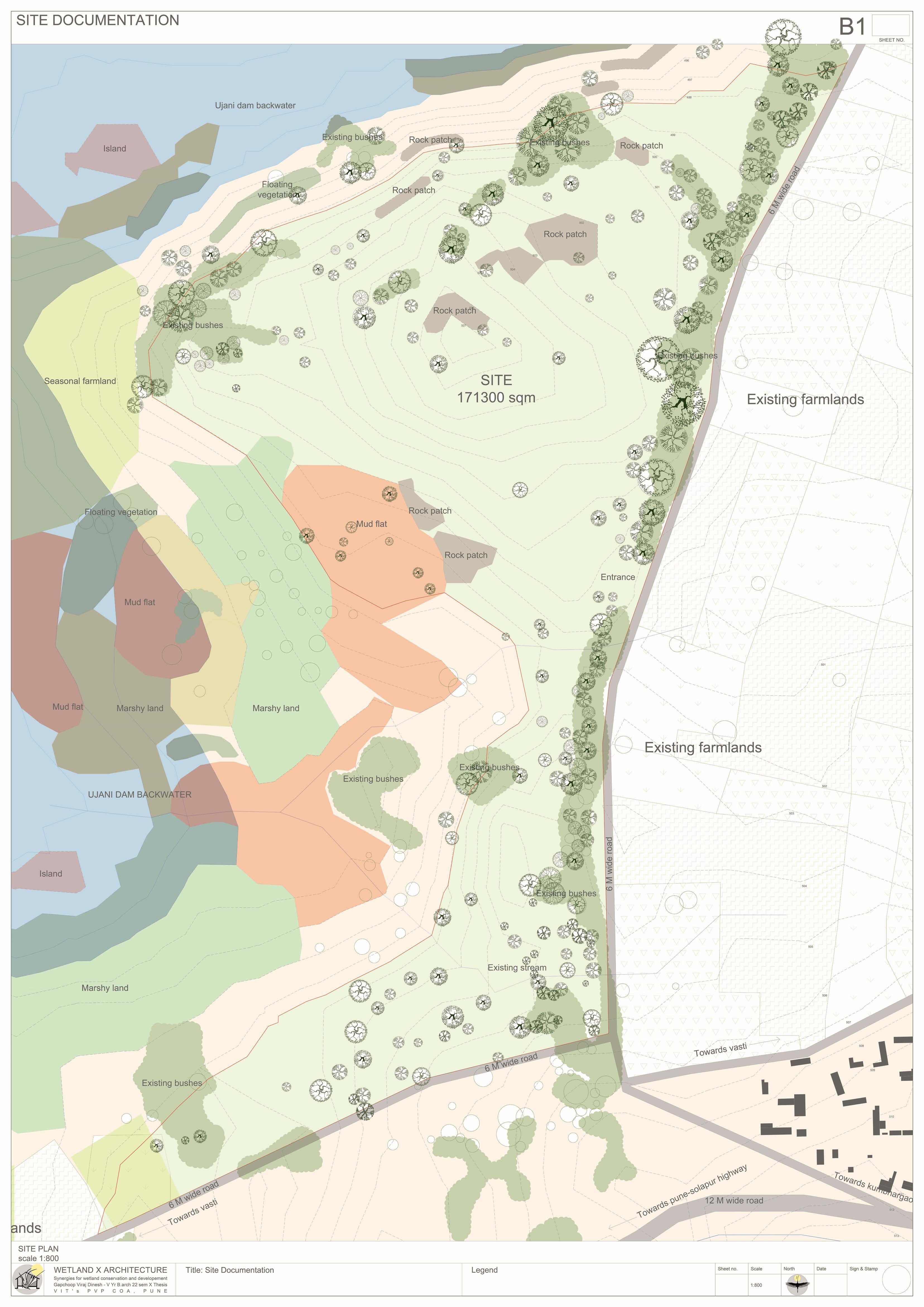
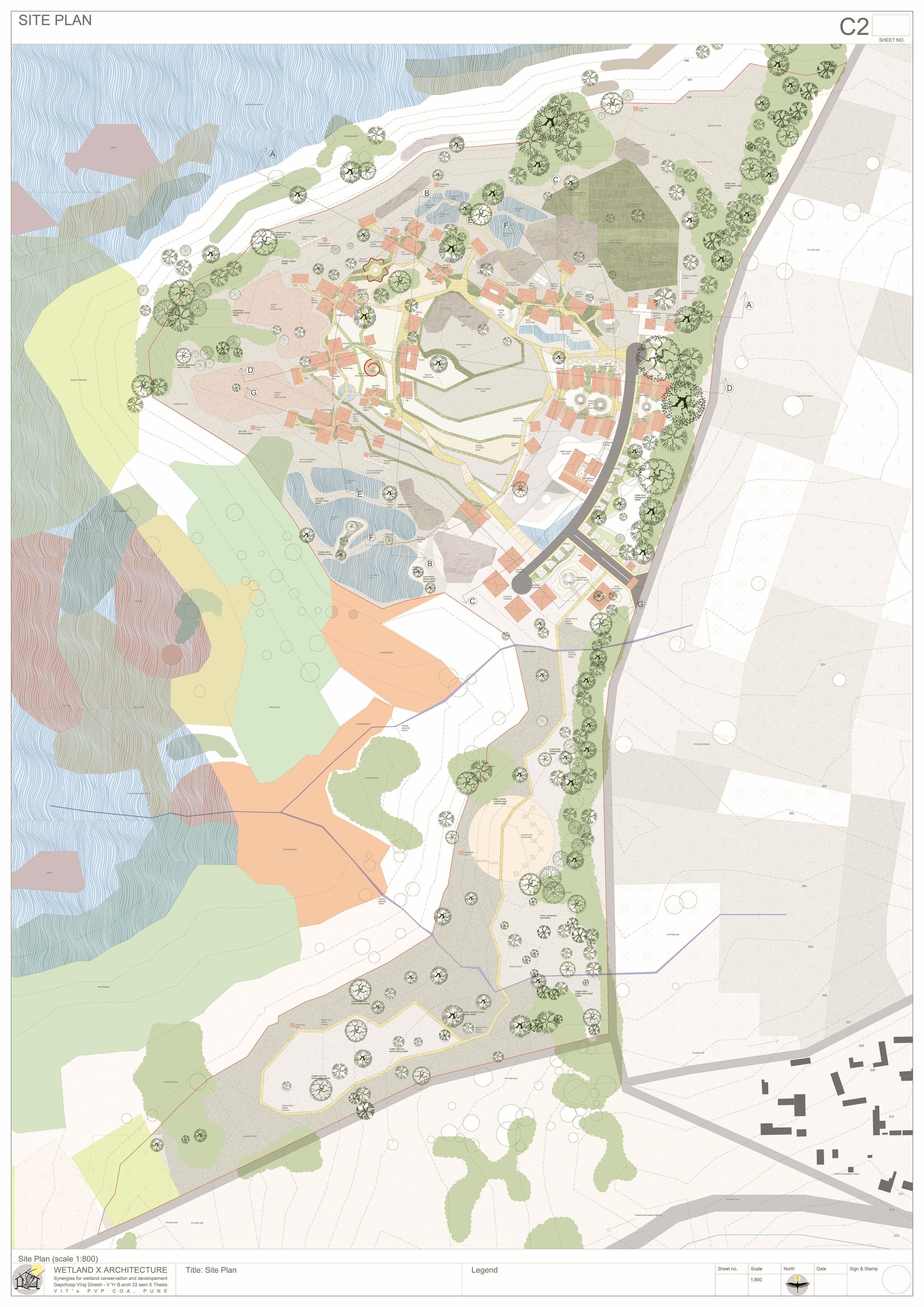
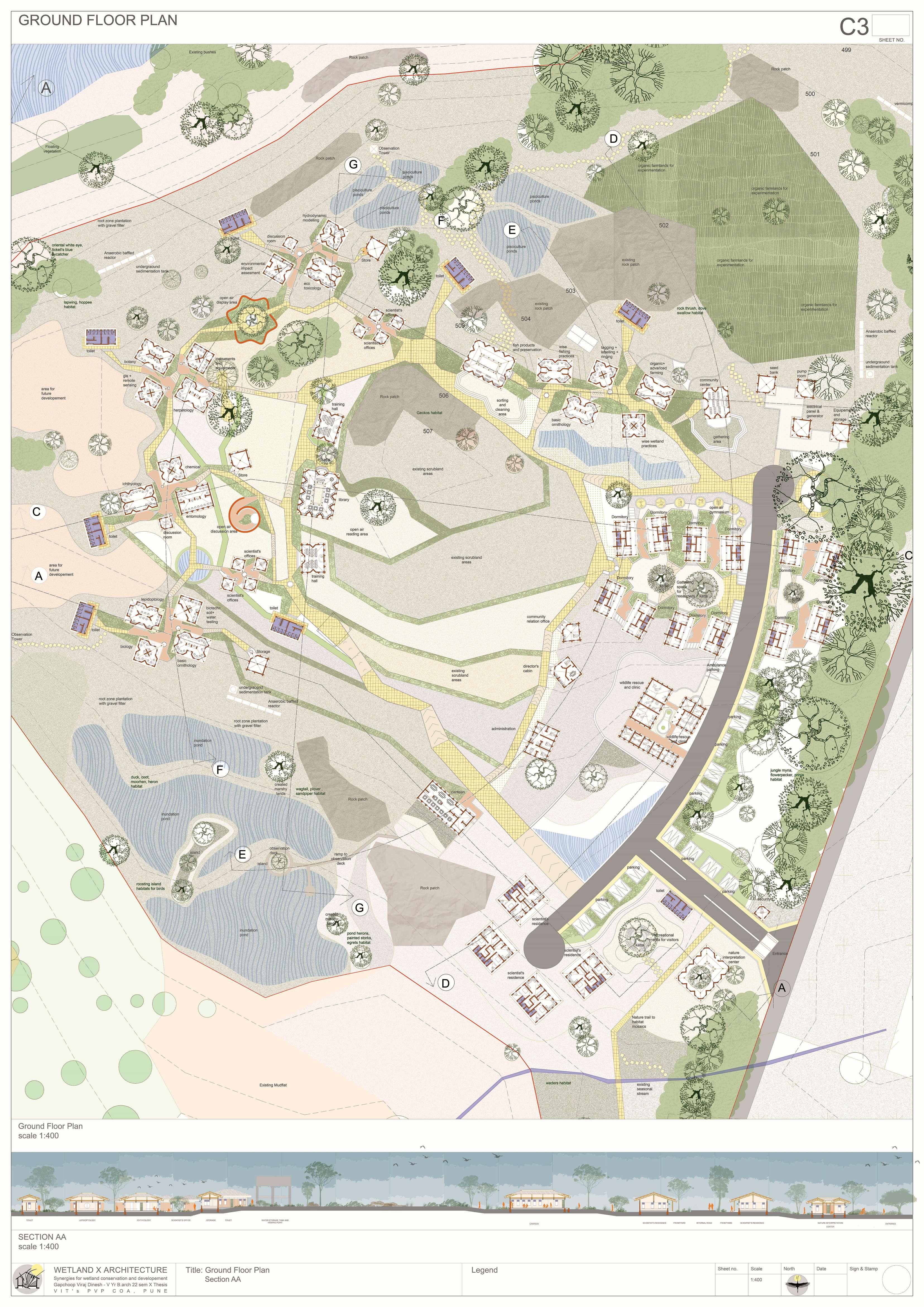
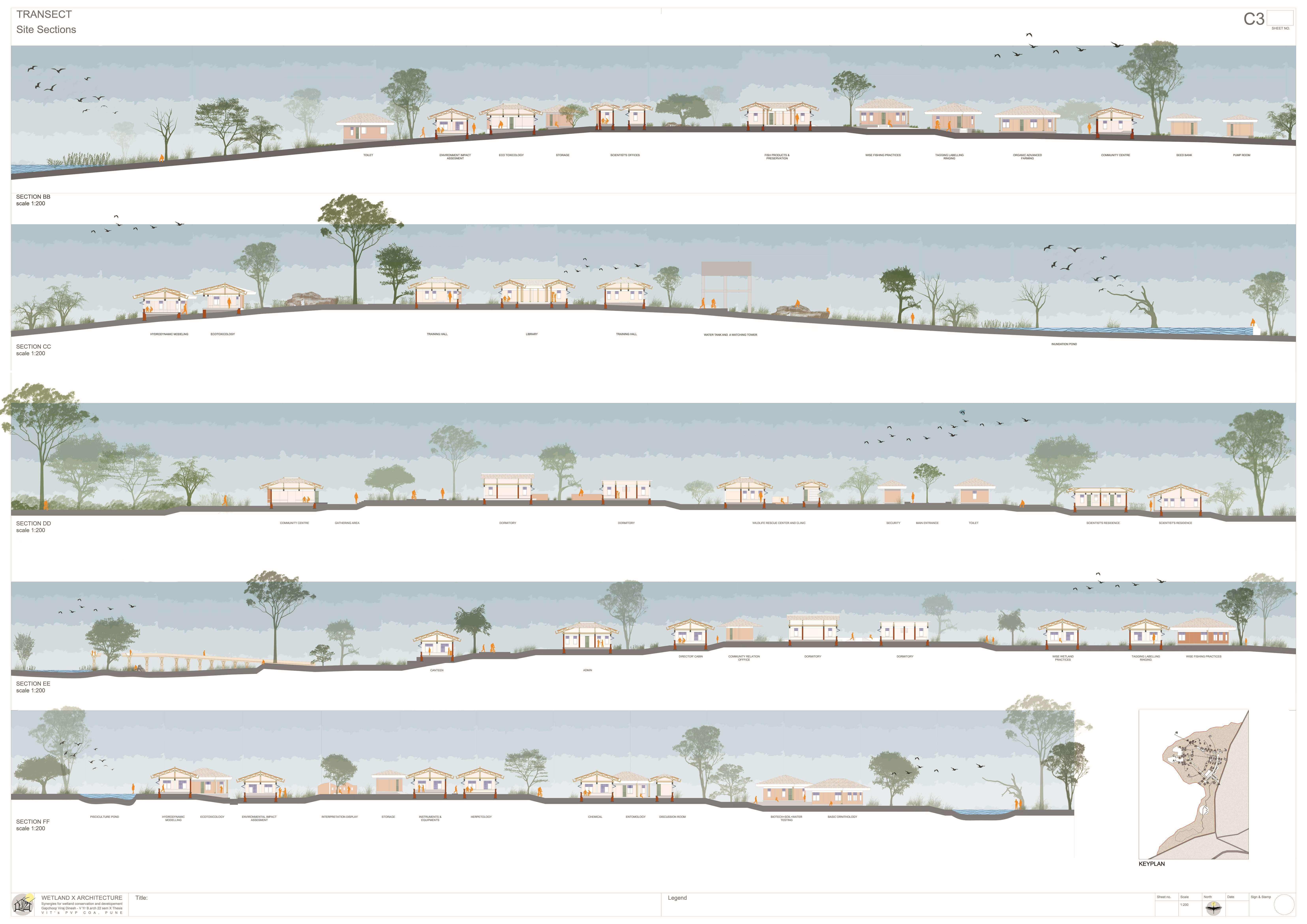
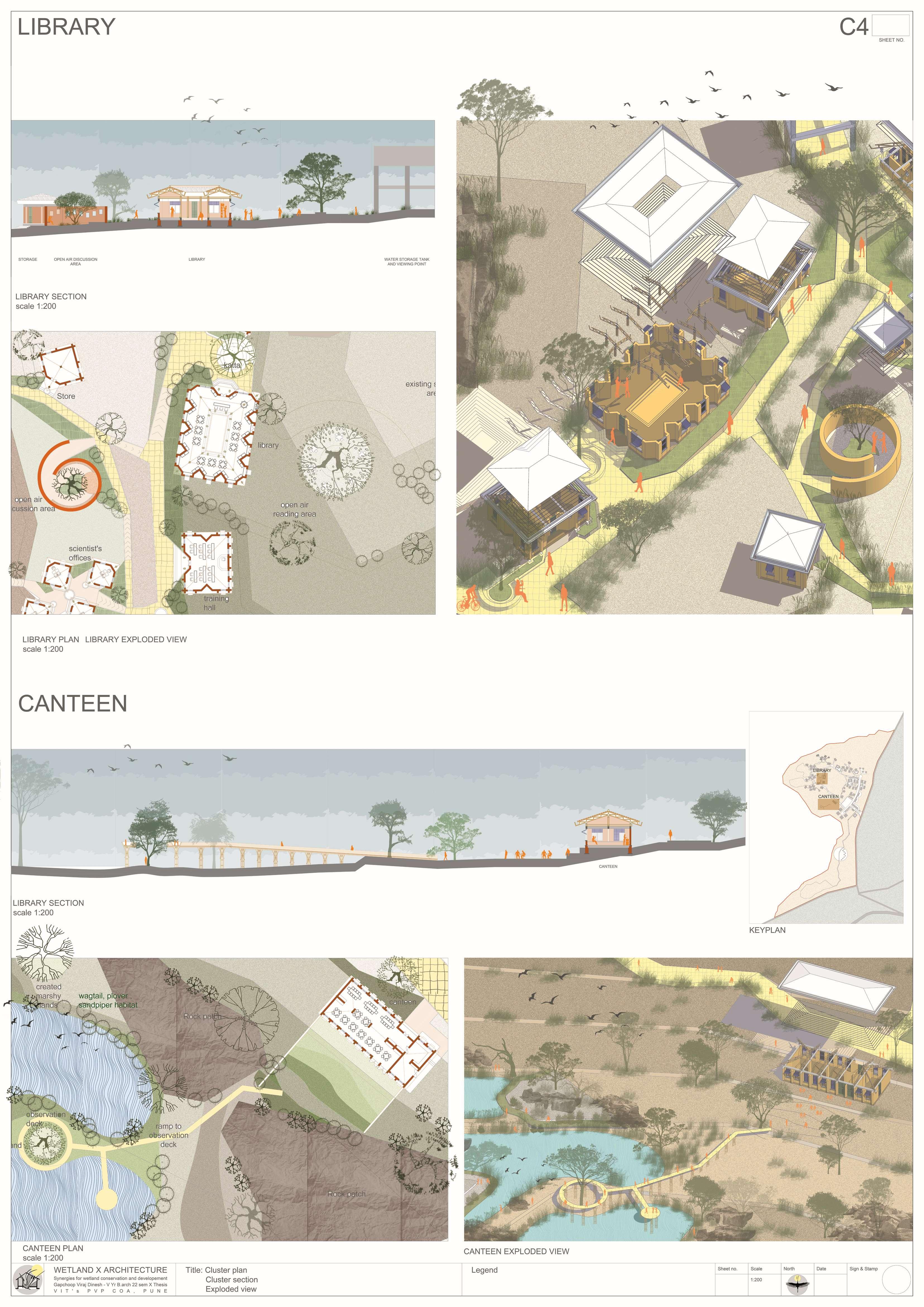
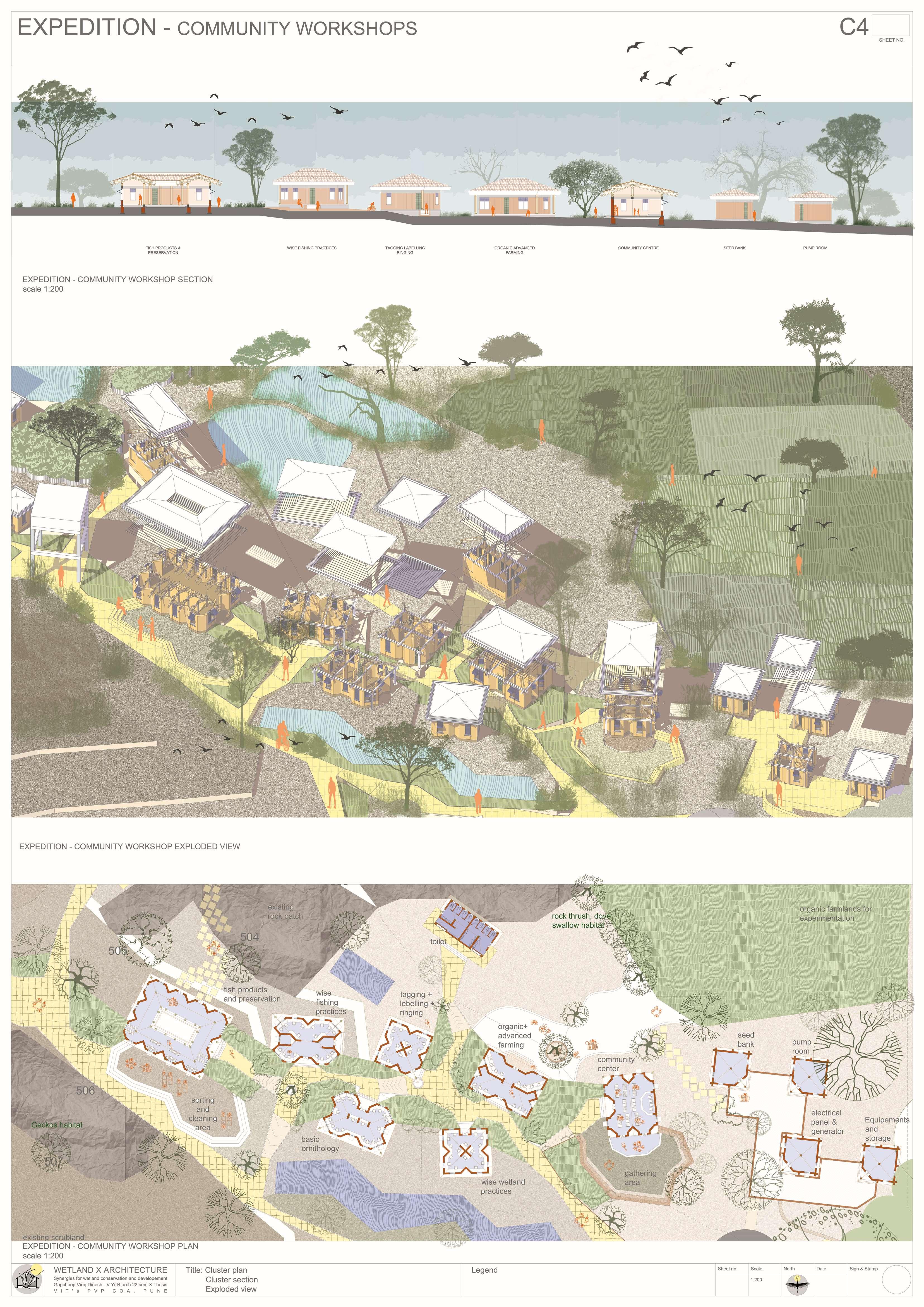
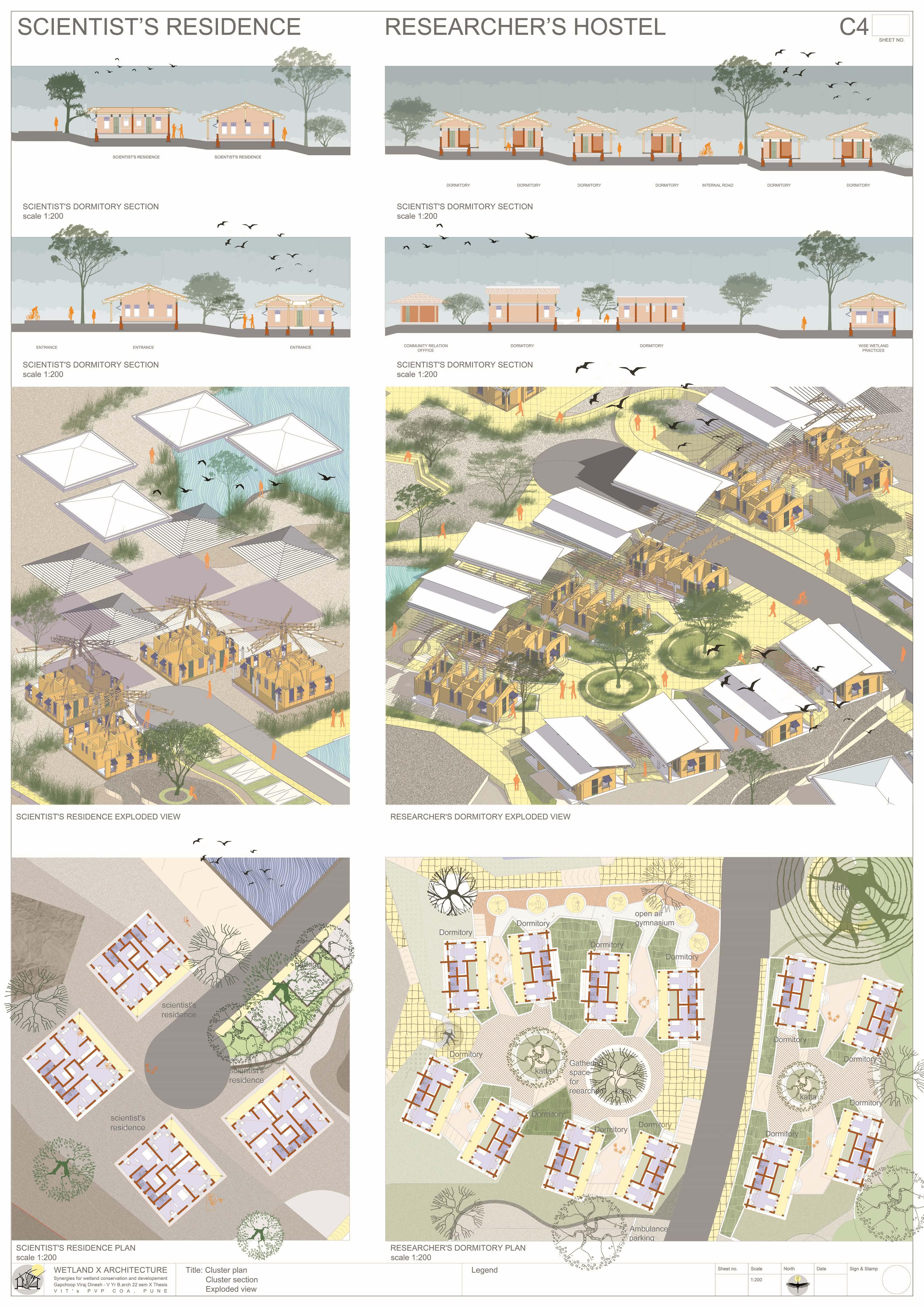
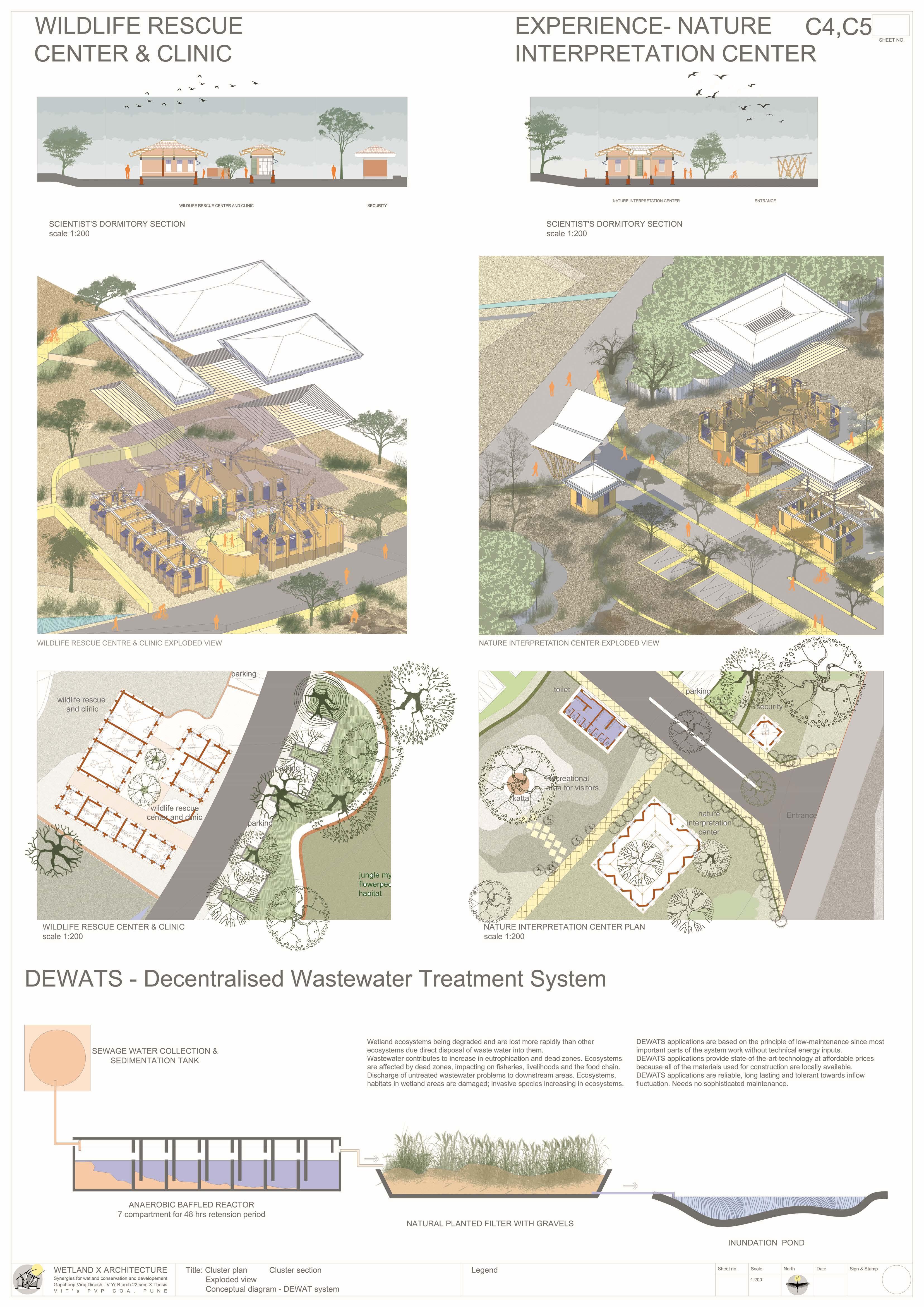
The Ujani wetland at Bhigwan is a vital ecological and economic resource, playing a crucial role in biodiversity conservation, water regulation, and sustaining livelihoods. This intricate ecosystem thrives on a delicate balance between human activities and ecological processes. However, increasing pollution, encroachment, and mismanagement, coupled with fragmented conservation policies, threaten its sustainability. Bhigwan’s wetland supports diverse ecological, traditional, religious, commercial, recreational, and transportation-related activities, making it an essential economic zone. To preserve this ecosystem, it is imperative to safeguard the interdependent communities that rely on it. A strategic architectural intervention can serve as a bridge, integrating human engagement with ecological preservation. This project proposes a multi-layered design approach, incorporating research hubs, eco-tourism, and conservation-focused infrastructure to foster collaboration among researchers, policymakers, and local