
7 minute read
Disc filters and solution to clogging problems in water distribution networks
The main objective of installing filtration systems is the protection of all the elements that make up the system. The installation of filter equipment enables the following:
- Improvements of hydraulic performance in the lines.
Advertisement
- Reduction in maintenance work for the control elements, protection and measurements installed in the water distribution networks.
- Reduction in the necessary maintenance for the safety filters.
- Elimination of particles, which are big enough to produce clogging in microirrigation systems.
For the suitable selection of a filtration system we need to know the origin and type of clogging that can occur:
TYPES OF CLOGGING
According to the size of particles that can cause clogging, these can be classified as follows:
- Particles with a direct clogging capacity, due to their size can block certain installation elements. - Clogging caused by large particles can be prevented by means of installing filtration equipment that is suitable for the water quality.
- Particles with no clogging capacity, not initially at least however these can acquire this capacity if the conditions are favourable.
Clogging can also be produced by very fine particles that go through the filters and under certain conditions (prolonged presence of water in the interior of the lines and variations in the water circulation speed) can form larger sized particles.
To prevent this, filter dimensions should be suitable to ensure that the filter grade is correct.
On the other hand, according to the origin of the matter causing the clogging, it can be caused by physical, chemical or biological origin particles:
- Physical origin particles produced by particles of inorganic nature. Two different types:
- Internal Clogging. Caused by physical matter (sand, silt, clay) present in the water source destined for irrigation. - External clogging. Produced by matter that is introduced from the exterior into the interior of the system through: line joints, air relief valves, cracks in the distribution network, emitters in negative pressure conditions, etc…
- CHEMICAL ORIGIN PARTICLES
Caused by precipitation in the interior of the installation containing fertilizers or substances, which are dissolved in the irrigation water that passes through the filters. There are also two types.
- Direct chemical clogging. Those generated by precipitate in-situ.
- Indirect chemical clogging. Clogging generated by particles which come from the detachment of chemical precipitates generated above the point where the clogging has finally taken place. Their behaviour and treatment is the same as for inorganic particles.
- BIOLOGICAL ORIGIN PARTICLES
Causes by organisms or organic remains: These can be classified in two groups:
- Inorganic particles with no proliferation capacity. Vegetal and animal organic remains in suspension
11
in the water flow. Their behaviour and treatment is the same as for inorganic particles.
- Particles with proliferation capacity.
Organisms present in the water (small insects, algae, micro-organisms…) that initially do not have direct clogging capacity but it is acquired due to their proliferation (multiplication or development) inside the flow and distribution networks.
CHOICE OF SYSTEM
When choosing between different filtration systems, one should evaluate the water flow, properties of the water to be filtered and the quality sought; as well as subsequent cleaning operations and maintenance that will have to be carried out, the intrinsic characteristics of each type of filter, the filtration system safety and maintenance throughout its useful lifespan.
The number of filters and the size, with the chosen filtration system and necessary filter grade, must be suitable to be able to cover the requirements in periods of maximum demand. One must take into account that these periods normally coincide with the lowest levels of water quality.
APPROPRIATE FOR SYSTEM
For this reason, and before the existence of different filtration systems, we must check whether the chosen system is appropriate for our installation system and complies with the following characteristics:
1. High safety filter quality faced with variable conditions of:
- Water quality: types of solids in suspension.
- Circular water flow.
- Work pressure.
- Existing differential pressure.
- Frequency of maintenance work.
2. Efficiency of backwash system in the automatic equipment. 3. Minimum water use possible with highly efficient filtering and cleaning.
4. Long-term stability of properties.
5. Easy maintenance work.
The disc filtration systems provide the solution to problems that can come up in the distribution network due to solids that the water carries in suspension. The main features that highlight these filters are as follows:
These retain all types of particles, no matter their nature (organic or inorganic), as long as their size is greater than the filter grade.
These carry out filtration in depth. Not just the particles that have a greater size than the filter grade are retained by the filter element, but a high percentage of smaller sized particles can also be retained. If a particle that has not been trapped on the surface enters the disc channel, the probability of it being retained depends on the following:
- Size and form of the particle in relation to the dimensions of the channel: transversal area (directly linked to the filter grade) and its length.
- Nature of the particle.
- Existence of other particles already retained inside the channel that

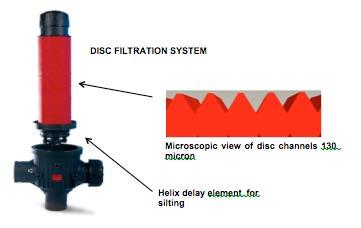
12 DISC FILTERS
act as an obstacle for the rest and provide retention. In other words, an increase in efficiency is achieved as the number of particles retained rises (pressure differential increases), therefore, we can assure that as the grade of silting increases there is an increase in the quality of the filtration.

Resistance of the filtering element under high differential pressures levels, without causing its breakage. This is due to the high resistance carried by the disc set that is compressed and housed in the interior structure.
EASY TO ADAPT TO WORK CONDITIONS
Faced with changeable conditions in water quality or in the use and destination of the filtered water, through grooved discs the filtration system can allow for the change of the filtration grade easily, quickly and economically, carrying out this operation without using tools.

MAXIMUM SAFETY THROUGHOUT ITS USEFUL LIFESPAN
Unlike other filtration systems, this system does not reduce the quality of filtration even when working under pressure differential at all times, or handled improperly, or the duration of use. Pic: Detail of HELICAL ELEMENT silting delayer. Situated in the base of the disc cartridge, it creates a helical effect in the water that takes the particles away from the filter element, thus, noticeably delaying its silting.
Reduced water consumption during the backwash process compared to other filtration systems:
One must take into account, that it is essential to know the “useful capacity” of the filter when purchasing filtering elements of the same nature and it is important to consider the existence of auxiliary elements that improve the effectiveness and efficiency equal to the surface use. These elements are the so-called “silting delayers”, that are able to reduce the frequency with which cleaning has to be carried out, whether it is manual or automatic.
EFFICIENCY
Most importantly, remember to not cut corners when planning the filtration section of your irrigation system. As mentioned, the success of filtration will determine the efficiency and sustainability of the entire system. Do not allow your filters to cause a weak link in your system. By I. Reubin
A FEW TIPS TO REMEMBER:
Do not underestimate the importance of regular maintenance in filter success
Do not omit the extra water required for a back-flush cycle in total flow calculations
Remember that a minimum working pressure will be required during the back-flush cycle of a filter
Do not install the water meter before the filter, if you do not want to measure your back-flush water
Do not release back-flush water back into the irrigation water source near the intake
Make sure that each filter bank is equipped with the correct type and size air valve
Calculate the diameter and length of the back-flush pipe correctly
Assure that PD switches are set up correctly and that backflush intervals and durations are set up correctly on the flush controller
Drain filters and switch off the power to the back-flush unit in off seasons
Keep in mind that a filter bank with two large filters might be less efficient than a bank with three or more smaller filters








