
35 minute read
Dr Tansen Chaudhari
Exclusive Interaction with: Dr. Tansen Chaudhari, COO, Fluid Controls Private Limited and the winner of Railway Innovator of the Year 2020 Global Award
Dr. Tansen Chaudhari is the Chief Operating Officer at Fluid Controls Private Limited since 2011. He has a Ph.D in Mechanical Engineering from IIT Bombay.
Advertisement
Tansen has over 20 years of rich experience in Research & Development as well as Enterprise Sales and General Management. His experience includes a stint in the USA at the GE (General Electronic) Global Research for over 5 years and management roles with GE Business for another 5 years. Tansen has 5 US Patents to his credit and has published more than 20 papers in international journals.. He is a Lean Six Sigma Master Black Belt and DFSS Black Belt.
In a recent conversation with Urban Transport News, Dr. Tansen shared his thoughts on how Fluid Controls is achieving its milestones in the global market by innovating quality products.
First, kindly accept our heartiest congratulations on receiving the “Railway Innovator of the Year” Global Award at Rail Infra and Mobility Business Digital Awards 2020.

It is really an honour to receive such a prestigious award. The awards received by Fluid Controls recognize the vision of the company to design, develop and deliver high quality, high-performance products that delight customers.
Please tell our readers about your professional journey and leadership experience in the industry?
My previous stint before joining Fluid Controls include a career at GE (General Electric), including Global research and management roles with GE Business. I joined Fluid Controls Private Limited in year 2011. My role at Fluid Controls enabled me to implement the learnings from my previous assignments. Post my joining at Fluid Controls we have developed more than 25 new products. Design & Development along with Testing is the foundation of our business, which is in line with the Fluid Controls Vision statement as well. Across the Rail and Metro industry, expectations from vendors are very stringent and process focused. Personally, I have presented at all the Rail & Metro Design Centers, and have enjoyed the technical know-how exchanges. Indeed, my journey at Fluid Controls has been engaging and full of leanings.
Give us a brief overview in respect to the vision, mission and business /operations of Fluid Controls Private Limited.
Fluid Controls Private Limited was established in 1974 by Dr. Y.E. Moochhala, a Ph.D. from Northwestern University, the USA with a Vision to be a Global Leader in the field of hydraulic fittings, valves and allied application solutions.
customer expectations by developing and delivering innovative solutions and providing them quality products and services. Within a framework of continuous improvement, we operate our organisation safely, efficiently and profitably, and provide a challenging work environment for our employees.
Integrity, Innovation and Reliability (I2R) are core values of Fluid Controls business operations which helps us stand uniquely for our People, and hence the Products and Services Globally!
Fluid Controls is a “Vocal for Local” company with over 45 years of experience in engineering fittings and connections for rail & metro brake piping assemblies. We offer customers comprehensive end-to-end “Make in India” solutions for locomotive and coach brake piping arrangements –from design & engineering services to supply of high-performance connectors and installation services.
Fluid Controls is the recipient of the CII Industrial Innovation Award for Medium Scale Manufacturing Organizations and has been recognized as one of the Top 25 Innovative Companies of the Year at the Indian R&D Ecosystem Conclave 2019. Other recognitions include the “Top 10 Urban Infra Solution Provider of Year” by Urban Transport News and the award for “Excellence in Technical Innovation” by ISA Maharashtra Section at PPA Meet 2020.
Tell our readers about some innovative products recently developed by Fluid
Controls for Rail & Metro sectors.
Over the years, Fluid Controls has built a comprehensive expertise for manufacturing, by identifying the right materials and ensuring "fit and forget" assembly. For Rail & Metro applications, we started with Double Ferrule Fittings, and Clamps. Recently we have added • Complete fitment of brake piping components • Engineering and site installation services • Pre-piped assemblies for easy site fitment
How do you view Govt. of India’s ambition to create smart urban infrastructure and public transport systems in various cities? What role do you see your company playing there?
In India, people used to say that we measure distance by time taken, i.e. time to cover the distance. This myth has been broken with the revolution in Rail Transportation across cities. Indeed, this Rail-revolution has brought connectivity, and helped the economy to be connected across geography. Within the same town, distance now is narrowed, and this has paved the path for all-around development of cities. In the good old days, the train station and around used to be only the hub for commercial establishments. With last mile rail and metro transport connectivity, now industrial and commercial establishments have spread. Fluid Controls has supplied brake system components to many Metro establishments such as Delhi, Chennai, Pune, etc. and we look forward to expand our supply in the forthcoming projects of this transport revolution.
Tell our readers about some valueadded products, services and solutions being offered by Fluid Controls to overcome the industry challenges.
Fluid Controls realised the importance of customer wanting to have a system than buying components, and assembling these components together. In fact, if this assembled system develops some issues, each component manufacturer highlights how their supplied component is okay with respect to others. To address this, Fluid Controls started offering engineering and site installation services, pre-piped assemblies for easy site fitment, and specialised products such as Across Frame Connectors, FlexiGripTM Connectors and so forth. This service provides our customers with an end-toend solution as they have a single source vendor for engineering and design, connectors supply and fitment.
Traditionally, the Indian Railways has sourced brake piping parts from individual suppliers, and the installation of the piping was carried out at the site by separate vendors. With the expansion in the manufacture of carriage and locomotive rolling stock, it is imperative that the railways have zero-defect, leakfree connections in the pneumatic brake piping system as this is a critical safety item which requires superior materials and precise expert installation. manufacturing connectors, our understanding of tube and end connector performance and our decades of experience of swaging and accurate tube bending, Fluid Controls offers customers a complete end-to-end engineered supply and installation solution. With this, working flexibility in the system is established, keeping the same performance.
What are the key challenges faced by Fluid Controls due to the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in the country and how are you addressing them?
Due to the current pandemic Fluid Controls, like all other industries has faced Supply, Transport and People challenges. Currently, we have teams who are working from home. We are working with our suppliers so that supplies can be better planned.
Though, given the project nature of our business, we continue to receive orders as there is activity in the infrastructure segment which constitutes our business.
At Fluid Controls, we “Engineer Connections Everyday”. In the COVID19 situation we are in today, we are also committed to “Staying Safe Everyday” and ensuring business continuity as well as the health and safety of our employees, their families, our customers, and our business partners. With a systems and process focused approach, we have restructured our operations and have put in place detailed guidelines for operations and conducted extensive training of our employees. The core of our EPRP Protocol is the “Fluid Controls Focus Five” to ensure safe working. We have also re-structured our facilities and offices to ensure compliance with government guidelines and have modified our manufacturing processes to ensure safe production and inward & outward material handling. In addition, all our employees are provided with individual PPE kits which are tailor made for their area of operation and have been provided with adequate insurance. As a responsible citizen, Fluid Controls has also reached out to the wider community and have extended support to NGOs such as UnLtd India, OSCAR Foundation, Masoom and Goonj who are involved with COVID Relief Work.
What is your personal vision for Fluid Controls and where do you see it five years down the line both in terms of the brand and revenues?
I joined Fluid Controls as an employee in year 2011, and now I am a Shareholder in the Company as well. This clearly shows the professionalism and the trust, of the Board of the Directors. Along with our Managing Director Ms. Sophie Moochhala, and a Winning Team, we have grown Fluid Controls 10 times in last 9 years!
We would like to expand the Fluid Controls’ footprint globally in coming years. Currently we have a manufacturing tie-up in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, and we would like to have one or two more geographically. We would also like to tie up with one or two global universities, and fund a Research Project for Fluid Controls. A key part of our future plans is to tap into the brake piping business for the emerging high-speed train operations. We are also focusing on global supplies to Europe, North America and SE Asia.
Anything else, you want to tell our readers about the business strategy and future expansion plan of your company.
Trustworthy, Transparent, and Walk-theTalk Brand is what any customer of Fluid Controls would describe us as. Unyielding Integrity in our People and Products is an added tag! Like the Rail and Metro transport industry, which is growing globally, I want to grow Fluid Controls multi-folds by taking everyone along, and contributing to our nations development!

Showcase your brand with Urban Transport Infrastructure Magazine and Urban Transport Infra Business Newsletter


•Print Advertising •Digital Advertising •Content Based Advertising
How Indian Railways can emerge as a key driver of the Indian economy?

Amitabh Kant CEO, NITI Aayog Govt. of India
Since the first passenger train chugged out of Bombay in 1853, Indian Railways has gone on to employ over 1.2 million people and generate approximately Rs 2 lakh crore annually. Not to forget the extraordinary scale of Indian Railways— its network spans around 68,000 route kilometres! Undisputedly, the railways is a major contributor to jobs, GDP, and mobility. It is, however, due for modernization and increase in capacity to become a key driver of India’s growth in the post-Covid era. In fact, given its size, scale and scope, modernization will make the entire travel experience not just palatable, but also world class. High quality in transit experience needs to be supplemented by best-in-class railway stations. All this will transform the overall experience of the common man.
Efficient and optimal use of the railways could add up to 1% to India’s GDP. The Government of India cannot conduct this massive operation alone; it needs to involve the best resources via public private partnership (PPP) to help bring in the latest technology, leading practices and efficiencies. In 2018–19, the reserved passenger volume was 16% of the total originating non-suburban passengers (3.65 billion). In a telling statistic, almost 8.85 crore of waitlisted passengers could not be accommodated in 2018–19, which needs to be rectified.
The recent opening up of public-private partnership (PPP) opportunities by Indian Railways is a clear indicator that a reform-driven agenda is being implemented. It is a controlled foray into PPP, where market forces will help enhance the quality of services and intransit experience, without the Government relinquishing control over public safety and security.
The purpose of PPP in certain routes is to facilitate the introduction of new technology, provide high-level service and reduce travel time. With the imminent commissioning of Dedicated Freight Corridors and other infrastructure development, it is likely there would be availability of additional paths for operation.
The broad contours of the proposal feature a list of 109 pairs of routes through 151 trains (rakes), divided into clusters with at least 12 rakes to be operated. Journey time will be, within a range of 10%, similar to the fastest Indian Railways train on that path. Proposed routes for long distance travel include Delhi – Mumbai, Delhi – Chennai, Mumbai – Chennai, and others. This is a follow up of last year’s launch of the IRCTC-run Tejas Express on the Lucknow–New Delhi and Ahmedabad–Mumbai routes, along with the Kashi Mahakal Express plying on the Varanasi–Indore route.
Critically, Indian Railways will be nondiscriminatory in its treatment towards trains operated under PPP. No similar regular train scheduled will depart within 15 minutes of the PPP-operated train on the same origin route, and the PPP operator will be responsible for maintaining its trains.
Safety certification of the rakes will be in line with all safety and security parameters laid down by Indian Railways. The concession period will be for 35 years, and the PPP operator may procure its trains and locomotives as per its choice as long as they are compatible with predetermined specifications and standards. With regard to introducing new rolling stock, the validation will be done by an accredited independent safety assessor on an Indian Railways track, until such time RDSO adopts testing norms as set out in UIC 518 or other internationally accepted norms.
The broad objectives of this proposal are to bring in PPP operators to finance, procure, operate and maintain the allocated trains. Indian Railways will be paid predetermined haulage charges, among other payments such as energy charges as per actual consumption, and a share in gross revenue as determined through a transparent bidding process. This is expected to bring in cutting-edge technologically advanced rolling stock, shorter journey times, enhanced job growth, better safety, and best-in-class service standards. And, crucially, bridge the demand-and-supply deficit for passengers. It is expected that the investment from the PPP will be in the range of Rs 30,000 crore—all in a Make in India–led growth strategy.
PPP has been actively deployed as a mechanism in Europe and Japan. In Germany, the Deutsche Bahn has gone the autonomous entity way. In fact, it been divided into two distinct entities: DB Netz for infrastructure and DB AG as operator, which remains state-owned and continues to operate most inter-city services. Entities in Britain and Italy too have gone the PPP way, while Japan has made several forays into PPP in its rails and stations. In the 1980s, seven forprofit companies were made as a result of the bifurcation of Japan Railways under the PPP umbrella. The other key initiative is the redevelopment of railway stations through a PPP model, remaining costneutral to Indian Railways. Initially, 50 stations will be bid out and funded through land monetization as well as user charges. The modernization and redevelopment of stations will be conducted primarily through Indian Railway Stations Development Corporation Limited, Rail Land Development Authority and other Central Government entities. The PPP basis is under the Design, Build, Finance, Operate and Transfer (DBFOT) model. The lease period of the land has been notified to allow an increase to 99 years for residential development around the railway stations as part of the project, and commercial development to 60 years. To add to the viability of this project, all clearances will be single-window, and plans will be approved in consultation with urban local bodies and authorities to ensure a collaborative exercise.
It entails utilizing the potential of real estate for excess land and air space in and around the stations for development through PPP. Comprehensive technoeconomic feasibility studies of stations across the country are and will continue to be conducted. Already, development at Gandhinagar and Habibganj railway stations is at an advanced level, expected to be completed by the end of the year. The redevelopment of Anand Vihar, Gomtinagar, Bijwasan, and Chandigarh railway stations has already been agreed to and work is commencing. The 50 big stations have been planned to be bid out through the PPP route aimed at bringing in investments exceeding Rs 50,000–60,000 crore, and a paradigm shift in travel experience. While 8 stations have been bid out, the two large stations of New Delhi and Mumbai will be in the market soon. The balance 40 stations are expected to soon hit the market.
In any structural reform of this nature, there will be challenges. One of the primary challenges will be independence of adjudication in matters of dispute. An independent regulator could go a long way towards allaying concerns of equitable treatment in the minds of PPP operators, and ought to be considered strongly. Other issues that could factor in will be the pricing strategy in order to remain competitive yet stay profitable, given the competition through air, road, and to some extent, water transport. It will be important to address the challenges in order to ensure this is a success and a sustainable model.
The introduction of PPP into Indian Railways is a welcome step, and can lead to the kind of reforms that can help transform India and make Indian Railways a global leader.

Dr. Amudhan Valavan Public Transport Expert
Smart Bus Maintenance in Public Transport by Using Internet of Things (IoT)
Dr. Amudhan Valavan possess over 26 years of experience in Public Transport and Urban Mobility related fields since 1993. From 2016, he has worked as an Independent consultant and Adviser to leading Companies like Thriveni Earthmovers, Thriveni Sainik and also RTA, Dubai and KPTC, Kuwait etc. on several technical assistance and training projects in India & the Middle-East and managed a number of projects involving numerous experts and multi-disciplinary teams.
In most of the Indian Public Transport firms there is no advancement in the level of maintenance system. Properly maintaining the Buses will not only ensure its safety and dependability but also greatly reduce operational costs and down times. As the National and Central Governments have invested huge amount for the STU’s, maintenance of the Public Transport Vehicles has to reach levels and standards in par with most developed countries.
In Indian STU’s fleet, the error codes can be predicted easily only in vehicles like Volvo, Mercedes Benz and Scania Buses from the Vehicle ECU’s through Digital System Signals. But the process is slightly difficult in Ashok Leyland, Tata, Mahindra Corana, AMW, etc. as most of the functions contain Analogue System without sensors. If Indian public transport needs to shine alongside with many developed countries, it needs to adopt IoT and other digital concepts as quick as possible.
As we enter the 4th wave of the Industrial revolution, the Utilisation of Internet of Things (IoT) in Public Transport is focused greatly on Vehicle utilisation, operational cost, worker productivity etc. IoT is all about connecting low-cost sensors to gather Vehicle data and using advanced analytics to draw meaningful insights. It is estimated that IoT will allow Public
Transport/Operators to increase their productivity by 30% The maintenance strategy that employs advanced analytics to predict machine failures is known as Predictive Maintenance. At present, Reactive and Periodic Maintenance are being carried out in Indian Public Transport STU’s. For the better efficiency in Vehicle maintenance, normally western countries are doing Predictive and Proactive modes of maintenance.
In a survey carried out by the World Economic Forum (WEF), the most widely cited application of the IoT is predictive maintenance and it is rightly so. Predictive maintenance allows the persons involved in Vehicle Maintenance to lower maintenance costs, extend equipment life, reduce downtime and improve production quality by addressing problems before they cause vehicle components failures. Predictive analytics helps us to predict future outcomes using past data. Together, we can help Operators to focus on their core operations and not worry too much about things like asset utilisation and equipment uptime. (See Figure 1)
IoT defines a new concept in the transport industry that enhances the current solutions with Remote Diagnostics and Technical information Functions. IoT focus is always oriented towards the optimization of the: Driving Performance & Bus Breakdown times, Fleet Management and Workshop Repair Times.
IoT facilitate the smart approach for the Bus maintenance and will provide the definitive solution for the management of industrial vehicle fleets. All of this contributes to the increase in benefits, thus providing a better service for your customers. (See Figure 2)
DIFFERENT TYPES OF MAINTENANCE
Fix or Repair w hen the Vehicle Components Fail
Figure 1
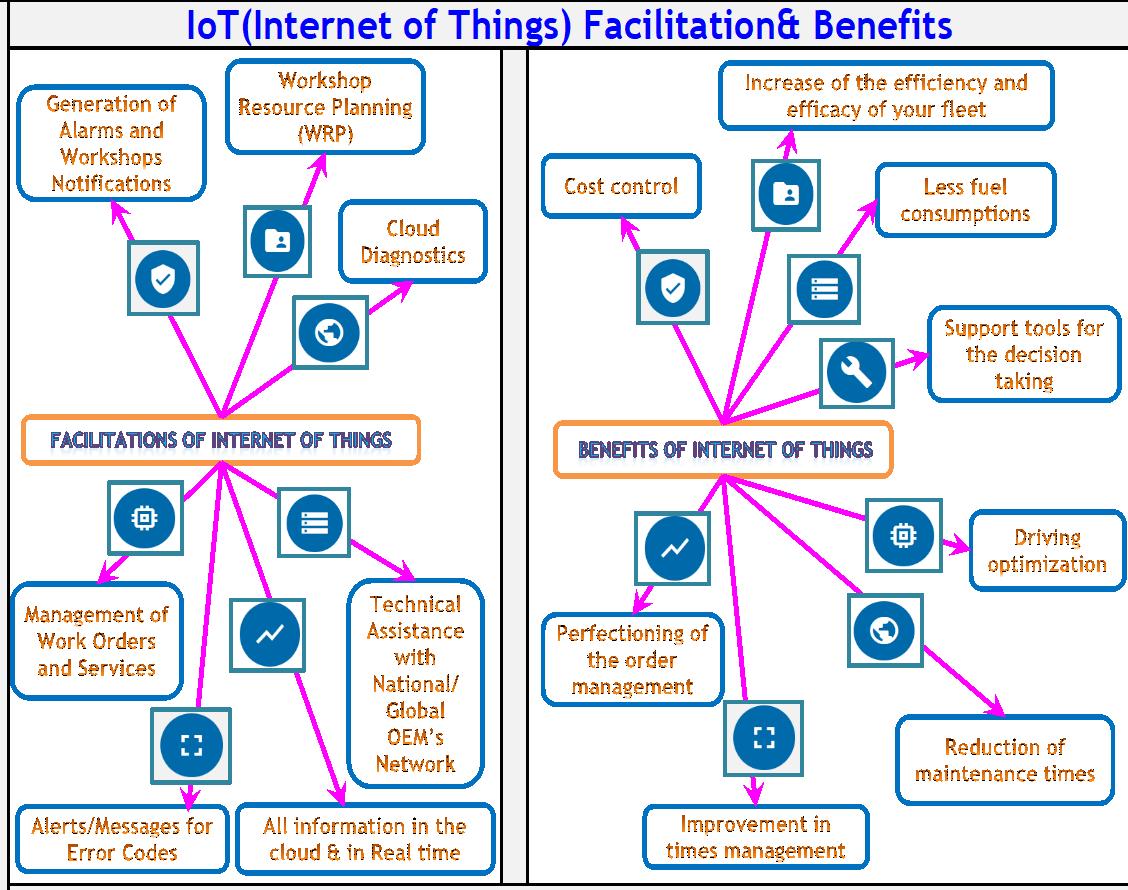
IoT introduces in an exclusive way ‘the concept of remote diagnosis in real time’, thus contributing to the correct maintenance and prevention of problems through error reading in the electronic systems installed in each vehicle. With Internet of things (IoT), it is possible to recognize three roles of the application: the fleet manager, the workshop and the driver. With IoT one will have a continuous and fluent communication between the fleet manager, the workshop manager and the vehicle driver. Each of them will have a role inside the system. Through the web portal, one will be able to access all information in real time from any place in the world. The Platform is accessible from any device (PC, tablet, Smartphone…) with an Internet connection and support for multilanguage can greatly increase the scope for further collaborations and development. Web Site platform includes the following features: Location, Alarms, Messages, Diagnosis,Tachograph Data , Reports etc. The most significant available functionalities are detailed below in the Another new development in IoT and transport maintenance is the Tire Pressure Monitoring System. A system designed to measure and monitor tire pressure and temperature using sensors in real time. Most punctures are caused by driving with wrong air pressure or a slow loss of pressure. TPMS system availability in the vehicle reduces the risk of a tyre bursting by a high percentage. Besides, with this system, it is possible to monitor if the tyres are in proper condition even in very high temperature or if there will be a potential problem in the axle or in the brake system. Correctly monitored tyres can reduce costs, consumption, emissions, as well as extend tyre life and increase road safety.
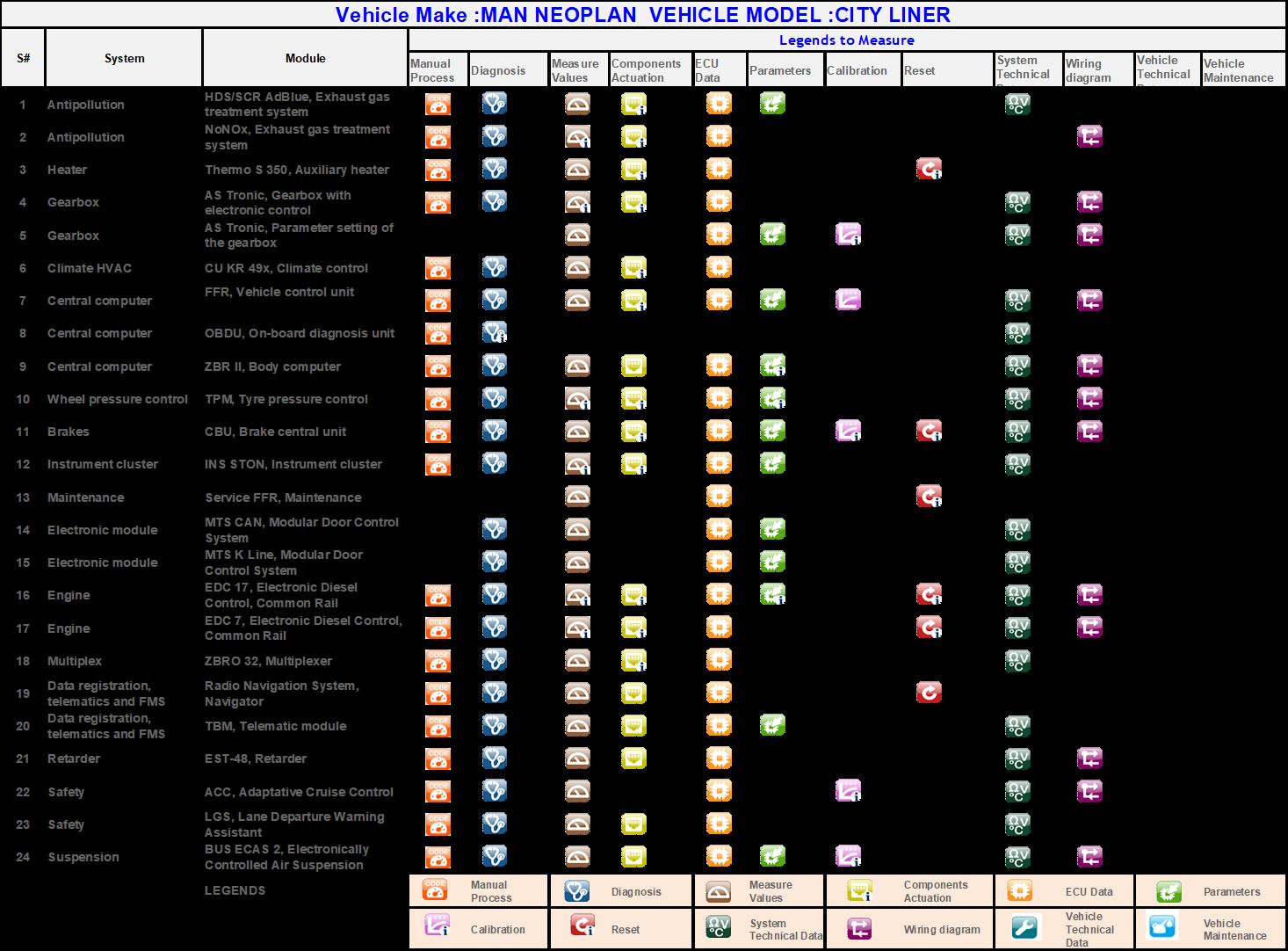
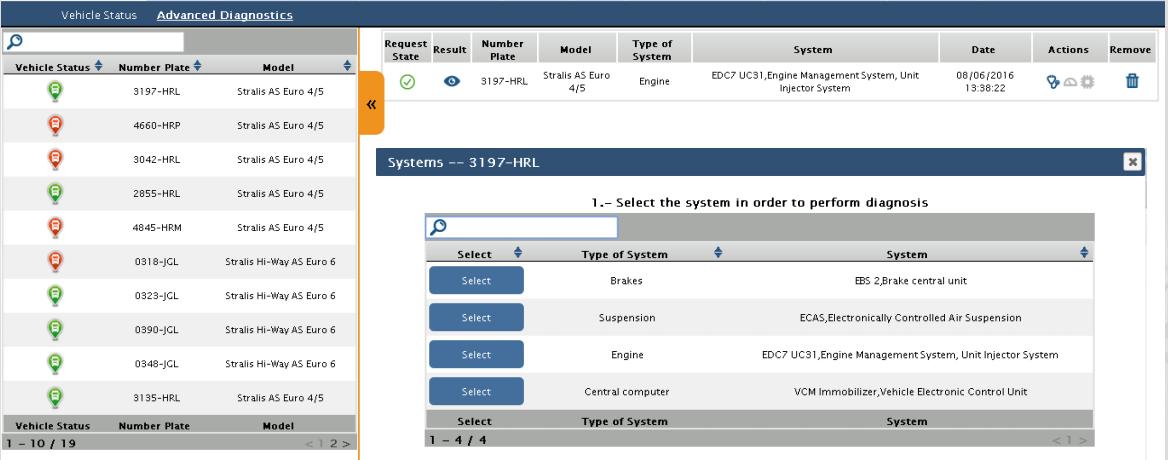
The current diagnostics tool works in delivering data to respective departments. The constraint in the present system is that it requires a dedicated computer system that must be connected physically with the ECU of the vehicle to obtain data after every run. The process is tedious and time consuming. Though the technology eliminates the huge hassle of manually examining and identifying errors, it still has many numbers of limitations. It must be done individually for one vehicle at a time. Solution to most of the restrictions posed in already existing digital diagnostic system is by connecting the fleet wirelessly through IoT Implementation. This enables easy monitoring of all vehicles thereby reducing operational cost that arises in conventional maintenance procedures. It also paves way to Proactive and Predictive maintenance when infused with technologies like AI prediction and cloud processing thereby monitoring every activity in real time and giving the management team full control over the maintenance process. The figure 4. gives all the possible data points through which valuable information can be extracted by introducing sensors and smart connectivity technology. When IoT is implemented in a large scale, it can greatly increase the profit margins for transport companies. showing error codes through detailed in the Figure 5. IoT are
Application of these smart technologies is must. In India, there are a more number of Analogue Vehicles with conventional maintenance mechanisms following time consuming, resource inefficient routines. Knowing the kind of
figure.3

positive impact smart technology can
Figure 3 offer, many developed countries have long back adopted Digital System Signals in their vehicles. The revelation of amount of ease in which most of the cumbersome maintenance process can be transformed calls for shift to Digital System Signals that needs to be integrated into the Vehicle as seen in Volvo, Mercedes Benz & Scania. Indian Vehicle Manufacturers need to quickly make the transition as the requirements of the competitive markets change from time to time.
Figure 4

Gurpreet Singh Sehmi Research Consultant, Sustainable Mobility for All (SuM4All) Image Credit: Roland Magnusson
Three ways COVID-19 is reshaping how we collect and use data in transport?
The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of leveraging data and evidence to make decisions. Key indicators, such as new cases or hospitalizations, are shaping how government leaders around the world plan or adapt their public health interventions.
But it is not just the health sector that relies on data. Evidence-based decisions are the bedrock of sustainable development outcomes, especially in the transport sector. Under the leadership of the Sustainable Mobility for All (SuM4All) coalition, the international transport community has reached a consensus on clear policy goals and developed the first-ever global tracking framework for transport (GTF). However, the unprecedented events of 2020 have challenged many assumptions about how we assess and track progress on sustainable mobility.
This article highlights some emerging opportunities that can be leveraged by the transport sector in light of the current context:
Redefining the way countries and share transport data collect
Many individuals worldwide can use their mobile phones or smartwatch to monitor their mobility patterns (distances walked in a day, time spent cycling per week, etc.). By contrast, many governments still struggle to compile those same metrics at the city or country level. In many instances, public authorities rely on traditional data collection methods that are often inefficient, time-consuming, and expensive. The rippling effect is inaccurate, incomplete, or outdated data.
According to a 2020 report from UNDESA, 96% of national statistical offices have fully or partially stopped face-toface data collection since the COVID-19 pandemic began. Meanwhile, technology companies such as Google, Moovit, Apple, and Tomtom have increasingly made harmonized data available by leveraging innovative technologies. Perhaps, national statistical bodies should be considering how this type of proprietary data can be expanded and further coordinated to create transport indicators to fill the gap.
The basis for new targets and indicators
Over the last few years, the international community has adopted several landmark initiatives directly relevant to transport, such as the Decade of Action for Road Safety and the Paris Climate Agreement.
These efforts brought attention to the unsustainability of the global transport system, and strove to catalyze action through the same basic approach: set clear targets, develop indicators, monitor the results closely. COVID-19 is now shining a light on other transport challenges that had been largely overlooked until now, from public health concerns to the lack of mobility options for vulnerable groups. Some examples include disabled persons whose constrained mobility options in the preCOVID world were exacerbated, refugees whose access to asylum was curtailed, and women and children who lack alternatives when public transport is shut down as part of pandemic lockdown measures. With this, the international transport community has an opportunity to revisit how we assess sustainability and include other critical aspects of safety, inaccessibility, and public health risks.
Data can help address challenges and guide the transformation immediate long-term
COVID-19 has shown just how critical big data could be in shaping policies and making informed decisions. Although data use in transport had been growing significantly over the past few years, the pandemic has increased the urgency to innovate. Cities and large corporations have partnered to use open-source data to assess mobility patterns and decide how to curtail the virus’ spread. Decisionmakers are leveraging data platforms to ensure a safely phased reopening of business activities around the world. City leaders could use a similar approach to re-imagine urban design and make room for walkable, cyclable, safe, accessible, congestion-free, and climate-friendly streets.
The work continues, and our ability to process information faster than ever before will only increase the potential of data for transport. But data is only as good as the people who handle it. We should keep in mind that wrong interpretations and premature conclusions could hinder progress toward sustainable mobility for all. To make the most of data, transport practitioners must strive to be both rigorous and adaptable to integrate the new trends and opportunities outlined in this article. If we get it right, data will go a long way in building a better, more sustainable transport future for all of us.
(Input Credit: The World Bank Blog)
Make in India: How ‘Make in India’ initiative is giving impetus to the High Speed Rail projects?

NHSRCL
Recognised among the fastestgrowing bilateral ties in the entire Asia region, the IndoJapan partnership has come a long way. With both the countries now joining hands to introduce in India its first High-Speed Rail or the Bullet Train, the partnership is only set to strengthen further. The 508 km long Mumbai-Ahmedabad High Speed Rail Project will augment connectivity between 12 stations across the corridor. Their names being BKC (Mumbai) –Thane – Virar –Boisar – Vapi – Bilimora – Surat – Bharuch – Vadodara – Anand Ahmedabad-Sabarmati. This partnership has also given impetus to another cause that’s close to India Inc.’s heart- that of giving boost to India’s economy through ‘Make in India’ .
What is Make in India?
The Make in India initiative was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in September 2014 as part of a wider set of nation-building initiatives. Devised to transform India into a global design and manufacturing hub, it quickly became a rallying cry for India’s innumerable stakeholders and partners and an invitation to potential partners and investors around the world. As a result, in a short span of time, the idea has helped drive investment, foster innovation, develop skills, protect Intellectual Property (IP) and build best-in-class manufacturing infrastructure within the country. The most striking indicator of progress is the unprecedented opening of key sectors – including railways, defence, insurance and medical devices – to substantially higher levels of Foreign Direct Investment. The initiative aims to lift the share of manufacturing in India's $2 trillion economy to 25 per cent and create 100 million jobs by 2022.
Role of ‘Make in India’ in MumbaiAhmedabad High Speed Rail Project
As part of the agreement, through the Mumbai - Ahmedabad High Speed Rail (MAHSR) project, India will focus on promotion of its two key drivers: ‘Make in India’ & ‘Transfer of Technology’. The amalgamation of Japan’s technology and India’s expertise in creating worldclass parts can prove to be a boon for the project. As part of Transfer of Technology (ToT) aspect of the project, for the parts that are to be made in India, Japan will share their blueprints and methodology behind their creation with their Indian counterparts. Further then, India, under the ‘Make in India’ scheme, will then replicate and recreate these elements related to the project as per the terms of the plan.
It is through the promotion of these two drivers that India will set up manufacturing facilities in the country, generate new jobs, upgrade the skills of its existing workforce, give a boost to allied industries (steel, cement, electrical components & infrastructure etc.) and get a toehold on the new and upcoming technologies being used by Japan.
that the project can spur growth and create employment opportunities with upto 20,000 during the construction phase, 4,000 direct employment in maintenance & operations & another estimated 20,000 indirect jobs.
Not only this, the project is also expected to boost social development along the route. Moreover, the trickle-down effect of the project can be understood from the fact that by setting up production bases across the country, its effect will spill over and open avenues for creation of logistic hubs, modern townships, industrial units and much more.
How ‘Make in India’ implemented in the project? is being
For the success of any project, discussion, collaboration, exchange of ideas and execution form a vital aspect. Since, the aim of the Mumbai Ahmedabad High Speed Rail (MAHSR) project is also to showcase India being at the forefront of technology and at par to build international standards of engineering and service, no stone is being left unturned to create an entire ecosystem of high performance through proper planning. Here’s looking at few key action points that have been taken so far under MAHSR project guidelines to meet the ‘Make in India’ objectives.
Frequent deliberations with regards to action required to meet the “Make in India” objectives of MAHSR project is being held under the convenorship of key stakeholders like Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP) & Japan External Trade Organisation (JETRO).
Timely & regular discussions and meets are held among the 4 key sub-groups, namely Track, Civil, Electrical & S&T, and Rolling Stock; to identify potential items and sub-systems of ‘Make in India’ and take immediate action as and when required. These groups constitute of senior representatives from Indian industry, Japanese industry, Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion (DIPP), NHSRCL and JETRO (Japan External Trade Organisation).
The discussion criterion that is being followed to further the ‘Make in India’ component of the agreement and promote collaboration between Indian & Japanese companies can divided into 3 broad categories:
• Sub Group Meetings- These are attended by representatives from
Department of Industrial Policy and
Promotion (DIPP), Ministry of
Railways, National High Speed Rail
Corporation Ltd (NHSRCL), MLIT,
Japan External Trade Organisation (JETRO), Japanese Embassy, Japan
Railway East (JRE), Indian Industry representatives including representatives form Industry associations like
Confederation of Indian Industry (CII),
Federation of Indian Chambers of
Commerce & Industry (FICCI) and The
Associated Chambers of Commerce and
Industry of India (ASSOCHAM) among others.
• Workshops: Regular workshops are being organised, in India & Japan, for the various stakeholders involved in the project. These day long workshops are advertised well-in advance to ensure complete participation from the existing partners as well as to invite potential investors and interested firms. The workshops are being followed by B2B meetings and discussions as a platform for interaction between Indian and
Japanese firms. In recent times, a workshop was organised in Tokyo which concluded with Japanese firm visit by
Indian firms the next day.
• Task Force Meetings: The purpose of these meetings is to check on the progress of the plans already implemented and also discuss the road ahead with regards to the project. At a recent meeting held in DIPP, a review on the progress of sub group meetings and workshops was done alongside finalisation of the action plan for the future. These review meetings were attended by representatives from DIPP,
Ministry of Railways, NHSRCL,
Ministry of Land, Infrastructure,
Transport and Tourism (MLIT),
JETRO, Japanese Embassy, and JRE among others.
By reaching out to construction companies, manufacturers and entrepreneurs across India and Japan through such workshops & meeting, the MAHSR project is facilitating a positive trade tie-ups between the two nations and opening up bigger horizons for technological advancement in India.
As per the joint agreement under Make in India, various components of HSR project are being planned to be added in the list.
Target items lists for ‘Make In India’ ‘Transfer of Technology’ for Track Works:
Target items ‘Transfer of Works: lists for ‘Make In Technology’ for India’ & Electrical

Target items lists for ‘Make In India’ & ‘Transfer of Technology’ for Civil Works:
You can also find brief details on the other items like OHE Steel Mast, Rail Turnover Prevention Device, Embedded Inserts, Cement Asphalt Mortar (CAM) under “Make In India” on NHSRCL’s website. Besides these, there will be many more items in the list which will be made in India and used extensively during the making of India’s first High Speed Rail. Efforts are constantly being made to identify the need at this stage and align sources for the implementation of the same.

Can ‘Make in India’ prove to be a winwin proposition for both India & Japan?
The project will certainly be a new feather in the cap of India Inc. For a growing nation like ours, years there can be no better news than a spurt of economic activities happening across sectors. Japanese firms are welcome to set up partnerships, manufacturing bases in India. Indian firms should avail this opportunity for technical upgradation. They would also have access to the big and growing Indian Railways and Metro Railway market. Lower cost of production in India will make Japanese product cost competitive for exports to other countries. Along with the Japanese, India too stands to gain by assimilation of better technology, manufacturing and construction practices. Thus, it is win-win proposition for both the countries!
The first High Speed Rail corridor to be implemented in the Country, with technical and financial assistance of Government of Japan, has been identified from Mumbai to Ahmedabad. With total twelve stations in the States of Maharashtra, Gujarat and Union Territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli, the corridor will have a length of 508.17 Km. Where high speed rail will cover 155.76 kms in the state of Maharashtra (7.04 Kms in Mumbai suburban, 39.66 kms in Thane district & 109.06 kms in Palghar district), 4.3 kms in union territory of Dadra & Nagar Haveli and 348.04 kms in the state of Gujarat.
High speed rail will cover total 12 stations namely Mumbai, Thane, Virar, Boisar, (in Maharashtra), Vapi, Bilimora, Surat, Bharuch, Vadodara, Anand, Ahmedabad and Sabarmati (in Gujarat). Where a limited stop (in Surat & Vadodara) service will cover this distance in 1 hr. and 58 mins and all stops service will take 2 hr. 57 min to cover this distance.
High speed rail will be operating at a speed of 320 Km/hr at an elevated (10 to 15 m) track above the ground on a viaduct all along except 26 kms in Mumbai, which will be underground. All stations will be elevated except Bandra Kurla Complex station (Mumbai), which will be
underground.
PRESENTS A M E G A V I R T U A L E X H I B I T I O N O N URBAN RAIL AND EQUIPMENT BUSINESS 2021

1 FEB – 15 MAR 2021
w w w. u r b a n t ra n s p o r t e v e n t s . c o m
B E N E F I T S O F V I R T U A L E X H I B I T I O N
Very low cost exhibition opportunity: No need to worry about high expenses on transportation, shipping, hotels, hospitality and booths Very Safe and effective mode of showcasing products and services in the front of global audience and end users. No need to worry about infection of COVID-19. Lead Retrieval and Follow Up is also much easier as information of all visitors recorded in our database automatically. Green initiative towards saving environment: We can save thousands of trees as there is no more printing, branding and handing outs thousands of flyers required. We put all information in digital and downloadable form for visitors. Real-time response: Visitors and exhibitors can interact directly through video chat platform.
V I S I T O R S P R O F I L E
Officials from Govt./Ministry/PSU/Nodal Authorities Decision makers and Industry leaders from Metro Rail Authorities, Indian Railways, Construction, EPC, Public & Freight Transportation, Logistics, Smart Cities, Mobility industry OEMs, Suppliers, Consultants, City Planners, Architectures, Export/Import Business, Infra Project Financers etc. Engineering Institutions, R & D Organisations, Think Tanks and Game Changers Students and Academicians, Researchers, Surveyors etc.
Support requested from:
EXHIBITION & SPONSORSHIP PACKAGE
EXHIBITORS
• Indian: INR 50000 • International: USD 800
SPONSORS
For more information, please contact:
Mr. Vinod Shah | Mr. Surya Prakash
M: +91-9716454505 | M: +91- 9340632433
E-mail: bizdev@urbantransportnews.com
BOOK YOU VIRTUAL STALL AND SPONSOR NOW

Last Date 15 January 2020 Save 25%

EVENT CALENDER 2020


Dates
September 8-9
October 6-8
October 20-22
November 09
November 25-26
November 30-Dec 02
December 03-04
December 17-18 Event Name
Arab Transport Development & Integration Conference
GeoSmart India 2020
Transport India 2020 Expo
Urban Mobility India Conference & Expo 2020
Rail Asia Expo 2020
Rail Live 2020
Rail India Conference & Expo 2020
Asian Rail Infrastructure & Modernisation (ARIM) Venue
Dubai, UAE
Hyderabad, India
New Delhi, India
New Delhi, India
Bangkok, Thailand
Madrid, Spain
New Delhi, India
Ho Chi Minh, Vietnam
!! Special Announcement !!
In view of spread of the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak in India and to ensure safety of Industry leaders and delegates, we have cancelled our all physical events. And now we are launching an interactive and exclusive virtual platform which can help business entities to exhibit and showcase their business worldwide at minimal cost. We have launched a mega virtual exhibition on Urban Rail & Equipment Business 2021 to facilitate Rail, Infra and Mobility Business Industry.







