Sustainability Report 2022



This report is presented in accordance with the GRI 2021 Guidelines Standards framework, through which the Ternova Group’s management during the year 2022 is accurately reported. It also addresses the Global Compact’s Ten Principles in relation to the 17 Sustainable Development Goals, compliance with the United Nations Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights and the Women’s Empowerment Principles established by UN Women.
For the preparation of this document, the stakeholders that interact with the Company in the activities related to Ternova Packaging, have been considered,
in an attempt to respond to their expectations and interests in a reasonable manner.
Ternova chooses to manage resources using a responsible and sustainable approach with the aim of generating economic, social, environmental and integrity value to society in general.
Significant economic, social and environmental impacts are identified prior to each action through planning and the establishment of inspection points. This report describes those most susceptible to programmed monitoring.
The management indicators contain
information on economic, social, environmental or good governance aspects in the period from January 2022 to December 2022, in order to report on annual performance in relevant sustainability issues.
The information presented in this report was built with records documented in the internal archive of the company. The report is faithful to the results obtained in the topics associated with sustainability, whether positive or negative, with the purpose of [object of] establishing a real balance of the information from the business units that make up Ternova Packaging and the areas of
management systems, finance, organizational development, human talent, logistics, corporate affairs and sustainability.
At Ternova we are ready to face the future with great enthusiasm and with the desire to contribute in generating value—for all those who have placed their trust in us— through the promotion of a more dynamic and efficient business sector that protects labor rights, promotes diversity and inclusion, complies with environmental requirements and also assumes new roles to contribute to sustainable development through innovation, production and responsible consumption, the creation of employment and sustainable solutions, as well as the preservation of business ethics.
At Ternova Group we carry the DNA of sustainability because we are aware and interested in our surroundings, we understand the environment and we use reality as the starting point to motivate change. We have a proactive mentality, able to inspire by example, ensuring a vision that
incites action to impact the present and visualize the results in the future.
We remain committed to the United Nations Global Compact Initiative and its ten principles of responsible behavior based on the Sustainable Development Goals since, at Ternova, we focus on generating a triple impact (economic, social and environmental). Being signatories to this initiative allows us to firmly integrate sustainability into the business strategy, in addition to providing the appropriate framework to reinforce the long-term commitment to responsible and ethical business practices.
We are the first Central American company to heed the Ellen MacArthur Foundation-World Wildlife Fund’s corporate call for a global treaty against plastic pollution and, together with the world’s leading companies and financial institutions, we welcome the
decision by UN member states to begin negotiations for a legally binding treaty to end plastic pollution.
With winning alliances such as the ones we have with our clients Nestlé and Walmart in recycling, through Recicla 503, we have generated a positive impact that allows us to have an active community participating in recycling processes with brand presence in each of their facilities and activating people already sensitized, who in turn educate in the voluntary delivery of recyclable materials, building together credibility credentials that open new doors in other companies.

Grupo Termoencogibles was founded in 1970 as a family company dedicated to the manufacture of packaging. The dream of the Tona Giolitti family began as a venture with three brothers manufacturing bags by hand. Five years ago, we decided to transform and adopted a new name: Ternova.
Ternova means intelligent transformation and innovation towards the future; we seek to make available the latest technology to continue co creating packaging and products that transcend and help maintain the value proposition of your company, reaffirming its commitment to sustainability. In this way, the business group seeks to consolidate its position as a world leader in intelligent solutions to tomorrow’s problems.
Ternova has a presence in the following territories:

Production plants
1) Renova (Plan de la Laguna)
2) Plan de la Laguna (Plan de la Laguna)
3) Maquilishuat (Puerto de La Libertad)
4) Merliot 1 (Merliot Industrial Zone)
5) Merliot 2 (Merliot Industrial Zone)
6) Vietnam
Distribution Centers
1) Termoencogibles El Salvador
2) Termoexport El Salvador
3) Termoencogibles Guatemala City
4) Termoencogibles Xela
5) Termoencogibles Tegucigalpa 1
6) Termoencogibles Tegucigalpa 2
7) Termoencogibles San Pedro Sula
8) Termoencogibles Managua, Nicaragua
9) Termoencogibles Alajuela, Costa Rica
10) Termoencogibles Howard, Panamá
11) Termo Vietnam
Commercial Offices
1) Logistics and Distribution Office, El Salvador
2) Branch Office Honduras, Tegucigalpa
3) Branch Office Guatemala, Guatemala City
4) Branch Office Nicaragua, Managua
5) Branch Office Costa Rica
6) Branch Office Panama
Ternova Packaging is focused on smart transformation and innovation into the future to continue co-creating flexible packaging and products that transcend and help us maintain the value proposition of companies and their environmental commitments.


Ternova Packaging is divided into the following categories, which concentrate the different products we develop:
B2B
INDUSTRIAL PACKAGING
B2C
MASS CONSUMPTION PACKAGING
B2D
RETAIL PACKAGING



In the B2B industrial market, we provide solutions to the textile sector, where we serve large industrial customers, for whom we design and produce the best packaging to make their brands stand out from the very first moment.
In response to the [of] segmented industries, in TERNOVA we deliver products specially created for various productive sectors, with greater emphasis on food, mass consumption, home care, personal care and luxury products, making packaging that stand out for having a high content of recycled raw materials and for being customized with a variety of applications.
At Ternova we cultivate excellent relationships with our customers, who we support as strategic allies and reliable experts within the value chain by providing them with flexible packaging that goes beyond the main function and allows them to deliver
more attractive, competitive and eco-friendly products, betting together on the growth of their businesses in a responsible way to the final consumer and the environment, thus evolving in the world of materials.
B2C’s current portfolio seeks to make a positive contribution to the planet, offering different alternatives that meet the needs of each consumer, making the most of resources and following strict procedures throughout the manufacturing process to reduce the impact on the environment.
Ternova has three categories of eco-friendly packaging available in the largest supermarkets in Central America:


Ternova create state-of-the-art Post Industrial Recyclate (PIR) and PostConsumer Recycled (PCR) pellets in our recycling plant to contribute to the creation of circular economic models in the flexible packaging industry, incorporating postconsumer recycled materials that allow the production of packaging from recycling.
As an innovative element, at Ternova manufacture films for industrial packaging with a significant certified PCR content, thanks to the CO2 Neutral certification with which we convert traditional flexible packaging into recyclable ones with 30-100% PCR and PIR content, replacing PET/PE (polyethylene terephthalate/polyethylene) structures with LDPE structures
(low density polyethylene) by using Reifenhäuser’s co-extrusion technology.

This product meets international standards of ASTM D6954 with the three stages of the oxobiodegradation process in the presence of sunlight, heat and oxygen:
1. Degradability: accelerated degradation and plastic breakdown.
2. Biodegradability: reintegration into the ecological cycle by means of microorganisms that eat the material, converting it into carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O) and biomass through the metabolism of the microorganisms.
3. Ecotoxicity: ensures the absence of toxic residues and heavy metals.
Ternova´s compostable packaging is an excellent sustainable solution, as it is made from plantbased resources and has the same strength and quality as conventional packaging.
With this type of product, we accompany the client and the consumer to carry their purchases and, later, to give other uses to the packaging [when they get home].


Ternova also serve the retail segment with our distributors group, with whom we cover the demand of most supermarkets and multiple commercial establishments in Latin America.

Ternova Packaging serves hundreds of consumers around the world.
North America: food
Central America and the Caribbean: food, home, and personal care.
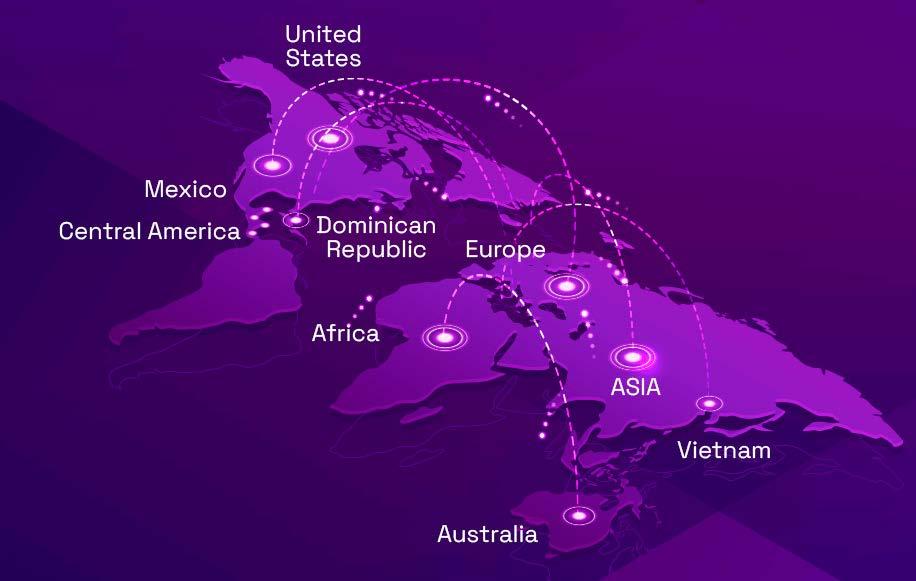
North America and Central America: textiles
Southeast Asia: textiles
At Ternova we are a team of collaborators who act in accordance with our culture of innovation and sustainability through transformation, being faithful to our purpose and management philosophy.
Regardless of the country where we are located, each of our commercial and corporate upgrades are aimed at fulfilling our purpose and we find a common ground in our cultural model, mission, vision and values, through our behaviors.

At Ternova we define the values and behaviors with which we want to conduct ourselves on a daily basis, not only as collaborators of a responsible group, but also as members of a family and members of society.
We live these values in our work and in our relationships, thus conditioning our way of thinking, acting and interacting with reality.
Below, we present the values on which Ternova has based its work ethic and with which we have differentiated ourselves from the rest:
We always do what is right.
We preserve life, care for the environment and contribute to the prosperity of current and future generations.
We are in a continuous search for new and better ways of doing things.
We generate business models that maximize the value delivered to customers.
We know that through building alliances, we have the power to change the world.
Our commitment to human well-being is and will always be unwavering.
Ternova’s organizational structure is innovative, and it is designed to facilitate the fulfillment of our responsibilities with greater efficiency and to enhance growth, without losing sight of the core business.
We transformed ourselves into Ternova, as we focus on the quest to impact the world through innovation, technology and sustainability, with the conviction that we can influence and

contribute to make it a better place than it is today.
This transformation led to a change in the organizational structure, a change that currently allows us to fulfill the Company’s tasks with the bold vision of consolidating our position as a strategic ally in the region and the world.
Blanca Villela
Hugo Tona Giolitti
Arturo Tona Giolitti
Hugo Eduardo Tona
This structure is concerned with taking the company to another level, sharing and facilitating knowledge for the construction of innovative solutions that open new doors and business opportunities for industries.
Arturo Alfredo Tona
Cristian Leñero
José Carlos Bonilla
In Ternova, the governance structure established for decision-making and determining the best course of action is managed by various groups, beginning with the Board of Directors, the Steering Committee, and specialized departments. These entities align and consider the recommendations of the committees currently in operation within the company.

is a TRIPLE IMPACT corporation.
It has various operational nodes dedicated to specific value propositions for customers.

Steering Committee is the team that directs and leads strategic planning, profitability and diversification through operational excellence and corporate innovation.








4 Committees led by members of the Board of Directors.
1.
2.
3.
4.
AUDIT AND RISK COMMITTEE
José Carlos Bonilla (president)
Hugo Eduardo Tona
Ana Pérez
Elena Lazo
Melania Parada
Raúl Aguilar
Eduardo Vidal
Rodrigo Samayoa
ETHICS COMMITTEE
Hugo Eduardo Tona
Rodrigo Samayoa
Miguel Argueta
STRATEGIC TALENT COMMITTEE
Cristian Leñero
Blanca Villeda
Miguel Argueta
SUSTAINABILITY COMMITTEE
Hugo Eduardo Tona
Rodrigo Samayoa
Miguel Argueta
Jorge Murillo
Elena Lazo
Raúl Aguilar
















We know that we cannot achieve the greatest impacts when working for sustainability by ourselves; therefore, we work to become actors committed to the sustainable development of each country where we operate, establishing strategic alliances that contribute to our commitment to sustainability.

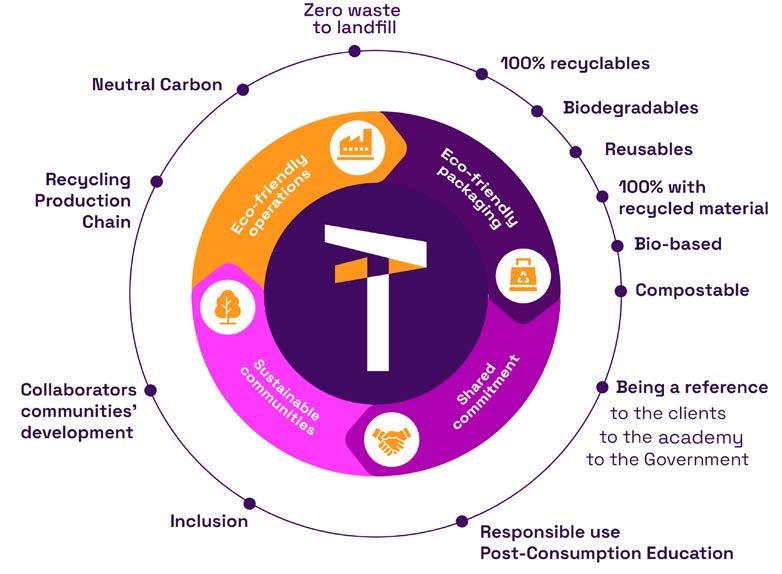
At Ternova, we understand sustainability as the balance between economic growth, environmental conservation and social well-being, which allows us to guarantee a long-term business model. Therefore, we guide our operations with the following strategy.

In 2022 we became the first Central American company to heed the Ellen MacArthur Foundation - World Wildlife Fund corporate call for a global treaty against plastic pollution.
Thus, together with the world’s leading companies and financial institutions, we welcomed the decision of UN member states to begin negotiations for a legally binding treaty to end plastic pollution.
This treaty includes:
Upstream and downstream policies, with the aim of keeping plastics in the economy and out of the environment, reducing the production and use of virgin plastic and decoupling plastic production from the consumption of fossil resources.
Setting a clear direction to align governments, companies and civil society around a common understanding of the causes of plastic pollution and a shared approach to addressing them.
For companies and investors, this creates a level playing field and avoids a patchwork of disconnected solutions, while setting the right enabling conditions to make a circular economy work in practice and at scale.

It provides a robust governance structure to ensure country participation and compliance, with common definitions and harmonized standards applicable to all. This facilitates investments to scale innovations, infrastructure and skills in countries and industries most in need of international support.
We are constantly evaluating and researching the best options for sustainable production. One of the best examples are our 100% recycled, biodegradable and compostable TermoBio
bags. These products comply with international standards that guarantee accelerated biodegradability in the 3 stages of the oxo-biodegradation process in the presence of sunlight, heat and oxygen.
Degradability: accelerated degradation and breakdown of plastic.
Biodegradability: reintegration into the ecological cycle by means of microorganisms that eat the material, transforming it into carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O) and biomass through the metabolism of microorganisms.
Eco-toxicity: ensures the absence of toxic residues and heavy metals.
Among the international commitments that govern our sustainability strategy as of 2020 are the 10 Global Compact Principles related to Human Rights, Decent Work, Environment and AntiCorruption:

Fight corruption in all its forms including extortion and bribery.
Encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies.
Conduct environmentally responsible activities.
Support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights.
Ensure that business practices are not complicit in human rights abuses.
Uphold the freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining.
Adopt a precautionary approach to environmental challenges.
Eliminate all forms of forced and compulsory labor.
Eliminate discrimination in employment and occupation.
Abolish child labor.

In addition, we have made commitments to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation to sustain them until 2030:
Working with brand owners to reduce packaging per functional unit, where possible.
Providing reuse and secondary use alternatives for all our retail customers, and to other types of customers, when relevant.
Working with local authorities, associations and communities to lead the creation of a realistic supply chain for recycling in our markets.
Providing biodegradable or bio-based resin alternatives for 100% of our product lines.
Committing to consume at least 50% recycled material, on average, in all the products we manufacture.
Recycling more than 25,000 metric tons of plastic annually.
Investing in the development of better recycling technologies and improving our supply chain.



The recycling alliance with our clients Nestlé and Walmart, through our initiative Recicla 503, generates an impact by having an active community participating in recycling processes, with brand presence in each of its facilities, and activating sensitized people who in turn educate in the voluntary delivery of recyclable materials, building together credibility credentials that open new doors in other companies.

1. We brought together the Ternova Packaging teams.
2. We identified the stakeholders of the business units.
3. We evaluated the issues by influence and impact weighting.
a. Influence: Degree to which each stakeholder group has the capacity to propose solutions and make decisions.
Weighting Description
01 02
This stakeholder group only receives information on the decision taken.
This stakeholder group is considered to assess their needs in relation to a decision.
03
This stakeholder is an expert in its area and is therefore consulted for decisions.
04
All decisions must be approved by this group.
b. Impact: Level at which each stakeholder contributes to the achievement of the organization’s objectives.
Weighting Description
01 02
This stakeholder group only executes specific actions, but not transversal actions in the chain.
This stakeholder can be easily substituted and does not represent an operating cost.
03
This stakeholder is an expert in its area, so it cannot be replaced.
04
This stakeholder is indispensable for the whole strategy to work together.
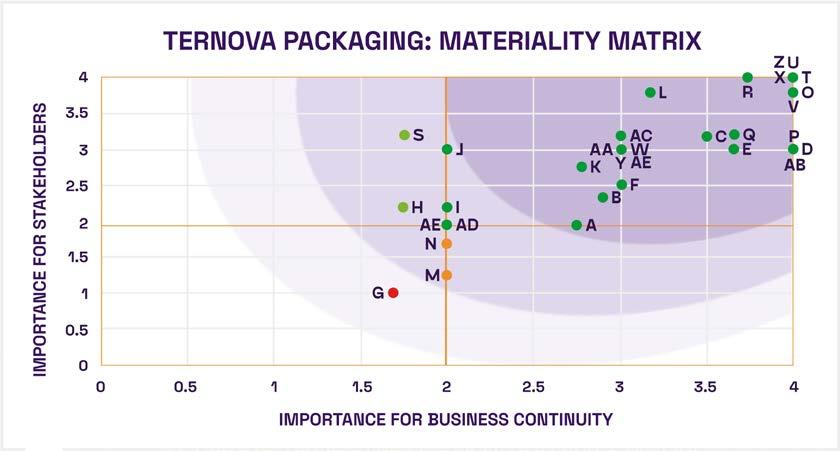
4. We developed a Stakeholder map with a matrix where each quadrant contains the type of prioritization of influence vs. impact they represent for the organization.
H - SHAREHOLDERS
T - BOARD OF DIRECTORS
A - STEERING TEAMS
X - BRAND OWNER CLIENTS
P - EMPLOYEES
E - MUNICIPAL GOVERNMENTS
D - RAW MATERIAL SUPPLIERS
G - ACADEMY
AD - CERTIFICATION BODIES
O - INTERMEDIARIES - RETAILERS - DISTRIBUTORS
AB - FINANCIAL INSTITUTIONS
TERNOVA PACKAGING: STAKEHOLDERS MATRIX

However, the map of material issues has been drawn, where all the issues are important. On this occasion, we will focus on the issues of quadrant D to develop a strategy. It is important to review and analyze the stakeholder map by quadrant to define an effective communication mechanism.
VERY HIGH PRIORITY ISSUES
Circular Economy
C
AA Liquidity
License to operate
D
Specific regulations
Eco-friendly product portfolio
Energy efficiency projects Environmental education programs
Plastic neutrality
Eco-friendly business philosophy
Social-environmental reputation
Adherence to clients’ sustainability objectives
GPTW ranking
Women Empowerment Principles
Business ethics
Developing the maximum potential of our collaborators
K
Inclusion policies
L Corporate image
O Price negotiation with suppliers
P Agreed service levels
Q Supplier credit limits
R
Customer credit limits
T Profits and earnings
U Strategic objectives compliance
V
Medium- and long-term strategic plans
Inventory risk
X Profitability
Y Ambidexterity
Z Attractive value proposition
Compliance with socially related laws
Impact projects with soft loans
HIGH PRIORITY ISSUES M
Generating a culture regarding the use of plastics
LOW PRIORITY
G Environmental education programs
Salvadoran Association of Industrialists (ASI)
Salvadoran Association of the Plastics Industry (ASIPLASTIC)
CENTRARSE Guatemala
Ellen MacArthur Foundation
United Nations Global Compact U.S. Agency for International Developmentl (USAID)
Business Coalition for a Global Plastics Treaty
American Chamber of Commerce of El Salvador (AmCham)
German Chamber of Commerce and Industry of El Salvador (AKH)
Chamber of Commerce and Industry of El Salvador (CAMARASAL)
El Salvador Exporters Corporation (COEXPORT)
Chamber of Industry of Guatemala
Salvadoran Business Council for Sustainable Development (CEDES)
Executive Autonomous Port Commission (CEPA)
Business Foundation for Social Action (FUNDEMAS)
El Salvador Environmental Investment Fund (FIAES)
Zoological Foundation of El Salvador (FUNZEL)
INTEGRARSE
Latitud R
UN Women: Women’s Empowerment Principles (WEPs)
United Nations Environment Program (UNEP)
Nature Foundation El Salvador
Exporter of the Year 2022
Great Place to Work Latin America, 8th place.



Great Place to Work El Salvador.
Disabilities Awards granted by the British Embassy in El Salvador.


TERNOVA has the following certifications that help us maintain high quality standards in our production processes and support the quality of our eco-friendly flexible packaging.

ISO 9901:2015 Certification (Icontec)


Certification INet (Management System)


Food Safety Systems Certification - FSSC 22000 (Icontec)

Carbon Neutral Certification (CN-CER-201)
Graphic Measures International (GMI) Certification

Global Recycled Standard

Labour, health and safety environmental performance and ethics
Green Certified Supplier 2015-2017 y 2017-2019; Supply Chain Security Audit
Great Place to Work (GPTW) 2020 Central America Certification


At Ternova, we continually seek new and better ways of doing things, proposing solutions for a better world, preserving life, caring for the environment and contributing to the prosperity of current and future generations.

We are the ideal strategic ally for companies around the world that want to join the transformation of sustainable flexible packaging of the future as elements that add value to their products and contribute to the customer’s circular economy strategy.
For more than ten years, we have been working to integrate sustainability into the entire Ternova structure, in the constant search for solutions that optimize
our capacity for continuous improvement and help us move forward with that innovative spirit capable of bringing about the changes in which we believe, which we seek, and finally, materialize.
We are focused on leading the transformation of intelligent solutions for a better world, forming a corporation in which every employee knows his or her sustainable role in the company and who, beyond watching over productivity and growth, drives actions in favor of social, environmental and economic balance.
We are proud to say that we are continually reinventing ourselves to generate value for the future. This helps us to remain a leading company in sustainable flexible packaging with operations in the Americas and Southeast Asia, committed to creating a better world through sustainable innovation.
Inclusion of the “Innovation and Sustainability” criterion in the evaluation of business associates.
Participation of business associates in recycling campaigns and activities together with Ternova’s environmental initiative, Recicla 503.
We work on different action fronts with the aim of increasing our contribution to the circularity and sustainability cycle with our recycling efforts through the environmental initiative Recicla 503.
Talks given to Ternova Packaging collaborators and third parties on Eco-efficiency - Focus: Transportation.
Fleet Renewal Project.
Digitalization of the Maintenance Process.
Products based on recycled raw materials.
Recicla 503 is a sustainable initiative of Ternova, born in 2019 with the purpose of bringing our recycling process closer to the population by establishing strategic alliances with companies that become enablers of material collection points.

At Recicla 503, we have two ways of processing recyclable material collected in El Salvador:


The objective of Recicla 503 is the collection of plastic waste (such as straws, bags and plastic caps), which is then processed in our recycling plant.
In addition, we offer an educational platform on the separation, handling and processing of solid waste which, at the end of the chain, can generate economic development opportunities in El Salvador.
1. Flexible plastic and highdensity plastic, processed in our Recycling Plant.
2. All other recyclable materials are sent to other specialized centers.
Our deployment as a facilitator for recycling in the region entails the following:
Creating alliances with companies and institutions.
Collecting in homes. Developing volunteer programs and social hours.
Receiving recyclable materials at different points.
Working with collection centers. Providing donations. Educating on recycling issues.
500 households on the collection route.
Alliances with educational institutions to develop the student social service program.
90% of the recyclable materials we receive are delivered to collection centers.
6 alliances with collection centers.
170,933 kg of recyclable material processed by Recicla 503.
The transportation provider participated in the campaign by loading approximately 1.5 tons of recyclable material for delivery to the post-consumer resin production plant. This project was executed over a period of 6 months.
Mechanical recycling has proven that it will be the fastest growing future plastic packaging solution in the next decade. Therefore, we want to lead the transformation of mechanical recycling in the world, creating alliances in North America, South America and Asia. To achieve this, we have the goal of turning the recycling plant into a world-scale solution.


Currently, our flexible polyethylene plant is the largest and most modern in the Central American region, with which we close the product cycle under Circular Economy criteria.
During 2022, we transformed more than 17,000 tons of flexible
polyethylene into recycled raw material ready for the production process. This is [why] we stand firm on our goal to recycle the equivalent of 66 million pounds of plastic bags in the next 5 years. We know that the greatest sustainability impacts are achieved through collaborative work, which
16,900 tons of recyclable materials recovered.
17 collection centers and 2 purchasing companies strengthened.
More than 1,000 people trained in various topics.
6 collection center infrastructures improved and 5 equipped with machinery for pre-processing.
341 grassroots recyclers registered.
350 grassroots recyclers received work kits.
110 collection centers received “business acceleration” (ITE) scholarships.
is why we work to become actors committed to the sustainable development of each country where we operate, establishing strategic alliances that contribute to our commitment to sustainability. We have been key players in strengthening the recycling value chain in El
Salvador together with FUNDEMAS, USAID El Salvador and more than 14 organizations and companies, achieving the following goals through the inclusive recycling project:
386 officials sensitized on the Integrated Waste Management and Recycling Promotion Act (LEGIR); 226 participated in workshops for codesign and validation of municipal ordinances.
12 municipal ordinances.
2,256 people sensitized with recycling talks.
19,180 pounds of recyclable material recovered in various campaigns.
624 people have taken e-learning courses on recycling.
368 students have collected 16,029 pounds in the “Eco recycling promoters” program.

The minimum standards for effluent discharge water quality are determined in compliance with ANDA regulations, since the effluent is finally discharged into the sewage system administered by ANDA, which consists of the following set of analyses performed once a year in order to obtain the discharge permit.
The system consists of the following phases:
1. Capture of wastewater generated in the roller washer: Each cycle of the washer generates 90 liters of wastewater. The storage tank or buffer tank receives the water directly from the outlet of the anilox washer; this tank has a capacity of 3,100 liters. At this stage, the wastewater is stabilized prior to treatment.
The treatment process consists of the following phases:
Primary Treatment: This consists of the automatic dosage of 200 ml of PH regulator, 500 grams of coagulant material and 12 grams of flocculant (the whole dosage is formulated to treat one cubic meter of wastewater).
Subsequently, the contents of the container are agitated with a compressed air system for ten minutes and distributed over the width of the container with a manifull type device. Then, it is allowed to rest so that flocs are formed and precipitate, leaving it for 4 hours.
Secondary Treatment:
2. Treatment of 1 cubic meter batches of wastewater: El tratamiento de las aguas residuales se realiza en lotes de un metro Wastewater treatment is carried out in batches of one cubic meter each, giving the facility to treat wastewater according to the demand of the process, in an efficient manner and making the best use of the physical resources and reagents. Five cubic meters of water are treated weekly.
Once the flocculant and coagulant dosing is completed, the cubic meter of water is pumped to a second twin tank of equal capacity (1 m3), which is equipped with an activated carbon and gravel filter, in which the water is left to stand for a period of two hours.
In 2022, fuel consumption was 18,500 gallons of diesel and 22,514 gallons of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), representing a net increase of 3.41% in fuel consumption (5.93% for diesel consumption and 1.44% for LPG gallon consumption) compared to 2021, when 17,465 gallons of diesel and 22,196 gallons of LPG were consumed.
During the previous period, there was a 9.37% reduction in the outgoing volume, from 246,157 tons to 223,095 tons in 2022, while the net inventory position increased by 87.7% and 60.60%
for raw materials and finished product, respectively, thus experiencing an increase in the total volume moved.
Accordingly, in 2022, 44.8 tons of CO2 were emitted per thousand tons of inventory moved, a reduction of 3.86% with respect to the previous period, when emissions were 46.6 tons of CO2 per thousand tons moved.
The methodology used by Ternova to measure diesel consumption is done directly according to the refueling of the transport units through the pump inside the facilities, and in the case of LPG, direct consumption is measured according to the purchase and replacement of cylinders.
Direct Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 1)
Ternova has no biomass combustion processes, so there are no records of anthropogenic biogenic greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
The greenhouse gases emitted by the company are carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O) and hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HFC). Table 3 shows the list of gases emitted according to the sources identified.
The emission factors used for the calculations are taken from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) reported combustion factors. The other emission factors are taken from US EPA publications. Category
Emission source
Fossil fuel consumption
Leakage - Fire
Process leakage
Electricity
Greenhouse gas emissions from the generation of externally generated electricity consumed by the organization is 7,468.762 tons CO2e. The organization does not generate indirect emissions from imported energy such as steam, heating, cooling and compressed air.
Emission factors for the calculation of energy emissions have been purchased directly from the International Energy Agency.
Ternova emits 0.148 tCO2e per ton produced.
In 2022, we certified the GHG Emissions Reduction Project for the production of plastics made mainly from other post-consumer recycled plastics at Ternova’s facilities in El Salvador. The purpose of this was the recovery and recycling of plastic materials (high- and low-density polyethylene and polypropylene) which allowed the following:
Preventing such materials from reaching final disposal sites such as landfills.
Processing such waste as intermediate products or final products, thus avoiding the production of virgin materials, displacing the use of energy in the process.
We developed the Emissions Reduction Project on a voluntary basis as part of the company’s commitment to the current climate change situation and its neutrality declaration.
The project is part of an initiative to generate the reduction of emissions that will be used to offset the residual emissions in its production processes and thus meet the criteria for the neutrality certification that we have achieved from 2019 to 2021. Before 2021, Ternova offset its emissions through the purchase of carbon credits. From that same year, we have been able to offset the Carbon Footprint thanks to this internal project. The project began in 2017 and will end in 2025.
During 2022, this initiative resulted in the reduction of 7,063 tons of CO2e. As a result, we have residual emissions of 902 tons of CO2e that will be offset by the reductions from this project.
All data presented are preliminary data that will be subject to a carbon neutral certification audit in 2022.

We do our best not to use substances that deplete the ozone layer. Our R-22 gas air conditioning equipment has been replaced by R-410 refrigerant gas and, in addition to carrying out the appropriate maintenance procedures, the investment in new equipment and proper maintenance has enabled us to stop recharging refrigerant by 2022. In addition, we do not directly emit ozone-depleting substances or other significant substances.
We sought to determine the presence and concentration of volatile organic compounds derived from the products used in the manufacturing process of printed bags and films, and to determine whether the concentrations are within the permitted limits, both for their possible impact on the environment and for the effects they may have on the health of workers. The compounds analyzed were toluene, ethyl acetate, propyl acetate, and propanol.
The results of the measurement and analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) carried out at various points distributed in the production area of Ternova’s plants established that we are complying with the requirements.
At Ternova, we believe that the business of the future, beyond focusing on products or services, must be centered on people. Therefore, our management is based on focusing our attention on collaborators, clients, consumers, suppliers, communities, authorities and allies, in addition to actively listening to their expectations and ways of approaching them.
We have developed the Business-toHuman (B2H) business model which, as a company, leads us to connect with potential customers through a common ideal and the shared responsibility we have with the environment in which we operate, which makes sustainability and its 3 components key and guiding aspects of the business of the future.
The adoption of a sustainable strategy based on ESG criteria and Ternova’s solid foundations in our history of growth allow us to continue providing value for the
future in increasingly unpredictable environments, which are possible to overcome if the best professionals, teams, and structures are in place to develop the capacity to compete and achieve success on a global scale.
Gone are the days when planning and good resource management were enough to ensure positive results in a company. Businesses are now vulnerable to a highly competitive and changing environment, in which companies must adapt quickly to remain relevant and competitive.
At Ternova we focus on the human side of the consumer. Whether it is business to business, business to distribution or business to consumer is irrelevant, since in the Business to Human (B2H) model all changes are seen as an opportunity to generate trust among the people with whom we relate.

All of Ternova’s actions are geared towards creating a diverse, equitable, and inclusive organization. With this vision in mind, an internal assessment was conducted, leading to a comprehensive action plan with the implementation of initiatives such as the following:
1. Formation of the 1st Inclusion Champions Cohort, comprised of dedicated leaders committed to fostering an inclusive culture.
2. Approval and dissemination of the “Corporate Policy for Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion in Grupo Ternova,” which reaffirms, within a legal and compliance framework, all actions to be taken in the areas of diversity, equity, and inclusion.

3. Sensitization campaigns at all operational levels of Ternova.
4. Establishment of strategic partnerships with public and private institutions, such as:
a. Salvadoran Red Cross

b. University of El Salvador’s Student Disability Support Unit
c. Survivor and Disability Network Foundation
d. Association of the Blind of El Salvador (ASCES)




e. House of Culture for the Blind, Ministry of Culture
f. Ministry of Labor and Social Welfare

5. Recruitment and talent selection with a priority focus on vulnerable populations: women and individuals with disabilities. The following are the achieved goals:
% OF WOMEN IN THE PRODUCTION FLOOR.
18% = 188 women hired in production processes.
% OF INDIVIDUALS WITH DISABILITIES.
1.9% = 31 individuals with disabilities hired.
6. We became signatories to the Women’s Empowerment Principles launched by UN Women. Equality Means Good Business: In pursuit of this premise, the United Nations Global Compact and UN Women reached this document composed of seven principles that emphasize the business case for promoting gender equality and women’s empowerment.

In the years that have passed since their launch, and despite the progress made in this area, these Principles are still valid, in the hope that their application will inspire and intensify efforts to ensure the presence of women at all levels. They also offer a set of reflections designed to help the private sector focus on the key elements for promoting gender equality in the workplace, in the marketplace and in the community.

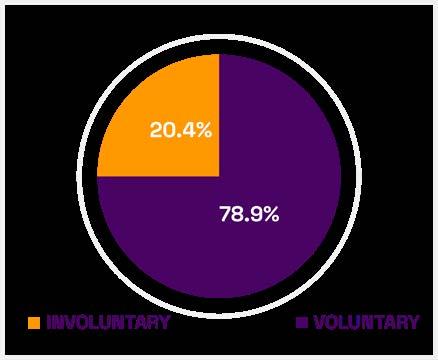
In 2022, we had an annual rotation of 14.7%, of which 11.6% was voluntary and 3.09% was involuntary. The main reasons for rotation during 2022 were as follows.

Our collaborators have the space to communicate and express their observations and concerns, and for this purpose, we have created committees of guardians at all of our campuses.
Each guardian committee had a work plan per session and their progress percentage at the close of 2022 is a great achievement for everyone in the organization:
Our Organizational Culture Pillars help us focus on initiatives that maximize the potential of our talent to achieve our strategic purpose. Our pillars are the following:
Identity
Role design
Community Leadership
Performance Management
Career Management
Compensations
Cultural Outreach
Objective:
That Ternova Group collaborators feel committed to continue developing the transformation process initiated by the company in 2021, adopting the New Culture Model and reflecting on the Convincing Future they have within the company.
Reach: 100% of collaborators from all subsidiaries, including Vietnam.
Implementation of Culture Workshops
952 participants
7616 training hours (8 hours of workshop per number of participants)
Institutional acknowledgments
Audit Awards
It is a recognition given to our collaborators who have accepted the challenge of training and being part of our team of Management System Auditors in the different certification schemes such as Quality, Safety, 6S.

We are proud to have collaborators who perform the role of internal auditor with high quality and prepare us to meet all the requirements of the systems in which we are certified.
In 2022, 13 supervisors were honored for having the highest standard of supervisor compliance and their employees qualified as the best in the evaluations. The most outstanding supervisor is selected by area and a celebration is held with their collaborators and leaders.
As a training team, our challenge is to develop operationally competent collaborators to ensure sustained growth. To fulfill this objective, we use methodologies and tools for the effective implementation of training, which increases the closing of identified gaps in knowledge and skills required in their jobs.
We believe in developing the maximum potential of our collaborators and one of the ways to do this is to provide them with the knowledge and skills to be successful in their jobs. Continuous training is one of the ways for collaborators to develop their potential.

English Language Program

With the growth of the company on a global scale, the integral development of our employees has become important. For this reason, we have included English as a key subject, so that our employees can be ready to take on challenges where this skill is indispensable.
The program covers 108 employees.

01. 02.
It is a program of specialized courses open for collaborators who want to add technical skills and strengthen their competencies for future mobility opportunities. By 2022, 281 participants were trained.
Topics: Flexible Packaging Quality, Teamwork, Self-management and English.
03.
We also have the AVANZA Program, which offers our collaborators the opportunity to study technical careers. For 2022, the following participants were registered:
17 7 6 18
Active collaborators in the Industrial Engineering Technician program. Collaborators graduated from Industrial Engineering Technician 2022. Collaborators in high school process. Female collaborators who start the scholarship benefit for 2023.
One of the best ways to acquire knowledge and develop skills is through experience, which is why we create alliances with educational institutions that give young people the opportunity to work as interns and foster their professional development.
41 trainees from universities and technical training centers
12 trainees from FUNDEPLAST

Since March 15th, 2010, all collaborators of the companies under the Ternova Group umbrella have access to an in-company health clinic which complies with the following legal requirements.
1. Authorization to operate from the Superior Council of Public Health.
2. Support agreement with the Salvadoran Social Security Institute (ISSS).
In this sense, we abide by the health care guidelines recommended by the ISSS for in-company clinics regarding all health programs.
Additionally, Ternova’s healthcare professionals hold the following certifications:
Occupational Hearing Conservationist No. 491044 by the Council for Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation. Hearing Conservation Program Supervisor No. 492172.
NIOSH/ATS spirometry training program. Student number SP000174-18.
American Heart Association Basic Life Support.
Manual handling of loads and repetitive motion evaluation with ISO standard (NIOSH and OCRA formula).
Regarding the health management of Ternova’s personnel, we have developed a surveillance program for employees exposed to the following:
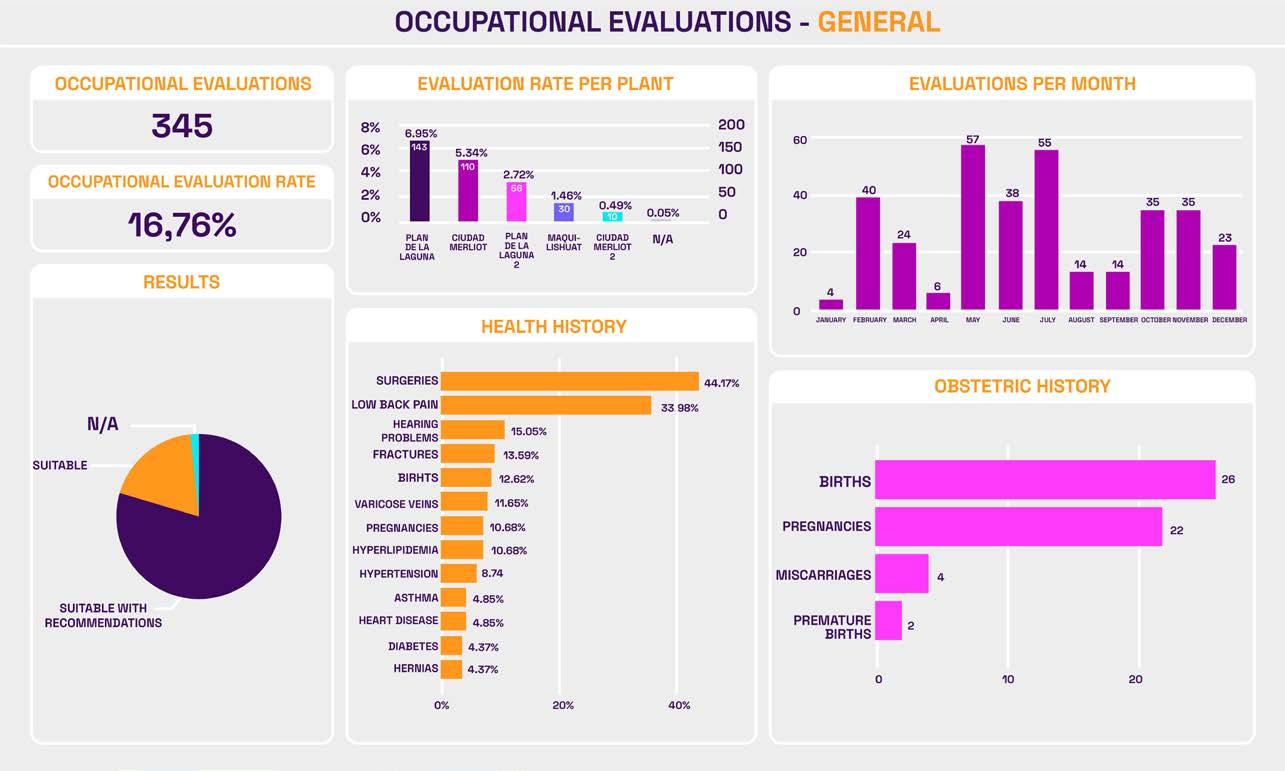
To create the clinical profiles of our work team, we evaluate the following parameters of all collaborators:
Health history
Occupational noise
Respiratory pollutants
Chemicals
Heat
Food packaging process
Family health history
Habits
Somatometry
General examination of stool, urine and smear microscopy
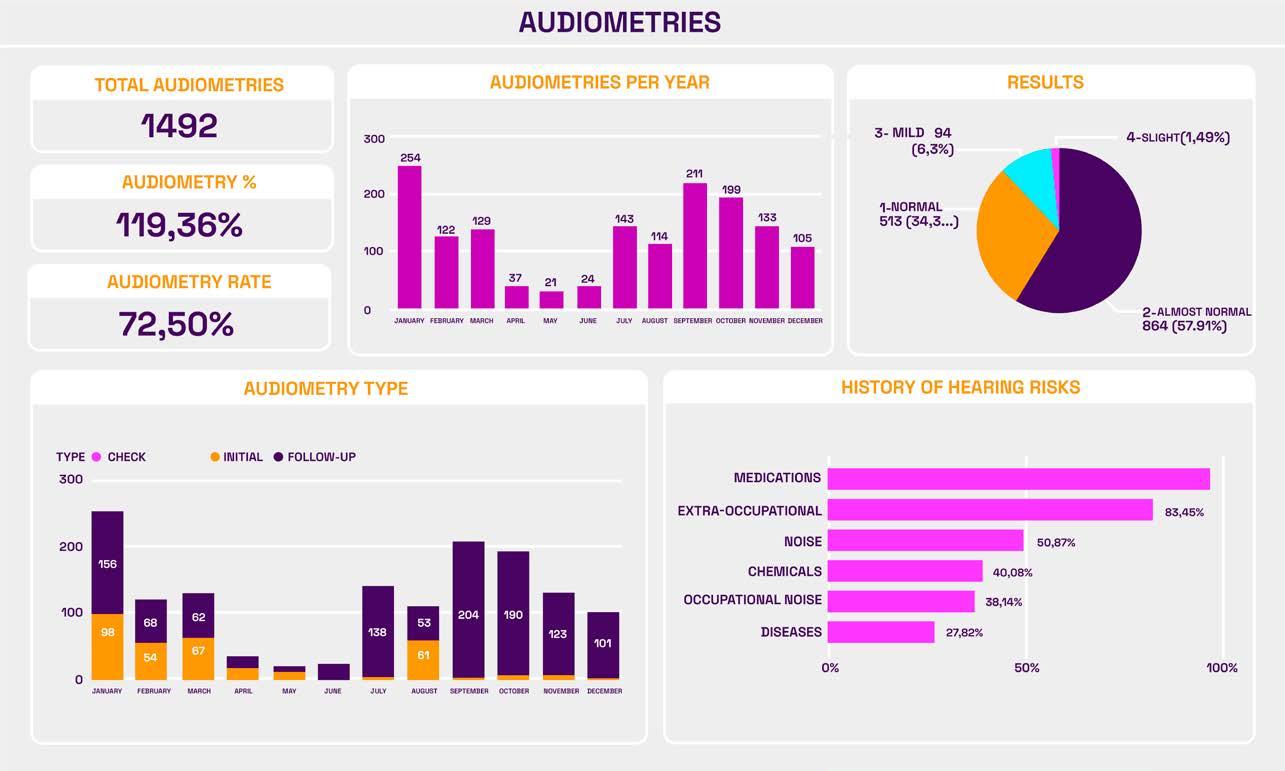
Audiometry
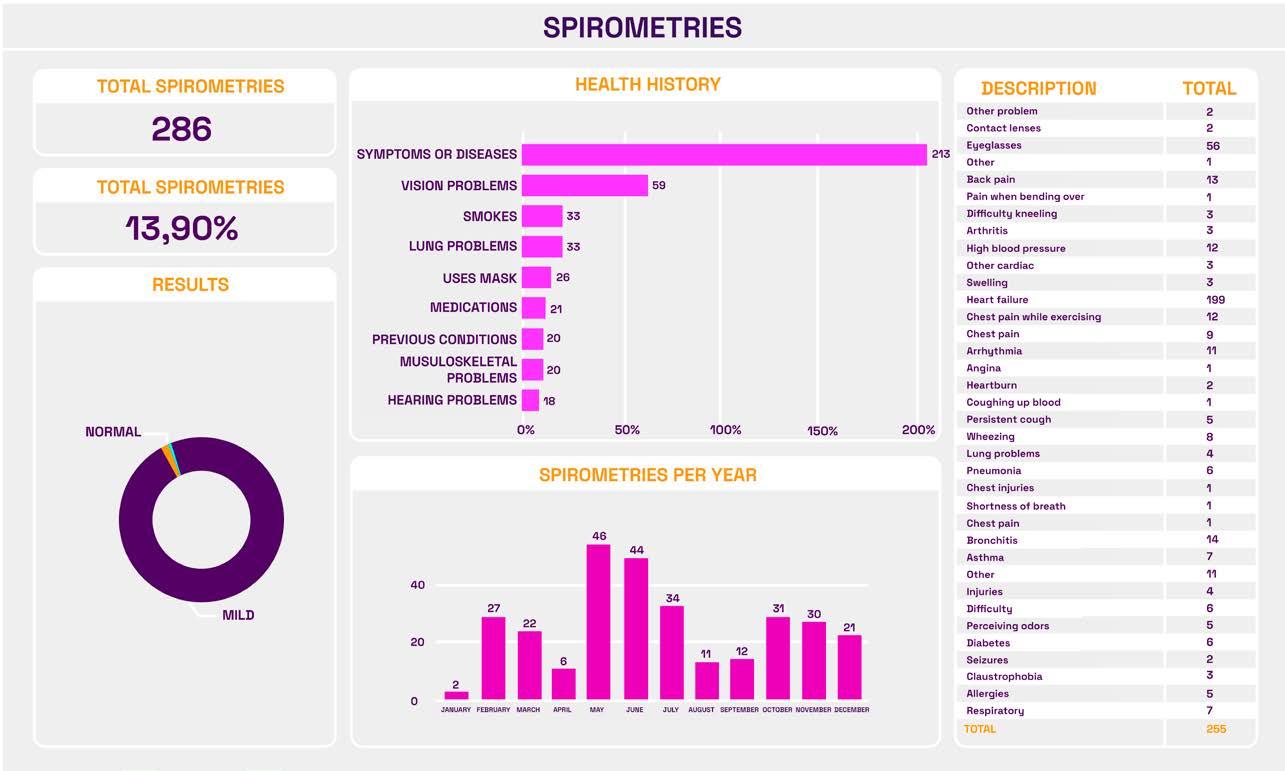
Spirometry
Electrocardiogram
Visual acuity and color distinction test
Comprehensive Health uses a digital platform to gather information from occupational evaluations, audiometries and spirometries, which allows processing the information in real time and maintaining updated and accessible indicators, protecting the information’s confidentiality. The information can be segregated by year, month, gender, plant in which he/she works and operative process to which he/she belongs.
Audiometries are performed under the guidelines of the Council for Accreditation in Occupational Hearing Conservation, CAOHC, and spirometry with recommendations from the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, NIOSH.

Hazard Identification, Risk Assessment
Workplace hazards are identified between health personnel and leaders. When conducting the round of occupational evaluations of personnel, hygiene studies and test results of the exposed population are reviewed.
4. Occupational noise
5. Respiratory pollutants
6. Chemical hazards
SCHEDULING OF OCCUPATIONAL ASSESSMENTS FOR 2022 AND 2023
Merliot 1 y 2
Maquilishuat
January - April
July
7. Biological hazards
The following methodology is used to identify and measure the level of risk:
Ternova Recycling Plant
Plan de la Laguna
The health risks explored are as follows:
1. Ergonomic risks
2. Manual handling of loads
3. Repetitive movements
August
September - December
5-6
SEVERITY LEVEL TABLE
Death, total or permanent disability (LTA), loss of resources and irreparable damage to materials, equipment and environment.
3-4
Permanent partial disability, temporary total disability for more than 3 months (LTA), serious, partially repairable damage to materials, equipment and environment.
0-2
A mishap that includes considerable but repairable damage to materials, equipment and environment, first aid or minor medical treatment.
5-6
Likely to occur immediately or within a short period of time
3-4 Will easily occur over time.
0-2 Likely to occur over time.
Processes that can be followed by workers who want to report health hazards:
Employees, through the Occupational Health and Safety Committees, have representatives and can escalate unidentified hazards
Other unidentified hazards are also explored in the specific questionnaires for respiratory surveillance and audiometry.
During the medical consultation, they may be notified or identified by the health personnel.

0-5
Tolerable risk
6-10 Medium risk
11-25 Significant risk
When a health risk is identified, a specific assessment is made for that hazard.
The results of the identification of health risks are reported to the Occupational Health and Safety Committee, which is responsible for following up on the elimination or reduction of risks.
In addition, various health campaigns are carried out throughout the year to bring health services closer to the personnel.









Humanity is facing three of the greatest environmental challenges: climate change, deforestation and biodiversity loss, which are closely linked in many of their most important aspects. At all levels, maintaining, protecting and promoting ecosystems that act as carbon sinks has proven to be an essential tool in the fight against climate change.
At Ternova Group, we are committed to the protection of carbon sinks in the country. For this reason, we joined Fundación Naturaleza to work together on the project “Reduction of Carbon Emissions as Part of a Citizen Science Strategy for Integral Fire Management” within the framework of the Sustainable Future Contest. This project seeks to have a positive impact on the forests and communities near the Sapo River, and has achieved great progress:
Strengthening local governance
Formation of community brigades
Equipping forest pumps in local communities and neighboring municipalities

Decrease in hunting
Species protection
Protection of carbon stock: 100 hectares of private land protected
For more than a decade, we have worked for the preservation of marine life, especially turtles, supporting the implementation of the project “Strengthening Local Governance around the Experiences Generated by the Management of a Sea Turtle Breeding Corral on the Beaches of Tasajera Island” of the Zoological Foundation of El Salvador (FUNZEL).


In the 2022 nesting season, a total of 1,419 nests were incubated, resulting in 136,186 sea turtle eggs. In addition, we managed to release a total of 124,094 hatchlings to the sea (91% release rate). To achieve this preservation mission, we had the support of the island community, who collaborated in the collection of 6,503 sea turtle eggs during collection days (known as “Closed Nights”). We also built a small interpretation center with information panels and solar energy, supervised by the FUNZEL team and financed by the Ternova Group.

During the last 13 years supporting the project, we have had a significant impact on Salvadoran beaches, releasing a total of 954,278 sea turtle hatchlings with a 91% success rate to the Conservation Program of the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources. This program, in turn, incorporates these efforts at the international level.
At the same time, we have involved the island community in sea turtle conservation and environmental awareness processes through the “Clean Beaches” program created and supervised by FUNZEL. We have also promoted the economic development of the island through work related to the project, directly benefiting 250 people and 500 people indirectly.

Corporate offices: Calle L-3, Polígono D, Lotes 1 y 2, Zona Industrial Merliot, Ciudad Merliot, La Libertad, El Salvador, Centroamérica.
PBX: (503) 2212-7300
Customer Service: (503) 2212-7471
Hana Sztarkman Aráuz
María José Valencia
Hugo Eduardo Tona
Rodrigo Samayoa Valiente
Photography
Archivos de Comunicación
Organizacional
Design and Layout
Carolina Reina
Graciela Rivera
Content Coordinator Graciela Rivera