of Covid



Prof. Carlo Federico Perno
Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital


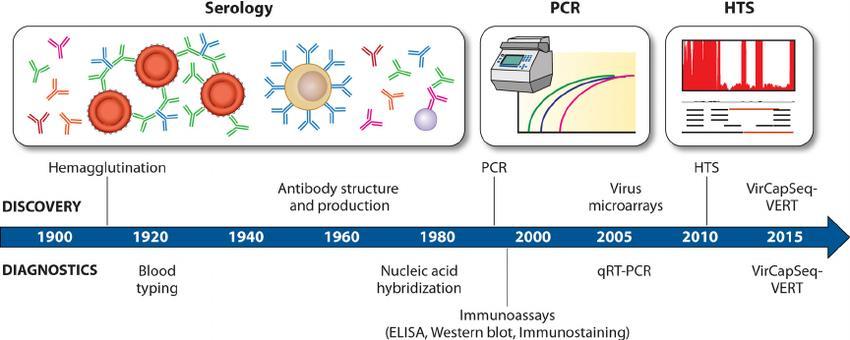
A modern approach to viral diagnosis
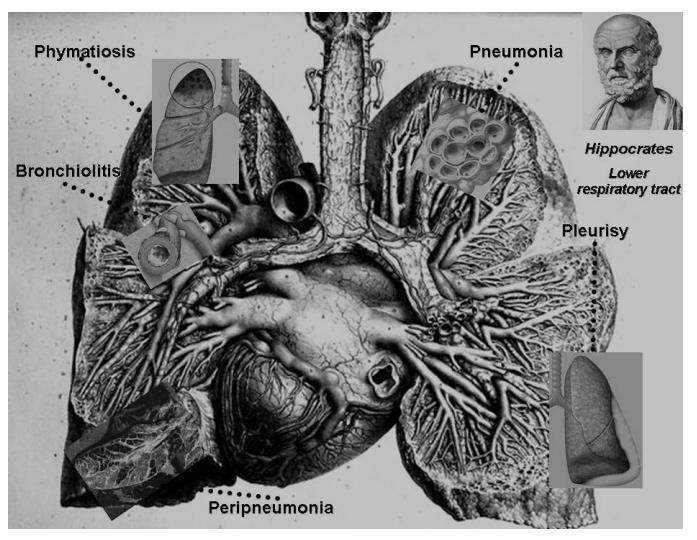
«COUGH OF PERINTHUS»

First influenza epidemic of human history
Corpus Hippocraticum: Books Epidemics II


Alexandria; late 2°-1° c. BC
Pathology of the lower respiratory track insed
Corpus Hippocraticum.

Lung anatomy, Anatomie del l’homme, Bourgery and Jacob, Guérin Editions, Paris 1862
2
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid

Discovery of human influenza virus (Smith, Andrewes, Iaidlaw)



Scagnolari et al., Expert review of anti-infective therapy, 2016


3
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid


Scagnolari et al., Expert review of anti-infective therapy, 2016


 Discover of PCR (Salki, Mullis)
Discover of PCR (Salki, Mullis)
4
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid

Influenza A
R&D Systems, a Biotechne Brand


SARS MERS SARS-CoV2 H1N1/
5
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid



Subbarao et al.,
2020 6
Immunity
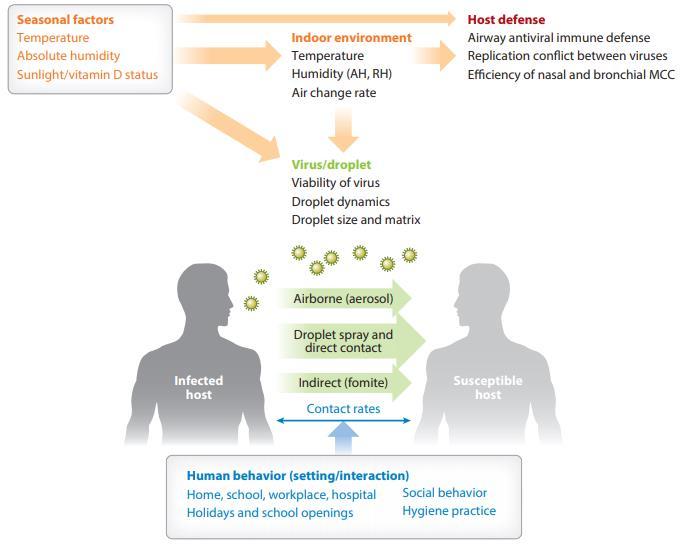
Seasonal determinants in the epidemics of respiratory viruses include seasonal changes in temperature, absolute humidity (AH), sunlight, vitamin status, and host behavior.
Environmental factors affect host susceptibility by modulating airway defense mechanisms and affect viability and transmission of respiratory viruses.
Human behavioral patterns affect the contact rates between infected individuals and susceptible individuals.

Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid


7
Moriyama et al., Annu. Rev. Virol. 2020
The extrathoracic and tracheal mucosal surface defense is directly affected by the seasonal changes in temperature and water content of the inhaled air on both infected and susceptible hosts.

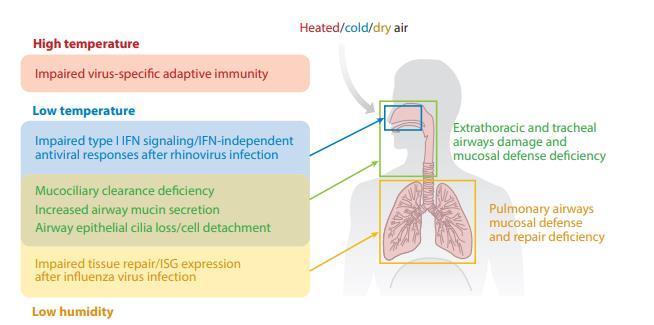
Proper mucus hydration is required for the efficient mucous transport. Dehydration caused by dry breathing air leads to increased viscoelasticity of the mucous layer and immobilizes cilia, which are pressed down by the reduced height of the dehydrated periciliary layer.

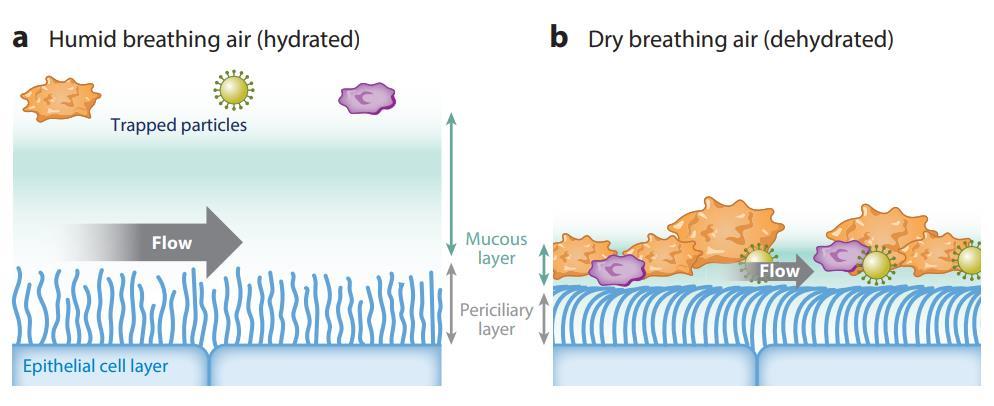
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid

8
Moriyama et al., Annu. Rev. Virol. 2020
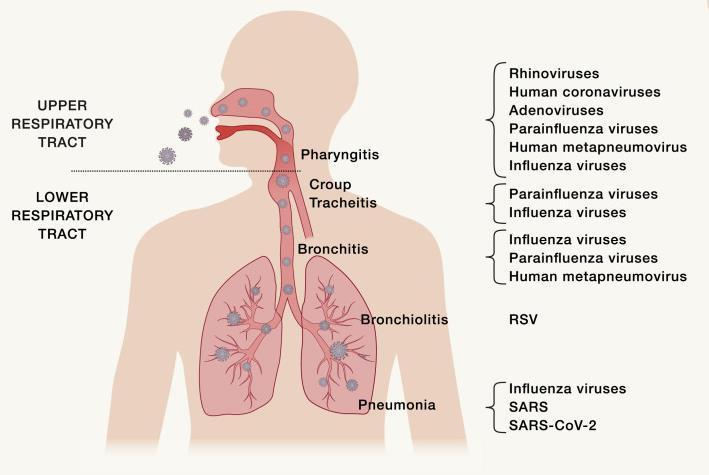
Respiratory viruses are classified according to their seasonal epidemics
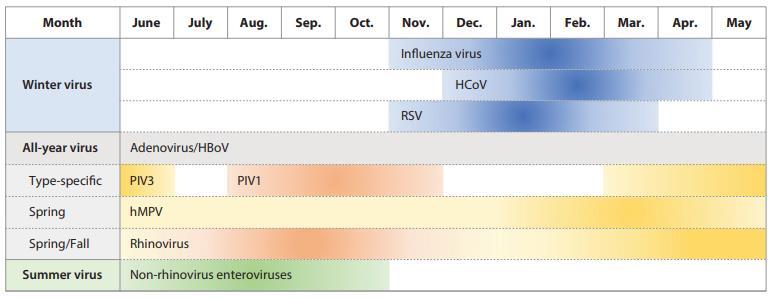


Replication conflicts among those respiratory viruses can contribute to the nonoverlapping peak incidence with respect to one another. Interference between respiratory viruses has been recognized by epidemiological observation that influenza viruses and RSV do not share peaks during the same period even though both are prevalent in winter

Moriyama et al., Annu. Rev. Virol. 2020
9 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Gomez GB et al., Science 2021

During the pandemic, circulation patterns of respiratory viruses other than severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) have been disrupted.

This could mean a future shift in the epidemiology of respiratory diseases, potential for new epidemic threats, or larger outbreaks than previously observed.

Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid

10
• Since WHO declared the COVID-19 pandemic on March 11th 2020, non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPI), including mask wearing and social distancing, have been implemented worldwide to counteract the spread of SARS-CoV-2


• These measures have resulted in a reduced circulation of other respiratory viruses commonly responsible for winter seasonal infections in the pediatric population

Sullivan SB et al., Eur Surveill 2020
11 A
modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
But... the scenario has changed once again


12 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Number of different viral pathogens detected in January-December 2019 (a), in January-December 2020 (b) and January-October 2021(c).

0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 Jan-21 Feb-21 Mar-21 Apr-21 May-21 Jun-21 Jul-21 Aug-21 Sep-21 Oct-21 -10 10 30 50 Jan-19 Feb-19 Mar-19 Apr-19 May-19 Jun-19 Jul-19 Aug-19 Sep-19 Oct-19 Nov-19 Dec-19 0 10 20 30 40 50 Jan-20 Feb-20 Mar-20 Apr-20 May-20 Jun-20 Jul-20 Aug-20 Sep-20 Oct-20 Nov-20 Dec-20 N ° pathogens detected April 22nd, 2021: easing restrictive measures March 9th, 2020: national lockdown 2019 2020 2021 (b) (c) (a)
Mattana et al, submitted
All virus can cause overlapping clinical presentation making it difficult to distinguish the causative agents without a solid laboratory analysis


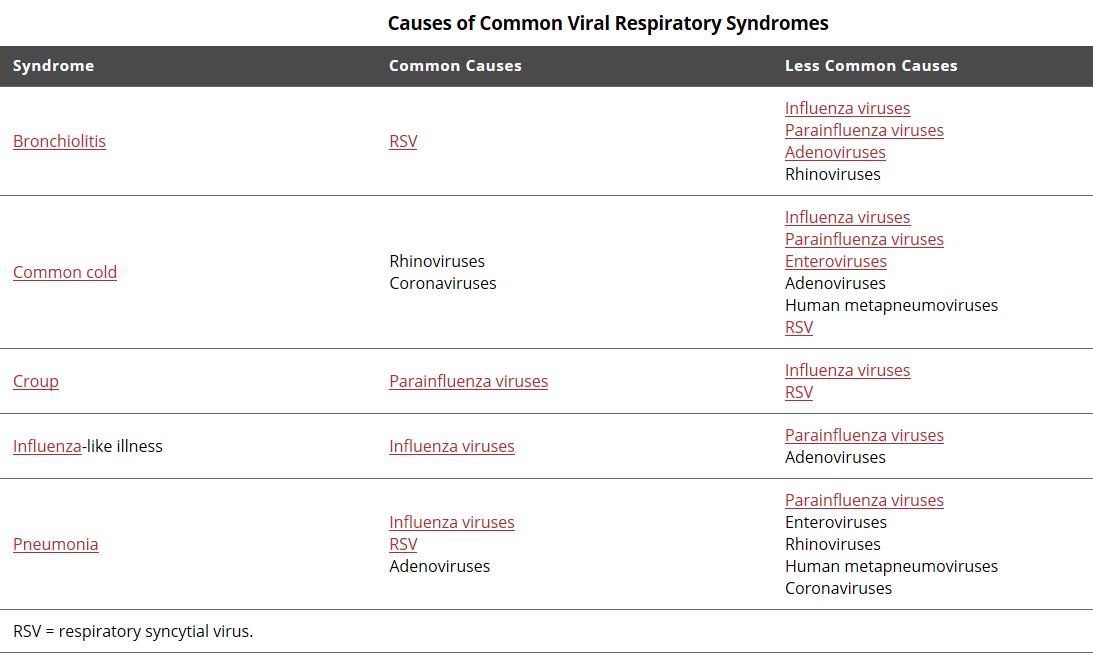
14 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
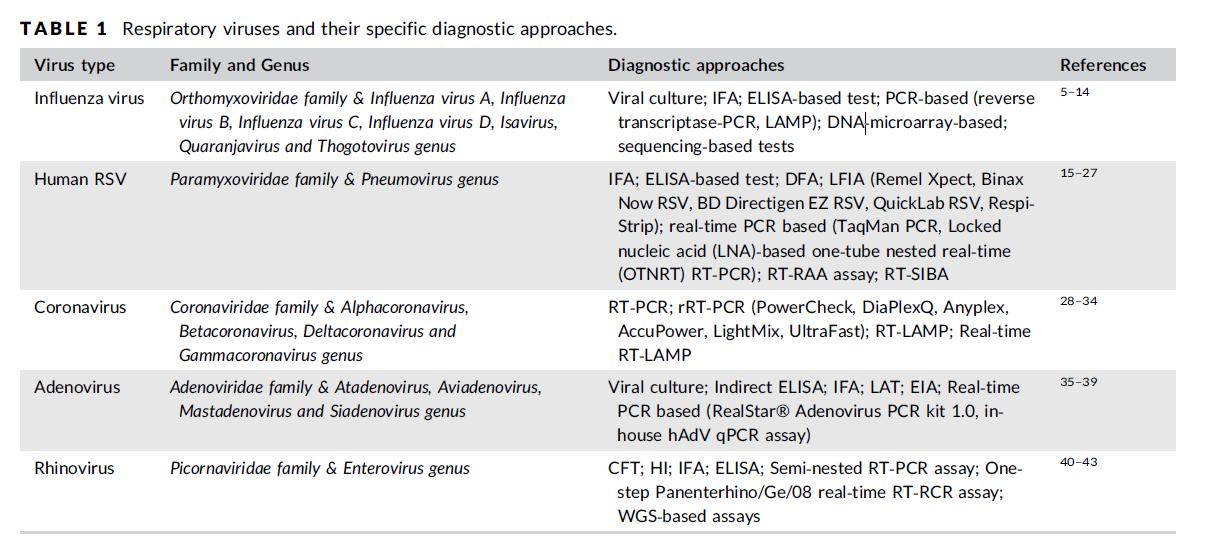



Zhang et al., J Med Virol. 2020 15 A
modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Acute respiratory tract infections are one of the leading causes of childhood morbidity and mortality worldwide, and it has been estimated that globally, respiratory infections are responsible for about 2 million deaths in children between 0 and 5 years of age.
Approximately 80% of these respiratory infection cases are caused by viral pathogens such as influenza A and B, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) A and B, parainfluenza virus types 1–3, adenovirus, rhinovirus, human metapneumovirus (hMPV), and others.

The non-specific clinical presentation of respiratory infections poses a considerable challenge to the differential diagnosis of these pathogens.

Early and accurate diagnosis of the causative pathogens in respiratory infections is essential to administer appropriate antiviral or antibacterial therapy, initiate effective infection control measures, and reduce the length of hospital stay.
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid

16
Das et al, frontiers in microbiology, 2018
DIAGNOSIS

Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid

17
The cornerstones of SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis
DIRECT DETECTION OF (PARTS OF) THE VIRUS
GOLD STANDARD
• Detection of nucleic acids via amplification (RT-PCR), ± sequencing
IMMUNOLOGICAL TESTS
• Detection of virusspecific antibodies
SCREENING,

PRESUMPTIVE

• Detection of one or more proteins (antigenic test)
• Definition of cellular immune response
• Culture
IS STILL RESEARCH (?) 18 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
DIAGNOSIS RESEARCH
for SARS-CoV-2

• Rapid diagnostic test (RDT)
• Simple and rapid test, based on lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) technology. It can be a point-of-care (POC) test or a self-test, with results available in 10-30 min.

• Chemiluminescence immunoassay (CLIA)
• High-throughput laboratory-based assay with high level of analytical agreement, and average time-to-result of 1-2 h.
• Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
• High-throughput laboratory-based assay with high level of analytical agreement, and average time-to-result of 2-5 h.
• Neutralization assay
• Lab-based test that uses live virus and cell culture methods. This test must be performed in laboratories with designated biosafety certificates to culture SARS-CoV-2-infected cells and has a time-toresult of 3–5 days.
There are four major types of serological diagnostic tests
TURNAROUND TIME 19 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Cell culture has a lower sensitivity than molecular techniques, the turnaround time and hands-on time required to perform cell culture compared to molecular testing are increased, and the technical expertise for performing cell culture is often not available.
Positive viral culture results would not impact the management of healthy children hospitalized for illness attributed to community acquired respiratory viral infection due to the delay in time to culture positivity


modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
DFA and IFA assays do not require viable viruses and the turnaround times are short (4 h)

DFA/IFA technologies are labor-intensive, require a skilled technologist to read and interpret results, require a fluorescence microscope, and are subject to reader error. Furthermore, the hands-on time required per test is not structured for high-throughput result reporting.
Compared to molecular detection methods, DFA and IFA assays have significantly reduced sensitivity and specificity
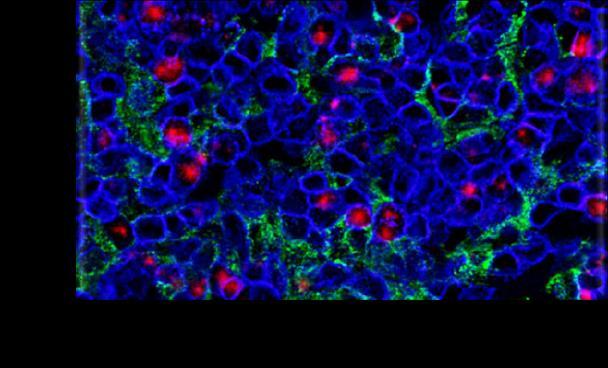 Charlton et al. Clinical Microbiology Reviews January 2019
Charlton et al. Clinical Microbiology Reviews January 2019
20
A
The mainstay of laboratory diagnosis of viral respiratory infections is the rapid identification of viral antigens and/or genetic material (either DNA or RNA) in freshly collected respiratory specimens, by a number of molecular assays:
Molecular tests are more sensitive, specific and accurate than other rapid diagnostic tests such as immunochromatography, allowing the detection of one or more respiratory viruses in biological samples


21 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT)

The clinical signs and symptoms of acute respiratory tract infections (RTIs) are not pathogen specific.

Highly sensitive and specific nucleic acid amplification tests have become the diagnostic reference standard for viruses, and translation of bacterial assays from basic research to routine clinical practice represents an exciting advance in respiratory medicine. How best to use newer molecular tests for RTI in combination with clinical judgment and traditional methods can be bewildering given the plethora of available assays and rapidly evolving technologies.

22
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
The detection power of PCR was better than that of traditional antigen tests and virus cultures when considering the detection of respiratory viruses
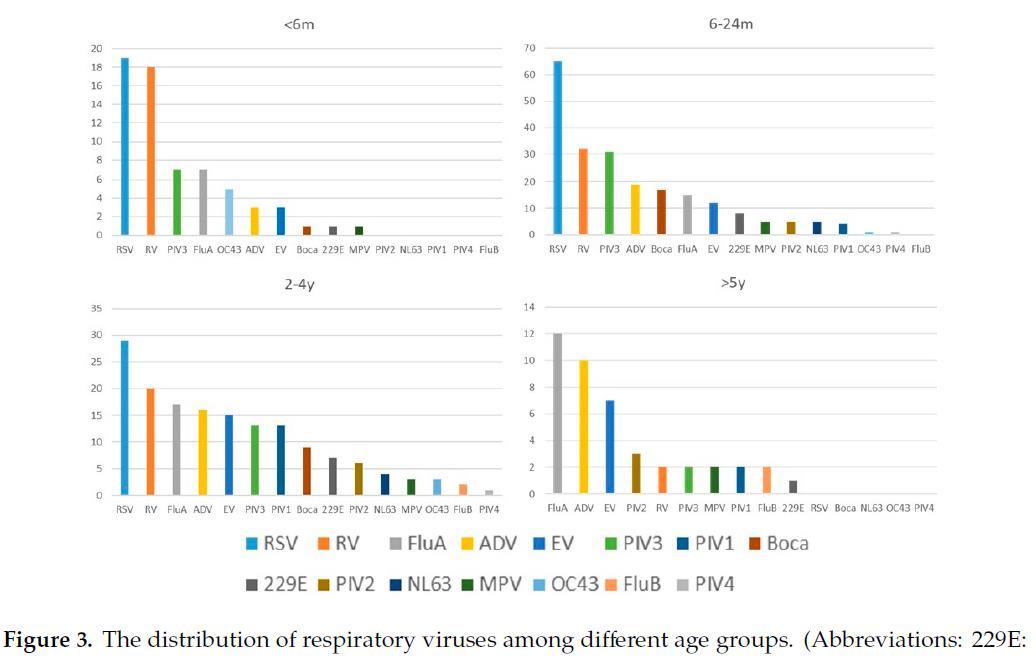
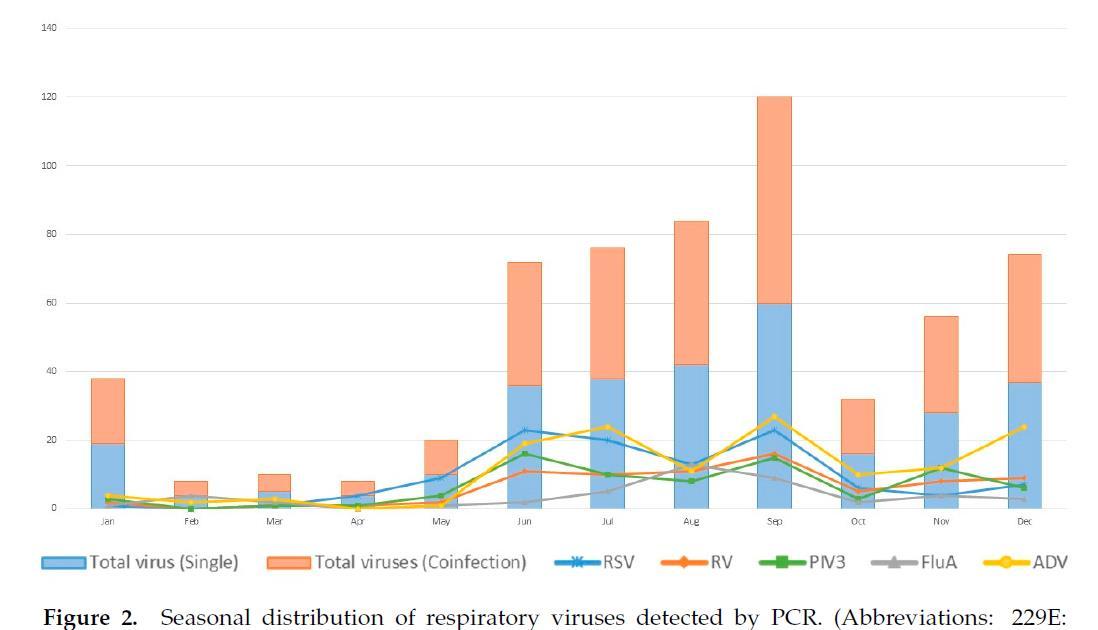
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid



Chien-Yu Linet al., Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020
23
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid



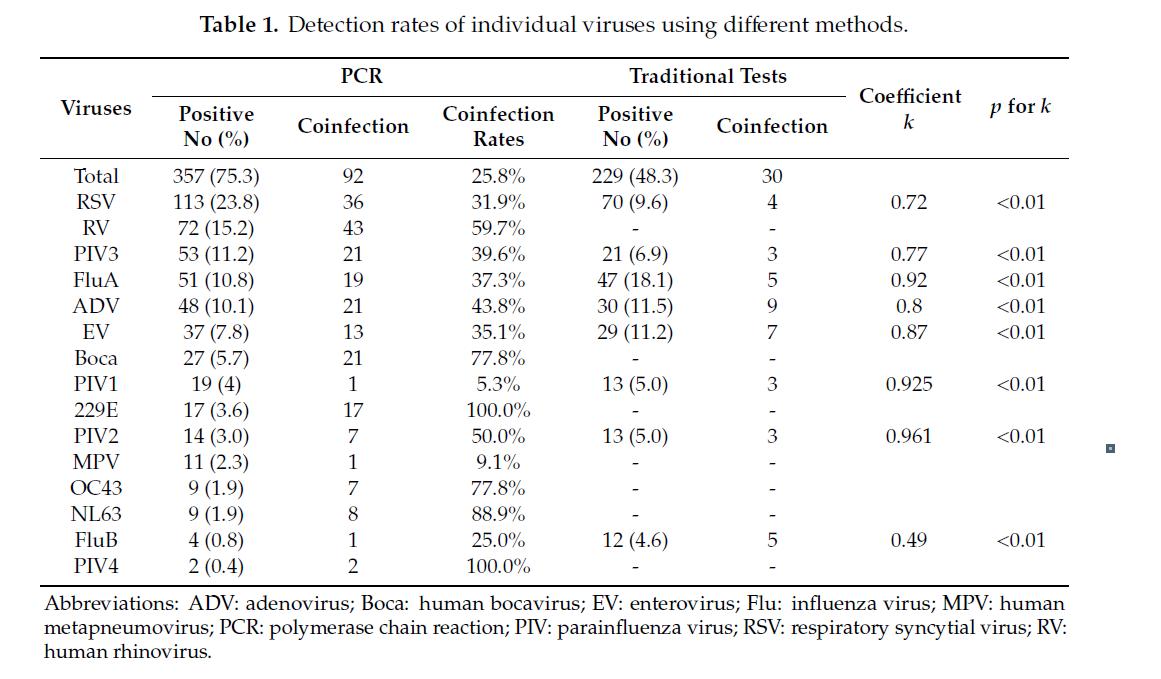

24
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
RT-PCR cycle-threshold values <20 were one of the strongest predictors of inhospital death, both in univariate (HR: 8.38 [2.66-26.37], p=0.00015), both in multivariate-analysis (HR: 3.94 [1.758.87], p=0.001; along with comorbidities presence, creatinine, D-dimers, and Creactive protein).

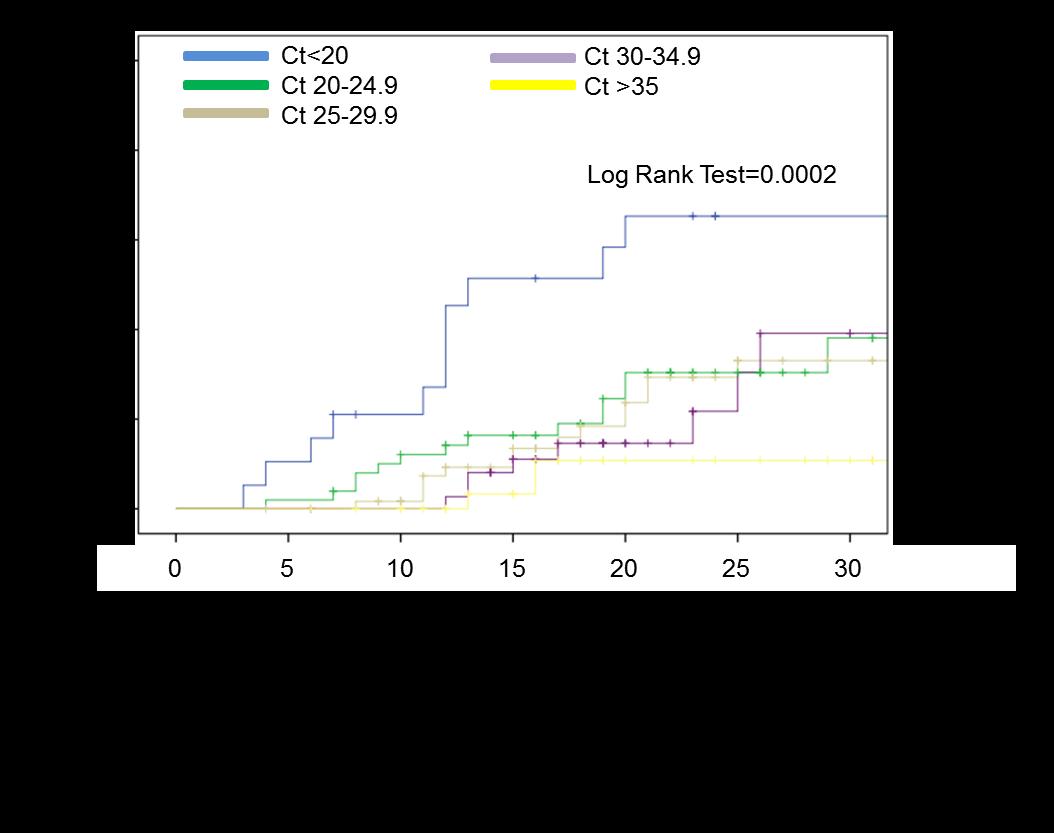
Alteri C. et al., Clin Inf Dis 2020

Kaplan-Meier curves showed a progressive increase of 30day in-hospital mortality, by increase in nasopharyngeal SARS-CoV-2 load
25
Multiplex RT-qPCR method advantages

Although single respiratory viruses can be detected in patients with symptoms, other respiratory viruses may also exist simultaneously.
Children, especially those under 5 years of age, present with a higher frequency of coinfections.

Multiplex assays that contain more than one viral gene target in a single tube have the advantage of rapid detection of several potential viral pathogens simultaneously.
Multiplex real‐time PCR has allowed simultaneous detection of multiple respiratory viruses in a short time.
Compared with the singleplex approach, the multiplex diagnostic approach has higher sample throughput (96 samples per run), shorter turnaround time (5 hours), and a smaller amount of sample requirement
26 A
modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid




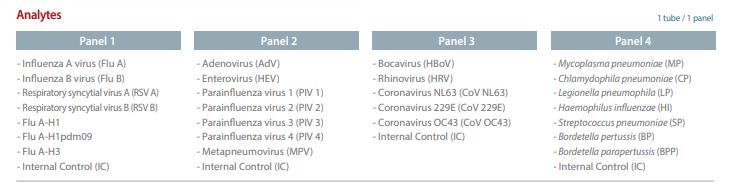


27
Sindromic Respiratory Panel



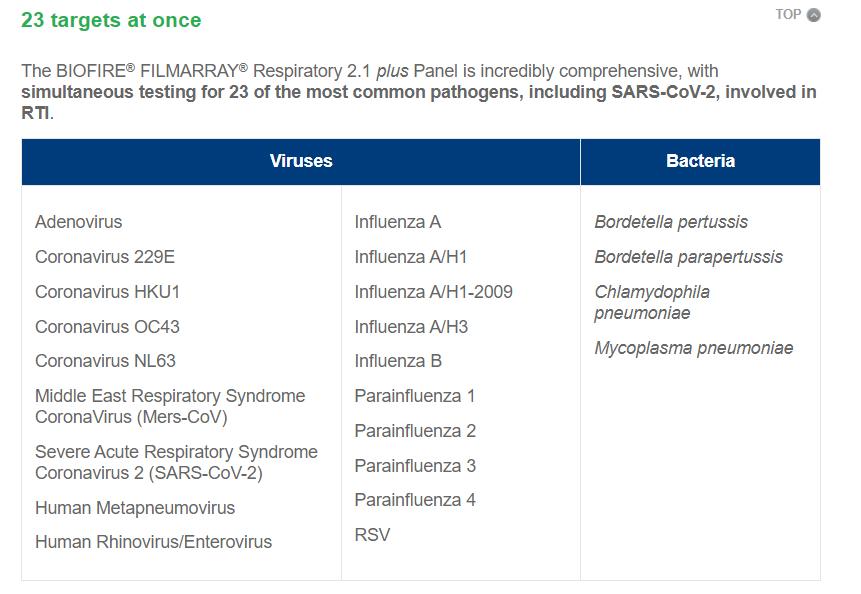
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid


28
POCT o Rapid Test:


Results in less than 30 min, relatively inexpensive and Easy to perform.
The sensitivities of these assays in pediatric and adult populations varied but were considered to be poor, and the assays could not be used to rule out infection
The lateral-flow immunoassay:
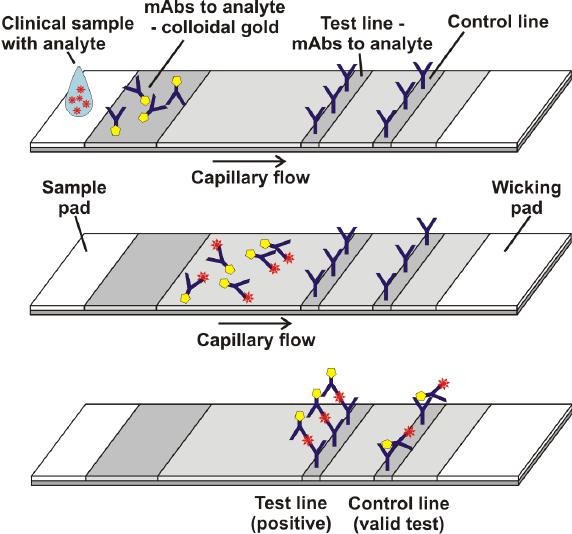 Das et al, frontiers in microbiology, 2018
Das et al, frontiers in microbiology, 2018
29 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
The use of POCT can increase the efficiency of a hospital ward, however…….
…

.the competence of the staff performing the tests can impact the quality and accuracy of

POCT results:
To ensure that POCT is performed safely and correctly, all hospital POCTs must be supervised by the central laboratory;
The laboratory director must monitor performance standards in all domains of the POCT, including pre-analytical, analytical and post-analytical aspects.
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
30
Point-of-care tests (POCTs) o Rapid Test:
Manufacturer Product Virus Detected
Luminex VERIGENE® Respiratory Pathogens Flex Test
GenMark Diagnostics eSensor® Respiratory Viral Panel (RVP)
Hologic Panther Fusion® Respiratory Assays
Seegene Allplex™ Respiratory Panel Assays
Adenovirus, Parainfluenza 1-4, Human Metapneumovirus, Influenza A (Flu AH1, Flu A-H1pdm09, Flu A-H3), Influenza B, Rhinovirus, Respiratory syncytial virus A-B
Adenovirus, Human Metapneumovirus, Influenza A (Flu A-H1, Flu A-H3), Influenza B, Rhinovirus, Respiratory syncytial virus A-B
Personalized Respiratory Testing: Influenza A virus, influenza B virus, respiratory syncytial virus, adenovirus, human metapneumovirus, rhinovirus, parainfluenza 1-4, SARS-CoV-2

Influenza A virus (Flu A-H1, Flu A-H1pdm09, Flu A-H3), Influenza B virus (Flu B), Respiratory syncytial virus A-B, Adenovirus, Enterovirus, Metapneumovirus, Parainfluenza 1-4, Bocavirus 1-4, Human rhinovirus, Coronavirus (229E, NL63, OC43)
Applied BioCode

BioCode® Respiratory Pathogen Panel (RPP)
Siemens Healthcare FTD Respiratory Assays
Adenovirus, Coronavirus (229E, OC43, HKU1, and NL63), Parainfluenza1-4, Respiratory Syncytial Virus A/B, Rhinovirus/Enterovirus, Human Metapneumovirus A/B, Influenza A (including subtypes H1, H1 2009 Pandemic, and H3), Influenza B
Adenovirus, Bocavirus, Coronavirus (229E; HKU1; NL63; OC43)
Enterovirus, Human metapneumovirus A/B, Parechovirus, Influenza A (H1N1), Influenza B, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Parainfluenza virus 1-4, Respiratory syncytial virus A/B, Rhinovirus
“ a diagnostic test that is performed near the patient or treatment facility, has a fast turnaround time, and may lead to a change in patient management” .
31 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Point-of-care tests are particularly suitable to detect COVID-19 positive
individuals in order to start self-isolation and contact tracing as soon as possible, with benefits on the spread of the infection


Forest plot of studies evaluating rapid antigenic tests
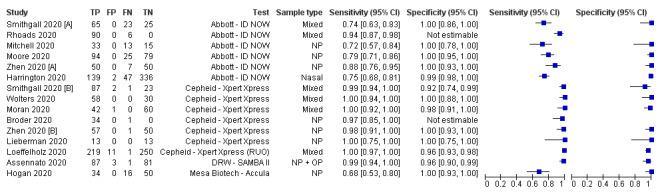
Forest plot of studies evaluating rapid molecular tests
 Dinnes et al., Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021
Dinnes et al., Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021
32 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Antigenic assays

There is a wide variety of commercially available FDA approved Rapid Antigenic Test (RATs) for the laboratory diagnosis of viral respiratory infection, based on either immune-chromatographic or immunofluorescence techniques.
They do not require laboratory support and the time to result is generally less than 30 minutes, so they are usually performed as POCTs, allowing their inclusion into the clinical decision-making algorithm.

34 Amodern
to viral
of
approach
diagnosis
Covid
Currently, commercial RATs availability is limited to the detection of influenza A virus, influenza B virus, RSV and SARS-CoV-2 These include latex agglutination tests, horizontal flow devices, lateral flow devices and optical immunoassay

Validation study of a rapid antigen test as a screening tool for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
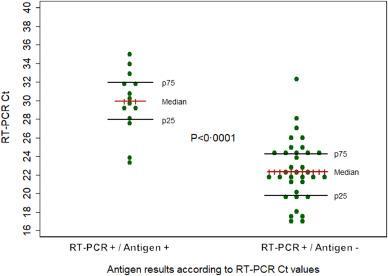
Regrettably, their suboptimal sensitivity limits the clinical utility in the viral respiratory infection diagnosis

Fernandez-Montero et al, The Lancet 2021 35 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Is COVID-19 Testing going HOME?


By mid-September, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had authorized emergency, overthe-counter use of 7 at home rapid antigen tests by both symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals.

36 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Speed vs Sensitivity


Rapid antigen tests are increasingly used worldwide
Rapid antigen tests are cheaper and provide answers within minutes instead of a day or 2 (or 5 or 6) like PCR tests, which detect genetic material from SARS-CoV-2.
• research is beginning to suggest that they aren’t as sensitive in the real world as they appeared to be in clinical trials …

•
BUT
37 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
The third-generation LumiraDx test has a sensitivity of 91% for samples with Ct ≤ 29 (high viral-load), and of 34% for samples with Ct > 29 (low viral-load)


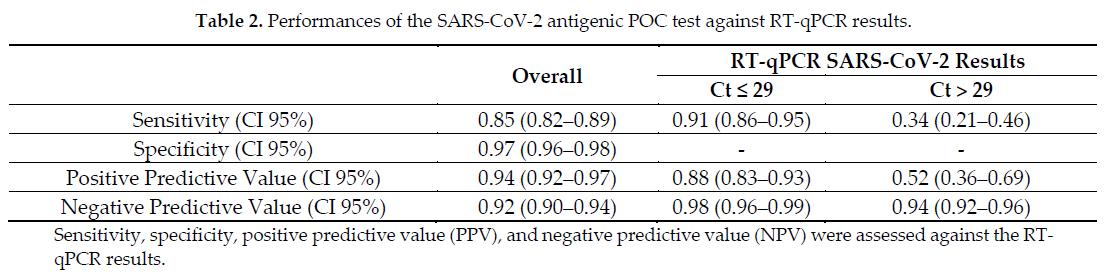
Cento V et al., Viruses 2021 38 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Not Positive About Negatives
«you could possibly still have COVID-19 even though the test is negative»

The antigen tests’ lower sensitivity translates into a higher rate of false negatives than with PCR-testing (is even lower in people who don’t have symptoms)
If not CONFIRMED by RT-PCR you can miss diagnosis …

39 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
The mainstay of laboratory diagnosis of viral respiratory infections is the rapid identification of viral antigens and/or genetic material (either DNA or RNA) in freshly collected respiratory specimens, by a number of molecular assays:
Molecular tests are more sensitive, specific and accurate than other rapid diagnostic tests such as immunochromatography, allowing the detection of one or more respiratory viruses in biological samples


Serologic diagnosis is of considerable help epidemiologically, but it cannot detect the presence of the virus in the early stage of infection and is therefore of limited use in all those conditions that require a prompt response to infection (including the isolation of patient and/or the initiation of antiviral therapy)
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
40
Diagnostic testing for respiratory viruses has been revolutionized by recent advances that have made rapid and highly accurate tests accessible to clinical laboratories




41 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
CRISPR-based DETECTR technology

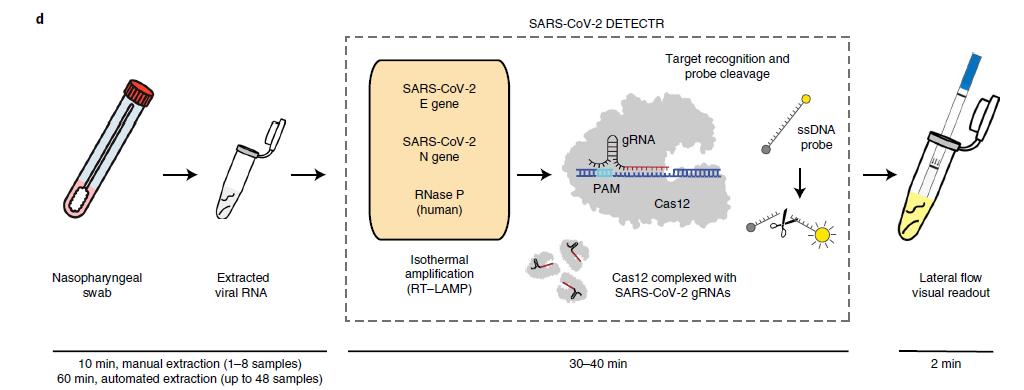
A diagnostic method that can be readily adapted to detect infection from emergent viruses is urgently needed.
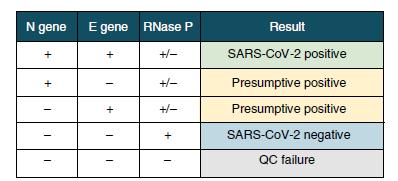
The future development of portable microfluidic-based cartridges and lyophilized reagents to run the assay could enable point-of-care testing outside of the clinical diagnostic laboratory, such as airports, local emergency departments and clinics and other locations.

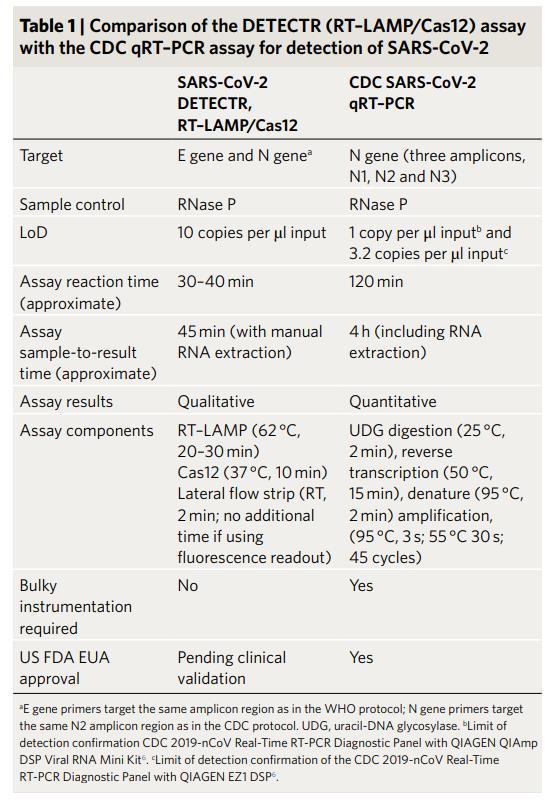
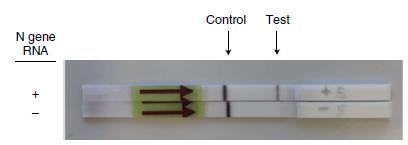
Broughton et al. Nature Biotechnology 2020
42 A
modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
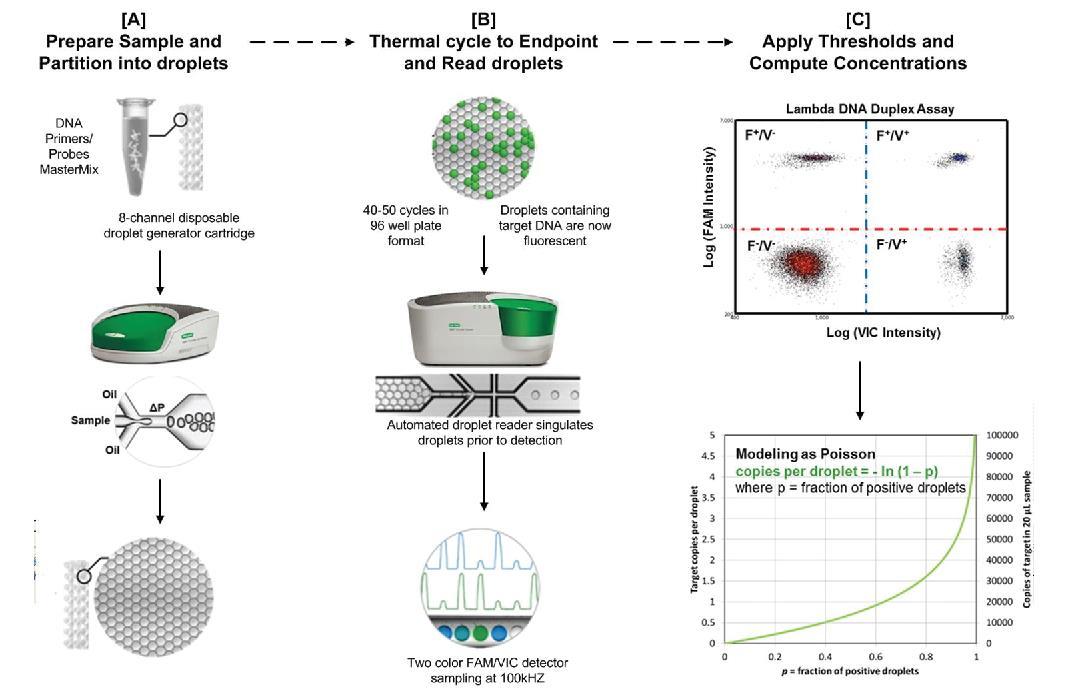





Droplet Digital™ PCR (ddPCR™) Technology 43 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid



Alteri et al., Plos ONE 2020 44 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
A severe COVID-19 manifestation characterized 14 of the 19 patients with a ddPCR confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection (73.7%)


ID Hospitalization date Symptoms Pulmonary involvement COVID-19 typical presentation Disease severitya SARS-CoV-2 viral load at hospitalization IgG resultsd (month, year) copies/mLb copies/100,000 RNAsePc 1 March, 2020 Fever, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 30 58 na 2 March, 2020 Fever, Cough, Lobar Pneumonia yes Moderate 30 21 + in a serum sample collected 3 days after the swab 3 March, 2020 Fever, Cough, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 49 30 + in a serum sample collected 80 days after the swab 4 March, 2020 Fever, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Moderate 56 44 na 5 April, 2020 Fever, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 60 50 + in a serum sample collected 15 days after the swab 6 April, 2020 Fever, Cough, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 84 47 + in a serum sample collected 16 days after the swab 7 March, 2020 Fever, Cough, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 111 8 + in a serum sample collected 22 days after the swab 8 March, 2020 none none no Asymtomatic/Milde 120 16 na 9 April, 2020 Fever, Cough, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 120 107 + in a serum sample collected 27 days after the swab 10 March, 2020 Fever, Cough, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Moderate 128 25 + in a serum sample collected 3 days after the swab 11 March, 2020 Fever, Dyspnea Pneumonia with pleuritis no Severe 163 16 + in a serum sample collected 24 days after the swab 12 May, 2020 Dyspnea Lung cancer no Severe 207 40 na 13 April, 2020 Fever, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 280 110 na 14 April, 2020 Fever, Cough, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 300 459 + in a serum sample collected 31 days after the swab 15 March, 2020 Cough, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 390 558 + in a serum sample collected 3 days after the swab 16 March, 2020 Fever, Coght, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Moderate 411 558 + in a serum sample collected 10 days after the swab 17 March, 2020 Fever, Cough, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 441 356 + in a serum sample collected 3 days after the swab 18 March, 2020 Fever, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 604 293 + in a serum sample collected 17 days after the swab 19 March, 2020 Cough, Dyspnea Bilateral interstitial pneumonia yes Severe 1800 3136 + in a serum sample collected 3 days after the swab Alteri et al., Plos One 2020 45
A
modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid


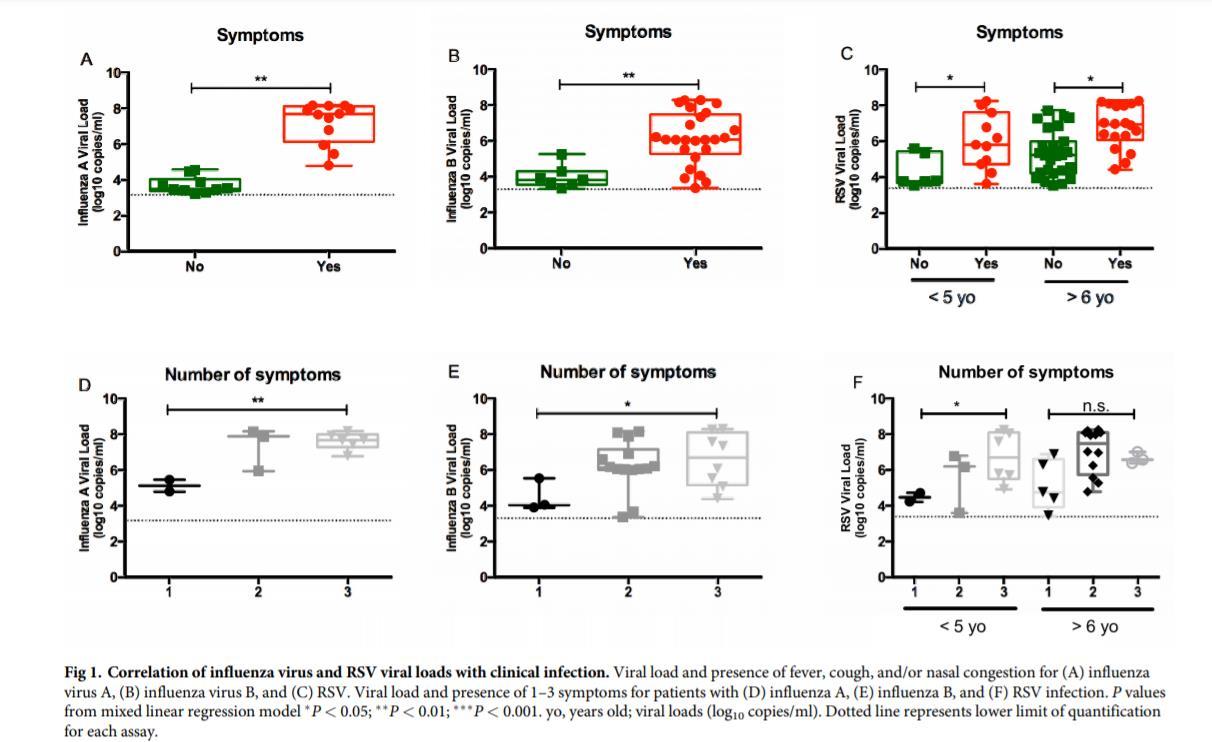


Bouzas et al., Journal of Clinical Virology 2018; Hijano et al., Plos ONE 2019 46 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
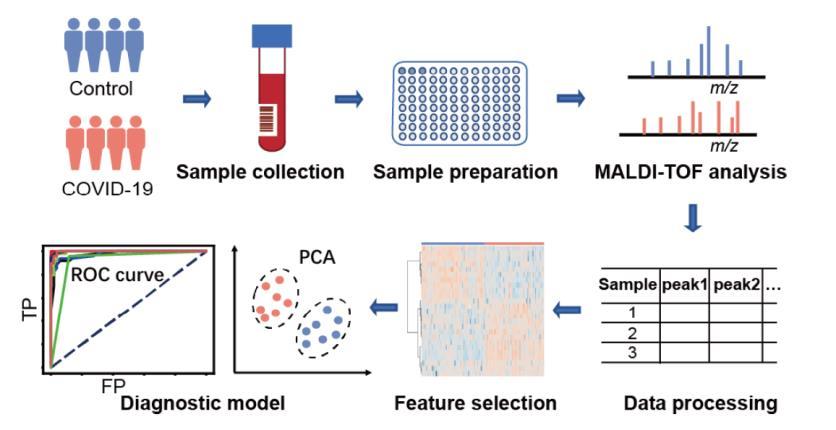




Yan et al., Anal Chem 2021; Iles et al., Diagnostics 2020 MALDI-TOF
47 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
and Respiratory Virus: great potential for screening, routine surveillance, and diagnosis in large populations
Evolution of «use-cases» during COVID-19 pandemics
INITIAL PHASE

• Triage of at-risk presymptomatic and symptomatic individuals
• Diagnosis of symptomatic individuals
• Differential diagnosis
PRE-VACCINE
• Triage of at-risk presymptomatic and symptomatic individuals
• Diagnosis of symptomatic individuals
• Differential diagnosis
• Confirmatory testing
• Testing of patients with previous COVID-19
• Surveillance and environmental monitoring
POST-VACCINE
• Triage of at-risk presymptomatic and symptomatic individuals

• Diagnosis of symptomatic individuals
• Differential diagnosis
• Confirmatory testing
• Testing of patients with previous COVID-19
• Surveillance and environmental monitoring
• Definition of vaccinebreakthrough infections
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
48
cases had been declining, and

shifted resources to vaccinating people Weekly COVID-19 testing. Data provided by the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control –

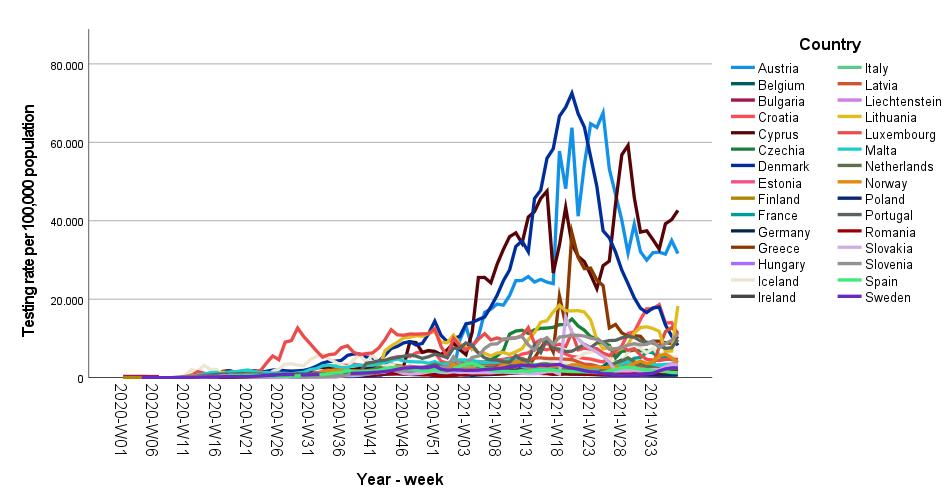
23 September 2021 49 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Many countries have now reduced testing because
they
FDA advisory panel recommends Pfizer vaccine for kids ages 5 to 11
A panel of independent advisers to the Food and Drug Administration is recommending that the agency issue an emergency use authorization for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in children ages 5 to 11 years old.
The vote was 17 in favor and one abstention.

The FDA panel accepted Pfizer’s data indicating the vaccine is safe and 90.7% effective in preventing COVID-19 infections in this age group.

50
26, 20214:43 PM ET 50 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
October
OPBG SARS-CoV-2 surveillance of variants


51 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid


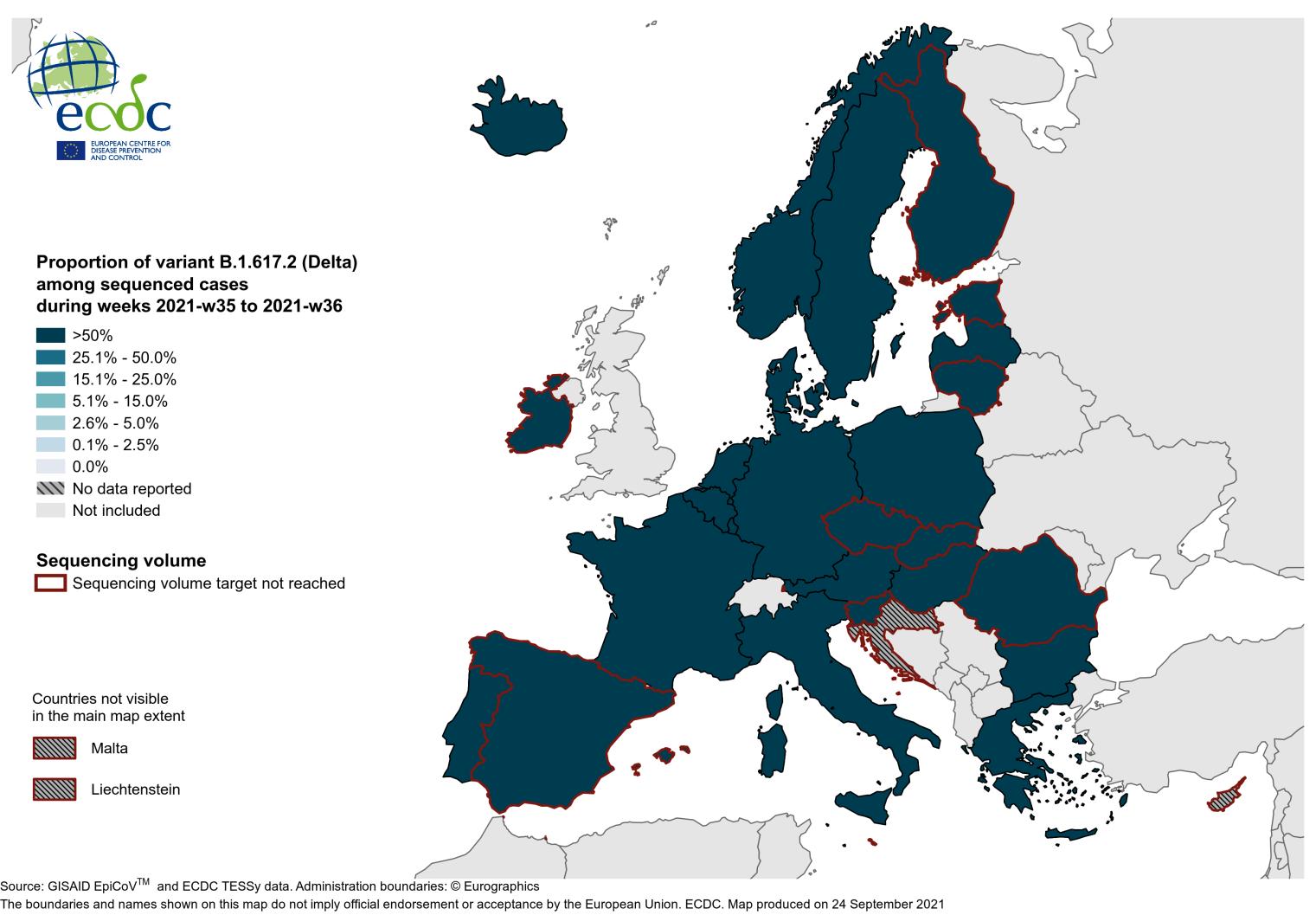
52
First SARS-CoV-2 diagnoses with Ct<29 in the overall and in patients aged <18years from March 2020 to September 2021


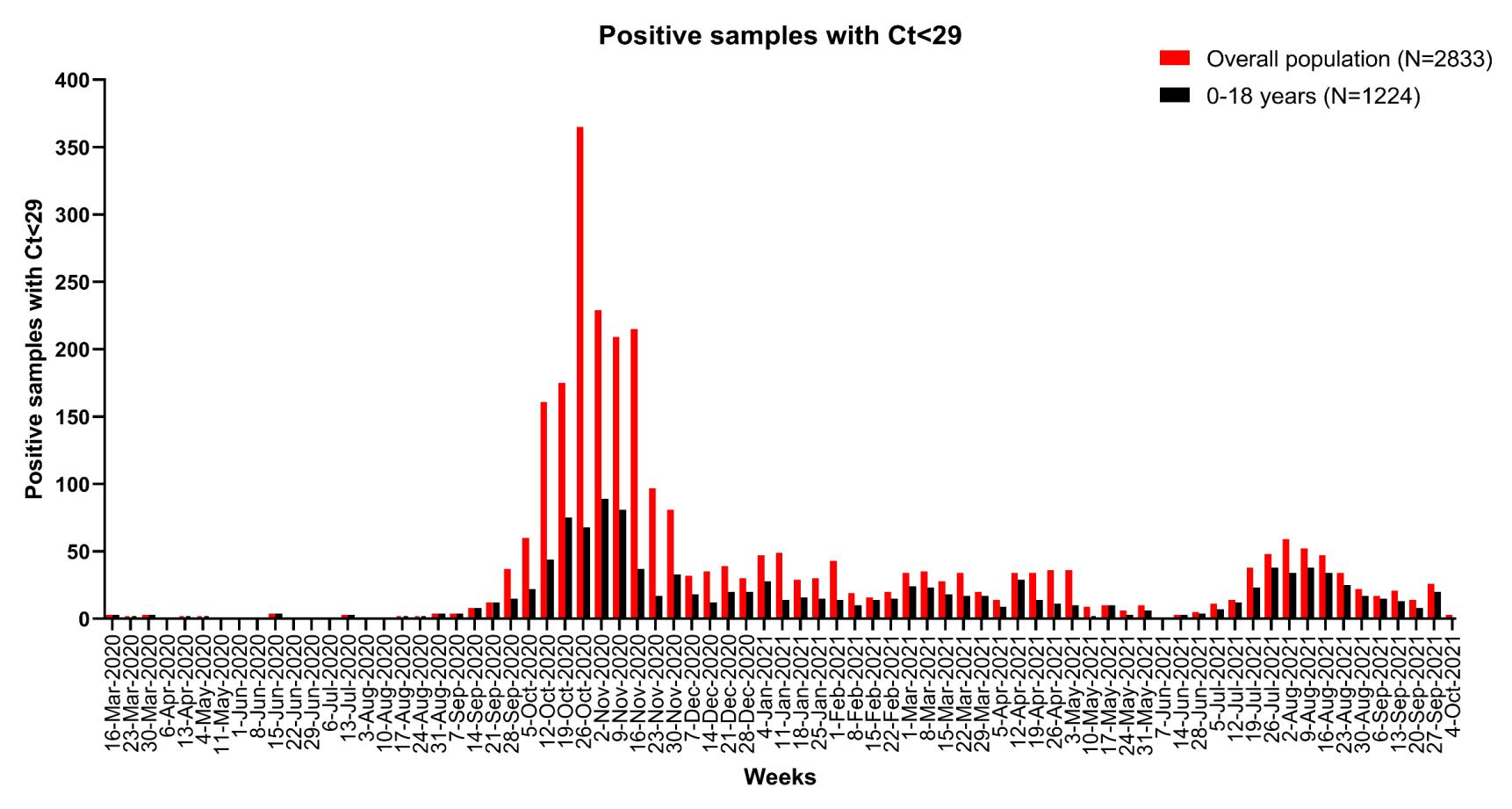
53 A
modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid


Others: B.1.221, B.1.236, B.1.258, B.1.258.14, B.1.258.17, B.1.351, B.1.36, B.1.367, B.1.396, B.1.398, B.1.416, B.1.525, B.1.586, C.36, C.36.3
54 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 800 850 900 950 1000 16 March 2020 30 March 2020 13 April 2020 11 May 2020 08 June 2020 22 June 2020 06 July 2020 03 August 2020 17 August 2020 31 August 2020 14 September 2020 28 September 2020 12 October 2020 26 October 2020 09 November 2020 23 November 2020 07 December 2020 21 December 2020 04 January 2021 18 January 2021 01 February 2021 15 February 2021 01 March 2021 15 March 2021 29 March 2021 12 April 2021 26 April 2021 10 May 2021 24 May 2021 07 June 2021 28 June 2021 12 July 2021 26 July 2021 09 August 2021 23 August 2021 06 September 2021 13 September 2021 27 September 2021 Cumulative Count B.1/B.1.1 B.1.177 B.1.1.7 P.1/P.1.1 B.1.617.2
Distribution of lineages from March 2020 to September 2021
The SARS-CoV-2 genome encodes approximately 25 proteins that are required for infection and replication, including four major structural proteins: spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N).
The S protein plays a critical role in fusion and entry into the host cell, and it comprises an N-terminal S1 receptor-binding domain (RBD), N-terminal domain (NTD), and a C-terminal S2 subunits. The primary function of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein (NP) is binding and packing of the viral RNA genome into a helical nucleocapsid structure during viral replication.

Studies on the serum of recovered COVID-19 patients suggest that host-neutralizing antibodies primarily work against S and N proteins. Consequently, the likelihood of predicting immunity status could increase in serological tests that target various regions of S or N proteins.

Therefore, the characterization of specific SARS-CoV-2 antigen domains targeted by the humoral immune response becomes an integral part of the serological test development

55 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Serological, or antibody, tests detect immunoglobulins produced by the host’s plasma B cells following exposure to foreign antigens.
• The S protein forms a transmembrane homotrimer protruding from the viral surface to attach to the host cellular receptor ACE2.

The SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) trimeric glycoprotein is a focus of vaccine development because it is the primary target of host immune defenses.

• S comprises two functional subunits: subunit S1 responsible for binding to the cell surface receptor ACE2 and subunit S2 responsible viral fusion to the cell membrane. Wrapp
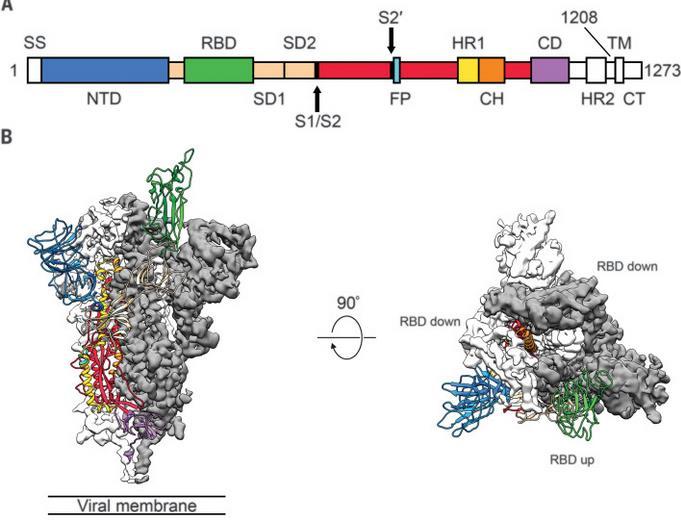
The Spike (S) protein (of about 150kDa) is the major antigen presented on the surface of SARSCoV-2
D et al. Science. 2020
56 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
965 HCWs vaccinated at the Bambino-Gesu Children Hospital, Rome, Italy (292 [30.2%] males, median age: 46 years [IQR:3656]).

Serum samples were available before the first dose and at 7, 21, and 28 days afterwards.
All HCWs had a negative SARS-CoV-2 status by molecular (Allplex2019-nCov, Seegene) and antibody assays

Presence and titers of anti-spike (S) antibodies in serum samples were evaluated by Elecsys®Anti-SARS-CoV-2- S (Roche, cut-off:0.8U/mL) detecting antibody against the S1-receptor- bindingdomain (RBD) and the LIAISON® SARS-CoV-2 TrimericS IgG assay (DiaSorin, cut-off: 13 AU/mL), detecting IgG against the trimeric S protein.
Recipients were stratified according to age (2355 or ≥56 years) and sex.

Zaffina et al., 2021
57 A
modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
The highest anti-S titers were detected in samples at day 28, when 99.8% of subjects showed a median anti-RBD titer of 2003(IQR:1089- 2,500, Similar results were observed for the anti-trimeric S titers (Fig. 1B).
At day 7, while only few individuals had low positive titers (2 to antiRBD:3.31 and 6.95 U/mL, and 5 to the S protein: median 26 [IQR:21–31]) (Fig .1A–B), a primary cellular response was already present.

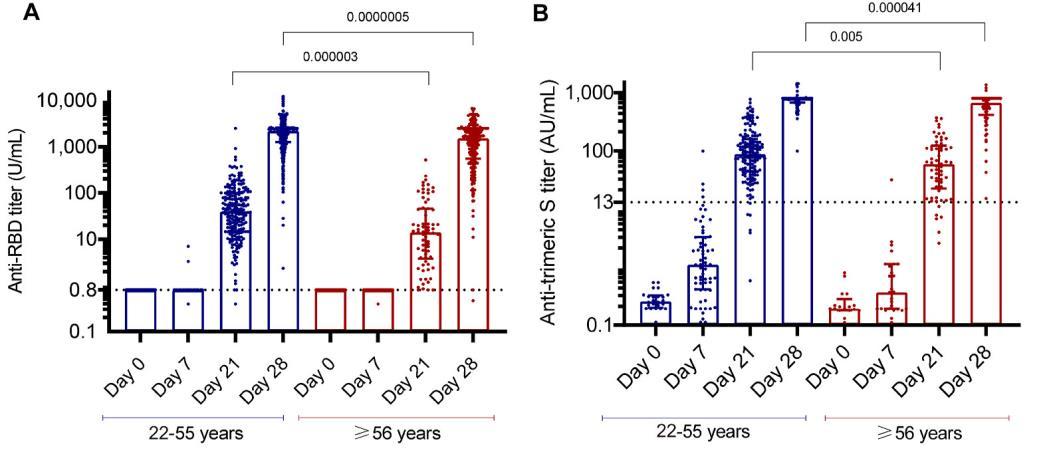
At day 21 (before the second administration), 97.5% of individuals showed positive anti-RBD antibodies, though with modest titers (median:54[IQR:26–109], Fig. 1A). Similar results were observed for antitrimeric S antibodies (Fig. 1B).

Zaffina et al., 2021

58 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
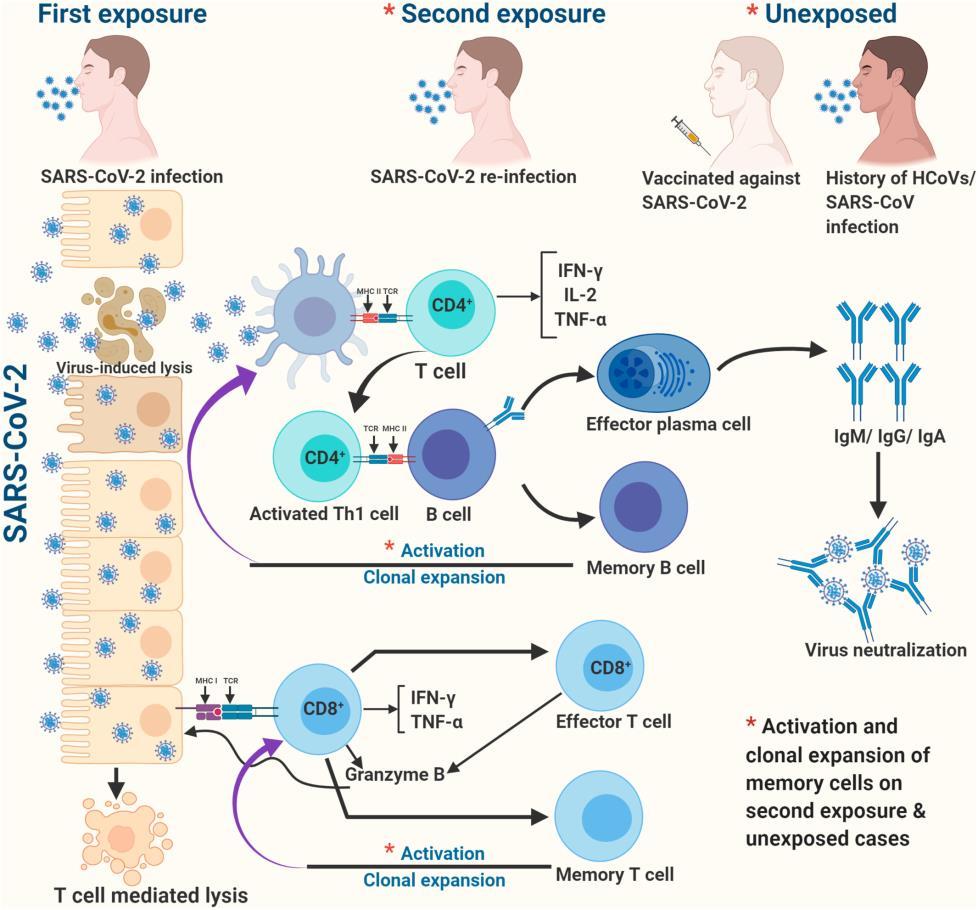
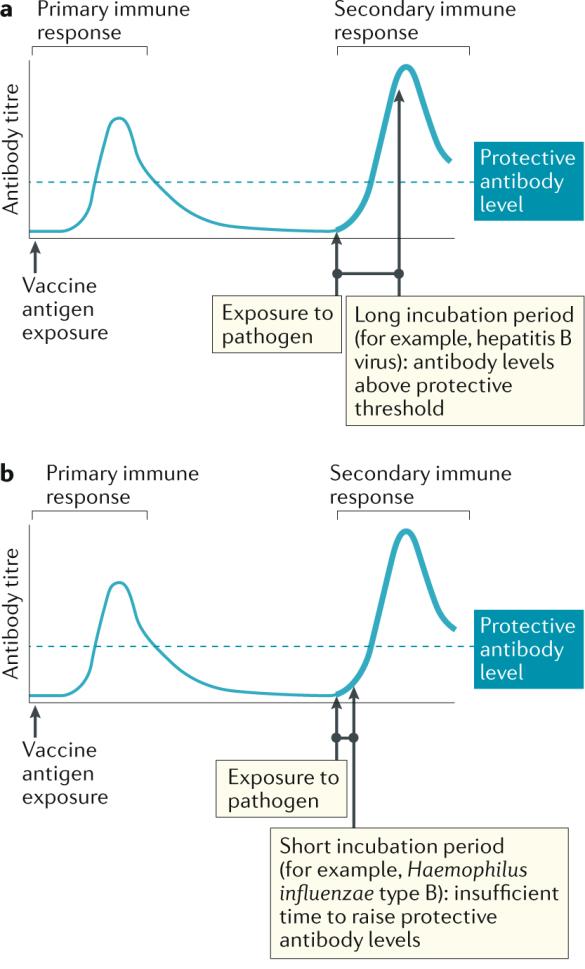
Hypothetical illustration of protective immunity against COVID-19.


59 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Study summary and key findings.(A) Cohort design and objectives. Longitudinal samples were collected from SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals and measured for both antibodies and memory B cells. (B) Distinct patterns of antibody and memory B cell responses to mRNA vaccination in SARS-CoV-2 naïve and recovered individuals. (C) Age-associated differences in antibody and memory B cell responses to mRNA vaccination. (D) Baseline memory B cells in SARS-CoV-2 recovered individuals contribute to recall responses after mRNA vaccination. Goel



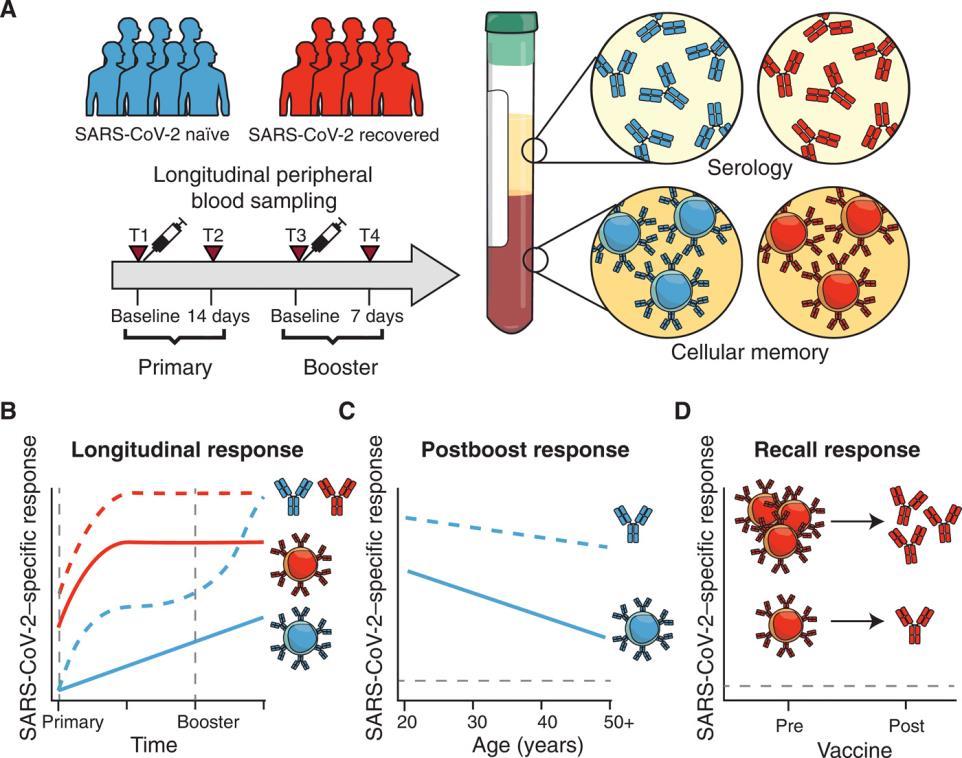
S
Immunology 15 Apr 2021 60
et al.,
cience
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid



Highly Specific Memory B Cells Generation after the 2nd Dose of BNT162b2 Vaccine Compensate for the Decline of Serum Antibodies and Absence of Mucosal IgA. Cells. 2021; 10(10):2541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102541 61 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Gating strategy for the detection of memory B cells specific for Trimeric Spike.

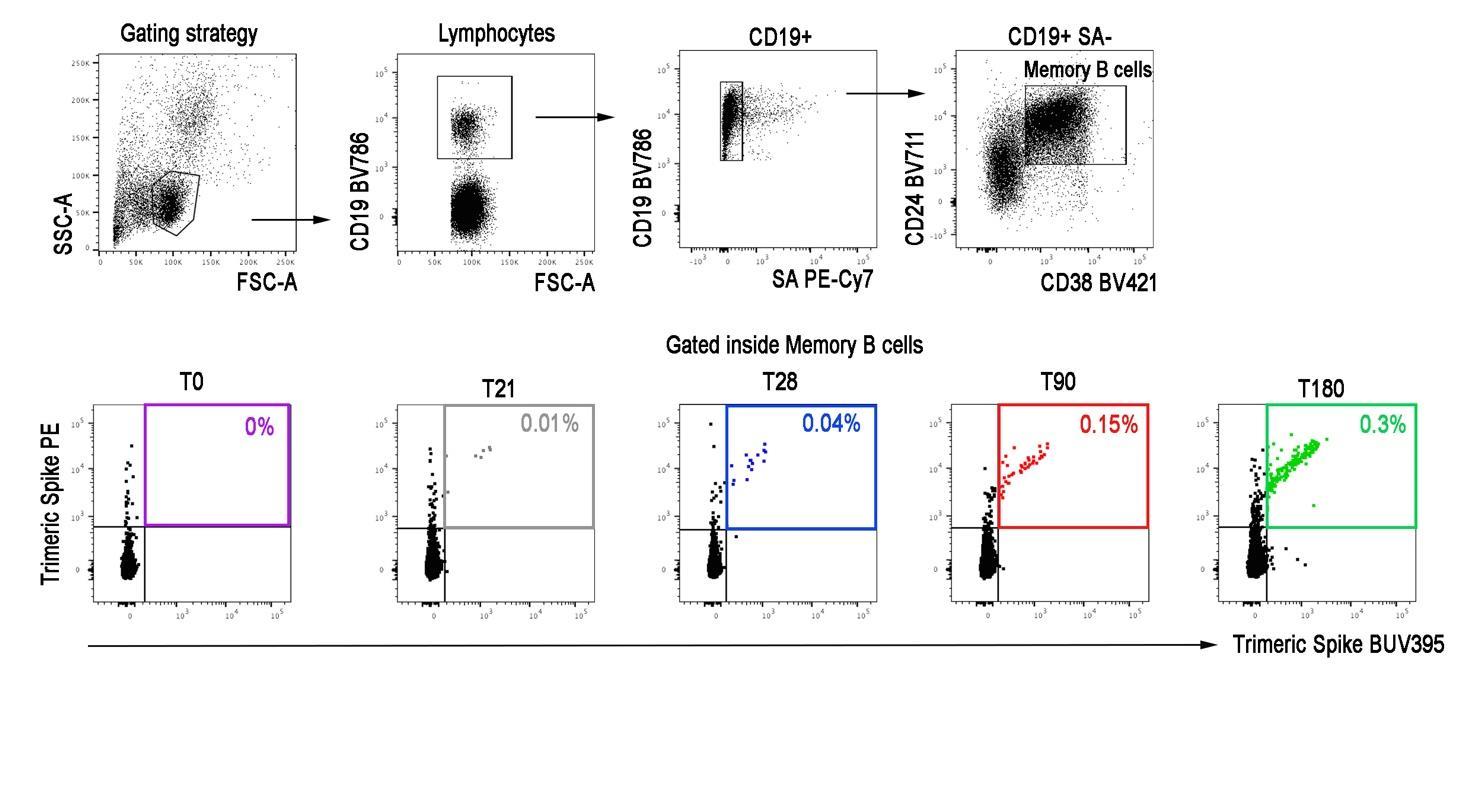
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid

62
Serum specific

2. PERSISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MEMORY B CELLS
antibodies
to RBD and Trimeric Spike
decline further six months after a complete vaccine cycle
Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid

T0 1w 3mo 6mo 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 A n t iT r i m e r i c S p i k e s p e c i f i c I g G ( B A U / m L ) ******** **** **** **** **** after 2nd dose T0 1w 3mo 6mo 0 2000 4000 6000 8000 T o t a l a n t iR B D a n t i b o d i e s ( B A U / m L ) ******** *** **** **** after 2nd dose
63
The decline of serum specific antibodies months after vaccination is a physiological event.
It occurs after every vaccine and in every individual

Nature Reviews Immunology volume 21, pages83–100(2021)

64 A
modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
In contrast, Spike-specific memory B cells continue to increase six months after vaccination


T0 1w 3mo 6mo 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.6 0.8 % o f S p i k es p e c i f i c M B C s **** **** ** **** **** **** after 2nd dose
65 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
2. PERFORMANCE OF SPECIFIC MEMORY B CELLS

In 17 HCWs with breakthrough infections, specific antibodies against Spike and RBD rapidly increase in the serum and reach the highest levels 4-6 days after the positive NPS.

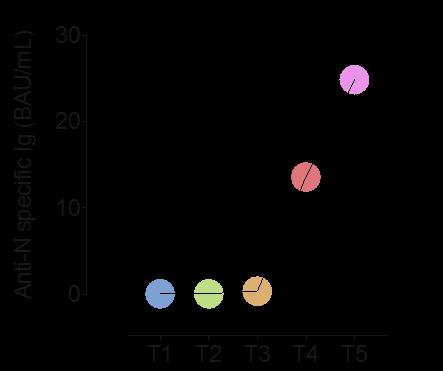
In contrast, Anti N antibodies start to increase after 10 days.
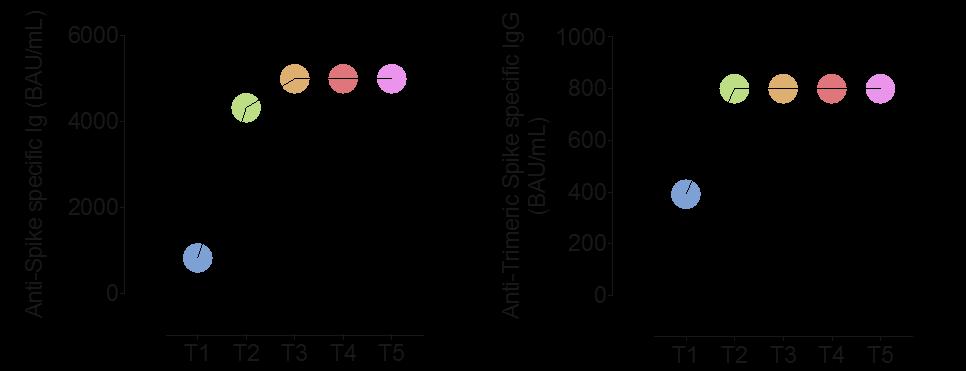
66 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Upon encounter with the pathogen for which they are specific MBCs have the function of rapidly producing antibodies in the serum and at the site of invasion, the oropharinx for SARSCoV-2


exCOVID-19vaccinated3movaccinated6mo T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 5 20 S a l i v a r y I g A ( r a t i o ) **** **** **** **** ** **** **** ** *** ** ** ** **** ** *** * * 0.058 Salivary IgA rapidly increase 67 A
modern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
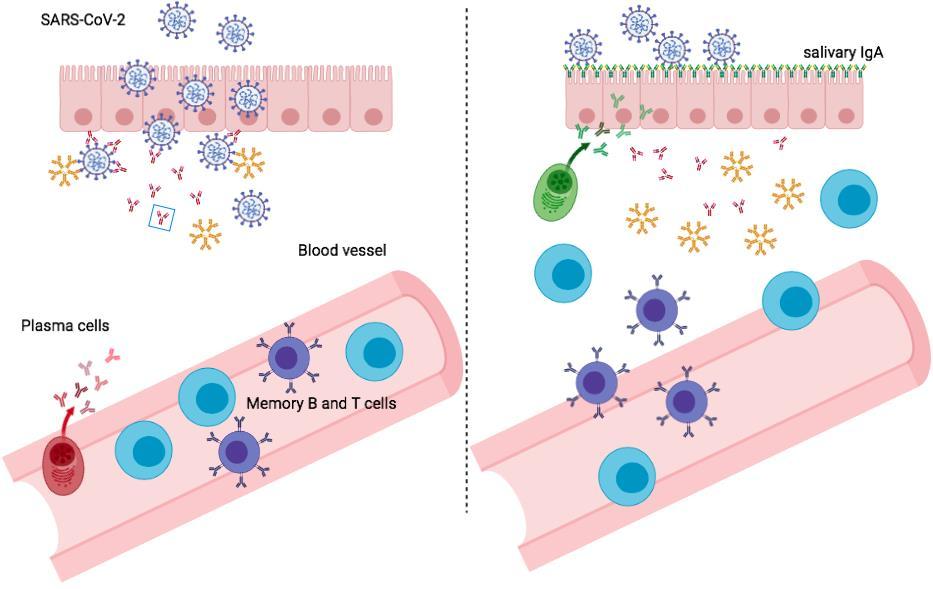


After vaccination In response to a breakthrough infection 68 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid



69 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
What can we conclude…..?
Accurate and fast diagnosis of SARS CoV2 is mandatory in order to:

Save people’s lives
Stop the epidemics
But is also part of proper management to

Reduce unnecessary use of antibiotics
Select appropriate treatment for fragile patients

70 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid
Accurate detection of respiratory viruses is important in patient care, as it guides both therapy and infection control measures.


In any infectious disease outbreak, accurate and accessible diagnostic testing must be one of the pillars of control-measure policies to understand and minimize the spread of disease

71 Amodern approach to viral diagnosis of Covid























 Discover of PCR (Salki, Mullis)
Discover of PCR (Salki, Mullis)






































 Charlton et al. Clinical Microbiology Reviews January 2019
Charlton et al. Clinical Microbiology Reviews January 2019

















 Das et al, frontiers in microbiology, 2018
Das et al, frontiers in microbiology, 2018

 Dinnes et al., Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021
Dinnes et al., Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021












































