




Every phase of e-commerce fulfillment and delivery is important, but there's one stage that receives more attention than any other – the last mile of delivery.
Consumer buying behaviors have changed, especially when it comes to online shopping Today’s consumers expect cheap or, better yet, free and fast delivery. A big part of this boils down to a company’s last mile delivery process That means, for a company to survive in this market, they need to find ways to improve efficiency in this area
Last mile delivery refers to the final stage of the delivery process when a finished customer order is transported from a fulfillment center to the final destination, usually a residential address
Put simply, the purpose of the last mile delivery process is to get orders to the final delivery destination as quickly as possible Delivery is one of the most important touchpoints in the e-commerce customer journey, thus the last mile is key to ensuring customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
With the continued growth of e-commerce, last mile delivery has become more important than ever for consumers and more challenging for shippers
The last mile is typically the most expensive leg of the entire supply chain, accounting for 53% of overall shipping costs The last mile is also unpredictable, with delivery destinations and timelines unknown until a consumer places an order.
Besides, these concerns last mile logistics is considered the most difficult stage of the fulfillment and delivery process to be implemented Getting the product to the doorstep in a timely, efficient, and most importantly cost-effective manner is a tough prospect for supply chain partners Combine that with various fulfillment and fleet types for shippers to choose from, and the last mile distribution process becomes even more complex and challenging.
Getting the delivery experience right is of utmost importance for shippers and carriers in an increasingly e-commerce-driven world.
Product and price are no longer the only considerations to winning sales and delighting consumers. Delivery has taken center stage as a key factor that consumers evaluate when deciding where to purchase their online goods A great delivery experience is a great competitive advantage
With 83% of customers now expecting a guaranteed delivery date and 80% a specified delivery time slot, this leaves very little room for error in your last mile logistics These rising expectations are causing a boom in the last mile delivery market, with an estimated growth of 15.62% between 2022 and 2027.
Supply chain leaders, whether e-commerce retailers, grocery chains, restaurants or manufacturers, need to revisit their last mile delivery strategy
Companies need to dramatically simplify the most complicated aspects of delivery logistics, especially in the last mile For shippers and carriers, getting the last mile delivery experience right is critical in an increasingly e-commerce driven world
Exhibit 1
Industry Analysis

Breaking down last-mile delivery expenses helps merchants to understand where Last-mile delivery is costing them the most and identify where they can make improvements.
Long, indirect routes to deliver packages cause fuel expenses to add up quickly, especially when out-ofroute miles are difficult to avoid on many last-mile deliveries Moreover, traffic congestion and long idling times can impact overall fuel efficiency, especially within busy metro areas
Estimates indicate that indirect routes and out-ofroute miles can increase fuel consumption by 2030% Furthermore, traffic congestion and idling can further reduce fuel efficiency by 10-15%
Delivery personnel play a pivotal role in last-mile delivery operations To ensure timely deliveries, delivery drivers and couriers require training on how to deliver packages correctly and avoid failed deliveries, in addition to wages, benefits, and insurance
Labor costs are also liable to fluctuate throughout the year in line with peak season and the availability of delivery staff.
Training costs for delivery drivers and couriers can range from $500 to $2000 per employee Seasonal fluctuations may lead to a 10-20% increase in labor costs during peak seasons.
Maintenance of your delivery vehicle fleet is essential to keep delivery operations running smoothly. Because businesses require a large number of delivery trucks – even for a relatively small volume of packages – these costs can escalate quickly
The last mile contributes significantly to an order’s total shipping costs, due to the many unique delivery addresses that delivery vehicles need to reach within one journey Shipping cost is also heavily influenced by factors like shipping distance, DIM weight, and delivery speed
All orders need to be packaged correctly to stay in optimum condition during transit Warehouse staff need to pay close attention to product characteristics to ensure they are selecting the appropriate packaging, such as using extra filler or bubble wrap for fragile items Some packages may require additional handling and labeling, such as orders bound for hazmat shipping
When a customer decides to return or exchange a product, this can add significantly to last-mile delivery costs.
Repackaging and reconditioning returned merchandise may cost 10-20% of the item's original price Flexible pickup and delivery schedules can increase return logistics costs by 10-15%.
Exhibit 2
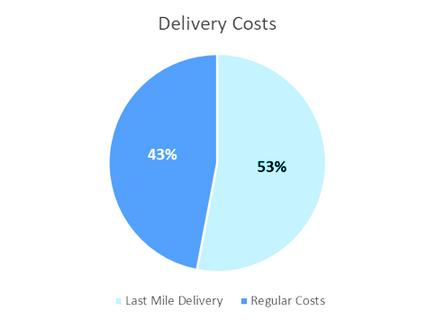
Delivery Costs
Source: Insider Intelligence
Consumers aren’t just shopping online more frequently; they’re also expecting ever-faster delivery times from e-commerce brands In fact, 41% of shoppers say they hope to receive their order within 24 hours or less. This means there’s little room for error within the last-mile delivery process, putting more strain on operational resources through the use of expensive expedited shipping or delivery scheduling systems But if brands don’t offer competitive delivery timeframes, they stand to lose a lot of sales.
A McKinsey & Company study found that offering faster delivery options can increase conversion rates by up to 35%
Peak season activity, such as the holiday season or one-off sales events, adds significant pressure to lastmile delivery logistics During peak seasons, delivery volumes can increase by 200% or more. When order volumes increase suddenly, this can slow down order fulfillment and shipping dispatched, resulting in extended delivery timeframes and higher transportation costs, especially if additional delivery trucks and drivers are needed to meet delivery targets. A survey revealed that 63% of businesses struggle to meet delivery timeframes during peak seasons
When delivery journeys are not planned out to reduce out-of-route miles, a delivery driver ends up traveling much longer distances and using greater amounts of fuel This can cause customer satisfaction to take a hit, and the need to invest in more resources to offset inefficient operations. Inefficient routes can increase delivery times by 20% and fuel costs by 30%
A study by Geotab found that using route optimization software can reduce out-of-route miles by an average of 15%.
A lack of proactive communication with customers
Brands need to communicate with their customers post-purchase to confirm their order and tell them when it has been dispatched for shipping A lack of information about delivery can make customers feel anxious and frustrated, which may dissuade them from shopping with you in the future. 63% of customers say they are frustrated by a lack of communication about their deliveries Moreover, if customers aren’t sure when their order is supposed to arrive, this may result in a failed delivery, resulting in additional trips and expenses. Companies that proactively communicate with customers about their deliveries can experience a 5% reduction in failed deliveries
One of the biggest challenges of the last mile is the number of delivery scenarios that couriers will encounter in a single delivery journey The average last-mile delivery contains 3.4 stops. Package dropoffs may include a mixture of apartments, townhouses, P.O. boxes, long driveways, and more. Finding the right address and figuring out the correct place to leave each parcel can add costly minutes and idling time to each drop-off, which reduces overall efficiency. Studies show that deliveries to apartments take 20% longer than deliveries to single-family homes
3
Unpacking supply chain costs
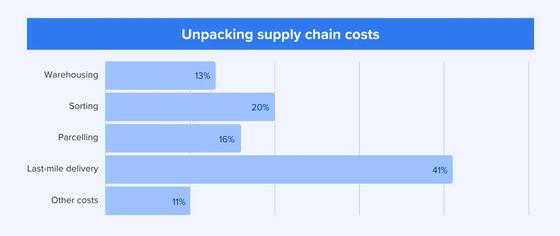
Last mile deliveries are made complicated by differing drop off points. Some customers are located in rural areas, which means delivery drop off points are located miles away from each other Transportation costs account for 61% of the lastmile delivery cost One might think that dropping off packages in urban areas will be easier, but it's not. This is because the shorter distance between drop off points is offset by congested roads and scarce parking in many cities A Department of Energy study found that urban deliveries average 5 miles per gallon, while rural deliveries average 10 miles per gallon.
There's a lot of idling going on when drivers are driving and dropping off goods in cities. Delivery trucks idle for an average of 30% of their operating time. Drivers are dealing with diverse vehicles, numerous traffic lights, and winding streets on a daily basis A delivery truck, on average, uses around 0 84 gallons of fuel per hour when idling, which can add up quickly. The average cost of idling a truck is $40 per hour.
Drivers tend to lose track of their dispatchers' route plans given the high number of individual stops they make especially if those routes aren’t easy to refer back to Unfortunately for shippers, a study shows that out-of-route miles usually account for 10 percent of the overall delivery fleet's mileage Eliminating out-of-route miles can save companies up to $500 per vehicle per month.
Unlike large-scale shipping and distribution, which usually involve large volumes, last mile delivery means transporting lots of small packages to single destinations. Without any economies of scale, the cost per delivery in the last mile is high The last-mile delivery cost per package is 20-30 times higher than the cost per package for long-haul transportation
Companies that distribute goods to supply chain partners or delivery hubs don't have to deal with failed deliveries. In contrast, businesses that deliver to the end consumer are grappling with the problem of failed deliveries every day Even a single digit percentage of failed deliveries (and the industry average is around 5%) can add up to considerable costs quite rapidly. A single failed delivery can cost a company $15 or more
There are multiple reasons why failed deliveries happen
The customer was not at home because the driver missed the delivery window
The customer was unavailable as he or she was not expecting the delivery
There were no options provided to customers in terms of delivery scheduling
The business has the wrong address
The average return rate of ecommerce products is a whopping 20%, which makes ecommerce fulfillment a particular challenge. If you sell consumer products online, you can expect at least one in five customers to send their purchased product back, either for a refund or for a different item (which you’ll have to deliver for free)
Efficient last mile delivery relies heavily on technology, Routing Software, Tracking System, Customer Management Systems, Warehouse and Distribution Centers: Costs for operating facilities that store and dispatch products.
Exhibit 4
Distribution of Cost


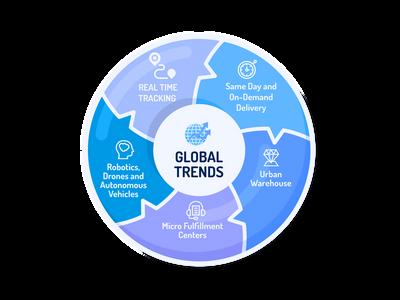
Customer expectations are changing quickly in the fast-paced world of e-commerce, with an increased focus on convenience and speed of delivery Due to this, same-day and on-demand delivery have become two crucial last-mile trends that are changing the logistics industry.
Benefits:
• Customer Satisfaction
The immediate demands of clients are met via sameday delivery, which boosts customer satisfaction and encourages return business.
• Competitive Edge
Same-day delivery services provide businesses with a competitive edge over slower competitors
• Reduced Abandoned Carts
Customers are more likely to finish orders when they know they will receive their items quickly, therefore immediate delivery options help reduce cart abandonment rates
An urban warehouse is a strategically located distribution centre or fulfilment facility within or near urban centres that allows for faster access to customers
• Proximity to Customers
By situating distribution centers closer to urban areas, companies can significantly reduce the distance traveled during the last mile This proximity enables faster order processing, reduced delivery times, and enhanced responsiveness to customer demands
• Quick Delivery Turnaround
Urban warehouses enable rapid order fulfillment and delivery. With products located nearby, companies can pick, pack, and dispatch orders within a short timeframe This expedites the final leg of the delivery process, ensuring customers receive their purchases swiftly
Urban warehouses enable effective inventory management and optimization. Businesses can reduce stockouts, improve product availability, and boost overall supply chain resilience by strategically distributing stock across multiple urban warehouses
3. Micro Fulfillment Centers
Micro Fulfilment Centers (MFCs) have emerged as a prominent last-mile delivery trend, revolutionizing how products are delivered to consumers
Micro Fulfillment Centers Benefits
• Proximity to Customers
MFCs are typically located near densely populated areas, allowing retailers and e-commerce businesses to reach customers more quickly
• Rapid Order Processing
With the help of automation and advanced technologies, MFCs facilitate faster order processing Orders can be picked, packed, and prepared for delivery in record time, optimizing the efficiency of the last mile.
• Efficient Space Utilization
MFCs are designed to make the most of limited urban space These centers are often compact and vertical, allowing for optimal utilization of real estate in densely populated areas where space is at a premium.
The convergence of robotics, drones, and self-driving vehicles has emerged as a transformative force in last-mile delivery, reshaping how goods reach consumers.
Exhibit 5
Global Trends
Milkbasket began when its founder, Mr. Anant Goel, had a very simple yet very deep thought. When Goel was in the UK, he noticed the comfort of having fresh milk delivered to his door every morning This experience sparked a eureka moment in his mind, why don’t just repeat this model in India, where we have a very deep and profound love for dairy products? Spotting an opportunity in the Indian dairy market, Goel and his partners, Anurag Jain, Ashish Goel, and Yatish Talvadia, decided to shake up the entire system the way Indians received their daily necessities. From the humble stall to an apartment complex in Gurugram, it was the beginning of what was to become a rapidly growing delivery business
Milkbasket focused on solving the high cost of lastmile delivery and the problem of getting an acceptable AOV in the price-sensitive Indian market Last-mile delivery, a final part of the supply chain, consumes about 30% to 50% of the total supply chain costs.
Furthermore, consumers in India are very pricesensitive therefore, it was a challenge to go beyond the average order value of Rs 500 In general, quick commerce, due to its true nature of a small order size, is unprofitable, and the delivery cost cannot be distributed evenly as it can be in a traditional ecommerce situation
One of the top strengths of Milkbasket lies in the fact that milk is an essential part of daily routine, which creates 100% loyal customers Despite the very thin margin on dairy items, the company perceived how important milk in the Indian diet is and it could be viewed as a way to compete and win the customer's trust and loyalty.
Pre-order System for Next-Day Morning Delivery:
Milkbasket invests time and gasoline that could be wasted for intensive deliveries during the day by having customers place their orders by midnight for
delivery the next morning Using this approach, Milkbasket contributes to saving on the distribution cost and the company extends the radius of its delivery to more places while the need for multiple warehouses is minimized
Dispatching orders at one time has helped cut down delivery costs, expanding much of fast commerce companies This incorporates the optimal method, which is not only beneficial to the efficiency of operation but also contributes to the overall profit of the business.
Milkbasket enlarged its delivery range for up to 15 kilometres with the pre-order system and, in turn, switched to a less dense warehouse distribution system. helping the business save money as a result of a more cost-effective expansion strategy
Minimizing Need for Multiple Warehouses:
Through grouping orders and broadening the area of delivery, Milkbasket has considerably reduced the number of quick commerce providers and their costs that are normally highly concentrated on logistics
Part-time Delivery Staff:
Part-time delivery staff is one of the core factors that cost Milkbasket less. By employing a flexible workforce, Milkbasket will utilize its logistics operations more efficiently and decrease expenses resulting from regular staff
Exhibit 6
Breakup of Milkbasket’s Finances
Delhivery, one of India's leading logistics and supply chain services companies, has significantly impacted the e-commerce logistics landscape with its innovative last-mile delivery solutions Established in 2011, Delhivery has expanded its services across the country, providing end-to-end supply chain solutions.
Geographical Diversity: India's vast and diverse geography presents significant challenges for lastmile delivery, from urban congestion to remote rural areas.
Infrastructure Issues: Poor road infrastructure in many parts of the country can delay deliveries and increase costs
Customer Expectations: Rising customer expectations for faster and more reliable deliveries put pressure on logistics companies to improve efficiency.
Operational Costs: High costs associated with lastmile delivery, including fuel, labor, and infrastructure, can impact profitability
1 Technological Integration:
Data Analytics: Delhivery utilizes advanced data analytics to optimize delivery routes, predict demand, and manage inventory efficiently.
Real-time Tracking: Implementing GPS tracking and real-time updates enhances transparency and customer satisfaction
Machine Learning Algorithms: Predictive algorithms help in forecasting delivery times and managing workforce allocation.
2 Network Optimization:
Hub-and-Spoke Model: Delhivery employs a huband-spoke model to streamline its logistics network, reducing transit times and operational costs.
Micro Warehousing: Establishing micro-warehouses closer to high-demand areas helps in reducing lastmile delivery time
3 Operational Efficiency:
Automated Sorting Centers: Automated systems in sorting centers increase efficiency and accuracy in package handling
Delivery Fleets: A diverse fleet, including bikes, vans, and electric vehicles, ensures flexibility and costeffectiveness.
4 Partnerships and Collaborations:
Local Partnerships: Collaborating with local delivery partners helps in navigating local challenges and expanding reach.
E-commerce Integration: Strategic partnerships with major e-commerce platforms ensure a steady volume of deliveries and optimized operations
Improved Delivery Times: Delhivery's technological and operational strategies have significantly reduced delivery times, enhancing customer satisfaction
Cost Efficiency: Optimized routes and efficient fleet management have led to reduced operational costs
Scalability: The scalable model allows Delhivery to handle increasing volumes, especially during peak seasons like festivals and sales events
Customer Satisfaction: High levels of transparency and reliability have bolstered customer trust and satisfaction.
Delhivery's innovative last-mile delivery approach and utilizing technology, has established it as a leader in the Indian logistics industry. Overcoming unique market challenges and consistently enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction, it sets a benchmark for the sector
Exhibit 7
Key statistics of Delhivery’s strategy’s impact

Yulu, a leading micro-mobility service provider in India, partnered with Zomato, a prominent food delivery platform, to tackle last-mile delivery challenges This collaboration aimed to enhance delivery efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and improve the delivery experience for both customers and delivery partners. The partnership leverages Yulu’s electric vehicles (EVs) to navigate urban environments more effectively, addressing common issues such as traffic congestion and delivery delays
The primary goals of the partnership were to improve delivery efficiency, lower operational costs, promote sustainability, and provide a better mode of transport for delivery partners. By leveraging Yulu's electric bikes (Yulu Miracle), both companies aimed to create a more efficient and environmentally friendly delivery system
The partnership saw the deployment of Yulu’s electric bikes within Zomato’s delivery network in key cities These bikes were seamlessly integrated with Zomato’s delivery app, enabling real-time tracking and optimized routing Training programs were conducted to familiarize Zomato’s delivery partners with the new electric vehicles. Additionally, incentive programs were introduced to encourage adoption, offering reduced rental rates compared to traditional fuel-based vehicles
The collaboration led to significant improvements in delivery efficiency, with a noticeable reduction in average delivery times and an increase in the number of deliveries per hour. Operational costs were lowered due to reduced fuel expenses, and delivery partners benefited from lower maintenance costs The use of electric vehicles resulted in a substantial reduction in carbon emissions, contributing to better urban air quality. Delivery partners also reported higher satisfaction levels, citing the comfort and costeffectiveness of the electric bikes.
Despite the success, the partnership faced challenges such as initial resistance from some delivery partners who were reluctant to switch from traditional bikes to electric vehicles There were also infrastructure limitations, with the need for adequate charging stations in urban areas to support the fleet. Addressing these challenges required ongoing communication, education, and investment in charging infrastructure to ensure the sustainability and scalability of the initiative.
Looking ahead, the partnership aims to expand to more cities and increase the fleet size Enhancements in charging infrastructure and operational support are planned to further improve efficiency. There is a continued focus on sustainability, with initiatives to reduce carbon footprints and engage in community programs promoting eco-friendly transportation solutions. The long-term vision includes exploring new technological advancements and partnerships to further optimize delivery operations and maintain leadership in sustainable urban mobility
The Yulu x Zomato partnership serves as a successful model of how micro-mobility and delivery platforms can collaborate to drive efficiency, cost savings, and sustainability in last-mile delivery This case study provides valuable insights for similar ventures aiming to revolutionize urban delivery logistics with innovative and eco-friendly solutions. By demonstrating the practical benefits and addressing the challenges, it sets a precedent for future collaborations in the field of sustainable transportation. Leveraging Yulu's electric bikes has enabled Zomato to reduce its carbon footprint significantly, showcasing a commitment to environmental stewardship With a focus on scalability and adaptability, the partnership paves the way for widespread adoption of green technologies in the logistics sector..
1. Traffic congestion
Urban regions are particularly susceptible to severe traffic congestion because of the high vehicle density and poor road infrastructure Delivery times are extended, fuel consumption rises, and operational expenses rise as a result of the delivery trucks’ slower delivery speeds. Furthermore, traveling through heavy traffic might result in missed delivery deadlines, irate clients, and a general decline in delivery effectiveness
2. High costs
The last-mile delivery segment is expensive for both the business and the customers With the sudden increase in demand, businesses find it costly to integrate the infrastructure to handle the demand for cost-effective and timely deliveries.
Businesses need to allocate money for sophisticated routes, extra stops, failed deliveries, driver’s salaries, and robust fleet management. If, unfortunately, a package is delayed or fails because of friction in the last-mile delivery logistics or entire supply chain, the delivery cost doubles up and can result in severe losses
3. Limited access to remote areas
Logistical challenges arise when delivering to isolated or rural areas is inadequate and poor Deliveries may be delayed or possibly fail if some places are inaccessible
4. Last-mile delivery costs
As already mentioned, supply-chain networks are under tremendous pressure as a result of the rising needs of continuously shifting client demands Additionally, when customers are ready to pay more for these expedited shipping alternatives, maintaining such a rigid distribution network still presents a significant logistical challenge
5. Seasonal demand fluctuations
Peaks in demand around holidays and special events can put a strain on delivery resources, causing
deliveries to be delayed and personnel to be overworked.
6. Real-time visibility
Depending on the drivers’ calls from pit stops or the daily activity logs that were kept Inefficiencies such as communication, breakdowns, and the inability to handle emergencies quickly. This leads to the failure to maintain the consistency of route optimization Such inefficiencies might rapidly turn into significant issues given the intense competition today
Bringg’s January 2022 survey found that 61% of retailers lack visibility once orders are out for delivery
7. Delayed deliveries
One of the major difficulties that shipping and delivery businesses face is the delay in deliveries. Businesses incur costs when they are unable to meet deadlines Delays in delivery damage a brand’s reputation, boost customer attrition and hurt your business’s bottom line.
Therefore, you require a same-day delivery strategy that enables you to make deliveries on schedule The answer is to develop a system for route planning and to guarantee openness and seamless communication at all levels.
Exhibit 8
Expectations of consumers on last mile delivery
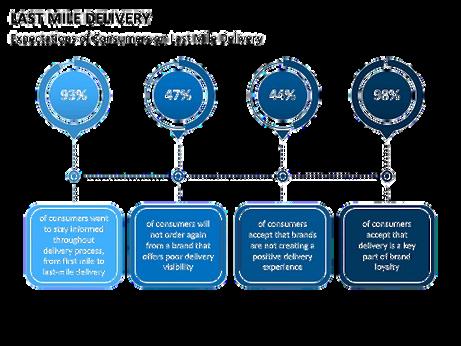
1. Streamlined delivery operations
Order segregation and allocation take up huge time and effort. For this, businesses also need a huge team of human professionals to check new orders, categorize them as per different parameters, find the right vehicle and driver for the delivery, and perform other functions. By integrating final mile delivery software, all these tasks can be automated, and hence, completed within the blink of eyes with less human intervention
2. Automated route planning
Finding efficient routes for delivery is yet another challenge in front of businesses Use of last-mile delivery software can overcome this problem and ensure more deliveries can be done in one day Another goal that businesses can achieve with automated route planning is to bring the vehicle back to the source in the expected time This would make the vehicle ready for the next delivery or secondary trip and will save costs significantly According to a report by McKinsey, efficient last-mile deliveries can reduce costs by 30%.
3. Real-time consignment tracking
Last-leg delivery software makes it possible for the vendor as well as the end customer to track the consignment in real-time and ensure that it is being delivered within the expected time. Around 84% of customers say that same-day delivery would make them more likely to shop again Also, both the vendors and customers can check the reasons for the delay, if any. This would also reduce the number of calls to the customer support center along with minimizing the rate of return of origin
4. Better visibility
The feature of the final mile delivery software facilitates the end-customers in checking the estimated time of delivery for the customers Moreover, they can
also make changes to the delivery time or address, if they are not available on location at the expected time of delivery
5. Increased productivity
Automation of various processes helps businesses to manage more customers effortlessly and focus on other business operations Last mile delivery practices have the potential to create numerous job opportunities with around 1,75,00 jobs created in the United States alone. They can increase business productivity by saving time, cost, and effort.
6. More successful first delivery attempts
When no one is at home, the driver has to return without delivering and try again the next day. Successful last-mile delivery solutions can be used to send a precise ETA directly to the customer To increase reliability, the ETA calculation includes historical traffic data, construction sites, driving and rest times, and vehicle-specific average speeds.
7. Reduced fuel consumption
Route optimization tools can help dispatchers find the most efficient route, avoid congestion, and reduce idle time. This in turn reduces overall fuel consumption, transport costs, and CO2 emissions.
8. Increased productivity
It ensures that customers experience shorter time windows for receiving their orders, leading to improved overall satisfaction and higher customer retention rates. It not only meets customer expectations but also builds trust and loyalty, encouraging repeat business Streamlined delivery processes mean quicker turnaround times, which can also reduce operational costs for the company. Additionally, by optimizing delivery routes, companies can better manage their resources and workforce, leading to a more sustainable and profitable operation Ultimately, the focus on efficient last-mile delivery creates a competitive advantage in the market, attracting more customers and fostering long-term growth,
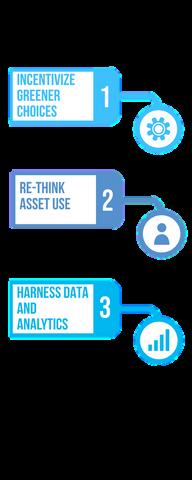
3 fundamentals for the last-mile ecosystem to create a more sustainable last mile
1. Incentivize greener choices:
Most users while ordering something online with a single click don’t focus on delivery methods for their purchase It is so easy that how the mode of delivery, where, when and how their delivery is fulfilled impacts the environment.
The root issue here is the lack of consumers awareness the overall last mile process should be made more transparent about how the delivery systems affects the environment and the customers should be availed with greener and sustainable methods for delivery.
43% of consumers are more likely to choose retailers that offer more sustainable delivery options.
These “choice architectures” run the gamut from greenshipping buttons to GHG calculators to consolidating multiple individual deliveries into one There are also options to incentivize consumers to pick up parcels at local fulfilment centres by offering value-add experiences or discounts.
If all customers within 1 kilometre of a fulfilment centre were to collect their deliveries on foot, 14% of London’s deliveries would have a zero emission last mile
These kinds of services can be availed to the customers withing big market apps like amazon, or they can be provided through separate apps dedicated to last mile delivery services, say FedEx Other than these options like usage of low emission vehicles and electric vehicles can be provided to the costumers Cities can incentivize further action by investing in electric vehicle charging infrastructure, making them convenient for delivery companies They can also offer GOV (green occupancy vehicle) driving lanes, express parking, ticketing and toll exemptions, or carbon credits for green vehicles
The use of low-emissions vehicles accounted for 51% of the total decrease in London’s delivery van emissions from 2020 to 2025.
2. Rethink asset use:
Assets have a fixed role in the traditional last mile Warehouses and fulfilment centres store the inventory. Delivery fleets run the routes. Every delivery organization invests in its own infrastructure, technology, people and vehicles
Retailers have been reinventing their best asset the physical store for years amid the e-commerce boom. Pandemic lockdowns that kept shoppers at home created new challenges, closing stores But retailers have and continue to repurpose stores into local fulfilment centres, transforming them into omnichannel fulfilment hubs. These are hybrid spaces for shopping, collecting and returning deliveries.
Delivery companies can also enhance cooperation and move to share assets in new ways Access to each other’s networks can eliminate costly redundancies and reduce emissions.
At the same time, cities and regulators can encourage asset sharing One way to do this is by creating points on the outskirts of cities where deliveries are concentrated for all carriers.
Bringing new life to such spaces can generate income for towns, cities, and local authorities while enabling sustainable last-mile development Making it a reality demands supportive zoning, tax incentives and creative city planning.
Exhibit 10
The path to sustainability
The more the ecosystem knows about who will buy what, where, and when, the more successful local fulfillment can be and the more delivery companies can plan greener routes.
While local fulfillment makes a bigger impact on the last mile than route optimization alone, they can further reduce emissions by between 7& & 9% in the cities.
Developing this insight goes beyond traditional customer segmentation & inventory optimization It is highly targeted With contextual insights into what specific customer groups in specific geographic areas need, retailers can stock the right SKUs locally. Doing this well involves analyzing a mix of internal and third-party data, social listening, and monitoring local trends and events
Take anticipatory shipping, for example. Delivery companies use customer and geolocation data to ensure a package is delivered the first time By using geolocation to see that a customer isn’t home, the delivery company can automatically leave the package in an alternative location per the recipient’s known preference. This eliminates exceptions that add cost and extra trips that increase the carbon footprint
Considering that every failed delivery costs about $5 and that 5 to 10% of all last-mile deliveries this is a much-needed improvement.
Data insight can also help delivery companies get more value out of route optimization Harness data and analytics are typically seen from traditional strategies.
When route optimization is applied with local fulfillment, delivery vehicles drive 140 million kilometers less.
All of these data inputs can optimize routes while reducing complexity and downtime Cross-ecosystem data sharing via the cloud is key to making it happen
The last-mile supply chain made possible by local fulfillment centers could lower last-mile emissions by between 17 and 26% by 2025. Using local fulfillment for even half of e-commerce orders between 2020 and 2025 could lead to significant impacts.
Roles different elements of the market can play in supporting sustainability
Entice consumers to choose in-store fulfillment. Transform supply chains to store networks to include dark stores, partial dark stores, and market fulfillment centers
Educate consumers on the value of consolidating deliveries
Put data at the heart of operations to prioritize new green practices
Explore partnerships and ways to invest in shared assets.
Electrify the delivery fleet with purpose-built, lastmile vehicles
Governments
Align sustainable last-mile strategy with economic stimulus and jobs.
Support and promote green transport initiatives
Encourage the repurposing of urban spaces for local fulfillment
Consumers
Choose the greenest delivery option possible. Take advantage of incentives to bundle deliveries
Consolidate trips to pick up parcels at local fulfillment centers
The final leg of the delivery process, known as last mile delivery, plays a critical role in ensuring customer satisfaction It's the part where goods move from distribution centers to the customers' doorsteps, directly influencing how customers perceive the service they receive.
Businesses recognize the importance of last mile delivery and are investing heavily to enhance this aspect of their operations. With the rising demand for faster and more convenient delivery options, companies are constantly innovating to find efficient and cost-effective solutions Projections suggest that the global last mile delivery market will witness substantial growth, reaching a value of $121.1 billion by 2030.
Significance of last mile delivery in driving customer satisfaction:
Speed of Delivery: Customers expect their orders to arrive swiftly, and timely delivery greatly influences their satisfaction
Condition of Goods: The condition in which goods are delivered significantly affects customers' perception of the service quality.
Real-time Tracking: Providing customers with the ability to monitor their deliveries in real-time instils a sense of control and confidence, contributing to overall satisfaction.
Moreover, last mile delivery constitutes a significant portion of retail logistics expenses. This underscores the importance for businesses to optimize this process to reduce costs and enhance customer satisfaction.
Invest in Technology: Utilize advanced delivery management systems, route optimization software, and real-time tracking tools.
Offer Delivery Options: Cater to diverse customer preferences by offering multiple delivery options
Leverage Data: Analyze customer data to identify trends and improve delivery performance
Customer Expectations and how to impress them with Last Mile Delivery
The current market landscape is characterized by heightened customer expectations for last mile delivery. Industry giants have revolutionized the industry with their provision of free and fast delivery, setting new benchmarks for last mile delivery and enhancing customer satisfaction
While meeting customer expectations is a critical first step, it merely forms the basis for competition; businesses must strive to exceed these expectations. One way to achieve this is by exploring the cheapest ways to ship large packages, thereby offering customers the highest level of service for the lowest fee, which greatly contributes to customer satisfaction. Another efficient method involves implementing eco-friendly delivery options.
The adoption of green logistics e g , electric delivery vehicles offers a sustainable alternative to traditional delivery methods. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also caters to the growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible practices.
Alternatively, businesses can exceed customer expectations by offering unique and convenient delivery options Smart locker systems for deliveries are a flexible solution for customers, enabling them to receive their packages at their convenience, any time of the day. Such innovative delivery methods cater to modern consumers’ desire for flexibility and convenience, thereby enhancing the overall customer experience and satisfaction
The Boom and the Burden: E-commerce & Last-Mile Delivery in India
India's e-commerce market is on a stellar trajectory, expected to reach a staggering USD 350 billion by 2030 However, this growth story faces a crucial challenge: last-mile delivery Delivering products efficiently to customers' doorsteps presents unique complexities in the Indian context.
Challenges: A Roadblock to Efficiency
1 Infrastructure Bottlenecks: Congested roads, poor addressing systems, and limited parking space in urban areas significantly hinder smooth deliveries. A 2023 Invest India study found a staggering 72% of logistics companies consider infrastructure limitations a major hurdle
2 Fragmented Market: The presence of numerous small and medium-sized delivery players creates a fragmented market, making consolidation and optimization difficult Frost & Sullivan estimates over 2,500 independent delivery companies operate in India, posing challenges in streamlining operations
3. Delivery Agent Management: Ensuring a reliable and well-trained workforce across a vast geographical landscape proves demanding. Attrition rates among delivery personnel can be high due to demanding schedules and competitive wages in other sectors
The Indian Perspective: Cost, COD, and Tier 2/3 Cities
1 Cost Sensitivity: Price is a major concern for Indian consumers A 2024 PwC survey revealed that 78% of Indian online shoppers consider delivery costs when making purchasing decisions. Delivery companies must find a delicate balance between speed and affordability
2 Cash on Delivery (COD): A significant portion of Indian e-commerce transactions rely on COD, requiring robust cash handling infrastructure. Nearly 52% of all e-commerce orders in India are paid for via COD, according to a 2023 Razor pay report
3. Rise of Tier 2 & 3 Cities: E-commerce penetration in smaller cities is increasing, demanding adaptable delivery solutions for diverse environments. By 2025, tier 2 and 3 cities are expected to contribute over 65% of India's ecommerce sales volume
The Indian last-mile delivery landscape is transforming, driven by technology, evolving models, and a focus on sustainability Here are some key trends to watch:
1. E-mobility Boom: Electric vehicles (EVs) are gaining traction in last-mile delivery By 2023, EVs secured over 20% market share due to cost savings and environmental benefits The electric twowheeler market in India is projected to reach a staggering 43 million units by 2030.
2 Micro-fulfillment Centers: Strategically placed micro-fulfillment centers in urban areas will enable faster deliveries within smaller radii Experts predict a 150% growth in micro-fulfillment centers in India by 2025.
3. Hyperlocal Delivery: Partnerships with local stores will ensure quick deliveries of everyday essentials, fostering convenience and supporting local businesses. The hyperlocal delivery market in India is expected to reach USD 7.5 billion by 2024.
1 Drone Deliveries: Technological advancements are making drone deliveries a viable option, especially in remote areas and for critical goods like medicines. The drone delivery market in India is projected to reach USD 1.2 billion by 2025 Regulations are still evolving, but pilot programs are underway
2. Automation & AI: AI-powered tools like route optimization, automated guided vehicles in warehouses, and data-driven analytics will enhance efficiency and cost reduction
The Last Mile of the delivery journey has evolved from a mere logistical function to a strategic imperative that significantly impacts customer satisfaction, brand loyalty, and overall business performance.
As e-commerce continues its rapid expansion, with global online sales projected to reach $7.4 trillion by 2025, the pressure on businesses to optimize last-mile operations has never been greater.
Our research underscores the complexities and challenges inherent in this final leg of the supply chain While advancements in technology, such as Route Optimization Software and Real-Time Tracking, have improved efficiency, the industry still grapples with issues like Traffic Congestion, Rising Fuel Costs, and the last-mile 'Delivery Desert' in rural areas
Key findings reveal that average delivery times have decreased by 27% over the past five years, but consumer expectations for faster and more convenient delivery options continue to rise A study by McKinsey found that 57% of consumers expect same-day or next-day delivery. Moreover, the cost of last-mile delivery accounts for a significant portion of total logistics expenses, ranging from 28% to 53% of overall shipping cost
To thrive in this competitive landscape, businesses must adopt a holistic approach. This includes investing in technology, cultivating strong partnerships with delivery service providers, and prioritizing sustainability For example, Amazon's investment in Drone Delivery Technology demonstrates a commitment to innovation in the last mile Additionally, offering flexible delivery options, such as same-day delivery, delivery lockers, and click-and-collect services, is crucial to meet evolving customer demands.
The last mile is no longer merely a logistical function; it's a strategic imperative By delivering products swiftly, reliably, and sustainably, businesses can foster customer loyalty, enhance brand reputation, and gain a competitive edge. As the industry evolves, those who can master the last mile will be wellpositioned to reap the rewards of a rapidly expanding e-commerce market
However, challenges such as the Increasing Costs of Urban Delivery, Labor Shortages, and the Environmental Impact of last-mile operations persist
To address these issues, the industry must collaborate with Policymakers, Infrastructure Providers, and Technology Companies to develop sustainable and efficient solutions
In conclusion, the last mile is a complex and dynamic ecosystem that requires continuous adaptation and innovation. By prioritizing Customer Satisfaction, Leveraging Technology, and Adopting Sustainable Practices, businesses can overcome challenges and create a competitive advantage in the evolving ecommerce landscape.
Kromer, Sven Grunwald, Alexander El Nassabi, Housni Bohler, Christian (October 28, 2022) Keeping up the Pace- The new face of Last Mile Delivery Accenture 4-10
https://www.accenture.com/content/dam/accenture/final/industry/retail/document/Accenture-Last-MileDelivery-Retail.pdf
Kammerer, William Mohney, Kevin Chinnareddy, Siddarth Neff, Deborah (June 5, 2020) The Last Mile: Enabling Last Mile through speed and flexibility upstream Deloitte 3-8
https://www2 deloitte com/content/dam/Deloitte/us/Documents/process-and-operations/us-the-last-mile pdf
Jayatilake, Priyanka. Perera, Kamaya. Watawana, Thisara. Karunathare, Hasitha. (April 2020). Last Mile Delivery Optimisation: The three success factors for online retailers to focus on during and post-COVID-19 KPMG 2-5
https://assets kpmg com/content/dam/kpmg/lk/pdf/last-mile-delivery-optimisation pdf
Xiaong, William. qing Li, Shang. Yan Qiang, Autumn. Zhou, Bryan. Chen, Kevin. Zhen, Jane. (2023). Global Smart Logistics Last Mile Outlook Deloitte 12-16, 32-40
https://www2 deloitte com/content/dam/Deloitte/cn/Documents/consulting/deloitte-cn-consulting-2023global-smart-last-mile-logistics-outlook pdf
Andrea, Barbara. Maurer, Andreas. Piermartini, Roberta. Teh, Robert. Carzaniga, Antonia. (June 19, 2010). World Trade Report 2019: The future of Services trade World Trade Organization 26-28, 48, 72 https://www wto org/english/res e/booksp e/00 wtr19 e pdf
Pharand, Andre. Banks, Sarah. Baker, Gemma. Cartwright, Henry. Olivier Desumers, Pierre. Holst, Alexander. Peters, Marius. Reers, Juergen. Strom Nordness, Simen. Whitehouse, Sean. The Sustainable Last Mile. Accenture. 12-16
https://www accenture com/content/dam/accenture/final/a-com-migration/r3-3/pdf/pdf-148/accenturesustainable-mile-pov pdf
Samet. Alexandra. (October 12, 2023). Last Mile Delivery Logistics: What it means for retailers. Emarketer. https://www.emarketer.com/insights/last-mile-delivery-shipping-explained/
Flora, Meredith (May 28, 2024) Last Mile Delivery 101: How a 3PL works with Last Mile Carriers for Bestin-Class Fulfillment ShipBob
https://www.shipbob.com/blog/how-last-mile-delivery-works/
Simrat Luthra Secretary simrat.22239@sscbs.du.ac.in
Shitiz Dhar Coordinator shitiz 22227@sscbs du ac in
Diya Bhargava Associate diya.23042@sscbs.du.ac.in
Dikshit Arora Associate dikshit.23325@sscbs.du.ac.in
Meet Mandhan Associate
meet 23533@sscbs du ac in
Parth Batra Associate parth 23351@sscbs du ac in

APICS SSCBS Chapter apicssscbs@sscbs.du.ac.in

@apics.sscbs
Diksha Garg Coordinator diksha.22068@sscbs.du.ac.in
Parth Khanna Treasurer
parth.22538@sscbs.du.ac.in
Aryaman Bahree Associate aryaman 23151@sscbs du ac in
Pranshi Garg Associate pranshi 23084@sscbs du ac in
Atishay Jain Associate atishay 23155@sscbs du ac in

