IN THE BAHAMAS
A Circular Business Model for the Island of Andros - A Prototype for Modular Ecotourism
Anushka Reddi and Atharva Belsare"Empowering
Andros Island with sustainable growth through ecologically designed, locally inspired modular lodges, fostering cultural integrity and environmental stewardship in every build."



The International Ecotourism Society (TIES) defines ecotourism as “responsible travel to natural areas that conserve the environment, sustains the well-being of the local people, and involves interpretation and education.”
Revolutionizing Ecotourism with Circular Business Models and Modular Lodges

Circular Economic Business Model
Implementing a sustainable and regenerative approach to tourism development

Modular Construction of Lodges
Utilizing innovative building techniques for eco-friendly and adaptable structures

Cultural Sensitivity and Sustainability
Incorporating the rich heritage, materials, and traditions of Andros Island into the lodge design



A Circular Ecotourism Business Model developed to leverage the natural resources of Andros, empower the community and generate cultural and environmental awareness.








A Circular Ecotourism Business Model developed to leverage the natural resources of Andros, empower the community and generate cultural and environmental awareness.
Monetary profits and Environmental Awareness

Project Development

Leveraging Natural Resources
Collaboration with Local Workers

Modular Construction – Kit of Parts


Ecological and Locally Sound Design

Accessibility of product on the Internet

Client Selection Process

Team sent to Site
Exploring the Fundamental Components Influencing Ecotourism Lodge Development
Cultural Sensitivity and Sustainability Practices
Incorporate respect for local culture and implement sustainable practices for environmental protection.

Options for Modular Lodges Available on the Website
Provide customers with the flexibility to explore and choose from a range of modular lodge options conveniently on the company's website.

Design Inspired by Local Ecology, Culture, and Traditions
Create lodge designs that harmonize with the natural environment and reflect the cultural heritage of the region.
Understanding How Clients Choose Modular Lodges for Ecotourism Resort Development

Clients Choose Modular Lodges
Clients actively participate in selecting modular lodges for construction.

Modular Materials Kit
The startup offers modular materials in a kit of parts for construction.


On-Site Construction Support
The project managers and construction team transport and assemble the lodges on-site in collaboration with local construction workers and artists.
Implementing Collaborative Approaches with Local Workers

Collaborative Development
Engaging closely with local workers to foster community involvement and skill development.

Local Building Techniques
Embracing and integrating local building methods and traditions to preserve cultural heritage.

Ecological Sustainability
Prioritizing ecological balances and sustainable practices throughout the construction process.



Leveraging Natural Resources and Community
Engagement for Sustainable Development

Utilizing Island's Resources for Development
- Maximizing natural resources of Andros to drive sustainable development and economic growth.
- By embracing this model, Andros can safeguard its natural resources, ensuring availability for future generations and aligning with Andros’ dedication to protecting the island's beauty and biodiversity.

Engaging Community Members, Experts, and Artists
- Fostering collaboration among locals, specialists, and creatives to enrich ecotourism offerings and experiences.
- The model will open doors to new jobs in sustainable industries, aligning with Andros Apartments' commitment to promoting local economic growth and development.

Promoting Sustainable Practices and Local Engagement
Advocating for eco-friendly initiatives and involving the community in conservation efforts to ensure long-term environmental preservation and community prosperity. Implementing a circular economic model will minimize waste and pollution, fostering a cleaner and healthier environment for residents and visitors.
Natural Resource - Water


 Capella Lodge, Australia
Resende Villas and Barracuda Hotel, Brazil
Z9 Resort, Thailand
Capella Lodge, Australia
Resende Villas and Barracuda Hotel, Brazil
Z9 Resort, Thailand


 Pedras Salgadas
Hotel TRI, Sri Lanka
Woodhouse Hotel, China
Natural Resource - Forest
Pedras Salgadas
Hotel TRI, Sri Lanka
Woodhouse Hotel, China
Natural Resource - Forest
- Earth



 Coastal Pavilions, Coles Bay, Australia
Resort Makenna, Brazil
Encuentro Guadalupe, Baja, California Natural Resource
Coastal Pavilions, Coles Bay, Australia
Resort Makenna, Brazil
Encuentro Guadalupe, Baja, California Natural Resource
Innovative Product Offering: Modular lodges that are sustainable and customizable to reflect local cultural and ecological themes.
Local Collaboration: Partnership with local artisans and construction workers, enhancing community involvement and acceptance.
Sustainability: Emphasis on environmental stewardship aligns with global trends towards eco-friendly tourism.
Scalability: Modular design allows for scalability and adaptability to various locales beyond Andros.
Rich Biodiversity, Sustainable Tourism Potential, Local Community Support
Partnership with Hospitality Industry, Diversification of Renewable Energy Sources, Eco-friendly Infrastructure Development
Growing Ecotourism Market: The increasing popularity of sustainable travel provides a significant market opportunity.
Government and NGO Support: Potential for support from government and environmental NGOs, which could include grants, incentives, and endorsements.
Marketing Edge: Unique selling proposition (USP) of culturally sensitive and eco-friendly lodges can attract a niche market.
Educational and Community Development: The project can be used as a platform for educational programs about sustainability and local culture, enhancing its value proposition.
Dependency on Local Infrastructure: Success is heavily reliant on the existing infrastructure of Andros, which may be limited.
High Initial Costs: The upfront investment for developing modular kits and transporting materials and crew to Andros might be substantial.
Complex Logistics: Managing the logistics of transporting modular components and assembling them in a remote location can be challenging.
Regulatory Challenges: Ensuring compliance with both local and international building codes and environmental regulations.
Limited Infrastructure, Reliance on Imports, Vulnerability to Natural Disasters
Climate Change Effects, Competition for Resources, Regulatory Changes
Economic Instability: Economic fluctuations can affect tourism and thereby impact the viability of the project.
Environmental Risks: Being located on an island, the project may face risks from natural disasters like hurricanes, which are prevalent in the Caribbean.
Competition: Competitors might replicate the modular eco-lodge concept or offer lower prices by compromising on sustainability.
Resistance to Change: Potential resistance from local communities or stakeholders who may be skeptical of new developments or external interventions.
The platform business model for EcoModular Constructs' ecotourism lodges would involve creating a digital and physical infrastructure that facilitates interactions among multiple users connected by the common interest in sustainable, culturally integrated ecotourism. The platform would sell modular lodge kits and foster a community around eco-conscious development, creating value for tourists, local artisans, construction professionals, environmentalists, and property developers.
Sales of Modular Lodge Kits: Primary source of revenue through the sale of customizable lodge kits.
Commission on Marketplace Sales: A fee from transactions between local artisans and buyers on the platform.
Service Fees: Charges for using the platform to book construction teams or local experiences.
Subscription Fees: Optional subscription for enhanced listing features for artisans and other service providers.
Advertising Fees: For businesses wanting to promote their services or products related to ecotourism.
Website and App Interface: Serve as the central hub for interaction - lodge designs, booking construction services, and facilitating community engagement.
Marketplace: A feature where local artisans can sell crafts, construction materials, and other services directly to lodge developers and tourists.
Service Booking: Allow developers and tourists to book construction teams, local guides, artisan workshops, and other ecotourism experiences directly through the platform.
Lodge Developers/Investors: Individuals or companies interested in building ecotourism lodges.
Tourists: Eco-conscious tourists looking for sustainable accommodation options.
Local Artisans and Workers: Local community members providing crafts, labor, and traditional expertise.
Environmental NGOs: Organizations interested in promoting and maintaining sustainable practices on the platform.
To Developers: Provides a streamlined process to design, order, and build sustainable lodges with local cultural authenticity.
To Tourists: Offers unique, sustainable, culturally rich lodging options that can be directly booked.
To Local Artisans and Workers: Delivers access to a broader market, professional growth opportunities, and the ability to collaborate on large projects.
To Environmental NGOs and Local Authorities: Facilitates monitoring and promoting sustainable development practices.
Platform Management and Maintenance: Ensuring the platform operates smoothly and efficiently, with high usability and reliability.
Community Engagement and Support: Organizing workshops, training, and support for local artisans and workers to enhance their skills and offerings.
Marketing and Outreach: Promoting the platform to potential lodge developers, tourists, and local community members.
Technology Infrastructure: Robust IT systems to support website and app functionality, including user management, payment processing, and data security.
Partnership Networks: Strong relationships with local communities, government bodies, NGOs, and tourism boards.
Marketing and Customer Service Teams: Dedicated teams to handle promotions, customer inquiries, and service facilitation.
User Trust and Safety: Implement rigorous verification processes for all service providers and robust security measures for user data.
Cultural Sensitivity: Continuously engage with local stakeholders to ensure the platform respects and promotes local culture and practices.
Environmental Impact: Regular audits and updates to construction practices and platform operations to minimize ecological footprint and ensure sustainability standards are met.
Context


Range of Rooms Available



Development Process

Development Process – Components

Development Process – Life Span

Modular Lodges

Modular Lodges

Modular Lodges

Modular Lodges

Modular Lodges

Modular Lodges

Modular Lodges
 Deluxe Room
300 Sq. ft Living Space + 200 Sq. ft Patio Iteration with 2 modules together
Deluxe Room
300 Sq. ft Living Space + 200 Sq. ft Patio Iteration with 2 modules together
Modular Lodges
 Deluxe Room
300 Sq. ft Living Space + 200 Sq. ft Patio Iteration with 4 modules together
Deluxe Room
300 Sq. ft Living Space + 200 Sq. ft Patio Iteration with 4 modules together
Modular

Modular

Modular Lodges
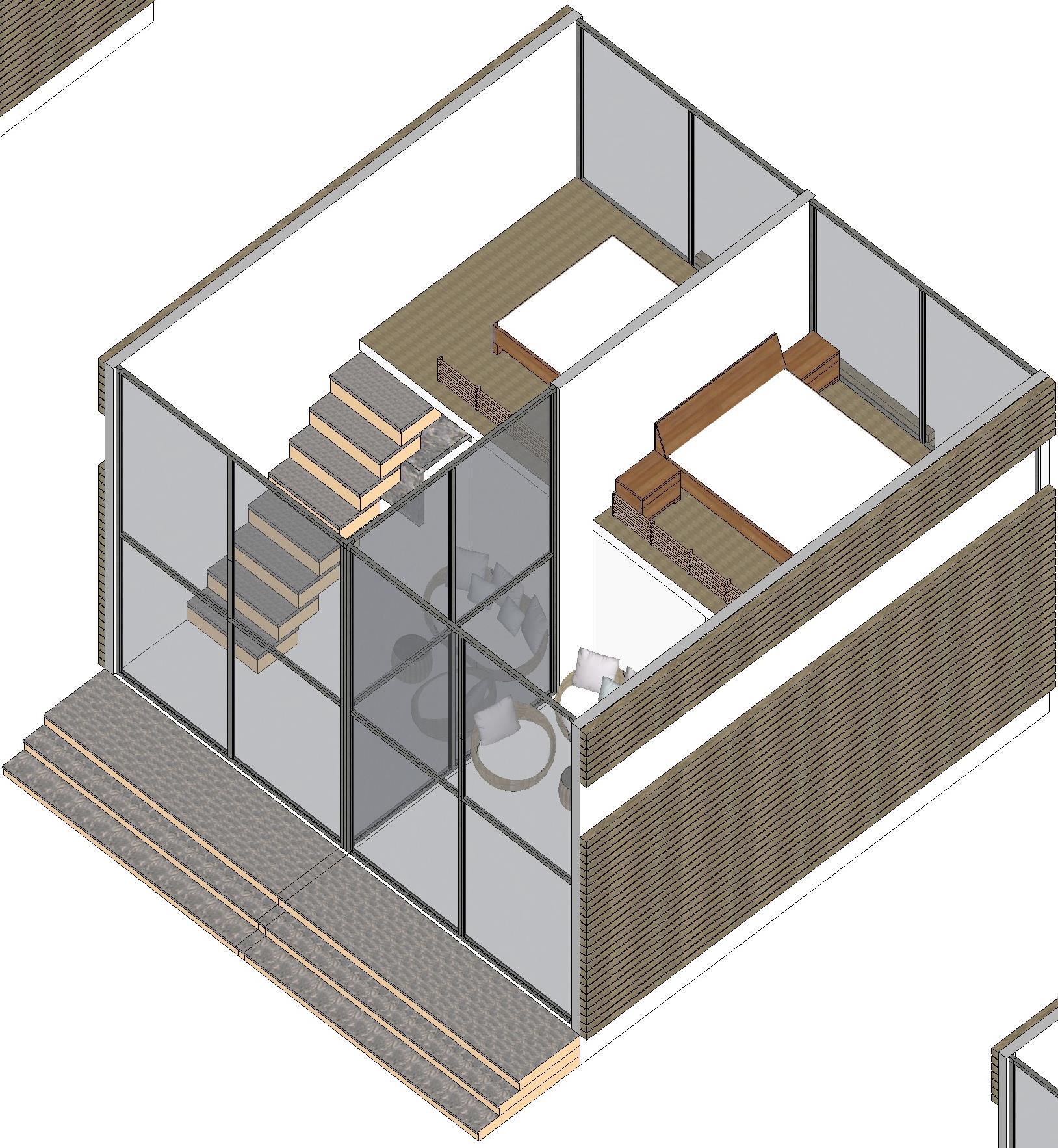 Family Room
Family Room
Modular Lodges
 Family Room
Family Room
Modular Lodges

Modular Lodges

Modular Lodges
 Housing Unit
300 Sq. ft Living Space + 200 Sq. ft Patio Iteration with 2 modules together
Housing Unit
300 Sq. ft Living Space + 200 Sq. ft Patio Iteration with 2 modules together
Modular Lodges
 Housing Unit
300 Sq. ft Living Space + 200 Sq. ft Patio Iteration with 4 modules together
Housing Unit
300 Sq. ft Living Space + 200 Sq. ft Patio Iteration with 4 modules together




