July 2024
Prosperity
in Heath, Barking and Dagenham
Findings from the Prosperity in east London 2021–2031
Longitudinal Study



About this bulletin
Overview
This bulletin reports on levels of prosperity in Heath, a Lower Super Output Area (LSOA) in the London Borough of Barking and Dagenham.
The bulletin uses data from the Prosperity in east London 2021-2031 10-year study, including household survey data collected between December 2021 and June 2022, and structural equation modelling to report on prosperity in Heath.
What?
The study tracks prosperity using the Citizen Prosperity Index - new metrics co-designed with citizen social scientists based on in-depth research about lived experiences and local determinants of prosperity in east London. It also addresses the lack of research around the long-term impacts of regeneration on prosperity, life chances, and quality of life, while offering a hyper-local look at who benefits and how from regeneration investments.
Where?
15 areas in 5 east London Boroughs
When?
3 waves of data collection between 2021-2031
How?
Uses a mixed methods approach that combines household surveys with qualitative research undertaken by citizen social scientists - local residents employed and trained by the UCL Citizen Science Academy to work and social scientists.
Main findings
Citizen Prosperity Index data suggests livelihood insecurity is becoming entrenched in east London.
Households in Heath are experiencing multiple forms of livelihood insecurity. Income is especially low compared to other areas in the study – 83% of respondents earn less than the national median income. Women earn less than men, and black residents report lower incomes than other ethnic groups. Financial stress tends to be high and access to key public services, such as affordable childcare and public transport connections, is relatively low. Compared to the average of all study sites, Heath performs worse in every Index subdomain, except Voice and Influence.
Prosperity measures that report on what people say makes a meaningful difference to their lives, rather than conventional metrics such as employment and income, reveal patterns that challenge mainstream policy assumptions about how to generate prosperity.
Hyper-local Citizen Prosperity Index data identifies the particular pressure points that local communities are experiencing. Aggregate secondary data of the kind that currently informs regeneration strategies masks the hyper-local nature of these experiences and the intersectional complexities that affect outcomes for individuals from different backgrounds.
Overview
Prosperity in east London
2021-2031 (PieL) is a 10year study examining the prosperity of over 4,000 households in 15 areas of east London where largescale and long-term urban regeneration is driving rapid physical, economic, and social changes in local communities.
It is the first longitudinal study in the UK to use the Citizen Prosperity Index: a new way of measuring prosperity that reports on what matters to local communities. The Citizen Prosperity Index was co-designed with a team of citizen scientists based on in-depth qualitative research about lived experiences and local determinants of prosperity in east London¹. Unlike traditional approaches to measuring prosperity that focus on household income and employment, the Citizen Prosperity Index has five domains: Foundations of Prosperity; Opportunities and Aspirations; Power, Voice, and Influence; Health and Healthy Environments; and Belonging, Connections and Leisure.
Prosperity in east London 2021-2031 is a mixed methods study. It combines data from the Citizen Prosperity Index Household Survey and Obstacles to Prosperity qualitative research, undertaken by citizen scientists –local residents employed and trained by the UCL Citizen Science Academy to work as social scientists in their neighbourhoods. Data will be collected in three waves between 2021 and 2031.
Research questions
Prosperity in east London 2021-2031 explores how the ‘prosperity gains’ from regeneration investments are shared in and between local communities. It looks at how regeneration affects the prosperity of people from different backgrounds and neighbourhoods in the longterm, asking:
• Who benefits and how?
• What are the obstacles to prosperity for different groups?
By examining these core questions, Prosperity in east London 2021-2031 aims to address specific gaps in knowledge about the long-term, hyper-local, and unequal impacts of regeneration on prosperity, life chances, and quality of life. See About the Study for a discussion of the knowledge gaps this research aims to address.
Research sites
Prosperity in east London 2021-2031 examines the experiences of households in 15 areas that are part of, or neighbour, large-scale and long-term strategic regeneration programmes. The 15 areas have been selected because they include ‘established’ communities – places where households often experience multiple forms of deprivation and inequality – as well as ‘new’ mixed-income communities –places where new housing development and job opportunities are changing the demographic make-up of local areas. The 15 areas in the study are sites of rapid socio-economic change, having experienced deindustrialisation and population loss, followed by regeneration, economic transformation, repopulation and demographic change within mere decades.
Each of the 15 research sites is a Lower Super Output Area (LSOA) – small geographic areas with an average of approximately 1,500 residents or 650 households. Prosperity in east London 2021-2031 has adopted a small-area research design to address a lack of evidence about the hyper-local impacts and outcomes of urban regeneration. Evidence from four decades of regeneration in London shows that gains are not equitably shared². Strategic regeneration programmes often target ‘under-developed’ areas, often former industrial sites, where investments in housing, commercial spaces, and transport infrastructure are intended to drive economic development, job growth, and deliver improved social outcomes such as tackling worklessness and housing need. Strategic regeneration sites are often surrounded by low-income neighbourhoods, where long-term residents struggle to access high-quality jobs created by new employers, and are disproportionately affected by rising living costs linked to the redevelopment of affordable housing and the loss of affordable community and commercial spaces³.
The 15 LSOAs in the study are in 5 London Boroughs –Newham, Tower Hamlets, Hackney, Waltham Forest, and Barking & Dagenham – and span 4 Opportunity Areas where long-term urban regeneration is taking place. These are:
– The Olympic Legacy Opportunity Area (OA). – Royal Docks and Beckton Riverside OA. – Poplar Riverside OA.
– London Riverside OA.
This report focuses on Heath in Barking and Dagenham.
1 The Citizen Prosperity Index is based on empirical work from community-led research in five east London neighbourhoods and reflects issues of specific concern to individuals and communities in east London (Moore and Woodcraft 2019; Woodcraft and Anderson 2019).
2 Two decades of urban regeneration in London and other UK cities shows an uneven and inequitable distribution of gains from regeneration investments (Tallon 2013; Atkinson and Bridge 2010; Butler and Rustin 1996).
3 Low-income households are disproportionately affected by rising land values following the development of ‘vacant’ post-industrial areas (Imrie, Lees, and Raco 2009). This has been linked to increasing social inequalities (Poynter and MacRury 2009), displacement (Bernstock 2014; Watt 2013; Cohen 2013), and the suburbanisation of poverty (Bailey and Minton 2018). New hyper-local geographies of inequality and exclusion have emerged with ‘established’ and ‘new’ communities facing starkly different life opportunities, quality of life and levels of prosperity in the wake of regeneration interments (Tallon 2013).
Overview
About the Citizen Prosperity Index Household Survey
The data presented in this report is the preliminary evidence from the first wave of the Citizen Prosperity Index Household Survey carried out between December 2021 and June 2022.
The survey sampled 4,093 households, representing 7,741 residents. Considering recent Census population data, the survey covered about 20 per cent of the total population of all the surveyed sites in the study, providing a representative account of current socio-economic conditions in east London.
IGP researchers designed the survey questionnaire to cover questions about the five domains of prosperity identified in research about the determinants of prosperity for people living in east London4. The survey recorded an overview of household members. The survey includes questions from national surveys such as Understanding Society5, Eurobarometer, and locally developed questions. It builds on the Prosperity Index Pilot Study, which ran in five research sites in east London in 20176


4 Moore and Woodcraft (2023).
5 Understanding Society: Waves 1-12, 2009-2021 and Harmonised BHPS: Waves 1-18, 1991-2009. 17th Edition. UK Data Service. SN: 6614, http://doi.org/10.5255/UKDA-SN-6614-18
6 Woodcraft and Anderson (2019).
Demographic profiles East London and Heath
Survey sampling overview
In 2020, east London had an estimated population of 2,869,200 (32% of the total population in London) – the largest among all five sub-regions of London7. Black or other ethnic minorities comprised 44% of residents in east London – higher than the London average of 40%8. East London also had the second-largest population density (6,214 residents per km2) and the second fastest population growth (13% increase from 2010 to 2020)8. These statistics are highly mirrored in our sample.
The sampling strategy aimed for a fully representative sample of the population in each LSOA surveyed⁸. 267 households in Heath (of a total of 888) were surveyed.
Income, education and age distributions
The two heatmap visualisations (Figures 3-4) show income distribution across various demographic slices. In the first plot, income is broken down by gender and ethnicity across Heath. The colour gradients represent income levels, with purple indicating higher income brackets and orange indicating lower income⁹. The data shows that men are more likely to have higher incomes than women in most ethnic groups with the exception of black women, who have higher incomes than men.
The second heatmap depicts income distribution across age groups and gender in Heath showing that earnings tend to be relatively higher for those aged 30 to 55. However, the survey shows that overall, Heath has the lowest income levels across the 15 LSOAs, with less than 20% of its households earning more than £30,000 a year and 83% of respondents earning less than the national median.
Figures 5 and 6 describe the demographic composition of Heath, each focusing on a different attribute: gender, education level, and age. By using a structured sampling strategy for the household survey, the gathered population data closely follows current Census findings, especially in these three areas10
This not only includes households with larger families and more children but a large proportion who share accommodation including students and professionals living together.
7 Trust for London. (2022). Key population statistics for London and its sub-regions.
8 ONS. (2020). Lower layer Super Output Area population estimates.
9 The income levels are shown by the different colours on the graph. The purple scale shows incomes from £17,500 to £100,000, with darker shades of purple showing higher incomes within this range. The orange scale shows incomes between £0 and £17,499, with the orange getting darker as incomes drop within this range. Questions about income were answered by roughly 50% of respondents, so sample sizes in these charts are smaller than total households in the study area. To get more responses, income was asked in ranges (e.g: £25,000 – £29,999)
10 The Appendix includes summary statistics and further demographic composition of Figures 1-5.
Citizen Prosperity Index
Foundations of Prosperity
Secure livelihoods
An inclusive economy
A good start in life
Opportunities and Aspirations
Good quality basic education
Lifelong learning
Freedom, choice and control
Power, Voice and Influence
Political inclusion
Voice and influence
Belonging, Connections and Leisure
Social relationships
Sense of community
Arts, leisure and sports
Health
and Healthy Environments
Healthy bodies and healthy minds
Healthy, safe and secure neighbourhoods
Sustainable and resilient communities
The Citizen Prosperity Index measures current levels of prosperity in east London. Unlike most indicators and metrics that are decided by experts in government, universities, or business and assumed to be relevant to communities everywhere, the Citizen Prosperity Index reports on what matters to local communities.
The Index is based on in-depth qualitative research about lived experiences and local determinants of prosperity in east London, carried out by a team of citizen social scientists. This research identified five prosperity ‘domains’ visualised in the Citizen Prosperity Index model (figure 7).
Foundations of Prosperity Domain
This domain assesses efforts to foster a local economy that prioritises the building blocks of prosperity - livelihood security, fairness, equity, and sustainable local value creation for those facing the most significant challenges.
Opportunities and Aspirations Domain
The Opportunities and Aspirations domain encompasses three subdomains: Good Quality Education, Lifelong Learning, and Freedom, Choice and Control, incorporating 5 indicators. It aims to evaluate the educational standards, lifelong learning opportunities, and individuals’ sense of autonomy and control over their future, aligning with the domain’s primary objective of assessing prosperity through inclusivity and equitable opportunities for all.
Power, Voice, and Influence Domain
The third domain, Power, Voice, and Influence, consists of two subdomains: Political Inclusion, and Voice and Influence, with two composite indicators. This domain measures the level of political participation and trust in institutions, focusing on inclusivity and empowerment, while also considering individuals’ perceptions of the impact of their participation on social change.
Belonging, Connections, and Leisure Domain
The Belonging, Connections, and Leisure domain includes three subdomains: Social Relationships, Sense of Community, and Arts, Leisure and Sports, covering eight individual indicators. This domain takes account of the levels of social connectedness and community involvement through formal and informal participation in community activities, along with equitable access to arts, sports, and leisure activities.
Health and Healthy Environments Domain
Health and Healthy Environments incorporates three subdomains: Healthy Bodies and Healthy Minds; Healthy, Safe and Clean Neighbourhoods; and Sustainable and Resilient Communities, with 7 indicators. This domain measures individuals’ well-being and health, including mental and physical health, life satisfaction, and access to related services. It also assesses the quality of housing, safety, cleanliness, and access to green spaces in neighbourhoods. The Sustainable and Resilient Communities sub-domain is calculated using the Natural Environment indicator, which is based on survey data around the satisfaction of residents with the local natural environment.
Prosperity in Heath, Barking and Dagenham
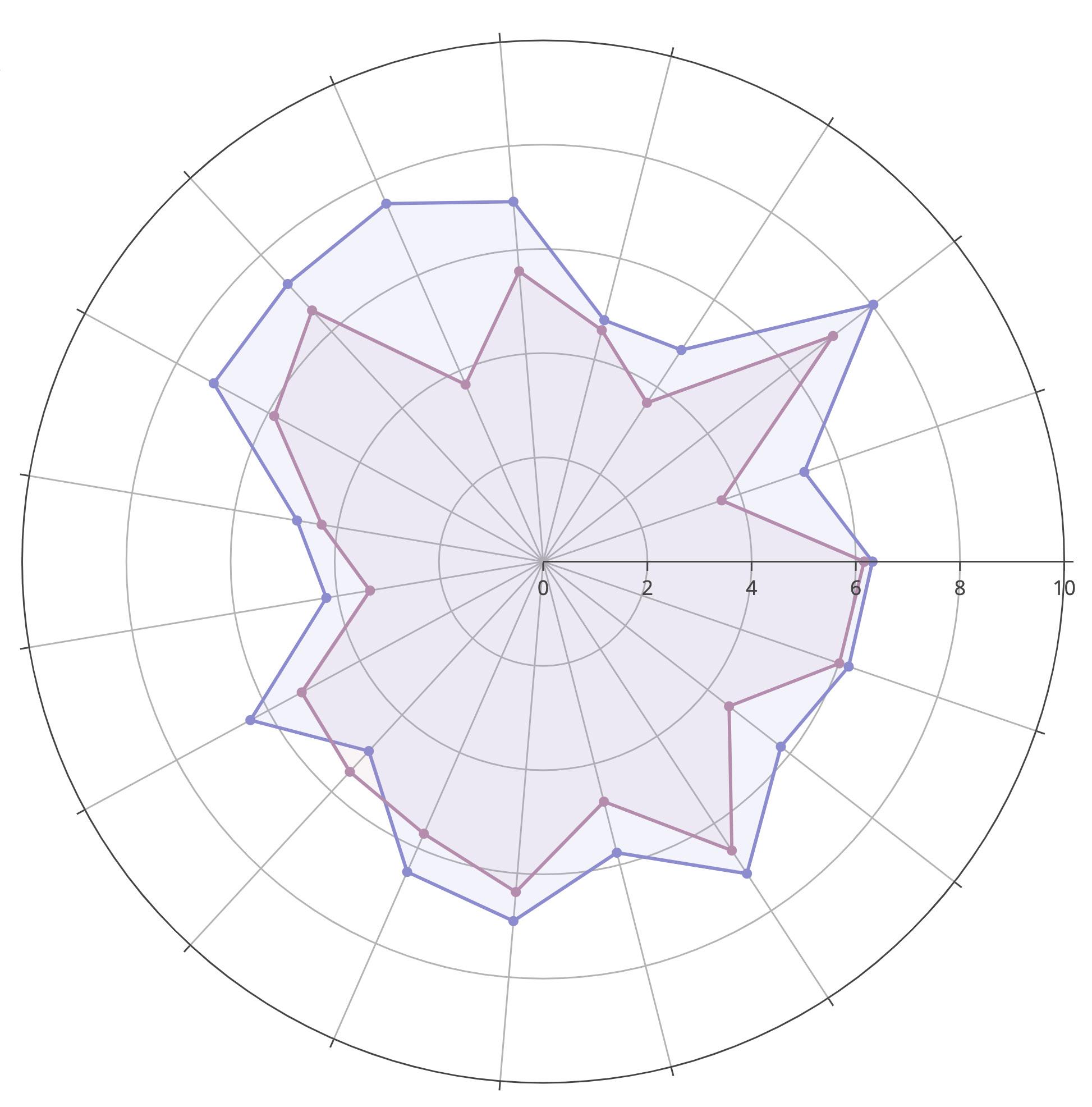
We use data from the Citizen Prosperity Index Household Survey and a simultaneous equation model to estimate values reflecting levels of prosperity in Heath. Figure 8 presents the prosperity scores for Heath compared to the average of the 15 sites in the study using a ‘spider-chart’.
Prosperity ‘scores’ in the model range from 0 to 10 (the lowest and highest values). The score determines how far each point radiates from the centre to the spiderchart’s periphery. The greater the value, the farther the point is from the centre.
Heath scores under the average for every subdomain, except Voice and Influence, which is a reflection of how people feel about their capacity to influence decisions in their local area.
Scores for Food and Energy Security and Affordable Housing – key Livelihood Security indicators – are similar to the study average, which is low for all sites. Other Livelihood Security indicators – Secure and Good Quality Work, Feeling Secure About the Future, Freedom from Financial Stress, and Access to Key Services (affordable childcare and public transport) are markedly lower than the study average.
These observations resonate with the findings of earlier studies that identify livelihood insecurity as the main obstacle to prosperity for people in east London. Community-based research by citizen scientists conceptualises Livelihood Security as more than work and income. Livelihood security depends on an interconnected infrastructure of crucial ‘assets’ such as secure income, stable and quality employment, affordable housing, access to vital public services, food and energy security, and digital inclusion11. Low levels of livelihood security continue to pose challenges in east London. Recognising these complexities, the Citizen Prosperity Index places livelihood security at its core.
The post-pandemic global economy, marked by rising inflation, higher interest rates, and an energy crisis, has had a detrimental impact on Heath. Income levels are much lower than the London average and than our east London average, despite unemployment being relatively low. In-work poverty seems to be an issue in the area, but it is only part of the intertwined challenges that the Citizen Prosperity Index shows.
Indicators of health and wellbeing show additional challenges. Over 36% perceive their health as poor or fair (compared to about 18% in Teviot Estate in Tower Hamlets) and 28% in Gascoyne Estate in Hackney, for example, Heath is among the five LSOAs with the lowest levels of happiness and three with highest feelings of loneliness. Moreover, only 43% of respondents think they could access healthcare services if they had a mental health condition.
Conclusion
This Citizen Prosperity Index bulletin offers an initial analysis of prosperity as a lived experience for residents of Heath in Barking and Dagenham.
Using new indicators co-produced with citizen scientists and based on extensive qualitative research about the determinants of prosperity for residents of east London, the Index offers rich and nuanced insights about socio-economic and spatial patterns of prosperity. Conventional prosperity measures focus on earnings, employment, disposable income and household wealth, with attention being paid more recently to personal wellbeing as a supplementary measure. This bulletin shows that prosperity measures reporting on what people say makes a meaningful difference to their lives, reveal patterns that challenge mainstream policy assumptions about how to generate prosperity. Index data shows deep-rooted challenges of livelihood insecurity that do not map straightforwardly onto employment status. Levels of financial stress, food and energy insecurity, and debt burdens vary significantly within communities that report similar levels of income security for example, and preliminary analysis of prosperity levels by gender and for different ethnic groups indicate intricate, place-specific patterns of experience.
While the current cost of living crisis might explain low levels of livelihood security, the consistent pattern Heath, and throughout the 15 areas in the longitudinal study, is cause for concern. Earlier waves of research undertaken by the IGP and citizen scientists in 2015 and 2017 identified livelihood insecurity as the main obstacle to prosperity in east London12,13. New Citizen Prosperity Index data suggests livelihood insecurity is becoming entrenched in east London.
Prosperity in east London 2021-2031 is a mixed methods study. Qualitative research undertaken by citizen scientists alongside the household survey identifies the complex strategies that people living with high-levels of insecurity employ to mitigate its effects, from local food bank use to relying on family or neighbours for childcare to enable people to manage short-term or temporary work. Such activities often rely on voluntary support in communities already under great pressure14,15. This research also identifies how histories of deindustrialisation, economic development, migration, and welfare interventions such as post-war social housing, have place-specific legacies that continue to exert concrete effects on peoples’ daily lives. Housing tenure, for example, is closely linked to housing affordability, housing security, and housing quality, which intersect with heath, wellbeing, and household disposable income, among other factors shaping lived experiences of prosperity.
More research is needed to understand the long-term social, cultural, and psychological effects of living with insecurity for individuals and for networks in communities exposed to multiple forms of insecurity. Future waves of Prosperity in east London 2021–2031 qualitative research by citizen scientists and IGP researchers will explore these issues.
The hyper-local focus of the Citizen Prosperity Index identifies the particular pressure points that local communities are experiencing today, and provides a framework for measuring social, economic and spatial changes over time. It has been designed to offer decision-makers a new, and nuanced, kind of evidence about the strengths, needs, and vulnerabilities in local communities, and to identify meaningful and sustainable pathways to prosperity that can offer new directions for regeneration planning. Aggregate secondary data of the kind that currently informs regeneration strategies masks the hyper-local nature of these experiences and the intersectional complexities that affect outcomes for individuals from different backgrounds. In a context of sustained cuts to local government budgets, strategic investments in urban regeneration are being expected to work harder to deliver ‘social value’ in the form of better social, economic and health outcomes for local communities, as well as housing, commercial and retail space, and built environment improvements. The Citizen Prosperity Index provides a framework to understand how to regeneration planning, policy, and investment, can be more effectively targeted.
Future bulletins will investigate how health and wellbeing outcomes vary across research sites and intersect with gender, ethnicity, livelihood insecurity, and community connectedness. In 2024, IGP will launch an open-access Citizen Prosperity Index dashboard to share analysis and data. Prosperity in east London 2021–2031 is a rich resource that will yield detailed insights and evidence about who benefits, and how, from investments in urban regeneration in the years to come.
12 Moore and Woodcraft (2019).
13 Woodcraft and Anderson (2019).
14 Alexis, (2022). Repackaging poverty. UCL Institute for Global Prosperity. Available at: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/igp/publications/zines/ repackaging-property Terry and Twinkle, (2022). The abandoned side of North Woolwich. UCL Institute for Global Prosperity. Available at: https:// www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/igp/publications/zines/abandoned-side-northwoolwich Terry, (2022). A tale of two sides. UCL Institute for Global Prosperity. Available at: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/igp/publications/ zines/tale-two-sides
15 Moore and Woodcraft (2023).
Partners and Funders
Prosperity in east London 2021-2031 is an innovative cross-sector research collaboration that brings together university, government, voluntary sector, business, citizen scientists, local residents, and community organisations. Managed by the Institute for Global Prosperity’s (IGP) Prosperity Co-Laboratory UK (PROCOL UK), the study was co-designed with members of the London Prosperity Board – a cross-sector partnership between the IGP, London government, local councils, public agencies, businesses, the third sector, and local communities in London, to change the way decision-makers think and act for prosperity by developing new forms of evidence and new ways of working. The study is jointly funded by London Prosperity Board members: Royal Docks, Lendlease, London Legacy Development Corporation, Hill Group, Poplar HARCA, and the London Boroughs of Hackney, Waltham Forest, and Barking and Dagenham.





































About us References
The Institute for Global Prosperity
The Institute for Global Prosperity aims to rethink what prosperity means for people around the globe. Our vision is to help build a prosperous, sustainable, global future, underpinned by the principles of fairness and justice, and allied to a realistic, long-term vision of humanity’s place in the world. The IGP undertakes pioneering research that seeks to dramatically improve the quality of life for current and future generations. Its strength lies in the way it allies intellectual creativity to effective collaboration and policy development. Of particular importance to the IGP’s approach is the way in which it integrates non-academic expertise into its knowledge generation by engaging with decision-makers, business, civil society, and local communities.
PROCOL UK
Prosperity Co-Lab (PROCOL) UK is an innovative initiative to develop transformational thinking and action on shared prosperity for the UK. Our goal is to achieve a sustained shift in public debate, policymaking, investment and community action for shared prosperity. Led by the IGP at UCL, PROCOL UK brings together citizen-led research, cutting-edge academic research, and collaborative, multistakeholder partnerships with communities, government, business and researchers, to develop new forms of knowledge and new ways of working that bring about transformational change. PROCOL UK’s work addresses the question ‘What are the pathways to shared prosperity in the UK?’ in the context of pressing challenges facing British society: climate emergency, rising social and financial inequalities, Brexit, austerity and public services, and the changing nature of work in the era of AI and robotics. We work across major challenges to identify the new forms of knowledge, governance and ways of working for shared prosperity.
London Prosperity Board
The London Prosperity Board is an innovative crosssector partnership established by the Institute for Global Prosperity (IGP) to rethink what prosperity means for London. The goal of the London Prosperity Board is to change the way decisionmakers think and act for prosperity by developing new forms of evidence and new ways of working that make shared and inclusive prosperity a reality.
Alexis, (2022). “Repackaging poverty”. UCL Institute for Global Prosperity. Available at: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/igp/publications/zines/ repackaging-property
Atkinson, Rowland, and Gary Bridge, (2010). ‘Globalisation and the New Urban Colonialism’. In The Gentrification Debates: A Reader, 51-. New York and Oxon: Routledge
Bailey, Nick, and Jon Minton, (2018). ‘The Suburbanisation of Poverty in British Cities, 2004-16: Extent, Processes and Nature’. Urban Geography 39 (6): 892–915. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/02723638.2017.1405689
Bernstock, Dr Penny, (2014). Olympic Housing: A Critical Review of London 2012’s Legacy. Surrey; Burlington: Ashgate Publishing, Ltd.
Butler, Tim, and Michael Rustin, eds. (1996). Rising in the East: Regeneration of East London. London: Lawrence & Wishart Ltd.
Cohen, Phil, (2013). On the Wrong Side of the Tracks? East London and the Post-Olympics. London: Lawrence & Wishart.
Imrie, Rob, Loretta Lees, and Mike Raco, (2009). Regenerating London: Governance, Sustainability and Community in a Global City. Taylor & Francis.
Poynter, Gavin, and Iain MacRury, (2009). Olympic Cities: 2012 and the Remaking of London. Routledge.
Moore, Henrietta, and Saffron Woodcraft, (2019). “Understanding Prosperity in East London: Local Meanings and ‘Sticky’ Measures of the Good Life.” City & Society 31 (June). https://doi.org/10.1111/ciso.12208
Moore, H. L., Davies, M., Mintchev, N., & Woodcraft, S, (2023). “Rethinking Livelihood Security” In ‘Prosperity in the Twenty-First Century: Concepts, Models and Metrics’, UCL Press, chapter 4, pp.105-121.



Office for National Statistics (UK), (2020). Lower layer Super Output Area population estimates. Avaliable at: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/ populationandmigration/populationestimates/datasets/ lowersuperoutputareamidyearpopulationestimates
Tallon, Andrew, (2013). Urban Regeneration in the UK. 2nd ed. London: Routledge. Available at: https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203802847
Terry and Twinkle, (2022). The abandoned side of North Woolwich. UCL Institute for Global Prosperity. Available at: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/igp/publications/zines/ abandoned-side-north-woolwich
Terry, (2022). A tale of two sides. UCL Institute for Global Prosperity. Available at: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/igp/ publications/zines/tale-two-sides
Trust for London, (2022). Key population statistics for London and its sub-regions. Understanding Society: Waves 1-12, 2009-2021 and Harmonised BHPS: Waves 1-18, 1991-2009. 17th Edition. UK Data Service. SN: 6614, http://doi.org/10.5255/UKDA-SN-6614-18.
Watt, Paul, (2013). ‘“It’s Not for Us”’. City 17 (1): 99–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/13604813.2012.754190.
Woodcraft, S. and Anderson, B. (2019). ‘Rethinking Prosperity for London: When Citizens Lead Transformation’. London: Institute for Global Prosperity UCL.
Woodcraft, S; Collins, H; McArdle, I; (2021) Re-thinking livelihood security: Why addressing the democratic deficit in economic policy-making opens up new pathways to prosperity. UCL Institute for Global Prosperity: London, UK.
Appendix
The following tables show all the measures that make up the Citizen Prosperity Index. Each of these represents a survey question (e.g ‘thinking about your main job, how many hours excluding meal breaks but including overtime do you work in a normal week?’ = Satisfactory Hours (49h or less/week) indicator). We aggregate these measures under composite ‘headline indicators’, such as ‘Secure Income and Good Quality Work’, which is informed by 11 measures. And these headline indicators belong to specific subdomains, which are part of the five wider domains that make up the Prosperity model.
1. Foundations of Prosperity
Secure livelihoods Secure income and good quality work
Pre-tax income
Real household disposable income
Proportion of Permanent Contracts
Commute time
Satisfactory leisure time
Overall job satisfaction
Satisfaction with opportunities for promotion
Satisfaction with quality of available jobs
FOUNDATIONS OF PROSPERITY
OPPORTUNITIES AND ASPIRATIONS
POWER, VOICE AND INFLUENCE
BELONGING, CONNECTIONS AND LEISURE
HEALTH AND HEALTHY ENVIRONMENTS
Genuinely affordable and secure housing
Affordable housing
Size of House
Mortgage (i.e., whether they have a mortgage or not)
House ownership
Ability to keep up-to-date with bills
Freedom from financial stress
Food and energy security
Access to key basic services: public transport, internet and childcare
Feeling secure about the future
An inclusive economy Fairness and equity
A good start in life
Childhood poverty
Adolescent transitions to work or study
Debt burden
Ability to save
Eating less due to lack of money
Use of food banks
Ability to keep accomodation warm
Affordable public transport
Satisfaction with public transport
Mode of transportation for work/education
Internet access
Having social support when in need
Anticipation of moving out of the area
Childcare spending
Part time or full time Job
Ability to save
Income Inequality
Use of Childcare
Household Size
Children present in the household
Students leaving key stage 4 and transitioning to any sustained educational destination
Unemployment
School attendance
Appendix
The following tables show all the measures that make up the Citizen Prosperity Index. Each of these represents a survey question (e.g ‘thinking about your main job, how many hours excluding meal breaks but including overtime do you work in a normal week?’ = Satisfactory Hours (49h or less/week) indicator). We aggregate these measures under composite ‘headline indicators’, such as ‘Secure Income and Good Quality Work’, which is informed by 11 measures. And these headline indicators belong to specific subdomains, which are part of the five wider domains that make up the Prosperity model.
2. Opportunities and Aspirations
Subdomain
Good quality basic education
Lifelong learning
Freedom, choice and control
Headline (Composite) Indicator
Access to good quality education
Access to skills and training for work
Opportunities for self-improvement and personal development
Freedom from discrimination
Having choices and control over one’s future
Measures (survey question description)
Level of education attained
Satisfaction with education
Participation in professional training through work
Participation in adult learning classes
Degree to which people with different backgrounds can live in harmony
Degree to which different cultures, beliefs and identities can flourish in the area
Feeling free to make decisions about one’s life
Degree to which people feel they can take steps to improve their life
FOUNDATIONS OF PROSPERITY
OPPORTUNITIES AND ASPIRATIONS
POWER, VOICE AND INFLUENCE
BELONGING, CONNECTIONS AND LEISURE
HEALTH AND HEALTHY ENVIRONMENTS
3. Power, Voice and Influence
Subdomain
Political inclusion
Headline (Composite) Indicator Measures (survey question description)
Political inclusion
Voice and influence
Feelings of influence
Trust in the Local Authority / Council
Trust in political parties
Trust in the Parliament
Trust in the police
Trust in the British legal system
Trust in the Greater London Authority (GLA)
Trust in the National Government
Taking part in political party activities
Degree to which people feel they can influence decisions about their local area
Taking part in demonstrations
Boycott
Contacted a politician, local, non-local government official
Appendix
The following tables show all the measures that make up the Citizen Prosperity Index. Each of these represents a survey question (e.g ‘thinking about your main job, how many hours excluding meal breaks but including overtime do you work in a normal week?’ = Satisfactory Hours (49h or less/week) indicator). We aggregate these measures under composite ‘headline indicators’, such as ‘Secure Income and Good Quality Work’, which is informed by 11 measures. And these headline indicators belong to specific subdomains, which are part of the five wider domains that make up the Prosperity model.
4. Belonging, Connections and Leisure
Subdomain
Social relationships
Headline (Composite) Indicator Measures (survey question description)
Regular contact with family, friends, and neighbours
Sense of community Community cohesion
FOUNDATIONS OF PROSPERITY
OPPORTUNITIES AND ASPIRATIONS
POWER, VOICE AND INFLUENCE
BELONGING, CONNECTIONS AND LEISURE
HEALTH AND HEALTHY ENVIRONMENTS
Arts, leisure and sports
Getting involved in community life
Having contact with family at least 2-3 times per week
Having contact with friends at least 2-3 times per week
Having contact with neighbours at least 2-3 times per week
Feelings of loneliness
Feeling like they belong to the neighbourhood
Plans to remain in the neighbourhood for a number of years
Feeling like the friendships and associations in their neighbourhood mean a lot to them
Trusting people in their neighbourhood
Feeling like their neighbours will help them
Borrowing and exchanging favours with neighbours
Volunteer work
Membership in civic and voluntary organisations
Participation in local social activities
Participation in arts, sport, and leisure activities
Participation in organised arts or cultural activities
Membership in club (e.g., sports club)
Appendix
The following tables show all the measures that make up the Citizen Prosperity Index. Each of these represents a survey question (e.g ‘thinking about your main job, how many hours excluding meal breaks but including overtime do you work in a normal week?’ = Satisfactory Hours (49h or less/week) indicator). We aggregate these measures under composite ‘headline indicators’, such as ‘Secure Income and Good Quality Work’, which is informed by 11 measures. And these headline indicators belong to specific subdomains, which are part of the five wider domains that make up the Prosperity model.
5. Health and Healthy Environments
Subdomain
Headline (Composite) Indicator
Healthy bodies and healthy minds Healthy bodies
Wellbeing
FOUNDATIONS OF PROSPERITY
OPPORTUNITIES AND ASPIRATIONS
POWER, VOICE AND INFLUENCE
BELONGING, CONNECTIONS AND LEISURE
HEALTH AND HEALTHY ENVIRONMENTS
Access to health and care services
Healthy, safe and clean neighbourhoods Good quality housing
Safe and clean neighbourhoods
Access to green space
Sustainable and resilient communities Natural Environment
Measures (survey question description)
Subjective health
Health and disability status
Visited Nature Recently
Number of days where respondent walked more than 10 minutes in past 10 days
Happiness
Life satisfaction
Feeling life is worthwhile
Anxiety
Access to mental healthcare
Access to physician for physical health problems in your local area
Satisfaction with quality of health services
Satisfaction with local housing quality
Satisfaction with living conditions
Safety at night
Safety in the day
Satisfaction with green/open spaces
Satisfaction with local natural environment
Summary statistics
The following Table and Figures show the key summary statistics for the surveyed population across Heath. These statistics include essential demographic characteristics, employment, housing and educational attainment information.
Main descriptive statistics*
*Please note: full sample Size: 267. Minimum: 255.

Contact
Visit: www.prosperity-global.org www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/igp/ Email: londonprosperity@ucl.ac.uk
Stay connected
@glo_pro
Institute for Global Prosperity @glo_pro


