Commodity distribution in e-tailing
businesses more control over the platform and allows them to customize it to meet their specific needs However, on-premise platforms can also be more expensive and complex to set up and maintain. There are a number of leading ecommerce platform providers, including Shopify, BigCommerce, Magento, WooCommerce, and Wix These platforms offer a variety of features and functionalities to meet the needs of businesses of all sizes.
Types of E-commerce
1. Hosted E-commerce Platforms: These platforms are hosted by third-party providers, and users pay a subscription fee to access the platform Examples include Shopify, BigCommerce, and Volusion
2. Open-Source E-commerce Platforms: These platforms are free to use and allow users to customize the source code to meet their specific needs. Examples include WooCommerce (WordPress plugin),Magento, and PrestaShop
3. SaaS (Software as a Service) E-commerce Platforms: Similar to hosted platforms, SaaS platforms are hosted by third-party providers, but they typically offer more flexibility and customization options Examples include Shopify Plus and BigCommerce Enterprise
4 Marketplace Platforms: These platforms allow numerous sellers to list, market, and sell a wide range of products in a centralized marketplace, fostering competition and consumer choice Examples include Amazon, eBay, and Etsy
5. Social Commerce Platforms These platforms integrate e-commerce functionality with social media networks, allowing users to buy and sell products directly within the social media environment. Examples include Facebook Marketplace and Instagram Shopping.
6. Mobile Commerce Platforms (M- commerce): These platforms are specifically designed for mobile devices, allowing users to browse, shop, and make purchases using smartphones and tablets They optimize the shopping experience for smaller screens and mobile interfaces, often incorporating features like mobile wallets and one-click purchasing Examples include mobile apps from retailers like Amazon, Walmart, and eBay
7. Dropshipping Platforms: These platforms enable entrepreneurs to start an e-commerce business without managing inventory, by facilitating direct shipping from suppliers to customers This model reduces upfront costs and inventory risks, allowing for more flexible product offerings Examples include Oberlo (for Shopify) and AliExpress
8. Subscription E-commerce Platforms: These platforms focus on selling products or services through subscription models, where customers pay a recurring fee for regular access This model drives customer loyalty and predictable revenue Examples include Birchbox, Dollar Shave Club, and Blue Apron.
9. B2B E-commerce Platforms: These platforms are designed for businesses to sell products or services to other businesses, offering features like bulk ordering, account management, and ERP system integration They enable streamlined procurement processes and stronger supplier relationships Examples include Alibaba com and SAP Commerce Cloud
10. Niche E-commerce Platforms: These platforms cater to specific industries, interests, or demographics, offering specialized products or services. They often create niche communities around their offerings, providing tailored experiences and exclusive access to products that resonate with their target audience. Examples include Houzz (for home improvement products) and StockX (for sneaker resale).
Omni Channel
Omnichannel is a term used in ecommerce and retail to describe a business strategy that aims to provide a seamless shopping experience across all channels, including in store, mobile, and online
How Omni Channel Works
General principles apply to all implementations are:-
First, businesses understanding of behaviors need to have their customers' a strong needs and
Second, businesses need the resources to manage all aspects of an omnichannel strategy This means having a team in place that can coordinate efforts across channels and ensure that everyone is on the same page
Last, businesses need to be prepared to evolve their omnichannel strategy constantly. That means being open to new ideas, trying new things, and adjusting as necessary
Omnichannel Vs. Multi-channelVs.
Single-channel
The industry is rewriting the rules of omnichannel retail and the evolution of the store.
A single-channel approach is when a business onlyuses one channel, such as a brick-and-mortar storeor an online store A multichannel approach is when a company uses multiple channels, but there's no coordination between them.
For example, a business might have an online store, a brick-and-mortar store, and a catalog, but each one operates independently from the others.
Benefits of omnichannel commerce
1. Customer expectations: 41% of leaders say ecommerce is their most effective sales route, beating out in- person (37%) and video (31%),
1 Source: WTO
according to a new McKinsey & Co omnichannel survey By the start of 2022, only 15% of business- to-business (B2B) sellers expect in- person to be the norm going forward
2. Price flexibility: A good experience trumps price for many consumers, with customers being willing to pay 17% more for items, says American Express. That means businesses can provide high- quality products and high levels of service without worrying excessively about the costs.
3. Less stagnant inventory: Omnichannel systems share stock data across channels, decreasing the risk of inventory staying static and unsold. Decreasing storage and opportunity costs. Cross-channel inventory management is the “endless aisle” concept practiced by retailers such as Coach, Kohl's, Best Buy, and Walmart.
4. Increased profits: Investing in customer experience can have a considerable impact on revenue, with Qualtrics research estimating that companies that earn $1 billion gain an average of $700 million annually within three years of focusing on customer experience.
5. More upsell and cross-sell opportunities: With the data and access to customers that cross-channel strategies provide, businesses can send emails, texts, push notifications. In- store, an excellent example of this idea is the ship-to-store feature, opening opportunities for instore purchases of complimentary items or impulse buys.
Future of Omni-channel
Omnichannel provides the ability for retailers to achieve higher availability, drive increased sales and traffic, and integrate all customer touchpoints. An omnichannel strategy across retail and commerce will continue to improve your customer’s experience and provide more channels for customer purchases.
Case Studies
Case Studies Critical elements that influence success in the Indian e-commerce sector:
Case Study 1: Flipkart, one of the biggest online retailers in India, Flipkart was established in 2007 by Sachin and Binny Bansal The business began as an online bookstore and then gradually broadened its domain in a variety of goods –including electronics, apparel, and household goods Its unwavering focus on client happiness is one of themain causes of Flipkart’s success Via a user- friendly website and mobile app, a variety of payment choices, and a strong delivery network, the company offered a seamless and personalised client experience The idea of cashon-delivery was also introduced by Flipkart, which addressed the concerns of convenience and trust for customers who were hesitant to make online payments Flipkart has established a number of milestones and won various awards for its unique business strategy and customer-focused outlook over the years.
Case Study 2: Myntra Myntra is an online retailer of fashion and lifestyle products that have revolutionised the Indian fashion market with its creative thinking and dedication to the customer experience. Offering a large selection of reasonably priced, fashionable products with an emphasis on customer preferences and personalisation has helped Myntra stand out among rival retailers The business has also made use of technology to offer features like chatbots for client help, customised recommendations, and virtual try-on Myntra rapidly responded to the COVID-19 outbreak by starting projects like virtual fashion shows and contactless deliveries. It also collaborated with local manufacturers to make face masks and other necessary products Several honours and awards have been given to Myntra in recognition of its success, including the title of Most Admired & Valuable Power Brand in India in 2020
Case Study 3: Nykaa Nykaa is an online retailer with headquarters in Mumbai that focuses on health and cosmetic supplies The company’s distinctive value proposition, which includes a large selection of products from both domestic and foreign brands, low pricing, and a seamless customer experience, is responsible for its success With a focus on social media and influencer collaborations, Nykaa has made significant investments in marketing and branding. Nykaa’s strong Net Promoter Score (NPS), which is among the highest in the e-commerce sector at 70, demonstrates its dedication to client pleasure The valuation of Nykaa was over $1.2 billion in 2020, and it has aspirations to increase its product lineup and retail presence over the next few years
Supply Chain
A supply chain is the network of all the individuals, organizations, resources, activities and technology involved in the creation and sale of a product
Exhibit 3 Supply Chain Overview
Raw Material
The staff that need to transfer to new items through production.
Factory Responsible for producing the goods.
Retail Selling the product.
Supplier
Supply the raw materials
Distribution Transport to factory, store, and market.
Customer
Purchase the goods and items.
A supply chain encompasses everything from the procurement of raw materials to the delivery of the product to the consumer Distribution channel is the supply chain segment that deals with the delivery of finished goods from the manufacturer to the consumer
1 Source: WTO
Steps in the supply chain
The fundamental steps of a supply chain in order are as follows:
• Sourcing raw materials
• Refining those materials into basic parts
• Combining those basic parts to create a product
• Sales
• Product delivery
• Customer support and return services
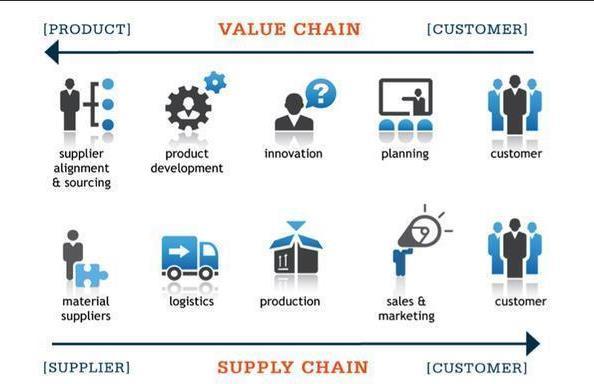
Supply Chain vs Value Chain
Supply chain and value chain are two different terms that are often used interchangeably. The supply chain aims to meet market demand, whereas the value chain seeks to add value to the product The value chain is used to give the company has an advantage in the industry. The supply chain encompasses all the steps involved, right from the procurement of raw materials to the delivery of the product The value chain consists of steps taken to make a product valuable and promising.
Exhibit 4 Supply Chain vs Value Chain
Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management (SCM) is the oversight of materials, information and finances as they move in a process from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer and then to the consumer
The three main flows of the supply chain are the product flow, the information flow and the finances flow. These occur across three main stages:
strategy, planning and operation. SCM involves coordinating and integrating these flows both within and among companies
Supply Chain Models
Establishing and running a global supply chain is a complex activity, and using the wrong supply chain model can expose an enterprise to risks and disruptions, increasing costs and potentially damaging the brand. Selecting the right model for your business requirements is thus a critical task.
Continuous Flow
Among the models on the list, this one is the most conventional For enterprises and sectors with a high degree of operational reliability, the continuous flow model is ideal. For this model, stability is crucial because it's needed at both the manufacturer's and the customer's ends Businesses that can anticipate a steady level of market demand and create a consistent set of items are ideally suited for this approach. As the name implies, this model, which is predicated on the stability of supply and demand in the market, involves a constant flow of commodities.
Fast chain
The Fast chain model is suitable for businesses with shorter life cycles It is an emerging name in supply chain models For example, a fashion designer launches a special clothing line for a particular season. Designers will try to take it to the market to earn profits as the fashion industry changes rapidlybased on the trends
Efficient Chain
For hyper-competitive industries, the efficient chain model has been crafted. It is primarily used by those industries where the end result is to maximise the efficiency In this model, disruption in production or sales could result in disturbance in supply chain. For instance, shortage of raw materials or a labour strike could cause long delays and ultimately the company will have to bear the loss
Agile
The agile model is well-suited for businesses dealing with specialty items where products may require extra care in the supply chain. The agile model is known for the expertise it requires to transport the goods from point A to point B and not so much for the automation or technology involved.
Custom-configured
The custom-configured model needs custom setups in the assembly and production stages It is a mix of agile and continuous flow methods where the product that is being manufactured may require some extra customization, but it needs to operate on an end-to-end basis It is usually used for prototype design and manufacturing of small batches.
Flexible
The flexible model is used to handle high demand during peak season and also accommodate a lean period with low demand.
Supply Chain Constraints
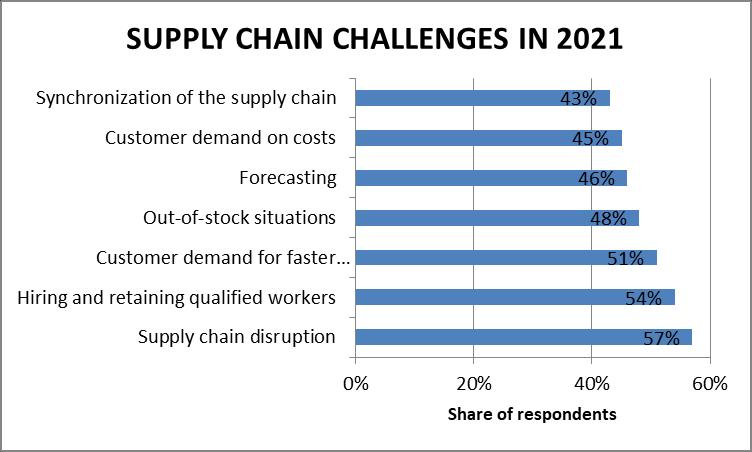
The supply chain in e-commerce comes with a unique set of challenges at the best of times. However, with the various supply issues caused by the Covid-19 pandemic, ecommerce companies have had to fiercely adapt to continue to meet consumer demands.
In a 2021 survey, over half of surveyed supply chain professionals stated that they found supply chain disruptions and shortages extremely or very challenging. During the survey, demand-side challenges, such as faster response time were cited among the most difficult hurdles supply chain companies face
Infrastructure deficiencies
Successful e-commerce operations depend on high functioning warehouse infrastructure. This involves 3 key components:
1. Visibility- Using software to keep constant track of inventory.
2. Mobility- Effective management of ingoing and outgoing inventory.
3. Flexibility- Having the means in place to adjust and adapt to continue meet orders when errors and issues occur.
Making sure the warehouse operates efficiently and productively is one of the main ways an ecommerce business can optimize order fulfillment and ensure deliveries both contain the right items and arrive on time
Issues with warehouse packing
In addition to infrastructural issues in the warehouse, the activities of warehouse personnel themselves can sometimes cause problems Labour is often the most expensive portion of warehouse costs, but this budget should also extend to extensive and thorough training of labour staff This involves training them on compulsory protective items (e g gloves, protective wear), and guidance on how to pick and pack products correctly and efficiently. Making sure you have the right warehouse team and good training in place will help prevent problems such as lost inventory, product breakages and losses, among other costly errors.
Transport and shipping logistical issues
Whether an ecommerce business handles its own deliveries or uses a third-party delivery service, issues can arise when it comes to logistics. These issues include inexperienced delivery personnel damaging goods in transit, unexpected delays and high delivery costs Ensuring you work with experienced and reliable delivery companies with well trained personnel, or indeed ensuring your own delivery staff is well equipped and trained, can help eliminate the risk of some of these issues Taking into account potential issues and having solutions and back up plans in place can also help prevent errors leading to serious problems with delivery
Exhibit 5 The various supply chain challenges faced
ValueChain
The value chain is a concept introduced by Michael Porter in his book "Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance." It refers to a series of activities that organizations undertake to deliver a valuable product or service to customers These activities encompass the entire process, from the initial creation of raw materials to the final delivery of the product or service to the end consumer
The two primary types of activities within the value chain are:
Primary Activities: These are directly involved in the production, marketing, delivery, and support of the product or service There are typically five primary activities:
• Inbound Logistics: Activities related to receiving, storing, and managing inputs or raw materials
• Operations: Processes involved in transforming raw materials into finished products or services
• Outbound Logistics: Activities associated with storing, distributing, and delivering the finishedproducts to customers
• Marketing and Sales: Activities involved in promoting and selling the product or service to customers
• Service: Activities related to providing after- sales support and maintenance
1 Source: WTO
Support Activities: These are essential for enabling and enhancing the primary activities There are four main support activities:
• Procurement: Activities related to sourcing and acquiring inputs, such as materials, equipment, and services, necessary for the production process.
• Technology Development: Activities focused on research and development, technological innovation, and infrastructure to support the value chain activities.
• Human Resource Management: Activities involved in recruiting, training, developing, and managing the workforce required for the value chain operations
• Firm Infrastructure: Activities that provide the overall management, planning, finance, and administrative support necessary for the organization's functioning.
ValueChain Analysis
• Importance of value chain analysis in identifying opportunities for cost reduction, process improvement, and value creation.
• Tools and methodologies for conducting value chain analysis, such as SWOT analysis, Porter's Five Forces, and benchmarking.
• Case studies illustrating successful implementation of value chain analysis in various industries
Examples of Value Chain
Trader Joe's
Another example is privately held grocery store Trader Joe's, which also has received much pressure about its tremendous value and
competitive edge.Because the company is private, there are many aspects of its strategy that we don't know However, when you enter a Trader Joe's store, you can readily observe instances of Trader Joe's business that reflect the five primary activities of the value chain.
1. Inbound logistics: Unlike traditional supermarkets, Trader Joe's does all of its receiving, shelving, and inventory-taking during regular store hours Although potentially maddening for shoppers, this system creates a ton of cost savings in terms of employee wages alone. Moreover, the logistics of having this work take place while customers are still shopping sends the strategic message that "we're all in this together "
2. Operations: Here's an example of how a company could apply the value chain creatively In primary activity number two above, "converting raw materials into finished product" is cited as an "operations" activity. However, because converting raw materials is not an aspect of the supermarket industry, we can use operations to mean any other regular grocery store function. So, let's substitute "product development," as that operation is critical for Trader Joe's
The company selects its products carefully, featuring items that you generally can't find elsewhere Its private-label products account for more than 80% of its offerings, which often have the highest profit margins, as Trader Joe's can source them efficiently in volume.
Another vital piece of product development for Trader Joe's is its taste-testing and chef-partnership programs, which ensure high quality and continuous product refinement
3. Outbound logistics: Many supermarkets offer home delivery, but Trader Joe's does not. Yet here, we can apply the activity of outbound logistics to mean the range of amenities that shoppers encounter once they are inside a Trader Joe's store. The company has thought carefully about the kind of experience it wants us to have when we visit its stores
Among Trader Joe's many tactical logistics are its instore tastings. Usually, there are a few product tastings happening simultaneously, which create a lively atmosphere, and often coincide with the seasons and holidays. The tasting stations feature both new and familiar items that are prepared and served by staff
4. Marketing and sales: Compared to its competitors, Trader Joe's barely does any traditional marketing. However, its entire in-store experience is a form of marketing. The company's copywriters craft product labels to appeal specifically to its customer base Trader Joe's' unique branding and innovative culture indicate that the company knows its customers well which it should, as the firm has actually chosen the type of customers it prefers and has not deviated from that model.
5. Service: Customer service is paramount for Trader Joe's. Generally, you see twice as many employees as shoppers in their stores Whatever work they are doing at the moment, the friendly, knowledgeable, and articulate staff are there primarily for you. Employees welcome shoppers' interruptions and will instantly rush to find your item or answer your question In addition, the company has always employed a no-questionsasked refund program. You don't like it, you get your money back period.
Supply Chain Disruption
Supply chain disruption refers to the interruption in the procurement, production, sales and distribution of goods and services. A standardized supply chain plays a crucial role in regulating the quality right from the starting to the end unit and is also useful in ensuring effective and efficient use of resources.
Levels of Supply Chain Disruption Severity
Supply chain disruptions can come in many forms but they can usually classified into two broad categories; first one being probability of occurrence- which refers to the likelihood of it
happening; and severity- which refers to the degree of impact which can be classified in three levels, they are as follows:
1. Low: These disruptions generally have short-term effects and are often resolved once a specific issue is analysed and eliminated For example, delay in order delivery or logistics issues
2. Medium: These are the disruptions that can generally obstruct the production or normal functioning from weeks to months. These disruptions will lead to losses that are included in quarterly financialstatements of an organisation. An example of this is damage to the warehouse.
3. High: High severity disruptions will have a paramount impact and long-term effects on time, money, and the supply chain in general Examples include COVID-19, Russia-Ukraine war etc
Causes of Supply Chain Disruption
There are various internal and external factors thatcan disrupt the supply chain Below are some of the potential causes that industries and businessesmust be aware of:
Cyber and security ransom ware and prominent examples. attacks: Security breach, data leakage are some
Financial and company viability: Internal conflicts between the management can hinder the functioning of the company
Transportation or logistics: This includes problems caused by weather or shipping damage.
Man-made: Human errors such as, warehouse explosion, gas leakage.
Geopolitical instability: Disturbance caused by political events or foreign affairs. Political strife or war between two countries is a prominent example
Natural disasters: Drastic damages caused by earthquakes, tsunamis, floods can severely impact the supply chain
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, supply chains across the globe have suffered significant disruption with Europe being no exception In a market with approximately 150 million more people than the United States, for sectors such as e-commerce it is vital that supply chains operate with as little disruption as possible The situation is also exacerbated by the continuation of the war in Ukraine, where the transportation and commerce industries have suffered a total loss of 47 billion U.S. dollars’ worth of damage.
Effects of Supply Chain Disruption
Global cost of disruptions brought by various scenarios like wars, pandemics have always been enormous Such disruptions usually impact the whole chain and can lead to serious repercussions Below are the known effects of supply chain disruptions:
1. Shortages: Due to material insufficiency, scarcity of certain products can be seen.
2. Inflation: Prices get inflated as the demandof the product increases.
3. Factory/store closures: Low level of production can lead to factory shut down.
4. Unemployment: Like a domino effect, all these factors collaborate and result in an increase in unemployment.
5. Threat to national security: Ability of the nation to protect its citizens during such situations is one of the hidden and paramount impacts of the supply chain disruption.
The infamous 2021 Suez Canal obstruction by Ever Given cargo ship is an example of a possible human error in cargo consolidation and disruption The cargo ship blocked Egypt’s canal for almost 7 days and disrupted global trade, which cost almost $10 billion in losses per day.
The impact of disruptions in various industries substantially affects the global supply chain and the global economy Surveys of 200 supply chain executives done by Ernest & Young LLP in the United States, shows that 72 percent of the companies reported that these disruptions adversely affected their operations and that only 2 percent responded that they were prepared for the challenges.
QUICK COMMERCE
First generation, E-Commerce: - This was the generation in which shopping was associated with self-service rather than home delivery wherein people would go and purchase the required items in their own private vehicles, and most of the products were available at their local Kirana stores
Second generation, E-commerce: - In this generation people got to know about the concept of home delivery and slowly and gradually they became habitual of the concept of home delivery which was done usually through large delivery trucks.
Third Generation E-commerce: - In this generation the delivery time further reduced and it came down to less than 1 hour from 2-3 days and the delivery was done from local stores or warehouses on two-wheeled vehicles and in this generation
OUTLOOK FOR QUICK COMMERCE
In India In descending order, the following players are on the springboard of success:
Zomato and Swiggy: both grocery and food delivery platforms boast of a large fleet which has offer membership base to keep the high utilization rates They benefits to their customer customers they acquire.
BigBasket and Blinkit(ex-Grofers): Big Basket and Grofers had an early start in expanding their warehouses Some of these can convert to mother hubs that communicate with the dark store network. Unlike Swiggy and Zomato, however, their rider fleet is considerably smaller despite stocking a more diverse catalog of household staples
Zepto, Dunzo: According to a study by AI-platform Bobble, Zepto holds the record for user growth( 946% within 90 days) In terms of the time spent on the app, Dunzo beat all the other q-commerce players, Zepto included with the entry of food and grocery-delivery players such as Swiggy and Zomato, India’s gaining on its American counterparts, i e Uber Eats and Gopuff Put simply, the idea of convenience shopping is shaping up
CHALLENGES OF QUICK ECOMMERCE
Finding the right delivery partners: Securing reliable and efficient delivery partners is crucial for Quick Commerce platforms to ensure timely order fulfillment However, finding and managing a network of delivery partners that can consistently meet service level agreements (SLAs) while adhering to quality standards can be challenging,
Ensuring on-time deliveries within 60 minutes: Meeting the promise of ultra-fast delivery within a tight timeframe, such as 60 minutes or less, requires meticulous planning and execution. Quick Commerce companies must optimize delivery routes, minimize transit times, and prioritize orders based on proximity to the customer's location to achieve on-time deliveries consistently.
Tackling on-ground dynamics: Quick Commerce operations are heavily influenced by on-ground dynamics such as traffic congestion, weather conditions, and other logistical challenges. Navigating these factors effectively requires realtime monitoring, adaptive routing, and contingency planning to mitigate potential disruptions and ensure smooth operations.
Managing customer emphasis on speed Commerce platforms expectations: With the and convenience, Quick face the challenge of managing customer expectations effectively. This includes providing accurate delivery estimates, communicating transparently about potential delays, and offering responsive customer support to address any issues or concerns promptly.
Balancing cost and profitability: Operating a Quick Commerce business model involves significant upfront investments in technology, infrastructure, and workforce Balancing the need for fast delivery with cost-effectiveness can be challenging, especially as companies strive to achieve profitability in a competitive market environment
Regulatory compliance: Quick Commerce companies must navigate regulatory requirements and compliance standards related to food safety, labor laws, vehicle emissions, and other regulatory frameworks. Ensuring compliance with local regulations while scaling operations can pose logistical and administrative challenges for companies operating in multiple jurisdictions
INVENTORY MANAGEMENT
Managing inventory to create higher inventory turnover and just in time delivery practices is one of the most important processes for online retailers Flexible systems that respond to customer demand and inventory uncertainties are most important in e-commerce.
Inventory Management Challenges
DEMAND
FLUCTUATION retailers have to account for
- Most of the online the demand fluctuations which are caused due to the seasonality and product popularity For example, during the time when most of the schools reopen in India after the summer vacation, the online stationery retailers face a mammoth challenge to supply all the necessary items which a school goingkid needs because this is the time when the demand will fluctuate more due to seasonality.
REVERSE LOGISTICS - It is one of the greatest challenges that online retailers have to manage to enhance the customer satisfaction and generate more business Because of high product returns, the management of reverse logistics is crucial for survival. Returned products have to be organized into distinct categories to see if they can be reused or distributed into smaller pieces.
STOCKOUTS – Sometimes the online retailers carry lesser inventory to reduce cost and the benefits of carrying lower inventory are widely acknowledged but such a policy increases the risk of stockouts Retailers who experience stockouts face declining sales and declining customer satisfaction, so they might switch to competitors leading to more back end costs.
MANAGING SKU – This challenge is mostly faced by the online apparel retailers where they have the problem of managing inventory information for various SKUs for each product shown on the website
MULTI CHANNEL SHOPPERS – inventory control is more challenging than ever because of the evolution of customers into multichannel shoppers. Consumers now browse, research, purchase and return products through multiple mediums
Inventory Management Models
Marketplace model
Also known as zero inventories, this organization creates a platform where the dealer can frame its products and maintain stock in a store A certain commission is changed on the order by the facilitator from the merchant. Examples include Snapdeal, Flipkart, and eBay.
Inventory model
A product is chosen by a buyer from an online shopping platform post and the company takes care of the process In this model, the organization maintains the distribution centre for the stock inventory and the order is dispatched to the customer’s doorstep
Hybrid Model
Amazon and Flipkart have recently shifted towards the hybrid model due to current FDI inflows in India. This model is a mixture of inventory and marketplace models Fulfilment services like FBA, Snapdeal Plus and Flipkart Advantage are included in the marketplace model Sellers can make the choice of self-fulfilment or marketplace fulfilment.
Bibliography
Placik, Martin. (March 11, 2024). Supply Chain Challenges 2021. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1182057/global-supply-chain-challenges/
Evolution of E-Commerce in India. Pwc. 3-7 https://www.pwc.in/assets/pdfs/publications/2014/evolution-of-e-commerce-in-india.pdf
Jain, Karan. Sarin, Raghav. Saxena, Vinayak. (April 2021) . Sector Flash: E-commerce market in India. Grant Thornton. 7-18
https://www.grantthornton.in/globalassets/1.-member-firms/india/assets/pdfs/sector-flash-ecommercemarket-in-india.pdf
The evolution of e-commerce globally. (March 23, 2022). Neilseniq https://nielseniq.com/global/en/insights/analysis/2022/the-evolution-of-e-commerce-globally/ (September 9, 2023). Leading Causes of supply chain issues in Europe. Statista https://www.statista.com/statistics/1415887/leading-causes-supply-chain-issues-central-europe/
(July, 2024) Supply Chain Management Market Size, Share, and Trends 2024to 2033 https://www.precedenceresearch.com/supply-chain-management-market
Tarda, Carli. (July 30, 2024) Value Chain: Definition, Model, Analysis, and Example https://www.investopedia.com/terms/v/valuechain.asp
Caldwell, Austin. (August 29, 2022) What Is Omnichannel? Benefits and Strategies https://www.netsuite.com/portal/resource/articles/ecommerce/omnichannel.shtml
(January, 2020) McK_Retail-Ops-2020_FullIssue-RGB-hyperlinks-011620.pdf https://www.mckinsey.com/~/media/McKinsey/Industries/Retail/Our%20Insights/Future%20of%20retail%2 0operations%20Winning%20in%20a%20digital%20era/McK_Retail-Ops-2020_FullIssue-RGB-hyperlinks011620.pdf
Authors
Rakshit Gupta Associate rakshit.22188@sscbs.du.ac.in
Diksha Garg Coordinator diksha 22068@sscbs du ac in
Dheer Kheria Associate dheer 23393@sscbs du ac in
Manav Mahajan Associate manav.23343@sscbs.du.ac.in
Agrima Chhabra Associate agrima 23009@sscbs du ac in
Ravi Bhatti Associate ravi.23092@sscbs.du.ac.in
Shitiz Dhar Coordinator shitiz.22227@sscbs.du.ac.in
Siddhi Jangid Associate siddhi 22412@sscbs du ac in
Meidhaa Ailawadi Associate meidhaa 23287@sscbs du ac in
Manya Gupta Associate manya 23205@sscbs du ac in
Sheen Sapru Associate sheen.23434@sscbs.du.ac.in