Pests and Disease Connection



Pests play a significant role in the transmission of various diseases to humans. Understanding the link between pests and disease transmission is crucial for public health. This presentation will explore common pests associated with disease transmission, the mechanisms involved, influential factors, impacts on public health, preventive measures, integrated pest management strategies, and the role of public health agencies.




Mosquitoes are notorious for spreading vector-borne diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, and Zika virus. They transmit pathogens through their bites, making them a major public health concern.

Rodents, including rats and mice, can carry diseases like hantavirus and leptospirosis. Their urine and droppings contaminate food and surfaces, leading to disease transmission.
Ticks are vectors for diseases such as Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. They attach to hosts and transmit pathogens through their bites, posing risks to humans and pets.

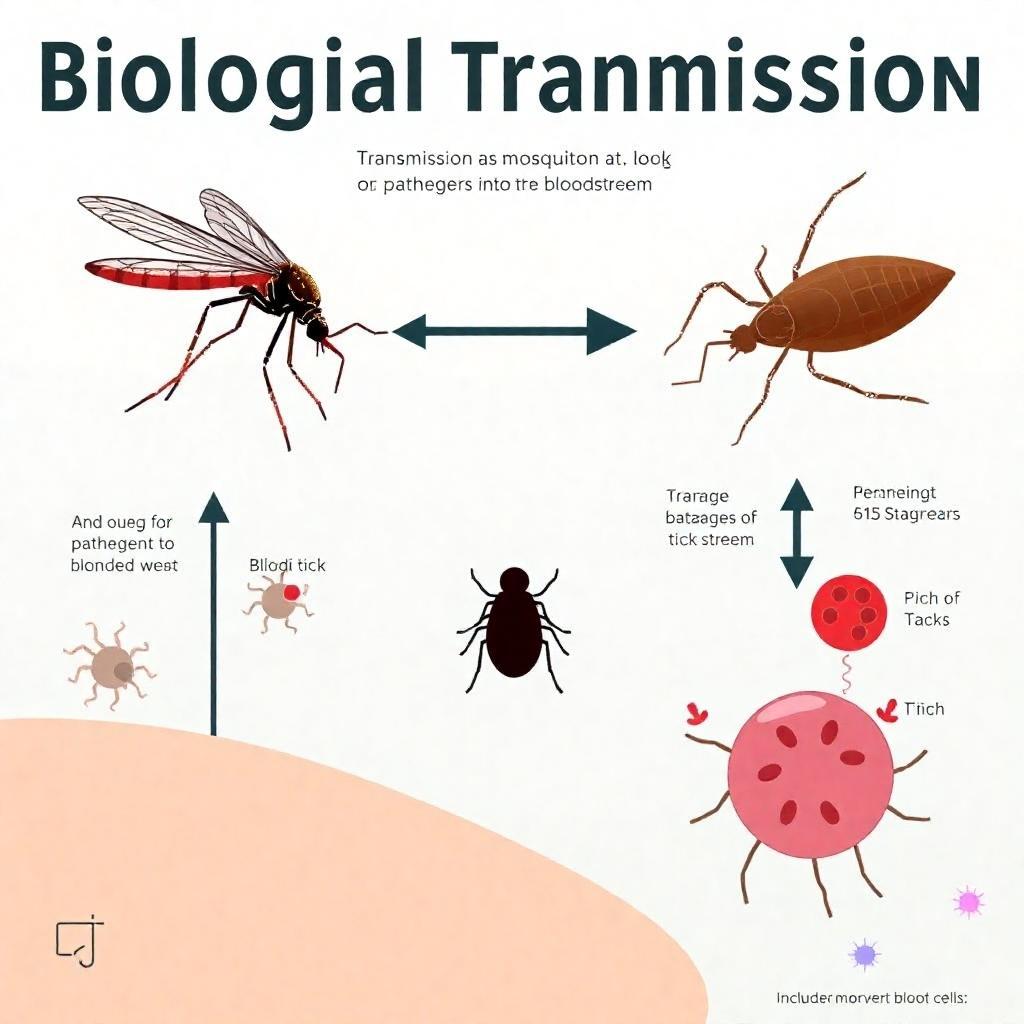
In biological transmission, pests like mosquitoes and ticks introduce pathogens into the host's bloodstream during feeding. This method often involves a complex life cycle of the pathogen within the pest.
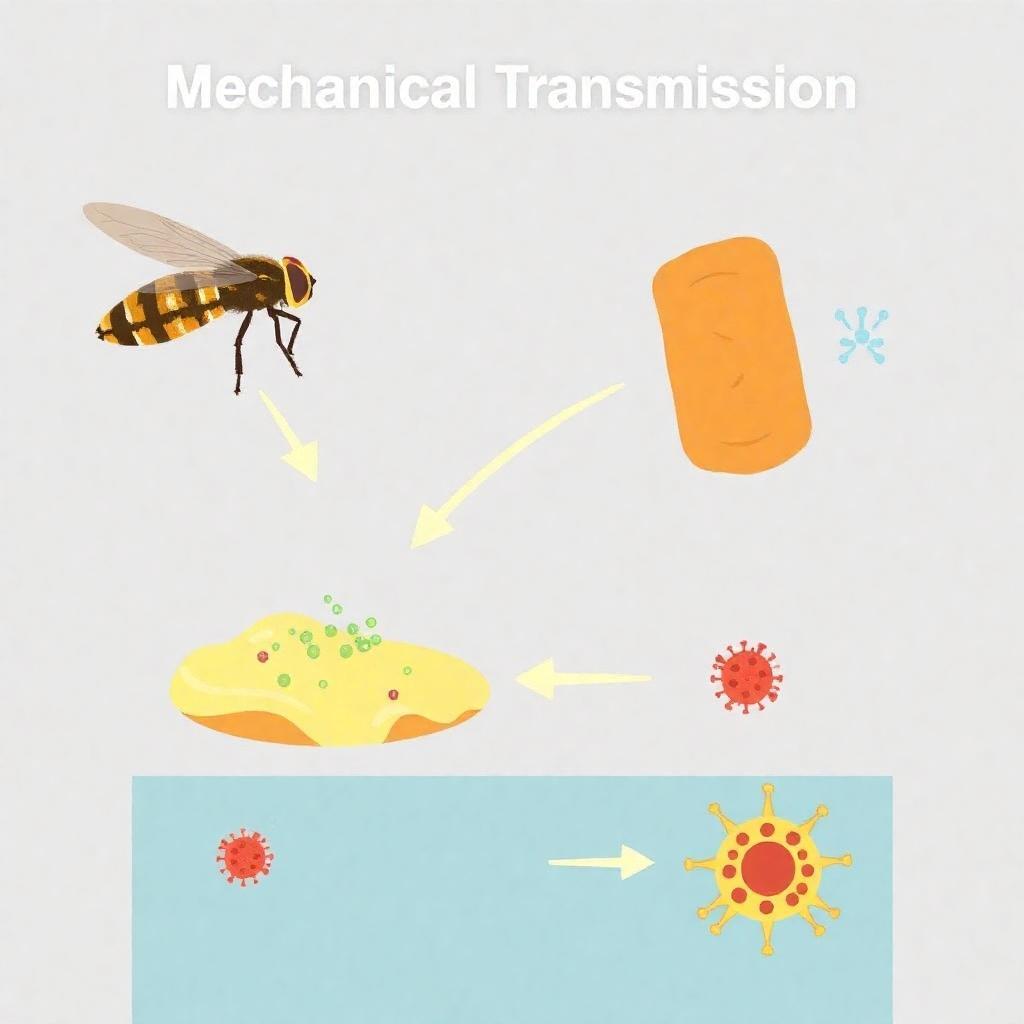
Mechanical Transmission
Mechanical transmission occurs when pests carry pathogens on their bodies or mouthparts and transfer them to hosts inadvertently. This can happen with flies that land on contaminated surfaces before touching food.

Climate, humidity, and urbanization can influence pest populations and their ability to transmit diseases.
Warmer temperatures can increase mosquito breeding and tick activity.
The immune status of hosts, including age and health, can affect susceptibility to diseases transmitted by pests. Individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk.
The behavior, reproduction rate, and habitat preferences of pests can impact disease transmission dynamics. Some pests may adapt to urban environments, increasing their interaction with humans.

Pests are responsible for the spread of numerous infectious diseases, leading to public health crises. This can strain healthcare systems and resources.
Pests such as cockroaches and dust mites can trigger allergies and respiratory issues in sensitive individuals. Their droppings and body parts contribute to indoor allergens.
The economic impact of pest-related diseases includes healthcare costs, loss of productivity, and pest control expenditures. This burden can be significant for communities and governments.
Insecticides and repellents can effectively reduce pest populations and minimize disease transmission risks. Proper application is essential to ensure effectiveness and safety.
Effective waste management and sanitation reduce pest breeding sites and food sources. Keeping environments clean is crucial for preventing infestations.
Community-based vector control programs can help manage pest populations and reduce disease transmission. Collaboration with public health agencies enhances these efforts.


Accurate identification and monitoring of pest populations are vital for effective management. This helps in understanding pest behaviors and planning control measures.
Non-chemical control methods, such as habitat modification and biological controls, can be effective in managing pests. Preventive measures are essential for long-term pest control.
When necessary, targeted pesticide applications can minimize environmental impact while controlling pest populations. Integrated approaches ensure sustainable pest management.

Public health agencies conduct surveillance and monitoring to track pest populations and disease outbreaks. This data informs response strategies and preventive measures.
Educational campaigns raise awareness about the risks associated with pests and how to mitigate them.
Community involvement is crucial for effective pest management.
Collaborations between public health, environmental, and agricultural sectors enhance pest control efforts. A multi-sector approach is essential for comprehensive pest management.
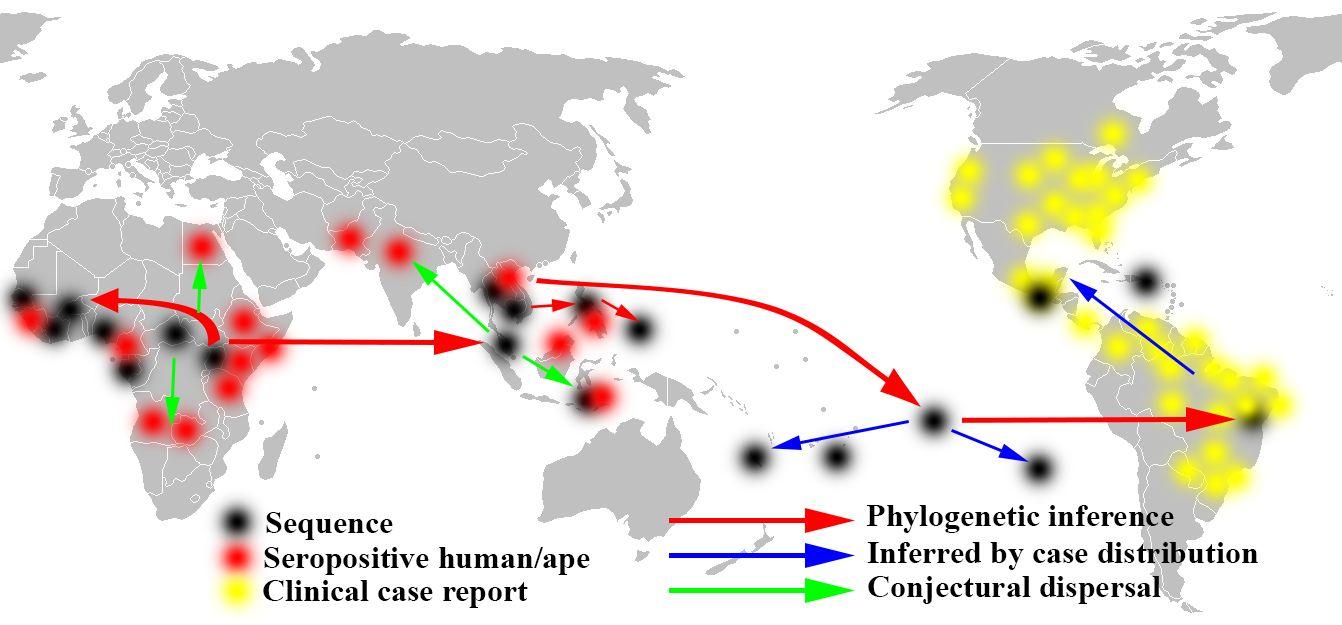


The Zika virus outbreak highlighted the role of mosquitoes in disease transmission. Public health responses included vector control and community education.
Hantavirus outbreaks emphasize the risks associated with rodent infestations. Preventive measures focused on rodent control and public awareness.
Lyme disease cases have increased due to expanding tick populations. Education on prevention and tick control measures is vital for public health.


In conclusion, pests significantly impact public health through disease transmission. Understanding their role and implementing effective management strategies is essential. Future directions in pest management should focus on sustainable practices, community engagement, and continued collaboration among public health agencies to mitigate the risks associated with pests and protect public health.
Contact:
Email: info@trustpestcontrolmelbourne.com.au
Address: 12/45 Vere Street, Richmond, VIC 3121
Phone: 03 8595 9881

Website: www.trustpestcontrolmelbourne.com.au