
A flock of tourists
A company of actors
A mob of rioters
A shoal/school of fish
A litter/pack of dogs
An opera of canaries
A drove of bullocks
A scuttle of crabs
A chain/group of islands
A series of events
A network of roads
A network of computers
A block of apartments
1. Name the type of noun and then, make a sentence.
a shawl:
b Himachal Pradesh:
c a parliament of owls:
d grandmother:

e acorn:

2. Complete each sentence with the collective noun in the box.
Hint Box: pack pile flock pride cluster
a A of ducks swam across the pond in a neat row.
b A of lions looked for a place to keep themselves warm.
c Dadijaan stacked a of books high on the library shelf.
d Nicki watched a of stars twinkling brightly in the night sky.
e A of wolves prowled through the forest, hunting for their next meal.
Concrete Nouns Nouns refer to physical things, people or places. They can be recognised by seeing, touching, hearing, smelling or tasting them.
phone, laptop, chair, girl, lion
Material Nouns These are also concrete nouns but they specifically refer to the material that something is made of. gold, iron, plastic, cement
Abstract Nouns These refer to ideas, feelings, emotions, anything that is not physical and cannot be recognised by using our senses. science, liberty, generosity, childhood, sympathy
3. Read the underlined nouns. Write C for concrete nouns, A for abstract nouns and M for material nouns.
a Nicki’s Dadijaan knitted a shawl using colourful wool which she carefully chose from a variety of colours.
b Nicki felt love for his Dadijaan when she gave him the shawl and he hugged her tightly.
c Kaku Dada brought different shades of wool so that Dadijaan could knit.
d The animals showed friendship by sharing the shawl, although it was very cramped inside.
e The last leaf of autumn fell as Dadijaan finished knitting the shawl, and the first snowflakes began to fall.
f Nicki wore a scarf made of silk, which shimmered beautifully under the lights.
We can make abstract nouns by adding a suffix to the root word.
• A suffix is a series of letters such as -ness, -ity and -tion.
• The root word can be a verb or adjective.
For example:
kind (adj/adv) kindness (abstract noun)
possible (adj) possibility (abstract noun) silly (adj/(adv) silliness (abstract noun)
Check the spelling—the -e in the root word could fall away and -y may change to i.
4. Add suffixes to the root words to form abstract nouns.
a forgetful
b happy
c responsible
d determine
e diverse
In your notebook, use the abstract nouns you made above in sentences of your own.


Listen Well

Listen to the text here.
Listen carefully to the text and fill in the blanks with the words from the text.
a In our neighbourhood, we started a community project.
b Mr Patel helped plant .
c Mrs Singh watered the every morning.
d Every , the community members gathered to share ideas and work together.
e They planted vegetables like and .
f Soon the garden expanded and became a place where people wanted to time.





Community helpers, such as construction workers, doctors, taxi drivers, shopkeepers, salespeople and bank employees perform important jobs that benefit everyone in the community.





a Choose a community worker and mime what he or she does. Your partner must guess which role you have chosen.
b Next, role play being the community worker you have chosen. Your partner will ask you questions.
i Begin with a greeting.
ii Ask questions about the job, for example, the hours worked, what is enjoyable and not enjoyable and a funny incident that happened while doing the job.
iii Finish the conversation by thanking your partner for their contribution.


Write an ending to the story given. When writing an ending make sure to think about what happened in the story so far and how the ending can be written to make the story meaningful and complete.
In a small town called Sunnyville, a group of neighbours noticed that the local park had no playground for the children. The kids often played in an empty area between buildings but they needed a safe place with swings, slides and climbing equipment. The neighbours decided to come together and build a playground for everyone to enjoy. Each neighbour contributed something special. Mrs Khan, a landscaper, designed the playground. Mr Kumar, a teacher, organised a fundraiser to buy the materials and Mr Singh, a carpenter, offered his help. The local youth group volunteered their time to help with the construction. Little did they know what the project would lead to.
Complete the story by writing an ending in about 60–70 words. Write a creative ending that will leave the readers satisfied.
Project Overview:
In this project, you will write a postcard to a classmate and visit the post office to send it.
What You Need:
• A postcard

















• A pen or pencil
• A postage stamp
Steps:
• As a class, pick a chit from the bowl to find out to whom you will send a postcard.
• Visit a nearby post office or a stationery store to get a postcard and a stamp. You may ask an adult to accompany you.
• Write the date on your postcard and include a message to the person, focusing on their quality or skill that you admire and want to learn from them.
For example: 16 July 2025
Dear Nishant,
I really admire the confidence with which you give your oral presentations. You are always so prepared. I hope you can give me a few tips on how to boost my confidence.
Your friend, Sanya
• Paste a postage stamp in the top-right corner of your postcard.
• Write the correct address of the person to whom you are sending the postcard. You may ask your friend or teacher for help.

• Ask an adult to take you to the post office. When you get there, give your postcard to the postman or drop it in the mailbox.
• While visiting the post office, take a moment to observe how letters, postcards, and couriers are processed and delivered. You could ask someone to share some information with you.

Final Presentation:
On the presentation day, sit in a group and share the postcard you received. Talk about:
• who sent you the postcard.
• the date it was sent and the date when you received it.
• how long it took to reach you.
• the message you received.
• how you felt when receiving the postcard.
• what you learnt at the post office.





Share your story in class. Get Set
What are some naughty things you have seen pet animals do?
The narrator’s grandfather brings home a pet monkey named Toto, but Toto does a lot of things no one expects. Let us read to find out what happens.



Grandfather bought Toto from a tonga driver for the sum of five rupees. Toto was a pretty monkey. His bright eyes sparkled with mischief beneath deep-set eyebrows, and his teeth were a pearly white. But his hands looked dried up. Yet, his fingers were quick and wicked, and his tail, while adding to his good looks, also served as a third hand. He could use it to hang from a branch; and it was capable of scooping up any delicacy that might be out of reach of his hands.
Grandmother always fussed when Grandfather brought home some new bird or animal. So it was decided that Toto’s presence should be kept a secret from her. Grandfather and I put him away in a little closet opening into my bedroom wall, where he was tied securely—or so we thought—to a peg fastened into the wall.
A few hours later, when Grandfather and I came back to release Toto, we found that the walls, which had been covered with some ornamental paper, now stood
Why was Toto kept as a secret from Grandmother?

mischief: playful troublemaking delicacy: a special, tasty treat fussed: worried securely: safely; in a manner to avoid escape
peg: a small hook or pin used to hang things ornamental: decorative naked: (here) bare, without paint or wallpaper
Toto was now transferred to a big cage in the servants’ quarters where a number of Grandfather’s pets lived very sociably together—a tortoise, a pair of rabbits, a tame squirrel, and, for a while, my pet goat. But the monkey wouldn’t allow any of his companions to sleep at night; so Grandfather, who had to leave Dehradun the next day to collect his pension in Saharanpur, decided to take him along.
A big black canvas kit bag was provided for Toto. When the strings of the bag were tied, there was no escape. His efforts to get out only had the effect of making the bag roll about on the floor or occasionally jump into the air.
Toto remained in the bag as far as Saharanpur, but while Grandfather was producing his ticket at the railway turnstile, Toto suddenly poked his head out of the bag and gave the ticket-collector a wide grin.
The poor man was taken aback, but he said, ‘Sir, you have a dog with you. You’ll have to pay for it accordingly.’ Toto was classified as a dog by the ticket collector, and three rupees was the sum handed over as his fare.
When Toto was finally accepted by Grandmother, he was given a comfortable home in the stable, where he had for a companion the family donkey, Nana.
A great treat for Toto during cold winter evenings was the large bowl of warm water given to him by Grandmother for his bath. He would cunningly test the temperature with his hand, then gradually step into the bath until he was in the water up to his neck.
What are some things Toto did that made him stand out?

sociably: in a friendly way pension: a regular income made by the government or a private company to someone who no longer works due to old age or ill health railway turnstile: a gate at an entrance that allows one person to pass at a time
taken aback: surprised or shocked classified: labelled companion: friend cunningly: cleverly

One day, Toto nearly succeeded in boiling himself alive. A large kitchen kettle had been left on the fire to boil for tea. And Toto, finding himself with nothing better to do, decided to remove the lid. Finding the water just warm enough for a bath, he got in, with his head sticking out from the open kettle. This was just fine for a while, until the water began to boil. He continued hopping up and down for some time, until Grandmother arrived and hauled him, halfboiled, out of the kettle.

One day, at lunchtime, a large dish of pulao-rice stood in the centre of the dining table. We entered the room to find Toto stuffing himself with rice. My grandmother screamed, and Toto threw a plate at her.
Toto picked up the dish of pulao and made his exit through a window. We found him in the branches of the jackfruit tree, the dish still in his arms. He remained there all afternoon, eating slowly through the rice, determined to finish every grain. Obviously, Toto was not the sort of pet we could keep for long. Even Grandfather realised that. So Grandfather found the tonga driver, and sold Toto back to him—for only three rupees.
What made Grandfather realise that they could not keep Toto for long?
hauled: dragged or pulled stuffing: (here) eating a lot of food
Listen to all the keywords here.



1. Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the story.
a Toto’s were described as ‘quick and wicked’.
b Grandfather and the narrator put Toto in a in the narrator’s bedroom.
c Toto wouldn’t let his in the servants’ quarters sleep at night.
d At the railway station, the ticket collector was taken when Toto stuck his head out of the bag.
e Toto sat on the branches of the tree, determined to finish every grain of the pulao-rice.
2. Write True or False.
a Grandfather wanted to hide Toto because he was worried how Grandmother would react.
b Toto improved over time, and by the end of the story, he had become a well-behaved pet.
c Grandmother was welcoming towards Toto. Therefore, Grandfather felt comfortable bringing home more unusual pets.
d Toto was not fond of warm baths as he would always check the temperature of water.
e Grandfather sold Toto for less than what he had bought him for.
3. Answer the questions in three to four sentences.
a How did Toto’s appearance contribute to his mischievous nature?
b What happened when Grandfather and the narrator left Toto in the closet?
c How did Toto create trouble during Grandfather’s train journey?
d Ruskin Bond uses humour to make the story fun and engaging. Describe the event in the story that according to you was the most humorous.
e Which event made Grandfather change his mind about keeping Toto as a pet?




1. In your notebook, write the words from the story that mean the same as the words below. Read the sentences they have been used in and then use the words in sentences of your own.
mischievous smartly firm and resolute
2. What do the actions of the following characters tell you about their qualities?
Hint Box: helpful caring accepting supportive adaptable enthusiastic confused compassionate
Narrator
• He seems excited about Toto’s presence.
• He doesn’t show any objections to Grandfather bringing home new pets.
Grandmother


• She eventually accepts Toto and gives him a comfortable home in the stable.
• She gives Toto warm baths.

Grandfather chose to keep an uncommon pet and the family faced many problems. We often read or hear about people with unusual pets.
Sit in a group of five. List a few such pets and discuss the possible challenges that people can face.
List the problems that an unusual pet might cause in a household:
Reflect on how people might overcome such challenges:


Singular means one person, animal, thing or idea. Plural means more than one person, animal, thing or idea.
For most nouns, add -s to the end of the singular form to make it plural. pet petS
For nouns ending in -s, -c, -z, -ch or -sh, add -es to form the plural. bus buses box boxes match matches quiz quizzes
For nouns ending in a consonant + -y, change -y to -ies for the plural form.
For nouns ending in a vowel + -y, add -s after -y for the plural form. cherry cherries key keys
For most nouns ending in -f or -fe, change -f or -fe to -ves for the plural form.
For some nouns ending in -f, add -s to form the plural. knife knives leaf leaves roof roofs handkerchief handkerchiefs
Some nouns do not follow the regular rules and have unique plural forms. tooth teeth child children
1. In your notebook, write the plurals of the words. Use the plural forms to make sentences.

2. Fill in the blanks with the correct singular or plural forms of the nouns.
a He packed his (sandwich) in his lunchbox.
b She picked some fresh (berry) from the bush.
c The (sheep) grazed in the field.
d There were many (butterfly) in the garden.
e The (leaf) have dried.
3. Choose the correct words to replace the words in the brackets.
Suffixes are letters or groups of letters that are added to the end of words to make new words.
a This (active) helps Nishant stay fit.
i activement ii activity
b The (dark) scared the little boy.
i darkment ii darkness
c They celebrated their (achieve).
i achieveness ii achievement
d The book gave us a lot of (inform).
i information ii informness
e Her (happy) was visible on her face.
i happyment ii happiness

Go Grammar

Subject-Verb-Object
In a sentence, the subject is the doer of the action and the object is the receiver of the action.









A sentence can be divided into the following parts:
The subject is who the sentence is about. It is the doer of the action.
The verb is the action or the state of being. The object is usually the receiver of the action or who/ what the action is about.
For example: Grandfather bought Toto. For example: Grandfather bought Toto. For example: Grandfather bought Toto. Grandfather is the doer of the action.
Bought is the action. Toto is the receiver of the action.
1. Read the sentences and fill in the columns.
Toto threw a plate at Grandmother. Toto threw (What did Toto throw?) a plate
Toto’s tail scooped up the banana.
The parrot picked a card from the deck.
Grandfather paid the tonga driver for Toto.
The ticket collector took the money.
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
• Transitive verbs are verbs that need an object, which means they include the receiver of the action in the sentence.
For example: Toto grabbed the dish of pulao. Here, the verb grabbed needs the object (the dish of pulao).
‘Toto grabbed’ is an incomplete thought that does not make sense.
• Intransitive verbs do not need an object to make a complete sentence.
For example: Toto jumped.
Here, even if we do not add any more details, the sentence is complete and conveys meaning.

2. Underline the verbs and write T for transitive verbs and I for intransitive verbs.
a Grandfather finds the tonga driver.
b We realised Toto was naughty.
c My grandmother screamed.
d The ticket collector classified Toto as a dog.
e Toto seemed to laugh behind his hand.
3. In your notebook, use the verbs below to make sentences of your own. Mark them as T or I (as in the previous exercise).
chased barked caught laughed threw
The subject of the sentence must agree with the verb in person and in number.
1. The verb to be must match the person (the subject of the sentence).
First person (I) am/was/have (We) are/were/have Second person (You) are/were/have (You) are/were/have Third person (He/She/It) is/was/has (They) are/were/have
2. In the simple present, the verb takes an -s/-es if the subject is He/She or It. The verbs match the subject.
Toto jumps into the kettle. The children jump into the bath. (He) (They)
3. Agreement in number means that if the subject is singular the form of the verb must be singular and if the subject is plural the form of the verb must be plural.
Uncountable nouns take the singular form of the verb.
Collective nouns usually take the singular form of the verb.
If the subjects are joined with and the verb will be plural.
If the subjects are joined with or, either/or, neither/nor, the verb will be singular or plural depending on the noun closest to the verb.
If the subject is a singular pronoun like each, nobody, everyone, every, the verb will be singular.
Plural pronouns like several, many, few, a few, both take the plural form of the verb.
When using here or there, the subject comes after the verb. The verb may be singular or plural depending on the subject.
When some is used with the subject, the verb will be singular or plural depending on the subject.
The titles of books, movies or other works are treated as singular.
The pulao tastes great.
The stack of cookies looks good.
Toto and the donkey fight.
Neither the Grandfather nor the narrator tells the Grandmother.
Either the Grandmother or the other pets push Toto out of the house.
Everybody laughs at Toto. Each pet gets a gift on Christmas. Nobody goes to bed on an empty stomach.
Several neighbours complain about Toto. Many children run when they see Toto. A few of them get hurt.
Here is hot water.
There are pets in the house.
Some rice is left. Some pets are unwell.
‘The Adventures of Toto’ is a popular story.

4. Fill in the blanks with verbs that agree with the subjects. Write the verbs in the present tense.
a Grandfather and I (put) Toto in a little closet, and we (hope) he will stay there.
b The dish of pulao (tempt) Toto, and he cannot resist it.
c Each member of the family (be) upset with Toto for a different reason.
d Neither Grandmother nor Grandfather (want) to keep Toto.
e ‘The Lord of the Rings’ (be) Grandfather’s favourite movie.
f Some animals (run) away when they see Toto. Listen to the text here.


Listen carefully to the story and fill in answers.
a What was the name of the clever crow?
b What food did the farmer have?
c From whom did Kulu get a banana?
d What did Kulu use to distract the kids in the park?
e What did the villagers do when they saw Kulu’s clever antics? Practise speaking here.



Sit in a group of six. Take turns to share a humorous incident from your life. Choose the incident that the group likes most and write a short skit. Practise the skit and present it in class.


Practise your lines, focussing on clear pronunciation and expressive delivery.
Use objects around you as props to make your performance engaging.
Use voice modulation, gestures and facial expressions.


To summarise is to briefly retell the main events in a story. A summary is always shorter than the actual story, because it covers only the main events written in the correct order.
Beginning:
Who are the characters?
Where does the story take place?
What is the problem?
Model Answer
Middle: End:
What happens?
How is the problem solved?
Beginning Middle End
Nikki was a young boy who lived in Himachal Pradesh. Dadijaan knitted a pure white shawl for him. One day, while playing outside, Nikki dropped the shawl in the snow and couldn’t find it.
A mole found the shawl and crawled under it for warmth. He was joined by a rabbit, a porcupine, an owl, a marmot, a fox, a bear and a mouse who found a place on the bear’s nose.
When the mouse’s whiskers tickled the bear’s nose, he gave a huge sneeze which made all the animals scatter. Nikki noticed his shawl in the air and ran to catch it. He had found his shawl!
In the notebook, summarise the story ‘The Adventures of Toto’ in your own words.




Get Set

Think about a hero from history or a hero in a TV programme or film. Choose three qualities that you think are important for someone to be a hero. Make notes and share with your partner why you chose these qualities. You may consider qualities like these:
bravery kindness strength determination intelligence compassion
In the freezing winter of 1925, a serious illness spread through Nome, Alaska. Read the story of how a brave dog helped to get medicine to the people there.



I never thought I’d owe my life to a dog, but then I never imagined being so sick. It all started in the harsh winter of 1925 in our small town of Nome, Alaska. Diphtheria had struck, and without the life-saving antitoxin, many of us, especially the children, were in grave danger.
Why were the children in grave danger?
I remember lying in bed, shivering, my strength fading. The air was so cold it felt as if ice was cutting through my lungs. My only hope was that we would get the antitoxin in time, but the only supply was in Anchorage, which was hundreds of miles away. The stormy weather made it impossible to use planes or boats.
Sled dogs, like Balto, can pull heavy loads over long distances. They often run more than 80 kilometres a day in difficult conditions.
owe: to feel grateful for the help received Diphtheria: a serious bacterial infection that affects the respiratory tract and can be dangerous without treatment
Why couldn’t the boats and planes be used to transport the vaccine?
antitoxin: medicine that works against the germs that cause an illness grave: very serious


Our last hope was the brave sled dog teams and their mushers who volunteered to bring the medicine to us.
Balto was a Siberian husky, part of one of these heroic teams. Led by musher Gunnar Kaasen, Balto was not even the lead dog at first. Many didn’t believe he could lead, but fate had a different plan. With temperatures dropping to –40°C and winds howling fiercely, the journey was dangerous.
Balto and the other dogs ran tirelessly, their paws bleeding from the ice. They crossed frozen rivers, climbed over steep mountains, and pushed through blizzards that blinded them. Along the way, some dogs and mushers lost their lives in the harsh weather. Balto, however, seemed to have an unbreakable spirit.
When the lead dog of the team was hurt, Balto stepped up, taking the lead. It was as if he understood the urgency of his mission. He guided the team through the icy wilderness with incredible determination. The team had to run in total darkness, guided only by Balto’s instincts.
sled: vehicle used for travelling over snow mushers: persons who drive a sled pulled by dogs
fate: something that happens that you have no control over blizzards: heavy snowstorms with strong winds
stepped up: took the necessary action urgency: the importance of acting quickly and immediately instincts: natural feelings or abilities that guide behaviour without needing to think
After five long days and nights, Balto and his team finally reached Nome. The town erupted in cheers, but my tears were of relief. The medicine was here, and with it, hope. Balto had made it, saving countless lives, including mine.
For days, I could only think of the bravery and endurance of that amazing dog. Balto became a hero, a symbol of hope and courage. He showed us that even in the darkest times, light can shine through the most unexpected places.
Balto lived the rest of his life in Cleveland Zoo, where he was nursed back to health, loved, and honoured. Today, a statue of Balto stands in Central Park, New York, celebrating his incredible journey and reminding us of the power of perseverance and bravery. Each time I hear the story of Balto, I feel a surge of gratitude for the dog that saved my life and the lives of so many others. Balto, our four-legged hero, will forever be remembered.
What feelings does the narrator experience when remembering the story of Balto?
endurance: the ability to keep going when things are tough perseverance: the quality of not giving up
How did Balto demonstrate his unbreakable spirit?

Listen to all the keywords here.




1. Fill in the blanks.
a This story takes place in in during a very cold winter.
b The only thing that could save the people who were struck by the disease called was a life-saving .
c When planes and boats couldn’t help, the town’s only hope was the and their .
d On their long trip, and the other dogs kept running even when their were bleeding from the ice.
e After a dangerous trip through and , Balto and the team reached their goal, bringing hope to the town.
2. Fill in the graphic organiser with information from the story.
Solution: Setting: Place: Weather: Mood: (at start and in the end)
Title of the story:
Characters:
Problem faced by the people
3. Answer the questions in two to three sentences.
a Where did the antitoxin have to come from? Can you think of a reason why?
b What kind of weather did Gunnar Kaasen and his team of dogs face? Describe it in detail.
c How did Balto’s role in the team change during the journey?
d How did the people of the town react on seeing Balto and his team? How was the narrator’s reaction different?
e What were the narrator’s feelings towards Balto?



A story can be told from different points of view. These are:
First person: The story is told by a character using I, we, me and our. You see the story through a character’s eyes.
Third person: The story is told by someone outside the story, using he, she, it, or they to describe characters.
1. Tick () the point of view from which this story is told.
First person
Third person
Write two sentences from the text that show the point of view.
2. Read the information and write which qualities these actions show. You can choose from the list or use your own words.
Hint Box: selflessness determination trust fearlessness wisdom bravery leadership daring confidence courage






Balto
Gunnar Kaasen
When the lead dog of the team was hurt, Balto stepped up, taking the lead.
Balto and the other dogs ran tirelessly, their paws bleeding from the ice.
He guided the team through the icy wilderness relying on his instincts.
He volunteered to bring the medicine to Nome.
He travelled in tough weather conditions, with temperatures dropping to –40°C and winds howling fiercely.
The team had to run in total darkness.
Based on the qualities of Balto and Gunnar, write the theme of the story.
The theme is the main idea or the message of the story. For example: Kindness


Balto and Gunnar Kaasen showed heroism and bravery. There are others in our country who have shown courage and bravery to save the lives of others.
Do research about one such person. Sit in a group of four and share your findings.
Discuss the following:
• The name of the person.
• What the person did.
• Were they rewarded for their heroic deed?
• What lesson did you learn from them?


Collocations are pairs or groups of words that are often used together. They can be thought of as word partners. They sound natural because they commonly appear together in speech and writing.
For example: fading strength grave danger unbreakable spirit natural instincts
How to use a dictionary to find collocations
• If you are looking for collocations for ‘heroic’ find ‘heroic’ in the dictionary.
• Under the entry for ‘heroic,’ you might find collocations like heroic deed or heroic figure.
1. Using the dictionary, identify collocations for the words. Underline the correct words and use them in the sentences.
• harsh: dog/weather
• catch: a cold/fright
• thoughtful: deed/work
• brave: doing/effort
• warm: laugh/smile
a The firefighters made a to rescue the people trapped in the building.
b Despite the , the team completed the marathon.
c Her made everyone feel welcome at the party.
d Be sure to wear a jacket so you don’t in this chilly weather.
e His of helping his neighbour with groceries made her day brighter.
2. Match the words to form collocations. In your notebook, use the word pairs to make sentences.
kind
act express
words
charitable offer tender
gratitude
generous care



Pronouns are words used in place of a noun. Personal pronouns stand for the names of people, animals and things.
For example:
Rohan went to the market. He bought a new shirt. Personal pronouns can be subjects or object.
Person
Singular Plural Singular Plural
First person I we me us
Second person you you you you
Third person he, she, it they him, her, it them
Possessive, Demonstrative, Interrogative and Reflexive Pronouns
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to show that something belongs to someone.
First person: mine, ours
Second person: yours
Third person: his, hers, theirs
This bag is yours and that one is mine. Please give the box to Neha. It is hers.
Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. The answer to the question should be a noun.
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns point to the objects to which they refer.
these, those, this, that
This is my dog. That is my house. These are ours. Those are yours.
Reflexive Pronouns
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a sentence are the same person or thing. It reflects the action of the verb back to the subject. who, what, which, whom, whose and which. myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves and themselves
Which is your favourite season? Who got the medicines?
The musher prepared himself for the journey. The dog cleaned itself after eating.
1. Fill in the blanks with the appropriate possessive pronouns.
a Balto’s determination saved the town. The determination was .
b The sled dogs’ efforts were crucial. The efforts were .
c The musher ’s leadership guided the team. The leadership was .
d The mushers volunteered their services. The idea of fetching the antitoxin was .
2. Fill in the blanks with the correct demonstrative pronouns.
a was an incredibly tough journey.
b dogs over there were part of the team.
c is the same map they used to navigate.
d medicines in my hand are the ones we needed.
3. Read each statement below and frame a question using the appropriate interrogative pronoun.
a Statement: The team leader guided the dogs through the blizzard.
Question:
b Statement: The path behind the mountain was considered the safest path.
Question:
c Statement: You borrowed the musher’s map.
Question:
d Statement: The musher ’s jacket was left at the campsite.
Question:
4. Complete the sentences with the most appropriate reflexive pronouns.
a The musher prepared the sled .
b I reminded to stay focused.
c The dog licked after the injury.
d We must get the medicine .



Listen Well

Listen and trace the route on the map.
Listen to the text here.
The destination you will reach is the .





Pay attention to the directions, especially the turns (left or right) and landmarks mentioned.
Refer to the compass on the map to ensure you are moving in the correct direction (North, South, East, West).

Practise speaking here.
Sit in pairs. Look at the map and choose a place where you and your partner are standing. Now, ask your partner to decide where he wants to go.
Give step-by-step instructions to reach the place.
Turn left at the… Go straight along until you reach… Head North from… Start at the… and go…
You will pass the… on your… After the…, turn… When you see the… you are almost there.
When you reach… your destination… will be on your…
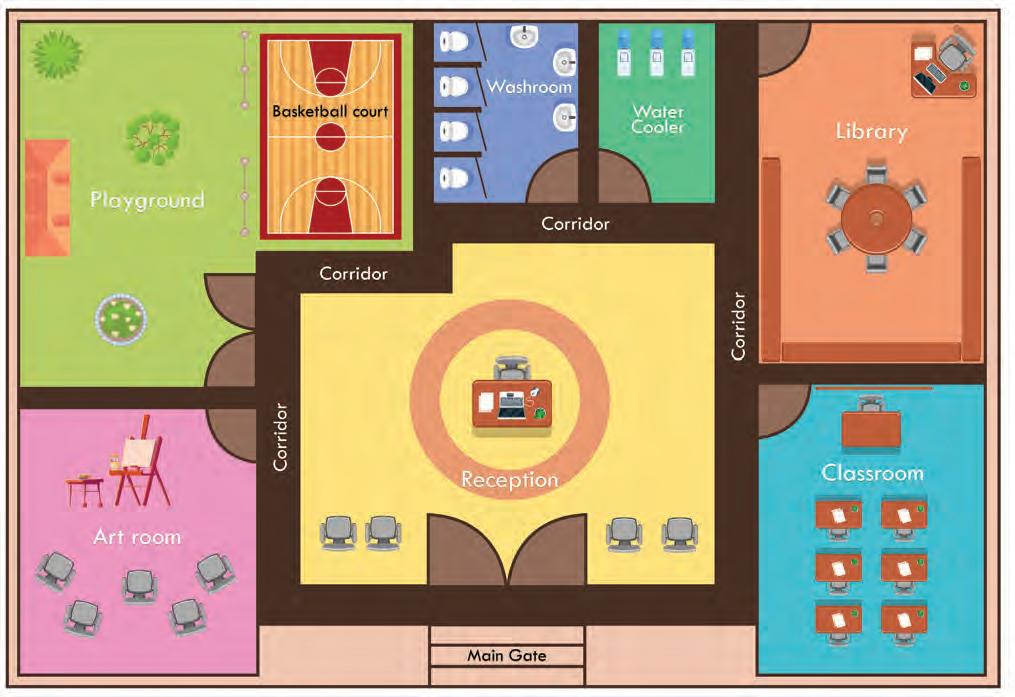



Share the exact starting point.
Use correct words to indicate turns and directions (go straight along, left and right; East, West, North and South).
Mention landmarks on the way.

A notice is a written or printed announcement that is used to inform a group of people about an event or provide information. Notices are displayed in public places or distributed to ensure that people get the information.
A notice must…
• give all the necessary information, for example, the time, venue, date, last date to register and who to contact for more information.
• mention the purpose of notice clearly.
• use impersonal language (write in the third person and avoid using I and you.
• be placed in a box.
• be concise (60–80 words).

25 July 2025
Kindly note that an Annual Science Fair is being organised by our school. This will give the students an opportunity to showcase their innovative projects and experiments. The details are:
Date: 10 August 2025
Time: 9:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m.
Venue: School Auditorium
All students from Grade 5 and 6 are encouraged to participate. Interested students must register by 3 August 2025. Registration forms are available at the Science Department office.
There will be prizes for the best projects. For more information, please contact Mr Sharma in the Science Department or email him at sharma@example.com.
Nidhi Yadav Secretary Science Club
Name of the institution
Header Date
Title/Subject
Body of the Notice
• Purpose of the notice
• Date, time, venue, etc.
• What the readers should do
• Contact information
Signature
Details of the person in charge
You are the Head Boy of your school. In your notebook, write a notice to inform the students about an upcoming bake and sale event to raise funds for a local shelter. Include details about the date, time and location of the event, and how they can contribute or participate.

—Edger Albert Guest


There are many stories that tell us how one kind word or act has changed people’s lives forever.
Think of your own life. How has something someone said or did made a big difference in your life?
Who was the person?
What was the situation and what did the person do or say?
How did this change the situation or your life?
If you want to, share what you wrote with your classmates.
Even the smallest acts of kindness can show others that we care about and respect them. A smile here and a kind word there can make all the difference. Let’s see what the poem says about the importance of kindness.



One never knows
How far a word of kindness goes; One never sees
How far a smile of friendship flees.
Down through the years,
The deed forgotten reappears.
One kindly word
The souls of many here has stirred.

Do we always know how our kind acts affect others? Which words in the poem tell us this?
flees: (here) how far it spreads reappears: appears again
stirred: makes people think or feel something deeply
Man goes his way
And tells with every passing day, Until life’s end:
“Once unto me he played the friend.”
We cannot say What lips are praising us today.
We cannot tell
Whose prayers ask God to guard us well.
But kindness lives
Beyond the memory of him who gives.

There are many Heroes of Kindness in India like KR Ushakumari who has been trekking through a dangerous forest and rowing across a river for 17 years to teach 14 children in a tiny village school.

unto: an old English way of saying ‘to’ praising: saying good things about someone guard: protect
Think and Tell
How does kindness live on?
Listen to all the keywords here.




1. Fill in the blanks with words from the poem.
a A word of kindness may go .
b A friendly smile can be remembered for many .
c An act of kindness, though forgotten, eventually .
d A single word of kindness has many people’s hearts.
e We’re unaware of who might be saying for our well-being.
2. Answer the questions in one to two sentences.
a According to the poem, what happens to a kind deed over time?
b Write ‘Once unto me he played the friend’ in your own words.
c Why does the poet say we cannot tell whose prayers are asking God to guard us?
3. Read the lines from the poem and answer the questions.
Down through the years, The deed forgotten reappears. One kindly word The souls of many here has stirred. Man goes his way And tells with every passing day, Until life’s end: Once unto me he played the friend.
a According to the poem, what effect does one kindly word have?
b How do people remember acts of kindness, according to the poet?





The poem ‘Kindness’ and the story ‘A Life-Saving Dog’ reflect the theme of Compassion and Humanity.
Name and discuss any other text that has a similar theme with your partner. A text may be a story, an article in the news, a movie, a cartoon or a TV programme.
Name: . Text


That reminds me of the text because Text (text in the Coursebook) In the poem/the story


1. Match the words to form collocations. a word of hand generous heart selfless spirit helping deed warm kindness
In your notebook, use the pairs to write sentences of your own.

2. Replace the underlined words with a synonym from the box. Then, rewrite the sentence using the new word.
Hint: Use a dictionary wherever needed!
Hint Box: gentle compassion bond companionship
a Showing kindness is important when dealing with people and animals.
Synonym:
b I appreciated his friendship even more when times were hard.
Synonym:
c A soft answer can calm an upset friend.
Synonym:
d Good pals have a special connection.
Synonym:



Personification is when a non-living thing is given a human quality. For example: The chair sits in one corner.
1. In your notebook, write a line from the poem where kindness has been personified. Also, explain what the poet means by the line.
2. What is the theme of the poem? State the poet’s message.
3. If you were to rename this poem, what title would you give it? Provide the new title and a reason for your choice.





Which situation would you prefer being in? Why? Get Set
Two old friends have a disagreement which ruins their friendship. Let’s find out what the fight is about and how it is resolved.




In a village in Punjab, old Jaideep and his neighbour Balbir had been best friends for as long as they could remember. They had been through life’s ups and downs together and had stood shoulder to shoulder in good times and in bad. In their old age, they only had their farms and each other.
One day, however, their friendship hit a bump. It started with a quarrel about a stray calf. The calf had wandered onto Balbir’s land, so he thought it was his.
‘Balbir, that calf belongs to me,’ Jaideep insisted.
‘Jaideep, you always think everything is yours! It’s on my land, so it’s mine!’ Balbir retorted.
‘You always want to take what’s mine!’ Jaideep shouted.
‘And you never share!’ Balbir yelled back. Their faces had turned red with rage. Let’s Read
stood shoulder to shoulder: supported each other
hit a bump: faced a problem or difficulty quarrel: a verbal argument or fight about something
stray: an animal that has wandered away from its owner’s home retorted: replied quickly and sharply yelled: shouted rage: anger
Both men were too stubborn to back down, so they stopped talking to each other. Jaideep felt quite gloomy about it but he did not want to be the first one to give in. They ignored each other for weeks until something unexpected happened.
Why did Jaideep and his neighbour have a fight?
One morning, there was a knock on Jaideep’s door. He opened it to find a woman carrying a toolbox. She had kind eyes and a gentle voice.
‘Hello, I’m a carpenter looking for work. Do you have anything I can help you with?’ she asked.
Jaideep was confused. He had not called for a carpenter. His eyes strayed towards Balbir’s farm and an idea struck him. He welcomed her inside and offered her water.
‘I have a job for you,’ Jaideep said, pointing through the kitchen window. ‘See that farm over there? That’s my neighbour Balbir’s. He has dug a ditch between our farms to divert water from the upper pond to his land. He is just being spiteful.’
What did Balbir do to hurt Jaideep?
‘Since he holds a grudge against me,’ Jaideep continued, ‘I want you to build a big fence between us. I don’t want to see him again or to continue our friendship.’
The carpenter understood what was needed.
Jaideep had to go to town for supplies, so he got his bullock cart ready and showed the carpenter where everything was in the store room.
She worked quickly and efficiently, measuring, sawing and nailing planks together. As the sun began to set, Jaideep returned from town. To his surprise, instead of a fence, he saw a beautiful bridge with sturdy handrails over the ditch.
Even more surprising, Balbir was walking across the bridge with his hand outstretched. ‘Jaideep, you’re truly amazing to build this bridge. I never would have thought of it. Let bygones be bygones. I’m so glad we can be friends again,’ Balbir said.
stubborn: unwilling to change one’s mind back down: give in diverting: changing the direction of something spiteful: mean and hurtful holds a grudge: continues to be angry efficiently: quickly and effectively
sturdy: strong and not easily broken handrails: bars that you can hold on to for support, usually on stairs or bridges outstretched: extended (to) let bygones be bygones: to forget the past and move on

Jaideep, full of emotion, hugged his friend and confessed, ‘The calf is yours. I’ve always known it. I’m sorry.’
The old friends decided to bury the hatchet and laughed at how obstinate they had been. As the carpenter started packing her tools, Jaideep called out, ‘Wait! Please stay. I have many more projects for you.’
The carpenter smiled warmly. ‘I’d love to stay, Jaideep, but I can’t. There are more bridges to build…’.
How did the friends reconnect?

confessed: admitted or told the truth about something bury the hatchet: to end a fight obstinate: unwilling to change one’s mind
Listen to all the keywords here.




1. Match the actions with the underlying thoughts or motivations.
Actions
Balbir insists the calf is his.
Jaideep asks the carpenter to build a fence.
The carpenter builds a bridge instead of a fence.
Balbir walks across the bridge with his hand outstretched.
The carpenter decides to leave after finishing the bridge.
Thoughts/Motivations
I have been stubborn, he is a good friend and we need to make up.
These two old men need each other, I must reunite them.
The calf belongs to me as it was on my land.
Another friendship is saved, there is more work to do elsewhere.
Balbir has dug a ditch out of spite, I do not want to see him again.
Idioms are phrases where the actual words may mean something different from how we use the idiom, for example, to bury the hatchet means to make peace, whereas the words actually mean to dig a hole and bury the hatchet.
2. Check how the following idioms are used in the text and use them to make your own sentences in your notebook.
a to stand shoulder to shoulder
c to back down
e to let bygones be bygones
b to hit a bump
d to hold a grudge
f to bury the hatchet
3. In your notebook, summarise the story in your own words using the clues given. Then, share it with your partner.
The story is about...
They started to...
But, Balbir and Jaideep...
So, Balbir...
Then, Jaideep...
Finally, the carpenter...


4. Answer the following questions in two to three sentences.
a Explain how the argument about the calf becomes an even bigger and more hurtful fight.
b What else does Balbir do to upset Jaideep? What does Jaideep do in response?
c Why does the carpenter build a bridge instead of a fence?
d What is Balbir ’s reaction when he sees the bridge? Why?
e Which positive characteristics do the men display in the story? Which negative traits do they display?



Symbolism is when an object, a person or an event stands for something more than what it usually means, giving it a deeper meaning in the story.
1. Fill in the table with words or phrases that you associate with a fence and a bridge. Fence Bridge
In two short sentences write what these things symbolise (stand for) in the story.
2. What is the theme of the story ‘Old Jaideep and the Carpenter ’? What can we learn from the story?



An argument about a simple matter can often lead to hurtful things being said. Think about a time when you had a disagreement with a friend or family member.
a Describe what the disagreement was about and what happened.

b What could you have done differently to handle the situation better?


Compound adjectives are adjectives made up of two or more words that work together to describe a noun. They are often connected by a hyphen to show that they form a single idea.
For example:
• The peace-loving community built a strong bridge.
• They had a heartwarming reunion after their disagreement.
1. Read each sentence and choose the correct compound adjective to describe the situation.
a The village elder is known and trusted by everyone in the community.
i well-respected ii warm-hearted iii open-minded
b The children were excited and played with great energy.
i soft-spoken ii high-spirited iii clear-headed
c The villagers were ready to accept new ideas.
i full-hearted ii soft-spoken iii open-minded
d The leader gave instructions in a calm and gentle manner. i soft-spoken ii well-known iii high-spirited
e The doctor made decisions quickly and wisely during the emergency. i open-minded ii full-hearted iii clear-headed
2. Complete each sentence with the appropriate compound adjectives in the box.
Hint Box: kind-hearted peace-loving good-natured easy-going level-headed
a The volunteers worked tirelessly to help those in need.
b In our family, we support each other and do not allow our differences to divide us.
c Despite the chaos, he remained and found a solution quickly.
d His nature made him very approachable and friendly.
e My friend welcomed everyone with a smile.

Homographs are words that are spelt the same but have different meanings and are sometimes even pronounced differently.
3. Replace the words in brackets with the homographs in the box. Each homograph will be used twice.
Hint Box:
contract conduct row refuse
Hint: Use the Internet to find the pronunciation of the homographs.
Search: Pronunciation of <word>
a The students were standing in a (queue).
b The conductor will (lead) the orchestra tonight.
c The neighbours had a nasty (quarrel).
d He will (decline) the offer to join the new project.
e They signed a/an (agreement) to maintain peace between the two nations.
f The teacher praised the students’ (behaviour) during the assembly.
g Wool can (shrink) when it is not washed correctly.
h The park was littered with (garbage) after the festival.


Indefinite articles a and an are used before singular nouns. These articles are called indefinite because they refer to any one place, animal, person or thing and do not specify which one.
We use a for words starting with consonant sounds and an for words starting with vowel sounds.
For example:
• Old Jaideep and Balbir lived in a village in Punjab.
(We are not specifying which village)
The articles a, an and the are used before nouns.
For example:
• The carpenter needed an axe to chop logs of wood.
(We are not specifying which axe)
The definite article the is used before plural nouns or nouns that are known or have been previously mentioned. The is called a definite article because it refers to a particular place, animal, person or thing and specifies the noun.
We also use the before superlatives, proper nouns and abstract nouns followed by ‘of ’.
For example:
• The village where Old Jaideep and Balbir lived was flooded.
(We are specifying the noun)
• The Green Revolution started in Punjab.
(Before a proper noun)
For example:
• Balbir is the best friend Jaideep could ask for.
(Before a superlative)
• The stubbornness of the two men ruined their friendship.
(Before abstract nouns followed by ‘of’)
1. Complete the paragraph with the correct articles. Then add two more sentences to the story using the correct articles.
This story comes from the State of Bengal. Aarav and Meera lived on opposite sides of picturesque river connected by bridge. Aarav, who was an artist, painted vibrant scenes on bridge that connected their homes. One day, two friends argued about theme that Aarav had chosen for his art.
Modal Verbs
Modal verbs are helper verbs that express conditions related to the main verb.
• In sentences, modal verbs come before the main verb.
• In questions, modal verbs come before the subject.
• In negative sentences, modal verbs come before ‘not’ + the main verb.

Can It is used to express ability.
For example:
I am so glad we can be friends again. Can we be friends again?
I can not stay upset with you.
May It is used to seek permission, suggest possibilities, or make suggestions.
For example:
She may build a bridge instead of a fence. (possibility)
May I build a bridge over the stream? (permission)
You may not enter my farm without my permission.
Should It is used to give advice.
For example:
Balbir and Jaideep should sort out their differences. Shouldn’t Balbir and Jaideep talk about their issues?
You shouldn’t interfere with their conflict.
Must It is used to express obligation.
For example:
One must never go to bed without resolving differences.
2. Fill in the blanks with the correct modal verbs.
a We (ability) spread joy by sharing smiles and helping others.
b You (possibility) find forgiveness easier than to hold a grudge.
c One (advice) not be cruel towards animals.
d People (obligation) save this planet by conserving resources.
e Every small gesture (ability) make a difference.
3. Make questions starting with these modal verbs:
a can:
b may :
c should:
d must:



Listen Well

Listen carefully to the text and choose the correct answers.
a What was the disagreement in the village about?
i Building a new school.
iii Starting a new market.
b Where did the villagers hold the meeting?
i At the school
iii At the market
c How did the villagers resolve the conflict?
Listen to the text here.
ii Cutting down trees.
iv Making a playground.
ii On the square
iv In the park
i They decided not to build new houses. ii They ignored the problem.
iii They would plant new trees and build. iv They moved to another village.
d What did the groups do after the meeting?
i They continued to argue. ii They worked together.
iii They built a new market.
e How did the villagers feel about the solution?
iv They forgot about the issue.
i Angry ii Unhappy
iii Confused



iv Satisfied Practise speaking here.
A persuasive speech is made to convince listeners that a particular point of view is correct. This is done by giving arguments that are supported by facts and examples and by making emotional appeals.
Sit in groups of three. Choose a topic from the list, prepare for five minutes and deliver a persuasive speech to your friends in the group.
The importance of reading.
Use bicycles to travel short distances.
Adopt a pet.
Reduce the use of electricity. Plant trees to save the planet.




Make points that will be of interest to your listeners. Begin with an introduction to the topic, talk about the advantages/ benefits and conclude with a call to action.
Use expressive body language and maintain eye contact while speaking. Use real-life examples and factual information to make your points more engaging.

A formal letter is one written to a person of authority such as a school teacher, principal or local officials. It needs to follow a proper format and be written using formal language.
Read the letter written to the Apartment manager requesting him for a community library.
45 Lakeview Apartment
Gandhinagar
Delhi 56789
15 July 2025
The Manager Lakeview Apartment
Gandhinagar
Delhi 56789
Subject: Establishment of a Community Library
Dear Mr Kumar,
I would like to make a proposal that will greatly benefit the residents of our apartment complex. I suggest that we establish a community library in our building. A library will have many advantages for both children and adults. It can act as a quiet space for studying as well as a place to gather and discuss books.
Sender’s address with pincode Date
Receiver’s address with pincode
Subject line
Dear [Receiver’s Name] [Receiver’s Title]
Introduction (Purpose of your letter)
Specific details about the request
I suggest that we use the common room that is hardly used. We could organise a book drive where the residents can donate their books.
Thank you for considering my suggestion. I look forward to your positive response.
Yours sincerely, Amit Sharma
Clearly state what you are requesting
Thank you message.
Yours sincerely/Yours respectfully/Yours faithfully Your Name
Write a formal letter to the principal of your school asking for new sports equipment for your school.



Get Set

• What are some of the things that make you laugh?
• Who do you laugh with the most?
Share the funniest moment of your life.
Imagine stepping into a world where everything around you – from the trees and streams to the very air you breathe – is alive with laughter and joy. Let’s read the poem and feel the excitement as the poet William Blake paints a picture of a world filled with fun and laughter.


When the green woods laugh with the voice of joy, And the dimpling stream runs laughing by; When the air does laugh with our merry wit, And the green hill laughs with the noise of it;
When the meadows laugh with lively green,
And the grasshopper laughs in the merry scene,
When Mary and Susan and Emily
With their sweet round mouths sing “Ha, ha he!”
When the painted birds laugh in the shade,
Where our table with cherries and nuts is spread: Come live, and be merry, and join with me,
To sing the sweet chorus of “Ha, ha, he!”
What are the different elements of nature that the poet mentions?

Who in the poem is described as having a sweet laugh?

William Blake was a famous English poet. He was born in 1757 and died in 1827. Blake’s most notable collections of poetry include ‘Songs of Innocence’ and ‘Songs of Experience’ in which he explores themes of childhood, nature and the human spirit.
dimpling: dimples are the small hollows in your cheeks when you laugh – here, imagine that the ripples in the stream look like dimples
merry: happy wit: playful intelligence
meadows: large, open fields of grass and wild flowers
painted: (here) with bright and colourful feathers
chorus: a part of a song that is repeated after each verse
Listen to all the keywords here.




1. Tick () the correct options.
a Which of the following best describes the main theme of the poem?
i The joy of growing old.
ii The joy found in nature and childhood.
iii How beautiful birds and insects are.
iv The importance of hard work.
b The repeated use of ‘Ha, ha he!’ in the poem:
i creates a sense of confusion.
ii show how women have fun.
iii shows that streams also like laughing.
iv highlights the idea of joy and laughter.
c Which of the following best describes the relationship between humans and nature in the poem?
i conflicting ii distant
iii independent iv harmonious
d The poem suggests that laughter can be found in…
i nature and human activities.
ii only in the beauty of nature.
iii all human interactions. iv only in children’s play.
e Based on the poem, which statement is most likely true about the speaker?
i The speaker prefers being alone to being around people.
ii The speaker finds joy in both nature and human company.
iii The speaker likes children.
iv The speaker is unhappy.
2. Answer the following questions.
a Write a line from the poem where nature reflects the sound of human laughter.
b What does ‘merry wit’ mean in the poem?
c How does the colour green add to the meaning of the poem?
d Why does the poet describe the birds as painted?

e What do these lines tell you about the theme of the poem?
Come live, and be merry, and join with me, To sing the sweet chorus of “Ha, ha, he!


Sit in a group of four. Discuss and create a mind map with the phrase ‘Nature’s Joy’ at the centre. Add words associated with the phrase to your mind map. You will need a large sheet of paper and sketch pens.
• Sights that bring you joy in nature.
• Sounds of nature that make you happy.
• Natural scents you find pleasant.
• Textures in nature you enjoy.
• Activities you like to do in nature.


Chart paper/ A3 sheet
Materials Needed
Sketch pens
1. Use a dictionary to find the meaning of the words. Write the meaning that matches how the word is used in the poem.
chorus:
wit:
dimpling: merry: Now, use the words to complete the sentences.
a The surface of the lake reflected the gentle sunlight.
b As the sun set, the forest was filled with the songs of birds.
c Sitting under the ancient oak tree, we heard the hills echoing human and laughter.
d As we walked through the meadow, a harmonious of crickets and frogs serenaded us.

2. Replace the underlined words in the sentences with the appropriate synonyms in the box. Rewrite the sentences in your notebook.
Hint Box: cleverness joyful field song decorated
a The cattle grazed contentedly in the meadow, where the grass was lush and green.
b The chorus of birds filled the morning air with a harmonious melody.
c The festival was a merry occasion, with people dancing and singing throughout the night.
d The room was painted with vibrant colours, creating an atmosphere of creativity and inspiration.
e His wit often left his friends amazed and entertained.



Poetic and Sound Devices: These are techniques that poets use to enhance the sound and meaning of a poem and evoke the emotions of the reader.
Personification: Giving human qualities to non-human things or ideas. For example: The green woods laugh.
Rhyme: Words with similar ending sounds. They often appear at the end of the line. For example: wit/it
Imagery: Descriptive language that appeals to the senses (sight, sound, touch, taste, smell). For example: painted birds
Repetition: When the same word or phrase is used multiple times to emphasise a point or theme. For example: “Ha, ha, he!”
Alliteration: The repetition of the first sound of words that appear near each other in a text. For example: The white whale wallowed in the water.
1. The poem uses various poetic devices to create a joyful atmosphere and convey the theme. Analyse the use of personification, alliteration and imagery in the poem by completing the following table.
Poetic device
Words or lines from the poem How it affects the meaning
Personification
Repetition
Imagery

2. Put on the poet’s hat. Follow the pattern used in the poem and write the missing lines to add another stanza to the poem.
a Use personification.
b Use repetition or imagery.
c Remember to follow the rhyme scheme of the poem.
d Remember the theme of the poem.
When the with , (natural element) (joyful action/emotion) ; When the playing children shout with glee, .




In this project, you will explore the theme of peace and harmony and present ways to promote it within your community, school or family.
What You Need:
• A poster board or a digital tool for your presentation.
• Art supplies (crayons, markers, or paints).
• Materials for your hands-on activity (craft materials, recycled items, etc.).
• Research materials (books, internet access, or discussions with family/teachers).
Steps:
1. Choose a Peace and Harmony Topic: Form a group and pick an idea related to peace and harmony that you would like to explore. For example:
• How to resolve conflicts peacefully.
• The importance of kindness and empathy.
• Working together as a team or community.
• Celebrating cultural diversity and respecting differences.
• Acts of kindness that spread peace.
2. Research and Write:
• Brainstorm, research and briefly describe your chosen peace and harmony topic. (100–150 words)
• Explain why this topic is important and how peace and harmony can make the world a better place. For example:
If you choose Resolving Conflicts Peacefully, you could explain how talking, listening, and finding solutions together helps resolve arguments and fights.


3. Create a Hands-On Project:
• Make a visual presentation that reflects the theme that you have chosen. It could be a poster, a peace tree, a skit, a role play.
For example, you could create a peace tree, where each leaf has a word or phrase that promotes harmony, such as ‘kindness,’ ‘sharing,’ or ‘understanding’.
4. Present to the Class:
• Present your project to your classmates.
• Explain the topic you have chosen, why it is important, and how people can work together to promote it.
• Show your project and describe how it represents your topic.
• Reflect on what you learned and share your thoughts on how you can promote peace and harmony in your daily life.


Keep your project simple, clear, but thoughtful. Use bright visuals and key messages to make your presentation more engaging.
Share stories, quotes or examples that inspire peace and harmony.



Get Set

What would you like to become one day? Write a few steps you can take to fulfil your dream.
I would like to become . A few steps that I can take are:
1. 2. 3.
Sit in pairs and discuss what you have written with your partner.
NASA’s space missions have always excited people. These missions, on space shuttles like the Columbia, involve important experiments and explore the mysteries of space. Each trip brings new discoveries and inspires people to dream about the stars. Now, let’s read about an astronaut who made her mark.



Kalpana Chawla was a remarkable astronaut who made history as the first woman of Indian origin to travel to space. Her journey, from a small town in India to the stars, is truly inspiring, and shows that with hard work and determination, anyone can achieve their dreams.
Kalpana Chawla was born on 17 March 1962, in Karnal, a town in the state of Haryana, India. As a child, she was fascinated by aeroplanes and the night sky. She would gaze at the stars and wonder what it would be like to travel to space. Kalpana Chawla was a bright student who loved to learn new things. Her curiosity about space and flying grew as she got older.

After finishing school, Kalpana Chawla decided to pursue her dream of becoming an aerospace engineer. She went to Punjab Engineering College. Her professors tried to discourage her from choosing aeronautical engineering, stating that there were limited career opportunities for girls in India. However, she was adamant and after completing her degree, she moved to the United States where she earned a master’s degree and a Ph.D. in aerospace engineering.
What did Kalpana Chawla’s professors advise and why?
Kalpana’s hard work and dedication were rewarded when she was selected by NASA, the American Space Agency, to become a trainee astronaut. This was a huge achievement and a dream come true. She trained hard to prepare for her journey to space and forged ahead even when the training was tough. She knew that reaching for the stars required effort and determination.
space shuttles: vehicles used to travel in outer space
origin: where her family came from determination: the quality of not giving up easily
aerospace engineer: a person who designs and builds planes, rockets, and other flying machines adamant: refused to be persuaded

In 1997, Kalpana Chawla made her first trip to space aboard the space shuttle Columbia. This mission was called STS-87. Kalpana and her team conducted many important experiments, and she got to see Earth from outer space. She was thrilled by the beauty of space and the excitement of floating in zero gravity. Kalpana Chawla’s second mission was in 2003, again aboard the space shuttle Columbia. This mission was called STS-107. The team conducted more than 80 experiments such as studying the reproduction of plants in microgravity and the behaviour of different materials in space. Kalpana was proud to be a part of this important work that would help scientists understand more about space
However, on 1 February 2003, tragedy struck. As the space shuttle Columbia was returning to Earth, it broke apart, and all seven astronauts on board lost their lives. It was a sad day for the entire world. People mourned the loss of the brave astronauts who had dedicated their lives to exploring space.



Did You Know?
Laika was the first dog to travel around the Earth. She was launched on a spacecraft called Sputnik 2 on 3 November 1957.
aboard: on or in a vehicle like a ship, train, or spacecraft zero gravity: a condition where there is no force of gravity, making objects and people float mission: an important job or task, often with a target goal microgravity: when there is almost no gravity mourned: felt very sad about someone’s death
What were the names of the missions that Kalpana Chawla was a part of?
Kalpana Chawla was deeply committed to promoting science education for young girls in India. From 1998, she helped to send two girls from her secondary school to NASA’s United Space School in Houston each year. She was involved in selecting and interviewing fourteen Indian students for the program over the years. Her life and achievements remind us that gender is no barrier to achieving greatness.
How does Kalpana Chawla continue to inspire young people?
Many schools, scholarships, and space programmes have been named in her honour. She brought fame to India and proved that with determination and perseverance the sky’s the limit. Kalpana Chawla will always be remembered as a pioneer in space exploration and remain a role model for aspiring astronauts around the world.
pioneer: a person who is the first to do something new or important aspiring: wanting to become something or achieve a goal



Listen to all the keywords here.
1. Sequence the following events, 1–7, in the correct order.
a Kalpana Chawla goes on the STS-107 mission and conducts more than 80 experiments.
b Kalpana Chawla is discouraged from pursuing her dream of being an astronaut.
c Kalpana Chawla is selected as a trainee by NASA.
d She goes to America and obtains her masters degree and a doctorate.
e Kalpan Chawla completes her Ph.D. in aeronautical engineering.
f Kalpana Chawla goes on the STS-87 mission.
g The space shuttle Columbia breaks apart and is lost.


2. In your notebook, summarise the great things Kalpana Chawla did. Use these headings:
• Her education
• Highlights from her space missions
• Her social initiatives
3. Answer the questions in two to three sentences.
a How did Kalpana Chawla’s childhood interest relate to her career?
b What challenge did Kalpana face as a student in India? What was her response to it?
c Describe Kalpana Chawla’s second mission to space.
d What impact did Kalpana Chawla’s achievements have on her home country and the United States? Provide one specific example for each.



1. Perseverance is the ability to continue working towards a goal despite facing challenges or setbacks.
How did Kalpana show perseverance in her journey to becoming an astronaut? Provide examples from the text and explain how she demonstrated this quality.
2. A stereotype is a belief that certain things are only for certain people. For example, some people might think only boys can be engineers.
What stereotypes did Kalpana break?


Reflect on a goal or dream you have for your future. How can Kalpana Chawla’s story inspire you to overcome potential challenges?
a What is a goal or a dream you would like to achieve?
b Name three of Kalpana Chawla’s qualities that you most admire.
c How can the qualities you mentioned above help you achieve your dreams?


1. Use a dictionary to find the meaning of the words in the box. Then, use the words to complete the sentences.
Hint Box: astronaut microgravity aerospace engineer space shuttle experiments
a The astronauts conduct many in space.
b An designs rockets and satellites, and they often work on projects that involve space exploration.
c A can be used to travel to space and back more than once which makes it a reusable spacecraft.
d In , everything floats around because there is very little gravity.
e An trains hard to travel to space, and undergoes rigorous physical and mental preparation.
Phrasal Verbs
Phrasal verbs are phrases that combine a verb with a preposition or adverb, creating a new meaning different from the original verb.
For example: lift off—The rocket will lift off at dawn. touch down—The space shuttle will touch down on Earth after its mission.
2. Use the dictionary to write the meaning of the phrasal verbs. Then, make sentences of your own in your notebook. set out blast off carry out take over look up to



Adverbs are words that describe or modify verbs, adjectives or other adverbs. They provide additional information about how, when, where and to what extent something happens.
Adverbs of Manner
These tell us the manner in which something happens.
They answer the question, How?
For example: carefully, casually, skilfully, smoothly, silently
The astronaut moved cautiously during the spacewalk to avoid any accidents.
Adverbs of Time
These tell us when something happens.
They answer the question, When?
For example: now, then, yesterday, today, tomorrow, soon, later, always
The rocket will launch tomorrow, and the mission will begin.
Adverbs of Degree
These tell us about the intensity or degree of an action, adjective or another adverb.
They answer the question, To what extent?
They are often written before the word they modify.
For example: very, quite, almost, too, enough, just, so, extremely
The telescope provides very clear images of distant galaxies.
Adverbs of Frequency
These tell us how often something happens.
They answer the question, How often?
They are usually written before the main verb but after the verb ‘to be.’
For example: always, often, frequently, sometimes, rarely, never Comets rarely pass close enough to be seen without a telescope.
1. Read the beginning of the space adventure story. Name the type of adverb in the order that they appear in the text.
The astronauts carefully prepared for their mission. They eagerly anticipated the moment they would lift off. The rocket would soon take them to the International Space Station. Because they frequently checked their equipment, they knew there would be no challenges. They spoke excitedly about the experiments they would conduct in space. As the countdown began they were extremely excited about the mission.
2. Use the adverbs given to complete the story.
Hint Box: frequently soon bravely extremely smoothly skilfully



The rocket engines roared to life, and the astronauts felt a strong push as they faced the journey ahead. , they passed through the Earth’s atmosphere and entered the vastness of space. They navigated the spacecraft, making adjustments. Inside the cabin, they worked hard, setting up their living quarters and preparing for the upcoming experiments. They floated through the cabin, enjoying the peacefulness of zero gravity. As they approached the International Space Station, they manoeuvred the spacecraft into the docking position. They were ready to begin their mission.




Listen Well
Listen to the text here.
Listen carefully to the text and complete the table with details on Astronaut Zara’s routine.


Practise speaking here.
An anecdote is a short, entertaining story about a real incident or person. Anecdotes can be about personal experiences or stories heard from others.
An anecdote should:
• be brief and to the point.
• be based on actual events or personal experiences.
• illustrate a point, provide an example, or entertain.
• involve personal experiences, making them relatable and engaging.
Think of an interesting anecdote and share it with the class.
Preparation:
a Think of a personal story or anecdote that is interesting or meaningful to you. It can be something funny, surprising, adventurous or touching.
b Plan the beginning, middle and end of your story.
Then, something unexpected happened... I/we noticed... Suddenly, we...
In the middle of our…, we discovered…
One sunny day, I/we decided to…
A few years ago, I…
In the end, I/we realised… Finally, we reached…
From that day on, I always...
In conclusion, the experience taught me...


An article is a piece of writing that is published in a newspaper, magazine, journal, or online. Articles can cover a wide range of topics, including news, opinion, research, reviews, and more. They are written to inform, entertain, or persuade readers.
An article includes the following:
Title: The title should be clear and indicate the topic of the article.
Byline: This is where the writer’s name is mentioned.
Introduction: Start with a hook to grab the reader’s attention. Introduce the topic and provide some background information. State the purpose of the article.
Body: Organise the main points in paragraphs. Each paragraph should cover one main point or idea. Use facts, details, examples, and explanations to support each point.
Conclusion: Summarise the main points and end with a final thought or call to action.
Write an article of 100–120 words on ‘The Importance of Scientific Discoveries’.




Imagine that you are onboard a fast rocket travelling through space. What are some things you can see? Fill in the mind map and share what you wrote with your partner.
This poem takes you on a journey in a speedy rocket. You’ll be surprised at how fast it moves! Let’s read the poem aloud and find out more about this experience.


This rocket’s going fast!
Super-fast!
Faster than light, it’s out of sight!
A zipping zapping rocket on a slipstream trip. It rides it rips through the Milky Way it dips. It whips, it slips, meteors it clips!


The first Indian rocket, named Rohini-75, was launched on 10 August 1969, from Kerala. This marked India’s debut in space exploration. Did You Know?
How does the rocket travel through the Milky Way?
slipstream: the smooth, fast-moving air behind an object that moves quickly meteors: large rocks in space clips: to hit something quickly or lightly debut: first try

It zips, it tips, this rocket shakes its hips! This super-duper-blooper rocket sliding on a beam of light, it’s bright, a fright, it swerves incredibly tight. This rocket’s so wonderfully fast, It arrives at night time before night!
It’s a dream-exploding, Mind-imploding, zooming melody of thought-dissolving, whizzing cacophony of engine thrust and time revolving!
An incredible super-speedy rocket ship.

swerves: changes direction suddenly imploding: falling inward on itself suddenly melody: a soft tune or music that is pleasant and soothing to hear cacophony: a loud mixture of sounds that are not pleasant thrust: a strong force that pushes something forwards or upwards
What are some adjectives the poet uses to describe the rocket?
Listen to all the keywords here.



1. Tick () the correct answers.
a What is the main focus of the poem? A rocket…
i exploring new planets.
ii racing against other rockets.
iii demonstrating incredible speed.
iv collecting space samples.
b How does the rocket interact with meteors in the poem?
i It avoids them completely.
ii It collides with them head-on.
iii It barely touches them as it passes.
iv It collects them along the way.
c What is the relationship between the rocket’s speed and time?
i Time slows down for the rocket.
ii The rocket moves faster than time itself.
iii Time has no effect on the rocket.
iv The rocket experiences time normally.
d What do the words dream-exploding and mind-imploding suggest about the speed of the rocket?
i It is unimaginably fast.
ii It implodes on itself.
iii It is only a dream.
iv It explodes in space.
e What unusual ability does the rocket have because of its speed?
i It can change colours.
ii It can split into multiple rockets.
iii It can arrive before dawn.
iv It can travel forward in time.

2. Match the lines from the poem and their meaning.
Faster than light, it’s out of sight!
It zips, it tips, this rocket shakes its hips!
It arrives at night time before night!
Whizzing cacophony of engine thrust.
Sliding on a beam of light.
The rocket seems to move without effort.
The engines make a very loud noise.
The rocket travels at a speed faster than light.
The rocket is faster than time itself.
The rocket does not travel in a straight line.
3. Assonance is when the same vowel sound is repeated in nearby words.
For example: In the line ‘Whips, it slips’ the short i sound is repeated.
Find another example of assonance in the poem. Write the line.
4. Onomatopoeia is when a word imitates the sound it describes, like ‘whizzing’.
Find another example of onomatopoeia in the poem. Write the word here:


Think about a time when you felt a sense of speed and excitement, similar to the rocket in the poem.
• Describe the experience: Where were you and what were you doing when you felt this thrill?
• Feelings and senses: How did it make you feel? What did you see, hear or feel during this experience?
• Connection to the poem: How is your experience similar to the rocket’s journey in the poem?


1. Create a word web using the words ‘Speed’ and ‘Excitement’. Write words or feelings that you associate with the two words.
2. Read how the phrases are used in the poem. In your notebook, use them in sentences of your own.
dream-exploding beam of light zipping zapping time revolving out of sight



Imagery is when a writer uses words to create pictures in the reader’s mind. It helps make the poem (or story) feel more real by describing how things look, sound, smell, taste, or feel.
The poem uses imagery to help us imagine the rocket’s speed and movement.
Speed imagery:
a Write a line from the poem that helps you imagine how fast the rocket is moving.
b Describe in your own words what you see in your mind when you read that line.
Movement imagery:
a Write a line from the poem that describes how the rocket moves through space.
b Describe in your own words what you see in your mind when you read that line.

1. Underline the nouns and write the type of noun you underlined.
a Mr Sharma, a retired doctor, lived in D N Nagar.
b He had an orchard of apple trees.
c This group of friends lived near Mr Sharma’s house.
d Every September, they picked apples.
2. Use the collective nouns to form sentences of your own.
a A group of volunteers
b A crowd of neighbours
c A crew of workers
d A gathering of parents
3. Underline the abstract nouns, circle the concrete nouns and tick () the material nouns.
a The villagers greet tourists with friendliness.
b It is a village filled with harmony and positivity.
c The mud houses show people’s love for simple living.
d Their dedication to health is remarkable.
e Many of the homes are still built from clay but they are maintained with care.
4. Use suffixes to make abstract nouns from the given words.
a cooperate
b generous
c good
d civil
e communicate
Now, make a sentence with each abstract noun you created.
a
b
c d e

1. Underline and write S (subject), V (verb) and O (object) in the sentences below.
a The playful dog caught the frisbee.
b We feed our fish every morning.
c Mithu repeats whatever I say.
d My hamster spins on a wheel all the time.
e His cat is napping in the sun.
2. Underline the verbs and identify them as ‘Transitive’ or ‘Intransitive’.
a The cat chased the mouse.
b The baby slept soundly.
c The principal addressed the students.
d The sun rises in the east.
e The flowers bloomed beautifully.
1. Rewrite the sentences with the correct subject-verb agreement.
a The monkeys is eating bananas.
b Neither the teacher nor the students was ready for the test.
c Which group of students are making such a noise?
d Everyone in the village know the crow is cheeky.
e A basket of chapatis were lying on the ground.
f The Gopi Diaries are a book by Sudha Murthy.

1. Rewrite each sentence with a demonstrative pronoun or a possessive pronoun depending on the clue given.
a The gifts belong to them. (possessive pronoun)
b The book is about our school. (demonstrative pronoun)
c The flowers over there belong to them. (demonstrative pronoun)
d That cake sale poster was made by me. (possessive pronoun)
e The old photo belongs to her. (possessive pronoun)
2. Read each question and fill in the correct interrogative pronoun to complete the sentence.
a organised the charity event last weekend? What Whose Who
b is that book on the table? Whom Whose What
c did the volunteers help at the shelter? Who Whom What
d is the most remarkable act of kindness that you have experienced? What Who Whose
e poster should we use for the cake sale? Who Which Whom
3. Match the sentences with the correct reflexive pronouns.
Column A Column B
She reminded to always be kind. yourself
He congratulated on a job well done. herself
I taught the importance of empathy. ourselves
You can reward by having a cup of chai. himself
We reminded to keep trying. myself

1. Correct the articles in the paragraph.
In an bustling city park, a elderly woman named Margaret sat alone on the bench, her eyes were filled with sorrow. The young girl named Lily skipped through a park, her laughter rang out like the melody. Without hesitation, a little girl approached Margaret and asked, ‘Why are you so sad?’ Surprised by a child’s question, Margaret started talking to her. Their growing friendship showed an effect that human connections could have.
2. Use the correct modal verbs in the questions.
a you organise a neighbourhood picnic to get everyone together? (ability)
b I suggest your name for the community service project? (permission)
c We visit all villages in this area to assess how happy people are. (advice)
d They not quarrel about petty issues like who uses the swing first. (obligation)
3. Make negative sentences using the given modal verbs.
a must:
b can:
c may:
d should:
e must:
1. Read the sentences below and underline the adverbs. Then, label each adverb according to the type: manner, frequency, time, or degree.
a The astronaut carefully prepared for thespace mission.
b The rocket launches weekly at the space centre.
c The space station will be visited soon by the international crew.
d The experiment was extremely successful.
e They will land on the Moon tomorrow.
f The rover moved smoothly across the lunar surface.
g They always follow safety procedures before launching.
h The astronaut floats gently from one side of the capsule to the other.
2. Fill in the blanks with the adverbs in the box.
Hint Box: rarely yesterday quietly quickly very
a The astronaut moved through the spacecraft to avoid making a noise.
b A space shuttle is used more than four times.
c The team celebrated the successful launch .
d The telescope provided clear images of distant galaxies.
e The rocket was assembled in the launch facility.
3. Write one sentence for each type of adverb.
a happily:
b often:
c slightly:
d later:

Name of the Student:
Class: 5
Roll Number:
Section:
Date:
Section – A (Reading and Vocabulary—25 marks)
Read the text and answer the questions.
Compassion is the ability to care for others and help them when they need it most. Some famous people in history have shown us how powerful compassion can be.
Mother Teresa was Albanian but she spent her life caring for the poor and sick in India. She believed that no one should feel unloved or forgotten. Mahatma Gandhi taught the world about kindness and peaceful protest. He helped India gain its freedom by standing up against violence and choosing peaceful solutions. In South Africa, Nelson Mandela fought against injustice. After spending twentyseven years in prison, he forgave his enemies and worked to unite the people of the country.
The change brought about by these inspiring leaders, proves that compassion can create real and lasting change in the world.
1. Choose the correct answer. (4 marks)
a What does ‘compassion’ mean?
i To ignore others
iii To help others with work
b Who helped the poor and sick in India?
i Mahatma Gandhi
iii Mother Teresa
ii To defeat others
iv To show concern for others
ii Nelson Mandela
iv Martin Luther King Jr.
c What did Mahatma Gandhi use to help India gain freedom?
i Harmless action
iii Forgiveness
ii Peaceful resistance
iv Violence
d How did Nelson Mandela respond after being in prison for twenty-seven years?
i He sought revenge
iii He left South Africa
ii He forgave his enemies
iv He chose to stay silent
2. Write True or False. (4 marks)
a Mother Teresa was born and worked in India.
b Mahatma Gandhi did not believe in peaceful solutions.
c Nelson Mandela’s ability to forgive after years in prison helped to unite his country.
d The actions of Mother Teresa, Gandhi and Mandela all demonstrate how kindness and compassion can lead to positive change.
3. Find the words in the story that have the same meaning as the words below. Then, write your own sentences using the words you filled in. (3 marks)
a well-known (paragraph 1)
b looking after (paragraph 2)
c motivating (paragraph 3)
4. Answer the questions in two to three sentences. (4 marks)
a What did Sister Theresa want for every person?
b Why do you think forgiveness is an important part of compassion, as shown by Nelson Mandela’s story?

Read the poem and answer the questions that follow.
The Kindness of Arjun
Arjun saw the boy alone, Sitting on the schoolyard stone, He shared his lunch without a word, The quiet act went unobserved.
Each day he smiled, gave what he could, Not for praise, but because he should. His heart was light, his hands were kind, Helping others brought peace of mind.
One day, the boy stood tall and bright, And thanked Arjun with all his might. For every gentle thing he’d done, The gift of kindness, quietly won.
5. Choose the correct meaning of the phrases given in the following questions. (5 marks)
a What does the word ‘unobserved’ mean in the line ‘The quiet act went unobserved’?
i Everyone was disturbed by the act. ii It happened without being noticed.
iii Arjun didn’t stop the boy.
iv No one cared about the act.
b Which line from the poem gives the reason why Arjun was kind and generous?
i He shared his lunch without a word.
ii The quiet act went unobserved.
iii Each day he smiled, gave what he could.
iv Not for praise, but because he should.
c What does the phrase ‘his heart was light’ suggest about Arjun?
i He felt happy and free. ii He was tired of helping others.
iii He didn’t care about anything. iv He lost weight quickly.
d Which of these is NOT a correct interpretation of the underlined words? One day, the boy stood tall and bright,
i The boy had grown up. ii He was happy and confident.
iii He did not need help anymore. iv He was challenging Arjun.
e Which word is NOT a synonym for the underlined word?
For every gentle thing he’d done, i soft
iii compassionate
ii thoughtful
iv kind
6. Answer the questions in two to three sentences. (5 marks)
a Name two kind things that Arjun did.
b How did the boy react to Arjun’s kindness at the end of the poem?
c What was special about the way in which Arjun gave?
d What lesson can we learn from the way Arjun showed his kindness?
Section – B (Grammar—10 marks)
7. Fill in the blanks with verbs that agree with the subjects. Write the verbs in the present tense. (5 marks)
a When Arjun (see) the boy alone, he immediately (decide) to share his lunch.
b The boy (be) grateful when Arjun (share) his lunch with him.
c Each day, Arjun (show) kindness without expecting anything in return.
d Arjun’s quiet acts of kindness (make) a big difference in the boy’s life.
e Many people (not appreciate) the little things others (do) for them.

8. Complete the following sentences with the correct collective nouns. (5 marks)
a A of judges sat to decide on the case.
b As the of fish swam past, the villagers caught them
c A of dogs attacked the tiger in the village.
d A of unfortunate events led to the riots in the village.
e A company built a of apartments for their employees to live in.
9. Summarise this story in four sentences. Write the key events from the beginning, middle and end. (5 marks)
Anaya saw her classmate Meena sitting alone under a tree. Meena had lost her cell phone and was very upset. Anaya knew how Meena felt, and she wanted to cheer her up. She went home and asked her mother if Meena could have the extra cell phone that Anaya was not using. Anaya’s dad had given her the phone when he got an upgrade. When she handed the phone to Meena the next day, her face lit up with joy. Meena thanked Anaya and hugged her. She was so happy, not just because of the cell phone, but because of Anaya’s kindness. From that day on, they became best friends and always looked out for each other.
10. Complete the story in about 70–80 words. Remember to give the story a satisfying ending. (10 marks)
In a bustling Indian town, young Aisha found a dusty old lantern while cleaning her attic. Intrigued, she polished it, and to her surprise, it started to glow. The lantern hummed softly, and a gentle voice whispered, “Hello, Aisha.” Astonished, Aisha watched as a tiny fairy appeared from the lantern.
The fairy told Aisha that she could grant her one wish. Excited but uncertain, Aisha thought carefully about what to wish for. She wanted to help her community but wasn’t sure how best to use the wish.
The fairy asked her to decide by the end of the day. Aisha started to think about her options and wondered how her wish could make a real difference. Should she wish for something that would benefit everyone, or should she focus on helping a specific person in need?
With the magical lantern glowing softly beside her, Aisha thought about what she should do. The fairy waited patiently, ready to grant her wish.
Name of the Student:
Class: 5
Roll Number:
Section:
Date:
Section – A (Reading and Vocabulary—25 marks)
Read the text and answer the questions.
Microplastics are tiny pieces of plastic, smaller than a grain of salt, that are all around us. They come from items like plastic bottles, bags and packaging materials that break down into tiny pieces over time. They also come from our clothes when we wash them, and even from the tyres of cars as they wear down. These microplastics end up in the air we breathe, the water we drink and the food we eat. Scientists have detected microplastics in human blood, muscles and even in people’s brains.
So, how can we reduce the risk of consuming plastic? Start by using your own reusable bags instead of buying food in plastic packaging. When cooking, use stainless steel or cast iron pans instead of nonstick ones, which can release microplastics when heated. Another good tip is to filter your tap water to remove microplastics. We need to take action to reduce the use of plastic so that we can protect our bodies from the harmful effects of microplastic.
1. Find the words in the passage that mean the same as the words given below. (4 marks)
a found (paragraph 1)
c give off (paragraph 2)
b taking in (paragraph 2)
d keep safe (paragraph 2)
2. Write True or False. (3 marks)
a The plastic we use every day turns into microplastic immediately.
b Microplastics are present all around us.
c Research is being done on microplastics and where they are found.
3. Answer the questions in two to three sentences. (8 marks)
a What does the suffix micro- in the word microplastics mean?

b Name three ways that microplastics enter the environment.
c Name three ways that humans can take in microplastics.
d How can the choices we make every day help reduce the amount of microplastics in our bodies and the environment?
Read the poem and answer the questions. Let’s take care of our Earth today, In simple and thoughtful ways.
Turn off lights when you leave the room, Save Earth’s energy in any way you can.
Walk or cycle, don’t always drive, Keep our planet’s air alive.
Plant a tree, let it grow tall, Help the animals, big and small.
Use less plastic, make a change, These little steps aren’t so strange.
Together we can do our part,
Sustain the world, we have to start!
4. Choose the correct answer. (4 marks)
a In which way can we save energy according to the poem?
i By planting trees
iii By turning off lights
ii By recycling bottles
iv By walking
b Which of the following will not improve air quality?
i Planting trees
iii Driving
ii Using bicycles
iv By walking
c What does it mean to sustain the Earth? Choose the best answer.
i Give it food and water
iii Save trees for animals
d What is the main idea of the poem?
ii Keep it alive and well
iv Keep humans safe
i Recycling is the most important thing.
ii Saving energy is very important.
iii Driving is bad for the environment.
iv Take care of the Earth in simple ways.
5. Answer the questions in two to three sentences. (6 marks)
a Name four ways to save Earth according to the poem.
b Explain two ways how planting a tree will help animals.
Section – B (Grammar—10 marks)
6. Fill in the blanks with the correct articles. (6 marks)
a Walking or biking is good way to reduce pollution in cities.
b We all have important role in protecting the environment.
c Recycling plastic helps reduce amount of waste that ends up in landfills.
d Planting trees is essential step in fighting climate change.
e Turn off lights when you leave the room to save energy.
f Using reusable bags is simple way to cut down on plastic waste.

7. Use the modals given to form questions about the environment. (4 marks) can: may: should: must:
8. Your school is starting a recycling program to encourage students to manage waste better. Write a notice to inform your classmates about the program. Include the following details in your notice: (7 marks)
i Title: Give your notice a clear and informative title.
ii Date and Time: Mention when the Recycling Program will start.
iii Location: Specify where the recycling bins will be placed.
iv Purpose: Explain why the Recycling Program is important.
v What to Recycle: List the items that can be recycled.
vi Contact Information: How can students get more information or ask questions?
9. Write an 80–100-word paragraph on why conserving water is so important. Use the following guidelines to help you structure your paragraph: (8 marks)
i Start with a Topic Sentence: Clearly state why conserving water is important.
ii Include Key Points: Mention the benefits of saving water, such as protecting natural habitats and ensuring water availability for future generations.
iii Give Examples: Provide a simple example of how people can conserve water in their daily lives.
iv End with a Conclusion: Summarise the importance of water conservation.

























































Dhruv was reading a newspaper. He came across news about different states in India that participated in the COVID vaccination drive and the number of vaccinations given until August 2023. Given below is the data of four states.
While reading the news, Dhruv got confused and could not read the numbers given in the data. The numbers of vaccinations given were either 7-digit numbers or 8-digit numbers.
7-digit Numbers 8-digit Numbers
Place Value, Face Value and Expanded Form
Every digit in a number has a fixed position called the place of a digit. The value of the digit depends on its place or position in the number. So, the place value of a digit is the value represented by the digit on the basis of its position in the number.
The face value of a digit is the value of the digit itself.
Reading and Writing 7-Digit and 8-Digit Numbers
We know that the greatest 6-digit number is 999999.
Now, if we add 1 to this number, we get 1000000.
999999 + 1 = 1000000
Chapter 1 • Numbers up to 8 Digits
1000000 is the smallest 7-digit number and is read as “Ten Lakhs”.
Let us show the number of vaccinations administered in Sikkim, 1360477, in the place value chart.
Lakhs Thousands Ones
Ten Lakhs (TL) Lakhs (L) Ten Thousands (TTh) Thousands (Th) Hundreds (H) Tens (T) Ones (O)
1 3 6 0 4 7 7
9999999 is the greatest 7-digit number and if we add 1 to this number, we get 10000000. 10000000 is the smallest 8-digit number and is read as “One crore”.
Now let us show the number of vaccinations administered in Delhi, 37409161, in the place value chart.
Crores Lakhs Thousands Ones
Crores (C) Ten Lakhs (TL) Lakhs (L) Ten Thousands (TTh) Thousands (Th) Hundreds (H) Tens (T) Ones (O)
3 7 4 0 9 1 6 1
Let us write the face value and place value of 37409161.
37409161 Face Value Place Value
1 ones = 1 × 1 = 1
6 tens = 6 × 10 = 60
1 hundreds = 1 × 100 = 100
9 thousands = 9 × 1000 = 9000
0 ten thousands = 0 × 10000 = 0
4 lakhs = 4 × 100000 = 400000
7 ten lakhs = 7 × 1000000 = 7000000
3 crores = 3 × 10000000 = 30000000
periods place periods place

The place value of zero is always 0. It may hold any place in a number, but its value is always 0.
When place values of all the digits are added to form a number, it is known as the expanded form of the number.
The expanded form of 37409161 can be given as:
30000000 + 7000000 + 400000 + 9000 + 100 + 60 + 1 = 37409161
Form Standard Form


Place value of a digit = face value of a digit × value of the place.
+ 400000
Error Alert!
Never write the plural form of ‘periods’ while writing number names. 36,57,648
Thirty-six lakhs fifty-seven thousands six hundreds forty-eight

Thirty-six lakh fifty-seven thousand six hundred forty-eight
Example 1: Rewrite the numbers in a place value chart. Also, write them in words.
1 54879509 2 6509808 S.
Number Names:
1 Five crore forty-eight lakh seventy-nine thousand five hundred nine
2 Sixty-five lakh nine thousand eight hundred eight
Example 2: Write the numbers for the given number names.
1 Seventy-eight lakh nine thousand one hundred nine = 7809109
2 Nine crore five lakh ten thousand two hundred = 90510200
Example 3: Write the expanded form of the number 64870977.
Expanded Form: 60000000 + 4000000 + 800000 + 70000 + 0 + 900 + 70 + 7
1 • Numbers up to 8 Digits
The Indian number system includes the ones period, the thousands period, the lakhs period and the crores period.
There is another number system used globally, called the International number system.
In the Indian number system, we put commas after each period, starting with the ones. But the same number in the international system will be read differently.
For every number in each system, the value of each digit is 10 times the value of the digit on its right.
So, from the above table, we can say that:
1 lakh = 100 thousands; 10 lakhs = 1 million; 1 crore = 10 millions
Let us represent the number 98710325 on the place value chart.
Indian Number System
Standard Form: 9,87,10,325
Number Name: Nine crore eighty-seven lakh ten thousand three hundred twenty-five.
Expanded form: 9,00,00,000 + 80,00,000 + 7,00,000 + 10,000 + 300 + 20 + 5 International Number System
Standard Form: 98,710,325
Number Name: Ninety-eight million seven hundred ten thousand three hundred twenty-five.
Expanded form: 90,000,000 + 8,000,000 + 700,000 + 10,000 + 300 + 20 + 5 Indian Number System International Number System

Example 4: Write the numbers in the international number system using commas and number names. Write their expanded forms.
1 79027348 2 90710946
1 79,027,348 = Seventy-nine million twenty-seven thousand three hundred forty-eight = 70,000,000 + 9,000,000 + 20,000 + 7,000 + 300 + 40 + 8
2 90,710,946 = Ninety million seven hundred ten thousand nine hundred forty-six = 90,000,000 + 700,000 + 10,000 + 900 + 40 + 6

















Write the place value and face value of the underlined digit in the following numbers.
a 7409230 b 8656023 c 93260075 d 29543002
e 61752812 f 10081824 g 43889385 h 57131060
Write the standard form of the numbers in the Indian and International number systems.
a 21643332 b 1200621
c 46207219 d 95910158
Write the number names and expanded form of the given numbers.
a 4,41,90,887 b 1,90,81,702
c 81,085,432 d 19,854,004
Write the numerals for the following number names.
a Sixty lakh eight thousand ninety-eight b Twenty million five hundred sixty-nine
c Four million ninety thousand d Eight crore one thousand two
Fill in the blanks.
a 10 million = crore b 1 million = lakh
c 1 crore = thousands d There are zeroes in 20 million.
The Amazon Rainforest covers approximately 2722000 square miles. Write the number in the Indian and the international number system.
Do as directed.
a Write the greatest 7-digit number that has the smallest odd digit at its hundreds, ten thousands and lakhs place.
b Write the smallest 8-digit number that has the digit 7 at all its odd positions, starting from the ones place.
India got its independence in 1947. Its population at that time was 353 million. Write the population as a numeral.
During COVID, India offered support to 150 affected countries in the form of vaccines, medical equipment and medicines. Given below is the data of the number of vaccine doses supplied by India to four different countries.
Rahul: Which country did India supply the greatest number of vaccine doses to?
Bran: We could compare the numbers to find the country to which India supplied the greatest number of vaccine doses.
What if Rahul wanted to compare the number of vaccines sent to Nepal and Australia? Let us find out.
Since 94,99,000 has 7 digits and 3,09,13,200 has 8 digits, 3,09,13,200 > 94,99,000.
Thus, Australia was sent more vaccine doses.

number with more digits is always greater.
Now, what if we want to compare two numbers with the same number of digits? Let us consider 4,13,23,456 and 4,13,23,657.
Step 1: Write the numbers in a place value chart and check the number of digits. Both the numbers have the same number of digits, that is, 8 digits.
Step 2: Start comparing the digits from the left until we find different digits. The number with the greater digit is greater.
Here, the digits are the same until the thousands place. Now, we compare the digits in the hundreds place.
We see that 4 < 6.
So, 4,13,23,456 < 4,13,23,657.

Example 5: Compare the numbers 6,47,17,389 and 6,47,00,508.
6 = 6 4 = 4 7 = 7 1 > 0
So, 6,47,17,389 > 6,47,00,508
Aryabhata (476–550 CE) was the first mathematician who was known for his significant contributions to the place-value system, where he used letters of the alphabet to denote numbers, expressing quantities.
Do you remember the number of vaccine doses donated by India to different countries? Let us read them again.
Can you rearrange them in ascending order?
To arrange the number of vaccine doses in ascending order, follow the given steps.
1. Compare the two 7-digit numbers. 94,99,000 < 98,02,000 So, 94,99,000 is the smallest number.
2. Compare the two 8-digit numbers. 3,09,13,200 > 2,80,82,800 So, 3,09,13,200 is the greatest number.
The ascending order is 94,99,000 < 98,02,000 < 2,80,82,800 < 3,09,13,200.

The predecessor of a number is just before the number. So, it is always less than that number. For example, 100 is the predecessor of 101 and 100 < 101.
Chapter 1 • Numbers up to 8 Digits
Can you arrange these numbers in descending order?
Example 6: Arrange 38,65,080; 10,00,000 and 4,50,50,809 in descending order.
Descending order
4,50,50,809
38,65,080
10,00,000
4,50,50,809 > 38,65,080 > 10,00,000 is the descending order.
Example 7: Arrange 8,15,64,205; 8,13,54,610; 65,99,090; 8,76,01,006 in descending order. 65,99,090 is the smallest number since it has the least number of digits. 8,76,01,006 is the largest number. 8,15,64,205 > 8,13,54,610.
Thus, the descending order of the numbers is 8,76,01,006 > 8,15,64,205 > 8,13,54,610 > 65,99,090.
Let us understand this using an example. Let us say we are given the digits 9, 5, 1, 0, 6, 7 and 3.
Let us try forming some numbers such that each digit appears exactly once.
Can you form more such numbers?
Now, what if we wanted to form the greatest and the smallest 7-digit numbers using these digits only once?
Greatest number: Write the digits in descending order.
9 7 6 5 3 1 0
Smallest number: Write the digits in ascending order. 0 will appear in the second position; otherwise it forms a 6-digit number if 0 comes in the leftmost position.
1 0 3 5 6 7 9
Now, what if we want to form a number by repeating 1 digit?
Greatest number: Repeat the greatest digit. We get an 8-digit number.
9 9 7 6 5 3 1 0
Why did we choose to repeat the greatest digit?

Smallest number: Repeat the smallest digit. We get an 8-digit number.
Example 8: Form the greatest and the smallest 8-digit number using the digits 1, 8, 6, 0, 9, 2, 5 and 4. No repetition of digits is allowed.
Greatest number = 98654210; Smallest number = 10245689
Example 9: Find the greatest and smallest 8-digit number using the digits 5, 4, 7, 6, 0, 1 and 3 but repeating any one digit only once.
The given digits are 5, 4, 7, 6, 0, 1 and 3.
To form the greatest number, we will repeat the digit 7.
Greatest 8-digit number formed using the given digits = 77654310
To form the smallest number, we will repeat the digit 0.
Smallest 8-digit number formed using the given digits = 10034567

















Which is smaller: 76,24,578 or 87,90,213?
Fill in the blanks with <, > or =.
a 35,72,123
d 6,24,58,110 6,24,59,211 e 82,60,154
Match the numbers so that the number in the second column is 1,00,000 more than the number in the first column.
a 99,00,000 10,00,000
b 2,89,52,468 3,00,52,468
c 9,00,000 1,00,00,000
d 2,99,52,468 2,90,52,468
Arrange the following numbers in ascending order and descending order.
a 1,00,36,782; 5,00,00,367; 8,87,21,460; 93,12,820
b 92,56,890; 36,81,910; 6,92,10,350; 8,26,00,031
c 5,00,21,138; 6,04,50,821; 6,50,24,567; 9,45,21,823
Write the greatest and the smallest 7-digit numbers using all the digits only once.
a 5, 3, 4, 0, 8, 9, 1 b 5, 7, 6, 2, 1, 3, 8 c 1, 0, 3, 5, 6, 2, 4
Write the greatest and the smallest 8-digit numbers using all the digits but repeating any one digit exactly once. a 2, 7, 1, 0, 8, 6, 4 b 8, 3, 9, 4, 7, 1, 6 c 7, 5, 2, 0, 4, 9, 3
Rearrange all the digits of the number 5,48,79,802 to form the largest and the smallest 8-digit number.
Write the greatest 8-digit number and the smallest 7-digit number using: a two different digits b four different digits c five different digits
The total areas of 4 countries in sq. km are given below. Arrange the names in descending order of their area.
Russia - 17,098,242; India - 3,287,590; China - 9,706,961; Australia - 7,692,024.
Create a word problem on comparing two 8-digit numbers.
Remember, the number of vaccine doses donated by India to Bangladesh was 2,80,82,800.
But what if we wanted to convey this number to a friend? The number 2,80,82,800 is very inconvenient to read and say out loud.
What if we just said that India donated about 3,00,00,000 vaccines to Bangladesh. It still gives a fair idea of how many vaccines were donated. This is called rounding off a number.
While rounding off numbers, terms like “about” and “approximately” are added to convey that the number is close to being exact.
Let us learn how to round-off numbers to different places.
If the ones digit is less than 5, then the ones digit is replaced by 0.
rounded off to
The diameter of the Sun is approximately 14,00,000 km.
5 4, 7 0, 8 2 3 5 4, 7 0, 8 2 0
3 < 5
If the ones digit is greater than or equal to 5, then the ones digit is replaced by 0 and the tens digit is increased by 1.
rounded off to
2, 6 4, 8 0, 0 2 7 2, 6 4, 8 0, 0 3 0 7 > 5 2 + 1 = 3

To round off to the nearest 100s, we look at the tens digit. If the tens digit is less than 5, then the ones and tens digits are replaced by 0.
rounded off to
4, 3 0, 7 0 8
0 < 5
If the tens digit is greater than or equal to 5, then the ones and tens digits are replaced by 0 and the hundreds digit is increased by 1.
rounded off to
6
To round off to the nearest 1000s, we look at the hundreds digit. If the hundreds digit is less than 5, then the ones, tens and hundreds digits are replaced by 0.
rounded off to
7 8, 5 1, 4 2 3
4 < 5
8, 5 1, 0 0 0
If the hundreds digit is greater than or equal to 5, then the ones, tens and hundreds digits are replaced by 0 and the thousands digit is increased by 1. 2, 8 3, 4 9, 6 2 7
rounded off to
How do you think the number of vaccine doses donated by India to Bangladesh was rounded off ? Explain.
Example 10: Round off 3,76,87,519 to the nearest 10s, 100s and 1000s.
To the nearest 10s: 3,76,87,519 is rounded off to 3,76,87,520.
To the nearest 100s: 3,76,87,519 is rounded off to 3,76,87,500.
To the nearest 1000s: 3,76,87,519 is rounded off to 3,76,88,000.
















2

Round off the following numbers to the nearest tens. a 85,48,749 b 89,05,462 c 6,07,85,888 d 1,56,48,950
Round off the following numbers to the nearest hundreds. a 1,25,89,183 b 87,52,368 c 68,67,790 d 77,59,910
Chapter 1 • Numbers up to 8 Digits
Round off the following numbers to the nearest thousands.
a 8,97,00,110 b 53,12,069 c 8,21,58,701 d 5,89,89,929
The distance of the Moon from the Earth is 238,855 miles. What is the approximate distance between the Moon and the Earth when rounded off to the nearest thousand?
Shekhar participated as a volunteer in the municipal corporation drive to plant trees and provide a habitat for various species of birds, insects and other wildlife. The municipal corporation spent ₹65,94,830 on the project. Rewrite the amount spent by rounding off the number to the nearest 1000s. Have you ever planted trees?
Use the given information to form the greatest 7-digit numbers using the digits 6, 0, 3, 2, 1 and 9. Round off the numbers formed to the nearest thousands.
a Repeat the greatest digit only once. b Repeat the smallest digit only once.

Objective: To solve puzzles involving large numbers by identifying missing digits based on the given clues.
Setting: In pairs

Materials Required: Puzzles or worksheets with missing digit problems, Pencils
Method:

Prepare puzzles where certain digits of large numbers are missing. Provide clues to identify the missing digits (e.g., “The digit in the millions place is double the digit in the ten thousands place”).
Students work in pairs to solve the puzzles and fill in the missing digits.
The team which solves the puzzle first wins.
Once the students have completed their puzzles, bring the class together to discuss the solutions.


Rewrite the following numbers in figures and words using both the Indian and international number systems. Also, write their expanded form.
a 3507681 b 42087950
c 63565842 d 91500084
Write the numbers for the following number names in both number systems.
a Sixty million seven hundred fifteen thousand two hundred thirty-nine
b Eight crore nine lakh fifty thousand two
c
thirty-nine

Round off the following to the nearest tens, hundreds and thousands.
a 6,45,87,123 b 89,09,008
Fill in the blanks using <, > or =.
a 6,56,52,567 6,48,90,650
b 90,00,518 90,76,757
c 34,57,879 34,57,879
d 13,05,885 6,74,38,989
Arrange the following numbers in ascending order.
a 23,56,475; 9,08,04,365; 8,91,63,896; 90,87,687
b 6,76,12,895; 6,76,87,980; 4,35,46,576; 3,24,35,678
Arrange the following numbers in descending order.
a 4,56,45,768; 5,36,45,787; 2,40,85,167; 43,56,787
b 80,88,428; 4,90,76,837; 9,09,87,897; 80,68,964
List all the numbers that are rounded off to the nearest tens as 16,48,240.
Under the Vaccine Maitri initiative, India supplied COVID-19 vaccines to various countries. India supplied around 3,151,324 vaccines to UK. Write the expanded form of the number in both numeral systems.
A certain 8-digit number has only fives in the ones period, only sevens in the thousands period, only nines in the lakhs period and only ones in the crores period. Answer the following questions.
a Write the number in figures and words using both the Indian and international number systems.
b Round off the number to the nearest tens, hundreds or thousands.
Critical Thinking
1 Sanya wants to solve a 7-digit secret code in a safe. Use the given clues to help Sanya solve the secret code.

a The digit in the hundreds and ones place is 6.
b The digit in the lakhs place is 4 less than the digit in the ones place.
c The digit in the ten lakhs and ten thousands place is the smallest odd number.
d The face value of the digit in the thousands place is 5.
e The digit in the tens place is the biggest 1-digit number.

2 Write the greatest 8-digit odd number using only 5 digits. Do not repeat any digit more than twice.

The population of different countries is shown using a table. Read the data carefully and answer the questions.

1 Which country has the least population?
a Italy
c Poland

b Germany
d United Kingdom
2 Which country has the greatest population?
a Poland
c Italy

b United Kingdom
d Germany
3 Which country has approximately double the population than that of Poland?
4 Arrange the countries in ascending order as per their population.
5 If all the digits in the population of each country are rearranged to form the greatest number, then which country will have the greatest population? Cross Curricular





























































Sahil’s father runs a bakery. At the end of each year, they calculate the total sales for the different types of baked goods they sold.
Father: We made ₹2,50,678 by selling cakes and ₹1,56,240 by selling cookies this year.
Sahil: Wow! How much did we make last year?
Father: Last year, we made a total of ₹3,15,500.
Sahil wonders whether they have made more or less this year!
Sahil wants to know the total sales they made this year. He also wants to know whether they have made more or less this year than last year.
How will Sahil do that? Let us help him out!
If Sahil wants to find the total sales they made this year, he will have to add the numbers ₹2,50,678 and ₹1,56,240.
Add: ₹2,50,678 + ₹1,56,240
So, Sahil’s father made ₹4,06,918 this year.
Example 1: Add 1,98,794, 52,250 and 21,000. Using the steps, we can add the numbers as: 1,98,794 + 52,250 + 21,000 = 2,72,044.
Example 2: A company produced 4,56,360 boxes in 2019. The same company produced 3,60,780 boxes in 2018 and 90,995 boxes in 2017. How many boxes have they produced in three years?
Boxes produced in 2019 = 4,56,360
Boxes produced in 2018 = 3,60,780
Boxes produced in 2017 = 90,995
Total number of boxes produced = 4,56,360 + 3,60,780 + 90,995 = 9,08,135
So, the company produced 9,08,135 boxes in three years.
Sahil found that they earned ₹4,06,918 this year, which is more than the money they earned last year, which was ₹3,15,500. Now, Sahil wants to know how much more they have earned this year.
Let us subtract the sales made last year from the sales made this year.

Changing the order of addends does not change the sum.
₹4,06,918 − ₹3,15,500 = ₹91,418. Therefore, they earned ₹91,418 more this year than last year.
Example 3: Find the difference of 57,588 and 6765.
We know that we subtract the smaller number from the larger number as shown: Therefore, 57,588 − 6765 = 50,823.
Example 4: A pen company manufactures 9,28,667 pens in total, out of which 58,475 are red pens. Find the total number of pens that are not red.
Total number of pens = 9,28,667
Number of red pens = 58,475
Number of pens that are not red = Total number of pens Number of red pens
Therefore, 9,28,667 − 58,475 = 8,70,192.

Always write the smaller number below the larger number.

















Write True (T) or False (F).

a When the number is subtracted from itself, the difference is zero.
b When 0 is subtracted from a number, the difference is zero.
c When the order of the addends is changed, the sum remains the same.
d The order of the numbers involved in subtraction can be changed.
Add the given numbers. a
The difference of two numbers is 3,98,460. If the smaller number is 5,05,090, find the greater one. 1
Subtract the given numbers. a
Write the numbers in columns and add.
a 1,72,744 and 5,56,200 b 3,44,567, 78,456 and 39,894
c 5,89,569, 1,24,887 and 56,758
Find the difference of the given numbers.
3,86,565, 2,34,567, 56,468 and 46,568
a 87,687 and 5789 b 9,87,609 and 56,000
c 5,68,978 and 3,21,098 d 7,99,098 and 2,67,548
A factory manufactured 59,899 blazers in the year 2020, 78,906 blazers in the year 2021 and 1,34,145 blazers in the year 2022. How many blazers did they manufacture in these three years?
What is the difference between the diameters of Jupiter and Saturn if Jupiter’s diameter is about 142,984 kilometres and Saturn’s diameter is about 120,536 kilometres.
An NGO collected ₹2,89,230 for a charity fund in one year and ₹3,97,500 in another year. They used ₹3,05,700 out of the total amount collected in the two years. How much money are they left with now? Do you volunteer for any charity activities?
Jay runs a toy store. He has marbles in all shapes, sizes and colours. Each jar of marbles contains 1225 marbles. Sometimes, the customers want to buy more than one jar. Sometimes, they want to buy only a few marbles from the jar. How do you think Jay calculates the number of marbles a customer is buying?
Let us say, a customer wants to buy 2 jars of marbles. Jay will have to multiply 1225 by 2 to find the total number of marbles he will give.
So, Jay will give 2450 marbles.
Now let us say that a customer wants to give marbles from one jar to 5 of his friends.
To find out how many marbles each friend will get, he will have to divide 1225 by 5.
Each friend will get 245 marbles. Let us see some properties of multiplication and division.
1 Order Property: Two numbers can be multiplied in any order. The product will always be the same. For example: 12 × 4 = 48 and 4 × 12 = 48
2 Grouping Property: Two or more numbers can be grouped in any way. The product will be the same. For example: (3 × 5) × 6 = 15 × 6 = 90 and 3 × (5 × 6) = 3 × 30 = 90
3 Distributive Property: The product of a sum of two or more numbers is equal to the sum of the products. For Example: 4 × (2 + 3) = (4 × 2) + (4 × 3) = 8 + 12 = 20 and 4 × (2 + 3) = 4 × 5 = 20
A customer wants to buy 10 marble jars. How can he find the total number of marbles?

We know that he will have to multiply the number of marbles in one jar by the number of jars he wants. He will have to multiply 1225 by 10.
Step 1
Multiply the non-zero digits.
1225 × 1 = 1225
Step 2
Put the remaining 0s at the end of the product.
1225 × 10 = 12,250
So, he will get 12,250 marbles.
Step 1
Multiply the non-zero digits.
1225 × 1 = 1225
Step 2
Put the remaining 0s at the end of the product.
1225 × 100 = 1,22,500
So, he will get 1,22,500 marbles.

The product of any number multiplied by 1 will always be the number itself. The product of any number multiplied by 0 will always be 0.
Step 1
Multiply the non-zero digits. 1225 × 1 = 1225
Step 2
Put the remaining 0s at the end of the product.
1225 × 1000 = 12,25,000
Thus, he will get 12,25,000 marbles.
So, when we multiply a number by 10, 100, 1000 and so on, we add as many 0s to the right of the multiplicand, as there are 0s in the multiplier to get the product.
Example 5: Multiply 7865 by 30.
Step 1
Multiply the non-zero digits.
7865 × 3
TTh Th H T O
2 1 1
7 8 6 5 × 3
2 3 5 9 5
Step 2
Put the remaining 0s at the end of the product.
7865 × 30 = 2,35,950
Therefore, the product of 7865 × 30 is 2,35,950.
Example 6: A book contains about 1244 letters on one page. If there are the same number of letters on each page, then how many letters will there be on 200 pages?
Number of letters on 1 page = 1244
Number of letters on 200 pages = 1244 × 200 = 2,48,800
Therefore, the book has 2,48,800 letters in total.
Radha wants to buy 125 jars of 1225 marbles each, from Jay’s store. Let us find the total number of marbles using multiplication.
Thus, if Radha buys 125 jars of 1225 marbles each, she will get a total of 1,53,125 marbles.
Mr Sharma is a businessman. He visited Jay’s store and wants to buy 1121 jars of marbles.
To find the total number of marbles he is buying, we will have to multiply 1225 by 1121. We will first expand 1121 = 1000 + 100 + 20 + 1 = 1 thousand + 1 hundred + 2 tens + 1 one.
TTh Th H T
So, if Mr Sharma buys 1211 jars of 1225 marbles each, he will have a total of 13,73,225 marbles. Example 7: Multiply 3479 by 452.
Zero was invented by the great Indian mathematician Aryabhata in the 5th century.

Anything multiplied by zero is zero.
452 = 400 + 50 + 2
1: Multiply the ones: 3479 × 2
2: Multiply the tens: 3479 × 50
Step 3: Multiply the hundreds: 3479 × 400

Example 8: There are 1500 students in a school. The school is planning to take all the students for a trip. Each student has to contribute ₹555. What is the total amount collected by the school?
We know that: Total amount collected = Total amount paid by 1500 students
The amount to be paid by 1 student is ₹555.
The amount to be paid by 1500 students = 1500 × ₹555 = ₹8,32,500
So, the total amount collected by the school is ₹8,32,500.
Jay, the owner of the toy store, has 40,000 marbles apart from the marbles in the jars. He wants to put them equally into other jars. He can either put them into 10 jars, 100 jars or 1000 jars.
Division by 10
Division by 100
1 digit from the right is the remainder
2 digits from the right is the remainder
Division by 1000 3 digits from the right is the remainder
Remaining is the quotient
Remaining is the quotient
Remaining is the quotient
Number of marbles in each jar
40,000 ÷ 10
Remainder = 0
Quotient = 4000
40,000 ÷ 100
Remainder = 00
Quotient = 400
40,000 ÷ 1000
Remainder = 000
Quotient = 40
Jay will put 4000 marbles in each jar.
Jay will put 400 marbles in each jar.
Jay will put 40 marbles in each jar.
We can conclude that the same number of digits, as the number of 0s in the divisor from the right of the dividend, form the remainder. The remaining digits are the quotient.
Let us see some more properties of division.
1 When 0 is divided by any number then the quotient is always 0.
2 When a number is divided by 1, the quotient is always the number itself.
3 When a number is divided by itself then the quotient is 1.
Example 9: Divide 15,679 by 100.
15,679 ÷ 100 = 156, with a remainder 79.
Thus, quotient = 156 and remainder = 79.
The remainder can never be greater than the divisor.

If it is more than the divisor, that means the long division is incomplete or incorrect.
Example 10: Divide 98,562 by 1000.
98,562 ÷ 1000 = 98, with a remainder 562.
Thus, quotient = 98 and remainder = 562
Jay wonders if he could divide all of the 40,000 marbles into 120 smaller jars.
Look at the division house to see how 40,00 is divided by 120 to get 333 as the quotient and 40 as the remainder.
So, Jay can only put 333 marbles in each jar, and he will be left with 40 marbles.
Let us check to see if the quotient is correct.
Dividend = Quotient × Divisor + Remainder
Here, the Dividend = 40,000.
Quotient × Divisor + Remainder
= 333 × 120 + 40 = 40,000.
Since the answer is the same as the dividend, our answer is correct.
Example 11: Divide 76,545 by 115. 665 115 76545 –690 754
Dividend = 76,545
Quotient × Divisor + Remainder = 665 × 115 + 70 = 76,475 + 70 = 76,545
So, our answer is correct.
Example 12: A room is large enough for 256 people to sit. How many rooms will be required for 32,000 people to sit?
We know that 256 people can sit in 1 room.
So, 32,000 people can sit in 32,000 ÷ 256 rooms. Therefore, the required number of rooms is 125.

















Write True (T) or False (F).

a The divisor and remainder in a division sum can be the same.
b The result of multiplication is called the multiplicand.
c When a number is divided by another number, it is called the difference.
d Anything multiplied by zero is zero.
Multiply the given numbers by 10, 100 and 1000. a
Divide the given numbers by 10, 100 and 1000. a 25,000
Find the product of the given numbers. a 2675 × 23
Divide the given numbers.
How many hours are there in one leap year?
Find the product of the largest 3-digit and 2-digit number.
Divide the largest 5-digit number by the smallest 3-digit number.
Mrs Gupta earns ₹78,562 every month. How much does she earn in 3 years?
The book Romeo and Juliet by Shakespeare has about 24,645 words. Each page contains 155 words. How many pages are there in the book?
The owner of a shop makes a profit of ₹98,000. He decides to keep ₹30,000 for himself and distribute similar stationery kits among 100 kids in an orphanage. What is the cost of each stationery kit? Have you ever donated anything to an orphanage?
On a school trip, there were 6 teachers who accompanied one group out of 2 equal groups in a class of 54 students. On the day of the trip, 2 groups of 5 students each were absent. Ram, a student on the trip, wonders how many people including the teachers, are on the trip. Let us help him find out.
Ram tries putting the number and operators in a problem. He comes up with: 6 + 54 ÷ 2 − 2 × 5
Seeing so many operations in a single problem, Ram cannot figure out how to solve it. To solve this problem, he will have to use DMAS. What is DMAS? When we have two or more operations in a problem, we carry out these operations in a certain order. This order is called DMAS.
Now, let us help Ram figure out how many people are there on the trip.
Let us help Ram solve the problem: 6 + 54 ÷ 2 – 2 × 5
We always move from left to right. We will follow the following steps of DMAS:
Step 1
Simplify division (÷)
= 6 + 54 ÷ 2 − 2 × 5
= 6 + 27 − 2 × 5
Step 2
Simplify multiplication (×)
= 6 + 27 − 2 × 5
= 6 + 27 − 10
D Division ÷
M Multiplication ×
A Addition +
S Subtraction
Step 3
Simplify addition (+)
= 6 + 27 − 10
= 33 − 10
Therefore, there are 23 students and teachers on the trip.
Example 13: Simplify: 42 ÷ 7 + 3 × 9 − 1
42 ÷ 7 + 3 × 9 − 1
= 6 + 3 × 9 − 1
= 6 + 27 − 1
= 33 − 1 = 32
Step 4
Simplify subtraction (−)
= 33 − 10 = 23
A teacher has 72 apples. He distributes them equally among 4 bags and keeps only 1 bag for himself. Then, 4 students give the teacher 10 apples each. Finally, all of them together eat 20 apples from the bag.
Calculate the number of apples left with the teacher. The teacher puts the apples equally in 4 bags. That is, 72 ÷ 4. 4 students give him 10 apples each. So, he has 4 × 10 more apples.
That is, 72 ÷ 4 + 4 × 10.

Now, all of them ate 20 apples. So, the apples left in the bag are:
72 ÷ 4 + 4 × 10 − 20
= 18 + 4 × 10 − 20
= 18 + 40 − 20
= 58 − 20 = 38
Are multiplication and division related?
Example 14: Tarun has 2 sets of 10 toy cars. His father gives him 5 more toy cars. Tarun then wants to give 4 cars to his friend. How many cars will he be left with?
Cars in sets of 2 = 2 × 10
Father gives him 5 more cars = 2 × 10 + 5
Tarun gives 4 cars to his friend = 2 × 10 + 5 − 4
Number of cars left = 20 + 5 − 4 = 25 − 4 = 21

Therefore, Tarun will be left with 21 toy cars.

If we do not follow DMAS, will we get the same answer?














Tick () the correct answer.

a The order of DMAS is:
d 20 + 50 ÷ 2 – 5 = e 16 + 8 ÷ 2 – 1 × 5= f 25 – 4 × 12 ÷ 4 + 3 = 1 2 3 Chapter 2 • Operations
b 100 × 10 – 100 + 2000 ÷ 100 =
979
c 100 ÷ 10 + 10 × 10 =
920
d 63 ÷ 9 + 12 × 4 – 5 = i 71 ii 50 iii 23 iv 7
Write True (T) or False (F).
a In DMAS, we first perform addition/subtraction and then division/multiplication.
b In DMAS, the last step is subtraction.
c 5 × 4 + 12 ÷ 3 = 24
d 36 ÷ 6 – 3 × 2 = 2
Fill in the blanks.
a 82 × 3 + 20 = b 28 ÷ 7 + 8 × 5 = c 55 ÷ 11 + 7 =
a 120 – 12 + 36 ÷ 3 × 5 b 279 + 321 ÷ 3 – 57 × 2 c 676 + 835 × 45 ÷ 15 – 10
Alex has saved ₹120. He wants to buy a toy for ₹28 and a book. The book is half the price of the toy. How much money will he have left after buying the toy and the book?
Anish had 50 stickers. He gave 3 stickers to each of his 4 friends. He then bought 10 more stickers. How many stickers does Anish have now?
Sahil has 15 pencils. He wants to distribute them among his 3 friends. All three friends already have 2 pencils. If he gives each friend the same number of pencils, find the total number of pencils each friend has. Do you also share things with your friends?
Solar Panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity using photovoltaic (PV) cells made of semiconductor materials like silicon. In a school with 350 students, the administration wants to install solar panels to help the environment and teach students about renewable energy. On Monday, 25 students were absent. The rest of the students brought ₹230 each for the project. How much money did the students bring?

Communication & Collaboration
Setting: In pairs
Materials Required: 3 dice, a pencil and paper.
Method:

Divide the students into pairs.
Each pair should have a pencil and paper.

One student from each pair would roll the 3 dice.
From the three numbers obtained, one student from each pair will form the largest and the smallest number. The other student will multiply the two numbers.
Note down the number obtained on a sheet of paper.

Keep repeating the above process, and each time add the results obtained after multiplication to find the sum.
The student who gets the sum of 6,00,000 or more first wins.


Find the sum of the given numbers.
a 56,789 and 23,456 b 9,87,654 and 45,774
c 6,73,778 and 5,67,433 d 2,53,621, 12,365 and 36,586

Subtract the given numbers.
a 54,676 and 34,575 b 8,64,826 and 96,537
c 8,68,636 and 65,365 d 9,54,863 and 8,45,622
Multiply the given numbers by 10, 100 and 1000.
a 896 b 4546
c 6457 d 9876
Divide the given numbers by 10, 100 and 1000.
a 2100 b 4086
c 51,200 d 74,562
Find the product of the given numbers.
a 6789 and 432 b 8646 and 200
c 4321 and 2981 d 1256 and 3251
Divide the given numbers using long division.
a 54,767 and 231 b 56,785 and 314
c 88,757 and 768 d 99,866 and 982
Simplify.
a 18 ÷ 2 × 3 b 12 × 6 − 2 + 18 ÷ 3
34
The product of two numbers is 25,290. If one number is 562, find the other number.
Find the difference of the largest 6-digit number and the smallest 6-digit number.
Raj and his team are census workers, whose job is to collect the population. In Ghaziabad city, there are 3,81,53,154 men, 3,15,31,873 women and 6,81,231 children. How many people are there in Ghaziabad?
Isha is planning a road trip that covers a total distance of 7500 km. She plans to drive 150 km each day. In how many days will Isha complete the trip?
Ooty organises a botanical flower show every year. A garden is divided into 60 equal sections. Each section has 1280 flowers. 30 of these sections are replanted with the same number of new flowers, and the rest remain the same. How many new flowers are there in the garden now?
An auditorium has a capacity of 64,070 people. If one row can seat 430 people, how many rows are there in the auditorium?
Maya has 80 marbles. She gives 5 marbles each to 6 of her friends. Then, she finds 15 more marbles. How many marbles does Maya have now?
Neha’s annual income is ₹98,780. She spends ₹50,000 and saves the rest. How much money will she save in 10 years?
What number must be subtracted from the sum of 5,00,000 and 3,00,000 to make it equal to their difference?
There are 5565 mangoes. The number of oranges is twice the number of mangoes. How many oranges will each box contain if the shopkeeper keeps an equal number of oranges in 5 cartons?
Shreya had ₹45,000 in her bank account. She got her salary and the amount in her bank account became three times what it was before. She donated ₹14,500 to an emergency relief fund for the soldiers on the Indian border. How much money was left in her bank account? Have you ever collected funds for a charity event?
Write a word problem with one 6-digit number and two 5-digit numbers. The word problem should have addition, division and subtraction.
1 The population of Hassan is 1,88,000. The population of Mysore city is 12,61,000.
Read the statements and answer the question given below.

Statement 1: The population of Belgaum is 7,83,000, which is 5,95,000 more than the population of Hassan.
Statement 2: The population of Hassan and Belgaum together is less than the population of Mysore.
Is statement 1, 2 or both true? Show your working.

2 Ravi has two bank accounts A and B. The combined balance of the two accounts is ₹8,75,632. What is the balance in account B?
Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Statement 1: The balance in Account A is ₹3,56,289.

Statement 2: Account B has more balance than account A.
a Statement 1 alone is sufficient to answer.
b Statement 2 alone is sufficient to answer.
c Both statements together are sufficient to answer.
d Both statements together are not sufficient to answer.




Cross Curricular
Our country is the largest rice-producing country. Most of the states in our country produce rice, and most of the rice varieties are exported to different parts of the world. The table shows the amount of rice produced by the state in 2 months.
State
Karnataka
Tamil Nadu

Bihar
Madhya Pradesh
5,04,975 kg
8,20,965 kg
7,05,136 kg
4,94,814 kg
1 The total weight of the rice produced by Karnataka and Bihar is .
2 Write True (T) or False (F).

a Tamil Nadu produces 4,67,870 kg more rice than Madhya Pradesh.
b Karnataka produces 3,15,990 kg less rice than Tamil Nadu.
3 Tamil Nadu wants to deliver 78,432 kg of rice in 456 bags to a relief camp. What will be the weight of rice in each bag?

4 24,430 kg of rice from Bihar and 20,510 kg of rice from Karnataka are to be mixed and put equally in 214 containers. What will be the weight of the rice in each container?




























































For a group dance event, 12 dancers were to enter the stage together. The dance teacher made all the dancers stand in a single line, but all of them could not fit on the stage.












So, she decided to try different ways in which the dancers could fit onto the stage.
2 rows of 6 dancers 4 rows of 3 dancers 3 rows of 4 dancers




































She noticed that all the dancers could fit when she made 3 rows of 4 dancers.
So, here we saw four different ways to make 12 dancers stand in lines having equal rows and columns.
1 × 12 2 × 6 4 × 3 3 × 4
Can there be more ways to arrange the dancers in lines having equal rows and columns?
1, 12, 2, 6, 3 and 4 are all the numbers we multiplied to get 12. Therefore, we can say that 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12 are all factors of 12.

The numbers that are multiplied to get a product are called its factors.
Let us look at the factors of 12 once more.
• 1 is its smallest factor. 1 is the smallest factor of every number.
• 12 is the greatest factor of itself. Every number is the greatest factor of itself.
• Every factor of 12 is less than or equal to 12. The factors of a number are always equal to or less than the number.
We know that multiplication and division are opposite operations. Thus, we can also define factors in terms of division.
The factor of a number is a number that divides the given number evenly or exactly, leaving no remainder.
In our example, the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12 are all factors of 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 exactly without leaving any remainder.
We can find the factors of a number by recalling the multiplication facts of numbers. We begin with the multiplication table of 1 and gradually move on to higher tables to see where the given number appears.
Let us try to find the factors of 18 using multiplication.
1 × 18 = 18; 2 × 9 = 18; 3 × 6 = 18
The multiplication table of 4 does not give 18 as a product.
The multiplication table of 5 does not give 18 as a product.

When finding factors by multiplication, always:
• Start with the multiplication table of 1.
• Stop when any factor starts repeating.
6 × 3 = 18. This is the same as 3 × 6 = 18, which is already covered. Thus, we will stop at the multiplication table of 6.
So, the factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9 and 18.
To find the factors of a number, we can also look for numbers that divide the given number exactly, without leaving any remainder.
Let us find the factors of 36 using the division method.
36 ÷ 1 = 36 0 1 and 36 are factors of 36.
36 ÷ 2 = 18 0 2 and 18 are factors of 36.
36 ÷ 3 = 12 0 3 and 12 are factors of 36.
36 ÷ 4 = 9 0 4 and 9 are factors of 36.
36 ÷ 5 = 7 1 5 and 7 are not factors of 36.
36 ÷ 6 = 6 0 6 is a factor of 36.
36 ÷ 7 = 5 1 7 and 5 are not factors of 36.
36 ÷ 8 = 4 4 8 and 4 are not factors of 36.
36 ÷ 9 = 4 0 STOP! 9 and 4 are already covered above.
When factors are repeated, no further division takes place.
So, the factors of 36 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18 and 36.
Example 1: Find the factors of 20 using multiplication.
1 × 20 = 20
2 × 10 = 20
The multiplication table of 3 does not give 20 as a product.
4 × 5 = 20.
5 × 4 = 20. This is the same as 4 × 5 = 20, which is already covered above.
Thus, we will stop at the multiplication table of 5.
So, the factors of 20 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10 and 20.
Example 2: Find the factors of 30 using the division method.
30 ÷ 1 = 30 0 1 and 30 are factors of 30.
30 ÷ 2 = 15 0 2 and 15 are factors of 30.
30 ÷ 3 = 10 0 3 and 10 are factors of 30.
30 ÷ 4 = 7 2 4 and 7 are not factors of 30.
30 ÷ 5 = 6 0 5 and 6 are factors of 30.
30 ÷ 6 = 5 0 STOP! 6 and 5 are already covered above.
When factors are repeated, no further division takes place.
So, the factors of 30 are 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15 and 30.
Numbers which have only two factors, namely 1 and the number itself, are called prime numbers. Numbers with more than two factors are called composite numbers.

When 2 numbers have 1 as their common factor, they are called co-prime numbers. For example, 4 and 7 have 1 as their common factor.
When 2 numbers have only one composite number between them, they are called twin prime numbers. For example, (3, 5), (11, 13), (17, 19).
Example 3: Which is a prime number, 16 or 17?
Factors of 16 = 1, 2, 4, 8 and 16.
Factors of 17 = 1 and 17
17 has 2 factors, so it is a prime number.



• 0 and 1 are neither prime nor composite.
• 2 is the lowest and the only even prime number.














Find the factors of the numbers using the multiplication method.

Find the factors of the numbers using the division method.
Sort the given numbers as prime or composite numbers.
How many prime numbers are there between 10 and 20? List them.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a bacteria which is responsible for tuberclosis. It has a slower replication time and typically divides every 17 minutes (approx.). How many factor are there for the number 17?
An event manager is getting chairs arranged for a stage show. He wants to put the same number of chairs in rows as the total number of rows. How many chairs will be there in each row, if he has 169 chairs?
a word problem to find factors of a number.
The rules of divisibility will help you find the numbers that divide other numbers without leaving any remainder.
The divisibility of a number by 2, 5 and 10 can be checked by looking at the last digit of the number. Look at the table below:
A number is divisible by: If the last digit is:
A number is divisible by 2 and 5 if it is divisible by 10.
Example 4: Is 64 divisible by 2?
64 ends with the digit 4.
So, 64 is divisible by 2.
Divisibility by 3 and 9
Example 5: Is 45 divisible by 5?
45 ends with the digit 5.
So, 45 is divisible by 5.
To test the divisibility of a number by 3 or 9, we add the digits of the number. If the sum is divisible by 3 or 9, the number itself is divisible by 3 or 9, respectively.
A number is divisible by: If the sum of the digits is divisible by:
A number is also divisible by 3 if it is divisible by 9.
Example 6: Is 54 divisible by 3?
5 + 4 = 9
9 is divisible by 3.
So, 54 is divisible by 3.


Example 7: Is 452 divisible by 9?
4 + 5 + 2 = 11
11 is not divisible by 9.
So, 452 is not divisible by 9.















Circle the numbers that are divisible by 2.
Circle the numbers that are divisible by both 5 and 10.
Circle the numbers that are divisible by 3.
Circle the numbers
are
by 9.

A secret passage has a number lock. Below are the clues to the correct number needed to open the lock. Which of the given numbers shows the secret code?
• The number is divisible by 3 and 5.
• The number has 0 as the last digit.
a 660 b 530 c 130 d 370
Anu is distributing gifts to the poor kids in her neighborhood. There are 10 kids in all. She has 40 pencils, 20 erasers, 55 candies and 20 notebooks. Which are the items that she can divide equally among the kids?
A prime factor of a number is a factor that is also a prime number.
A composite number can be expressed as the product of prime factors. This is called prime factorisation.
A factor tree can be used to find the prime factors of a number. Let us find the factors of 120 using a factor tree.
Step 1: Write the number at the top of the factor tree and draw two branches below
Step 2: Fill in the branches with a factor pair of the number above. We chose 12 and 10 as the factor pair.
Step 3: Continue until each branch ends in a prime number.
Prime factorisation of the number = Product of prime numbers found by factor tree
Prime factorisation of 120 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5

Prime factorisation can be checked by multiplying all the factors. The product should be equal to the given number.
Prime factors can also be found using repeated division. In this method, we start dividing the given number by the smallest possible prime number and continue dividing it by prime numbers until we reach 1.
Let us factorise 81 by the division method.

There is only one unique product of prime factors for any number. For example, prime factors of 40 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 5. There is no other possible set of prime numbers that can be multiplied to make 40.
So, the prime factorisation of 81 = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3.
Example 8: Draw a factor tree for the number 36 and then express the number as a product of its prime factors.
Example 9: Use repeated division to find the prime factors of 84. Express the number as a product of its prime factors.
So, 36 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3.


So, 84 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 7.















Which of the following represents the prime factorisation of 80?
Which of the following has 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 7 as its prime factorisation?
Draw factor trees to find the prime factorisation of the given numbers.
Find the prime factorisation of the following using the division method.
The Earth completes its revolution around the Sun in 365 days. What are the prime factors of 365?

Mrs Gupta has 18 students in her class today, and her fellow teacher, Mrs Mehra, has 27 students. The teachers want to combine the classes for a group activity that requires groups of equal size.
The teachers aim to maximise the number of students in each group.
The teachers want to divide their students into groups. Thus, the factors of the total number of children can represent the group size and number of groups.
Total number of children in the class = Number of groups × Students per group.
Mrs Gupta’s class
Mrs Mehra’s class
Possible group size = 27, 9, 3 and 1.
Possible group size = 18, 9, 6, 3, 2 and 1.
Notice that all the possible group sizes are factors of the class sizes. Now, let us list the possible group sizes that are equal in the two classes. We do this in the following manner:
Thus, 1, 3 and 9 are possible equal group sizes for the two classes. These are the common factors of the two numbers. We can say that 1, 3 and 9 are common factors of 18 and 27.
A common factor is a number that can evenly divide a set of two or more numbers without leaving any remainder.
How can we find the common factors of any two numbers?
We list the factors of each number and then identify the common factors among them.
Let us try to find the common factors of 16 and 40.
Factors of 16 = 1 , 2 , 4 , 8 and 16.
18 Factors
27
Factors of 40 = 1 , 2 , 4 , 5, 8 , 10, 20 and 40.
Common Factors of 16 and 40 = 1 , 2 , 4 and 8.
Example 10: Find the common factors of 15 and 20.
Factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5, and 15.
Factors of 20 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 10 and 20.
The common factors of 15 and 20 are 1 and 5.
Example 11: Find the common factors of 12 and 16.
Factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
Factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16.
The common factors of 12 and 16 are 1, 2, and 4.
Factor Method

When two or more numbers have the same factor, that factor is called a common factor.

1 is the common factor of every two or more given numbers.
The following are the possible group sizes that can be formed in Mrs Gupta’s and Mrs Mehra’s classes:
Mrs Gupta’s class of 18: 18, 9, 6, 3, 2 and 1.
Mrs Mehra’s class of 27: 27, 9, 3 and 1
The common factors represent the equal numbers of group sizes that can be formed. These are 1, 3 and 9.
For the activity, the teachers wanted to maximise the number of students per group. The biggest group size that can be achieved is 9!
So, 9 is the highest common factor, or simply, the HCF. 9 is the HCF of 18 and 27.
Let us see how we can find the HCF of any two numbers, say 12 and 18. We proceed using the following steps:
Factors of 12 = 1 , 2 , 3 , 4, 6 and 12
Factors of 18 = 1 , 2 , 3 , 6 , 9 and 18.
Common Factors of 12 and 18 = 1 , 2 , 3 and 6 .
The highest common factor (HCF) of 12 and 18 is 6.
The largest of the common factors is the HCF of the two numbers.
Example 12: Find the HCF of 56 and 70.
Factors of 56 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 14, 28 and 56.
Factors of 70 are 1, 2, 5, 7, 10, 14, 35 and 70.
The common factors of 56 and 70 are 1, 2, 7 and 14.

The HCF of the given numbers cannot be bigger than any one of the given numbers.
The highest common factor (HCF) of 56 and 70 is 14.

Example 13: Mike has 16 blue marbles and 8 white marbles. If he wants to place them in identical groups without any marbles being left over, what is the largest number of groups Mike can make?
Number of blue marbles: 16
Number of white marbles: 8
As we need to find the greatest number of groups, we will find the HCF.
Factors of 16 = 1, 2, 4, 8, 16
Factors of 8 = 1, 2, 4, 8
Common factors = 1, 2, 4, 8
Highest common factor = 8
Hence, the greatest number of groups that Mike can make is 8.
Let us now use the prime factorisation method to find the HCF of 24 and 32.
1. Find the prime factorisation of both numbers.
24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3
32 = 2 × 2 ×
2. Find the common factors of both numbers.
3. Multiply the combination of common factors to get the HCF of the numbers.
= 2 × 2 × 2 = 8.

The HCF of two or more numbers is the product of their common prime factors.
Example 14: Find the HCF of 12, 18 and 24.
12 = 2 × 2 × 3
18 = 2 × 3 × 3
24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3
The common factors of 12, 18, and 24 are 2 and 3.
Hence, HCF = 2 × 3 = 6.
In this method, we divide the greater number by the smaller number. The remainder of this division becomes the new divisor, and the previous divisor becomes the new dividend. We continue this process until the remainder is 0. The last divisor obtained is the HCF of the given numbers.
Let us find the HCF of 18 and 48 using the long division method.
Remainder 12 becomes the new divisor.
Remainder is 0.
So, the last divisor 6 is the HCF.
Divisor 18 becomes the new dividend.
Example 15: Find the HCF of the given numbers using the long division method.
Example 16: Three pieces of fabric, measuring 42 m, 49 m and 63 m long have to be divided into curtains of the same length. What is the greatest possible length of each curtain?
Length of pieces of fabric = 42 m, 49 m and 63 m.
Greatest possible length of each curtain = HCF of 42 m, 49 m and 63 m.
Hence, the greatest possible length of each curtain is 7 m.
















Find the common factors for the 2 numbers.


Find the HCF by finding all the factors.
a 16, 24 b 15, 90 c 25, 45 d 27, 47 e 27, 81 f 28, 42 g 40, 50 h 33, 55
Draw factor trees to find the HCF of the given numbers.
a 12, 15 b 26, 65 c 36, 54 d 24, 40, 56
Find the HCF of the following numbers by using the long division method.
a 18, 24 b 14, 84 c 20, 120 d 81, 108
The length, breadth and height of a box are 75 cm, 85 cm and 95 cm, respectively. Find the length of the longest tape which can measure the three dimensions of the box exactly.
Rice takes 120 days to mature, while maize takes 150 days to mature. A farmer wants to plant and harvest both crops in such a way that they can start planting both crops again on the same day after the crops have matured and been harvested. How many days will it take for this cycle to repeat?
Setting: In groups of 4
Materials Required: Number chart for numbers 1 to 100, coloured pencils
Method:
Colour the number 1 on the number chart as 1 is neither prime nor composite.
Circle the number 2 and put a blue dot for all the numbers divisible by 2.
Circle the number 3 and put a red dot for all the numbers divisible by 3.
Circle the number 5 and put a green dot for all the numbers divisible by 5.
Find the next number that is neither circled nor has a dot. Circle that number and put a different colour for all the numbers that are divisible by this new number.
List the numbers that have dots of all the colours.
All the circled numbers are prime numbers, and the numbers that have dots are composite numbers.
Write the number of prime numbers between 1 and 100.
Write the number of composite numbers between 1 and 100.
Sort
Find the factors of the numbers using the multiplication method.
a 16 b 20 c 24 d 42
Find the factors of the numbers using the division method.
a 28 b 36 c 56 d 80
Use the divisibility rules to check if the given numbers are divisible by 2, 3, 5, 9, 10.
a 35 b 93 c 450 d 700
Draw factor trees to find the prime factorisation of the given numbers.
a 88 b 102 c 112 d 140
Use the repeated division method to find the prime factorisation of the numbers.
a 75 b 21 c 128 d 164
Find the common factors of each pair of numbers.
a 25, 45 b 75, 125 c 33, 55 d 120, 156
Find the HCF by finding all the factors.
a 16, 60 b 25, 65 c 48, 120 d 150, 225
Find the HCF using the prime factorisation method.
a 34, 38 b 34, 51 c 60, 225 d 105, 180
Find the HCF of the following numbers by using the long division method.
a 36, 63
b 119, 187 c 45, 89 d 136, 170
Write a 3-digit number such that both 420 and the number have 2 as a common factor.
Rainwater harvesting is a simple technique of collecting, filtering and subsequently storing rainwater into reservoirs or tanks. Two tanks contain 250 litres and 425 litres of rainwater, respectively. What will be the maximum capacity of a bucket that can measure the water in both tanks an exact number of times?
Kirti is making identical balloon bunches for a party. She has 24 white balloons and 16 orange balloons. She wants each bunch to have the same number of balloons of each colour. What is the greatest number of bunches she can make if she uses every balloon?
Jose is making a game board that is 66 inches by 24 inches using square tiles only. What is the largest square tile he can use, and how many tiles will he need?
Neeta wants to distribute refreshments at a party. She has 240 cupcakes and 160 sandwiches. She wants to equally distribute the food items among her classmates in packets. What is the maximum number of packets she can make, and what will be the contents of each?
Anita baked 30 oatmeal cookies and 48 chocolate chip cookies to package in plastic containers to giveaway at an old age home. She wants to divide the cookies into identical containers with each container having the same number of each type of cookie. If she wants each container to have the greatest number of cookies possible, how many plastic containers does she need? Have you ever visited an old age home?

1 Find the greatest number that divides 178 and 128, leaving a remainder of 8 in each case.

2 ‘I am twice the number that divides two numbers without leaving any remainder. One number is 2 more than half a century, and the other number is 16 more than a century.’ Who am I?

Cross Curricular


Jewellery making is an art. The stones used in making a jewel goes through a lot of chemical processes. Rubies are red in colour and are made from the corundum mineral. Emerald is made from beryl mineral and it is green in colour. Pearls are obtained below the sea and are white in colour. Jade comes in vibrant colours and is obtained from jadeite.

A jeweller has a few pearls, emerald, ruby and jade. He customises jewellery according to the needs of the customer.



1 A customer asks him to make a pearl bracelet with an odd number of strings. The total number of pearls in the bracelet is 72. If the number of strings is also a prime number, then which of these can be the number of strings?

2 A girl asks the jeweller to use emeralds and rubies to make bangles. The jeweller has 18 rubies and 24 emeralds. What is the maximum number of stones he can use in each, such that the number of rubies and emeralds are equal in the bangles?

3 A girl orders 32 pairs of earrings. She also asks the jeweller to pack them per his choice. If the jeweller decides to pack them in prime factors, draw the factor tree for the same.

4 The jeweller decides to use 24 jades and 36 emeralds to make identical necklaces without any stones left. What is the greatest number of necklaces that the jeweller can make?




























































Ajay is very fond of music. He attends music classes on every fifth day of the month. The rest of the month, he practises what he has already learnt in the class.
Ajay wants to mark every fifth day on the calendar so that he does not forget to attend his music classes.
So, Ajay skip counts by 5 to make a list of the days on which he will attend his music class in the month of August.
Here, the list prepared by Ajay gives the first six multiples of 5.
When any number is multiplied by 1, 2, 3, 4, …, we get the multiples of that number.
For example, we get the multiples of 7 by multiplying 7 with 1, 2, 3, 4, … and so on.
7 × 1 = 7, 7 × 2 = 14, 7 × 3 = 21, 7 × 4 = 28, …
Hence, multiples of 7 are 7, 14, 21, 28, …
Do all the numbers when Ajay attends the music classes appear in the multiplication table of 5? What do we call such numbers?
Look at the multiplication sentence given below. 7 and 2 are the factors of 14. 14 is the multiple of 7 and 2.
7 × 2 = 14
Factors of 14
Multiple of 7 Multiple of 2

Multiple of a number = Number × Any number

This is the same as recalling the multiplication tables of those numbers.
For example, multiples of 9 are the numbers in the 9 times table.
We can also find the multiples of a number by skip counting on the number line.
When we skip count by a number, we get the multiples of that number.
The numbers 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 and 14 are the first seven multiples of 2.
Another way to create a list of multiples of a number is to start at the number and add it repeatedly to the sum. The repeated addition method is one of the simplest methods to find the multiples of any given number.
For example, the multiples of 25 can be found by: Using the Multiplication Tables
25 × 1 = 25
Here, 25, 50, 75, 100 and 125 are a few multiples of 25.
Hence, it is possible to find the multiples of any number by repeated addition of that number or by recalling the times table of that number.
Look at the multiples of 25 once more.
25 is a multiple of itself. A number is a multiple of itself.
25 is a multiple of 1.
Each multiple of 25 is either greater than or equal to 25.
There are countless multiples of 25.
Every number is a multiple of 1.
Every multiple of a number is greater than or equal to the number itself.
There is no end to the multiples that you can find for a number.
You can also check if a number is a multiple of a given number by using division. If the remainder is zero, then the bigger number (dividend) is a multiple of the smaller number (divisor).
For example:
On dividing 91 by 7, we get 0 as the remainder. So, 91 is a multiple of 7.
Example 1: Show the first eight multiples of 8, on a number line.
So, 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56 and 64 are the first eight multiples of 8.
Example 2: What is the 9th multiple of 7?
The 9th multiple of 7 is 7 × 9 = 63.
Example 3: Is 78 a multiple of 3? 2 6 3
On dividing 78 by 3, we get no remainder. So, 78 is a multiple of 3.

















Write the first 5 multiples of the given numbers.
2 Is 7209 a multiple of 9? Justify.
3 The kumbh mela is a major pilgrimage and festival in Hinduism. The ‘Purna Kumbh mela’ is organised every 12 years. The last Purna Kumbh mela was organised in 2013. When will the next three Purna Kumbh melas be organised?
4 Select any number with 0 in its ones place and write its first ten multiples. State whether the multiples are odd or even.
5 Cicadas are large and winged insects known for their distinct, loud sound. Two species of cicadas emerge from the ground every 13 years and 17 years respectively. If both species emerged in 2021, will they emerge together over the next century?

Apart from music classes, Ajay also attends art classes every fourth day in the month of August.
Ajay marks every fourth day on the calendar and completes the list of the days on which he will attend his music and his art classes in the month of August.
Ajay looks at the lists to see if there are any days on which he has to attend both—his music and his art classes. He finds that 20th August is the date when he would have to attend both the classes.
So, 20th of August is the only day in August when Ajay will be attending both the classes.
When a number is a multiple of two or more numbers, it is called a common multiple of those numbers. Let us list the multiples of 5 and 6.
30 is a common multiple of 5 and 6. 60 is a common multiple of 5 and 6.
30 and 60 are known as common multiples of 5 and 6. If the pattern is extended, you will find that 90 and 120 are also common multiples of 5 and 6.
Out of these numbers, 30 is the lowest common multiple, or LCM, of 5 and 6.
The smallest number among the common multiples is called the lowest common multiple or LCM. It is also the smallest number which can be divided by each of the given numbers.
Aryabhata was an Indian mathematician who helped us understand how to find the least common multiple (LCM) of numbers, which is useful for solving problems where we need to find a common time or number for different things to happen together.
Example 4: Find the LCM of 3 and 5.
30 is a common multiple of 3 and 5. 15 is a common multiple of 3 and 5.
of 5: 5
15 is the lowest of all common multiples. So, 15 is the LCM of 3 and 5.
15 is the lowest among the common multiples, it is the LCM of 3 and 5.
Example 5: Find the LCM of 6, 4 and 8.
Common multiples of 6, 4 and 8 = 24, 48, …
Since 24 is the lowest among all the common multiples, so it is the LCM of 6, 4 and 8.

















Which of the following is a common multiple of 25, 75 and 50?
a 75 b 100 c 125 d 150
2 Find the common multiples of the given numbers. Write their LCM. a 12 and 15 b 9 and 63 c 5 and 55 d 8 and 10 e 6, 12 and 18 f 6, 10 and 15 g 12, 15 and 20 h 15, 25 and 30
3 Which of these will have the same lowest common multiple as 4 and 15?
a 4 and 20 b 6 and 25 c 5 and 12 d 8 and 30
4 The U.S. presidential elections are held every 4 years, while Senate elections are held every 6 years. If both elections are held in 2024, in which year will they next occur together again?
5 A machine requires maintenance every 12 days, and another machine requires maintenance every 18 days. If both machines are maintained today, in how many days will they both need maintenance on the same day again?
6 Two sisters, one in a primary school and the other in a middle school, have lunch together when their school bells ring at the same time. The bell of the primary school rings every 30 minutes, while the bell of the middle school rings every 40 minutes. If both bells ring together at 8:30 a.m., when will they ring together again?
7 Create a question based on LCM.

In this method, we first find the prime factorisation of each number. We then multiply each factor the maximum number of times it occurs in any given number.
For example, to find the LCM of 60 and 45, follow the steps given below:
Step 1: Write the prime factorisation of the numbers.
60 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
45 = 3 × 3 × 5
So, LCM of 45 and 60 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5 = 180
Step 2: Multiply each factor the greatest number of times it occurs in the prime factorisation.
We take 2 two times, 3 two times, and 5 one time and multiply
Example 6: Find the lowest common multiple of 84 and 90.
84 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 7 90 = 2 × 3 × 3 × 5
So, LCM of 84 and 90 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 7 = 1,260
Example 7: Find the LCM of 36, 48 and 56 by the prime factorisation method.
36 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 48 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 56 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 7

LCM of 36, 48 and 56 = 3 × 3 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 7 = 1,008















Find the prime factorisation of the numbers.

a 35 and 75 b 44 and 88 c 48 and 12 d 25 and 115
2 These numbers have already been factorised for you. Find the LCM of the pairs given below.
8 = 2 × 2 × 2 25 = 5 × 5 16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 10 = 2 × 5
a 8, 10 b 8, 16 c 16, 10 d 25, 10
3 Find the LCM of the given numbers using the prime factorisation method.
a 16, 24 b 25, 35 c 36, 45 d 63, 105 e 18, 40 and 45 f 72, 96 and 108 g 48, 56 and 70 h 30, 60 and 90
4 Rohan writes the prime factorisation of the numbers 12, 24 and 56 as shown below.
12 = 2 × 2 × 3 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 56 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 7
He says that the LCM of the numbers is 24. Is he right? Why or why not?
5 The T20 cricket world cup is held every 2 years while the FIFA world cup is held every 4 years. Both the world cups were last held together in 2022. How many times will both world cups be held together till 2040 after 2022?
6 Create a word problem on finding the LCM of 2 numbers.
Let us see how we can find the LCM of 25 and 45 using the short division method.
Step 1: Arrange the numbers in a line.
Step 2: Start dividing the numbers by common prime number, which, in this case, is 5.
5 25, 45 5 5, 9 3 1, 9 3 1, 3 1, 1
Step 4: Multiply all the prime factors to get the LCM.
LCM = 5 × 5 × 3 × 3 = 225
Step 3: Continue dividing until we get 1 as the quotient for all the numbers.
Example 8: Find the LCM using the short division method.
1 6, 12 and 15
3 6, 12, 15
2 2, 4, 5
2 1, 2, 5
5 1, 1, 5 1, 1, 1
LCM = 3 × 2 × 2 × 5 = 60


2 12, 16 and 20
2 12, 16, 20 2 6, 8, 10
2 3, 4, 5
2 3, 2, 5
3 3, 1, 5 5 1, 1, 5 1, 1, 1
LCM = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 = 240















Find the LCM using the short division method.
a 21, 24 b 25, 30 c 32, 48 d 60, 75
e 28, 42, 56 f 75, 100, 150 g 21, 63, 105 h 90, 135, 180
2 Rohit finds the common prime factors of 42 and 56 using short division as shown below.
He says that the LCM of 42 and 56 is 28. Is he right? Why or why not?
3 Match the following.
LCM of 42, 70 90
LCM of 63, 105 45
LCM of 30, 45 48
LCM of 9, 15
LCM of 12, 48
2 42, 56
7 21, 28
2 3, 4

4 Jupiter takes around 12 years to revolve around the Sun while Saturn takes around 30 years to revolve around the Sun. If Jupiter, Saturn and the Sun are in a straight line at the beginning of their revolution cycle, after how many years will they be in their original positions again?
When do we use LCM?
When we need to find the smallest number that is a multiple of all the numbers in a group.
When do we use HCF?
When we need to find the largest number that evenly divides all the numbers in a group.
Let us look at some examples to understand this better.
A store is distributing freebies to its loyal customers. Every third customer receives a free keychain, and every fourth customer receives a free pen. Which customer will be the first to receive both a keychain and a pen?
List the multiples of 3 and 4.
12 is a common multiple of 3 and 4. 24 is a common multiple of 3 and 4.
The Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 3 and 4 is 12.
The first customer to get both a keychain and a pen is the 12th customer.
The fifth-grade class is conducting an activity. There are 32 girls and 40 boys who want to participate. Each team must have the same number of girls and the same number of boys. What is the greatest number of teams that can be formed?
List the factors of 32 and 40. Then, write the common factors.
The class can divide 32 girls into 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 teams.
The class can divide 40 boys into 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, and 40 teams.
The common factors of 32 and 40 are 1, 2, 4, and 8.
The HCF of 32 and 40 is 8.
So, the greatest number of teams that can be formed is 8.
Let us now understand the relationship between HCF and LCM.
Example 9: The product of two numbers is 864. If the LCM of the two numbers is 72, what is the HCF of the two numbers?
We know that the Product of two numbers = HCF × LCM
864 = HCF × 72
So, the LCM = 864 ÷ 72 = 12
Example 10: At a school carnival, every 4th student to enter the carnival gets a candy and every 10th student gets a chocolate. Which student was the first to get both the candy and the chocolate? Find the answer using the prime factorisation method.
Let us find the LCM of 4 and 10.
4 = 2 × 2
10 = 2 × 5
So, LCM of 4 and 10 = 2 × 2 × 5 = 20
Thus, the 20th student will get both the chocolate and the candy.
Example 11: For a morning walk, three people step out together. Their steps measure 80 cm, 85 cm, and 90 cm respectively. What is the minimum distance that each should walk before they are together again?
We need to find the minimum distance they have walked so that they are together again.
Now, the distance walked by them will be greater than 80 cm, 85 cm, and 90 cm.
So, we need to find the LCM in this case.
LCM = 2 × 5 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 17 = 12,240 cm
Therefore, the minimum distance walked so that they are together again = 12,240 cm.
2 80, 85, 90
5 40, 85, 45
2 8, 17, 9
2 4, 17, 9
2 2, 17, 9
3 1, 17, 9
3 1, 17, 3
17 1, 17, 1 1, 1, 1

Example 12: Three pieces of cloth 84 cm, 98 cm and 126 cm long need to be divided into table mats of the same length. What is the greatest possible length of each mat?
Here the pieces of cloth need to be divided into table mats of the greatest possible length. So, the length of each table mat would be less than the lengths of the given pieces of cloth.
So, we need to compute the HCF in this case.
Required length = HCF of 84 cm, 98 cm and 126 cm
84 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 7
HCF = 2 × 7 = 14.
98 = 2 × 7 × 7
Therefore, the required length of each table mat is 14 cm.


126 = 2 × 3 × 3 × 7















endra attends drawing classes which are scheduled once every seven days, starting from the 7th of August. He marks all the dates on a calendar. Write the dates that he will mark for the classes scheduled in the month of August.
2 There are 12 boys and 18 girls in Mrs. Mehra’s maths class. Each activity group must have the same number of boys and the same number of girls. What is the greatest number of groups Mrs. Mehra can make if every student must be in a group?
3 A milkman has 75 litres of milk in one can and 45 litres in another. What is the maximum capacity of a container which can measure the milk in either container an exact number of times?
4 An electronic device beeps every 60 seconds. Another device beeps every 62 seconds. They beep together at 10:00 a.m. What will be the time they beep together again?
5 A school is organizing a sports event. There are 72 soccer balls and 96 basketballs. The organizers want to divide the balls into the largest possible equal groups, such that each group has the same number of soccer balls and basketballs. How many soccer balls and basketballs will be in each group?
6 The HCF of two number is 4 and their LCM is 48. If one of the number is 12, what is the second number?
7 Three different species of flowers have different blooming cycles, depending on their species and types. The sunflowers bloom every 10 weeks, the roses bloom every 5 weeks and the tulips bloom every 3 weeks. If all three species bloom today, after how many weeks will they all bloom together again?
8 Three sets of books, containing 336 English, 240 Mathematics and 96 Science books, need to be stacked in such a way that all the books are stored subject-wise. The height of each stack is the same with the maximum possible number of books. What is the total number of stacks?
9 Create a word problem on finding the HCF.
Setting: In groups of 3

Experiential Learning & Collaboration
Materials Required: Crayons of three colours—blue, orange, and green, and a notebook.
Method:

The students will make a grid of 10 rows and 10 columns in their notebooks.
The students will write the numbers from 1 to 100 in them.

The teacher will ask the students to find the LCM of three numbers, say, 3, 6 and 8.
The students will highlight 3 and its multiples using blue crayons, 6 and its multiples using orange crayons and 8 and its multiples using green crayons. The students can be asked to shade one-third of the cell in each colour.

5 The teacher will tell the students that the numbers which are shaded with all 3 colours are the common multiples of 3, 6 and 8. The teacher will then ask the students to locate the smallest common multiple of 3, 6, and 8 on the grid.


1 Colour the multiples of 9 in the number chart shown below.
2 Ajit picked a number and multiplied it by 7. Which of the following numbers cannot be the result of this multiplication?
3 What will be the 9th multiple of the numbers given?
4 Select the common multiples of 30 and 45 from the following options. 30 = 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210, 240, … 45 = 45, 90, 135, 180, 225, …
a Only 180 b 90, 180 c Only 90 d 30, 45

5 In the following table, the prime factorisation of two numbers A and B is given. Complete the table by finding the LCM of A and B.
a 2 × 3 × 3
2 × 5 × 7
b 2 × 3 × 5 3 × 3 × 5
c 2 × 3 × 3 × 7 2 × 3 × 11
6 Find the LCM of the given numbers using prime factorisation.
a 18, 27 b 35, 14 c 5, 9, 15 d 25, 40, 60
7 Which of the following is the smallest number that is divisible by 9, 12 and 15?
a 360 b 90 c 120 d 180
8 Find the LCM by the short division method.
a 12, 20 and 32 b 93, 62 and 120 c 15, 36 and 40 d 45, 18 and 63
9 Aakash noticed that the number of questions given for homework is divisible by both 3 and 13. What is the smallest possible number of questions that could have been given?
10 Three bells ring at intervals of 20 minutes, 30 minutes and 45 minutes respectively. After how many minutes will the bells ring together?
11 El Niño and La Niña are opposite phases of a natural climate pattern across the tropical Pacific Ocean. If El Niño occurs every 3 years and La Niña every 7 years, starting from 2020 when both were observed, in what future year will both phenomena occur together again?
12 The product of 2 numbers is 2025. What is the LCM of two numbers if their HCF is 15?
Critical Thinking
1 A teacher asks the students to name any number that has 75 as a multiple. Rahul says 15, Sahil says 25, and Ajay says 12.
Which of the statements given below is correct regarding this scenario?
a Rahul and Ajay are correct.
c Rahul and Sahil are correct.

b Ajay and Sahil are correct.
d Only Rahul is correct.
2 Read the given statements. Choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): The LCM of 3 and 9 is 9.
Reason (R): The LCM of any two numbers is always greater than their HCF.

a Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c A is true, but R is false.
d A is false, but R is true.



Riya and Samir are school friends. They live at equal distance from their school but in opposite directions. They use the local bus to go to their school. Riya’s bus arrives every 15 minutes, while Samir’s bus arrives every 20 minutes.
For Earth Day, they decided to plant trees together, outside the school, to increase awareness about saving the environment. For this, they wanted to reach the school at the same time. The buses arrived at their respective bus stands at 8:00 a.m. but both of them missed their buses.

Now, answer the following questions.
1 How often do the buses arrive at the same time?
a Every 30 minutes
c Every 75 minutes

b Every 60 minutes
d Every 90 minutes
2 When should Riya and Samir take the next bus so as to reach school at the same time?
a 8:15 a.m.
c 8:45 a.m.

b 8:30 a.m.
d 9:00 a.m.
3 When they finished planting trees, Riya said, “The number of trees I planted is a multiple of 2.” Samir said, “The number of trees I planted is a multiple of 5.” They both planted the same number of trees. What is the lowest multiple of trees planted that is common to both?

4 On the way back home, Riya’s bus arrives every 10 minutes and Samir’s bus arrives every 15 minutes at the school’s bus stand. If the last time that both the buses arrived together was at 3:30 p.m., when will they arrive at the school bus stop together again?
5 Have you ever taken part in such plantation drives? Give a reason for your answer.



























































Richa and Amit are in their art and craft class.
Richa: Amit! I have a colourful square origami sheet with me.
Amit: I have one too! Let us draw lines on it and see the patterns that come out of it.
Richa and Amit drew lines on their sheets in the following way.
Look at the pattern on the origami sheet carefully. What do you see?
We see 8 triangles on Richa’s sheet. Each triangle is exactly equal in size!
What part of the square is each triangle? Since the square sheet is divided into 8 equal parts, one part is 1 out of 8 or 1 8 of the square sheet.
What about Amit’s sheet? Here, 4 equal triangles divide the square. So, each part is 1 out of 4 or 1 4 of the square sheet.
Improper Fractions:
Examples: 459919 ,,,, 445611 Examples: 4 1 11 and 1 2 2
Examples: 23456 ,,,, 77777
Example 1: Which of the following are like fractions?
1 4 5 and 1 5
Examples: 46263 ,,,, 5791113
and 1 3
1 As the denominators of 4 5 and 1 5 are the same, they are like fractions.
2 As the denominators of 3 6 and 1 3 are different, they are unlike fractions.
Example 2: Classify the fractions 25179 , , 3, , 537105 as proper fractions, improper fractions or mixed numbers.
Let΄s see how we can convert fractions with the help of examples.
An improper fraction shows the same number of parts as a mixed number. Both show a value greater than 1. Here we see each square divided into 4 equal parts.

Improper Fraction
Parts each shape is divided into = 4
Total parts shaded = 11 11 4
Convert 4 4 5 into an improper fraction.
1 Split the mixed number into a whole number and proper fraction.
Quick way:
2 Write the whole number part as a proper fraction.
Step 1: Multiply the denominator with the whole number part.
Step 2: Add the result obtained in step 1 to the numerator.
Mixed Number
Wholes shaded = 2
Parts shaded = 3 out of 4 2 3 4
3 Multiply the numerator and denominator by the denominator of the fractional part.
4 Add the numerators to get the improper fraction.
Step 3: Write the result obtained in step 2 over the denominator.
Divide the numerator by the denominator.
The divisor is the denominator of the fraction. The quotient becomes the whole number part. Example 3:

The fractional part of a mixed number cannot have the numerator bigger than the denominator.

















Are the given pairs of fractions like or unlike?
a 4 7 and 1 4 b 5 8 and 4 8 c 1 4 and 1 5 d 3 7 and 5 7 e 6 18 and 7 18
Classify the following fractions as proper fractions, improper fractions or mixed numbers.
a 461585171297122684 , , 4, , 5, , , , 6, , , 7,15 52758111539291797
b461585171297122684 , , 4, , 5, , , , 6, , , 7,15 52758111539291797
c 461585171297122684 , , 4, , 5, , , , 6, , , 7,15 52758111539291797
f 461585171297122684 , , 4, , 5, , , , 6, , , 7,15 52758111539291797 g 461585171297122684 , , 4, , 5,
d 461585171297122684 , , 4, , 5, , , , 6, , , 7,15 52758111539291797 e 461585171297122684 , , 4, , 5, , , , 6, , , 7,1 52758111539291797
461585171297122684
, 4, , 5, , , , 6, , , 7,15 52758111539291797 j 461585171297122684 , , 4, , 5, , , , 6, , , 7,15 52758111539291797
Match the mixed numbers and the improper fractions of the same value.
Convert between improper and mixed fractions.
87 rice packets are distributed among 5 families during floods. How many packets of rice does each family get? Express your answer as a mixed number. Have you ever helped flood victims? Use fraction strips to represent 15 6 as an improper fraction and a mixed number.
Remember Richa and Amit had drawn lines on their origami sheets. Now, Richa and Amit cut parts of their origami sheets in the given way. The white part shows the sheet that is removed.

Notice that Amit and Richa have the same size of paper cutouts!
Richa has cut 2 out of 8 parts. So, she now has 2 8 of the entire sheet.
Amit has cut 1 out of 4 parts. So, he now has 1 4 of the entire sheet.
Since both Amit and Richa have the same size of paper, we can say 1 4 = 2 8 .
These are called equivalent fractions.
We can multiply the numerator and the denominator by the same number to find any equivalent fraction.
2 8 and 1 4 are equivalent fractions.
Example 4: Write three equivalent fractions for 3 7 .
3 7 = 32 72 × × = 6 14 3
We can also divide the numerator and the denominator by the same number to find more equivalent fractions.
To convert a fraction to its simplest form, divide the numerator and the denominator by the highest common factor.
Convert 4 8 to its simplest form.
HCF of 4 and 8 = 4.
Checking for Equivalent Fractions
Check whether 4 5 and 12 15 are equivalent or not.
1 Cross multiply the denominator of one fraction with the numerator of the other fraction and vice versa. × 4 5 12 15
2 Check if the products of both the multiplications are the same. If the products are the same, the fractions are equivalent. 4 × 15 = 60 5 × 12 = 60 Hence, 4 5 and 12 15 are equivalent.
Another way:
Check whether 4 5 and 12 15 are equivalent or not.
Reduce both the fractions to their lowest form and check if they are equal.
4 5 is already in its lowest form.
12 15 = ÷ ÷ 123 153 = 4 5
Both the fractions are equal, so 4 5 and 12 15 are equivalent.
Example 5: Write any three equivalent fractions for 90 120 using division.
Example 6: Express 42 91 in the simplest form.
Factors of 42 = 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21, 42; Factors of 91 = 1, 7, 13, 91.
HCF of 42 and 91 = 7.
42 91 = 427 917 ÷ ÷ = 6 13
Thus, 6 13 is the simplest form for 42 91 .
Example 7: Check whether the 602 and 903 are equivalent or not. ÷ = ÷ 603022 and 903033
As = 22 , 33 hence 602 and 903 are equivalent.
Example 8: Fill in the box to make the given fractions equivalent. = 5 1155
Since the denominator 11 × 5 = 55; hence, the numerator 5 × 5 = 25.
Thus, = 525 1155 .

















Find any two equivalent fractions by using multiplication for each of the given fractions.

Find any two equivalent fractions by using division for each of the given fractions.
Express the given fractions in their lowest form.
Check whether the given fractions are equivalent or not.
and
Fill in the boxes to make the given fractions equivalent.
Richa and Amit had cut out different parts of their origami sheet.
Although the sizes of both their sheets were the same, are each of the single triangles in their sheets the same size? Let us see!
Single triangle in Richa’s sheet = Fraction of the sheet = 1 8
Single triangle in Amit’s sheet = Fraction of the sheet = 1 4 = 2 8
To compare like fractions, compare the numerators.
Greater the numerator, greater the fraction.
2 > 1. Thus, 2 8 > 1 8 .
Richa’s sheet Amit’s sheet
We can also see above that the shaded portion in Amit’s sheet is bigger than that in Richa’s sheet.
For unlike fractions with the same numerator, we compare the denominators. The fraction with the greater denominator is smaller.
Compare 2 7 and 2 8 . 7 < 8. Thus, 22 78 > .
But, what if both the numerators and the denominators are different?
Method 1: Make the fractions like, using the LCM Method.
Compare 1 4 and 2 6 .
Step 1: Find the LCM of the denominators.
The LCM of 4 and 6 is 12.
Step 2: Find the equivalent fractions of 1 4 and 2 6 such that their denominators are 12.
of 4 and 6 =12
Method 2: Cross-multiplication Method
Compare 1 5 and 2 7 .
Cross multiply the denominators with the numerators.
1 × 7 = 7 and 5 × 2 = 10
7 < 10. Thus, 1 5 < 2 7 .
Example 9: Which fraction is smaller? 6 8 or 10 15
LCM of 8 and 15 = 120
6 8 = 615 815 × × = 90 120 10 15 = 108 158 × × = 80 120
90 120 > 80 120 .
Hence, 10 15 is the smaller fraction.
Step 3: Now that the fractions are like fractions, compare the numerators and identify which fraction is larger.
3 < 4 So, 34 1212 < . Thus, 12 46 < .
Example 10: Which fraction is bigger? 4 7 or 5 8
Apply the cross-multiplication method.
4 × 8 = 32 5 × 7 = 35 32 < 35 Thus, 5 8 is bigger than 4 7 .

Example 11: Lila has two pieces of ribbon. One piece is 3 4 of a metre long, and the other piece is 2 3 of a metre long. Which piece of ribbon is longer?
To compare 3 4 and 2 3 , we find a common denominator, which is 12. × == × 3339 44312 ; × == × 2248 33412
Since 9 12 is greater than 8 , 12 piece of the ribbon that is 3 4 of a metre long is longer.
Arrange 1324 ,,, 5757 in ascending order.
Step 1
Convert all the fractions into like fractions.
LCM of 5 and 7 is 35.
1 5 = 17 57 ×× 17 57 × = 7 35 3 7 = 3 7 × 5 5 = 15 35
2 5 = × 27 57 ×× 27 57 = 14 35 4 7 = 45 75 ×× 45 75 × = 20 35
Step 2
Since the denominators are the same, compare the numerators and order the fractions.
7 < 14 < 15 < 20 So, 7141520 35353535 <<< . Thus, 1234 5577 <<< .
Example 12: Arrange the fractions 3 4 , 9 13 , 4 26 , 1 2 in descending order.
LCM of 2, 4, 13 and 26 = 52.
331339 441352 =×=
1313452 =×= 4428 2626252 =×=
39 > 36 > 26 > 8
So, 3936268 52525252 >>> . Thus, 3914 413226 >>> . Chapter 5 • Fractions
















Compare the following fractions using >, <, =.

Put a tick () for the statements which are correct and a cross () for the statements which are wrong.
a 4 5 > 2 3 b 6 12 = 5 10 c 7 8 < 15 17 d 14 12 > 12 11
Arrange the following in ascending order.
a 213 , , 467 b 2151 ,,, 3562 c 35517 , ,,, 13712412 d 7845 ,,, 815812
Arrange the given fractions in descending order.
a 3131 ,,, 8456 b 3811 ,,, 8932 c 1111 ,,, 111496 d 43421 ,,,, 5151136
Represent visually 2 fractions greater than the fraction 1 4
Shashank studied for 6 13 hours while Reshma studied for 11 23 hours. Who studied for a longer duration?
Create a word problem on your own on comparing two fractions.

Experiential Learning & Collaboration
Aim: To understand how to represent equivalent fractions.
Materials Required: Paper strips.
Setting: In groups of 4
Method:
Each group should choose a fraction like

Fold one strip to show the chosen fraction (e.g., fold in half for 1 2 )
Mark the folds and label each part.

Fold and mark the other three strips to show three equivalent fractions.
Compare the strips and discuss how they show equivalent fractions.



Convert the given mixed numbers into improper fractions.
Convert the given improper fractions into mixed numbers. a 18 4
Find any three equivalent fractions using multiplication. a 2 6
Find any three equivalent fractions using division. a 16 24
Write the following fractions in the simplest form.
Compare the fractions and put the correct symbol >, <, =.
and
Arrange the following fractions in ascending order.
Reading books is a relaxing activity, that reduces stress levels and enhances brain connectivity. Three friends, Alex, Bailey, and Casey borrowed some books from the library. Alex took 1 4 , Bailey took 3 8 , and Casey took 3 12 of the total borrowed books. Who took the least fraction of the borrowed books and who took the greatest fraction?
The approximate population of the 6 continents of the world as fractions are given below. Arrange them in ascending order.

1 If 4 fractions 1 2 , 3 8 , 5 4 and 5 6 are placed on the number line, which fraction will be to the extreme left?
2 Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): 1 2 > 1 3 > 1 4 .
Reason (R): In unit fractions, the denominators are compared. The smaller the denominator, the smaller the fraction.
a Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c A is true but R is false.

d A is false but R is true.


Value Development & Cross Curricular
Mrs Gupta’s class is learning about recycling and the importance of sorting waste correctly. For their science project, they decide to organise a recycling drive. The students need to sort paper, plastic, and glass into different bins.

The bins are labelled with different fractions representing how full they can be before being emptied:
Paper Bin: 3 6 full; Plastic Bin: 3 4 full; Glass Bin: 4 5 full Tanvi, one of the students, notices that the fractions on the bins look different but wonders if they might actually be the same.
Answer these Questions:


1 Which of the following fractions is equivalent to the paper bin? a 2 6 b 1 2 c 3 8 d 4 6
2 Which option shows the fractions from the bins arranged in ascending order? a 334 ,, 645 b 334 ,, 465 c 433


3 The fraction of the glass bin is equivalent to 10 .
4 The fraction of the plastic bin is an improper fraction. (True/False)

5 Tanvi realises that sorting recyclables correctly helps keep the environment clean and conserves resources. Why is it important to recycle and sort waste properly?



























































Shagun celebrated her birthday. Her mother made apple pies for the party.
Shagun: I will eat 2 slices of the apple pie.
Arvind: I will eat 3 slices of the apple pie.
All her other friends also had the apple pie.
There are 8 slices in one apple pie.
Shagun ate 2 8 of the apple pie. Arvind ate 3 8 of the apple pie.
What part of the apple pie did they both eat together?
What if the denominators of the two fractions added, are not the same?
We first make the denominators the same, that is, make them like fractions. We can then easily add the fractions.
Let us add the unlike fractions 2 5 and 1 15 .
Remember!

Sum of like fractions = Sum of numerators Common denominator
We first find the LCM of the denominators of the two fractions.
Step 1
Find the LCM of the denominators.
LCM of 5 and 15 = 15
Step 2
Find the equivalent fractions of the two fractions so that the denominators of both become the LCM.
2 5 = 2 5 × 3 3 = 6 15 1 15 = 1 15 × 1 1 = 1 15
Step 3
Add the numerators after the denominators become the same.
6 15 + 1 15 = 6 + 1 15 = 7 15
Step 4
Reduce the fraction to its simplest form, if required. 7 15 is already in its simplest form.
Thus, 2 5 + 1 15 = 7 15
Example 1: Add 6 9 and 5 12 .
LCM of 9 and 12 = 36 6 9 = 6 9 × 4 4 = 24 36 5 12 = 5 12 × 3 3 = 15 36 24 36 + 15 36 = 24 + 15 36 = 39 36
Example 2: Add 2 7 and 5 9 . LCM of 7 and 9 = 63
Example 3: Suhani spent 5 7 hours on a project on Saturday and 11 14 hours on Sunday. How many hours did she spend on the project together?
Fraction of hours spent on Saturday = 5 7 hours
Fraction of hours spent on Sunday = 11 14 hours
Total hours spent = 5 7 + 11 14 = 10 + 11 14 = 21 14 = 3 2 hours = 11 2 hours [LCM of 7 and 14 = 14]

Remember Shagun, who had a birthday party?
Her friends ate 2 whole apple pies and 5 6 of an apple pie. 3 3 6 of the apple pies was left.
How much apple pie was there in total? Here the two mixed numbers are like.
Method 1: When the mixed numbers to be added are like, we can add the whole number to the whole number and the fraction to the fraction.
Add 5 2 6 and 3 3 6 .
Add the whole number to the whole number.
Add the fractional part to the fractional part.
Convert the fraction to a mixed number.
Add the results of step 1 and step 3.
What if the total apple pie eaten was 1 2 3 and the apple pie left was 1 3 2 , then how much apple pie was there in total?
Method 2: When the mixed numbers to be added are unlike, we convert the mixed numbers to improper fractions and then add.
Add 1 2 3 and 1 3 2 .
Convert the mixed numbers to improper fractions.
Example 4: Add 1 3 3 and 1 5 4 .
Example 5: Rakesh has two ropes of length 1 3 3 m and 5 1 6 m. What is the total length of the ropes?
Length of both the ropes = 1 3 3 m and 15 6 m
Total length of the ropes = 3 + 1 +
Hence, the total length of rope is 1 5 6 m.
Remember, Shagun and Arvind had eaten 5 8 of an apple pie.
Let us see how much apple pie was left with them. A whole is represented as 1.
Apple pie left = 1 5 8 = 85 88 = 85 8 = 3 8
Thus, 3 8 of the apple pie was left.
What if 3 4 of the apple pie was left and Shagun ate 1 3 of the apple pie from the leftover?
Let us find out.
Make the fractions like using the LCM method.
To find the leftover pie, we will subtract 1 3 from 3 4 .

LCM of 3 and 4 = 12 3339 44312 =×= 1144 33412 =×=
Subtract the like fractions. 94 945 12121212 −==
Thus, 3 4 1 3 = 5 12
Example 6: Find 7 8 − 1 4 .
Convert the fractions into like fractions.
LCM of 8 and 4 = 8 7717 8818 =×= 1122 4428 =×= 72725 8888 −==
Thus, 7 8 1 4 = 5 8 .
Subtracting Like Mixed Numbers

Difference of like fractions = Difference of numerators Common denominator
If the total apple pie available was 1 5 3 and the portion eaten was 2 2 3 , then how much apple pie would be left?
To find the leftover pie, we will subtract 2 2 3 from 5 1 3 .
(23)262 28 2 3333
Subtracting Unlike Mixed Numbers
If the total apple pie available was 2 4 5 and the portion eaten was 1 2 3 , then how much apple pie would be left?
Example 7: Simplify +− 515 21 9318
Mahavira, in his work "Ganita Sara Samgraha," provided systematic rules for dealing with fractions. He discussed how to reduce fractions to their lowest terms and how to handle operations with mixed numbers.
5223 29 1818 11 1 18
Example 8: Niharika bought 3 4 4 litres of milk from the milk parlour. She was left with 5 2 8 litres of milk after preparing a sweet dish. How much milk did she use in the sweet dish?
Amount of milk bought = 3 4 4 litres
Amount of milk left = 52 8 litres

Amount of milk used in the dish = 42351921 4848 −=− 3821171 2 888 === litres.

















Add the fractions and write the answer in the simplest form.
Find the difference.
Simplify.
Answer the questions.
a Subtract the
b Subtract
A basket has 2 1 5 kg of mangoes. Rajiv puts 2 2 5 kg more mangoes in it. What is the total weight of the mangoes in the basket?
Earth’s atmosphere is composed of many gases. The atmosphere is composed of about 39 50 nitrogen and about 21 100 oxygen. What is the fraction of all the other gases in the atmosphere?
Sanjay sent 50 1 2 kg of wheat to help the flood victims. 10 3 4 kg of wheat was spoilt. What quantity of wheat reached the victims? What else can be done to help flood victims?
Mithun, a shopkeeper, sells dairy products like milk, curd and paneer.
He packs milk in 1 4 litre packets.
Mithun packed 8 packets of 1 4 litre of milk each. Let us see what quantity of milk he packed.
To show this using fraction strips, we can say that there are 8 groups of 1 4 .
What will we get when 8 one-fourths are put together?
8 groups of 1 4 is the same as 8 × 1 4 .
The steps to multiply the whole number 8 by a fraction 1 4 are given below.
Step 1
To multiply a whole number with a fraction, multiply the whole number by the numerator of the fraction. The denominator remains the same.
8 × 1 4 = 81 4 × = 8 4
Step 2
Convert the improper fraction into a mixed number.
8 2 4 =
Thus, the total quantity of milk packed is 2 litres.
Example 9: Multiply 5 and 6 7 . 5 6 6 5 77 × ×= 30 7 =
Example 10: Mahesh reads 2 5 pages of a book. The total number of pages in the book is 100. How many pages has he read?
Total number of pages = 100
Fraction of pages read = 2 5

Number of pages read = 2 5 of 100 = 2 10040 5 × = pages.
Hence, Mahesh read 40 pages.
Multiply 2 5 and 3 7
Let us multiply the above 2 fractions using pictures.
1 To show 2 5, divide the rectangle vertically into 5 equal parts. Shade 2 out of 5 parts.
2 Then, to show 3 7, divide the rectangle horizontally into 7 equal parts.
3 Draw crosses in 3 out of 7 parts, horizontally.
4 Count the number of equal parts which have both the shading and the cross (×). 6 out of 35 parts, both have the green colour and the cross (×).
Fractions can be multiplied using two methods.
Method 1: Multiplying the numerators and multiplying the denominators.
Method 2: Cancelling out the common factors in the numerators and denominators.
Fraction of a fraction: ‘of’ means multiplication when multiplying fractions.

Example 11: Multiply 2 3 by 7 8 . 27 2714 383824 × ×== × ÷ == ÷ 141427 2424212
Thus, 277 3812 ×=
Example 12: Find 4 9 of 7 2 . 4 9 of 7 2 = 47 92 × ×=×=×=
Example 13: In a grid 4 5 of the squares are shaded. If 3 7 of the shaded squares are blue, what fraction of the entire grid is made up of blue squares?
Fraction of square shaded = 4 5
Fraction of shaded squares that are blue = 3 7
Fraction of grid made up of blue squares = 4312 5735 ×=
Hence, 12 35 of the grid is blue.
Lalit has to pack 2 cakes in boxes. Each box can hold 1 2 of the cake. How many cake boxes are needed?
We need to find 2 ÷ 1 2 .
To find the number of boxes packed by Lalit, let us first understand the concept of reciprocal. Reciprocal of a Number
The reciprocal of a number or a fraction is obtained by interchanging the numerator and the denominator of the fraction.
What is the reciprocal of 5? 5 5 1 =
Reciprocal of 5 = 1 5
What is the reciprocal of 1 5 ?
Reciprocal of 1 5 = 5 1 or 5.

Two numbers are said to be reciprocals of each other when their product is 1. Thus, reciprocals are the multiplicative inverse of each other.
Now, let us find the number of boxes packed by Lalit.
There are 2 boxes. Each box can hold 1 2 of the cake.
So, we need to find 2 ÷ 1 2 or how many halves will fit into 2 wholes.
Let us see, using the figures.
2 ÷ 1 2 means how many halves will fit into 2 wholes.
Thus, 4 boxes of cake were packed by Lalit.

Example 15: Sarah follows an exercise routine. She runs 3 4 miles in a day. How many days will it take her to achieve her running goal of 12 miles?
Running goal of Sarah = 12 miles
Number of miles she runs in a day = 3 4 miles
Number of days required to reach the goal = ÷=×= 34 121216 43 days
Hence, Sarah will take 16 days to achieve her goal.
Dividing a Fraction by a Whole Number
Divide
Let us understand this in another way.
1 Write the whole number as a fraction.
2 Reverse the ‘÷’ symbol to ‘×’.
Example 16: Divide 1 3 by 6.
3 Write the reciprocal of the fraction.
4 Multiply the fractions to get the answer.
Example 17: Divide 4

Example 18: Megha has 5 6 of a watermelon. She wants to share it equally with her 5 friends. What fraction of watermelon will each of her friends get?
Fraction of watermelon with Megha = 5 6
Number of friends she wants to divide the watermelon among = 5
Fraction of watermelon each friend will get = ÷=×==
Hence, each friend will get 1 6 of the watermelon.
Dividing a Fraction by a Fraction
Divide 1 2 by 1 6 .
Method 1
Example 19: Divide 1 3 by 1 6 .
How many one-sixths will fit into one-third?
Example 21: A water tank is filled to 2 3 of its capacity. Rahul wants to empty the tank using buckets that can hold 1 6 of the tank’s capacity. How many buckets are needed to empty the tank?
Volume of water in the tank = 2 3 of its capacity
Volume of water each bucket can hold = 1 6 of the tank’s capacity
Number of buckets needed to empty the tank = 212 64 363 ÷=×= buckets
Hence, 4 buckets are needed to empty the tank.
















Do It Yourself 6B

Find the reciprocal of the given fractions.
Multiply the fractions using fraction strips.
Multiply.
Divide.
Answer the questions.
a What is 3 4 of 2 hours?
b How many days are 2 7 of 1 week?
Sushen and his friends ate 3 4 of a cake at his party. The total weight of the cake was 2 kg. What weight of cake was eaten?

Ravi has 21 kg of rice. He packs the rice in packets of 3 4 kg each. How many such packets does he pack?
A car has 50 litres of petrol in its fuel tank. 3 5 of the fuel is used up to travel from one place to another. What quantity of fuel is left in the fuel tank? What should we do to utilise fuel efficiently? How many bottles of capacity 3 4 L can be filled from a container of capacity 57 4 L?
a fraction.

Aim: To understand fractions and add fractions.
Setting: In pairs
Method:

Materials Required: Fraction bingo cards, markers or coloured pencils
Create the fraction bingo cards and the list of fractions that are to be called out.

Each pair gets a fraction bingo card and a coloured pencil or marker.
Call out the fractions along with the operation that needs to be done.
The pairs will perform the operation and check if the answer is on their bingo card. If found they will circle the answer.


The pairs that gets all the answers in a row, column or diagonal says Bingo and wins!

Find the multiplicative inverse of the given fractions.
Write True or False.
a The reciprocal of every fraction is a proper fraction.
b 0 ÷ any fraction = 0.
c The reciprocal of 0 is 0.
d The multiplicative inverse of any fraction is always greater than 1.
Add the given fractions.
Subtract the fractions and express the answer in its simplest form.
Multiply to find the product. Also, write the answer in its simplest form.
5 6 9 ×
Divide and find the quotient.
Answer the following questions.
a Which is more: the difference of 1 2 8 and 1 8 4 or the sum of 1 2 4 and 1 4 3 ?
b Which is less: the product of 5 and 4 5 or the sum of 1 1 4 and 4 2 5 ?
c What is the difference between the product of 4 and 1 5 , and the product of 2 5 and 3?
Delhi is the capital city of India. The age distribution in Delhi is given as; Children29 100 , Adults13 20 and Elderly people3 50 . What fraction of the population of Delhi are not children?
A boy was travelling to his grandmother’s home. He travelled 41 7 km by bicycle, 23 4 km on foot and 101 2 km by car. What is the total distance covered by him?
The Delhi metro is a rapid rail system that connects Delhi to its adjoining cities. About 65 km of the total length was constructed in phase 1, about 125 km in phase 2 and about 167 km in phase 3. About 11 2 times of the length of phase 1 was constructed in phase 4. What is the length constructed in Phase 4?
3 4 of a parking lot is full when there are 66 cars in it. How many cars can be parked inside the parking lot?
14 cans can hold 1441 2 litres of water. What is the capacity of each can?
Radhika purchased 20 m of cloth. She used 112 5 m of cloth for the curtains and 35 6 m of cloth for a bed sheet. How much cloth does she have left?
Create a word problem to divide a fraction by a whole number.

1 A recipe requires 5 6 cup of grated cheese. With the help of 6 cheese cubes, you get 3 5 of the amount you need. How much more grated cheese (in cups) do you need? How many more cheese cubes should you grate?

2 Read the given statements. Choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): Shefali has 2000 marbles, out of which 1 4 are red and the rest are green. 2 5 of the red marbles are defective. The total number of non-defective red marbles is 300.
Reason (R): To add two unlike fractions, first the denominator is made the same by finding the equivalent fractions and then the numerators are added.

a Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c A is true but R is false.
d A is false but R is true.



It is summer holidays for Sonia. Her mother signed her up for different social service classes. Sonia goes to a different class each day of the week. The table below shows how much time Sonia spends in each class. Read the table and answer the questions.


1 How much time does Sonia spend in Community Clean-up Programs in the entire week?


2 If Sonia wants to add another 1 1 2 hours for a gardening and farming class on Sunday, how many fewer hours will she spend in the class on Sunday than on Wednesday? a 1 2 4 hours b 3 4 hours c 1 4 hours d 3 3 4 hours

3 Sonia’s friend Misha goes to animal care and welfare classes but spends 45 minutes less time there than Sonia. How much time does Misha spend in the class?
4 Sonia learnt how to create art from recycled materials and made small pots for gardening. Look for some recyclable materials around you and use them to create something new.



























































Alfred, the carpenter, goes to the market to purchase nails and screws.
The weight written on the packet of nails is 2.5 kg.
Alfred gets confused when he sees a weight which is not a whole number. Let us help him out by reading the number!
The number that uses a decimal point followed by digits is called a decimal number.
Decimals have a whole number part and a fractional (or decimal) part, which is separated by a decimal point.
When 1 whole is divided into 10 equal parts, then each part is called one-tenth.
Fractional representation = 1 10
Decimal representation = 0.1
Let us see some more tenths.
Each whole is divided into 10 equal parts

Let us see how to read 0.6. It is written as zero and six tenths.
Write the decimal for the shaded part.
Whole number part
part
point

The decimal part after the decimal point is always less than 1 whole.
As we move towards the right-hand side of the decimal point, the value of the digit decreases 10 times. Let us write the expanded form of decimals up to tenths.
Write 14.6 and 45.7 in the place value table and in their expanded form.
(value of 6 is 6 10 or 0.6) Ones (value of 4 is 4) Tens (value of 1 is 10)
form: 10 + 4 + 6 10
Expanded form of 45.7 = 40 + 5 + 0.7
=
+ 4 +
Example 1: Write the decimal number of the coloured portion. Also, write the decimal number in words.
Thus, the coloured part represents 2.2 in decimal form.
In words: Two point two or two and two tenths.
Example 2: Fill in the blanks.
Figures
6.2
11.6
Words
Six and two tenths
Eleven and six tenths 51.9
760.5
Fifty-one point nine
Seven hundred sixty point five
Example 3: Write the decimals 15.7 and 23.9 in the place-value table. Also, write these in words and in expanded form.
15.7 is written as fifteen and seven tenths.
15.7 = 10 + 5 + 7 10 Or 15.7 = 10 + 5 + 0.7
23.9 is written as twenty-three and nine tenths.
23.9 = 20 + 3 + 9 10 Or
When 1 is divided into 100 equal parts, then each part is equal to one-hundredth.
Fractional representation = 1 100
Decimal representation = 0.01
One-hundredth is the same as one-tenth further divided into 10 equal parts. Let us see a few more hundredths.

Let us learn how to read decimal numbers up to hundredths. 15.54 fifteen fifty-four hundredths and fifteen point five four
Let us note down the above number in the place value chart and write its expanded form.
15.54 1 5 . 5 4
Expanded form: 10 + 5 + 5 10 + 4 100 Or 15.54 = 10 + 5 + 0.5 + 0.04
Example 4: Fill in the blanks.
Three and fourteen hundredths 14.36
Fourteen and thirty-six hundredths 12.91
Twelve point nine one 104.05 One hundred four point zero five
Example 5: Write 34.18 in expanded form.
Expanded form: 30 + 4 + 1 10 + 8 100 Or 34.18 = 30 + 4 + 0.1 + 0.08
Thousandths
When 1 is divided into 1000 equal parts, then each part is equal to one-thousandth.
Fractional representation = 1 1000
Decimal representation = 0.001
One-thousandth is the same as one-hundredth further divided into 10 equal parts.
Reading and Writing Thousandths
Let us read and write decimal numbers in thousandths.
Write 14.179 in the place value chart.
one hundred seventynine thousandths and
The expanded form of the above number using the place value chart can be given as:
Equivalent decimals are decimal numbers which have the same value. They are also called equal decimals. For example:
If we place zeroes before the end of the decimal, then it changes the value of the number, and thus the decimal numbers are not equivalent. For example: 0.5 and 0.05 are not equivalent decimals.

When we place zeroes on the right-hand side of a decimal number, its value remains the same.

Example 6: Fill in the blanks.
Figures Words
14.814
16.005
514.047
Fourteen and eight hundred fourteen thousandths
Sixteen and five thousandths
Five hundred fourteen point zero four seven 5.407
Five point four zero seven
Example 7: Write 76.103 in the expanded form.
76.103 = 70 + 6 + 1 10 + 3 1000 Or 76.103 = 70 + 6 + 0.1 + 0.003
Example 8: Write any three equivalent decimals for 14.3.
14.3 = 14.30 = 14.300 = 14.3000
Now, let us learn how to convert fractions to decimals and vice versa.
Let us convert 1 5 into a decimal number.
Step 1: Multiply the denominator and the numerator by the same number so that we get a power of 10 in the denominator.
Step 3: Insert a decimal point before the number of places equal to the number of zeroes in the denominator from the rightmost side. 1 5 = 1 × 2 5 × 2 = 2 10 = 0.2
Let us now convert 0.25 to a fraction.
Step 1: Write the decimal with a denominator of 1.
Aryabhata, an astronomer and mathematician from ancient India, represented fractional values in a way that contributed to the development of the modern decimal system.
Step 2: Write a fraction with the denominator as 10, 100 or 1000.
So, 1 5 is the same as 0.2.
Step 2: Convert the denominator into multiples of 10, 100 or 1000 to eliminate the decimal point. Chapter 7 • Introduction to Decimals
0.25 = 0.25 1 = 0.25 × 100 1 × 100 = 25 100 = 25 ÷ 25 100 ÷ 25 = 1 4
Step 3: Express the fraction in its simplest form.
Example 9: Convert the given fractions into decimals.
1 1 2 = 1 × 5 2 × 5 = 5 10 = 0.5
2 3 25 = 3 × 4 25 × 4 = 12 100 = 0.12
3 3 8 = 3 × 125 8 × 125 = 375 1000 = 0.375
Do we convert all the fractions into fractions with denominator of 10, 100, 1000 to convert them into decimals?
Example 10: Convert the decimals into fractions.
1 4.2 = 4.2 1 = 4.2 × 10
2 0.174 = 0.174
Percentages
Let us look at the given grid. How will we write it as a fraction or a decimal?
40 out of 100 squares are shaded.
Fraction of the shaded part = 40 100
Decimal of the shaded part = 0.40
40 100 can also be written as 40 percent since percent is per hundred.
Percentage is represented by ‘%’.
So, 40 percent is also written as 40%.
Converting Fractions to Percentages
Fraction Multiply by 100% Percentage
For example: 53 100 = 53 100 × 100% = 53%
4 5 = 4 5 × 100% = 80%
Converting Decimals to Percentages
Multiply by 100 and shift the decimal point two places to the right.
For example:
0.45 = 0.45 × 100% = 45%
3.25 = 3.25 × 100% = 325%
Converting Percentages to Fractions
Percentage Divide by 100 Fraction
For example:
47% = 47 100
48% = 48 100 = 12 25
Converting Percentages to Decimals
Divide by 100 and shift the decimal point two places to the left.
For example:
69.4% = 69.4 ÷ 100 = 0.694 84% = 84 ÷ 100 = 0.84

Example 11: Convert the given percentage to a fraction and a decimal.
1 18%
As a fraction: 18% = 18 100 = 18 ÷ 2
As a decimal: 18% = 18 ÷
Example 12: Do as directed.
1 Convert 5 into a percentage.
5 = 5 × 100% = 500%
2 Convert 12.306 into a percentage.
12.306 = 12.306 × 100% = 1230.6%


2 25%
As a fraction: 25% = 100 100 = 1 4
As a decimal: 25% = 25 100 = 0.25
Percent is derived from a Latin word ‘per centum’ which means ‘per hundred’.














o It Yourself 7A

Write the decimals in words.
Write the decimal numbers.
a Four hundred thirteen and two tenths b Seventy-two point three three c Three hundred sixty-one point zero four d Fifty-two and four hundred two thousandths
Shade to show the decimals and then write them in words.
Write the expanded form of the given decimal numbers.
Write in decimal form.
Convert the fractions into decimal numbers and percentages.
Rewrite the decimals as fractions and percentages.
a
Write any two equivalent decimals for the given decimal numbers.
Write as fractions, decimals and percentages.
a Two and one tenth b Thirty-five hundredths
c Five hundred twenty-four thousandths d Three and one hundred twenty thousandths
Insert >, < or = in the blanks.
In 2021, Shivraj Dhananjay Thorat registered his name in the Asia Book of Records by covering a distance of 455.89 km in a day. Express the distance covered in expanded form.
Rakesh a contractor got a contract to build a ramp of a house. He completed 5 8 of the work in 7 days. What is the decimal form for the work completed?
The tiger is the national animal of India. There are approximately 3600 tigers in India whereas there are about 6000 tigers in the world. What percentage of the world’s tiger population is there in India?
Sanjana and her friends were measuring their heights.
Sanjana is 1.32 m tall, Sana is 1.2 m tall, Reshma is 1.26 m tall and Muskan is 1.4 m tall.
Like
Let us learn about the types of decimals.
Like Decimals
1.32 and 1.26 have 2 digits after the decimal point. 1.2 and 1.4 have 1 digit after the decimal point.
Same number of digits after the decimal point. 1.32 1.26
Decimal numbers which have the same number of digits after the decimal point are called like decimals. Thus, 1.32 and 1.26 are like decimals.

Decimal numbers which have a different number of digits after the decimal point are called unlike decimals.
Example: 1.32 and 1.2 are unlike decimals.
Example 13: Sort the groups of like decimals out of the following decimal numbers.
1.4, 5.64, 5.5, 48.14, 38.6, 147.47
Group 1: (With 1 digit after the decimal point) 1.4, 5.5, 38.6
Group 2: (With 2 digits after the decimal point) 5.64, 48.14, 147.47
Example 14: Which option shows unlike decimals?
a 14.2, 54.8, 23.6 b 71.25, 89.35, 41.51 c 13.147, 879.78
Option (a) and (b) are groups of like decimals. The numbers in (c) are unlike decimals since 13.147 has 3 decimal places and 879.78 has 2 decimal places.
Let us learn how to convert unlike to like decimals.
Consider 1.3 and 1.46.
Same number of digits after the decimal point Add 1 zero
Unlike decimals can be converted into like decimals by finding the equivalent decimal.
Put zeroes at the end of the decimal number such that the number of digits after the decimal point is the same.
Example 15: Convert 14.5, 74.543 and 15.64 into a group of like decimals.
Convert each of the decimal numbers into equivalent decimals with 3 decimal places by adding 0s at the end.
14.5 = 14.500 74.543 = 74.543 15.64 = 15.640

Thus, 14.500, 74.543 and 15.640 are a group of like decimals.
















Which of the following are a group of like decimals?
a 1.2, 5.4, 8.9, 6.54, 1.3 b 2.23, 4.26, 4.89, 4.2, 6.584
c 7.89, 7.2, 64.594, 45.2, 56.5
d 81.564, 78.512, 453.125, 486.154, 86.15
Tick () if the decimals are like and cross () if the decimals are unlike.
a 4.2 and 6.25 b 17.23 and 691.56 c 11.3 and 17.8 d 5.157 and 64.581
Identify the number of zeroes to be added to the decimal numbers to convert them into like decimals.
a 1.45, 1.6 b 81.566 and 12.2 c 17.98 and 14.221 d 11.001 and 11
Convert the unlike decimals into like decimals.
a 13.15, 1.2 b 3.48, 1.2 c 4.8, 1.526
Convert the fractions into like decimals.
,
The value of different currencies in terms of Indian rupees can be given as:
Japanese Yen = ₹0.54; Canadian Dollar = ₹60.9; US Dollar = ₹83.394. Convert all decimals into like decimals.
Create a word problem to convert two unlike decimals to like decimals.
Bhawna volunteered at her school’s sport event, where a long jump competition took place.
She diligently recorded the jumps of the participants.
Suhani jumped 3.2 m, Sobhita jumped 3.15 m, Kiran jumped 3.18 m and Mridula jumped 3.7 m.
Bhawna wanted to compare the lengths of the jumps of the participants. Let us see how we could do this!.
Let us compare the jumps of Suhani and Mridula.
3.2 3.7
The coloured part in 3.2 is less than the coloured part in 3.7
Since 3.2 < 3.7, Mridula jumped longer than Suhani.
Let us learn a quicker way to compare decimal numbers.

Compare 3.15 and 3.18.
Compare the whole numbers. The number with a larger whole number will be bigger. If the whole numbers are the same, compare the tenths. If the tenths are the same, compare the hundredths.
Follow the same process until you find unequal digits.
Example 16: Which of the given numbers is smaller—16.47 or 16.42?
Look at the digit in the hundredths place: 7 > 2.
So, 16.42 < 16.47. 16.42 is smaller.
Remember Bhawna? She now wants to compare the jumps of all the participants and announce the winner.
Let us see how she finds the winner!
Let us compare 3.2 m, 3.15 m, 3.18 m and 3.7 m.
If the number of digits in a number is more, then the number is not necessarily bigger.
To compare unlike decimals, make all the decimals like decimals. Then, compare the like decimals.
3.70 is the biggest number. Thus, Mridula jumped the farthest and is the winner.
Example 17: Which of the following decimals is bigger—48.25 or 48.251?

Look at the thousandths digit: 0 < 1.
So, 48.251 is bigger.
The distances jumped by 4 players are: Suhani– 3.2 m, Sobhita– 3.15 m, Kiran– 3.18 m and Mridula– 3.7 m. Arrange the distances in order, from the longest jump to the shortest.
Convert the given decimals into like decimals.
Compare the decimals and arrange them.
Thus, 3.70 > 3.20 > 3.18 > 3.15
Example 18: Arrange 12.14, 12.4, 12.04, 12.41 in ascending order.
Make the decimals like:
So, 12.04 < 12.14 < 12.40 < 12.41.
In a 100 m race, Rupali completed the race in 20.3 seconds and was the winner.
Rupali’s coach wanted to know approximately how many seconds it took her to complete the race.
Mark the decimal number on the number line.
Check which whole number is closer to the decimal number.
20.3 is closer to 20 and farther away from 21.
Thus, 20.3 rounds off to 20 when rounded off to the nearest whole number.
Let us now understand the other way for rounding off decimal numbers to the nearest whole number.
Check the digit in the tenths place. The digit in the tenths place = 3

If the digit in the tenths place is less than 5, then round down; or else, round up. Here, 3 < 5, so we will round down. 20.3 is rounded off to 20.
Example 19: Round 14.7 to the nearest whole number.
14.7 lies between 14 and 15.
Digit in the tenths place = 7 7 is greater than 5
So, 14.7 will round up to 15.

















Colour and compare using >, < or =.
Write if True(T) or False(F).
a If the digit in the tenths place is 5, then the number rounds up to the nearest whole number.
b 12.2 rounds up to 13 when rounded to the nearest whole number.
c 99.9 rounds up to 100 when rounded to the nearest whole number.
Find the greater decimal number.
a 4.2 or 4.15
Round off the numbers to the nearest whole number.
Arrange the decimal numbers in ascending order.
a 14.14, 14.1, 14.01, 14.101 b 84.56, 84.5, 84.6, 84.55, 84.65
c 184.2, 184.23, 184.1, 184.112 d 64.23, 54, 64.32, 64.22, 64.33
Round off the numbers to the nearest whole number first and put the correct symbol <, >, =.
In May 2023, Bangalore Urban recorded 205.8 mm of rainfall. What is 205.8 rounded off to the nearest whole number?
In a racing competition, three athletes finish the race in 24.54 minutes, 24.68 minutes and 24.36 minutes, respectively. Arrange the numbers in descending order.
The population (in crores) of different states in India (in 2011) is given. Arrange the states in ascending order according to their population.
Collaboration & Experiential Learning
Aim: To understand and practise recognising with decimal numbers.
Setting: Whole class
Materials Required: Small sheets of paper with decimal numbers written on them, a pencil,
Method:
Prepare a sheet with a grid of decimal numbers from 1.1 to 6.6, spaced out evenly.
Each decimal number should appear only once on the sheet.
Each student takes a turn to roll the dice twice.
The first roll gives the whole number part of the decimal (e.g., rolling a 3 means the whole number is 3).
The second roll gives the decimal part (e.g., rolling a 5 means the decimal part is 0.5).
Combine these rolls to form the decimal number (e.g., 3 and 7 become 3.7).
Students then cross out this number on their sheet.
If a student rolls a number that has already been crossed out, they roll again.
The game continues until all the decimal numbers on the sheet have been crossed out by any one student.
Shade the grid and write the expanded form of the decimals.

Write the decimal number in words.
a 15.2 b 71.65 c 814.36 d 176.801
Write as decimal numbers.
a Forty point one zero one b One hundred three and five hundredths
c Four hundred twenty and eleven thousandths d Thirty-one and five thousandths
Place the numbers in the place value chart and write the expanded form of the decimal numbers.
a 11.1 b 16.54 c 490.02 d 843.033
Convert the fractions into decimal numbers and percentages.
a 1 8 b 4 5 c 12 20 d 36 40
Identify the number by which the decimal has to be multiplied and then convert it into a fraction and percentage.
a 12.6 b 52.2 c 20.8 d 25.315
Circle the smaller decimal number and put a square on the greater decimal number.
a 12.3 and 12.4
b 14.5 and 14.55
c 222.22 and 222.02 d 3.003 and 3.033
Round off the decimal numbers to the nearest whole number.
1.3
Arrange the numbers in descending order.
a 1.3, 1.31, 1.2, 1.33
b 19.4, 19.44, 19.54, 19.501
c 555.5, 555.55, 555.05, 555.555 d 748.01, 748.101, 748.11, 748.1
Show two like decimals using square grids.
Regular cycling strengthens leg muscles, improves joint mobility, and enhances overall body flexibility. Mr Raj and his family took part in a bicycle race. The time taken by each of them is given below. Who won the race?
Raj: 14.3 minutes Rekha: 15.2 minutes Utkarsh: 13.92 minutes Ali: 13.99 minutes
Mr Jadeja spent $12.99, Sarah spent $13.01, Alice spent $12.9 and Jacob spent $13.1. Arrange the amounts spent in ascending order.

1 Look at the numbers shown below. Which number does not follow the pattern? 0.9, 0.91, 0.93, 0.97, 1 and 1.05

2 Read the statements and identify which of the following options is correct.
Assertion (A): The decimal number 0.78 is less than the decimal number 0.7801.
Reason (R): When comparing two decimal numbers, the number with more digits to the right of the decimal point is always larger.
a Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.

b Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
c A is true, but R is false.
d A is false, but R is true.
e Both A and R are false.



Cross Curricular
John got a school project in which he had to find the heights of multiple skyscrapers of the world. John made a list of 6 skyscrapers. Based on the list of the height of the skyscrapers, answer the questions given below.



a Merdeka 118


1 Which of the following skyscrapers is the shortest?
b CITIC Tower
c Jin Mao Tower d Wuhan Greenland Centre
2 Which of the following skyscrapers is the tallest?
a Shanghai Tower
b CITIC Tower
c Lotte World Tower d Merdeka 118
3 What is the ascending order of the heights of the given skyscrapers?

4 What are the heights of the towers when rounded to the nearest whole number?
5 Write the expanded form of the heights of the skyscrapers.


























































Ana and her father went to order sweets for a wedding.
Ana: Father, how many sweets do we want to give to each guest?
Father: Ana, we will give 1.2 kg of laddoos and 1.5 kg of barfi to each of our guests.
Let us find the total weight of sweets that they are giving to each guest.
To find the total weight of sweets, add 1.2 and 1.5.
Step 1
Represent 1.2 and 1.5 visually.
Step 2
Add the wholes with the wholes and tenths with the tenths. 1 whole + 1 whole 2 tenths + 5 tenths = 7 tenths
Thus, the total weight of sweets that each guest gets 2.7 kg.
Let us learn another way to add decimals.
Write the digits in columns and align the decimal points.
Add the numbers. Use regrouping, if required.
Put the decimal point in the answer at the same place as it is in the numbers above it.
Let us add some more decimal numbers.
Example 1: Find the sum of the given numbers using the column method.
Example 2: Nikhil requires 3.5 kg of rice and 2.25 kg of sugar for his home. What is the total weight of rice and sugar that Nikhil requires?
Weight of rice = 3.5 kg
Weight of sugar = 2.25 kg
Total weight = weight of rice + weight of sugar = 3.5 kg + 2.25 kg
Thus, Nikhil requires 5.75 kg of rice and sugar.
Remember!

Decimal numbers with the same number of decimal places are called like decimals.
Let us see how can we subtract two decimal numbers using the column method.
Subtract: 17.2 – 16.84

Write the digits in columns and align the decimal points and the digits.
Remember to convert the decimals to like decimals if required. Subtract. Use regrouping if required.
Put the decimal point in the answer at the same place as it has been put in the numbers above it.
Let us see how to subtract decimals using a grid.
Example 3: Find the difference of the numbers visually.
1
Example 4: When Sushil was born, his weight was 3.75 kg. After 1 year, his weight increased to 8.5 kg. By how much did Sushil’s weight increase in 1 year?
Sushil’s weight when he was born = 3.75 kg
Sushil’s weight after 1 year = 8.5 kg
Increase in weight = 8.5 kg – 3.75 kg
Thus, Sushil’s weight increased by 4.75 kg in 1 year.
Chapter 8 • Operations with Decimals

















Add the tenths and hundredths visually and find the sum.
0.1 + 0.2
Subtract visually and find the difference.
a 1 – 0.3 b 1.23 – 0.46
+ 0.38
Add the numbers using the column method.
Subtract using the column method.
Compare using >, < or =.
Ramesh is a milkman. He has two cows. One is a Gir cow and the other is a Sahiwal cow. The Gir cow yields 13.4 litres of milk in a day while the Sahiwal cow yields 8.55 litres of milk in a day. How much more milk does the Gir cow yield than the Sahiwal cow?
Raman is 1.65 m tall and his brother is 0.18 m shorter than him. What is his brother’s height?
The weight of a frog is around 3.3 kg while the weight of a tadpole is 0.005 kg. What is the total weight of the frog and the tadpole?
In a relay race, Rashi covers 1.548 km, Prerna covers 2.328 km and Navya covers 1.986 km. What is the total distance (in km) covered by the three girls?
Read the table showing the weight of 4 students. Answer the questions below.
a What is the total weight of Rakesh and Ismail?
b What is the total weight of John and Shahid?

Priya travelled from point A to point B via bus and from point B to point C via auto. How much distance does she need to cover if she walks from point C to point D?
Rashmi had ₹5555.5 in her wallet. She bought a saree for ₹555.5 and an umbrella for ₹55.5. She paid ₹5.5 to buy a packet of biscuits to feed a hungry dog. What was the total amount of money she had left?
Ana’s father wanted to give sweets to 10 of his staff members, with each box weighing 0.5 kg.
Ana wanted to know the total weight of sweets given to the staff members.
How will they find the total weight?
Let us learn!
Multiplying Decimals by 10, 100, 1000…
Weight of each box = 0.5 kg
Total number of boxes = 10
Total weight of 10 boxes = 10 × 0.5 = 5 kg
Multiplication by 10
When we multiply any decimal number by 10, we move the decimal point 1 place to the right.
10 × 0.614 = 6.14 0 . 6 1 4
Multiplication by 100
When we multiply any decimal number by 100, we move the decimal point 2 places to the right.
100 × 0.614 = 61.4 0 . 6 1 4
























When we multiply any decimal number by 1000, we move the decimal point 3 places to the right.
1000 × 0.614 = 614 0 . 6 1 4
Thus, we move as many decimal places to the right as there are 0s in the multiplier (10, 100 or 1000).


Remember!

614 is never written as 614.0 as we do not put a decimal point at the end of the number that has no decimal value.
Example 5: Solve. 1
Move the decimal point 1 place to the right.
4.52 × 10 = 45.2

Adding 0s at the end of the decimal number does not change the value. Move the decimal point to the right while multiplying by 10, 100 or 1000.
×
= 12.5400
= 1254
Move the decimal point 2 places to the right.
23.48 × 100 = 2348
Move the decimal point 3 places to the right.
1.413 × 1000 = 1413
We can multiply a decimal number with a whole number. Let us multiply 4 by 0.4.
4 × 0.4 = 0.4 + 0.4 + 0.4 + 0.4 = 1.6
Steps to multiply 4 by 0.4 using the column method.
1. Ignore the decimal point in the decimal number and multiply the whole numbers. 4 × 4 = 16
Move the decimal point 3 places to the right. 32.4 × 1000 = 32400
2. Count the total number of digits after the decimal point in both the numbers. There is 1 digit after the decimal point for this question.
3. Place the decimal point in the product so as to obtain as many decimal places as there are in the decimal number. So, 4 x 0.4 = 1.6
Example 6: Multiply 0.6 and 3 visually.

Example 7: Multiply using the columnmethod. 506 × 1.06
5 0 6 × 1 0 6
3 0 3 6
0 0 0 0 + 5 0 6 0 0
5 3 6 3 6
Put the decimal point in the product so that it has 2 decimal places. 506 × 1.06 = 536.36
Bhaskara II’s work "Lilavati" (1150 CE) includes operations involving decimal fractions. He provided methods for calculations that made use of the decimal point to represent fractions more accurately.
We can multiply a decimal number with another decimal number as well.
Let us multiply 1.5 by 2.6.
Steps to multiply 1.5 by 2.6 using the column method.
1. Ignore the decimal point in the decimal numbers and multiply them as whole numbers.
15 × 26 = 390
2. Count the total number of digits after the decimal point in both the numbers.
Sum of the decimal places in the given decimal numbers = 1 + 1 = 2
3. Put the decimal point in the product so that it has 2 decimal places. So, 1.5 × 2.6 = 3.90
Example 8: Multiply.
1 15.46 × 36.1 1 5 4 6 × 3 6 1 1 5 4 6 9 2 7 6 0 + 4 6 3 8 0 0
5 5 8 1 0 6
15.46 × 36.1 = 558.106
1 5 1 decimal place × 2 . 6 1 decimal place
3 9 0 (1 + 1) = 2 decimal places
What is the product of the smallest 4-digit number and 45.623?
2 + 1 = 3 decimal places.
Example 9: The cost of 1 kg of apples is ₹126.5. What is the cost of 2.5 kg of apples?
Cost of 1 kg of apples = ₹126.5
Weight of apples required = 2.5 kg
Total cost of 2.5 kg of apples = 2.5 × ₹126.5
Thus, the cost of 2.5 kg of apples is ₹316.25.
decimal places.
Anaʼs father travelled all over the world for business. Whenever he visited a country, he exchanged Indian currency for the currency of that country.
Consider the chart which shows how many Indian rupees we can get when we exchange the money of different countries.
*rates tabulated are not specific and subject to change
How many Indian Rupees are there in 5 Nepalese Rupees? (1 NPR = ₹0.62)
1 NPR = ₹0.62
5 NPR = 5 × ₹0.62 = ₹3.10
Thus, 5 NPR = ₹3.1
Example 10: How many Indian rupees are there in $6? ($1 = ₹82.67)
$1 = ₹82.67
$6 = 6 × ₹82.67
Thus, $6 = ₹496.02

Example 11: Rihan’s father came back from South Korea. He wanted to exchange the South Korean currency (Won) at the airport. He had 15,51,000 Won with him. How much money will he get in Indian currency? (1 Won = ₹0.062)
Amount of money with Rihan’s father in Won = ₩15,51,000
We know that, 1₩ = ₹0.062
So, ₩15,51,000 = 15,51,000 × ₹0.062 = ₹96,162
Thus, Rihan’s father will get ₹96,162 in exchange for ₩15,51,000.

















Multiply the decimal number by the whole number visually.
a 0.2 × 4
b 0.4 × 5
Multiply.
a 45.6 × 10
c 63.157 × 1000
b 15.478 × 100
d 4 × 2.5
e 12 × 14.945 f 12.3 × 35.69
Compare using >, < or =.
a 5.15 × 10 515 b 83.482 × 1000 83482
c 6 × 1.658 10.948 d 715.15 × 8 5720.12
e 2.13 × 31.4 6.5882 f 1.5 × 634.71 94.2065 1 1 1
Fill in the blanks.
a 12.15 × = 121.5
c 61.235 × = 612.35
b 15.26 × = 15260
d 14.1 × = 14100
e 6 × 1.645 = f 1.1 × 47.503 =
How many Indian rupees are the same as 1000 Euros? (1 Euro = ₹89.19)
Matthew was solving a puzzle based on decimal numbers. The first step is to think of a number and then find six times of that number. If he thinks of 4.6, what is the final answer?
There are 24 workers at a factory. 11 workers are given ₹252.54 each and the rest of them are given ₹364.52 each. How much money is given to the workers in total?
Suresh’s father is working in U.A.E. He gets 800 dirham as a salary. Saurav’s father who is working in Sri Lanka gets 2200 Sri Lankan rupees. Who gets more Indian rupees as salary and by how much? (1 dirham = ₹22.51 and 1 LKR = ₹0.25)
New dustbins were to be purchased for Sanchita's school. The school ordered 96 dustbins and each dustbin costs ₹123.65. What was the total cost of the dustbins? Why do we need dustbins at home, in schools, and in public places?
Anjali is fond of collecting different currency notes. She has 2 Pounds, 5 Rand, 6 US Dollars, 5 Euros and 15 Yuan. How much money does Anjali have in Indian Rupees? (1 pound = ₹104.06, 1 rand = ₹4.43, 1 US dollar = ₹82.67, 1 Euro = ₹89.19, 1 yuan = ₹11.51)
If Ana’s father bought 92.5 kg of fruit. He wants to make 10 baskets of fruit. How much fruit will be there in each basket?
Let us learn how to find the answer!
Total fruit bought = 92.5 kg, Total baskets = 10
Fruit in each basket = 92.5 ÷ 10 = 9.25 kg
Let us now divide 987.1 by 10, 100 and 1000.
Division by 10
When we divide any decimal number by 10, move the decimal point 1 place to the left.
987.1 ÷ 10 = 98.71
9 8 7 . 1
Division by 100
When we divide any decimal number by 100, move the decimal point 2 places to the left.
987.1 ÷ 100 = 9.871
9 8 7 . 1
Division by 1000
When we divide any decimal number by 1000, move the decimal point 3 places to the left.
987.1 ÷ 1000 = 0.9871
9 8 7 . 1

Thus, when we divide by 10, 100 or 1000, we move as many decimal places to the left as there are 0s in the divisor.
Example 12: Divide.
1 453.2 ÷ 10 = 45.32
2 471.12 ÷ 1000 = 0.47112
3 53 ÷ 100 = 0.53
4 65.001 ÷ 1000 = 0.065001
Divide 0.6 by 3.
Remember!

Adding a 0 before any number does not change its value.
Step 1: Place the decimal point directly above the decimal point in the dividend.
Step 2: Divide as we divide whole numbers. Divide the ones.
6 tenths are put in 3 equal parts which is equal to 2 tenths in each part.
0.6 � 3 = 0.2
Steps
Step 3: Divide the tenths.
Step 4: Divide the hundredths.
When the dividend is less than the divisor (1.45 ÷ 5)
When the dividend is more than the divisor (6.48 ÷ 4)
8 • Operations with Decimals
When there is a remainder while dividing (4.5 ÷ 2)
Add an extra zero at the hundredths place to complete the division. Adding a zero to the dividend on the right side does not change the value of the number.
Example 13: Find the quotient.
Thus, 5.62 ÷ 4 = 1.405

















Divide the given decimal numbers visually.
0.8 ÷ 4
Fill in the blanks.

Find the quotient.
a 120.6 ÷ 6
c 37.905 ÷ 7 d 18.9 ÷ 4
e 105.1 ÷ 5 f 252.3 ÷ 6
Compare using >, < or =. a 13.25 ÷ 5 2.65
How many pounds should Hari take with him to England, if the total expenses for the trip add up to ₹1,04,200? (Given: 1£ = ₹104.2 approximately)
Rajat works at a grocery store. He received nine cartons of items at his store. The total weight of 9 cartons is 37.8 kg. Find the weight of one carton.
Sakshi helps her mother in saving money by managing the grocery expenses of her house. She sees an offer on the internet where six 1-litre bottles of oil cost $37.92. Should she buy it if the rate of the same oil bottle is $6.5 per bottle in the market?
Create a word problem for division of a decimal number by a whole number.
Objective: To reinforce the understanding and application of decimal operations.
Setting: In groups of 4.
Materials Required: Printed maze worksheets with each intersection or decision point in the maze having a decimal operation problem (addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division), pencils
Method:
1 Distribute the maze worksheet to each group.
2 Ask the students to start at the “Entrance” of the maze.
3 One student from each group solves one decimal problem in their notebooks, which leads to next problem.
4 The group which performs the correct decimal operations first, and reaches the exit of the maze, wins.
Add or subtract the numbers visually.
a 0.23 + 0.47 b 1.4 – 0.62
Find the product of the numbers visually.
a 6 × 0.2 b 5 × 0.6
Add or subtract the numbers using the column method. a 45.61 + 17.513 b 1.14 + 45.2 c 18.963 + 14.517
64.51 – 12.718
Fill in the blanks.
a 45.12 × = 451.2 b 184.351 × = 184351 c 2.517 × = 251.7 d 2.002 × = 20.02 e 81.36 × = 81360 f 1.001 × = 1001
Fill in the blanks.
d 1.21 ÷ = 0.00121 e 14.2 ÷ 1000 = f 123.321 ÷ = 1.23321
Find the product of the numbers. a 12 × 1.54
18 × 3.251
9 × 32.14 d 1.2 × 21.36
41.5 × 12.45
Divide to find the quotient.
Simplify.
Match the following. a 1.51 + 23.72
b 27.63 – 2.78 22.8852 c 4 × 6.17
× 7.02

Divide to find the quotient.
a 56.8 ÷ 5 b 22.49 ÷ 2 c 189.2 ÷ 8
d 313.5 ÷ 6 e 356.1 ÷ 5
f 535.47 ÷ 6
Read the exchange rate chart of different countries given in the chapter. Answer the questions.
a What is 6000 Won in Indian Rupees?
c Convert 850 Rand into Indian Rupees.
b What is €150 in ₹?
d What is 100.5 Dirham in ₹?
Jason bought an item for ₹45.8. He gave the shopkeeper ₹50. How much money will he get back from the shopkeeper?
Raj wants to buy a DVD player for $47.85, a DVD holder for $21.36 and a stereo for $22.01. If he has $90, how much more money does he require?
George’s friend returned from the USA. He exchanged $168 for Indian currency. If he has to give $1 for every $20 as a tax for the exchange, what amount of Indian currency does he have? ($1 = ₹89.12)
Rohan owns a carpool agency that takes people from Meerut to Gurgaon everyday. If the cars run for 4 hours each day and consume 6.5 L of petrol each hour, for how many days will the cars run with 130 litres of petrol?
Create a word problem on multiplication of two decimal numbers.
Critical Thinking
1 John’s weight is 0.89 times that of Harry’s and Harry’s weight is 0.56 times that of Jacob’s. If Jacob weighs 51.25 kg, what is John’s weight?

2 Read the statements and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): When multiplying two decimal numbers, the product is always less than both of the original numbers.
Reason (R): Multiplying any two numbers between 0 and 1 results in a number that is smaller than each of the original numbers.

Options:
a Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c A is true, but R is false.
d A is false, but R is true.
e Both A and R are false.




Cross Curricular & Value Development
In 2023, India experienced diverse weather patterns across its various cities. The government meteorological department recorded the rainfall in several major cities to analyse the effects of these patterns. The data is essential for urban planning, agricultural forecasts, and water resource management.
Read the questions and answer.

1 What is the total rainfall in Mumbai, Delhi and Bangalore? a 3981.4 mm b 3871.4 mm c 3791.4 mm d 3971.4 mm
2 Find the difference in rainfall between Chennai and Kolkata. a 256.6 mm b 265.5 mm c 248.4 mm d 268.2 mm

3 If the rainfall in Pune doubles next year, how much rainfall is expected in the next year?
4 Find the difference between the rainfall in Mumbai and the total rainfall in Delhi, Bangalore and Chennai combined.
5 Find the average rainfall of the 6 cities? Hint: Average = Total Rainfall Total number of cities

6 Why is it important for us to save rain water?




Name of the Student:
Time: 1 Hour
Total Marks: 50
1 Choose the correct option. (4 marks)
A The place value of 5 in 74095230 is ___________.
i 50 ii 500 iii 5000 iv 50,000
B Sixty-six lakh one thousand four hundred seventy in figures is ___________.
i 6,14,720 ii 66,10,470 iii 6,60,147 iv 66,01,470
C The expanded form of 13294190 in Indian number system is ___________.
i 10,00,000 + 3,00,000 + 20,000 + 9,00,000 + 4000 + 100 + 90
ii 1,00,00,000 + 30,00,000 + 2,00,000 + 90,000 + 4000 + 100 + 90
D 10 million is equal to ___________.
i 1 crore ii 1 lakh iii 10 crores iv 10 lakhs
2 Add and subtract the given fractions. (4 marks)
A 17 24 − 5
3 Form the greatest and the smallest 8-digit number using the digits 1, 8, 6, 0, 9, 5, 2 and 4, without repeating any digit. (2 marks)
4 Look at the Venn diagram. Answer the questions. (8 marks)
A The factors of 18 are ____________.
B The common factors of 12 and 8 are ____________.
C The factors that are common to 12 and 18 and not to 8 are ____________.
D The HCF of 8, 12 and 18 is ____________.
5 Solve to find the answer. Show your work. (4 marks)
A 87,687 + 46,568
B 7,99,098 – 2,67,548
6 Spot the errors in the given factor tree and redraw the factor tree correctly. Also write the prime factorisation of the number 120. (4 marks)
7 Shade the grids to show the decimals. Convert the decimals into fractions. (4 marks)
1.2
8 Write the fractions shown in the given figures. Arrange them in ascending order. (4 marks)
9 Which is more—the products of 5 and 4 5 or the sum of 1 1 4 and 2 4 5 ? (4 marks)
10 Multiply 2.4 × 1.2. (4 marks)
11 Find the LCM of 12, 16 and 20. (4 marks)
12 A town has a total population of 4,00,000. The population of females is 1,20,500 and the population of males is 1,50,800. Read the statements and answer the question given below.
Statement 1: The population of children is 1,28,700, which is 8,200 more than the population of females in the town.
Statement 2: The population of females and children together is less than the population of males. Is statement 1 true or statement 2? Are they both true? (4 marks)

Do It Yourself 1A
1. a. 9000; 9 b. 50000; 5 c. 90000000; 9 d. 20000000; 2
e. 60000000; 6 f. 800; 8 g. 3000000; 3 h. 100000; 1
2. a. Indian System: 2,16,43,332; International System: 21,643,332
b. Indian system: 12,00,621; International System: 1,200,621
c. Indian system: 4,62,07,219; International System: 46,207,219
d. Indian system: 9,59,10,158
3. a. 4,00,00,000 + 10,00,000 + 90,000 + 800 + 80 + 7
Four crore forty-one lac ninety thousand eight hundred eighty-seven
b. 1,00,00,000 + 90,00,000 + 80,000 + 1000 + 700 + 2
One crore ninety lac eighty-one thousand seven hundred two
c. 80,000,000 + 1,000,000 + 80,000 + 5000 + 400 + 30 + 2
Eighty-one million eighty-five thousand four hundred thirty-two
d. 10,000,000 + 9,000,000 + 800,000 + 50,000 + 4000 + 4
Nineteen million eight hundred fifty-four thousand four
4. a. 60,08,098 b. 20,000,569 c. 4,090,000
d. 8,00,01,002 5. a. 1 b. 10 c. 10,000 d. 7
6. Indian number system- 27,22,000
International number system- 2,722,000
7. a. 91,19,199 b. 170,70,707 8. 353,000,000
Do It Yourself 1B
1. 76,24,578
2. a. < b. = c. > d. < e. < f. <
3. a. 1,00,00,000 b. 2,90,52,468 c. 10,00,000
d. 3,00,52,468
4. a. Ascending order: 93,12,820 < 1,00,36,782 < 5,00,00,367 < 8,87,21,460
Descending order: 8,87,21,460 > 5,00,00,367 > 1,00,36,782 > 93,12,820
b. Increasing order: 36,81,910 < 92,56,890 < 6,92,10,350 < 8,26,00,031
Decreasing order: 8,26,00,031 > 6,92,10,350 > 92,56,890 > 36,81,910
c. Increasing order: 5,00,21,138 < 6,04,50,821 < 6,50,24,567 < 9,45,21,823
Decreasing order: 9,45,21,823 > 6,50,24,567 > 6,04,50,821 > 5,00,21,138
5. a. 98,54,310; 10,34,589 b. 87,65,321; 12,35,678
c. 65,43,210; 10,23,456
6. a. 8,87,64,210; 1,00,24,678 b. 9,98,76,431; 1,13,46,789
c. 9,97,54,320; 2,00,34,579
7. 9,88,75,420 and 2,04,57,889
8. a. 9,99,99,998; 10,00,000 b. 9,99,99,876; 10,00,023
c. 9,99,98,765; 10,00,234
9. Descending Order = Russia, China, Australia, India
10. Answers will vary. Sample answer.
The government of a country has allocated its national budget for the upcoming fiscal year. The budget for the education sector was ₹45,678,912 and for healthcare was ₹45,345,678. Which sector had a greater budget?
Do It Yourself 1C
1. a. 85,48,750 b. 89,05,460 c. 6,07,85,890
d. 1,56,48,950
2. a. 1,25,89,200 b. 87,52,400 c. 68,67,800
d. 77,59,900
3. a. 8,97,00,000 b. 53,12,000 c. 8,21,59,000
d. 5,89,90,000 4. 239,000 approximately
5. The municipal corporation spent ₹65,95,000 on planting trees.
6. a. 99,63,210; 99,63,000 b. 96,32,100; 96,32,000
1. a. Indian system: 35,07,681; Thirty-Five Lakh Seven Thousand Six Hundred Eighty-One; 30,00,000 + 5,00,000 + 7000 + 600 + 80 + 1; International system: 3,507,681-Three Million Five Hundred Seven Thousand Six Hundred Eighty-One; 3,000,000 + 500,000 + 7000 + 600 + 80 + 1
b. Indian system: 4,20,87,950; Four Crore Twenty Lakh Eighty-Seven Thousand Nine Hundred Fifty; 4,00,00,000 + 20,00,000 + 80,000 + 7000 + 900 + 50
International system: 42,087,950; Forty-Two Million Eighty-Seven Thousand Nine Hundred Fifty; 40,000,000 + 2,000,000 + 80,000 + 7000 + 900 + 50
c. Indian system: 6,35,65,842; Six Crore Thirty-Five Lakh Sixty-Five Thousand Eight Hundred Forty-Two; 6,00,00,000 + 30,00,000 + 5,00,000 + 60,000 + 5000 + 800 + 40 + 2
International system: 63,565,842; Sixty-Three Million Five Hundred Sixty-Five Thousand Eight Hundred Forty-Two; 60,000,000 + 3,000,000 + 500,000 + 60,000 + 5000 + 800 + 40 + 2
d. Indian system: 9,15,00,084; Nine Crore Fifteen Lakh EightyFour; 9,00,00,000 + 10,00,000 + 5,00,000 + 80 + 4
International system: 91,500,084 - Ninety One Million Five Hundred Thousand Eighty-Four; 90,000,000 + 1,000,000 + 500,000 + 80 + 4
2. a. 60,715,239; 6,07,15,239 b. 8,09,50,002; 80,950,002
c. 1,100,039; 11,00,039
3. a. 6,45,87,120; 6,45,87,100; 6,45,87,000
b. 89,09,010; 89,09,000; 89,09,000
4. a. > b. < c. = d. <
5. a. 23,56,475 < 90,87,687 < 8,91,63,896 < 9,08,04,365
b. 3,24,35,678 < 4,35,46,576 < 6,76,12,895 < 6,76,87,980
6. a. 5,36,45,787 > 4,56,45,768 > 2,40,85,167 > 43,56,787
b. 9,09, 87, 897 > 4,90,76,837 > 80,88,428 > 80,68,964
7. 16,48,235; 16,48,236; 16,48,237; 16,48,238; 16,48,239; 16,48,240; 16,48,241; 16,48,242; 16,48,243; 16,48,244
8. 3,151,324
Indian number system - 31,51,324 = 30,00,000 + 1,00,000 + 50,000 + 1,000 + 300 + 20 + 4
International number system- 3,000,000 + 100,000 + 50,000 + 1,000 + 300 + 20 + 4
9. a. Indian number system: 1,99,77,555
One Crore Ninety-Nine Lakh Seventy-Seven Thousand Five Hundred Fifty-Five; International Number system: 19,977,555 Nineteen Million Nine Hundred Seventy-Seven Thousand Five Hundred Fifty-five
b. 1,99,77,560; 1,99,77,600; 1,99,78,000
Challenge 1. 12,15,696 2. 99887765
Case Study
1. Option c 2. Option d 3. Germany
4. Poland, Italy, France, United Kingdom, Germany
5. Germany
Do It Yourself 2A
1. a. True b. False c. True d. False
2. a. 89,285 b. 2,64,859 c. 15,54,313
3. a. 91,660 b. 71,092 c. 9,21,018
4. a. 7,28,944 b. 4,62,917 c. 7,71,214 d. 7,24,168
5. a. 81,898 b. 9,31,609 c. 2,47,880 d. 5,31,550
6. 9,03,550 7. 2,72,950 blazers 8. 22,448 kilometres
9. ₹3,81,030
Do It Yourself 2B
1. a. False b. False c. False d. True
2. a. 5,65,670; 56,56,700; 5,65,67,000
b. 4,78,520; 47,85,200; 4,78,52,000 c. 8,25,870; 82,58,700; 8,25,87,000 d. 19,84,540; 1,98,45,400; 19,84,54,000
3. a. 2500; 250; 25 b. 35,400; 3540; 354 c. 89,500; 8950; 895 d. 98,700; 9870; 987
4. a. 61,525 b. 27,36,600 c. 78,71,525 d. 1,46,55,870 e. 3,03,57,504 f. 4,45,49,588 g. 4,72,86,288 h. 5,35,25,760
5. a. Quotient = 183; Remainder = 134 b. Quotient = 124; Remainder = 228 c. Quotient = 159; Remainder = 280 d. Quotient = 161; Remainder = 219 e. Quotient = 233; Remainder = 366 f. Quotient = 135; Remainder = 365 g. Quotient = 136; Remainder = 15 h. Quotient = 102; Remainder = 219
6. 8784 days 7. 98,901 8. Q = 999 R = 99 9. 28,28,232 10. 159 pages 11. ₹680
Do It Yourself 2C
1. a. (ii) b. (ii) c. (ii) d. (ii)
2. a. False b. True c. True d. False
3. a. 266 b. 44 c. 12 d. 40 e. 15 f. 16
4. a. 168 b. 272 c. 3171
5. ₹78 6. 48 stickers 7. 7 pencils 8. ₹74,750
Chapter Checkup
1. a. 80,245 b. 10,33,428 c. 12,41,211 d. 3,02,572
2. a. 20,101 b. 7,68,289 c. 8,03,271 d. 1,09,241
3. a. 8960; 89,600; 8,96,000 b. 45,460; 4,54,600; 45,46,000 c. 64,570; 6,45,700; 64,57,000 d. 98,760; 9,87,600; 98,76,000
4. a. Quotient = 210; Quotient = 21; Quotient = 2, Remainder = 100
b. Quotient = 408, Remainder = 6; Quotient = 40, Remainder = 86; Quotient = 4, Remainder = 86
c. Quotient = 5120; Quotient = 512; Quotient = 51, Remainder = 200
d. Quotient = 7456, Remainder = 2; Quotient = 745, Remainder = 62; Quotient = 74, Remainder = 562
5. a. 29,32,848 b. 17,29,200 c. 1,28,80,901 d. 40,83,256
6. a. Quotient = 237; Remainder = 20 b. Quotient = 180; Remainder = 265 c. Quotient = 115; Remainder = 437
d. Quotient = 101; Remainder = 684
7. a. 27 b. 76 c. 43 d. 179 8. 45
9. 8, 99, 999 10. 7,03,66,258 people 11. 50 days
12. 38,400 flowers 13. 149 rows 14. 65 marbles
15. ₹4,87,800 16. 6,00,000
17. 2226 oranges in each carton
18. ₹1,20,500 19. Answer may vary. Sample answer: A company manufactures 1,86,320 pencils and 98,346 erasers. The company packs 2 pencils and 1 eraser in a packet. How many pencils and erasers will be left unpacked?
Challenge 1. Both statements are true. 2. Option a Case Study
1. 12,10,111 kg 2. a. False b. True
3. 172 kg 4. 210 kg
Do It Yourself 3A
1. a. 1, 2, 7 and 14 b. 1, 2, 17 and 34
c. 1 and 37 d. 1, 2 , 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24 and 48
e. 1, 5, 11 and 55 2. a. 1, 3, 5 and 15 b. 1 and 41
c. 1, 3, 7, 9, 21 and 63 d. 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36 and 72
e. 1, 3, 9, 27 and 81
3. Prime numbers: a, c, g, i Composite Number: b, d, e, f, h, j
4. 4 prime numbers - 11, 13, 17 and 19 5. 2 factors
6. The chairs will be arranged in 13 rows with 13 chairs in each row.
7. Answer may vary. Sample answer Alika has a ribbon of length 27 m. In how many ways she can cut the ribbon equally?
Do It Yourself 3B
1. b, c, e 2. d, e 3. a, b, d 4. a, b 5. 660
6. pencils, erasers and notebooks
Do It Yourself 3C
1. b 2. c 3. a. 8 = 2 × 2 × 2 b. 20 = 2 × 2 × 5
c. 24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 d. 33 = 3 × 11 e. 63 = 3 × 3 × 7
f. 72 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 g. 90 = 2 × 3 × 3 × 5
h. 112 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 7
4. a. 16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 b. 22 = 2 × 11 c. 30 = 2 × 3 × 5
d. 45 = 3 × 3 × 5 e. 51 = 3 × 17 f. 60 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
g. 100 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 h. 148 = 2 × 2 × 37 5. 1, 5, 73, 365
Do It Yourself 3D
1. a. 1 b. 1 c. 1, 7 d. 1, 3 e. 1, 3, 5, 15
f. 1, 2, 3, 6 g. 1, 2 h. 1, 5
2. a. 8 b. 15 c. 5 d. 1 e. 27 f. 14 g. 10
h. 11 3. a. 3 b. 13 c. 18 d. 8
4. a. 6 b. 14 c. 20 d. 27 5. 5 cm 6. 30 L
Chapter Checkup
1. Prime Numbers: b and c Composite number: a and d
2. a. 1, 2, 4, 8 and 16 b. 1, 2, 4, 5, 10 and 20
c. 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24 d. 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21 and 42

3. a. 1, 2, 4, 7, 14 and 28 b. 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18 and 36
c. 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 14, 28 and 56
d. 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, 20, 40 and 80
4. a. divisible by 5 b. divisible by 3
c. divisible by 2, 3, 5, 9 and 10 d. divisible by 2, 5 and 10
5. a. 88 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 11 b. 102 = 2 × 3 × 17
c. 112 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 7 d. 140 = 2 × 2 × 5 × 7
6. a. 75 = 3 × 5 × 5 b. 21 = 3 × 7
c. 128 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 d. 164 = 2 × 2 × 41
7. a. 1,5 b. 1, 5, 25 c. 1, 11 d. 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12
8. a. 4 b. 5 c. 24 d. 75 9. a. 2 b. 17 c. 15
d. 15 10. a. 9 b. 17 c. 1 d. 34
11. Answers may vary. Sample answer: 120 12. 25 litres 13. 8 bunches 14. 6 inches; 44 15. 80; 3 cupcakes; 2 sandwiches 16. 6 containers
Challenge 1. 10 is the greatest number that divides 178 and 128 leaving remainder as 8.
2. HCF is 4. Twice the HCF is 4 × 2 = 8. So, the number is 8. Case Study
1. d 2. b 3. 32
4. 12 necklaces
Do It Yourself 4A
1. a. 8, 16, 24, 32, 40 b. 11, 22, 33, 44, 55
c. 21, 42, 63, 84, 105 d. 25, 50, 75, 100, 125 e. 50, 100, 150, 200, 250 2. Yes, 7209 is completely divisible by 9. 3. 2025, 2037, 2049 4. Answers may vary. Sample answer 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100; Even. 5. No
Do It Yourself 4B
1. d 2. a. 60 b. 63 c. 55 d. 40 e. 18 f. 30
g. 60 h. 150 3. c 4. 2036 5. 36 days 6. 10:30 a.m. 7. Answers may vary. Sample answer.
A shopkeeper sells candles in packet of 12 and candle stands in packets of 8. what is the least number of candles and candle stands Rita should buy so that there will be one candle for each candle stand?
Do It Yourself 4C
1. a. 35 = 5 × 7; 75 = 3 × 5 × 5
b. 44 = 2 × 2 × 11; 88 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 11
c. 48 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3; 12 = 2 × 2 × 3
d. 25 = 5 × 5; 115 = 5 × 23 2. a. 40 b. 16 c. 80 d. 50
3. a. 48 b. 175 c. 180 d. 315 e. 360 f. 864 g. 1680 h. 180
4. No, LCM of 12, 24, and 56 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 7 = 168
So, Rohan is not right.
5. 4 times
6. Answers may vary. Sample answer.
Find the least length of a rope which can be cut into whole number of pieces of length 45 cm and 75 cm.
Do It Yourself 4D
1. a. 168 b. 150 c. 96 d. 300 e. 168 f. 300 g. 315 h. 540
2. No, Rohit’s calculation is incorrect, as he didn’t consider all the prime factors.
3. A B
LCM of 42, 70 210
LCM of 63, 105 315
LCM of 30, 45 90
LCM of 9, 15 45
LCM of 12, 48 48
4. 60
Do It Yourself 4E
1. August 7, 14, 21, 28. 2. 6 groups
3 15 litres 4. 10:31 a.m. 5. 24 balls
6. 16 7. 30 weeks 8. 3360 stacks
9. Answers may vary. sample answer.
Three pieces of ribbons 42 cm, 49 cm and 63 cm long need to be divided into the same length. What is the greatest possible length of each ribbon?
Chapter Checkup
1. 9, 18 and 27 2. a 3. a. 63 b. 81
c. 99 d. 117 4. b 5. a. 630 b. 90 c. 1386
d. 6930 e. 180 6. a. 54 b. 70 c. 45 d. 600
7. d 8. a. 480 b. 3720 c. 360 d. 630 9. 39 10. 180 minutes 11. 2041 12. 135
Challenge 1. c. Rahul and Sahil are correct. 2. a
Case Study
1. b. Every 60 minutes 2. 9:00 a.m.
3. 10 4. 4:00 p.m. 5. Answers may vary.
Chapter 5
Do It Yourself 5A
1. a. Unlike fractions b. Like fractions c. Unlike fractions
d. Like fractions e. Like fractions
2. Proper fractions: 41212 ,,� 51529
Improper fractions: 658179 ,,,� 25113
Mixed numbers: 157 4,5,6� 789
3. a. 61 15 b. 14 20 15 c. 79 15 d. 15 e. 44
4. a. 2 4 3 b. 2 8 7 c. 2 5 5 d. 3 7 6 e. 8 7 9
f. 9 2 g. 18 7 h. 55 9 i. 35 3 j. 135 11
6. Mixed Number 2 3 6 Improper Fraction 15 6
Do It Yourself 5B
1. Answers may vary, sample answers:
a. 1218 , 1421 b. 1218 , 3045 c. 2233 , 3451 d. 2436 , 4060
2. Answers may vary. Sample answers:
a. 63 , 105 b. 72 , 288 c. 1510 , 2114 d. 168 , 2412
3. a. 2 5 b. 3 7 c. 1 3 d. 4 5
4. a. Not equivalent b. Equivalent
c. Equivalent d. Equivalent
5. a. 28 b. 56 c. 2 d. 70 6. d.
7. Answer may vary. Sample answer. = =
Do It Yourself 5C
1. a. < b. < c. > d. <
2. a. b. c. d.
3. a. 132 674 << b. 1125 5236 <<<
c. 31575 13412127 <<<< d. 5487 128158 <<<
4. a. 3311 5846 >>> b. 8131 9283 >>>
c. 1111 691114 >>> d. 42431 5311156 >>>>
5. Answer may vary. Sample answer.
6. Reshma 7. Answer may vary. Sample answer.
Shalini studied for 14 9 hours, Priya studied for 8 3 hours.
Who studied for more hours?
Chapter Checkup
1. a. 15 2 b. 17 3 c. 103 8 d. 51 8
2. a. 2 4 4 b. 1 8 5 c. 1 24 6 d. 11 4 19
3. Answers may vary. Sample answers:
a. 468 ,, 121824 b. 234 ,, 182736
c. 101520 ,, 162432 d. 223344 ,, 284256
4. Answers may vary. Sample answers:
a. 842 ,, 1263 b. 1284 ,, 21147 c. 25155 ,, 653913
d. 543618 ,, 664422
5. a. 3 4 b. 11 14 c. 3 5 d. 9 17
6. a. 114 2 25 < b. 434 6 54 < c. 24 8 3 =
7. a. 1514 61225 <<< b. 1313 5825 <<<
c. 2126 5237 <<< d. 14311 27512 <<<
8. Least: Alex and Casey; Greatest: Bailey
157 6 39 =
9. Australia < South America < North America < Europe < Africa < Asia
Challenge 1. 3 8 2. Option a
Case Study
1. b 2. a 3. 8 10 4. False 5. Answer will vary
Do It Yourself 6A
9. Answers may vary. Sample answer.
Neeta filled 2 3 4 litres of petrol in her car. After a day she again filled 1 1 4 litres of petrol. Next day she went to visit her grandparents and used 3 3 4 of the petrol. How much petrol is left in her car?
Do It Yourself 6B

8. 20 L 9. 19 bottles
10. Answers may vary. Sample answer.
Roy ran 4 5 of a km each day for 6 days. How many kms did he run in all?
1. a. 5 4 b. 17 18 c. 14 78 d. 5
2. a. False b. True c. False d. False
3.
6.
7.
1
9. 11 17km 28 10. Phase 4: 97 1 2
11. 88 cars 12. 9 10litres 28 13. 23 4m 30
14. Answers may vary. Sample answer.
A glass of water holds cups of water. How many 1 4 cups will it take to fill the glass?
Challenge 1. 1 3 cup; 4 cheese cubes 2. b
1. c 2. b 3. 1 13 20 hours
4. Students will create something using recyclable materials.
Do It Yourself 7A
1. a. forty-five point five or forty-five and five tenths
b. twelve point three or twelve and three tenths
c. forty-two and fourteen-hundredths or forty-two point one four
d. one hundred seventy-eight point six four or one hundred seventy-eight and sixty-four hundredths
e. four hundred fifty-seven point one eight or four hundred fiftyseven and eighteen hundredths
f. twenty-five and one hundred twenty-seven thousandths or twenty-five point one two seven
g. one hundred seventy-four and two hundred one thousandth or one hundred seventy-four and two zero one
h. seven hundred sixty-five and four thousandths or seven hundred sixty-five point zero zero four
2. a. 413.2 b. 72.33 c. 361.04 d. 52.402
and six-tenths.
one point seven two or one and seventy-two hundredths
4. a. 40 + 5 + 1 10 or 40 + 5 + 0.1
b. 700 + 80 + 9 + 4 10 or 700 + 80 + 9 + 0.4
c. 40 + 5 + 1 10 + 3 100 or 40 + 5 + 0.1 + 0.03
d. 400 + 80 + 6 + 7 10 + 2 100 or 400 + 80 + 6 + 0.7 + 0.02
e. 900 + 70 + 6 + 7 100 or 900 + 70 + 6 + 0.07
f. 10 + 5 + 6 100 + 2 1000 or 10 + 5 + 0.06 + 0.002
g. 70 + 8 + 6 10 + 2 1000 or 70 + 8 + 0.6 + 0.002
h. 100 + 50 + 4 + 3 100 + 1 1000 or 100 + 50 + 4 + 0.03 + 0.001
5. a. 4.1 b. 867.17 c. 16.106 d. 489.982
6. a. 0.9, 90% b. 0.32, 32% c. 0.34, 34%
d. 0.475, 47.5%
7. a. 13 10 , 130% b. 627 50 = 1254%
c. 803 23 = 3212% d. 1151 500 = 230.2%
8. Answers may vary. Sample answers.
a. 187.2 = 187.20 = 187.200
b. 87.02 = 87.020 = 87.0200
c. 963.14 = 963.140 = 963.1400
d. 189.221 = 189.2210 = 189.22100
9. a. 21 10 , 2.1, 210% b. 7 20 , 0.35, 35%
c. 131 250 , 0.524, 52.4% d. 78 25 , 3.120, 312%
10. a. > b. < c. = d. <
11. 400 + 50 + 5 + 8 10 + 9 100 or 400 + 50 + 5 + 0.8 + 0.09
12. 0.625 13. 60%
Do It Yourself 7B
1. None
2. a. b. c. d.
3. a. 1 b. 2 c. 1 d. 3
4. a. 13.15, 1.20 b. 3.48, 1.20 c. 4.800, 1.526 d. 1.400, 47.584
5. a. 0.6 and 0.2 b. 0.35 and 0.50 c. 0.625 and 0.750 d. 0.80 and 0.25
6. 0.540, 60.900 and 83.394
7. Answers may vary. Sample answer.
Mahika bough 1.5 L of milk and 3.245 L of curd. Convert both the decimals into like decimals.
Do It Yourself 7C
1. a.
< b. 0.9 > 0.89
2. a. True b. False c. True
3. a. 4.2 b. 15.67 c. 87.654 d. 294.98
4. a. 3 b. 8 c. 48 d. 15
5. a. 14.01 < 14.1 < 14.101 < 14.14
b. 84.5 < 84.55 < 84.56 < 84.6 < 84.65
c. 184.1 < 184.112 < 184.2 < 184.23
d. 54 < 64.22 < 64.23 < 64.32 < 64.33
6. a. < b. = c. = d. <
7. 206 8. 24.68 > 24.54 > 24.36.
9. Telangana, Rajasthan, Bihar, Maharashtra, Uttar Pradesh Chapter Checkup
1. a.
1.2 = 1 + 0.2 = 1 + 2 10 b.
1.48 = 1 + 0.4 + 0.08 = 1 + 48 10100 +
2. a. fifteen and two-tenths or fifteen point two
b. seventy-one and sixty-five tenths or Seventy-one point six five
c. eight hundred fourteen and thirty-six hundredths or eight hundred fourteen point three six
d. one hundred seventy-six and eight hundred one thousandths or one hundred seventy-six point eight zero one
3. a. 40.101 b. 103.05 c. 420.011 d. 31.005
4. a. 10 + 1 + 1 10 or 10 + 1 + 0.1
b. 10 + 6 + 54 10100 + or 10 + 6 + 0.5 + 0.04
c. 400 + 90 + 2 200 or 400 + 90 + 0.02
d. 800 + 40 + 3 + 33 1001000 + or 800 + 40 + 3 + 0.03 + 0.003
5. a. 0.125, 12.5% b. 0.8, 80% c. 0.6, 60% d. 0.9, 90%
6. a. 63 10; 5 ; 1260% b. 261 10; 5 ; 5220%
c. 104 10; 5 ; 2080% d. 5063 1000; 200 ; 2531.5%
7. a. 12.4 12.3 < b. < 14.55 14.5
c. > 222.22 222.02 d. < 3.003 3.033
8. a. 1 b. 100 c. 100 d. 1000
9. a. 1.33 > 1.31 >1.3 > 1.2
b. 19.54 > 19.501 > 19.44 > 19.4
c. 555.555 > 555.55 > 555.5 > 555.05
d. 748.11 > 748.101 > 748.1 > 748.01
10. Answers may vary. Sample answer. 3.7 3.2
11. Utkarsh
12. 12.9 < 12.99 < 13.01 < 13.1
Challenge 1. 0.97 2. Option c
Case Study
1. Option c 2. Option d
3. Jin Mao Tower, Wuhan Greenland Centre, CITIC Tower, Lotte World Tower, Shanghai Tower, Merdeka 118
4. 679 m; 528 m; 421 m; 599 m; 476 m; 632 m
5. 678.9 = 600 + 70 + 8 + 9 10
527.7 = 500 + 20 + 7 + 7 10
420.5 = 400 + 20 + 5 10
599.1 = 500 + 90 + 9 + 1 10
475.6 = 400 + 70 + 5 + 6 10
632.0 = 600 + 30 + 2

Do It Yourself 8A
1. a. ; 0.3 b. ; 0.7
c. ; 0.4 d. ; 0.63
4. a. = b. >
5. 1000 pounds 6. 4.2 kg 7. Yes
8. Answer will vary. Sample answer.
A community centre received a donation of 47.5 litres of hand sanitizer to be distributed equally among 5 local schools. How much hand sanitizer will each school receive to ensure an equal distribution?
Chapter Checkup
1. a. 0.7 b.
2. a. 0.7 b. 0.77
3. a. 35.9 b. 79.19 c. 117.882 d. 1052.518
4. a. 3.2 b. 0.58 c. 8.94 d. 110.803
5. a. < b. > c. = d. >
6. 4.85 litres 7. 1.47 m 8. 3.305 kg 9. 5.862 km
10. a. 70.88 kg b. 83.735 kg 11. 3.45 km 12. ₹4939
Do It Yourself 8B
1. a. ; 0.8 b. ; 2.0
2. a. 456 b. 1547.8 c. 63,157 d. 10 e. 179.34 f. 438.987 3. a. < b. = c. < d. > e. > f. >
4. a. 10 b. 1000 c. 10 d. 1000 e. 9.87 f. 52.2533 5. ₹89,190 6. 27.6 7. ₹7516.7 8. Suresh’s Father, ₹17,458 9. ₹11,870.4; Answer may vary. 10. ₹1344.89
Do It Yourself 8C
1. a. 0.2
b. 0.2
2. a. 1.56 b. 0.5123 c. 0.012 d. 0.032561 e. 0.0231 f. 0.2
3. a. 20.1 b. 9.13 c. 5.415 d. 4.725 e. 21.02 f. 42.05
d. 46.39 e. 23.65 f. 12.142 8. a. 33.07 b. 85.971 c. 55.33 d. 37.399 e. 50.605 f. 24.512 9. a. 25.23 b. 24.85 c. 24.68 d. 22.8852 10. a. 11.36 b. 11.245 c. 23.65 d. 52.25 e. 71.22 f. 89.245 11. a. ₹372 b. ₹13,378.5 c. ₹3,765.5 d. ₹2,262.255 12. ₹4.2 13. $1.22 14. ₹14,259.2 15. 5 days 16. Answer may vary. Sample answer.
John’s car consumes 0.08 gallons of fuel per mile. If he drives 45.7 miles, how many gallons of fuel does he use?
Challenge 1. 25.543 kg 2. option d
Case Study
1. Option c 2. Option a 3. 1444.6 mm 4. 790 mm 5. 1288.78 mm 6. Answers may vary






Circle the names of five nutrients from the given word search.
Think about how plants in a garden need different things like sunlight, water and good soil to grow strong and healthy. Our bodies too need a variety of nutrients to grow, perform various functions, and be healthy and strong. We get these nutrients from the healthy foods we eat every day. Different foods provide different nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, proteins, and carbohydrates. These nutrients are the building blocks of our health. Let’s learn about these essential nutrients, what they do for our bodies, and where we can find them.
Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for our body. The different forms of carbohydrates are starches and sugars. Carbohydrates can be found in foods like wheat, rice, potatoes, sugar, honey, corn, etc.
When we eat carbohydrates, our bodies break them down into simple sugars like glucose, which gives us the energy to stay active throughout the day.








We can imagine fats as the storage units for our bodies. While carbohydrates give us instant energy, fats store energy for later use. They also protect our organs like a cushion, help in the absorption of certain vitamins, and help to keep our bodies warm.
Fats can be found in foods like nuts, seeds, avocados, butter, ghee, cheese and oil. We require fats in very small amounts.





Not all fats are good for us. Unhealthy fats, found in fried and processed foods, cause health problems. Error Alert!
Proteins are essential for building, maintaining, and repairing muscles, blood, skin, bones, and other tissues and organs in the body. Because of this important function,
processed food: food changed from its natural state, often to make it last longer or taste better

they are known as “body-building nutrients”. Foods rich in protein include meat, eggs, dairy products, fish, beans, soya and pulses.
Growing children and sick people should include more protein-rich food in their meals.
When you get cut yourself, your body works hard to heal and repair itself. Proteins play a crucial role in this healing process by helping to repair and build tissues.







Although needed in small amounts, vitamins are crucial for maintaining good health. They are required in very small amounts by our body. You can find vitamins in a variety of foods like fruits, vegetables, dairy products and meats. Vitamins help our body fight against infections. They help to heal wounds and keep our bones and gums strong.
Minerals are another group of essential nutrients that help our bodies to stay healthy. Some important minerals include sodium, potassium, calcium, iron, phosphorus and iodine. Calcium is important for strong bones and teeth, while iron helps in carrying oxygen in our blood. Minerals can be found in foods like dairy products, nuts, fruits and green leafy vegetables.
Vitamins and minerals are collectively known as “protective foods” as they are necessary for good health and protecting our body.

Water doesn’t provide any nutrients to our body. However, it’s an important component of food. It’s often referred to as our “body’s lifeblood” because it plays a critical role in almost every bodily function. It aids in digestion, regulates body temperature, maintains skin health, and helps in transporting nutrients to the different parts of the body. We should drink plenty of water every day.
The body of an adult human being consists of about 60% water.
Roughage, also known as dietary fibre, is the indigestible part of food. Roughage plays an important role in digestion. It promotes smooth passage of food through the digestive system, preventing constipation. It adds bulk to the food and helps to get rid of the undigested food from the body. Fibre-rich foods like whole grains, fruits and vegetables provide the roughage our bodies need to maintain a healthy digestive system.

Aim: To analyse the nutrient content in a packet of chips.
Materials Needed: a packet of chips (of your choice)
Method:
Step 1: Choose your favourite packet of chips. Make sure the packet includes nutritional information.
Step 2: Look at the nutritional information on the packet. Focus on key nutrients: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins and minerals.
Step 3: Now look at the amount of salt, sugar, food colours and preservatives.
Findings: A packet of chips contains very high amounts of salt, food colour, oil and preservatives. These items, in such quantities, are not good for health if consumed on a regular basis.
Conclusion: This experiment helps you see the nutrient content in things like a packet of chips. This will help you make healthier choices in terms of what you eat.
Write any two food items rich in each of the nutrients listed below.
1. Carbohydrates
2. Fats
3. Proteins
4. Vitamins
5. Minerals
indigestible: something that cannot be digested constipation: a condition in which stool becomes hard and is difficult to pass

Being healthy means your physical and mental well-being. A healthy person eats a balanced diet rich in nutrients, practises good hygiene, maintains good posture, exercises regularly, gets enough rest and sleep, and keeps their surroundings clean. They feel good physically as well as mentally.
A balanced diet means eating a variety of foods from all the major food groups to get the nutrients that are required by the body. A balanced diet provides all the essential nutrients for the proper growth and functioning of our body.


A balanced diet should contain all the nutrients.
Create your own balanced meal! Draw a plate and divide your plate into sections and label each with different food items that make up a balanced meal.

Hygiene is essential for staying healthy and preventing illness. This includes practices that help remove or reduce the number of germs on your body and in your environment. Some hygiene practices that we should follow to stay healthy are listed below.
• Wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds when they are dirty, before and after meals, and after using the toilet.
• Brush your teeth twice a day. Use a tongue cleaner to clean your tongue.
• Regularly shower to keep your skin clean. Always wear neat and clean clothes after bathing.
• Keep your nails trimmed and clean to prevent the accumulation of dirt and germs, which can cause infections.
• Regular cleaning of kitchens, toilets and bathrooms should be done.





Hygienic practices
Posture is how we hold our body while standing, sitting, moving or lying down. Good posture means positioning our body in ways that reduce stress on muscles. It helps keep bones and joints strong. Always make sure to keep your back straight while standing, sitting and walking. Correct posture makes your body appear smarter and improves flexibility in joints.
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy body and mind. Walking, cycling, jogging, running, yoga and swimming are some exercises that keep us fit and healthy. Let’s learn about some benefits of regular exercise.
• It makes our bones and muscles strong and healthy.
• It improves the circulation of blood in our body. When we exercise, our heart pumps blood at a faster rate, which leads to more intake of oxygen and better functioning of the body.
• It keeps our body in good shape.
• It makes our body healthier and more flexible.
• It keeps us active and energetic throughout the day.
• It improves our quality of sleep.

accumulation: to collect or gather We should exercise daily.
Rest and sleep are important for your body to recover and work well. When you sleep, your brain stores memories, helping you to learn better. Your muscles repair themselves, making you feel strong. Sleep also boosts your immune system, so you don’t get sick easily. Besides sleep, taking breaks during the day helps to reduce stress and tiredness, giving your body and mind time to recharge.


A clean surrounding reduces the risk of infections and other health issues. Let’s learn about how to keep our surroundings clean.
• Regularly clean your room by dusting, sweeping and organising your belongings to reduce the presence of dust.
• Always throw garbage in dustbins.

• All drains in the house should be covered and cleaned properly.
• Avoid letting dirty water accumulate in your surroundings, as it can become a breeding ground for mosquitoes and harmful germs.
A disease is a condition in which our body or any part of it is not in a healthy condition. Diseases can be caused by improper diet, or lack of hygiene, rest and exercise. Diseases can be classified into two main types: communicable and non-communicable diseases.
These diseases don’t spread from person to person. Some non-communicable diseases are caused due to the lack of nutrients. These are called deficiency diseases. Let’s first learn about some deficiency diseases.
Names of deficiency diseases
Night blindness
Beriberi
Scurvy
Rickets
Anaemia
Goitre
Caused by deficiency of
Vitamin A
Vitamin B
Vitamin C
Vitamin D
Iron
Iodine
Apart from deficiency diseases, there are a few other kinds of non-communicable diseases such as:
1. Allergy: Some people are highly sensitive towards certain food items, dust or chemicals. When people are exposed to any of these things, they might sneeze, cough or even become ill. This state or condition is called an allergy.
2. Obesity: This occurs due to excess consumption of oily, fried and processed foods or by overeating. Obese people are more prone to heart diseases and diabetes.
3. Diseases like arthritis and diabetes are caused due to malfunctioning of body parts like the joints and the pancreas.
Reflect on your own eating and exercise habits. What is one healthy change you can make to reduce the risk of diseases?
4. Diseases like cancer can be caused due to environmental pollution, smoking or consumption of alcohol.
5. Some people have heart disease from birth which they inherit from their parents.
These diseases can spread from one person to another or through the environment. These are caused by germs such as bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa.
The germs causing communicable diseases can spread in several ways. Let’s learn about them.
Not all microbes are bad. Microbes help us in many ways. They are used to make food such as curd, yogurt, cheese and bread. They also help in digestion of food. Scientists use microbes to make medicines like antibiotics.
• Direct Contact: Germs can transfer through physical contact like shaking hands with the infected person. Communicable diseases can also spread by touching or using the belongings, like clothes and utensils, of the infected person. Diseases such as chickenpox, whooping cough, common cold, measles and tuberculosis spread through direct contact.

• Dirty food and water: You might have noticed a lot of mosquitoes, flies and cockroaches sit on the uncovered food and dirty water. These insects carry germs on their bodies and pass them to the uncovered food and water. Consumption of infected food items spreads diseases such as typhoid and cholera.
• Insects or carriers: Some insects, such as mosquitoes, can bite and transmit germs into a person. When the female Anopheles mosquito bites a person already infected with malaria, it sucks in the germs along with the blood of the person. Then, this mosquito bites a healthy person and causes malaria
inherit: to pass from parents to children






to him/her as well. Some other carriers of diseases include Aedes mosquitoes (causing dengue) and rat fleas (causing plague).
Kerala, a beautiful state in southern India, is known for its rich history in the spice trade. Spices from Kerala have been traded with ancient civilisations across the world. These spices are packed with vitamins and minerals that boost our immune system and add a variety of nutrients to our diet.


nutrients: the essential components found in food that our body needs to function properly roughage: a dietary fibre that aids in digestion communicable diseases: diseases that spread from one person to another non-communicable diseases: diseases that don’t spread from person to person
Scan the QR code to know more about the skeletal system.
• Nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals, are essential for the body to function properly.
• Eating a balanced diet ensures that the body gets all the essential nutrients it needs.
• Proper hygiene, regular exercise, sleep and rest are important for us to stay healthy.
• Communicable diseases spread from one person to another through various means.
• Non-communicable diseases don’t spread from one person to another.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of the following nutrients primarily provides energy for the body?
B. Which of the following must be included in a balanced diet?
All nutrients only Nutrients with water and roughage
Only water
Only roughage
C. Which of the following is a non-communicable disease?
Whooping cough
Diabetes Tuberculosis Malaria
D. Which of the following is caused by consuming dirty food and water?
Dengue Malaria Plague Cholera
2. Fill in the blanks. communicable proteins roughage water
A. helps in the growth, repair and maintenance of tissues.
B. aids in digestion and regulates body temperature.
C. helps to prevent constipation.
D. Diseases that spread from one person to another are called diseases.
3. Write True or False.
A. Good posture helps reduce strain on muscles and joints.
B. Cancer and arthritis are non-communicable diseases.
C. Exercise can help to improve our health.
D. A balanced diet means avoiding all kinds of fats.
4. Match the following.
Diseases
Caused by the deficiency of
A. Night Blindness i. iodine
B. Beriberi ii. vitamin A
C. Scurvy iii. iron
D. Rickets iv. vitamin C
E. Goitre v. vitamin D
F. Anaemia vi. vitamin B
5. Short-answer questions.
A. How do fats help the body besides providing energy?
B. What is the role of roughage in digestion?
C. Why do we need to maintain good posture?


D. Write two benefits of exercise.
E. What happens when we don’t take proper rest and sleep?
F. Why are vitamins and minerals called protective foods?
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Explain the importance of a balanced diet and how it benefits the body.
B. Differentiate between communicable and non-communicable diseases. Give examples for each.
C. Describe the different ways in which communicable diseases can spread. Give an example for each.
7. Picture-based questions.
A. Which of these actions affect the spread of communicable diseases?
B. How do actions like washing hands and covering your mouth when sneezing help prevent the spread of communicable diseases? What might happen if people don’t follow these habits?

One day, during the monsoon, Latika had a plate of golgappas from a seller outside her school. The next morning, she became unwell. What do you think could have happened and why? What are the two things she should take care of to avoid falling sick like this in future?

Make a meal plan for yourself and your family for a week. Make sure that all the meals are balanced. Stick the meal plan on the refrigerator door or a cupboard from where it can be easily seen. Stick to the meal plan and share your experience in the class.



The Human Skeletal System
What Makes Up Our Skeletal System Joints Muscles
Parts of the Skeletal System

Get Set

Look at the pictures of the organ systems and label them.
Circulatory system Skeletal system Digestive system Respiratory system
Our body is made of different organ systems such as the digestive, respiratory, muscular, and skeletal systems. Of these systems, the skeletal system provides shape, support and strength to our body. Let us learn more about the skeletal system.

The human skeletal system is a framework of bones. It has many parts. Some of the main parts are the skull, the backbone, the ribcage, limb bones, and joints.
Bones
Bones are the hard structures that make our skeleton system. Although we cannot see them, but we can feel them as hard structures beneath our skin. They are made of calcium phosphate. A bone has three main parts:
• A hard outer layer called the compact bone.
• An inner layer called the spongy bone.
• The jelly-like material in bones is called the bone marrow. It is the site for making new blood cells. It also stores fat.
Just like a helmet protects our head against injury, similarly, our skeletal system also protects our internal organs. It also system provides support, shape and strength to the body and helps in the movement of different body parts.
A newborn baby has 305 bones. Some bones fuse and an adult human is left with only 206 bones.
The main parts of the skeletal system are the skull, spine, ribcage and limbs (forelimbs and hindlimbs).
The skull is the framework of the head and it protects the brain from injuries. An adult human skull has 22 bones. All the bones of the skull, except the lower jaw, do not move and are fused together. The movable lower jaw allows us to speak and chew food. The skull has sockets for the eyes, nose and ears. Teeth are present both in the upper and the lower jaws.



The spine is also called the backbone or the vertebral column. It is made up of 33 small bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae attach the skull to the spine. The spine protects the spinal cord that is present in it. The spine also allows us to stand upright, bend, stretch, twist and turn. It also helps us to maintain our balance.


spine helps us bend and stretch.
Run your fingers from the underarms and move towards the waist. Do you feel some thin hard structures under the skin? These are ribs. Ribs are thin, flat and curved bones. We have 12 pairs of ribs that forms our ribcage. The function of the ribcage is to protect the heart and the lungs.
Out of 12 pairs, 10 pairs of ribs are joined to the breastbone (or sternum) in front and to the spine at the back. The last two pairs are ribs are attached only to the spine. They are not attached to the breastbone and are called floating ribs.
Our body has two pairs of limbs. These are forelimbs, or arms, and hindlimbs, or legs.
Forelimbs
The forelimb has two parts: the upper arm and the lower arm. The upper arm has a single bone called the humerus. The lower arm has a pair of bones that are connected to the humerus at the elbow. The hand is attached to the lower arm and has many small bones.
Hindlimbs
The hindlimb has two parts: the upper leg and the lower leg. The upper leg is made of a single bone called the femur or thigh bone. The lower leg has
breastbone: a flat bone in the chest

two bones that are joined to the femur at the knee. Many small bones make up the feet.

The femur is the longest bone in our body.




























































































































































Joints are movable or immovable.












































Look at the pictures. Write the names of the parts of the skeleton.









elastic: not rigid











































































































































Joints are the places where two or more bones are connected. The bones are held together at the joints by strong tissues called ligaments. At joints, the surface of bones has cartilage. Cartilage is a tough elastic tissue that prevents the bones at the joints from rubbing against each other.

















The hard but flexible tip of your nose and ears is not made up of bones. It is made of cartilage and therefore we can bend them.
The joints that allow movement of body parts are movable joints. There are four types of movable joints in our body—hinge joint, ball and socket joint, pivot joint and gliding joint. Let’s discuss about each of them in detail.
Observe the direction in which the door of your room opens. Does it open only in one direction? See the movement at its hinges (the piece of metal that joins its edges). A hinge joint allows the movement of bones only in one direction. Bones of the elbows, knees, toes and fingers have hinge joints. Hinge joint

A ball-shaped end of one bone fits into the cup-shaped end of the other bone. It allows movement in many directions. Our shoulders and hips have ball and socket joints.
The pivot joint allows up, down, and side-to-side movement. It is found in our neck.
A gliding joint allows two flat bones to move past each other in any direction. The wrists and ankles have gliding joints.



Sit on a chair. Your feet should touch the ground. Now move your knees in all possible directions. Now do the same for your shoulders. Which one of these moves in all directions? Which one moves only in one direction?

Immovable joints do not allow any movement. The bones at these joints are fixed and therefore they are also called fixed joints. The joints between the bones of the skull are immovable joints. They do not have cartilage between the bones. Fixed joints

Aim: To know the joints used to do various actions.
Materials Needed: a paper, a pen, a book lying on the floor and a football Method:
Step 1: Get into groups of five.
Step 2: One student in the group to perform certain actions such as nodding, moving their head in right and left directions, lifting a book from the floor, rotating an arm, or kicking a football.
Step 3: Other students in the group will identify the joint that is being used for that action. Observe the type of movement that joint allows. Record the observations in your notebook.

1. Nodding: Pivot joint; allows up-down movement of the neck
2. Moving the head right and left: Pivot joint; allows turning the neck
3. Rotate your arm: Ball and socket joint;
4. Kick a football:
Conclusion: Joints allow movements of body parts. The range of allowed movements differs for different joints.
Muscles are the tissues that connects two bones. They are attached to the bones by strong tissues called tendons. Our body has about 650 muscles. There are three types of muscles in our body: voluntary, involuntary and cardiac muscles.
The muscles of our body make up the muscular system.
We can control the movement of voluntary muscles. Voluntary muscles are also called skeletal muscles as they are joined to our bones. They have bands or stripes and are also called striped muscles. The muscles of our arms and legs are voluntary muscles.
We cannot control the movements of involuntary muscles. These muscles do not have stripes on them. So, they are also called smooth muscles. The muscles in our digestive system are smooth muscles.
The muscles in the heart are cardiac muscles. Even though the cardiac muscles are striped, yet they are not voluntary muscles. They work continuously on their own without stopping even for a second.




Read these statements on voluntary muscles. Write T for true and F for false.
1. They are also called smooth muscles.
2. They work automatically.
3. They are present in the heart.
4. They are striped.
Yoga originated in India around 5,000 years ago. Maharishi Patanjali is popularly known as the ‘Father of Yoga’. He wrote a book Yoga-sutra, which talks about the different aspects of yoga. Today, 21 June is celebrated all over the world as Yoga Day.
bones: hard structures that make our skeleton system
bone marrow: the jelly-like material in bones
skull: the framework of the head which protects the brain from injuries vertebrae: small bones that make the spine joints: the places where two or more bones join ligaments: strong tissues that join the bones at joints cartilage: a tough elastic tissue at the surface of bones of movable joints tendons: strong tissues that join muscles to bones


Scan the QR code to know more about the skeletal system.
• The skeletal system protects the internal organs, gives the body a shape and helps in movement.
• The human skeletal system is made up of the skull, spine, ribcage and limbs.
• Joints allow the movement of body parts. These can be movable or immovable.
• Muscles in our body are involuntary, voluntary and cardiac.

1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. The organ system made of bones is
Skeletal system
Digestive system
Muscular system
Circulatory system
B. Which of the following is not a part of the skeletal system?
skull spine ribcage cardiac muscles
C. The number of bones in our skull is 12 22 8 33
D. The only movable bone of our skull is in the head upper jaw lower jaw collar bone
2. Fill in the blanks. cartilage ligaments ribs floating vertebrae
A. Our spine is made of small bones called .
B. The ribcage is made up 12 pairs of .
C. The ribs that are attached only to the spine are called ribs.
D. The bones are held together at the joints by strong tissues called .
E. is a tough elastic tissue that prevents the bones from rubbing against each other at the joints.
3. Write True or False.
A. The ribcage protects the heart and lungs.
B. The breastbone is also called the sternum.
C. Our spine has a total of 23 bones.
D. Our body has around 200 muscles.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. What are the functions of the skeletal system in our body?
B. What is the significance of bone marrow in our body?


C. Why is the spine important?
D. Where are immovable joints located in our body?
E. How are forelimbs different from hindlimbs?
5. Long-answer questions.
A. Describe the structure of a bone with the help of a diagram.
B. Explain the different types of joints with an example of each.
C. Differentiate between the different types of muscles. Draw their diagrams.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. Name the type of muscle marked as A.
B. Name the type of muscle marked as B.
C. Which of these muscles is involuntary?

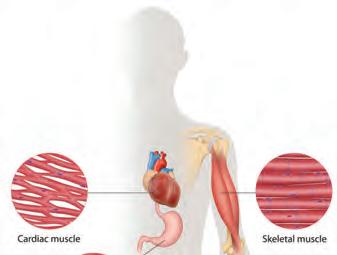
What would have happened if the muscles in our limbs were involuntary muscles?





Complete the following to find out the names of various organ systems.
1. This system provides shape and structure to our body.
S L T YS M
2. This system breaks down food and absorbs it.
D ES VE S T
3. This system consists of the nose, windpipe and lungs.
R S R T RY Y T
4. This system comprises of the heart, blood and the blood vessels.
I C L OR S S M
The brain, the spinal cord and the nerves constitute our nervous system. It is responsible for things like sensing and responding to stimuli. Let us learn more about our nervous system.
An organ system consists of a group of organs that work together to perform specific functions in our body.
The brain acts as the control centre of our body. It is located in the head and is protected by the skull. It sends and receives information from all the parts of the body, through a network of nerves. The brain is further divided into three parts—cerebrum, cerebellum and medulla. Let us learn about them.
Brain Spinal cord
Nerves
Human nervous system
Cerebrum
Medulla
It is the largest part of our brain. It is the in-charge of our sense organs. It gives us the capacity to think, talk, remember, recall and learn.
This part of the brain is located at the back, below the cerebrum. It enables us to maintain the balance of our body, its movement and muscle coordination. Without the cerebellum, we won’t be able to stand or walk properly.
Cerebellum
Human brain
What would happen to our body movements if the cerebrum is damaged?
It is a stem-like structure which lies at the bottom of the brain. Due to its structure, it is also known as the brain stem. It connects the brain and spinal cord. It controls involuntary activities, like digestion, blood circulation and breathing. This part of the brain keeps working, even when we are asleep.
coordination: working together smoothly and efficiently involuntary: an action done without one’s own choice

Make a list of any ten things that we continue doing even in sleep and ten things that we have to stop doing when we sleep. Write them a table as shown below.
Activities
Continue while sleeping Stop while sleeping
Name the following.
1. The part of the nervous system that is the control centre of the body.
2. The part of the brain that connects the brain to the spinal cord.
3. The part of the brain that helps us to maintain the body balance.
4. The largest part of the brain.
The spinal cord is a tube-like structure that extends from the medulla to the lower end of the spine. It is surrounded by the bony vertebral column. The spinal cord connects the brain to the remaining parts of the body through nerves. It also transmits information between the brain and other body parts.
The spinal cord controls some automatic and involuntary actions that do not involve the brain. Such actions are known as reflex actions. For example, when we step on something pointed by mistake, we immediately pull our feet away due to a reflex action. Some other examples of reflex action are the blinking of eyes and watering in the mouth when looking at tasty food.
transmit: to send something from one place to another
Brain
Cerebellum
Spinal cord
Nerves
Nerves are long, thread-like structures that transmit messages between the brain or spinal cord and other parts of the body. The nerves in the head and neck connect to the brain, while nerves from the rest of the body connect to the spinal cord. There are three types of nerves in our body: sensory nerves, motor nerves and mixed nerves. Let us learn about each of them.
Sensory nerves carry messages from the sense organs of our body to the brain and spinal cord. These nerves help us sense the world around us. For example, when you touch something hot, the sensory nerves in your skin send a message to your brain, letting you know that it is hot.
Motor nerves carry messages from the brain and the spinal cord to the muscles in the body. These messages tell the muscles to move. For example, when you decide to pick up a book, motor nerves send a signal from your brain to your hand muscles to make them move.
Mixed nerves have both sensory and motor nerves. This means they perform both sensory and motor functions. These nerves can carry messages to the brain or the spinal cord to other body parts and vice-versa. Mixed nerves help coordinate many activities in the body by sending and receiving messages.
Our sense organs are special organs in our body that help us experience the world around us. They allow us to see, hear, smell, taste, and feel. These organs collect and send information to our nervous system through sensory nerves. Our brain further processes the information and lets us know about what are we experiencing through

our sense organs. There are five sense organs in our body—eyes, ears, nose, tongue and skin. Let’s learn about them.
Eyes help us see different things around us. They are very sensitive organs. Therefore, these are protected by eyelids and eyelashes from dust, dirt and bright light. Our eyes are complex organs and have many parts. Let us learn about them.
Cornea: It is a thin transparent layer that covers and protects the front part of the eye.
Iris: It is the round and coloured part that lies behind the corner of the eye. It can be blue, black, brown or grey.
The lens: The transparent part of the iris. It is located behind the iris.
Pupil: It is the black spot in the centre of the eye that lets light in.
Retina: It is a thin lining present at the back of the eye. It is like a screen. The retina is connected to the brain through optic nerves. These nerves send signals to the brain, which then interprets the signals as images.
The size of the pupil depends on the brightness of light entering our eyes. The pupil becomes bigger in dim or low light. On the other hand, the pupil becomes smaller in bright light.
Our ears allow us to hear sounds. Each ear is divided into three parts: the outer, middle and inner ear.
The outer and visible part of the ear is called the pinna. It receives sound and directs it to the eardrum through the ear canal. The eardrum is located in the middle ear.
The middle ear is composed of three small bones, including the eardrum, that transmit sound waves to the inner ear.
The inner ear converts these sound waves into nerve signals and sends them to the brain via the auditory nerve. The brain then interprets these nerve signals, allowing us to hear different sounds.
interpret: to understand information auditory: related to hearing
The tongue helps us speak, and taste a variety of food. The surface of our tongue is covered with many taste buds. The taste buds send signals to the brain, which then interprets these signals as different tastes. Our taste buds can detect four major tastes: sweet, sour, salty and bitter.
How would it be if we had no taste buds present on our tongue? Discuss with your classmates.
Our nose helps us smell and breathe. It has two openings called nostrils. Inside the nostrils, tiny hairs and mucus trap dust particles. Our nose has special nerve cells that detect different smells and send messages to the brain. The brain then interprets these messages, allowing us to recognise what we are smelling.
Tongue

The skin is our largest sense organ. There are many nerve endings in the skin that help us feel touch and sensations like hotness, coldness and pain. The skin has different types of receptors that detect different sensations. Our skin also has pores on its surface that allow body waste to exit as sweat. Besides protecting our internal organs, our skin also helps to regulate body temperature.

Experiment: To demonstrate how the tongue helps us identify different tastes.
Materials Needed: Food items cut into pieces (apple, cucumber, carrot, mango, peach, pear, lemon) and a blindfold
Step 1: You can do this experiment with a friend or a family member. Arrange the different food items on a table.
Step 2: Ask your friend or the family member to volunteer to be blindfolded. Then, let him/her taste one item at a time. Make sure you give the person enough time to taste the item properly.
Step 3: Ask him/her to guess the taste of the food item and then its name.
recognise: to identify sensation: a type of feeling

Step 4: You can volunteer to be blindfolded and taste a different set of food items.
Findings: We can identify the taste of different food items without actually seeing what food it is.
Conclusion: Our tongue helps us taste various food items.
Tip: Please arrange different food items per their availability.

Our sense organs are essential for experiencing the world around us. They help us see, hear, smell, taste and feel. It’s important to take good care of them for their proper functioning. Here are some tips on how to take care of each of our five sense organs.
Eyes
• Avoid staring at screens for too long. Take breaks every 20 minutes to rest your eyes.
• Maintain a proper distance while watching computer screens or TV.
• Avoid reading in dim lights or while travelling when the book.
• Don’t touch your eyes with dirty hands. Wash your hands before touching your eyes.
Ears
• Clean the outer part of your ears with a damp cloth.
• Never put sharp objects inside your ears.
• Don’t listen to loud music for too long. Plug your ears with your fingers if you are in a noisy place.
• If you have trouble hearing, visit a doctor as soon as possible.
Nose
• Gently blow your nose to clear out mucus and dust. Don’t pick your nose.
• Stay away from strong chemicals and smoke that can irritate your nose.
Tongue
• Always clean your tongue using a tongue cleaner.
• Don’t eat foods which are too hot as they can burn your tongue.
Skin
• Bathe regularly with mild soap and water to remove dirt and sweat.
• Always wear clean and washed clothes.
• Eat raw fruits and vegetables and plenty of water to keep your skin healthy.
• Keep any open cut or wound away from dust and dirt and ask an adult to put an antiseptic cream on it.
damp: slightly wet or moist




The Garden of Five Senses in Delhi is designed to stimulate all our sense organs through visually appealing flowers, fragrant plants, and different textures to touch. It also offers sounds from nature, creating a joyful experience that engages our sight, smell, touch, hearing and taste.
nerves: long thread-like structures that carry messages between the brain, spinal cord and the other parts of the body reflex actions: involuntary actions that are automatic and in which the brain is not involved nostrils: two openings present on the nose receptors: special cells in our body that detect and respond to different types of signals, like light, sound or touch lens: the transparent part of the iris

Scan the QR code to know more about brain.
• The nervous system comprises the brain, spinal cord and nerves.
• The brain is the control centre of the body.
• The spinal cord is a tube like structure consisting of nerves that runs from the brain to the lower spine, transmitting information between the brain and the body.
• Nerves are thread-like structures that carry messages between the brain, spinal cord and the body.
• Sense organs help us experience the world. There are five sense organs in our body—eyes (seeing), ears (hearing), nose (smelling), tongue (tasting) and skin (feeling).

1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Where is the brain located and how is it protected?
In the chest, protected by ribs
In the head, protected by the skull
In the abdomen, protected by muscles
In the neck, protected by bones.
B. What is the function of motor nerves?
Carry messages from the body to the brain
Carry messages from the brain to the body
Carry messages from the brain to the spinal cord
Control movement of the body parts
C. What do our sense organs help us do?
Move our muscles
Experience the world around us
Digest food
Grow
D. What is the function of the nose besides smelling?
Tasting Hearing
Breathing Seeing
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. The connects the brain to the remaining parts of the body through nerves.
B. nerves carry messages from the sense organs to the brain and spinal cord.

C. nerves carry messages from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles in the body.
D. The surface of our tongue is covered with many buds that detect different tastes.
3. Write True or False.
A. The cerebellum is the largest part of the brain.
B. There are only two types of nerves in our body.
C. Mixed nerves have both sensory and motor nerves.
D. The spinal cord transmits information between the brain and other body parts.
4. Match the following.
A. eyes
B. ears
C. nose
D. skin
E. tongue
5. Short-answer questions.
A. Why is the nervous system important?
i. sight
ii. taste
iii. smell
iv. sensation
v. hearing
B. How are sensory nerves different from motor nerves?
C. Write two ways to take care of your skin.
D. Which part of the nervous system is responsible for reflex actions?
E. Name and describe three parts of the eye.
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Describe the main parts of the brain. Mention the function of each part.
B. Describe reflex action with an example.
C. Explain how motor nerves help us move our muscles with the help of an example.
D. Draw and describe the three parts of the ear and their functions.


7. Picture-based questions.
A. What is shown in the image?
B. Label the parts in the image.
C. Mention the function of the part labelled as 2.

Which parts of the nervous system work together to make us wake up in the morning?
Think about a friend you know who might have trouble seeing or hearing well. List some activities where this friend might find it hard to do things because of their vision or hearing issues. Write down some ideas on how you can help this friend make these activities easier for them. Offer to help your friend and share your ideas with others to encourage them to be supportive too.


Safety and First Aid

Importance of Safety Safety on Roads First Aid
Safety at Home

Get Set

Solve the following riddles.
I am in your car and keep you tight, If there’s a sudden stop, I hold you right. Put me on before you start, For safety’s sake, I’m a crucial part.
What am I?
I protect your head and keep it sound. When you’re riding your bike around Strap me on before you go. For safety first, that’s what you should know.
What am I?

We should always be alert and aware to decrease the chances of accidents. An accident is an unexpected event that causes harm, injury or damage. Accidents can occur if we are not cautious. To prevent accidents and ensure our safety, it is important to follow certain safety rules. Let us learn more about them in this chapter.
• Always cross the road at the zebra crossing. Look both ways before crossing the street.
• Do not run up or down the staircase.
• Do not play with sharp objects, fire, electrical appliances.
• Whenever there is an accident, help the injured. Don’t panic in such situations.

Use zebra crossing to cross roads.
Imagine you are responsible for creating a safety plan for a school field trip. What are the key safety measures that you would include?
We spend a lot of time at home, so it is very important to follow safety rules to stay safe. Let us discuss different situations where we need to be cautious while at home.
Have you ever seen anyone cutting fruits and vegetables with a knife? They always cut them very carefully to avoid any injury.
To stay safe while handling sharp objects, follow the following rules:

• If you are carrying scissors, keep the sharp sides pointing downwards. Use sharp objects under adult supervision.
alert: fully aware cautious: being careful
• Never run while holding a sharp object.
• Keep all sharp objects away from children.
• Be careful with your fingers when using a knife. Do it under adult supervision only.
We need to be careful while using electrical appliances. To be safe around such appliances, follow these rules:
• Do not use electrical appliances with wet hands.
• Always operate them under adult supervision.
• Wear rubber slippers when handling them.
• Avoid plugging too many devices into a single socket, as it may lead to a short circuit and cause a fire.

Sharad noticed a peculiar smell coming from the gas stove. He quickly called his father. His father asked Sharad to stay away and quickly turned the gas cylinder off.
The gas cylinders have an added smell in them that makes the detection of gas leaks easy. In case of a gas leak, follow the steps mentioned below.
• Warn everyone in the house about the leak.

• Open all the doors and windows to let the smell out.
• Don’t operate any electrical appliances, as these can produce sparks.
• Call the gas company or mechanic immediately to repair the leak.
In case of a fire, follow the steps given below:
• Inform an adult and immediately call the fire brigade.
• If the fire is at a plug point, do not throw water on it. Either use the fire extinguisher or sand.

Use a fire extinguisher to control fire. supervision: monitoring of someone over an activity peculiar: strange

• If the fire is due to oil or petrol, again, use the fire extinguisher instead of water.
• If the fire is out of control, immediately evacuate that area.
We use chemicals, like detergents and disinfectants, in our homes. Some chemicals, like vinegar and baking soda, are also used in cooking. We also keep medicines at home for emergencies. To stay safe around these things, follow these rules:
• Always keep chemicals and medicines out of the reach of children.
• Take all medicines only under adult supervision.

Wear gloves while using chemicals.
• Always wear gloves while handling chemicals like disinfectants and floor cleaners.
• Wash your hands thoroughly after handling chemicals, even if you were wearing gloves.
• Seek medical help immediately if you accidentally swallow chemicals or get them in your eyes.

Nowadays, the internet plays a crucial role in our daily lives, including helping with homework and projects. However, it is essential to follow certain guidelines to ensure online safety.
• Never share your personal details online without your parents’ permission.
• Create strong, unique passwords for your online accounts and don’t share them with anyone.
• Only chat with people you know in real life.
• Spend a balanced period of time online.
Tick ( ) the correct statement about internet safety.
1. We should share our personal details with an unknown person.
2. We should spend a balanced period of time online.
3. We should share passwords with everyone.
4. We should chat with everyone.
evacuate: to leave an area urgently unique: different from others

Ravi is riding his bike on the footpath. He has a helmet on to protect his head. As he rides, he makes sure to stay on the footpath and look both ways before crossing the lane. Why is it essential to wear a helmet? A helmet helps to protect your head if you fall or bump into something. Without it, Ravi could hurt himself more easily. Wearing a helmet keeps you safe while riding your bike! Let us learn more about road safety.
To be safe on roads, follow these rules:

Always wear helmet while riding bicycle.
• Look left and right before crossing. Wait for the traffic to come to a complete stop before crossing.
• Obey traffic signals and road signs. Green means go, red means stop and yellow means prepare to stop.
• Don’t jump off or get on moving vehicles.
• Never stick your hands or face out of a moving vehicle.
• Don’t play near roads. Play in parks or playgrounds instead.

Many think only drivers need to follow traffic rules, but that’s not true. Cyclists and pedestrians must also follow road-crossing rules. Error Alert!
Make some posters showing road signs for display in your classroom. You can discuss their importance with your teachers, school bus drivers and your parents.
Since accidents can happen anywhere and anytime, it is wise to know what to do during an emergency. First aid is the immediate help given to someone who is hurt or sick before a doctor can attend to it.
The following first-aid measures should be taken in case of a cut or wound.

Never keep your body parts out of the moving vehicle.


• Cuts and wounds can happen at any time, and knowing how to provide first aid is essential for proper care and healing.
• Never ignore a wound, no matter how small it seems. Keep hygiene in mind when giving first aid, as germs can easily enter through cuts.
An ice pack is a bag filled with ice or a cold substance used to reduce swelling and pain from injuries.
• Wash your hands with soap and water before treating a wound.
• Clean the wound with water, soap, and antiseptic lotion.
• Cover it with a bandage to prevent infection and control bleeding.
• If the bleeding continues, apply a tight bandage above the wound to reduce heavy bleeding.
• For deep wounds, take the person to a doctor immediately, as stitches may be needed. If the cut is from a rusty object, an anti-tetanus injection may be necessary to prevent tetanus.
Burns can be caused by touching something hot, like a stove or a flame, hot liquids like boiling water or steam and chemicals.
• If a person’s clothes catch fire, tell them to lie down and roll on the ground to extinguish the flames, as fire spreads upward.
For minor burns, run cool water over it
• Wrap the person in a blanket to cut off the air supply and put out the fire.
• The person should not run, as this will fan the flames and make the fire spread.
• Do not apply ointment or cream to burns.
• For minor burns, run cool water over it. Apply an antiseptic cream over the burn.
• For serious burns, cover the area with sterile gauze and a loose bandage.
• Avoid puncturing any blisters.
A fracture occurs when there is a crack in the bone. Use a splint to prevent the moving of the fractured part. Seek medical help immediately.
A sprain indicates an injury to the ligament. A ligament is the tissue connecting the bones at the joints. When a ligament is torn or stretched, it causes sprain. This usually occurs due to falling or twisting.

Use a splint in case of a fracture.
blister: small bubble formed on the skin due to burns (usually have water in it) splint: a stiff support used to keep broken bone in place
• Keep the injured joint still to avoid any other injury.
• Apply an ice pack over the injured area to reduce swelling. Keep it on for at least 15 minutes.
• Wrap the injured part with an elastic bandage to provide support.
• Raise the injured part above the level of the heart to reduce swelling.
On hot, dry days, a nosebleed may occur when tiny blood vessels in the nose burst. The following first-aid measures should be taken in case of a nose bleed:
• Loosen clothing around the neck.
• Have the person sit upright with their head slightly forward.
• Pinch the bleeding side of the nose and ask the person to breathe through their mouth.
• Apply an ice pack or wet cloth to the nose and neck.


• Advise the person not to blow their nose for a few hours after the bleeding stops.
• If the bleeding is heavy, consult a doctor immediately.
Dehydration happens when your body loses more water than it takes in. This can happen if you don’t drink enough water, especially on hot days or after lots of exercise. Signs of dehydration include feeling thirsty, tired, dizzy, or having a dry mouth.
• Give the person small sips of water or an oral rehydration solution (ORS) to drink.
• Move the person to a cool, shaded area to rest.
• If the person feels very weak or dizzy, seek medical help immediately.
Insect bites or stings can be very painful. It can cause redness, swelling and itching in the affected area.
• Wash the bite area with soap and water. Use an antiseptic lotion over the infected area. Remove the insect sting with the help of a tweezer.
• For a bee sting, apply toothpaste or sting relief cream over the bite area.






For a snake bite, tightly tie a cloth above the bite area. This will prevent bleeding and the spreading of poison in the body. Seek medical help immediately.
Traditional remedies, such as using Neem leaves for insect bites, are helpful for first aid. Neem has antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties that can reduce itching and prevent infection. It is still commonly used as a natural solution for insect bites.

first aid: the immediate help given to someone who is hurt or sick before a doctor can take over fracture: a crack in the bone sprain: when a ligament gets torn or stretched, it causes sprains

Scan the QR code to know more about first aid.
• Accidents can happen with anyone and at any time.
• We should always be alert and aware to prevent accidents.
• In case of accidents, first aid measures should be followed.
• Stay calm and help the patient in case of an accident till the doctor arrives.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What should you do if you burn yourself slightly?
Apply ice directly on the burn
Cover it with a heavy cloth
Run cool (not cold) water over the burn
Pop any blisters that form

B. Why is it important to wear a helmet while riding a bicycle?
To look fashionable
To protect your head in case of an accident
To ride faster
To keep your hair in place
C. When crossing the road, what should you always do?
Run quickly across Look left and right first Cross at any point you like Follow the car ahead of you
D. Which of the following is a sign of dehydration?
Sweating Increased urination
Dizziness
2. Fill in the blanks.
Feeling energetic
A. An is an unexpected event that causes harm, injury or damage.
B. A is a break or crack in the bone.
C. happens when our body loses more water than it takes in.
D. Use creams to prevent infection.
3. Write True or False.
A. You should perform first aid before calling for medical help in an emergency.
B. Pedestrians should follow traffic signals, just like vehicles.
C. Leaning your head back is the best way to stop a nosebleed.
D. It’s okay to ignore an insect bite and not wash the area.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. Write any two ways to stay safe on the road.
B. What should be done in case of a kitchen fire?
C. Mention the first aid to be given in case of dehydration.
D. How can you help someone with an insect bite?
E. Write two ways that you should follow for internet safety.


5. Long-answer questions.
A. What is an accident? Why should we follow safety rules?
B. How would you provide help to a person with a nosebleed?
C. What precautions should you take when handling medicines and chemicals?
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What kind of an accident is shown in the given image?
B. Mention the first aid to be given in this case.


If a family member gets a deep cut while using a sharp tool at home, what immediate actions would you take to stop the bleeding and prevent infection?
In small groups, choose a common household accident, such as burns, cuts, or electric shocks. Each group will act out how to give first aid for that situation and follow safety rules. After the role-play, discuss how to prevent such accidents and why staying calm is important during emergencies. This activity helps everyone understand the steps needed to stay safe and handle emergencies at home.






Solve the following riddles.
I am round with many layers, not a fruit or a treat. I spin through space, yet you stand on your feet.
What am I?
I have no colour, but I am everywhere, I fill the oceans and float in the air.
What am I?
It was a regular school day, and Siya was enjoying her science class. Then, it started raining heavily, and the rain kept getting stronger. The principal announced that school would end early because of flooding in many places. Siya wanted to learn more about flooding, so she asked her teacher. The teacher explained to her that flooding is a type of natural calamity. Let us learn more about natural calamities. A natural calamity is a sudden event caused by natural forces that can cause a lot of damage to the environment, life and property.

Some common natural calamities are earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis, floods, cyclones and droughts. Let us learn about each of them in detail.
An earthquake occurs when the ground shakes suddenly. Earthquake is also called as tremor or quake.
An earthquake is a sudden shaking of the Earth’s surface caused by movements within the Earth. The Earth’s crust consists of large and small rock plates called tectonic plates that move slowly past each other. Sometimes, these plates pull apart, collide, or slide under one another, causing vibrations that result in earthquakes. They can range from mild to severe, leading to significant damage to life and property.

The point on the Earth’s surface directly above where the earthquake starts is called the epicenter, which feels the strongest effects. The focus is the point below the ground at which the earthquake originates. Aftershocks are smaller tremors that may occur within a few days after the main quake as the rocks settle back into place.
Earthquakes are measured with a seismograph, and their intensity is recorded on the Richter scale. Richter scale was developed by Charles Richter in 1935. Earthquakes rated between 6 and 8 on this scale can cause major destruction, with the extent of damage depending on the earthquake’s location and intensity. A value of 1 on the Richter scale indicates a minor earthquake.
• An earthquake can cause the ground to vibrate and shake which leads to the collapsing of buildings, roads and bridges.
• Many people lose their lives as they get trapped under the collapsing buildings.
• The shaking ground during an earthquake can crack gas pipes, leading to fires. This results in more damage to the people and buildings.
intensity: strength or force of something


Effects of earthquake

• If you are indoors, cover your head and neck with your arms. Take shelter under a sturdy piece of furniture, like a table or desk.
• If you are outside, stay away from tall buildings, trees and power lines. Move to an open space such as a field or park.
• If you are inside a tall building, evacuate it as soon as possible.

Take shelter under a piece of furniture.
• Do not use elevators during an earthquake as they may get stuck or malfunction. Instead, take the stairs.
Gather information about the Bhuj earthquake that occurred in 2001. You may take help of the internet or an adult. Make a report of it in your scrapbook. Collect and paste pictures and news clippings related to this disaster to make your report more informative.
Name the following.
Discuss how families and schools can prepare for an earthquake. What should be included in an emergency kit? Where are the safest places to take cover?
1. Instrument used to measure the intensity of an earthquake.
2. Scientists who study and observe earthquakes.
3. Small tremors felt after the earthquake.
4. Large plates of rocks that make up the earth’s crust.
Volcano
A volcano is an opening in the earth’s surface through which molten rock called magma comes out . When this magma reaches the earth’s surface, it is called lava. It comes from the inner layers of the earth and reaches the outer layer through cracks. Eruptions happen when pressure builds up inside the earth. Eruption of volcanoes can cause a lot of damage to life and property. It is difficult to control such type of natural calamity.
sturdy: strong; malfunction: to function incorrectly; magma: hot, melted rock found beneath the Earth’s surface; lava: hot, melted rock that comes out of a volcano during an eruption; eruptions: sudden explosion

Active volcano: These volcanoes can erupt at any time or have erupted recently. For example, Barren Island in Andaman and Nicobar islands, Mount Vesuvius and Mount Fuji.
Dormant volcano: A volcano that has not erupted in recent years but can erupt in the near future is known as a dormant volcano. For example, Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania and Mauna Kea in Hawaii.


Extinct volcano: Volcanoes that have stopped erupting and have no chances of erupting in the future are known as extinct volcanoes. For example, Mount Popa in Myanmar and Zuidwal volcano in the Netherlands.
Tides are the regular rise and fall of sea levels caused by the pull of the moon and the sun. When the Sun, the Moon, and Earth are in a straight line, tides can be higher than usual. Tidal waves can occur due to storms or earthquakes.


Tsunamis are very large waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions. The term “tsunami” means “harbor wave” in Japanese and is often confused with tidal waves. When a tsunami occurs, the waves can travel in all directions and can reach heights of up to 100 feet when they reach the shore, causing massive destruction in seconds.
While tidal waves and tsunamis cannot be controlled, people can be advised to move to higher ground for safety. Many coastal areas have tsunami warning centers that help alert residents about potential tsunamis.
The Indian Ocean tsunami was triggered by a massive undersea earthquake off the coast of Sumatra, Indonesia, on December 26, 2004. The tsunami measured 9.1 on the Richter scale. Sri Lanka, India, Maldives, Somalia and Thailand were the countries affected by the tsunami.
Floods happen when a river overflows its banks. Heavy rainfall is the major cause of floods. When air pressure in coastal areas changes, it causes sudden strong storms. These are called cyclones, typhoons, hurricanes or tropical storms, depending on their locations.

These storms bring heavy rain, strong winds and can cause big waves. These can be dangerous and affect coastal areas, causing damage to homes, trees and sometimes flooding.
• Both these disasters cause damage to life and property.
• Floods wash away the crops and destroy them.
• Floods result in water logging, which affects traffic movements and causes diseases such as cholera, dengue, typhoid and malaria.
Preventive
• Floods can be prevented by building, checking and maintaining dams regularly.
• We should construct raised embankments or bunds near residential areas to prevent the overflow of water.
• We should plant trees along river banks to avoid the overflow of water.


• To prepare for cyclones, early warning system that alerts coastal areas about approaching storms should be maintained.:

Aim: To show how flooding affects different surfaces.
Materials Needed: Two trays, soil, stones or grass (for one tray), water, and a watering can or cup.
Method:
Step 1: Fill both trays with soil. In one tray, add stones or grass on top of the soil. Leave the other tray with just soil.
Step 2: Slowly pour water over both trays to depict heavy rain or a flood.
water logging: collection of too much water on the ground embankments: raised barrier or mound built to prevent flooding or support roads and railways

Step 3: Observe how the water affects both trays.
Findings: The tray with only soil shows more erosion and water runoff. The tray with stones or grass shows less soil movement and more water absorption.
Conclusion: Natural coverings like grasses and stones help reduce the effects of floods by preventing soil erosion and controlling water flow. This shows how important it is to protect the environment to reduce the impact of floods.
A drought occurs when a region receives little to no rainfall for an extended period, sometimes lasting for years. This leads to higher temperatures and shortages of food and water.
Effects of Drought
• It dries up water bodies, making it difficult to grow crops. This causes great problems for farmers and other people.
• If drought lasts for a longer period of time, famines can occur due to food shortage. Deforestation can reduce rainfall and create drought-like conditions. In India, regions such as eastern and southern Maharashtra, northern Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Gujarat, Telangana, and Rajasthan are prone to drought.
Preventive Measures
• Plant more and more trees in our surroundings.
• Save water by using it wisely at home and in agriculture.
• Planting crops that need less water to grow.

• Communities can also build reservoirs to store water during rainy seasons to use during dry periods. This practice is called rainwater harvesting.
A common misconception about droughts is that they are just short periods without rain. In reality, droughts can last for months or even years, severely impacting water availability.
By studying how natural calamities like earthquakes, floods and droughts occur, we learn to ask important questions and find solutions to protect ourselves. This careful observation helps us better prepare for and respond to such events.
famines: extreme scarcity of food reservoirs: artificial lakes made to store water

Match the natural disasters with their respective causes.
Natural disasters Causes
1. Volcanoes
2. Earthquakes
3. Droughts
4. Floods
5. Tsunamis
A. Causes excessive shaking of the ground
B. Caused by eruption of molten lava
C. Caused by heavy rainfall
D. Caused by less rainfall and water scarcity
E. Caused by underwater earthquake
We cannot predict or control natural calamities. But we can be prepared beforehand for any such disaster. We should spread awareness about these calamities.
Although we cannot control the disasters from happening, we can help the victims in many ways. We can donate money, clothes, food items and other essential supplies to the disaster-affected people.
• Early Warning Systems: Use weather monitoring and forecasting to predict floods and cyclones early.
• Community Preparedness : Educate people about the risks of natural calamities and what to do in emergencies, such as conducting mock drills.
• Evacuation plans: This include taking measures to lead people out of danger and take them to safe places.
NGOs are Non-Governmental Organisations that provide help to victims. One of the well-known NGOs is the Red Cross society. Other organisations that work towards public welfare are WHO and UNICEF. Let us discuss how each of them helps the disaster-hit victims.
Human beings should help each other in times of crisis.


forecasting: guessing or predicting; emergencies: sudden and unexpected situations


1. Red Cross Society: It is an organisation that helps people in emergencies, like natural disasters or accidents. It provides food, shelter and medical care to those in need.
2. WHO (World Health Organization): They help countries by giving advice on how to prevent and treat diseases, and they also help during health emergencies like outbreaks of new diseases.
List any two ways in which you can help the disaster-hit victims.
3. UNICEF (United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund): It is an organisation that helps children all around the world. They work to make sure that every child has what they need to grow up healthy and happy.
The Sundarbans, located in the delta region of West Bengal, are the largest mangrove forests in the world. These mangroves act as a natural shield against natural calamities like cyclones. When a cyclone hits, the dense mangrove roots and trees help absorb the impact of strong winds and waves, reducing the damage to nearby areas. Sunderbans

natural calamity: a sudden event caused by natural forces that can cause widespread damage earthquake: the sudden and violent shaking of the ground epicenter: the point on the Earth’s surface directly above where the earthquake starts volcano: a mountain that erupts to let out to a pool of molten rock (magma) from below the Earth’s surface floods: a situation when too much water covers land

Scan the QR code to know more about natural disasters.
• Natural calamities can cause widespread destruction to the environment.
• Some of the common natural calamities include earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis, floods, cyclones and droughts.
• We can donate money, clothes and other essential stuff to the calamity-affected people.
• The government and the NGO’s play an important role in disaster management.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of these values on the Richter scale indicates a mild earthquake?
1 7 9 8
B. How many types of volcanoes are there?
Two Three Four Five
C. Which of these is a common effect of drought?
Flooding Water scarcity Strong winds Earthquakes
D. What should you do during an earthquake?
Run outside immediately.
Stand near windows.
Take cover under a sturdy piece of furniture.
Use the elevator to get to a higher floor.
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. The intensity of an earthquake is measured by an instrument called .
B. There are types of volcanoes in nature.
C. is a hot, melted rock found beneath the Earth’s surface.
D. can be prevented by building dams.
E. A is a huge ocean wave caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions.


3. Write True or False.
A. NGO’s do not have any role to play in dealing with calamities.
B. It is important to have early warning systems in place to deal with a natural calamity.
C. Active volcanoes can erupt at any time.
D. The Richter scale is used to measure the intensity of an earthquake.
E. We should use the elevator during an earthquake.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. What causes earthquakes?
B. How do we measure earthquakes?
C. How can we prevent floods?
D. What happens during a drought?
E. Name any three organisations that help disaster-hit victims.
5. Long-answer questions.
A. Explain different types of volcanoes with an example of each.
B. What are the preventive measures implemented by the government to deal with natural calamities?
C. What is a drought? Mention any two causes of droughts and two measure that can be taken to prevent droughts.
6. Picture-based questions.

A. Identify and name the natural calamity shown in the image.
B. What happens during this calamity?


Imagine you are part of a disaster management team in your town. Discuss three strategies you would propose to improve community preparedness for natural disasters like floods or earthquakes.
We can help people affected by natural calamities in many ways. Collecting and giving relief materials like food, water, and clothes is important. Organising fundraisers and donating money to trusted groups can support their recovery. Volunteering to help distribute supplies or offer shelter also makes a big difference. Raising awareness through social media and creating care packages with essentials like food and blankets can bring comfort to families in need. Together, we can help rebuild communities after a disaster.




Flower: A Reproductive Part
Growing Plants from Seeds
Growing Plants from Roots
Growing Plants from Stems
Growing Plants from Leaves Agriculture

Get Set

Write the names of these parts of a plant. Do you know their functions?



Look at the plants around you, you will see that some have flowers while others do not. Flowers often have bright colours and pleasant smell, and some of them eventually turn into fruits. Fruits such as apples, oranges and papaya, contain seeds inside. We plant seeds in the soil, and they then grow into new plants. However, some plants can be grown without seeds. Plants reproduce in two ways:
• through seeds
• through roots, stems and leaves

When you walk through a garden, the first thing that catches your eye is usually the colourful, fragrant flowers. Each flower is unique in size, shape, colour and scent. These flowers play a vital role in a plant’s life. They serve two purposes:
• To attract insects that aid in pollination

• To form seeds that will develop into new plants
Sepals: These are small, green, leaf-like structures which protect the flower when it is still a bud. Generally, sepals are green in colour.
Petals: These are brightly coloured and vary enormously in shape. The main function of the petals is to attract insects and birds to the flower.
Stamens: The stamen is located within the flower. It is the male reproductive part of the flower. Each stamen consists of a long filament with an anther at the top. The anther contains pollen grains.
Carpels: The carpel is the central part of the flower. It is also known as pistil. It is the female part of the flower contains a stigma, a style and an ovary. The style connects the stigma to the ovary, which contains one or more ovules that later become seeds.
Take a hibiscus or any other flower, carefully dissect it, and observe its different parts.

Plants reproduce in a fascinating way to create new life. One important process in this is seed formation, which involves several steps. Here is how seeds are formed:
• For a seed to form, pollen must travel from the anther to the pistil and then down to the ovary. You may have noticed insects feeding on flower nectar. As they do so, pollen grains from the anther stick to their bodies. When the insect moves to the stigma of a similar flower, the pollen grains transfer to the stigma. This process is called pollination. Insects are the main agents of pollination, helping to carry pollen from one flower to another.
• The stigma produces a sweet nectar that attracts insects. When insects land to drink nectar, they transfer the pollen on their bodies to the stigma. Once the pollen reaches the stigma, it forms a pollen tube that grows through the style to the ovary. The contents of the tube combine with the ovules, forming seeds.
• As this happens, the ovary swells and turns into a fruit, encasing the seeds inside. If the stigma does not receive pollen, the flower cannot reproduce, and will wither and die.
This process helps plants reproduce, continue their life cycle and maintain balance in nature.
Answer the following in one word.
1. It is the green leaf-like structure of a flower.
2. It is the colourful part of the flower that attracts insects.
3. It is the male part of the flower.
4. It is the female part of the flower.
encasing: as to cover or to enclose

Let us understand the structure of a seed and how it grows into a full-grown plant.
Seeds are found inside the fruit. The size, shape and structure of seeds of different plants vary considerably, but the basic structure of most the seeds is similar. A seed has three main parts—the seed coat, cotyledons (or seed leaves) and the embryo (or baby plant).
Seed Coat: The external covering of a seed is called the seed coat. It protects the baby plant that lies inside the seed.
Cotyledons or Seed Leaves: These store food for the growing embryo. Until the plant grows its own green leaves, it uses the food stored in the cotyledons to grow.
Embryo or Baby Plant: It is the baby plant that will turn into a seedling or a young plant.
Germination is the process by which a seed begins to grow into a seedling. For a seed to sprout, it needs to be planted in the right soil and provided with water, air and warmth. However, not all seeds turn into plants, as some are destroyed by rain, wind, insects, or birds, while others don’t get the right conditions to grow. The process of germination follows several stages:
• The seed is planted in soil and regularly watered while receiving air and warmth.
The Giant Sequoia Tree produces seeds that are so tiny they can weigh less than a grain of sand. Despite their small size, these seeds can grow into some of the largest trees on earth.


Stages of seed germination
• It absorbs water, causing the seed coat to break open.

• Once the seed coat breaks, a seedling emerges while drawing nutrients from the cotyledons initially before taking them from the soil.
• Tiny roots begin to grow along with a shoot.
• The seedling develops leaves and branches, eventually growing into a full plant.
Error Alert!
Be careful not to overwater your seeds when you plant them. Too much water can prevent air from reaching the seeds, stopping their growth.
Some seeds grow very close to each other and their parent plant, leading to competition for water, nutrients, light and space. This means that only a few seeds may survive while others perish. To improve their chances of survival, plants use various agents such as explosion, wind, water and animals to spread their seeds away from the parent plant. The process of scattering seeds away from the parent plant is known as seed dispersal. The following are some of the natural ways of seed dispersal:
• Dispersal by Wind: Seeds that are dispersed by the wind are small and light. Some examples include cotton and dandelion seeds which have tufts of hair, while maple seeds have wings to help them float in the air. Some other examples include drumstick and teak.
• Dispersal by Water: Plants near water disperse seeds and fruits through water. The examples include coconut seeds which have a fibrous covering that helps them float and lotus seeds which are found in spongy fruit that floats on water.
• Dispersal by Animals: Animals, birds and humans eat fleshy fruits like mangoes and discard the seeds, which can grow into new plants. Some seeds have hooks, spines or hairs that stick to animal fur or feathers and are carried to new places; examples include xanthium, tiger nail and spear grass.
• Dispersal by Explosion: Some plants like poppy, peas and beans have fruits that burst open when they are ripe and scatter seeds in all directions. This method of dispersal is called explosion.




perish: to die
Write True or False.
1. The seed coat is the internal covering of a seed.
2. Cotyledons store food for the growing embryo.
3. Seeds will germinate if it is too cold.
4. Mango seeds are dispersed by wind.
5. Animals do not play any role in seed dispersal.
Some plants can grow from their roots, without needing the seeds. For example, sweet potatoes, carrots, radishes, turnips and dahlias.

Aim: To observe and understand how a new plant can grow from the top of a carrot. Materials Needed: A fresh carrot with its top (about 2–3 cm), a small shallow dish or bowl, water, cotton balls or a small piece of sponge and a space for enough sunlight
Method:
Step 1: Take a fresh carrot and cut off the root part, leaving about 2–3 cm of the carrot attached to the green leafy top.
Step 2: Place a few cotton balls or a small piece of sponge in the shallow dish or bowl. Place the carrot top on the cotton balls or sponge, with the cut side facing down.
Step 3: Pour a small amount of water into the dish, enough to keep the cotton balls wet.
Step 4: Put the dish near a window where it can get plenty of sunlight.
Findings: Over the next few days, observe the carrot top for signs of new growth. The green leafy top should begin to grow taller, and small roots may start to develop at the bottom.
Conclusion: Some plants, like carrots, can grow from their roots.

Plants like potatoes, ginger and onions have underground stems. These stems have many buds that can grow into new plants when conditions are right.
The buds on a potato are called eyes. If you plant a piece of potato with an eye in moist soil, it will grow into a new plant in a few days. Plants such as lilies, tulips and chrysanthemums grow from underground stems called bulbs.

Some plants can be grown from stem cuttings. For example, rose, sugarcane and money plant can grow from a piece of the plant’s stem.
Growing a rose plant from stem cutting.
• Choose a healthy rose stem about 6–8 inches long. Cut it just below a leaf node and remove the lower leaves.
• Plant the cut end in a pot with moist soil.
• Place the pot in a bright spot (but not in direct sunlight) and keep the soil moist. After a few weeks, new leaves should appear, indicating the cutting has rooted and is growing.




Some plants have special leaves that develop buds along their edges. These leaves are thick and fleshy. For example, Bryophyllum and Begonia. In these plants, the buds along the leaf edges can grow into new plants.

Identify the part of the plant through which the following plants can reproduce.

Plants provide us with food, oxygen, medicine, timber and many other resources. We cultivate plants extensively to meet our needs. This large-scale cultivation of plants for food products and other uses is known as agriculture.
The plants that are cultivated in large amounts in a specific area are referred to as crops. There are different types of crops:
• Food Crops: These are grown for human consumption, such as rice, wheat and vegetables.
• Cash Crops: These are grown to sell, like cotton and coffee.

• Feed Crops: These are grown to feed animals, like corn and hay.
To grow healthy crops, farmers needs to work hard and take care of the plants throughout the year. Here are the steps to grow healthy crops:
Ploughing: The soil is turned and loosened to prepare it for planting seeds. The loose soil allows air and water to pass through.
Sowing: In this process, seeds are carefully planted in the soil.
extensively: in a large scale or quantity




Watering (Irrigation): Regular and measured watering of plants.
Adding Manure and Fertilisers: Crops need nutrients from the soil. Manures enrich the soil by adding humus, while fertilisers give specific nutrients to help plants grow strong.

Weeding

Weeding: Farmers remove unwanted plants, called weeds, from the field so they do not take the water and nutrients meant for the main crops.
Protecting Crops: Crops need protection from birds, insects, rats and pests. Farmers use scarecrows to keep birds away and spray pesticides to protect crops from insects and animals.

Harvesting

Protecting crops
Harvesting: When the crops are fully grown, farmers cut and collect them.
Storage: After harvesting, crops are safely stored to keep them fresh until they are used or sold.

manures: the waste matter from animals that is mixed with soil to make plants grow better fertiliser: a substance added to the soil to provide specific nutrients to the plants nutrients: substances that are needed to keep a living thing alive and to help it grow

India is the world’s largest producer of pulses and jute, and ranks as the second largest producer of rice, wheat, sugarcane, groundnut, vegetables, fruit and cotton.
pollination: the transfer of pollen from the male part to the female part in flowers embryo: the baby plant inside a seed germination: the process by which a seed grows into a new plant seed coat: the outer covering of a seed that protects it cotyledons (seed leaves): parts of a seed that store food for the baby plant dispersal: the process by which seeds are spread to new areas agriculture: the practice of growing plants on a large scale for food and other uses crops: plants grown in large quantities by farmers humus: decomposed plant and animal matter in the soil pesticides: chemical substances that are meant to kill insects that destroy crops harvesting: the process of gathering mature crops from the fields

Scan the QR code to learn more about reproduction in plants.
• Plants are living organisms that breathe, grow, produce food and reproduce.
• Flowers attract insects for pollination and form seeds for new plants.
• Plants reproduce through the process of pollination.
• Seeds need water, air and the right temperature to germinate into new plants.
• Seeds disperse through wind, water, animals or explosions to avoid overcrowding.
• Plants can also grow from roots, stems or leaves besides seeds.
• Farmers grow crops on a large scale to provide food and other materials.

1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What is the primary function of petals in a flower?
Protect the flower Store food Attract insects Disperse seeds
B. Which part of the seed stores food for the growing embryo?
Seed coat Cotyledons Embryo Root
C. The baby plant inside a seed is called the:
Seed coat Cotyledons Embryo Ovary
D. What do seeds need to germinate?
Light, soil and fertiliser
Only water and soil
Water, air and suitable temperature
Only sunlight
E. Seeds dispersed by animals often have: Wings Hooks or spines
Fibres to float in water The ability to explode out from the shell
F. Which of the following plants can grow from roots?
Rose Potato Carrot Mango
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. The external covering of a seed is called the .
B. The of a flower develops into a fruit.
C. store food for the growing embryo.
D. of some plants like sweet potatoes can grow into new plants.
E. Manures and fertilisers provide to crops.
3. Write True or False.
A. Sepals are usually brightly coloured.
B. Insects are main agents of pollination.
C. Seeds need both air and water to germinate.

D. Plants can grow from stem cuttings too.
E. Watering is necessary for crops to grow.
4. Short-answer questions.
A. Describe the process of pollination.
B. What conditions are necessary for seed germination?
C. What is the significance of seed dispersal?
D. How do seeds dispersed by water adapt to their environment?
E. How can a new plant grow from a stem cutting?
F. Why do farmers use fertilisers?
5. Long-answer questions.
A. Describe the structure of a seed and its parts.
B. Discuss the importance of seed dispersal and the different methods by which seeds are dispersed.
C. What are the main steps involved in agriculture? Write one line about each.
D. With the help of a labelled diagram, explain the structure of a flower.
6. Picture-based questions.
A. What do you think the bee is doing in the picture?
B. What is this process called?
C. What is the result of this process?



1. How would the absence of insects affect the reproduction of flowering plants?
2. What are the advantages of growing plants from roots instead of seeds? Provide examples of plants that can be grown this way.
Crops are important for our food supply, and farmers work very hard to cultivate them. They plant seeds, water the plants, and care of them until they are ready to be harvested. You can help your family and friends understand a farmer’s hard work, and the importance of not wasting food. Also, encourage your family to buy local and seasonal fruit and vegetables.

INTEGRATED


Habitat of Animals
Animal World
Feeding Habits of Animals
Adaptations in Animals Migration in Animals

Get Set

Help the animals find their homes.
Like us, animals also need food and shelter to survive. But how do animals survive against heat or cold? And how do different animals live in different places? We will find answers to these questions in this chapter.

The natural home of animals is called their habitat. Habitats provide food, water, shelter to animals. Several kinds of plants and animals live in the same habitat. For example, the ocean is a habitat because it is a natural home for various aquatic plants and fish.
Only the natural home of an animal can be called a habitat. For example, a zoo is not the habitat of a tiger because it is not its natural home.
There are different types of habitats such as forests, deserts, the polar regions, freshwater bodies (rivers, lakes and ponds), and oceans. Let us learn about them.
A forest is a large area covered with trees. They are important because they are home to many animals, they clean the air we breathe and offer us resources such as wood and paper.
Some animals that live in forests are elephants, tigers, leopards, baboons, foxes, wolves, snakes and bats. Many kinds of birds, like eagles, owls, kingfisher and mynas and peacocks live in forests.
A desert is an extremely dry area as it receives very little rainfall. Animals such as camels, scorpions, desert snakes and hedgehogs are found in deserts. These animals have thick skin to reduce water loss through sweating. Some find shelter in burrows to escape the heat, while others store water and food in their bodies. These adaptations enable them to survive in the harsh, water-scarce environment of the desert.


An area in a desert where water and plants can be found is called an oasis.
shelter: a place that protects from weather or danger resources: anything available in our environment that can be used to fulfil our needs
Polar regions refer to the areas near the north (Arctic) and south (Antarctica) poles of the Earth. These high-altitude regions are covered with ice and snow all year round. In the Southern Hemisphere, you can find animals like penguins, whales and seals, while the Northern Hemisphere is home to polar bears, Arctic foxes and Arctic hares. These animals have thick fur and a layer of fat underneath their skin to stay them warm.
A freshwater habitat is a naturally-occurring water body on the Earth’s surface. There, the water is not salty. Rivers, lakes, ponds and streams are some examples of freshwater habitats. Many animals live in freshwater. Some of these animals include catfish, trout, frogs, turtles, water snakes, ducks, kingfishers and swans.
An ocean is a huge body of saltwater that covers most of the Earth’s surface. Many animals live in oceans. Oceans are the largest habitats on Earth. Some of the animals found here are crabs, octopuses, whales, jellyfish, turtles, eels, angelfish, sharks and dolphins.
Name the following habitats.
1. A large area covered with trees.



2. A huge body of salty water that covers most of the Earth’s surface.
3. An area that remains covered with ice for most of the year.
4. A very dry place where hardly any rain falls.

We all know that our body needs energy to be alive, to grow and to perform various activities. We get this energy from the food we eat. If we do not eat food, we become weak and tired. We can even fall sick. Just like us, all animals also get energy from the food they eat. Animals can be grouped by what they eat. Some animals eat only plants, some eat only other animals and some eat both. This shows how different animals have different dietary habits.
Herbivores are animals that eat only plants. Their food includes leaves, grass, flowers, fruits, seeds and roots. They have a dental pad on the upper jaw and sharp front teeth, called incisors, on the lower jaw for biting. Their broad back teeth—molars and premolars, help them grind and chew their food. Some examples of herbivorous animals are deer, zebras, cows, sheep, horses, rabbits, elephants and giraffes.

We have learnt that herbivores eat plants and grass. They must grind their food into a paste before swallowing it, which requires strong, flat teeth. Have you ever seen how cows chew on grass? A cow’s mouth moves up and down to bite and from side to side to grind food easily.
Carnivores are animals that hunt and eat other animals. Some examples of carnivorous animals are foxes, wolves, lions, sharks, tigers, crocodiles, eagles, cats, frogs and snakes.
Carnivores have sharp canine teeth to tear meat, and strong molars to crush bones. Birds of prey such as eagles, have sharp, hooked beaks for tearing flesh. grind: to press and break something into very small pieces

Omnivores are animals that eat both plants and animals. Some examples of omnivorous animals are human beings, mice, bears, pigs and hens.
Omnivores have flat teeth at the back for grinding food and sharp teeth at the front for tearing it.
Scavengers feed on the flesh of animals that are already dead. They have sharp beaks or teeth to tear flesh. Examples of scavengers include vultures, jackals and hyenas.
Lice, ticks and fleas are parasites. They live on the body of another living being, and suck their blood for their food.
Match the following.

Column I Column II
A. Omnivores i. Sharp teeth
B. Carnivores ii. Flat and sharp teeth
C. Herbivores iii. Strong and flat teeth
A fish can live in water but a camel cannot. The features of a fish help it to live inside water, however, the features of a camel are best suited for survival in a desert. These features that plants and animals develop to survive in their natural habitats, such as seas and deserts, are called adaptations.
The different ways in which plants and animals adapt to their habitats include:
• Body Covering
• Breathing Organs
• Organs for Movement
Body Covering
One way animals adapt is through their body covering, which can include fur, feathers, scales, shells or skin. These coverings help animals stay safe, find food, and survive in different climates.


Fur: Polar bears have thick fur to keep them warm in the icy polar regions. Their fur is also water-resistant, helping them stay dry after swimming.
Feathers: Birds have feathers that help them fly, stay warm, and sometimes even help them blend into their surroundings. Penguins have waterproof feathers to keep them dry while swimming.


Scales: Fish have scales that protect their bodies and help them swim smoothly.
Shells: Turtles and snails have hard shells on their back that protect them from predators and harsh environmental conditions. They can pull their heads, legs and tails into their shells for safety.

A camel’s thick skin helps protect it from the hot sun in the desert. Camels can also close their nostrils to keep out the sand during sandstorms.
Animals live in different places, like water, land and air. They have special adaptations for breathing in each of these places. Let us learn how different animals have adapted their breathing organs to survive.
Animals such as fish, crabs and prawns breathe using gills. Gills are feather-like organs located in pouches on either side of the animal’s head that absorb oxygen from water.
water-resistant: to not allow water to pass through easily predator: an animal that kills and eats other animals
Reptiles, birds and mammals breathe using lungs. Humans are also mammals. Air enters through the nose and travels down the windpipe to the lungs where gas exchange occurs between air and blood.
Insects breathe through tiny openings on their bodies called spiracles. These spiracles lead to a network of tubes known as trachea that extends to every part of their body, allowing air to enter through this network.
Error Alert!
Whales and dolphins have lungs too, but they don’t have a nose. They come to the surface to breathe air through blowholes.





































Fish have fins that help them swim smoothly through water. They have streamlined bodies that allow them to swim quickly and easily. Some animals, like frogs and ducks, have webbed feet for swimming in water.














Animals such as frogs and toads are called amphibians. They can live both on land and in water. Young amphibians use gills to breathe in water, but adults depend on lungs and moist skin when on land.
Animals move from one place to another in search of food, shelter or safety from predators or natural disasters. This ability to move is known as locomotion. Different animals use different body parts for movement.

Birds have wings that help them to fly. Their wings are strong and covered with feathers which help them lift off the ground and glide through the air. Birds have light, hollow bones that make it easier for them to fly.
streamlined: a shape that is narrow at the front and broad at the back

Animals such as deer and horses have strong legs that help them run fast to escape from predators. Their legs have muscles that give them the power to run and jump.


Snakes do not have legs. Instead, they use their muscles to slither smoothly across the ground.
Choose an animal you find interesting and research more about it on the internet. Create a poster with pictures along with facts about its habitat, diet, behaviour, etc.
Give one word for the following.
1. The features that help plants and animals survive in their natural habitats.
2. The body covering that keeps polar bears warm in icy polar regions.
3. The breathing organs in fish that absorb oxygen from water.
4. The body part that helps fish swim smoothly through water.
5. The tiny holes in insects’ bodies used for breathing.
Migration is the regular movement of animals from one area to another, caused mainly due to unfavourable weather conditions, the search for new habitats, or food shortages. This movement occurs at specific times and during certain seasons. Animals may also migrate due to natural disasters such as earthquakes, droughts and floods. Some species travel to specific areas at specific times of the year to give birth to their young ones; these locations are known as breeding grounds.
slither: to move by sliding from side to side along the ground




Certain birds, known as migratory birds, migrate twice a year during spring and autumn. They do this to avoid harsh weather and to find food. For instance, the Arctic tern breeds near the north pole in summer and migrates all the way to Antarctica in autumn to escape extreme cold.
What could happen to a bird if it did not migrate when its food sources became scarce? Discuss with your classmates.
Other animals, like caribou, elk and whales, also migrate in search of food. Certain insects, such as butterflies and moths, also migrate. The monarch butterfly, for instance, migrates from Canada to Mexico during winter.

Flamingos are known for their long migrations, and every year thousands of them travel to India. These beautiful birds fly from regions like Siberia and the Middle East to wetlands in Gujarat and Maharashtra. They come to India during the winter months, searching for food and a safe place to breed.
habitat: a natural home of an animal or a plant

adaptation: the features that plants and animals develop to live in a habitat
fur: the soft thick hair that covers the bodies of some animals
scale: a small rigid plate that grows out of the skin of a fish
shell: a hard covering that protects some animals
spiracles: a respiratory organ in insects
migration: the movement of animals from one place to another in search of food, better climate and shelter

Scan the QR code to learn more about habitats.

• The natural home of animals is called its habitat.
• Since animals eat different types of food, they can be classified based on the food they eat: herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, scavengers and parasites.
• The features that plants and animals develop to survive in their natural habitats are called adaptations.
• Animal migration is when animals move from one place to another at certain times of the year to find food, better weather or safe places to raise their young ones.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. Which of the following is not an example of a habitat?
Desert Nest Forest Ocean
B. Which of the following animals have fins for movement?
Tiger Fish Frog Camel
C. Which organ helps animals breathe underwater?
Lungs Spiracles Gills Blowhole
D. Which animal has scales as its body covering?
Dog Butterfly Fish Duck
E. Why do some animals, like polar bears, have thick fur?
To look bigger To keep warm in cold climates
To help them swim To scare predators
2. Fill in the blanks.
A. The natural home of animals is called a .
B. Fish have that help them swim smoothly in water.
C. Polar regions are covered with for most part of the year.
D. are the habitats of camels.
3. Match the following.
A. Desert i. Elephants
B. Forest ii. Penguins
C. Ocean iii. Camels
D. Freshwater habitats iv. Whales
E. Polar regions v. Swans
4. Write True or False.
A. Deserts receive a lot of rainfall.
B. Both day and night are extremely hot in the deserts.
C. Soil remains frozen in the polar regions.
D. It is easier for us to breathe air under water than on land.
5. Short-answer questions.
A. What is a habitat?
B. Write a short note on the feeding habit of carnivores.
C. Provide an example of a living organism that has adapted to the following environments:
a. In polar regions b. In deserts c. In water
D. Define parasites, with examples.
E. Briefly explain the importance of shells in snails and turtles.
F. Give two differences between the teeth of carnivores and herbivores.
6. Long-answer questions.
A. Why do animals migrate? Explain with the help of three examples.
B. Explain the differences in the way fish and insects breathe.
C. How do the following features help a fish adapt to its habitat?
a. Shape
7. Picture-based questions.
b. Scales c. Fins
A. Identify the animal shown in the image and name its habitat.
B. How does its thick fur and layer of fat help it survive in the cold polar region?
C. What special adaptations does it have to walk on snow in this icy habitat?




How do you think climate change might affect animals living in the Arctic circle and Antarctica?
Just like how adapt, we also need to learn how to handle changes around us. It could be starting a new school, making friends in a new place, or facing surprises like bad weather. Being able to adjust helps us become stronger. Write a diary entry about a challenge you faced and the ways you found to overcome it.





Let's play a fun game to understand our surroundings better.
Step 1: Take a paper chit. Write the name of something that you commonly see around you—it could be plants, animals, vehicles, a plastic bag or books.
Step 2: Make more such chits and put them into a bowl on the teacher's table. Mix them up.
Step 3: Now, one by one, pick a chit. Read what's written on it.
Step 4: Let others decide if that thing is good or bad for our surroundings. Also, discuss why.
Environment is everything that surrounds us. It includes living things like plants and animals, and non-living things like soil, air and water. A clean and healthy environment is important for the well-being of all living beings. However, human activities have increasingly harmed the environment, resulting in various form of pollution. Let us learn about pollution and its effects on our environment.

Pollution occurs when harmful or poisonous substances are introduced into the environment. These substances can make air, water and land, unsafe for humans, animals, and plants. Such harmful substances are known as pollutants. There are four major types of pollution—air pollution, water pollution, land pollution and noise pollution. Let us learn about each of them in detail.

Imagine you are travelling by bus or car, and you see a truck in front of you releasing a thick black smoke. That black smoke is an example of pollutant, making the air dirty and hard to breathe. Air pollution occurs when harmful substances like gases, dust, or smoke enter the air and affect the quality of air we breathe. Some causes of air pollution are:
• Burning fossil fuels (like, coal and petroleum) and garbage releases toxic gases such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and methane into the air. These gases are very harmful and can cause respiratory diseases like asthma and lung cancer.
• Natural activities like volcanic eruption and forest fires release ash and gases into the air and pollute it.
• Spraying pesticides and fertilisers can also lead to air pollution.



Gases like carbon dioxide and methane trap the Sun’s heat, raising the temperature of the Earth. This phenomenon is known as the greenhouse effect and these gases are called greenhouse gases. This increase in Earth’s temperature due to this effect is called global warming.
containing poison
related to breathing
Mention two ways in which you can help reduce air pollution.

Let us see the effects of air pollution. Take two identical plastic bottles and fill them with cotton balls. Cover one bottle with a thin layer of cloth and leave the other bottle uncovered. Place the bottles outside for a day. Position one bottle in a busy area (like near a road) and the other bottle in a less polluted area (like in a garden). At the end of the day, compare the cotton balls in both bottles to see how much dust and pollutants were collected. Discuss how air pollution affects our lungs similarly.
Imagine visiting a beach and finding it littered with plastic or seeing a river filled with garbage—this is the result of water pollution. It affects not only the animals living in the water but also the water we drink and use every day.
The addition of harmful substances in water bodies like rivers, lakes, seas and oceans causes water pollution. This makes the water dirty and unsafe. Water pollution can occur in various ways:
• Throwing household garbage, plastics and untreated industrial wastes into water makes it dirty and unfit for use. Consuming dirty water can cause diseases like jaundice, typhoid, cholera and dysentery.
• Human activities, such as washing clothes and bathing in water bodies, cause water pollution.
• Pesticides and fertilisers get mixed with rain and enter water bodies, thereby polluting them.
• Oil spills from ships cover the surface of oceans and seas. Due to this, aquatic life finds it difficult to breathe and survive.



Aim: To study the effects of different pollutants on water.
Materials Needed: clear plastic containers, clean water, various pollutants (soil, oil, food colouring, small pieces of plastic, paper scraps), a spoon, small nets, cotton balls or coffee filters
Method:
Step 1: Fill the clear plastic container with clean water. This represents a clean water source.

Step 2: Ask students to take turns one by one and add different pollutants to the water (soil to represent dirt runoff, oil to represent oil spills, food colouring to represent chemical pollutants, and small pieces of plastic and paper to represent litter).
Step 3: Stir the water gently with a spoon to mix the pollutants.
Step 4: Observe the water and note changes in its appearance, colour and clarity. Discuss how each pollutant affects water.
Findings: Larger pollutants are easier to remove from water with the help of nets. However, smaller and finer particles are difficult to remove from water.
Conclusion: Any kind of impurity (small or large) is harmful to water. These pollutants contaminate water and make it unsafe for consumption.
It is a common mistake to think that polluted water is always dirty or smelly. Sometimes, water can look clear and still be polluted with harmful chemicals or germs that you cannot see.
Imagine you are walking in a beautiful park, but you see trash everywhere—plastic bottles, candy wrappers and old newspapers. How would you feel? You will not feel good at all. All this litter contributes to land pollution. Let us learn more about it.
When harmful substances are added to the soil or land, making it dirty, unhealthy or unsafe, it is called land pollution. It can happen in various ways:

1. Throwing solid wastes, such as plastic bags, metal containers, and glass bottles on the ground can pollute the soil and harm wildlife.
2. The roots of trees hold the soil in place. Deforestation causes strong winds and rain to wash away the top layer of the soil, causing soil erosion.
3. Extracting minerals from the earth can cause the land to become polluted and degraded.
Clean air, water and land are the basic requirements for life to flourish.
Imagine you are trying to read your favourite book, but there is loud music playing, dogs barking and cars honking outside. Will you be able to focus? All these loud sounds together can be very annoying and even harmful. This is called noise pollution.
When loud noises are produced by the honking of vehicles, loudspeakers and construction sites, it causes noise pollution. If we hear these loud noises for a long period, it may lead to deafness. Noise pollution can cause stress, hearing loss, sleep disturbances, and other health issues. Loud noises can disturb animals, affecting their behaviour and habitat.
Choose the odd one out.


1. Burning of fuels Air pollution Dysentery Smoke
2. Carbon dioxide Methane Oxygen Greenhouse gases
3. Noise pollution Deafness Loud speakers Water pollution
1. Factories should be located away from the residential areas. They should have filters so that the harmful gases and smoke are processed and not released out in the air.
2. We should plant more and more trees in our surroundings.
Are there any rules or guidelines that could help keep noise levels down in public places? Discuss with your classmates.
3. Different types of waste should be treated before getting dumped.
4. We should avoid using plastic bags and bottles.

deafness: unable to hear





5. We should use natural fertilisers for agricultural purposes.
6. The government should ban unnecessary honking of horns on the roads.
7. We should adopt the formula of the 3R’s (reduce, reuse and recycle) to prevent pollution.
Due to the actions taken by the Namami Gange river conservation plan, around 4,000 Indian river dolphins have returned to the Ganga and its tributaries. This shows that the rivers are slightly cleaner than before, and it has encouraged the people and the government to put in more effort to prevent river pollution in India.


environment: all living and non-living things in our surroundings pollutants: the harmful substances that cause pollution
air pollution: the addition of harmful particles in the atmosphere
water pollution: the addition of harmful chemicals, waste and plastic in water bodies
land pollution: polluting of the soil due to garbage, plastic waste and deforestation
noise pollution: loud noise that affects the health of humans and animals

• All living and non-living things in our surroundings make the environment.
• Pollution is caused by the addition of harmful substances into the environment.
• There are four main types of pollution—air, water, land and noise.
• We should follow measures to reduce pollution and save our environment.
1. Tick ( ) the correct option.
A. What is air pollution?
The contamination of water by harmful substances.
The contamination of soil by harmful substances.
The contamination of air by harmful substances.
The contamination of noise by harmful substances.
B. Which of the following is a major cause of water pollution?
Planting more trees. Using solar energy.
Disposing industrial waste into rivers. Riding bicycles.
C. How can we reduce land pollution?
By throwing garbage everywhere. By burning plastic waste. By recycling and reusing materials. By cutting down trees.
D. What is noise pollution?
The presence of harmful chemicals in water.
The excessive and harmful levels of noise in the environment.
The presence of unwanted materials in the soil.
The increase in the earth’s temperature.

2. Fill in the blanks.
respiratory noise water global warming
A. Air pollution can cause problems like asthma and lung cancer.
B. The increase in the Earth’s temperature by greenhouse gases is called .
C. pollution can cause diseases like jaundice, typhoid and dysentery.
D. pollution is caused by the honking of vehicles, loudspeakers and construction sites.
3. Write True or False.
A. Throwing garbage into rivers and lakes causes water pollution.
B. Factories that burn coal and gas to produce energy release pollutants into the air.
C. Gases like carbon dioxide and methane are called greenhouse gases.
D. Noise pollution can cause stress and hearing loss.
4. Circle the correct alternative in each of the following.
A. Air / Water pollution occurs when harmful substances enter into air.
B. Water / Noise pollution makes water dirty and unsafe for use.
C. Land / Noise pollution can cause stress, hearing loss and sleep disturbances.
D. We should prefer to use natural / chemical fertilisers for agricultural purposes.
5. Short-answer questions.
A. Name two diseases caused by air pollution.
B. What is the greenhouse effect? Which gases are responsible for the greenhouse effect?
C. Mention ways to prevent water pollution.
D. How is land pollution caused?
E. Mention one harmful effect of noise pollution.

6. Long-answer questions.
A. Explain air pollution and factors causing air pollution. Mention its effects on environment as well.
B. How is noise pollution caused? What will happen if we are exposed to loud noises for a longer time period?
C. List some ways to prevent pollution.
7. Picture-based questions.
A. Which type of pollution is depicted in the given image?
B. What major cause of the pollution is being shown in the above image?
C. Write one harmful effect of the above-mentioned pollution on human health.


If you were the governor of your city, what steps would you take to ensure that local water bodies, the land and the air are not polluted by the residents?

With the help of your neighbours, volunteer to clean one neighbourhood park. Sort the wastes into different types: all the recyclable wastes in one bag and the non-recyclables in another. Also try to plant grass and local plants and trees in the park.

Objective: Students will understand how a volcano erupts.
Materials Needed: A small bottle, baking soda, vinegar, red food colouring, clay, a cup, a tablespoon and a tray
Step 1: Learn about Volcano and Their Different Types: Study about the volcano and its various types. You can take the help of school textbooks or the internet.

Step 2: Build Your Volcano: Place the plastic bottle in the centre of the tray. Shape clay around the bottle to create a volcano, leaving the top open.
Step 3: Prepare the Eruption:
• Add two tablespoons of baking soda to the bottle.
• In a separate cup, mix ½ cup of vinegar with a few drops of red food colouring.
Step 4: Erupt the Volcano: Carefully pour the vinegar mixture into the bottle and watch the eruption!
Tip: Take the help of an adult while pouring the vinegar mixture into the bottle.
Step 5: Document Your Observations: Take pictures of or draw each step of your project, especially the eruption. Write down what happened and any similarities to real volcanoes.
Project Output: Now you have your own volcano model. Share your volcano model and pictures with the class. Explain how it works and what you learnt about volcanic eruptions.
Final Outcome: This hands-on project not only allows you to create a fun and exciting volcano model but also helps you understand the scientific principles behind volcanic eruptions and encourages teamwork, observation and communication skills.
Read the given conversation. Answer the questions given below.
Aarav: Hi, Meera! I just got a new game on my computer. I can even chat with people while playing!
Meera: That sounds fun, Aarav! But remember, we need to be careful when talking to people online.
Aarav: Why? It’s just a game.
Meera: Well, some people online might not be who they say they are. It’s important to only talk to people you know in real life like friends or family.
Aarav: Oh, I didn’t think about that. What else should I do to stay safe?
Meera: Make sure you have a strong password and never share it with anyone. Also, don’t click on links or download anything from people you don’t know. It could be dangerous.
Aarav: Good idea! I’ll be careful. What if I see something weird or someone is mean to me?
Meera: You should tell a trusted adult, such as your parents or a teacher, right away. They can help you report it, if needed.
Aarav: Thanks, Meera! I’ll remember these tips to stay safe online.
1. Which of the following is a good practice to stay safe while using the internet?
A. Sharing your full name and address with friends online
B. Using a strong password and not sharing it with anyone
C. Clicking on any link you find interesting

2. What should you do if you see something online that makes you feel uncomfortable?
A. Ignore it and continue using the internet
B. Click on it to learn more about it
C. Report it to a trusted adult
3. Imagine you are playing an online game and someone you don’t know sends you a message. Mention any two steps you would take to ensure your safety.
4. Aarav is excited to play his new game online, but he is asked to create a password. What are some important things Aarav should keep in mind while creating his password, and why is it important to have a strong password?
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.

Name of the Student:
Time: 1 Hour
Total Marks: 40
1 Tick () the correct answer. (1 × 5 marks)
A Which of the following nutrients provides energy to the body?
a Proteins
c Carbohydrates
B What is the function of motor nerves?
b Vitamins
d Minerals
a Carry messages from the brain to the body
b Control movement of the body parts
c Carry messages from the brain to the spinal cord
d Carry messages from the body to the brain
C Which of the following is a sign of dehydration?
a Increased urination
c Feeling energetic
b Sweating
d Dizziness
D Which is the only movable bone in our skull?
a Collar bone
c Upper jaw
b Lower jaw
d Head
E Which of these is NOT an example of a habitat?
a Desert b Ocean
c Nest d Forest
2 Fill in the blanks. (1 × 5 marks) seed coat water magma ligaments gills
A Bones are held together at the joints by strong tissues called .
B is hot, melted rock found beneath the Earth’s surface.
C pollution can cause diseases like jaundice, typhoid and dysentery.
D The external covering of a seed is called the .
E enable fish to breathe underwater.
3 Write ONE word for the following.
A A dietary fibre that aids digestion
B The point on the Earth’s surface directly above where the earthquake starts
C Respiratory organs in insects
D Special cells in our body that detect and respond to different types of signals
E A crack in the bone
(1 × 5 marks)
4 Write True or False. (1 × 5 marks)
A Insects are the main agents of pollination.
B The cerebellum is the largest part of the brain.
C Gases like carbon dioxide and methane are called greenhouse gases.
D The breastbone is also called the sternum.
E Arthritis is a communicable disease.
5 Picture-based questions. (1 + 2 + 1 marks)
A What process is being performed by the bee in this picture?
B Describe the steps in this process.
C What is the result of this process?
6 Answer the following questions in short. (2 × 4 marks)
A Write any two ways to stay safe on the road.
B Why do animals like turtles and snails have shells?
C Name two diseases caused by air pollution.
D How are sensory nerves different from motor nerves?
7 Answer the following questions in detail. (4 × 2 marks)
A Explain the different types of volcanoes. Provide one example for each.
B What is the importance of a balanced diet? How does it benefit the body?



Chapter Overview

Shape of the Earth
The Globe

Poles and Hemispheres
Latitudes, Longitudes and Grids


Read the poem given below aloud along with your classmates.
The Earth is round, like a big blue ball, It spins and spins, never will it fall.
From space, it looks so small and bright, A circle of wonder, day and night.
Though it seems flat below our feet, It is round and whole, a special feat.
From oceans deep to mountains high, The Earth’s a circle, under the sky.

In this chapter, we will learn more about our planet, Earth, and what the vertical and horizontal lines on the globe and maps mean.

We have already studied that the Earth is round. In ancient times, people used to believe that the Earth is flat. They believed that if a person will walk towards the end of the Earth and keep walking, then the person will fall off the edge of the Earth. From where we stand, the Earth looks flat because our eyes can only see a small part of it. The Earth is so vast that we cannot see its shape from the ground. Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese navigator, sailed around the Earth and proved it is round. You can only see the Earth’s curve from space.
Studying the whole of Earth is not easy because it is so large. To make it easier, geographers use different methods to represent the Earth on a smaller scale. Two essential tools for this are maps and globes.


Chandani has always wondered what the Earth would look like. One day she asked her teacher, “Ma’am how does the Earth look?” Her teacher showed her a globe kept in the school library. She told her that a globe is a model of the Earth. Chandani was excited to see the globe and wanted to know more about it.
The globe is a small model of the Earth. It shows how oceans, continents and seas are spread across the Earth. We can see the location of countries on a globe. It helps us see the shape of countries, and some cities. We can only see one half of the globe at a time. To view the other half of the globe, we must rotate it. The globe can be turned around, just like the Earth turns around an imaginary line which passes through it. This line is called the axis. The axis is not straight. It is tilted at an angle of 23½°.
Even though a globe is a representation of the Earth, we cannot always use it due to the following reasons:
• It is big and difficult to carry around.
• It can only show a part of the Earth at once.
edge: the boundary line of a surface or an area vast: very large essential: very important

• It cannot show all the specific details about a place and its people.
• Globes lack the detail needed for complete understanding.
• Globes cannot be folded and included in books for easy access.
Circle the correct word.
1. People in ancient times believed the Earth was round/flat.
2. Geographers/Philosophers use different methods to study Earth’s features.
3. The axis/equator is an imaginary line passing through the centre of the Earth.
The axis of rotation has two end points called the poles. They are the North Pole and the South Pole. These poles are at the very top and bottom of the planet. The North Pole is in the middle of the Arctic Ocean and is covered by ice. The South Pole is in the middle of the coldest continent, called Antarctica, which is also covered by ice.












and Hemispheres
At the centre, between the two poles there runs an imaginary line that circles the planet. It is called the Equator. It divides the Earth into two equal halves. These halves are called hemispheres. Towards the north is the Northern hemisphere and towards the south is the Southern hemisphere.
On the globe, horizontal and vertical lines are drawn for the ease of locating places. The imaginary horizontal lines that run from east to west on the globe are called Latitudes. The Equator is one of them. The latitudes are also called lines of latitude or parallels of latitude as they all run parallel to each other. There are 180-degree latitudes in total. The units degree (°) and minutes (`) are used to measure the latitudes. Sixty minutes (60`) are equal to one degree (1°).


The Equator lies at the 0°. At the 90° north, there is the North Pole. At 90° south, we have the South Pole. Therefore, with the help of latitudes, we can know the distance we have travelled towards north or south. For example, a place which is located 45° south, lies between the Equator and the South Pole. Similarly, 60° south will be nearer to the South Pole.
Important latitudes on the Earth:
• At 23½°N, we have the Tropic of Cancer.
• At 66½°N, we have the Arctic Circle.
• At 23½°S, we have the Tropic of Capricorn.
• At 66½°S, we have the Antarctic Circle.
Properties of Latitudes
• The parallel lines are at an equal distance from each other, and they do not meet.
• The Equator is the longest latitude and other latitudes become smaller when moving towards the poles.
• The North Pole and South Pole are just points. There are no lines there.
• Latitude affects climate, with locations near the Equator being warmer and locations near the poles being colder.
With the help of the internet, look for five countries from the Northern hemisphere and five countries from the Southern hemisphere.
The vertical, imaginary lines drawn from the North Pole to the South Pole are called Longitudes. The longitude that runs through Greenwich near London is at 0°. It is called the Prime Meridian. As this meridian passes through the observatory at Greenwich in London, United Kingdom, it is also called the Greenwich Meridian.

Meridian line at Greenwich
There are 360° of longitude: 180° towards the east of the Prime Meridian and 180° towards the west of the Prime Meridian. The longitude divides the Earth into Eastern hemisphere
observatory: a place with special equipment like telescopes, where scientists watch and study the stars, planets, and weather
and the Western hemisphere. The 180th degree of the Eastern and Western hemisphere meet at a single line. It is called as International Date line or the 180° longitude.
In total, there are 360 longitudes: the Prime Meridian at 0°, the International Date line at 180°, 179 meridians in the Eastern hemisphere and 179 meridians in the Western hemisphere. The longitudes, therefore, tell us how far east and west we have travelled.
• These lines are semi-circles that run from the North Pole to the South Pole.
• The lengths of the meridians are the same.
• The distance between the lines is broader at the centre and lesser at the poles.

Distance between the lines is less at the poles.
The International Date Line is not a straight line. It is drawn as a zig-zag line to maintain a consistent time zone in the countries and islands that it passes near.
Latitudes and longitudes intersect each other at right angles, forming a network of lines called grids. By knowing the degrees of latitude and longitude, we can pinpoint the exact location of a place. The point where the latitude and longitude intersect marks the location of a place.

Latitudes and longitudes forming a grid
Norway experiences the longest night or darkness of the year in its northern regions during the winter, a phenomenon known as “polar night.”
The time at the point of the Prime Meridian, or the Greenwich Meridian, is considered as the mean time and called as the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). The countries on the eastern side of this meridian get to see the sunrise earlier than the countries on the western side of the meridian. The local time of a particular place is calculated based on the distance from Greenwich and the time at Greenwich.


Every country has a particular longitude fixed to calculate the time of that country. Many longitudes pass through one single country. To avoid confusion, one longitude is chosen. In India, 82½°E longitude is chosen to calculate the time. It almost divides India into two equal parts. This longitude passes through Mirzapur, Uttar Pradesh. This standard time is called the Indian Standard Time (IST). By calculating its distance from Greenwich and the time at Greenwich, Indian Standard Time is 5½ hours ahead of the Greenwich Mean Time.
Find out the current time in India and in Greenwich. Write them in your notebook.

How would the lives of people of India be different if India had different time zones? Discuss with your friends.
Jantar Mantar in Jaipur, built in the 18th century, is a place with special instruments used to measure time, predict eclipses, and observe stars and planets. It is famous for its role in advancing ancient Indian astronomy and science. It is also a UNESCO World Heritage site.

geographer: a person who studies the Earth’s features axis: an imaginary line around which the Earth spins poles: the points on the Earth’s surface where the axis ends latitude: horizontal lines drawn around the globe longitude: vertical lines drawn around the globe

Scan the QR code to learn more about how to find the location of a place using latitudes and longitudes.
• Ferdinand Magellan, a Portuguese explorer, sailed around the Earth and proved that it was round.
• Latitudes are the imaginary horizontal lines and longitudes are the imaginary vertical lines which help to find the location of a place.
• The important latitudes are the Equator, Tropic of Cancer, Tropic of Capricorn, Arctic Circle and the Antarctic Circle; and the important longitudes are the Prime Meridian and International Date Line.
• Indian Standard Time (IST) is 5½ hours ahead of Greenwich Mean Time.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. The axis of the Earth is titled at which angle?
a. 66½°
B. The 0° Longitude is called
b. 23½°
c. 90°
a. Greenwich Meridian b. International Date Line c. Equator
C. The total number of longitudes are
a. 180
b. 181
D. The total number of latitudes are
a. 90
b. 181
2. Fill in the blanks. east to west north to south poles grids
c. 360
c. 180
A. The latitudes and longitudes intersect and form a network of lines called .
B. Latitudes run from .
C. Longitudes run from .
D. The points on top and bottom of the Earth are called .

3. Write True or False.
A. Longitudes affect the climate in both hemispheres.
B. The 23½°S latitude is called the Tropic of Cancer.
C. Latitudes are also called parallels.
D. The Equator is also called the Prime Meridian.
4. Match the following.
A. Latitude
B. Longitude
C. 23½°
D. 66½°N
5. Short answer questions.
A. Define latitudes and longitudes.
i. Arctic Circle
ii. Axis of rotation
iii. Prime Meridian
iv. Equator
B. What is a globe? Write one advantage and one disadvantage.
C. What is the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT)?
D. What are grids? How are they useful?
6. Long answer questions.
A. What are the properties of latitudes?
B. What are the properties of longitudes?
C. What is Indian Standard Time? How is it calculated?
7. Picture-based questions.
A. Name any one continent the Equator is passing through.
B. Which line divides the Earth into the Eastern hemisphere and the Western hemisphere?

1. If you travel directly from the Equator to the North Pole, how will the environment around you change? Describe what you might observe about the climate, daylight and landscapes as you move from 0° to 90°N latitude.
2. India has only one time zone, the Indian Standard Time (IST), which is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of Greenwich Mean Time. Considering the vast geographical spread of India, what could be some advantages and disadvantages of having a single time zone for the entire country?

Connect to a friend/relative who is living in a different country and find out the difference in time, weather, food and culture. Present the details to your class.




Maps and Directions
Globes and Maps
Types of Maps
Directions and Sub-directions

Reading a Map


Shreyas is new to his school. At lunch time, he asks his classmate Mahima to tell where the school canteen is. Mahima gives him the directions to these. She tell him to first go to the north block of the school, and then take a left from there. The canteen would be on his right.
Do you also give directions to others to help them reach a particular place?
In this chapter, we will learn about maps and directions.
In the previous chapter, we have learnt that a globe is a miniature model of the Earth. It accurately represents the shape, size and location of places. It helps us study the distribution of water and land on the Earth’s surface.
miniature: very small
However, globes have some limitations:
• Large globes are hard to carry around.
• You can only see one-half of the Earth at a time.
• They don’t show all the details of the Earth.
What are some ways in which maps can be more convenient than globes? Discuss with your partner.
• Making a large, detailed globe is difficult. To overcome these issues, we use maps. A map is a flat representation of the Earth’s surface, usually on paper. Since the Earth is curved, it is impossible to flatten it perfectly on paper. This leads to some inaccuracies in the shapes and sizes of landmasses on maps. Mapmakers work to reduce these inaccuracies. Maps may have distortions, but they can still show small areas precisely. This makes them useful for studying the Earth. However, maps can be outdated and need to be updated from time to time.
Maps can show the entire world or specific areas like continents, countries, cities or neighbourhoods. They come in various sizes. Larger maps, such as those of the world, tend to have more errors due to the broad area they cover. In contrast, smaller maps, like those of a neighbourhood, can provide more accurate details. A wall map of the world may be large because it includes many details, but it can be rolled up or folded for easy transport. There are various types of maps:
• Political maps: They show the boundaries of continents, countries, states and cities.
Why do you think we use different maps for a place or region instead of including all details on a single map?
During the 16th century, Gerardus Mercator, a map-maker, was the first to compile and publish a collection of maps in the form of a book.
• Physical maps: They highlight natural features such as rivers, plateaus, mountains and plains.
limitations: restrictions inaccuracies: errors or mistakes distortions: changes that make something unclear or wrong precisely: exactly or accurately contrast: comparison

• Climatic maps: They display information on rainfall and climate across different places.
• Thematic maps: They include details on railways, roads and airline routes.
• Resource maps: They show industries, crops, minerals, soils, wildlife, forests and natural resources. A book of maps is called an atlas.
Underline the correct answer.
1. A map/globe is a small model of the Earth.
2. Maps that show the boundaries of continents or countries are known as physical/ political maps.
3. Using maps, we can see the whole/half world at once.
To use any map, it is important to follow a set of directions. A direction is an indication leading towards a place. There are four major directions: North, South, East and West. These are known as cardinal directions. On a map, the top usually represents the North, the bottom represents the South, the right side represents the East, and the
left side represents the West. Often on a map, an arrow pointing to the North is marked with the letter ‘N,’ which helps you identify the other directions.
In addition to the cardinal directions, there are also intermediate directions that provide more precise guidance.
The area between North and East is called Northeast, and the area between North and West is called Northwest. Similarly, the area between South and East is called Southeast, and the area between South and West is called Southwest.
The directions
Maps provide us with detailed information about the world, a country, or a specific place. However, to effectively read a map, we need to understand certain features that guide us. These features are known as the elements of a map. Here are some basic elements:
Maps convey information about mountains, rivers, dams, lakes, bridges, landforms, airports, railway tracks and much more. Since everything cannot be written out on a map, symbols are used to represent these features. For example, cities are often marked by small circles and mountain peaks by triangles. These symbols make it easier to understand the information being given by the map.
In early maps, symbols were often more artistic with detailed drawings representing cities or mountains. Did You Know?
Map symbols


A map condenses a large area, such as the entire world, a country or a state, into a much smaller size. It is not feasible to draw a map of the same size as the actual place.
To address this, scales are introduced. A scale helps compare the actual size of an area to a smaller representation on the map.
For instance, a scale might show that 1 cm on the map equals 200 km in reality. This ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground is called the scale.

Create a map showing the route from your school to your home. Mark landmarks like libraries, hospitals, parks, etc. with your own symbols and use blue for any water bodies along the way.
Different colours are used on maps to represent various features, and most maps follow similar colour patterns. For example, generally on a physical map, mountains are shown in shades of brown, yellow represents plateaus, and green represents plains. Water bodies are shown in shades of blue, with light blue representing shallow waters and dark blue indicating deeper waters. Typically, a key is provided in the upper or lower right corner of the map. This key helps us understand what the different colours on the map represent.
Climatic regions of the world
condenses: makes something smaller or compact feasible: possible or practical to do

Indore celebrated India’s 75th Independence Day in a unique way. Over 5,000 people, including students and social workers, came together to form a giant human chain shaped like India’s map. This incredible achievement earned them a spot in the World Book of Records for creating the largest human chain forming a geographical shape. The participants carefully created the outline of the map, including the tricolor flag and the Ashok Chakra emblem in the centre.
map: a flat representation of the Earth’s surface, usually on paper atlas: a collection of maps, typically bound together in a book direction: an indication that leads to a particular point cardinal directions: the four main directions—north, south, east and west intermediate directions: the directions in between the cardinal directions elements: the features used on a map that guide you to read the map easily symbols: small pictures or icons that represent different features and landmarks scale: ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground

Scan the QR code to learn more about the symbols and colours used on maps.
• Maps may be distorted since the curved Earth cannot be represented perfectly on flat paper.
• Smaller maps show details more accurately, while larger maps may be less precise.
• An atlas contains different types of maps, such as political, physical, climatic, thematic and resource maps, each serving a specific purpose.
• There are four directions and four intermediate directions that help us to locate places on the map.
• The basic elements used on a map include symbols, scales and colours.

1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. A collection of maps is called
a. a map book b. a globe
c. an atlas
B. Political maps show information about a. states and cities b. rivers and plateaus c. temperature
C. Landmarks are represented on maps by a. colours b. symbols c. scales
D. The directions between the cardinal directions are called directions.
a. in-between
b. medium
c. intermediate
E. Plateaus are shown on maps in a. brown b. green c. yellow
2. Fill in the blanks.
intermediate directions resource maps thematic maps globe scale
A. shows the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground.
B. give the details of minerals, crops, industries and soil.
C. is a miniature model of the Earth.
D. give details on railway, roads and airline routes.
E. Northeast, Northwest, Southeast and Southwest are called .
3. Write True or False.
A. Water bodies are always represented in shades of green.
B. There are four cardinal directions and four intermediate directions used in a map.
C. Physical map gives information on rivers, plateaus, etc.
D. Plains are represented in shades of light green and dark green.
E. Large maps are easy to handle and read.
4. Match the following.
A. States and continents i. Climate map
B. Rivers and plateaus ii. Physical map
C. Railway and airports iii. Political map
D. Rainfall iv. Resource map
E. Crops and minerals v. Thematic map
5. Short answer questions.
A. What are the uses of maps?
B. What are symbols? Why are they used on a map?
C. What are the different elements used on a map?
D. How is the scale used on a map?
E. What does a colour key on a map mean?
6. Long answer questions.
A. What are cardinal directions and intermediate directions? Explain.
B. Name three different types of maps and describe what they represent.
7. Picture-based questions.
A. What type of map is this?
B. What does this type of map tell us?
C. What information do you get from the key of this map?



Why do you think it is important to know which direction is north, south, east or west while reading a map? Support your reason with examples.
Two friends are lost in the woods and need to find their way back to the camp! Start at the ‘START’ and follow the arrows to reach the ‘FINISH’. There might be different paths, but try to find the quickest one. Write the directions in the empty circles to guide the campers.



Rotation of the Earth
Revolution of the Earth Equinox and Solstice


Solve the riddles related to the seasons given below.
I am hot, full of sunlight, ice cream, pools and lots of fun. Who am I?
Snow games and cold winds blow, cozy sweaters and ice that glows. Who am I?
Flowers bloom and birds take flight, nature wakes, fresh and bright. Who am I?



We know that the Earth spins around its own axis. We also know that it moves around the Sun. In this chapter, we will learn more about how these movements cause day and night; and different seasons.
In ancient times, there was a belief that the Earth was flat. However, an Indian astronomer, Aryabhata, was among the first to propose that the Earth is spherical and propose: to suggest an idea, plan or action

rotates on its axis. People did not believe it until astronomers like Nicolaus Copernicus and navigators like Ferdinand Magellan provided evidence to support their findings. Today, satellite images of the Earth clearly show that it is spherical in shape.
You can learn more about the Earth and its features using a globe.
The Earth is spherical but slightly flattened at the poles and slightly bulging at the equator. As a result, gravity is stronger at the poles than at the equator.
The Earth rotates on its axis. It takes about 24 hours to complete one full rotation. The rotation of the Earth is responsible for causing day and night. As the Earth rotates from west to east, we see the Sun rising in the east and setting in the west.
To understand how day and night happens in a better way, try this activity: Take a globe and shine a flashlight on it. You will observe that light shines on only one-half of the globe, leaving the other half in darkness. This is similar to what happens on the Earth. Because the Earth is spherical, when the Sun's rays shine on one side, that side experiences day. The opposite side remains dark because the Sun's rays do not reach there, creating night. This cycle repeats regularly, creating our daily cycle of day and night.
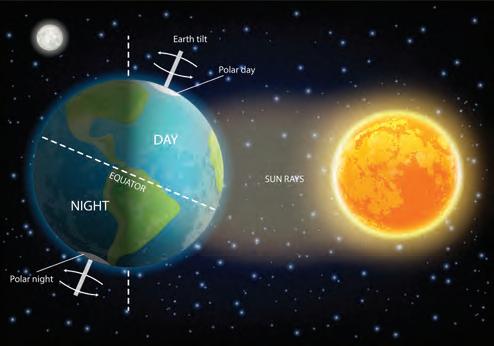
A globe is a small model of the Earth.
The Earth moves around the Sun in an oval-shaped path called an orbit. This movement of the Earth around the Sun, in a fixed path, is called revolution. It takes about 365¼ days for the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun. The 1/4 day
evidence: facts, information or objects that help prove whether something is true or false
adds to one full day every fourth year. To keep our calendar accurate, we add this extra day to February of that fourth year. This creates a leap year with 366 days.
As the Earth revolves around the Sun, different parts of the Earth get varying amounts of sunlight. This causes the seasons: summer, winter, spring and autumn. Because the Earth’s axis is tilted, the part that gets more direct sunlight experiences summer, while Southern Hemisphere is titled away from the Sun. So, that part of the Earth experiences winter, with shorter days and longer nights. From October to February, this is reversed the Southern Hemisphere experiences summer, while the Northern Hemisphere experiences winter. Can you guess what season does Australia have in the month of June?
Error Alert!
Although it looks like the Sun moves around the Earth, it is actually the other way round: it is the Earth that moves around the Sun.
Underline the correct answer.
1. A leap year occurs every 6/4 years.
2. Camera/Satellite images of the Earth confirm that it is a sphere.
3. The Earth takes 40/24 hours to complete one rotation.
reverse: opposite

Equinox and solstice are important positions in Earth’s revolution around the Sun. These times of the year help us note the change of seasons.
An equinox is a time of the year when the length of day and night are nearly equal. This happens twice a year: on 21 March and 23 September.
In an equinox, the axis of the Earth is neither tilted towards the Sun nor away from the Sun.
21
On December 22, the Sun's rays fall directly on the Tropic of Capricorn. So, in the Northern Hemisphere, it is the shortest day and is called the winter solstice. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is the longest day and is called the summer solstice.
Solstices are two days in a year when the Sun shines directly on one of the two tropics.
On June 21, the Sun’s rays fall directly on the Tropic of Cancer. So, in the Northern Hemisphere, it is the longest day and is called the summer solstice. In the Southern Hemisphere, it is the shortest day and is called the winter solstice.
– December 22
At the poles during the solstices, the Sun does not set or rise for extended periods. For instance, in the Arctic Circle, on the summer solstice, the Sun remains above the horizon for 24 hours. This creates a unique phenomenon known as the “midnight sun,” where the Sun is visible even at night.
On Sunday morning, when Shreya was playing outside with her brother, she noticed that it was turning dark. They quickly went inside, and Shreya asked her mother, “Why is it turning dark now? It is 11’o clock in the morning.” Shreya's mother replied, “It is because there is a solar eclipse today.”
Eclipses occur when the Earth or the Moon fall into the shadow of each other. This happens because the Earth revolves around the Sun, and the Moon revolves around the Earth. During an eclipse, the Sun, Earth and Moon are aligned in a straight line.
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, partially or completely blocking the Sun’s rays over an area on the Earth. This event can only happen on a new moon day. Because the Sun’s rays are blocked, this phenomenon is called a solar eclipse. We should not look directly at the Sun during a solar eclipse, as it can be harmful for our eyes.
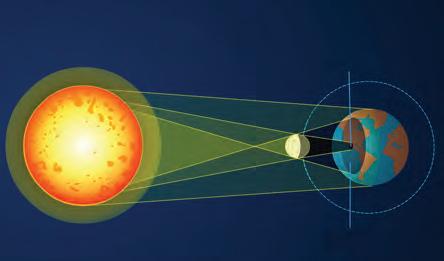
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, partially or completely covering the Moon in its shadow. This is also known as lunar eclipse. It happens on full moon nights. Since the Moon does not produce its own light, it is safe to look at it during a lunar eclipse. During a lunar eclipse, the Moon often appears reddish and generally lasts for a few hours.


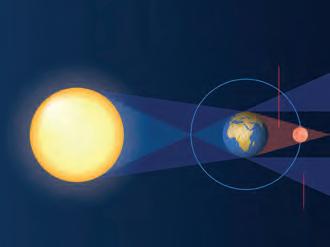
Create a simple model using two balls of different sizes to represent the Moon and the Earth. Use a torch to represent sunlight. Arrange the balls in a straight line. First, shine the torchlight with the smaller ball in front of the bigger ball to understand solar eclipse. Then, exchange their places to understand lunar eclipse.
The Nehru Planetarium in Bangalore is one place where you can look at creative models of the Earth’s rotation and revolution to understand things like the axis, the Earth’s tilt, day and night, seasons, equinoxes and solstices, and eclipses.


astronomers: people who study space, including stars, planets and other objects in the universe
rotation: the spinning of the Earth on its axis which is an imaginary line that runs from the north pole to the south pole
orbit: the curved path that one celestial object takes around another celestial object
revolution: the movement of the Earth around the Sun
leap year: the year with 366 days instead of 3651/4
equinox: a time of the year when the day and the night are the same length everywhere on the Earth
solstice: the time of year when the Sun shines directly on one of the tropics

Scan the QR code to learn more about eclipses.
• The Earth takes 24 hours to complete one rotation. The rotation of the Earth causes day and night.
• The Earth moves around the Sun in an oval-shaped orbit and takes 365¼ days to complete one revolution. The revolution of the Earth causes seasons.
• Equinoxes are times in a year when the day and the night are almost equal. It happens twice a year: 21 March and 23 September.
• Solstices are times in a year when the Sun shines directly on one of the tropics. It happens twice a year: 21 June and 22 December.
• During a solar eclipse, the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth.
• A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon. This causes the Earth’s shadow to fall on the Moon.
• Solar eclipses happen on new moon days. Lunar eclipses happen on full moon nights.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. How many hours does the Earth take to complete one rotation?
a. 23 hours
b. 24 hours
c. 30 hours
B. What is the pathway along which the Earth revolves around the Sun called?
a. Orbit
b. Axis
c. Equator
C. On which of these days does the Summer Solstice occur in the Northern Hemisphere?
a. June 21
b. March 21
c. December 22
D. During which event does the Moon pass between the Sun and the Earth?
a. Solar Eclipse
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Lunar Eclipse
c. Solstice
winter solstice solar eclipse axis leap year
A. When the Sun’s rays fall on the Tropic of Capricorn, it is known as in the Northern hemisphere.
B. The Earth rotates on an imaginary tilted line called .
C. A occurs once every four years.
D. It is harmful for our eyes if we look directly at the Sun during a
3. Write True or False.
A. The Earth moves around the Sun in an oval-shaped orbit.
B. During a lunar eclipse, the Moon comes in between the Sun and the Earth.
C. During an equinox, the Sun’s rays shine directly on the tropics.
D. The seasons are caused due to the revolution of the Earth.

4. Match the following.
A. Equinox i. Axis
B. Solstice ii. 366 days
C. Imaginary line iii. March 21
D. Leap year iv. June 21
5. Short answer questions.
A. What causes day and night?
B. How are seasons caused?
C. What is an equinox?
D. What is a solstice?
6. Long answer questions.
A. Differentiate between solar eclipse and lunar eclipse.
B. Differentiate between summer solstice and winter solstice.
7. Picture-based questions.
A. What does this image show?
B. What is the cause of this eclipse?


What do you think would happen if the Earth’s axis was not tilted?

Talk to an elder in your family or your community. Ask them about any folktales or stories related to eclipses.


Weather and Climate
The Atmosphere
Weather and Seasons
Climate and the Factors Influencing It
Climatic Zones


Look at the pictures and think about the type of weather these places would have. Write it in the space given below the pictures.


In this chapter, we will learn more about weather and climate.
The atmosphere is the layer of air that surrounds the Earth, and supports life by providing oxygen and protecting us from harmful rays of the Sun.
The atmosphere has several layers. The temperature changes in each layer depending on how much heat from the Sun is absorbed.

Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time. Has it ever happened that you were out and it was dark and cloudy, but suddenly it became bright and sunny? This happens because weather can quickly change from day to day and hour to hour. Weather can be hot, cold, windy, dry or humid.
Different seasons occur because of changes in weather patterns. In India, we have three main seasons: summer, monsoon and winter. These seasons affect the food we eat and grow, what we wear, our daily activities and the kinds of houses we build.



Climate is the weather pattern of a specific place for a longer period of time. We know that the climate of hilly areas is generally cold and chilly, while deserts have a hot and dry climate. Climate affects things like transportation, food and housing. Scientists who study the climate are called climatologists.
Have you ever wondered why different places have different climates?
Did You Know?
The coldest place where people live is Oymyakon, a remote village in Siberia, Russia. During winter, temperatures here can drop below –50°C.
For example, if you compare the climate of Mumbai and Leh, you will note that Mumbai is warm and humid, while Leh is cold and dry, even though they are both in the same country. Several factors influence the climate of a place. Let us learn about them.
Latitude is the distance of a place from the equator. The Earth is spherical, with the equator as an imaginary line around its middle. The equator receives direct sunlight. In contrast, the North and South Poles receive sunlight at an angle. That is why, the
contrast: to show how two or more things are different from each other
Sun's rays have to travel a longer distance through the atmosphere to reach the Earth's surface around poles. As a result, the rays lose much of their heat by the time they get there. This is why regions near the equator are warmer, while areas near the poles are colder.
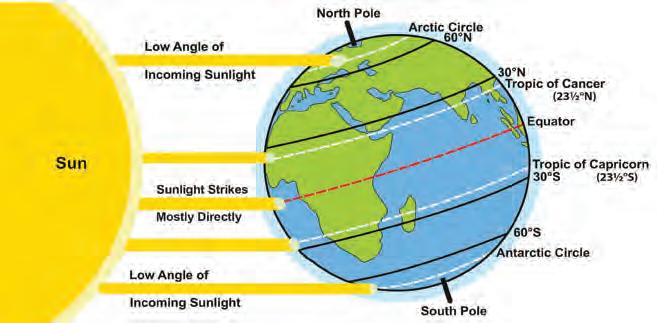
Altitude means the height of a place when measured from the sea. Since the sea level is the same everywhere on Earth, so it is used as a reference point for measuring altitude. The climate of a place is significantly affected by its altitude. The layer of air near the Earth's surface is thicker and can absorb and retain more heat. Therefore, areas at lower altitudes tend to be warmer. However, as altitude increases, the air becomes thinner and absorbs less heat. This is why mountain regions are colder, even in the summer, and often have freezing temperatures in winter.


The distance from the sea significantly impacts a region's climate. Coastal areas, like Mumbai, experience a moderate climate due to the sea’s influence. Seas get heated up and cooled down at a slower rate compared to land. That is why coastal areas are cooler in summer than areas which are far from the sea. Similarly, coastal areas are warmer in winters than other areas.

Places that are far from the sea, like Delhi, face extreme temperatures. Without the sea’s moderating effect, these areas experience very hot summers and very cold winters.
Chile is one of the driest places on Earth, with less than 0.04 inches of rain per year.

Winds are the horizontal movements of air. They play a significant role in influencing the climate of a place. Hot winds can increase the temperature of an area, while cold winds can lower it. Winds also help bring rainfall to certain regions. When winds blow from the sea to the land, they are called sea breezes. These winds carry moisture, making the area humid and warm, and they often bring rainfall. On the other hand, when winds blow from the land toward the sea, they are called land breezes. These winds are dry and do not significantly affect the temperature of the area. In India, the south west monsoon wind brings rainfall from June to September.
Humidity is the amount of water vapour in the air. The heat of the Sun causes faster evaporation in the regions around the equator, which leads to heavy rains in those areas. In regions with less evaporation of water, there is little humidity, leading to dry land and very little rain throughout the year.

Humidity Meter
How is the climate in Shimla different from the climate of the Thar Desert? Discuss with your partner and think of any 2 differences.
Fill in the blanks.
1. The south west monsoon winds bring to India.
2. is the distance of a place from the equator.
3. areas experience moderate climate due to the sea’s influence.
The world is divided into three climatic, or heat, zones. These three zones are the Torrid Zone, the Temperate Zone and the Frigid Zone.
The Torrid Zone lies between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. It receives direct rays from the Sun, resulting in high temperatures and heavy rainfall. It is typically hot and humid throughout the year. This zone generally receives a lot of rainfall.

The Temperate Zone is located between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle in the Northern Hemisphere, and between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle in the Southern Hemisphere. These regions receive slanting rays from the Sun, so the climate is neither too hot nor too cold.
The Frigid Zone is found near the poles, between the Arctic Circle and the North Pole in the Northern Hemisphere, and between the Antarctic Circle and the South Pole in the Southern Hemisphere. It is very far from the equator and receives very slanted rays of the Sun. This zone remains frozen for most of the year. Due to global warming, the ice caps in the polar regions are melting. We must play our part in reducing air pollution and protecting environment so that we can stop global warming.
Polar regions are not always cold and dry. Coastal areas in Antarctica can be humid, and some Arctic regions of Alaska and Canada experience significant snowfall and milder temperatures at certain times during the year.

Gulmarg in Jammu and Kashmir is the ultimate snowy paradise in India. With its breathtaking snow-covered landscapes, fantastic skiing opportunities, and some of the heaviest snowfall in the country, it is the perfect destination for snow enthusiasts.

atmosphere: the layer of air surrounding the Earth temperature: a measure of how hot or cold something is weather: the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time climate: the average weather conditions over a long period climatologists: scientists who study climate and weather patterns latitude: distance from the equator altitude: height of a place above the sea level humidity: the amount of moisture in the air


Scan the QR code to learn more about factors that are affecting climate change.
• The atmosphere is the layer of air that surrounds the Earth.
• The local weather and climate significantly influence people's lifestyles, including their clothing, food and housing.
• Climate is the weather pattern of a place for a longer duration of time.
• The main factors affecting climate include latitude, altitude, distance from the sea, direction of winds and humidity.
• The world is divided into three climatic zones, which are the Torrid Zone, the Temperate Zone and the Frigid Zone.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. The atmosphere is a layer of air that surrounds the
a. Mountains
b. Earth
B. Altitude is the height of a place above the
a. Ground level
b. Sea level
C. The imaginary line that circles the middle of the Earth is
a. Axis
b. Equator
D. How many climatic zones is the Earth divided into?
a. 3
b. 5
c. Water bodies
c. Mountain level
c. Orbit
c. 4
2. Fill in the blanks.
moisture sea breezes climatologists Tropic of Capricorn
A. The people who study the climate are called .
B. Humidity is the measure of present in the air.
C. The Torrid Zone is located between the Tropic of Cancer and the .
D. blow from the sea to the land, bringing moisture, warmth and often rainfall.
3. Write True or False.
A. The atmosphere consists of several layers.
B. Winds blowing from the sea toward the land are called land breezes.
C. The Torrid Zone is situated between the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle.
D. The Frigid Zone is far from the equator and remains cold for most of the year.
4. Match the following.
A. Distance from the equator i. Atmosphere
B. Height above sea level ii. Poles
C. Layer of air around Earth iii. Latitude
D. Frigid zone iv. Altitude
5. Short answer questions.
A. Name the factors that influence the climate.
B. What is humidity and how does it affect the climate?
C. Differentiate between sea breeze and land breeze.
D. Differentiate between latitude and altitude.
6. Long answer questions.
A. How does the distance from the equator and the sea affect the climate of a place?
B. Describe the three climatic zones of the Earth.

7. Picture-based questions.
A. What kind of place is this?
B. What will be the climate of this place?
C. What type of clothes should people wear in this place?



What role do trees and forests play in affecting the climate of a place? Mention any two points.

Talk to your grandparents or some older neighbours from your community. Ask them about how weather patterns have changed over the years. Here are some questions you can ask:
1. What was the weather usually like when you were my age?
2. Have you noticed any changes in the weather patterns from the time of your childhood till the present day?

Chapter Overview

During Disasters


Name the situations the given pictures are telling about. Use can take help from the hints given along with the pictures.


(Hint: When there are
(Hint: When the Earth shakes continuous rains.) and shocks are felt.)
The pictures above are of natural disasters. A natural disaster is a crisis or a calamity caused by nature. These disasters occur without warning and can cause a lot of damage. They even harm people, animals and the environment. Earthquakes, floods, droughts and cyclones are some of the different kinds of natural disasters. In this chapter, we are going to learn about them.

An earthquake is the sudden shaking of the ground. One of the major reasons for an earthquake is movements under the surface of the Earth. These movements cause sudden tremors on the Earth’s surface.
The intensity of an earthquake is measured on a scale called the Richter scale. A value of 1–2 on the Richter scale indicates mild earthquakes, while that of 6 or above is considered extremely powerful. A machine that records and measures how strong an earthquake is is called a seismograph. The point from where an earthquake originates is called the focus. The place directly above the focus on the Earth’s surface is called the epicentre of the earthquake. The effects of the earthquake are maximum at the epicentre.

The Himalayas and its surrounding areas experience frequent earthquakes. They are also frequent in Japan, the Philippines and on the edges of the Pacific Ocean.
Safety tips to follow during an earthquake:
• Drop to the ground, take cover under a sturdy table or desk and hold on until the shaking stops.
• Move away from windows, glass objects and anything that could fall, like bookshelves or heavy pictures.
• If you are inside, stay there until the shaking stops. Do not use lifts; use stairs instead.
On 26 January 2001, Gujarat was struck by a violent earthquake that recorded 7.7 intensity in the Richter scale. It caused a huge loss of life and property.
Have you ever noticed how the roads in your city sometimes become waterlogged? Sometimes, when the rain is too much for the drains to handle, water starts to collect and cannot flow away easily. This waterlogging is like a small version of what happens during a flood. Floods happen when a lot of water covers the land due to water logging or overflowing of water bodies.
tremors: the shaking or vibration of the Earth's surface sturdy: something that is strong and solid or thick
Floods are often caused by heavy rainfall, cloudbursts and melting snow. Sometimes, when a dam breaks or gets damaged because of heavy rains; all the stored water can rush out quickly and flood the areas downstream of the dam. During floods, buildings are destroyed because of water filling inside them, thereby causing them to collapse. There is so much build up of water that it covers roads, enters homes, and can even sweep away everything in its path. There is loss of crops as floods can wash away crops too. Floods also cause loss of lives of animals. There is a rise in epidemics, like malaria and diarrhoea, after flooding. Assam, West Bengal, Bihar and Uttar Pradesh are frequently affected by floods.
Safety tips to follow during floods:

• Go to a high place like a rooftop or a hill where the water cannot reach you.
• Help in rescuing older people, children and pets who are caught in the water.
• Try to swim away from electronic appliances or heavy furniture.
• If the flow of water is too strong, try to swim to a sturdy pole or a tree, and hold on to it.
• Always listen to the instructions given by rescue officers.
Do and Learn
With the help of internet, prepare an evacuation plan for your family in case of floods. Include the steps to take before, during and after the floods. Share your plan with your friends as well.
Write True or False.
1. Roads become filled with water when floods occur.
2. Earthquakes are measured using the Doppler scale.
3. The breaking of dams can cause floods.
cloudburst: sudden violent rainstorm epidemics: when a large number of people in a specific area get sick from the same disease at the same time

Cyclones are violent storms that form over seas and oceans. They cause great damage when they reach the shore. During cyclones, there is heavy rainfall, and strong winds. In India, the states of Odisha, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu are frequently hit by cyclones.
Safety tips to follow during cyclones:
• Do not go close to the sea or the ocean. If you are out in the open, take shelter immediately. Avoid sheltering beneath trees.

• Stay indoors if you live in apartments or other kinds of pucca houses.
• Stay away from electrical appliances.
Another natural disaster near the coastal regions is a tsunami. They are huge ocean waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions. Large waves come rushing towards the land and cause flooding in minutes. The height of the waves can vary between 10 feet to 100 feet. Tsunamis can flood coastal areas and destroy homes, buildings and roads. The sudden impact of a tsunami can cause numerous people to lose their lives and others to get injured. The salty sea water brought in by the tsunami can make the soil less fertile, affecting farming and plant growth.
Safety tips to follow during a tsunami:

• If you hear a tsunami warning, quickly move to higher ground.
• Pay attention to emergency alerts and warnings from local authorities.
• Do not go to the beach to watch the waves.
• Use evacuation routes to reach safer areas.
numerous: too many
evacuation: safe escape

A drought occurs when there is not enough rain for a long time. This causes a shortage of water for plants, animals, and people. As the underground water levels reduce, availability of water for drinking and other daily purposes becomes scarce. The geographical location of a place plays an important role in determining places affected by droughts. Deforestation, caused due to overgrazing and excessive cutting of trees is also a factor that causes droughts. During a drought, streams, lakes and wells may dry up, leading to a shortage of clean water for families. This makes it hard to cook, drink and wash properly. Farmers are most affected by droughts. Crops dry up and die, which makes it difficult for farmers to grow food. This results in famine and starvation. Animals also struggle because there is not enough water to drink. Some ways to stop the spreading of droughts are:

• The best way to tackle droughts is by planting more trees. This is known as afforestation. For example, Rajasthan has suffered less droughts after planting more trees.
• Rainwater harvesting techniques should be implemented.
• Water conservation projects should be implemented in states that are prone to droughts.
It is believed that droughts can only happen in very hot places. But that is not true. Droughts can occur in various climates, including temperate and even cold regions, when there is a prolonged lack of rain or snowfall.
A natural disaster can occur anytime. We must be trained and ready to keep ourselves and our family and friends safe if any natural disaster occurs. We must follow these steps in the event of a natural disaster.
• Remain calm and listen to instructions from adults or authorities.
• Move to a safe place away from danger, such as staying indoors during cyclones or going to higher grounds during tsunamis or floods.
scarce: so less in quantity that almost nothing is left famine: extreme scarcity of food


• Organise help and rescue operations.
• Stay updated through radio, TV or official announcements about what is happening and when it is safe to return to normal activities.
• Help people who are affected by natural calamities by donating clothes, money, food and medicines to help them rebuild their lives.

Rescue efforts at an earthquake site
The government also provides help during natural disasters. It invests in advanced technologies to detect natural disasters early. In India, the NDMA (National Disaster Management Authority) lays down policies for effective disaster management. Sometimes, the army is also involved to move people to safer places.
During natural calamities, apart from the government, some other organizations and agencies also help the affected people. Let us talk about some of them.
1. Red Cross Society: Their symbol is a huge red cross on a white background, which is visible on all its vehicles, equipment and clothing worn by its volunteers. The Red Cross provides medical relief to the victims and helps in rehabilitating them.
2. WHO (World Health Organisation): The WHO helps during natural disasters by giving medical care and making sure people have clean water, food and healthcare. This organisation also prevents the spreading of diseases and helps communities get their health services back quickly.
3. UNICEF (The United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund): UNICEF provides financial assistance and essential items, particularly to children. It also ensures that orphans and people with disabilities receive care and support after a natural disaster.


The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) is an Indian force dedicated to helping and rescuing people during natural disasters. It is made up of 16 battalions, each consisting of about 1,149 personnel. The NDRF's rapid and effective response to major disasters has been possible due to its extensive training and the use of advanced technology. NDRF rescuing people during floods
rescue: save from a difficult situation rehabilitating: restoring someone to normal life
natural disaster: a crisis or a calamity caused by nature earthquake: sudden shaking of the ground
seismograph: a machine used to record and measure an earthquake flood: a lot of water on land which also enters homes, etc.
cyclones: violent storms that form over the sea or the ocean
tsunami: a huge ocean wave caused by an underwater earthquake or volcanic erruption drought: when there is not enough rain for a long time

Scan the QR code to learn more about flood prevention management.
• Natural disasters are sudden events that cause widespread death, destruction and damage.
• Earthquake, volcano, flood, tsunami and drought are some examples of natural disasters.
• The government and some other agencies provide rescue and relief support to people affected by natural disasters.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which of the following is a natural disaster?
a. Afforestation
b. Tsunami
c. Deforestation
B. Which instrument measures the intensity of an earthquake?
a. Seismograph
b. Thermometer
c. Barometer

C. Which organisation provides relief, particularly for children?
a. WHO
b. UNICEF c. Red Cross
D. A drought occurs when there is .
a. Less rainfall
b. Thunderstorm c. Flooding
2. Fill in the blanks. famine coastal floods cyclone
A. Cyclones and Tsunamis occur in regions.
B. A is always accompanied by heavy rainfall and strong winds.
C. Epidemics, such as malaria and diarrhoea, are common after .
D. A drought can result in a .
3. Write True or False.
A. Drought-hit areas experience heavy rainfall.
B. The army does not play any role during natural disasters.
C. Weather updates over the radio can help during natural disasters.
D. WHO provides relief during natural disasters.
4. Match the following.
A. Drought
B. Tsunami
i. Ground shakes violently
ii. Extreme scarcity of rain
C. Earthquake iii. Overflowing of water everywhere
D. Flood
5. Short answer questions.
iv. Huge ocean wave formed due to underwater earthquake
A. How can you identify whether the earthquake is mild or severe?
B. How does a drought occur?
C. How does a tsunami affect people?
D. Name any two organizations that provide help during a natural calamity.
6. Long answer questions.
A. Write two measures each to prevent floods and droughts.
B. What are the effects of a cyclone? How can we be safe during a cyclone?
C. What is NDMA? What does it do?
7. Picture-based questions.
A. Identify the natural calamity shown in the image.
B. What are the two after effects of this calamity?

C. Give two safety measures to be followed during this calamity.


Imagine a drought occurs in the Northern Plains of India. What do you think could happen as a result, and how would it affect the country?

Natural disasters, like floods, earthquakes and cyclones, can have a huge impact on the people and the environment. Talk to your parents, neighbours or elders and ask them if they have ever experienced a natural disaster. Find out what happened, how they prepared for it and how they stayed safe. Share the learnings with your classmates.

With the help of your teachers and friends, present a short skit on how to stay safe during an earthquake. You pretend that an earthquake happens while you are at school. Talk about what you would do to keep yourself and your friends safe during the earthquake. Then, present the skit.






Look at the pictures. Put a tick () against the images that are good for the environment.



The environment is made up of all living and non-living things around us. It also includes human-made things. We create human-made things to make our lives easier. These include vehicles, houses, electrical appliances, roads, etc. However, human-made things have also damaged the environment in many ways, like the release of smoke into the air from factories. The damage caused to the environment results in pollution.
Pollution is the introduction of harmful substances in our environment (air, water, land). These harmful substances are called pollutants. Pollution is caused by things like factories and vehicles releasing smoke into the air and the act of littering. There are three main types of pollution—air pollution, water pollution and land pollution. Let us learn about each of them.
When harmful gases, toxic particles, or a lot of dust are released into the air, they cause air pollution. Air pollution is caused when factories, power plants and vehicles release harmful gases and smoke into the air. Burning fossil fuels, like petrol releases a lot of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Also, various natural phenomena such as volcanic eruptions, forest fires and dust storms cause air pollution.



• Gases like carbon dioxide and methane trap the sun’s heat and increase the temperature of the Earth. This leads to global warming, which is the increase in the Earth’s temperature by these gases (especially carbon dioxide).
• The ozone layer is a layer in the atmosphere that protects us from the harmful rays of the sun. But certain gases damage this layer, thereby exposing us to the sun's harmful rays.
• When various harmful gases rise and combine with water vapour in the atmosphere, it results in acid rain. Acid rain damages buildings and forests and is harmful for living beings as well.
• Air pollution causes several diseases such as asthma, lung cancer and bronchitis.

People get diseases due to air pollution.
littering: throwing of waste on the ground or in a public place global warming: the increase in the temperature of the Earth due to the trapping of the sun's heat by gases such as carbon dioxide


Pollution is not something that happens outside only. Indoor air pollution is as harmful as outdoor air pollution. Major pollutants of indoor pollution include vapours from paints, and dust from tiles and cement.
• Encourage afforestation or the planting of trees and plants.
• Use public transport for travelling. Try carpooling with your friends and family rather than using private vehicles. Try to walk wherever possible.
• Recycle garbage instead of burning them.
• Reduce the use of things that use up or burn fossil fuels. For example, electricity comes from burning huge amounts of coal. Switching off lights and fans when not using them reduces the use of electricity, thereby reducing the amount of coal used.
Have you ever seen people throwing garbage into rivers or washing their clothes on the river bank? What do you think happens to the river water due to this?
When things like chemicals, garbage and sewage are dumped into our water bodies, they cause water pollution. Water pollution severely affects aquatic plants and animals and cause a lot of diseases in us.
Many things cause water pollution. Some of them are:
• Domestic chores, like bathing and washing clothes in rivers, ponds or lakes.
• Dumping untreated waste from homes and factories or immersing idols in rivers, ponds or lakes.
• Oil spills caused from oil tankers or oil mining sites pollute the ocean, severely harming marine life. It takes a very long time for the ocean waters to be clean again.


• The consumption of dirty and polluted water causes several diseases like jaundice, cholera, typhoid and dysentery.
• Oil spills make a layer of oil on the surface of the water that reduces the amount of oxygen dissolving in the water. This causes marine plants and animals to choke and die due to lack of oxygen.

• Never throw garbage near or in water bodies such as rivers, lakes or ponds.
• Reuse water to prevent dirty water to be drained into rivers. For example, reuse kitchen water for cleaning your car and watering your plants.
• Use more eco-friendly products so that there is less chemical waste released from your homes.
• Use reusable items instead of items that are thrown away after being used once. For example, reusing glass bottles instead of using and throwing away a plastic bottle.
• Join cleaning drives to voluntarily clean local water bodies like ponds and streams.
Urmi and her father went to the park one evening for a walk. They noticed a garbage dump in a corner. It caused the park to smell, attracted flies, and spoilt the way the park looked. Her father told her that the dumping of waste materials on land is a cause of land pollution.

Land pollution happens when land or soil gets contaminated by harmful substances such as solid waste, garbage, and harmful chemicals. Another cause of land pollution is deforestation. The roots of the trees hold the soil firmly. But when trees are cut down, the fertile soil gets washed away due to running water and strong winds, thereby causing its erosion.
Dumping of non-recyclable waste such as polythene bags, plastic bottles, chemical waste and e-waste (old laptops, mobile phones, televisions and computers) on land causes pollution. Excessive use of fertilizers and pesticides for agricultural purposes, and animal and human waste also cause land pollution.

• Most plants need soil to grow. We get our food from plants. Plants grown in polluted soil may contain harmful substances that reach us through the food we eat. This can cause several diseases.
• Some animals and plants die due to soil contamination and hence, the food chain gets disturbed.
• Chemicals in the soil also leak into the ground water or get washed into rivers during rains. This contaminates the water we use for our domestic purposes, and cause diseases.
pesticides: chemical sprays used to kill insects on crops


• Create less waste. For example, carry your water bottle instead of purchasing a new one, each time you go out.
• Plant more trees and use organic manure for agricultural purposes.
• Dispose of waste properly. Throw biodegradable wastes into green bins and non-biodegradable wastes into blue bins.
Complete the following sentences.
1. The increase in the Earth’s temperature is called .
2. Oil spills in oceans reduce the supply of dissolved .
3. One of the main causes of land pollution is .
Materials that are no longer useful to people are called waste. It is important to dispose of waste properly. Otherwise, it can lead to pollution and the spreading of germs and diseases. Waste is sorted into two types:
• The waste that can be broken down by worms and bacteria when mixed with the soil is called biodegradable waste. Fruit and vegetable peels, paper and leaves are some examples of biodegradable waste. It is useful for the environment. It can be converted into manure, which can be used to improve the fertility of the soil. This is done through a process called composting. In this process, biodegradable waste is buried in the soil for around two months.

Use separate bins for different types of wastes
• Waste that cannot be broken down by worms and bacteria when mixed with the soil is called non-biodegradable waste. Plastic items, metal cans, glass bottles, etc. are examples of non-biodegradable waste.
During waste disposal, biodegradable waste should be thrown in green-coloured dustbins while non-biodegradable waste should be thrown in blue-coloured dustbins.
What are the benefits of using separate dustbins for different types of waste? Is it necessary to do so? Discuss with your classmates.


We should follow the policy of the 3Rs to protect our environment. The 3Rs are: Reduce, Reuse, Recycle.
Reduce: Reduce your usage of things that generates more non-biodegradable waste. We should reduce our usage of plastic since it cannot be broken down in the soil and it creates waste. We should only buy as much as we need so that excess items do not have to be thrown away.

Reuse: Some items can be used again and again. We can reuse plastic bottles to store water instead of throwing them away. We can reuse cloth bags to carry grocery instead of plastic bags. Plastic containers can be used to store things around the house.
Recycle: Items that cannot be reused can be made into other useful items. This process is called recycling. Old newspapers can be used to make paper bags. Waste objects made of metal are melted in factories to make other items. Even water can be recycled. The water that we use to cook food can be used to water plants.
Following the policy of the 3Rs in our daily lives will help us protect our environment and keep it clean and green.
Gather old newspapers, magazines, empty plastic bottles, cardboard boxes and other unusable items from your home. Use your creativity to make new items such as a flower vase, pot holders, pen stands, etc., from these materials. Decorate your new item with the materials of your choice.

The Bishnoi community in Rajasthan is known for their deep respect for nature and wildlife. The Bishnoi people are popularly known for their efforts to save trees from being cut down.

pollution: the addition of harmful substances into the environment pollutants: harmful substances that pollute the environment

afforestation: planting of trees and plants
deforestation: cutting down trees and forests over a large area of land biodegradable waste: waste from natural materials that can be broken down non-biodegradable waste: waste that cannot be broken down

Scan the QR code to know more about air pollution.
• Pollution is the introduction of harmful substances into the environment.
• There are three major types of pollution—air pollution, water pollution and land pollution.
• When harmful gases or toxic particles are released into the air, they cause air pollution.
• When land or soil gets contaminated by harmful substances such as solid waste, garbage, and metal containers, it causes land pollution.
• When chemicals, wastes and sewage are added into water bodies, these pollute water and cause water pollution.
• Waste can be sorted into two types: biodegradable and non-biodegradable.
• The policy of Reduce, Reuse, Recycle can help us protect our environment.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. One cause of air pollution is
a. burning of fossil fuels. b. sounds from factories.
c. sewage.
B. Water pollution causes diseases like a. cholera. b. asthma.
c. high blood pressure.
C. We can tackle land pollution by a. recycling.
c. cutting down trees.
D. The 3Rs stand for
a. Reject, Redeem, Repurpose
c. Refuse, Redo, Remember
b. throwing garbage in the open.
b. Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
2. Fill in the blanks. pollution acid afforestation biodegradable
A. is the introduction of harmful substances into our environment.
B. rain has harmful effects on buildings and living beings.
C. We should throw waste into green dustbins.
D. Planting of trees is called .
3. Write True or False.
A. Air pollution can cause respiratory problems.
B. Water pollution does not affect aquatic life.
C. Planting trees helps reduce air pollution.
D. Recycling means creating new things out of old objects.
4. Match the following.
A. Air pollution
B. Land pollution
C. Water pollution
D. Biodegradable waste
5. Short answer questions.
A. Define pollution and pollutants.
i. Soil-borne diseases, skin allergies
ii. Cholera, typhoid, dysentery
iii. Asthma, lung cancer, bronchitis
iv. Generated from natural things
B. Mention one harmful effect of land pollution on humans.
C. What is global warming?
D. What are the 3Rs about protecting the environment?

6. Long answer questions.
A. Write a note on the causes and ways to control air pollution.
B. What are the two types of waste? How are they different?
C. In what can we apply the 3Rs in our lives to prevent environmental pollution? Give any three ways.
7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. Which type of pollution is shown in the given image?
B. How will this type of pollution affect the plants and animals that depend on water?

C. Write two ways that we can use to reduce this type of pollution.


1. A forested area was cleared to build a highway. How do you think this will affect the environment?
2. What would happen if we keep polluting our environment? How do you think it will affect our future generations? Explain in 2 points.

Ask your family and neighbours about how they recycle things at home. Then, discuss with them about more ways of reusing and recycling things that would further reduce the amount of waste produced at home and in your neighbourhood.

With your parents and neighbours, organise a cleanliness drive for a nearby water body. Collect and separate waste into different coloured garbage bags. You can use green colour bags for biodegradable waste and blue/black bags for non-biodegradable waste. Make a note of 5 items you put in each bag.



Chapter Overview Get Set
Vegetation



Read the poem given below. It is about a beautiful country, the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
In Congo’s heart, the rivers flow, Through forests deep where wild things grow. With mountain peaks that kiss the sky, And vibrant sunsets waving goodbye. From Kinshasa’s streets to jungle’s call, The spirit of Congo unites us all.
A land of beauty, rich and wide, Here culture and nature, side by side.

Republic of the Congo Lifestyle

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is located in central Africa. The Equator passes through the northern part of the country. It is the second largest country in Africa. The capital of the DRC is Kinshasa. Its neighbouring countries are the Central African Republic, South Sudan, Rwanda, Burundi, Uganda, Tanzania, Angola and Zambia.
The DRC was ruled by Belgium until 1960.
The Congo is the main river in the DRC. The Congo basin is huge and covers almost the entire country. The southern part of the DRC has plateaus. High mountains are present in the east.
Since the DRC is near the Equator, the climate is hot and humid all year round. The north of the DRC receives heavy rainfall in the afternoon almost every day. Due to this, it is one of the wettest regions in the world. The southern part of the DRC is drier and has less rainfall.

What are some ways in which the Congo River might be important to the people of the DRC? Discuss with your classmates.
Most of the DRC is covered in dense vegetation. The hot and humid climate is suitable for the growth of tropical rainforests. These are evergreen forests. The trees here are very tall and closely
The Congo rainforest is the second largest rainforest in the world. It is also called the ‘Lungs of Africa’.
basin: the area of land around a large river from which smaller rivers and streams run down to it

packed together. Their branches get tangled with each other and form a canopy of leaves at the top. This canopy prevents sunlight from reaching the ground.
Evergreen forests have trees that remain green throughout the year since they lose old leaves and grow new leaves continuously.
In the south, the climate is not as hot and wet as in the north. So instead of dense forests, there are grasslands like the savanna. The forests and savannas of the DRC are very rich in wildlife. Animals such as chimpanzees, baboons, elephants, buffaloes, rhinoceroses and hippopotamuses are commonly found in the forests. Lions, leopards, zebras, giraffes and wolves can be found in the savannas. Crocodiles are present in large numbers in the rivers. Many kinds of birds, insects and snakes can also be found in the forests.


Find pictures of 2 plants and 5 animals found in the DRC, other than the ones shown in this chapter. Paste them in your scrapbook and write their names next to their pictures.
Write True or False.
1. The Congo is the longest river in Africa.
2. The equator passes through the DRC.
3. The DRC experiences heavy rainfall in the afternoon every day.
4. The DRC has deciduous forests.
canopy: the uppermost branches of the trees in a forest, forming a continuous layer of leaves


In the DRC, the main industries are mining and agriculture. The country is rich in minerals like cobalt, which is used in batteries, and diamonds, which are precious gems. The country also has gold, which is used for making jewellery, and electronics and coltan, which is used in phones and computers. These industries help support the DRC’s economy.
Agriculture is also important, with people growing crops like cassava, rice, maize, coffee, cocoa, rubber and cotton. Most of these are exported as well. Dams have been built on rivers in DRC, providing hydroelectricity.
Water transport is the major means of transport in the DRC. Railways and road networks connect different cities.


The DRC has a significant population, but much of it is rural, with many people living in villages. They live in huts which are built on raised platforms to protect them from the heavy rainfall. They grow crops like cassava and plantains.
The DRC is home to different tribes with unique customs and traditions. For example, the Bambuti people, also known as Pygmies, live in the rainforest and have a special bond with the forest. They are known for their small size and they use traditional hunting skills to find food. The Twa people also live in the forest and have similar customs.
The Babinga people live in the southern part of the country and are known for their colourful clothes and intricate beadwork.
People in the DRC often wear bright, patterned clothing made from local fabrics. Customs and festivals are an important part of life. For example, people celebrate with dances, music, and traditional ceremonies that have been passed down through generations. Life in the DRC is rich in culture and sense of community.


India has supported various UN peacekeeping missions in the DRC to maintain stability and support the local population. These initiatives reflect India’s commitment to international cooperation and its role in global affairs.

A UN peacekeeper soldier
tropical rainforest: dense and warm rainforests with high rainfall usually found between 10° north and south of the equator
savanna: grassy plains in tropical and sub-tropical regions
tribes: a group of people who have the same language, customs and live in their separate society

Scan the QR code to learn more about the Congo River of the DRC.
• The Congo is the main river in the DRC.
• The DRC is rich in minerals like cobalt, used in batteries, and diamonds, which are precious gems.
• Lions, leopards, zebras, giraffes and wolves can be found in the savannas.
• People in the DRC often wear bright, patterned clothing made from local fabrics.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. Which is the main river in the DRC?

B. Which of the following tribes live in the rainforest of the DRC?
a. Bambuti b. Banjaras c. Inuits
C. Which of these crops are grown in the DRC?
a. Wheat
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Millets c. Rubber
Babinga Coltan Savanna Canopy
A. The tribe in the DRC is known for its beadwork.
B. The tall trees in the forests of the DRC form a which prevents sunlight from reaching the forest floor.
C. is used in phones and is found in the DRC.
D. In the south of the DRC, there are grasslands called the .
3. Write True or False.
A. The DRC has tropical rainforests.
B. The DRC is the second largest country of Africa.
C. Republic of the Congo is the capital of the DRC.
D. The southern part of the DRC has plateaus.
4. Match the following.
A. Savanna i. Batteries
B. Kinshasa ii. Giraffes
C. Cobalt iii. Gold
D. Jewellery iv. Capital of the DRC
5. Short answer questions.
A. Why does it rain every day in the DRC?
B. Name any three crops grown in the DRC.
C. Name any two neighbouring countries of the DRC.

6. Long answer questions.
A. What kind of lifestyle do the people of the DRC have?
B. Describe the wildlife of the DRC in the north.
C. What type of climate does the DRC have?
7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the questions that follow.
CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC
CAMEROON
EQUATORIAL GUINEA
REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
DEMOCRATIC REPUBLIC OF THE CONGO
SOUTH SUDAN
ATLANTIC OCEAN
A. Which countries border the DRC in the north and in the west?
B. Which ocean is closest to the DRC?

Compare the climate of the Democratic Republic of Congo with the climate in your state. How are they similar or different? Write any 3 points.
The Congo Rainforest are called the ‘Lungs of Africa’. With the help of the internet, research on the Congo Rainforest. Then, write 5 points on how it helps the environment of the DRC and of Africa. You may make this as a poster. Share your findings with your class.




Greenland: The Land of Ice and Snow
Location and Climate Vegetation and Wildlife Occupations and Transport
Lifestyle


Which of the following places will be the coldest? Put a tick (✓) against it.



Greenland is located in the Atlantic Ocean, to the northeast of North America. It is a territory of Denmark. Its capital is Nuuk. Sisimiut is another important town.
The North Pole and the South Pole are located at 90-degree north and 90-degree south latitudes, respectively.
Greenland is the largest island in the world. The Arctic Circle passes through the southern part of Greenland. It lies in the frigid zone, which means it experiences very cold temperatures throughout the year.
The climate of Greenland is extremely cold, with long, icy winters and short, cool summers. Temperatures can drop below –30°C in winter and rise only slightly above the freezing point in summer. Most of this island is covered in ice.

GREENLAND (DENMARK)
Upernavik
Ittoqqortoormiit (Scoresbysund)
Sisimiut (Holsteinsborg)
Nuuk (Godthab)
The southwestern part of Greenland is warmer, and hence, most people live in this part.
Most of the plants grow in the tundra region, towards the coast and away from the ice sheets in central and north Greenland. Low-growing plants like dwarf birch and whortleberry, as well as mosses and lichens, can be found in this region.
Animals, like the polar bear, reindeer, seal, wolf, arctic fox and musk ox, are found here. All these animals are able to withstand extreme cold.

Many kinds of fish and birds, like the white-tailed eagle, are also found here. Seals and walruses are some of the large marine animals found in this region. Many species of whales, such as fin, minke, humpback, narwhal, beluga (white whale) and blue whale are found in Greenland.
A walrus and her pup
lichens: a group of tiny plants that grow on rocks, walls and trees



Animals are very important to people in the tundra region. Their meat, bones, skin and milk are used by the people for food, clothing and shelter.
Polar bears are the largest carnivorous land mammals on Earth. They are also very strong swimmers. They can swim continuously for many days.
Write True or False.
1. Greenland is very fertile with lots of vegetation.
2. The Antarctic region is situated between 66.5°S and 90°S.
3. Seals, whales and walruses are found in Greenland.
The most important occupations in Greenland are hunting and fishing. Sheep are also reared in small numbers in the southwestern part of the country. Vegetables, such as potatoes, are grown in the southwest part of Greenland.
Since most of Greenland is always covered with ice, it is not possible to build roads and railways throughout the island. People travel by sledges, which are drawn by reindeers or dogs found there. A sledge is a vehicle that has blades instead of wheels and is used in places that are covered with snow. People also go out into the sea in small boats called kayaks and umiaks. Kayaks are narrow boats that can carry one or two people. Umiaks are larger open boats, made of animal skin stretched over a wooden frame and can carry ten or more people at a time.



carnivorous: an organism that eats flesh of other animals mammals: animals that give birth to babies instead of laying eggs and feed the babies milk from their own bodies

Most people in Greenland are Inuits who have lived there for thousands of years. The Inuit people are known for their special skills in surviving in freezing temperatures. Many people in Greenland live in small towns or villages along the coast. The houses are made of strong materials, like wood, stones, or even concrete, with thick walls, to keep out the cold. Central heating is also common in modern homes.
What are the different ways in which the lives of the people of Greenland are influenced by its environment?

In the past, the Inuit people led a nomadic life, which means they did not settle at one place and kept moving from one place to another. They lived in igloos during the winter and in tent-houses made of leather during the summer. Igloos are dome-shaped houses made from blocks of snow. An igloo
Make a chart about the Inuit people of Greenland. Paste pictures and write about their food habits, clothing, occupations, modes of transport and festivals. Give the chart a creative title. Do and Learn
People in Greenland eat food that comes from the sea, like fish, seals and whales. Earlier people used harpoons to hunt, but now they use guns. They also eat reindeer, birds and imported foods from other countries. Hunting and fishing are still important activities in their culture, helping them survive the cold environment.
People here mostly wear clothes made of animal skin and fur to keep themselves warm. A jacket with hoods and lined with animal fur is quite popular here. It is called parka. They wear long boots made of seal skin, which makes it easy to walk in snow and keep their feet warm.
Most people live in the southwestern part since it is less cold there. Modern facilities, like schools, hospitals, permanent homes, electricity, etc., are present in these areas.

harpoon: a spear-like instrument that is attached to a long rope and thrown by hand


The Siachen glacier is one of the longest glaciers outside the polar regions. It is located in Ladakh, India.

sledge: a vehicle without wheels that is used to travel in snow kayak: a small, narrow boat with a small opening at the top for a person to sit in umiak: an open boat made of animal skin stretched over a wooden frame igloo: a dome-shaped house made of snow parka: a jacket with a hood and lined with animal fur

Scan the QR code to learn more about life in Greenland.
• Greenland is the largest island in the world.
• The Arctic Circle passes through the southern part of Greenland.
• The most important occupations in Greenland are hunting and fishing.
• Since Greenland is mostly covered in ice, plants like mosses and lichens grow here.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer.
A. In which region is Greenland located?
a. The Torrid
b. The Temperate c. The Polar
B. What are the native people of Greenland called?
a. Inuits
b. Babingas c. Bengalis
C. In the past, what did people use for hunting?
a. Hooks
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Harpoons c. Crossbows
A. Greenland is a territory of .
B. is the capital of Greenland.
C. is an important town in Greenland.
D. Inuits live in in winters.
3. Write True or False.
A. Most of Greenland is permanently covered with ice.
B. Greenland has a large network of railways.
C. Lots of vegetation is found in Greenland.
D. Greenland is located in the Atlantic Ocean.
4. Match the following.
A. Umiak i. A jacket with hood, lined with animal fur
B. Sledge ii. A boat that can carry many people
C. Parka iii. A boat meant for one person
D. Kayak iv. A vehicle without wheels
5. Short answer questions.
A. What are some of the occupations of the people of Greenland?
B. Name any three species of whales found in Greenland.
6. Long answer questions.
A. How is the climate of The Democratic Republic of the Congo different from that of Greenland?
B. How does the location of Greenland influence the life of the people there? Mention any three points.
C. What kind of clothes do people wear in Greenland?

7. Picture-based questions.
Look at the given picture and answer the following questions.
A. What is the boat in the picture called?
B. Do you think roads and railways can be used in the place shown in the picture? Why or why not?


Imagine you had to live in Greenland for a month. Write about the following:
1. Two things you would eat.
2. Two things you would wear.
3. Two ways in which you will travel around.
4. Two things you will do there.

Houses are built depending on the weather and the climate of the area in which they are built. With the help of your parents or elders, understand how the houses in your region are designed to suit the climate there.


Chapter Overview Get Set
Cities and Some Places of Interest


We know that deserts have extreme climatic conditions. Name two plants that grow in deserts.


Major desert regions of the world
Saudi Arabia is a country in the western part of Asia. It is located in the Arabian Peninsula. A peninsula is a land which is surrounded by water on its three sides. Saudi Arabia has the Red Sea on the west and the Persian Gulf on the east. Riyadh is the capital of Saudi Arabia. Some of its neighbouring countries are Jordan and Iraq to the north; Kuwait to the northeast; Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; and Oman and Yemen to the south. It is the largest country in West Asia.
map of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia has the world’s largest continuous stretch of desert land. Deserts and plateaus cover the central and eastern parts of the country. The desert region is covered with hills of sand called sand dunes. The western part of Saudi Arabia is mountainous. Saudi Arabia does not have any

lakes or perennial rivers. Streams called wadis are occasionally formed after rainfall, but they disappear quickly. Due to this, Saudi Arabia has very little freshwater. In some places in deserts, underground bodies of water rise to the surface. These are called oases.

Do you think wadis and oases are important for the animals which live in the desert? Discuss with your classmates.
The Tropic of Cancer passes through Saudi Arabia, dividing the country into two halves. During summers, it has extremely hot weather with temperatures above 50° C at times. In the desert, the temperature varies greatly from day to night as well. It is very hot during the day and cold at night. The climate throughout the year is extremely dry as Saudi Arabia receives very little rainfall.
The plants that grow here have adapted to the hot and dry climate. They mostly have very long roots that go deep into the earth in search of water. They have thick, fleshy stems which can store water. Many of them have spines instead of leaves in order to minimise water loss. Some of the plants that can be found here are cacti, thorny bushes and shrubs. Trees like date palms grow in and around the oases.

How does having spines instead of leaves help trees in minimising water loss?


Deserts have very harsh climatic conditions. All the animals that live in the desert have to adapt to conditions like the shortage of food and water, and extreme heat to survive. A wide variety of animals are found in Saudi Arabia. Horses from Arabia are known all over the world for their speed. Other fast animals like gazelles, foxes and jackals can also be found in the Saudi Arabian desert. They can move across the desert very quickly in order to find food. Small animals like scorpions and snakes burrow into the sand during the day to escape the extreme heat. They come out at night to hunt for food.
We have previously learnt that the camel is known as the ‘ship of the desert.’ Camels have special adaptations that enable them to survive in the desert. They can store water in their bodies for many days. The food that they eat is stored in their hump. This allows them to survive without food or water for many days. Camels also have thick eyelids and nostrils which prevent sand from entering them. They can eat the thorny vegetation that is found in the deserts since they have rough tongues. They have wide, padded feet that do not sink into the sand. So, they can travel across the desert easily.
Bustards, pigeons, and quails are some of the birds that can be found in the desert. They are usually found around the oases.
In the mountainous regions of Saudi Arabia, animals like ibex, wolves, hyenas and wild cats are found. The coastal areas of the country are rich in marine life. Sea birds like pelicans are found here.



Write whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Riyadh is the capital of Saudi Arabia.
2. The Tropic of Capricorn passes through Saudi Arabia.
3. Arabian horses are called the ship of the desert.
adaptations: changes through which living beings become better suited to their environment
The discovery of oil in Saudi Arabia in 1937 transformed the country and the lifestyle of the people greatly. Saudi Arabia’s main industry is oil. Saudi Arabia is one of the largest producers of petroleum in the world. It exports petroleum to different countries all over the world.
Iron and steel, cement and construction are also important industries in the country. It is very difficult to carry out agricultural activities in Saudi Arabia due to the harsh environment. Only a small part of the country is suitable for growing crops. Crops such as wheat, rice and alfalfa are grown. The water required for irrigation is obtained through the desalination of seawater.
The export of petroleum has made Saudi Arabia a wealthy country. This has contributed to its rapid development. It has modern cities which have very good infrastructure. The standard of living of the people who live in the cities is very high. Saudi Arabia has a traditional society. Women generally wear abaya. Abaya is a robe worn over clothes which covers from head to toe. Men wear loose-fitting white robes called thobe. Their heads are covered with a chequered cloth called keffiyeh.
Saudi Arabia is a monarchy, which means it is ruled by a king. Arabic is the main language spoken by the people. How do you think the ruler in a monarchy is chosen?
One of the native Arab tribes in Saudi Arabia are the Bedouins. They are nomadic people. They travel on camels in groups known as caravans. They rear camels, goats, sheep and horses.
alfalfa: a kind of legume infrastructure: the systems and facilities available in a place robe: a long, flowing outer garment nomadic: living by travelling from place to place




The animals are very important to the Bedouin. They provide them with milk, meat and animal hide. During summers, they camp in and around oases where their animals can graze. In winter, they travel along those desert routes where water can be found.

Make a chart about the Bedouin people. Paste pictures and write about their clothes, food habits and houses. Give a title to your chart and display it in the class.
The capital of Saudi Arabia is Riyadh. Most of the government ministries and public service headquarters are located here. It is full of skyscrapers, parks, hospitals, educational institutions and markets.
Jeddah is a port city. It is a very important centre of trade and manufacturing. It is also known as the commercial capital of Saudi Arabia.
Mecca is the most important site of pilgrimage for Muslims in the whole world. Medina is another city of great religious importance. Both these cities are located in Saudi Arabia.



The Thar Desert in India is home to many different species of birds and animals. It is the native place of the Great Indian Bustard, which is at a great risk of dying out. In 2013, the government of Rajasthan launched Project Great Indian Bustard for the conservation of this species.
animal hide: animal skin that can be used to make tents or clothes skyscrapers: a very tall building in a city

wadis: temporary streams formed after rainfall in the desert
oases: underground bodies of water in deserts that rise to the surface
desalination: a process through which salt is removed from seawater
monarchy: a type of government where the king is the ruler of the country
Bedouin: one of the native Arab tribes with a nomadic lifestyle caravan: a group of people travelling together in a desert

Scan the QR code to learn more about Saudi Arabia.
• A desert is a large area of land which receives very little rainfall and has little to no vegetation.
• Saudi Arabia has the world’s largest continuous stretch of desert land. The capital of Saudi Arabia is Riyadh.
• Saudi Arabia has extremely hot and dry weather conditions. It is hot during the day and cold during the night.
• Camels have special adaptations that enable them to survive in the desert.
• Saudi Arabia is one of the largest producers of petroleum in the world.
• Saudi Arabia is a monarchy.
1. Tick ( ) the correct answer:
A. What is the capital of Saudi Arabia?
a. Jeddah
b. Riyadh
B. What kind of government is in Saudi Arabia?
a. Republic
b. Democracy
c. Medina
c. Monarchy

C. Which animal is called the ship of the desert?
a. Camel
b. Ibex
c. Hyena
D. Which of the following is a neighbouring country of Saudi Arabia?
a. Afghanistan
2. Fill in the blanks.
b. Syria
c. Oman
Bedouin Jeddah oil date palms
A. Saudi Arabia is one of the largest producers of in the world.
B. are trees that grow in and around oases.
C. is known as the commercial capital of Saudi Arabia.
D. The are a nomadic Arab tribe in Saudi Arabia.
3. Write True or False.
A. Mecca is the most important pilgrimage site for Muslims.
B. The Bedouin people do not have permanent homes.
C. The main language spoken by the people of Saudi Arabia is Arabic.
D. Desert plants have big leaves from which a lot of water can evaporate.
4. Match the following.
A. Bedouin
B. Monarchy
C. Camel
D. Wadis
5. Short answer questions.
A. Where is Saudi Arabia located?
i. Temporary streams
ii. Nomadic herders
iii. Ruled by kings
iv. Ship of the Desert
B. What is the main industry in Saudi Arabia?
C. What is an oasis?
D. How is water obtained for irrigation in Saudi Arabia?
E. Name the types of clothes worn by the people in Saudi Arabia.
6. Long answer questions.
A. What are some of the adaptations that camels have that make them suited to the desert climate?
B. What is the lifestyle of the Bedouin people like?
7. Picture-based questions.

A. Which physical feature is seen in the above image?
B. How is this feature formed?
C. Name one tree that grows in and around this feature.

In what ways do you think the discovery of oil in Saudi Arabia played an important role in the growth of the country and the changing lifestyle of the people of Saudi Arabia?

Saudi Arabia is the world’s largest producer of petroleum. Petroleum is a fossil fuel, and the burning of fossil fuels is harmful to the environment. Make a poster to show why fossil fuels are harmful for the environment. Paste pictures and cutouts of newspaper headlines. Give the poster a title.

Objectives: Students will understand the importance of reusing and recycling materials to protect the environment.
Materials Needed: Used plastic bottles, cans, cardboard, scissors, glue, tape, paint or markers, paper, pencils
Step 1: Learn About Reuse and Recycle

Study the basics of Reuse and Recycle, as concepts, from textbooks or online resources. Understand their importance and how they impact the environment.
Step 2: Collect Reusable Items
Gather items from home that are usually thrown away—plastic bottles, cardboard and aluminium cans.
Step 3: Sort the Items
Sort the collected items based on whether they can be reused or recycled.
Step 4: Reuse
Use the sorted items to create something useful, such as turning plastic bottles into plant pots or aluminium cans into pencil holders.
Step 5: Recycle
Work together with your friends or classmates to collect all the recyclable items, like glass and paper. You can then give it away to a scrap dealer for recycling.
Project Output: Now you have created useful items from waste, and contributed to recycling of materials. Share your experience in the class.
Final Outcome: This hands-on project will help you understand the importance of reusing and recycling materials; and how they can positively impact the environment by reducing waste output. To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.
Read this news article. Answer the questions given below.
On Monday, a powerful cyclone named Cyclone Vara hit the coastal city of Vardhanpur, causing heavy rain and strong winds. The cyclone warning was issued two days before the storm, giving the local government time to prepare. Early preparations included evacuating people from low-lying areas and closing schools and offices. Emergency shelters were set up, and rescue teams were kept on standby. Despite these efforts, the cyclone damaged many homes, uprooted trees, and disrupted electricity supply across the city. The local hospital reported a few injuries but, fortunately, no loss of life.

After the cyclone passed, the government quickly began the repair work. Workers cleared fallen trees and restored power lines. Roads were repaired, and relief camps provided food and water to those whose homes were destroyed. The city’s mayor praised the efforts of the citizens and emergency workers in their timely response to the crisis. Although Vardhanpur is recovering, it will take time for the city to return to normal.
1. What was the name of the cyclone that hit Vardhanpur?
a. Cyclone Vara
c. Cyclone Titli
b. Cyclone Vayu
d. Cyclone Phailin
2. Why were people evacuated from low-lying areas before the cyclone?
a. To protect buildings
c. To ensure safety from flooding
3. How did the cyclone harm the city?
b. To prevent waterlogging
d. To stop traffic jams
4. Imagine you are the mayor of Vardhanpur. What additional steps would you take to make sure the city is better prepared for future cyclones? Write any two steps.
To be read aloud and explained in the mother tongue by the teacher, as needed.

Name of the Student:
Time: 1 Hour
Total Marks: 40
1 Tick () the correct answer. (1 × 5 marks)
A What is the 0° longitude called?
a Equator
c Tropic of Capricorn
b Prime Meridian
d International Date Line
B How many climatic zones is the Earth divided into?
a 6 b 4 c 3 d 2
C Which of these is the main river in the Democratic Republic of Congo?
a Nile b Ganga c Mississippi d Congo
D What is the capital of Saudi Arabia?
a Riyadh
c Jeddah
b Abu Dhabi
d Medina
E Which explorer sailed around the world and proved that the Earth is round?
a Christopher Columbus
c Ferdinand Magellan
b Vasco Da Gama
d Hernan Cortes
2 Fill in the blanks. (1 × 5 marks) cyclone green moisture axis Denmark
A The Earth rotates on an imaginary tilted line called .
B A is always accompanied by heavy rainfall and strong winds.
C We should throw biodegradable waste into dustbins.
D Greenland is a territory of .
E Humidity is the measure of present in the air.
3 Write ONE word for the following. (1 × 5 marks)
A The time of the year when the Sun shines directly on one of the tropics
B Scientists who study the climate and weather patterns
C Grassy plains in tropical and sub-tropical regions
D A native Arab tribe with a nomadic lifestyle
E A machine used to record and measure earthquakes
4 Write True or False.
A Water bodies are represented in shades of green on a map.
B The frigid zone is far from the equator and remains cold for most of the year.
C Latitudes are also called parallels.
D Recycling means using the same item again and again.
E The main language spoken in Saudi Arabia is Arabic.
5 Picture-based questions.
A What type of a map is this?
B What does this type of a map tell us?
C What information do you get from the key of this map?
(1 × 5 marks)
(1 + 2 + 1 marks)
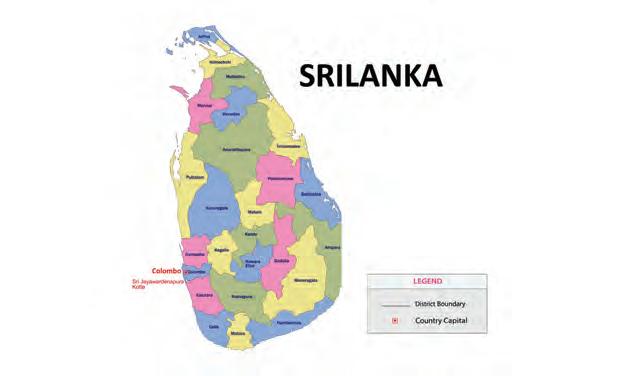
6 Answer the following questions in short.
A What is Greenwich Mean Time?
B Differentiate between land breeze and sea breeze.
C How is water obtained for irrigation in Saudi Arabia?
(2 × 4 marks)
D Name any two organisations that provide help during a natural calamity.
7 Answer the following questions in detail. (4 × 2 marks)
A How is the climate of Democratic Republic of Congo different from that of Greenland?
B What are the 3Rs? Write any 3 ways that we can apply them to our lives to prevent environmental pollution.

The leader of a country makes important decisions that affect people’s lives. They are chosen to lead countries. Let us learn about some of the leaders who were elected in the year 2024.
Vladimir Putin

He became the president of Russia for the fifth term in May after winning the 2024 Russian presidential elections. Previously, he served as Russia’s president from 2000 to 2008 and from 2012 to 2024.
Cyril Ramaphosa

He was elected the president of South Africa for the second time in June after the South African national elections of 2024. He has served as the president of South Africa since 2018.

Narendra Modi

He became the prime minister of India for the third time in June after the 2024 Lok Sabha elections. He served as India’s prime minister from 2014 to 2019 and 2019 to 2024.
Keir Starmer

He became the prime minister of the United Kingdom in July after winning the 2024 UK general elections. He was also the Leader of the Opposition from 2020 to 2024.
He became the president of Sri Lanka in September 2024 after winning the 2024 Sri Lankan presidential elections. He is the 9th executive president of Sri Lanka.

The leader of a country is responsible for making important decisions that affect the nation’s future. A good leader takes responsibility for his/her actions and sets a good example for others to follow.


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Name the leaders.
a Prime Minister of India
b Prime Minister of the UK
c President of Russia
d President of South Africa
e President of Sri Lanka
2 Fill in the blanks.
a Vladimir Putin was elected as the president of Russia for the term.
b Narendra Modi served as the prime minister of India from to and to 2024.
c Cyril Ramaphosa became the president of South Africa for the first time in the year .
d Keir Starmer was the from 2020 to 2024.
e Anura Kumara Dissanayke is the executive president of Sri Lanka.
3 Write the names of the countries led by the following leaders and the months in which they were appointed to their positions in 2024.
a Narendra Modi
b Vladimir Putin
c Cyril Ramaphosa
d Anura Kumara Dissanayake
e Keir Starmer







India gained its independence from British rule due to the efforts of its brave freedom fighters. Let us learn about them.
Mahatma Gandhi
He was a popular leader of India’s independence struggle. He led important movements like the Salt March and the Quit India Movement. He believed in nonviolence. His birthday, 2 October, is celebrated as Gandhi Jayanti.
He was a leader who joined the non-cooperation movement started by Gandhi. He founded the Indian National Army. He is also known as Netaji. His birthday, 23 January, is celebrated as Netaji Jayanti. Tum mujhe khoon do, mein tumhe azadi doonga (‘Give me blood and I will give you freedom’) is a famous declaration by Netaji.
Bhagat Singh
He was a courageous hero of the Indian freedom movement. He began to protest against British rule at a young age and fought for national independence. In his honour, the anniversary of his death, 23 March, has been declared as Shaheed Diwas. He made the slogan, Inquilab Zindabad (Long Live Revolution) popular.
Chandra Pal
He was a prominent Indian freedom fighter, social reformer and writer. He was one of the key members of the Swadeshi movement that encouraged people to use only Indianmade products. He was also a strong supporter of Swaraj (self-rule) for India.
Lala Lajpat Rai was a writer, politician and a famous leader in India’s struggle for independence. He was known as Punjab Kesari for his acts of protest against the British. Some of his most memorable writings include Unhappy India.





He was a scholar, teacher and a devoted leader. He played an important role in inspiring the nationalist movement. He earned the title Lokmanya. He also talked about the importance of education and unity among the people of India. ‘Swaraj is my birthright, and I shall have it’ is a famous statement he made.
Jawaharlal Nehru

He emerged as the leader of the country’s youth during India’s independence movement. He led a historic session at Lahore which declared complete independence as India’s political goal. After independence, he became the first prime minister of India in 1947.
Our freedom fighters fought for our country’s independence. They displayed courage, dedication and patriotism. We should be proud of our country and its history.






Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Write the titles given to these freedom fighters.
a Bal Gangadhar Tilak
b Lala Lajpat Rai
c Subhas Chandra Bose
2 Which freedom fighters popularised/said these words?
a Inquilab Zindabad.
b Swaraj is my birthright, and I shall have it.
c Tum mujhe khoon do, mein tumhe azadi doonga.
3 Write the dates of these events.
a Gandhi Jayanti:
b Shaheed Diwas:
c Netaji Jayanti:
4 Which hero of the Indian Freedom Movement am I?
a I became the first Prime Minister of India in 1947.
b I believed in nonviolence.
c My birth anniversary is celebrated as Netaji Jayanti.
d My death anniversary is celebrated as Shaheed Diwas.
e I wrote the book Unhappy India.
f I was one of the key members of the Swadeshi movement.

Hockey is a popular sport in India. It is played by two teams of 11 players each. The players use J-shaped sticks to hit the ball into the opposite team’s goal.

• Men’s team
• Women’s team
• Junior men’s team
• Junior women’s team
From 1928 to 1956, the Indian men’s hockey team won six consecutive gold medals at the Olympics.

The Indian Hockey Team, 1948
Due to hockey’s popularity, many people regard it as India’s national sport. However, this is a myth.
In 2012, the Sports Ministry undersecretary Shiv Pratap Singh Tomar clarified that there is no record from the ministry that hockey, or any other sport is our national game.
Major Dhyan Chand is known as the Wizard of Indian Hockey. He was a three-time Olympic gold medallist. On 29 August every year, his birthday is celebrated as the National Sports Day.

Some International Achievements
• It is the most successful team in the Olympics with 8 gold, 1 silver and 4 bronze medals.
• They have won medals in many other events:
- World Cup: Gold in 1975, silver in 1973 and bronze in 1971
- Asian Games: 4 gold, 9 silver and 3 bronze medals
- Asia Cup: 3 gold, 5 silver and 2 bronze medals
- Asian Champions Trophy: 5 gold, 1 silver and 1 bronze medal
Some International Achievements
• The women’s team represented India for the first time at the Olympics in 1980.
• The team has won medals at many events:
- Asian Games: 1 gold, 2 silver and 4 bronze medals
- Asia Cup: 2 gold, 2 silver and 3 bronze medals
- Asian Champions Trophy: 2 gold, 2 silver and 1 bronze medal.
Hockey is a high-energy sport that needs players to constantly move. It improves physical health and enhances the balance and coordination of a player.


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Answer the following correctly.
a The number of players in a hockey team:
b The number of Indian hockey teams:
c The shape of a hockey stick is like this letter:
d The years during which the men’s national hockey team won consecutive Olympic gold medals:
e The number of times Major Dhyan Chand won Olympic gold medals:
f The number of Olympic gold medals won by the men’s national hockey team:
2 Fill in the blanks.
a Major Dhyan Chand is known as the of Indian hockey.
b The Indian men's hockey team won consecutive gold medals at the Olympics.
c In World Cup, the Indian men's hockey team won gold in , silver in and bronze medals in 1971.
d The Indian women's hockey team represented India at the Olympics for the first time in the year .
3 HOTS Write down the number of medals won by the Indian hockey teams in the given tournaments.
a Asian Games
b Asia Cup
c Asian Champions Trophy
Tropical rainforests are dense forests that are warm and receive a large amount of rainfall. They are home to a large variety of animals and birds.

Sloths are found mostly in the rainforests of Central and South America. They live in trees. They have curved claws that are four inches long which enable them to hold onto branches and hang from the trees. They spend 15 to 20 hours per day sleeping.

Toucans are found in the rainforests of America. They spend most of their time nesting high in the forests. They take shelter in hollowed-out trees. Toucans have large bills that can be four times the size of their head!

Poison dart frogs are found in the rainforests of Central and South America. They are small frogs with brightlycoloured bodies. Their skin is poisonous! The golden poison frog is the most poisonous of all. This frog has enough poison to kill about 20,000 mice.

Orangutans are redhaired apes that live in the tropical rainforests on the islands of Sumatra and Borneo. They can weigh up to 100 kg which makes them the heaviest tree-dwelling animals. They have extremely long arms.

Okapi are found mainly in the Rainforest of Ituri in the, Democratic Republic of Congo, Africa. Although they have stripes like a zebra on their legs and a body like a horse, they actually belong to the giraffe family. The tongue of an okapi is long enough to clean its eyelids, ears and even its neck.



Boa constrictors are large rainforest snakes, found mainly in Central and South America. The anaconda, a member of the boa family, can grow as long as 9 metres! They are non-venomous. Boa constrictors give birth to babies, unlike other snakes that lay eggs.
Tropical rainforests once covered about 14% of the Earth’s surface, but now they only cover around 6%. They are being destroyed at an alarming rate. It is important to make efforts to save the rainforests in order to protect the environment.

1 Fill in the box with the correct number.

Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
a Sloths have claws that are inches long.
b Anacondas can grow as big as metres.
c The golden poison frog has enough poison to kill about mice.
d The bills of toucans can be times the size of their heads.
2 Where do I live?
a Orangutans are found in the rainforests of .
b Toucans are found mostly in the rainforests of .
c Sloths are found mostly in the the rainforests of
d Okapi are found in the rainforest of .
3 Complete the sentences.
a Other snakes lay eggs, while boa constrictors
b The long claws of sloths help them to
c The long tongues of the okapi help them to
4 HOTS Read the features. Then, write the names of the animals.
a It is a slow-moving animal that spends most of its time clinging to trees:
b It is the most poisonous frog:
c They have stripes like a zebra on their legs and a body like a horse.
d They are the heaviest tree-dwelling apes:
e They are birds with large, colourful bills:
On 7-07-2007, the New 7 Wonders Foundation (now an official partner of the UN) declared the new 7 wonders of the world. These wonders were chosen by the votes of more than 10 crore people across the world.

The Taj Mahal Agra, India
It is made of white marble and is located on the banks of the River Yamuna. The main structure has four pillars (minars) around it. It was built by Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife, Mumtaz Mahal.
The Great Wall of China China

This 21,196-km-long wall is one of the largest buildingconstruction projects in the world. It spreads from the eastern seaside to the western desert in northern China. The first emperor of China, Qin Shi Huang, ordered its construction to protect his people from nomads.
Machu Picchu
Andes mountains, Peru

It is a ruined, stone city of the Inca Empire. It was hidden in the middle of a mountain forest. Archaeologist, Hiram Bingham, found it in 1911. Thus, it is also called The Lost City of the Incas.


The Colosseum

Rome, Italy
It is the largest amphitheatre ever built. It could host about 50,000 people at once. It was built by the Romans as an entertainment venue and for hosting human fights and animal hunts.

Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
This 30-m-tall statue of Jesus Christ with open arms stands on top of Corcovado Mountain. It was viewed as a symbol of hope and peace for the people after World War I.
Chichén Itzá
Yucatán State, Mexico

It is the site of a ruined ancient Mayan city. It is most popular for its temple pyramid. The pyramid has 365 steps, for each day of a year. The complex also has the Temple of Warriors.
Petra, Jordan

It is a ruined city of an ancient Arab kingdom, located in a distant valley and surrounded by mountains. It is half-built and halfcarved into the rocks. It is also known as the RedRose City because of the colour of its rocks.
All monuments are an important part of our cultural heritage. We should protect them from damage and conserve them.



Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 In which cities are these new wonders located?
a Taj Mahal b Colosseum
c Christ the Redeemer
2 In which countries are these new wonders located?
a Chichén Itzá b Machu Picchu
c Petra
3 Fill in the blanks with the correct names of the wonders of the world.
a is a 30-metre-tall statue.
b has a famous temple pyramid.
c is the largest amphitheatre ever built.
d is the longest of all the new seven wonders of the world.
e was part of an Arab kingdom.
f was built by an emperor in memory of his late wife.
g is a ruined stone city in the middle of the forest.
4 Who am I?


a I am known as The Lost City, as I was found in the year 1911.


b The rose colour of my rocks gave me the name, The Red-Rose City
c I gave hope to people after a time of chaos during World War 1.






Films help us see and understand different people, places and stories. Many filmmakers from different parts of the world have inspired us with their films. Let us learn about some of them.

Satyajit Ray was an Indian filmmaker known for depicting intense emotions and social issues in his films. He received an Honorary Oscar in 1992 for his lifetime achievements and contribution to world cinema.
Major Films: Pather Panchali and Aparajito
North America
Quentin Tarantino is an American filmmaker and a two-time Oscar winner. His films are known for their sharp dialogue and complex stories.

Major Films: Pulp Fiction and Django Unchained
Haile Gerima is an Ethiopian filmmaker known for showing social realities of Black communities in his films. He has been a film professor at Howard University since 1975.

Major Films: Sankofa and Bush Mama


Jean-Pierre and Luc Dardenne are brothers from Belgium known for depicting strong emotions in their films. They made a lot of films on working-class themes and characters.

Major Films: The Child and Two Days, One Night South America
Fernando Meirelles is a Brazilian filmmaker known for his captivating films. His films touch upon different social issues and have received international acclaim.

Major Films: City of God and Blindness
Jane Campion is a filmmaker from New Zealand, known for having great visual effects and strong emotions in her films. She won the Oscar for Best Director in 2022 for the film, The Power of the Dog.

Major Films: The Piano and Bright Star
Films have a unique power to reach audiences on an emotional level. Through relatable characters and storytelling, they can highlight the importance of virtues like honesty and courage.






Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Name any two films made by each of the following filmmakers.
Filmmakers
a Quentin Tarantino
b Haile Gerima
c Jane Campion
d Satyajit Ray
Films
2 Sort the given filmmakers based on the parts of the world they come from.
Jean-Pierre and Luc Dardenne Jane Campion Haile Gerima
Fernando Meirelles Satyajit Ray Quentin Tarantino
a Asia
b Europe
c Africa
3 Which filmmaker am I?
d North America
e South America
f Oceania
a I am Ethiopian and I am known for films that depict realities of Black communities.
b I am from New Zealand and I am known for films which have great visual effects.
c I am American and I am known for films that have sharp dialogue and complex stories.
d We are brothers from Belgium known for depicting strong emotions in films.
e I am the only Indian director to receive an Honorary Oscar in 1992.
Kitchen gardening means growing food—fruit and vegetables in a small space —mostly for the everyday use of a family. One can grow a kitchen garden in any available space at home, like on the balcony, in a backyard or on a roof.
Grow Your Kitchen Garden

1. Choose a spot and decide the layout. Choose a spot in the backyard or balcony with enough sunlight for plant growth and decide the size of the kitchen garden.

4. Water the plants. Water the plants regularly according to their need. Avoid overwatering the plants.

2. Prepare the soil. Use nutrientrich soil for better plant growth. You can also add manure to it. Remove the stones and hard soil from the pot or patch.
5. Maintain plant health. Check the plants regularly to see if they are growing well or have pests. Check for weeds and remove them.

3. Seeds or seedlings. Gently, sow the seeds in the soil. We can buy seedlings from a nursery. We should plant seeds which grow best during the season when we are sowing.

6. Wait and harvest. The seeds take time to grow into fruit, leaves or vegetables. Gently harvest the fruit, leaves and vegetables. Avoid any damage to the plants.
y The food grown in a kitchen garden is much healthier than the food we buy from the market.
y A kitchen garden provides us with naturally grown food, free from any chemicals.
y It helps us to save money and utilise the free space in and around our house.
y We can grow many vegetables like lady finger, chilies, spinach and spring onions.
y We can grow fruit like tomatoes, strawberries, lemons and blueberries.
y We can also grow herbs like mint, coriander, basil and rosemary.
Growing food at home fosters healthy eating habits. Fresh, home-grown fruit and vegetables are nutritious and free from harmful chemicals, thus promoting good health and well-being.




Scan this QR code to see the quiz.

1 Name any four vegetables, herbs or fruit that we can grow in a kitchen garden.

2
Number the steps of kitchen gardening (1-4) in the correct order.

a Sow the seeds or seedlings. b Water the plants and check them regularly.


c Harvest the final produce. d Choose a spot for the kitchen garden.
3 Write whether the step is a Do or Don’t when growing a kitchen garden.
a We should select a place where there is enough sunlight.
b We should remove stones and hard soil before sowing seeds.
c We should not consider the seasons when selecting seeds.
d We should not add manure to the soil.
e We can buy seeds from a nursery.
f We should avoid overwatering the plants.
g We should not remove the weeds from the soil.
h We should damage the plants while harvesting.

A bank is a place that keeps and manages people’s money, with permission from the government.
A bank is an institution where money is kept and managed. We need to open an account with the bank. When we open a bank account, we get an account number.
When we put money into our bank account, it is called depositing money. It could be through cash, cheque or electronic transfer. We can take money out of our bank account as well to pay bills, shop or to pay other expenses. When we take our money out of the bank, it is called withdrawing money
We need money for different things in our lives. When people buy a car, a house or set up their own business, they need a lot of money. In such cases, people can take a loan from the bank. Taking a loan, means borrowing money from the bank with an agreement to return it later.
Banks have lockers. These lockers are in a secure room. Only the person who owns the locker can open it with their key. People keep valuable items, like jewellery and important documents, in their locker to keep them safe.
Having a good banking system is very important for a country. Banks help businesses function and create jobs. They help regulate the flow of money.


With the help of your parents, find out about the different steps to open a bank account.


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Choose the correct word from the brackets and fill in the blanks.
a A bank is a place where people can keep their . (clothes/money)
b We can put our money in a account. (bank/shop)
c Putting money in a bank is called money. (spending/depositing)
d Taking out our money from the bank is called money. (withdrawing/saving)
e When banks lend money to people, it is called a . (gift/loan)
f A in a bank is where people can keep their gold. (locker/drawer)
2 Write True or False.
a A bank is not a safe place to keep our money.
b We can put our money in a bank through cash or a cheque.
c Banks can gift people money on special occasions like their birthdays.
d People can also safely keep their important papers in a bank.
3 Write the correct reasons.
a People may need to borrow money from a bank for: , ,
b Banks are important because they: create , and help the
4 Help Rajiv, a businessman, reach the bank quickly as he has to take a loan for his new project.
In 2024, India took part in many sports events and had amazing performances, winning several important competitions around the world. Let’s take a look at some of India’s achievements in sports this year!

India won six medals at the 2024 Olympics, including one silver and five bronze medals. This event was held in Paris, France from 26 July 2024 to 11 August 2024. A total of 117 athletes represented India in 16 sports. India won medals in shooting, athletics, hockey and wrestling.

India won the ninth edition of the ICC Men’s T20 World Cup. They beat South Africa in the finals. This event was held in the United States of America and the West Indies from 1 to 29 June. This is India’s second T20 World Cup title.
India won 29 medals at the 2024 Paralympics, including seven gold, nine silver and thirteen bronze medals. This event was held in Paris, France from 28 August 2024 to 8 September 2024. This is India’s best performance in the history of the Paralympic games. India won medals in shooting, athletics, badminton, archery and judo.

India won in both the open and women’s categories at the 45th FIDE Chess Olympiad. This event was held in Budapest, Hungary from 10 to 23 September 2024. This is India’s first-ever win in the Chess Olympiad in both the categories. India is the third country to win in both categories in the same year.
Teamwork in sports has played a key role in helping India win many competitions. When team members work together, they support each other, learn from each other and make the team stronger.


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Write down the dates and the places where these events took place in 2024.
a Olympics
b Paralympics
c ICC Men’s T20 World Cup
d FIDE Chess Olympiad
2 Fill in the blanks.
a India won medals at the 2024 Olympics.
b athletes represented India at the 2024 Olympics.
c India won medals including gold, silver and 13 bronze at the 2024 Paralympics.
d India won the 2024 ICC Men’s T20 World Cup by beating in the finals.
e India won in both and categories at the 2024 FIDE Chess Olympiad.
f India is the country to win in both the open and women’s categories at the FIDE Chess Olympiad in the same year.
3 HOTS Tick ( ) the sports in which India won medals at the 2024 Olympics.
a Wrestling b Archery c Shooting d Hockey e Athletics f Swimming

An inventor is someone who thinks of a new idea and then makes something useful from that idea. Let us learn about some of the great inventors and their inventions.




Johannes Gutenberg is known for building the first mechanical printing press in the mid-1400s. His printing process was one of the greatest inventions. One of the known books he printed was the Gutenberg Bible.
Thomas Savery, an English engineer, built the first steam engine in the 1690s. He patented a steam pump in the year 1698. The steam engine uses steam to make machines work and powers things like trains and factories.
Samuel Morse was an American inventor. He developed an electric telegraph between 1832-1835. His invention allowed people to send messages over long distances using electric signals.
Guglielmo Marconi invented the radio in 1896. He developed a wireless communication system that sent radio signals over long distances, which led to the development of advanced radio technology. He received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1909.

The Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur Wright, invented the first airplane, that a pilot could control in 1903. The first airplane flew at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina for 12 seconds and covered a distance of 36 metres.






Use the internet to find the inventors of any three modern devices that you use in your daily life.


Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Match the following inventions and the years of the inventions.
a First mechanical printing press 1832–1835
b Steam pump 1903
c Electric telegraph Mid-1400s
d The radio 1698
e The first airplane 1896
2 Fill in the blanks.
a One of the famous books that Johannes Gutenberg printed was the .
b The steam engine uses steam to make work and things like trains and factories.
c Guglielmo Marconi developed a that sent radio signals over long distances.
d The first airplane flew for and covered a distance of .
e The electric telegraph allowed people to send messages over long distances using .
3
Who am I? Write the names of the inventors.
a I built the first steam engine.
b I built the first mechanical printing press.
c We invented the first airplane.
d I invented the radio.
e I developed an electric telegraph.
In India, many old cities have been renamed, but the vibrant lives of these cities remain the same. Let’s learn about them.
City: Prayagraj
Old name: Allahabad

Prayagraj in Uttar
Pradesh is a city of religious importance. The city is the meeting point of three rivers— the Ganga, Yamuna and the mythical Saraswati. The city’s name officially became Prayagraj on 16 October, 2018.
City: Kolkata
Old name: Calcutta

Kolkata is the capital city of West Bengal. It has a rich heritage of literature, art, music and theatre. It is famous for the the Howrah Bridge and the Victoria Memorial. The city’s name officially became Kolkata in January 2001, to match its Bengali pronunciation.

City: Kochi
Old name: Cochin

Kochi is a major port city of Kerala. It is known as the Spice Capital of the World. The city was renamed Kochi in 1996, to bring the name closer to its original Malayalam name. Kochi means a small lagoon.
City: Gurugram
Old name: Gurgaon

Gurugram in Haryana is one of India’s information technology and banking hubs. It is often called the Millennium City of India. The city’s name officially became Gurugram on 27 September 2016 in honour of its mythological relation to Guru Dronacharya.
City: Mumbai
Old name: Bombay

Mumbai is the capital city of Maharashtra. It is also called the business capital of India. The city is known for landmarks like the Gateway of India and the Marine Drive. The city’s name officially became Mumbai in 1995, in honour of the goddess of the region, Mumbadevi.
City: Chennai
Old name: Madras

Chennai is the capital city of Tamil Nadu. It is known as the Detroit of India, as it is the hub of the automobile industry. Its Marina Beach is the longest urban beach in India. The city’s name officially became Chennai on 17 July, 1996.
There are many other cities in India whose names have been changed. Use the internet to find out the names of any three such cities.



Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 What were the old names of the given cities?
a Kolkata b Chennai
c Prayagraj
d Gurugram
e Kochi f Mumbai
2 Name the city.
a Detroit of India:
b Millennium City of India:
c Business capital of India:
d Spice capital of the world:
e A major port city in Kerala:
f The city where the three riversGanga, Yamuna and Saraswati meet:
3 In which cities are these landmarks located? Write the new city names.
a Marina Beach
b Howrah Bridge
4 Neharika wants to visit Mumbai. She asks you to suggest places she should visit. Name three places that you would suggest to her.




Each country of the world has a flag. The flag’s colour, shape and symbols usually represent the history, land, culture, uniqueness and goals of the country it belongs to.
The Indian flag is a tricolour flag, also called the Tiranga, with three horizontal bands of saffron, white and green, respectively. Each colour represents something about India—saffron symbolizes strength and courage, white symbolizes peace and truth, and green shows the fertility, growth and richness of the land. At the centre of the white band, there is a navy blue Ashoka Chakra with 24 spokes representing continuous movement and progress throughout the 24 hours of the day.
India
This is the oldest , continuously used national flag in the world! It’s believed that the flag itself fell from the sky in 1219. But its current design was adopted in 1625. The red background represents the battles that the Danish people fought and the white stripes represent their religious faith.
This is the only flag in the world that is not rectangular or square. Instead, it has two triangles. They represent the Himalayan Mountains and the two major religions of the country—Hinduism and Buddhism. The symbols of the sun and moon signify the hope that Nepal will stand as long as the sun and the moon are shining.
There are only two countries in the world that have square flags.
Flags of some countries are almost identical except for the differences in their sizes and colours.
The flags of some countries may look alike but the meaning of the symbols differ. Japan is known as the ‘Land of the Rising Sun’. The sun is represented by the red circle in the middle of the flag. This flag is commonly called the Hinomaru meaning ‘Ball of the Sun’.








Just like Japan, the flag of Bangladesh also has a bright red circle in the middle. It has two meanings: 1. The rising sun of a new country; 2. The blood of the people who fought for the country’s independence. The dark-green background of the flag represents the lush vegetation of the land of Bangladesh.

A country’s flag is an important national symbol. We should take pride in our country’s flag and respect it.







Scan this QR code to see the quiz.
1 Look at the flags and name the countries they belong to.
2 Name the countries that have flags with similarities.
a Both the flags have a square shape: and
b Both the flags have red and white horizontal bands in reverse: and
c Both the flags have a red circle in the middle, representing the sun: and
3 Read the features of the flags and name the countries they belong to.
a It has a white cross in the middle of a red square background.
b It has two triangles stacked on top of each other.
c It has a red circle on a dark-green background.
d This tricolour flag is also known as the Tiranga.
e It is popularly known as the Hinomaru.
f It is the oldest, continuously used national flag in the world.
1. World Leaders, 2024
1. a. Narendra Modi b. Keir Starmer
c. Vladimir Putin d. Cyril Ramaphosa
e. Anura Kumara Dissanayake
2. a. fifth b. 2014, 2019, 2019 c. 2018
d. Leader of the Opposition e. 9th
3. a. India, June b. Russia, May
c. South Africa, June d. Sri Lanka, September
e. United Kingdom, July
2. Heroes of Indian Freedom
1. a. Lokmanya b. Punjab Kesari c. Netaji
2. a. Bhagat Singh b. Bal Gangadhar Tilak
c. Subhash Chandra Bose
3. a. 2 October b. 23 March c. 23 January
4. a. Jawaharlal Nehru b. Mahatma Gandhi
c. Subhash Chandra Bose d. Bhagat Singh
e. Lala Lajpat Rai f. Bipin Chandra Pal
3. Hockey in India
1. a. 11 b. 4 c. J d. 1928 to 1956
e. three f. 8
2. a. Wizard b. six c. 1975, 1973
d. 1980
3. Tournament
4. Animals of the Tropical Rainforest
1. a. four b. 9 c. 20,000 d. Four
2. a. The Island of Sumatra and Borneo
b. America c. Central and South America
d. Ituri, Democratic Republic of Congo, Africa
3. a. give birth to babies
b. hold branches and hang from trees
c. clean their eyelids, ears and neck
4. a. Sloth b. Golden poison frog
c. Okapi d. Orangutan e. Toucan
5. 7 New Wonders of the World
1. a. Agra b. Rome c. Rio de Janeiro
2. a. Mexico b. Peru c. Jordan
3. a. Christ the Redeemer b. Chichen Itza
c. The Colosseum d. The Great Wall of China
e. Petra f. Taj Mahal g. Machu Picchu
4. a. Machu Picchu b. Petra c. Christ the Redeemer
6. Renowned Filmmakers
1. a. Pulp Fiction, Django Unchained
b. Sankofa, Bush Mama
c. The Piano, Bright Star
d. Pather Panchali, Aparajito
2. a. Satyajit Ray
b. Jean-Pierre and Luc Dardenne
c. Haile Gerima
d. Quentin Tarantino
e. Fernando Meirelles
f. Jane Campion
3. a. Haile Gerima b. Jane Campion
c. Quentin Tarantino d. Jean-Pierre and Luc Dardenne e. Satyajit Ray
7. Kitchen Gardening
1. Spinach, Tomatoes, Coriander, Lemons
2. a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 1
3. a. Do b. Do c. Don’t d. Don’t
e. Do f. Do g. Don’t h. Don’t
8. Banks and Their Uses
1. a. money b. bank c. depositing
d. withdrawing e. loan f. locker
2. a. False b. True c. False d. True
3. a. Car, Home, Business b. jobs, businesses

9. India in Sports, 2024
1. a. 26 July 2024- 11 August 2024; Paris, France
b. 28 August 2024- 8 September 2024; Paris, France c. 1 June 2024- 29 June, USA and West Indies d. 10 September 2024 to 23 September 2024, Budapest, Hungary
2. a. six b. 117 c. 29, 7, 9 d. South Africa
e. Open, Women’s f. third
3. a. b. c. d. e. f.
10. Great Inventors
1. a. Mid-1400s b. 1698 c. 1832-1835
d. 1896 e. 1903
2. a. Gutenberg Bible b. machines, powers
c. wireless communications system
d. 12 seconds, 36 metres e. electric signals
3. a. Thomas Savery b. Johannes Gutenberg
c. The Wright Brothers d. Guglielmo
Marconi e. Samuel F.B. Morse
11. Old Cities, New Names
1. a. Calcutta b. Madras c. Allahabad d. Gurgaon e. Cochin f. Bombay
2. a. Chennai b. Gurugram c. Bombay d. Kochi e. Prayagraj
3. a. Chennai b. Kolkata
12. International Flags
1. a. United States of America b. Switzerland c. Bangladesh d. Denmark e. Romania f. Japan g. Vatican City h. Nepal
2. a. Switzerland, Vatican City b. Monaco, Poland c. Japan, Bangladesh
3. a. Switzerland b. Nepal c. Bangladesh d. India e. Japan f. Denmark
Introducing WISDOM, a 21st-century product for the learners of grades 3 to 5. It includes all curricular areas—English, Mathematics, Science, Social Science and General Knowledge. WISDOM is aligned with the NEP 2020 in terms of its design principles, and fulfils all recommendations of the NCF 2023.
Product Package
• Semester Books
• Uolo App
• Teacher Guide
• Focus on HOTS and Critical Thinking: Intellectually stimulating questions designed to encourage deep, analytical, critical and evaluative thought processes
• Digital Aids: Animated talking books, interactive quizzes for additional practice and curated learning videos
• Experiential and Applicative Learning: Projects and activities designed for real-life settings, like lab activities and community projects, to enable the development and practice of life skills
• Rootedness to India: Examples from India’s unique culture and history, linked to each topic, to inculcate a sense of pride and love for the nation
• Model Assessments: Test papers designed to evaluate the understanding of core concepts and the application of skills
Uolo partners with K-12 schools to provide technology-enabled learning programs. We believe that pedagogy and technology must come together to deliver scalable learning experiences that generate measurable outcomes. Uolo is trusted by over 15,000+ schools across India, Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
ISBN 978-81-980880-1-7
