
11 minute read
DIABETES
from He & She Oct 2018
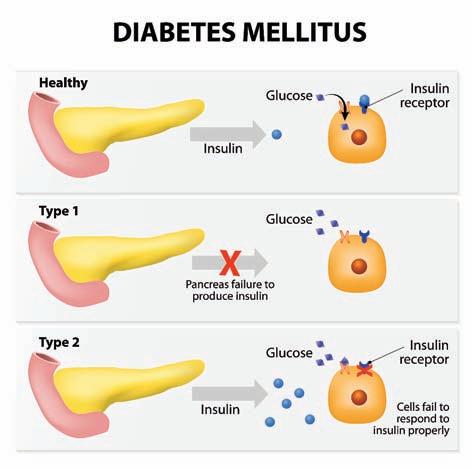
Diabetes Mellitusis a disease in which the level of blood glucose or blood sugar are too high. It is of two types; type 1 is where the body doesn’t make enough insulin, type 2 diabetes is more common. It’s when the body doesn’t use insulin well or develops a resistance for it. In both these cases, without enough insulin or insulin which is not well utilized the glucose stays in the blood and affects many body organs. Type 2 DM is a lifestyle disorder. Certain risk factors which predispose to developing diabetes like obesity or having an inactive lifestyle, high blood pressure, smoking, having a history of heart disease or stroke and having high levels of triglycerides (bad cholesterol) in your blood. In women, who have had diabetes during pregnancy or PCOS (polycystic ovarian disease syndrome) are also predisposed to developing type 2 DM. You can also have prediabetes. This means that your blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough to be called diabetes. Having prediabetes puts you at a higher risk of getting type 2 diabetes. Lastly, having family history of diabetes also predisposes one to have type 2 DM. Glucose comes from food and insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into the body’s cells to give
• Diabetes is a long-term condition that causes high blood sugar levels. • in 2013 it was estimated that over 382 million people throughout the world had diabetes (Williams textbook of endocrinology). • Type 1 Diabetes - the body does not produce insulin. Approximately 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1. • Type 2 Diabetes - the body does not produce enough insulin for proper function. Approximately 90% of all cases of diabetes worldwide are of this type. • Gestational Diabetes - this type affects females during pregnancy. • The most common diabetes symptoms include frequent urination, intense thirst and hunger, weight gain, unusual weight loss, fatigue, cuts and bruises that do not heal, male sexual dysfunction, numbness and tingling in hands and feet. • if you have Type 1 and follow a healthy eating plan, do adequate exercise, and take insulin, you can lead a normal life. • Type 2 patients need to eat healthily, be physically active, and test their blood glucose. They may FAST FACTS ON DIABETES
Advertisement
also need to take oral medication, and/or insulin to control blood glucose levels. • As the risk of cardiovascular disease is much higher for a diabetic, it is crucial that blood pressure and cholesterol levels are monitored regularly. • As smoking might have a serious effect on cardiovascular health, diabetics should stop smoking. • Hypoglycemia - low blood glucose - can have a bad effect on the patient. Hyperglycemia - when blood glucose is too high - can also have a bad effect on the patient.
DR SUDHA PRASAD Professor & IVF Coordinator Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, India

DIABETES Causes, Complications & Prevention
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is one of the world's major diseases. It currently affects an estimated 143 million individuals worldwide and this number is growing rapidly. It is also a big challenge for India and is potentially becoming epidemic. In India, about 5% of the population suffers from diabetes.
What is prediabetes? The vast majority of patients with type 2 diabetes initially had prediabetes. Their blood glucose levels where higher than normal, but not high enough to merit a diabetes diagnosis. The cells in the body are becoming resistant to insulin. Studies have indicated that even at the prediabetes stage, some damage to the circulatory system and the heart may already have occurred.
them energy. So, Insulin help utilize the glucose we eat. In DM, over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems. It can damage your eyes, kidneys, and nerves. Diabetes can also cause heart disease, stroke and even due to poor or no blood supply, the need to remove a limb. Pregnant women can also get diabetes, called gestational diabetes, which can affect both the mother and the child. Symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop slowly, usually over the course of several years. They can be so mild that you might not even notice them. Because of their indolent course, some people do not find out they have the disease until they have diabetes-related health problems, such as blurred vision or heart disease. Symptoms of diabetes include; increased thirst and uri
nation, increased hunger, feeling tired all the time, blurred vision, numbness or tingling in the feet or hands, sores that do not heal easily and unexplained weight loss. People with diabetes tend to develop heart disease at a younger age than people without diabetes. In adults with diabetes, the most common causes of death are heart disease and stroke. This is because over time, high blood glucose from diabetes can damage your blood vessels and the nerves that control your heart and blood vessels. The longer you have diabetes, the higher the chances that you will develop heart disease. Diabetes can damage the nervous system too resulting in diabetic neuropathy. It can lead to problems with your heart rate and blood pressure, digestive system, bladder, sex organs, sweat glands, and eyes. It can also cause loss in sensation in feet resulting in sores which aren’t noticed and can result in ulcers. It can cause damage to your eyes that can lead to poor vision or even blindness. The retina is the inner lining at the back of each eye. The retina senses light and turns it into signals that your brain decodes, so you can see the world around you. Damaged blood vessels can harm the retina and cause production of abnormal blood vessels, causing a disease called diabetic retinopathy.These abnormal new blood vessels can lead to serious vision problems. The part of your retina that you need for reading, driving, and seeing faces is called the macula. Diabetes can lead to swelling in the macula, which is called diabetic macular edema. Over time, this disease can destroy the sharp vision in this part of the eye, leading to partial vision loss or blindness. Other eye problems caused by diabetes include; early cataract and glaucoma. Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease. The main job of the kidneys is to filter body wastes and extra
tYPes of Diabetes type 1 diabetes The body does not produce insulin. Some people may refer to this type as insulin-dependent diabetes, juvenile diabetes, or early-onset diabetes. People usually develop type 1 diabetes before their 40th year, often in early adulthood or teenage years. Type 1 diabetes is nowhere near as common as type 2 diabetes. Approximately 10% of all diabetes cases are type 1. Patients with type 1 diabetes will need to take insulin injections for the rest of their life. They must also ensure proper blood-glucose levels by carrying out regular blood tests and following a special diet.
type 2 diabetes The body does not produce enough insulin for proper function, or the cells in the body do not react to insulin (insulin resistance). Approximately 90% of all cases of diabetes worldwide are type 2. Some people may be able to control their type 2 diabetes symptoms by losing weight, following a healthy diet, doing plenty of exercise, and monitoring their blood glucose levels. However, type 2 diabetes is typically a progressive disease - it gradually gets worse - and the patient will probably end up have to take insulin, usually in tablet form. gestational diabetes This type affects females during pregnancy. Some women have very high levels of glucose in their blood, and their bodies are unable to produce enough insulin to transport all of the glucose into their cells, resulting in progressively rising levels of glucose. Diagnosis of gestational diabetes is made during pregnancy. The majority of gestational diabetes patients can control their diabetes with exercise and diet. Between 10% to 20% of them will need to take some kind of blood-glucose-controlling medications. Undiagnosed or uncontrolled gestational diabetes can raise the risk of complications during childbirth.

comPlications linkeD to uncontrolleD Diabetes • eye complications - glaucoma, cataracts, diabetic retinopathy, and some others. • foot complications - neuropathy, ulcers, and sometimes gangrene which may lead to foot amputation • skin complications - people with diabetes are more susceptible to skin infections and skin disorders • heart problems - such as ischemic heart disease, when the blood supply to the heart muscle is diminished • hypertension - common in people with diabetes, which can raise the risk of kidney disease, eye problems, heart attack and stroke • mental health - uncontrolled diabetes raises the risk of suffering from depression, anxiety and some other mental disorders • hearing loss - diabetes patients have a higher risk of developing hearing problems • gum disease - there is a much higher prevalence of gum disease among diabetes patients • gastroparesis - the muscles of the stomach stop working properly • ketoacidosis - a combination of ketosis and acidosis; accumulation of ketone bodies and acidity in the blood. • neuropathy - diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage which can lead to several different problems. • hhns (hyperosmolar hyperglycemic nonketotic syndrome) - blood glucose levels shoot up too high, and there are no ketones present in the blood or urine. it is an emergency condition. • nephropathy - uncontrolled blood pressure can lead to kidney disease • PaD (peripheral arterial disease) - symptoms may include pain in the leg, tingling and sometimes problems walking properly • stroke - if blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood glucose levels are not controlled, the risk of stroke increases significantly • erectile dysfunction - male impotence. • infections - people with badly controlled diabetes are much more susceptible to infections • healing of wounds - cuts and lesions take much longer to heal

water out of your blood to make urine. Your kidneys also help control blood pressure and make hormones that your body needs to stay healthy. Over a period, damaged kidneys can result in hypertension and kidney failure. Sexual and urologic complications occur because of damage caused to blood vessels and nerves. Men may have difficulty with erections or ejaculation. Women may have problems with sexual response and vaginal lubrication. Urinary tract infections and bladder problems occur more often in people with diabetes. If you are at risk for diabetes, you may be able to prevent or delay getting it. Most of the things that you need to do involve having a healthier lifestyle. These changes will get other health benefits as well. You may lower your risk of other diseases, and you will probably feel better and have more energy. Changes such as exercise, weight control and sticking to your meal plan can help control your diabetes. You should also monitor your blood glucose level and take medicine if prescribed. Diabetes can be controlled and managed to prevent complications. Controlling weight is an important part of preventing diabetes. And once you lose the weight, it is important that you don't gain it back. This would involve: • Following a healthy eating plan. It is important to reduce the number of calories you eat and drink each day, so you can lose weight. The diet should include variety of foods from each food group, including plenty of whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, smaller portions and less fat and sugar. It's also a good idea to limit red meat and avoid processed meats. • Get regular exercise. Exercise has many health benefits, including helping you to lose weight and lower your blood sugar levels. These both lower your risk of type 2 diabetes. Try to get at least 30 minutes of physical activity 5 days a week. Smoking can contribute to insulin resistance, which can lead to type 2 diabetes. If you already smoke, try to quit. Along with following your diabetes care plan, you may need diabetes medicines, which may include pills or insulin injections. Over time, you may need more than one diabetes medicine to manage your blood glucose. Even if you don’t take insulin, you may need it at special
times, such as during pregnancy or if you are in the hospital. You also may need medicines for high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or other conditions. Various blood tests can show if you have diabetes. Another a very specific test, the HbA1C, can also check on how you have managed your diabetes over the last three months. Some people, especially who are on insulin require regular glucose monitoring. Too low (<70 ng/dl) blood glucose is also very dangerous. This is known as severe

hypoglycemia. Symptoms tend to come on quickly and include light-headedness, disorientation, blurred vision, headache and lots of sweating. Blood glucose level may become so low that you may fall unconscious. This condition is more common in people with type 1 diabetes. If you begin to feel one or more hypoglycemic symptoms, check your blood glucose. If your blood glucose level is below your target or less than 70, eat or drink something sugary immediately.










